Page 1

DG-BG4100N
150Mbps Wireless ADSL2/2+ Broadband Router
User Manual
V1.0
2012-11-06
As our products undergo continuous development the specifications are subject to change without prior notice
Page 2

DG-BG4100N User Manual
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2012 by this company. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or computer language, in
any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without
the prior written permission of this company.
This company makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to the contents
hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Any
software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the programs prove defective following their
purchase, the buyer (and not this company, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all necessary
servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential damages resulting from any defect in the software.
Further, this company reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the
contents thereof without obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Trademarks:
DIGISOL™ is a trademark of Smartlink Network Systems Ltd. All other trademarks are the property of the
respective manufacturers.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However, special
attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with electrical
equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacturer must therefore be allowed at all times to
ensure the safe use of the equipment.
2
Page 3

DG-BG4100N User Manual
INDEX
Product Information......................................................................................... 5
1
1.1 Safety Precautions ................................................................................ 6
1.2 System Requirements ...........................................................................7
1.3 Package contents .................................................................................. 7
1.4 LEDs and Interfaces .............................................................................. 8
2 Hardware Installation..................................................................................... 11
2.1 Software Installation ............................................................................13
3 About the Web Configuration ....................................................................... 22
3.1 Access the Router ...............................................................................22
3.2 Wizard ................................................................................................. 24
3.3 Status................................................................................................... 36
3.3.1 Device Info................................................................................ 36
3.3.2 LAN........................................................................................... 37
3.3.3 WLAN .......................................................................................38
3.3.4 WAN .........................................................................................39
3.3.5 Port Mapping ............................................................................39
3.3.6 Statistics....................................................................................40
3.3.7 ARP Table................................................................................. 42
3.4 Network ............................................................................................... 42
3.4.1 LAN........................................................................................... 42
3.4.2 WAN .........................................................................................53
3.4.3 WLAN .......................................................................................61
3.5 Service................................................................................................. 74
3.5.1 DNS .......................................................................................... 74
3.5.2 Firewall .....................................................................................78
3.5.3 UPNP........................................................................................ 85
3.5.4 IGMP Proxy ..............................................................................85
3.5.5 TR-069...................................................................................... 87
3.5.6 ACL........................................................................................... 89
3.6 Advanced............................................................................................. 92
3.6.1 Routing .....................................................................................92
3.6.2 NAT........................................................................................... 97
3
Page 4

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.6.3 Port Mapping ..........................................................................104
3.6.4 IP QoS .................................................................................... 105
3.6.5 SNMP .....................................................................................108
3.6.6 Others ..................................................................................... 109
3.7 Admin ................................................................................................ 113
3.7.1 Commit/Reboot....................................................................... 113
3.7.2 Update .................................................................................... 114
3.7.3 Log.......................................................................................... 116
3.7.4 Password ................................................................................ 117
3.7.5 Time........................................................................................ 118
3.8 Diagnostic.......................................................................................... 119
3.8.1 Ping......................................................................................... 119
3.8.2 Traceroute ..............................................................................121
3.8.3 OAM Loopback ....................................................................... 122
3.8.4 ADSL Statistics .......................................................................123
3.8.5 Diag-Test................................................................................. 124
4 Appendix………………………………………………………………………...125
4.1 Technical Specifications ....................................................................125
4.2 Troubleshooting................................................................................. 128
4.3 Glossary ............................................................................................ 130
4
Page 5

DG-BG4100N User Manual
1 Product Information
The ADSL access device supports multiple line modes. It provides four 10/100Base-T
Ethernet interfaces at the user end. Utilizing the high-speed ADSL connection, the device
provides users with broadband connectivity to the Internet or the Intranet for high-end users
like net bars and office users. It provides a downlink speed up to 24 Mbit/s and an uplink
speed up to 1 Mbit/s.
The device supports WLAN access, as WLAN AP or WLAN router, to internet. It is compliant
with IEEE 802.11,802.11b/g/n specifications and complies with WEP, WPA and WPA2
security specifications.
Other features of this wireless broadband router include:
Supports various line modes.
Supports external PPPoE dial-up access.
Supports internal PPPoE/PPPoA dial-up access.
Supports leased line mode.
Supports 1483B/1483R/MER access.
Supports multiple PVCs (eight at most) and these PVCs can be isolated from each
other.
Supports single PVC with multiple sessions.
Supports multiple PVCs with multiple sessions.
Supports the binding of the ports and the PVCs.
Supports the 802.1Q and 802.1P protocol.
Supports DHCP server.
Supports NAT / NAPT.
Supports static route.
Supports firmware upgrade: WEB/tftp/ftp.
Supports reset to factory default: reset, WEB.
Supports DNS relay.
Supports Virtual server.
Supports DMZ functions.
Supports two-level passwords and usernames.
5
Page 6

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Supports WEB interface.
Supports telnet CLI.
Supports System status display.
Supports PPP session PAP / CHAP.
Supports IP filter function.
Supports IP QoS function.
Supports remote access control.
Supports line connection status test.
Supports remote management (Telnet; HTTP).
Supports configuration file backup and restoration function.
Ethernet supported such as Crossover Detection, Auto-Correction and polarity
correction.
1.1 Safety Precautions
In order to keep the safety of users and your properties, please follow the safety instructions
as mentioned below:
Use the type of power marked in the volume label.
Use the power adapter packed within the device package.
Pay attention to the power load of the outlet or prolonged lines. An overburden power
outlet or damaged lines and plugs may cause electric shock or fire accident. Check the
power cords regularly. If you find any damage, replace it at once.
Proper space left for heat radiation is necessary to avoid any damage caused by
overheating the device. The long and thin holes on the Access Point are designed for
heat radiation to make sure the device works normally. DO NOT cover these heat
radiant holes.
DO NOT put this device close to a place where a heat source exists or high
temperature occurs. Avoid exposing the device to direct sunlight.
DO NOT put this device close to a place which is over damp. DO NOT spill any fluid on
this device.
DO NOT connect this device to any PC or electronic product, unless our customer
engineer or your broadband provider instructs you to do this, because any wrong
connection may cause any power or fire risk.
6
Page 7

DG-BG4100N User Manual
DO NOT place this device on an unstable surface.
1.2 System Requirements
The following system requirements are recommended:
A 10BaseT/100BaseT Ethernet card installed on your PC.
A hub or switch is available for connecting one Ethernet interface on the device and
several PCs.
Operating system: Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 98SE, Windows 2000,
Windows ME or Windows XP.
Internet Explorer V7.0 or higher, or Netscape V4.0 or higher, or firefox 1.5 or higher.
1.3 Package contents
Before you start using this router, please check if there’s anything missing in the package,
and contact your dealer of purchase to claim for missing items:
DG-BG4100N 150MBPS WIRELESS ADSL2+ BROADBAND ROUTER
Switching Power Adapter
POTS Splitter
Two RJ-11 cables
One RJ-45 patch cord
Quick Installation Guide
Installation Guide CD
7
Page 8
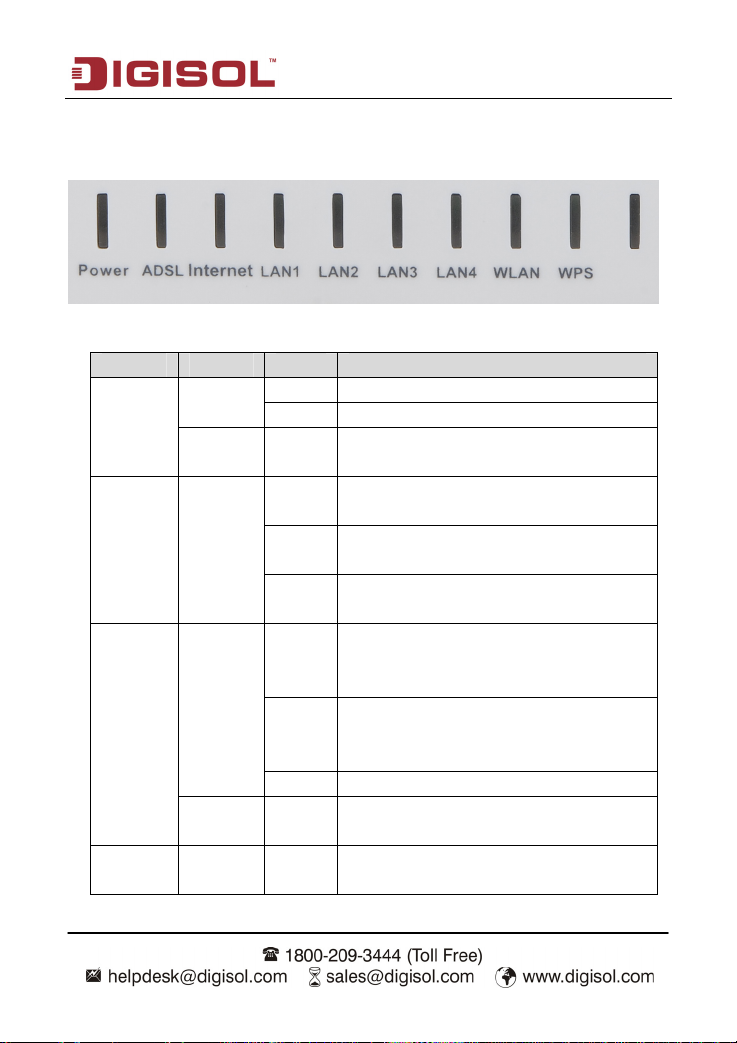
DG-BG4100N User Manual
1.4 LEDs and Interfaces
Top P a n el
The following table describes the LEDs of the device.
LEDs Color Status Description
Green
Power
Amber On
ADSL Green
On The initialization of the Router is successful.
Off The Router is powered off.
The Router is booting, or software upgrade is
under progress.
On
Slow
Blink
Fast
Blink
ADSL Signal between the Router and
Exchange is established.
No signal from Exchange is being detected.
The Router is syncronising with the
Exchange.
Internet
LAN
1/2/3/4
Blink
Green
On
Off The Router is in bridged mode.
Red On
Green
On
Internet data is being transmitted or received
(Routing mode)
Internet Connection is established (Routing
Mode)
The Internet connection failed/password
error.
The LAN connection is established and
activated.
8
Page 9
DG-BG4100N User Manual
Blink LAN data is being transmitted.
Off The LAN interface/cable is disconnected.
On Wireless connection has been activated.
WLAN Green
WPS Green
Blink Wireless data is being transmitted.
Off The Wireless connection is not activated.
Blink WPS process on the Router is initiated.
Off
WPS is disabled OR WPS process not
initiated.
9
Page 10

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Rear Panel
The following table describes the interfaces of the device.
Item
WLAN / WPS
ADSL
LAN4/3/2/1
Power
ON / OFF
Reset
Press the button and hold it for 1 second to enable WLAN.
Press the button and hold it for at least 3 seconds, to initialize WPS
negotiation.
RJ-11 interface, for connecting to the ADSL interface or a splitter
through a telephone cable.
RJ-45 interface, for connecting to the Ethernet interface of a computer
or the Ethernet devices through an Ethernet cable.
Power interface, for connecting to the power adapter.
Power switch, power on or power off the device.
Reset to the factory default configuration. Keep the device powered
on, and insert a pin into the reset hole for 3 seconds, then release it.
The device is reset to the factory default configuration.
Description
10
Page 11

