Dionex IONPAC AG9-SC GUARD COLUMN, 043185, 043186, IONPAC AS9-SC ANALYTICAL COLUMN Product Manual

for
IonPac® AG9-SC
IonPac
®
AS9-SC

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 1 of 28
PRODUCT MANUAL
for the
®
IONPAC
AG9-SC GUARD COLUMN
(4 x 50 mm, P/N 043186)
IONPAC® AS9-SC ANALYTICAL COLUMN
(4 x 250 mm, P/N 043185)
©DIONEX Corporation, 2008
Document No. 034656
Revision 06
November 2008

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 2 of 28
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 - INTRODUCTION...................................................................................................... 4
SECTION 2 - THE ION CHROMATOGRAPHY SYSTEM ........................................................ 5
SECTION 3 - INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................... 6
3.1 System Requirements.............................................................................................................................................. 6
3.1.1 System Requirements for 4-mm Operation ............................................................................................................... 6
3.1.2 System Void Volume................................................................................................................................................. 6
3.2 The Sample Concentrator ...................................................................................................................................... 6
3.3 The Injection Loop .................................................................................................................................................. 6
3.3.1 The 4-mm System Injection Loop, 10 - 50 μL......................................................................................................... 7
3.4 The IonPac AG9-SC Guard Column..................................................................................................................... 7
3.5 Installing the Anion Trap Column, ATC-3 .......................................................................................................... 7
3.6 Eluent Storage.......................................................................................................................................................... 8
3.7 The Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor, ASRS® -ULTRA............................................................................. 8
3.8 The Anion Atlas® Electrolytic Suppressor, AAES............................................................................................. 8
3.9 The Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor, AMMS® III ...................................................................................... 8
3.10 Using AutoRegen® with the ASRS-ULTRA orthe AMMS III in the Chemical Suppression Mode............ 8
3.11 Using Displacement Chemical Regernation (DCR) with the Chemical Suppression Mode........................... 9
3.12 Detector Requirements ........................................................................................................................................... 9
SECTION 4 - OPERATIONS ......................................................................................................... 10
4.1 General Operating Conditions............................................................................................................................. 10
4.2 IonPac AS9-SC Operation Precautions .............................................................................................................. 10
4.3 Chemical Purity Requirements............................................................................................................................ 10
4.3.1 Inorganic Chemicals ................................................................................................................................................ 10
4.3.2 Solvents.................................................................................................................................................................... 10
4.3.3 Deionized Water ...................................................................................................................................................... 11
4.4 Eluent Preparation ................................................................................................................................................ 11
4.4.1 Preparation of Carbonate Eluent Concentrates........................................................................................................ 11
4.4.2 Preparation of Carbonate Eluents ............................................................................................................................ 12
4.4.3 Preparation of Borate Eluents.................................................................................................................................. 12
4.5 The Borate Eluent System .................................................................................................................................... 12

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 3 of 28
4.6 Eluents that Contain Solvents .............................................................................................................................. 13
4.7 Regenerant Preparation for the AMMS III ....................................................................................................... 13
4.8 The Sample Concentrator .................................................................................................................................... 14
SECTION 5 - EXAMPLE APPLICATIONS................................................................................. 15
5.1 Production Test Chromatogram.......................................................................................................................... 16
5.2 Inorganic Anions Including Chlorate and Chlorite........................................................................................... 17
5.3 Resolution of Low-Concentration Analytes - EPA Water Matrix ................................................................... 18
5.4 Varying the Eluent System - 22 mM Borate....................................................................................................... 19
5.5 Varying the Eluent System - 10 mM Borate with Column Purge.................................................................... 20
SECTION 6 - TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ............................................................................ 21
6.1 High Backpressure ................................................................................................................................................ 21
6.1.1 Finding the Source of High System Pressure .......................................................................................................... 21
6.1.2 Replacing Column Bed Support Assemblies .......................................................................................................... 21
6.2 High Background Or Noise .................................................................................................................................. 22
6.2.1 Preparation of Eluents ............................................................................................................................................. 22
6.2.2 Borate Eluent Precautions ....................................................................................................................................... 22
6.2.3 A Contaminated Guard or Analytical Column ........................................................................................................ 23
6.2.4 A Contaminated Anion Trap Column, ATC-3 ........................................................................................................ 23
6.2.5 Contaminated Hardware .......................................................................................................................................... 24
6.2.6 A Contaminated Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor, ASRS-ULTRA ................................................................ 24
6.2.7 Contaminated Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor, AMMS III ............................................................................. 25
6.2.8 A Contaminated Anion Atlas Electrolytic Suppressor, AAES............................................................................... 25
6.3 Loss of Front End Resolution............................................................................................................................... 27
6.4 Poor Peak Resolution ............................................................................................................................................ 27
6.4.1 Loss of Column Efficiency...................................................................................................................................... 27
6.4.2 Poor Resolution Due to Shortened Retention Times............................................................................................... 27
6.5 Spurious Peaks....................................................................................................................................................... 27

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 4 of 28
SECTION 1 - INTRODUCTION
The IonPac® AS9-SC Analytical Column (P/N 043185) is designed for the analysis of inorganic anions including oxyhalides,
such as chlorate, chlorite and bromate.
