
CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 1
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
DKTCOMEGA CPE User Documentation

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 2
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Table of content
Introduction ................................................................................................................................ 3
The boot process of the CPE node ............................................................................................ 4
DHCP Settings ...................................................................................................................... 6
TFTP Settings ....................................................................................................................... 9
Custom configuration .......................................................................................................... 11
Device script commands .......................................................................................................... 13
Explanation of feature settings ................................................................................................ 19
VLAN settings ..................................................................................................................... 19
Provider mode (Double tagging, Q-in-Q) ............................................................................. 21
Isolate LAN ports ................................................................................................................. 22
Enable LAN ......................................................................................................................... 22
Set LAN Port Speed ............................................................................................................ 23
Set Port MTU size ............................................................................................................... 23
IGMP snooping ................................................................................................................... 23
Ingress rate limitation .......................................................................................................... 25
Egress rate limitation ........................................................................................................... 28
Configuration of SNMP values ............................................................................................ 28
Syslog ................................................................................................................................. 28
Surveillance via SNMP ........................................................................................................ 29
CATV setup ......................................................................................................................... 29
Quality of Service (QoS) ...................................................................................................... 30
Reboot ................................................................................................................................. 32
Save configuration to flash .................................................................................................. 32
DHCP Option 82 ................................................................................................................. 33
LLDP/EDP/CDP .................................................................................................................. 34
Support for SSH .................................................................................................................. 35
VoIP ATA Plug-in module ........................................................................................................ 38
DHCP/TFTP based provisioning ......................................................................................... 38
Web Interface ...................................................................................................................... 39
System Parameters ............................................................................................................. 39
VoIP Accounts ..................................................................................................................... 44
VoIP Parameters ................................................................................................................. 45
SIP Parameters ................................................................................................................... 46
IPBX Parameters ................................................................................................................ 48
Regionalization .................................................................................................................... 50
Subscription Services .......................................................................................................... 56
User Configuration .............................................................................................................. 62
Feature Code Assignments (*55 - *99) ................................................................................ 64
Wifi Plug-in module .................................................................................................................. 66
TFTP based provisioning .................................................................................................... 66
System Parameters ............................................................................................................. 66
Appendix 1 – ATA configuration file ......................................................................................... 73
Appendix 2 – Wifi configuration file .......................................................................................... 90

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 3
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Introduction
This is the documentation of the DKTCOMEGA managed CPE product line.
The hardware consists of a switch with a fiber WAN port and 4 RJ45 LAN ports.
These ports are connected together with a powerful programmable layer 2 switch.
A CPU is attached to the switch. Initial the switch is setup only to accept traffic
between the CPU and the WAN port, first in the end of the CPU boot process are
the LAN ports enabled.
As an option a VoIP (SIP based) plug-in module can be installed, which will give 2x
RJ-11 analogue phone connections.
The CPE is provisioned via DHCP/TFTP, however also SNMP can be used to for
surveillance and settings.
Following DKTCOMEGA product codes are supported:
10/100 Mbps #79204, from now on referred to as 100Mb
100/1000 Mbps #79403, from now on referred to as 1Gb
10/100 Mbps w/ VoIP #79265
100/1000 Mbps w/ VoIP #79275
100/1000 Mbps w/ VoIP + Wifi #79550, special release only!
VoIP Plug-in module #65699, for now on referred to as VoIP

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 4
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
The boot process of the CPE node
The boot process is split in two:
- First the node issue a dhcp request with dhcp option 60 set to <file
name>vx_xx (where x_xx is the version number of the firmware).
- Afterwards the node start it's operation system (OS). The OS also issue a dhcp
request, with dhcp option 60 set to the version of the software.
When a new node is unpacked it doesn’t contain any firmware, and before it can
be used in must be updated with the latest revision. This mean that when the
node is installed at the customer premise, it will be required to remotely update
with firmware, before it will be working. It is highly recommended to visit
www.dktcomega.com -> support -> firmware for latest boot loader and firmware
revision.
The managed node depends on DHCP negotiation. Through this negotiation the
firmware ID of the managed node is exchanged for a configuration file. The DHCP
server hands out the configuration file depending on the firmware ID.
Bootstrap (Part of boot loader).
A small piece of code that is able to setup critical CPU specific registers such as
CPU clock, flash interface and SDRAM timing. The bootstrap code is automatically
loaded by the CPU into internal RAM of the CPU and executed. Bootstrap loads a
larger general boot-loader; U-boot.
U-boot (Part of boot loader).
This is a larger chunk of boot-loader software, which is able to setup network and
other more complex features of the CPU. U-boot use DHCP to get network setup.
U-boot is able to download firmware updates using TFTP.
Linux (Main Firmware).
This is the main software with full network support and features to use the
complete hardware platform. The network is configured using DHCP, and the
system configuration is downloaded using TFTP.
The first bootp/dhcp request from the device can be used to remote upgrade the
firmware. If a bootfile and a bootserver is given in the bootp response then the file
is downloaded via tftp and executed by the device.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 5
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
The device is configured to not pass any traffic per default, so in order to pass
traffic through the switch engine, the switch --enable-lan command must be
provisioned to the device. Also telnet daemon must be started, with the use of
telnetd -l /bin/sh command in the script
DHCP
DKTCOMEGA
DHCP Discover – Vendor class ID (DKT_Firstboot, option 60)
DHCP Offer – IP Address + DKT_firmware info (filename, server info, etc)
TFTP Request – ”filename”
TFTP transfer of firmware
DHCP Discover – configuration (option 66, 67)
DHCP Offer – configuration (filename, server info, etc)
TFTP Request – ”configuration”
TFTP transfer of configuration
Ensures correct device settings and automatically firmware upgrade without user interaction
Firmware and configuration are provisioned by the operator
}
At device start-up
configuration is
provisioned automatically.
Firmware is provisioned
by request, either at first
boot or when applicable
DHCP Request – request parameter list, incl network info
DHCP Release – Release IP
DHCP ACK – respond parameter list, incl network info + “file name”
DHCP Request – request parameter list, incl network info
DHCP ACK – respond parameter list, incl network info + “configuration”
Bo
ot
lo
ad
Li
nu

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 6
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
DHCP Settings
The CPE requires a dhcp server connected to the fiber WAN port before power on.
As an example we have used Linux Kubunto platform and installed the following
component via adept
dhcp3
tftpd
Make sure that DHCP server has its unique static IP address settings, so it doesn’t
conflict with its own leasing of IP Addresses.
It is important that the DHCP server is properly configured, and that it responds to
the DHCP options requested by the CPE. Otherwise communication with the
internal CPU of the CPE can’t be obtained.
For more information about DHCP options in dhcp3, please refer to:
http://pwet.fr/man/linux/formats/dhcp_options
1) CPE requests in its BOOTLOADER discoverer:
Option: 53, 57, 60, 55
2) DHCP Server offers in it responses:
Option: 53, 54, 51, 1, 3

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 7
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
3) CPE requests in its LINUX Boot-up process, where configuration file is requested:
Option: 53, 61, 60, 50, 54, 55, 1, 3, 28, 66, 67
To edit DHCP Server Setup for dhcp3, edit the DHCP setup configuration file:
sudo kate /etc/dhcp3/dhcpd.conf
# DHCP SECTION: insert the following

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 8
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
default-lease-time <SECONDS>;
# Ex: default-lease-time 600
max-lease-time <SECONDS>;
# Ex: max-lease-time 7200
# --------------FIRMWARE UPGRADE PART -----------------
class "Upgrade Firmware after boot loader upgrade" {
match if option vendor-class-identifier = "DKT_firstboot";
filename = "dkt_fw_02_01.img";
}
# DHCP request in U-boot has got an option 43 field with
bootloader/U-boot software version information (ex. the text string
"14" for revision 1.4). This information is available from boot
loader revision 2_00 and forward
---# --------------- END OF UPGRADE -------------------
# The following is needed in order for the CPE to download the
configuration. Remember to place this configuration file in TFTPBOOT
directory. Remember to assign correct eth interface, subnet/mask, IP
address range, TFTP-server name and bootfile-name below
subnet <Subnet> netmask <Subnet mask> #
Ex: subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
{
interface <Ethernet Interface>;
# Ex. interface eth0
range <Min IP Address> <Max IP Address>;
# Ex: range 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.30
option tftp-server-name "<TFTP Server IP Address>";

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 9
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# Ex: option tftp-server-name “192.168.1.1”
option bootfile-name "<Configuration_File_Name";
# Ex: option bootfile-name “cpe_settings.txt”
option broadcast-address <Broadcast IP Address>;
# Ex: option broadcast-address 192.168.1.255
option routers <Router IP Address>;
# Ex: option routers 192.168.1.1
server-name "<Server IP Address Name>";
# Ex: server-name “192.168.1.1”
option next-server <Server IP Address Name>;
# Ex: next-server 192.168.1.1
option subnet-mask <Subnet Mask>;
# Ex: option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0
}
To restart DHCP Server
Any change in the dchp configuration implies a server reset. For the
DHCP server used for this purpose the following instruction is
necessary:
sudo /etc/init.d/dhcp3-server restart
TFTP Settings
After the DHCP server is configured a TFTP server should be configured, so
firmware image and configuration file for the CPE can be downloaded correctly.
As an example we have used Linux tftpd and xinetd
The TFTP configuration file must be edited. And a tftpboot directory must be
created in root and made accessible from CPEs
mkdir tftpboot

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 10
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# creates tftpboot directory
chmod a+wrx tftpboot
# changes rights so directory is readable, writeable and executable
from CPEs
sudo kate /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
# starts an editor where TFTP settings can be inserted
Insert the following:
service tftp
{
protocol = udp
port = 69
# CONFIGURATION FILE SECTION: insert the following
socket_type = dgram
wait = yes
user = nobody
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = /tftpboot
disable = no
}

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 11
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Custom configuration
When the OS issue a dhcp request a filename of a configuration file can be sent to
the node. This configuration file is then downloaded by tftp during the boot
process and issued instead of the default configuration. In this way it is possible to
persist settings for each customer (by mapping the hardware address of the node
and the customer number).
The server and the filename of the configuration file should be sent in respective
tftp-server-name (option 66) and bootfile-name (option 67) from the dhcp server.
Notice these options are different from the bootfile/bootserver used in the bootp
response.
If it is not feasible that the dhcp server distinguish the customers configurations
base on the hardware address an alternativ method can be used. The dhcp server
sends out the name of a generic configuration. This configuration can then include
instruction to the node of fetching a node specific configure by tftp where the
requested filename is a combination of the node hardware address.
In the generic configuration script, which is common for all devices and that will
provisioned during boot up, the following instructions can be inserted:
source /etc/dhcp.vars
export WAN_MACADDR=$(ip addr show dev eth0 | grep "ether" | cut -d "
" -f6 | tr -d :)
tftp -g -r my_conf_$WAN_MACADDR -l /tmp/config.sh $TFTP_SERVER
save_configuration
source /tmp/config.sh
An example of a configuration file1 could be the following:
####################################################################
# DKT configuration
# Firmware version: 02_05
####################################################################
switch --enable-lan # enable LAN ports
# VLAN SETTINGS FOR WAN PORT
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=0:2
# Sets the WAN port in check mode, allows untagged on
ingress if VID (incl default) is present in VTU
switch --set-port-default-vid=0:102
# Default VLAN for WAN port
switch --add-vtu-entry 102:2:1:1:1:1:2:0
# Management VLAN, enables contact to CPU - untagged on
egress
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=1:3
# Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=2:3
1
Please notice that text editors using Carrier Return for each line is NOT supported. The text editor should use
Line Feed for line separation.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 12
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=3:3
# Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=4:3
# Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --add-vtu-entry 104:3:2:2:1:1:2:0
# put WAN and LAN port into VLAN - untagged on egress,
IPTV VLAN
switch --set-port-default-vid=1:104
# Default VLAN for LAN port 1, IPTV VLAN
switch --set-port-default-vid=2:104
# Default VLAN for LAN port 2, IPTV VLAN
switch --add-vtu-entry 106:3:1:1:2:1:2:0
# put WAN and LAN port into VLAN - untagged on egress,
DATA VLAN
switch --set-port-default-vid=3:106
# Default VLAN for LAN port 3, DATA VLAN
switch --add-vtu-entry 105:3:1:1:1:2:2:0
# put WAN and LAN port into VLAN - untagged on egress,
VoIP VLAN
switch --set-port-default-vid=4:105
# Default VLAN for LAN port 4, VoIP VLAN
#
# QoS Settings
#Uplink rate (DATA port 3 and 4, ingress rates of 1 Mbps)
switch --set-port-ingress-rate-limit 3:0:1000:3:FC
# port=3, bucket=0, rate=1000kb/S,
bytecounter=layer3,limitaction=flowcontrol
switch --port-map-to-pirl-bucket 4:0
# join port 4 to bucket 0. Please notice that thisfeature
is NOT valid for the Gigabit CPE
#Downlink rate (Total for WAN 2Mbps)
switch --set-port-ingress-rate-limit 0:1:2000:3:FC
# port=0(WAN), bucket=0, rate=2Mb/S, bytecounter=layer3,
limitaction=flowcontrol
#
# Turn CATV module off
switch -c 0
#
# The following command enables TELNET access from WAN
telnetd -l /bin/sh
# End of DKT configuration
####################################################################

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 13
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Device script commands
The following commands are supported in the script that will be
downloaded to the CPE via TFTP during boot-up process.
This command is used to configure the switch in the unit. The command
takes one or more of the following parameters, with the syntax switch --
nn.
Please note that the commands are valid from firmware version 01_06 or
later.
Basic settings:
-s, --simple-switch
Setup port based VLAN for a simple switch.
-e, --enable-lan
Enables LAN ports so traffic can be switched between WAN and LAN.
-v, --version
Prints the firmware version number.
-h, --help
Prints this help text.
--set-arp-mirroring=PORT:enable
Enable/disable ARP mirroring to the CPU port, works from firmware
revision 02_13 and later
--get-arp-mirroring=PORT
Get state of ARP mirroring to the CPU port, works from firmware
revision 02_13 and later
CATV:
-c, --catv=(1|0)
Turns on/off the CATV module.
Unicast:
--add-uca=PORT:aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff
Adds the Ethernet address statically into the ATU.
--del-uca=aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff
Removes the Ethernet address from the ATU.
--dump-atu
Dumps the current content of the ATU, Ethernet addresses and Port
no.
Multicast:
--add-mca=PORT:aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
Adds the IP multicast address statically to the ATU.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 14
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
--del-mca=PORT:aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
Removes the IP multicast address from the ATU.
--enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=PORT:(1|0)
Blocks all Ethernet frames with Destination Address not present in
the ATU.
--get-enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=PORT
Prints the status of blocking all Ethernet frames with Destination
Address not present in the ATU.
--enable-port-igmp-snooping=PORT:(1|0)
Enables/disables IGMP snooping for the individual port.
--get-enable-port-igmp-snooping=PORT
Prints the status if IGMP snooping is enabled for the port.
--set-port-mtu=PORT:(0|1|2)
Sets the MTU size for the port 0…5, where 0 indicates support for
1522 bytes, 1 indicates support for 2048 bytes and 2 indicates
support for 10240 bytes
--get-port-mtu=PORT
Get the MTU size for the port
Link status:
--get-port-link-status=PORT
Gets the links status of the port
Speed and duplex mode:
--set-port-autonegotiation=PORT:(1|0)
Enable or disable autonegotation on the port
--get-port-autonegotiation=PORT
Gets the autonegotiation status of the port
--set-port-speedmode=PORT:(1000FD|1000HD|100FD|100HD|10FD|10HD|AUTO|FD|HD)
Sets the speed and duplex mode of the port
--get-port-speed-mode=PORT
Gets the speed and duplex mode of the port
Flow control:
--enable-port-flowcontrol=PORT:(1|0)
Enables/disables flow control on the port
--get-enable-port-flowcontrol=PORT:(1|0)
Prints the status of flow control on the port
Rate control:

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 15
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
--dump-pirl-buckets
Prints the status of the PIRL buckets.
--set-port-egress-rate-limit=PORT:rate
Sets the egress rate for the port. Rate is in kbps range: 0,
128..1000000 - 0=unlimited
--get-port-egress-rate-limit=port
Display egress rate for the port.
--set-port-ingress-rate-limit=port:bucket:rate:layer:(DROP|FC)
Sets a Port Input Rate Limit(PIRL) bucket.
--get-port-ingress-rate-limit=port
Gets a list of enabled Port Input Rate Limit(PIRL) buckets.
--disable-pirl-bucket=bucket (100Mb)
--disable-pirl-bucket=port:bucket (1Gb)
Disables a PIRL bucket.
--port-map-to-pirl-bucket=port:bucket (100Mb)
Adds/maps a port to a Port Input Rate Limit(PIRL) bucket, note that
the rate limitation will be a shared between the ports.
--port-del-from-pirl-bucket=port:bucket (100Mb)
Removes a port from a Port Input Rate Limit(PIRL) bucket.
--port-enable-vid-nrl=port:enable (100Mb)
Enables/disables per port the Non rate limit for VLANs with the NRL
bit enabled.
QoS:
--set-port-ieee-tag-priority=PORT:(1|0)
Enables prioritized frames based on their IEEE priority tags
--get-port-ieee-tag-priority=PORT
Prints the status of Enable prioritized frames based on there IEEE
priority tags
--set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=PORT:(1|0)
Enables prioritized frames based on their IP4/IP6 priority fields
--get-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=PORT
Prints the status of Enable prioritized frames based on their
IP4/IP6 priority fields
--set-port-map-rule=PORT:(1|0)
This makes IEEE tags to used priority to IP4/IP4 fields if both
exists.
--get-port-map-rule=PORT
Prints the status of if IEEE tags is prioritized over IP4/IP4 fields
if both exists.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 16
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
--set-ieee-queue-map=PRIO:QUEUE
Used to map IEEE tag priority 0-7 to internal queue 0-3.
--get-ieee-queue-map=PORT
Prints the queue of a mapped IEEE tag priority.
--set-ip4ip6-queue-map=PRIO:QUEUE
Used to map IP4/IP6 priority 0-63 to internal queue 0-3.
--get-ip4ip6-queue-map=PORT
Prints gets the queue of a mapped IP4/IP6 priority.
--set-sa-da-frame-priorityoverride=PORT:SA_FRAME_PRIO_OVERRIDE:DA_FRAME_PRIO_OVERRIDE (100Mb)
Source Address(SA) or Destination Address(DA) Frame Priority
Override on an ATU match.
FRAME_PRIO_OVERRIDE=0..1
--set-sa-da-queue-priorityoverride=PORT:SA_QUEUE_PRIO_OVERRIDE:DA_QUEUE_PRIO_OVERRIDE (100Mb)
Source Address(SA) or Destination Address(SA) Queue Priority
Override on an ATU match.
QUEUE_PRIO_OVERRIDE=0..1
--get-sa-da-frame-priority-override=PORT (100Mb)
Source Address(SA) or Destination Address(DA) Frame Priority
Override on an ATU match.
FRAME_PRIO_OVERRIDE=0..1
--get-sa-da-queue-priority-override=PORT (100Mb)
Source Address(SA) or Destination Address(DA) Frame Priority
Override on an ATU match.
FRAME_PRIO_OVERRIDE=0..1
--set-queue-priority=PORT:PRIORITY:ENABLE (100Mb)
Used to force queue priority for a port.
The priority will be superseeded by VTU, SA, DA or ARP priority.
PRIORITY=0..3, ENABLE=0..1
--get-queue-priority=PORT´ (100Mb)
Used to force queue priority for a port.
The priority will be superseeded by VTU, SA, DA or ARP priority.
This will return 1 if enabled, 0 if disabled.
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN:
--set-port-admit-only-tagged-frames=PORT:ENABLE
This will make sure that all frames received on the port is blocked
unless they are tagged with a VLAN ID.
--get-port-admit-only-tagged-frames=PORT
Prints the status of blocking untagged frames
# Note from firmware revision earlier than 02_05
--add-vtu-entry=VID:WAN:LAN1:LAN2:LAN3:LAN4:CPU:NRL-ENABLE
Adds an entry to the VTU table.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 17
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# Note from firmware revision 02_05 or later
--add-vtu-entry=VID:WAN:LAN1:LAN2:LAN3:LAN4:CPU:NRLENABLE[:PRIORITY]
Modes for the ports
0=egress unmodified, so the frames's VID tag will not be modified
1=not member, frames belonging to the VLAN will not be
present on the port
2=egress untagged, frames with VID tag will have this tag
stripped
3=egress tagged, frames will have the VID tag inserted
If the VID should be omitted in rate limitation, the NRL-ENABLE
should be set to 1, then PIRL bucket will be bypassed.
PRIORITY is optional parameter, a Class of Service value can be
associated to the specific VLAN. Value 0…7 is accepted. If
parameters is omitted no changes will be made to priority tag.
The parameter is only valid for firmware revision 02_05 or later.
--del-vtu-entry=VID
Removes the VTU entry for the VID.
--dump-vtu
Dumps the VTU table
--clear-vtu
Removes all entries of the VTU.
--set-port-default-vid=PORT:VID
Sets the default VLAN ID(VID) for a port.
--get-port-default-vid=PORT:VID
Prints the default VLAN ID(VID) for a port.
--set-port-force-default-vid=PORT:ENABLE
Forces the tagging of VID on all frames on the port.
--get-port-force-default-vid=PORT
Gets the status of force tagging of VID on all frames on the port.
--set-port-802dot1q-mode=PORT:MODE
Sets the IEEE 802.1Q mode for the ingress port.
Mode either
0=disable, disables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, used for port
based VLANs
1=fallback, enables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, fallback mode
2=check, enables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, check mode
3=secure, enables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, secure mode
--get-port-802dot1q-mode=PORT
Prints the 802.1Q mode for the ingress port.
Mode either
0=disable, disables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, used for port
based VLANs
1=fallback, enables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, fallback mode
2=check, enables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, check mode
3=secure, enables IEEE 802.1Q for the port, secure mode

