Page 1

D-Command
Version 7.0
™
Page 2

Copyright
© 2006 Digidesign, a division of Avid Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. This
guide may not be duplicated in whole or in part without the express written
consent of Digidesign.
Avid, Digidesign, Pro Tools and Pro Tools|HD are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of Avid Technology, Inc. in the US and other countries. All other
trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Product features, specifications, system requirements, and availability are
subject to change without notice.
PN 9106-18919-00 REV A 07/06
Warning
This product contains chemicals, including lead, known to the State of California
to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm.
handling
.
Wash hands after
Communications & Safety Regulation Information
Compliance Statement
The models D-Command and XMON comply with the following standards
regulating interference and EMC:
• FCC Part 15 Class A
• EN55103 – 1, environment E4
• EN55103 – 2, environment E4
• AS/NZS 3548 Class A
• CISPR 22 Class A
• ICES-003 Class A
Canadian Compliance Statement:
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du
Canada.
CE Compliance Statement:
Digidesign is authorized to apply the CE (Conformité Europénne) mark on this
compliant equipment thereby declaring conformity to EMC Directive
89/336/EEC and Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC.
Australian Compliance:
Radio and Television Interference
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Communications Statement
This equipment has been tested to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device. Changes or modifications to this product not authorized by Digidesign,
Inc., could void the Certification and negate your authority to operate the product.
This product was tested for CISPR compliance under conditions that included the
use of peripheral devices and shielded cables and connectors between system
components. Digidesign recommends the use of shielded cables and connectors
between system components to reduce the possibility of causing interference to
radios, television sets, and other electronic devices.
Safety Statement
This equipment has been tested to comply with USA and Canadian safety
certification in accordance with the specifications of UL Standards: UL60065 7th
/IEC 60065 7th and Canadian CAN/CSA C22.2 60065:03. Digidesign Inc., has
been authorized to apply the appropriate UL & CUL mark on its compliant
equipment.
Warning
Important Safety Instructions
1) Read these instructions.
2) Keep these instructions.
3) Heed all warnings.
4) Follow all instructions.
5) Do not use this apparatus near water.
6) Clean only with dry cloth.
7) Do not block any ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions.
8) Do not install near any heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves,
or other apparatus (including amplifiers) that produce heat.
9) Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or grounding-type plug. A
polarized plug has two blades with one wider than the other. A grounding type
plug has two blades and a third grounding prong. The wide blade or the third
prong are provided for your safety. If the provided plug does not fit into your
outlet, consult an electrician for replacement of the obsolete outlet.
10) Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched particularly at plugs,
convenience receptacles, and the point where they exit from the apparatus.
11) Only use attachments/accessories specified by the manufacturer.
12) Unplug this apparatus during lightning storms or when unused for long
periods of time.
13) Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when
the apparatus has been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug
is damaged, liquid has been spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the
apparatus has been exposed to rain or moisture, does not operate normally, or
has been dropped.
Page 3

Do not attempt to service the equipment. There are no
user-serviceable parts inside. Please refer all servicing to authorized
Digidesign personnel.
Any attempt to service the equipment will expose you to a risk of
shock and will void the manufacturer’s warranty.
SPECIAL WARNING REGARDING VENTILATION:
Do not install D-Command anywhere or in any way that blocks free
air flow at any time around the back panel of the unit.
SPECIAL WARNING REGARDING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE:
Before powering on the D-Command unit, be sure to allow it to reach
room temperature. The unit includes some components that are
senstive to cold temperatures, so it is recommended that you
unpack the unit and allow it to acclimate before turning it on for the
first time.
This symbol on the product or its packaging indicates that this product must not
be disposed of with other waste. Instead, it is your responsibility to dispose of
your waste equipment by handing it over to a designated collection point for the
recycling of waste electrical and electronic equipment. The separate collection
and recycling of your waste equipment at the time of disposal will help conserve
natural resources and ensure that it is recycled in a manner that protects human
health and the environment. For more information about where you can drop off
your waste equipment for recycling, please contact your local city recycling office
or the dealer from whom you purchased the product.
Page 4

Page 5
Contents
Part I Introduction
Chapter 1. Introduction to D-Command
D-Command Features
D-Command System Components
System Expansion Options
Operational Requirements
Connection Requirements
System Requirements
Chapter 2. D-Command Overview
D-Command Main Unit
D-Command Fader Module
D-Command XMON Interface
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Part II Installation
Chapter 3. Setting Up the Fader Module
Assembling an Expanded System
Chapter 4. Connecting D-Command
D-Command Connections
Audio Connections
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Chapter 5. Configuring D-Command
Starting Up and Shutting Down the System
Software Configuration
Setting D-Command Preferences
System Calibration
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Part III Reference
Chapter 6. Channel Strip Controls
Channel Strips
Global Controls Section
Miscellaneous Controls
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Contents
v
Page 6

Chapter 7. Plug-in Controls
Plug-ins and D-Command
Dynamics Section
EQ Section
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Chapter 8. Transport and Navigation Controls
Transport Section
Zoom/Navigate Section
Nudge/Bank Section
Chapter 9. Management Sections
Window Management Section
Session Management Section
Soft Keys Section
Chapter 10. Monitor and Meter Sections
Monitor Section Controls
Meter and Time Code Displays (Main Unit)
Setting D-Command Meters for Different Reference Levels
Chapter 11. Operating Modes
Normal Mode
Custom Fader Modes
Entering Utility Mode
Navigating Utility Mode
Exiting Utility Mode
D-Command System Info Page
D-Command Name Page
D-Command Test Pages
Resetting D-Command to Factory Defaults
D-Command Preferences
25-Pin Female Connector Pinouts
15-Pin Connector Pinouts
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Tech Pubs Style Guide
vi
Page 7

Part I: Introduction
Page 8

Page 9
Chapter 1: Introduction to D-Command
Welcome to the D-Command™ worksurface for Digidesign®
ICON systems.
D-Command System Components
D-Command provides hands-on control of Pro Tools®, and
offers powerful options for customizing the Pro Tools mix environment.
D-Command Features
The D-Command system provides controls for most Pro Tools
recording, editing and mixing tasks, and a versatile remote-controlled audio monitoring system.
Control Features
• Touch-sensitive, motorized 100mm faders
• Touch-sensitive, multi-purpose rotary controls
• Dedicated controls for assignment and activation of inputs,
outputs, inserts and sends
• Flexible display of pan, insert, send, plug-in and mic pre
controls
• Dedicated EQ and dynamics plug-in control sections
• Dedicated controls for all channel strip functions including
recording and input monitoring modes, mute, solo, and
channel select
• Dedicated controls for automation mode, enable and safe
status
• Custom Fader Mode for flexible channel and parameter
mapping
• Full transport and navigation controls, including location
commands and scrub/shuttle capability
Monitoring Features
• 6-channel control room monitoring system supports mono
through 5.1 surround monitoring, with up to 5 possible input sources and 3 selectable output paths
• 2-channel cue system with 4 separate outputs and selectable
talkback feed
• Built-in talkback microphone and external talkback mic Input
• Standalone mode for monitoring without Pro Tools
• External source metering
The following components are included in a D-Command
8-channel or 24-channel system:
Main Unit
• D-Command Main Unit
• AC power cord
• Ethernet cable
• Ethernet “crossover” cable (for direct connection to CPU
without a hub)
• Ethernet loopback plug (for Ethernet testing)
• 9/64-inch hex driver (for removing side panels)
• 5/32-inch hex driver (for connecting Main Unit and
Fader Module)
Fader Module
(Required for 24-Channel System)
• D-Command Fader Module unit
• AC power cord
• Ethernet cable
XMON Monitoring System
• XMON Interface
• AC power cord
• XMON cable
System Expansion Options
An additional 16-channel Fader Module can be added to
D-Command, for a total of 24 faders. For details on D-Command expansion and customization options, visit the Digidesign Web site (www.digidesign.com).
Chapter 1: Introduction to D-Command
3
Page 10

Operational Requirements
Temperature and Ventilation
D-Command should be installed and operated in a climate-controlled environment, away from heat sources, and
with adequate ventilation. D-Command should be operated
at an ambient temperature that does not exceed 100 degrees F
(35 degrees C).
The back panel and the front half of the bottom panel of each
unit should be exposed to ambient air. Blocking or partially
blocking the back panel or bottom panel of a D-Command
unit may cause the unit to malfunction and may void your
warranty.
Audio Connections
All external analog audio inputs and outputs for control room
monitoring and studio communication are connected to the
XMON interface. D-Command connects to the XMON interface with a single 15-pin cable (included). All analog inputs
and outputs on the XMON use DB-25 connectors.
Audio Cables for D-Command Monitoring
Digidesign offers a range of DigiSnake cabling options for connecting Digidesign interfaces and external sources to the
XMON monitoring system. For details, visit the Digidesign
Web site (www.digidesign.com).
Water and Moisture
D-Command units should be operated away from sources of
moisture or humidity and should be protected from liquid
spills.
Cleaning and Maintenance
If you need to clean the D-Command top surface, apply a
non-chlorine bleach based cleaning solution to a cloth or paper towel, then carefully wipe the surface. Do not use abrasives, cleaning solutions with chlorine bleach, or spray cleaners.
Connection Requirements
Power Connections
Each unit (D-Command Main Unit, Fader Module, and
XMON Monitor Interface) requires its own power connection.
Make sure your power source is correctly rated for the number
of units you are connecting. A surge protected power source
(not included) is highly recommended.
System Requirements
D-Command requires the following system components:
• Pro Tools|HD® system (which includes at least one
Pro Tools|HD audio interface)
An expanded Pro Tools|HD system is required for higher track
counts.
For complete system requirements, visit the Digidesign Web
site (www.digidesign.com).
Compatibility Information
Digidesign can only assure compatibility and provide support
for hardware and software it has tested and approved. For a list
of Digidesign-qualified computers, operating systems, and
third-party devices, refer to the Digidesign Web site
(www.digidesign.com).
Ethernet Connections
Each D-Command unit communicates with Pro Tools using
Ethernet. A single Main Unit can be connected to the host
computer without an Ethernet hub. To connect multiple
D-Command units to the host computer, a 10-BaseT Ethernet
hub (not included) is required.
D-Command Guide
4
Page 11

Chapter 2: D-Command Overview
D-Command Main Unit
Main Unit Top Panel
Meter
section
Rotary Encoder
section
Channel Strip
Display controls
Channel Strip
Mode controls
Talkback Microphone
Dynamics Section
EQ Section
Main Time Scale display
Monitor Section
Miscellaneous
controls
Soft Keys
section
Channel
faders
Modifier
keys
Figure 1. D-Command Main Unit top panel
Global
controls
Automation Mode
controls
Transport
Section
Custom Fader
controls
Window
Management
section
Session
Management
section
Zoom/Navigation
section
Nudge/Bank
section
Chapter 2: D-Command Overview
5
Page 12

Meter Display
Soft Keys Section
The Meter display on the D-Command Main Unit can be set
to show the output levels, or levels associated with a track or
plug-in. See “Meter and Time Code Displays (Main Unit)” on
page 87.
Main Time Scale Display and Location Indicator
The Main Time Scale display and Location indicator mirrors
the Main Time Scale in Pro Tools. See “Meter and Time Code
Displays (Main Unit)” on page 87.
Dynamics and EQ Sections
The D-Command Main Unit provides dedicated Dynamics
and EQ sections for plug-ins that support Dynamics and EQ
plug-in mapping. See “Plug-ins and D-Command” on
page 45.
Monitor Section
The Monitor section on the D-Command Main Unit includes
a full set of controls for the control room, headphone/cue,
and talkback/listenback sections of D-Command. See “Monitor Section Controls” on page 79.
Zoom/Navigation Section
The Zoom/Navigate section on the D-Command Main Unit is
used to control navigation, display, and selections in the
Pro Tools Edit window. See “Zoom/Navigate Section” on
page 67.
Nudge/Bank Section
The Nudge/Bank section on the D-Command Main Unit is
used to control the display of Pro Tools tracks on the control
surface. See “Nudge/Bank Section” on page 67.
The Soft Keys section on the D-Command Main Unit provides
access to a wide range of Pro Tools commands directly from
the control surface. It also provides access to preferences and
settings specific to D-Command. See “Soft Keys Section” on
page 71.
Transport Section
The Transport section on the D-Command Main Unit includes a full set of transport controls, switches for setting the
transport mode, scrub/shuttle controls, as well as advanced
audition and locate controls. See “Transport Section” on
page 63.
Global Controls
The Global controls are a set of channel-related controls in the
center of the D-Command Main Unit, allowing easy access to
powerful assignment, display, and channel function controls.
See “Global Controls Section” on page 35.
Custom Fader Controls
The Custom Fader mode switches on the D-Command Main
Unit invoke a special set of D-Command modes, called
tom Fader modes
nel strips for display and editing of a variety of functions. See
“Custom Fader Controls” on page 39.
, which let you set aside and customize chan-
Cus-
Automation Mode Controls
The Automation Mode controls mirror the function of the
on-screen Automation Mode selector for each track, and let
you change automation modes during playback. See “Automation Mode Controls” on page 40.
Window Management and Session Management Sections
The Window Management and Session Management sections
on the D-Command Main Unit include controls for opening
and closing Pro Tools windows, and managing and saving
Pro Tools sessions. See “Window Management Section” on
page 69 and “Session Management Section” on page 70.
D-Command Guide
6
Page 13

Main Unit Back Panel
Power switch
AC Power
Figure 2. D-Command Main Unit back panel connectors
AC Power
The AC Power connector accepts a standard AC power cable.
The D-Command Main Unit is auto power-selecting (100V to
240V) and automatically works with a standard modular
power cord when connected to an AC receptacle in any
country.
Power Switch
The Power switch applies power to the D-Command Main
Unit.
Footswitch Jack
The footswitch jack on the back panel of the D-Command
Main Unit is a 1/4-inch TRS jack that supports two footswitch
connections. See “Footswitch Connections” on page 16.
Footswitch jack
Ethernet connector
XMON Monitoring System
connector
Ethernet Connector
The Ethernet connector on the back panel of the D-Command
Main Unit provides communication to Pro Tools. See “Ethernet Connections” on page 15.
XMON Monitoring System Connector
The 15-pin connector on the back panel of the D-Command
Main Unit provides remote control of all audio monitoring
functions from the D-Command Monitoring section. See
“XMON Monitoring System Connection” on page 17.
Chapter 2: D-Command Overview
7
Page 14

D-Command Fader Module
Fader Module Top Panel
Meter
section
Rotary Encoder
section
Channel Strip
Mode controls
Channel Strip
Function controls
Channel faders
Modifier keys
Figure 3. D-Command Fader Module top panel
Meter Section
The Meter section on the D-Command Fader Module can display track levels, plug-in meters, and other parameters depending on D-Command metering preferences.
Channel Strip
Each channel strip on the D-Command Fader Module has
identical channel controls, including two touch-sensitive rotary encoders, display and mode controls, and a touch-sensitive fader. See “Channel Strips” on page 29.
Modifier Keys
Each D-Command Fader Module has a set of four switches in
its lower left corner that duplicate the function of the
Pro Tools computer keyboard modifiers. See “Modifier Key
Switches” on page 34.
Channel Strip
Fader Module Back Panel
AC Power
The AC Power connector accepts a standard AC power cable.
The D-Command Fader Module is auto power-selecting (100V
to 240V) and automatically works with a standard modular
power cord when connected to an AC receptacle in any
country.
Power Switch
The Power switch applies power to the Fader Module.
Ethernet Connector
The Ethernet connector on the back panel of the D-Command
Fader Module provides communication to Pro Tools. See
“Ethernet Connections” on page 15.
D-Command Guide8
Page 15

D-Command XMON Interface
XMON
D-Command monitoring is based on the XMON analog interface, which is remotely controlled from the D-Command
monitoring section.
XMON Front Panel
XMON
Power
Figure 4. XMON front panel
switch
Mute indicator
Mute button
MIDI Receive indicator
Power Switch
The Power switch applies power to the XMON Interface.
Mute Indicator
The Mute indicator shows the mute status of XMON.
MIDI Receive Indicator
The MIDI Receive indicator shows MIDI activity between
XMON and D-Command.
Mute Button
The Mute button mutes all XMON outputs. It is not possible
to unmute XMON with this button. The XMON mute state
can only be cleared from the D-Command Monitor section
(see “Monitor Section Controls” on page 79).
Chapter 2: D-Command Overview 9
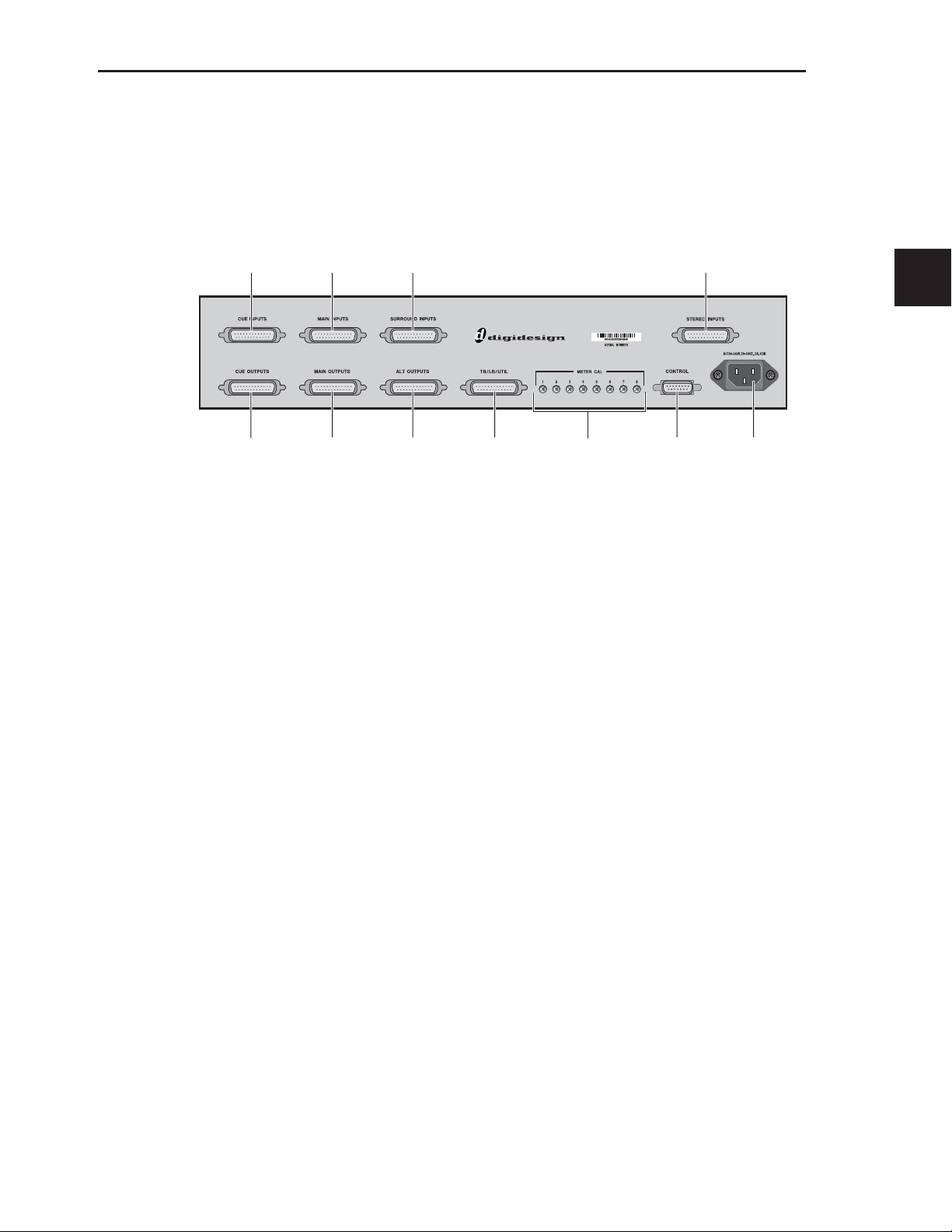
Page 16
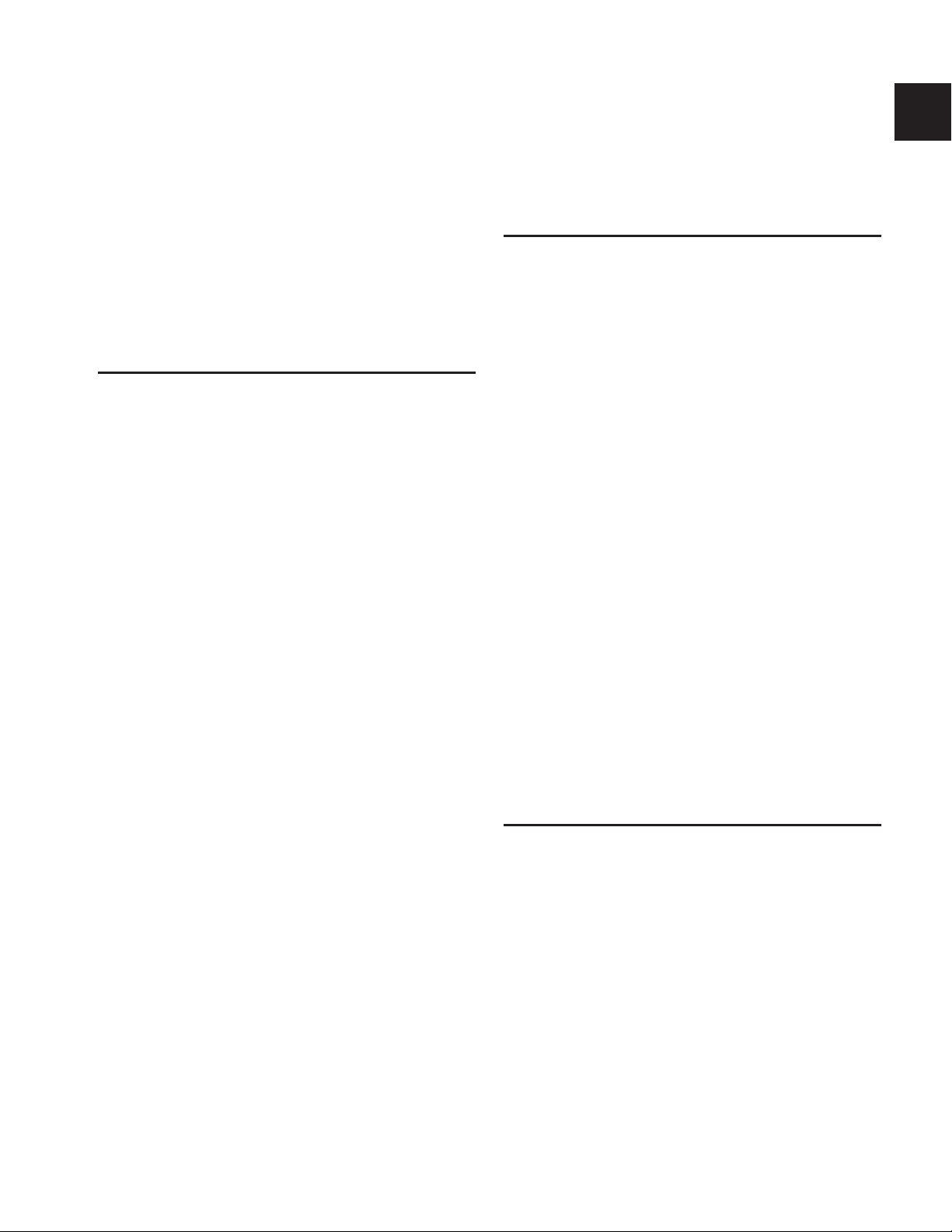
XMON Back Panel
The back panel of the XMON interface includes connectors for all external analog audio inputs and outputs for D-Command. See
“Audio Connections” on page 17.
Cue Inputs
Cue Outputs
Figure 5. XMON back panel
Main Inputs Surround Inputs Stereo Inputs
Main Outputs Alt Outputs Talkback/ Meter Calibration Control Surface AC Power
Listenback/
Utility
Screws
D-Command Guide10
Page 17

