Page 1
cchhiippKKIIT
T
™
™
NNeettwwoorrkk SShhiieelldd
BBooaarrdd RReeffeerreennccee MMaannuuaal
l
Revision: June 27, 2012
1300 NE Henley Court, Suite 3
Pullman, WA 99163
(509) 334 6306 Voice | (509) 334 6300 Fax
Overview
The chipKIT Network Shield is an input/output
expansion board designed for use with the
chipKIT Max32™. It provides the additional
circuitry and connectors to allow the advanced
communications features of the
PIC32MX795F512L on the Max32 to be
utilized.
The Network Shield provides a 10/100 Mbps
Ethernet PHY to allow connection to an
Ethernet network. It provides the connectors
and load switch to support use of the USB 2.0
OTG controller to implement USB device, USB
host or OTG operation. It also provides two
CAN transceivers and connectors to allow
connection to two independent CAN networks.
Connectors are provided to allow connection to
two of the I2C busses supported by the Max32.
In addition to the communications features, the
Network Shield also adds a 256Kbit I2C
EEPROM for non-volatile data storage and a
32.768Khz oscillator to allow use of the Real
Time Clock/Calendar (RTCC) peripheral in the
PIC32 microcontroller.
The Network Shield is designed to the same
form factor as the Max32 board.
Features:
SMSC LAN8720 10/100 Ethernet PHY
RJ45 connector with integral magnetics
USB Device and Host Connectors
Two MCP2551 CAN Transceivers
Two 12-pin header connectors for CAN
Two I2C daisy chain connectors
256Kbit I2C EEPROM
32.768 Khz Oscillator
Doc: 502-211 page 1 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 2
chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
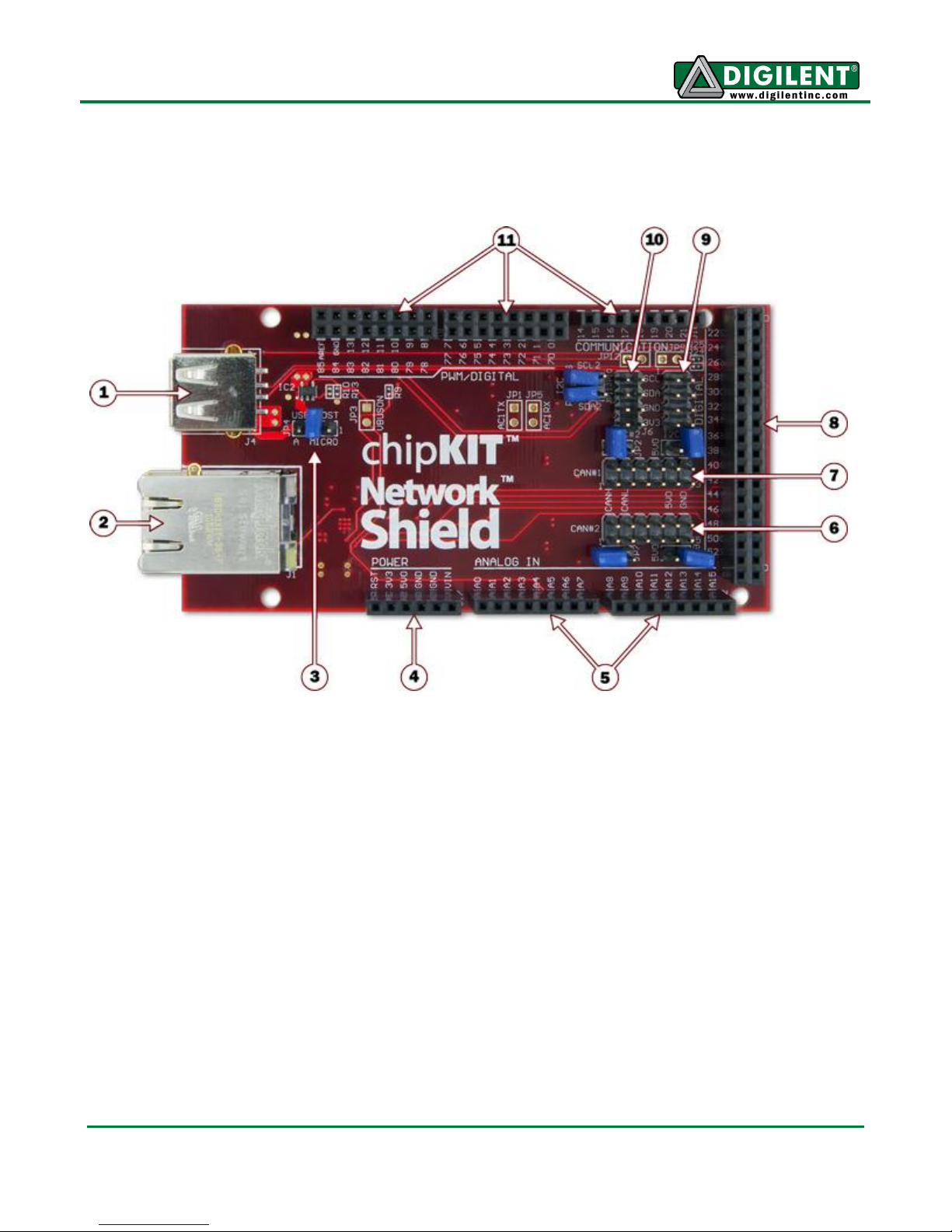
chipKIT Network Shield Hardware Overview
The Network Shield has the following hardware features:
1) USB Connectors
The connector on the top of the board is a standard USB A type receptacle. This is used
when the Max32/Network shield is used as a USB host. Immediately below this connector
is a USB Micro-AB connector. Tis connector is used when the Max32/Network Shield is
used as a USB device, or when using it as an On-The-Go (OTG) device.
2) Ethernet Connector with Integral Magnetics
This connector is used to connect the Max32/Network Shield to an Ethernet network..
3) JP4 – USB Host Connector Selection
When the Max32/Network Shield is used as a USB host, this jumper is used to select
