Page 1
doepfer
System A - 100
1. Introduction
VC Phaser
A-125
Level
CV
Audio
In
CV 2
CV
Audio
Out
A-125
VCP
Shift
Resonance
Mix
Module A-125 (VC Phaser) is a voltage controlled
phase shifter.
Phase shifting can be controlled either manually or by
voltage control.
Other parameters which can be controlled are reso-
nance (governing the depth of the comb filtering, and
tonal color - see page 3) and
original signal which is added to the phase-shifted
signal).
(the amount of the
mix
1
Page 2
A-125
VC Phaser
System A - 100
doepfer
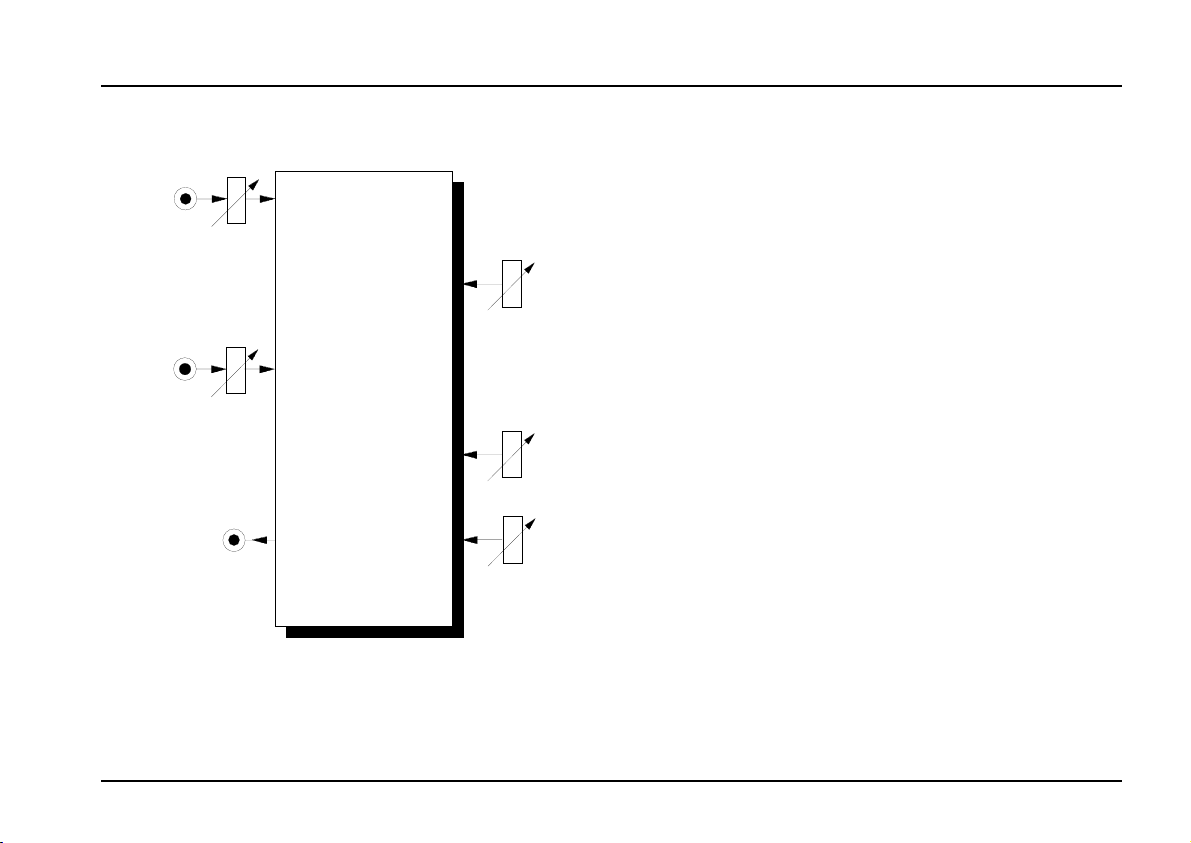
