Diodes ZVN4525E6 User Manual
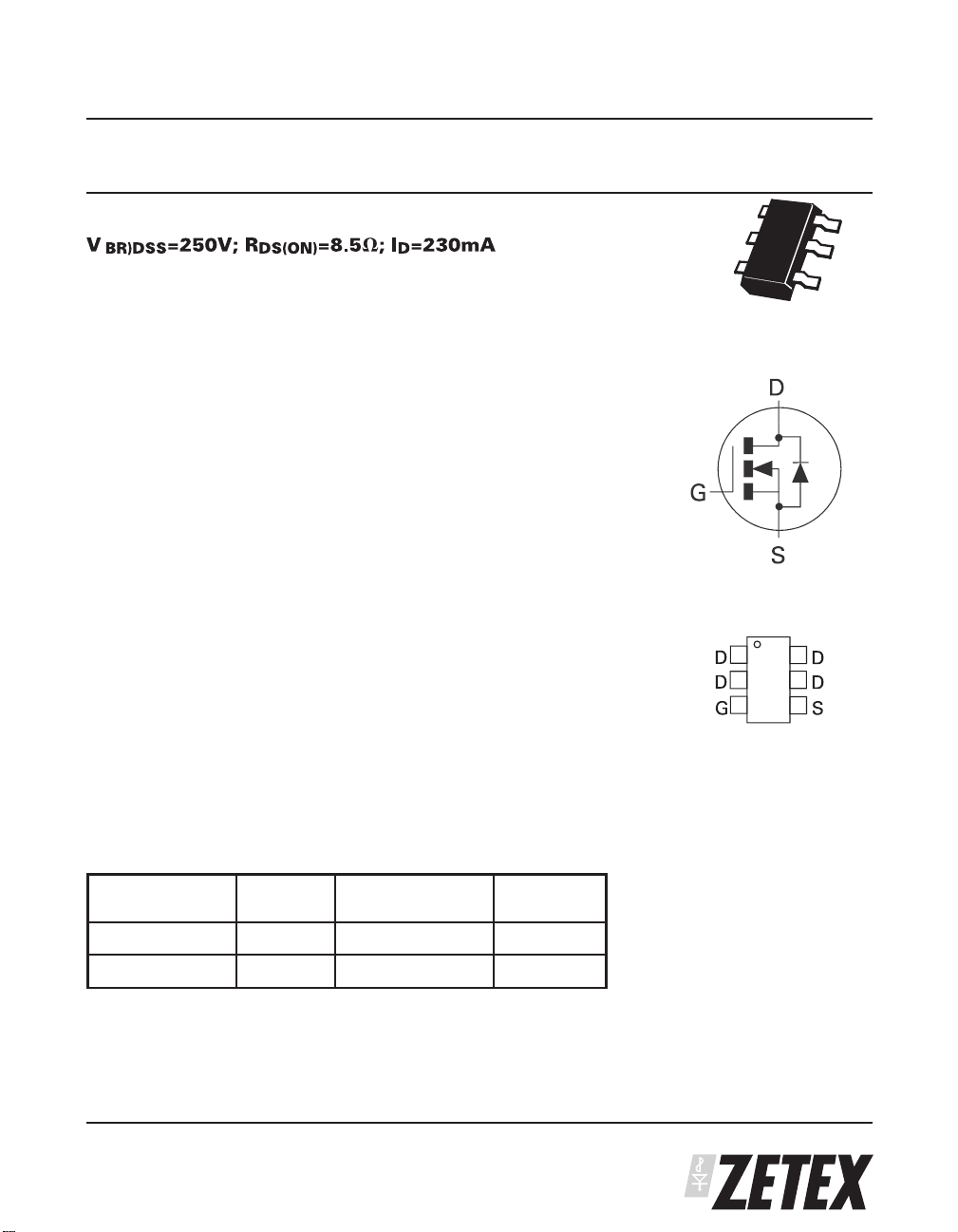
250V N-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET
SUMMARY
(
DESCRIPTION
This 250V enhancement mode N-channel MOSFET provides users with a
competitive specification offering efficient power handling capability, high
impedance and is free from thermal runaway and thermally induced
secondary breakdown. Applications benefiting from this device include a
variety of Telecom and general high voltage circuits.
SOT89 and SOT223 versions are also available.
FEATURES
High voltage
•
Low on-resistance
•
• Fast switching speed
• Low gate drive
• Low threshold
• Complementary P-channel Type ZVP4525E6
• SOT23-6 package
APPLICATIONS
•
Earth Recall and dialling switches
•
Electronic hook switches
•
High Voltage Power MOSFET Drivers
•
Telecom call routers
•
Solid state relays
ORDERING INFORMATION
DEVICE REEL SIZE
(inches)
ZVN4525E6TA 7 8mm embossed 3000 units
ZVN4525E6TC 13 8mm embossed 10000 units
TAPE WIDTH (mm) QUANTITY
PER REEL
ZVN4525E6
SOT23-6
Top View
DEVICE MARKING
•
N52
ISSUE 1 - MARCH 2001
1
ZVN4525E6
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS.
