Page 1
doepfer
A-117
System A - 100
1. Introduction
Module A-117 (DNG) is a combination module, including a
Digital Noise Generator A-117
digital noise generator
and an
808 source
.
DNG / 808
Noise/
Clo c k Out
Ext.
Clock In
Mix 2
Mix 6
Rate
The digital noise generator uses random sequences of
square waves, (18-band, with multiple slewed feedback loops), whose rate can go from
pure noise. The colour of the noise is very different
from the analog noise produced by the A-118.
In addition to a manual setting, the rate can be controlled by an external clock - eg. VCO, LFO or MIDI clock).
The 808 Source aims to re-create the sort of multi-
oscillator array
and 606 drum machines as the basis of the sound of
the hi-hat, cymbals and cowbell. The cowbell mix
uses two oscillators, and the cymbals mix six.
that was used in
random clicks
Roland’s TR-808
to
1
Page 2

A-117
Digital Noise Generator
System A - 100
doepfer
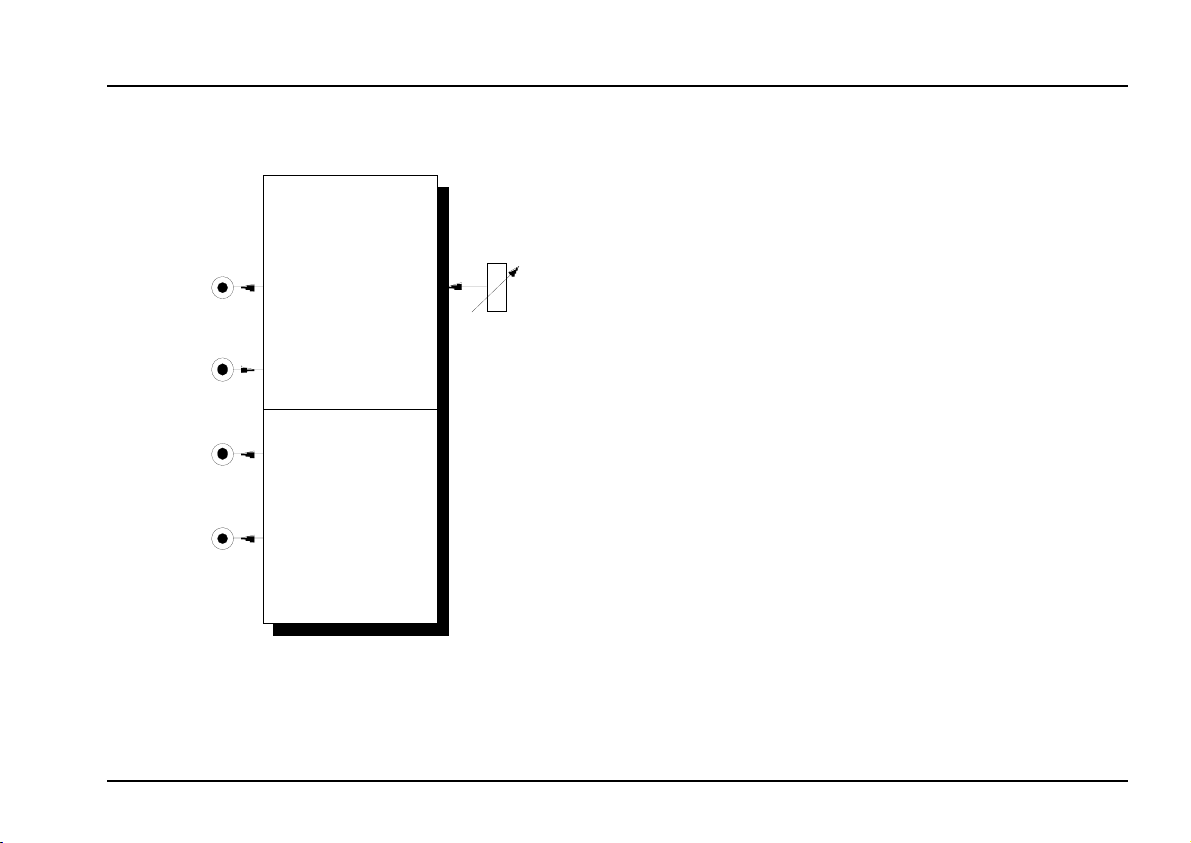
2. DNG / 808 - Overview
DNG
DIG. NOISE/ 808 Source
DNG /
RND CLK
➊
0
EXT. CLK
➋
808 Sound Source
➌
➍
6 Oscillators
2 Oscillators
Rate
10
➀
Controls:
: Pulse rate control for random clock /
Rate
1
noise output
!
In / Outputs:
! DNG / RND CLK : Output for random clock / digital
noise
EXT. CLK : Input for external clock signal
"
§ 6 Osc. : Output for 808 source (6 oscillators)
2 Osc. : Output for 808 source (2 oscillators)
$
2
Page 3

