Dodge Clutch SRM 2006 Service Manual
DR CLUTCH 6 - 1
CLUTCH
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CLUTCH
WARNING .....................................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH ....................................2
SPECIFICATIONS
CLUTCH ....................................5
SPECIAL TOOLS ...............................7
DISC-CLUTCH
REMOVAL .....................................8
INSTALLATION ................................9
ADJUSTMENTS
PRESSURE PLATE DIAPHRAGM SPRINGS . .. 10
DISC-CLUTCH SRT10
REMOVAL ....................................12
CLEANING ...................................12
INSTALLATION ...............................13
BEARING-CLUTCH RELEASE
REMOVAL ....................................14
INSTALLATION ...............................14
BEARING-CLUTCH RELEASE SRT10
REMOVAL ....................................15
INSTALLATION ...............................15
FLYWHEEL
DESCRIPTION ................................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FLYWHEEL .................................17
REMOVAL ....................................18
INSTALLATION ...............................18
FLYWHEEL-SRT10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FLYWHEEL-SRT10 ..........................19
REMOVAL ....................................19
INSTALLATION ...............................19
BEARING-PILOT
REMOVAL ....................................20
INSTALLATION ...............................20
LINKAGE
REMOVAL ....................................21
INSTALLATION ...............................21
LINKAGE-SRT10
REMOVAL ....................................23
INSTALLATION ...............................23
SWITCH-CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SWITCH-CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION .........25
SWITCH-CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SRT10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SWITCH-CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SRT10 . . 26
REMOVAL ....................................26
INSTALLATION ...............................27

6 - 2 CLUTCH DR
CLUTCH
WARNING
WARNING: Exercise care when servicing clutch components. Factory installed clutch discs do not contain
asbestos fibers. Dust and dirt on clutch parts may contain asbestos fibers from aftermarket components.
Breathing excessive concentrations of these fibers can cause serious bodily harm. Wear a respirator during
service and never clean clutch components with compressed air or with a dry brush. Either clean the components with water dampened rags or use a vacuum cleaner specifically designed to remove asbestos
fibers and dust. Do not create dust by sanding a clutch discs. Replace the disc if the friction material is
damaged. Dispose of all dust and dirt containing asbestos fibers in sealed bags or containers. This will
minimize exposure to yourself and to others. Follow all recommended safety practices prescribed by the
occupational safety and health administration (OSHA) and the environmental safety agency (EPA), for the
handling and disposal of products containing asbestos. Failure to follow these instructions may result in
personal injury or death
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH
Road test and inspect components to determine a clutch problem. Road test the vehicle at normal speeds. Shift the
transmission through all gear ranges and observe clutch action. If clutch chatters, grabs, slips or does not release
properly, remove and inspect clutch components. If problem is noise or hard shifting, further diagnosis may be
needed to the transmission and driveline component.
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION
Contamination is a frequent cause of clutch malfunctions. Oil, water or clutch fluid on the clutch disc and pressure
plate surfaces will cause chatter, slip and grab. Oil contamination indicates a leak at either the rear main seal or
transmission input shaft. Clutch fluid leaks are usually from damaged slave cylinder push rod seals. Heat buildup
caused by slippage between the pressure plate, disc and flywheel can bake the oil residue onto the components.
The glaze-like residue ranges in color from amber to black.
Road splash contamination is dirt/water entering the clutch housing due to loose bolts, housing cracks. Driving
through deep water puddles can force water/road splash into the housing through such openings.
IMPROPER RELEASE OR CLUTCH ENGAGEMENT
Clutch release or engagement problems can be caused by worn or damage clutch components.
Release problems can cause hard shifting and noise. Look for leaks at clutch cylinders, connecting line and loose
slave cylinder bolts. Also worn/loose release fork, pivot stud, clutch disc, pressure plate or release bearing.
Engagement problems can cause slip, chatter/shudder and noisy operation. The causes may be clutch disc con-
tamination, wear, distortion or flywheel damage.
CLUTCH MISALIGNMENT
Clutch components must be in proper alignment with the crankshaft and transmission input shaft. Misalignment
caused by excessive runout or warpage of any clutch component will cause grab, chatter and improper clutch
release.
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC RUNOUT
Check the clutch disc before installation. Axial (face) runout of a new disc should not exceed 0.50 mm (0.020 in.).
Measure runout about 6 mm (1/4 in.) from the outer edge of the disc facing. Obtain another disc if runout is excessive.
Check condition of the clutch before installation. A warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause grab and incomplete release or engagement. Be careful when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort the cover, diaphragm
spring, release fingers and the hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalignment which
could result in cover distortion and disc damage.