which USB connector is being used.
4) J17 – Power Pass-through Connector
This connector passes the power connector from the Max32 through the Network Shield
board, and powers the Network Shield from the Max32.
5) J9 & J12 – Analog Signal Pass-Through Connectors
These connectors pass the analog input pins on the Max32 through the Network Shield
board.
www.digilentinc.com page 2 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
6) CAN2 Connector
This connector provides access to the signals for CAN2.
7) CAN1 Connector
This connector provides access to the signals for CAN1.
8) Digital Signal Connector
This connector provides most of the signals used by the Ethernet and USB interfaces from
the Max32 board to the Network Shield board. The remaining signals are passed through
the Network Shield.
9) J7 – I2C #1 Daisy Chain Connector
This is a 2x4 pin header connector that provides access to the I2C signals SDA and SCL
as well as power from the 3.3V power bus and ground. This can be used to extend the I2C
bus off of the board and to power external I2C device. Digilent has cables and a selection
of I2C peripheral modules that can be accessed using this connector.
10) J7 – I2C #2 Daisy Chain Connector
This is a 2x4 pin header connector that provides access to the I2C signals SDA and SCL
as well as power from the 3.3V power bus and ground. This can be used to extend the I2C
bus off of the board and to power external I2C device. The jumpers for disabling the onboard pull-ups are adjacent to this connector.
11) Digital Signal Connectors
Some of the signals used by the Network Shield are provided on these connectors. The
rest of the signals are passed through the Network Shield.
www.digilentinc.com page 3 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 4

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
chipKIT Network Shield Hardware Description
Introduction
The following describes the hardware provided
by the Network Shield and its use. Appendices
at the end provide pin-out and connection
tables.
The Network Shield is designed to be used
with the chipKIT Max32 board. When used in
combination, the two boards provide the
necessary supporting hardware and
connectors to make use of all of the advanced
communications and networking features of
the PIC32MX795F512L microcontroller on the
Max32.