Part II: Installation
Page 18

Page 19
Chapter 3: Setting Up the Fader Module
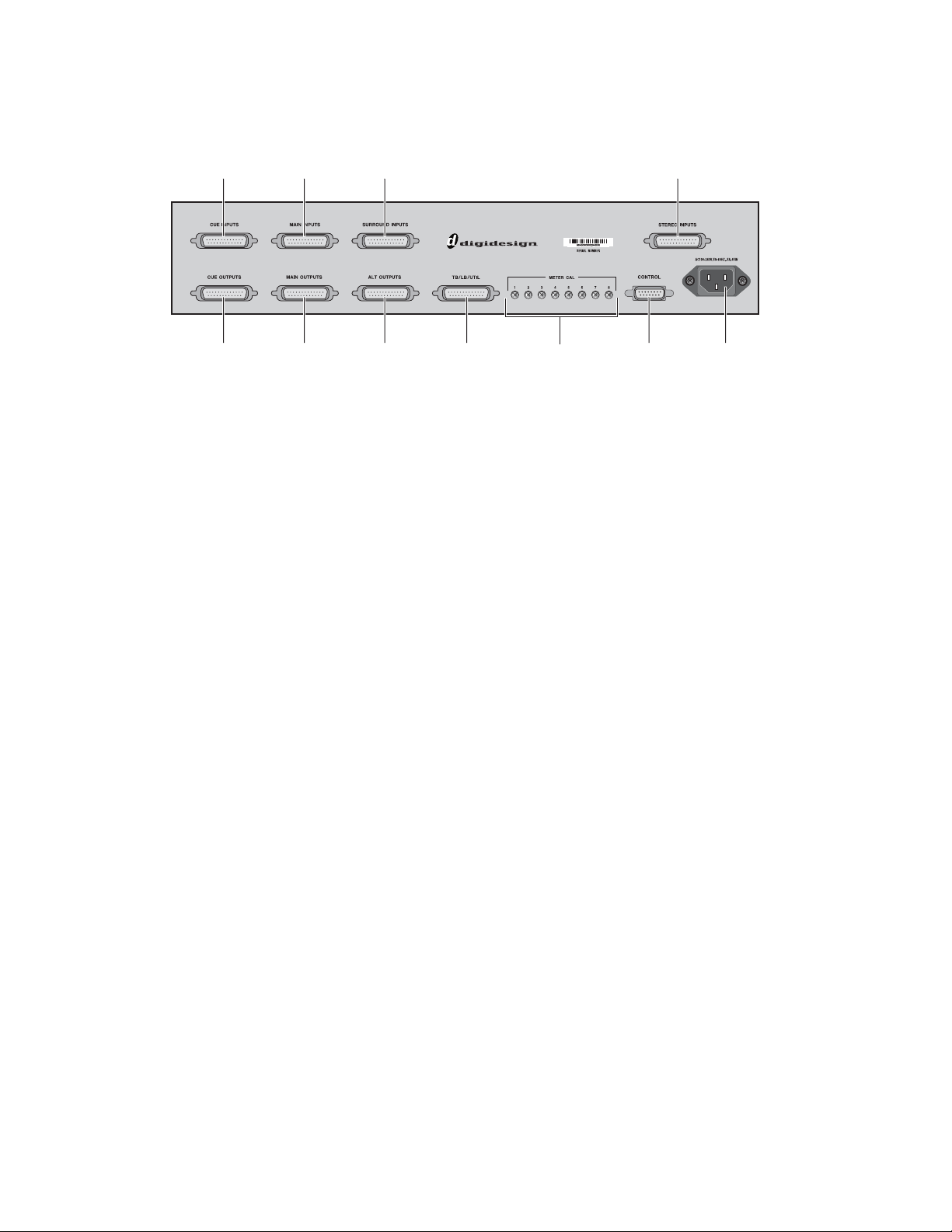
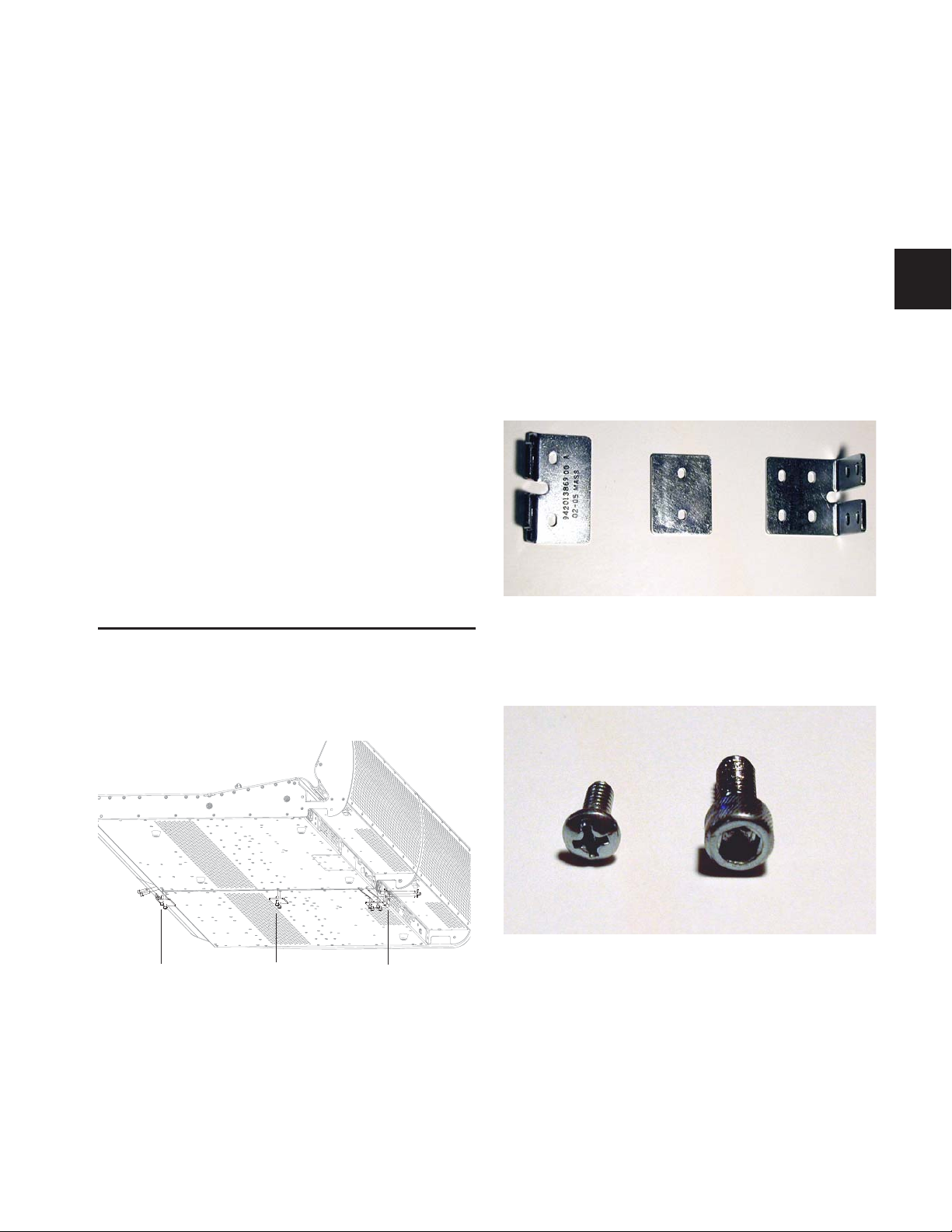
Front bracket Center bracket Rear bracket
10-32 x 3/4-inch
socket cap screw
6-32 x 3/8-inch
Philips pan head screw
This chapter explains how to add the Fader Module to the
D-Command Main Unit.
Placement of D-Command Fader Module
When placing the D-Command Fader Module in studio furniture or on a table top, make sure to account for the dimensions of the assembled system, allowing for at least 1 inch
(2.5 cm) of open space behind the finished unit. This meets
the ventilation requirements for the D-Command units.
When bracketing together your system, you will need additional clearance on either side of the unit to push the Fader
Module and the Main Unit together, as well as sufficient clearance in front and behind the units to allow you to attach the
brackets. You will also need access to the rear of the unit to
make cable connections.
The Fader Module is designed to be attached to the left of the
D-Command Main Unit.
Assembling an Expanded System
The D-Command Main Unit can be attached to the D-Command Fader Module, using the front, middle, and rear brackets included with the D-Command Fader Module.
Assembly Hardware
The following hardware is provided with the D-Command
Fader Module (spare pieces may be included).
Brackets
• Front Bracket
• Center Bracket
• Rear Bracket
Figure 2. D-Command expanded system connecting brackets
Screws
• (10) 10-32 x 3/4-inch socket cap screw
• (4) 6-32 x 3/8-inch Philips pan head screw
Front bracket Center bracket Rear bracket
Figure 1. D-Command with Fade Module (bottom view)
Figure 3. Screws for D-Command connecting brackets
Chapter 3: Setting Up the Fader Module 13
Page 20

Attaching the Units
D-Command
To attach the D-Command Fader Module to the Main Unit:
1 Remove the plastic end cap from the left end of the Main
Unit.
2 Place the Fader Module to the left of the Main Unit, and
press the D-Command units together.
3 Slide both units forward far enough to have complete access
to the front bracket screw holes.
4 Attach the front bracket, using four 10-32 3/4-inch socket
cap screws.
When bracketing together a D-Command system, leave all
screws on the Fader Module loose enough to allow you to adjust the position of the units relative to each other. After all
three brackets are installed, and the units are pressed fully
together, you will fully tighten the Fader Module screws.
5 Slide the connected units backwards far enough to have
complete access to the rear screws.
6 Remove the four Philips head screws indicated in Figure 4.
Fader Module
Remove screws
Figure 4. Rear view of D-Command and Fader Module
7 Attach the rear bracket, using four 10-32 3/4-inch socket cap
screws and four 6-32 x 3/8-inch Philips pan head screws.
8 Carefully slide the connected units forwards far enough to
have complete access to the center bracket screw holes.
9 Attach the center bracket, using two 10-32 3/4-inch socket
cap screws.
10 Press the D-Command units together. If necessary, use a
ratcheting nylon strap to press the units together by running
the strap around the two units. Make sure the nylon strap does
not contact any switches or encoders on the surface.
11 Tighten the bracket screws on the Fader Module.
12 Attach the plastic end cap to the Fader Module.
D-Command Guide14
Page 21

Chapter 4: Connecting D-Command
D-Command Connections
D-Command units require power and Ethernet connections to operate with Pro Tools. An optional footswitch connection is also
available on the Main Unit. The connectors on the back panel of the D-Command Main Unit are shown in Figure 5.
Be sure to make all connections with your D-Command units and computer turned off.
Ethernet connector
Footswitch jack
Figure 5. D-Command Main Unit back panel connectors
Power Connections
Each D-Command unit (Main Unit and Fader Module) and
the XMON Monitor Interface requires its own power connection. D-Command Main Units, Fader Modules, and XMON Interfaces are auto power-selecting (100V to 240V) and automatically work with a standard modular power cord when
connected to an AC receptacle in any country. A power cable
is provided with each D-Command unit and the XMON
interface.
To make D-Command power connections:
■ For each D-Command unit and the XMON Interface, con-
nect the included AC power cord the unit and to a power
source.
XMON Monitoring System connector
Ethernet Connections
Each D-Command unit communicates with Pro Tools using
Ethernet. An Ethernet cable is included with each D-Command unit.
A 10-BaseT Ethernet hub (not included) is required to connect
multiple D-Command units to the host computer.
To connect a single D-Command unit:
■ Connect one end of the supplied crossover Ethernet cable to
the port on the back of the D-Command unit, and the other
end to the Ethernet port on the computer.
To connect multiple D-Command units:
1 Install the Ethernet hub according to its instructions, apply
power to it, and verify that it is functioning properly.
2 Connect the Ethernet hub to the Ethernet port on your
computer.
3 For each D-Command unit, connect one end of the supplied
Ethernet cable to a port on the Ethernet hub, and the other
end to the Ethernet port on the back of the unit. Do not use
any port labelled for LAN connections.
Connection sequence to the Ethernet hub does not matter, because the order of the units can be configured
from within Pro Tools.
Chapter 4: Connecting D-Command 15
Page 22

