Page 1
1300 Henley Court
Pullman, WA 99163
509.334.6306
www.digilentinc.com
Cmod S6™ Reference Manual
Revised January 30, 2014
This manual applies to the Cmod S6 Rev A
DOC#: 502-282
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 1 of 4
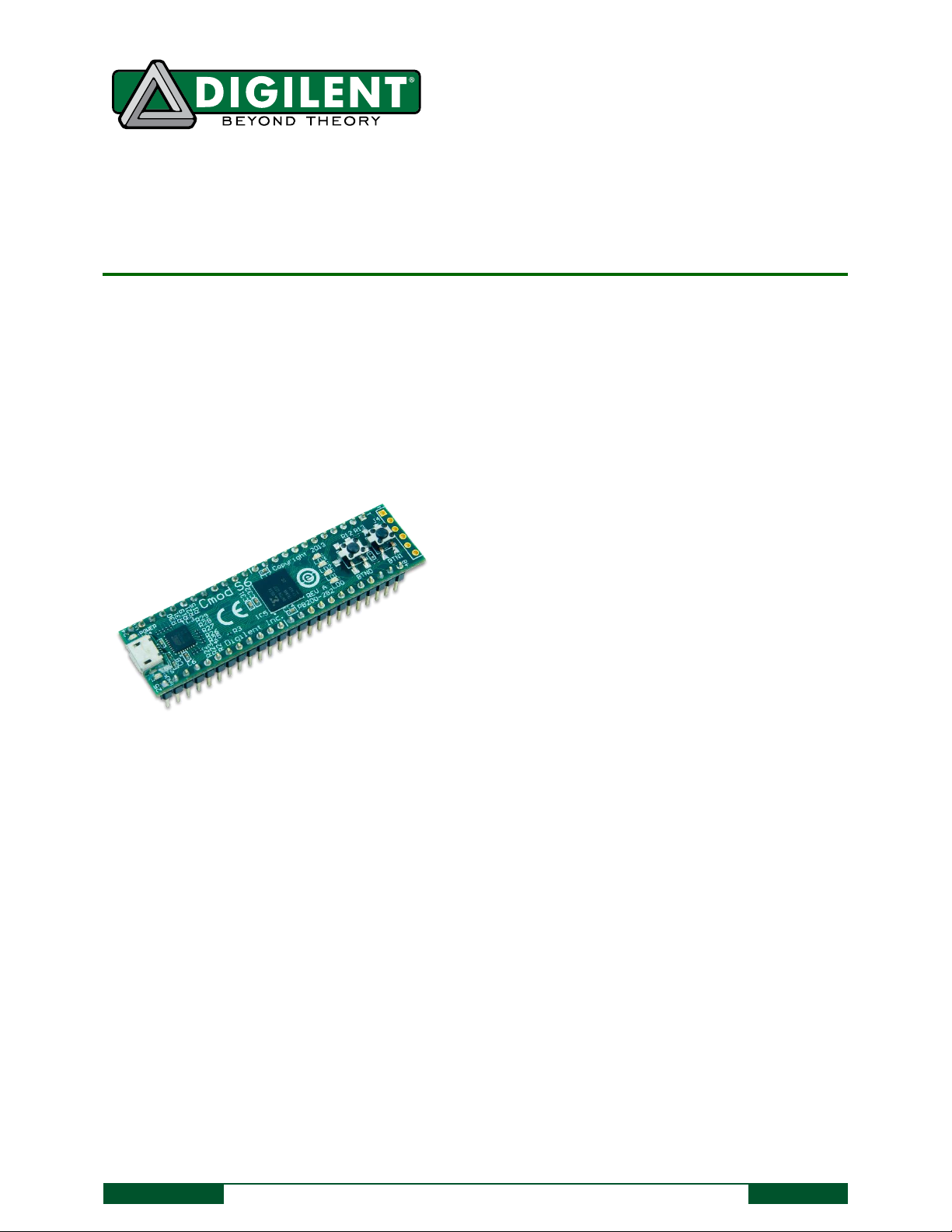
The Cmod S6.