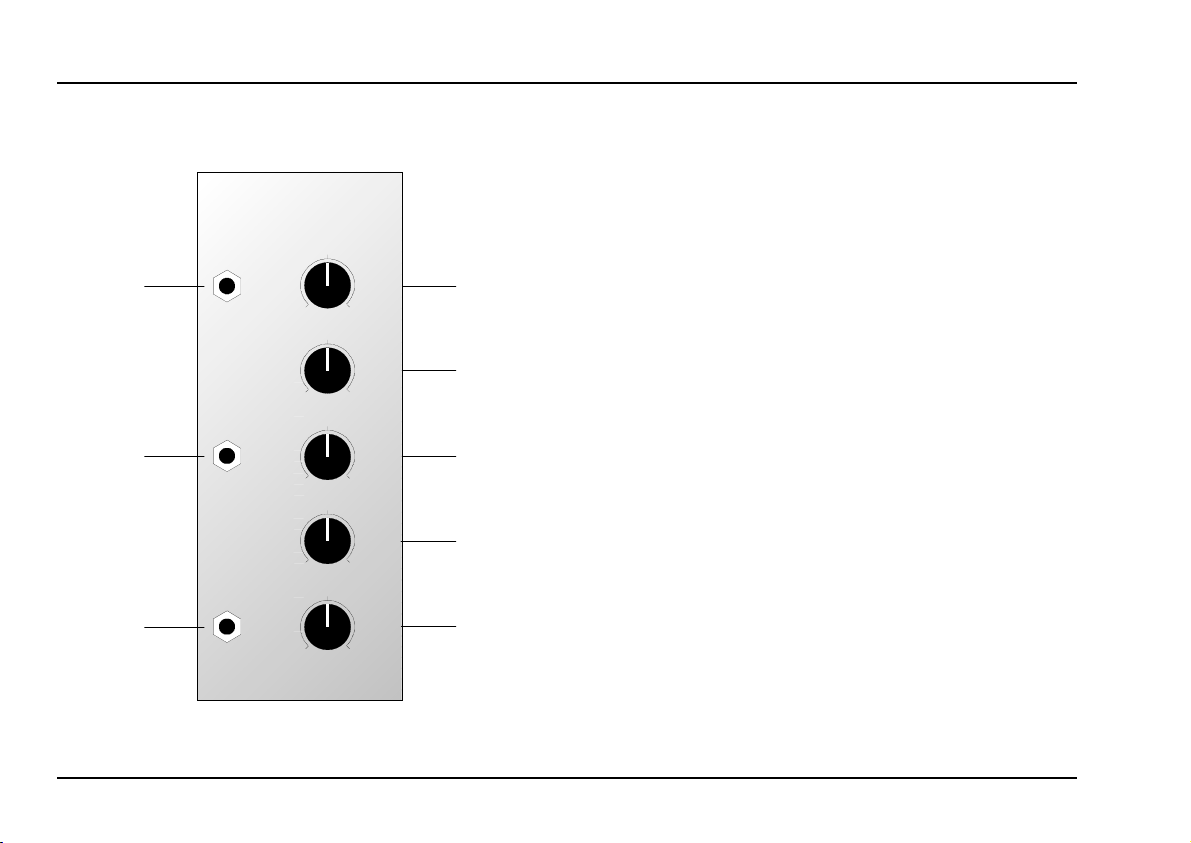
2. VC Phaser - Overview
A-125 VCP
VC PHASE SHIFTER
Audio In
0
0
CV
0
0
Audio Out
0
Level
10
Shift
10
10
Res.
10
Mix
10
CV
➀
➁
➂
➃
➄
Controls:
1 Level : Attenuator to control the level of the
signal at input
Shift : Control for manually setting the
2
!
amount of phase shift
: Attenuator for the phase shift voltage
CV
3
control signal at input
: Resonance control
Res.
4
Mix : Control for setting the amount of the
5
"
original signal added to the phaseshifted signal
In / Outputs:
Audio In : Audio input
!
