Page 1

DG-FS1526
Layer 2 Fast Ethernet W
eb Managed Switch
User Manual
V1.4
2012-4
-5
A
s our products undergo continuous development the specifications are subject to change without prior notice
Page 2

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
2
COPYRIGHT
Copy
right © 2010 by this company. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any
language or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of this
company
This company makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with
respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or
fitness for any particular purpose. Any software described in this manual is sold or licensed
"as is". Should the programs prove defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not this
company, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all necessary servicing,
repair, and any incidental or consequential damages resulting from any defect in the software.
Further, this company reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from
time to time in the contents thereof without obligation to notify any person of such revision
or changes.
T
rademarks:
DIGISOL
™ is a trademark of Smartlink Network Systems Ltd. All other trademarks are the
property of the respective manufacturers.
Safety
T
his equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it.
However, special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity
when working with electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer
manufacturer must therefore be allowed at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
Page 3

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
3
Index
1
Precautions
........................................................................................................6
2
Overvie
w............................................................................................................7
2.1
Product Featu
res...................................................................................7
3 T
echnical Specifications.....................................................................................8
3.1
Environment Re
quirements...................................................................8
3.2
Power Inte
rface .....................................................................................8
3.3
Power Co
nsumption..............................................................................8
3.4
Ethernet Inte
rface..................................................................................8
3.5
Ph
ysical Characteristics ........................................................................9
4
Device Inst
allation and Description....................................................................9
4.1
Prep
aration Before Installation..............................................................9
4.1.1
Package Content
s............................................................................9
4.1.2
Optional Accessories
and T ools.......................................................9
4.1.3
Choosing the Ins
tallation Location.................................................10
4.1.3.1
Inst
alling the DG-FS1526 on the Work Platform.......................10
4.1.3.2
Inst
alling the DG-FS1526 on a Rack........................................10
4.2
Hard
ware Description.......................................................................... 11
4.2.1
Front Pan
el..................................................................................... 11
4.2.2
Rear Panel.....................................................................................
12
4.3
Electrical Setup
....................................................................................12
4.3.1 Setting Up the P
ower Interface......................................................12
4.3.2
Setting Up the Et
hernet Interfaces.................................................12
5
Device S
tartup..................................................................................................14
5.1
Check Before Po
wer-On......................................................................14
5.2
Powering
On the Device......................................................................14
6
Device Upgrade
...............................................................................................15
7
W
eb Configuration and Management ..............................................................15
Page 4

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
4
7.1
Preparation Before Login.....................................................................15
7.2
Logging In to the
Switch......................................................................16
7.3
S
ystem Management...........................................................................18
7.3.1
Authentication Configuration..........................................................
18
7.3.2 System IP Configuration.................................................................19
7.3.3
System
Status................................................................................20
7.3.4
Loading Default
Settings................................................................20
7.3.5
F
irmware Update............................................................................21
7.3.6
Reboot the Device..........................................................................21
7.4 Port Managem
ent................................................................................22
7.4.1
Port Configu
ration..........................................................................22
7.4.2
Port Mi
rroring .................................................................................24
7.4.3
Bandwid
th Control..........................................................................25
7.4.4
Broadcast S
torm Control................................................................26
7.5 VLAN Configurat
ion.............................................................................27
7.5.1
VLAN Mode....................................................................................
28
7.5.1.1
VLAN Based on
Port.................................................................28
7.5.1.2
VLAN Based on
Tag .................................................................29
7.5.2
VLAN Me
mber................................................................................30
7.5.2.1
VLAN Based on
Port.................................................................30
7.5.2.2
VLAN Based on
Tag .................................................................31
7.5.3
M
ulti to 1 Setting Configuration......................................................33
7.6
Per Port C
ounter..................................................................................34
7.7
QoS Configu
ration...............................................................................36
7.7.1
Priority M
ode..................................................................................37
7.7.2
Class of Service
Configuration - 1..................................................38
7.7.3
Class of Service
Configuration - 2..................................................39
7.8
Securit
y................................................................................................41
7.8.1
M
AC Address Binding ....................................................................42
7.8.2
TCP/UDP
Filter...............................................................................44
7.9
S
panning T ree .....................................................................................45
Page 5

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
5
7.9.1
STP Bridge Settings.......................................................................46
7.9.2
STP
Port Settings...........................................................................48
7.9.3
Loopback Detect
ion: ......................................................................50
7.10
T
runking...............................................................................................51
7.11 DHCP Relay Agent..............................................................................54
7.1
1.1
DHCP
Relay Age nt.........................................................................54
7.1
1.2
Relay Server ..................................................................................
55
7.1
1.3
VLAN M
AP Relay Agent.................................................................55
7.12
Configuration Backup and Recovery...................................................56
7.13 Miscellaneous Configuration
...............................................................57
7.14
SNMP
Settings ....................................................................................58
7.15
Logout
..................................................................................................59
8
T
roubleshooting................................................................................................60
9
Glossary
...........................................................................................................61
Page 6

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
6
1 Precautions
Power supply sockets with too heavy load or broken cables and plugs may
cause electric shock or fire. Users should check the power supply wires and
cables regularly. If there is any breakage, please replace the cable at once.
Do not open the case of the device, especially during device power-on.
The device should be installed at position with good ventilation and without
high temperature or direct sunshine, so as to avoid faults of the device and its
corresponding components due to overheat.
Do not put this device close to a damp or watery place. Do not spill any fluid on
this device.
Keep proper space for heat dissipation, to avoid any damage to the device
caused by overheating. The holes on the shell are designed for heat dissipation,
to ensure that the device works normally. Do not cover the heat dissipation
holes.
Keep the power plug clean and dry, if abnormal phenomenon occurs, such as
smoke, abnormal sound, abnormal smell, switch off the power.
Page 7

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
7
2 Overview
The DG-FS1526 i
s an intelligent Layer 2 Ethernet switch. It provides 24 10M/100M selfadaptive Ethernet ports and 2 gigabit combo ports. The combo ports can be flexibly
connected to gigabit copper cable or backbone fiber. You can select 1000BASE-LX,
1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-T interface according to the transmission distance. The DGFS1526 supports VLAN classification, SNMPv1, port mirroring, port trunking, and QoS.
You can configure the device easily through web interface.
2.1 Product Features
24 10M/100M self-adaptive FE ports and 2 10M/100M/1000M self-adaptive
GE ports. 2 SFP slots are shared with GE ports. You can connect the switch to
other switches through copper cable or fiber .
Manage the switch through web page. Network administrator can monitor and
configure the switch through any Ethernet port.
Support the following standards: IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, IEEE802.3x, and
IEEE802.1Q.
VLAN: Support up to 32 Tag VLANs and up to 26 Port Based VLANs.
Support 4K MAC addresses.
Other functions: CoS, broadcast storm control, port management, bandwidth
control, spanning tree protocol, and simple network management.
Page 8

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
8
3 Technical S
pecifications
3.1 Environment Require
ments
The whole device
can survive in a wide range of operating temperature and can work
normally and stably in tough environment.
Operating temperature: 0˚C—40˚C
Storage temperature: -10˚C—70˚C
Relative humidity: 10%—90% (non-condensing)
Storage Relative Humidity: Maximum 95% (non-condensin g)
3.2 Pow
er Interface
Power
input: 100V AC ~240V AC, 50/60Hz
3.3 Pow
er Consumption
W
hole device consumption: < 18 W
3.4 Ethernet Interface
Standard: IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, and IEEE802.3x.
Transmission rate: Port 1 ~ Port 24 are 10 M/100 M self-adaptive.
Port 25 ~ Port 26 are 10 M/100 M/1000 M self-adaptive.
Working mode: full duplex, half duplex, self-adaptive.
Port type:
–
24 x 10/1
00Base-TX self-adaptive Ethernet ports.
–
2 x 10/10
0/1000Base-TX self-adaptive Ethernet ports.
–
2 x SFP
fiber ports. They are shared with 10/100/1000Base-TX self-adaptive
Ethernet ports.
Page 9

