Page 1
1300 Henley Court
Pullman, WA 99163
509.334.6306
www.store. digilent.com
Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Revised August 31, 2017
This manual applies to the Pmod CAN rev. B
SKU: 410-353
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 1 of 8
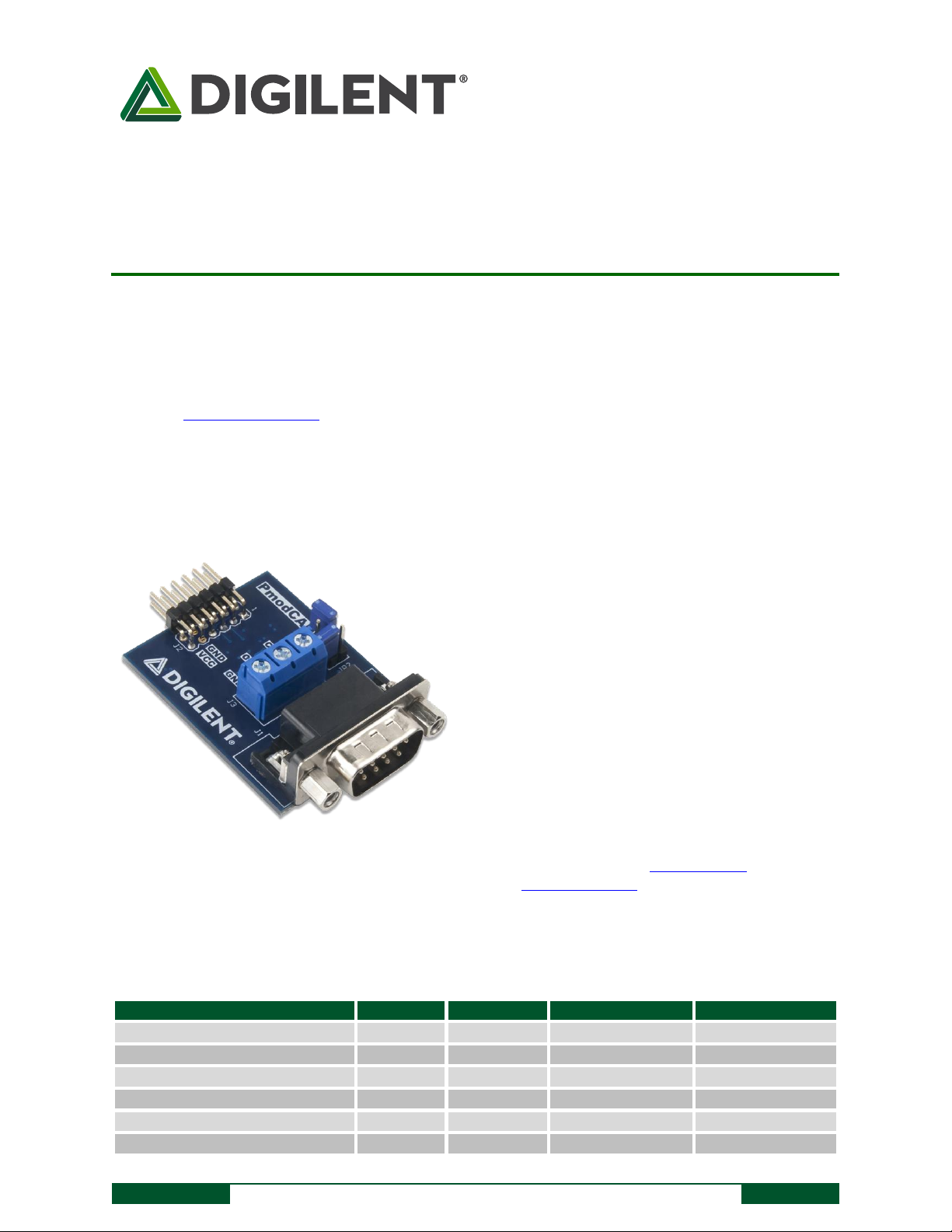
Overview
The Digilent Pmod CAN (Revision B) is a CAN 2.0B controller with an integrated transceiver. The
embedded Microchip MCP25625 chip connects directly to the physical CAN bus and meets automotive
requirements for high-speed (1 Mb/s), low quiescent current, electromagnetic compatibility, and electrostatic
discharge.