PARAMETER SYMBOL LIMIT UNIT
Drain-Source Voltage V
Gate Source Voltage V
Continuous Drain Current (V
=10V; TA=25°C)(a)
GS
(V
=10V; TA=70°C)(a)
GS
Pulsed Drain Current (c) I
Continuous Source Current (Body Diode) I
Pulsed Source Current (Body Diode) I
Power Dissipation at T
Linear Derating Factor
=25°C (a)
A
Operating and Storage Temperature Range T
I
D
I
D
DM
S
SM
P
DSS
GS
D
j:Tstg
THERMAL RESISTANCE
PARAMETER SYMBOL VALUE UNIT
Junction to Ambient (a) R
Junction to Ambient (b) R
θJA
θJA
250 V
±40
230
183
mA
mA
1.44 A
1.1 A
1.44 A
1.1
8.8
mW/°C
-55 to +150 °C
113 °C/W
65 °C/W
V
W
NOTES
(a) For a device surface mounted on 25mm x 25mm FR4 PCB with high coverage of single sided 1oz copper,
in still air conditions
(b) For a device surface mounted on FR4 PCB measured at t⭐5 secs.
(c) Repetitive rating - pulse width limited by maximum junction temperature. Refer to Transient Thermal
NB High Voltage Applications
For high voltage applications, the appropriate industry sector guidelines should be considered with regard to
voltage spacing between conductors.
ISSUE 1 - MARCH 2001
2
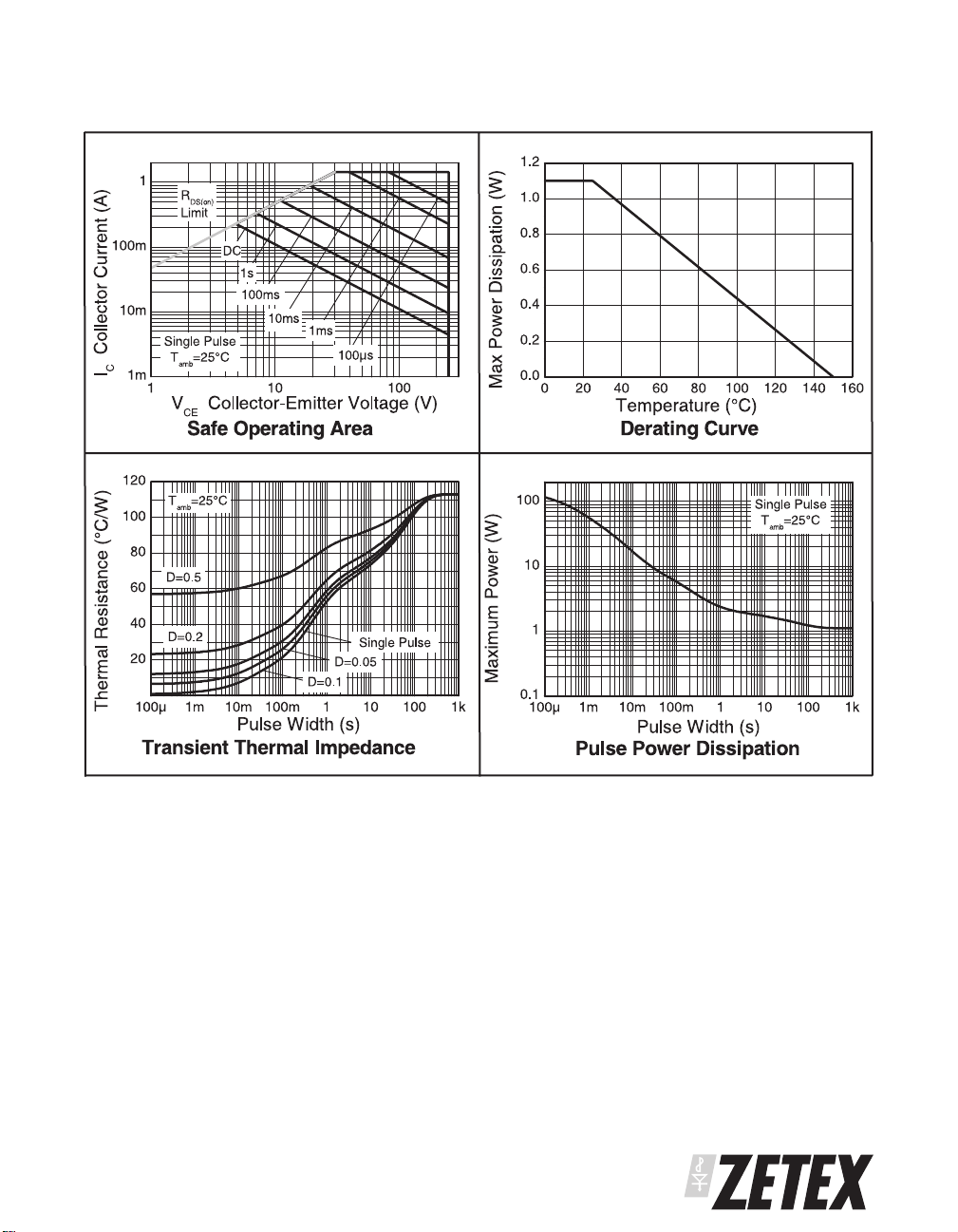
CHARACTERISTICS
ZVN4525E6
ISSUE 1 - MARCH 2001
3
 Loading...
Loading...