DR CLUTCH 6 - 3
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tightening.
FLYWHEEL RUNOUT
Check flywheel runout whenever misalignment is suspected. Flywheel runout should not exceed 0.08 mm (0.003
in.). Measure runout at the outer edge of the flywheel face with a dial indicator.
Common causes of runout are:
• heat warpage
• improper machining
• incorrect bolt tightening
• improper seating on crankshaft flange shoulder
• foreign material on crankshaft flange
Flywheel machining is not recommended. The flywheel clutch surface is machined to a unique contour and machining will negate this feature. Minor flywheel scoring can be cleaned up by hand with 180 grit emery or with turning
equipment. Remove only enough material to reduce scoring (approximately 0.001 - 0.003 in.). Heavy stock removal
is not recommended. Replace the flywheel if scoring is severe and deeper than 0.076 mm (0.003 in.). Excessive
stock removal can result in flywheel cracking or warpage after installation; it can also weaken the flywheel and
interfere with proper clutch release.
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the flywheel. Dirt and grease on the flange surface may cock the flywheel causing excessive runout. Use new bolts when remounting a flywheel and secure the bolts with Mopar™
Lock And Seal or equivalent. Tighten flywheel bolts to specified torque only. Overtightening can distort the flywheel
hub causing runout.
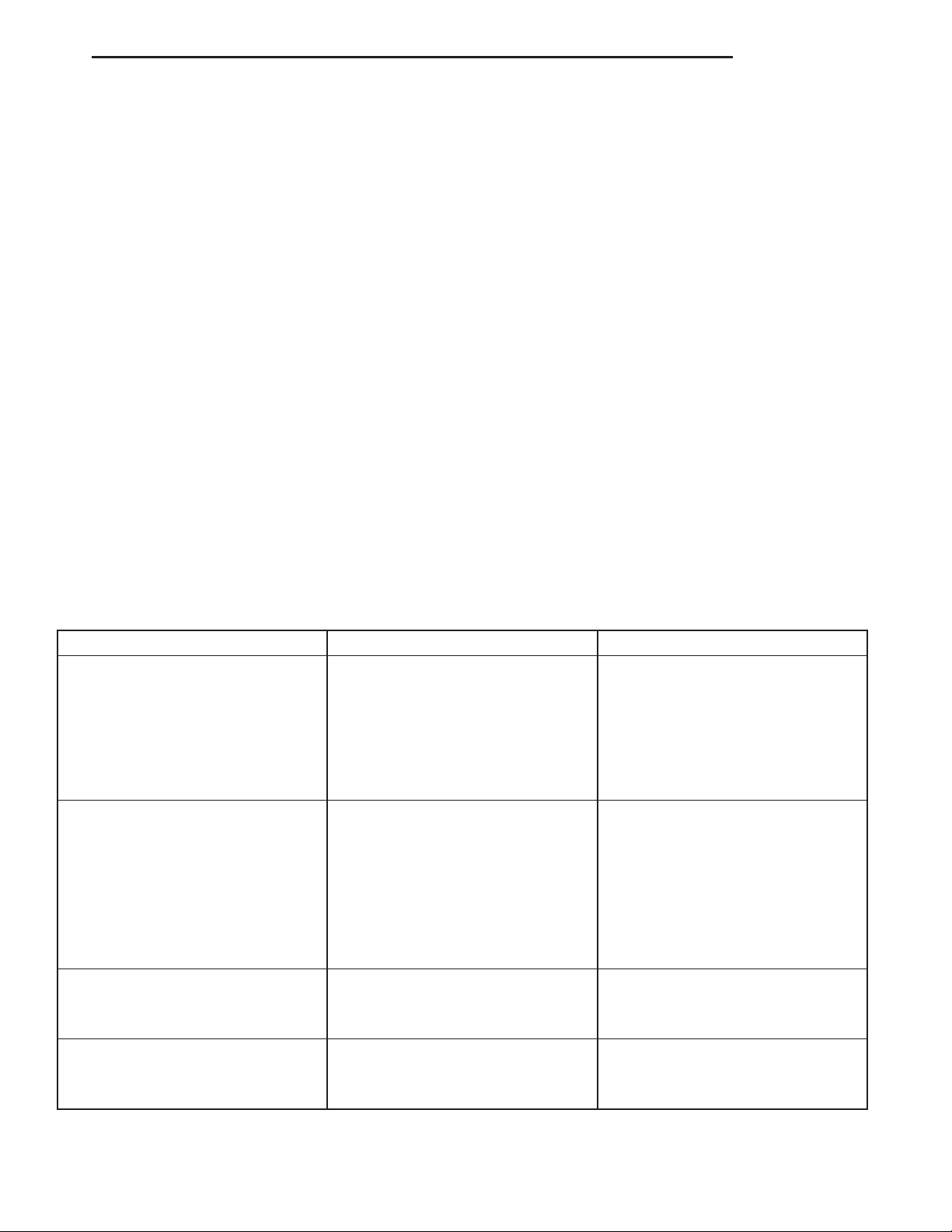
DIAGNOSIS CHART
The diagnosis charts Diagnosis Chart describe common clutch problems, causes and correction.