1 Specifications
Parameter
Min
Typical
Max
Units
Power Supply Voltage (Vcc)
2.7 5.5
V
High-Level Input Voltage (RxCAN)
2 - Vcc+1
V
Low-Level Input Voltage (RxCAN)
-0.3 - 0.15*Vcc
V
High-Level Output Voltage (TxCAN)
Vcc-0.7 - -
V
Low-Level Output Voltage (TxCAN)
- - 0.6 V Bit Frequency
14.4 - 1000
kHz
The Pmod CAN.
Standalone CAN 2.0B controller with an
integrated CAN transceiver
Compatible with ISO-11898-1, ISO-11898-2, and
ISO-11898-5
Suitable for automotive applications
Up to 1 Mb/s operation
Up to 10 MHz SPI clock speed
3 Transmit buffers with prioritization and abort
feature
2 Receive buffers
6 Filters and 2 masks with optional filtering on
the first two data bytes
Interrupt output pin
Standard DB9 connector for a secure connection
Suitable for 12 V and 24 V systems
Small PCB size for flexible designs 1.4 in x 1.8 in
(3.6 cm x 4.6 cm)
12-pin Pmod connector with SPI interface
Follows the Digilent Pmod Interface
Specification 1.1.0
Page 2
Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 2 of 8
Transmitter
Min
Typical
Max
Units
Recessive Bus Output Voltage
(CANH & CANL)
2.0
0.5 Vcc
3.0
V
Dominant Output Voltage (CANH)
2.75
3.50
4.50
V
Dominant Output Voltage (CANL)
0.50
1.50
2.25
V
Dominant Differential Output
Voltage
1.5
2.0
3.0
V
Receiver
Min
Typical
Max
Units
Recessive Differential Input
Voltage (normal mode)
-1.0 - +0.5
V
Dominant Differential Input
Voltage (normal mode)
0.9 - Vcc
Parameter
Value
Units
Standby Current
10
μA
1.1 Pinout Table Diagram
Header J1
Pin
Signal
Description
1
N/C
Not Connected
2
CANL
CAN Low-Level Voltage I/O
3
GND
Power Supply Ground
4
N/C
Not Connected
5
N/C
Not Connected
6
GND
Power Supply Ground
7
CANH
CAN High-Level Voltage I/O
8
N/C
Not Connected
9
N/C
Not Connected
S1
GND
Power Supply Ground
S2
GND
Power Supply Ground
Header J2
Pin
Signal
Description
1
CS
Chip Select
2
MOSI
Master-Out-Slave-In
3
MISO
Master-In-Slave-Out
4
SCK
Serial Clock
5
GND
Power Supply Ground
6
VCC
Power Supply (3.3V/5V)
7
INT
Interrupt
8
RST
Reset
9
Rx0BF
Receive Buffer 0 Full Interrupt
10
Rx1BF
Receive Buffer 0 Full Interrupt
11
GND
Power Supply Ground
12
VCC
Power Supply (3.3V/5V)
Page 3
Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3 of 8
Header J3
Pin
Signal
Description
1
CANL
CAN Low-Level Voltage I/O
2
CANH
CAN High-Level Voltage I/O
3
GND
Power Supply Ground
Jumpers
Pin
Signal
Description
JP1
Loaded/ Unloaded
End of bus terminated with a combined 120Ω impedance/ Do not
terminate the end of the bus
JP2
Loaded/ Unloaded
Terminate the CAN bus lines with a capacitor to ground/ No termination
1.2 Physical Dimensions
The pins on the pin header are spaced 100 mil apart. The PCB is 1.8 inches long on the sides parallel to the pins on
the pin header and 1.4 inches long on the sides perpendicular to the pin header.