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
9
Transmission distance: < 100m, Cat. 3/5 UTP. The transmission distance of SFP
port is determined by optical module.
Auto-MDI/MDI-X. Automatically distinguish crossover cable from straight
through cable.
3.5 Ph
ysical Characteristics
Dimension (L x W x H):440 mm x 208 mm x 44 mm
Net Weight: 2.9 kgs
Gross Weight: 3.9 Kgs
4 Device Inst
allation and Description
4.1 Prep
aration Before Installation
4.1.1 Packag
e Contents
DG-FS1526 Fast Ethernet Switch
Power Cord
Bracket Mounting Kit containing two brackets and six screws for
attaching the brackets to the switch
CD containing User Manual
Four adhesive foot pads
4.1.2 Optional
Accessories and Tools
Screwdriver
ESD straps
Ethernet crimping pliers, 8P8C crystal heads
Ethernet (either crossover or straight through) cable
Page 10

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
10
4.1.3 Choo
sing the Installation Location
T
he DG-FS1526 can be installed in either of the following ways as required:
On the work platform
On a rack
4.1.3.1 Installing the
DG-FS1526 on the Work Platform
T
he common way is to install the DG-FS1526 on a clean work platform. Pay attention to
the following precautions:
Ensure that the work platform is flat and stable.
Ensure good ventilation of air ports on both sides of the device.
Do not put heavy objects on the device.
4.1.3.2 Installing the
DG-FS1526 on a Rack
Befor
e installing the DG-FS1526 on a rack, you need to install the provided L- Clamps on
both sides of the DG-FS1526.
Page 11
DG-
FS1526 User Manual
4.2 Hardw
are Description
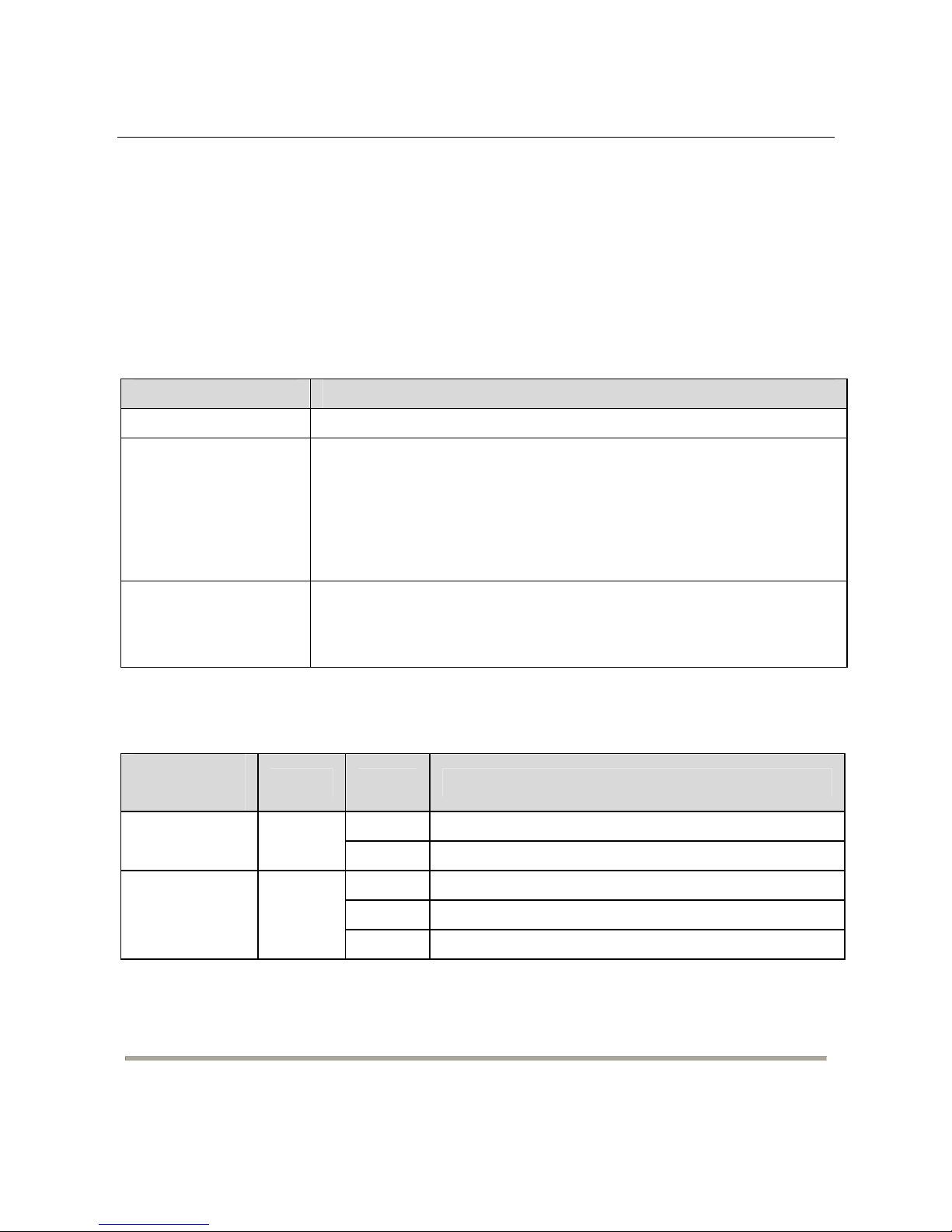
4.2.1 Front Pan
el
The following tabl
e describes the interface of the DG-FS1526.
Interfa
ce/Button
Descrip
tion
1~24 24 x RJ-45 Ethernet interfaces, 10
M/100 M self-adaptive.
25,
26
Two groups of fiber-copper combo ports. T he copper ports are 10
M/100 M/1000 M self-adaptive Ethernet ports and the fiber ports
are SFP optical module ports. I f the combo ports are preferred to
serve as fiber ports, that is, if the ports connect to a fiber port, the
copper port is disabled.
Reset
Keep the device p
owered on and push a paper clip into the hole.
Press down the button for about 5 seconds. The system restores the
factory default settings.
The follo
wing table describes the twenty-seven LED indicators of the DG-FS1526.
LED
Indica
tor
Color St
atus
Descrip
tion
Of
f The power is off.
Power Green
On T
he power is on.
Of
f The LAN interface is not connected.
Blinks Data is being trans
mitted.
1 ~ 24,
25, 26
Link/Act
Green
On The network connection is established.
11
Page 12

