Page 1
doepfer
Audio
In
A-128
Fixed
Filter
Bank
Audio
Out
50 Hz
75 Hz
110 Hz
11 kHz
System A - 100
1. Introduction
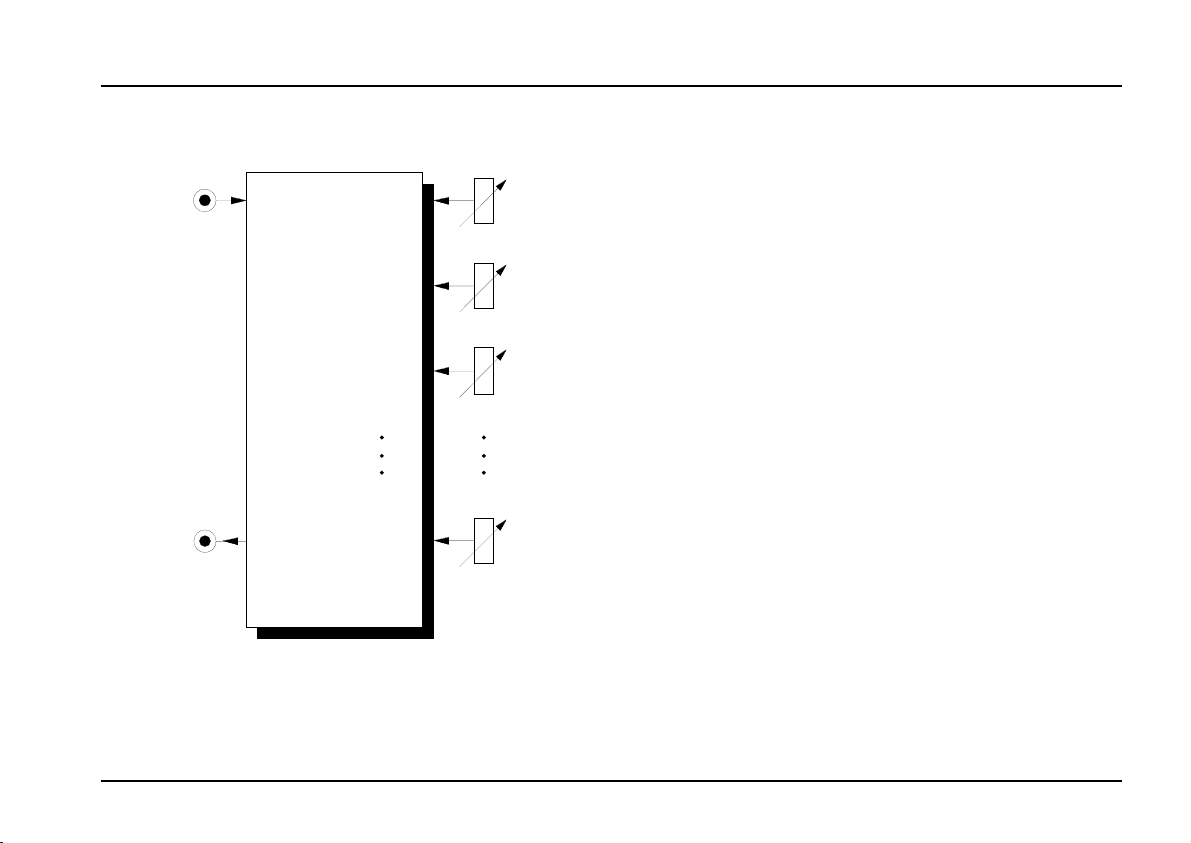
Module A-128 (Fixed Filter Bank) is a filter bank,
made up of
fixed middle frequencies and bandwidth:
50 Hz 350 Hz 2.2 kHz
75 Hz 500 Hz 3.6 kHz
110 Hz 750 Hz 5.2 kHz
150 Hz 1.1 kHz 7.5 kHz
220 Hz 1.6 kHz 11.0 kHz.
Each band pass filter has its own amplitude control
knob, with which that frequency band can be attenuated. The bandwidth of each of the filters is approximately half an octave.
The signal at the output of the A-128 contains a mix of
all the filters, depending on the position of each one’s
amplitude control knob.