2 Functional Description
The Pmod CAN utilizes the Microchip MCP25625 to enable CAN communication with a variety of external devices.
A complete CAN solution with a controller and transceiver can be implemented on a system board by
communicating with the host board via the SPI protocol in SPI mode 0 or 3. The two differential lines on the
transceiver, CANH and CANL, enable balanced differential signaling to eliminate most of the electromagnetic field
(EMF) and provide high noise immunity within the system.
2.1 Serial Communication
The Pmod CAN communicates with the host board via the SPI protocol. By driving and keeping the Chip Select line
(pin 1) at a logic level low, users may communicate back and forth with the Pmod depending on whether or not
both sets of data lines are enabled. The embedded chip on the Pmod operates in SPI Mode 0 or 3, with data
captured on the rising edge of the clock and data transferred on the falling edge of the clock, and a minimum clock
cycle time of 100 nanoseconds as per Table 7-6 (page 70) of the Microchip MCP25625 datasheet.
Nine SPI instructions are available to read the status of the receiver, load a transmit buffer, modify bits in a register
and more. Most of the instruction commands are single byte instructions followed by an address byte. More
information is available in the Quick Start section as well as Section 5 (page 55) of the MCP25625 datasheet.
2.2 Register Details
2.2.1 CANINTE
The CANINTE register (page 51) enables the generation of interrupts on Pin 7.
Page 4

Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 4 of 8
CANINTE 0x2B
Bit Name
Bit Number
Bit Description
Bit Values
Functional Description
MERRE
[7]
Message Error Interrupt Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt on error during
message reception or
transmission/0-Disabled
WAKIE
[6]
Wake-up Interrupt Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt on CAN bus
activity/0-Disabled
ERRIE
[5]
Error Interrupt Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt on EFLG error
condition change/0-Disabled
TX2IE
[4]
Transmit Buffer 2 Empty Interrupt
Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt on TXB2
becoming empty/0-Disabled
TX1IE
[3]
Transmit Buffer 1 Empty Interrupt
Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt on TXB1
becoming empty/0-Disabled
TX0IE
[2]
Transmit Buffer 0 Empty Interrupt
Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt on TXB0
becoming empty/0-Disabled
RX1IE
[1]
Receive Buffer 1 Full Interrupt
Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt when message
received in RXB1/0-Disabled
RX0IE
[0]
Receive Buffer 0 Full Interrupt
Enable Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt when message
received in RXB0/0-Disabled
¹ – This is the default value on power-up or reset
2.2.2 CANINTF
The CANINTF register (page 51) holds the flags of all the interrupts that are enabled through the CANINTE register.
If an interrupt flag is set, it must be cleared by the system board to reset the interrupt condition.
CANINTF 0x2C
Bit Name
Bit Number
Bit Description
Bit
Values
Functional Description
MERRF
[7]
Message Error Interrupt Flag Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
WAKIF
[6]
Wake-up Interrupt Flag Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
ERRIF
[5]
Error Interrupt Flag Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
TX2IF
[4]
Transmit Buffer 2 Empty Interrupt
Flag Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
TX1IF
[3]
Transmit Buffer 1 Empty Interrupt
Flag Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
TX0IF
[2]
Transmit Buffer 0 Empty Interrupt
Flag Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
RX1IF
[1]
Receive Buffer 1 Full Interrupt Flag
Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
RX0IF
[0]
Receive Buffer 0 Full Interrupt Flag
Bit
0¹
1-Interrupt pending/0-No
interrupt pending
¹ – This is the default value on power-up or reset
2.2.3 CANSTAT
The CANSTAT register (page 54) provides the status of the CAN controller and the source of the interrupt flag.