Ethernet Interface
The Network Shield provides the ability to
interface with 10Mbps or 100Mbps Ethernet
networks. The PIC32MX795 microcontroller on
the chipKIT Max32 board contains a 10/100
Ethernet Medium Access Controller (MAC).
The Network Shield provides an SMSC
LAN8720 Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
(PHY). Together, the MAC and PHY provide a
complete 10/100 Ethernet interface.
The RJ45 connector, J1, provides the physical
connection to an Ethernet network using a
standard Ethernet cable.
When the Ethernet controller is enabled in the
PIC32 microcontroller, it takes over the use of
a number of the microcontroller pins. All of the
signals from these pins are taken from
connector J10 on the Network Shield
(connector J8 on the Max32). Three of these
signals are also shared with connector J7 on
the Max32 and are analog pins A11, A12, and
A13. When the Ethernet interface on the
Network Shield is being used, these pins are
not available for other use, and nothing should
be connected to them to avoid interference
with the operation of the Ethernet interface.
All devices on an Ethernet network must have
a unique address. This address is used to
direct packets on the network to a specific
device and to identify the device that originated
a packet. An Ethernet MAC uses a 48-bit
address value, commonly called the ‘MAC
Address’. These address values are globally
unique to ensure that no two devices on a
network can have conflicting addresses. MAC
addresses are assigned by the IEEE. The
address to use with the Network Shield is
printed on a sticker attached to the bottom of
the board. The address is a twelve digit
hexadecimal number of the form:
00183Exxxxxx, where xxxxxx represents six
hexadecimal digits. This value is used to
initialize the Ethernet Controller MAC Station
Address registers in the Ethernet controller of
the PIC32MX795 microcontroller.
In order to connect to and operate with an
Ethernet network, the PIC32 microcontroller
must be running network protocol stack
firmware. Normally, the TCP/IP (Transmission
Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) network
protocol is used and “TCP/IP Stack” software
will be used. The Ethernet library provided for
use with the Network Shield board provides the
necessary stack support for use of the chipKIT
Max32/Network Shield from within the MPIDE
programming environment.
If the board is being used outside the MPIDE
programming environment, The Microchip
Applications Library, available for download
from the Microchip web site provides full
protocol stack support compatible with the
PIC32MX795 MAC and the LAN8720 PHY.
Microchip also provides numerous example
programs illustrating the use of their network
protocol stack for various applications.
When not using the either the chipKIT Ethernet
library or the Microchip network protocol stack,
refer to the manufacturer documentation for
the PIC32MX795 and LAN8720, plus network
www.digilentinc.com page 4 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 5

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
protocol documentation, for operation of the
Ethernet interface.
The PIC32MX795 microcontroller provides two
alternate sets of pins that can be used to
connect the MAC to the external PHY. It also
provides two alternate standard MAC/PHY
interface signaling conventions. The chipKIT
Max32/Network Shield are designed to use the
standard (not the alternate) pins, and to use
the RMII (not the MII) interface signaling
convention. These options are selected using
the configuration variables in the PIC32
microcontroller and are specified using the
#pragma config statement. To enable the
Ethernet controller in the correct configuration,
the following statements must appear in the
main program module:
#pragma config FETHIO=ON
#pragma config FMIIEN=OFF
The boot loader in the chipKIT Max32 board
sets this configuration by default. When using
the Network Shield within the MPIDE
environment no additional work is necessary.
When using it outside the MPIDE environment,
these configuration settings must be made.
The LAN8720 PHY has a reset signal, labeled
NRST in the schematic, that is used to reset
the PHY. This signal is connected to the
INT2/RE9 pin on the PIC32 microcontroller.
This pin is chipKIT digital pin 7 on the Max32
board. The NRST signal is active low.
Configure the microcontroller pin as an output
and drive it low to reset the PHY, or drive it
high to allow the PHY to come out of reset and
begin operation. The NRST signal is pulled low
on the Network Shield board, so that the PHY
is held in reset by default. To allow the PHY to
operate, this pin must be driven high. This
reset operation is not part of the Microchip
network protocol stack, and so driving NRST
high must be done before initializing the
Microchip network stack. When using the
chipKIT Ethernet library for the Network Shield,
this is done automatically by the library.
