Page 1
doepfer
A-163
VDIV
System A - 100
1. Introduction
Module A-163 is a voltage controlled audio frequency divider.
The frequency of the input signal (preferably the rectangle output of a VCO) is divided by an integer factor
(N = 1, 2, 3, 4 ... up to about 20). The
N
waveform is rectangle with 50% duty cycle.
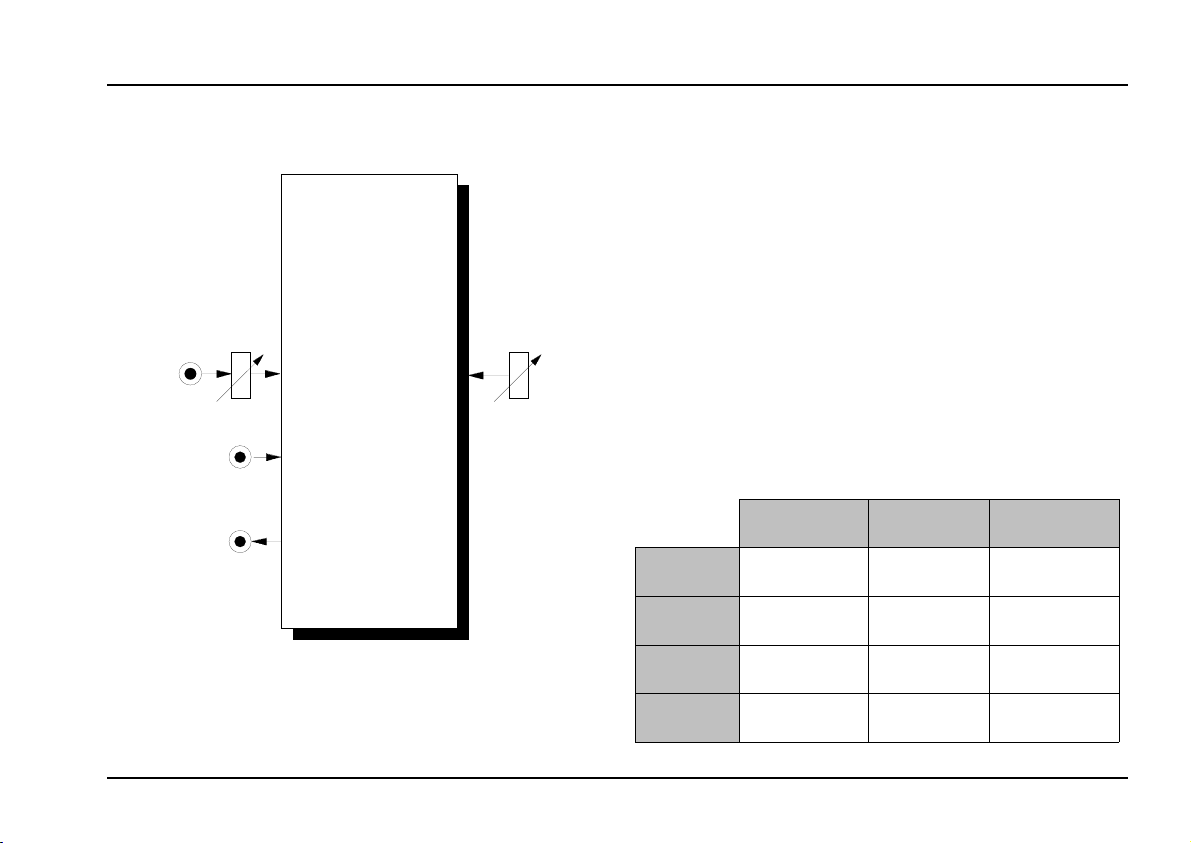
VC Frequency Divider
A-163
output
CV
CV In
In
Out
Manual
The
divisor N
can be adjusted
manually
and modulated with an external control voltage (e.g. from LFO,
ADSR, Random, MIDI-to-CV, Theremin, Light-to-CV,
analog sequencer) with attenuator.
The following table shows the differences between the
divider modules available in the A-100 system.
A-115 A-113 A-163
Divisor
setting
Divisor
range
No. of
outputs
Output
waveform
fixed manually voltage contr.