Page 5

Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 5 of 8
CANSTAT 0xXE
Bit Name
Bit Number
Bit Description
Bit
Values
Functional Description
OPMOD2
[7]
Operation Mode Bit 2
1¹
See the Operation Mode Bit
Table
OPMOD1
[6]
Operation Mode Bit 1
0¹
See the Operation Mode Bit
Table
OPMOD0
[5]
Operation Mode Bit 0
0¹
See the Operation Mode Bit
Table
--
[4]
Unimplemented
0¹
Unimplemented - read as '0'
ICOD2
[3]
Interrupt Flag Code Bit 2
0¹
See the Interrupt Flag Code Bit
Table
ICOD1
[2]
Interrupt Flag Code Bit 1
0¹
See the Interrupt Flag Code Bit
Table
ICOD0
[1]
Interrupt Flag Code Bit 0
0¹
See the Interrupt Flag Code Bit
Table
--
[0]
Unimplemented
0¹
Unimplemented - read as '0'
¹ − This is the default value on power-up or reset
2.2.4 Operation Mode Bit Table
Operation Mode Bit Table
Bit values for Operation Mode bits 2,1,0
Mode
0,0,0
Device is in Normal Operation Mode
0,0,1
Device is in Sleep Mode
0,1,0
Device is in Loopback Mode
0,1,1
Device is in Listen-Only Mode
1,0,0
Device is in Configuration Mode
2.2.5 Interrupt Flag Code Bit Table
Interrupt Flag Table
Bit values for Interrupt Flag bits 2,1,0
Interrupt
0,0,0
No Interrupt
0,0,1
Error Interrupt
0,1,0
Wake-up Interrupt
0,1,1
TBX0 Interrupt
1,0,0
TBX1 Interrupt
1,0,1
TBX2 Interrupt
1,1,0
RBX0 Interrupt
1,1,1
RBX1 Interrupt
2.3 Quick Start
Here is the series of SPI commands to set up, transmit, and receive data on the Pmod CAN:
2.3.1 Setup
1. Set CAN control mode to configuration
Page 6

Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 6 of 8
1. Send modify register SPI command (0x05)
2. Send the address of the control MCP_CANCTRL (0x0F)
3. Send a mask to get things prepared (0x80)
4. Send the command to place the module in config mode (0x80)
2. Set config rate and clock for CAN
1. Send a write SPI command (0x02)
2. Send the address of the register to modify followed by the value to set
3. Three registers are manipulated in this way with a variety of settings; for more details see
Section 4.4 (page 47) in the MCP25625 datasheet. The following three commands set a CAN
speed of 250 kBPS with a CAN clock of 20 MHz.
1. CNF1 (0x2A) set to 0x41
2. CNF2 (0x29) set to 0xFB
3. CNF3 (0x28) set to 0x86
3. Initiate can buffer filters and registers
1. Set the receive filters to either standard or extended identifiers
1. For all standard inputs and in the demo code, set registers 0x00 through 0x0B, registers
0x10 through 0x1B, and registers 0x20 through 0x27 to a value of 0x00. The transmit
register flags and settings are also all cleared by setting registers 0x30 through 0x3D,
0x40 through 0x4D, and registers 0x50 through 0x5D to a value of 0x00. This can be
done for each register by performing the following steps:
2. Send a write SPI command (0x02)
3. Send the register address of interest
4. Send the value to be written (0x00)
4. Set the CAN mode for any message type
1. Send modify register SPI command (0x05)
2. Send the address of the control RXB0CNTRL (0x60)
3. Send a mask to get things prepared (0x64)
4. Send the actual command to accept any message type (0x60)
5. Set CAN control mode to normal mode
1. Send modify register SPI command (0x05)
2. Send the address of the control MCP_CANCTRL (0x0F)
3. Send a mask to get things prepared (0x80)
4. Send the actual command to put in config mode (0x00)
2.3.2 Receive
1. Send the Read Status SPI command (0xA0) to see if any flags have been set. The Pmod will respond with a
single byte detailing a number of flags status as follows:
Bit 7* (MSB) is TX2IF Transmit Buffer 2 Empty interrupt Flag bit (bit 4 in CANINTF (0x2C)), must be
cleared by system to be reset
Bit 6 is TXREQ Message Transmit request bit (bit 3 in TXB2CTRL register 0x50) auto cleared on
message sent
Bit 5* is TX1IF Transmit Buffer 1 Empty interrupt Flag bit (bit 3 in CANINTF (0x2C)), must be
cleared by system to be reset
Bit 4 is TXREQ Message Transmit request bit (bit 3 in TXB1CTRL register 0x40) auto cleared on