USB Interface
The PIC32MX795 microcontroller on the
Max32 contains a USB 2.0 Compliant, Full
Speed Device and On-The-Go (OTG)
controller. This controller provides the
following features:
USB full speed host and device support
Low speed host support
USB OTG support
Endpoint buffering anywhere in system
RAM
Integrated DMA to access system RAM
and Flash memory.
Connector J4 on the top left side of the board
is a standard USB type A receptacle. This
connector will generally be used when the
Max32/Network Shield has been programmed
to operate as a USB host. The USB device is
connected either directly, or via cable to this
connector.
Connector J2, on the bottom left side of the
Network Shield board is the Device/OTG
connector. This is a standard USB micro-AB
connector. Connect a cable with a micro-A
plug (optionally available from Digilent) from
this connector to an available USB port on a
PC or USB hub for device operation.
When the USB controller in the PIC32
microcontroller on the Max32 board is in use, it
takes over the use of several of the pins. The
signals provided by these pins appear on
connector J13 on the Network Shield
(connector J9 on the Max32). Two addition
signals are used, when doing USB hosting.
These signals appear on AN5 and digital pin 2.
These pins are not available when using the
USB interface.
When operating as a USB device, the chipKIT
Max32/Network Shield will normally be a self
powered device. To operate as a self powered
device, an external power supply should be
connected to the external power connector, J2
on the Max32 board. If the external power
supply is a regulated 5V supply, jumper JP1 on
www.digilentinc.com page 5 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 6

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
the Max32 should be set in the BYP position to
bypass the on-board 5V regulator.
The Max32/Network Shield can also be
operated as a self powered device powered by
the USB connector, J1, on the Max32. This is
the connector used by the USB Serial
converter. When operated this way, the
Max32/Network Shield will be a bus powered
device from the perspective of the USB port
connected to J1, and a self powered device
from the perspective of the port connected to
the USB connector J2 on the Network Shield.
Operation of the Max32/Network Shield as a
bus powered device is possible although not
recommended in most cases. The USB bus
voltage from USB connector J2 appears on pin
1 of jumper JP4. Remove the shorting block
from JP4, and jumper from pin 1 to any point
on the board that connects to the 5V bus,
VCC5V0. The VCC5V0 bus can be accessed
from power connector J17, pin 3. It can also be
accessed from either pin of J14, the uppermost
two pins on the connector on the right edge of
the board. When operating the board in this
way, be aware that if the USB serial converter
on the Max32 is connected to a live USB port,
the 5V power supplies of the two USB ports
(the one connected to the Max32 and the one
connected to the Network Shield) will be
shorted together. If these are not the same
power supply (i.e. both USB ports are on the
same PC), one or both USB ports and/or the
Max32/Network Shield may be damaged.
When operating as a USB host, the
Max32/Network Shield should be externally
powered. Connect a power supply to the
external power connector, J2, on the Max32. If
the external supply is a regulated 5V supply,
place JP1 on the Max32 in the BYP position to
bypass the 5V regulator. The power supply
used must be able to supply enough current to
power both the Max32/Network Shield, and the
attached USB device, as the Max32/Network
Shield provides power to the attached USB
device when operating as a host.
Jumper JP4 on the Network Shield is used to
route power to the host connector being used.
Place the shorting block in the “A” position
when using the standard USB type A (host)
Connector, J4. Place the shorting block in the
“MICRO” position for use with the USB microAB (OTG) connector, J2.
When operating as a USB host, the
PIC32MX795 microcontroller controls
application of power to the connected device
via the VBUSON control pin (labeled VBUSON
in the schematic). Bus power is applied to the
USB bus by driving the VBUSON pin high.
Power is removed from the bus by driving the
VBUSON pin low. The VBUSON pin is
accessed via bit 3 of the U1OTGCON register.
The VBUSON signal is shared with same
microcontroller pin as analog input A5 and
digital pin 59.