2, 4, 8, 16 1... 24
4
(mixed)
rectangle sawtooth rectangle
integer
4
(mixed+single)
+ manually
1... 20
integer
1
1
Page 2
A-163
VC Frequency Divider
System A - 100
doepfer
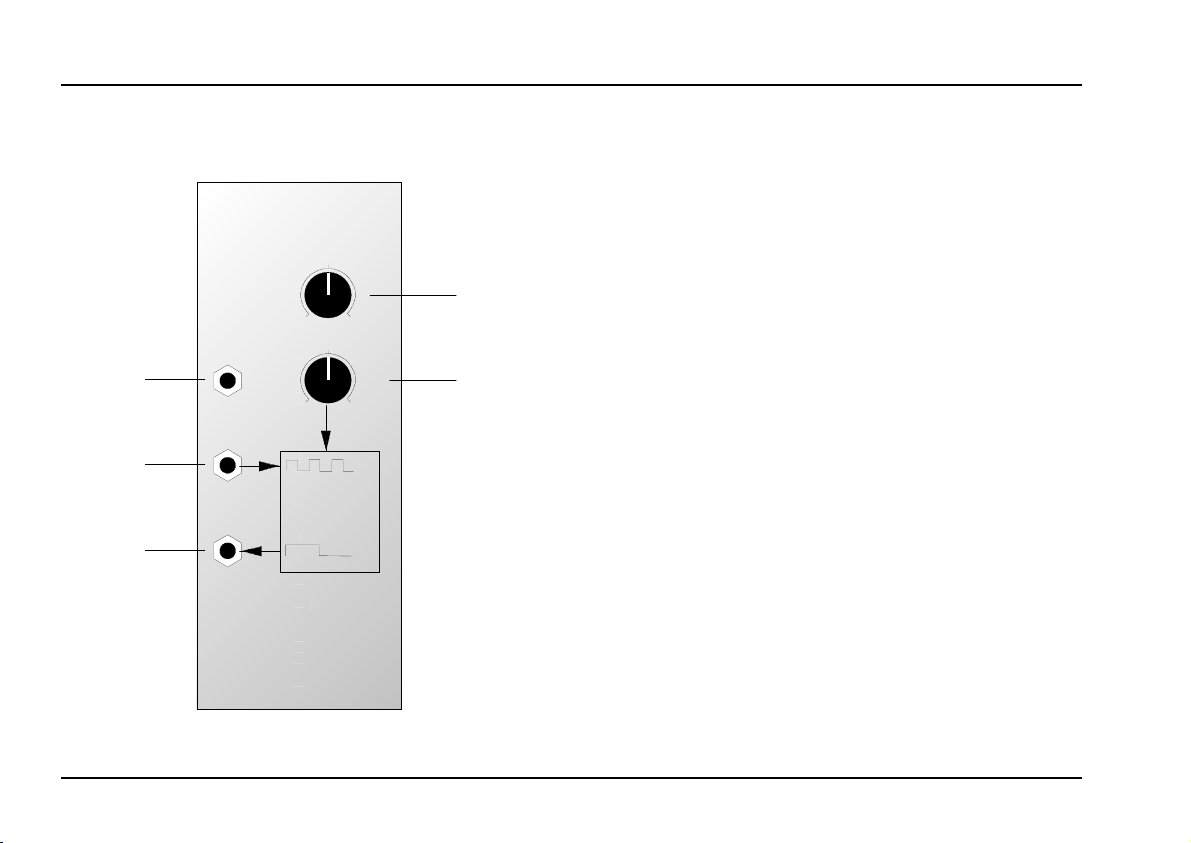
2. Overview
A-163
VDIV
VC Frequ. Divider
Manual
0
CV In
-5
In
Out
Divide
by N
Controls:
Manual: Control for manual setting of the integer
1
dividing factor N
: Symmetric (negative-0-positive) attenua-
CV
2
tor for control voltage at input
!
• fully clockwise: max. positive level
➀
10
CV
+5
➁
For the first production series the inscription of the CV
2
knob
formations in this manual are correct, i.e. left stop = 5, middle position = 0, right stop = +5.
is wrongly 0...10 instead of -5...0...+5. The in-
middle position: level 0
•
• fully counterclockwise: max. negative
level
In- / Outputs:
! CV In : Control voltage input
In : Audio input (preferably the rectangle
"
output of a VCO or LFO), i.e. the master
frequency for the divider
Out : Audio output of the frequency divider
§
(rectangle)
2
Page 3

doepfer
System A - 100
VC Frequency Divider
A-163
3. Controls
1 Manual
With knob 1 the divisor N is manually adjusted.
Integer division of an audio frequency leads to the
so-called subharmonics. The table in fig. 1 shows the
subharmonic frequencies and pitches of an audio signal C5 (= 523,2 Hz) as master frequency input for the
A-163.