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 18
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Port based VLAN:
--set-port-vlan-table=port:WAN_ENABLE:LAN1_ENABLE:LAN2_ENABLE:
LAN3_ENABLE:LAN4_ENABLE:CPU_ENABLE
Enable which ports are enabled for communication.
PORT_ENABLE is in the range 0..1
--get-port-vlan-table=port
Prints the port based VLAN mapping
RMON:
--get-rmon-histogram-mode
Sets the mode for the RMON counters.
0 = Rx only, 1 = Tx only, 2 = Sum of Rx and Tx.
--set-rmon-histogram-mode=MODE
Sets the mode for the RMON counters.
Mode must be between 0 and 2; 0 = Rx only, 1 = Tx only, 2 = Sum of
Rx and Tx.
--flush-all-rmon-counters
Flushes all counters on all ports.
--flush-port-rmon-counters=PORT
Flushes all counter for a single port.
--get-port-rmon-counters=PORT, Prints the RMON counters for a port.
DHCP Option 82:
supported from firmware revision 03_00 and later, in the 794xx
series (1 GbE CPE).
--set-port-dhcp-option82=PORT:enable[:<optional text>] (1Gb)
Enable or disable DHCP option 82 (DHCP relay agent).
1=enable, 0=disable
The optional text will be written in the "Option82 Agent
Circuit ID
Sub-option" field. If the optional text contains white space,
the text must be enclosed in "".
--get-port-dhcp-option82=PORT (1Gb)
Is DHCP option 82 (DHCP relay agent) enabled?
1=enable, 0=disable
"Option82 Agent Circuit ID Sub-option" text.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 19
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Explanation of feature settings
VLAN settings
In SECURE mode, the VID for the given frame must be contained in the VTU, and
the Ingress port must be a member of the VLAN or the frame will be discarded.
In CHECK mode, the VID for the given frame must be contained in the VTU or the
frame will be discarded (the frame will not be discarded if the Ingress port is not a
memeber of the VLAN).
In FALLBACK mode, Frames are not discarded if their VID's are not contained in the
VTU. If the frame's VID is contained in the VTU, the frame is allowed to exit only
those ports that are members of the frame's VLAN; otherwise the switch 'falls back'
into Port Based VLAN mode for the frame.
Egress Tagging for a member port of a Vlan has the following three choices:
1. Unmodified
2. Untagged
3. Tagged
The default configuration defines no VLAN.
The following ports can be included in the VLAN setup:
WAN port = port <0>
LAN port 1 = port <1>
LAN port 2 = port <2>
LAN port 3 = port <3>
LAN port 4 = port <4>
CPU port = port <5>, this is the interface between the internal switch and
CPU engine (management and VoIP processor, if applicable)
Each LAN port can be setup up to tagged traffic there ingress the port with a given
vlan identifier. When the traffic egress the LAN port the vlan tag is removed. The
syntax for the command is:

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 20
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# VLAN SETTINGS FOR WAN PORT, WAN PORT WILL BE MEMBER OF ALL VLANS, SEE SETTINGS UNDER EACH VLAN
DEFINITION
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode 0:3 # WAN port is in secure mode, allows tagged frames only
switch --add-vtu-entry 500:3:1:1:1:1:2:2:0 # puts WAN and CPU into vid 500, THIS IS MANAGEMENT VLAN
#
# VLAN SETTINGS FOR LAN PORT 1
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode 1:3 # LAN port 1 is secure mode, allows tagged frames only
switch --add-vtu-entry 111:3:3:1:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN1 into vid 111, LAN1 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 121:3:3:1:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN1 into vid 121, LAN1 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 131:3:3:1:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN1 into vid 131, LAN1 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 141:3:3:1:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN1 into vid 141, LAN1 is tagged on egress
#switch --set-port-default-vid 1:111 # If untagged frames ingress on port 1, place these into VLAN 111 (first VLAN)
#
# VLAN SETTINGS FOR LAN PORT 2
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode 2:3 # LAN port 2 is secure mode, allows tagged frames only
switch --add-vtu-entry 211:3:1:3:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN2 into vid 211, LAN2 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 221:3:1:3:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN2 into vid 221, LAN2 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 231:3:1:3:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN2 into vid 231, LAN2 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 241:3:1:3:1:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN2 into vid 241, LAN2 is tagged on egress
#switch --set-port-default-vid 2:211 # If untagged frames ingress on port 2, place these into VLAN 211 (first VLAN)
#
# VLAN SETTINGS FOR LAN PORT 3
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode 3:3 # LAN port 3 is secure mode, allows tagged frames only
switch --add-vtu-entry 311:3:1:1:3:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN3 into vid 311, LAN3 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 321:3:1:1:3:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN3 into vid 321, LAN3 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 331:3:1:1:3:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN3 into vid 331, LAN3 is tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 341:3:1:1:3:1:2:0 # puts WAN and LAN3 into vid 341, LAN3 is tagged on egress
#switch --set-port-default-vid 3:311 # If untagged frames ingress on port 3, place these into VLAN 311 (first VLAN)
#
# VLAN SETTINGS FOR LAN PORT 4, DUMMY VLAN
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode 4:3 # LAN port 4 is secure mode, allows tagged frames only
Also a combination of tagged/untagged frames that ingress a port is possible. The
following example has VLAN 211 and VLAN 221 defined for WAN and LAN port 1.
VLAN 211 will be tagged egress on WAN and LAN port 1, whereas VLAN 221 will be
tagged egress on WAN and untagged egress on LAN port 1. It is expected that VLAN
211 is tagged ingress on both WAN and LAN port 1, whereas VLAN 221 is tagged
ingress on WAN and untagged ingress on LAN port 1. All other ports are not
member of the VLANs. A management VLAN 951 is defined (untagged), which
enables communication between system operator and CPE for management
purposes (untagged).

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 21
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=0:3 # Sets the WAN port in check mode, allows untagged on ingress if VID (incl
default) is present in VTU
switch --set-port-default-vid=0:951 # Default VLAN for WAN port
switch --add-vtu-entry 951:2:1:1:1:1:2:0 # Management VLAN, enables contact to CPU - untagged on egress
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=1:3 # Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=2:3 # Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=3:3 # Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --set-port-802dot1q-mode=4:3 # Sets the LAN port in secure mode
switch --add-vtu-entry 211:3:3:1:1:1:2:0 # put WAN and LAN port 1 into VLAN - tagged on egress
switch --add-vtu-entry 221:3:2:1:1:1:2:0 # put WAN and LAN port into VLAN - untagged on egress
switch --set-port-default-vid=1:221 # Default VLAN for LAN port 1
Provider mode (Double tagging, Q-in-Q)
In provider network environments, it is very common to use double VLAN tagging
to pass along the customer tag through the provider network by adding a provider
tag on top of the customer tag. Double Tagging is a way to isolate one IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN from other IEEE 802.1Q VLANs in a hierarchical fashion that is compatible
with IEEE 802.1Q aware switches. This method places an extra or Double Tag in
Operator
Network
WAN:
VID 211 (tagged)
VID 221 (tagged)
VID 951 (untagged)
DHCP Server
VID 951 (untagged)
VID 221 (untagged)
VID 211 (tagged)
Port 1:
VID 211 (tagged)
VID 221 (untagged)
Voice service: VID 221
data service: VID 211

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 22
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
front of a frame’s normal tag (assuming the frame was already Tagged), increasing
the frame size by 4 bytes.
Provider mode works for the WAN port only, and is simply enabled with the
following syntax. The ingress ports default VLAN VID will be used as the double
tag.
Note: Client ports must have their ingress 802.1Q mode set to disable
# Syntax is switch --set-port-802dot1q-provider-mode = Enable # Note default VLAN must be defined for the ports
# Sets the IEEE 802.1Q provider mode for the WAN port.
# ENABLE is either
# 0=disable, disables IEEE 802.1Q (Q-in-Q) double tagging
# 1=enable, enables IEEE 802.1Q (Q-in-Q) double tagging
# The tag value is set by the --set-port-default-vid=0:VID option
# Example
switch --set-port-802dot1q-provider-mode = 1
from firmware revision 03_19, there is support configuration of the Ethertype value. Default is 0x9100.
switch --set-port-802dot1q-provider-mode=ENABLE[:ethertype]
# The ethertype value is interpreted as hexadecimal number ethertype defaults to 0x9100 if not given.
Isolate LAN ports
The default is that the traffic can be switch between the LAN ports. The LAN port
can be isolated by each other by issuing the command:
# Syntax for a port based VLAN is:--set-port-vlan-table=port:WAN_ENABLE:LAN1_ENABLE:LAN2_ENABLE:
LAN3_ENABLE:LAN4_ENABLE:CPU_ENABLE
# Enable which ports are enabled for communication.
# PORT_ENABLE is in the range 0..1
# Example, LAN1, LAN2, LAN3 and LAN4 can communicate with WAN but not between the LAN ports
switch –set-port-vlan-table=0:1:1:1:1:1:1
switch –set-port-vlan-table=1:1:1:0:0:0:0
switch –set-port-vlan-table=2:1:0:1:0:0:0
switch –set-port-vlan-table=3:1:0:0:1:0:0
switch –set-port-vlan-table=4:1:0:0:0:1:0
# Please note that the ingress port setting mode for the client ports must be set to disable
switch –set-port-802dot1q-mode=1:0
switch –set-port-802dot1q-mode=2:0
switch –set-port-802dot1q-mode=3:0
switch –set-port-802dot1q-mode=4:0
Enable LAN
The LAN ports are disabled per default. Therefore the configuration file should
enable the LAN ports by issuing the command:

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 23
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
switch --enable-lan
Set LAN Port Speed
All ports are default configured to 100 Mbit/s full duplex. Change of this setting is
possible by using the following command:
switch --set-port-speed-mode=<port>:<mode>
# <port> is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4
# <mode> is 100FD|100HD|10FD|10HD|AUTO
# For 1 GbE CPE 1000FD|1000HD|100FD|100HD|10FD|10HD|AUTO
# WAN port, from firmware revision 02_09 Auto negotiation is not possible for WAN port, due to missing support
for 100 BASE-FX
# For 1 GbE CPE auto negotiation is supported
Set Port MTU size
The MTU size can be programmed for each port. The following syntax can be used:
switch --set-port-mtu=[PORT]:[Jumbo Mode]
#Where [PORT] is 0…5
#Where [Jumbo Mode] = 0 for 1522 bytes, 1 for 2048 bytes and 2 for 10240 bytes
IGMP snooping
The device supports IGMP snooping, and join messages received from clients on
the LAN ports will be handled by the CPE CPU, which will control which ports that
belongs to which multi cast group. IGMP snooping has to be enabled per port but is
running per default:
# Enable IGMP snooping on port 2, 3
switch --enable-port-igmp-snooping=2:1
switch --enable-port-igmp-snooping=3:1
# Also unknown multicast traffic should be blocked. This can be done via the following commands
switch --enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=1:1
switch --enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=2:1
switch --enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=3:1
switch --enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=4:1
switch --enable-port-block-unknown-multicast=5:1 # Important to include CPU port, alternatively a membership
to any of the multicast groups could cause the CPU to be overloaded.
# It is recommended NOT to block unknown multicasts on port 0 (WAN), as all client broadcasts are blocked, as
broadcasts are considered as multicasts
# This will prevent unknown multicast traffic to be passed out on any of the LAN ports. So it requires a join
message on the specific LAN port, from a set-top box, in order to have traffic passed on to that LAN port

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 24
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# The IGMP can be shut off via SNMP, use dkt_fe.mib OID named “feIGMPSnooping”, input parameter 0 = stops
IGMP snooping. Alternatively in the configuration file add the following: “mv /etc/init.d/igmp /etc/init.d/igmp2”
Note that blocking multicasts for port 5, will result in a blocking of ARPs originated
for the WAN port also, as all broadcasts are considered as multicasts. In order to
ensure that ARPs from the DHCP Server is still passed through, ARP mirroring
function must be enabled.
switch --set-arp-mirroring=0:1 # Enables ARP mirroring, so ARPs received on WAN port will be redirected to CPU
port, despite the fact that multicast/broadcasts are blocked on the CPE port
When an IGMP join is seen for a multicast group, then switch ATU is configured
with a filter setting for this group, allowing traffic for the group to be bridged to
the specific port.
Per default, the filter settings are kept until appropriate IGMP leave is seen for the
particular multicast group.
This means that once a device has joined a multicast channel then the address will
be present in the switch ATU until a leave is received by the IGMP snooper.
It is possible to enable a timeout in the IGMP snooper with default timeout values,
the user must put this line in the CPE configuration file:
ENABLE_IGMP_TIMEOUT=1 /etc/init.d/igmp restart
#or “enable_igmp_timeout=1 /etc/init.d/igmp restart”
When the CPE detects IGMPv2/v3 join packet, and will establish a filter for the
multicast group for the specific port seen, and set a default time-out value (for
IGMPv2 the specified time-out value in the RFC, for IGMPv3 the value extracted
from the join packet) for this specific multicast group. The switch filter will start
to decrease this value immediately.
It is expected that a IGMP Query is present, followed by a IGMP report from the
client, saying that it is still a member of the group
In some cases race conditions can occur, if the CPE filter times out before a client
has responded to an IGMP query, hence signal will be lost, as CPE expect that the
client is no longer member of the multicast group.
Therefore it is possible to change the default time-out values for the IGMP
snooping.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 25
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
To enable timeout and to increase timeout from defaults in the IGMP snooper, the
user must put this line in the CPE configuration file (example with additional 77
seconds timeout):
ENABLE_IGMP_TIMEOUT=1 ADDITIONAL_IGMP_TIMEOUT=77 /etc/init.d/igmp restart
#or “enable_igmp_timeout=1 additional_igmp_timeout=77 /etc/init.d/igmp restart”
Ingress rate limitation
The CPE includes 12 Port Ingress Rate Limitation buckets2, that can be assigned to
any of the CPE ports, both WAN and LAN ports.
Bytes to be counted:
Accounts for all bytes
Accounts for all bytes, Count all Layer 1 bytes:
o Preamble (8bytes) + Frame's DA to CRC + IFG (12bytes)
Accounts for all bytes, Count all Layer 2 bytes:
o Frame's DA to CRC
Accounts for all bytes, Count all Layer 3 bytes:
o Frame's DA to CRC - 18 - 4 (if frame is tagged)
Please notice that from firmware release 03_09 and later Ingress rate
limitation: Added support for traffic based rate limitation for the types:
Broadcast (BC), Multicast (MC) and Unknown multicast or unicast Traffic
(UT).
o Broadcasts, BC # this should be used to limit any broadcast traffic
o Unknown multicast, UMC # this should be used as you don’t know
the destination of any multicast traffic
o Known multicasts, MC # this should be used only if you know the
multicast traffic, must be present in the ATU
2
Please note that Gigabit CPE doesn’t support a multi port bucket based structure, as ingress rate limitation
works at a port based level, so not more than one port can be associated with a bucket.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 26
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Non-Rate Limitation (NRL) overrides can be programmed for VLAN Id’s.
The following example creates two buckets:
Bucket 1 includes LAN port 3 and 4, which totally has an ingress data limitation of
1 Mbps, counted from layer 3 and upwards. Layer 1 and layer 2 statistics are not
included/counted in this bucket.
Bucket 2 includes WAN port, which has an ingress data limitation of 2 Mbps,
counted from layer 3 and upwards. Layer 1 and layer 2 statistics are not
included/counted in this bucket.
This would match a situation where the service provider is offering a 2048/1024
kbps broadband connection to the Internet. Since the service provider may want to
offer VoIP and/or IPTV, these services should not be counted in the bucket. A NonRate Limitation setting for the services can be made with the use of the VLAN Id’s.
In the example VLAN VID 100 is excluded from the buckets, and therefore they do
not have any rate limitations assigned.
The following rate limitation structure for ingress must be followed:
64kbps ~ 1Mbps : increments of 64kbps
1Mbps ~ 100Mbps : increments of 1Mbps
100Mbps ~ 200Mbps : increments of 10Mbps
The valid values are:
64, 128, 192, 256, 320, 384,..., 960
1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, ..., 100000
110000, 120000, 130000, ..., 200000
switch --add-vtu-entry 100:3:1:1:2:2:2:1
# put WAN and LAN port 3 and port 4 into VLAN 100, which could be IPTV. Notice NRL bit is set, so this VLAN will
bypass buckets
switch --add-vtu-entry 200:3:1:1:2:2:2:0
# put WAN and LAN port 3 and port 4 into VLAN, which could be data. Notice NRL bit is not set, so this VLAN will
not bypass buckets
#Uplink rate (DATA port 3 and 4, ingress rates of 1 Mbps)
#
# port=3, bucket=0, rate=1000kb/S, byte counter=layer3, limitation = drop
switch --set-port-ingress-rate-limit 3:0:1000:3:DROP
# join port 4 to bucket 0, Please notice that this feature is NOT valid for the Gigabit CPE
switch --port-map-to-pirl-bucket 4:0
#Downlink rate (Total for WAN 2Mbps)
#
switch --set-port-ingress-rate-limit 0:1:2000:3:DROP # port=0(WAN), bucket=0, rate=2Mb/S,
bytecounter=layer3, limitation=drop
#
# Non-Rate Limitation settings
# Enable NRL for all ports. If a VLAN is defined with “--add-vtu”, see first command in this example, having NRL
bit set, then traffic from this VLAN (VID 100) is not counted inside the bucket
switch --port-enable-vid-nrl=1:1

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 27
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
switch --port-enable-vid-nrl=2:1
switch --port-enable-vid-nrl=3:1
switch --port-enable-vid-nrl=4:1

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 28
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Egress rate limitation
The egress rate can be set by each port. The default is full 100Mbit access.
The integer part of the value could be used********* to set the egress rate for a
given port:
switch --set-port-egress-rate-limit=0:8192 # set the WAN port to 8Mbit/sec.
switch --set-port-egress-rate-limit=1:256 # set the LAN1 port to 256kbit/sec.
switch --set-port-egress-rate-limit=2: 1024 # set the LAN2 port to 1Mbit/sec.
switch --set-port-egress-rate-limit=3:8192 # set the LAN3 port to 8Mbit/sec.
switch --set-port-egress-rate-limit=4:512 # set the LAN4 port to 512kbit/sec.
# Note, syntax is depending on firmware revision
# Firmware version 01_06_06 or older, following rates can be programmed:
128|256|512|1024|2048|4096|8192|16384|32768|65536
# Firmware version 01_06_07 supports any rate, egress rate limitation parameter is entered in kbps. No longer a
fixed value.
Because the egress rate of the WAN port is in opposite direction than the LAN port
the egress rate can be used to limit the upload rate.
Configuration of SNMP values
The following SNMP values can be set by the configuration file:
SysContact the administrate contact for the network
echo "syscontact techsupport@example.com" >> /etc/snmp/snmpd.local.conf
SysLocation for the location of the system
echo "syslocation somewhere" >> /etc/snmp/snmpd.local.conf
SysName the name of the system e.g the customer identification
echo "sysname customerXYZ" >> /etc/snmp/snmpd.local.conf
Syslog
Support for remote logging via syslog (RFC 3164)
To start syslog, enter the following line in your configuration file

