Page 1
1300 Henley Court
Pullman, WA 99163
509.334.6306
www.digilentinc.com
chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Revised November 6, 2013
This manual applies to REV E of the board.
DOC#: 502-269
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 1 of 11
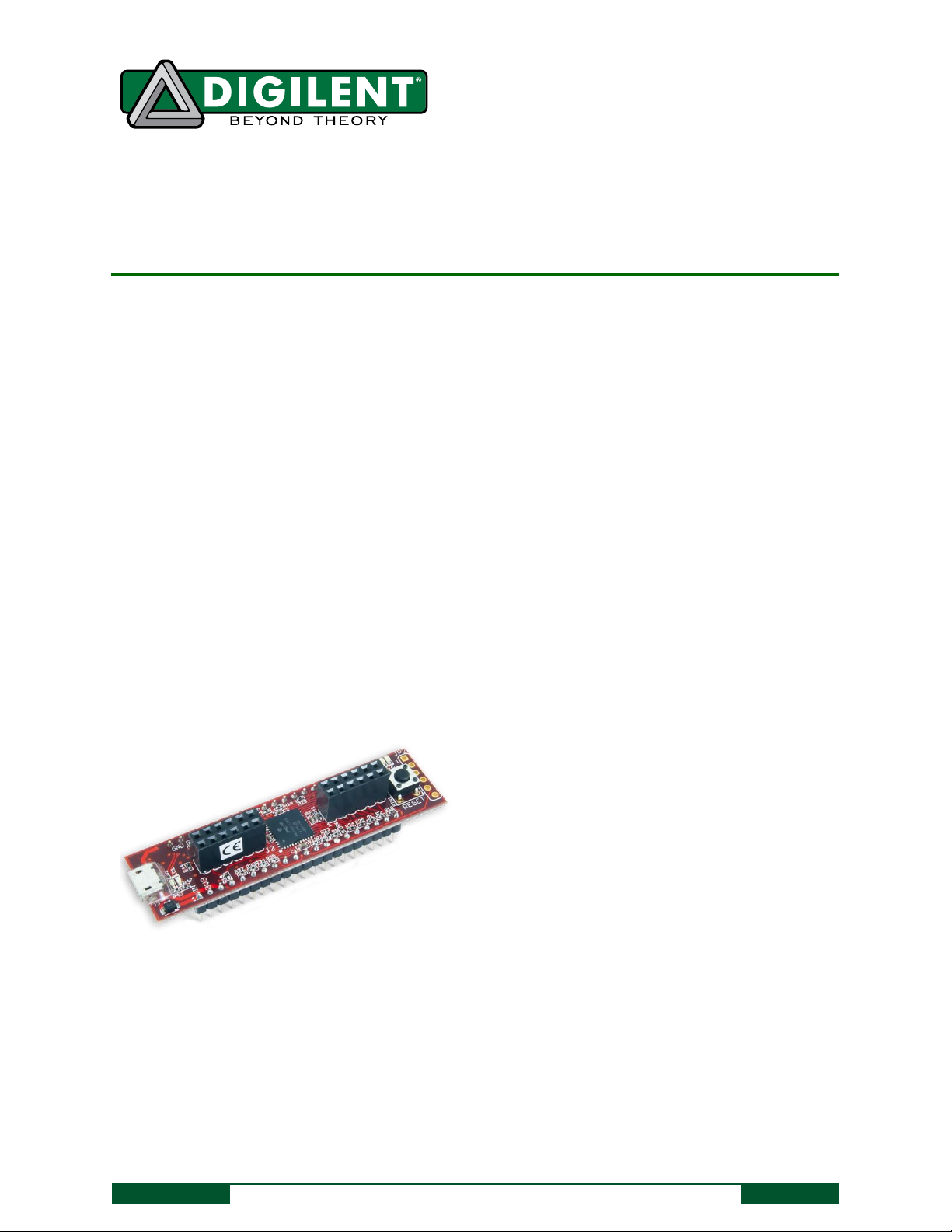
The chipKIT Cmod.
Microchip® PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller
(40/50 Mhz 32-bit MIPS, 128K Flash, 32K SRAM)
Convenient 600-mil, 2x20-pin DIP package
5V – 12V recommended operating voltage
33 available I/O pins
Two user LEDs
PC connection uses a USB A to micro B cable (not
included)
13 analog inputs
3.3V operating voltage
Two Pmod connectors for Digilent peripheral
module boards
Overview
The chipKIT Cmod is a chipKIT/MPIDE compatible board from Digilent. It combines a Microchip®
PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller with a convenient 600-mil, 40-pin DIP package and two Digilent Pmod
connectors. Digilent’s Cmod boards are ideally suited for breadboards or other prototype circuit designs where the
use of small surface mount packages is impractical.