Divisor Freq. [Hz]
1523,2C
2261,6C
3174,6F
4130,8C
5103,8As
687,3F
773,4D
865,4C
Fig. 1: Subharmonics of an audio signal with pitch C5
It becomes apparent that the subharmonics are equivalent to the tones of the
Pitch
5
4
3
3
2
2
2
2
minor chord scale
.
The term "subharmonic " is not quite correct as
H
the A-163 output waveform is rectange with a
marked harmonic spectrum in contrast to the
“pure” sine waves used in the harmonics theory.
For details concerning harmonic contents of
different waveforms please refer to the A-110 or
A-111 manual (VCO´s). For details about subharmonics please refer to the A-113 manual.
2 CV
The positive/negative attenuation and inversion of
the control voltage fed into socket ! is adjusted with
control 2. The following connections are valid :
Position Amplification Effect
-5 -1 invertierted CV
0 0 full attenuation
5 1 original CV (not inverted)
The manual setting of control 1 and the exter-
H
nal control voltage fed into socket ! and attenuated/inverted with control 2 are internally
added to generate the resulting control voltage
that defines the divisor N.
3
Page 4

A-163
VC Frequency Divider
System A - 100
doepfer
4. In- / Outputs
! CV In
The external control voltage (e.g. from an LFO or
ADSR) used to modulate the divisor N is fed into the
CV input ! .
" In
Socket " is the audio input of the module. This input
is connected to the audio source (waveform preferable
rectangle from an VCO or LFO). The frequency of this
signal (= master frequency) is divided by N.
§ Out
Socket § is the output of the module. Here the
harmonic (rectangle) is available.
Frequency division of control signals
The output § of the module is AC-coupled. This
means that no slow signals (e.g. 0.5 Hz LFO) can be
divided. To obtain a DC-coupled output the capacitor
C7 on the A-163 pc board has to be replaced by a
jumper (short circuit). This modification leads to a
0/+5V rectangle output that can be used for slowly
changing signals too. Please refer to the service manual for the position of C7.
sub-
5. User Examples
Sub-Oscillator
With the A-163 an audio sub-oscillator can be realized
very simply. The rectangle output of a VCO is connected to the audio input of the A-163. The audio outputs
of the VCO (e.g. sawtooth) and the A-163 are mixed
together e.g. with an A-138b. Thus one obtains a VCO
with sub-oscillator to enhance the bass sound of the
VCO. The interval between VCO and sub-oscillator
can be set manually or voltage controlled.
Subharmonic Glissando
One obtains very interesting effects if a dynamically
changing control voltage (e.g. from ADSR, LFO, Joy
Stick, Theremin, Random or similiar) is used to define
the divisor N of the A-163. This leads to a special kind
of glissandos containing only the subharmonics of the
master frequency.
4
Page 5

doepfer
System A - 100
VC Frequency Divider
A-163
In fig. 1 the triangle signal of a LFO (e.g. A-145) is
used to control the divisor N of the A-163. As only
integer divisors occur both time and frequency quantization takes place. A so-called "subharmonic glissando" appears, i.e. separate tones with the same
length are generated (subharmonics derived from the
master frequency of the VCO signal).
CV
+5 V
0 V
Sub-Osz.
Out
Frequency Multiplication
In combination with the PLL module A-196 frequency
multiplication can be obtained. For details refer to the
A-196 manual.
t
: Subharmonic glissando
Fig. 1
5
Page 6

A-163
VC Frequency Divider
6. Patch-Sheet
System A - 100
doepfer
The following diagrams of the module can help you
recall your own Patches. They’re designed so that a
complete 19” rack of modules will fit onto an A4 sheet
of paper.
Photocopy this page, and cut out the pictures of this
and your other modules. You can then stick them onto
another piece of paper, and create a diagram of your
own system.
Make multiple copies of your composite diagram, and
use them for remembering good patches and set-ups.
P • Draw in patchleads with colored pens.
• Draw or write control settings in the little
white circles.
A-163
VDIV
VC Frequ. Divider
Manual
0
CV In
-5
In
Out
Divide
by N
A-163
VDIV
VC Frequ. Divider
10
CV
+5
Manual
CV In
In
Out
0
-5
Divide
by N
10
CV
+5
A-163
VC Frequ. Divider
Manual
CV In
In
Out
0
-5
Divide
VDIV
10
CV
+5
by N
6
 Loading...
Loading...