DG-
FS1526 User Manual
4.2.2 Rear Pan
el
Interfa
ce
Descrip
tion
100-
240VAC 50/60Hz
The power interface.
The power input is 100 V ~ 240 V AC, 50 Hz ~ 60Hz.
4.3 Electrical Setup
4.3.1 Setting
Up the Power Interface
After placing t
he DG-FS1526 to a flat and stable surface, insert the supplied power cable
to the power socket, and connect the other end of the cable to the power interface of DGFS1526.
4.3.2 Setting
Up the Ethernet Interfaces
The DG-FS1526 provides twenty
-four auto-MDI/MDI-X Ethernet service interfaces of
standard RJ45 connectors. You can use either the crossover or straight through cable to
connect an interface.
12
Page 13
DG-
FS1526 User Manual
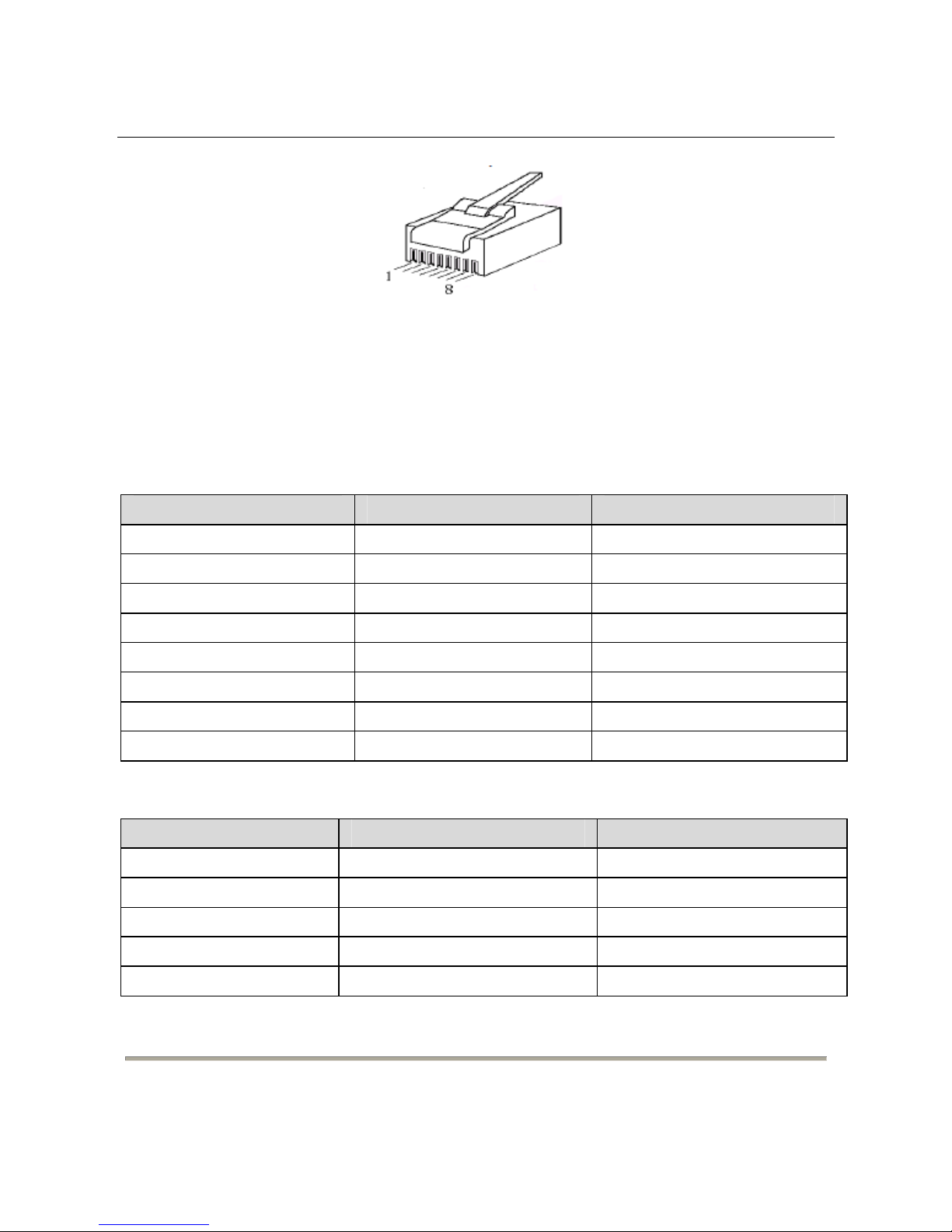
The following figure describes the line sequence of Ethernet cable:
F
igure 1 Pinout of Ethernet interfaces
Crossover cable: Refer to 0 to connect one end of the ne
twork cable. Refer to 0 to connect
the other end.
Straight-through cable: Refer to 0 to connect both ends of the network cable.
T
able 1.
Pinout of RJ-
45 straight-through cable
No. Defini
tion
Color
1 T
XD+ Orange and white
2 TXD- Orange
3 RXD+ Green and white
4 -
Blue
5 -
Blue and white
6 RXD- Green
7 -
Brown and white
8 -
Brown
T
able 2.
Pinout o
f RJ-45 crossover cable
No. Defini
tion
Color
1 RXD+ Green and white
2 RXD- Green
3 T
XD+ Orange and white
4 -
Blue
5 -
Blue and white
13
Page 14
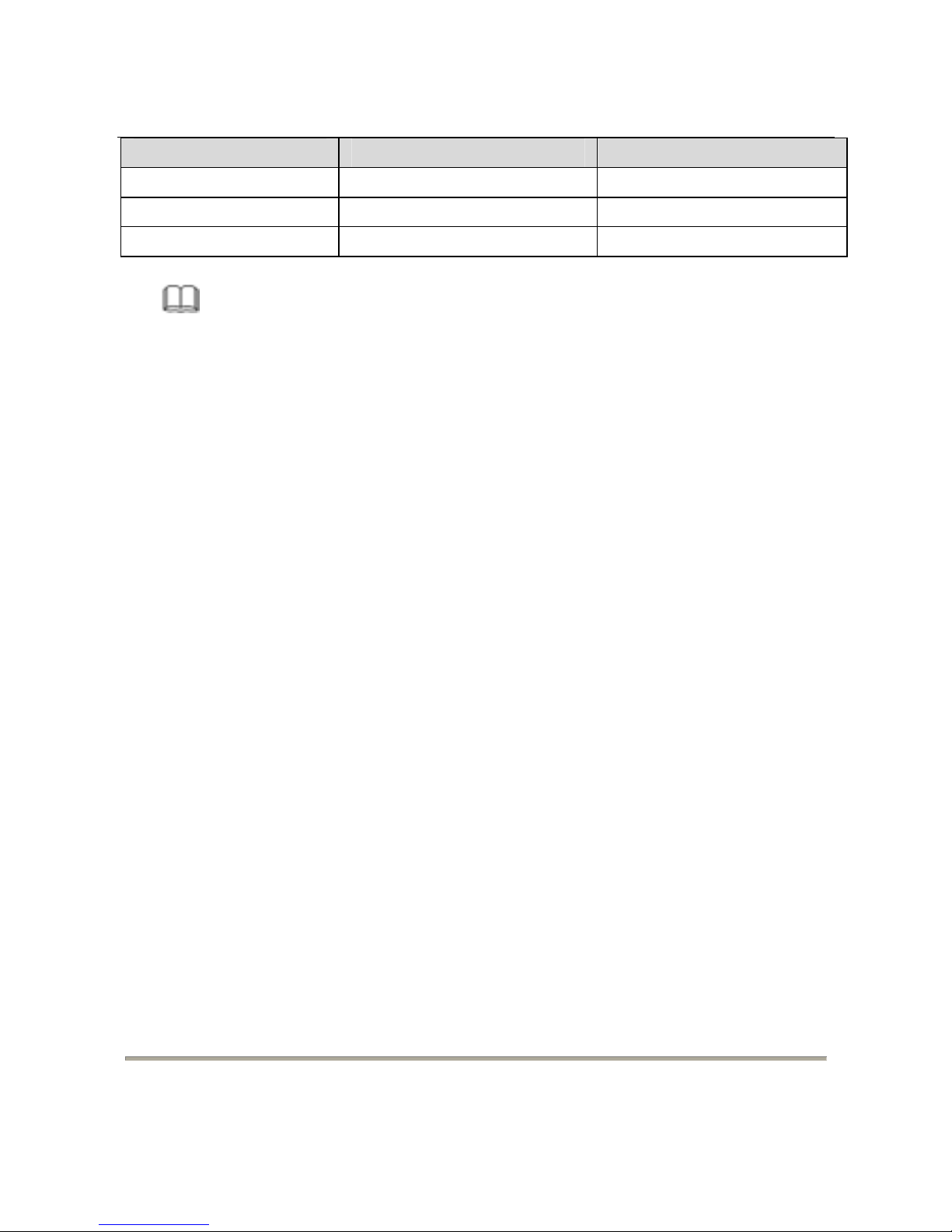
DG-
FS1526 User Manual
No. Defini
tion Color
6 TXD- Orange
7 -
Brown and white
8 -
Brown
Note
:
T
o ensure good quality of the data signal, the length of the network cable connected to
the Ethernet interface should be shorter than 100m.
5 Device S
tartup
5.1 Check Befo
re Power-On
Befor
e powering on the device, check the following:
Whether the voltage of the power supply is consistent with the power
requirement of the device.
Whether the power cable is correctly connected.