The chipKIT Cmod takes advantage of the powerful PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller. This microcontroller
features a 32-bit MIPS processor core running at 40Mhz, 128K of flash memory, and 32K of SRAM data memory.
The chipKIT Cmod can be programmed using the Multi-Platform Integrated Development Environment, MPIDE, an
environment based on the open source Arduino IDE modified to support the PIC32 microcontroller. The board
provides everything needed to start developing embedded applications using the MPIDE.
The chipKIT Cmod is also fully compatible with the advanced Microchip MPLAB® IDE. To develop embedded
applications using MPLAB®, a separate device programmer/debugger, such as the Digilent chipKIT PGM or the
Microchip PICkit™3 is required.
Features Include:
Page 2
chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 2 of 11
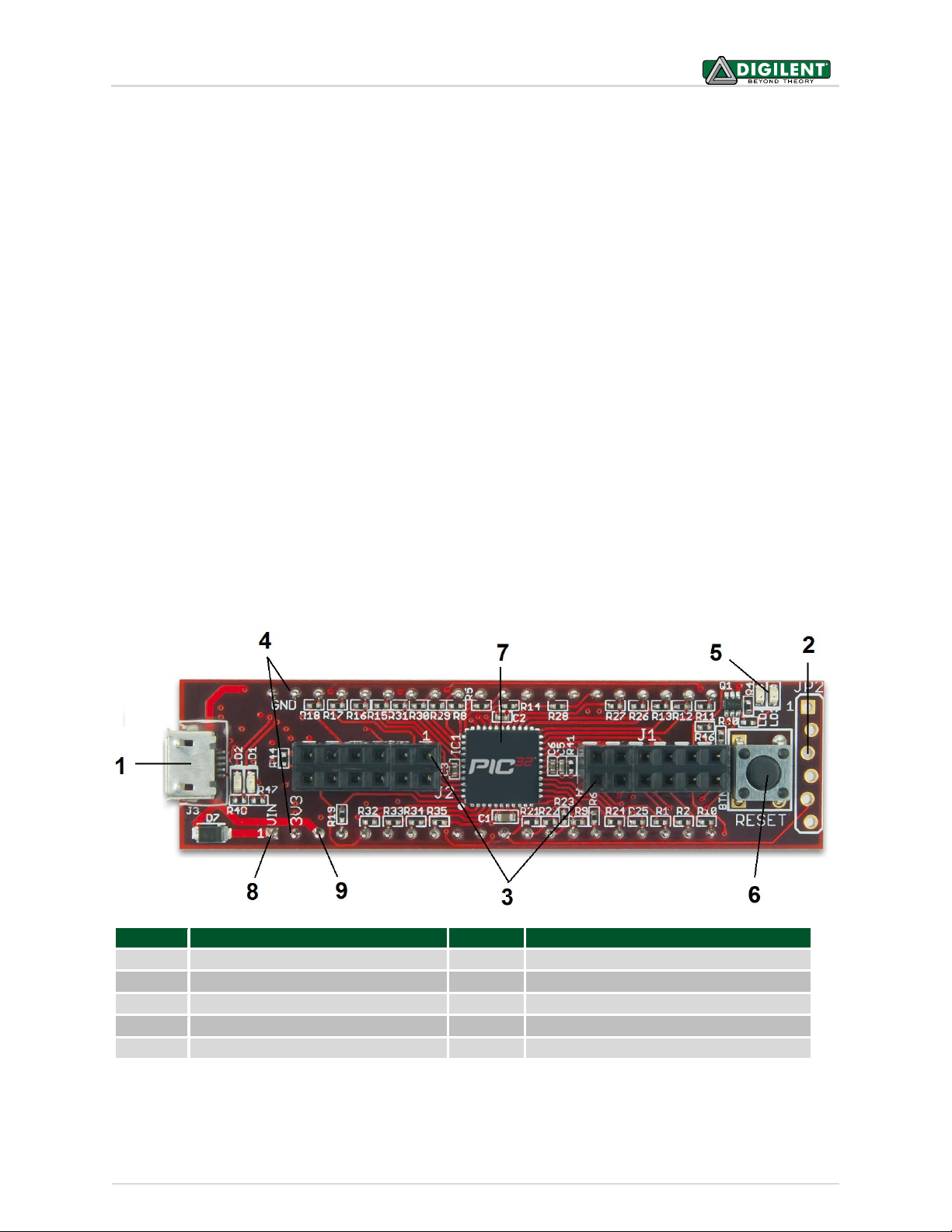
Call Out
Component Description
Call Out
Component Description
1
J3 USB Connector for USB Serial Converter
6
Reset Button
2
JP2 Microchip ICSP Connector
7
PIC32 Microcontroller
3
J1-J2 Digilent Pmod Connectors
8
DIP Pin 1 External Power Connector
4
40 Pin DIP connector
9
DIP Pin3 USB 5.0V Power Connector
5
User LEDs
1 Functional Description
The PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller features a 32-bit MIPS processor core capable of running at up to 50 MHz.