Diagnosis Chart
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Disc facing worn out 1. Normal wear. 1. Replace cover and disc.
Clutch disc facing contaminated with
oil, grease, or clutch fluid.
Clutch is running partially
disengaged.
2. Driver frequently rides (slips) the
clutch. Results in rapid overheating
and wear.
3. Insufficient clutch cover
diaphragm spring tension.
1. Leak at rear main engine seal or
transmission input shaft seal.
2. Excessive amount of grease
applied to the input shaft splines.
3. Road splash, water entering
housing.
4. Slave cylinder leaking. 4. Replace hydraulic clutch linkage.
1. Release bearing sticking or
binding and does not return to the
normal running position.
2. Replace cover and disc.
3. Replace cover and disc.
1. Replace appropriate seal.
2. Remove grease and apply the
correct amount of grease.
3. Replace clutch disc. Clean clutch
cover and reuse if in good condition.
1. Verify failure. Replace the release
bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer as necessary.
Flywheel below minimum thickness
specification.
1. Improper flywheel machining.
Flywheel has excessive taper or
excessive material removal.
1. Replace flywheel.
6 - 4 CLUTCH DR
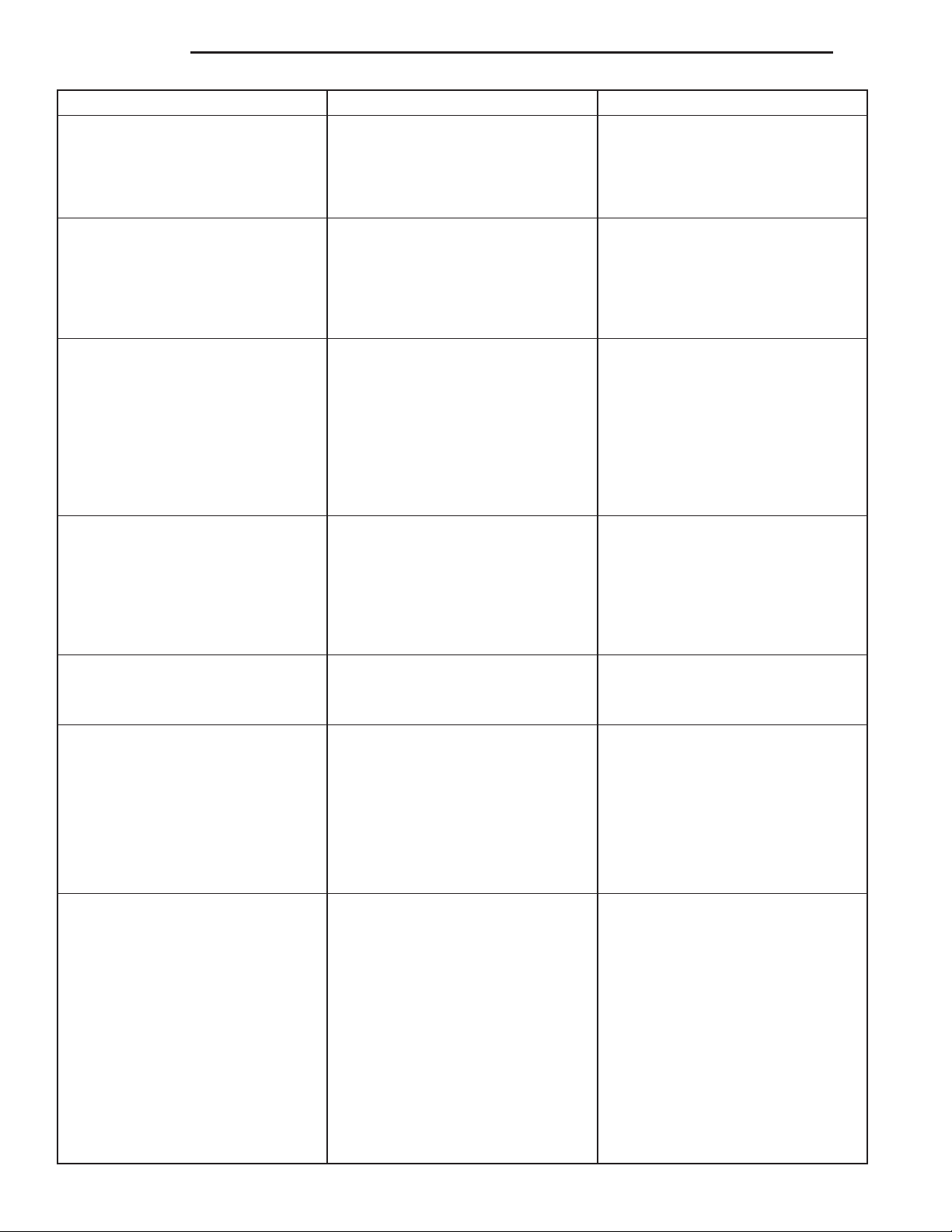
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Clutch disc, cover or diaphragm
spring warped or distorted.