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 29
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
syslogd [-l <log level>] -R <Remote server IP>
The syslog daemon sends logging information in UDP packets - port 514.
If all IP addresses are handled by the DHCP server, then there is also a way that
the syslog daemon may be started by the DHCP client:
echo "-O logsrv" > /tmp/dhcp_requests.txt
/etc/init.d/udhcpc restart
The daemon will be started by the DHCP client if the log server parameter (DHCP
option 7) is received in the DHCP response.
The following is supported from firmware release 03_08 and onwards:
You may control which extra DHCP options that are requested in DHCP option 55.
It is done by creating a file /tmp/dhcp_requests.txt containing just one line
with a list of request commands to the DHCP client.
The format of the line is:
-O <option name> [-O <option name>] ...
The following values for <option name> are currently supported:
Name
DHCP
Option
Description
dns 6 Domain name server IP
logsrv
7
Log server IP address
hostname
12
Hostname of the box
domain
15
Domain name
serverid
54
DHCP server identifier
Surveillance via SNMP
Various information about the node and the switch can be access via SNMP. Some
of these can also be set by snmp - but the setting is lost during a power reset. To
persist a setting it must be set as part of the configuration file.
The MIBs for SNMP management is available at www.dktcomega.com -> support ->
firmware. These can be loaded into a standard MIB browser or 3rd party SNMP
management system.
CATV setup
CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 30
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
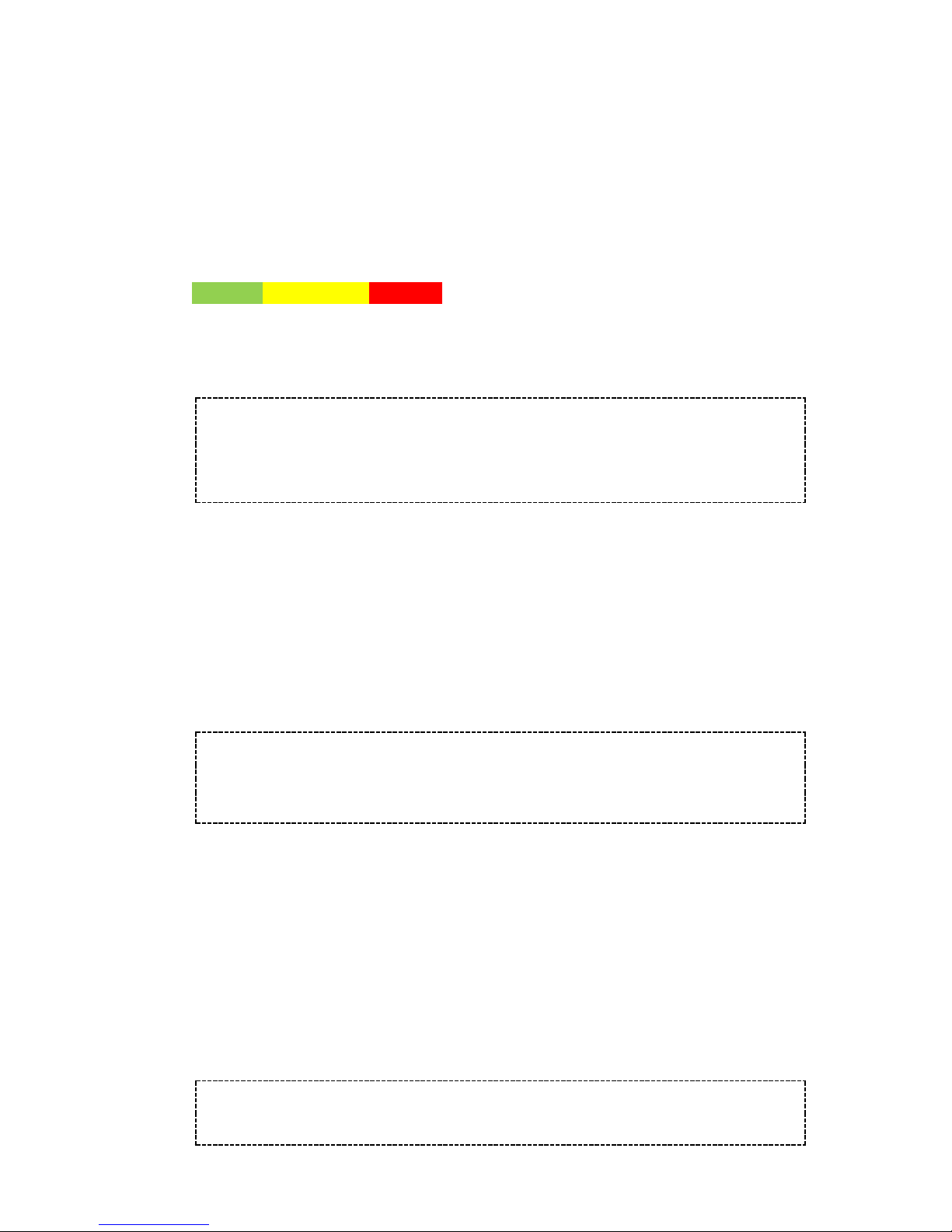
The CATV module has a LED indicator, for 79204, 7926x, 79403 and 7927x series
the color coding is as follows:
CATV optical signal level:
<-10dBm
-3 to -10dBm
>-3dBm
low
normal
High
The CATV module can be setup, on/off mode:
switch -c 1
switch -c 0
# Turn CATV module off
switch -c 0
# Turn CATV module on
switch -c 1
Quality of Service (QoS)
Per default all ports and traffic types have equal priority. Some time it is
necessary to differentiate the priority based on source/destinations
ports/addresses or traffic types.
Example, CPU port should have high priority in order to always enable
management traffic to pass. Internet traffic on LAN port 1, VoIP traffic on
LAN port 2, IPTV traffic on LAN port 3
switch --set-queue-priority=5:3:1 # Port 5 (CPU port) will have highest priority, feature is enabled
switch --set-queue-priority=1:0:1 # Port 1 (Internet traffic port) will have lowest priority, feature is enabled
switch --set-queue-priority=2:2:1 # Port 2 (VoIP traffic port) will have medium priority, feature is enabled
switch --set-queue-priority=3:2:1 # Port 3 (IPTV traffic port) will have medium priority, feature is enabled
Same scenario can be made based on traffic type and/or
Source/Destination MAC addresses
DKTCOMEGA is recommending that CPU port always is granted high priority as it
will ensure that management traffic is passed to the internal CPU on the device.
Furthermore prioritization based on packet ToS or DiffServ value can be made.
Below is an example of prioritization based on ToS value, where the switch engine
will inspect the value from 0 – 7. The switch holds 4 queues per port, where 3 is
highest priority and 0 is lowest.
switch --set-port-ieee-tag-priority=0:1 #Enables prioritization for WAN port
switch --set-port-ieee-tag-priority=1:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port1

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 31
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
switch --set-port-ieee-tag-priority=2:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port2
switch --set-port-ieee-tag-priority=3:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port3
switch --set-port-ieee-tag-priority=4:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port4
switch --set-port-ieee-tag-priority=5:1 #Enables prioritization for CPU port
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=7:3 # ToS value of 7 will go to queue with highest priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=6:3 # ToS value of 6 will go to queue with highest priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=5:2 # ToS value of 5 will go to queue with next highest priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=4:2 # ToS value of 4 will go to queue with next highest priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=3:1 # ToS value of 3 will go to queue with low priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=2:1 # ToS value of 2 will go to queue with low priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=1:0 # ToS value of 1 will go to queue with lowest priority
switch --set-ieee-queue-map=0:0 # ToS value of 0 will go to queue with lowest priority
Using a traffic analyzer, where we have defined 8 traffic classes, each sending
12.5% in an over subscription configuration, we can see that Class_0 programmed
with ToS value = 7, Class_1 programmed with ToS value =6 … Class_7 programmed
with ToS value = 0 will be prioritized according to the specification above.
The same goes for Differentiated Services, where the value can be between 0 – 63.
switch --set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=0:1 #Enables prioritization for WAN port
switch --set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=1:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port1
switch --set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=2:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port2
switch --set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=3:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port3
switch --set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=4:1 #Enables prioritization for LAN port4
switch --set-port-ip4ip6-priority-field=5:1 #Enables prioritization for CPU port
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=63:3 # DiffServ value of 63 will go to queue with highest priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=62:3 # DiffServ value of 62 will go to queue with highest priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=61:2 # DiffServ value of 61 will go to queue with next highest priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=60:2 # DiffServ value of 60 will go to queue with next highest priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=59:1 # DiffServ value of 59 will go to queue with low priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=58:1 # DiffServ value of 58 will go to queue with low priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=57:0 # DiffServ value of 57 will go to queue with lowest priority
switch --set-ip4ip6-queue-map=56:0 # DiffServ value of 56 will go to queue with lowest priority

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 32
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Using a traffic analyzer, where we have defined 8 traffic classes, each sending
12.5% in an over subscription configuration, we can see that Class_0 programmed
with DiffServ value = 63, Class_1 programmed with DiffServ value =62 … Class_7
programmed with DiffServ value = 56 will be prioritized according to the
specification above.
The IEEE 802.1 Prioritization remapping supports 8 priorities, parameter value
0…7. If the 802.1Q is enabled for the ports a prioritization can be associated to
each VLAN
# Syntax is switch --add-vtu-entry=VID:WAN:LAN1:LAN2:LAN3:LAN4:CPU:NRL-ENABLE[:PRIORITY]
switch --add-vtu-entry=100:3:2:2:1:1:2:5 # priority tag of 5 will be associated with VLAN id 100.
Reboot
The device can be accessed via TELNET, and is rebooted with the use of “reboot”
command. TELNET access must however be configured in the configuration file.
# The following command enables TELNET access from WAN
telnetd -l /bin/sh
Save configuration to flash
Per default device configuration is provisioned via DHCP at boot, and it will be
stored in device RAM memory, which means that the device would need to have
the configuration loaded at every boot.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 33
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
From firmware revision 02_11/boot loader revision 02_05 and later a possibility
exists to save the last configuration provisioned to flash memory.
Concept is if dhcp service is out, the device will restore its latest saved – the latest
saved configuration is the incident where there is a difference between saved
configuration and provisioned configuration. Also the CPE will get an ad-hoc linklocal IP address, which is an auto configuration algorithm described in the IETF
Draft "Dynamic Configuration of IPv4link-local addresses".
Procedure is to
- upgrade boot loader to version 02_05 (dkt_boot_02_05.img)
- upgrade firmware to version 02_11 (dkt_fw_flashdisk_02_11.img)
- insert a syntax in the configuration file “save_configuration”
Please note that the syntax “save_configuration” will be filtered by the device, so
if you do a “cat /tmp/config.sh” or “cat /mnt/flash/config.sh” this command is
not visible.
When dhcp service comes back, then the device will lease an IP address again, but
not fetch any new configuration, as it will keep its restored configuration until
next boot process.
# The following command allows the configuration to be saved to flash memory, and this will be restore if dhcp
service is out.
save_configuration
DHCP Option 82
DHCP Option 82 relay feature is supported from firmware revision 03_00 and later.
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 is an extension to the Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP), and is defined in RFC 3046 and RFC 3993. DHCP
Option 82 can be used to send information about DHCP clients to the
authenticating DHCP server. DHCP Option 82 can as an example identify the VLAN
number, port number as well as a customer ID of a client, during any IP address
allocation. When DHCP Option 82 is enabled on the CPE, it inserts the per port
defined information into the DHCP packets as they pass through the CPE on their
way to the DHCP server. The DHCP server stores the IP allocation record. The CPE
will strip off the DHCP reply from the DHCP server, so the clients will never see
the DHCP option 82 information.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 34
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
The DHCP Option 82 information can hold a 32 char string per port.
# Syntax is switch --set-port-dhcp-option82=PORT:enable[:<optional text>]
switch --set-port-dhcp-option82=1:1:”VLAN 100, LAN port 1”
switch --set-port-dhcp-option82=2:1:”VLAN 200, LAN port 2”
switch --set-port-dhcp-option82=3:1:”VLAN 300, LAN port 3”
switch --set-port-dhcp-option82=4:1:”VLAN 400, LAN port 4”
LLDP/EDP/CDP
LLDP/EDP/CDP feature is supported from firmware revision 03_00 and later. The
feature is enabled using the following syntax in the configuration script:
# Syntax is /etc/init.d/lldpd start [-OPTIONAL MODE <C | E | F>]
/etc/init.d/lldpd start # Starts LLDP on WAN port
/etc/init.d/lldpd start –C # Starts LLDP and CDP on WAN port
/etc/init.d/lldpd start –E # Starts LLDP and EDP on WAN port
# combinations of the above is also possible
/etc/init.d/lldpd start –CEF # Starts LLDP and CDP/EDP/Foundry DP on WAN port

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 35
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Support for SSH
Please note that support for SSH is available for all DKTCOMEGA CPE platforms
except HW revision “FE1 0” or earlier. HW revision can found via SNMP OID -
.1.3.6.1.4.1.27304.10.1.0
Alternatively with DKT-GENERIC-MIB::hwVersion.0
HW with values of "ERROR" or "FE1 0" do not support SSH.
In order to have SSH support, please make sure that flashdisk image is used (e.g.
dkt_fw_flashdisk_02_15.img) and remember to insert the following
command in the configuration script:
# SSH daemon is started with the following command
/etc/init.d/sshd start
The CPE is preconfigured with a login for SSH, please consult DKTCOMEGA for user
name and password.
The first time the SSH daemon is started; two secret key files are generated.
Please note that it takes a while to generate the secret key files. The secret key
files are not automatically stored to flash.
Save the SSH secret key files to flash using save_configuration in the configuration
file:
# Save configuration to flash memory, same SSH key is used at every boot
save_configuration
Now it is possible to log into the CPE as the user ”Administrator” (case sensitive)
through SSH.
ssh Administrator@<IP address>
or
ssh -l Administrator <IP address>
or using e.g. Putty application
When logged in as Administrator, it is not possible to make any changes, as you
must switch user to root with this command:
su

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 36
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Now it is possible to run all of the configuration commands, and it is possible to
change the password of the user with the command
passwd <username>
If password is changed remember save to flash with the save_configuration
command.
When finished, type exit to return to the Administrator user.
To log out, type exit again.
The daemon is started by the normal configuration file by inserting the following
commands (the lines should replace the telnetd command):
# Some configuration commands
# Start SSH daemon
/etc/init.d/sshd start
# Save configuration and SSH secret files to flash
save_configuration
The sshd script automatically restores password- and SSH key files from flash
before the SSH daemon is started.
Procedure for changing SSH password on all CPE units.
If password for Administrator is to be changed for all CPE's do the following:
1) Log into one CPE via ssh
2) change user to root with command su
3) cd /etc
4) change password of the CPE
5) Now copy the shadow file to a tftp server, typing "tftp -p -l shadow -r
shadow <TFTP Server IP Address>"
This file has to be pushed to all CPE's
6) you can edit CPE's configuration files by inserting the following commands:
tftp -g -r shadow -l /tmp/shadow <TFTP Server IP Address> #
This will get the shadow file for Administrator from TFTP
server and temporarily store this in /tmp directory
chown root /tmp/shadow # change owner of shadow
chmod 600 /tmp/shadow # change rights of shadow
mv /tmp/shadow /etc/ # move the shadow file to correct
directory

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 37
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
save_configuration # save configuration to flash memory, now
the password is saved locally on each CPE

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 38
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
VoIP ATA Plug-in module
DHCP/TFTP based provisioning
The ATA will gets it configuration from a TFTP server with the use of DHCP option
66/67, as for the CPE and will act as a separate network entity.
An example is shown below, example of dhcp configuration, where a specific host
with the MAC Address 00:19:9f:01:02:03 will get the "dktata2_test1.cfg"
configuration file offered during boot process.
host 1
{
hardware ethernet 00:19:9f:01:02:03;
option bootfile-name "dktata2_test1.cfg";
}
The configuration file holds all ATA specific parameters, as listed in the following
sections and can be tailored specifically for each ATA unit, please refer to
Appendix 1 – ATA configuration file
Firmware3 can be provisioned to the ATA in a similar manner as for the CPE, with
the use of DHCP option 60.
class "ATA Firmware upgrade"
{
match if option vendor-class-identifier="DKT_ATA_Firmware_v5_05_00";
filename "dkt2code_5_05_00.ece";
}
A bridge between the ATA and the CPE Linux has to be established. If the ATA has
to be configured on a separate VLAN than for CPE management (untagged), the
following command should be used:
enable_voip [VID]
# example ATA packets will be tagged via a VID of 100
enable_voip 100
If ATA packets should be untagged along with the CPE management, the following
command should be used:
3
Please notice that for firmware revision 5_05_16 or earlier, in very rare cases if the ATA boot loader has to be
upgraded then the following procedure must be conducted for each ATA.
1. telnet to each ATA
2. ata tftpup <tftp server ip address> <remote file name> <local file name>
3. reboot ATA
4. upgrade firmware via dhcp option 60 using appropriate dhcp.conf settings, as mentioned in the above
section
Ex.: ata tftpup 192.168.10.1 dkt2boot_5_05b4_secure.ece ata2boot.ece # NOTE: Pay attention to the filename of
the boot loader.
For firmware revision 5_05_17 or later this is irrelevant, as the runtime firmware automatically will upgrade the
boot loader, please refer to the firmware release note for further details.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 39
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# example ATA packets will be untagged
enable_voip
Web Interface
Alternatively the ATA can be managed via HTTP browser by inserting http://<IP
Address>
User name: <to be disclosed by DKTCOMEGA>
Password: <to be disclosed by DKTCOMEGA>
System Parameters
Generic settings for the ATA plug-in module can be configured under System
ATA Manager Logon
Date/Time
Network Device Configuration
Static Network Configuration
Dynamic Network Configuration
Remote Configuration Access
NAT Transversal Parameters
Update Parameters
ATA Maintenance
System Identification
Accounts:
Parameter
Description
Default
ata service name
Brand or service name used by telephone service
provider
VoIP Service Plan
Name
ata admin name
Administrator configuration access name, Please
consult DKTCOMEGA for user name and password
************
ata admin password
Administrator password, Please consult
DKTCOMEGA for user name and password
************
ata user name
User configuration access name
ata user password
User password
ata user message
Message which is displayed to the user when they
access the ATA web interface
Thank you for
purchasing this
DKTCOMEGA ATA
Date/Time:
Parameter
Description
Default
ata date
Current date
2004/7/4
ata time
Current time
12:00:00
ata time zone
Number of hours to subtract from GMT to form
local time
-5
ata daylight savings enable
Enable local application of daylight savings time
Enabled
ata timeserver enable
Enable use of network timeserver
Enabled

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 40
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ata timeserver domain name
Fully qualified domain name (including an optional
port number) for the NTP/SNTP timeserver server
time-a.nist.gov
Network Device Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
net assigned router name
Manually configured router device name
DKTCOMEGA_ATA
net assigned host name
Manually configured host device name (or name
automatically assigned and saved)
DKTCOMEGA _ATA
net assigned domain name
Manually configured domain name
(empty)
net assigned mtu
Manually configured maximum transmit unit size
(range of 576 to 1500)
1492
net assigned cloned mac address
Alternate Ethernet MAC address used for cloning an
existing device (required for special situations
only)
(empty)
Static Network Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
net static config enable
Enable static network configuration
Disabled
net static ip address
Manually configured IP address (or address
automatically assigned and saved)
0.0.0.0
net static netmask
Manually configured local network mask (or
netmask automatically assigned and saved)
255.255.255.0
net static gateway address
Manually configured gateway IP address (or address
automatically assigned and saved)
0.0.0.0
DNS Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
net dns primary address
Manually configured IP address of primary domain
name server (DNS)
0.0.0.0
net dns secondary address
Manually configured IP address of backup domain
name server (DNS)
0.0.0.0
net dns parallel search mode
Uses both DNS servers concurrently when enabled
Disabled
Dynamic Network Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
net isp dhcp enable
Enable use of DHCP for automatic local IP address
configuration
Enabled
net isp pppoe enable
Enable use of PPPoE for automatic local IP address
configuration and public network access
Disabled
net isp user name
PPPoE or PPTP user name
(empty)
net isp password
PPPoE or PPTP password
(empty)
net isp dhcp discover duration
A parameter to enable DHCP retries. This
parameter is in units of seconds and sets how long
after a DHCP timeout that the ATA will restart
sending DHCP discovers.
0 (Disabled)
net isp connect on demand enable
Enable PPPoE or PPTP connection on demand
Disabled
net isp connect on demand interval
Idle period for disconnection in seconds
0
net isp keep alive enable
Keep PPPoE or PPTP connection active when
enabled
Disabled
net isp keep alive interval
Interval for keep alive messages in seconds
0
net isp reconnect on link loss
Enable automatic reconnection on link loss (retains
initial configuration if disabled), CURRENTLY NOT
IMPLEMENTED
n/a

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 41
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
net isp save as assigned
Enable saving of results acquired automatically as
the assigned address, netmask and gateway for
later restarts. When this is enabled the ATA saves
the IP information (IP address, netmask, gateway,
DNS servers) obtained from a DHCP response in the
appropriate parameters ('net static ip address', 'net
static netmask', 'net static gateway address', 'net
dns primary address', 'net dns secondary address')
Disabled
Remote Access Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
ata web external server enable
Enable access to configuration procedures from
external IP addresses
Enabled
ata web internal server enable
Enable access to configuration procedures from
local IP addresses
Enabled
ata web server port
Port number for configuration web server
0 (Defaults to 80)
ata web server language
Language selection
English
ata telnet server enable
Enable remote access via telnet protocols
Enabled
ata telnet port
Telnet Port no
ata ftp server enable
Enable remove access via ftp protocols
Enabled
ata ftp port
FTP Port no
NAT Transversal Parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default
nat stun enable4
Enables use of STUN for discovery of network
address translation (NAT) mapping
Enabled
nat stun server domain name
Fully qualified domain name (including optional
port number) for the STUN server
stun.fwdnet.net
nat stun symmetric deterministic enable
Enables STUN deduction for a symmetric
deterministic firewall
Enabled
nat turn enable
Enables use of TURN for discovery of network
address translation (NAT) mapping
Disabled
nat turn server domain name
Fully qualified domain name (including optional
port number) for the STUN server
(empty)
nat ice enable
Enables use of ICE for discovery of network address
translation (NAT) mapping and exchange via SIP
Disabled
Update Parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default
ata local update enable
Control to enable a manual update operation
from a local PC running the provided ATA local
update services
Disabled
ata local update domain name
Fully qualified domain name (including an
optional port number) for the update server
(empty)
ata update domain name
Fully qualified domain name (including an
optional port number) for the update server
TBD
ata configuration update enable
Control to enable automatic updating of
configuration
Enabled
ata configuration update on reset
Control to enable automatic update of
configuration on reset
Enabled
4
If STUN is enabled the ATA will wait until STUN completes or times out before it will send the INVITE on an
outgoing call or begin to ring on an incoming call. Please notice that this can cause delays in making and receiving
calls if the STUN service is not used, but enabled.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 42
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ata configuration update from sip
Control to enable automatic update on receipt of
SIP message
Disabled
ata configuration request message
SYSLOG message body sent when requesting a
configuration update
(empty)
ata configuration success message
SYSLOG message body sent when configuration
update completed successfully
Configuration update
successful
ata configuration failed message
SYSLOG message body sent when configuration
update completed unsuccessfully
Configuration update
failed
ata configuration update periodic delay
Periodic delay in seconds between configuration
update checks
3600
ata configuration update random delay
Uniform random delay in seconds applied when
contact with the update server fails
240
ata configuration update error retry
delay
Fixed delay in seconds applied when the
configuration update operation fails
120
ata firmware update enable
Control to enable automatic updating of
firmware
Enabled
ata firmware update on reset
Control to enable automatic update of firmware
on reset
Enabled
ata firmware request message
SYSLOG message body sent when requesting a
firmware update
(empty)
ata firmware success message
SYSLOG message body sent when firmware
update completed successfully
Firmware update
successful
ata firmware failed message
SYSLOG message body sent when firmware
update completed unsuccessfully
Firmware update
failed
ata firmware update periodic delay
Periodic delay in seconds between firmware
update checks
86400
ata firmware update random delay
Uniform random delay in seconds applied when
contact with the update server fails
240
ata firmware update error retry delay
Fixed delay in seconds applied when the
firmware update operation fails
120
ATA Maintenance:
Parameter
Description
Default
ata help url
URL for ATA configuration help (default page says
no help available here)
help.html
ata logo url
URL for ATA logo (default logo is stored in ATA
when manufactured)
Atalogo.jpg
net syslog enable
Control to enable transmission of SYSLOG messages
Disabled
net syslog server
Fully qualified domain name (including an optional
port number) for the SYSLOG server
(empty)
net debug enable
Control to enable transmission of developer debug
messages
Disabled
net debug server
Fully qualified domain name (including an optional
port number) for the debug server
(empty)
net debug level ata
Debug message level hex bitmask for ATA layer
function
7
net debug level sip
Debug message level hex bitmask for SIP layer
function
307
net debug level mgcp
Debug message level hex bitmask for MGCP layer
function
307
net debug level net
Debug message level hex bitmask for NETWORK
layer function
7
net debug level omc
Debug message level hex bitmask for OMC layer
function
7
net debug level pmp
Debug message level hex bitmask for PUMP layer
function
7
System Identification:
Parameter
Description
Default
ata copyright notice
DKTCOMEGA’s copyright notice
(C) 1994-2009
DKTCOMEGA