When used with MPIDE, thechipKIT Cmod operates the microcontroller at 40Mhz by default. The microcontroller
features 128 KB of flash program memory and 32 KB of SRAM data memory. Programming the chipKIT Cmod can
be done using the Multi-Platform Integrated Development Environment (MPIDE) or with the advanced Microchip
MPLAB® IDE with the addition of a PICKit3 or chipKIT PGM in-system programmer/debugger.
The chipKIT Cmod provides 33 I/O pins located on the 40-pin DIP package. Some pins share functions with the
onboard circuits such as the on-board LEDs, the UART data lines used by the USB serial converter, or the Pmod
connectors (see the schematic for details). If these peripherals are needed in the design, then the microcontroller
can be reconfigured to allow these pins to be used for other purposes. Thirteen of the digital I/O pins can also be
used as analog input pins.
The PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller supports peripheral functions such as UART, SPI, and I2C, as well as pulsewidth-modulated outputs. To use the peripheral functions the PIC32MX1xx family of microcontrollers features a
mappable I/O system called peripheral pin select (PPS), which allows select peripheral functionality to be mapped
to multiple pins on the device. The default chipKIT Cmod board support files provide a specific mapping of
peripheral functions to microcontroller pins. This default pin mapping can be over-ridden by the user’s sketch if a
different mapping is desired.
1.1 ChipKIT Cmod Hardware Overview
Page 3

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3 of 11
2 ChipKIT Cmod Hardware Description
MPIDE and USB Serial Communications
The chipKIT Cmod board is designed to be used with the Multi-Platform IDE (MPIDE). The MPIDE development
platform was created by modifying the Arduino™ IDE. It is backwards-compatible with the Arduino IDE.
The MPIDE uses a serial communications port to communicate with a boot loader running on the chipKIT Cmod
board. The serial port on the board is implemented using an FTDI FT232R USB serial converter. Before attempting
to use the MPIDE to communicate with the board, the appropriate USB device driver must be installed.
The chipKIT Cmod uses a standard micro-USB connector for connection to a USB port on the PC. A USB-A to MicroB cable, not supplied, is used to connect the board to a USB port on the host computer.
When the MPIDE needs to communicate with the chipKit Cmod board, the board is reset and starts running the
boot loader. The MPIDE then establishes communications with the boot loader and downloads the program to the
board.
When the MPIDE opens the serial communications connection on the PC, the DTR pin on the FT232R chip is driven
low. This pin is coupled through a capacitor to the MCLR pin on the PIC32 microcontroller. Driving the MCLR line
low resets the microcontroller, restarting execution with the boot loader. See the net labeled P32_RST in the
schematic for further detail about this connection. The P32_RST net is also brought out to DIP pin 9.
Two red LEDs (LD1 and LD2) will blink when data is being sent or received between the chipKIT Cmod and the PC
over the serial connection.
Power Supply
The chipKIT Cmod is designed to be powered via USB (J3) or from an external power supply connected to pin 1 of
the DIP package.
The chipKIT Cmod has a single voltage regulator which regulates either 5V from USB, or a maximum of 15V
external voltage. A series diode between the DIP pin 1 (VIN) and DIP pin 3 (USB5V0) prevents an external voltage
applied to pin 1 being fed back onto the USB 5V supply when powering the board via DIP pin 1. All power supply
options are regulated to 3.3 V to provide power to the VCC3V3 bus that powers the PIC32 microcontroller. The
output of the on-board 3.3V regulator is available at DIP pin 2 and can be used to power external circuitry.
The 3.3V regulator is a Microchip MCP1703. The regulator is rated for a maximum output current of 250mA. The
absolute maximum input voltage for the MCP1703 is 16V. This regulator has internal short circuit protection and
thermal protection. It will get noticeably warm when the current consumed by the VCC3V3 bus is close to the
250mA maximum.
5V Compatibility
The PIC32 microcontroller operates at 3.3V. There are two issues to consider when dealing with 5V compatibility
for 3.3V logic. The first is protection of 3.3V inputs from damage caused by 5V signals. The second is whether the
3.3V output is high enough to be recognized as a logic high value by a 5V input. When driving a high impedance
input (typical of CMOS logic), the output high voltage from the PIC32 microcontroller will be close to 3.3V. Some
Page 4

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 4 of 11
5V devices will recognize this voltage as a logic high input, and some won’t. Many 5V logic devices will work
reliably with 3.3V inputs. Please check the datasheet for the 5V components you are using to ensure that 3.3V will
satisfy the logic high conditions for the components.
