Page 1

The Digilent Pmod COLOR (Revision A) is a color sensor module with the ability to sense red, green, blue and clear light.
The onboardAMS TCS3472integrates an IR blocking filter to accurately determine the color of objects as well as sense
ambient light under varying lighting conditions and through attenuating materials.
Pmod COLOR Reference Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Page 4

Red, green, blue, and clear light sensing
IR-blocking filter
WhiteLEDfor reflective measurements
Suitable for use behind darkened glass
Small PCB size for flexible designs 0.8“ × 1.25” (2.0 cm × 3.2 cm)
6-pin Pmod connector with I²C interface
Pass-through Pmod host port for daisy chaining
Follows DigilentPmod Interface Specification Type 6
Library and example code available on theResource Center
Parameter Min Typical Max Un
Power Supply Voltage 2.7 3 3.6 V
Parameter Channel Min Max Un
Responsivity to blue light (λ = 465 nm) Red Channel¹ 0% 15% counts/
Features
Specifications
Page 5

¹ - Percent values are with respect to the counts measured by the clear (non-color filtered) channel
Parameter Min Typical Max Un
Green Channel¹ 10% 42% counts/
Blue Channel¹ 65% 88% counts/
Clear Channel 11.0 16.6 counts/
Responsivity to green light (λ = 525 nm) Red Channel¹ 4% 25% counts/
Green Channel¹ 60% 85% counts/
Blue Channel¹ 10% 45% counts/
Clear Channel 13.2 20.0 counts/
Responsivity to red light (λ = 615 nm) Red Channel¹ 80% 110% counts/
Green Channel¹ 0% 14% counts/
Blue Channel¹ 5% 24% counts/
Clear Channel 15.6 23.4 counts/
Parameter Value Un
Output Resolution 16 bi
Header J1 Header J2 Jumper JP
Pin Signal Description Pin Signal Description Pin Status
1 IO1/~INT I/O pin 1 or
active low
interrupt
1 IO1/~INT I/O pin 1 or
active low
interrupt
SCL Loaded/
Unloaded
2 IO2/LED_EN I/O pin 2
orLEDenable
2 IO2/LED_EN I/O pin 2
orLEDenable
Jumper JP2
3 SCL Serial Clock 3 SCL Serial Clock SDA Loaded/
Unloaded
4 SDA Serial Data 4 SDA Serial Data Jumper JP3
Pinout Table Diagram
Page 6

The pins on the pin header are spaced 100 mil apart. The PCB is 1.34 inches long on the sides parallel to the pins on the
pin header and 0.8 inches long on the sides perpendicular to the pin header.
The Pmod Color utilizes the TCS3472 to detect color in the near vicinity. While communicating with the host board via
theI²C protocolusing an I²C address of 0x29 users can measure color. A user controlled whiteLEDis also provided to
help illuminate the object and improve color determination; theLEDis very bright so it is recommended that users do not
stare at the light.
The Pmod COLOR communicates with the host board via theI²C protocol. By first sending the 7-bit I²C device address
of 0101001 (0x29), users may receive the color data from the TCS3472. Each of the fourADCchannels (red, green, blue,
and clear) sends it's conversion from theADCto the host buffer simultaneously.
The TCS3472 can set the gain and integration time for each round of data collection. Integration time provides more time
for the color sensor to collect more data, providing accurate data and helping to prevent the data from disproportionately
capturing any overexposure that may occur. Each set of the 16-bit data is organized in a low-byte, high-byte arrangement.
Each of the three colors (RGB) and the clear color byte has two registers to store the high and low data bytes for each
measurement. The data registers are arranged in a low byte, high byte arrangement.
Header J1 Header J2 Jumper JP
Pin Signal Description Pin Signal Description Pin Status
5 GND Power Supply
Ground
5 GND Power Supply
Ground
~INT Loaded/
Unloaded
E
6 VCC Power Supply
(3.3V)
6 VCC Power Supply
(3.3V)
Jumper JP4
LED_EN Loaded/
UnloadedEt
Data Registers addresses 0x14 to 0x1B
Address Register Name
0x14 Clear Data Low Byte
0x15 Clear Data High Byte
Physical Dimensions
Functional Description
Serial Communication
Register Details
Data Registers
Page 7