The 4 x 250 mm IonPac AS9-SC Analytical Column has an ion exchange capacity of approximately 30 μeq/column. This resin
is composed of a highly cross-linked (55%) 13 micron polyethylvinylbenzene/divinylbenzene substrate agglomerated with anion
exchange latex that has been completely aminated. The latex has a polyacrylate backbone and carries the actual ion exchange sites.
The IonPac AS9-SC has nominal efficiency for sulfate using standard operating conditions of at least 14,000 plates/meter.
The IonPac AS9-SC can be operated at flow rates up to 3.0 mL/min with eluents that have a pH between 2 and 11. Eluents may
contain organic solvents from 0 - 100% in concentration. Optimally, the IonPac AS9-SC should operate at a backpressure less
than 1,100 psi at 1.0 mL/min. However, the column is capable of operating at backpressures up to 4,000 psi.
CAUTION
Eluent pH must be maintained between 2-11 or irreversible damage to the column will result.
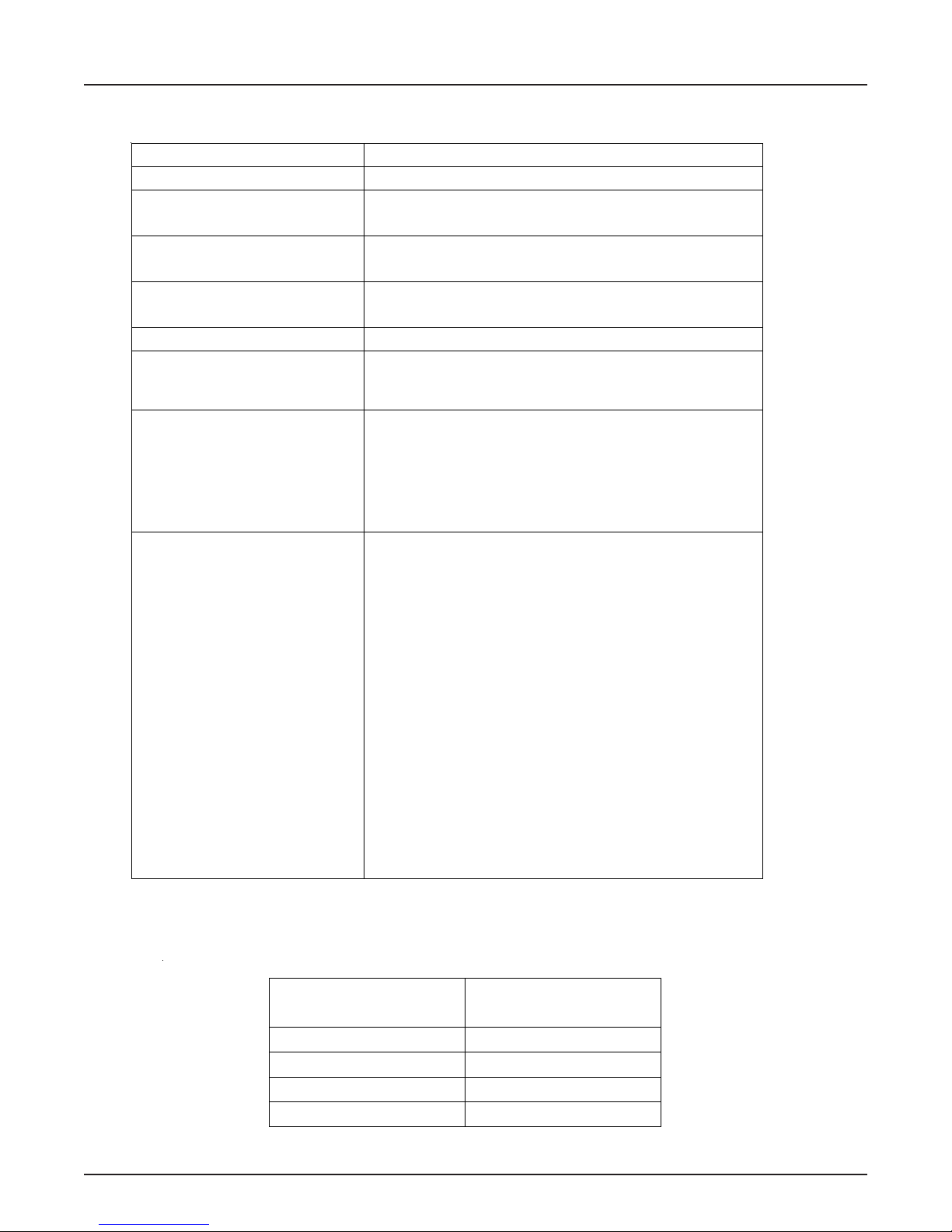
Table 1
AS9-SC/AG9-SC Packing Specifications
Column Particle Substrate Latex Latex Column Functional Hydrophobicity
Diameter X-Linking Diameter X-Linking Capacity Group
μm% nm%μeq/column
AS9-SC 13 55 110 20 30-35 Alkyl Medium-low
(4 x 250 mm) quaternary
ammonium
AG9-SC 13 55 110 20 6-7 Alkyl Medium-low
(4 x 50 mm) quaternary
ammonium
Table 2
AS9-SC/AG9-SC Operating Parameters
Column Typical Back Pressure Standard Maximum
psi (MPa) at 30°C Flow Rate Flow Rate
mL/min mL/min
AS9-SC (4 x 250 mm) Analytical
< 950 (6.55) 1.0 3.0