DG-BG4100N User Manual
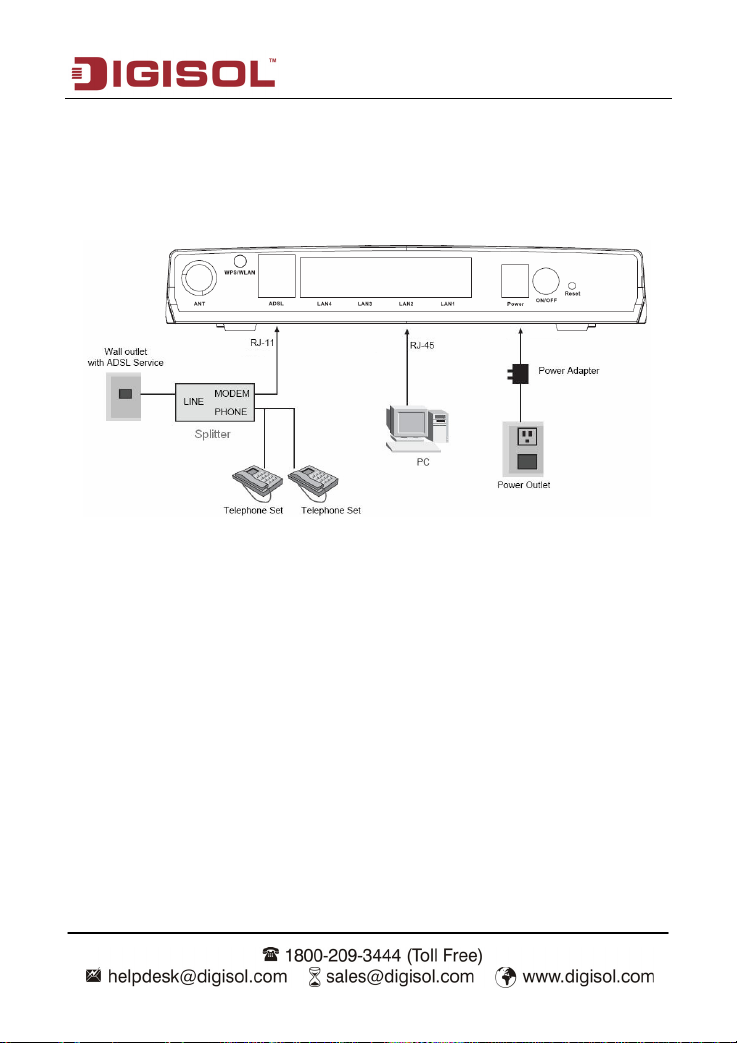
2 Hardware Installation
Step 1 Connect the ADSL interface of the device and the router interface of the splitter
through a telephone cable. Connect the phone to the Phone interface of the
splitter through a telephone cable. Connect the incoming line to the Line interface
of the splitter.
The splitter has three interfaces:
Line: Connect to a wall phone jack (RJ-11 jack).
Router: Connect to the ADSL jack of the device.
Phone: Connect to a telephone set.
Step 2 Connect the LAN interface of the device to the network card of the PC through an
Ethernet cable (MDI/MDIX).
Note:
Use twisted-pair cables to connect to the hub or switch.
11
Page 12
DG-BG4100N User Manual
Step 3 Plug one end of the power adapter to the wall outlet and connect the other end to
the Power interface of the device.
The following figure shows the application diagram for the connection of the router, PC,
splitter and the telephone sets.
12
Page 13

DG-BG4100N User Manual
2.1 Software Installation
Insert the Setup CD into your CD-ROM drive of notebook/desktop computer.
Explore the CD and execute the “India_autorun.exe” file. Screen given below will be
displayed. Click ‘Start’ to continue.
13
Page 14
DG-BG4100N User Manual
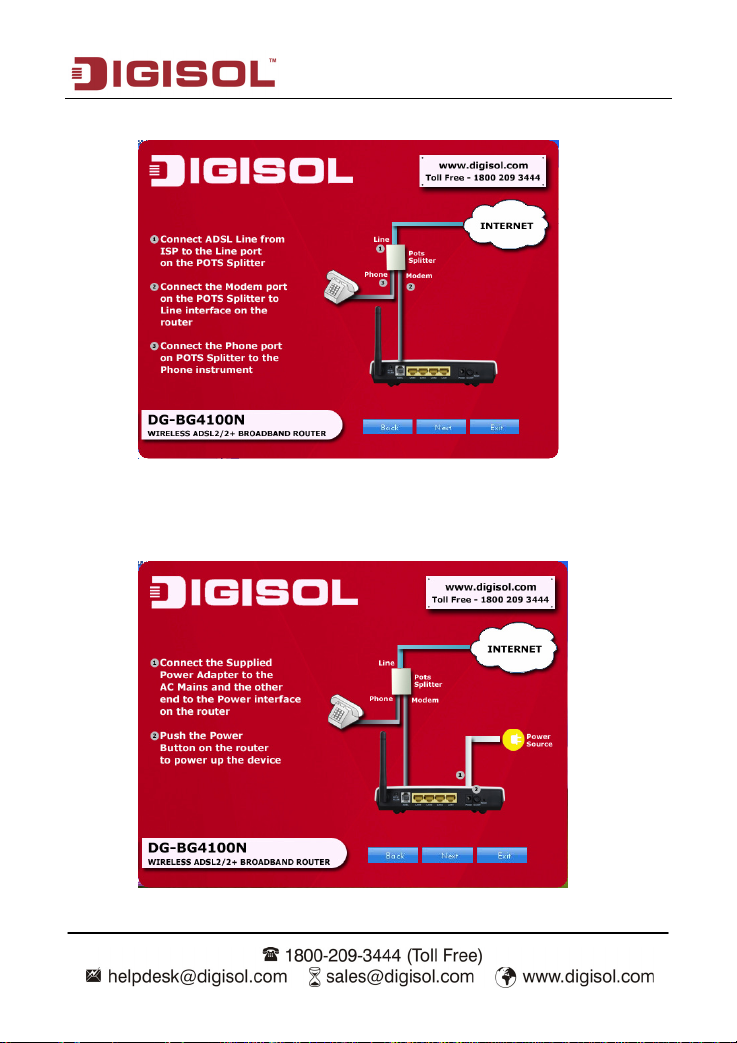
Connect the ADSL line and the phone line to the router. Click ‘Next’.
Connect the power adapter to the AC Mains and the other end to the power interface
on the router. Push the power button on the router to power up the device. Click
‘Next’.
14
Page 15
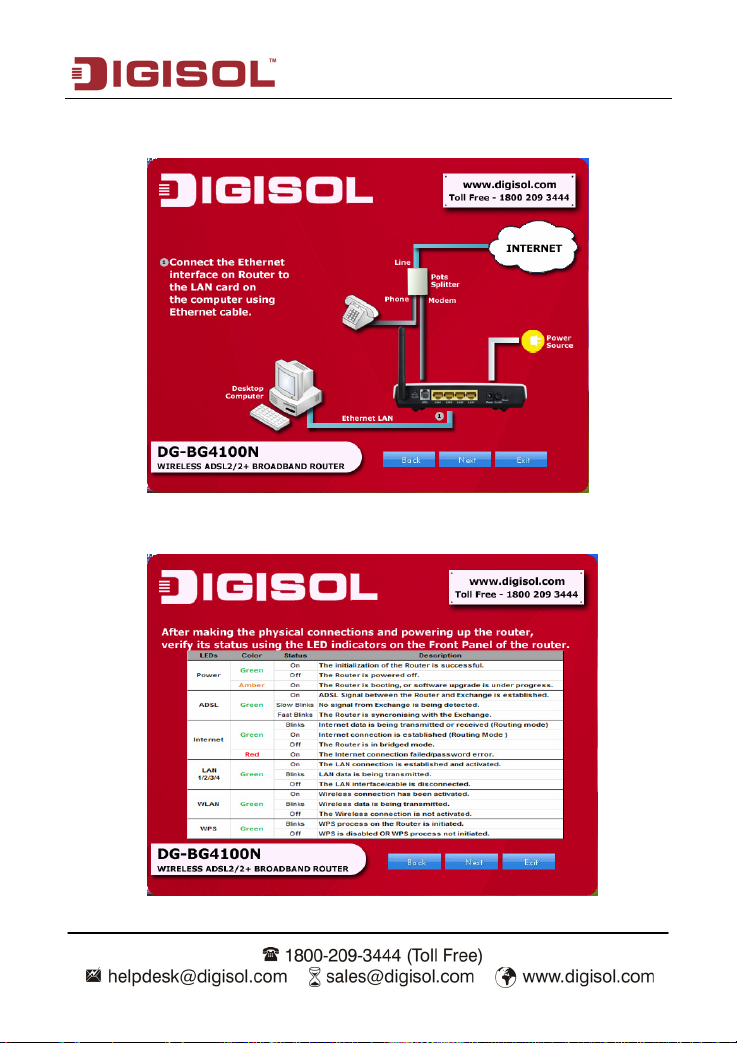
DG-BG4100N User Manual
Connect the Ethernet interface on the router to the LAN card on the computer using
the Ethernet cable. Click ‘Next’.
After powering up the router, verify the status of the LED indicators on the front panel of
the router. Click ‘Next’.
15
Page 16
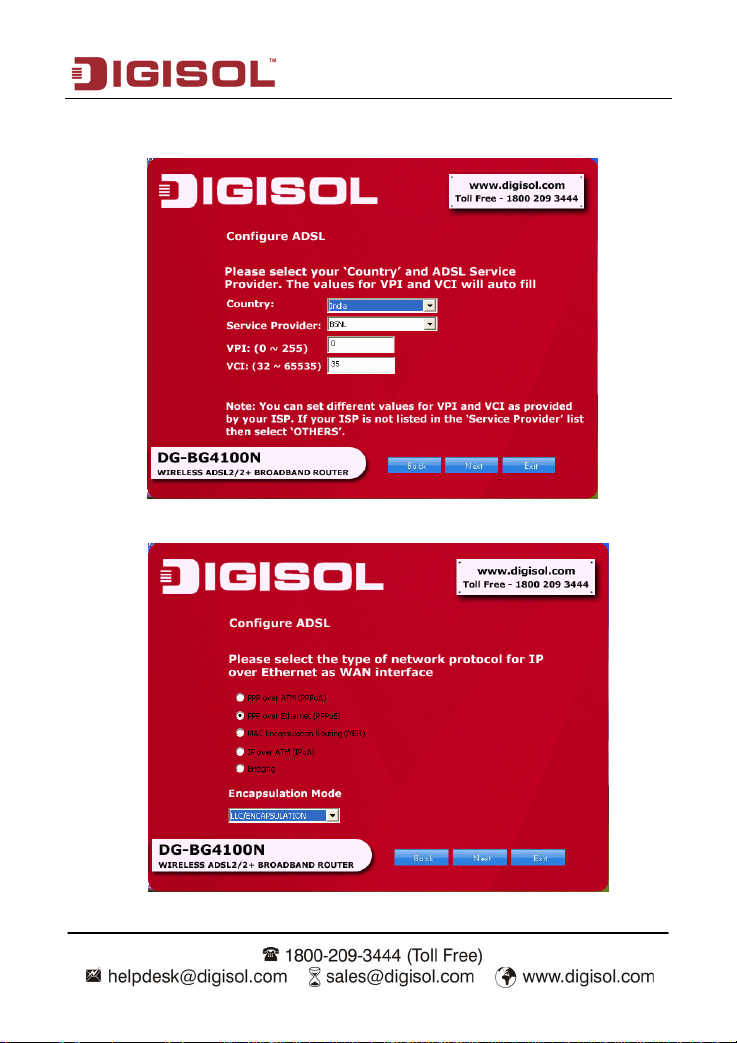
DG-BG4100N User Manual
Please select your ‘Country’ and ADSL service provider. VPI and VCI values will auto
fill.
Select the network protocol for WAN interface. Click ‘Next’.
16
Page 17
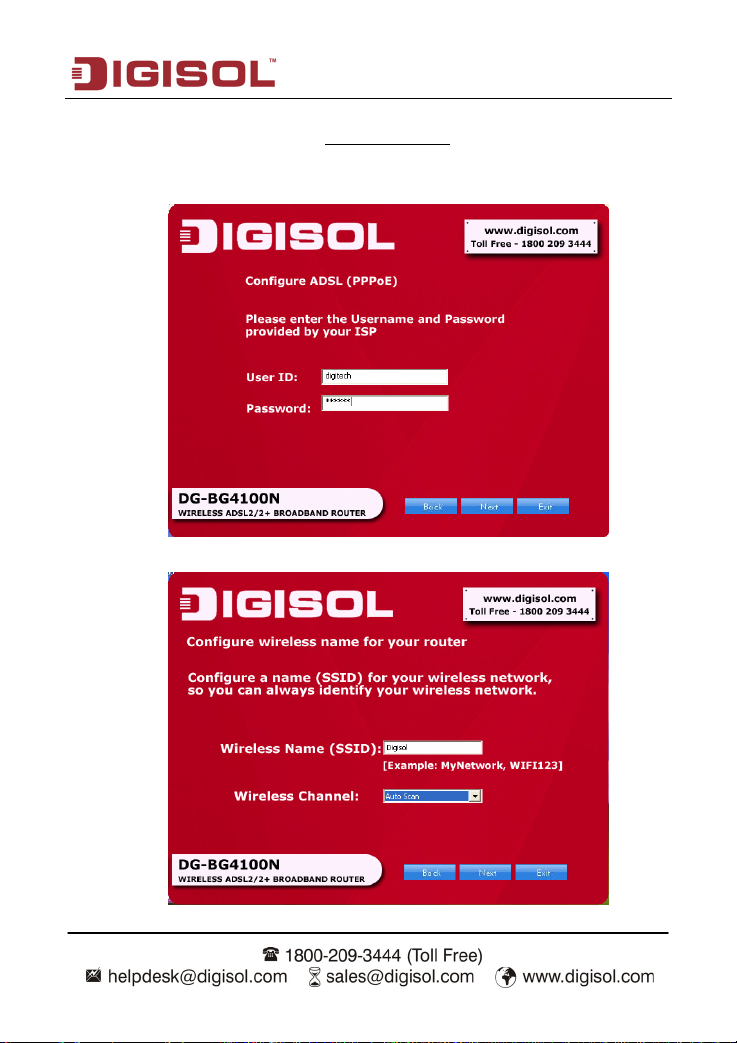
DG-BG4100N User Manual
All the utility installation steps till here are the common steps to be followed for the modes.
Following are the steps for configuring PPPoE connection
Enter the username and password provided by your ISP. Click ‘Next’.
Configure a wireless name (SSID) for your router. Click ‘Next’.
:
17
Page 18
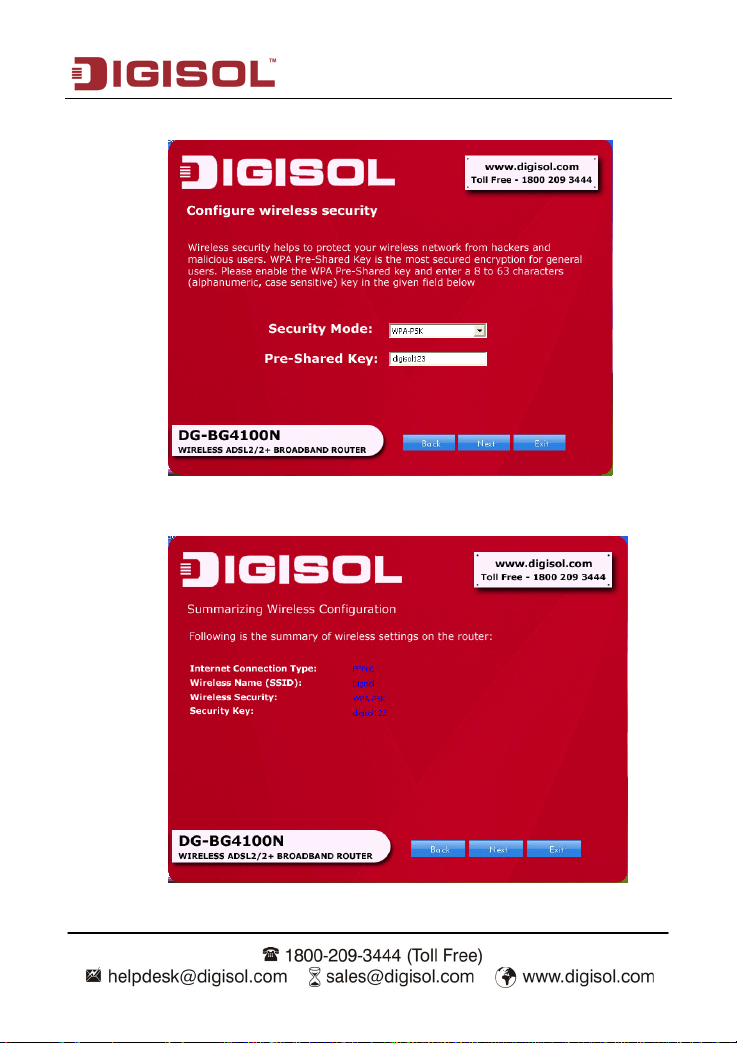
DG-BG4100N User Manual
Configure the wireless security. Click ‘Next’.
The next screen is a summary of the wireless settings of the router.
18
Page 19