The Command register controls the functionality of the internal address pointer and clears interrupts.
¹ - This is the value on power-up and reset ² - See theTransaction Tablebelow ³ - See theAddress Field and Special
Function Tablebelow
³ - See theAddress Field and Special Function Tablebelow
0x16 Red Data Low Byte
0x17 Red Data High Byte
0x18 Green Data Low Byte
0x19 Green Data High Byte
0x1A Blue Data Low Byte
0x1B Blue Data High Byte
Bit Name Bit Number Bit Description Bit Values Functional Description
CMD 7 Command 0¹ Select the command register; must be se
TYPE 6-5 Type 00¹ Selects the type of data transfer²
ADDR/SF 4-0 Address/Special Field 00000¹ Register address field and special functio
Transaction Table
Bit Values Transaction Type
00 Repeated bytes at the same register
01 Auto-increment to the next register
10 Reserved - Do not write
11 Special function³
Address Field and Special Function Field
Bit Values Read Value
Command Register
Transaction Table
Address Field and Special Function Table
Page 8

The Control Register (0x0F) sets the gain factor applied to theADCcolor data.
¹ - This is the value on power-up and reset ² - See theGain Value Tablebelow
The Status register (0x13) is a read-only register that provides the state of the channel interrupt and if the ADCs have
completed a data collection.
Address Field and Special Function Field
Bit Values Read Value
00110 Clears any pending interrupts and self clears
Other Reserved - Do not write
Control Register
Bit Name Bit Number Bit Description Bit Values Functional Description
Reserved 7-2 Reserved 000000¹ Reserved - Write as 0
AGAIN 1-0 Analog gain 00¹ RGBC Gain Control²
RGBC Gain Value Table
Bit Value RGBC Gain Value
00 1x gain
01 4x gain
10 16x gain
11 60x gain
Status Register
Bit
Bit
Bit
Control Register (0x0F)
RGBC Gain Value Table
Status Register (0x13)
Page 9