Using D-Command on an Ethernet Network
Footswitch Connections
You can purchase a combined 10/100-BaseT Ethernet hub
that can simultaneously support D-Command over 10-BaseT
and other network traffic over 100-BaseT. This will let you use
D-Command over a local area network.
Moderate network traffic (such as e-mail) should not affect
communication between D-Command and the computer. If
your network experiences heavy traffic, you may want to create a dedicated Ethernet network for D-Command.
Controlling Pro Tools Systems Over a Network
When D-Command is connected to an Ethernet network, it
will be available to be declared by any Pro Tools system on
that network. This lets you control different Pro Tools systems
on the network with a single D-Command console. (You can
only control one Pro Tools system at a time.)
You can connect two SPST (single-pole, single-throw) footswitch units to the D-Command Main Unit to control any of
the following functions:
• Starting and stopping Pro Tools playback
• Starting Pro Tools recording
• Toggling Talkback on and off
The footswitch connector is a single 1/4-inch TRS jack on the
back panel of the D-Command Main Unit.
To wire a TRS connector for the D-Command footswitch jack:
■ Use the following wiring convention: Tip = Footswitch 1,
Ring = Footswitch 2, Sleeve = Ground.
D-Command Guide16
Page 23
Audio Connections
D-Command monitoring is based on the XMON analog interface, which is remotely controlled from the D-Command monitoring section. All external analog audio inputs and outputs for control room monitoring and studio communication are connected
to the XMON interface.
XMON provides 18V phantom for its three external mic inputs (External Talkback Mic, Listen Mic 1, Listen Mic 2).
All audio connections are made with standard DB-25 connectors. The back panel of the XMON is shown in Figure 6.
Cue Inputs
Cue Outputs
Figure 6. XMON back panel
Main Inputs Surround Inputs Stereo Inputs
Main Outputs Alt Outputs Talkback/ Meter Calibration Control Surface AC Power
Listenback/
Utility
Screws
XMON Monitoring System Connection
D-Command connects to XMON with a single 15-pin XMON cable. A 50-foot (15.25 m) cable is included with the D-Command
Main Unit. The system supports up to an 80-foot (24.5 m) cable.
To connect the XMON to D-Command:
1 Connect the included AC power cord to the back panel of the XMON and to a power source. A surge protected power source
is highly recommended.
2 Connect one end of the included XMON cable to the Control Surface port on your XMON unit, and the other end to the 15-pin
XMON Monitoring System connector on the back panel of the D-Command Unit.
Chapter 4: Connecting D-Command 17
Page 24
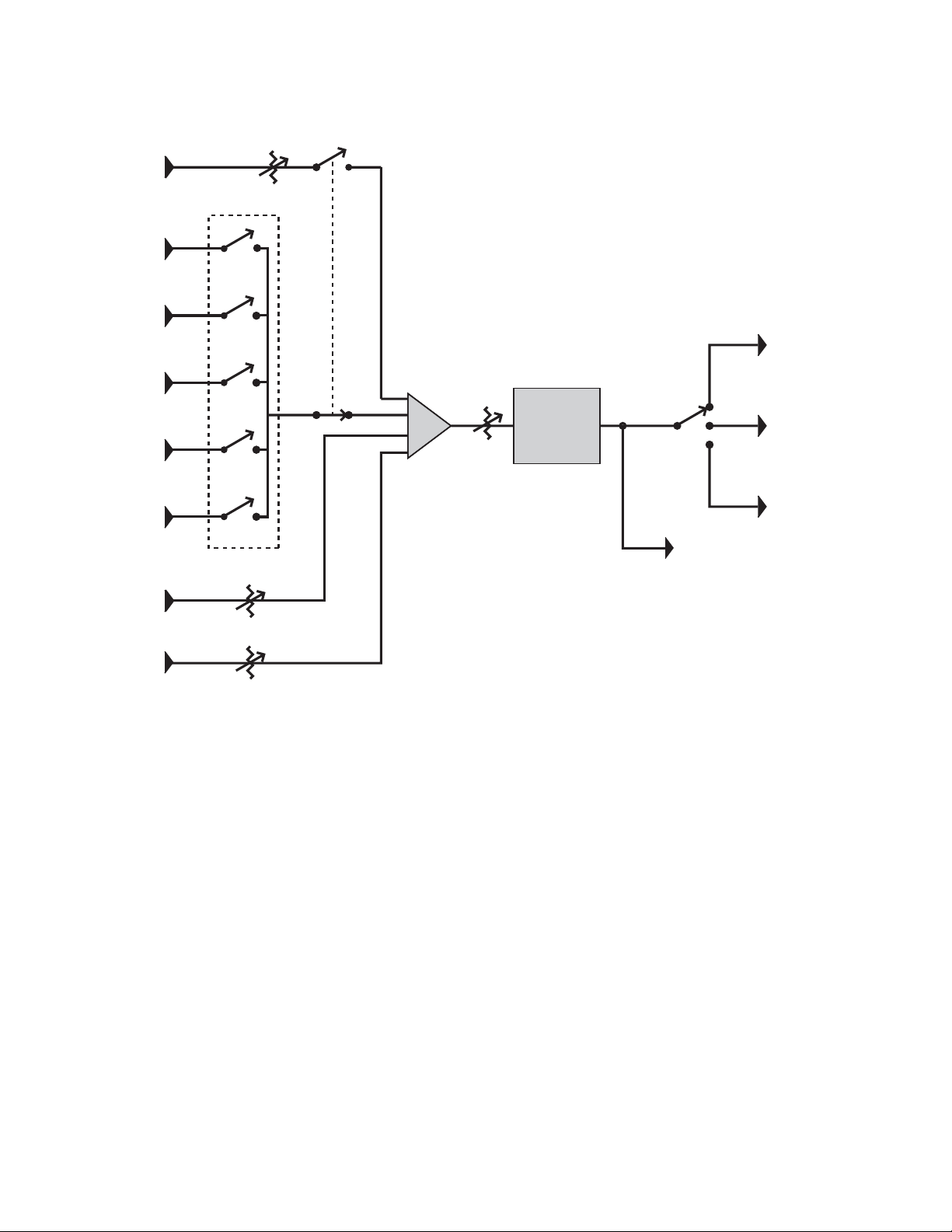
Control Room Monitoring Connections
AFL/PFL
Input
(2 channels)
Main
Input
(6 channels)
Surround
Input
(6 channels)
Stereo 1
Input
(2 channels)
Stereo 2
Input
(2 channels)
Stereo 3
Input
(2 channels)
Listen
Mic 1
Level
AFL/PFL
Level
Input
Source
Select
Pro Tools
Solo
Command
Σ
Level, Dim,
Solo, Mute,
Trim + Cal
Mono
Summing
Control Room
Output Select
[To Cue System]
Main Output
(6 channels)
Alt Output
(6 channels)
Mini Output
(2 channels)
Listen
Mic 2
Figure 7. Control room monitoring system block diagram
Level
Inputs
• Main Inputs (6 channels), balanced, +4 dBu (from Pro Tools)
• Surround Inputs (6 channels), balanced, +4 dBu
• Stereo 1 Inputs (2 channels), balanced, +4 dBu/–10dBV
• Stereo 2 Inputs (2 channels), balanced, +4 dBu/–10dBV
• Stereo 3 Inputs (2 channels), balanced, +4 dBu/–10dBV
• AFL/PFL Inputs (2 channels), balanced, +4 dBu
• Listen Mic 1 (external), mic level (XMON provides 18V phantom power)
• Listen Mic 2 (external), mic level (XMON provides 18V phantom power)
Outputs
• Main Control Room Outputs (6 channels), balanced or unbalanced, +4 dBu
• Alt Control Room Outputs (6 channels), balanced or unbalanced, +4 dBu
• Mini Control Room Outputs (2 channels), balanced or unbalanced, +4 dBu
D-Command Guide18
Page 25
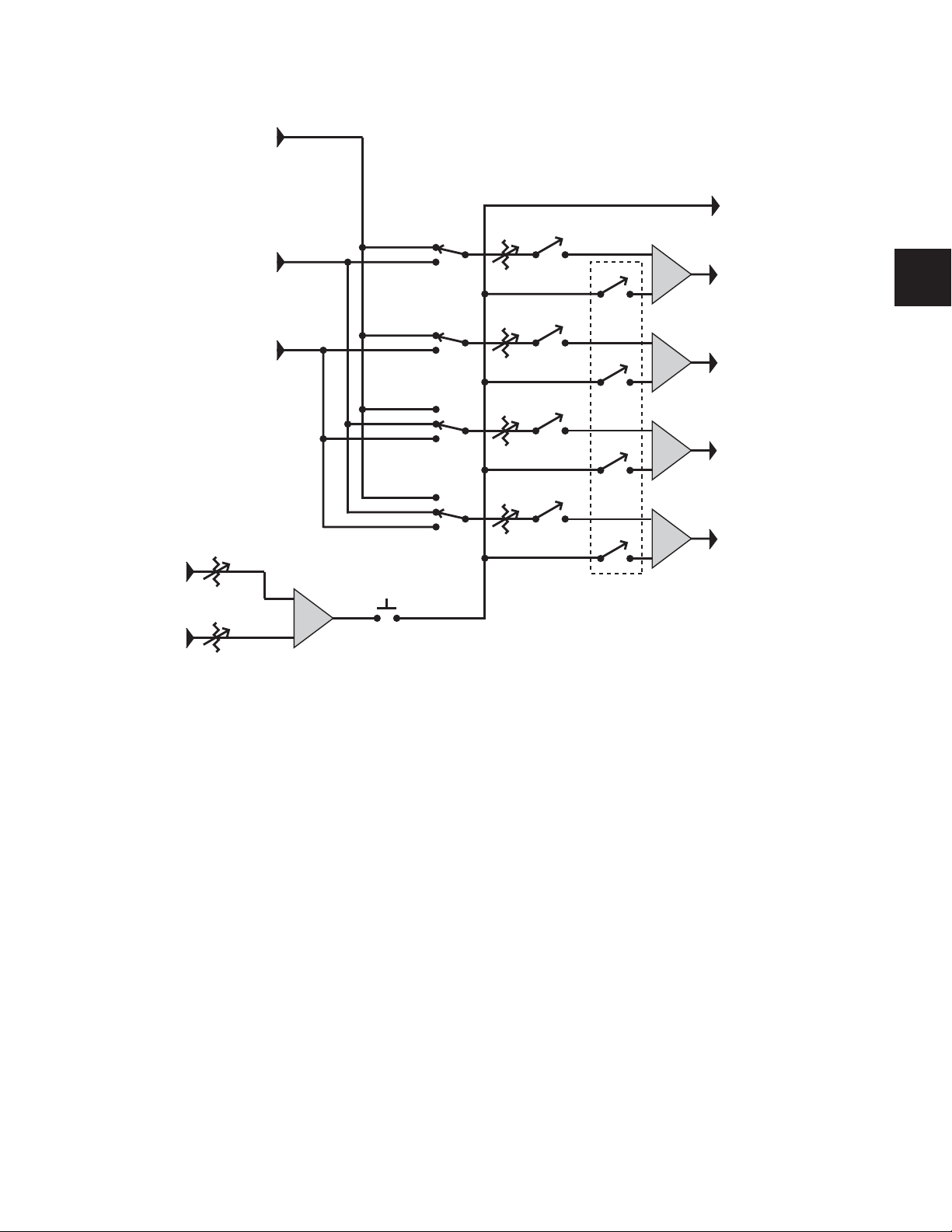
Headphone/Cue System Connections
Main Monitor
Input
(2 channels)
[from Control Room System]
Cue 1
Input
(2 channels)
Cue 2
Input
(2 channels)
Σ
Σ
Σ
Talkback/Slate Out
(1 channel)
Cue 1 Out
(2 channels)
Cue 2 Out
(2 channels)
HP Out
(2 channels)
Internal
Internal
Talkback
Input
External
Talkback
Input
Figure 8. Headphone/Cue system block diagram
Talkback
Level
External
Talkback
Level
Talkback
switch Talkback
Σ
Inputs
• Main Monitor Input (2 channels)
• Cue 1 Input (2 channels), balanced, +4 dBu
• Cue 2 Input (2 channels), balanced, +4 dBu
• Internal Talkback Mic (from internal mic)
• External Talkback Mic, mic level (XMON provides 18V phantom power)
Outputs
• Cue 1 (2 channels), +4 dBu
• Cue 2 (2 channels), +4 dBu
• Headphone (2 channels), to internal headphone jack
• Studio Loudspeaker (2 channels)
• Talkback/Slate Output (1 channel)
Assign
Σ
Studio LS
(2 channels)
Chapter 4: Connecting D-Command 19
Page 26

D-Command Guide20
Page 27
Chapter 5: Configuring D-Command
Starting Up and Shutting Down the System
Your D-Command-based system must be started up and shut
down in a specific order.
Start your D-Command-based system in this order :
1 Turn on external hard drives first. Wait 10 to 15 seconds for
them to come up to speed.
2 Turn on the D-Command units.
3 If you plan to work with MIDI equipment, turn on MIDI in-
terfaces and other MIDI devices.
4 Turn on all Pro Tools audio interfaces.
5 Turn on the computer.
6 Turn on the XMON interface.
7 Turn on monitor amplifiers or self-powered speakers.
Shut down your D-Command-based system in this order:
1 Turn off monitor amplifiers or self-powered speakers.
2 Turn off the XMON interface.
Software Configuration
All D-Command software is included when Pro Tools software
is installed. The Pro Tools software installer places the D-Command Personality folder on the system drive.
Refer to the Getting Started Guide that came with your system
for instructions on installing or updating Pro Tools software.
Updating System Firmware
Each release of Pro Tools software includes the most current
D-Command firmware. When you declare a D-Command
unit in the Pro Tools Peripherals dialog, Pro Tools compares
the firmware of all connected units to the version available in
Pro Tools software, and prompts you if an update is available.
If you are prompted to update firmware, follow the on-screen
instructions to load the latest firmware to each D-Command
unit.
Declaring D-Command Units in Pro Tools
Communication between D-Command and Pro Tools is configured from Pro Tools.
3 Turn off all Pro Tools audio interfaces.
4 Shut down the computer.
5 If using MIDI equipment, turn off MIDI interfaces or con-
trollers.
6 Turn off the D-Command units.
7 Turn off external hard drives.
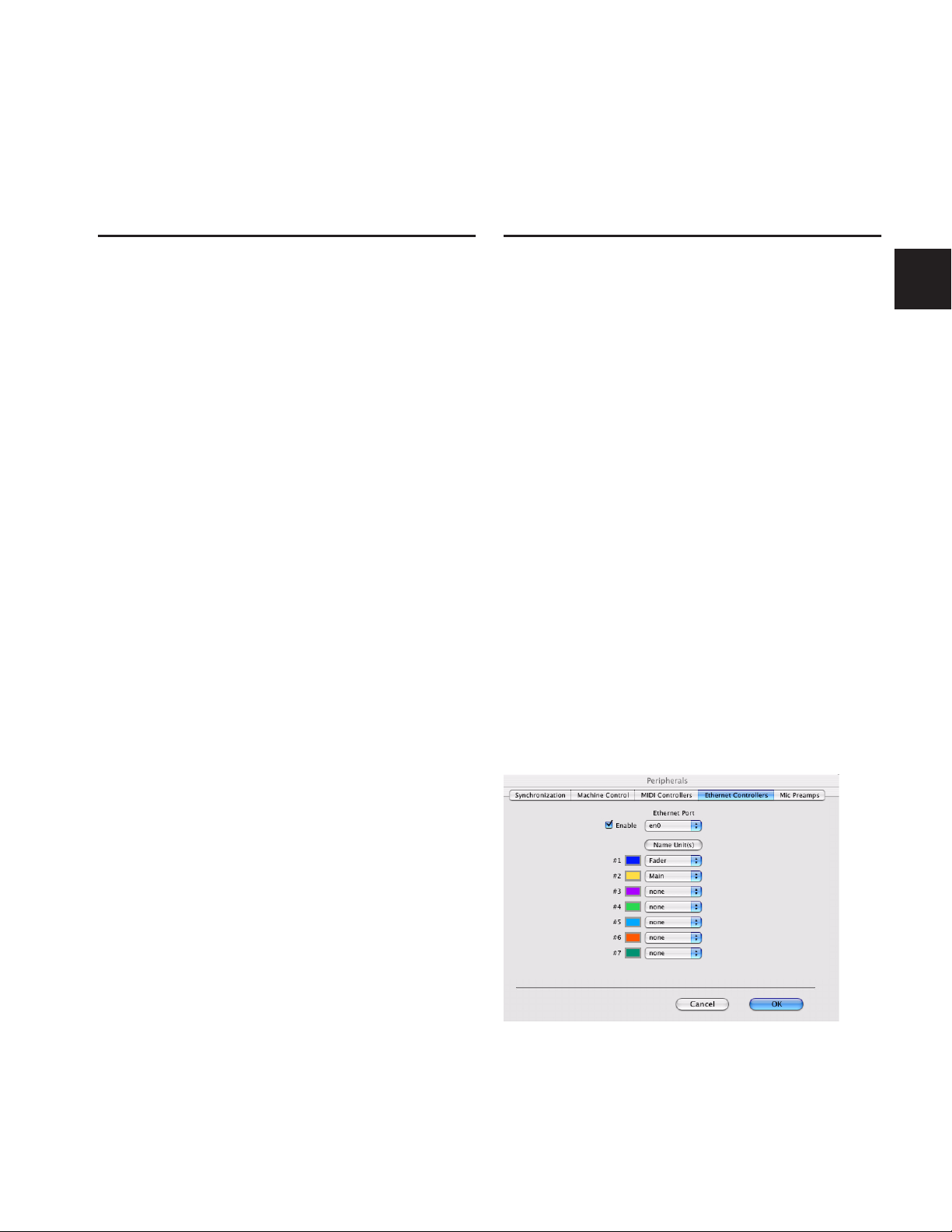
To declare D-Command units in Pro Tools:
1 Choose Setups > Peripherals, and click Ethernet Controllers.
Ethernet Controllers display in the Peripherals dialog
2 Select Enable. Pro Tools scans the Ethernet connection for
any Ethernet controllers connected to the system.
Chapter 5: Configuring D-Command 21
Page 28
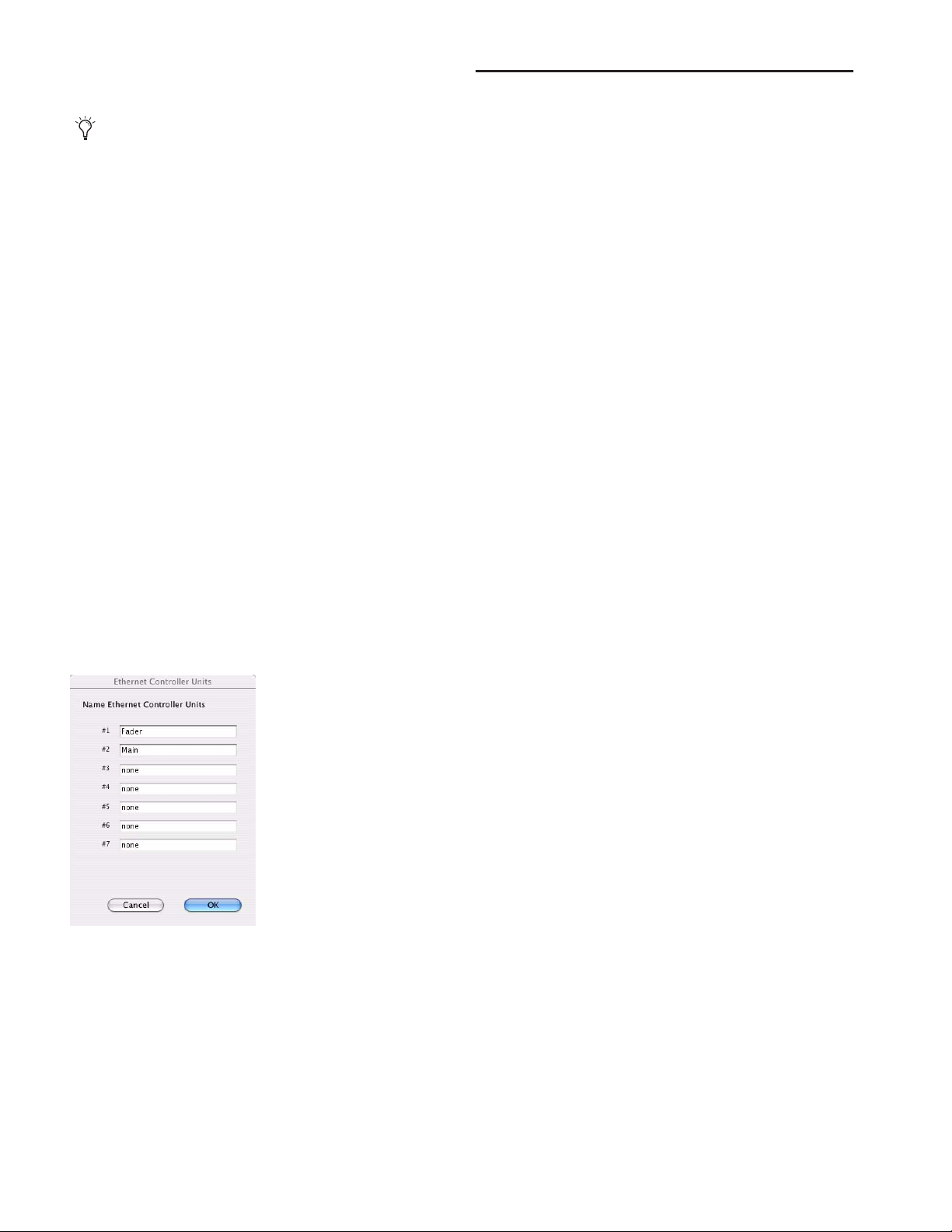
3 Select the units in the order you want them arranged left to
right.
Setting D-Command Preferences
It is not necessary to declare units in the same sequence
as they are physically arranged.
As each unit is selected, Pro Tools scans it and brings it online.
The current status of each unit is indicated in the Peripherals
dialog in the following ways:
• Bold indicates a connected unit.
• Italics indicate an offline or disconnected unit.
• Underlining indicates that the selected unit is in use by
another Pro Tools system.
4 After declaring one or both units, click OK to close the Pe-
ripherals window.
When communication is established, Pro Tools displays colored outlines identifying each bank of Pro Tools tracks.
The colors in each unit row are used to identify controller focus on-screen in Pro Tools. The bank, track, insert, send, or
other element currently the focus of D-Command is outlined
in the color associated with each unit.
Naming D-Command Units in Pro Tools
You can set the names for D-Command units from Pro Tools.
This section describes the settings and preferences for D-Command that are set directly from the control surface. For details
on preferences that are set from Pro Tools, refer to the
Pro Tools Reference Guide.
Fader and Switch Preferences
The following settings and preferences affect operation of the
faders and switches on D-Command.
Bank Justification
The Bank Justification preference determines whether banks
of channels in Normal mode are left-, center-, or right-justified on the control surface.
To set bank justification:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “BnkJus” to choose
between the “Left,” “CentrL,” “CentrR,” and “Right” settings.
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch twice to
exit.
To name D-Command units in Pro Tools:
1 Choose Setup > Peripherals, and click Ethernet Controllers.
2 Click Name Units.
Naming D-Command units
3 Enter the names for the units and click OK.
You can also set the names for D-Command Main Units and
Fader Modules directly from the units themselves, by using
Utility mode. For details on naming D-Command units in
Utility mode, see “D-Command Name Page” on page 102.
Custom Fader Justification
The Custom Fader Justification preference determines
whether channels in Custom Fader mode are left-, center-, or
right-justified on the control surface.
To set Custom Fader justification:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “CF Jus” to choose be-
tween the “Left,” “CentrL,” “CentrR,” and “Right” settings.
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch twice to
exit.
D-Command Guide22
Page 29
Maximum Custom Fader Bank Size
Encoder Preferences
The Maximum Custom Fader Bank Size preference determines
the number of channels to be used when displaying channels
in the Custom Fader modes. Options are 4 and 8 faders for a
Main Unit, and 4, 8, 16 and 24 faders for an expanded system.
To set the maximum Custom Fader bank size:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Do one of the following:
• To increment the maximum number of channel strips
used by the Custom Fader modes, press the Soft Key that
corresponds to “Max CF.”
• To decrement the maximum number of channel strips
used by the Custom Fader modes, hold Shift and press
the Soft Key that corresponds to “Max CF.”
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch twice to
exit.
Select Switch Latch Mode
The Select Switch Latch mode determines whether channel
Select buttons follow latching or non-latching (exclusive-or)
behavior when in Select mode.
To set the Select switch mode:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “Select” to toggle the
setting between the “Latch” and “ExclOr” (non-latching) settings.
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch twice to
exit.
The following preferences affect operation of the rotary encoders on D-Command.
Rotary Encoder Mode
The Rotary Encoder mode affects responsiveness of rotary encoder knobs. Fixed mode is at normal resolution. The velocity
modes set different rates of encoder acceleration. In Fine
mode, response is fixed and at fine resolution.
To set the Rotary Encoder mode:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Press the upper Soft Key that corresponds to “Rotary” to step
through the “Fixed,” “Vel-Sl” (velocity-sensitive, slow),
“Vel-Md” (velocity-sensitive, medium), “Vel-Fa” (velocity-sensitive, Fast), and “Fine” settings.
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch twice to
exit.
Encoder Order
The Encoder Order preference determines whether inserts,
sends, and pan controls will be displayed in order from
top-to-bottom or bottom-to-top on D-Command rotary encoders.
To set the Encoder Order preference:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section twice.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “Encod” to toggle the
setting between “Bot-Tp” (bottom-to-top ordering) and
“Tp-Bot” (top-to-bottom ordering).
Faders On/Off
The Faders On/Off preference lets you temporarily turn off
D-Command faders to prevent fader movement when monitoring a mix.
To toggle D-Command faders on and off:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section twice.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “Faders” to toggle all
faders on and off.
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
Chapter 5: Configuring D-Command 23
Page 30