Whether the device is correctly connected to the ground on the rear side.
5.2 Pow
ering On the Device
Af
ter connecting the power cable, turn on the power switch. When the Power indicator
turns on, the system starts to initialize. When other indicators blink three times and the
Power indicator is always on in green, the power works normally.
14
Page 15
DG-FS1526 User Manual
6 Device Upgrade
You can upgrade software through any Ethernet port for DG-FS1526. After software
upgrade is complete, the system reboots automatically.
7 Web Configuration and Management
The system does not support the CLI and telnet management. It supports the web
management only. This section describes the web configuration and management.
7.1 Preparation Before Login
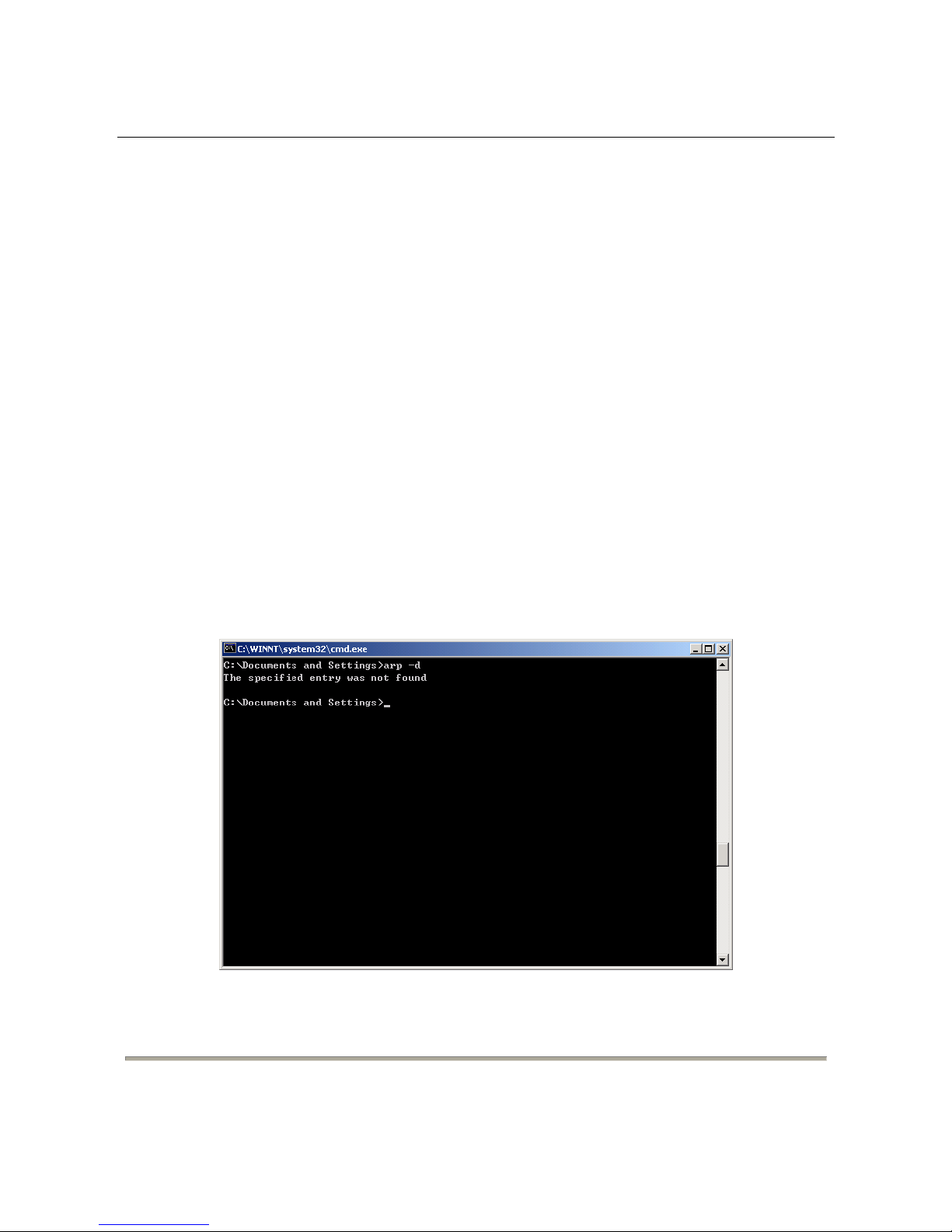
Before accessing the switch, ensure the communication between PC and switch is normal.
Check the communication as follows.
1. Set the IP address of the PC to 192.168.2.X (2~254) and the subnet mask to
255.255.255.0.
2. Enter arp -d or arp -d 192.168.2.1 in the DOS window. See the following figure.
15
Page 16
DG-FS1526 User Manual
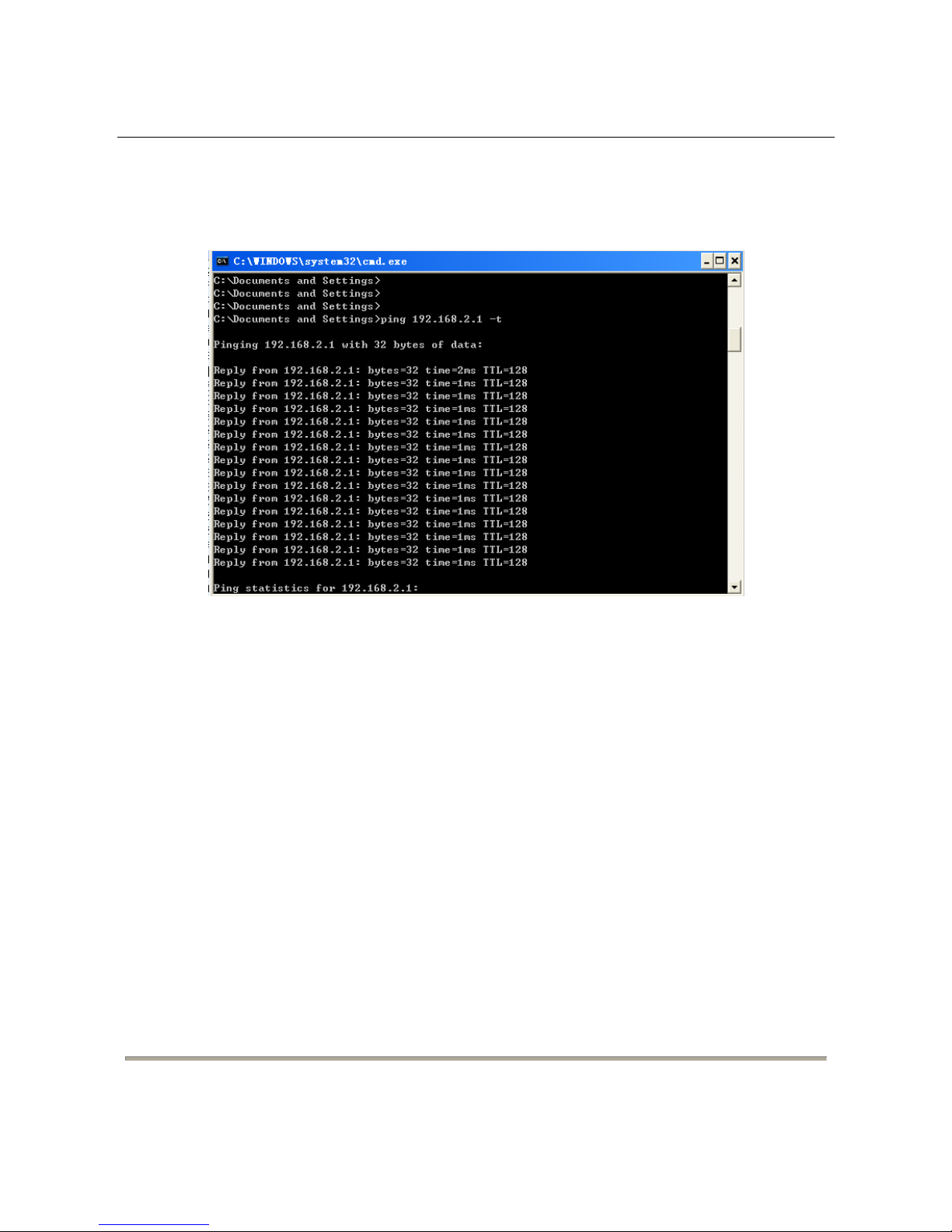
3. Ping the maintenance IP address (192.168.2.1 by default) of the switch. See the
following figure.
If the PC can read the MAC address of the switch and can ping through the maintenance IP
address of the switch, that means the communication of the PC and the switch is normal.
7.2 Logging In to the Switch
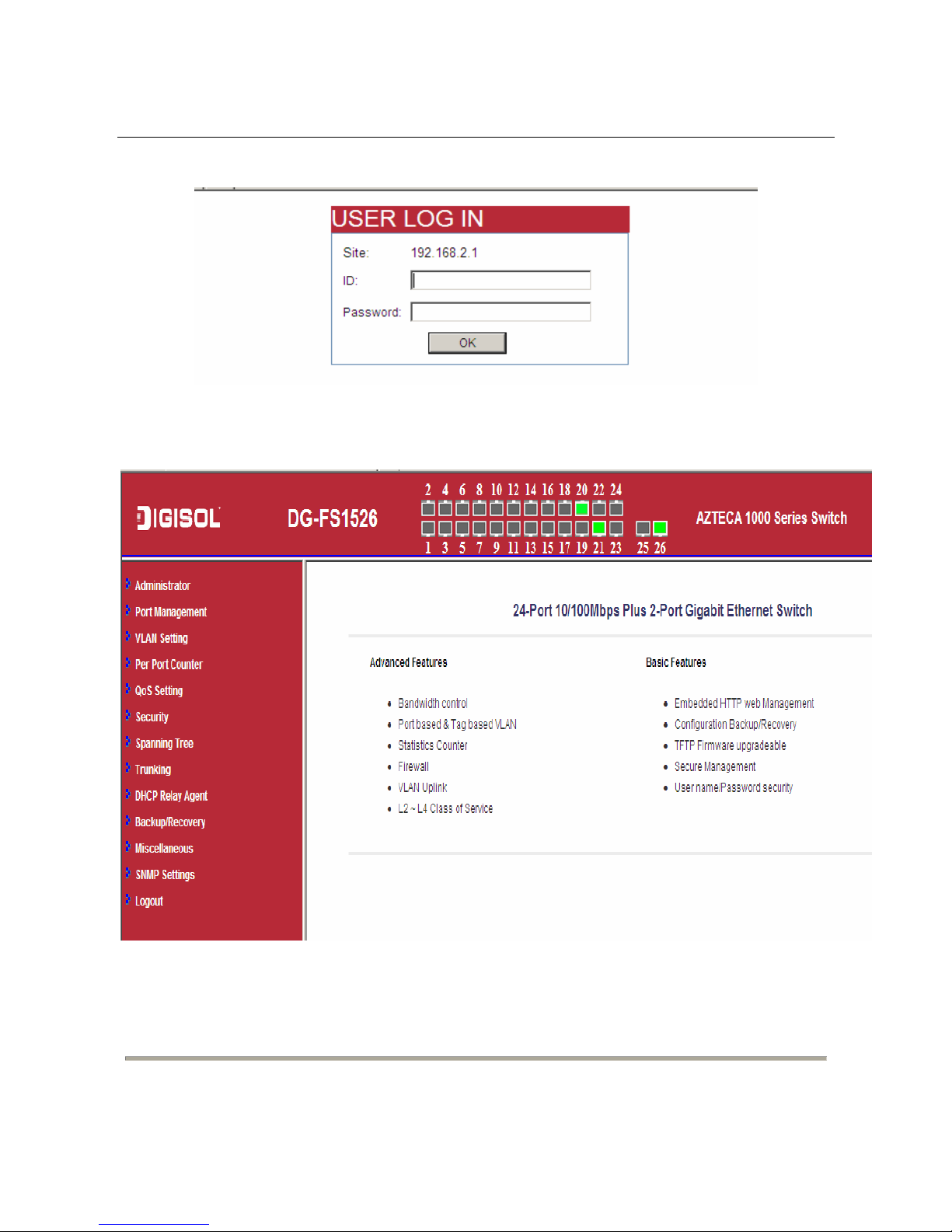
1. Open the web browser, and type the default IP address of switch in the address bar
as ‘http: //192.168.2.1’.
2. Enter the ID and the password. The default ID is admin and password is system.
16
Page 17
DG-FS1526 User Manual
3. Click OK to log in.
After logging in to the switch successfully, the following page appears.
17
Page 18