doepfer
System A - 100
Digital Noise Generator A-117
3. Controls
1 Rate
This is used to adjust the pulse rate of the random
clocks generated. At low pulse rates, individual pulses
can be heard (see Fig.1, top), but with higher pulse
rates (see Fig.1, bottom) the sound merges into
DNG/
Clock
Out
DNG/
Clock
Out
Fig. 1: A-117 output signals at different pulse rates
noise
4. In / Outputs
! DNG / RND CLK
Output !!!! produces random clock pulses or digital
noise, depending on the pulse rate set.
.
" EXT. CLK
Input " is a normalled socket, so that the rate knob
controls pulse rate, unless a signal is patched into this
socket.
This external clock can be provided eg., by a square
wave from a VCO or LFO, or from a MIDI clock, etc.. In
this case, control 1 has no effect. Pulse rate is then
simply decided by the frequency of the external clock.
§ 6 Oscillators
Output § delivers a six-oscillator mix, like the raw
material of the TR-808’s cymbal sound.
$ 2 Oscillators
Output $ delivers a two-oscillator mix, like the raw
material of the cowbell sound on the Roland TR-808.
3
Page 4

A-117
Digital Noise Generator
System A - 100
doepfer
5. User examples
Module A-117 is an inexhaustible source of scraping,
lip-smacking, bell or other untuned percussion sounds,
so the following examples should be taken just as
starting points for further experimentation.
Random clock pulses
With low pulse rate settings, the A-117’s output ! is a
source of randomly sequenced clicks or clocks. You
can use these for modulating a variety of things - for
instance the final ADSR in a patch, to produce sudden
sharp peaks in the filter cut-off point.
Alternatively, you can use the clock pulses to control
the voltage controlled switches A-150 and A-151, or
the
clock divider / sequencer
patches can be found in the manual sections fo r the
respective modules.
The patch in Fig. 2 shows another application, where
the clock pulses are used with a filter for sound
creation
It uses the ability of a filter to ‘ring’: if you patch a pulse
with a steep rising edge into a filter, it can set the filter
into a brief burst of resonance. Depending on the filter
.
A-160/161. Relevant
type, different settings of the cut-off point and resonance amount can lengthen a click into bell-like
sounds.
For example, if you use the 12dB band pass filter
output on the A-121, with the cut-off set at around 5,
and resonance set just below self-oscillation, you can
create effective dripping sounds. A slow LFO (c. 5
Hz) modulating the filter cut-off point, makes each drip
sound different.
A-117
Fig. 2
Use the filter’s resonance control to adjust the nature
of the sound, from a drier, cracking / clicking type of
sound (with little resonance) to a wetter, tinkly / belllike sound (with the resonance set high, just below
self-oscillation).
RND
ADSR
: random production of dripping sounds
A-121
6
FCV
LFO
4
Page 5