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 43
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ata manufacturer
Manufacturer name
DKTCOMEGA.
ata model number
Product model number
TBD
ata serial number
Serial number assigned during manufacture
(as assigned)
ata hardware revision
Hardware revision
0.30
ata boot rom revision
Boot code revision
3.28.00
ata firmware revision
Run-time code revision
3.31.01
ata configuration revision
Configuration file revision
3.28.00
net hardware mac address
Ethernet MAC address assigned during manufacture
(as assigned)
net unique device id
Unique device ID including Ethernet MAC used for
DHCP and update operations
(as assigned)

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 44
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
VoIP Accounts
The VoIP Provider Parameters configure the user account access for up to four
providers. Following are brief descriptions of the parameters available for each
account.
VoIP Account #1 - #4:
Parameter
Description
Default
voip provider 1.provider name
Name of VoIP provider
(empty)
voip provider 1.provider type
Type of VoIP provider
Disabled
voip provider 1.distinctive ring type
Distinctive ring type
1
voip provider 1.dialing prefix
Dialing prefix to select provider (such as
10288)
(empty)
voip provider 1.preferred codecs
List of numeric codec types in order of
preference
(empty)
voip provider 1.incoming mode
Incoming call distribution mode (ring all,
hunt all, ring group or hunt group)
Ring All
voip provider 1.group line 1 enable
Line 1 enable for group
Enable
voip provider 1.group line 2 enable
Line 2 enable for group
Enable
voip provider 1 use outbound proxy
voip provider 1.display name
Outgoing caller ID display name
(empty)
voip provider 1.user name
User name such as an E.164 number
(empty)
voip provider 1.domain name
Authentication domain name (or realm)
(empty)
voip provider 1.auth user name
User name for authentication
(empty)
voip provider 1.auth domain name
Fully qualified domain name used as the
authentication realm
(empty)
voip provider 1.auth user password
User password for authentication
(empty)
voip provider 1.proxy domain name
Fully qualified domain name (with optional
port number) for the SIP proxy server
(empty)
voip provider 1.register domain name
Fully qualified domain name (with optional
port number) for the SIP registration server
(empty)
voip provider 1.reregister interval
Re-registration period in seconds
120
voip provider 1.subscription domain
name
Fully qualified domain name (with optional
port number) for the SIP subscription server
(empty)
voip provider 1.resubscribe interval
Re-registration period in seconds
0
Dial Prefix Contains the dial string pattern matching used to distinguish and route
calls to a VoIP service provider.
VoIP Provider Defaults:
Parameter
Description
Default
voip default display name
Display name used as the name in the caller
ID
default_display_name
voip default user name
Login user name
default_user_name
voip provider default1
Default provider selection
1
voip provider alternate1
Alternate provider to use when selected
provider is unavailable (0 to disable)
0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 45
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
voip provider default line 1
Default provider selection for line 1
1
voip provider alternate line 1
Alternate provider for line 1 to use when
selected provider is unavailable (0 to
disable)
0
voip provider default line 2
Default provider selection for line 2
1
voip provider alternate line 2
Alternate provider for line 2 to use when
selected provider is unavailable (0 to
disable)
0
VoIP Parameters
The VoIP Protocol Parameters control various common aspects of the ATA device.
These include:
Audio Settings
RTP Protocol Parameters
SDP Protocol Parameters
SDP Audio Codec Names
Audio Settings:
Parameter
Description
Default
voip preferred codecs
List of numeric codec types in order of preference
18 0
voip silence supression enable
Enables comfort noise/silence processing
Disabled
voip echo canceller enable
Enables the G.168 echo canceller
Enabled
voip echo canceller mode
Sets the echo canceller operating mode
2
voip echo canceller tail length
Specifies length of echo canceller in msec
16
voip fax processing mode
Control for FAX processing method: off, pass
through (uLaw or Alaw) or real-time FAX (T.38)
Off
voip fax processing rate
Controls the fax processing rate (0 to 5 for 2400 to
14400 respectively)
5
RTP Protocol Parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default
rtp port minimum
The minimum RTP port number to be used
1234
rtp port maximum
The maximum RTP port number to be used
65535
rtp public external ip address
Force a specific external IP address for SDP
messages sent (disabled when 0.0.0.0)
0.0.0.0
rtp public external port min
Specifies the fixed RTP port mapping performed by
a NAT firewall associated with the minimum RTP
port number (disabled when 0)
0
rtp tos value
Type of service (TOS) value or DIFFServ DSFIELD
used for SIP messages as a hexidecimal value
0x68
rtp packet duration
The duration in msec for frame-based codecs
30
rtp stream duration
The duration in msec for sample stream-based
codecs
20
rtp session timeout interval
The session timeout interval in seconds
120
rtp jitter buffer start depth
Jitter buffer depth at startup in msec
20
rtp jitter buffer minimum depth
Jitter buffer minimum depth
20

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 46
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
SDP Protocol Parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default
DP Session Name
-
SDP Session Owner
DKTCOMEGA
SDP ignore stun
Parameters are passed on to end-point for outgoing calls only
SDP Audio Codec Names:
Parameter
Description
Default
sdp g711u codec name
G.711 ulaw codec name
PCMU/8000
sdp g711a codec name
G.711 alaw codec name
PCMA/8000
Sdp cn codec name
Comfort noise codec name
CN
sdp g729 codec name
G.729/G.729A codec name
G729/8000
sdp g729b codec name
G.729B codec name
G729B/8000
Sdp NSE codec name
Named Signaling Event codec name
X-NSE/8000
SDP Audio Codec Dynamic Code Points:
Parameter
Description
Default
sdp g711u codec dyn pt
G.711 ulaw dynamic payload type
0
sdp g711a codec dyn pt
G.711 alaw dynamic payload type
0
Sdp cn codec dyn pt
Comfort noise dynamic payload type
0
sdp g729 codec dyn pt
G.729/G.729A dynamic payload type
0
sdp g729b codec dyn pt
G.729B dynamic payload type
109
sdp NSE codec dyn pt
Named Signaling Event dynamic payload type
100
SIP Parameters
The SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) Parameters control particular aspects of the
SIP protocols. These parameters include:
SIP Protocol Parameters
SIP Response Codes
SIP Distinctive Ring Names
SIP Protocol Timers
SIP Protocol Parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default
sip user agent
User-Agent header for outbound responses if not
empty
DKTCOMEGA 3.27
sip require user name
Require username to match for incoming calls
Disabled

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 47
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
sip local port
Local UDP port used for sending/ receiving SIP call
control messages
5060
sip public external ip address
Force a specific external IP address for SIP
messages sent (disabled when 0.0.0.0)
0.0.0.0
sip public external sip port
Force a specific external UDP port for SIP messages
sent (disabled when 0)
0
sip tos value
Type of service (TOS) value or DIFFServ DSFIELD
used for SIP messages as a hexidecimal value
0x68
sip accept language string
Specifies the language for user viewable messages
used in the SIP accept message
(empty)
sip send response to src port
Respond to the sender’s IP address/UDP port used
by SIP request message
Enabled
sip max forwards
Maximum forward value
15
sip ringing retransmit
Enables ringing invite retransmission
Enabled
sip use nat discovery
Enable use of NAT discovery procedures to obtain
an external IP address/UDP port mapping for SIP
messages
Enabled
sip use received via info
Use VIA header IP address/UDP port parameters in
received messages as external IP address/UDP port
Disabled
sip nat keep alive enable
Send periodic SIP messages to keep port mapping
active
Disabled
sip nat keep alive interval
Periodic interval in seconds for SIP keep alive
messages
15
sip nat keep alive domain name
Fully qualified domain name (including an optional
port number) for the destination of SIP keep alive
message (sends to the proxy server if empty)
(empty)
sip nat keep alive message
Type of message to be sent as SIP keep alive:
empty, notify or register
(empty)
sip prack enable
Enables support for Provisional Response
ACKnowledgement, PRACK (supported from
firmware 05_05b6 or later)
Disabled
SIP Response Codes:
Parameter
Description
Default
sip response code sit1
SIP response code which plays the SIT1 tone
sequence
0
sip response code sit2
SIP response code which plays the SIT2 tone
sequence
0
sip response code sit3
SIP response code which plays the SIT3 tone
sequence
0
sip response code sit4
SIP response code which plays the SIT4 tone
sequence
0
sip response code try backup
SIP response code to use backup server
0
sip response code retry registration
SIP response code to retry the registration
30
SIP Distinctive Ring Names:
Parameter
Description
Default
sip distinctive ring names 1
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 1
Belcore-r1
sip distinctive ring names 2
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 2
Belcore-r2
sip distinctive ring names 3
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 3
Belcore-r3
sip distinctive ring names 4
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 4
Belcore-r4
sip distinctive ring names 5
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 5
Belcore-r5
sip distinctive ring names 6
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 6
Belcore-r6
sip distinctive ring names 7
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 7
Belcore-r7

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 48
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
sip distinctive ring names 8
Telephone event name to produce distinctive ring
pattern 8
Belcore-r8
SIP Protocol Timers:
Parameter
Description
Default
sip timer invite expires
Invite expiration in seconds
180
sip timer reinvite expires
Re-invite expiration in seconds
180
sip timer registration min
Registration period minimum in seconds
1
sip timer registration max
Registration period maximum in seconds
7200
sip timer registration retry
Registration expiration in seconds
30
sip timer no answer duration
No answer duration in seconds
300
sip session time
Session expiration in seconds
1800
SIP Server Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
sip allow incoming subscription
Disabled
sip subscribe authentication
Disabled
sip incoming resubscribe interval
Resubscribe interval in seconds
3600
sip allow incoming registration
Disabled
sip register authentication
Disabled
sip incoming reregister interval
Reregister interval in seconds
3600
sip invite authentication
Disabled
sip bye authentication
Disabled
sip notify authentication
Disabled
sip incoming auth user name
(empty)
sip incoming auth realm
(empty)
sip incoming auth password
(empty)
IPBX Parameters
IPBX Parameters:
The parameters in the following three sections control the connection to the local
phone (FXS) port on the ATA. This includes control of both the SLIC (Subscriber
Line Interface Circuit) and SLAC (Subscriber Line Audio Circuit) that together make
up the FXS port. The first section, below, offers separate control for voice and
tone signals, of parameters including transmit and receive levels, and of DTMF
tone characteristics.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx voice rx gain
Additional voice receive gain in dB units
0
ipbx voice tx gain
Additional voice transmit gain in dB units
0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 49
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx tone gain
Additional tonal signal gain in dB units
0
ipbx tone max
Maximum tonal signal level in dBm
-12
dtmf low tone gain
Low frequency group DTMF tone level in dBm
-9
dtmf high tone gain
High frequency group DTMF tone level in dBm
-7
dtmf tone on time
DTMF generation on time in msec
80
dtmf tone off time
DTMF generation off time in msec
80
dtmf detect abcd
DTMF detection enable for ABCD dual tone pairs
Enabled
dtmf generate abcd
DTMF generation enable for ABCD dual tone pairs
Enabled
dtmf pad duration
DTMF out-of-band on time in msec
100
dtmf wait duration
DTMF out-of-band off time in msec
50
dtmf playout min duration
DTMF out-of-band minimum on time in msec
100
Timers:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx brief pause duration
Time in 10 msec units before tone
50
ipbx initial dial duration
Timeout in 10 msec units from off-hook to first
dialed digit
1500
ipbx warm line duration
Timeout in 10 msec units from off-hook to first
dialed digit before warm dial
400
ipbx interdigit duration
Timeout in 10 msec units between digits after dial
string already matches a possible pattern
500
ipbx dialing duration
Timeout in 10 msec units after each digit until next
digit
1000
ipbx hangup disconnect duration
Hangup disconnect duration in 10 msec units
85
ipbx hangup silence duration
Hangup silence duration in 10 msec units
1000
ipbx pause wait duration
DTMF dial string pause duration in 10 msec units
300
ipbx timeout tone duration
Duration of busy in 10 msec units after aborted
dialing or aborted answer (glare)
6000
ipbx timeout pause duration
Pause in 10 msec units between busy and alert tone
100
ipbx timeout warning duration
Duration of alerting tone in 10 msec units when off
hook for too long
0
ipbx timeout hold duration
Duration of time in 10 msec units before call
holding tone
1000
ipbx timeout hold drop duration
Duration of time in 10 msec units before dropping
holding call
6000
ipbx no answer duration
No answer duration in seconds
20
ipbx call back duration
Callback duration in seconds
1800
ipbx call back retry duration
Callback retry duration in seconds
30
ipbx call back ring wait duration
Callback ring wait duration in seconds
1
ipbx message waiting refresh duration
Message waiting refresh duration in seconds
1800
ipbx hookflash maximum
Time in msec for maximum hookflash
900
ipbx hookflash minimum
Time in msec for minimum hookflash
100
ipbx hookflash delay
Time in msec to delay hookflash action in case of
hangup
200
ipbx answer hangup delay
Time in msec for answer side hangup delay
0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 50
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Other:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx concurrent line count
Number of concurrent line permitted
2
ipbx concurrent voip count
Number of concurrent VoIP segments permitted
including conferences
3
ipbx epoch clock limit
Call progress, ringer and display synchronization
period in samples (16000 for two seconds and 48000
for six seconds)
16000
ipbx hook debounce
Debounce test count for hook on/off transitions
10
ipbx hookflash enable
A parameter added to disable hook flash processing
1
Regionalization
The Regionalization settings are used to configure the ATA for local operating
conventions. These include:
Call Progress Tones
Default Ringing Patterns
Distinctive Ringing Patterns
Distinctive Call Waiting Patterns
LED Patterns and Priority
Voice and Tone Parameters
SLAC Configuration
Command Strings
Call Progress Tones:
Call progress tones are specified by a list of values indicating the number of tones,
number of on/off transitions, frequency/signal level pairs and tone on/off times
according to the following format:
no_of_tones, no_of_times, duration, {tone_element1_freq,
tone_element1_db, tone_element2_freq, tone_element2_db, …},
{tone_on_time1, tone_off_time1, tone_on_time2, …}
no_of_tones is the number of tone elements that are combined to form a
tone. Each tone element has an associated frequency and amplitude. Up to
four tone elements can be combined – to form a chord, or played in
sequence – as a tune (see no_of_times). A negative no_of_tones indicates
that the tones will be synchronized to a two-second timer (relevant for
multi-port ATAs only).
no_of_times is the total of both on-to-off and off-to-on transitions in the
tone pattern. If this value is positive, it produces a composite tone. If it is
negative, the tones are played in sequence. Zero produces a continuous
composite tone
duration is the length of time in seconds that the call progress tone will
be played. A value of zero means that the tone will be played until
instructed otherwise.
tone_elementX_freq and tone_elementX_db represent the frequency (Hz)
and signal level (dB) of each tone. A negative frequency is used to

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 51
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
modulate the prior tone components summed together. A negative dBm
level can be offset by ipbx_tone_gain.
tone_on_timeX and tone_off_timeX are interleaved Tone On and Tone
Off durations in msec. A value of zero for a Tone On time indicates a
continuous tone. A value of zero for a Tone Off time produces silence,
while a negative value (-1) terminates the tone pattern, removing the
silencing. (With silencing, the voice channel is blocked until the tone
pattern is stopped.)
Allowed values for frequency are from 0 to 3000Hz. Allowed values for dB levels
are from –1 to –40 dB. The maximum number of tones is 4. The maximum number
of on-to-off and off-to-on times counted individually is 9.
F
or example, the default setting for initial dial tone is “{2, 0, 0, {350, -19,
440, -19}, {0}}”. “2” is the number of frequency/dB pairs, “350, -19” and
“440, -19”. “0” is the number of on/off transitions in the tone pattern, which
means that it is a constant tone. The second “0” indicates that the tone will be
played until otherwise instructed. The first pair of frequency/dB “350, -19”
means that the first tone is at 350Hz with a level of -19dB. The second pair “440,
-19” means that the second tone is at 440Hz with a level of -19dB. The final
“{0}” means that there are no on/off times and that the tone is constant.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx initial dial tone
Initial composite dial tone pattern
{2, 0, 0, {350, -19, 440, 19}, {0}}
ipbx alternate dial tone
Alternate dial tone pattern used with
primary VoIP provider not available
{1, 0, 0, {400, -16}, {0}}
ipbx secondary dial tone
Outside line composite dial tone pattern
{2, 0, 0, {420, -19, 520, 19}, {0}}
ipbx stuttered dial tone
Stuttered composite dial tone pattern
{2, 7, 0, {350, -19, 440, 19}, {100, 110, 100, 110,
100, 110, 0}}
ipbx message wait dial tone
Message waiting composite dial tone
pattern
{2, 2, 0, {350, -19, 440, 19}, {160, 160}}
ipbx call forward dial tone
Call forward composite dial tone pattern
{2, 3, 0, {350, -19, 440, 19}, {250, 400, 0}}
ipbx pre ringback tone
Pre-ringback tone pattern sequence
{4, -8, 0, {440, -16, 494, 19, 523, -19, 587, -19},
{340, 160, 340, 160, 340,
160, 340, 160}}
ipbx ringback tone
Ringback composite tone pattern
{2, 2, 0, {440, -19, 480, 19}, {2000, 4000}}
ipbx call waiting tone default
Non-blocking call waiting single tone
pattern
{1, 2, 0, {440, -16}, {300,
9700}}
ipbx station call waiting tone default
Non-blocking call waiting single tone
pattern for station to station calls
{1, 2, 0, {440, -16}, {300,
9700}}
ipbx call holding tone
Non-blocking call holding single tone
pattern
{1, 4, 0, {1200, -16}, {100,
200, 100, -1}}
ipbx call hold disconnect tone
Non-blocking call hold disconnect single
tone pattern
{1, 4, 0, {350, -16}, {50,
100, 50, -1}}
ipbx call disconnect tone
Call disconnect tone pattern
{2, 2, 0, {480, -19, 620, 19}, {500, 500}}
ipbx call conference tone
Non-blocking conference call tone
pattern
{1, 2, 0, {350, -16}, {100,
15000}}
ipbx busy tone
Normal busy composite tone pattern
{2, 2, 0, {480, -19, 620, 19}, {500, 500}}
ipbx reorder tone
Re-order (network/fast busy) composite
tone pattern
{2, 2, 0, {480, -19, 620, 19}, {250, 250}}