The VBUSON pin drives the enable input of a
TPS2051B Current-Limited Power Distribution
Switch to control the application of USB power
to the host connector. This switch has overcurrent detection capability and provides an
over-current fault indication by pulling the
signal USBOC low. The over-current output pin
can be monitored via the INT1/RE8 pin on the
PIC32MX795 microcontroller. This signal
appears on connector J14, pin 5 on the Max32
board, and is chipKIT digital pin 2. Details
about the operation of the TPS2051B can be
obtained from the data sheet available at the
Texas Instruments web site.
The VBUSON signal is shared with same
microcontroller pin as analog input A5 and
digital pin 59. This pin is not available for other
uses when operating as a USB host. If the
Max32/Network Shield is not being used as a
USB host, the use of A5/pin 59 can be
recovered by cutting the trace on the bottom of
JP3. USB Host capability can be restored by
soldering a two pin header to JP3 and
installing a shorting block.
The PIC32 USB controller can be accessed
using the chipKIT USB libraries for use within
the MPIDE environment.
www.digilentinc.com page 6 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 7

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
When using the Max32/Network Shield outside
the MPIDE environment, the Microchip
Application Library provides USB stack code
that can be used with the Max32/Network
Shield. There are reference designs available
on the Microchip web site demonstrating both
device and host operation of PIC32
microcontrollers. These reference designs are
suitable to use for developing USB firmware for
the Max32/Network Shield.
CAN Interfaces
The Controller Area Network (CAN) is a control
networking standard originally developed for
use in automotive systems, but has since
become a standard used in various industrial
control and building automation networking
applications as well.
The PIC32MX795 microcontroller on the
Max32 contains two independent CAN network
controllers. These CAN controllers in
combination with two Microchip MCP2551
CAN transceivers on the Network Shield allow
the Max32/Network Shield to operate on one
or two independent CAN networks.
When not using the MPIDE environment, refer
to the PIC32MX7XX data sheet and the PIC32
Family Reference Manual, plus CAN network
documentation for information on operation of
the CAN controllers and CAN networking in
general.
The PIC32MX795 microcontroller provides two
sets of pins that can be used to connect the
CAN controllers to the external transceivers.
The Max32/Network Shield is designed to use
the alternate (not the standard) pins. This
selection is made using the configuration
variables in the microcontroller, set using a
#pragma config statement. To select the use
of the alternate interface pins, the following
statement must appear in the main program
module:
#pragma config FCANIO=OFF
When using the Max32/Network Shield within
the MPIDE environment, the boot loader on the
Max32 boards sets this configuration
automatically, so nothing needs to be done in
this case. When using the boards outside the
MPIDE environment, this configuration setting
is required.
The pins on the PIC32MX795 microcontroller
used by signals for the CAN1 controller to
connect to its transceiver are shared with two
of the signals for UART3B and SPI port 3A.
These signals appear on pins 14 & 15 of
connector J4 on the Max32 board. To recover
the use of these pins if both CAN networks are
not needed, jumpers JP1 and JP5 are provided
on the Network Shield. There are cut-able
traces on the bottom of the board between the
pins of JP1 and JP5. Cut these traces to
disconnect the transceiver for CAN1. To
restore the connection, load two pin headers
for JP1 and JP5 and install shorting blocks on
the two jumpers.
The pins on the PIC32MX795 microcontroller
used by the signals for CAN2 appear on
connector J13 on the Network Shield
(connector J9 on the Max32), pins 15 and 16.
These are digital pins 22 and 23. These pins
are not available for other use when using
CAN2.
There is no standard connector for use with
CAN networks. The Network Shield provides
two 2x6 pin header connectors for access to
the CAN signals. Connector J3 provides
access to the signals for the CAN1 network
controller, and connector J5 provides access to
the signals for CAN2. Refer to the schematic
for the Network Shield board or the tables at
the end of this document for information on the
connectors and signals. Digilent 6-pin or 2x6 to
dual 6-pin cables can be used to daisy chain
Digilent boards together in a CAN network. A
Digilent 6-Pin cable in combination with a
Digilent PmodCON1 Screw Terminal
Connector module can be used to connect the
Max32/Network Shield to other network wiring
configurations.
www.digilentinc.com page 7 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 8

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
The CAN network standard requires that the
nodes at each end of a network provide 120
ohm termination. The Network Shield provides
the termination resistors and jumpers to
enable/disable them depending on the location
of the board in the network. Jumper JP6 is
used to enable/disable the termination resistor
for the CAN1 network, and JP8 is used to
enable/disable the termination resistor for
CAN2. Install a shorting block on the jumper
pins to enable the termination resistor, or
remove the shorting block to disable the
termination resistor.