doepfer
Change the band pass for a high pass filter, put the
cut-off to high and the resonance to minimum, and
summon up a hailstorm.
System A - 100
A-117
Digital Noise Generator A-117
RND
VCA
A-138
P
Experiment with different filter kinds, and
settings for cut-off and resonance. You’ll
find all sorts of combinations of settings and
filter types that produce well usable percussion sounds.
The A-117 as noise generator
At higher pulse rates, digital noise is available at
output !. For example, you can add this unfiltered to
other sounds. In Fig. 3, a patch for an 808-like bass
drum sound uses a VCA, two ADSRs (one with a very
short envelope) and a band-pass filter, to create a
burst of bass energy. This standard bass drum sound
benefits from filter ringing - see above.
P Again, this basic patch will work well with
other filter types, and cut-off and resonance
settings, to produce different sounds like tom
and snare drums.
ADSR 1
Gate
Fig. 3: Producing bass drum sounds
ADSR 2
A-121
Band
"Playable" noise
If you patch a VCO’s square wave output into the
external clock input, the frequency of the digital noise
follows the pitch of the VCO, to produce a sort of
pitched noise. Best for this is the High End VCO
A-111, which has a greater usable frequency range
than the standard VCO A-110.
5
Page 6

A-117
Digital Noise Generator
System A - 100
"Octave noise"
Patch the digital noise into an A-115
and create extra sub-octave bands in the character
of the noise.
Audio Divider
A-117
2 Oscil.
A-121
Band
doepfer
VCA
P
The A-117’s digital noise is an excellent
sound source for the synthesis element in
the A-129 vocoder.
Producing percussion sounds á la TR-808
To produce a sound like the TR-808’s cowbell, use
output $ (2 oscillators). Fig. 4 shows the relevant
patch.
With that same patch, you can also produce hi-hat
and
cymbal
this case, the filter cut-off point neds to be about 10
kHz.
sounds, using output § (6 oscillators). IN
P Instead of the band pass filter, you can use a
low pass filter for the cowbell sound, and a
high pass filter will work for hi-hat and cymbal sounds.
Try other settings for filter cut-off and resonance, and other types of filter, to produce all
sorts of different percussive sounds.
6
ADSR
Gate
Fig. 4: producing a TR-808 cowbell sound.
Use full range digital noise as source material for
noises and percussive sound effects, patching it
into an A-128 fixed
is controlled by an ADSR. Experiment with all sorts of
different combinations of filter bank settings.
Another thought: the 6 oscillator signal at output § of
the A-117 works very well as an excellent sound
source
(A-129/2).
for the synthesis section of the A-129
filter bank
and VCA, which in turn
vocoder
Page 7

doepfer
System A - 100
Digital Noise Generator A-117
7
Page 8

A-117
Digital Noise Generator
6. Patch-Sheet
System A - 100
doepfer
The following diagrams of the module can help
you recall your own Patches. They’re designed so
that a complete 19” rack of modules will fit onto an
A4 sheet of paper.
Photocopy this page, and cut out the pictures of
this and your other modules. You can then stick
them onto another piece of paper, and create a
diagram of your own system.
Make multiple copies of your composite diagram,
and use them for remembering good patches and
set-ups.
P • Draw in patchleads with colored
pens.
• Draw or write control settings in the
little white circles.
DIG. NOISE/ 808 Source
DNG
DNG /
RND CLK
EXT. CLK
808 Sound Sou rce
6 Oscillators
2 Oscillators
Rate
10
0
DIG. NOISE/ 808 Source
DNG
DNG /
RND CLK
EXT. CLK
808 Sound Sou rce
6 Oscillators
2 Oscillators
Rate
10
0
DIG. NOISE/ 808 Source
DNG
DNG /
RND CLK
EXT. CLK
808 Sound Source
6 Oscillators
2 Oscillators
Rate
10
0
8
 Loading...
Loading...