The filter bank’s main job is to emphasise individual
sections of the whole audio frequency range. It’s like
a passive 15-band EQ.
Fixed Filter Bank
15 parallel band pass filters
A-128
, all with
1
Page 2
A-128
Fixed Filter Bank
System A - 100
doepfer
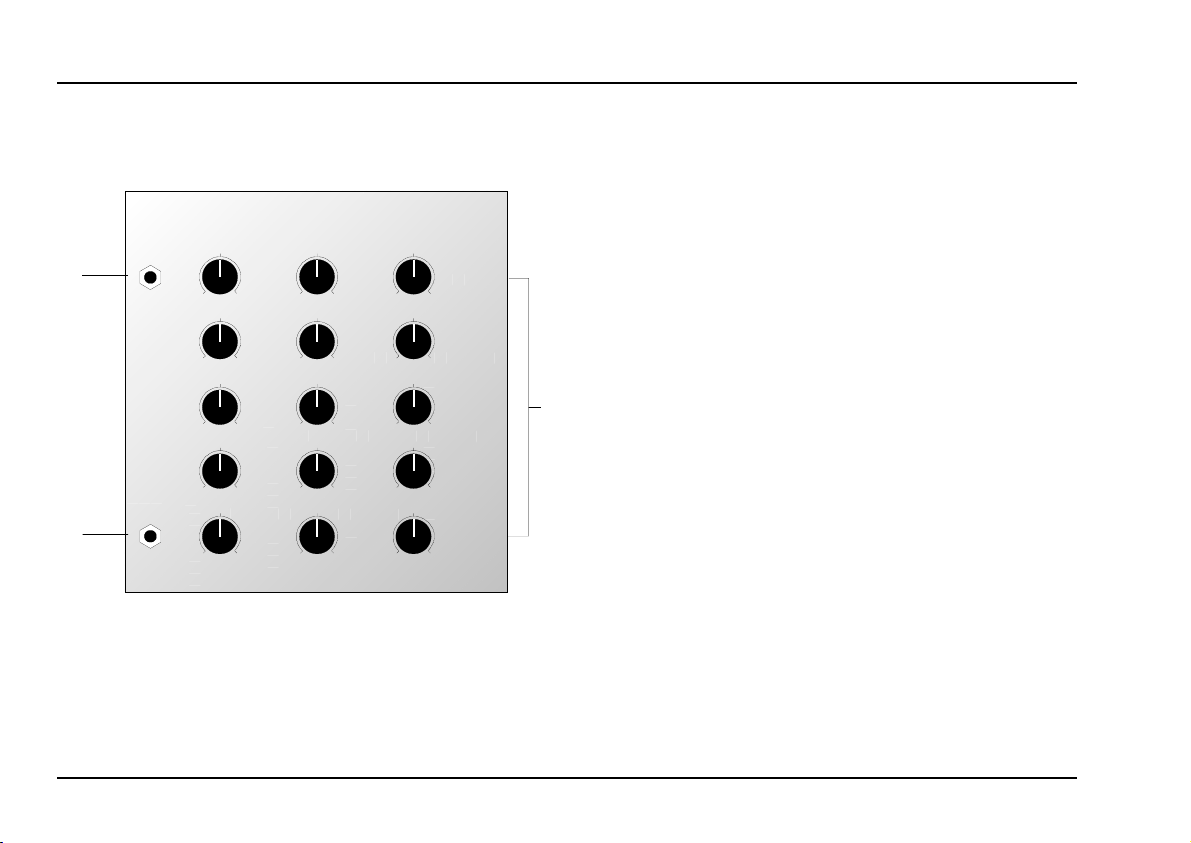
2. A-128 - Overview
A-128
Audio In
0
0
0
0
Audio Out
0
FIXED FILTER BANK
50
10
0
75
10
0
110
10
0
150
10
0
220
10
0
Controls:
50 ... 11000 : Amplitude controls (attenuators) for
1
the individual band pass filters
350
10
500
10
750
10
1100
10
1600
10
2200
10
0
3600
10
0
5200
10
0
7500
10
0
11000
10
0
In / Outputs:
!