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 52
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx off hook warning tone
Off-hook warning composite tone pattern
{4, 2, 0, {1400, 11, 2050,
11, 2450, 11, 2600, 11},
{100, 100}}
ipbx sit1 tone
Sit tone #1 tone sequence
{3, -6, 0, {985, -16, 1428,
-16, 1777, -16}, {330, 5,
330, 5, 330, 1000}}
ipbx sit2 tone
Sit tone #2 tone sequence
{3, -6, 0, {914, -16, 1371,
-16, 1777, -16}, {330, 5,
330, 5, 330, 1000}}
ipbx sit3 tone
Sit tone #3 tone sequence
{3, -6, 0, {985, -16, 1428,
-16, 1777, -16}, {380, 5,
380, 5, 380, 1000}}
ipbx sit4 tone
Sit tone #4 tone sequence
{3, -6, 0, {985, -16, 1428,
-16, 1777, -16}, {380, 5,
380, 5, 380, 1000}}
ipbx prompt tone
Prompt composite tone
{2, 0, 0, {520, -19, 620, 19}, {0}}
ipbx confirm tone
Confirmation single tone
{1, 2, 0, {600, -16}, {400,
0}}
ipbx input error tone
Input error composite tone pattern
{2, 2, 0, {480, -19, 620, 19}, {250, 250}}
ipbx number error tone
Number error composite tone pattern
{2, 2, 0, {480, -19, 620, 19}, {250, 250}}
Standard Ringing Patterns:
Ring patterns are specified by a list of values indicating the frequency, number of
on/off transitions and Ring On/Ring Off times according to the following format:
ring_frequency, no_of_times, duration, {ring_on_time1,
ring_off_time1, ring_on_time2, ring_off_time2, …}
ring_frequency specifies the frequency of the ringing tone in Hz for
sinusoidal and trapezoidal ringing. This value is only used if the default
ringer parameter slac_ring_frequency is zero.
no_of_times is the total of both on and off transitions in the ring pattern.
This can be zero for a continuous ring signal (which may not be desirable
and may exceed the rated power capacity of the ATA).
duration is the length of time in seconds to ring. A value of zero means
until instructed otherwise.
ring_on_timeX and ring_off_timeX are interleaved Ring On and Ring Off
durations in msec. A value of zero for a Ring On time indicates a continuous
tone. A value of zero for a Ring Off time produces continuous silence.
Possible values for frequency are between 0-60Hz. The maximum total of on and
off times summed together is 9.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx call ring default
Default ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {2000, 4000}}
ipbx call station ring default
Default station call ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {1000, 3000}}
ipbx call holding rering
Call on hold reminder re-ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {500, 0}}
ipbx call back ring
Call back success ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {1500, 0}}
ipbx call back ring splash
Call back in progress ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {700, 0}}
ipbx call forward ring splash
Call forward reminder ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {500, 0}}
ipbx message waiting ring splash1
Audible message waiting ring pattern
{20, 2, 0, {500, 0}}

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 53
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Distinctive Ringing Patterns:
The distinctive ring feature allows a different ring to be sent to the telephone as
per the values of the Distinctive Ring parameters 1 - 8. Support for up to 8
distinctive rings is available to the user. The syntax for each of the distinctive ring
parameters is the same as the default ring parameter where the frequency,
number of On/Off transitions, and the Ring On/Ring Off times can be set as
desired.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx distinctive ring 1
Distinctive ring pattern #1
{20, 2, 0, {2000, 4000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 2
Distinctive ring pattern #2
{20, 4, 0, {1000, 1000, 1000,
3000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 3
Distinctive ring pattern #3
{20, 6, 0, {300, 200, 1000,
200, 300, 4000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 4
Distinctive ring pattern #4
{20, 4, 0, {800, 400, 800,
4000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 5
Distinctive ring pattern #5
{20, 4, 0, {400, 200, 400,
2000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 6
Distinctive ring pattern #6
{20, 2, 0, {1000, 3000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 7
Distinctive ring pattern #7
{20, 4, 0, {300, 200, 1500,
2000}}
ipbx distinctive ring 8
Distinctive ring pattern #8
{20, 4, 0, {800, 400, 800,
2000}}
Distinctive Call Waiting Patterns:
A distinctive call waiting tone is played when an incoming call arrives while the
phone is in use. Support for up to 8 distinctive call waiting tone patterns is
available. The syntax for each of the distinctive call waiting tone parameters is
the same as the default call waiting tone parameter where the number of tones,
number of On/Off transitions, Frequency/Signal level pairs and the tone On/Off
times can be set as desired.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx call waiting tone 1
Non-blocking call waiting #1 single tone
pattern
{1, 2, 0, {440, -16}, {300,
9700}}
ipbx call waiting tone 2
Non-blocking call waiting #2 single tone
pattern
{1, 6, 0, {440, -16}, {100,
20, 100, 20, 100, 9660}}
ipbx call waiting tone 3
Non-blocking call waiting #3 single tone
pattern
{1, 4, 0, {440, -16}, {100,
100, 100, 9700}}
ipbx call waiting tone 4
Non-blocking call waiting #4 single tone
pattern
{1, 6, 0, {440, -16}, {100,
100, 100, 100, 100, 9500}}
ipbx call waiting tone 5
Non-blocking call waiting #5 single tone
pattern
{1, 2, 0, {620, -16}, {300,
9700}}
ipbx call waiting tone 6
Non-blocking call waiting #6 single tone
pattern
{1, 6, 0, {620, -16}, {100,
20, 100, 20, 100, 9660}}
ipbx call waiting tone 7
Non-blocking call waiting #7 single tone
pattern
{1, 4, 0, {620, -16}, {100,
100, 100, 9700}}
ipbx call waiting tone 8
Non-blocking call waiting #8 single tone
pattern
{1, 6, 0, {620, -16}, {100,
100, 100, 100, 100, 9500}}
SLAC Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
slac port impedance
Synthetic impedance matching network control for
a choice of one in ten common world-wide
configurations
600 ohm
slac port rx gain (GR)
SLAC receive gain in dB units
-3
slac port tx gain (GX)
SLAC transmit gain in dB units
6

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 54
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
slac audio clamp
slac caller id type 1 mode
Caller ID type 1 (on-hook) mode (None, Belcore
MDMF, SDMF, ETSI WINK, ETSI RING and DTMF)
Belcore MDMF
slac caller id type 2 mode
Caller ID type 2 (off-hook) mode (None, Belcore
MDMF, SDMF, ETSI WINK, ETSI RING and DTMF)
Belcore MDMF
slac message waiting mode
Message waiting mode (None, Belcore VMWI, ETSI,
DTMF)
Belcore VMWI
slac ring type
Selects ring waveform type of sinusoidal or
trapezoidal
sinusoidal
slac ring frequency
Ringer frequency in Hz (zero to use ring pattern
frequency specification)
25
slac ring transition
Trapezoidal transition time in msec
15
slac ring amplitude
Ringer voltage in volts
85
slac ring bias
Ringer bias in volts
0
slac message waiting type
Selects visual message waiting waveform type of
sinusoidal or trapezoidal
Sinusoidal
slac message waiting frequency
Visual message waiting frequency in Hz
25
slac message waiting transition
Trapezoidal transition time in msec
15
slac message waiting amplitude
Visual message waiting voltage in volts
50
slac message waiting bias
Visual message waiting bias in volts
0
slac dtmf caller id start code
The parameters 'slac dtmf caller id start code' and
'slac dtmf caller id end code' allow you to configure
the start and end codes respectively.
slac dtmf caller id end code
The parameters 'slac dtmf caller id start code' and
'slac dtmf caller id end code' allow you to configure
the start and end codes respectively.
slac dtmf caller id polarity reversal
DTMF polarity reversal as per ETSI EN 300 659-1:
Subscriber line protocol over the local loop for
display (and related) services ; Part 1 : On-hook
data transmission. The parameter 'slac dtmf caller
id polarity reversal' allow you to enable to disable
polarity reversal during DTMF caller ID
transmission. This function will invert voltage when
DTMF tones are transmitted on the analogue
interface (Caller Id) before ringing.
Disabled
SLAC Command Strings:
Parameter
Description
Default
slac initialization commands
100
slac impedance commands 1
SLAC commands to synthesize 600 ohm impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 2
SLAC commands to synthesize 900 ohm impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 3
SLAC commands to synthesize 600 ohm + 1.0uF
impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 4
SLAC commands to synthesize 900 ohm + 2.16uF
impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 5
SLAC commands to synthesize 270 ohm + 750 ohm
|| 150nF impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 6
SLAC commands to synthesize 220 ohm + 820 ohm
|| 120nF impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 7
SLAC commands to synthesize 220 ohm + 820 ohm
|| 115nF impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 8
SLAC commands to synthesize 370 ohm + 620 ohm
|| 310nF impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 9
SLAC commands to synthesize 200 ohm + 680 ohm
|| 100nF impedance
(many)
slac impedance commands 10
SLAC commands to synthesize 800 ohm + 50nF
impedance
(many)

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 55
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 56
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Subscription Services
Subscription Services configure the ATA for the specific advanced services
permitted and/or supported. These include:
Subscription Services
Port Configuration
Subscription Service Parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx call waiting service
Enables customer use of call waiting service
Enabled
ipbx caller id inbound service
Enables customer use of incoming caller ID service
Enabled
ipbx caller id outbound service
Enables customer use of outgoing caller ID service
(i.e. always send caller ID information)
Enabled
ipbx call waiting caller id service
Enables customer use of incoming caller ID during
call waiting service
Enabled
ipbx call back service
Enables customer use of call back service
Enabled
ipbx call return service
Enables customer use of call return service
Enabled
ipbx speed dial service
Enables customer use of speed dial service
Enabled
ipbx do not disturb service
Enables customer use of do not disturb service
Enabled
ipbx block anonymous service
Enables customer use of anonymous call block
service
Enabled
ipbx call forward service
Enables customer use of call forward service
Enabled
ipbx busy forward service
Enables customer use of call forward when busy
service
Enabled
ipbx no answer forward service
Enables customer use of no answer call forward
service
Enabled
ipbx priority forward service
Enables customer use of priority call service
Enabled
ipbx distinctive ring service
Enables customer use of distinctive ring service
Enabled
ipbx disturb accept service
Enables customer use of do not disturb accept
service
Enabled
ipbx blocked number service
Enables customer use of blocked number service
Enabled
Ipbx outgoing block number service
Enables outgoing block service
Enabled
ipbx forward last call service
Enables customer use of forward to last caller
service
Enabled
ipbx distinctive ring last call service
Enables customer use of distinctive ring for last
caller service
Enabled
ipbx disturb accept last call service
Enables customer use of do not disturb accept last
caller service
Enabled
ipbx block last call service
Enables customer use of block last caller service
Enabled
ipbx three way calling service
Enables customer use of three way calling service
Enabled

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 57
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx three way conference service5
Enables customer use of three way conference
service
Enabled
ipbx attended transfer service
Enables customer use of attended call transfer
service
Enabled
ipbx unattended transfer service
Enables customer use of unattended call transfer
service
Enabled
ipbx message waiting service
Enables customer use of message waiting service
Enabled
ipbx visual message waiting service
Enables customer use of visual message waiting
service. If enabled the ATA will send FSK data to
the phone indicating the presence or non-presence
of a message. The ATA supports the Belcore SDMF
and Belcore MDMF standards of visual message
waiting indication.
Enabled
ipbx remote feature code service
Enables sending all features codes to remote
service provider
Disabled
ipbx default feature code service
Enables sending all unprocessed feature codes to
remote service provider
Disabled
Port Configuration:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx line 1 enable
Enables use of physical line 1
Enabled
ipbx line 2 enable
Enables use of physical line 2
Enabled
ipbx line 1 number
Assigned local number for line 1
L1
ipbx line 2 number
Assigned local number for line 2
L2
ipbx line 1 name
Assigned name for line 1
(Empty)
ipbx line 2 name
Assigned name for line 2
(Empty)
5
As far as conferencing goes, the ATA can handle two simultaneous media connections. If both ports are in use,
local conferencing inside the ATA is not possible.
If three way conferencing is enabled:
Scenario 1 (while in call):
1. Hookflash puts current call on hold.
2. Dial and connect second call.
3. Hookflash conferences the calls together.
4a. Hookflash hangs up the second call.
or
4b. Hanging up will transfer the 2 remote calls together (attended transfer).
Scenario 2 (while in call):
1. Incoming call received (call waiting).
2. Hookflash to accept call waiting call.
3. Hookflash to switch back to first call.
4. Hookflash to switch back and forth between calls.
Scenario 3 (while in call and local processing of feature codes is enabled):
1. Hookflash puts current call on hold.
2. Dial *98 followed by a phone number.
3. Current call will be transferred to number dialed in step 2 (blind transfer).
The difference between scenarios 1 and 2 is the direction of the second call. In scenario 1 the second call was an
outgoing call from the ATA. In this case the ATA is able to conference the two calls together. In scenario 2 the
second call was incoming to the ATA. In this case conferencing is not available. If three way conferencing is
disabled the behavior is the same as scenario 2 regardless of whether the second call was incoming or not (i.e.
hookflashing will switch between the two active calls).

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 58
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Operating Mode:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx mode
ATA operating mode (ASS, SIHT, IHT, SIOT, IPBX)
ASS (A Simple Service):
The simplest mode passes all digits, as well as * and
#, to the pattern matches for VOIP or PSTN calls. In
this mode there is absolutely no feature codes,
speed dialing or manual call routing.
SIHT (Simple Internet Home Termination):
This mode provides dialing priority for a VoIP call
and almost eliminates all special codes for access
to other stations. This is best used for a maximum
of 2 to 4 stations. The most significant
simplification is for placing a call on hold and
picking it up. No transfer/pickup codes are
needed. Picking up both lines conferences them
together. A line may press * or # to get a new line
to place their own call. Very limited feature
sequences are needed.
IHT (Internet Home Termination):
This mode provides dialing priority for a VoIP call
and requires special codes for access to other
stations. This can be scaled from 2 to 8 stations
(and possibly more by increasing the number of
digits used for station identification).
SIOT (Small Internet Office Termination):
This mode is a simplified IBX/enhanced IHT
IPBX (Internet Private Branch Exchange):
This mode provides dialing priority for station-tostation calls and requires dialing 8 or 9 to place
PSTN and VoIP calls. This can be scaled from 2 to
99 (or 999) stations with the use of more digits for
station identification.
SIHT, value ‘1’
ipbx voip primary provider unavailable
Dial tone to be generated when the primary
provider is not available
Standard Dial
Tone
ipbx voip no provider available
Dial tone to be generated when all VoIP providers
are not available
Alternate Dial
Tone
ipbx pstn not available
Dial tone to be generated when no VoIP provider is
available and no PSTN dial tone is available
No Dial Tone
ipbx dial direct
Direct dial processing mode (VoIP, PSTN, BOTH or
DIRECT)
BOTH
ipbx dial after 8
Processing mode after an 8 prefix (VoIP, PSTN,
BOTH or DIRECT)
PSTN
ipbx dial after 9
Processing mode after a 9 prefix (VoIP, PSTN, BOTH
or DIRECT)
VoIP
ipbx dial after pound 8
Processing mode after a #8 prefix (VoIP, PSTN,
BOTH or DIRECT)
BOTH
ipbx dial after pound 9
Processing mode after a #9 prefix (VoIP, PSTN,
BOTH or DIRECT)
BOTH
ipbx dial speed dial
Processing mode for speed dial (VoIP, PSTN, BOTH
or DIRECT)
VoIP
ipbx input pattern voip
Pattern match for VoIP dialing
[3469]11|*xx|**|
1900r7x!| 976r4!|
1800r7x|[^1]r6x|
1r3x[^1]r6x|
1010Se#e*p2r*x|
0Se#e*p2r*x
ipbx input pattern pstn
Pattern match for PSTN dialing
911
ipbx hot line dialing
Enables automatic hot-line dialing
Disabled
ipbx warm line dialing
Enables shorter duration timeout for warm line
dialing
Disabled
ipbx hotwarm dial string
Hot/warm dial string
(empty)
ipbx polarity dialing
Sets the SLAC line polarity during dialing (forward
or reverse)
Forward

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 59
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx polarity dial done
Sets the SLAC line polarity after dialing is done
(forward or reverse)
Forward
ipbx polarity connect
Sets the SLAC line polarity during connect (forward
or reverse)
Forward
ipbx polarity answer
Sets the SLAC line polarity during answer (forward
or reverse)
Forward
ipbx polarity idle
Sets the SLAC line polarity during idle (forward or
reverse)
Forward
Ipbx party line enable
Enables the two lines to be bridged with the use of
hock flash
Disabled
VoIP Dial Pattern:
The VoIP Dial Pattern and the PSTN Dial Pattern together determine how the ATA
handles dial strings when someone dials a number from an attached phone. For
units without an FXO port, the PSTN Dial Pattern is ignored. In a given location,
there are generally only a few types of dialed numbers that need to be defined.
There is dialing for local calls, there is dialing for domestic toll calls, and there is
dialing for international toll calls. In addition, there are specific short strings that
are set aside for emergency dialing, and there may be other special strings that
invoke telephone features.
By default, the ATA is configured to handle number patterns in every country in
the world. For models with an FXO port, emergency calls are by default routed to
the PSTN, and all other calls are routed via VoIP. You can use the Dial Patterns to
change which calls are sent via VoIP, and which are sent to the PSTN. For
example, you may want to send all local calls via the PSTN, because these may be
free on your PSTN line. You may also want to tailor the Dial Patterns to precisely
reflect the format of telephone numbers in your location. For example, the
default configuration recognizes that a local number may be from 5 to 10 digits
long. If local numbers are always 8 digits, this means that the ATA will wait a few
seconds after the 8th digit has been dialed, to see if any digits follow. You could
redefine the local dial string always to expect 8 digits, and to immediately send
the number to the service provider once someone had dialed 8 digits.
Parameter
Description
“|”
separates different possible patterns
"r"
repeat by following a number (1-9), letter (a-z for 10 to 35 times) or "*", “+” or "." to mean any
number of times (255 times)
"."
repeat previous digit any number of times (0 to 255)
"+"
repeat previous digit any number of times (0 to 255)
"x"
match any numerical digit (0-9)
"~"
match any digit (0-9, A-D, *, #) excluding any specified terminators
"!"
disallows pattern
"$"
indicates secondary dialing to follow - used only by fixed dial strings
"<:>"
replace group to replace left digit(s) with right digit(s)
"[]"
selection group of candidate digits
"[^]"
exclusion group of digits

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 60
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
"[0-9]"
selection range of candidate numerical digits
"[a-d]"
selection range of candidate letter digits
"s"
seize on string as only candidate if match to this point
"e"
specify ending termination digit which follows (usually * or #)
"f"
pause timeout causes failure instead of dial
"p"
set digit pause to number of seconds which follow (1-9) for current pattern
"t"
set digit timeout to default for current pattern
"-"
human readable spacing which is ignored
" "
human readable spacing which is ignored
Interdigit timeout, or pause: By default, the device allows five (5) seconds
between dialed digits. To change this default, you must insert the “p” parameter
before the point in the match string that you want this parameter to change. For
example, if you would like a nine (9) second delay after each digit is pressed, then
you would need to enter “p9” at the beginning of the pattern matching string.
Similarly, if you would like a shorter timeout of three (3) seconds towards the end
of a dial string, you would need to enter “p3” before the last entry in the pattern
matching string: …p3r*x.
Examples of dial strings:
Each parameter in a pattern match string represents a single digit. The only
exceptions are parameters that include a repeat operator. We will illustrate these
features by examining the entries in the default VoIP dial string:
[346]11|*xx|**[1-9]e#r5xp3r*x|p8[1-9]e#r5xp3r*x|#[1-9]e#r5xp3r*x
|1010Se#p2r*x|0Se#r5xp2r*x[3469]11
Recognize the sequences 311,411, 611 and 911, and send them to the service
provider when complete.
[3469] means “either 3 OR 4 OR 6 OR 9” . The entire string means “either 3 OR 4
OR 6 OR 9” followed by “11”.
*xx
This string allows the ATA to recognize and forward feature codes to the service
provider. However, note that by default, feature codes are handled locally, in the
ATA. The ATA refers to this string only if the remote or default feature code
parameters are enabled, or if Pass Through mode is enabled. In those cases, this
string must be included in the pattern matching string, so that the ATA will
forward feature codes to the service provider.
**[1-9]e#r5xp3r*x
This string pertains to VoIP provider “area codes”. The “**” prefix is a signal for
the service provider to forward this call to another VoIP service provider. The
three digits following “**” constitute the VoIP provider “area code.” Recognize a
string starting with “**”, and proceeding with any of the digits 1-9. “e#” defines

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 61
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
“#” as the terminating character. If someone dials “#” at any point after the 1-9,
the ATA sends out all digits dialed to that point to the service provider. If the
person doesn’t dial a “#”,collect five more digits (“’r5x”), switch from the
default inter-digit timeout of five (5) seconds to a shorter inter-digit timeout of
three (3) seconds (“p3”), and continue collecting digits until a timeout occurs
(“r*x”). This string will be forwarded only if the ATA is in Pass Through Mode.
p8[1-9]e#r5xp3r*x
This is the workhorse string of the default pattern for dialing. It matches dialing
for VoIP calls, and for local dialing in most countries. It also matches dialing for
domestic long distance dialing under the North American dial plan. This string is
identical to the preceding string, except for the first two characters. Where the
preceding string calls for a match to the prefix “**”, this string redefines the
interdigit timeout. This value has been increased to eight (8) seconds. This
timeout value persists until the first digit plus five other digits have been
collected, at which time the timeout value is reduced to three (3) seconds. From
that point onward, the ATA continues to collect digits until the user pauses three
seconds, at which point, the ATA sends the dialed string to the service provider.
#[1-9]e#r5xp3r*x
This string is identical to the previous two, except for the first digit. This string
supports cases where service providers use strings that start with “#” for various
special features or control purposes. This string is forwarded to the service
provider only if the Mode is set to Pass Through.
1010Se#p2r*x
This string is included to supported cases where North-American style dial-around
dialing is available. The “S” means that if someone dials 1010 as the first four
digits of a dial string, this is the only string the ATA should match to from that
point on. “e#” means that the user can indicate the completion of dialing at any
time by entering “#”. “p2” means that after someone dials 1010, the timeout
between subsequent digits is reduced to two (2) seconds. “r*x” means that the
ATA will continue to collect dialed digits until there is a timeout.
0Se#r5xp2r*x
This is the second workhorse string of the default pattern matching string.
International calls in almost every country, and domestic long distance calls in
most countries outside North America, all match this pattern. Any number that
starts with zero (0) matches this string. The user may dial # at any time to indicate
the number dialed is complete. After the user dials the sixth digit, the inter-digit
timeout is reduced to two seconds. After that point, the ATA continues to collect
digits until the user pauses two seconds. Then the ATA sends the dialed string to
the service provider.