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click on ‘Next’, the following screen will appear.
Once the connection is established, the router connection status will appear.
19
Page 20

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Bridging Mode:
To configure the router in bridge mode select “Bridging” option. Click ‘Next’.
Configure a wireless name (SSID) for your router. Click ‘Next’.
20
Page 21

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Configure the wireless security.
Click on ‘Next’ the following screen will appear.
21
Page 22
DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click on ‘Finish’ to complete the configuration of the router in Bridge mode.
3 About the Web Configuration
This section describes how to configure the router by using the Web-based configuration
utility.
3.1 Access the Router
The following is the detailed description of accessing the router for the first time.
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer (IE) browser and enter http://192.168.1.1.
Step 2
In the Login page that is displayed, enter the username and password.
The username and password of the super user are admin and admin.
The username and password of the common user are user and user.
22
Page 23
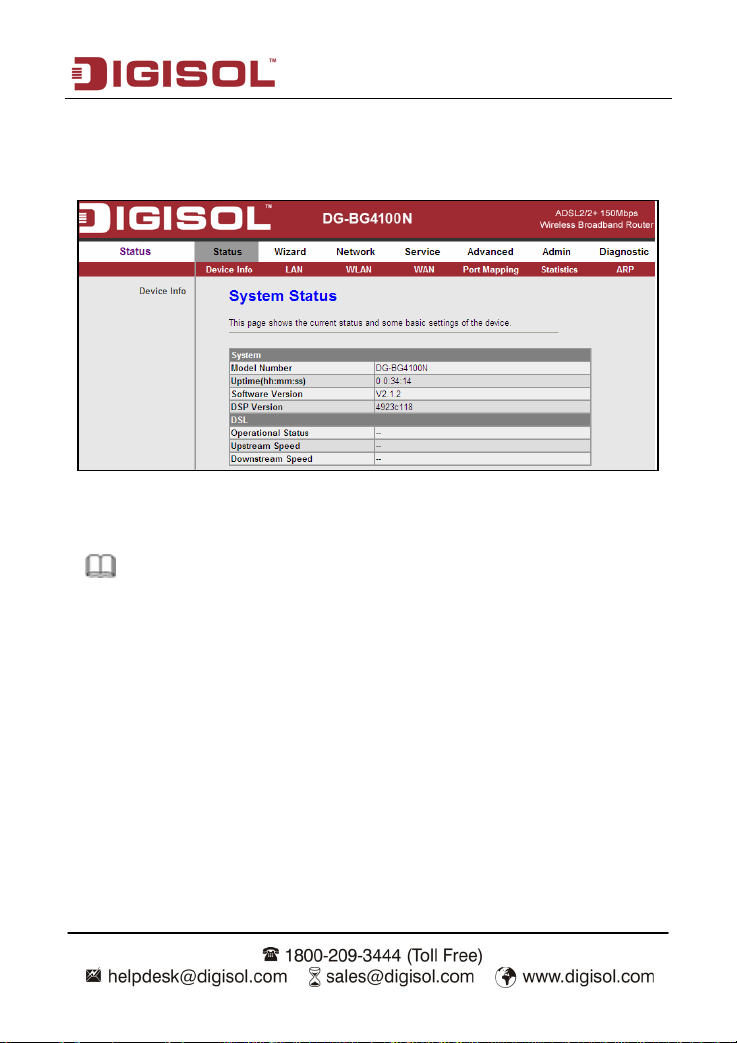
DG-BG4100N User Manual
If you log in as a super user, the page shown in the following figure appears. You can check,
configure and modify all the settings.
If you log in as a common user, you can check the status of the router, but can not configure
most of the settings.
Note:
In the Web configuration page, you can click Apply Changes to save the settings temporarily.
If you want to save the settings of this page permanently, click save of Attention that appears
at the bottom of the Web page after the configuration.
23
Page 24
DG-BG4100N User Manual
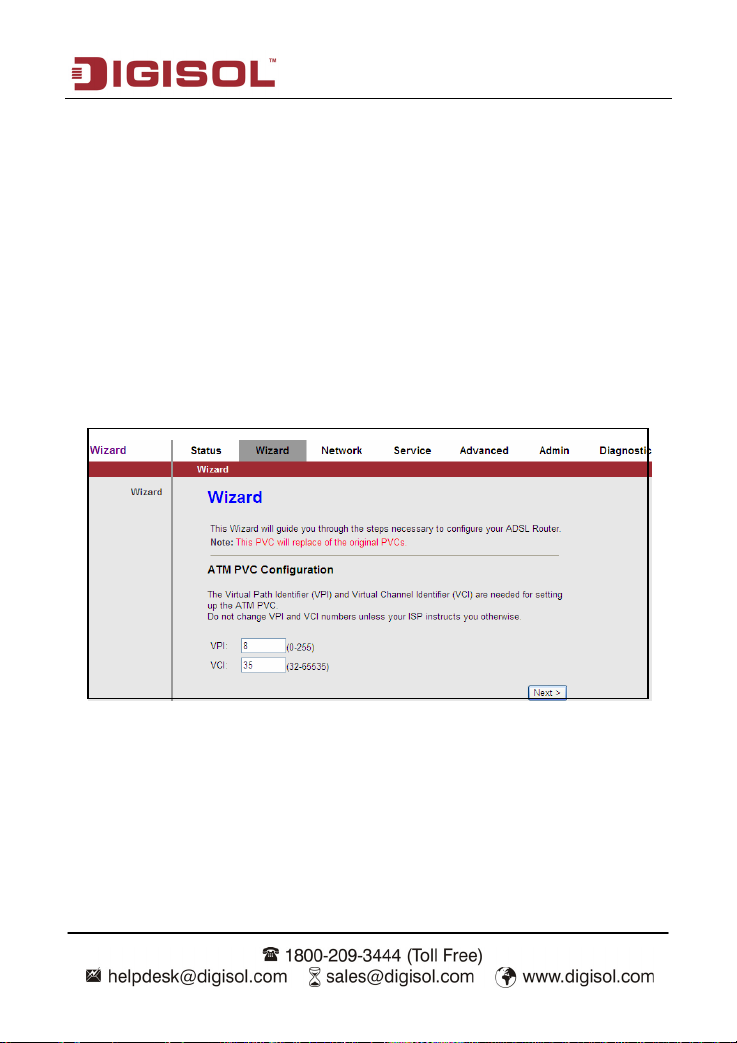
3.2 Wizard
When subscribing to a broadband service, you should be aware of the method by which you
are connected to the Internet. Your physical WAN device can be either PPP, ADSL or both.
The technical information about the properties of your Internet connection is provided by your
Internet Service Provider (ISP). For example, your ISP should inform you whether you are
connected to the Internet using a static or dynamic IP address, and the protocol that you use
to communicate on the Internet.
In the navigation bar, choose Wizard. The page shown in the following figure appears. The
Wizard page guides fast and accurate configuration of the Internet connection and other
important parameters. The following sections describe these various configuration
parameters. Whether you configure these parameters or use the default ones, click NEXT to
enable your Internet connection.
24
Page 25
DG-BG4100N User Manual
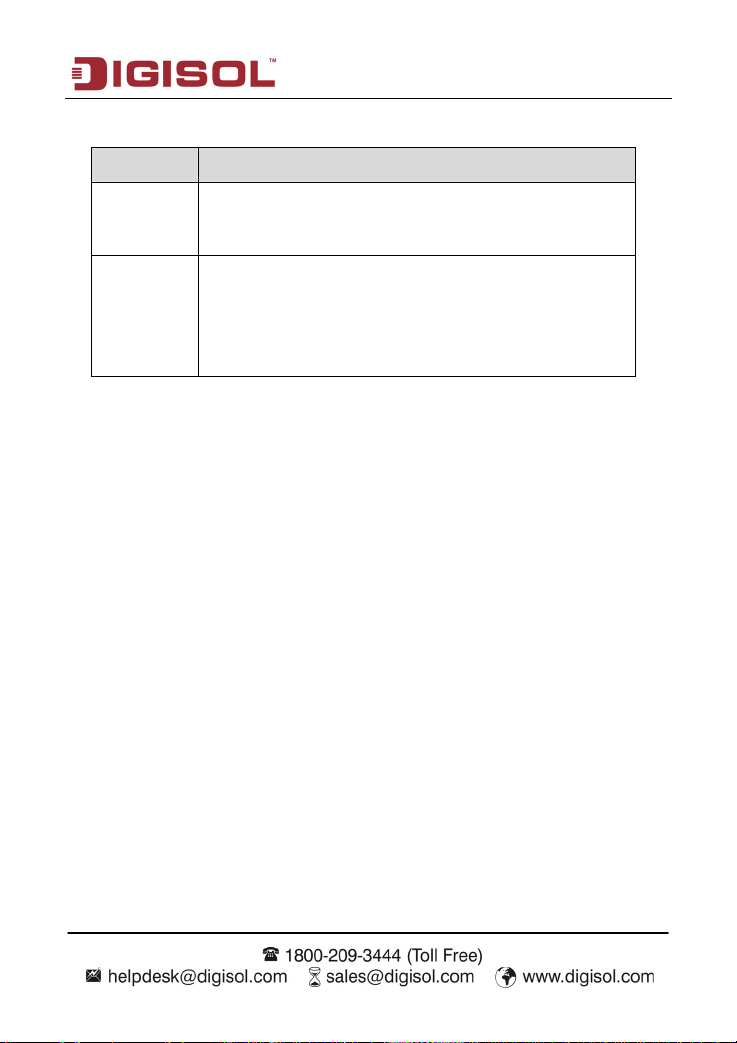
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
Virtual path identifier (VPI) is the virtual path between two points in
VPI
VCI
an ATM network. Its valid value is in the range of 0 to 255. Enter the
correct VPI provided by your ISP. By default, VPI is set to 0.
Virtual channel identifier (VCI) is the virtual channel between two
points in an ATM network. Its valid value is in the range of 32 to
65535. (0 to 31 is reserved for local management of ATM traffic)