Facing on flywheel side of disc torn,
gouged or worn.
Clutch disc facing burnt. Flywheel
and cover pressure plate surfaces
heavily glazed.
Clutch disc binds on input shaft
splines.
1. Rough handling. Impact bent
cover, spring, or disc.
2. Improper bolt tightening
procedure.
1. Flywheel surface scored or
nicked.
2. Clutch disc sticking or binding on
transmission input shaft.
1. Frequent operation under high
loads or hard acceleration
conditions.
2. Driver frequently rides (slips)
clutch. Results in rapid wear and
overheating of disc and cover.
1. Clutch disc hub splines damaged
during installation.
1. Replace disc or cover as
necessary.
2. Tighten clutch cover using proper
procedure.
1. Correct surface condition if
possible. Replace flywheel and disc
as necessary.
2. Inspect components and
correct/replace as necessary.
1. Correct condition of flywheel and
pressure plate surface. Replace
clutch cover and disc. Alert driver to
problem cause.
2. Correct condition of flywheel and
pressure plate surface. Replace
clutch cover and disc. Alert driver to
problem cause.
1. Clean, smooth and lubricate hub
splines if possible. Replace disc if
necessary.
2. Input shaft splines rough,
damaged, or corroded.
Clutch disc rusted to flywheel or
pressure plate.
Pilot bearing seized, loose or rollers
are worn.
Clutch will not disengage properly. 1. Low hydraulic linkage fluid level. 1. Add hydraulic linkage fluid.
1. Clutch not used for an extended
period of time (e.g. long term
vehicle storage).
1. Bearing cocked during
installation.
2. Bearing defective. 2. Install a new bearing.
3. Bearing not lubricated. 3. Install a new bearing.
4. Clutch misalignment. 4. Inspect clutch and correct as
2. Clutch cover loose. 2. Follow proper bolt tightening
3. Clutch disc bent or distorted. 3. Replace clutch disc.
4. Clutch cover diaphragm spring
bent or warped.
5. Clutch disc installed backwards. 5. Remove and install clutch disc
6. Release fork bent or fork pivot
loose or damaged.
7. Clutch master or slave cylinder
failure.
2. Clean, smooth, and lubricate
shaft splines if possible. Replace
input shaft if necessary.
1. Sand rusted surfaces with 180
grit sanding paper. Replace clutch
cover and flywheel if necessary.
1. Install a new bearing.
necessary. Install and lubricate a
new bearing.
procedure.
4. Replace clutch cover.
correctly.
6. Replace fork or pivot as
necessary.
7. Replace hydraulic linkage
assembly.