Display Preferences
Meter Preferences
The following preferences affect the interaction of D-Command with on-screen display of elements in Pro Tools.
Target Track from Application
The Target Track from Application preference determines
whether selecting an Insert or Send on-screen makes its track
the focused track on the D-Command Main Unit. For details
on focusing a track on D-Command, see “Focusing a Track”
on page 91.
To set the Target Track from Application preference:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section twice.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “ApTrgt” to toggle the
setting between “Yes” and “No.”
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
Channel Window Display
The Channel Window display preference determines whether
displaying plug-in or send pan parameters (by pressing an encoder Select switch) on D-Command opens the corresponding
plug-in or send window on-screen in Pro Tools.
This preference also determines whether the Channel Select
switches in the Dynamics or EQ sections change the channel
display of multi-mono plug-ins.
◆ When this preference is set to “Yes,” the on-screen display
of plug-in and send windows changes to reflect the state of the
control surface.
◆ When this preference is set to “No,” the on-screen display of
plug-in and send windows does not change to reflect the state
of the control surface.
The following preferences affect operation of the meters on
D-Command.
Send Meters On/Off
The Send Meters On/Off preference toggles send metering on
and off. Send levels are displayed on the LED rings surrounding the D-Command rotary encoders. This metering follows
Send pre- or post-metering settings in Pro Tools.
To toggle send meters on and off:
1 Press the Meters switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys sec-
tion.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “SndMtr” to toggle
the setting On and Off.
3 Press the Meters Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
Insert Meter On/Off
The Insert Meters On/Off preference toggles insert metering
on and off. This preference applies when inserts are displayed
on the LED rings surrounding the D-Command rotary encoders.
To toggle insert meters on and off:
1 Press the Meters switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys sec-
tion.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “InsMtr” to toggle the
setting On and Off.
3 Press the Meters Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
To set the Channel Window display preference:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “ChanWn” to toggle
this setting between “Yes” and “No.”
3 Press the Operation Console Prefs Soft Key switch twice to
exit.
D-Command Guide24
Page 31
Meters Pre/Post Fader
The Meters Pre/Post Fader preference toggles channel metering between pre- and post-fader modes.
System Calibration
Recalibrating D-Command Faders
To toggle channel meters between pre- and post-fader metering:
1 Press the Meters switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys sec-
tion.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “Meters” to toggle the
setting between “PreFad” (pre-fader metering) and “PostFd”
(post-fader metering).
3 Press the Meters Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
Center Meters Track/Output
The Center Meters Track/Output preference toggles the
8-channel meter display on the Main Unit meter bridge between main output levels and the focused track.
When set to meter the focused track, you can view levels for
multichannel tracks up to 6 channels (5.1 surround).
To toggle the center meters between output and track metering:
1 Press the Meters switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys sec-
tion.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “CtrMtr” to toggle the
setting between “Output” and “Track.”
3 Press the Meters Console Prefs Soft Key switch to exit.
If a fader on a D-Command Unit shows response problems,
you can recalibrate the faders with the Recal command in
Utility mode. See “Recal” on page 105 for details.
Calibrating the Output Meters
You can calibrate the output meters on the Main Unit meter
bridge from XMON, in order to match metering levels in
Pro Tools with metering levels of external sources. The example below uses a Digidesign 192 I/O as the reference source.
To calibrate the D-Command output meters:
1 Set the reference level of your 192 I/O according to the in-
structions in the 192 I/O Guide.
2 With the 192 I/O analog output connected to the XMON
Main Input, send a calibration tone to the D-Command Main
Outputs, and note the output level on the D-Command
meters.
3 Disconnect the 192 I/O analog output from the XMON
Main Input and connect it to the XMON Alt Input.
4 Activate the Alt Output.
5 Adjust the trim pots on the back panel of the XMON until
the output level for each channel on the D-Command
matches the level displayed for the Main Output.
6 When you are finished, reconnect the 192 I/O analog out-
put to the XMON Main Input.
Calibrating SPL Indication on the Monitor Section
The D-Command Monitor section lets you display output
level in dB or dB SPL. You can calibrate the SPL display to reflect the sound pressure level at the mix position. See “Calibration Mode Switch” on page 85.
Chapter 5: Configuring D-Command 25
Page 32

D-Command Guide26
Page 33

Part III: Reference
Page 34

Page 35

Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls
Channel Strips
The D-Command Main Unit has 8 channel strips, and the
D-Command Fader Module has 16 channel strips. Each channel strip (Figure 1) has identical controls, including two
touch-sensitive rotary encoders, display and mode controls,
and a touch-sensitive fader.
auto
SEND E
Mute PreFlipClip
Select
Rotary Encoders
B M P
auto
SEND F
Mute PreFlipClip
B M P Select
Page Dn Page Up
Inserts
Byp Mute
Channel Strip
Pan
Sends
Mode controls
Rotary Encoder Section
Each channel strip has two touch-sensitive rotary encoders
with LED ring, alphanumeric display, mode switches, and status indicators. Rotary encoders control channel input, send,
pan, and mic pre parameters.
Encoder
LED ring
Encoder knob
Encoder
Automation Mode
indicator
Clip/Flip indicators
Select switch
Channel Strip Rotary Encoder
Encoder Knob
The encoder knobs on D-Command channel strips are
touch-sensitive. When you touch the encoder, the encoder
display switches from the parameter name to the parameter
value. Touch display of parameter values can be turned off.
auto
SEND E
Mute PreFlipClip
Select
B M P
Encoder display
Mute/Pre indicators
Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch
Record
Auto / Inpt
Sel
Solo
Mute
KICK
Auto Trim
WR
+12
TC
Automation Mode
and
Channel Status
indicators
LT
+6
TM
RD
0
GRP
-5
CF
-10
-15
-20
-30
-40
-60
-90
Figure 1. D-Command Channel Strip
Channel Strip
Function controls
Channel Fader
When you are automating a parameter on an encoder, touching the encoder knob starts writing automation.
When assigning a channel input or output, or an insert or
send, the encoder knob is used to scroll through available inputs, outputs, inserts, or sends.
Encoder LED Ring
Each encoder has a ring of 15 LEDs. Discrete or stepped information is shown by single LEDs, and continuously variable information is shown by an expanding series of LEDs.
In Normal mode, encoder LED rings can show send level, pan
position, plug-in parameter values, and mic pre settings. In
Flip mode, they show track level.
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 29
Page 36

Encoder Automation Mode Indicator
Bypass/Mute/Pre Switch
Below each encoder knob is an LED marked “auto,” which
lights when the corresponding parameter is enabled for automation. The indicator lights green for Read mode, yellow
when armed for automation in any of the Write modes, and
red when writing automation in any of the Write modes.
Encoder Display
Each encoder has a six-character display that shows parameter
names. When the corresponding encoder knob is touched or
moved, the display shows parameter values.
Encoder displays use color inversion to indicate the following:
• Green: Default color for input, insert, send, pan, and mic
pre parameter names and values
• Inverted green: Inactive input, inactive output, inactive
plug-in or inactive send names
Clip and Flip Indicators
When viewing inserts on an encoder, these LEDs light to indicate the send or insert has clipped (red LED) or has been
flipped to the fader (yellow LED).
Mute and Pre Indicators
When viewing sends on an encoder, these LEDs light to indicate that the send is muted (red LED) or set to pre-fader operation (green LED).
Encoder Select Switch
Each encoder has a Select switch that is used to assign an insert or send to that encoder, or to display send parameters for
editing.
Inserts
When assigning an insert, the encoder Select switch is used to
confirm the selection of the following elements on each level:
• Insert type (TDM plug-in, RTAS plug-in, Multi-Mono
TDM plug-in, Multi-Mono RTAS plug-in, or Hardware
Insert)
• Plug-in subfolder (such as EQ, Dynamics, Pitch Shift,
Reverb, or Delay)
• Individual insert or plug-in
Each encoder has a Bypass/Mute/Pre (B/M/P) switch whose
function depends on what is currently displayed on the encoder. With Sends, the function of the B/M/P switch also depends on the current Switch Mode setting.
See “Switch Mode Switch” on page 37 for more information
on changing the Switch mode and viewing the current function of the B/M/P switch.
Inserts
When a plug-in name is displayed on an encoder (in the top
level Inserts display), the B/M/P switch bypasses the corresponding plug-in. The B/M/P switch lights when the plug-in is
bypassed.
Sends
When a send name is displayed on an encoder, the B/M/P
switch does one of the following:
• If the Switch Mode is set to Mute, the B/M/P switch
mutes the corresponding send. The red Mute LED lights
to indicate that the send is muted.
• If the Switch Mode is set to Pre, the B/M/P switch toggles
the corresponding send between pre- and post-fader operation. The green Pre LED lights to indicate that the
send is set for pre-fader operation.
Mic Pre
In Mic Pre mode, mic pre parameters are displayed on a channel strip’s encoders. In addition, the B/M/P switches do the
following:
• Top encoder, page 1: toggles phantom power on and off
• Bottom encoder page 1: toggles mic pre Pad on and off
• Top encoder, page 2: toggles mic pre HPF on and off
• Bottom encoder page 2: toggles mic pre Polarity
• Top encoder, page 3: toggles phantom power on and off
• Bottom encoder, page 3: toggles mic pre Insert on and off
Sends
When assigning a send, the encoder Select switch is used to
confirm the selection of the following:
• Send type (interface or bus)
• Send assignment
When viewing a send, the encoder adjusts level. In Send Pan
mode, the fader adjusts level and the encoder adjusts Pan.
D-Command Guide30
Page 37

Channel Strip Mode Controls
Pan Switch
Each channel strip has a set of Channel Strip Mode controls
for displaying and editing pan, plug-in, mic pre, insert, or
send parameters on the encoder section of the D-Command
channel strip.
Page Down switch
Inserts switch
Bypass/Mute
switch
Channel Strip Mode controls
Page Dn Page Up
Inserts
Pan
Sends
Byp Mute
Page Up switch
Pan switch
Sends switch
Page Up and Page Down Switches
Control parameters are arranged on channel strip rotary encoders in pages, or groups of up to two parameters at a time.
The Page Up and Page Down switches light to indicate the
presence of additional pages of pan, plug-in, or mic pre parameters in the corresponding direction on each channel
strip. If no additional pages are available, neither switch is lit.
To move the page display of parameters on the encoders up or
down:
■ Press a lit Page Up or Page Down switch.
When you press the Pan switch, you enter Pan mode, and the
pan controls for the channel strip are displayed on the encoder displays. If there are additional pages of pan controls for
a multichannel track, its Page Up switch lights.
Mic Pre Mode
When you press a channel strip’s Inserts switch and Pan
switch simultaneously, you enter Mic Pre mode. In Mic Pre
mode, the controls for an available remote-controlled microphone preamplifier (such as the Digidesign PRE) are displayed
on the channel strip’s rotary encoders for editing. The Page Up
switch lights to indicate more available parameter pages.
Microphone preamplifiers are declared in the Pro Tools peripherals dialog, and assigned to channels in the Pro Tools I/O
Setup dialog.
Bypass/Mute Switch
The function of the Bypass/Mute switch depends on what is
currently displayed on the channel strip’s encoders.
Inserts
◆ In the top level Inserts view (when plug-in names are dis-
played on a channel strip’s encoders), the Bypass/Mute switch
bypasses all plug-ins on that channel.
Inserts Switch
When you press the Inserts switch, you enter Inserts mode,
and the plug-in names for the first two plug-ins on that channel strip are displayed on the encoder displays. If there are additional plug-ins on the channel, the channel’s Page Up
switch lights.
To open a plug-in window from any channel on D-Command:
■ Hold Start (Windows) or Control (Mac) and press the Select
switch for the plug-in.
To close the plug-in window:
■ Hold Start (Windows) or Control (Mac) and press the Select
switch again.
The Inserts switch flashes when a plug-in on that channel has
clipped. To clear a clip, press the Clear Clip switch in the Session Management section. See “Clear Clip Switch and Plug-in
Clip Indicator” on page 70 for more information.
Sends
◆ In the top level Sends view (when send names are displayed
on a channel strip’s encoders), the Bypass/Mute switch mutes
all sends on that channel.
Sends Switch
When you press the Sends switch, you enter Sends mode, and
the send names for the first two sends on that channel strip
are displayed on the encoder displays. If there are additional
sends on the channel, the channel’s Page Up switch lights.
The 10 available sends are displayed in five pairs (A–B, C–D,
E–F, G–H, I–J).
Send Pan Mode
Send Pan mode allows you to adjust send panning and level at
the same time. Send Level is controlled by the channel fader
and Send Pan is controlled by the encoder.
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 31
Page 38

To enter Send Pan mode:
1 Press the Sends switch to display sends on the channel’s en-
coders.
2 Press the encoder Select switch that corresponds to the send
you want to display.
Channel Strip Function Controls
Each channel strip has a set of Channel Strip Function controls for controlling channel selection and focus, mute, solo,
and record enable status, input monitor mode, and automation mode.
To return to the top level display of sends on the channel strip:
■ Press the Sends switch again.
MIDI Controls on Instrument Tracks
The Instruments View in Pro Tools contains MIDI controls
that can be displayed on the encoders of D-Command channel strips.
To display MIDI controls:
■ Hold the Inserts switch and press the Sends switch in the
Channel Strip Mode controls section of the channel strip.
The MIDI controls appear on the channel encoders as follows:
• Encoder #2 knob: MIDI Volume
• Encoder #2 B/M/P switch: MIDI Mute
• Encoder #2 LED ring: MIDI Velocity Meter
• Encoder #1 knob: MIDI Pan
To exit display of MIDI controls:
■ Press another switch in the Channel Strip Mode section.
Instrument Tracks and Flip Mode
When MIDI controls for Instrument tracks are displayed on
the encoders, they can be transferred (or “flipped”) to the
channel faders, allowing control of MIDI Volume or MIDI Pan
from the channel faders.
To transfer controls from the rotary encoders to the channel
faders:
■ Press the Flip switch that corresponds to the row of encod-
ers you want to transfer.
In Flip mode, Instrument track controls are transferred as follows:
• The fader on each channel controls the parameter (MIDI
Volume or MIDI Pan) that was assigned to the encoder, and
the encoder controls track Volume.
• The channel Mute switch controls the MIDI Mute function,
and the B/M/P switch on the encoder controls channel
mute.
Input Monitor Mode
Automation Mode
switch
Channel Select
switch
Mute switch
switch
Auto / Inpt
Sel
Solo
Mute
KICK
Auto Trim
Record
Record Enable switch
Solo switch
Channel display
Automation Trim
switch
Channel Strip Function controls
Input Monitor Mode Switch
The Input Monitor Mode switch toggles the input monitoring
mode for that channel between Auto Input and Input Only
mode. The switch lights when the channel is in Input Only
mode.
Record Enable Switch
The Record Enable switch toggles record enable status for the
channel. When the channel is record-enabled and the
Pro Tools transport is stopped, the switch flashes. During recording, the switch lights continuously.
Record Safe Mode To record safe a track from D-Command,
hold Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the
track’s Record Enable switch.
Channel Select Switch
The function of the Channel Select switch depends on the Select/Focus Mode setting. See “Select/Focus Mode Switch and
Indicators” on page 37 for more information on changing the
Select/Focus mode.
To exit Flip mode:
■ Press a lighted Flip switch.
D-Command Guide32
Page 39
Select Mode If the Select/Focus Mode is set to Select, the
Automation Mode
indicators
Group Status
indicator
Custom Fader Mode
indicator
AutoMatch
indicators
Channel
Fader
Channel Select switch selects the channel in Pro Tools. The
switch lights when the channel is selected. In this mode, the
Channel Select switch can be set to follow latching or exclusive-or (non-latching) behavior.
Focus Mode If the Select/Focus Mode is set to Focus, the Channel Select switch brings that channel’s Dynamics and EQ controls into the Dynamics and EQ sections of the Main Unit for
editing. In this mode, because only one track can be focused at
a time, the Select switch follows exclusive-or (non-latching)
behavior only.
In Focus mode, if the D-Command Focus Channel Strip Operations preference is set to Yes, the Channel Select switch also
places a duplicate of the focused channel in the channel strip
to the immediate left of the Global Controls section.
Solo Switch
The Solo switch toggles solo status for the channel. When a
channel is soloed, the Solo switch lights, and the Mute
switches on other channels in the session flash. The Solo
switch function follows the Pro Tools Operation preference
for latched operation.
Solo Safe Mode To solo safe a track from D-Command, hold
Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the track’s
Solo switch.
Mute Switch
The Mute switch toggles mute status for the channel. When a
channel is muted, the Mute switch lights continuously.
Channel Display
Each channel display shows the channel information in the
following display modes. In each mode, when the channel
fader is touched, the display shows the channel volume in dB.
Track Name Mode Shows the track name only.
Group/Name Mode Shows the group membership of the track
(by group letter) and an abbreviated track name.
Automation Mode Switch
The Automation Mode switch cycles the channel through the
Pro Tools automation modes (Write, Touch, Latch, Read and
Off). The active mode is shown by the Automation Mode LED
indicators to the left of each channel’s fader. When in Off
mode, none of the indicators is lit.
The Automation Mode switch lets you cycle the channel
through Touch, Latch, and Read modes during playback, but
it prevents you from entering Write of Off mode during playback. To directly enter Write or Off mode during playback, use
the Automation Mode controls in the lower left of the Main
Unit. (See “Automation Mode Controls” on page 40.)
Automation Trim Switch
The Automation Trim switch toggles the channel into the corresponding Trim mode for Write, Latch, Touch, and Read
modes. Active Trim mode is shown by the yellow Trim mode
LED indicator to the left of each channel’s fader. The Automation Trim switch has no effect while the channel is in Off
mode.
Fader Section
WR
+12
TC
LT
+6
TM
RD
0
GRP
-5
CF
-10
-15
-20
-30
-40
-60
-90
Track Position Number/Name Mode Shows the track position
number and an abbreviated track name.
Headroom Mode Shows the abbreviation “HR” followed by the
remaining headroom in dB.
Level Mode Shows the track volume level in dB only.
Channel displays use colors and backlighting to indicate the
following:
• Green: Channel names and values
• Inverted green: Inactive channel
Channel Strip Fader section
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 33
Page 40