Spartan 6 XC6SLX4-2CPG196 FPGA Features include:
600 slices (each with 4 LUTs and eight flip-flops);
8 DSP slices;
216Kbits of block RAM;
2 CMTs (4 DCMs and 2 PLLs).
Cmod S6 features include:
16Mbyte Spansion Quad SPI Flash for storing FPGA
configurations and/or user data;
46 FPGA GPIO signals brought to DIP pins;
Two on-board clock sources;
4 user LEDs and 2 user buttons;
On-board Adept USB2 port for configuration, test and
communications interfaces.
Overview
The Digilent Cmod S6 is a small, 48-pin DIP form factor board built around a Xilinx Spartan 6 LX4 FPGA. The board
also includes a programming ROM, clock source, USB programming and data transfer circuit, power supplies, and
basic I/O devices. There are 46 FPGA I/O signals that are routed to 100-mil-spaced through-hole pins, making the
Cmod S6 well suited for use with solderless breadboards. At just .7” by 2.6” inches, it can also be loaded in a
standard socket and used in embedded systems.
1 Configuration
The FPGA on the Cmod S6 can be configured using the on-board Adept USB interface or from the on-board Quad-
SPI Flash memory. Configuration files can be programmed using Xilinx’s ISE 14.2 (or higher) development tools,
using Digilent’s Adept system, or using older versions of the Xilinx tools if Adept is also installed. Xilinx’s ISE/Impact
programming tool and Digilent’s Adept tool will recognize the board and/or FPGA when the board is attached to a
PC using a Type-A to micro-B USB cable.
Xilinx’s iMPACT tool and Digilent’s Adept can both be used to program the FPGA, and iMPACT can also be used to
program the on-board QSPI Flash. Please refer to the ISE and/or Adept documentation for more information on
using the configuration software.
When using Digilent’s Adept software for programming, a dialog box available from the Config tab can be used to
select a configuraiton file. Pressing the Program button will program the FPGA with the selected file. This may
result in a warning that the configuration file was built for an unknown device; however, this warning can be
ignored.
When using Xilinx’s iMPACT 14.2 (or higher) software for programming, a .bit file can be associated with the FPGA
by right-clicking on the FPGA icon, selecting the desired .bit file, and clicking Program.
Page 2

Cmod S6™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 2 of 4
On power-up, if the FPGA detects a valid bitstream stored in the Quad SPI flash memory, the FPGA will
automatically configure itself with that bitstream. If necessary, the user can reconfigure the FPGA with a different
bitstream at any point after power-up using iMPACT or Adept.
2 FPGA
The Cmod S6 features a Xilinx Spartan 6 XC6SLX4-2CPG196 FPGA. Of the 92 available unshared FPGA I/O pins, 46
are routed to through-hole pins on the DIP module, 24 are not connected, 14 are used by the programming
interface, and 7 drive on-board I/Os (4 leds, 2 pushbuttons, and 2 clock inputs). Several of the 46 signals connected
to FPGA pins are routed to clock buffers, and several are routed to matched pairs. Please see the schematic for
more information.
The Spartan 6 LX4 FPGA includes 3,840 6-LUT logic cells, 4,800 flip-flops, 216Kb of block RAM, 8 DSP slices, and two
clock management tiles, each with two DCMs and one PLL. The fabric can support internal clock speeds above
400MHz, allowing the Cmod S6 to host high-speed or complex designs. Please see the Spartan 6 user manual
available at www.xilinx.com for more detailed information.
3 Power
The Cmod S6 can be powered either from a USB-connected computer, or from a power source connected to DIP
pin 24 that delivers voltage in the range of 5VDC to 15VDC (the power input on pin 24 is most useful when the
board is used in an embedded system or in a solderless breadboard). The two sources are diode-OR’ed on the
board, so both may be connected simultaneously.
The FPGA and other on-board devices require 3.3VDC and 1.2VDC – both of these voltages are generated from the
input supply using Texas Instrument’s TPS62170 switching regulators. Total current draw depends on FPGA
configuration. When about half the FPGA is configured and running at 8MHz, the board consumes about 180mA
from the main supply.
4 Clocks
An 8MHz and a 1Hz clock are available to the FPGA. Both are generated from the on board USB processor, both are
routed to clock inputs on the FPGA, and both run continuously. The 8MHz clock, called “FPGA-GCLK”, can be used
with the FPGA’s clock manager to create a wide range of frequencies, even beyond 200MHz. The 1Hz clock
provides a simple timing signal for basic experiments and low-frequency needs.