AG9-SC (4 x 50 mm) Guard < 225 (1.55) 1.0 3.0
AS9-SC Analytical Column + Guard < 1175 (8.10) 1.0 3.0
Always remember that assistance is available for any problem that may be encountered during the shipment or
operation of DIONEX instrumentation and columns through the DIONEX North America Technical Call Center
at 1-800-DIONEX-0 (1-800-346-6390) or through any of the DIONEX Offices listed in, “DIONEX Worldwide
Offices.”
IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 5 of 28
SECTION 2 - THE ION CHROMATOGRAPHY SYSTEM
CONDITION 4-mm
Eluent Flow Rate 3 mL/min Maximum Flow Rate
SRS Suppressor ASRS-ULTRA (4-mm)
(P/N 053946)
MMS Suppressor AMMS III (4-mm)
(P/N 056750)
AES Suppressor AAES
(P/N 056116)
Injection Loop 10 - 50 µL
System Void Volume Minimize dead volumes. Switching valves, couplers can be
used. Use the GM-2 , GM-3 or recommended gradient
mixers.
Pumps Use the GP40/GP50/IP20/IP25 in Standard-Bore
Configuration.
The GM-3 Gradient Mixer should be used for gradient
analysis on systems other than the GP40/GP50/IP20/IP25
and the DX-300 HPLC Pump.
Detectors AD20/AD25 Cell (10-mm, 9 µL, P/N 049393)
VDM-2 Cell (6-mm, 10 µL) P/N 043113
CD20, CD25, CD25A, ED40, ED50, or ED50A
Conductivity Cell with DS3
P/N 044130 or with shield P/N 044132
CDM-2/CDM-3 Cell P/N 042770
Either the TS-1 with the TS-2 can be used with the CDM-2
or the CDM-3. Do not use the TS-2 or the TS-1 with the
ED40/ED50 or the CD20/CD25.
DIONEX Back Pressure Regulator 75 psi rating (P/N
039760, 046480) or Tubing (see Table 3)
Ensure 50-75 psi back pressure.