¹ - This is the value on power-up and reset
Here is the series of commands to acquire a set of data from the Pmod COLOR via pseudo I²C code.
1. Power on the Pmod COLOR.
2. Provide a START condition and call the device ID with a write bit
I2CBegin(0x52); //device ID 0x29 with a write (0) bit
3. Wait to receive an ACK from the Pmod COLOR.
4. Provide a command to maintain the pointer address OR'd with the Enable register (0x00)
I2CWrite(0xA0); //Maintain the pointer address at the Enable register
5. Wait to receive an ACK from the Pmod COLOR.
6. Send the Enable Address and enable the oscillators.
I2CWrite(0x01); //0x01 enables the oscillators for the timers and ADC channels
7. Delay at least 2.4 mS before starting a data collection initiation.
8. Send the Enable Address and enable the ADCs for all 4 channels.
I2CWrite(0x02); //0x02 enables the ADC channels
9. Wait to receive an ACK from the Pmod COLOR and then send a STOP condition.
10. Delay 2.4 ms for the ADCs preparing themselves for data measurement and at least 2.4 ms by default for the
integration time during the data collection process.
11. Send a START condition and call the device ID with a write bit
I2CBegin(0x52); //device ID 0x29 with a write (0) bit
12. Wait to receive an ACK from the Pmod COLOR.
13. Provide a command to auto-increment the address pointer OR'd with the first data register (0x14)
14. Wait to receive an ACK from the Pmod COLOR
15. Provide a RESTART condition and call the device ID with a read bit
Name Number Bit Description Values Functional Description
Status Register
Bit
Name
Bit
Number Bit Description
Bit
Values Functional Description
Reserved 7-5 Reserved 000¹ Reserved
AINT 4 Analog Data
Interrupt
0¹ RGBC clear channel interrupt
Reserved 3-1 Reserved 000¹ Reserved
AVALID 0 Analog Data Valid 0¹ RGBC valid bit when the channels have completed
integration cycle
I2CWrite(0xB4); //Auto-increment the pointer address starting at the Clear Data Low Byte re
Quick Start
Page 10
I2CBegin(0x53); //device ID 0x29 with a read (1) bit
16. Wait to receive an ACK from the Pmod COLOR.
17. Collect all 8 data bytes corresponding to the low and high data byte registers of the clear, red, green, and blue data,
respectively, sending an ACK to the Pmod Color between each byte.
18. Send a STOP condition.
The Pmod COLOR is ideal for fun applications that perform different tasks based on the color of an object. This is perfect
for sorting different objects or controlling a motor based on the detected color temperature.
The AMS TCS3472 module has four differentADCchannels to detect red, green, blue, and clear ambient light data.
Colorimeters of this nature do not have perfect sensing capability so some of the color sensors, notably green and blue, do
not measure the full data range of the data
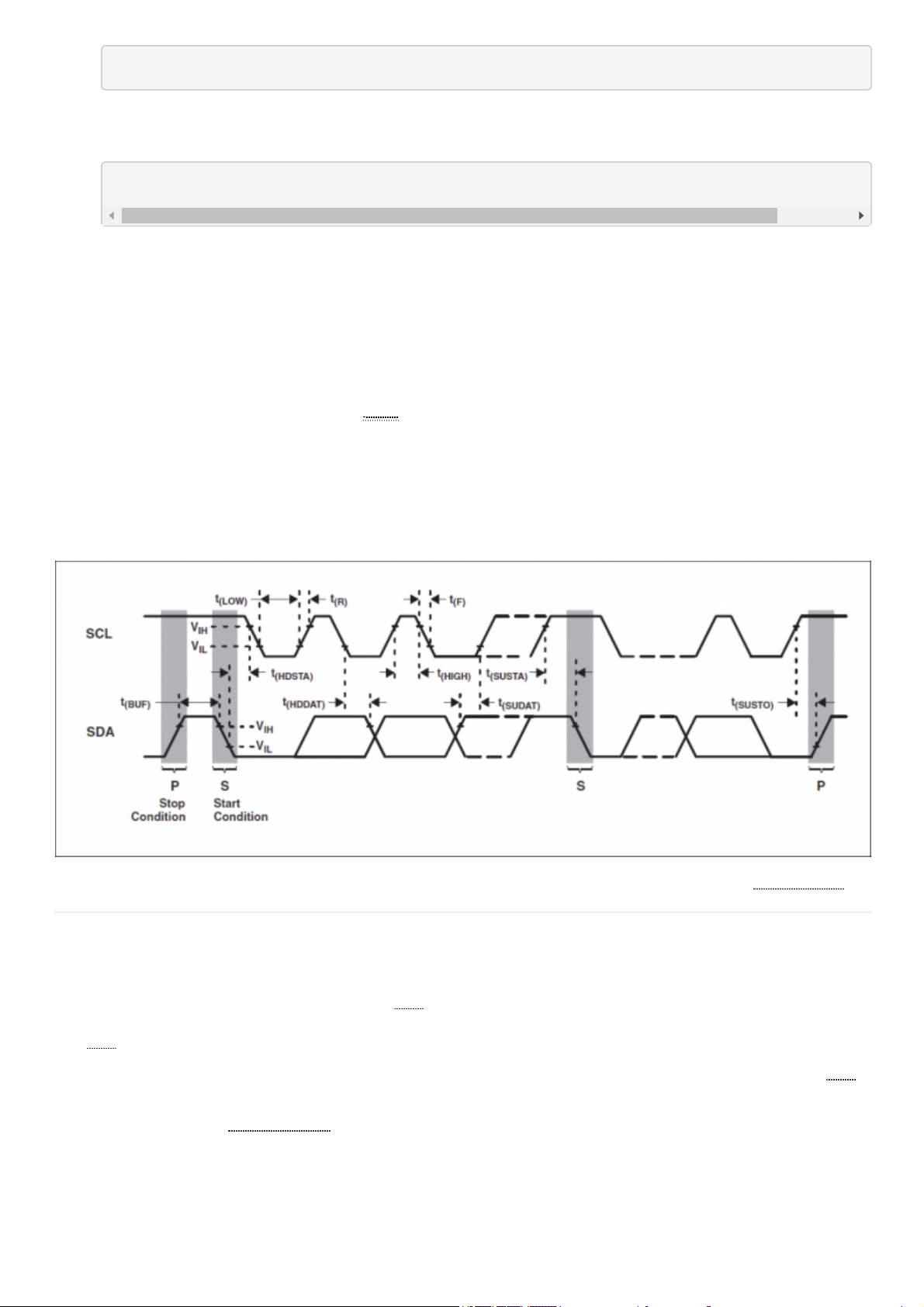
An example timing diagram for reading and writing to the Pmod COLOR taken from the AMS datasheet is provided
below:
When using an external power supply to run the Pmod, be sure to stay within the parameters provided inSpecifications.
The schematics of the Pmod COLOR are availablehere. Additional information about the color sensor including
communication modes and specific timings of the chip can be found by downloading its datasheet from the AMS website
herehere.
Example code demonstrating how to get information from the Pmod COLOR can be found on its Resource Centerhere.
If you have any questions or comments about the Pmod COLOR, feel free to post them under the appropriate section
(“Add-on Boards”) of theDigilent Forum.
I2CReadMultiple(8); //read in the 8 data registers taking advantage of the auto-incrementin
Applications Information
Data Conversion
Timing Diagrams
Additional Information
 Loading...
Loading...