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.3 System Management
Choose Administrator, and the sub-menus of Administrator are shown as below.
7.3.1 Authentication Configur ation
Choose Administrator > Authentication Configuration, and the following page appears.
Read the Note in the page, and change the user name and password. After proper
configuration, click Update to apply the settings and then Reboot the device for the
changes to take effect.
18
Page 19
DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.3.2 System IP Configuration
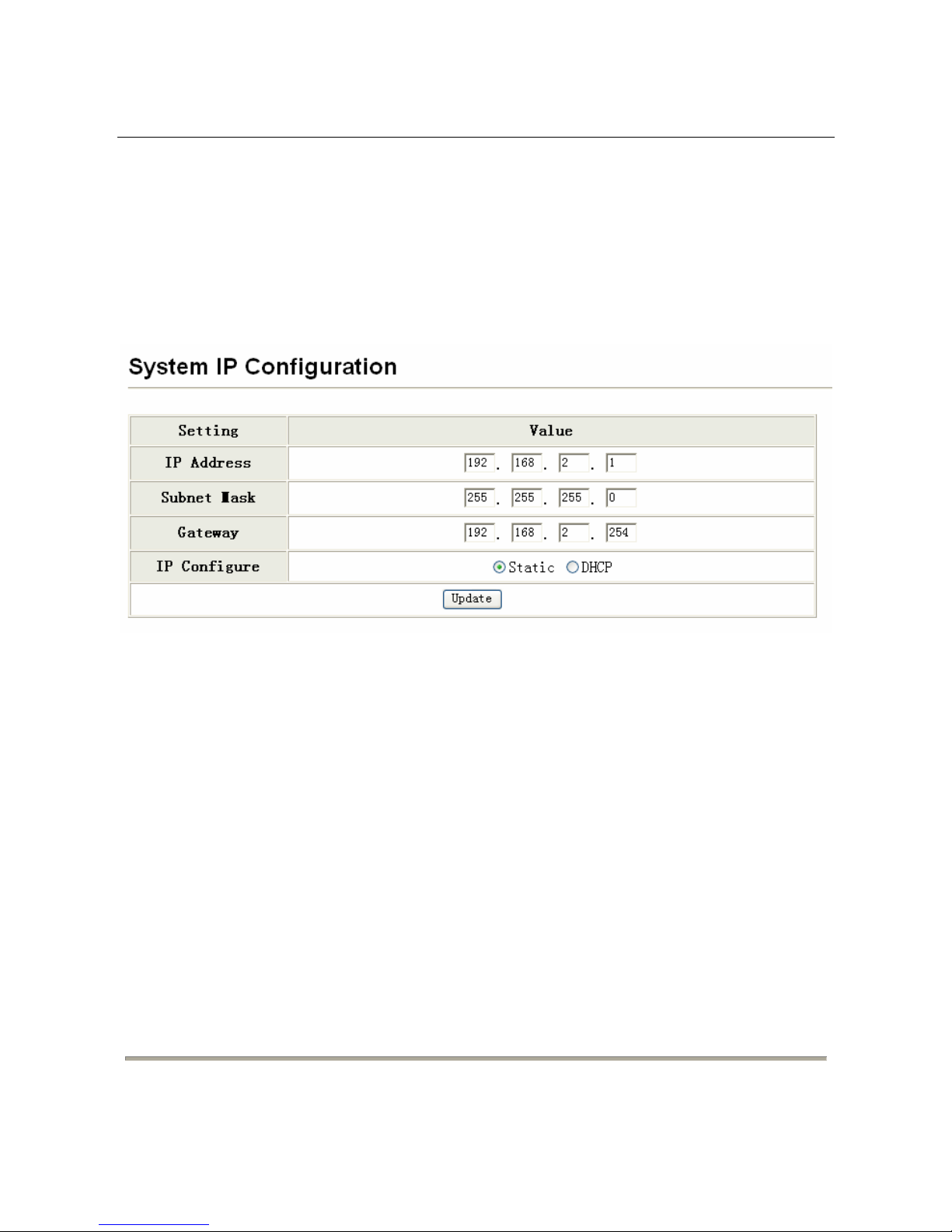
Choose Administrator > System IP Configuration, and the following page appears. In this
page, you can set the maintenance IP address of the switch, subnet mask, and gateway. After
proper configuration, click Update to apply the settings and then Reboot the device for the
changes to take effect.
19
Page 20