Enter the correct VCI provided by your ISP. By default, VCI is set to
35.
After setting, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
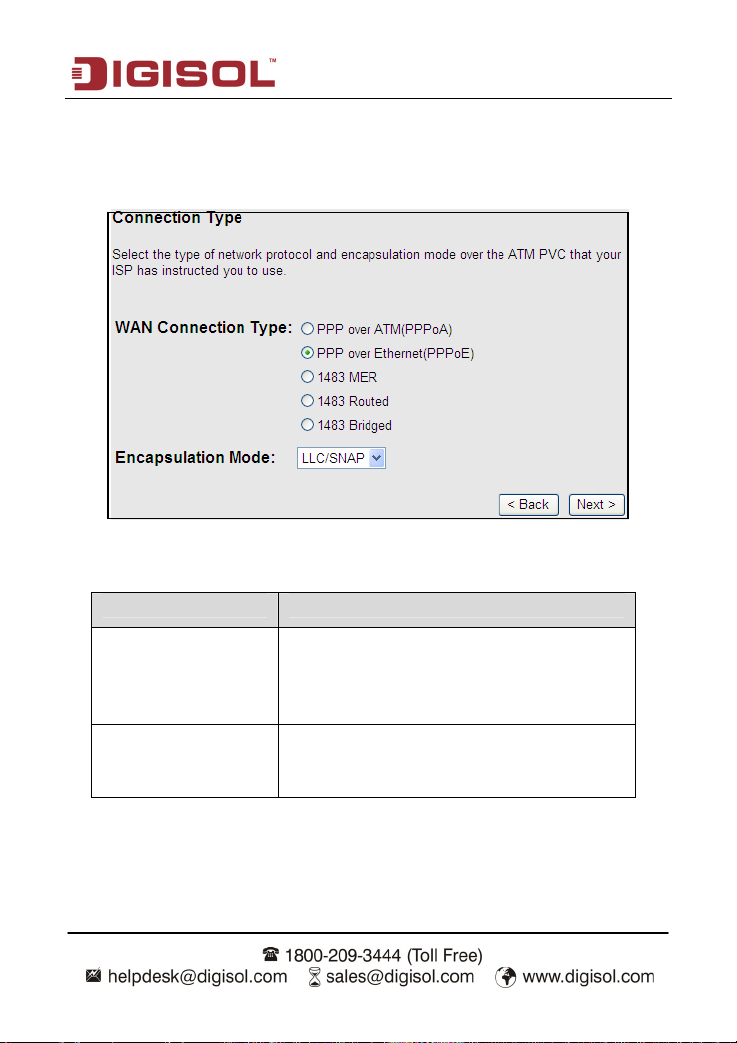
There are five WAN connection types: PPP over ATM (PPPoA), PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE),
1483 MER, 1483 Routed and 1483 Bridged. The following below describes them
respectively.
25
Page 26
DG-BG4100N User Manual
PPPoE/PPPoA
In the Connection Type page, set the WAN connection type to PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE),
the encapsulation mode to LLC/SNAP.
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
There are five WAN connection types: PPP over
WAN Connection Type
Encapsulation Mode
ATM (PPPoA), PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE), 1483
MER, 1483 Routed and 1483 Bridged. In this
example, the connection type is set to PPPoE.
You can select LLC/SNAP or VC-Mux. In this
example, the encapsulation mode is set to
LLC/SNAP.
26
Page 27
DG-BG4100N User Manual
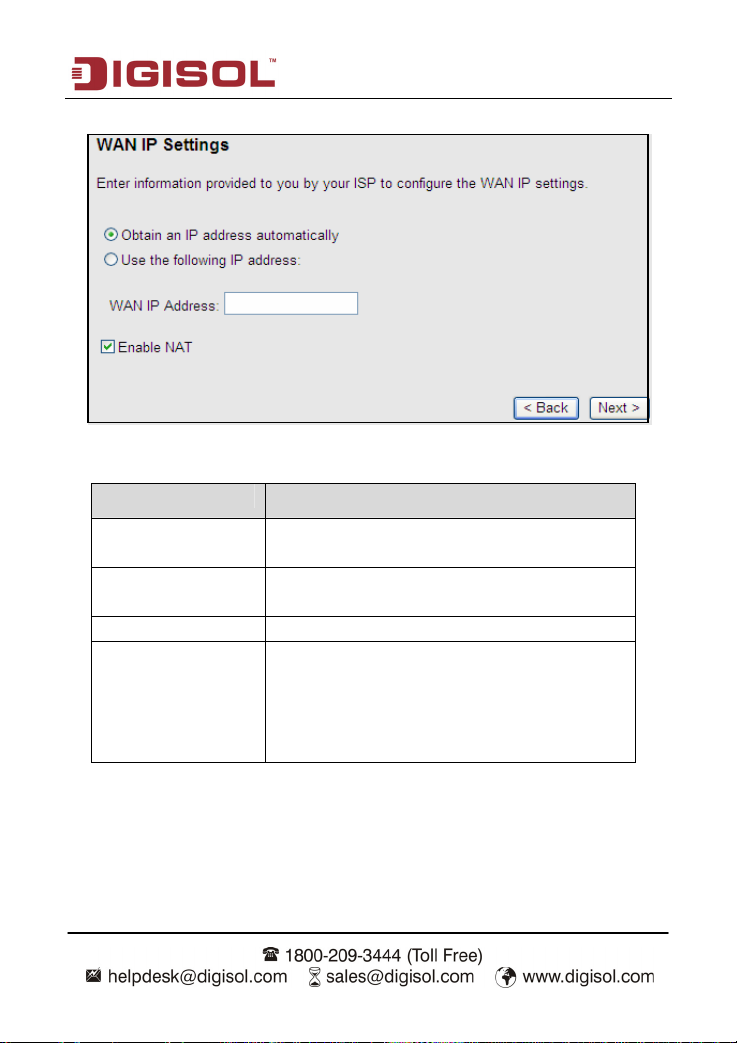
After the settings are done, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
Obtain an IP address
automatically
Use the following IP
address
WAN IP Address Enter the WAN IP address here.
Enable NAT
Select it, the DHCP assigns the IP address for PPPoE
connection.
Select it, you need to enter the IP address for PPPoE
connection, which is provided by your ISP.
Select the checkbox to enable network address
translation (NAT). If you do not select it and you want
to access the Internet normally, you must add a route
on the uplink equipment. Otherwise, the access to the
Internet fails. Normally, it is required to enable NAT.
27
Page 28
DG-BG4100N User Manual
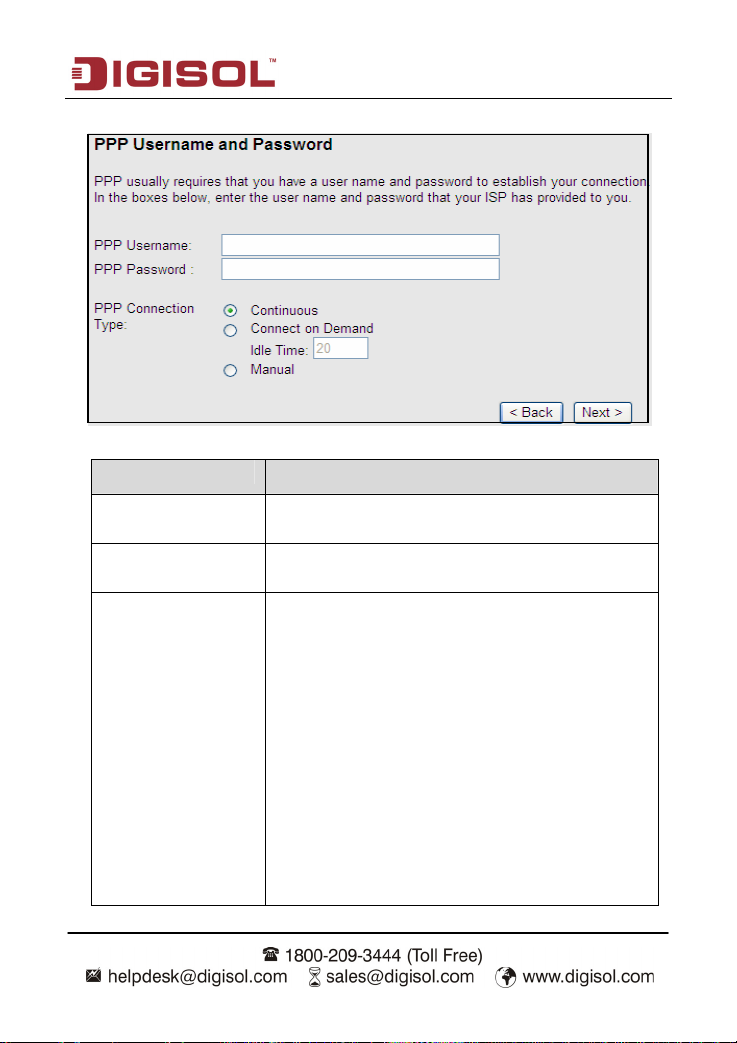
After the settings are done, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
PPP Username
PPP Password
PPP Connection Type
Enter the username for PPPoE dial-up, which is provided by
your ISP.
Enter the password for PPPoE dial-up, which is provided by
your ISP.
You can select Continuous, Connect on Demand, or
Manual.
Continuous: After dial-up is successful, PPPoE
connection is always on-line, no matter whether the
data is being transmitted or not. It is recommended
to select it.
Connect on Demand: After dial-up is successful,
within the preset idle time, no data is being
transmitted; the router automatically disconnects
the PPPoE connection.
In this case, you need to enter the idle time.
Manual: Select it, you need to dial up and
disconnect the connection mannually.
28
Page 29
DG-BG4100N User Manual
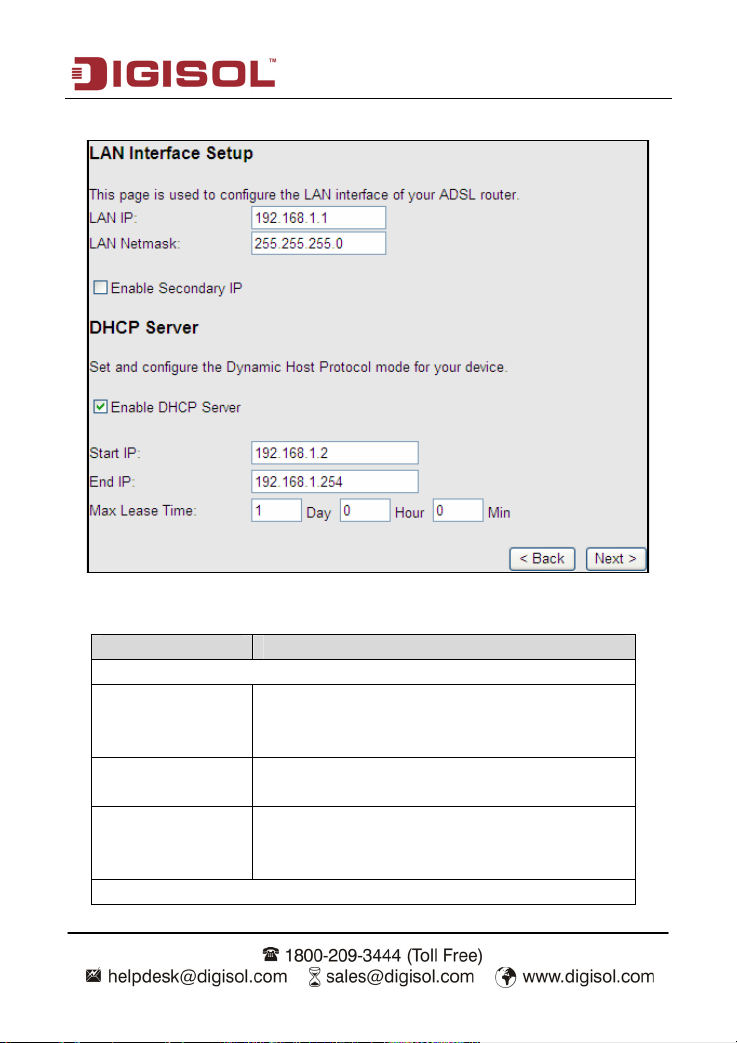
After the settings are done, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
owing table describes the parameters in this page:
The foll
Field Description
LAN Interface Setup
Enter the IP address of LAN interface. Its valid value is
LAN IP
LAN Netmask
Enable Secondary IP
DHCP Server
in the range of 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254. The
default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Enter the subnet mask of LAN interface. Its valid value
is in the range of 255.255.255.0 to 255.255.255.254.
Select the checkbox to enable the secondary LAN IP.
The two LAN IP addresses must be in different
networks.
29
Page 30