" CV : Input for pitch-shift voltage control
Audio Out
§
: Audio output
2
Page 3
doepfer
System A - 100
VC Phaser
A-125
3. Basic principles
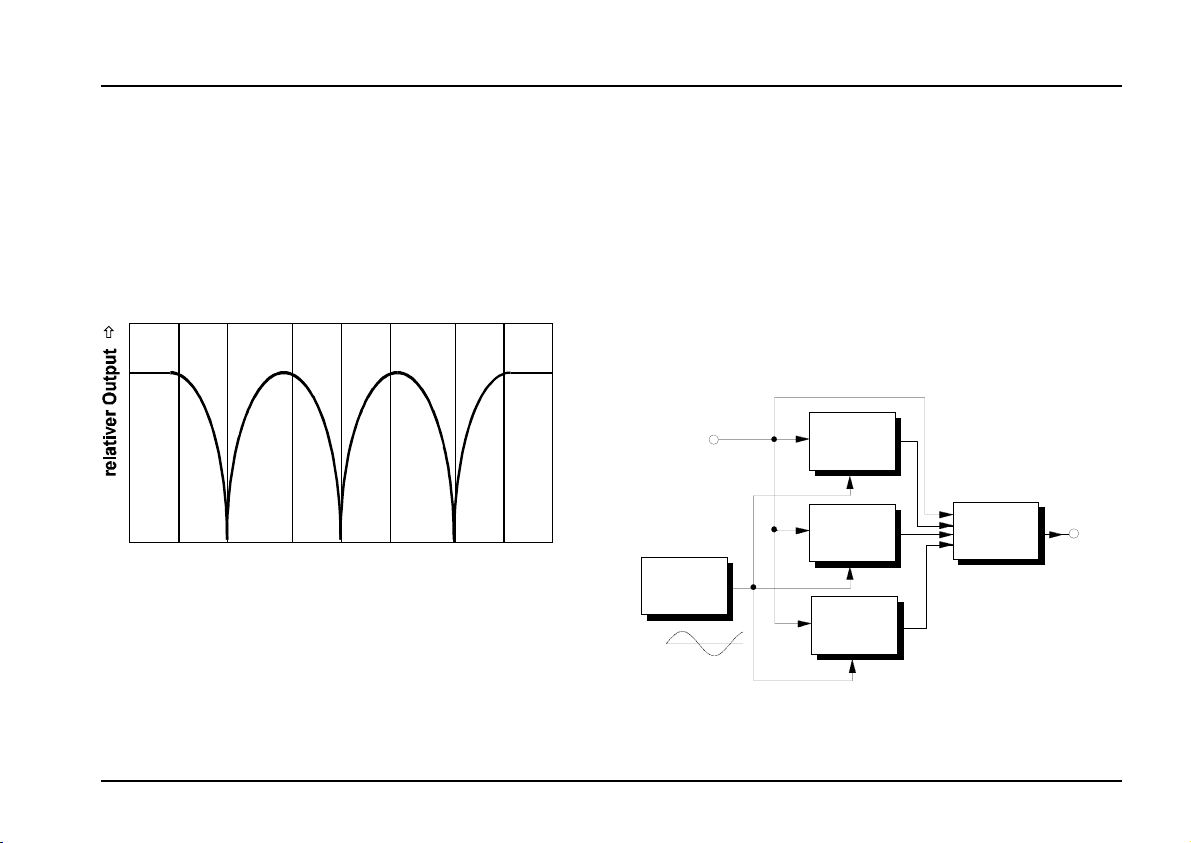
The phasing process relies on dynamic comb filtering.
The comb filtering produces a series of gaps in the
audio spectrum (in Fig. 1, at 200 Hz, 1 kHz and 5
kHz), by the cancelling process which is created byhaving identical sounds 180° out of phase with each
other (or ‘inverted’).
10k
20k
ÖÖÖÖ
50
100
200
500
1k
2k
5k
Frequenz [Hz]
Fig. 1: The principle of phasing
These zero points are continuously swept through the
audio spectrum, cancelling out different frequencies,
and producing the characteristic phasing sound.
The principle can be explained by looking at the diagram (Fig. 2) of a phaser created by three band pass
filters. Here, audio is input to the three filters BP1 to
BP3 (notch filters also work), set to different middle
frequencies. A slow LFO modulates the frequencies.
The outputs of the band pass filters are then mixed
with the original signal. Because of the phase reversal
inherent in the filter design (most apparent close to the
middle frequency), different areas of the audio
spectrum are cancelled out.