I2C Busses and Connectors
The Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2CTM) Interface
provides a medium speed (100K or 400K bps)
synchronous serial communications bus. The
I2C interface provides master and slave
operation using either 7 bit or 10 bit device
addressing. Each device is given a unique
address, and the protocol provides the ability
to address packets to a specific device or to
broadcast packets to all devices on the bus.
Refer to the Microchip PIC32MX7XX Data
Sheet and the PIC32 Family Reference
Manual for detailed information on configuring
and using the I2C interface.
The PIC32MX795 microcontroller on the
Max32 provides for up to five independent I2C
interfaces. The Network Shield is designed to
provide access to two of these interfaces I2C
#1 (SCL1, SDA1) and I2C #2 (SCL2, SDA2).
I2C #1 is the bus accessed through the
standard chipKIT Wire library. There are two
sets of connectors on the board for access to
the two I2C ports. Connector J7 provides
access to I2C port #1 while connector J6
provides access to I2C port #2.
The user should note that external interrupt 3
and SCL1 share the same pin on the
PIC32MX795. External interrupt 4 and SDA1
also share the same pin. Therefore, external
interrupts 3 and 4 should not be used
simultaneously with I2C bus #1.
One I2C device is provided on the Network
Shield. This is a 256Kbit EEPROM connected
to the I2C #1 bus.
I2C Connectors: Connectors J6 and J7 can be
used to extend the I2C busses off of the board
to connect to external I2C devices. These are
standard 2x4 pin header connectors with
0.100” spaced pins. They provide access to
the I2C signals, SCL and SDA, plus VCC3V3
and ground. The VCC3V3 can be used to
power external I2C devices.
The I2C bus uses open collector drivers to
allow multiple devices to drive the bus signals.
This means that pull-up resistors must be
provided to supply the logic high state for the
signals. The Network Shield provides 2.2Kohm
pull-up resistors on I2C #1. As I2C #1 is the bus
with the EEPROM, these pull-up resistors are
permanently connected.
Jumpers JP9 & JP12 are provided to allow I2C
#1 to be disconnected from the Network
Shield, if it not being used and is interfering
with the use of the associated pins. There are
cut-able traces on the underside of the board
between the pins of these jumpers. Cut these
traces to disconnect SCL1 and SDA1 from the
Network Shield. To restore the connection,
load two pin headers for JP9 and JP12 and
install shorting blocks. If this is done, it is still
possible to access the on-board EEPROM by
connecting SCL and SDA from I2C #2 by
installing jumper wires between connector J6
and J7. The EEPROM will then appear on I2C
bus #2.
The logic high pull-up for I2C #2 is provided by
sourcing current mirrors instead of resistors.
These current mirrors source approximately
1.7mA. The use of current mirrors provides
faster rise times on the I2C signals and
provides the ability to drive longer cable runs
reliably than would be the case with simple
pull-up resistors.
Generally, only one set of pull-ups are used on
the bus. Jumpers JP10 and JP11 can be used
to disable the on-board pull-ups on I2C #2 if a
www.digilentinc.com page 8 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 9

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
different value is needed or some other device
on the bus is providing the pull-ups or if I2C #2
isn’t being used and the pull-ups are interfering
with the use of the pins. The on-board pull-ups
are enabled by install shorting blocks on JP10
and JP11. Removing the shorting blocks
disables the pull-ups.
Digilent has several small I/O modules
available that can be connected using the I2C
connector. These include a 3-axis
accelerometer, 4-channel, 12-bit A/D
converter, serial character LCD panel, 3-axis
gyroscope, real-time clock/calendar, and I/O
expander.