message sent
Bit 3* is TX0IF Transmit Buffer 0 Empty interrupt Flag bit (bit 2 in CANINTF (0x2C)), must be
cleared by system to be reset
Page 7

Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 7 of 8
Bit 2 is TXREQ Message Transmit request bit (bit 3 in TXB0CTRL register 0x30) auto cleared on
message sent
Bit 1* is RX1IF Receive Buffer 1 Empty interrupt Flag bit (bit 1 in CANINTF (0x2C)), must be
cleared by system to be reset
Bit 0* (LSB) is RX0IF Receive Buffer 0 Empty interrupt Flag bit (bit 0 in CANINTF (0x2C)), must be
cleared by system to be reset
*-These interrupt flags are disabled by default in the CAN Interrupt Enable register (address
0x2B)
2. If a receive buffer has data in it, determine the length of the message through the four LSBs of the
associated DLC register for the receive buffer (0x65 for RXB0DLC and 0x75 for RXB1DLC)
3. Reset the interrupt flag that was triggered by clearing bit 0 (RX0IF) or bit 1 (RX1IF) as appropriate in the
CANINTF (0x2C) register after reading the data.
2.3.3 Transmit
1. Load data through a Load TX Buffer SPI command. 6 different starting locations are available
Transmit Buffer 0 starting at the standard identifier high register (0x31) – 0x40
Transmit Buffer 0 starting at the data byte register (0x36) – 0x41
Transmit Buffer 1 starting at the standard identifier high register (ox41) – 0x42
Transmit Buffer 1 starting at the data byte register (0x46) – 0x43
Transmit Buffer 2 starting at the standard identifier high register (ox51) – 0x44
Transmit Buffer 2 starting at the data byte register (0x56) – 0x45
2. Send a Request-To-Send SPI command for one or more of the three registers of interest
Transmit buffer 0 (TXB0) uses 0x81
Transmit buffer 1 (TXB1) uses 0x82
Transmit buffer 2 (TXB2) uses 0x84
Multiple transmit buffers can be simultaneously primed by OR'ing the SPI commands
Note that this command does not actually initiate a message transmission. The MCP25625 still
internally goes through arbitration on the bus line and only transmits the message when the bus
is available.
3. Upon completion, the bit set to indicate to the controller that a message is ready to be transmitted will be
cleared and an interrupt will be generated if the TXnIE bit in the CANINTE register is set.
3 Application Information
The CAN protocol uses two communication lines, CANH and CANL, to enable communication between multiple
CAN transceivers called nodes. The two bus lines are actively driven to produce a differential voltage greater than
1.5 V, resulting in the Dominant transmission state. CAN transceivers will interpret a dominant transmission as a
logic low state. A logic high state is created by neither bus driving their lines so that they idle at approximately the
same voltage, typically Vcc/2 as biased by the common mode transceiver. This state is a Recessive transmission
and typically has a differential voltage of less than ±100 mV.
Similar to UART, all nodes on a CAN network must operate at the same nominal bit rate as data is transmitted
without a clock signal in an asynchronous format. The Pmod CAN is compliant with CAN 2.0B (ISO-11898-2 and
ISO-11898-5). In additional to the de-facto RS-232 header, Header J1, screw terminals are provided on Header
J3 for other CAN devices that use twisted pair wiring.
Page 8

Pmod CAN Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 8 of 8
Timing diagrams from page 58 of the MCP25625 datasheet for the Pmod CAN for data coming in and out through
SPI are provided below. The timing values for the parameters shown in the images can be found in Table 7-6 (page
70) of the MCP25625 datasheet.
Figure 1. SPI input timing diagram from MCP25625 datasheet.
Figure 1. SPI output timing diagram from MCP25625 datasheet.
Page 9

Mouser Electronics
Authorized Distributor
Click to View Pricing, Inventory, Delivery & Lifecycle Information:
Digilent:
410-353
 Loading...
Loading...