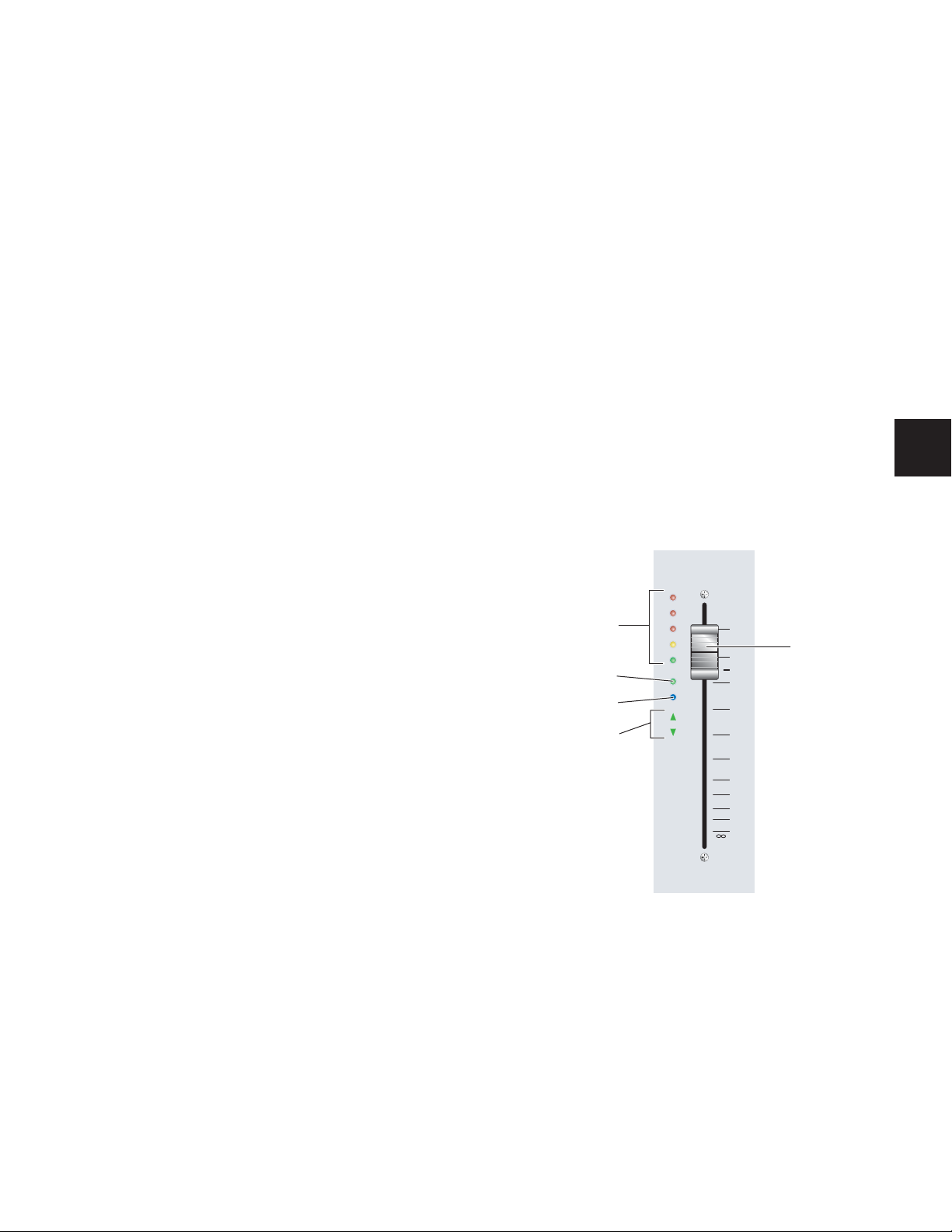
Fader
60
60
Modifier Key Switches
The touch-sensitive faders on D-Command channel strips
control channel volume in Normal mode, and a wide range of
parameters in Flip mode or the Custom Fader modes. When
you touch a fader, its channel strip display changes from track
name to track volume level (in Normal mode), or from parameter name to parameter value (in Flip modes or Custom Fader
modes). When you are automating a parameter on a fader,
touching the fader starts writing automation.
Automation Mode Indicators
The Automation Mode indicators, located to the left of each
channel’s fader, indicate the active automation mode.
WR (Write), TC (Touch) and LT (Latch) are red LEDs; TM
(Trim) is a yellow LED; and RD (Read) is a green LED.
When in Write, Touch or Latch modes, the corresponding indicator flashes until automation writing begins. When automation writing begins, the indictor lights solid.
If automation is turned off for the channel (Off), none of the
indicators is lit.
Group Status Indicator
The Group Status indicator (a green LED marked GRP), located
to the left of each channel’s fader, lights to indicate that the
channel is a member of an active Mix or Edit group in
Pro Tools.
If the channel is a member of an inactive group, or if groups
are suspended, this indicator is off.
Custom Fader Mode Indicator
The Custom Fader Mode indicator (a blue LED marked CF), located to the left of each channel’s fader, lights to indicate that
the channel is currently in Custom Fader Mode.
AutoMatch Indicators
The AutoMatch indicators (green arrow-shaped LEDs), located
to the left of each channel’s fader, light to indicate the direction you need to move the fader in order to match the automation level previously written for that track. This is especially useful when editing fader automation.
Each D-Command Main Unit and Fader Module has a set of
four switches in its lower left corner that duplicate the function of the Pro Tools computer keyboard modifiers.
-
-90
Shift Control Star t/Win (Windows)
Modifier Keys (Fader Module)
Option (Mac)
-
-90
Alt (Windows)
(Command) (Mac)
Shift Switch (Windows and Mac)
The Shift switch duplicates the function of the Shift key on
your computer keyboard.
Control Switch (Windows and Mac)
The Control switch duplicates the function of the Control key
on your computer keyboard.
Win Switch (Windows) or Option Switch (Mac)
The Win/Option switch duplicates the function of the Windows key (also called the Start key) or the Option key (Mac) on
your computer keyboard.
Alt Switch (Windows) or Command Switch (Mac)
The Alt/Command switch duplicates the function of the Alt
key (Windows) or the Command key (Mac) on your computer
keyboard.
The order of the modifier keys on the D-Command
reflects the order of the corresponding keys on a
Windows or Mac keyboard, from left to right.
D-Command Guide34
Page 41
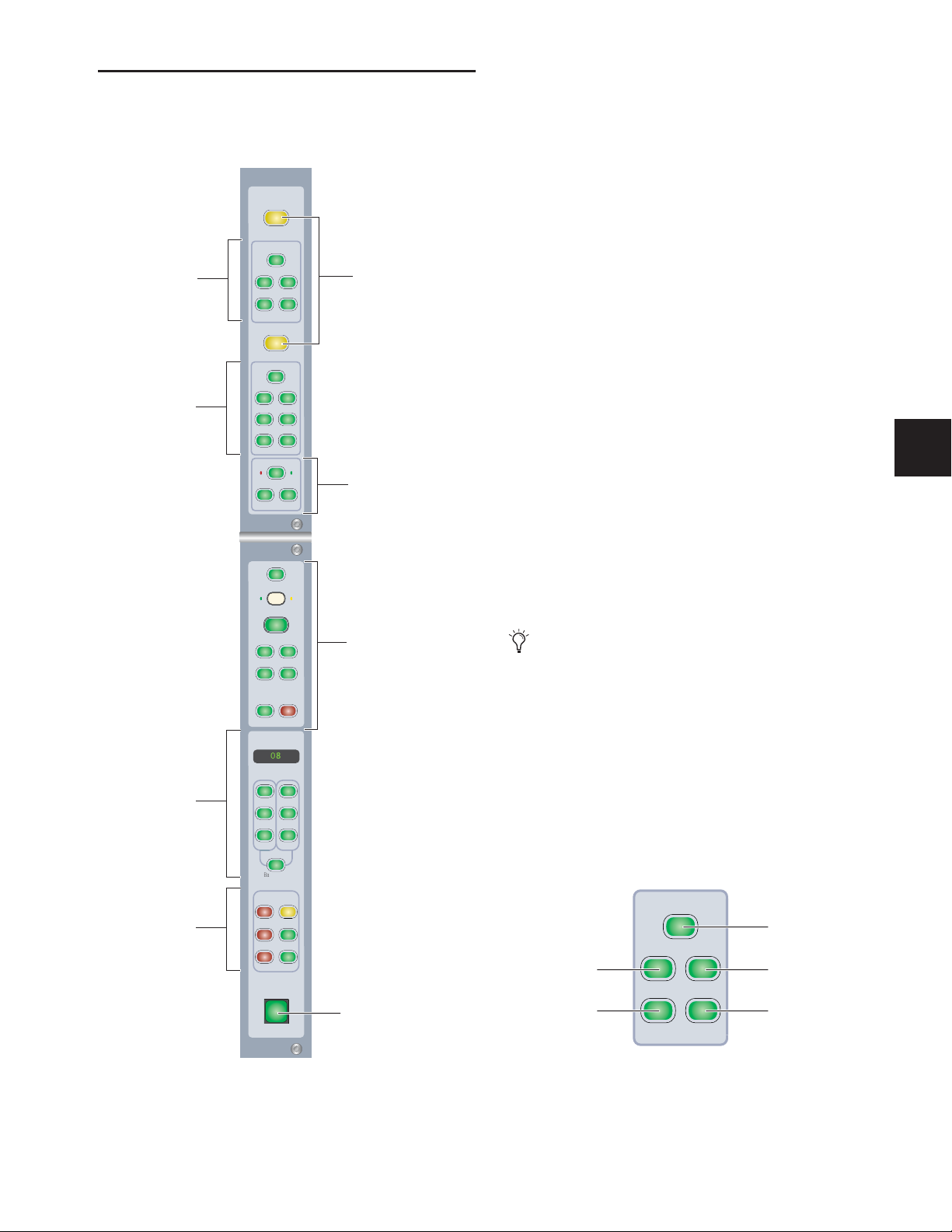
Global Controls Section
Start
Current
All
Enab
All
End
Auto Write
Automation
Write to Start
Write to Current
Parameter
Automation
Write to All
Automation
Write to End
Write to All Enabled
Parameters
switch
switch
switch
switch
switch
The Global Controls section (Figure 2) is a set of channel-related controls in the center of the D-Command Main Unit.
Flip Switches
The two yellow Flip switches in the Global Controls section
correspond to the two rotary encoders on the D-Command
channel strips.
Flip Mode
Automation Write
controls
Automation Enable
Automation Mode
controls
Custom Fader
controls
controls
Flip
Auto Write
Start
Current
All
All
End
Flip
Auto Enable
Plug-in
Send Lvl
Vol
Send
Pan
Mute
Send
Mute Pre
Sw Mode
Show
Info
Sw
Escape
Mode
Solo
Clear
Do to Sel Do to All
Mode
Disp
Susp Grp
Auto
Focus Channel
&
Custom Faders
Type
WindowPlug-In
Bank / Cycle
Auto Mode
Write Trim
Touch
Latch Off
Default
Lock
Read
The Flip switches invoke Flip mode, which transfers controls
from the corresponding rotary encoder to the fader on each
channel strip, allowing convenient editing and automation of
Flip
switches
Enab
send, pan, plug-in, and mic pre parameters directly from the
channel faders.
In Flip mode, the rotary encoder control swaps with the channel fader; the encoder Select switch swaps with the channel
Select switch; the encoder Bypass/Mute/Pre switch swaps with
the channel Mute switch; and the encoder display swaps with
the channel display.
Pan
Mute
In Flip mode, the Flip switch lights for the affected row of encoders, and the yellow Flip LED below each affected encoder is
lit.
Switch Information
controls
Val
To transfer controls from a row of rotary encoders to the channel
faders:
■ Press the Flip switch that corresponds to the encoder row.
FocSel
Global Modifier
controls
To exit Flip mode:
■ Press a lighted Flip switch.
When D-Command is in Flip mode and you enter Make
Inactive mode or Assign mode, it is temporarily taken out
of Flip mode, but the Flip switch remains lit. When you
exit Make Inactive mode or Assign mode, controls return
Susp
to their flipped positions.
Automation Write Controls
The Automation Write controls invoke the manual “Write to
MapGroups
Start/End/All” commands, the automatic “Write to
Start/End/All on Stop” automation commands, and the
“Write to Current Parameter” and “Write to All Enabled Parameters” snapshot automation commands in Pro Tools.
Dbl Press to Latch
Figure 2. Global Controls section
Talkback
Talkback switch
Automation Write controls
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 35
Page 42

Start Switch
All Enabled Switch
The Start switch writes the current automation value of all
write-enabled parameters to the start of a selection or track
when performing an automation pass.
To manually Write to Start:
■ Press the Start switch during playback.
To enable automatic Write to Start on Stop:
■ Hold the Start key (Windows) or the Control key (Mac) and
press the Start switch.
To disable automatic Write to Start on Stop:
■ Press the flashing Start switch.
All Switch
The All switch writes the current automation value of all
write-enabled parameters to an entire selection or track when
performing an automation pass.
To manually Write to All:
■ Press the All switch during playback.
To enable automatic Write to All on Stop:
■ Hold the Start key (Windows) or the Control key (Mac) and
press the All switch.
To disable automatic Write to All on Stop:
■ Press the flashing All switch.
End Switch
The End switch writes the current automation value of all
write-enabled parameters to the end of a selection or track
when performing an automation pass.
The All Enabled switch writes a snapshot of all current parameter values to all enabled automation parameters.
Automation Enable Controls
The Automation Enable controls are used to enable or suspend writing of each type of automation on all channels.
When writing is enabled for a type of automation, its corresponding switch is lit.
These Automation Enable controls mirror the function of the
corresponding buttons in the Pro Tools Automation Enable
window.
Auto Enable
Vol
Pan
Mute
Plug-in
Send Lvl
Send
Send
Pan
Mute
Enable Volume
Automation
switch
Enable Pan
Automation
switch
Enable Mute
Automation
switch
Automation Enable controls
Plug-in Switch
The Plug-in switch enables and suspends writing of automation for any automation-enabled plug-in parameters on all
tracks in the session.
Volume Switch
The Volume switch enables and suspends writing of channel
volume automation on all tracks in the session.
Pan Switch
Enable Plug-in
Automation
switch
Enable Send Level
Automation
switch
Enable Send Pan
Automation
switch
Enable Send Mute
Automation
switch
To manually Write to End:
■ Press the End switch during playback.
To enable automatic Write to End on Stop:
■ Hold the Start key (Windows) or the Control key (Mac) and
press the End switch.
To disable automatic Write to End on Stop:
■ Press the flashing End switch.
Current Switch
The Current switch writes a snapshot of the current parameter
value to the currently displayed automation parameter.
D-Command Guide36
The Pan switch enables and suspends writing of channel pan
automation on all tracks in the session.
Mute Switch
The Mute switch enables and suspends writing of channel
mute automation on all tracks in the session.
Send Level Switch
The Send Level switch enables and suspends writing of send
level automation on all tracks in the session.
Send Pan Switch
The Send Pan switch enables and suspends writing of send
pan automation on all tracks in the session.
Page 43
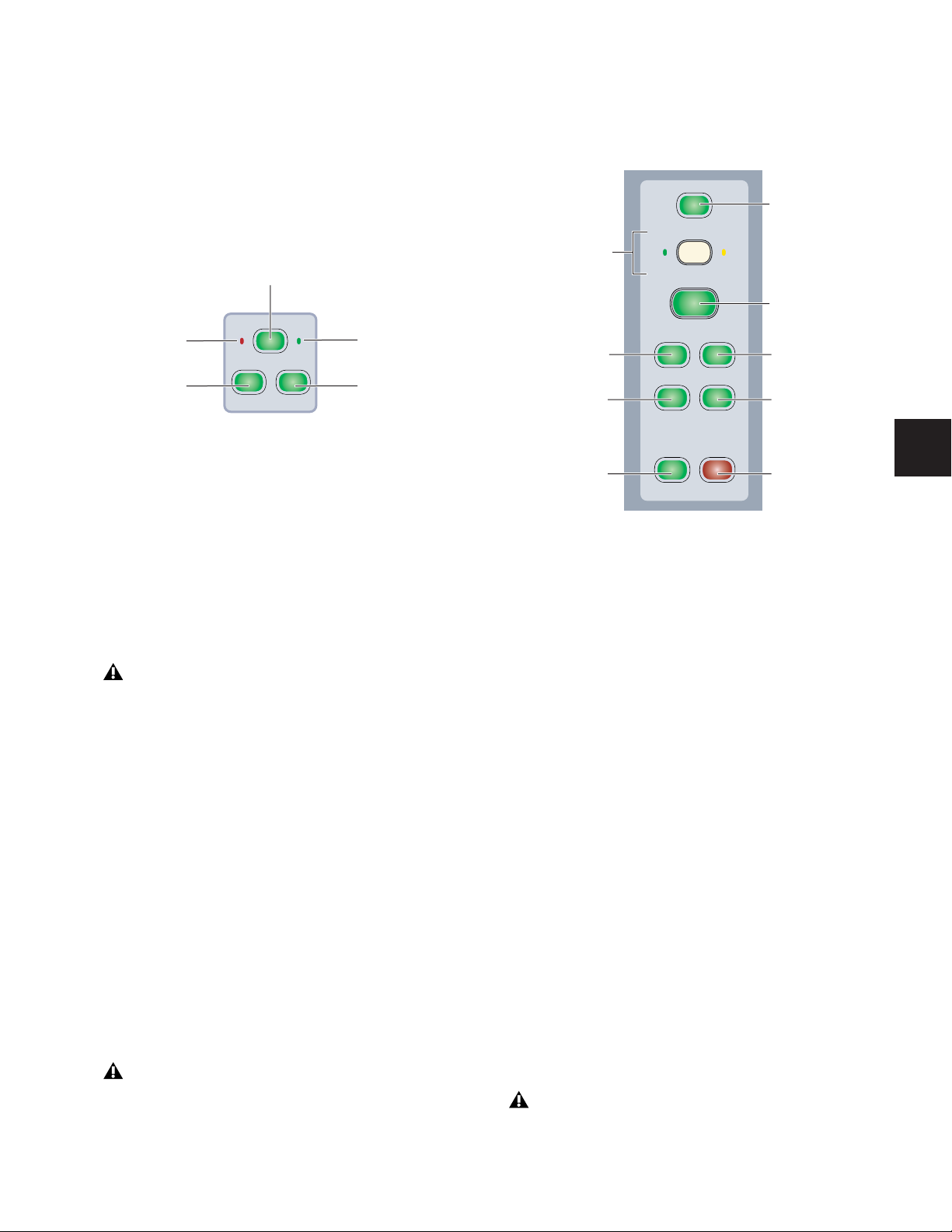
Send Mute Switch
Escape
Mode
Disp
Mode
Susp Grp
Do to Sel Do to All
Default
Auto
Susp
FocSel
Solo
Clear
Escape switch
Select/Focus Mode
Solo Clear switch
Display Mode
Suspend Automation
switch
Switch and indicators
Do to Selected
Set to Default
Do to All switch
Suspend Groups
switch
switch
switch
switch
Global Modifier Controls
The Send Mute switch enables and suspends writing of send
mute automation on all channels.
Switch Information Controls
The Switch Information controls are used to change the mode
and display of encoder Bypass/Mute/Pre switches, and globally show encoder parameter values.
Switch Mode switch
Mute Mode
indicator
switch switch
Switch Information controls
Switch Mode Switch
The Switch Mode switch toggles the function of encoder Bypass/Mute/Pre switches between Mute and Pre-Fader functions when displaying sends on the encoders.
• When the Switch Mode is set to Bypass, the encoder B/M/P
switch mutes the corresponding send.
• When the Switch Mode is set to Pre, the encoder B/M/P
switch toggles the corresponding send between pre- or
post-fader operation.
Mute Pre
Sw Mode
Show Val
Info
Sw
Pre-Fader Mode
indicator
Show ValuesSwitch Info
The Global Modifier controls are used to change modes for the
channel Select switches, channel displays, clear Solo and Mute
states, and globally suspend automation.
Global Modifier controls
Escape Switch
The Escape switch is used to exit modes and to cancel operations or on-screen dialogs. When an action has occurred that
can be exited or canceled with the Escape switch, the switch
flashes.
The Transport must be stopped to toggle sends between
pre- and post-fader operation.
To set the Switch Mode:
■ Press the Switch mode switch until the appropriate indica-
tor lights (Mute or Pre).
Switch Info Switch
The Switch Info switch can follow toggling or momentary behavior. If pressed briefly, it toggles the encoder display to
show the function assigned to the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on
each rotary encoder. If held, the function is shown until the
switch is released.
Show Values Switch
The Show Values switch can follow toggling or momentary
behavior. If pressed briefly, it toggles the encoder display between parameter name and parameter value. If held, parameter value is shown until the switch is released.
The operation of the Show Values switch is not affected by
the Touch Display of Parameter Values setting in the Operations Soft Key Section.
Select/Focus Mode Switch and Indicators
The Select/Focus Mode switch toggles the function of channel
Select switches between Select and Focus mode. In Select
mode, channel Select switches are used to select channels in
Pro Tools. In Focus mode, channel Select switches are used to
focus a channel in the Focus Channel section on the Main
Unit.
The LEDs on either side of this switch indicate the current
mode.
Do To All and Do To Selected Switches
The Do To All and the Do To Selected switches on D-Command can be used in two different ways: to apply actions to
multiple tracks in a Pro Tools session, and to change the display mode of multiple channel strips on D-Command.
The Do To All and Do To Selected switches can follow latching
or momentary behavior. If pressed briefly, they latch on and
flash until pressed a second time. If held, they apply to all controls moved until released.
The Do to All and Do to Selected switches can latch on, and
are not cleared by the Escape switch. Use them carefully.
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 37
Page 44