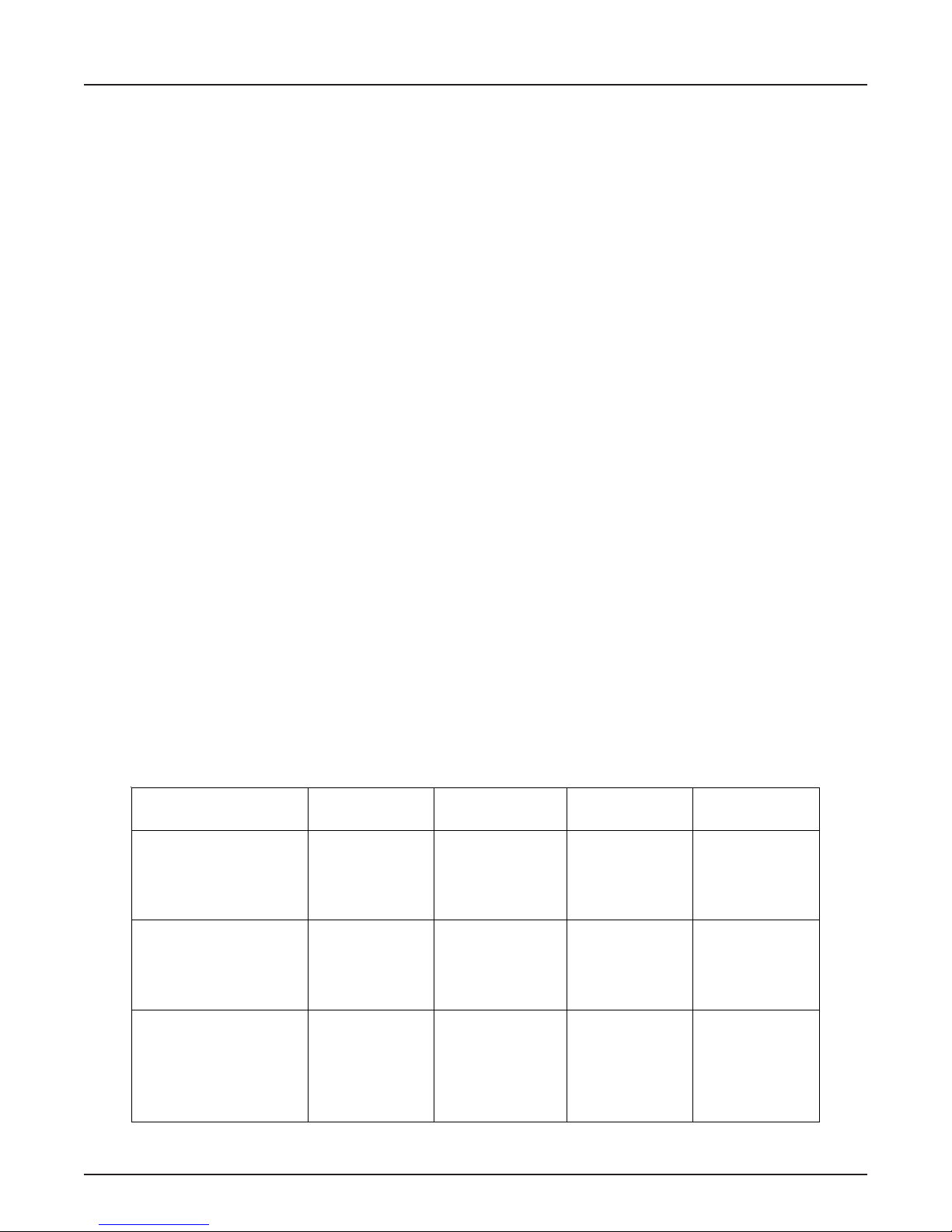
Table 3
Tubing Back Pressures
Tubing ID
in
0.005 111.4
0.007 29.0
0.010 7.0
0.012 3.4
H20 Back Pressure
Psi/ft at 1 mL/min
IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 6 of 28
SECTION 3 - INSTALLATION
3.1 System Requirements
3.1.1 System Requirements for 4-mm Operation
The IonPac AS9-SC 4-mm Guard and Analytical Columns are designed to be run on the following DIONEX Ion Chromatographs
equipped with suppressed conductivity detection. Isocratic analyses at flow rates of 0.5 mL/min or greater can be performed on
a GS50/GP50/GP40/IP25, Gradient Pump Module (GPM-2) or an Advanced Gradient Pump (AGP) with standard (1/8" pistons)
pump heads. For isocratic analyses at flow rates below 0.5 mL/min and gradient analyses, a Microbore GS50/GP50/GP40 or
Advanced Gradient Pump (1/16" pistons) must be employed.
3.1.2 System Void Volume
It is important to minimize system void volume. For best performance, all of the tubing installed between the injection valve and
detector should be 0.005" (P/N 044221) ID PEEK tubing, 0.010" ID PEEK tubing (P/N 042260) or 0.012" Tefzel tubing (see,
DIONEX Product Selection Guide). Minimize the lengths of all connecting tubing and remove all unnecessary switching valves
and couplers. If you need assistance in properly configuring your system contact the nearest DIONEX Worldwide Office (see,
DIONEX Worldwide Offices).