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 62
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
User Configuration
ATA settings made by the user include:
Speed Dials
Call Forwarding
Message Waiting
Timers
Distinctive Ringing
Do Not Disturb
Call Blocking
Call Waiting/Caller ID
Speed Dial:
The Speed Dial List can be modified by the telephone or via the web pages. Up to
28 numbers can be entered into the Speed Dial List. Each number can be up to 40
digits in length.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx speed dial array *20
Speed dial number corresponding to *20
(empty)
(repeated)
ipbx speed dial array *39
Speed dial number corresponding to *39
(empty)
ipbx speed dial array #0
Speed dial number corresponding to #0
(empty)
(repeated)
ipbx speed dial array #7
Speed dial number corresponding to #7
(empty)
ipbx hot warm dial string
Special number to be dialed when phone is picked
up
(empty)
Call Forwarding:
With Call Forward enabled, any call on this list will be forwarded to the number
stored in the Call Forward List (1-12). Up to thirty 40-digit numbers can be
entered.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx call forward enable
All call forward enable
Disabled
ipbx busy forward enable
Busy call forward enable
Disabled
ipbx no answer forward enable
No answer call forward enable
Disabled
ipbx priority forward enable
Priority call forward enable
Disabled
ipbx call forward dial string
Call forward destination
(empty)
ipbx busy forward dial string
Busy call forward destination
(empty)
ipbx no answer forward dial string
No answer call forward destination
(empty)
ipbx priority forward dial string
Priority call forward destination
(empty)
ipbx call forward list 1
Number to forward entry 1
(empty)
(repeated)
ipbx call forward list 30
Number to forward entry 30
(empty)

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 63
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Distinctive Ringing:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx distinctive ring enable
Allows numbers on Distinctive Ring List to ring with
a distinctive pattern
Enabled
ipbx distinctive ring list 1
Number for distinctive ringing entry 1
(empty)
(repeated)
ipbx distinctive ring list 30
Number for distinctive ringing entry 30
(empty)
Do Not Disturb:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx do not disturb mode
Enables Do Not Disturb Mode
Disabled
ipbx disturb accept enable
Enables only calls on the Disturb Accept List to ring
Disabled
ipbx disturb accept list 1
Number to accepted while in do not disturb state
entry 1
(empty)
(Repeated)
Call Blocking:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx block anonymous enable
Blocks anonymous numbers
Disabled
ipbx blocked number enable
Enables blocking of calls from numbers in the
Blocked Number List
Disabled
ipbx blocked number list 1
Numbers to block entry 1
(empty)
(repeated)
ipbx blocked number list 30
Numbers to block entry 30
(empty)
Outgoing Call Blocking:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx outgoing block enable
Enables outgoing blocking of calls from numbers in
the Blocked Number List
Disabled
ipbx outgoing block number list 1
Numbers to block entry 1
(empty)
(repeated)
ipbx outgoing block number list 30
Numbers to block entry 30
(empty)
Call Waiting/Caller ID:
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx call waiting enable
Enables call waiting for all calls
Enabled
ipbx caller id inbound enable
Enables caller ID for inbound calls
Enabled
ipbx caller id outbound enable
Enables caller ID for outbound calls
Enabled
ipbx caller id waiting enable
Enables caller ID during call waiting
Disabled
Message Waiting:
Parameter
Description
Default

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 64
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx message waiting
Enables message waiting indication
Off
Feature Code Assignments (*55 - *99)
The IPBX calling features are assigned the ranges *55 to *89 and *92 to *99. The
codes can be reassigned to better match common local conventions, but they must
be given codes within the assigned ranges.
Parameter
Description
Default
ipbx fc call waiting enable
Enable call waiting on all calls
55
ipbx fc call waiting disable
Disable call waiting on all calls
56
ipbx fc call trace
Call trace (reserved)
57
ipbx fc call waiting caller id enable
Enable call waiting caller ID generation
58
ipbx fc call waiting caller id disable
Disable call waiting caller ID generation
59
ipbx fc blocked number enable
Enable call blocking feature
60
ipbx fc distinctive ring enable
Enable distinctive ringing feature
61
ipbx fc caller id outbound disable
Block caller ID on all outbound calls
62
ipbx fc priority forward enable
Enable priority call forwarding feature
63
ipbx fc disturb accept enable
Enable do not disturb accept call feature
64
ipbx fc caller id inbound enable
Enable caller ID generation
65
ipbx fc busy number redial
Busy number redial
66
ipbx fc caller id outbound enable once
Unblock caller ID for one call
67
ipbx fc caller id outbound disable once
Block caller ID for one call
68
ipbx fc caller redial
Call the last caller
69
ipbx fc call waiting disable once
Deactivate call waiting for current call
70
ipbx fc call waiting enable once
Enable call waiting for current call
71
ipbx fc call forward enable
Enable call forwarding to number which follows
72
ipbx fc call forward disable
Cancel call forwarding of non-priority calls
73
ipbx fc one digit speed dial program
Program speed dials 2-9 (20-39 implemented)
74
ipbx fc two digit speed dial program
Program speed dials 20-49 (20-39 implemented)
75
ipbx fc block anonymous enable
Block all anonymous calls
77
ipbx fc do not disturb enable
Enter do not disturb state
78
ipbx fc do not disturb disable
Exit do no disturb state
79
ipbx fc blocked number disable
Cancel call lock - remove optional number from
blocked call list, or disable call blocking feature
80
ipbx fc distinctive ring disable
Disable distinctive ringing
81
ipbx fc caller id outbound enable
Unblock caller ID on all outbound calls
82
ipbx fc priority forward disable
Cancel priority call forward
83
ipbx fc disturb accept disable
Disable do not disturb accept call feature
84

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 65
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx fc caller id inbound disable
Disable caller ID generation
85
ipbx fc busy number redial cancel
Cancel busy redial
86
ipbx fc block anonymous disable
Unblock anonymous calls
87
ipbx fc hookflash simulation
88
ipbx fc caller redial cancel
Cancel calling last caller
89
ipbx fc no answer forward enable
Call forward when no answer - number follows
92
ipbx fc no answer forward disable
Cancel call forward when no answer
93
ipbx fc busy forward enable
Call forward when busy - number follows
94
ipbx fc busy forward disable
Cancel call forward when busy
95
ipbx outgoing block enable
96
ipbx outgoing block disable
97
ipbx fc unattended transfer
98

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 66
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Wifi Plug-in module
TFTP based provisioning
The Wifi Access Point will get its configuration via a TFTP request initiated by the
CPE, when the module is present and enabled.
The module is enabled using the following command in the CPE configuration
script.
enable_wifi <host-wifi-setup-filename> [-t optional-TFTPserver-IP] [-p optionalpassword] [-w optional-WiFi-IP-address]
# The default password for the admin user is "admin". If the
password is changed, this new password may be supplied as the
second parameter on the command line. The default IP address
of the wifi module is 192.168.1.250. If this is changed, then
both the password and the correct IP address must be supplied
on the command line. The default TFTP server is the same as
used for the CPE configuration file.
Note when Wifi is installed, LAN port 4 of the CPE switch is used as dedicated Wifi
port.
All VLAN and QoS parameters related to LAN port 4 must be configured AFTER the
“enable_wifi” command.
System Parameters
Configuration of the Wifi Access Point is done with the use of a configuration file,
including the following parameters, please refer to Appendix 2 – Wifi configuration
file for details.
Parameter
Description
Default
Default
Do not touch
-
WebInit
Do not touch
1
HostName
Wifi host name
DKTCOMEGA
Login
Administrator configuration access name, Please consult DKTCOMEGA for
user name and password
*********
Password
Administrator password, Please consult DKTCOMEGA for user name and
password
*********
OperationMode
Wifi Operation Mode
The following modes can be configured
- Access Point (0)
- Router (1)
- AP Client (2)
0
Platform
Wifi Module Platform, chip vendor
RT3050

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 67
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
wanConnectionMode
WAN Connection Type
DHCP
wan_ipaddr
Applicable to Router Operation Mode, WAN IP address
192.168.2.1
wan_netmask
applicable to Router Operation Mode, IP Subnet mask
255.255.255.0
wan_gateway
applicable to Router Operation Mode, IP Address of the WAN Gateway
192.168.2.254
wan_primary_dns
applicable to Router Operation Mode, DNS Server, primary
168.95.1.1
wan_secondary_dns
applicable to Router Operation Mode, DNS Server, secondary
168.95.192.1
wan_pppoe_user
applicable to Router Operation Mode, PPPoE Username
pppoe_user
wan_pppoe_pass
applicable to Router Operation Mode, PPPoW password
pppoe_passwd
wan_l2tp_server
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Server IP Address
l2tp_server
wan_l2tp_user
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Username
l2tp_user
wan_l2tp_pass
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Password
l2tp_passwd
wan_l2tp_mode
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Mode of Operation
0
wan_l2tp_ip
applicable to Router Operation Mode, IP Address of the Wifi
192.168.2.1
wan_l2tp_netmask
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Subnet mask of the Wifi
255.255.255.0
wan_l2tp_gateway
applicable to Router Operation Mode, IP Address of the Gateway
192.168.2.254
wan_pptp_server
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol,
Server IP Address
pptp_server
wan_pptp_user
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol,
Username
pptp_user
wan_pptp_pass
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol,
Password
pptp_passwd
wan_pptp_mode
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol,
Mode of Operation
0
wan_pptp_ip
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol, IP
Address of the Wifi
192.168.2.1
wan_pptp_netmask
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol,
Subnet mask of the Wifi
255.255.255.0
wan_pptp_gateway
applicable to Router Operation Mode, Point-to-point tunneling protocol, IP
Address of the Gateway
192.168.2.254
lan_ipaddr
LAN IP Address of the Wifi
192.168.1.250
lan_netmask
Subnet mask of the Wifi
255.255.255.0
dhcpEnabled
DHCP Server functionality, Enable or Disable. Clients connected to the Wifi
will get their IP Addressed by the Wifi.
0 (Disable)
dhcpStart
Applicable to DHCP Enable, Start IP Address in the range
192.168.1.100
dhcpEnd
Applicable to DHCP Enable, Stop IP Address of the rante
192.168.1.200
dhcpMask
Applicable to DHCP Enable, Subnet mask
255.255.255.0
dhcpPriDns
Applicable to DHCP Enable, Primary DNS Server IP Address
168.95.1.1
dhcpSecDns
Applicable to DHCP Enable, Secondary DNS Server IP Address
168.95.192.1
dhcpGateway
Applicable to DHCP Enable, IP Address of the Gateway
192.168.1.250
dhcpLease
Applicable to DHCP Enable, this is the DHCP lease time. When it is short,
the issued IP address to DHCP clients will be updated frequently. It is
recommended to keep default setting except for another purpose
86400 (24 hrs)
stpEnabled
Spanning Tree
0
lltdEnabled
Link Layer Topology Discovery, Enable or Disable
0
igmpEnabled
IGMP functionality, Enable or Disable
0
natEnabled
NAT functionality, Enable or Disable
1
IPPortFilterEnable
IP based port filtering, Enable or Disable
0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 68
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
IPPortFilterRules
IP based port filtering, Rules
PortForwardEnable
Port Forwarding, Enable or Disable
0
PortForwardRules
Port Forwarding, Rules
MacFilterEnable
MAC Filtering, Enable or Disable
MacFilterRules
MAC Filtering, Rules
DefaultFirewallPolicy
Default Firewall Policy – drop all or allow all
1
DMZEnable
De-Militarized Zone, Enable or Disable
0
DMZIPAddress
Input the IP Address of the computer that you want to expose to Internet.
TZ
Time zone
NTPServerIP
IP Address of the NTP Server
NTPSync
N/A
DDNSProvider
N/A
DDNS
N/A
DDNSAccount
N/A
DDNSPassword
N/A
BssidNum
Number of BSSID
4
SSID1
This device supports multiple SSID. Input the multiple SSID 1, 2, 3 in the
field to enable the function. With the field of Network Name (SSID), the
device supports maximum 4 SSIDs.
DKTCOMEGA1
WirelessMode
Wireless mode
9
TxRate
Tx rate
0;0;0;0
Channel
Channel
6
BasicRate
A bitmap represent basic support rate
15
BeaconPeriod
Beacons are the packets sending by Access point to synchronize the
wireless network. The beacon interval is the time interval between
beacons sending by this unit in AP or AP+WDS mode. The default and
recommended
User’s Guide 29
beacon interval is 100 milliseconds
100
DtimPeriod
This is the Delivery Traffic Indication Map. It is used to alert the clients
that multicast and broadcast packets buffer at the AP will be transmitted
immediately after the transmission of this beacon frame. You can change
the value from 1 to 255. The AP will check the buffer data according to
this value. For example, selecting “1” means to check the buffer data at
every beacon.
1
TxPower
Tx power
100
RxAckTimeout
The Acknowledgement Timeout means from remote to local data
transmission, one parameter to control both acknowledging action to
guaranty those packets have already be received. Usually, for short
distance, keep default setting is proposed. If there is long distance
application, have minor increased with this parameter will be proposed.
32
DisableOLBC
N/A
0
BGProtection
Default: Auto. You can select the other options including On and Off. The
B/G protection technology is CTS-To-Self. It will try to reserve the
throughput for 11bg clients association.
0
TxAntenna
N/A
RxAntenna
N/A
TxPreamble
0: long preamble, 1: Short preamble
0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 69
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
RTSThreshold
The RTS threshold determines the packet size at which the radio issues a
request to send (RTS) before sending the packet. A low RTS Threshold
setting can be useful in areas where many client devices are associating
with the device, or in areas where the clients are far apart and can detect
only the device and not each other. You can enter a setting ranging from 0
to 2347 bytes.
2347
FragThreshold
The fragmentation threshold determines the size at which packets are
fragmented (sent as several pieces instead of as one block). Use a low
setting in areas where communication is poor or where there is a great
deal of radio interference. This function will help you to improve the
network performance.
2346
TxBurst
The device will try to send a serial of packages with single ACK reply from
the clients. Enable this function to apply it.
1
PktAggregate
Package aggregate
1
TurboRate
N/A
0
StaLimitationEnable
N/A
0
StaLimitationNum
N/A
0
WmmCapable
Choose “Enable” to enable WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) function.
1;1;1;1
APAifsn
WMM parameters
3;7;1;1
APCwmin
WMM parameters
4;4;3;2
APCwmax
WMM parameters
6;10;4;3
APTxop
WMM parameters
0;0;94;47
APACM
WMM parameters
0;0;0;0
BSSAifsn
WMM parameters
3;7;2;2
BSSCwmin
WMM parameters
4;4;3;2
BSSCwmax
WMM parameters
10;10;4;3
BSSTxop
WMM parameters
0;0;94;47
BSSACM
WMM parameters
0;0;0;0
AckPolicy
WMM parameters
0;0;0;0
APSDCapable
Choose “Enable” to enable APSD (Automatic Power-Save Delivery) function.
0
DLSCapable
N/A
0
NoForwarding
Layer 2 isolation
0;0;0;0
NoForwardingBTNBSSID
No Forwarding between each BSSID interface.
0
HideSSID
Hide SSID
0;0;0;0
ShortSlot
Short slot
1
AutoChannelSelect=0
Auto channel selection function
0
SecurityMode
OPEN, SHARED, WEPAUTO, WPA RADIUS, WPA-PSK, WPA2 RADIUS, WPA2PSK, WPA/WPA2 PSK, WPA/WPA2 RADIUS, 802.1X.
0
VLANEnable
VLAN Support, one VLAN ID per SSID, Enable or Disable
0
VLANName
VLAN name
-
VLANID
VLAN VID for all SSIDs
0;0;0;0
VLANPriority
VLAN priority
0
WscConfMode
WPS function, bitwise.
0
WscConfStatus
It shows the current status of the WPS process.
2
WscAKMP
N/A
1

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 70
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
WscConfigured
It indicated whether the WPS is configured.
1
WscModeOption
N/A
0
WscActionIndex
N/A
9
WscPinCode
Input the 8-digits PIN of client.
-
WscRegResult
N/A
1
WscUseUPnP
N/A
1
WscUseUFD
N/A
0
WscSSID
N/A
DKTCOMEGAAP
WscKeyMGMT
N/A
WPA-EAP
WscConfigMethod
N/A
138
WscAuthType
N/A
1
WscEncrypType
N/A
1
WscNewKey
N/A
Scaptest
IEEE8021X
IEEE 802.1x function
0;0;0;0
IEEE80211H
N/A
0
CSPeriod
N/A
6
PreAuth
N/A
0;0;0;0
AuthMode
OPEN, SHARED, WEPAUTO, WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2
PSK, WPA/WPA2
WPAPSK;OPEN;O
PEN;OPEN
EncrypType
None, WEP, TKIP, AES, TKIPAES
TKIP;NONE;NON
E;NONE
RekeyInterval
Rekey Interval
3600
RekeyMethod
Rekey Method
DISABLE
PMKCachePeriod
PMK Cache Period
10
WPAPSK1
WPA/WPA2-PSK Pass Phrase (8-64 characters). Key 2
56655153
DefaultKeyID
Default Key ID
2;1;1;1
Key1Type
WEP Key 1 Type, 0: Hexadecimal, 1: ASCII
0;0;0;0
Key1Str1
WEP Key 1
-
Key2Type
WEP Key 2 Type, 0: Hexadecimal, 1: ASCII
0;0;0;0
Key2Str1
WEP Key 2
-
Key3Type
WEP Key 3 Type, 0: Hexadecimal, 1: ASCII
0;0;0;0
Key3Str1
WEP Key 3
-
Key4Type
WEP Key 4 Type, 0: Hexadecimal, 1: ASCII
0;0;0;0
Key4Str1
WEP Key 4
-
HSCounter
N/A
0
HT_HTC
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
1
HT_RDG
Applicable to HT Physical Mode, Reverse Direction Grant (RDG). This is the
11n performance parameter. Enable it if needed.
1
HT_LinkAdapt
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
0
HT_OpMode
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
0
HT_MpduDensity
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
5

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 71
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
HT_EXTCHA
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
1
HT_BW
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
1
HT_AutoBA
Applicable to HT Physical Mode, Auto Block ACK.
It is another aggregation technique which prevents sending ACK in the
communication to increase the throughput. If this option is enabled, the
device will activate this function when transmitting massive data.
1
HT_BADecline
Applicable to HT Physical Mode, Decline BA Request, Enable this option to
decline the Block ACK request addressed by the other devices.
0
HT_AMSDU
Applicable to HT Physical Mode, Aggregation MSDU (A-MSDU). The multiple
HT packets can be transmitted with single ACK reply packet. Enable it to
apply this function and reduce the network congestion.
0
HT_BAWinSize
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
64
HT_GI
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
1
HT_STBC
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
1
HT_MCS
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
33;33;33;33
HT_PROTECT
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
1
HT_MIMOPS
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
3
HT_40MHZ_INTOLERANT
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
0
HT_TxStream
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
2
HT_RxStream
Applicable to HT Physical Mode
2
NintendoCapable
N/A
0
AccessPolicy0
Access Policy, 0: Disable, 1: Allow all, 2: Reject all
0
AccessControlList0
Access Control List
-
AccessPolicy1
Access Policy, 0: Disable, 1: Allow all, 2: Reject all
0
AccessControlList1
Access Control List
-
AccessPolicy2
Access Policy, 0: Disable, 1: Allow all, 2: Reject all
0
AccessControlList2
Access Control List
-
AccessPolicy3
Access Policy, 0: Disable, 1: Allow all, 2: Reject all
0
AccessControlList3
Access Control List
-
WdsEnable
This device supports “Access Point”, “AP allows WDS”, “Bridge” and
“Repeater”. When selecting “Bridge”, this device provides WDS connection
only and doesn’t provide radio to the WLAN stations (clients). To provide
both AP and WDS connections, select “Repeater”.
0
WdsPhyMode
There are four modes including “CCK, OFDM, HTMIX, and Greenfield”.
Select one according the WDS devices. The CCK is for pure 802.11b WDS
network. OFDM is for pure 802.11g WDS network. HTMIX is for 802.11 g/n
WDS network. Greenfield is for pure 802.11n WDS network.
HTMIX;HTMIX;H
TMIX;HTMIX
WdsEncrypType
There are 4 types to support, NONE,WEP,TKIP,AES
NONE
WdsList
WDS list
-
WdsKey
Please input the key for encryption
-
WirelessEvent
N/A
0
RADIUS_Server
Input the IP Address of the Radius server
0;0;0;0
RADIUS_Port
Input the port of the Radius server. The default port is 1812.
1812;1812;1812;
1812
RADIUS_Key
Authentication Key
DKTCOMEGA;DK
TCOMEGA;DKTC
OMEGA;DKTCOM
EGA