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.3.3 System S ta t us
Choose Administrator > System Status, and the following page appears. In this page,
you can view the MAC address, number of ports, and system version. You can also set a
comment.
7.3.4 Loading Default Settings
Choose Administrator > Load default setting and the following page appears. In this
page, click Load to load the default settings that do not include IP address, user name, and
password.
20
Page 21

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.3.5 Firmware Update
Choose Administrator > Firmware Update, and the following page appears. In this page,
enter the login password. Then click Update. A pop up page will appear asking you to
select new file for updating the firmware.
Caution:
When firmware update is in progress, do not shut down the switch.
7.3.6 Reboot the Device
Choose Administrator > Reboot Device, and the following page appears. In this page,
click Confirm to reboot the device.
21
Page 22

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.4 Port Management
Choose Port Management, and the submenus of Port Management are shown as below.
7.4.1 Port Configuration
Choose Port Management > Port Configuration, and the following page appears. In this
page, you can set Tx/Rx Ability, Auto-Negotiation, Speed, Duplex, Pause,
Backpressure, and Addr. Learning of port.
22
Page 23

DG-FS1526 User Manual
23
Page 24

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.4.2 Port Mirroring
Choose Port Management > Port Mirroring, and the following page appears. In this
page, you can enable port mirroring service. The packets from source port transmit to
destination port.
Field Description
Dest Port You can select one or more.
Monitored Packets
You can select it from the drop-down list:
Source Port You can select one or more.
24
Page 25

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.4.3 Bandwidth Control
Choose Port Management > Bandwidth Control, and the following page appears.
25
Page 26

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
Port No. You can select the port number from the drop-down list.
Tx Rate The range of transmitting rate is 0 ~ 255. 0 means full speed.
Rx Rate The range of receiving rate is 0 ~ 255. 0 means full speed.
Speed Base
You can select Low or High from the drop-down list.
Low: The bandwidth resolution is 32 Kbps for all port.
High: The bandwidth resolution is 256 Kbps for port 1 ~ port
24. The bandwidth resolution is 2048 Kbps for port 25
and port 26. Port 25 and port 26 support 10 M/100
M/1000 M self-adaptive.
After proper configuration, click Update to apply the settings. Click Load Default to
restore the default settings.
7.4.4 Broadcast Storm Control
Choose Port Management > Broadcast Storm Control, and the following page appears.
26
Page 27

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
Threshold
The valid range is 1 ~ 63. This value indicates the number of broadcast
packets that are allowed to enter each port in one time unit. One time
unit is 50us for Gigabit speed, 500 us for 100Mbps speed, and 5000us
for 10Mbps speed.
Enable Port Select the corresponding port.
7.5 VLAN Configuration
In large networks, routers are used to isolate broadcast traffic for each subnet into separate
domains. This switch provides a similar service at Layer 2 by using VLANs to organize
any group of network nodes into separate broadcast domains. VLANs confine broadcast
traffic to the originating group, and can eliminate broadcast storms in large networks. This
also provides a more secure and cleaner network environment.
The system supports VLAN based on port and VLAN based on tag. You can change the
VLAN mode in the VLAN Mode page.
Choose VLAN Setting, and the sub-menus of VLAN Setting are shown as below.
27
Page 28

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.5.1 VLAN Mode
7.5.1.1 VLAN Based on Port
Choose VLAN Setting > VLAN Mode, and the following page appears. The default mode
is Port Based VLAN. Click Change VLAN mode to change the VLAN mode.
Once "Change VLAN mode" is selected, a warning message will appear. Select "Continue"
to change the mode or select "Back" to keep the existing vlan mode.
28
Page 29

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.5.1.2 VLAN Based on Tag
In the tag based vlan mode, you can modify the packet contents that are transmitted from
port. You can add tag or remove tag. If you do not want to modify the packets, select don't
care.
29
Page 30

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.5.2 VLAN Member
7.5.2.1 VLAN Based on Port
Choose VLAN Setting > VLAN Member, and the following page appears.
30
Page 31

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
Port Select the corresponding port from the drop-down list.
Dest PORT (check
box)
Select the corresponding port that is in the same VLAN of the
current port.
VLAN MEMBER
v indicates the following: The port in the row and the port in the
column are in the same VLAN.
7.5.2.2 VLAN Based on Tag
When the VLAN mode is tag, the VLAN Member Setting page is shown as the following
figure.
31
Page 32

DG-FS1526 User Manual
The following figure displays the VLAN configuration in the tag mode
Field Description
VID
Select the Vlan ID to be assigned to the VLAN and click on Add to
enter the VID. Once the VID is added it will appear in the drop down
list.
VLAN Member Port
Select the VID from the Dropdown list and then select the desired
member ports from the Table.
Port VID MAP
Port VID map shows the Port number corresponding to the VID to
which the same is assigned.
When the port receives the packets without tag, the system can check the VLAN table
according to the port VID. The system can add the tag according to the VID found in the
VLAN table.
32
Page 33