DR CLUTCH 6 - 5
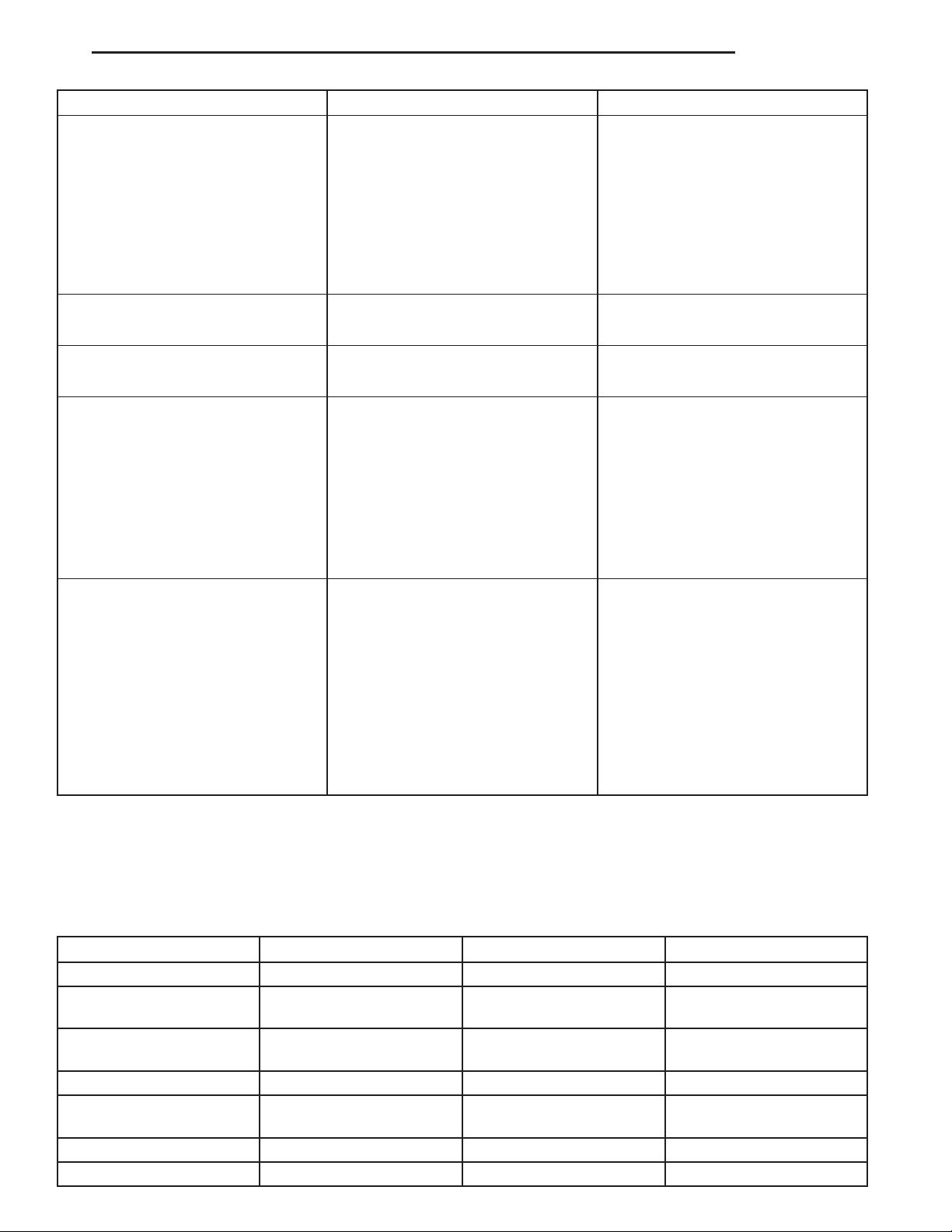
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Clutch pedal squeak. 1. Pivot pin loose. 1. Tighten pivot pin if possible.
Replace clutch pedal if necessary.
2. Master cylinder bushing not
lubricated.
3. Pedal bushings worn out or
cracked.
4. Rough surface on front bearing
retainer.
2. Lubricate master cylinder
bushing.
3. Replace and lubricate bushings.
4. Replace front bearing retainer.
Clutch master or slave cylinder
plunger dragging or binding
Release bearing is noisy. 1. Release bearing defective or
Contact surface of release bearing
damaged.
Partial engagement of clutch disc.
One side of disc is worn and the
other side is glazed and lightly
worn.
1. Master or slave cylinder
components worn or corroded.
damaged.
1. Clutch cover incorrect or release
fingers bent or distorted.
2. Release bearing defective or
damaged.
3. Release bearing misaligned. 3. Check and correct runout of
1. Clutch pressure plate position
incorrect.
2. Clutch cover, spring, or release
fingers bent or distorted.
3. Clutch disc damaged or
distorted.
4. Clutch misalignment. 4. Check alignment and runout of
1. Replace clutch hydraulic linkage
assembly.
1. Replace release bearing.
1. Replace clutch cover and release
bearing.
2. Replace the release bearing.
clutch components. Check front
bearing sleeve for damage/
alignment. Repair as necessary.
1. Replace clutch disc and cover.
2. Replace clutch disc and cover.
2. Replace clutch disc.
flywheel, disc, pressure plate and
clutch housing. Correct as
necessary.