5 Quad SPI Flash Memory
The Cmod S6 includes a non-volatile 16Mbyte Spansion Quad SPI Flash that can store FPGA configuration files as
well as user data. The Spansion device supports the standard 4-wire SPI protocol, as well as the newer Quad I/O
and Dual I/O protocols at speeds from 50 MHz to 133 MHz, depending on the protocol and command used. For
more information on the SPI Flash memory, please see the “S25FL128S and S25FL256S Data Sheet” at
www.spansion.com.
To achieve the fastest programming speed over the Digilent USB-JTAG connection, when generating the bitstream
in Project Navigator, change the SPI bus width to four and enable bitsream compression. To do this, simply select
“Generate Programming File” and navigate to Process>Process Properties. In the pop-up menu, enable –g
Compress under “Synthesis Options” and set –g SPI_buswidth to four under “Configuration Options”.
Page 3

Cmod S6™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3 of 4
Address (HEX
value)
Function
0 (0x0)
Stores the logic value present on pins 1 through 8
1 (0x1)
Stores the logic value present on pins 9 through 16
2 (0x2)
Stores the logic value present on pins 17 through 23
3 (0x3)
Stores the logic value present on pins 26 through 33
4 (0x4)
Stores the logic value present on pins 34 through 41
5 (0x5)
Stores the logic value present on pins 42 through 48
6 (0x6)
Controls the I/O state of pins 1 through 8
7 (0x7)
Controls the I/O state of pins 9 through 16
8 (0x8)
Controls the I/O state of pins 17 through 23
9 (0x9)
Controls the I/O state of pins 26 through 33
10 (0xA)
Controls the I/O state of pins 34 through 41
11 (0xB)
Controls the I/O state of pins 42 through 48
6 Digilent EPP Interface
The Cmod S6 implements the Digilent EPP interface (DEPP) for 8-bit parallel data transfers between the FPGA and
a computer attached via the USB Micro connector. DEPP is based on a set of API’s available in the Adept 2 public
SDK, available from the Adept product page at www.digilentinc.com. These APIs work in concert with firmware
running on the USB controller to provide a high-level software interface for transporting data between a PC and
the Cmod S6.
To use the DEPP interface, the host PC must use software built from the Adept SDK DEPP libraries, and the FPGA
has to be running a configuration that implements a DEPP controller. For a description of the DEPP library API,
refer to the “DEPP Programmer's Reference Manual” included with the Adept 2 SDK. For information on designing
a DEPP controller, refer to the “Digilent Asynchronous Parallel Interface (DEPP)” document, also included with the
Adept 2 SDK.
7 Factory Loaded User Demo
The Quad SPI Flash is loaded with a configuration file at the factory. When powered on, the file will configure the
FPGA such that the buttons control the states of two LEDs, while the other two LEDs toggle at a speed of about 1
Hz. The general purpose I/O pins are initially configured as inputs, and are pulled up internally by the FPGA to read
a logic level ‘1’. Each individual pin can be controlled using the DEPP interface to either drive the pin as an output,
or to read the logic level that is present on the pin as an input.
The I/O pins can be controlled by writing to specific DEPP register addresses. To test the interface, the “Register
I/O” tab within the Adept 2 application can be used. Table 1, shown below, gives a description of register
addresses and functions.
Table 1. DEPP Register Map for factory loaded configuration.
The least significant bit in any register corresponds to the smallest pin number that it controls. Registers 6 through
11 will set up a pin controlled by registers 0 through 5 as an input if the corresponding bit in the register is a logic
Page 4

Cmod S6™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 4 of 4
‘1’ and will set up the pin as an output if the corresponding bit in the register is a logic ‘0’. For example, if the value
stored in register 6 is 11110000 in binary (0xF0 in HEX), the pins 1-4 on the Cmod S6 will be set as outputs and pins
5-8 will be set as inputs. When a pin is configured as an output, it will initially be driven low (logic ‘0’).
The source code for this project can be found on the Cmod S6 product page of the Digilent website,
www.digilentinc.com.
 Loading...
Loading...