DG-FS1526 User Manual
33
To add vlan, enter a VID and select vlan member for this entry from vlan member list. Now
select “Add” button to add vlan entry to the table. Vl an entry can be modified by selecting
VID from the list and then select “Update” button.
To delete an entry from the vlan table, select VID from the drop-down list and select “Delete”
to remove the corresponding entry from the table.
7.5.3 Multi to 1 Setting Configuration
Choose VLAN Setting > Multi to 1 setting, and the following page appears. This feature
can disable communication between ports in order to improve the security.
After setting the multi to 1 setting, the VLAN original setting will be cleared. If
the VLAN is configured again, the multi to 1 setting will be cleared.
Multi to 1 Settings take effect only when “VLAN based on port” mode is
selected.
In this page, select the current port from the drop-down list. Then select the port from the
check box to isolate from the current port.
Page 34

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.6 Per Port Co unter
Choose Per Port Counter, and the Port Counter submenu is shown as below.
Choose Per Port Counter > Port Counter, and the following page appears. In this page,
you can view the packet quantity.
34
Page 35

DG-FS1526 User Manual
35
Page 36

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
Counter Mode
Selection
Select it from the drop-down list:
Click Update to view the corresponding packet quantity.
Refresh Click the button to refresh the counter information.
Clear Click the button to clear the counter information.
7.7 QoS Configuration
All switches or routers that access the Internet, rely on class information to provide the same
forwarding treatment to packets in the same class. Class information can be assigned by end
hosts, or switches or routers along the path. Priority can then be assigned based on a general
policy, or a detailed examination of the packet. However, note that detailed examination of
packets should take place close to the network edge so that core switches and routers are not
overloaded.
Switches and routers along the path can use class information to prioritize the resources
allocated to different traffic classes. The manner in which an individual device handles traffic
is called per-hop behavior. All devices along a path should be configured in a consistent
manner to construct a consistent end-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) solution.
36
Page 37

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Choose QoS Setting, and the sub-menus of QoS Setting are shown as below.
7.7.1 Priority Mode
Choose QoS Setting > Priority Mode, and the following page appears. In this page, you
can set the priority mode.
The system supports the following three priority modes.
First-In-First-Out
All-High-before-Low
Weight-Round-Robin
– Low weight: You can select 0 ~ 7 from the drop-down list.
– High weight: You can select 0 ~ 7 from the drop-down list.
37
Page 38

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.7.2 Class of Service Configuration - 1
Choose QoS Setting > Port, 802.1p, IP/DS based, and the following page appears.
The COS of port supports the following mode.
Based on port
Based on 802.1p: The priority is determined according to the value of
802.1p (bit [15:13]) in the VLAN Tag. Packets in which values of
802.1p (bit [15:13]) are 000-011 map to lower priority. Packets in which
values of 802.1p (bit [15:13]) are 100-111 map to higher priority.
38
Based on IP
/ DS:
Page 39

DG-FS1526 User Manual
39
For IPv4 packets, the priority is determined according to the value of
TOS [5:0] in the header. Packets in which values of TOS [5:0] are
101110, 001010, 010010, 011010, and 11x000 map to higher priority.
Packets in which TOS [5:0] are other values map to lower priority.
7.7.3 Class of Service Configuration - 2
Choose QoS Setting > TCP/UDP Port Based and the following page appears. COS based
on TCP/UDP port specifies the priority queues of packets or discards designated protocol
packets according to the application layer protocols of packets received at the port. COS
supports classifying packets into corresponding priority queues or discards packets
according to the port in the range of ports 1-65535, besides certain known protocols, such
as FTP, telnet, and SNMP.
Page 40

DG-FS1526 User Manual
DG-FS1526 User Manual
40
40
Page 41

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
Option
You can select it from the drop-down list:
User_Define
Port: The valid range is 1 ~ 65535.
Mask: The valid range is 0 ~ 255.
TCP/UDP port QoS
function
Override: When the "override" item is selected, the
Port_based, Tag based, IP TOS_based, CoS listed
previous will be ignored.
Not Override
7.8 Security
Choose Security, and the sub-menus of Security are shown as below.
41
Page 42

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.8.1 MAC Address Binding
Choose Security > MAC Address Binding and the following page appears. After MAC
address binding is enabled at a port, only devices whose MAC addresses are consistent
with the bound MAC address can communicate through the port. A port can be bound to a
maximum of three MAC addresses.
If MAC address binding is enabled, address learning is automatically disabled and
RSTP/STP is affected. It is recommended to disable STP on the port.
42
Page 43

DG-FS1526 User Manual
43
The configuration procedure:
Step 1 Enter the MAC address.
Step 2 Select the port that you want to bind MAC address.
Step 3 Select Enable from the drop-down list to enable the binding service.
Step 4 Click Update to apply the service of MAC address binding.
Page 44

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.8.2 TCP/UDP Filter
Choose Security > TCP/UDP Filter and the following page appears. TCP/UDP port filter
discards the set protocol packets at the secure WAN port. All ports can be set to secure
WAN ports, and the available protocols include FTP, HTTP, and TELNET.
44
Page 45

DG-FS1526 User Manual
The configuration procedure:
1. Select Enable from the drop-down list to enable the TCP/UDP filter service.
2. Select port filtering rule. Negative means the selected protocol will be dropped
and other protocols will be forwarded. Positive means the selected protocol will
be forwarded and other protocol will be dropped.
3. Select the protocol from the check box in the right area.
4. Select the secure WAN port.
5. Click Update to apply the settings.
7.9 Spanning Tree
Choose Spanning T r ee, and the sub-menus of Spanning Tree are shown as below.
45
Page 46

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.9.1 STP Bridge Settings
Choose Spanning T r ee > STP Bridge Settings, and the following page appears.
46
Page 47

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
STP Mode
You can select it from the drop-down list:
Bridge Priority
The valid range is 0 ~ 61440. The lower integer value for
precedence indicates the higher priority. And the integer should
be a multiple of 4096.
Hello Time
The valid range is 1 ~ 10. The unit is second. The hello time
indicates the interval of transmitting BPDU.
Max Age
The valid range is 6 ~ 40. The unit is second. It is the longest
waiting time of the blocking state turning into listening state.
Max Age >= 2*(Hello Time+1)
Forward Delay
The valid range is 4 ~ 30. The unit is second. It is the longest
waiting time of the listening state turning into learning state or
the learning state turning into forwarding state.
2*(Forward Delay-1) >= Max Age
After proper configuration, click Submit to apply the settings. In the mean time, you can
view the STP bridge status.
47
Page 48

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.9.2 STP Port Settings
Choose Spanning T r ee > STP Port Settings, and the following page appears.
48
Page 49

DG-FS1526 User Manual
49
Field Description
Port No. Select it from the drop-down list.
Priority The valid range is 0 ~ 240. It should be a multiple of 16.
RPC
Root Path Cost. The valid range is 1 ~ 200000000.
0 indicates Auto.
RPC determines the path cost that is from per port to root bridge. It is related with speed. The
following table lists the recommended value. You can modify it during actual using.
Speed IEEE Recommended Value Recommended Range
10Mbps 100 50~600
100Mbps 19 10~60
1000Mbps 4 3~10
10GMbps 2 1~5
After proper configuration, click Submit to apply the settings. In the mean time, you can
view the STP port status.
Page 50

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.9.3 Loopback Detection:
Choose Spanning Tree > Loopback Detection to configure loopback detection on an
interface. When loopback detection is enabled and a port receives it’s own BPDU, the
detection agent drops the loopback BPDU and places the interface in discarding mode. This
loopback state can be released automatically.
50
Page 51