Applying Actions to Multiple Tracks in Pro Tools
Changing Parameter Display on D-Command Channel Strips
The Do To All and Do To Selected switches are convenient for
performing tasks such as muting, soloing, assigning sends, or
assigning the same plug-in across multiple tracks in a session.
To apply actions to multiple tracks in a Pro Tools Session:
1 Press the Do To All or the Do To Selected switch.
2 Press any of the following switches to apply the correspond-
ing action to all tracks or all selected tracks in the current session:
• Channel Mute switch
• Channel Solo switch
• Channel Solo Safe: Control (Windows) or Command
(Mac) + Solo switch
• Automation Mode switch
• Automation Trim switch
• Channel Select switch (in Select mode)
• Record Enable switch
• Record Safe: Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) +
Record Enable switch
• Input Monitor Mode switch
3 Depending on the current channel strip display mode, you
can apply the following across all tracks or all selected tracks
in the session:
• Mic Pre Controls: Polarity, Pad, Impedance, Source, Gain
• Send Pre/Post: B/M/P switch in Send Pre/Post mode
• Send Mute: B/M/P switch in Send Mute mode
• Plug-in Bypass: B/M/P switch in Inserts mode
4 You can also carry out any of the following tasks across all
tracks or all selected tracks in the session:
• Assigning Inputs, Outputs, Inserts and Sends
• Activating/deactivating Inputs, Outputs, Inserts, Sends
and Tracks
• Resetting controls with the Set to Default switch
• Changing panner linkage
• Changing panner editor choice
5 When you are finished, press the flashing Do To All or Do To
Selected switch to exit the corresponding mode.
The Do To All and Do To Selected switches can be used to display and edit pan, mic pre, insert, or send parameters across
all channels on the D-Command surface.
The Do To All and Do To Selected switches are applied independently to channel strips in Normal mode and Custom
Fader mode. This independent operation lets you put banks of
channels in several display modes at once (for example, pan
on channels in Normal mode, and plug-ins on channels in
Custom Fader mode).
To change the display mode of D-Command channel strips:
1 Press the Do To All or the Do To Selected switch.
2 Press any of the following Channel Strip Mode switches on
any individual channel to apply the corresponding action to
all channels or to all selected channels on D-Command:
• Inserts switch
• Pan switch
• Bypass/Mute switch
• Sends switch
• Inserts + Pan switches (Mic Pre mode)
• Inserts + Sends (Instrument mode)
Page Down switch
Page Dn Page Up
Inserts switch
Bypass/Mute
switch
Channel Strip Mode controls
3 When you are finished, press the flashing Do To All or Do To
Inserts
Byp Mute
Pan
Sends
Page Up switch
Pan switch
Sends switch
Selected switch to exit the corresponding mode.
Display Mode Switch
The Display Mode switch toggles the channel display between
the five display modes: Track Name, Group/ Name, Channel
Number/Name, Headroom Value, and Level modes. See
“Channel Display” on page 33 for more information.
Set To Default Switch
The Set to Default switch lets you reset parameters that are
currently visible on the D-Command surface to their default
values. This switch works in both Normal and Custom Fader
modes.
The Set to Default switch can follow latching or momentary
behavior. If pressed briefly, it latches on and flashes until
pressed a second time. If held, its effect applies until released.
D-Command Guide38
Page 45

You can also use the Set to Default switch to remove
MapGroups
Lock
Tracks
WindowPlug-In
Focus Channel
&
Bank / Cycle
Custom Faders
Map switch
Lock switch
Window switch
Groups switch
Tracks switch
Plug-in switch
Bank/Cycle switch
Focus Channel
display
plug-in assignments from channels. See “Assign Inserts
Switch” on page 42.
While the Set to Default switch is pressed or latched on, the
following parameters can be reset:
To reset a channel’s track volume to 0 dB:
■ Press Set to Default + the channel Select switch.
To reset a channel’s pan control to 0 (center)
■ Press Set to Default + the pan encoder Select switch.
To reset a send’s level to 0 dB:
■ Press Set to Default + the send encoder Select switch. This
sets the send level to 0 dB, regardless of the Send default setting in Pro Tools Operation preferences.
To reset a channel’s mic pre gain to 0 dB:
■ Press Set to Default + the mic pre gain encoder Select switch
To set a plug-in’s parameters to their default values:
■ Press Set to Default + the Compare switch for the plug-in.
(The Compare switch appears in the D-Command Dynamics
and EQ sections, and in Custom Fader Expanded Plug-in
mode.)
Custom Fader Controls
The Custom Fader controls invoke a special set of D-Command modes, called Custom Fader modes, which let you set
aside and customize channel strips for display and editing of a
variety of functions. The Custom Fader modes are Groups
mode, Tracks mode, and Plug-in mode. See “Custom Fader
Modes” on page 94 for complete information on Custom
Fader modes.
Custom Fader controls
Suspend Groups Switch
The Suspend Groups switch suspends all groups in the session.
The Suspend Groups switch follows latching behavior, and
flashes to indicate groups are suspended. To exit Suspend
Groups mode, press the Suspend Groups switch again.
Automation Suspend Switch
The Automation Suspend switch suspends reading and writing of all automation on all tracks in the session. All channels
are left in their current automation mode, but automation operations are temporarily suspended.
The Automation Suspend switch flashes while automation is
suspended.
Solo Clear Switch
The Solo Clear switch clears all latched Solo switches in the
session. This switch flashes when any channel is soloed.
Focus Channel Display
◆ When a Custom Fader mode is active, the Focus Channel
display shows the name of the Custom Group, Mix/Edit
Group, or the plug-in displayed on the Custom Fader channels.
◆ When no Custom Fader mode is active, the Focus Channel
display shows the name of the focused channel.
Groups Switch
The Groups switch invokes Groups mode, which lets you select either Mix/Edit Groups or Custom Groups. Invoking
Mix/Edit Groups let you create, edit, and recall Pro Tools Mix
and Edit groups to the Custom Fader channels.
Invoking Custom Groups lets you create a custom collection
of channels and arrange them in any order in the Custom
Fader channels. Custom Groups are a D-Command feature,
and are not reflected on-screen in Pro Tools.
For more information about Custom Groups, see“Custom
Groups Mode” on page 95.
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 39
Page 46

To toggle between Custom Groups and Mix/Edit Groups:
■ Press the Bank/Cycle switch repeatedly until the appropri-
ate mode is displayed in the Focus Channel display (Custom
or Groups).
Tracks Switch
The Tracks switch invokes Track Type mode, which lets you
bring all Pro Tools tracks of a certain type (Audio tracks, Auxiliary Inputs, MIDI tracks, Instrument tracks, or Master Faders)
to the Custom Fader channels.
Plug-in Switch
The Plug-in switch invokes Plug-in mode, which lets you
bring the plug-in controls from the first insert of the currently
focused channel to the Custom Fader channels.
To cycle through the available inserts:
■ In Plug-in mode, press the Bank/Cycle switch repeatedly
until the desired insert is brought into the Custom Fader
channels.
Map Switch
Bank/Cycle Switch
◆ While in Custom Groups or Mix/Edit Groups mode, the
Bank/Cycle switch is used to bank faders within the Custom
Fader channels, if there are more channels than can be displayed at one time.
◆ While in Custom Fader Plug-in mode, the Bank/Cycle
switch cycles through the plug-ins on the focused channel,
displaying their controls on the Custom Fader channels.
◆ When no Custom Fader mode is active, the Bank/Cycle
switch cycles through the plug-ins on the focused channel,
displaying their names in the Custom Faders display.
Automation Mode Controls
The Automation Mode controls are used to display and set automation modes. These switches light to indicate that at least
one channel is in that automation mode. If multiple channels
are selected and set to different automation modes, all applicable mode switches are lit.
These Automation Mode controls let you change automation
modes during playback, and mirror the function of the
on-screen Automation Mode selector for each track.
The Map switch works with Custom Groups mode, Mix/Edit
Groups mode, and Plug-in mode. While in these modes, the
Map switch lets you further customize the control layout by
mapping individual rotary encoder controls to faders within
the Custom Fader channels.
The Map switch has no effect on other D-Command channels
in Normal mode.
Lock Switch
The Lock switch applies to Custom Fader Plug-in mode only.
This switch locks the plug-in that is currently displayed in the
Focus Channel display, so that it does not change when you
focus a different channel in the duplicate Focus Channel strip.
The Lock switch lights when the plug-in is locked.
◆ When Custom Fader Plug-in mode is active, the locked
plug-in appears in the Custom Fader channels, so you can focus a different channel in the Focus Channel section and keep
the locked plug-in in the Custom Fader channels.
◆ When Custom Fader Plug-in mode is not active, the locked
plug-in appears in the Focus Channel display, so you can focus
a different channel on the duplicate Focus Channel Strip and
keep the locked plug-in in the Focus Channel section. (When
you enter Custom Fader Plug-in mode, the locked plug-in will
be displayed on the Custom Fader channels.)
Window Switch
The Window switch opens and closes the plug-in window
on-screen for any plug-in whose name is displayed in the Custom Faders display.
Auto Mode
Automation Write
Mode switch
Automation Touch
Mode switch
Automation Latch
Mode switch
Automation Mode controls
Write Trim
Touch
Latch Off
Read
Automation Trim
Mode switch
Mode switch
Automation Read
Mode switch
Automation Off
switch
To set the automation mode of one or more channels:
1 Hold an Automation Mode switch (Write, Touch, Latch,
Trim, Read, or Off).
2 Press the Select switches on the channels whose automation
mode you want to set.
To set the automation mode of one or more selected channels:
1 Press the Do To Selected switch.
2 Press the Select switches on the channels whose automation
mode you want to set.
3 Press an Automation Mode switch.
4 Press the flashing Do To Selected switch.
To set the automation mode on all channels:
1 Press the Do To All switch.
2 Press an Automation Mode switch.
3 Press the flashing Do To All switch.
D-Command Guide40
Page 47

Write Switch
Timeline
controls
Assign
controls
Make Inactive
controls
Plug-in Automation
controls
Main Counter
switch
Link Edit and
Timeline switch
Edit/Timeline
Selection
switch and
indicators
The Write switch indicates or sets the automation mode for
the selected tracks to Write mode.
Talkback level is set with the Talkback controls in the Monitor
section. See “Talkback/Listen System” on page 84 for more information.
Touch Switch
The Touch switch indicates or sets the automation mode for
the selected tracks to Touch mode.
Latch Switch
The Latch switch indicates or sets the automation mode for
the selected tracks to Latch mode.
Trim Switch
The Trim switch indicates or sets the automation mode for the
selected tracks to Trim mode.
Read Switch
The Read switch indicates or sets the automation mode for the
selected tracks to Read mode.
Off Switch
The Off switch indicates or sets the automation mode for the
selected tracks to Off.
Talkback Switch
The Talkback switch, located at the bottom of the Global Controls section on the Main Unit, provides control of the
D-Command Talkback function.
Miscellaneous Controls
The Miscellaneous Controls section includes Timeline, Assign, Make Inactive, and Plug-in Automation controls.
Miscellaneous controls
Timeline Controls
Timeline controls
Main Counter Switch
The Main Counter switch cycles through the time code display modes (Bars:Beats, Min.Secs, Time Code, Feet+Frames
and Samples) on the Main Time Scale display.
Auto Mode
Write Trim
Touch
Read
Latch Off
Talkback switch
Talkback
Dbl Press to Latch
Talkback switch
The Talkback switch can follow momentary or latched behavior. If held, the switch is active only when pressed down.
If rapidly double-pressed, the switch latches on and flashes to
indicate that talkback is active. Press the switch again to turn
off talkback.
Talkback can be activated automatically. See “Auto Talkback
Switch” on page 84 for more information.
Link Edit and Timeline Switch
The Link Edit and Timeline switch toggles the Link Edit and
Timeline Selection command on and off. The switch is lit
when the selections are linked.
Edit/Timeline Switch and Indicators
The Edit/Timeline switch toggles the D-Command transport
function between the edit selection and the timeline selection. The indicators above the switch light to show which is
displayed. If Edit and Timeline Selections are linked, these values will be the same.
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 41
Page 48

Assign Controls
Assign Sends Switch
The Assign controls are used to assign inputs, outputs, inserts,
and sends to channels. Each switch puts D-Command into a
temporary Assign mode in which elements are assigned or removed from channels. The switch flashes while Assign mode
is in effect.
You can enter Assign mode while Pro Tools is playing back. To
confirm the assignment of inputs, outputs, and sends, the
transport must be stopped. You can, however, confirm the assignment of inserts during playback.
Assign Inputs
Assign Sends
Assign controls
switch
switch
Assign Outputs switch
Assign Inserts switch
Assign Inputs Switch
The Inputs switch invokes Assign Inputs mode, in which the
bottom row of encoders shows channel inputs.
When assigning an input, the Select switch on the bottom encoder is used to navigate down through Input menu levels,
and the encoder knob is used to scroll through available
choices at each level:
• Input type (Interface or Bus)
• Individual inputs
The Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the bottom encoder is used to
navigate back up the Input menu levels.
Assign Outputs Switch
The Sends switch invokes Assign Sends mode, in which the
channel encoders shows the sends on a channel.
When assigning a send, the encoder Select switch is used to
navigate down through Send menu levels, and the encoder
knob is used to scroll through available choices at each level:
• Send type (Interface or Bus)
• Individual sends
The Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on each encoder is used to navigate back up the Send menu levels.
Assign Inserts Switch
The Inserts switch invokes Assign Inserts mode, in which the
channel encoders show the inserts on a channel. When assigning an insert, the encoder Select switch is used to navigate
down through Insert menu levels, and the encoder knob is
used to scroll through available choices. The Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch on the bottom encoder is used to navigate back up the
Insert menu levels.
The order in which plug-ins appear in the Insert menu is determined by the Pro Tools Display preference for plug-in organization.
If the Organize Plug-in Menus by Category option is selected,
menu levels and choices include:
• Insert type (TDM plug-in, RTAS plug-in, Multi-Mono
TDM plug-in, Multi-Mono RTAS plug-in, or Hardware Insert)
• Plug-in category sub-folders (such as EQ, Dynamics,
Pitch Shift, Reverb, and Delay)
• Individual insert or plug-in
The Outputs switch invokes Assign Outputs mode, in which
the bottom row of encoders shows channel outputs.
When assigning an output, the Select switch on the bottom
encoder is used to navigate down through Output menu levels, and the encoder knob is used to scroll through available
choices at each level:
• Output type (Interface or Bus)
• Individual outputs
The Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the bottom encoder is used to
navigate back up the Output menu levels.
D-Command Guide42
If the Organize Plug-in Menus by Category option is not selected, the Plug-in subfolder level is not present.
Page 49

To assign an input, output, send or insert:
Inputs Inactive
switch
Sends Inactive
switch
Outputs Inactive
switch
Inserts Inactive
switch
1 Press an Assign switch to enter the corresponding Assign
mode.
2 On the channel where you want to make the assignment,
turn an encoder knob to select from the first level of menu
choices.
3 Press the encoder Select switch to move down and the By-
pass/Mute/Pre switch to move up through menu levels.
4 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing encoder Select switch or press the flashing Assign switch to confirm the assignment.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the assignment.
To assign multiple inputs, outputs, sends, or inserts:
1 Press an Assign switch to enter the corresponding Assign
mode.
2 Turn the encoder knobs and use the encoder Select and By-
pass/Mute/Pre switches to select each assignment.
3 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing Assign switch to confirm all the assignments at once.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel all the assignments.
To remove an input, output, send or insert:
1 Press an Assign switch to enter the corresponding Assign
mode.
To assign a MIDI Input or Output on an Instrument track:
1 Press the Assign Inputs or Assign Outputs switch to enter
the corresponding Assign mode. Encoder row #1 shows MIDI
inputs/outputs.
Assign Inputs
switch
Assignment controls
2 On each channel where you want to make an assignment,
Assign Outputs
switch
turn the encoder knob in encoder row #1 to select from the
first level of MIDI menu choices.
3 Press the encoder’s Select switch to move down and the By-
pass/Mute/Pre switch to move up through MIDI menu levels.
4 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing encoder Select switch or press the flashing Assign switch to confirm the assignments.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the assignments.
Make Inactive Controls
The Make Inactive controls are used to make tracks, inputs,
outputs, sends, or plug-ins inactive. Each switch puts D-Command into a temporary Make Inactive mode in which elements are made inactive or reactivated. The switch flashes
while Make Inactive mode is in effect.
2 For the assignment you want to remove, press the encoder
Bypass/Mute/Pre switch repeatedly until you reach top level
menu for the assignment.
3 Turn the encoder knob counter-clockwise until no assign-
ment is visible.
4 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing encoder Select switch or press the flashing Assign switch to confirm the removal.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the removal
and restore the assignment.
MIDI Inputs and Outputs on Instrument Tracks
The Assign Inputs and Assign Outputs switches can be used to
assign the MIDI Inputs and Outputs on Instrument tracks.
Make Inactive Controls
Making a Track Inactive
Tracks can be made inactive in any Make Inactive mode.
To toggle a track inactive/active:
1 Press any of the Make Inactive switches.
2 Press channel strip Select buttons to deactivate or reactivate
the corresponding tracks.
3 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode
Chapter 6: Channel Strip Controls 43
Page 50

Inputs Inactive Switch
Enable Parameters Switch
The Inputs switch invokes Inputs Inactive mode and displays
channel inputs in the bottom row of encoders. The Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the bottom encoder toggles the input inactive and active.
Outputs Inactive Switch
The Outputs switch invokes Outputs inactive mode and displays the main channel outputs in the bottom row of encoders. The Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the bottom encoder toggles the output inactive and active.
Sends Inactive Switch
The Sends switch invokes Sends Inactive mode and displays
the channel’s sends on its encoders. The Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch on each encoder toggles the corresponding send inactive and active.
Inserts Inactive Switch
The Inserts switch invokes Plug-ins Inactive mode and displays a channel’s inserts on its encoders. The Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch on each encoder toggles the corresponding insert inactive and active.
To toggle an input, output, send, or insert active/inactive:
1 Make sure the channel is showing the top-level view for the
element you want to make active/inactive.
2 Press a Make Inactive switch to enter the appropriate Make
Inactive mode.
3 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switches on encoders to deacti-
vate or reactivate their corresponding track elements.
4 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode.
Plug-in Automation Controls
The Plug-in Automation controls are used to enable parameters for automation and to place them in automation safe
mode.
Enable Parameter
Plug-in Automation controls
switch
Automation Safe switch
The Enable Parameters switch lets you enable parameters for
automation by touching or pressing their controls.
In Enable Parameters mode, the Enable Parameters switch is
lit. While in this mode, the Auto LED for any rotary encoder
enabled for automation is lit red, and the switch for any parameter enabled for automation is lit.
To toggle automation on and off for plug-in parameters:
1 Press the Enable Parameter switch.
2 Touch the rotary encoders or press the switches for the con-
trols for which you want to toggle automation on or off.
3 Press the Enable Parameter switch again to exit Enable Pa-
rameters mode.
You can also toggle automation for a plug-in parameter by
holding Control+Start+Alt (Windows) or Command+Control+Option (Mac) and touching the rotary encoder for the
parameter.
Automation Safe Switch
The Automation Safe switch invokes a mode in which the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch for each plug-in or send and the channel Select switch for each track become Safe switches.
Plug-ins and Sends
While in Automation Safe mode, pressing a Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch on a plug-in or send protects any automation on that
plug-in or send from being overwritten. The Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch for any protected plug-in or send is lit, reflecting the
state of the Safe button in the on-screen plug-in or send output window.
Tracks
While in Automation Safe mode, pressing a channel Select
switch protects volume, pan and mute parameters on that
track from being overwritten. The channel Select switch for
any protected track is lit, reflecting the state of the Safe button
in the on-screen track output window.
To toggle automation safe on and off:
1 Press the Automation Safe switch.
2 Press the channel Select switch on the tracks for which you
want to toggle automation safe status. The automation safe
status of the track is reflected by the Safe button in the track’s
on-screen output window.
3 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch for the plug-ins or sends
for which you want to toggle automation safe status.
4 Press the Automation Safe switch again to exit Automation
Safe mode.
D-Command Guide44
Page 51

Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls
5 Press the encoder Select switch to move down and the By-
Plug-ins and D-Command
pass/Mute/Pre switch to move up through menu levels.
D-Command provides dedicated Dynamics and EQ sections
for plug-ins that support dynamics and EQ plug-in mapping.
These sections include encoders and switches that map to
standard controls for each plug-in type.
Plug-ins of all types can be focused across multiple D-Command channels using Custom Fader Plug-ins mode. See
“Plug-In Mode” on page 97.
Plug-in Channel Formats
D-Command supports mono, stereo, multichannel and
multi-mono plug-in channel formats up to six channels wide.
With D-Command, you can display, edit, and link specific
channels of multi-mono dynamics and EQ plug-ins directly
from the Channel Select switches in the corresponding section.
Assigning and Removing Plug-ins
You can make plug-in assignments directly from D-Command
in several ways. In Inserts mode, plug-ins can be added on an
insert-by-insert basis. In Assign Inserts mode you can assign
plug-ins to insert positions on multiple tracks.
To assign a plug-in in Inserts mode:
1 Press the Inserts switch to display inserts on the channel
where you want to assign the plug-in.
2 If the insert location where you want to assign a plug-in is
not showing, press the Page Up or Page Down switches on the
channel where you want to make the assignment until the appropriate location is displayed.
6 When the plug-in you want to assign is displayed, press the
encoder Select switch to confirm your selection.
To assign plug-ins to multiple tracks:
1 Press the Assign Inserts switch to enter Inserts Assign mode.
The first two send or insert positions will show on the encoder
displays by default.
2 To display and edit other insert positions, press the Page Up
or Page Down switches on the channel where you want to
make the assignment.
3 At the insert position where you want to make the assign-
ment, turn the encoder knob to select from the first level of
menu choices.
4 Press the encoder Select switch to move down and the By-
pass/Mute/Pre switch to move up through menu levels.
5 When the plug-in you want to assign is displayed, press the
encoder Select switch to confirm your selection.
6 Repeat steps 2–5 to make additional insert assignments.
7 Press the flashing Assign switch to confirm the assignments
and exit Inserts Assign mode.
To remove a plug-in:
1 Press the Set to Default switch.
2 Press the encoder Select switch for each plug-in you want to
remove.
3 Press the flashing Set to Default switch to exit Set to Default
mode.
3 Do one of the following:
• If the insert location you want to use is empty, press the
corresponding encoder Select switch.
• If a plug-in is already present in the insert location you
want to use, press and hold the corresponding encoder
Select switch.
4 Turn the encoder knob that corresponds to the insert posi-
tion that you want to edit to select from the first level of menu
choices.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 45
Page 52

Focusing Plug-ins on D-Command
Opening Plug-in Windows On-Screen
A plug-in is focused when its controls are mapped to the knobs,
switches or faders on D-Command. Its parameters can then be
edited and automated from the control surface. D-Command
lets you focus a plug-in with or without displaying its window
on-screen.
You can focus plug-ins in multiple locations on D-Command:
in the Dynamics section, in the EQ section, and in the Custom
Faders section.
When a plug-in is focused on D-Command and displayed
on-screen in Pro Tools, a colored outline appears in the
plug-in window header.
To focus a plug-in in the Dynamics or EQ section:
1 Focus the plug-in’s track in the Focus Channel section by
pressing the track’s Select switch. The first dynamics and EQ
plug-ins on that track are automatically focused in the corresponding D-Command section.
2 Press the Cycle switch in the Dynamics or EQ section to fo-
cus successive dynamics or EQ plug-ins on that channel. (The
No Insert option is always available.)
To focus a plug-in in the Custom Faders section:
1 Focus the plug-in’s track in the Focus Channel section by
pressing the track’s Select switch. The name of the first plug-in
that is not a dynamics or EQ plug-in appears in the Focus
Channel display.
2 Press the Plug-in switch in the Custom Faders section. The
switch lights to indicate the mode is active. The plug-in name
and channel format appear in the Custom Fader channel displays, and the plug-in’s parameters appear in the Custom
Fader channel encoders.
3 In the Custom Faders section, press the Bank/Cycle switch
to cycle through the plug-ins on the focused channel. (The No
Insert option is always available.)
The plug-in whose name appears in the Custom Faders display
is focused in Custom Fader mode. See “Plug-In Mode” on
page 97.
When plug-in names are shown on the encoder displays, a
plug-in can be quickly brought into Custom Fader mode by
pressing its associated encoder Select switch.
There are several ways to open plug-in windows on-screen
from D-Command.
To open a plug-in window from any channel on D-Command:
■ Hold Start (Windows) or Control (Mac) and press the en-
coder Select switch for the plug-in.
To open a plug-in window on a focused track:
1 Focus a track in the Focus Channel section by pressing its Se-
lect switch.
2 In the Custom Faders section, press the Bank/Cycle switch
to cycle through the plug-ins on the focused track. Plug-in
names are shown in the Custom Faders display.
3 In the Custom Faders section, press the Win switch to open
the plug-in whose name is displayed.
To open a focused dynamics or EQ plug-in window:
■ Press the Window switch in the Dynamics or EQ section of
D-Command.
To open or close all focused plug-in windows:
■ Press the Plug-in switch in the Window Management sec-
tion.
To close all open plug-in windows:
■ Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) and press the Plug-in
switch in the Window Management section. This closes all
real-time and AudioSuite plug-in windows.
To set D-Command to automatically open plug-in windows:
1 Press the Operations switch in the D-Command Soft Keys
section twice.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “ChanWn” until its
value is “Yes.”
With this preference set to “Yes,” when you insert a new
plug-in, press an encoder Select switch to edit a plug-in, or cycle through plug-ins on the focused track, the plug-in window
will automatically open on-screen.
D-Command Guide46
Page 53

Managing Multiple Plug-in Windows
Making Plug-ins Inactive or Active
D-Command lets you open and swap multiple plug-in windows on-screen. This makes it possible keep multiple plug-in
windows open while focusing on different tracks (for example, in a session where several tracks have dynamics and EQ
plug-ins).
Targeting Plug-ins
A plug-in is said to be targeted on-screen when its target icon in
the plug-in window header is lit red. The first plug-in window
to be opened is automatically targeted.
◆ When a plug-in window is targeted, it is replaced when you
open any new plug-in window.
◆ When a plug-in window is not targeted (when its target icon
is grey) the plug-in window will remain on-screen.
To open multiple plug-in windows:
■ Hold Shift while opening each new window. The new
plug-in windows are not targeted.
To swap multiple plug-in windows while changing track focus:
1 Focus a track with multiple plug-ins (for example, dynam-
ics, EQ and pitch shift plug-ins) by pressing the track’s Select
switch.
2 Open multiple plug-in windows on the focused track while
holding the Shift modifier.
3 Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) while changing focus
to another track with multiple plug-ins by pressing that track’s
Select switch.
Focused plug-ins with open windows swap into new plug-in
windows on-screen, wherever plug-ins are present in the new
track.
You can toggle the active/inactive status of a plug-in directly
from a channel strip without putting D-Command into Make
Inactive mode.
To toggle a plug-in active/inactive directly from a channel strip:
1 Press the Inserts switch on a channel strip to display the
names of the plug-ins on the channel’s encoders.
2 If the insert location for the plug-in that you want to make
active/inactive is not showing, press the Page Up or Page
Down switches on the channel until the appropriate location
is displayed.
3 Hold Control+Start (Windows) or Control+ Command
(Mac) and press the encoder Select switch for the plug-in.
Copying and Pasting Plug-in Settings
You can copy plug-in settings from a plug-in and paste them
into another copy of the same plug-in directly from a channel
strip on D-Command.
To copy and paste plug-in settings:
1 Press the Inserts switch on a channel strip to display the
names of the plug-ins on that channel’s encoders.
2 If the insert location for the plug-in whose settings you
want to copy is not showing, press the Page Up or Page Down
switches on the channel until the appropriate location is displayed.
3 Copy the settings of a plug-in by holding Shift+Control
(Windows) or Shift+Command (Mac) and pressing the Select
switch under the name of the plug-in.
4 Paste the settings into another instance of the same plug-in
by pressing the B/M/P switch under the name of that plug-in.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 47
Page 54

Enabling Plug-in Automation
When plug-in names are displayed in top-level view on a
D-Command channel strip, you can quickly enable all parameters of a plug-in for automation.
You can also use the Do To All or Do To Selected switches on
D-Command to automate multiple plug-ins in the same insert
position in a session.
To toggle automation on and off for a parameter of a plug-in:
1 Press the Inserts switch in the Channel Strip Mode controls
of a track to show the top level Inserts display. Plug-in names
appear in the encoder displays of that track.
2 Press the Page Up or Page Down switch to display the name
of the plug-in you want to automate.
3 Press an encoder Select switch to display that plug-in’s pa-
rameters on the Custom Fader encoders.
4 Hold Control+Alt+Start (Windows) or Command+Op-
tion+Control (Mac) and touch the rotary encoder for the
plug-in parameters you want to enable for automation.
To toggle automation on and off for all parameters of a plug-in:
1 Press the Inserts switch in the Channel Strip Mode controls
of a track to show the top level Inserts display. Plug-in names
appear in the encoder displays of that track.
To toggle automation on and off for plug-ins in a given Insert
position on all selected tracks:
1 Select the tracks containing the plug-ins you want to enable
for automation.
1 Press the Inserts switch in the Channel Strip Mode controls
of a track to show the top level Inserts display. Plug-in names
appear in the encoder displays of that track.
2 Press the Page Up or Page Down switch to display the insert
position for the plug-ins you want to automate.
3 Press the Do To Selected switch in the Global controls sec-
tion.
4 Hold Control+Alt+Start (Windows) or Command+Op-
tion+Control (Mac) and touch the rotary encoder for any
plug-in at the insert position (Insert 1–5) where you want to
enable plug-in automation.
2 Press the Page Up or Page Down switch to display the name
of the plug-in you want to automate.
3 Hold Control+Alt+Start (Windows) or Command+Op-
tion+Control (Mac) and touch the rotary encoder for the
plug-in whose parameters you want to enable for automation.
To toggle automation on and off for all plug-ins in a given Insert
position:
1 Press the Inserts switch in the Channel Strip Mode controls
of a track to show the top level Inserts display. Plug-in names
appear in the encoder displays of that track.
2 Press the Page Up or Page Down switch to display the insert
position for the plug-ins you want to automate.
3 Press the Do To All switch in the Global controls section.
4 Hold Control+Alt+Start (Windows) or Command+Op-
tion+Control (Mac) and touch the rotary encoder for any
plug-in at the insert position (Insert 1–5) where you want to
enable plug-in automation.
D-Command Guide48
Page 55
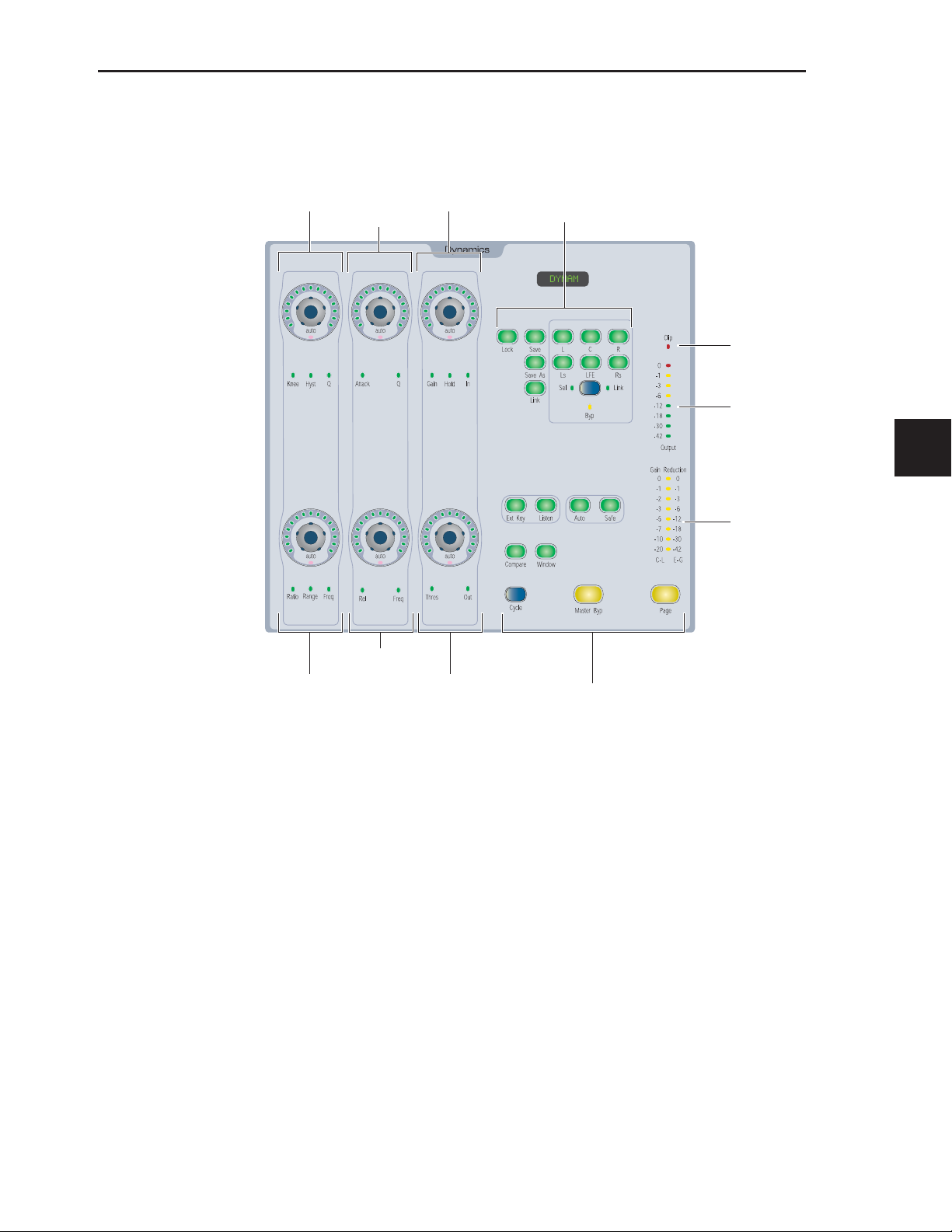
Dynamics Section
The Dynamics section includes standard controls for compressor, gate, and limiter plug-ins, an array of controls for managing the
display and editing of plug-in parameters, and for selecting or linking channels in multi-mono plug-ins.
Knee/Hysteresis/Q
control
Gain/Hold/Input Level
Attack/Q
control
control
Channel Select
switches
Clip
indicator
Output
meter
Gain Reduction
meter
Release/Frequency
control
Ratio/Range/Frequency
control
Threshold/Output Level
control
D-Command Dynamics section
Dynamics Plug-in Support
Dynamics processing plug-ins may have widely varying controls, depending on their applications. The D-Command Dynamics Section provides dedicated knobs and switches to accommodate a wide range of possible plug-ins. Not all plug-ins
will require all the Dynamics controls, while others may have
more parameters than can be displayed in the Dynamics section at one time. To display all controls in any plug-in, use
Custom Fader Plug-ins mode. (See “Plug-In Mode” on
page 97.)
Dynamics Edit/Display/Page controls
Displaying Dynamics Plug-ins
The D-Command Dynamics section automatically focuses the
first dynamics plug-in on the channel displayed in the Focus
Channel section on the Main Unit.
To display successive dynamics plug-ins that are on the focused channel, press the Cycle switch in the Dynamics section.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 49
Page 56

Knee/Hysteresis/Q and
Ratio/Range/Frequency Controls
Knee/Hysteresis/Q control
Hysteresis
indicator
Knee
indicator
Q
indicator
Attack/Q and Release/Frequency Controls
Attack/Q control
Attack
indicator
Q
indicator
Ratio/Range/Frequency
Ratio
indicator
control
Range
indicator
Frequency
indicator
Knee/Hysteresis/Q and Ratio/Range/Frequency controls in the
Dynamics section
Knee/Hysteresis/Q Control
The top encoder in this section controls the knee shape, the
hysteresis value, or the Q value for the current plug-in page,
depending on which indicator is lit. The Auto indicator under
the encoder knob lights when the displayed parameter is enabled for automation.
Ratio/Range/Frequency Control
The bottom encoder in this section controls the compression
ratio, the range value, or the filter frequency for the current
plug-in page, depending on which indicator is lit. The Auto
indicator under the encoder knob lights when the displayed
parameter is enabled for automation.
Release/Frequency
control
Release
indicator
Frequency
indicator
Attack/Q and Release/Frequency controls in the Dynamics section
Attack/Q Control
The top encoder in this section controls the attack value, or
the Q value for the current plug-in, depending on which indicator is lit. The Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights
when the displayed parameter is enabled for automation.
Release/Frequency Control
The bottom encoder in this section controls the release value
for the current plug-in, or the filter frequency for the current
plug-in page, depending on which indicator is lit. The Auto
indicator under the encoder knob lights when the displayed
parameter is enabled for automation.
D-Command Guide50
Page 57

Gain/Hold and Threshold Controls
Gain/Hold
control
Hold
Gain
indicator
Threshold
control
indicator
Input
indicator
Gain/Hold/Input Control
The top encoder in this section controls the gain (make-up
gain), the hold value for the current plug-in page, or the input
gain for the current plug-in, depending on which indicator is
lit. The Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when
the displayed parameter is enabled for automation.
Threshold/Output Control
The bottom encoder in this section controls the threshold
value for the current plug-in page, or the output gain for the
current plug-in, depending on which indicator is lit. The Auto
indicator under the encoder knob lights when the displayed
parameter is enabled for automation.
Threshold
indicator
Output
indicator
Gain/Hold and Threshold controls in the Dynamics section
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 51
Page 58

Dynamics Channel Select Controls
Dynamics display
Lock switch
Save and Save As switches
Master Link switch
Channel Select controls in the Dynamics section
Dynamics Display
The LED display in the Dynamics section show the name of
the focused plug-in by default. When any rotary encoder is
touched, the display shows the corresponding parameter
value.
Lock Switch
The Lock switch is used to lock the focus of the Dynamics section on the current plug-in. When the plug-in focus is locked,
the current plug-in remains in the Dynamics section, even
when a different track is focused on D-Command. This switch
lights when the plug-in focus is locked.
Channel Select switches
Select/Link/Bypass Mode switch
Bypass indicator
Save and Save As Switches
The Save and Save As switches perform the Save and Save As
commands in the Plug-in settings menu. The Save command
saves current parameter settings to the current plug-in settings
file, and the Save As command saves the parameter settings to
a new plug-in settings file.
To save a Dynamics plug-in setting from D-Command:
1 Press the Save or Save As switch in the Channel Select con-
trols of the Dynamics section. The Save or Save As switch
flashes while the Save Settings dialog is open.
2 Type a name for the plug-in setting.
3 Do one of the following:
• Click OK to save the settings and close the dialog.
• Press the flashing Save or Save As switch to save the settings and close the dialog.
• Press the Escape switch to exit the dialog without saving
the settings.
D-Command Guide52
Page 59