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Enable DHCP Server Select the checkbox to enable DHCP server.
Start IP Enter the start IP address that the DHCP sever assigns.
End IP Enter the end IP address that the DHCP server assigns.
The lease time determines the period that the PCs
Max Lease Time
After the settings are done, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
retain the assigned IP addresses before the IP
addresses change.
30
Page 31

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click BACK to modify the settings.
Click FINISH to save the settings.
Click RESET to cancel the settings.
Note:
If the WAN connection type is set to PPPoA, the parameters of the WAN
connection type are the same as that of PPPoE.
1483 MER / 1483 Routed
In the Connection Type page, set the WAN connection type to 1483 MER, the encapsulation
mode to LLC/SNAP.
After the settings are done, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
31
Page 32

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
Obtain an IP address
automatically
Use the following IP address
Obtain DNS server
addresses automatically
Use the following DNS server
addresses
Enable NAT
Select it, DHCP automatically assigns the IP
address for WAN connection.
Select it, you need to manually enter the IP
address, subnet mask and default gateway for
WAN connection, which are provided by your ISP.
Select it, DHCP automatically assigns DNS server
address.
Select it, you need to manually enter the primary
DNS server address and secondary DNS server
address.
Select it to enable network address translation
(NAT). If you do not select it and you want to
access the Internet normally, you must add a route
32
Page 33

DG-BG4100N User Manual
on the uplink equipment. Otherwise, the access to
the Internet fails. Normally, it is required to enable
NAT.
For subsequent configuration, refer to the description in the above section PPPoE/PPPoA.
Note:
If the WAN connection type is set to 1483 Routed, the parameters of the WAN connection
type
are the same as that of 1483 MER. For the parameters in these pages, refer to the
parameter
description of 1483 MER.
1483 Bridged
In the Connection Type page, set the WAN connection type to 1483 Bridged, the
encapsulation mode to LLC/SNAP.
33
Page 34

DG-BG4100N User Manual
After the settings are done, click Next, the page as shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters in this page:
Field Description
LAN Interface Setup
Enter the IP address of LAN interface. Its valid value is in
LAN IP
LAN Netmask
Enable Secondary IP
the range of 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.255.254. The default
IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Enter the subnet mask of LAN interface. Its valid value is
in the range of 255.255.0.0 to 255.255.255.254.
Select the checkbox to enable the secondary LAN IP. The
two LAN IP addresses must be in the different network.
34
Page 35

DG-BG4100N User Manual
DHCP Server
Enable DHCP Server Select the checkbox to enable DHCP server.
Start IP Enter the start IP address that the DHCP sever assigns.
End IP Enter the end IP address that the DHCP server assigns.
The lease time determines the period that the PCs retain
Max Lease Time
For subsequent configuration, refer to the description in the above section PPPoE/PPPoA.
Note:
You may configure at most eight ATM VCs. To add an ATM VC, refer
section 3.4.2.1WAN
the assigned IP addresses before the IP addresses
change.
35
Page 36

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3 Status
In the navigation bar, choose Status. The Status page that is displayed contains: Device Info,
LAN, WLAN, WAN, Port Mapping, Statistics and ARP.
3.3.1 Device Info
Choose Status > Device Info. The page that is displayed shows the current status and some
basic settings of the router, such as software version, DSP version, uptime, upstream speed,
and downstream speed.
36
Page 37

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3.2 LAN
Choose Status > LAN. The page that is displayed shows some basic LAN settings of the
router. In this page, you can view the LAN IP address, DHCP server status, MAC address,
and DHCP client table. If you want to configure the LAN network, refer to section 3.4.1.1 LAN
IP
37
Page 38

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3.3 WLAN
Choose Status > WLAN. The page that is displayed shows some basic settings of wireless
LAN (WLAN).
38
Page 39

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3.4 WAN
Choose Status > WAN. The page that is displayed shows some basic WAN settings of the
router. In this page, you can view basic status of WAN and DNS server. If you want to
configure the WAN network, refer to section 3.4.2.1 WAN
3.3.5 Port Mapping
Choose Status > Port Mapping. In this page, you can view the mapping relation and the
status of port mapping.
39
Page 40

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3.6 Statistics
Choose Status > Statistics. The Statistics page that is displayed contains Statistics and
ADSL Statistics.
3.3.6.1 Statistics
Click Statistics in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears. In this page,
you can view the statistics of each network port.
40
Page 41

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3.6.2 ADSL Statistics
Click ADSL Statistics in the left pane. The page shown in the following figure appears. In
this page, you can view the ADSL line status, upstream rate, downstream rate and other
information.
41
Page 42

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.3.7 ARP Table
Choose Status > ARP. In the ARP Table page, you can view the table that shows a list of
learned MAC addresses.
3.4 Network
In the navigation bar, click Network. The Network page that is displayed contains LAN,
WAN,
and WLAN.
3.4.1 LAN
Choose Network > LAN. The LAN page that is displayed contains LAN IP, IPv6 LAN Config,
DHCP and DHCP Static IP.
3.4.1.1 LAN IP
Click LAN IP in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
In this page, you can change IP address of the router. The default IP address is 192.168.1.1,
which is the private IP address of the router.
42
Page 43