Audio In
BP 1
f = x Hz
c
BP 2
f = y Hz
c
Mixer
Out
LFO
BP 3
f = z Hz
f ~ 3 Hz
: A phaser model using separate modules
Fig. 2
c
3
Page 4

A-125
4. Controls
VC Phaser
System A - 100
1 Level
Attenuator 1 controls the level of the input signal.
doepfer
5 Mix
Use control 5 to determine the exact balance of
phase-shifted and original signal. From minimum to
maximum produces the following:
2 Shift
Phase shift amount is controlled with this knob, in a
range from around 0° to 180°.
3 CV
As well as manual phase shifting, a control voltage at
input " can modulate the shift. Attenuator 3 sets the
level of voltage control.
As a rule, a slowly changing signal (eg LFO, ADSR,
Random, etc.) is used for this modulation.
4 Res.
This knob controls the resonance - the amount of the
output signal fed back to the input. With this you can
control the exact depth of the signal cancellation (see
Fig. 1). The resonance parameter controls the tonecolour of the sound; you can’t use resonance to make
the phaser self-oscillate like on a VCF.
4
Mix = 0 : just phase-shifted signal - "phase /
vibrato": the signal sounds somehow skewed.
Mix = 10 : 50% phase-shifted + 50% original signal
- phasing: typical swooshy phaser sound.
P
Try out different settings for resonance and
mix, to see how what effect these parameters have on the sound.
Page 5
doepfer
System A - 100
VC Phaser
A-125
5. In / Outputs
! Audio In
Socket ! is the phaser’s audio input.
" CV
The control voltage for modulating the speed of phase
shifting is input at socket ". You can set the level of
this CV with control 3.
§ Audio Out
Output § has the mix of phase-shifted and original
signals determined by the position of control 5.
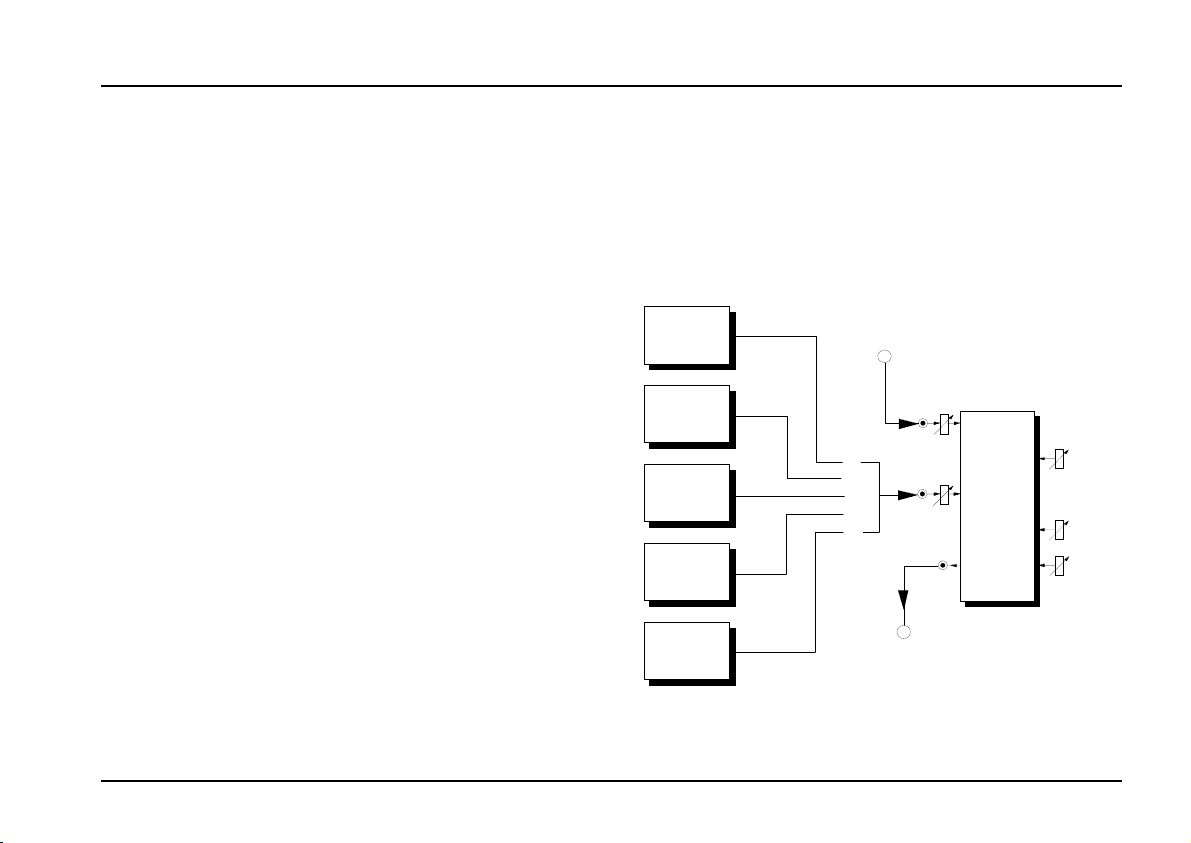
6. User examples
Standard set-up
Fig. 3 shows a typical patch, with various alternative
sources of slow-changing modulators affecting the
speed of the phase sweep.