Some of the digital I/O pins on the PIC32 microcontroller are 5V tolerant. The analog capable I/O pins are not 5V
tolerant. The following pins are 5V tolerant: 4-11, 14-15, 27, 31, and 33-38. The other pins are not 5V tolerant and
5V signals should not be applied to those pins. All I/O pins have a 200 ohm resistor in series between the
microcontroller pin and the connector pins to provide short circuit protection. These resistors will limit the output
drive strength of the pins to approximately +/- 2mA.
PmodTM Connectors
The chipKIT Cmod has two connectors for connecting Digilent Pmod peripheral modules. The Pmod connectors,
labeled J1 and J2, are 2x6, female pin header connectors.
The Pmod connectors on the chipKIT Cmod are both twelve-pin connectors. The connectors use standard pin
headers with 100-mil spaced pins. The twelve-pin connectors have the pins in a 2x6 configuration.
The twelve-pin connectors provide eight I/O signals, two 3.3V power pins, and two ground pins. The twelve-pin
connectors have the signals arranged so that one twelve-pin connector is equivalent to two of the six-pin
connectors. Pins 1–4 and 7–10 are the signal pins, pins 5 and 11 are the ground pins, and pins 6 and 12 are the
power supply pins.
The pin numbering that Digilent uses on the twelve-pin Pmod connectors is non-standard.
The upper row of pins are numbered 1–6, right to left (when viewed from the end of the connector), and the lower
row of pins are numbered 7–12, right to left. This is in keeping with the convention that the upper and lower rows
of pins can be considered to be two six-pin connectors stacked.
It is important to note that the Pmod connectors on the chipKIT Cmod are rotated 180 degrees in relation to each
other. Pin 1 of each Pmod connector is marked on the board. When viewing the top of the board, pin 1 of Pmod
connector J2 is the upper right pin, and pin 7 is immediately below it. For Pmod connector J1, pin 1 is in the lower
left corner and pin 7 is immediately above it. Connecting peripheral modules incorrectly could result in damaging
the peripheral module or the chipKIT Cmod.
See the attached pinout tables for more information about connecting peripheral modules and other devices to
the chipKIT Cmod. These tables describe the mapping between pins on the PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller and
the pins on the connectors.
Input/Output Connections
The chipKIT Cmod board provides 33 of the I/O pins from the PIC32MX150F128D microcontroller to pins on the DIP
connector.
The chipKIT Cmod and the MPIDE system uses logical pin numbers to identify digital I/O pins. All digital I/O pins
share their numbering with their DIP connector pin. Valid pin numbers on the chipKIT Cmod are 4-8, 10-27, and 29-
38. Pin numbers 1-3 and 39-40 refer to pins connected to power buses on the board and are not available for use
as I/O. Pin 9 can be used to reset the PIC32 microcontroller and pin 28 is unconnected. In addition, several of these
I/O pins share functionality with other devices on the board. See the attached pinout tables for more information.
Page 5

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 5 of 11
The DIP connector uses standard DIP package pin numbers. Pins 1- 20 count up from the square pad labeled ‘1’ on
the lower DIP connector. Pins 21-40 count up from the pin near the label ‘Q1’ to the pin labeled ‘GND’ on the other
DIP connector.
Pins 18 and 19 are normally the reference voltages for the microcontroller’s A/D converter, but can also be used as
digital I/O pins.
In addition to the connector pin, Pin 14 is also connected to the user LED LD3. Pin 12 also connects to the user LED
LD4.
In addition to digital I/O, there are analog inputs available on the board, called A0 through A12. These pins are
shared with digital pins 12, 13, and 16 through 26. Refer to the attached pinout tables for the correct mapping of
these signals.
Peripheral I/O Functions
The PIC32 microcontroller on the chipKIT board provides a number of peripheral functions. The following
peripherals are provided:
I2C: Synchronous serial interface. The I2C1 interface is available on pins 4 (SDA1) and 38 (SCL1). The I2C2 interface
is available on pins 22(SDA2) and 23(SCL2). Note that when using MPIDE, the only available I2C interface is I2C1.