DG-BG4100N User Manual
43
Page 44

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Enter the IP address of LAN interface. It is
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Secondary IP
IGMP Snooping
LAN Port
Link Speed /
Duplex Mode
MAC Address
Control
Add
Current allowed
MAC address table
recommended to use an address from a block that is
reserved for private use. This address block is
192.168.1.1 - 192.168.1.254.
Enter the subnet mask of LAN interface. The range of
subnet mask is from 255.255.0.0-255.255.255.254.
Select it to enable the secondary LAN IP address. The
two LAN IP addresses must be in different networks
When IGMP snooping is enabled, only hosts that
belong to the group receive the multicast packets. If a
host is deleted from the group, the host cannot receive
the multicast packets any more.
You can choose the LAN interface you want to
configure.
You can select the following modes from the
drop-downlist:100Mbps/FullDuplex,100Mbps/Half
Duplex,10Mbps/FullDuplex,10Mbps/HalfDuplex,Auto
Negotiation.
It is the access control based on MAC address. Select
it, and the host whose MAC address is listed in the
Current Allowed MAC Address table can access the
router.
Enter MAC address, and then click it to add a new MAC
address.
All the allowed MAC addresses added will be listed
here.
44
Page 45

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.1.2 IPv6 LAN Config
Click LAN IP in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears. In this page,
you can change IP address of the router. The default IP address is 192.168.1.1, which is the
private IP address of the router.
45
Page 46

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the RA parameters of this page.
Field Description
Global Address
RA Setting
Enable Enable or disable the Router Advertisement feature.
M Flag
O Flag
Max interval
Min Interval
Prefix Mode
DHCPv6 Setting
DHCPv6 Mode
Specify the LAN global ipv6 address, which may be
assigned by ISP.
Enable or disable the “Managed address configuration”
flag in RA packet.
Enable or disable the “Other configuration” flag in RA
packet.
The maximum time allowed between sending
unsolicited multicast Router Advertisements from the
interface, in seconds.
Note: The Max Interval must not be less than 4 seconds
and not greater than 1800 seconds.
The minimum time allowed between sending unsolicited
multicast Router Advertisements from the interface, in
seconds.
Note: The Min Interval must not be less than 3 seconds
and not greater than 0.75 * Max Interval.
Specify the RA feature prefix mode:
“Auto”: The RA prefix will use Wan dhcp-pd prefix.
“Manual”: User will specify the prefix Address, Length,
Preferred time and Valid time.
Specify the dhcpv6 server mode:
“None”: Close dhcpv6 server.
“Manual”: dhcpv6 server is opened and user specifies
the dhcpv6 server address pool and other parameters.
“Auto”: dhcpv6 server is opened and it can use Wan
dhcp-pd prefix to generate address pool.
46
Page 47

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.1.3 DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows the individual PC to obtain the TCP/IP
configuration from the centralized DHCP server. You can configure this router as a DHCP
server or disable it. The DHCP server can assign IP address, IP default gateway and DNS
server to DHCP clients. This router can also act as a DHCP server (DHCP Relay) where it
relays IP address assignment from an actual real DHCP server to clients. You can enable or
disable DHCP server.
Click DHCP in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
47
Page 48

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
If set to DHCP Server, the router can assign IP addresses,
DHCP Mode
IP Pool Range
Show Client
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask here.
Default Gateway Enter the default gateway of the IP address pool.
Max Lease Time
Domain Name
DNS Servers
Set VendorClass
IP Range
IP default gateway and DNS Servers to the host in
Windows95, Windows NT and other operation systems
that support the DHCP client.
It specifies the first and the last IP address in the IP
address pool. The router assigns IP address that is in the
IP pool range to the host.
Click it, the Active DHCP Client Table appears. It shows IP
addresses assigned to clients.
The lease time determines the period that the host retains
the assigned IP addresses before the IP addresses
change.
Enter the domain name if you know. If you leave this
blank, the domain name obtained by DHCP from the ISP
is used. You must enter host name (system name) on
each individual PC. The domain name can be assigned
from the router through the DHCP server.
You can configure the DNS server ip addresses for DNS
Relay.
Click it, the Device IP Range Table appears. You can
configure the IP address range based on the device type.
48
Page 49

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click Show Client in the DHCP Mode page, the page shown in the following figure appears.
You can view the IP address assigned to each DHCP client.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons in this page:
Field
IP Address
MAC Address
Expiry (s)
Type
Refresh Click it to refresh this page.
Close Click it to close this page.
Description
It displays the IP address assigned to the DHCP client from
the router.
It displays the MAC address of the DHCP client.
Each Ethernet device has a unique MAC address. The MAC
address is assigned at the factory and it consists of six pairs
of hexadecimal character, for example, 00-17-7C-00-02-12.
It displays the lease time. The lease time determines the
period that the host retains the assigned IP addresses
before the IP addresses change.
Automatic, means if the IP / MAC of the client are not binded
using the Static DHCP option.
Manual, means the IP/MAC are binded using the Static
DHCP Option.
49
Page 50

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click Set VendorClass IP Range in the DHCP Mode page, the page as shown in the
following figure appears. In this page, you can configure the IP address range based on the
device type.
In the DHCP Mode field, choose None. The page shown in the following figure appears.
50
Page 51

DG-BG4100N User Manual
In the DHCP Mode field, choose DHCP Relay. The page shown in the following figure
appears.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
If set to DHCP Relay, the router acts a DHCP Server and
DHCP Mode
Relay Server Enter the DHCP server address provided by your ISP.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
relays the DHCP requests and responses between the remote
server and the client.
51
Page 52

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.1.4 DHCP Static IP
Click DHCP Static IP in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears. You
can assign the IP addresses on the LAN to the specific individual PCs based on their MAC
address.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
IP Address Enter the specified IP address in the IP pool range,
which is assigned to the host.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of a host on the LAN.
Add After entering the IP address and MAC address, click
it. A row will be added in the DHCP Static IP Table.
Delete Selected Select a row in the DHCP Static IP Table, then click it,
this row will be deleted.
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
DHCP Static IP Table It shows the assigned IP address based on the MAC
address.
52
Page 53

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.2 WAN
Choose Network > WAN. The WAN page that is displayed contains WAN, Auto PVC, ATM
Settings and ADSL Settings.
3.4.2.1 WAN
Click WAN in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears. In this page, you
can configure WAN interface of your router.
53
Page 54

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Default Route Selection You can select Auto or Specified.
VPI
VCI
Encapsulation You can choose LLC and VC-Mux.
Channel Mode
Enable NAPT
Enable IGMP
The virtual path between two points in an ATM
network, ranging from 0 to 255.
The virtual channel between two points in an ATM
network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 are
reserved for known protocols)
You can choose 1483 Bridged, 1483 MER, PPPoE,
PPPoA, 1483 Routed or IPoA.
Select it to enable Network Address Port Translation
(NAPT) function. If you do not select it and you want
to access the Internet normally, you must add a
route on the uplink equipment. Otherwise, the
access to the Internet fails. Normally, it is enabled.
You can enable or disable Internet Group
Management Protocol (IGMP) function.
PPP Settings
User Name
Password
Type
Idle Time (min)
Enter the correct user name for PPP dial-up, which
is provided by your ISP.
Enter the correct password for PPP dial-up, which is
provided by your ISP.
You can choose Continuous, Connect on Demand,
or Manual.
If set the type to Connect on Demand, you need to
enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset
minutes, if the router does not detect the flow of the
user continuously, the router automatically
disconnects the PPPoE connection.
54
Page 55

DG-BG4100N User Manual
WAN IP Settings
You can choose Fixed IP or DHCP.
If select Fixed IP, you should enter the local IP
Type
Local IP Address
Netmask Enter the subnet mask of the local IP address.
Unnumbered
Add
Modify
Delete
Reset
Current ATM VC Table
address, remote IP address and subnet mask.
If select DHCP, the router is a DHCP client, the
WAN IP address is assigned by the remote
DHCP server.
Enter the IP address of WAN interface provided by
your ISP.
Select this checkbox to enable IP unnumbered
function.
After configuring the parameters of this page, click it
to add a new PVC into the Current ATM VC Table.
Select a PVC in the Current ATM VC Table, then
modify the parameters of this PVC. After finishing,
click it to apply the settings of this PVC.
Select a PVC in the Current ATM VC Table, then
delete the PVC.
Click reset to undo the settings entered in this page
and retain them to default settings.
This table shows the existing PVCs. It shows the
interface name, channel mode, VPI/VCI,
encapsulation mode, local IP address, remote IP
address and other information. The maximum item
of this table is eight.
55
Page 56

DG-BG4100N User Manual
After adding a PPPoE ATM VC to the table, click in the PPPoE mode, the page shown
in the following figure appears. In this page, you can configure parameters of this PPPoE
PVC.
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
The foll
Field Description
Protocol It displays the protocol type used for this WAN
connection.
ATM VCC The ATM virtual circuit connection assigned for this
PPP interface (VPI/VCI).
Login Name The user name provided by your ISP.
Password The password provided by your ISP.
Authentication Method You can choose AUTO, CHAP, or PAP.
Connection Type You can choose Continuous, Connect on Demand, or
56
Page 57

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Manual.
Idle Time (s) If you choose Connect on Demand, you need to enter
the idle timeout time. Within the preset minutes, if the
router does not detect the flow of the user
continuously, the router automatically disconnects the
PPPoE connection.
Bridge You can select Bridged Ethernet, Bridged PPPoE, or
Disable Bridge.
AC-Name The accessed equipment type.
Service-Name The service name.
802.1q You can select Disable or Enable. After enable it, you
need to enter the VLAN ID. The value ranges from 1 to
4095.
MTU (576-1492)
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page temporarily.
Return Click it to return to the Channel Configuration page.
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
Source Mac address The MAC address you want to clone.
MAC Clone Click it to enable the MAC Clone function with the
Maximum transfer unit is the Optimal MTU
configuration for PPPoE ADSL Connections, which is
set by ISP.
MAC address that is configured.
57
Page 58

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.2.2 Auto PVC
Click Auto PVC in the left pane, page shown in the following figure appears. In this page, you
can get PVC automatically through detecting function, and add or delete the PVC that you
want or do not want.
58
Page 59

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.2.3 ATM Settings
Click ATM Settings in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears. In this
page, you can configure the parameters of the ATM, including QoS, PCR, CDVT, SCR and
MBS.
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
VPI The virtual path identifier of the ATM PVC.
VCI The virtual channel identifier of the ATM PVC.
QoS The QoS category of the PVC. You can choose UBR,
CBR, rt-VBR or nrt-VBR.
PCR Peak cell rate (PCR) is the maximum rate at which cells
can be transmitted along a connection in the ATM
network. Its value ranges from 1 to 65535.
CDVT Cell delay variation tolerance (CDVT) is the amount of
delay permitted between ATM cells (in microseconds).
Its value ranges from 0 to 4294967295.
SCR Sustained cell rate (SCR) is the maximum rate that traffic
can pass over a PVC without the risk of cell loss. Its
value ranges from 0 to 65535.
59
Page 60

DG-BG4100N User Manual
MBS Maximum burst size (MBS) is the maximum number of
cells that can be transmitted at the PCR. Its value ranges
from 0 to 65535.
3.4.2.4 ADSL Settings
Click ADSL Settings in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears. In this
page, you can select the DSL modulation. Mostly, try to retain the factory default settings.
The router supports these modulations: G.Lite, G.Dmt, T1.413, ADSL2 and ADSL2+. The
router negotiates the modulation modes with the DSLAM.
60
Page 61