3.2 The Sample Concentrator
The Low Pressure Trace Anion Concentrator Column (TAC-LP1, P/N 046026), the Trace Anion Concentrator Column (TAC-2,
P/N 043101), the Anion MicroConcentrator, AMC-1, (P/N 051760) or the IonPac AG9-SC 4-mm Guard Column can be used for
trace anion concentration work required in high purity water analysis. The function of the TAC-LP1, the TAC-2, the AMC-1, or
the AG14A Guard Column in these applications is to strip ions from a measured volume of a relatively clean aqueous sample
matrix. This process “concentrates” all anionic analyte species onto the TAC-LP1, TAC-2, AMC-1 or the AG14A leading to a
lowering of detection limits by 2-5 orders of magnitude. The unique advantage to the analytical chemist of the TAC-LP1, the TAC2, the AMC-1, or the AG9-SC in these applications is the capability of performing routine trace analyses of sample matrix ions
at µg/L levels without extensive and laborious sample pretreatment.
3.3 The Injection Loop
Table 4
Smallest Injectable Volumes (μL)
Valve Type Using 0.012" ID
Tefzel Tubing
DIONEX
BF2 Valve
(8 µL Internal Volume)
(10 cm Loop)
DIONEX
MicroInject Valve
(10.5 µL Internal Volume)
(14 cm Loop)
Rheodyne
Microinjection Valve
Model 9126
(0.8 µL Internal Volume)
(10 cm Loop)
15.2 10.5 13.1 9.2
20.5 14.0 17.6 12.2
8.0 3.3 5.9 2.0
Using 0.007" ID
Tefzel Tubing
Using 0.010" ID
PEEK Tubing
Using 0.005" ID
PEEK Tubing

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 7 of 28
3.3.1 The 4-mm System Injection Loop, 10 - 50 μL
For most applications on a 4-mm analytical system, a 10 - 50 µL injection loop will be sufficient. Generally, do not inject more
than 10 nanomoles (100 - 200 ppm) of any one analyte onto the 4-mm analytical column. Injecting larger volumes of samples
can result in overloading the column which can affect peak efficiency and resolution.
3.4 The IonPac AG9-SC Guard Column
An IonPac AG9-SC Guard Column is normally used with the IonPac AS9-SC Analytical Column. Retention times will increase
by approximately 20% when a guard column is placed in-line prior to the analytical column. A guard is placed prior to the
analytical column to prevent sample contaminants from eluting onto the analytical column. It is easier to clean or replace a guard
column than it is an analytical column. Replacing the AG9-SC Guard Column at the first sign of peak efficiency loss or decreased
retention time will prolong the life of the AS9-SC Analytical Column.
3.5 Installing the Anion Trap Column, ATC-3
When performing a gradient anion exchange application, a borate eluent system should be used instead of a carbonate system
because of its low background conductivity. An IonPac Anion Trap Column (ATC-3 (4-mm), P/N 059660) should be installed
between the Gradient Pump and the injection valve. Remove the high pressure Gradient Mixer if present. The ATC is filled with
high capacity anion exchange resin which helps to minimize the baseline shift caused by increasing anionic contaminant levels
in the eluent as the ionic concentration of the eluent is increased over the course of the gradient analysis.
To install the ATC-3 (4-mm), complete the following steps:
A. Remove the Gradient Mixer, if installed between the gradient pump pressure transducer and the injection valve.
B. Connect the gradient pump directly to the ATC-3. Connect a waste line to the ATC-3 outlet and direct the line to a waste
container.
C. Flush the ATC-3 (4-mm) with 200 mL of 70 mM Na2B4O7 at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min.
D. Rinse the ATC-3 with the strongest eluent that will be used during the gradient analysis.
E. After flushing the ATC-3 with eluent, connect the ATC-3 to the eluent line that is connected to the injection valve.
The background conductivity of your system should be less than 7 µS when Na2B4O7 is being pumped through the chromatographic
system with the ASRS in-line and properly functioning. The baseline shift should be no greater than 10 µS during a borate gradient
eluent concentration ramp from 0 to 70 mM Na2B4O7. If the baseline shifts are greater than 10 µS, the ATC should be cleaned
using steps A - E above.