Note: The I2C bus uses open collector drivers to allow multiple devices to drive the bus signals. This means that
pull-up resistors must be provided to supply the logic high state for the signals. These pull-up resistors are not on
the chipKIT Cmod board and must be provided externally. The required resistance of the pull-up resistor to use
depends on the total number of devices on the bus, the length of wire, and the clock speed being used. It
essentially depends on distributed capacitance on the bus. The higher the distributed capacitance and the faster
the clock speed, the smaller the resistance should be. Values typically used are in the range of 2K to 10K ohms.
User LEDs: Pins 12 (LD4) and 14 (LD3). Both Pin 12 and Pin 14 are shared between a connector pin on the chipKIT
Cmod and an LED. Driving the pin high turns the LED on, driving it low turns it off.
External Interrupts: Only INT0 is hard-mapped on the microcontroller. It is connected to Pin 37 of the chipKIT
Cmod. The other external interrupts are accessible via PPS described below.
A/D Converter Reference: Pin 18 is used to provide an external voltage reference to determine the input voltage
range of the analog pins. The maximum voltage that can be applied to this pin is 3.3V. This pin can also be used as
digital pin 18.
Reset: The PIC32 microcontroller is reset by bringing its MCLR pin low. The MCLR pin is connected to the P32_RST
net on the circuit board. A reset button is located on the right side of the board. Pressing this button resets the
PIC32 microcontroller.
Reset of the PIC32 microcontroller can be initiated by the USB serial converter. The USB serial converter brings the
DTR pin low to rest the microcontroller. The P32_RST net is connected to Pin 9 of the DIP package. This allows
external circuitry to reset the microcontroller, or to ensure that the circuitry is reset at the same time as the
microcontroller.
Page 6

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 6 of 11
Peripheral Pin Select
An advanced feature of the PIC32MX1xx/2xx families of microcontrollers is the ability to re-map the locations of
peripheral devices. This advanced feature is available only in MPLAB® IDE or MPLAB® X. For more detailed
information, refer to the PIC32MX1XX/2XX Data Sheet available from www.microchip.com.
The PPS Peripherals are pre-assigned to the following pins when programming the chipKIT Cmod with MPIDE.
These assignments are also included in the Notes sections of the attached pinout tables.
Output Compare: Pin 29 (OC1), Pin 38 (OC2), Pin 4 (OC3), Pin 22 (OC4), Pin 13 (OC5). Output compare allows for
the implementation of pulse width modulated (PWM) signals using the analogWrite() function.
Input Capture: Pin 36 (IC1), Pin 10 (IC2), Pin 31 (IC3), Pin 37 (IC4), Pin 25 (IC5). Input capture allows for the
synchronization of timers with captured signals, along with the execution of interrupts.
External Timer Input: Pin 30 (TCK1), Pin 18 (TCK2), Pin 27 (TCK3), Pin 32 (TCK4), Pin 26 (TCK5) allows for timers to
be clocked from external sources.
External Interrupt: Pin 33 (INT1), Pin 13 (INT2), Pin 7 (INT3), Pin 37 (INT4) allows for external interrupts to be
triggered in their own ISRs. Interrupts may be edge triggered or level triggered, though only one of rising, falling,
high, or low, may be chosen for trigger sensitivity.
Change Notice Pins: All change notice pins are matched with their chipKIT pin numbers (e.g. CN4 is associated with
Pin 4). There is a change notice pin for each I/O pin.
UART: Asynchronous serial port. Pin 23 (U1TX), Pin 5 (U1RX). These pins use UART1 on the PIC32 microcontroller
and are connected to the FT232RQ serial converter. It is possible to use these pins to connect to an external serial
device when not using the USB serial interface. Pin 20 (U2TX) and Pin 21 (U2RX) are used to implement UART2 on
the PIC32 microcontroller.
SPI: Synchronous serial port. Pin 24 (SS), Pin 35 (MISO), Pin 25 (MOSI), Pin 16 (SCK). This uses SPI1 on the PIC32
Microcontroller. SPI2 is implemented as Pin 33 (SS), Pin 36 (MOSI), Pin 32 (MISO), and Pin 17 (SCK).
When using the chipKIT Cmod with MPIDE, the SPI ports are accessed using either the standard chipKIT SPI library
or using the Digilent DSPI library. The standard SPI library supports access to a single SPI port, SPI1. This is accessed
using the SPI object.
The DSPI library supports access to both SPI ports. The DSPI0 object class is used to access the default SPI port,
SPI1. The DSPI1 object class is used to access SPI2.
Microchip Development Tool Compatibility
In addition to being used with the MPIDE, the chipKIT Cmod board can be used as a more traditional
microcontroller development board using Microchip Development Tools.
Unloaded connector JP2 on the right side of the Reset button is used to connect to a Microchip development tool,
such as the PICkit™3. The holes for JP2 are staggered so that a standard 100-mil spaced 6-pin header can press fit
to the board without the need to solder it in place. Any Microchip development tool that supports the PIC32
microcontroller family, and can be connected via the same 6-pin ICSP interface as the PICkit™3, can be used.