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3 WLAN
Choose Network > WLAN. The WLAN page that is displayed contains Basic, Security,
Access Control List, MBSSID, Advanced, WPS, WDS and WDS Security.
3.4.3.1 Basic
Choose WLAN > Basic and the following page appears. In this page, you can configure the
parameters for wireless LAN clients that may connect to the router.
61
Page 62

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Choose the working mode of the router. You can choose
from drop-down list.
Band
Choose the network model of the router, which is varied
Mode
SSID
Channel Width Options available are 40 MHZ, 20 MHz and 40/20 MHz
Control Sideband
Channel Number
Radio Power (Percent) You can choose the transmission power of the radio
according to the software. By default, the network model
of the router is AP.
The service set identification (SSID) is a unique name to
identify the router in the wireless LAN. Wireless stations
associating to the router must have the same SSID.
Enter a descriptive name that is used when the wireless
client is connecting to the router.
There are two sidebands upper and lower bands. The
lower band comprises of channel numbers 1-9. The
upper band comprises of channel numbers 5-13.
A channel is the radio frequency used by 802.11b/g
wireless devices. There are 11 channels (from 1 to 11)
available depending on the geographical area. When You
may have a choice of channels (for your region) you
should use a different channel from an adjacent AP to
reduce the interference. Interference and degrading
performance occurs when radio signal from different APs
overlap.
Choose a channel from the drop-down list box.
62
Page 63

DG-BG4100N User Manual
signal. The default one is 100%. It is recommended to
choose the default value 100%.
Show Active Clients
Apply Changes
Click it to view the information of the wireless clients that
are connected to the router.
Click it to apply the settings temporarily. If you want to
save the settings of this page permanently, click Save in
the lower left corner which appears only after we apply
changes.
3.4.3.2 Security
Choose Wireless > Security and the following page appears.
63
Page 64

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Configure the wireless encryption mode. You can choose
None, WEP, WPA (TKIP), WPA (AES), WPA2 (AES), WPA2
(TKIP) or WPA2 Mixed.
Wired equivalent privacy (WEP) encrypts data frames
Encryption
before transmitting over the wireless network.
Wi-Fi protected access (WPA) is a subset of the
IEEE802.11i security specification draft.
WPA2 Mixed is the collection of WPA and WPA2
encryption modes. The wireless client establishes the
Set WEP Key
connection between the router through WPA or WPA2.
Key differences between WPA and WEP are user
authentication and improved data encryption.
It is available when you set the encryption mode to WEP.
Click it, the Wireless WEP Key Setup page appears.
Select Personal (Pre-Shared Key), enter the
pre-shared key in the Pre-Shared Key field.
Select Enterprise (RADIUS), enter the port, IP address,
WPA Authentication
Mode
and password of the Radius server.
You need to enter the username and password provided by
the Radius server when the wireless client connects the
router.
If the encryption is set to WEP, the router uses 802.1x
authentication, which is Radius authentication.
64
Page 65

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click Set WEP Key, as shown in the screen above and the following screen appears.
65
Page 66

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3.3 Access Control List
Choose WLAN > Access Control List and the following page appears. In this page, you can
configure the access control of the wireless clients.
Choose Allow Listed as the access control mode to enable white list function. Only the
devices whose MAC addresses are listed in the Current Access Control List can access the
router.
Choose Deny Listed as the access control mode to enable black list function. The devices
whose MAC addresses are listed in the Current Access Control List are denied to access the
router.
66
Page 67

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3.4 MBSSID
Choose Wireless > MBSSID and the following page appears. In this page, you can
configure the multiple SSID of the wireless clients.
It supports four virtual access points (VAPs). It is a unique name to identify the router in the
wireless LAN. Wireless stations associating to the router must have the same name. Enter a
descriptive name that is used when the wireless client connecs to the router.
67
Page 68

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3.5 Advanced
Choose WLAN > Advanced and the following page appears. In this page, you can configure
the wireless advanced parameters. It is recommended to use the default parameters.
Note:
The parameters in the Advanced link are modified by the professional personnel, it
is recommended to keep the default values.
owing table describes the parameters of this page:
The foll
Field Description
Authentication type
Select the router operating in the open system or encryption
authentication. You can choose Open System, Shared Key, or
Auto.
68
Page 69

DG-BG4100N User Manual
In the open system, the wireless client can directly
connect to the device.
In Shared key, the wireless client connects to the router
using the shared key.
The default is set to Auto, which allows either Open
Fragment treshold
RTS Treshold
Beacon Interval
DTIM Interval
Data Rate
System or Shared Key authentication to be used.
This value should remain at its default setting of 2346. It
specifies the maximum size for a packet before data is
fragmented into multiple packets. If you experience a high
packet error rate, you may slightly increases the “Fragment
Threshold” value within the value range of 256 to 2346.
Setting this value too low may result in poor network
performance. Only minor modifications of this value are
recommended.
This value should remain at its default setting of 2347. If you
encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor modifications are
recommended. If a network packet is smaller than the preset
“RTS threshold” size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will not be
enabled.
The Beacon Interval value indicates the frequency interval of
the beacon. Enter a value between 20 and 1024.
a beacon proportion (transmission quantity indication). Its
Dat
value range is 1—255 and the default value is 100.
Choose the transmission rate of the wireless data.
You can choose Auto, 1 M, 2 M, 5.5 M, 11 M, 6 M, 9 M, 12 M,
18 M, 24 M, 36 M, 48 M, 54M, MSC0 ~ MSC7.
Long Preamble: It means this card always uses long
PreambleType
Broadcast SSID
preamble.
Short Preamble: It means this card can support short
preamble capability.
Select whether the router broadcasts SSID or not. You can
select Enable or Disable.
Select Enable, the wireless client searches the router
69
Page 70

DG-BG4100N User Manual
through broadcasting SSID.
Select Disable to hide SSID, the wireless clients can not
Relay Blocking
Ethernet to Wireless
Blocking
Wifi Multicast to
Unicast
Aggregation
Short GI
Apply Changes
find the SSID.
Wireless isolation. Once this field is Enabled, the wireless
clients that are connected to the router cannot
intercommunicate.
Whether the wireless network can communicate with the
Ethernet network or not.
Enable it to use unicast to transmit multicast packets.
It is applied when the destination end of all MPDU are for one
STA.
It is not recommended to enable GI in obvious environment of
Multi-path effect.
Click it to apply the settings temporarily. If you want to save
the settings of this page permanently, click Save in the lower
left corner of the webpage. The save button appears only after
the ‘Apply Changes’ button has been clicked.
70
Page 71

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3.6 WPS
Choose WLAN > WPS and the following page appears.
There are
WPS. Click Regenerate PIN to generate a new PIN. In the wireless client tool, enter the PIN
which is generated by the router, start connection. The client will automatically establish the
connection with the router through the encryption mode, and you need not enter the key. The
other way is the wireless client generates PIN. In the above figure, enter PIN of the wireless
client in the Client PIN Number field, then click Start PIN to establish the connection.
two ways for the wireless client to establish connection with the router through
Note:
The wireless client establishes the connection with the router through WPS
negotiation. The wireless client must support WPS.
71
Page 72

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3.7 WDS
Choose WLAN > WDS, and the following page appears. In this page you can enable
wireless distribution system (WDS) so that the router can communicate with another AP.
owing table describes the parameters of this page:
The foll
Field Description
Enable WDS Check this box to enable WDS
MAC Address Wireless MAC address of the AP to be connected.
Comment Add comment for the WDS AP.
Current WDS AP List
All the MAC addresses of the AP to be connected will be
listed here
72
Page 73

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.4.3.8 WDS Security
Choose WLAN > WDS Security, and the following page appears. In this page, you can set
up wireless security for WDS.
The foll
owing table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
Encryption
Pre-shared Key Enter an encryption key.
Choose a WDS encryption algorithm from None, WEP,
TKIP and AES.
73
Page 74

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5 Service
In the navigation bar, click Service. The Service page that is displayed contains DNS,
Firewall, UPNP, IGMP Proxy, TR-069 and ACL.
3.5.1 DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet service that translates the domain name into IP
address. Because the domain name is alphabetic, it is easier to remember. The Internet,
however, is based on IP addresses. Every time you use a domain name, DNS translates the
name into the corresponding IP address. For example, the domain name www.example.com
might be translated to 198.105.232.4. The DNS has its own network. If one DNS server does
not know how to translate a particular domain name, it asks another one, and so on, until the
correct IP address is returned.
Choose Service > DNS. The DNS page that is displayed contains DNS, IPv6 DNS and
DDNS.
3.5.1.1 DNS
Click DNS in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
74
Page 75

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Attain DNS
Automatically
Set DNS
Manually
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Reset Selected Click it to start configuring the parameters in this page.
Select it, the router accepts the first received DNS assignment
from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER enabled PVC(s) during
the connection establishment.
Select it, enter the IP addresses of the primary and secondary
DNS server.
75
Page 76

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.1.2 IPv6 DNS
Click DNS in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page.
The foll
Field Description
Attain DNS
Automatically
Set DNS
Manually
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings of this page.
Reset Selected Click it to start configuring the parameters in this page.
Select it, the router accepts the first received DNS assignment
from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER enabled PVC(s) during
the connection establishment.
Select it, enter the IP addresses and choose the WAN interface of
the primary, the secondary and the tertiary DNS server.
76
Page 77

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.1.3 DDNS
Click DDNS in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is
used to configure the dynamic DNS address from DynDNS.org or TZO. You can add or
remove to configure dynamic DNS.
owing table describes the parameters of this page:
The foll
Field Description
DDNS
provider
Host Name The DDNS identifier.
Interface The WAN interface of the router.
Enable Enable or disable DDNS function.
Username The name provided by DDNS provider.
Choose the DDNS provider name. You can choose
DynDNS.org or TZO.
77
Page 78

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Password The password provided by DDNS provider.
Email The email provided by DDNS provider.
Key The key provided by DDNS provider.
3.5.2 Firewall
Choose Service > Firewall. The Firewall page that is displayed contains IP/Port Filter,
IPv6/Port Filter, MAC Filter, URL Filter, Anti-DoS and Software Forbidden.
3.5.2.1 IP/Port Filter
Click IP/Port Filter in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
Entries in the table are used to restrict certain types of data packets through the gateway.
These filters are helpful in securing or restricting your local network.
78
Page 79

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.2.2 IPv6/Port Filter
Click IPv6/Port Filter in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of ipv6 data packets from your local
network to the Internet through the Gateway.
79
Page 80

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.2.3 MAC Filter
Click MAC Filter in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears. Entries
in the table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to
Internet through the gateway. These filters are helpful in securing or restricting your local
network.
80
Page 81

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.2.4 URL Filter
Click URL Filter in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears. This
page is used to block a fully qualified domain name, such as tw.yahoo.com and filtered
keyword. You can add or delete the filtered keyword.
The foll
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
URL/KEYWORD
Blocking
Capability
You can choose Disable or Enable.
Select Disable to disable URL/KEYWORD blocking
function and keyword filtering function.
Select Enable to block access to the URLs and keywords
specified in the URL/KEYWORD Blocking Table.
URL/Keyword Enter the URL/keyword to block.
Add Click it to add a URL/keyword to the URL/KEYWORD Blocking
Table.
Delete Select a row in the URL/KEYWORD Blocking Table and click
Delete to delete the row.
URL/KEYWORD
Blocking Table
A list of URL (s) to which access is blocked will be displayed in
this table.
81
Page 82