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 72
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
RADIUS_Acct_Server
N/A
-
RADIUS_Acct_Port
N/A
1813
RADIUS_Acct_Key
N/A
-
session_timeout_interval
maximum idle time for this connection
0
idle_timeout_interval
N/A
0
staWirelessMode
Station’s Wireless mode
9
RemoteManagement
Remote management (via WAN): you can select “Deny” or “Allow” to
decide whether the WAN of the device can be accessed. If it isn’t
accessible, then you can’t open the web page from WAN.
1
WAN_MAC_ADDR
MAC Address of the WAN interface
RFICType
N/A
5
TXPath
N/A
5
RXPath
N/A
1
SSID2
This device supports multiple SSID. Input the multiple SSID 1, 2, 3 in the
field to enable the function. With the field of Network Name (SSID), the
device supports maximum 4 SSIDs.
DKTCOMEGA2
SSID3
This device supports multiple SSID. Input the multiple SSID 1, 2, 3 in the
field to enable the function. With the field of Network Name (SSID), the
device supports maximum 4 SSIDs.
DKTCOMEGA3
SSID4
This device supports multiple SSID. Input the multiple SSID 1, 2, 3 in the
field to enable the function. With the field of Network Name (SSID), the
device supports maximum 4 SSIDs.
DKTCOMEGA4
WPAPSK2
WPA/WPA2-PSK Pass Phrase (8-64 characters). Key 2
12345678
Key1Str2
WEP Key 1
-
Key2Str2
WEP Key 2
-
Key3Str2
WEP Key 3
-
Key4Str2
WEP Key 4
-
WPAPSK3
WPA/WPA2-PSK Pass Phrase (8-64 characters). Key 3
12345678
Key1Str3
WEP Key 1
-
Key2Str3
WEP Key 2
-
Key3Str3
WEP Key 3
-
Key4Str3
WEP Key 4
-
WPAPSK4
WPA/WPA2-PSK Pass Phrase (8-64 characters). Key 4
12345678
Key1Str4
WEP Key 1
-
Key2Str4
WEP Key 2
-
Key3Str4
WEP Key 3
-
Key4Str4
WEP Key 4
-
FixedTxMode
Fixed TX mode
HT;HT;HT;HT
MNGVLANID
Management VLAN ID
-

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 73
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Appendix 1 – ATA configuration file
Please notice that the ATA supports provisioning of the configuration file in both
clear text as well as in encrypted format. Default is clear text, if encrypted format
is preferred, please consult DKTCOMEGA for further details.
# Accounts
ata_service_name&3c0=DKTCOMEGA
ata_factory_name&300=Factory
ata_factory_password&300=1L60U5DdLQjh8DehGxpTCQ=
ata_admin_name&3c0=Administrator
ata_admin_password&3c0=VPxOk773305H+qh0NTnL1g=
ata_user_name&3d0=Username
ata_user_password&3d0=9oYkq64Q6wBNAg+FhkKrSw=
ata_factory_lock_bypass_enable&300=0
ata_user_message&3f0=Thank you for purchasing this DKT ATA
ata_user_email&310=
# Date/Time
ata_date&3d0=1970/1/1
ata_time&3d0=01:27:19
ata_time_zone&3dc=-5
ata_daylight_savings_enable&3dc=1
ata_timeserver_enable&3d0=1
ata_timeserver_domain_name&3dc=time-a.nist.gov
# Network Device Configuration
net_assigned_router_name&3d0=DKT_ATA
net_assigned_host_name&3d0=DKT_ATA
net_assigned_domain_name&3d0=
net_assigned_mtu&3d0=1492
net_assigned_cloned_mac_address&3d0=
# Router Command Strings
net_router_commands_&3d0=
_net_router_commands_1&3d0=
_net_router_commands_2&3d0=
_net_router_commands_3&3d0=
_net_router_commands_4&3d0=
_net_router_commands_5&3d0=
_net_router_commands_6&3d0=
_net_router_commands_7&3d0=
_net_router_commands_8&3d0=
_net_router_commands_9&3d0=
_net_router_commands_10&3d0=
# Static Network Configuration
net_static_config_enable&3dc=0
net_static_ip_address&3dc=0.0.0.0
net_static_netmask&3dc=255.255.255.0
net_static_gateway_address&3dc=0.0.0.0
# DNS Configuration
net_dns_primary_address&3dc=0.0.0.0
net_dns_secondary_address&3dc=0.0.0.0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 74
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
net_dns_parallel_search_mode&3d0=0
# Dynamic Network Configuration
net_isp_dhcp_enable&3dc=1
net_isp_pppoe_enable&3dc=0
net_isp_user_name&3dc=
net_isp_password&3dc=
net_isp_dhcp_discover_duration&3d0=1
net_isp_connect_on_demand_enable&3d0=0
net_isp_connect_on_demand_interval&3d0=0
net_isp_keep_alive_enable&3d0=0
net_isp_keep_alive_interval&3d0=0
net_isp_reconnect_on_link_loss&3d0=0
net_isp_save_as_assigned&3f0=0
# Remote Configuration Access
ata_web_external_server_enable&3f0=1
ata_web_internal_server_enable&3f0=1
ata_web_server_port&3f0=0
ata_web_server_language&3f0=0
ata_telnet_server_enable&3f0=1
ata_telnet_server_port&3f0=0
ata_ftp_server_enable&3f0=1
ata_ftp_server_port&3f0=0
# NAT Transversal Parameters
nat_stun_enable&3dc=1
nat_stun_dns_lookup_mode&3d0=0
nat_stun_server_domain_name&3dc=
nat_stun_symmetric_deterministic_enable&3dc=1
nat_turn_enable&3dc=0
nat_turn_server_domain_name&3dc=
nat_ice_enable&3f0=0
# Update Parameters
ata_local_update_enable&13f0=0
ata_local_update_domain_name&3f0=
ata_dhcp_update_enable&3c0=1
ata_update_domain_name&3fc=update.dktcomega.com:5070
ata_recovery_domain_name&300=recovery.dktcomega.com:5070
ata_finalize_domain_name&300=finalize.dktcomega.com:5070
ata_email_domain_name&300=email.dktcomega.com
ata_options_domain_name&300=options.dktcomega.com
ata_lcr_domain_name&300=lcr.dktcomega.com
ata_configuration_update_enable&3c0=0
ata_configuration_update_on_reset&3c0=0
ata_configuration_update_from_sip&3c0=0
ata_configuration_recover_enable&3c0=0
ata_configuration_request_message&3c0=
ata_configuration_success_message&3c0=Configuration update
successful
ata_configuration_failed_message&3c0=Configuration update
failed
ata_configuration_update_periodic_delay&3c0=3600
ata_configuration_update_random_delay&3c0=240
ata_configuration_update_error_retry_delay&3c0=120

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 75
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ata_firmware_update_enable&3fc=0
ata_firmware_update_on_reset&3c0=0
ata_firmware_recovery_enable&3c0=0
ata_firmware_request_message&3c0=
ata_firmware_success_message&3c0=Firmware update successful
ata_firmware_failed_message&3c0=Firmware update failed
ata_firmware_update_periodic_delay&3c0=86400
ata_firmware_update_random_delay&3c0=240
ata_firmware_update_error_retry_delay&3c0=120
# ATA Maintenance
ata_help_url&3c0=help.html
ata_logo_url&3c0=atalogo.jpg
net_syslog_enable&3c0=0
net_syslog_server&3c0=
net_debug_enable&3c0=0
net_debug_server&3c0=
net_debug_level_ata&3c0=7
net_debug_level_sip&3c0=307
net_debug_level_mgcp&3c0=307
net_debug_level_net&3c0=7
net_debug_level_omc&3c0=7
net_debug_level_pmp&3c0=7
# System Identification
ata_copyright_notice&12a0=ATA Ver 5.04 (C) 1994-2008 DKTCOMEGA
A/S
ata_manufacturer&12a0=DKT
ata_model_number&12a0=ATA2
ata_serial_number&12a0=3108
ata_hardware_revision&12a0=000
ata_boot_rom_revision&12a0=5.03
ata_firmware_revision&12a0=5.04
ata_configuration_revision&12a0=1.00.00
ata_processor_chip_id&1200=
ata_processor_die_id&1200=
net_hardware_mac_address&12a0=
net_unique_device_id&12a0=
#ata_processor_chip_id&1200=bf527
#ata_processor_die_id&1200=b0c090220b980c3989db2276c89d0000
#net_hardware_mac_address&12a0=00:50:c2:32:71:6c
#net_unique_device_id&12a0=DKT_ATA_0050c232716c
ata_system_info_1&300=
ata_system_info_2&300=
ata_system_info_3&300=
ata_system_info_4&300=
ata_system_info_5&300=
# VoIP Account 1 Information
voip_provider_1&3dc=
_voip_provider_1.provider_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_1.provider_type&3fc=1
_voip_provider_1.distinctive_ring_type&3fc=1
_voip_provider_1.dialing_prefix&3dc=
_voip_provider_1.preferred_audio_codecs&23fc=

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 76
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
_voip_provider_1.incoming_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_1.group_line_1_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_1.group_line_2_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_1.use_outbound_proxy&3d0=0
_voip_provider_1.dns_lookup_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_1.display_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_1.user_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_1.domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_1.auth_user_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_1.auth_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_1.auth_user_password&3fc=
_voip_provider_1.proxy_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_1.register_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_1.reregister_interval&23fc=120
_voip_provider_1.subscription_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_1.resubscribe_interval&23fc=0
# VoIP Account 2 Information
voip_provider_2&3dc=
_voip_provider_2.provider_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_2.provider_type&3fc=0
_voip_provider_2.distinctive_ring_type&3fc=0
_voip_provider_2.dialing_prefix&3dc=
_voip_provider_2.preferred_audio_codecs&23fc=
_voip_provider_2.incoming_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_2.group_line_1_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_2.group_line_2_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_2.use_outbound_proxy&3d0=0
_voip_provider_2.dns_lookup_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_2.display_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_2.user_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_2.domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_2.auth_user_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_2.auth_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_2.auth_user_password&3fc=
_voip_provider_2.proxy_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_2.register_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_2.reregister_interval&23fc=120
_voip_provider_2.subscription_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_2.resubscribe_interval&23fc=120
# VoIP Account 3 Information
voip_provider_3&3dc=
_voip_provider_3.provider_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_3.provider_type&3fc=0
_voip_provider_3.distinctive_ring_type&3fc=0
_voip_provider_3.dialing_prefix&3dc=
_voip_provider_3.preferred_audio_codecs&23fc=
_voip_provider_3.incoming_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_3.group_line_1_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_3.group_line_2_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_3.use_outbound_proxy&3d0=0
_voip_provider_3.dns_lookup_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_3.display_name&23fc=

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 77
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
_voip_provider_3.user_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_3.domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_3.auth_user_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_3.auth_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_3.auth_user_password&3fc=
_voip_provider_3.proxy_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_3.register_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_3.reregister_interval&23fc=120
_voip_provider_3.subscription_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_3.resubscribe_interval&23fc=120
# VoIP Account 4 Information
voip_provider_4&3dc=
_voip_provider_4.provider_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_4.provider_type&3fc=0
_voip_provider_4.distinctive_ring_type&3fc=0
_voip_provider_4.dialing_prefix&3dc=
_voip_provider_4.preferred_audio_codecs&23fc=
_voip_provider_4.incoming_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_4.group_line_1_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_4.group_line_2_enable&3d0=1
_voip_provider_4.use_outbound_proxy&3d0=0
_voip_provider_4.dns_lookup_mode&3d0=0
_voip_provider_4.display_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_4.user_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_4.domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_4.auth_user_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_4.auth_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_4.auth_user_password&3fc=
_voip_provider_4.proxy_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_4.register_domain_name&3fc=
_voip_provider_4.reregister_interval&23fc=120
_voip_provider_4.subscription_domain_name&23fc=
_voip_provider_4.resubscribe_interval&23fc=120
# VoIP Provider Defaults
voip_default_display_name&3e0=
voip_default_user_name&3e0=
voip_provider_default_line_1&3c0=1
voip_provider_alternate_line_1&3c0=0
voip_provider_default_line_2&3c0=1
voip_provider_alternate_line_2&3c0=0
# Audio Settings
voip_preferred_audio_codecs&3e0=18 0 8 109
voip_silence_suppression_enable&3e0=0
voip_echo_canceller_enable&3e0=1
voip_echo_canceller_mode&3e0=2
voip_echo_canceller_tail_length&3e0=16
voip_fax_processing_mode&3e0=0
voip_dtmf_transmit_method&3e0=0
# RTP Protocol Parameters
rtp_port_minimum&3e0=1234
rtp_port_maximum&3e0=65535
rtp_public_external_ip_address&3e0=0.0.0.0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 78
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
rtp_public_external_port_min&3e0=0
rtp_tos_value&3e0=68
rtp_packet_duration&3e0=30
rtp_stream_duration&3e0=20
rtp_session_timeout_interval&3e0=900
rtp_jitter_buffer_start_depth&3e0=20
rtp_jitter_buffer_minimum_depth&3e0=20
# SDP Protocol Parameters
sdp_session_name&3e0=sdp_session_owner&3e0=DKT
sdp_ignore_stun&3e0=1
# SDP Audio Codec Names
sdp_g711u_codec_name&3e0=PCMU/8000
sdp_g711a_codec_name&3e0=PCMA/8000
sdp_cn_codec_name&3e0=CN
sdp_g729_codec_name&3e0=G729/8000
sdp_g729b_codec_name&3e0=G729B/8000
sdp_NSE_codec_name&3e0=X-NSE/8000
sdp_AVT_codec_name&3e0=telephone-event/8000
# SDP Audio Codec Dynamic Code Points
sdp_g711u_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=0
sdp_g711a_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=0
sdp_cn_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=0
sdp_g729_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=0
sdp_g729b_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=109
sdp_NSE_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=100
sdp_AVT_codec_dyn_pt&3e0=101
# SIP Protocol Parameters
sip_user_agent&3e0=DKT 5.04
sip_require_user_name&3c0=0
sip_local_port&3e0=5060
sip_public_external_ip_address&3e0=0.0.0.0
sip_public_external_sip_port&3e0=0
sip_tos_value&3e0=68
sip_accept_language_string&3e0=
sip_send_response_to_src_port&3c0=0
sip_max_forwards&3e0=70
sip_ringing_retransmit&3c0=1
sip_use_nat_discovery&3e0=1
sip_use_received_via_info&3c0=0
sip_nat_keep_alive_enable&3c0=0
sip_nat_keep_alive_interval&3c0=15
sip_nat_keep_alive_domain_name&3c0=
sip_nat_keep_alive_message&3c0=
sip_prack_enable&3c0=0
# SIP Response Codes
sip_response_code_sit1&3c0=0
sip_response_code_sit2&3c0=0
sip_response_code_sit3&3c0=0
sip_response_code_sit4&3c0=0
sip_response_code_try_backup&3c0=0
sip_response_code_retry_registration&3c0=30

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 79
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
# SIP Distinctive Ring Names
sip_distinctive_ring_names_&3c0=
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_1&3c0=Belcore-r1
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_2&3c0=Belcore-r2
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_3&3c0=Belcore-r3
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_4&3c0=Belcore-r4
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_5&3c0=Belcore-r5
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_6&3c0=Belcore-r6
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_7&3c0=Belcore-r7
_sip_distinctive_ring_names_8&3c0=Belcore-r8
# SIP Protocol Timers
sip_timer_invite_expires&3c0=180
sip_timer_reinvite_expires&3c0=180
sip_timer_registration_min&3c0=1
sip_timer_registration_max&3c0=7200
sip_timer_registration_retry&3c0=30
sip_timer_no_answer_duration&3c0=300
sip_timer_reregister_interval&3c0=0
sip_session_timer&3c0=1800
# SIP Server Configuration
sip_allow_incoming_subscription&3c0=0
sip_subscribe_authentication&3c0=0
sip_incoming_resubscribe_interval&3c0=3600
sip_invite_authentication&3c0=0
sip_bye_authentication&3c0=0
sip_notify_authentication&3c0=0
sip_incoming_auth_user_name&3c0=
sip_incoming_auth_realm&3c0=
sip_incoming_auth_password&3c0=
# Voice and Tone Parameters
ipbx_voice_rx_gain&3f0=0
ipbx_voice_tx_gain&3f0=0
ipbx_tone_gain&3f0=0
ipbx_tone_max&3c0=-12
dtmf_low_tone_gain&3c0=-9
dtmf_high_tone_gain&3c0=-7
dtmf_tone_on_time&3c0=80
dtmf_tone_off_time&3c0=80
dtmf_detect_abcd&3c0=1
dtmf_generate_abcd&3c0=1
dtmf_pad_duration&3c0=100
dtmf_wait_duration&3c0=50
dtmf_playout_min_duration&3c0=100
# Timers
ipbx_brief_pause_duration&3c0=50
ipbx_initial_dial_duration&3c0=1500
ipbx_warm_line_duration&3c0=400
ipbx_interdigit_duration&3c0=500
ipbx_dialing_duration&3c0=1000
ipbx_hangup_disconnect_duration&3c0=85
ipbx_hangup_silence_duration&3c0=1000
ipbx_pause_wait_duration&3c0=300

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 80
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx_timeout_tone_duration&3c0=6000
ipbx_timeout_pause_duration&3c0=100
ipbx_timeout_disconnect_duration&3c0=85
ipbx_timeout_warning_duration&3c0=0
ipbx_timeout_hold_duration&3c0=1000
ipbx_timeout_hold_drop_duration&3c0=6000
ipbx_timeout_no_answer_drop_duration&3c0=120
ipbx_no_answer_duration&3c0=20
ipbx_call_back_duration&3c0=1800
ipbx_call_back_retry_duration&3c0=30
ipbx_call_back_ring_wait_duration&3c0=1
ipbx_message_waiting_refresh_duration&3c0=1800
ipbx_hookflash_maximum&3c0=900
ipbx_hookflash_minimum&3c0=100
ipbx_hookflash_delay&3c0=200
ipbx_answer_hangup_delay&3c0=0
# Other
ipbx_line_concurrent_line_count&3e0=2
ipbx_line_concurrent_voip_count&3e0=2
ipbx_epoch_clock_limit&3c0=16000
ipbx_hook_debounce&3c0=10
ipbx_hookflash_enable&3c0=1
# Call Progress Tones
ipbx_initial_dial_tone&3c0=1 0 0 425
ipbx_alternate_dial_tone&3c0=1 0 0 400 -16
ipbx_secondary_dial_tone&3c0=2 0 0 420 -19 520 -19
ipbx_stuttered_dial_tone&3c0=2 7 0 350 -19 440 -19 100 110 100
110 100 110 0
ipbx_message_wait_dial_tone&3c0=2 2 0 350 -19 440 -19 160 160
ipbx_call_forward_dial_tone&3c0=2 3 0 350 -19 440 -19 250 400
0
ipbx_pre_ringback_tone&3c0=4 -8 0 440 -16 494 -19 523 -19 587
-19 340 160 340 160 340 160 340 160
ipbx_ringback_tone&3c0=2 2 0 440 -19 480 -19 2000 4000
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_default&3c0=1 2 0 440 -16 300 9700
ipbx_call_station_call_waiting_tone_default&3c0=1 2 0 440 -16
300 9700
ipbx_call_holding_tone&3c0=1 4 0 1200 -16 100 200 100 -1
ipbx_call_disconnect_tone&3c0=2 2 0 480 -19 620 -19 500 500
ipbx_call_conference_tone&3c0=1 2 0 350 -16 100 15000
ipbx_busy_tone&3c0=2 2 0 480 -19 620 -19 500 500
ipbx_reorder_tone&3c0=2 2 0 480 -19 620 -19 250 250
ipbx_off_hook_warning_tone&3c0=4 2 0 1400 11 2050 11 2450 11
2600 11 100 100
ipbx_sit1_tone&3c0=3 -6 0 985 -16 1428 -16 1777 -16 330 5 330
5 330 1000
ipbx_sit2_tone&3c0=3 -6 0 914 -16 1371 -16 1777 -16 330 5 330
5 330 1000
ipbx_sit3_tone&3c0=3 -6 0 985 -16 1428 -16 1777 -16 380 5 380
5 380 1000
ipbx_sit4_tone&3c0=3 -6 0 914 -16 1371 -16 1777 -16 380 5 380
5 380 1000