Page 7

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 7 of 11
DIP
Pin #
chipKIT
Pin #
Connector
Pin #
PIC32
Pin #
PIC32 Signal
Notes
1 - -
-
N/A
VIN/External
Power
2 - -
28/40
VDD
VCC3V3
3 - -
-
N/A
USB5V0/External
5V Power for USB
4 4 -
1*
RPB9/SDA1/CTED4/PMD3/RB9
OC3
5 5 -
2*
RPC6/PMA1/RC6
U1RX 6 6
J1-08
3*
RPC7/PMA0/RC7
7 7 J1-07
4*
RPC8/PMA5/RC8
INT3
8 8 J1-10
5*
RPC9/CTED7/PMA6/RC9
9 - -
18*
MCLR
RESET
10
10 - 8*
PGED2/RPB10/CTED11/PMD2/RB10
IC2
11
11 - 9*
PGEC2/RPB11/PMD1/RB11
12
12/A12
-
10
AN12/PMD0/RB12
LD4
Typically, a right-angle male connector is used in JP2 so that a PICkit™3 can be attached coplanar with the chipKIT
Cmod. The connector can be loaded from the top, or it can be loaded from the bottom. In either case, the PICkit™3
will be upside-down (button and LEDs not visible) while the chipKIT Cmod board is upright (button, LEDs, and
Pmod connectors visible). In some cases, because of mechanical clearance limitations, it may be necessary to use a
6-wire cable to connect a PICkit™3 to the chpKIT Cmod board.
The Digilent chipKIT PGM can also be used in place of a PICkit™3 to program the chipKIT Cmod with the Microchip
Development tools. The chipKIT PGM has a smaller form factor and does not need a 6-pin cable to connect to JP2.
The Microchip MPLAB® IDE or the MPLAB® X IDE can be used to program and debug code running on the chipKIT
Cmod board. These programs can be downloaded from the Microchip web site.
Using the Microchip development tools to program the board will cause the boot loader to be erased. To use the
board with the MPIDE again, it is necessary to program the boot loader back onto the board. The boot loader
compiled image can be found on the chipKIT Cmod producg page on the Digilent web site. The source code project
for the boot loader is available on the Git server www.github.com.
Pinout Tables
The following tables give the relationship between the chipKIT digital pin numbers, the connector pin numbers,
and the microcontroller pin numbers.
In the following tables, columns labeled chipKIT pin # refer to the digital pin number. This is the value that is
passed to the pinMode(), digitalRead(), digitalWrite(), and other functions to refer to the pin.
The signals mapped by using Peripheral Pin Select are included in the following tables. They are listed with the
default pins assigned to them when using MPIDE. If the locations of peripheral devices are re-mapped, these
signals may no longer be associated with the same pin as listed below.
Pinout Table by DIP Connector/ChipKIT Pin Number
Page 8

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 8 of 11
13
13/A11
-
11
AN11/RPB13/CTPLS/PMRD/RB13