EEPROM: A 256Kbit (32Kbyte), I2C EEPROM
is provided using a Microchip 24LC256. This
EEPROM, IC5, is located on the bottom of the
board.
The EEPROM is on I2C bus #1, and its seven
bit I2C device address is ‘1010000’.
Digilent provides a library for accessing this
EEPROM. The library is available on the
Digilent web site and in the third party libraries
repository on github.
For complete technical documentation on the
24LC256, refer to the data sheet available on
the Microchip web site.
32.768Khz Oscillator
A 32.768Khz oscillator is provided to use as a
clock source for the Real Time Clock/Calendar
(RTCC) peripheral in the PIC32MX796
microcontroller on the Max32 board. The
output of this oscillator connects to pin 12 or
connector J11.
On the Max32 board, this signal connects to
signal RC13, which connects to pin 73 on the
PIC32 microcontroller. This pin provides the
secondary oscillator input, which can be used
to clock the RTCC in the PIC32
microcontroller.
www.digilentinc.com page 9 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 10

chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
chipKIT
Pin #
PIC32
Pin #
Pin
Signal
Notes
46
88
J10-8
C1TX/ETXD0/PMD10/RF1
ETXD0
45
87
J10-9
C1RX/ETXD1/PMD11/RF0
ETXD1
47
83
J10-7
ETXEN/PMD14/CN15/RD6
ETXEN
48
68
J10-6
RTCC/EMDIO/AEMDIO/IC1/RD8
EMDIO
49
71
J10-5
EMDC/AEMDC/IC4/PMCS1/PMA14/RD11
EMDC
53
14
J10-1
ERXCLK/AERXCLK/EREFCLK/AEREFCLK/SS2A/U2BRX/
U2ACTS/PMA2/CN11/RG9
EREFCLK
43
12
J10-11
ERXDV/AERXDV/ECRSDV/AECRSDV/SCL2A/SDO2A
UATX/PMA3/CN10/RG8
ECRSDV
40
35
J10-14
AN11/ERXERR/AETXERR/PMA12/RB11
ERXERR
42
41
J10-12
AN12/ERXD0/AECRS/PMA11/RB12
ERXD0
41
42
J10-13
AN13/ERXD1/AECOL/PMA10/RB13
ERXD1
7
19
J11-15
AERXD0/INT2/RE9
NRST
chipKIT
Pin #
PIC32
Pin #
Pin
Signal
Notes
27
57
J13-11
USBD+/RG2
26
56
J13-12
USBD-/RG3
25
51
J13-13
USBID/RF3
A5/59
20
J9-6
AN5/C1IN+/VBUSON/CN7/RB5
2
18
J11-5
AERXD0/INT1/RE8
chipKIT
Pin #
PIC32
Pin #
Pin
Signal
Notes
14
39
J16-8
AC1TX/SCK3A/U3BTX/U3ARTS/RF13
CAN1
15
40
J16-7
AC1RX/SS3A/U3BRX/U3ACTS/RF12
CAN1
22
7
J10-16
T3CK/AC2TX/RC2
CAN2
23
8
J10-15
T4CK/AC2RX/RC3
CAN2
Appendix A: chipKIT Network Shield Pinout Tables
Pins Used by the Ethernet Interface
Pins Used by USB Interface
Pins Used by CAN Interfaces
www.digilentinc.com page 10 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 11
chipKIT Network Shield Reference Manual
chipKIT
Pin #
PIC32
Pin #
Pin
Signal
Notes
66
21
J16-1
AETXCLK/SCL1/INT3/RA14
I2C1 – also attached to
EXT INT 3
67
20
J16-2
AETXEN/SDA1/INT4/RA15
I2C1 – also attached to
EXT INT 4
58
12
J8-9
SCL2/RA2
I2C2
59
13
J8-11
SDA2/RA3
I2C2
Pins Used by I2C Interfaces
www.digilentinc.com page 11 of 11
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved. Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
 Loading...
Loading...