SPECIFICATIONS
CLUTCH
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N·m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Slave Cylinder Nuts 23 17 -
Clutch Master Cylinder
Nuts
Pressure Plate Bolts - V6
&V8
Pressure Plate Bolts - V10 30 22 -
Pressure Plate Bolts -
Diesel
Release Bearing Pivot 23 17 -
Flywheel Bolts 95 70 -
28 21 -
50 37 -
30 22 -
6 - 6 CLUTCH DR
DESCRIPTION N·m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Dual Mass Flywheel To
Adapter Bolts
Dual Mass Flywheel
Adapter To Crankshaft
Bolts
55 40 -
137 100 -

DR CLUTCH 6 - 7
SPECIAL TOOLS
LINE DISCONNECT TOOL 6638A
6 - 8 CLUTCH DR
DISC-CLUTCH
REMOVAL
1. Support engine with wood block and adjustable
jack stand, to prevent strain on engine mounts.
2. Remove transmission and transfer case, if
equipped.
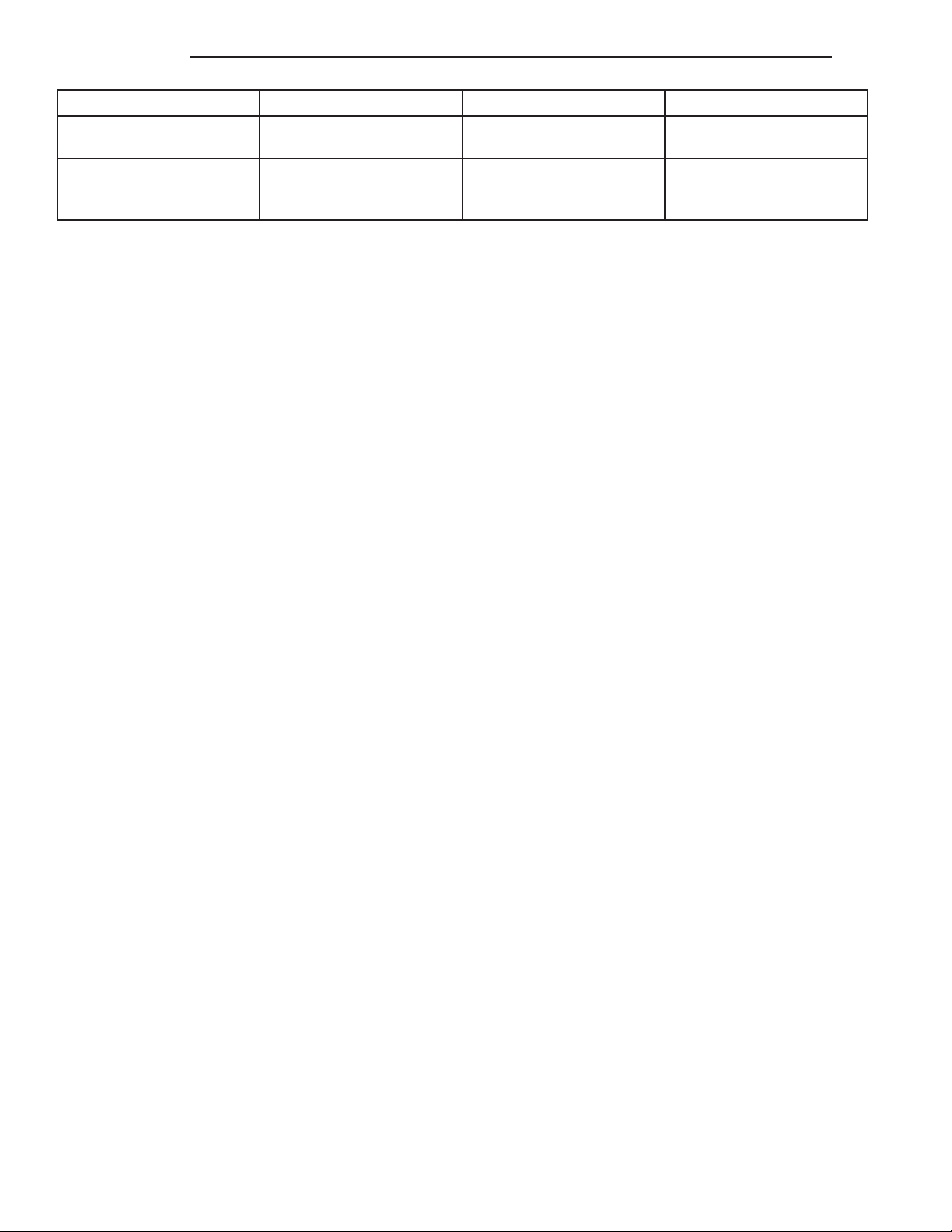
3. If pressure plate (3) will be reused, mark (2) the
position on flywheel (1) with paint or scriber. Also
note location marks on the pressure next to the
bolt holes. The mark will be a L or a circle with an
Xinit.