OC5/INT2
14
14 - 12*
PGED(4)/TMS/PMA10/RA10
LD3
15
15 - 13*
PGEC(4)/TCK/CTED8/PMA7/RA7
16
16/A10
J1-04
14
CVREF/AN10/C3INB/RPB14/SCK1/CTED5/PMWR/RB14
17
17/A9
J2-10
15
AN9/C3INA/RPB15/SCK2/CTED6/PMCS1/RB15
18
18/A0 - 19
VREF+/CVREF+/AN0/C3INC/RPA0/CTED1/RA0
TCK2
19
19/A1 - 20
VREF-/CVREF-/AN1/RPA1/CTED2/RA1
20
20/A2
J2-02
21
PGED1/AN2/C1IND/C2INB/C3IND/RPB0/RB0
U2TX
21
21/A3
J2-03
22
PGEC1/AN3/C1INC/C2INA/RPB1/CTED12/RB1
U2RX
22
22/A4
J2-01
23
AN4/C1INB/C2IND/RPB2/SDA2/CTED13/RB2
OC4
23
23/A5 - 24
AN5/C1INA/C2INC/RTCC/RPB3/SCL2/RB3
U1TX
24
24/A6
J1-01
25
AN6/RPC0/RC0
SS1
25
25/A7
J1-02
26
AN7/RPC1/RC1
IC5/SDO1
26
26/A8 - 27
AN8/RPC2/PMA2/RC2
TCK5
27
27 - 32*
TDO/RPA8/PMA8/RA8
TCK3
28 - -
- - Not connected
29
29 - 33
SOSCI/RPB4/RB4
OC1
30
30
J1-09
34
SOSCO/RPA4/T1CK/CTED9/RA4
TCK1
31
31 - 35*
TDI/RPA9/PMA9/RA9
IC3
32
32
J2-09
36
RPC3/RC3
TCK4/SDI2
33
33
J2-07
37*
RPC4/PMA4/RC4
INT1/SS2
34
34
J2-04
38*
RPC5/PMA3/RC5
35
35
J1-03
41*
PGED3/RPB5/PMD7/RB5
SDI1
36
36
J2-08
42*
PGEC3/RPB6/PMD6/RB6
IC1/SDO2
37
37 - 43*
RPB7/CTED3/PMD5/INT0/RB7
IC4/INT4
38
38 - 44*
RPB8/SCL1/CTED10/PMD4/RB8
OC2
39/40 - -
6/16/
29/39
VSS/AVSS
GND
Connector
Pin #
DIP
Pin #
chipKIT
Pin #
PIC32
Pin #
PIC32 Signal
Notes
J1-01
24
24/A6
25
AN6/RPC0/RC0
SS1
J1-02
25
25/A7
26
AN7/RPC1/RC1
IC5/SDO1
J1-03
35
35
41*
PGED3/RPB5/PMD7/RB5
SDI1
J1-04
16
16/A10
14
CVREF/AN10/C3INB/RPB14/SCK1/CTED5/PMWR/RB14
* Indicates 5V tolerant pin on the PIC32MX150F128D
Pinout Table by Pmod Connector Pin Number
Page 9

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 9 of 11
J1-05
39/40
-
6/16/
29/39
VSS/AVSS
GND
J1-06
2
-
28/40
VDD
VCC3V3
J1-07
7 7 4*
RPC8/PMA5/RC8
INT3
J1-08
6 6 3*
RPC7/PMA0/RC7
J1-09
30
30
34
SOSCO/RPA4/T1CK/CTED9/RA4
TCK1
J1-10
8 8 5*
RPC9/CTED7/PMA6/RC9
J1-11
39/40
-
6/16/
29/39
VSS/AVSS
GND
J1-12
2
-
28/40
VDD
VCC3V3
J2-01
22
22/A4
23
AN4/C1INB/C2IND/RPB2/SDA2/CTED13/RB2
OC4
J2-02
20
20/A2
21
PGED1/AN2/C1IND/C2INB/C3IND/RPB0/RB0
U2TX
J2-03
21
21/A3
22
PGEC1/AN3/C1INC/C2INA/RPB1/CTED12/RB1
U2RX
J2-04
34
34
38*
RPC5/PMA3/RC5
J2-05
39/40
-
6/16/
29/39
VSS/AVSS
GND
J2-06
2
-
28/40
VDD
VCC3V3
J2-07
33
33
37*
RPC4/PMA4/RC4
INT1/SS2
J2-08
36
36
42*
PGEC3/RPB6/PMD6/RB6
IC1/SDO2
J2-09
32
32
36
RPC3/RC3
TCK4/SDI2
J2-10
17
17/A9
15
AN9/C3INA/RPB15/SCK2/CTED6/PMCS1/RB15
J2-11
39/40
-
6/16/
29/39
VSS/AVSS
GND
J2-12
2
-
28/40
VDD
VCC3V3
- 1 -
-
N/A
VIN/External
Power
- 3 -
-
N/A
USB5V0/External
5V Power for USB
- 4 4
1*
RPB9/SDA1/CTED4/PMD3/RB9
OC3
- 5 5
2*
RPC6/PMA1/RC6
U1RX
- 9
18*
MCLR
Reset Button
-
10
10
8*
PGED2/RPB10/CTED11/PMD2/RB10
IC2
-
11
11
9*
PGEC2/RPB11/PMD1/RB11
-
12
12/A12
10
AN12/PMD0/RB12
LD4
-
13
13/A11
11
AN11/RPB13/CTPLS/PMRD/RB13