DG-FS1526 User Manual
These parameters are displayed:
Field Description
Loopback Detection Function Enables/Disables (Default: disable)
Auto Wake Up Configures the interface for automatic loopback
release.
Wake-Up Time interval Defines the time interval for the port that will be
released from the discarding state.
Interface status displays a list of ports with loopback detection status. Select “Reset All Ports”
option for manual release.
7.10 Trunking
This section describes how to configure static and dynamic trunks.
You can create multiple links between devices that work as one virtual aggregate link. A port
trunk offers a dramatic increase in bandwidth for network segments where bottlenecks exist,
as well as providing a fault tolerant link between two devices.
The switch supports both static trunking and dynamic Link Aggregation Control Protocol
(LACP). Static trunks have to be manually configured at both ends of the link. On the other
hand, LACP configur ed ports can automatically negotiate a trunked link with LACPconfigured ports on another device.
Choose Trunking, and the Link Aggregation Settings sub-menu is shown as below.
51
Page 52

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Choose Trunking > Link Aggregation Settings, and the following page appears.
52
Page 53

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
System Priority The valid range is 1 ~ 65535.
Link Aggregation
Algorithm
You can select it from the drop-down list:
Member
The system supports three link groups.
Link Group 1: It includes the following ports: 1, 2, 3, 4.
Link Group 2: It includes the following ports: 5, 6, 7, 8.
Link Group 3: It includes the following ports: 25, 26.
State You can select Disable or Enable.
Type
You can select it from the drop-down list:
Operation Key
When the type is LACP, there are some protocol parameters. Such
as operation key, transmitting LACP packets interactively or not.
Time Out
You can select it from the drop-down list:
It is the time out of trunking, when the link port does not receive
the corresponding LACPDU.
Activity
You can select it from the drop-down list:
One switch should be set to Active between two switches.
53
Page 54

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Note: When you configure trunking service, you need to disable the Pause
and Backpressure of corresponding port in the Port Configuration page in the
Port management navigation.
After pr
oper configuration, click Submit to apply the settings. Click Refresh to refresh the
state of link group. When the “--” in Member configuration turns into “A”, that indicates the
trunking service has established between the system and the corresponding end.
7.11 DHCP Relay Agent
Choose DHCP Relay Agent and the submenu shown as below appears.
7.11.1 DHCP Relay Agent
54
Page 55

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Field Description
DHCP relay State
Select Enable or Disable to start or Stop the DHCP relay agent
respectively.
DHCP relay Hop
count limit
Sets the maximum allowed number in the hops field of the
BOOTP/DHCP header.
DHCP relay option
82 State
Select Enable or Disable to start or Stop the DHCP relay option 82
respectively.
7.11.2 Relay Server
Choose Relay Server and the following page appears.
7.11.3 VLAN MAP Relay Agent
Choose VLAN MAP Relay Agent
After proper configuration, click Submit to apply the settings. Click Refresh to
refresh the state of link group.
55
Page 56

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.12 Configuration Backup and Recovery
Choose Backup/Recovery, and the following page appears. In this page, you can download
the switch configuration to PC, or upload the configuration file to switch according to the
page attention.
56
Page 57

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.13 Miscellaneous Configuration
Choose Miscellaneous, and the following page appears. In this page, you can enable
Aging, VLAN striding and set VLAN uplink.
57
Page 58

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.14 SNMP Settings
Choose SNMP Settings, and the following page appears. In this page, you can configure
SNMP related parameters.
Field Description
Community Name. The community name used by SNMP.
Access Right The right of community name.
System Description
System Contact
System Location
System related information.
Trap State Enable/disable SNMP trap.
58
Page 59

DG-FS1526 User Manual
7.15 Logout
Choose Logout, and the following page appears.
In this page, the system asks you whether to logout. Click Accept to logout. Click Back to
return to the previous page.
59
Page 60

DG-FS1526 User Manual
60
8 Troubleshooting
If a fault occurs, refer to the following table for troubleshooting:
Symptom Suggested Solution
The Power indicator is not
ON after the system is
started
Check whether the power is correctly connected.
Check whether the power switch is turned on.
The Power indicator is
ON but the Ethernet
indicator is off
Check whether the network cable is correctly
connected.
Check whether the configuration is correct.
Page 61

DG-FS1526 User Manual
61
9 Glossary
Auto-negotiation: Auto-negotiation is an Ethernet procedure by which two connected devices choose common
transmission parameters, such as speed, duplex mode, and flow control. In this process, the con nected devices first share
their capabilities as for these parameters and then choose the highest performance transmission mode they both support.
Backpressure: The build-up of data behind an I/O switch if the buffers are full and incapable of receiving any more
data; the transmitting device halts the sending of data packets until the buffers have been emptied and are once more capable
of storing information.
Flow-control: Flow control is the process of mana ging the pacing of data transmission between two nodes to p revent a
fast sender from outrunning a slow receiver. It provides a mechanism for the receiver to control the transmission speed, so
that the receiving node is not overwhelmed with data from transmitting node.
Address Learning: Address learning is a service that characterizes a learning bridge, in which the source MAC
address of each received packet is stored so that future packets desti ned for that address can be for warded only to the bridge
interface on which that address is located.
TCP: The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of
the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol (IP), and therefore the entire suite is
commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliable, ordered delivery of a stream of bytes from a program on one
computer to another program on another computer.
UDP: User Datagram Protocol. UDP provides a datagram mode for packet-switched communications. It uses IP as the
underlying transport mechanism to provide access to IP-like services. UDP packets are delivered just like IP packets –
connection-less datagrams that may be discarded before reaching their targets. UDP is useful when TCP would be too
complex, too slow, or just unnecessary.
FTP: File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to copy a file from one host to another over a TCP-
based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data
connections between the client and server.
Http:
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia
information systems.
TELNET: Telnet defines a remote communication facility for interfacing to a terminal device over TCP/IP.
ToS: Type of Service level, which processes the precedence part of the IP packet ToS (3 bi ts) as a n i ndex to the eight QoS
Class values.
Page 62

DG-FS1526 User Manual
Link-Aggregation: Link aggregation is a term which describes using multiple network cables/ports in parallel to
increase the link speed beyond the limits of any one single cable or port, and to increase the
redundancy for higher
availability.
COS: Class of Service is supported by prioritizing packets based on the required level of service, and then placing them in
the appropriate output queue. Data is transmitted from the queues using weighted round-robin service to enforce priority
service and prevent blockage of lower-level queues. Priority may be set according to the port default, the packet’s priority bit
(in the VLAN tag), TCP/UDP port number, IP Precedence bit, or DSCP priority bit.
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol. The application protocol in the Internet suite of protocols which offers
network management services.
QOS: Quality of Service. QoS refers to the capability of a network to provide better service to selected traffic flows using
features such as data prioritization, queuing, congestion avoidance and traffic shaping. These features effectively provide
preferential treatment to specific flows either by raising the priority of one flow or limiting the priority of another flow.
DHCP:
Dynamic Host Control Protocol. Provides a framework for passing configuration information to hosts on a
TCP/IP network. DHCP is based on the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP), adding the capability of automatic
allocation of reusable network addresses and additional configuration options.
DHCP OPTION 82: A relay option for sending information about the requesting client (or an intermediate relay
agent) in the DHCP request packets forwarded by the switch and in reply packets sent back from the DHCP server. This
information can be used by DHCP servers to assign fixed IP addresses, or set other services or policies for clients.
This product comes with Life time warranty. For further
details about warranty policy and Product Registration,
please visit support section of www.digisol.com
62
 Loading...
Loading...