4. Insert clutch alignment tool (3) through pressure
plate (2) and into pilot bushing, to hold disc in
place while removing bolts.
5. Loosen pressure plate bolts evenly, a few threads
at a time and in a diagonal pattern to prevent warping the plate.
6. Remove bolts completely and remove pressure
plate, disc and alignment tool.
DR CLUTCH 6 - 9
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Before installing a clutch disc on 5.9 L
Diesel with Dual Mass Flywheel and self-adjusting
pressure plate, the pressure plate must be reset.
Failure to reset the pressure will result in damage
to the clutch disc.
1. Check runout and free operation of new clutch
disc.
2. Lubricate crankshaft pilot bearing with a NLGI - 2
rated grease.
3. Install clutch alignment tool in clutch disc hub with
the raised side of hub is facing away from the flywheel.
NOTE: Flywheel side is imprinted on the disc face.
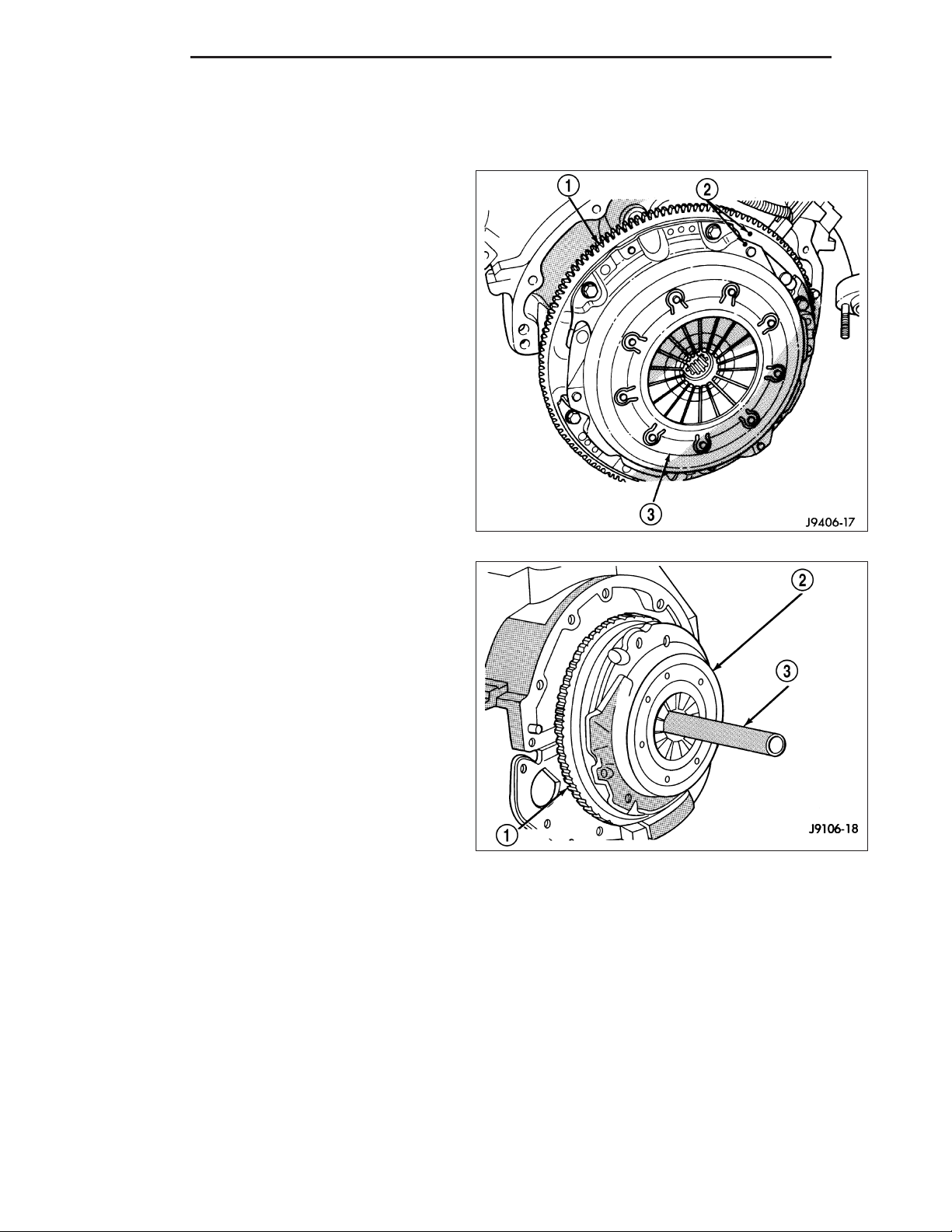
4. Install alignment tool (3) in pilot bearing and position disc on the flywheel (1).
5. Position pressure plate over disc (2) and onto the flywheel.
6. Align and hold pressure plate in position and install bolts finger tight.
7. Tighten bolts evenly and a few threads at a time in a diagonal pattern.
CAUTION: Bolts must be tightened evenly and to specified torque to avoid warping pressure plate cover.