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.2.5 Anti-DoS
Denial-of-Service Attack (DoS attack) is a type of attack on a network that is designed to
bring the network to its knees by flooding it with useless traffic.
A denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is an attempt to make a computer resource
unavailable to its intended users. One common method of attack involves saturating the
target machine with external communications requests, such that it cannot respond to
legitimate traffic, or responds so slowly as to be rendered effectively unavailable. Such
attacks usually lead to a server overload.
In general terms, DoS attacks are implemented by either forcing the targeted computer(s) to
reset, or consuming its resources so that it can no longer provide its intended service or
obstructing the communication media between the intended users and the victim so that they
can no longer communicate adequately.
Enable DoS Preventionto detect and prevent denial of service attacks through automatic rate
filtering or rules toprotect legitimate users during the DoS attacks.
82
Page 83

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click Anti-DoS in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears. In this
page, you can prevent DoS attacks.
83
Page 84

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.2.6 Software Forbidden
Click Software Forbidden in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
This interface realizes application control. Select an application from the drop-down list to
prohibit the application from accessing network resources.
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
The foll
Field Description
Current Forbidden
Software List
Add Forbidden
Software
A list of currently forbidden applications for accessing the
network.
Select an application to be forbidden from accessing the
network.
84
Page 85

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.3 UPnP
Choose Service > UPnP, and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is
used to configure UPnP. The system acts as a daemon after you enable it.
3.5.4 IGMP Proxy
Choose Service > IGMP Proxy, and the page shown in the following figure appears. IGMP
proxy enables the system to issue IGMP host messages on behalf of hosts that the system
discovered through standard IGMP interfaces. The system acts as a proxy for its hosts after
you enable it.
85
Page 86

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Field Description
Robust Count
Last member
query count
Query Interval
Query response
Interval
Group Leave
delay
The Robust Count allows tuning for expected packet loss
on a network. By default, the value is set to 2.
This parameter indicates last member query interval. It is
the maximum response time in seconds for an IGMP host
in reply to group-specific queries.
By default, the value is set to 2
This parameter indicates the query interval. It is the interval
in seconds (s) between general queries sent by the
querier.. Default is 60 sec.
This parameter indicates the query response interval. It is
the maximum response time in seconds for an IGMP host
in reply to general queries. By default, the value is set to
100.
The message is sent when a host leaves a group. Default
value is 2000.
86
Page 87

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.5.5 TR-069
TR-069 is a protocol for communication between a CPE and Auto-Configuration Server
(ACS).
Choose Service > TR-069, and the page shown in the following page appears. In this page,
you can configure the TR-069 CPE.
87
Page 88

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters of this page:
Field Description
ACS
URL The URL of the auto-configuration server to connect
to.
User Name The user name for logging in to the ACS.
Password The password for logging in to the ACS.
Periodic Inform Enable Select Enable to periodically connect to the ACS to
check whether the configuration updates.
Periodic Inform Interval Specify the amount of time between connections to
ACS.
Connection Request
User Name The connection username provided by TR-069
service.
Password The connection password provided by TR-069
service.
Path Identifies the PATH that the service should use.
Port Identifies the port number that the service should
use.
Debug
ACS Certificates CPE As vital data (like user names and passwords) may
be transmitted to CPE via TR-069 protocol it is
essential to provide secure transport channel and
always authenticate the CPE against the ACS.
Secure transport and authentication of the ACS
identity can easily be provided by usage of HTTPS
and verification of ACS certificate.
Show Message Select Enable to display ACS SOAP messages on
the serial console.
CPE sends GetRPC Select Enable, the router contacts the ACS to obtain
configuration updates.
88
Page 89

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Skip MReboot Specify whether to send an MReboot event code in
the inform message.
Delay Specify whether to start the TR-069 program after a
short delay.
Auto-Execution Specify whether to automatically start the TR-069
after the router is powered on.
3.5.6 ACL
Choose Service > ACL, the page shown in the following figure appears. In this page, you
can permit the data packets from LAN or WAN to access the router. You can configure the IP
address for Access Control List (ACL). If ACL is enabled, only the effective IP address in the
ACL can access the router.
Note:
If you select Enable in ACL capability, ensure that your host IP address is in
ACL list before it takes effect.
89
Page 90

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Direction Select
LAN ACL Switch Select it to enable or disable ACL function.
IP Address
Services Allowed
Add
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
Current ACL Table Displays the services that are added and are active.
Select the router interface. You can select LAN or WAN. In
this example, LAN is selected.
Enter the IP address of the specified interface. Only the IP
address that is in the same network segment with the IP
address of the specified interface can access the router.
You can choose the following services from LAN: Web,
Telnet, SSH, FTP, TFTP, SNMP, or PING. You can also
choose all the services.
After setting the parameters, click it to add an entry to the
Current ACL Table.
90
Page 91

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Set direction of the data packets to WAN, the page shown in the following figure appears.
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
The foll
Field Description
Direction Select
WAN Setting
IP Address
WAN Interface Choose the interface that permits data packets from
Select the router interface. You can select LAN or WAN.
In this example, WAN is selected.
You can choose Interface or IP Address. When IP
address option is selected only then IP address field will
appear.
Enter the IP address on the WAN. Only the IP address
that is in the same network segment with the IP address
on the WAN can access the router.
91
Page 92

DG-BG4100N User Manual
WAN to access the router.
You can choose the following services from WAN: Web,
Services Allowed
Add
Reset Click it to refresh this page.
Current ACL Table Displays the services that are added and are active.
Telnet, SSH, FTP, TFTP, SNMP or PING. You can also
choose all the services.
After setting the parameters, click it to add an entry to
the Current ACL Table.
3.6 Advanced
In the navigation bar, click Advanced. In the Advanced page that is displayed contains Bridge
setting Routing, NAT, Port Mapping, IP QoS, SNMP and Others.
3.6.1 Routing
Choose Advance > Routing, and the page shown in the following figure appears. The page
that is displayed contains Static Route, IPv6 Static Route and RIP.
3.6.1.1 Static Route
Click Static Route in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears. This
page is used to configure the routing information. You can add or delete IP routes.
92
Page 93

DG-BG4100N User Manual
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Enable Select it to use static IP routes.
Destination Enter the IP address of the destination device.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask of the destination device.
Next Hop Enter the IP address of the next hop in the IP route to the
destination device.
Metric The metric cost for the destination.
Interface The interface for the specified route.
Add Route Click it to add the new static route to the Static Route Table.
Update Select a row in the Static Route Table and modify the parameters.
Then click it to save the settings temporarily.
Delete Selected Select a row in the Static Route Table and click it to delete the row.
Show Routes Click it, the IP Route Table appears. You can view a list of
destination routes commonly accessed by your network.
Static Route
Table
A list of the previously configured static IP routes.
93
Page 94

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Click Show Routes, the page shown in the following figure appears. The table shows a list of
destination routes commonly accessed by your network.
3.6.1.2 IPv6 Static Route
Click IPv6 Static Route in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
This page is used to configure the routing information. You can add or delete IP routes.
The foll
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page.
Field Description
Destination Enter the IPv6 address of the destination device.
Prefix Length Enter the prefix length of the IPv6 address.
Next Hop Enter the IP address of the next hop in the IPv6 route to the
94
Page 95

DG-BG4100N User Manual
destination address.
Interface The interface for the specified route.
Add Route Click it to add the new static route to the IPv6 Static Route Table.
Delete
Selected
Select a row in the IPv6 Static Route Table and click it to delete
the row.
3.6.1.3 RIP
Click RIP in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears. If you are using
this device as a RIP-enabled router to communicate with others using Routing Information
Protocol (RIP), enable RIP. This page is used to select the interfaces on your devices that
use RIP, and the version of the protocol used.
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
The foll
Field Description
RIP Select Enable, the router communicates with other
RIP-enabled devices.
Apply Click it to save the settings of this page.
Interface Choose the router interface that uses RIP.
Receive Version Choose the interface version that receives RIP messages.
You can choose RIP1, RIP2, or Both.
95
Page 96

DG-BG4100N User Manual
Choose RIP1 indicates the router receives RIP v1
messages.
Choose RIP2 indicates the router receives RIP v2
messages.
Choose Both indicates the router receives RIP v1 and
RIP v2 messages.
Send Version The working mode for sending RIP messages. You can
choose RIP1 or RIP2.
Choose RIP1 indicates the router broadcasts RIP1
messages only.
Choose RIP2 indicates the router multicasts RIP2
messages only.
Add Click it to add the RIP interface to the Rip Config List.
Delete Select a row in the Rip Config List and click it to delete the
row.
96
Page 97

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.6.2 NAT
Choose Advanced > NAT, and the page shown in the following figure appears. The page
that is displayed contains Setup DMZ, Virtual Server, NAT Forwarding, ALG, NAT Exclude IP,
Port Trigger, FTP ALG Port and NAT IP Mapping.
3.6.2.1 Setup DMZ
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is used to provide Internet services without sacrificing
unauthorized access to its local private network. Typically, the DMZ host contains devices
accessible to Internet traffic, such as web (HTTP) servers, FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail)
servers and DNS servers.
Click DMZ in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
The following steps describe how to configure manual DMZ.
Step 1 Select Enable DMZ to enable this function.
Step 2 Enter an IP address of the DMZ host.
Step 3 Click Apply Changes to save the settings of this page temporarily.
97
Page 98

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.6.2.2 Virtual Server
Click Virtual Server in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
owing table describes the parameters of this page.
The foll
Field Description
You can select the common service type, for example,
Service Type
AUTH, DNS or FTP. You can also define a service name.
If you select Usual Service Name, the corresponding
parameter has the default settings.
If you select User-defined Service Name, you need to
enter the corresponding parameters.
Protocol
WAN Setting You can choose Interface or IP Address.
WAN Interface Choose the WAN interface that will apply virtual server.
WAN Port Choose the access port on the WAN.
LAN Open Port Enter the port number of the specified service type.
LAN IP Address
Choose the transport layer protocol that the service type
uses. You can choose TCP or UDP.
Enter the IP address of the virtual server. It is in the same
network segment with LAN IP address of the router.
98
Page 99

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.6.2.3 NAT Forwarding
Click NAT Forwarding in the left pane, the page shown in the following figure appears.
Under 1483MER or 1483Routed mode, if NAPT (Network Address Port Translation) is
enabled, the Local IP Address is configured as 192.168.1.3 and the Remote IP Address is
configured as 202.32.0.2, the PC with the LAN IP 192.168.1.3 will use 202.32.0.2 when it is
connected to the Internet via the router without NAPT control.
The foll
owing table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Field Description
Local IP Address
Remote IP
Address
Enable Enable the current configured rule.
Apply Changes Submit the configurations.
Reset Cancel the modification and reconfigure the settings.
Current NAT Port
Forwarding Table
Input a local IP address.
Input a remote IP address
Current configuration rule list.
99
Page 100

DG-BG4100N User Manual
3.6.2.4 ALG
Click ALG in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears. Choose the
NAT ALG and Pass-Through options, and then click Apply Changes.
3.6.2.5 NAT Exclude IP
Click NAT Exclude IP in the left pane, and the page shown in the following figure appears.
In the page, you can configure some source IP addresses which use the purge route mode
when accessing internet through the specified interface.
Field Description
IP range
Enter the IP address range, which do not require NAT
translation entries to be permitted by the router.
100
 Loading...
Loading...