The ATC-3 can be flushed, at the end of each operating day, to remove any impurities that may have accumulated on it. This will
minimize periodic maintenance and lost data.
A. Flush the ATC-3 with 30 mL of 70 mM Na2B4O
7.
B. Prior to next day use of the chromatographic system, flush the ATC-3 with 30 mL of the strongest eluent used in the
gradient program.
See the Product Manual for the IonPac ATC-3 (P/N 032697) for instructions on cleaning a contaminated Anion Trap Column.

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 8 of 28
3.6 Eluent Storage
IonPac AS9-SC columns are designed to be used with borate or bicarbonate/carbonate eluent systems. Storage under a helium
atmosphere ensures contamination free operation and proper pump performance (nitrogen can be used if eluents do not contain
solvents).
3.7 The Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor, ASRS® -ULTRA
An Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor should be used for applications that require suppressed conductivity detection. It is
compatible with solvent containing eluents and aqueous ionic eluents of all concentrations with which the systems and columns
are compatible. Aqueous ionic eluents can be used in all ASRS-ULTRA modes of operation.
NOTE
Solvent containing eluents should be used in the AutoSuppression External Water Mode.
If you are installing an IonPac AS9-SC 4-mm Analytical Column, use an ASRS-ULTRA (4-mm, P/N 053946).
For detailed information on the operation of the Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor, see Document No. 031367, the “Product
Manual for the Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor-ULTRA, the ASRS-ULTRA.”
3.8 The Anion Atlas® Electrolytic Suppressor, AAES
An Atlas Anion Electrolytic Suppressor (AAES) may be used instead of an ASRS-ULTRA for applications that require
suppressed conductivity detection. The AAES (P/N 056116) can be used for AS9-SC 4-mm applications using eluents up to 25
µeq/min.
For detailed information on the operation of the Atlas Anion Electrolytic Suppressor, see Document No. 031770, the “Product
Manual for the Atlas Anion Electrolytic Suppressor.”
3.9 The Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor, AMMS® III
An Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor, the AMMS III (P/N 056750) can also be used for applications that require suppressed
conductivity detection. It is compatible with all solvents and concentrations with which the systems and columns are compatible.
For detailed information on the operation of the Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor, see Document No.031727, the “Product
Manual for the Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor III, the AMMS III.”
NOTE
Do not run the AMMS III Suppressor over 40°C. If you are using an application where temperatures in excess
of 40°C are required, place the suppressor outside of the oven.
To minimize the baseline shift when performing an analysis that requires a borate gradient, a high regenerant flow rate (10 - 15
mL/min) is required. To save regenerant preparation time and reduce regenerant consumption and waste, DIONEX recommends
using an AutoRegen® Accessory (P/N 039594).
3.10 Using AutoRegen® with the ASRS-ULTRA orthe AMMS III in the Chemical Suppression Mode
To save regenerant preparation time and reduce regenerant consumption and waste, DIONEX recommends using an AutoRegen
Accessory (P/N 039594). For more detailed information on the use of the AutoRegen Accessory see the AutoRegen Accessory
manual (Document No. 032853). For more detailed information on the use of AutoRegen Regenerant Cartridges, see the “Product
Manual for the AutoRegen Regenerant Cartridge Refills” (Document No. 032852).
When using an AutoRegen System, specific contaminants are continuously removed from the regenerant solution to restore it to
the correct ionic state. It is necessary however to replace the regenerant on a regular basis. If solvents are used in the eluent, ionic
®

IonPacAS9-SC 034656-06 Page 9 of 28
contaminants from the solvent component of the eluent which are not removed by the Anion AutoRegen Regenerant Cartridge
may slowly accumulate in the regenerant. This results in slowly increasing background conductivity. The rate at which the
background conductivity increases versus the required analysis sensitivity will determine how often the regenerant must be
changed.
It is not necessary to change the Anion AutoRegen Regenerant Cartridge until it is completely expended and a sudden jump to
very high background conductivity is observed.
3.11 Using Displacement Chemical Regernation (DCR) with the Chemical Suppression Mode
DIONEX recommends using the Displacement Chemical Regeneration (DCR) Mode for chemical suppression using sulfuric acid
and the Anion MicroMembrane Suppressor (AMMS III). See the DCR kit manual, Document P/N 031664, for details.
SAFETY
Use proper safety precautions in handling acids and bases.
3.12 Detector Requirements
See Section 2, “The Ion Chromatography System,” for 4-mm system detector, cell and thermal stabilizer requirements.
 Loading...
Loading...