LFO
ADSR
Random
S&H
A-190
CV 2
Audio In
1
2
3
4
5
alternativ
Audio Out
Level
CV
Audio
CV 2
CV
Audio
Out
In
A-125
VCP
Resonance
Shift
Mix
Fig. 3: Typical phaser application
5
Page 6

A-125
R
VC Phaser
System A - 100
doepfer
The phaser is simply inserted in the audio path like
this. For modulation sources, you could use, for
instance, any of the following:
Alter-
native
P
Module Adjustment Effect
1
2
3
4
5
LFO
A-145
ADSR
A-140
Random
A-118
S&H
A-148
A-190
CV 2
With the last two of these alternative modulators particularly, you can optionally use an
A-170 Slew Limiter after them, to smooth out
sudden jumps of control voltage, and make
the phasing transitions less abrupt.
low frequency
(< 2 Hz)
slow envelope keyboard-
slow random
rate
any MIDI controller for CV 2
(eg. velocity)
free-running
phase-shift
controlled phaser
random phasing
random phasing
MIDI - controlled
phasing
"Stereo"-Phasing
Using two A-125s and the patch in Fig. 4 you can
create a wide pseudo-stereo phasing effect, with inverted signals coming out of each of the two audio
channels (Out
Typically, you can use a slow LFO to provide the
modulation for the phase shift, but any other modulator
will work, as with standard phasing. Phaser VCP 1 is
fed the modulation from the LFO directly, while an
A-175 voltage inverter is patched in before the second
phaser VCP 2, to invert the modulation.
Audio
In
: "Stereo" phasing
Fig. 4
und OutR).
L
LFO
VCP 1
Out
CV
A-175
CV
VCP 2
Out
L
6
Page 7
doepfer
7. Patch-Sheet
System A - 100
VC Phaser
A-125
The following diagrams of the module can help
you recall your own Patches. They’re designed so
that a complete 19” rack of modules will fit onto an
A4 sheet of paper.
Photocopy this page, and cut out the pictures of
this and your other modules. You can then stick
them onto another piece of paper, and create a
diagram of your own system.
Make multiple copies of your composite diagram,
and use them for remembering good patches and
set-ups.
P • Draw in patchleads with colored
pens.
• Draw or write control settings in the
little white circles.
A-125 VCP
VC PHASE SHIFTER
Audio In
10
0
10
CV
Audio Out
0
10
0
10
0
10
0
Level
Shift
CV
Res.
Mix
A-125 VCP
VC PHASE SHIFTER
Audio In
10
0
10
CV
Audio Out
0
10
0
10
0
10
0
A-125 VCP
Audio In
Level
Shift
CV
CV
Res.
Audio Out
Mix
VC PHASE SHIFTER
Level
10
0
Shift
10
0
CV
10
0
Res.
10
0
Mix
10
0
7
Page 8

A-125
VC Phaser
System A - 100
doepfer
8
 Loading...
Loading...