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 81
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx_prompt_tone&3c0=2 0 0 520 -19 620 -19
ipbx_confirm_tone&3c0=1 2 0 600 -16 400 0
ipbx_input_error_tone&3c0=2 2 0 480 -19 620 -19 250 250
ipbx_number_error_tone&3c0=2 2 0 480 -19 620 -19 250 250
# Standard Ringing Patterns
ipbx_call_ring_default&3f0=20 2 0 2000 4000
ipbx_call_station_ring_default&3f0=20 2 0 1000 3000
ipbx_call_holding_rering&3f0=20 2 0 500 0
ipbx_call_back_ring&3f0=20 2 0 1500 0
ipbx_call_back_ring_splash&3f0=20 2 0 700 0
ipbx_call_forward_ring_splash&3f0=20 2 0 500 0
ipbx_message_waiting_ring_splash&3f0=20 2 0 500 0
# Distinctive Ringing Patterns
ipbx_distinctive_ring_1&3f0=20 2 0 2000 4000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_2&3f0=20 4 0 1000 1000 1000 3000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_3&3f0=20 6 0 300 200 1000 200 300 4000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_4&3f0=20 4 0 800 400 800 4000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_5&3f0=20 4 0 400 200 400 2000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_6&3f0=20 2 0 1000 3000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_7&3f0=20 4 0 300 200 1500 2000
ipbx_distinctive_ring_8&3f0=20 4 0 800 400 800 2000
# Distinctive Call Waiting Patterns
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_1&3f0=1 2 0 440 -16 300 9700
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_2&3f0=1 6 0 440 -16 100 20 100 20 100
9660
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_3&3f0=1 4 0 440 -16 100 100 100 9700
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_4&3f0=1 6 0 440 -16 100 100 100 100 100
9500
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_5&3f0=1 2 0 620 -16 300 9700
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_6&3f0=1 6 0 620 -16 100 20 100 20 100
9660
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_7&3f0=1 4 0 620 -16 100 100 100 9700
ipbx_call_waiting_tone_8&3f0=1 6 0 620 -16 100 100 100 100 100
9500
# SLAC Configuration
slac_port_impedance&3c0=0
slac_port_rx_gain&3c0=-3
slac_port_tx_gain&3c0=2
slac_audio_clamp_duration&3c0=100
slac_caller_id_type_1_mode&3c0=1
slac_caller_id_type_2_mode&3c0=1
slac_message_waiting_mode&3c0=1
slac_ring_type&3c0=0
slac_ring_frequency&3c0=25
slac_ring_transition&3c0=15
slac_ring_amplitude&3c0=85
slac_ring_bias&3c0=0
slac_message_waiting_type&3c0=0
slac_message_waiting_frequency&3c0=25
slac_message_waiting_transition&3c0=15
slac_message_waiting_amplitude&3c0=50
slac_message_waiting_bias&3c0=0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 82
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
slac_dtmf_caller_id_start_code&3c0=0
slac_dtmf_caller_id_end_code&3c0=2
slac_dtmf_caller_id_polarity_reversal&3c0=0
# SLAC Command Strings
slac_initialization_commands&3c0=100
slac_impedance_commands_1&3c0=ca,40ed,98,3c,aa,32,ab,52,64,aa,
a3,b2,40bc,9a,a2,ba,a6,9f,4001,8a,0,f0,24,b0,33,a2,53,2c,71,d4
,0,3d,31,4026,88,15,10,13,3c,2b,b3,4b,2d,32,de,33,40a5,82,0,40
02,80,b3,4011,86,3a,42,a1,3b,1d,24,b8,7a,87,a4,fb,9f,a9,40f0,9
6,2e,4001,100
slac_impedance_commands_2&3c0=ca,4008,98,23,aa,32,ab,a4,b4,7d,
a3,34,40ac,9a,a4,ba,57,9f,4001,8a,7d,d0,42,a0,31,b3,e2,bd,b3,2
5,22,2d,24,4016,88,2b,20,22,3b,44,13,24,1c,33,a6,13,40b6,82,0,
4002,80,b3,4011,86,bd,42,51,22,13,b3,a8,f2,b6,b4,ea,8f,a2,40f0
,96,2e,4001,100
slac_impedance_commands_3&3c0=ca,4000,98,7a,b9,a2,d3,23,32,ab,
33,3a,40dc,9a,2c,a2,a3,22,40d0,8a,42,11,71,b0,13,a4,51,bc,22,2
c,d5,26,e4,4087,88,14,20,36,23,31,ba,7a,a7,c7,cc,0,4016,82,0,4
002,80,b3,4011,86,f5,5b,a1,ae,1c,23,b2,3b,24,a5,4a,c4,2c,4040,
96,b2,40d0,100
slac_impedance_commands_4&3c0=ca,4006,98,3b,4c,ad,bb,aa,8f,a3,
24,2a,40b7,9a,fd,b2,25,4d,4001,8a,c3,c0,23,a0,c3,45,31,37,22,3
5,c3,cc,31,40e5,88,32,20,23,b9,c2,41,3a,b9,c3,b2,12,402c,82,0,
4002,80,b3,4011,86,aa,49,80,2a,c,23,23,7a,a4,2a,52,c6,ea,4050,
96,2d,4001,100
slac_impedance_commands_5&3c0=ca,40dd,98,23,51,b2,32,2c,4c,3a,
aa,f3,4024,9a,a2,b2,a7,9f,4001,8a,3,f0,1c,10,12,b8,32,ac,13,15
,22,ce,24,408f,88,2b,20,b4,2f,f2,3b,6d,c3,b2,bc,c4,40a5,82,0,4
002,80,b3,4011,86,b2,52,32,98,3,a1,aa,24,b3,ac,4c,55,d3,4060,9
6,a5,40f1,100
slac_impedance_commands_6&3c0=ca,40e1,98,2b,31,bb,22,a3,7b,ab,
3a,bb,4043,9a,bd,42,97,9f,4001,8a,3,f0,1d,10,2c,e8,46,c3,c4,26
,1c,be,13,408f,88,14,30,24,16,13,2b,47,4,13,1d,3b,4026,82,0,40
02,80,b3,4011,86,a2,5a,22,d4,1b,a1,cb,25,b3,2b,42,b5,ca,4060,9
6,3b,40a1,100
slac_impedance_commands_7&3c0=ca,40ed,98,3c,aa,32,ab,52,64,aa,
a3,b2,40bc,9a,a2,ba,a6,9f,4001,8a,0,f0,14,b0,34,a2,32,ab,1c,54
,e4,ac,24,40a5,88,15,10,b2,3c,1b,b3,bb,2d,3a,ce,33,40a5,82,0,4
002,80,b3,4011,86,42,5c,22,ac,1c,a2,c3,5a,a6,29,fa,9f,4a,40f0,
96,2e,4001,100
slac_impedance_commands_8&3c0=ca,40dd,98,db,a3,ba,32,36,a2,a9,
f5,23,40ad,9a,53,b2,a6,1f,4001,8a,e,e0,14,20,be,2a,bb,2a,1b,cc
,a7,36,b3,405e,88,3a,10,48,75,d3,aa,32,b3,5a,2c,33,40a4,82,0,4
002,80,b3,4011,86,a2,53,32,4b,13,52,22,3b,b3,a2,42,b4,a2,4050,
96,a2,40a0,100
slac_impedance_commands_9&3c0=ca,40e2,98,ab,b1,ad,42,23,bb,a8,
7a,ca,40c3,9a,cb,a3,97,9f,4001,8a,3,f0,22,20,41,29,13,16,2b,c4
,12,bd,1d,4097,88,3a,20,3d,c4,24,aa,15,43,13,bc,31,4036,82,0,4
002,80,b3,4011,86,b2,5a,22,c5,12,a1,e2,34,b4,c4,64,97,39,40f0,
96,2e,4001,100
slac_impedance_commands_10&3c0=ca,4008,98,23,aa,32,ab,a4,b4,7d
,a3,34,40ac,9a,a4,ba,57,9f,4001,8a,7d,d0,42,a0,23,14,41,bd,2d,

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 83
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
25,32,2d,d4,4016,88,1b,20,23,3b,37,13,15,ab,2c,37,31,40c6,82,0
,4002,80,b3,4011,86,72,53,a1,42,1a,e2,b8,73,77,39,fa,3f,ab,40f
0,96,2e,4001,100
# Subscription Service Settings
ipbx_call_waiting_service&3e0=1
ipbx_caller_id_inbound_service&3e0=1
ipbx_caller_id_outbound_service&3e0=1
ipbx_call_waiting_caller_id_service&3e0=1
ipbx_call_back_service&3e0=1
ipbx_call_return_service&3e0=1
ipbx_speed_dial_service&3e0=1
ipbx_do_not_disturb_service&3e0=1
ipbx_block_anonymous_service&3e0=1
ipbx_call_forward_service&3e0=1
ipbx_busy_forward_service&3e0=1
ipbx_no_answer_forward_service&3e0=1
ipbx_priority_forward_service&3e0=1
ipbx_distinctive_ring_service&3e0=1
ipbx_disturb_accept_service&3e0=1
ipbx_blocked_number_service&3e0=1
ipbx_outgoing_block_service&3e0=1
ipbx_forward_last_call_service&3e0=1
ipbx_distinctive_ring_last_call_service&3e0=1
ipbx_disturb_accept_last_call_service&3e0=1
ipbx_block_last_call_service&3e0=1
ipbx_three_way_calling_service&3e0=1
ipbx_three_way_conference_service&3e0=1
ipbx_attended_transfer_service&3e0=1
ipbx_unattended_transfer_service&3e0=1
ipbx_message_waiting_service&3e0=1
ipbx_visual_message_waiting_service&3e0=1
ipbx_remote_feature_code_service&3e0=0
ipbx_default_feature_code_service&3e0=0
# Port Configuration
ipbx_line_1_enable&3e0=1
ipbx_line_2_enable&3e0=1
ipbx_line_1_number&3e0=L1
ipbx_line_2_number&3e0=L2
ipbx_line_1_name&3e0=
ipbx_line_2_name&3e0=
# Operating Mode
ipbx_mode&3f0=1
ipbx_voip_primary_provider_unavailable&3f0=0
ipbx_voip_no_provider_available&3f0=1
ipbx_pstn_not_available&3f0=2
ipbx_dial_direct&3f0=3
ipbx_dial_after_8&3f0=2
ipbx_dial_after_9&3f0=1
ipbx_dial_after_pound_8&3f0=3
ipbx_dial_after_pound_9&3f0=3
ipbx_dial_speed_dial&3f0=1

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 84
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx_input_pattern_voip&3f0=[3469]11|*xx|**p2r*x|1900r7x!|976r
4!|1800r7x|[^1]r7x|1r3x[^1]r6x|1010Se#e*p2r*x|0Se#e*p2r*x
ipbx_input_pattern_pstn&3f0=911
ipbx_hot_line_dialing&3e0=0
ipbx_warm_line_dialing&3e0=0
ipbx_hotwarm_dial_string&3e0=
ipbx_party_line_enable&3e0=0
ipbx_polarity_dialing&3e0=1
ipbx_polarity_dial_done&3e0=1
ipbx_polarity_connect&3e0=1
ipbx_polarity_answer&3e0=1
ipbx_polarity_idle&3e0=1
# Speed Dials
ipbx_speed_dial_array_&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_1&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_2&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_3&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_4&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_5&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_6&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_7&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_8&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_9&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_10&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_11&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_12&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_13&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_14&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_15&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_16&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_17&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_18&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_19&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_20&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_21&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_22&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_23&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_24&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_25&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_26&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_27&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_28&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_29&3df=
_ipbx_speed_dial_array_30&3df=
ipbx_hot_warm_dial_string&3d3=
# Call Forwarding
ipbx_call_forward_enable&3df=0
ipbx_busy_forward_enable&3df=0
ipbx_no_answer_forward_enable&3df=0
ipbx_priority_forward_enable&3df=0
ipbx_call_forward_dial_string&3df=
ipbx_busy_forward_dial_string&3df=

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 85
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx_no_answer_forward_dial_string&3df=
ipbx_priority_forward_dial_string&3df=
ipbx_call_forward_list_&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_1&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_2&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_3&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_4&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_5&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_6&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_7&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_8&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_9&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_10&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_11&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_12&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_13&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_14&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_15&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_16&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_17&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_18&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_19&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_20&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_21&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_22&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_23&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_24&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_25&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_26&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_27&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_28&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_29&3df=
_ipbx_call_forward_list_30&3df=
# Distinctive Ringing
ipbx_distinctive_ring_enable&3df=1
ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_1&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_2&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_3&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_4&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_5&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_6&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_7&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_8&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_9&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_10&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_11&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_12&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_13&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_14&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_15&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_16&3df=

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 86
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_17&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_18&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_19&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_20&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_21&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_22&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_23&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_24&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_25&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_26&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_27&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_28&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_29&3df=
_ipbx_distinctive_ring_list_30&3df=
# Do Not Disturb
ipbx_do_not_disturb_mode&13df=0
ipbx_disturb_accept_enable&3df=0
ipbx_disturb_accept_list_&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_1&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_2&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_3&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_4&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_5&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_6&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_7&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_8&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_9&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_10&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_11&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_12&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_13&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_14&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_15&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_16&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_17&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_18&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_19&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_20&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_21&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_22&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_23&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_24&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_25&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_26&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_27&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_28&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_29&3df=
_ipbx_disturb_accept_list_30&3df=
# Call Blocking
ipbx_block_anonymous_enable&3df=0
ipbx_blocked_number_enable&3df=0
ipbx_blocked_number_list_&3df=

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 87
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_1&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_2&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_3&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_4&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_5&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_6&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_7&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_8&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_9&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_10&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_11&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_12&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_13&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_14&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_15&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_16&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_17&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_18&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_19&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_20&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_21&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_22&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_23&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_24&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_25&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_26&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_27&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_28&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_29&3df=
_ipbx_blocked_number_list_30&3df=
# Outgoing Call Blocking
ipbx_outgoing_block_enable&3df=0
ipbx_outgoing_block_list_&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_1&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_2&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_3&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_4&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_5&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_6&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_7&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_8&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_9&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_10&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_11&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_12&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_13&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_14&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_15&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_16&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_17&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_18&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_19&3df=

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 88
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_20&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_21&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_22&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_23&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_24&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_25&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_26&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_27&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_28&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_29&3df=
_ipbx_outgoing_block_list_30&3df=
# Caller Waiting/Caller ID
ipbx_call_waiting_enable&3df=1
ipbx_caller_id_inbound_enable&3df=1
ipbx_caller_id_outbound_enable&3df=1
ipbx_caller_id_waiting_enable&3df=0
# Message Waiting
ipbx_message_waiting&13e0=0
# Feature Code Assignments (55-99)
ipbx_fc_call_waiting_enable&3e0=55
ipbx_fc_call_waiting_disable&3e0=56
ipbx_fc_call_trace&3e0=57
ipbx_fc_call_waiting_caller_id_enable&3e0=58
ipbx_fc_call_waiting_caller_id_disable&3e0=59
ipbx_fc_blocked_number_enable&3e0=60
ipbx_fc_distinctive_ring_enable&3e0=61
ipbx_fc_caller_id_outbound_disable&3e0=62
ipbx_fc_priority_forward_enable&3e0=63
ipbx_fc_disturb_accept_enable&3e0=64
ipbx_fc_caller_id_inbound_enable&3e0=65
ipbx_fc_busy_number_redial&3e0=66
ipbx_fc_caller_id_outbound_enable_once&3e0=67
ipbx_fc_caller_id_outbound_disable_once&3e0=68
ipbx_fc_caller_redial&3e0=69
ipbx_fc_call_waiting_disable_once&3e0=70
ipbx_fc_call_waiting_enable_once&3e0=71
ipbx_fc_call_forward_enable&3e0=72
ipbx_fc_call_forward_disable&3e0=73
ipbx_fc_one_digit_speed_dial_program&3e0=74
ipbx_fc_two_digit_speed_dial_program&3e0=75
ipbx_fc_block_anonymous_enable&3e0=77
ipbx_fc_do_not_disturb_enable&3e0=78
ipbx_fc_do_not_disturb_disable&3e0=79
ipbx_fc_blocked_number_disable&3e0=80
ipbx_fc_distinctive_ring_disable&3e0=81
ipbx_fc_caller_id_outbound_enable&3e0=82
ipbx_fc_priority_forward_disable&3e0=83
ipbx_fc_disturb_accept_disable&3e0=84
ipbx_fc_caller_id_inbound_disable&3e0=85
ipbx_fc_busy_number_redial_cancel&3e0=86
ipbx_fc_block_anonymous_disable&3e0=87
ipbx_fc_hookflash_simulation&3e0=88

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 89
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
ipbx_fc_caller_redial_cancel&3e0=89
ipbx_fc_no_answer_forward_enable&3e0=92
ipbx_fc_no_answer_forward_disable&3e0=93
ipbx_fc_busy_forward_enable&3e0=94
ipbx_fc_busy_forward_disable&3e0=95
ipbx_fc_outgoing_block_enable&3e0=96
ipbx_fc_outgoing_block_disable&3e0=97
ipbx_fc_unattended_transfer&3e0=98

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 90
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Appendix 2 – Wifi configuration file
#The following line must not be removed.
Default
WebInit=1
HostName=DKTCOMEGA
Login=*********
Password=*********
OperationMode=0
Platform=RT3050
wanConnectionMode=DHCP
wan_ipaddr=192.168.2.1
wan_netmask=255.255.255.0
wan_gateway=192.168.2.254
wan_primary_dns=168.95.1.1
wan_secondary_dns=168.95.192.1
wan_pppoe_user=pppoe_user
wan_pppoe_pass=pppoe_passwd
wan_l2tp_server=l2tp_server
wan_l2tp_user=l2tp_user
wan_l2tp_pass=l2tp_passwd
wan_l2tp_mode=0
wan_l2tp_ip=192.168.2.1
wan_l2tp_netmask=255.255.255.0
wan_l2tp_gateway=192.168.2.254
wan_pptp_server=pptp_server
wan_pptp_user=pptp_user
wan_pptp_pass=pptp_passwd
wan_pptp_mode=0
wan_pptp_ip=192.168.2.1
wan_pptp_netmask=255.255.255.0
wan_pptp_gateway=192.168.2.254
lan_ipaddr=192.168.1.250
lan_netmask=255.255.255.0
dhcpEnabled=0
dhcpStart=192.168.1.100
dhcpEnd=192.168.1.200
dhcpMask=255.255.255.0
dhcpPriDns=168.95.1.1
dhcpSecDns=168.95.192.1
dhcpGateway=192.168.1.250
dhcpLease=86400
stpEnabled=0
lltdEnabled=0
igmpEnabled=0
natEnabled=1
IPPortFilterEnable=0
IPPortFilterRules=
PortForwardEnable=0
PortForwardRules=
MacFilterEnable=0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 91
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
MacFilterRules=
DefaultFirewallPolicy=1
DMZEnable=0
DMZIPAddress=
TZ=
NTPServerIP=
NTPSync=
DDNSProvider=
DDNS=
DDNSAccount=
DDNSPassword=
BssidNum=4
SSID1=DKTCOMEGA1
WirelessMode=9
TxRate=0;0;0;0
Channel=6
BasicRate=15
BeaconPeriod=100
DtimPeriod=1
TxPower=100
RxAckTimeout=32
DisableOLBC=0
BGProtection=0
TxAntenna=
RxAntenna=
TxPreamble=0
RTSThreshold=2347
FragThreshold=2346
TxBurst=1
PktAggregate=1
TurboRate=0
StaLimitationEnable=0
StaLimitationNum=0
WmmCapable=1;1;1;1
APAifsn=3;7;1;1
APCwmin=4;4;3;2
APCwmax=6;10;4;3
APTxop=0;0;94;47
APACM=0;0;0;0
BSSAifsn=3;7;2;2
BSSCwmin=4;4;3;2
BSSCwmax=10;10;4;3
BSSTxop=0;0;94;47
BSSACM=0;0;0;0
AckPolicy=0;0;0;0
APSDCapable=0
DLSCapable=0
NoForwarding=0;0;0;0
NoForwardingBTNBSSID=0
HideSSID=0;0;0;0
ShortSlot=1
AutoChannelSelect=0

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 92
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
SecurityMode=0
VLANEnable=0
VLANName=
VLANID=0;0;0;0
VLANPriority=0;0;0;0
WscConfMode=0
WscConfStatus=2
WscAKMP=1
WscConfigured=1
WscModeOption=0
WscActionIndex=9
WscPinCode=
WscRegResult=1
WscUseUPnP=1
WscUseUFD=0
WscSSID=DKTCOMEGAAP
WscKeyMGMT=WPA-EAP
WscConfigMethod=138
WscAuthType=1
WscEncrypType=1
WscNewKey=scaptest
IEEE8021X=0;0;0;0
IEEE80211H=0
CSPeriod=6
PreAuth=0;0;0;0
AuthMode=WPAPSK;OPEN;OPEN;OPEN
EncrypType=TKIP;NONE;NONE;NONE
RekeyInterval=3600
RekeyMethod=DISABLE
PMKCachePeriod=10
WPAPSK1=56655153
DefaultKeyID=2;1;1;1
Key1Type=0;0;0;0
Key1Str1=
Key2Type=0;0;0;0
Key2Str1=
Key3Type=0;0;0;0
Key3Str1=
Key4Type=0;0;0;0
Key4Str1=
HSCounter=0
HT_HTC=1
HT_RDG=1
HT_LinkAdapt=0
HT_OpMode=0
HT_MpduDensity=5
HT_EXTCHA=1
HT_BW=1
HT_AutoBA=1
HT_BADecline=0
HT_AMSDU=0
HT_BAWinSize=64

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 93
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
HT_GI=1
HT_STBC=1
HT_MCS=33;33;33;33
HT_PROTECT=1
HT_MIMOPS=3
HT_40MHZ_INTOLERANT=0
HT_TxStream=2
HT_RxStream=2
NintendoCapable=0
AccessPolicy0=0
AccessControlList0=
AccessPolicy1=0
AccessControlList1=
AccessPolicy2=0
AccessControlList2=
AccessPolicy3=0
AccessControlList3=
WdsEnable=0
WdsPhyMode=HTMIX;HTMIX;HTMIX;HTMIX
WdsEncrypType=NONE
WdsList=
WdsKey=
WirelessEvent=0
RADIUS_Server=0;0;0;0
RADIUS_Port=1812;1812;1812;1812
RADIUS_Key=DKTCOMEGA;DKTCOMEGA;DKTCOMEGA;DKTCOMEGA
RADIUS_Acct_Server=
RADIUS_Acct_Port=1813
RADIUS_Acct_Key=
session_timeout_interval=0
idle_timeout_interval=0
staWirelessMode=9
RemoteManagement=1
WAN_MAC_ADDR=00:0C:43:30:50:66
RFICType=5
TXPath=5
RXPath=1
SSID2=DKTCOMEGA2
SSID3=DKTCOMEGA3
SSID4=DKTCOMEGA4
WPAPSK2=12345678
Key1Str2=
Key2Str2=
Key3Str2=
Key4Str2=
WPAPSK3=12345678
Key1Str3=
Key2Str3=
Key3Str3=
Key4Str3=
WPAPSK4=12345678

CPE User Guide v_04_07 Page - 94
DKTCOMEGA
Fanoevej 6
DK-4060 Kirke Saaby
+45 4646 2626
+45 4646 2625
mail@dktcomega.com
www.dktcomega.com
Key1Str4=
Key2Str4=
Key3Str4=
Key4Str4=
FixedTxMode=HT;HT;HT;HT
MNGVLANID=
 Loading...
Loading...