8. Tighten pressure plate bolts to:
• V6 & V8 Engines - 50 N·m (37 ft. lbs.)
• V10 & Diesel Engines - 30 N·m (22 ft. lbs.)
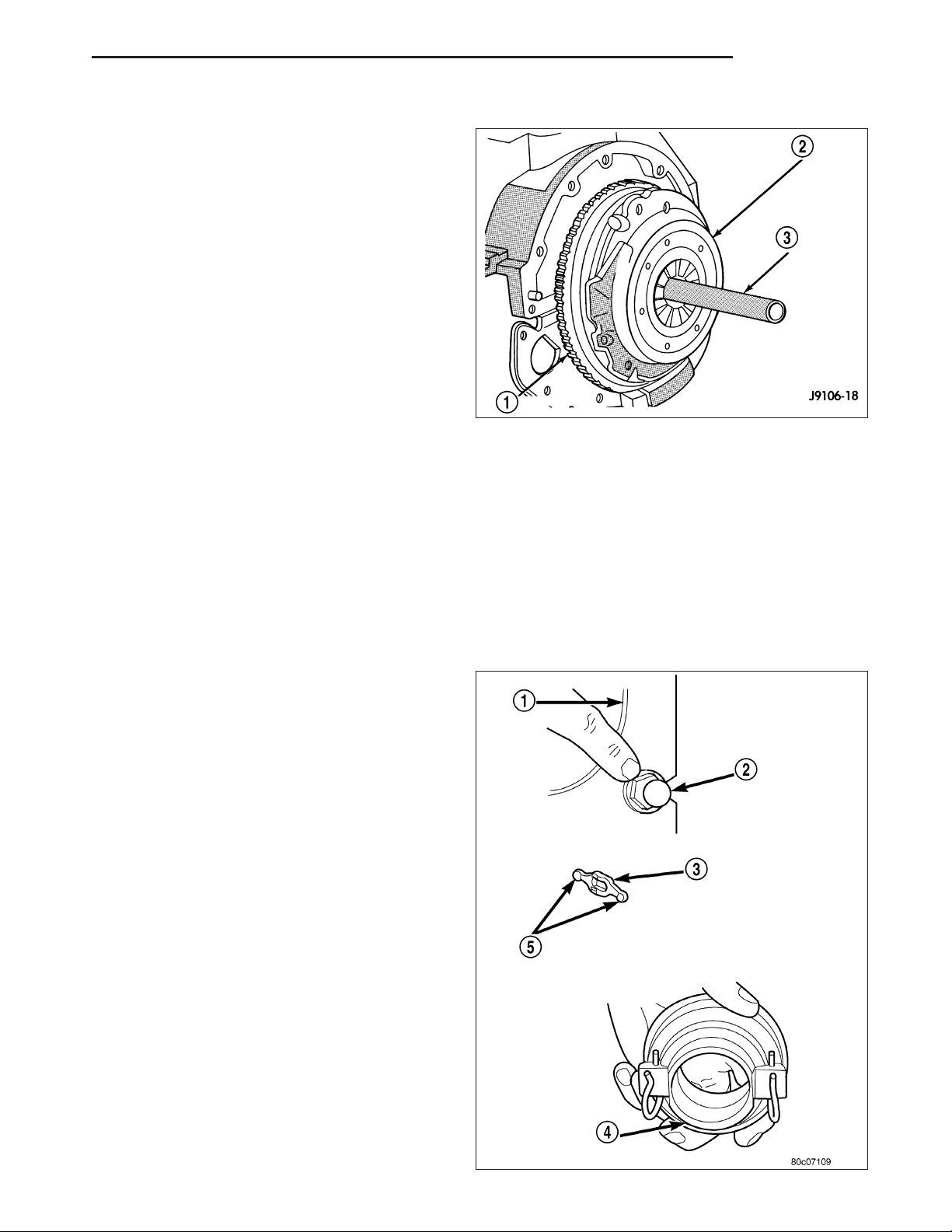
9. Remove release lever (3) and release bearing from
clutch housing (1). Apply Mopar™ high temperature
bearing grease to bore (4) of release bearing,
release lever (5) contact surfaces and release lever
pivot stud (2).
 Loading...
Loading...