OC5/INT2
-
14
14
12*
PGED(4)/TMS/PMA10/RA10
LD3
-
15
15
13*
PGEC(4)/TCK/CTED8/PMA7/RA7
-
18
18/A0
19
VREF+/CVREF+/AN0/C3INC/RPA0/CTED1/RA0
TCK2
-
19
19/A1
20
VREF-/CVREF-/AN1/RPA1/CTED2/RA1
-
23
23/A5
24
AN5/C1INA/C2INC/RTCC/RPB3/SCL2/RB3
U1TX
-
26
26/A8
27
AN8/RPC2/PMA2/RC2
TCK5
-
27
27
32*
TDO/RPA8/PMA8/RA8
TCK3
-
28
-
- - Not connected
Page 10

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 10 of 11
-
29
29
33
SOSCI/RPB4/RB4
OC1
-
31
31
35*
TDI/RPA9/PMA9/RA9
IC3
-
37
37
43*
RPB7/CTED3/PMD5/INT0/RB7
IC4/INT4
-
38
38
44*
RPB8/SCL1/CTED10/PMD4/RB8
OC2
PIC32
Pin#
DIP
Pin #
chipKIT
Pin #
Connector
Pin #
PIC32 Signal
Notes
1* 4 4
-
RPB9/SDA1/CTED4/PMD3/RB9
OC3
2* 5 5
-
RPC6/PMA1/RC6
U1RX
3* 6 6
J1-08
RPC7/PMA0/RC7
4* 7 7
J1-07
RPC8/PMA5/RC8
INT3
5* 8 8
J1-10
RPC9/CTED7/PMA6/RC9
6
39/40 - -
VSS/AVSS
GND
7
VCAP
8*
10
10
-
PGED2/RPB10/CTED11/PMD2/RB10
IC2
9*
11
11
-
PGEC2/RPB11/PMD1/RB11
10
12
12/A12
-
AN12/PMD0/RB12
LD4
11
13
13/A11
-
AN11/RPB13/CTPLS/PMRD/RB13
OC5/INT2
12*
14
14
-
PGED(4)/TMS/PMA10/RA10
LD3
13*
15
15
-
PGEC(4)/TCK/CTED8/PMA7/RA7
14
16
16/A10
J1-04
CVREF/AN10/C3INB/RPB14/SCK1/CTED5/PMWR/RB14
15
17
17/A9
J2-10
AN9/C3INA/RPB15/SCK2/CTED6/PMCS1/RB15
16
39/40 - -
VSS/AVSS
GND
17
AVDD
18* 9 -
-
MCLR
RESET
19
18
18/A0
-
VREF+/CVREF+/AN0/C3INC/RPA0/CTED1/RA0
TCK2
20
19
19/A1
-
VREF-/CVREF-/AN1/RPA1/CTED2/RA1
21
20
20/A2
J2-02
PGED1/AN2/C1IND/C2INB/C3IND/RPB0/RB0
U2TX
22
21
21/A3
J2-03
PGEC1/AN3/C1INC/C2INA/RPB1/CTED12/RB1
U2RX
23
22
22/A4
J2-01
AN4/C1INB/C2IND/RPB2/SDA2/CTED13/RB2
OC4
24
23
23/A5
-
AN5/C1INA/C2INC/RTCC/RPB3/SCL2/RB3
U1TX
25
24
24/A6
J1-01
AN6/RPC0/RC0
SS1
26
25
25/A7
J1-02
AN7/RPC1/RC1
IC5/SDO1
27
26
26/A8
-
AN8/RPC2/PMA2/RC2
TCK5
28 2 -
-
VDD
VCC3V3
29
39/40 - -
VSS/AVSS
GND
* Indicates 5V tolerant pin on the PIC32MX150F128D
Pinout Table by PIC32 Microcontroller Pin
Page 11

chipKIT Cmod™ Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 11 of 11
30
OSC1/CLKI/RPA2/RA2
X1, system
clock
oscillator
31
OSC2/CLKO/RPA3/RA3
X1, system
clock
oscillator
32*
27
27
-
TDO/RPA8/PMA8/RA8
TCK3
33
29
29
-
SOSCI/RPB4/RB4
OC1
34
30
30
J1-09
SOSCO/RPA4/T1CK/CTED9/RA4
TCK1
35*
31
31
-
TDI/RPA9/PMA9/RA9
IC3
36
32
32
J2-09
RPC3/RC3
TCK4/SDI2
37*
33
33
J2-07
RPC4/PMA4/RC4
INT1/SS2
38*
34
34
J2-04
RPC5/PMA3/RC5
39
39/40 - -
VSS/AVSS
GND
40 2 -
-
VDD
VCC3V3
41*
35
35
J1-03
PGED3/RPB5/PMD7/RB5
SDI1
42*
36
36
J2-08
PGEC3/RPB6/PMD6/RB6
IC1/SDO2
43*
37
37
-
RPB7/CTED3/PMD5/INT0/RB7
IC4/INT4
44*
38
38
-
RPB8/SCL1/CTED10/PMD4/RB8
OC2
- 1 -
-
N/A
VIN/Exter
nal Power
- 3 -
-
N/A
USB5V0/E
xternal 5V
Power for
USB
-
28 - -
N/A
Not
connected
* Indicates 5V tolerant pin on the PIC32MX150F128D
 Loading...
Loading...