Audio Out : Signal output
"
➀
Audio In
: Signal input
2
Page 3

doepfer
System A - 100
Fixed Filter Bank
A-128
3. Controls
1 Controls 50 Hz ... 11 kHz
With these controls you can set the amplitude of each
of the 15 bandpass filters (see Fig. 1).
50 75 110 150 ... Freq.
(6) (10) (3) (8)
Fig. 1: The effect of different amplitude levels on the
band pass filters.
4. In / Outputs
! Audio In
Socket ! is the filter bank’s input, into which you
patch the signal you want filtered.
" Audio Out
Output " carries the signal filtered by the 15 band
pass filters. The tonal quality will depend on the
settings of the individual amplitude controls.
3
Page 4

A-128
Fixed Filter Bank
System A - 100
doepfer
5. User examples
The main purpose of the Fixed Filter Bank is for
changing the colour of an audio signal (including external signals that can be patched in via an A-119 module) by attenuating certain frequency bands. This is
similar to an equalizer, except that an equalizer can
also boost frequency bands, while the fixed filter bank
only attenuates them.
Because each of the bands is very narrow (only about
half an octave or a musical fifth) drastic tonal changes
are possible - for instance ‘telephone-voice’ or
vocoder-like effects.
Also, even with each band’s amplitude control set to
identical positions, a tonal change occurs (see Fig. 2);
a neutral ‘straight-through’ setting isn’t possible.
Freq.
Emphasising certain frequencies
The patch in Fig. 3 shows how to
emphasise
frequencies using a filter bank.
The original signal and the output from the band pass
filter are both patched into an A-138 mixer.
This patch is really a special case (with no attenuation)
of the set-up on the following page.
A-138
In 1
Audio
In
A-128
MIXER
Input 1
In 2
Input 2
Fig. 3: Emphasising certain frequencies
Output
certain
Out
Audio
Out
Fig. 2: Filter response with all controls fully up
4
Page 5

doepfer
System A - 100
Fixed Filter Bank
A-128
Creating a multi-band equalizer
The patch in Fig. 4 shows how to model a simple
graphic equalizer. An A-138 Mixer is used to mix the
following signals:
Input 1: the signal from the audio output of the fil-
•
ter bank, via an A-175 inverter.
• Input 2
ter bank.
• Input 3: the original signal
Using the mixer pots "In 1", “In 2” and "In 3", you can
control the relative mix of the signals :-
• In 1
• In 2: Amount of boost
• In 3: Amount of original signal
To model an equalizer, you adjust the mixer pots as
per the above table. Naturally, any mix is possible, by
adjusting the pots according to the following formula :
Audio Out = - In 1 • filter signal
: the signal from the audio output of the fil-
:Amount of cut
+ In 2 • filter signal
+ In 3 • original signal
Pot
In 1
In 2
In 3
just the
original
0 0 0 0 ... 10
0 10 0 ... 10 0
10 0 10 10
just the
filter bank
original
+ boost
original
+ cut
P Patching a VCA in before the mixer’s inputs
can give voltage control of the relative
amounts.
Audio
In
A-128
A-175
Fig. 4: Creating a multi-band equalizer
A-138
In 1
MIXER
Input 1
In 2
Input 2
In 3
Input 3
Out
Output
Audio
Out
5
Page 6

A-128
Fixed Filter Bank
6. Patch-Sheet
System A - 100
doepfer
The following diagrams of the module can help
you recall your own Patches. They’re designed so
that a complete 19” rack of modules will fit onto an
A4 sheet of paper.
Photocopy this page, and cut out the pictures of
this and your other modules. You can then stick
them onto another piece of paper, and create a
diagram of your own system.
Make multiple copies of your composite diagram,
and use them for remembering good patches and
set-ups.
P • Draw in patchleads with colored
pens.
• Draw or write control settings in the
little white circles.
Audio In
Audio Out
A-128
50
10
0
75
10
0
110
10
0
150
10
0
220
10
0
FIXED FILTER BANK
350
10
0
0
0
0
0
0
500
10
0
750
10
0
1100
10
0
1600
10
0
2200
10
3600
10
5200
10
7500
10
11000
10
6
 Loading...
Loading...