Channel Select Switches
Master Link Switch
Multichannel Plug-ins
When you are working with a multichannel plug-in, all channels are controlled in tandem and the Channel Select switches
have no effect.
Multi-Mono Plug-ins
When you are working with a multi-mono plug-in, the controls for the channels are usually linked and edited together.
However, you can edit plug-in settings for individual channels
of a multi-mono plug-in by using the Channel Select switches
to unlink all of the channels, or to link specific channels.
There are Channel Select switches for the following channels:
• L (Left)
• C (Center)
• R (Right)
• Ls (Left Surround)
• Rs (Right Surround)
• LFE
A maximum of six channels (5.1 surround) may be in use at
any time.
Multichannel Plug-ins
When you are working with a multichannel plug-in, all channels are controlled in tandem, and the Master Link switch has
no effect.
Multi-Mono Plug-ins
When you are working with a multi-mono plug-in, the Master
Link switch toggles the Master Link button in the plug-in window, which links or unlinks all channels of the plug-in. When
the Master Link button is enabled, the Link switch is lit.
Select/Link/Bypass Mode Switch
The Select/Link/Bypass Mode switch determines the function
of the Channel Select switches with multi-mono plug-ins.
Select Mode In this mode, the Channel Select switches determine which channel of a multi-mono plug-in is the focus of
the plug-in controls. When a channel is selected, its switch is
lit. If any channels are linked, their switches follow linked behavior.
In Select mode, if the D-Command Channel Window Display
preference is set to Yes, the Channel Select switches also
change the channel display in the plug-in window.
Bypass Mode In this mode, the Channel Select switches determine which channels of a multi-mono plug-in are bypassed.
When a channel is bypassed, its switch is lit. If any channels
are linked, their switches follow linked behavior.
Link Mode In this mode, the Channel Select switches determine which individual channels of a multi-mono plug-in are
linked together. Linked channels are indicated by switches
that are lit.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 53
Page 60

Dynamics Edit and Display Controls
External Key switch
Window switch
Compare switch
Cycle switch
Edit and Display controls in the Dynamics section
Key Listen
switch
Automation switch
Master Bypass switch
External Key Switch
The External Key switch turns the Key Input on or off for
plug-ins that support side-chain processing with external input. This switch lights when Key Input is on.
Key Listen Switch
The Listen switch turns the Key Listen function on or off for
plug-ins that support auditioning the Key Input. This switch
lights when Key Listen is on.
Automation Safe switch
Page switch
To toggle automation on and off for all parameters of a Dynamics
plug-in:
1 Press the Automation switch.
2 Do one of the following:
• Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac).
– or –
• Hold Do to All.
3 Touch any rotary encoder or press any switches in the Dy-
namics section.
Automation Switch
The Automation switch lets you enable Dynamics parameters
for automation by touching or pressing their controls in the
Dynamics section only.
In Automation mode, the Auto switch is lit. While in this
mode, the Auto indicator for any rotary encoder enabled for
automation is lit red, and the switch for any parameter enabled for automation is lit.
To toggle automation on and off for individual Dynamics
parameters:
1 Press the Automation switch.
2 Touch the rotary encoders or press the switches in the Dy-
namics section for which you want to toggle automation.
3 Press the Automation switch again to exit Automation
mode.
4 Press the Automation switch again to exit Automation
mode.
Automation Safe Switch
The Automation Safe switch toggles the Safe button in the
plug-in window, which protects existing automation for that
plug-in from being overwritten.
Window Switch
The Window switch is used to open and close the on-screen
window for the currently focused plug-in.
Compare Switch
The Compare switch toggles the Compare button in the
plug-in window, which alternates between the currently
saved plug-in setting and any changes you have made.
D-Command Guide54
Page 61

Cycle Switch
Gain Reduction meter
Output meter
Clip Indicator
The Cycle switch steps through all available Dynamics
plug-ins on the focused channel.
Master Bypass Switch
The Master Bypass switch bypasses the plug-in.
Page Switch
With plug-ins that have more than one page of controls, the
Page switch lights. Pressing this switch steps through the
pages for the currently displayed plug-in.
The current function of the rotary encoders in the Dynamics
section is shown by the corresponding indicator LEDs. Active
controls are shown in the on-screen plug-in window by colored outlines.
Dynamics Gain Controls and Meters
Level meters in the Dynamics section
Output Meter and Clip Indicator
The Output meter shows the output level for the current
plug-in. The Clip indicator lights when a clip is reported by
the plug-in, and can be cleared by pressing the Clear Clip
switch in the Session Management section.
Gain Reduction Meter
The Gain Reduction meter shows the amount of gain reduction for Compressor/Limiter functions (using the range
shown on the left) and Expander/Gate functions (using the
range shown on the right).
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 55
Page 62
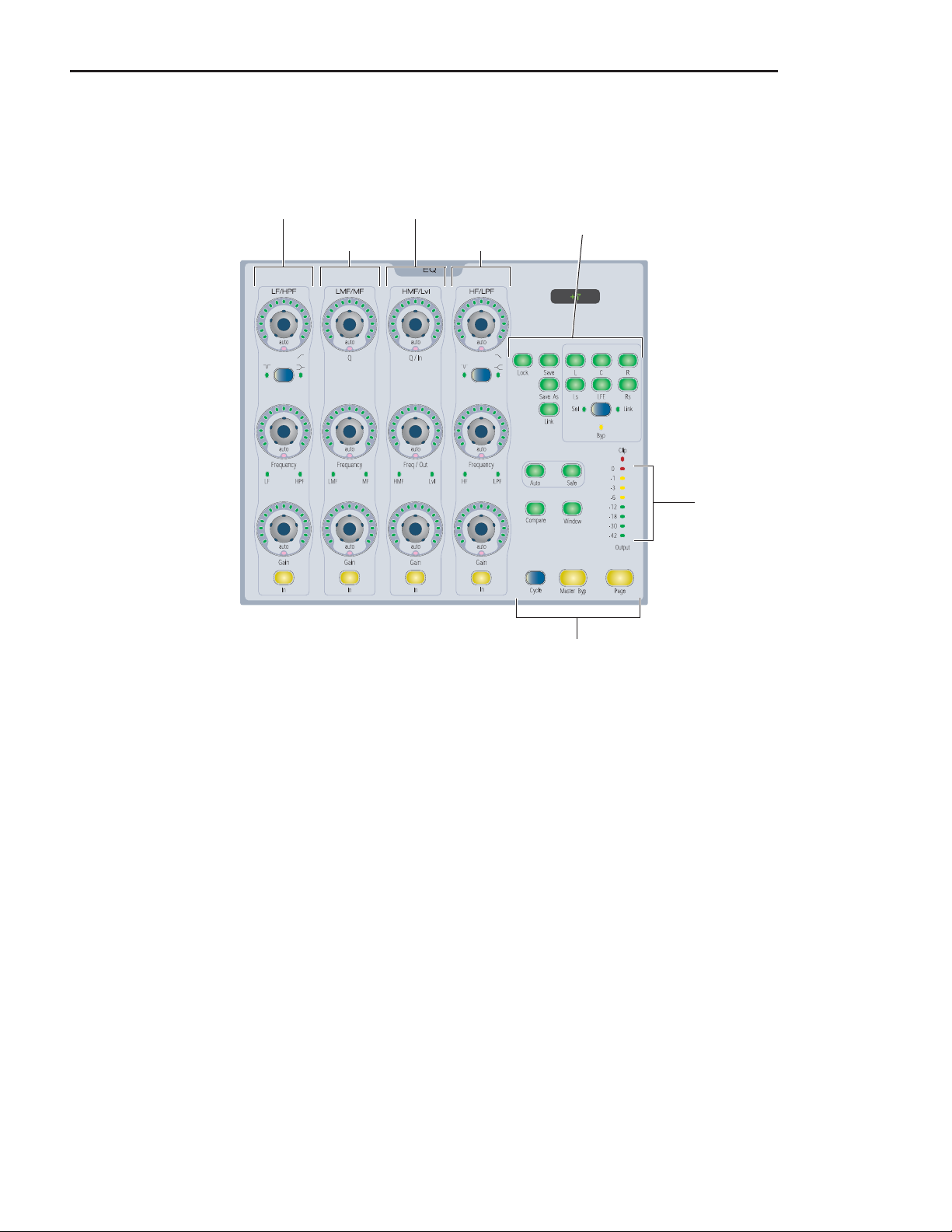
EQ Section
The EQ section includes standard controls for a variety of multi-band equalization plug-ins, an array of controls for managing the
display and editing of plug-in parameters, and controls for selecting or linking channels in multi-mono plug-ins.
Low Filter/
High-Pass Filter
controls
Low-Mid Filter/
Mid Filter
controls
High-Mid Filter/
Level
controls
High Filter/
Low-Pass Filter
controls
Channel Select
switches
Output
meter
D-Command EQ section
EQ Plug-in Support
EQ processing plug-ins may have widely varying controls, depending on their applications. The D-Command EQ section
uses paging to accommodate the widest range of plug-ins possible.
Each encoder column controls several frequency bands,
which are chosen by pressing the Page switch. LEDs light to
indicate the frequency band that is currently active for editing. Notch/Shape switches are located on the Low and High
band to change filter types.
To simultaneously display all controls in any plug-in, use Custom Fader Plug-ins mode. (See “Plug-In Mode” on page 97.)
EQ Edit and Display controls
Displaying EQ Plug-ins
The D-Command EQ section automatically displays the first
EQ plug-in on the channel that is focused in the Focus Channel section on the Main Unit.
To display successive EQ plug-ins that are on the focused
channel:
■ Press the Cycle switch in the EQ section.
D-Command Guide56
Page 63
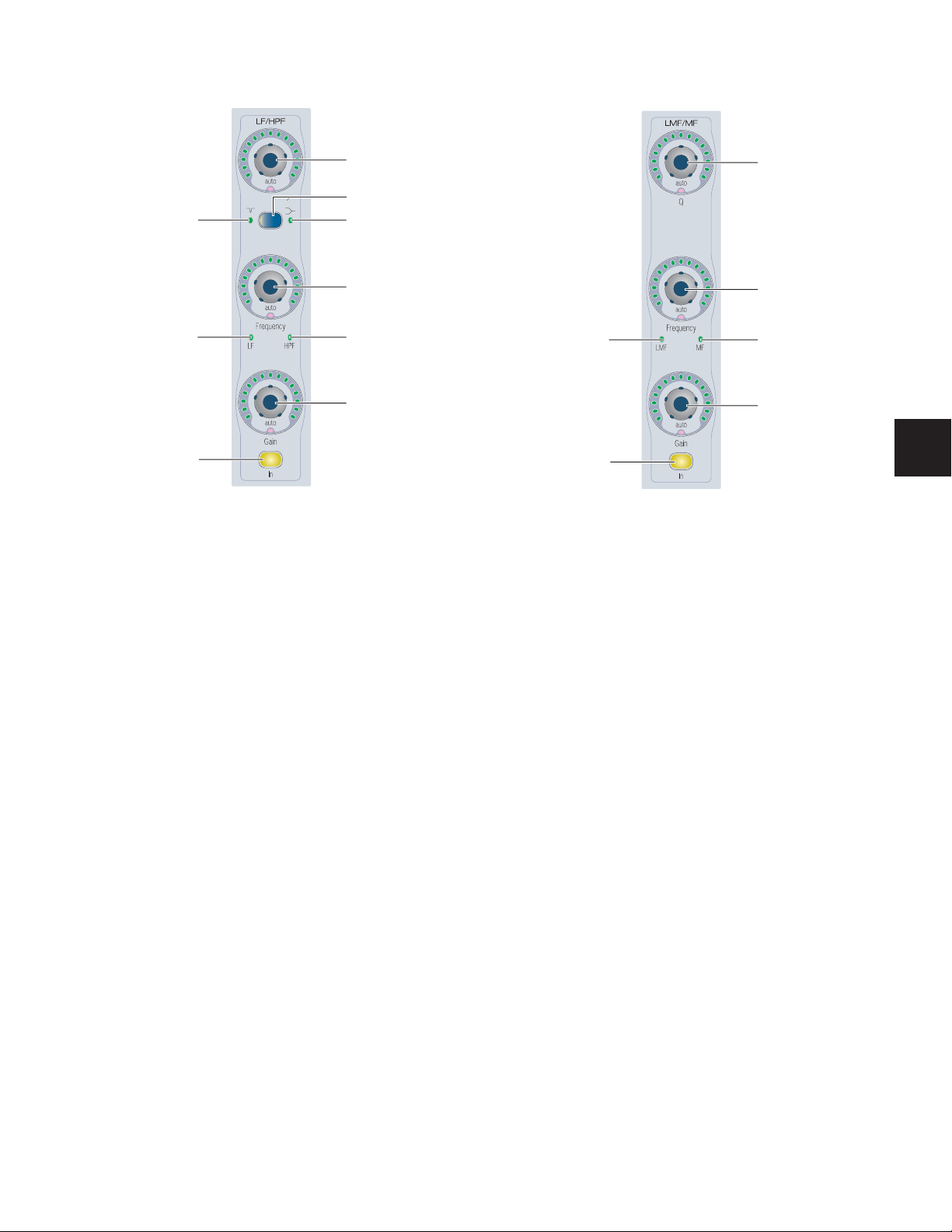
Low Filter and High-Pass Filter Controls
Q encoder
Filter In switch
Gain encoder
Mid Filter
indicator
Frequency encoder
Low-Mid Filter
indicator
Q encoder
Notch/Shape switch
Notch indicator
Shelf indicator
Frequency encoder
Low-Mid Filter and Mid Filter Controls
Low Filter
indicator
Filter In switch
Low Filter and High-Pass Filter controls in the EQ section
High-Pass Filter
indicator
Gain
encoder
Q Encoder
The top encoder controls the Q of the selected filter. The Auto
indicator under the encoder knob lights when the parameter
is enabled for automation.
Notch/Shape Switches and Indicator
The Notch/Shape switch let you switch between the two filter
types when they are available. The indicators on either side of
the switch light to show which type of filter is active.
Frequency Encoder
The middle encoder controls the filter frequency for the currently selected band. When the filter is a notch filter, the encoder controls the center frequency. When the selected filter
is a low-pass filter, the encoder controls the cutoff frequency.
The Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when the
parameter is enabled for automation.
Gain Encoder
Low-Mid Filter and Mid Filter controls in the EQ section
Q Encoder
The top encoder controls the Q of the selected filter. The Auto
indicator under the encoder knob lights when the parameter
is enabled for automation.
Frequency Encoder
The middle encoder controls the center frequency for the currently selected band. The Auto indicator under the encoder
knob lights when the parameter is enabled for automation.
Gain Encoders
The bottom encoder controls the gain for each band. The
Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when the parameter is enabled for automation.
Filter In Switch
The Filter In switch lets you engage or bypass the corresponding EQ band in the plug-in.
The bottom encoder controls the gain for each band. The
Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when the parameter is enabled for automation.
Filter In Switch
The Filter In switch lets you engage or bypass the corresponding EQ band in the plug-in.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 57
Page 64
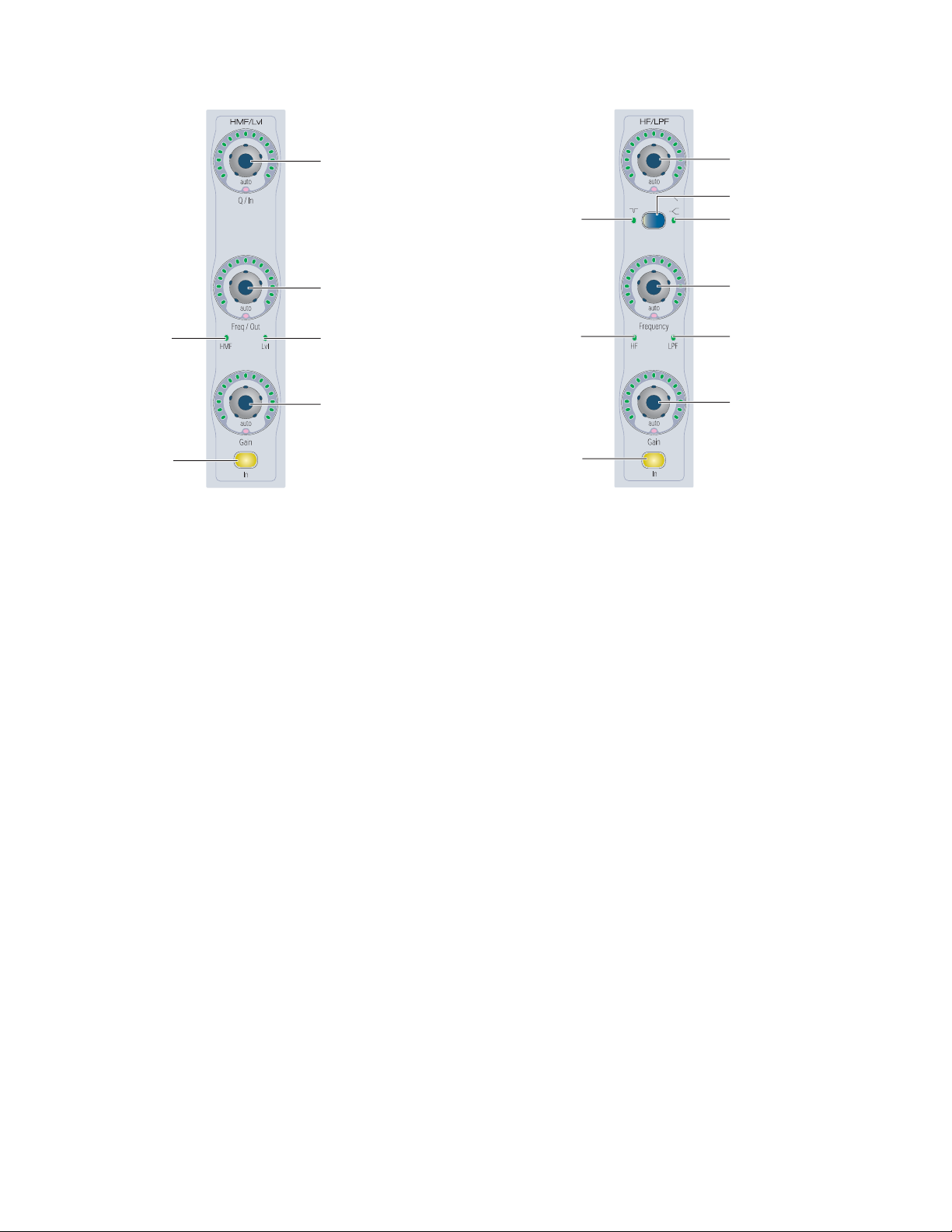
High-Mid Filter and EQ Level Controls
High Filter and Low-Pass Filter Controls
Q/Input level encoder
Frequency/Output level encoder
High-Mid Filter
indicator
Filter In switch
High-Mid Filter and EQ level controls in the EQ section
Level
indicator
Gain encoder
Q/Input level Encoder
The top encoder controls the Q of the High-Mid filter, or the
Input level. The Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights
when the parameter is enabled for automation.
Q encoder
Notch/Shape switch
Notch indicator
High Filter
indicator
Filter In switch
Low Filter and High Filter controls in the EQ section
Shelf indicator
Frequency encoder
Low-Pass Filter
indicator
Gain encoder
Q Encoders
The top encoder controls the Q of the selected band. The Auto
indicator under each encoder knob lights when the parameter
is enabled for automation.
Frequency/Output Level Encoder
The middle encoder controls the center frequency for the currently selected band, or the Output level. The Auto indicator
under the encoder knob lights when the parameter is enabled
for automation.
Gain Encoder
The bottom encoder controls the gain for the High-Mid band.
The Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when the
parameter is enabled for automation.
Filter In Switch
The Filter In switch lets you engage or bypass the corresponding EQ band in the plug-in.
Notch/Shape Switches and Indicator
The Notch/Shape switch let you switch between the two filter types when they are available. The indicators on either side of the switch light to show which type of filter is active.
Frequency Encoder
The middle encoder controls the filter frequency for the currently selected band. When the filter is a notch filter, the encoder controls the center frequency. When the selected filter
is a low-pass filter, the encoder controls the cutoff frequency.
The Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when the
parameter is enabled for automation.
Gain Encoder
The bottom encoder controls the gain for each band. The
Auto indicator under the encoder knob lights when the parameter is enabled for automation.
Filter In Switch
The Filter In switch lets you engage or bypass the corresponding EQ band in the plug-in.
D-Command Guide58
Page 65

EQ Channel Select Controls
EQ display
Lock switch
Save and Save As switches
Master Link switch Select/Link/Bypass Mode switch
Channel Select controls in the EQ section
EQ Displays
The LED display in the EQ section shows the name of the focused plug-in by default. When any rotary encoder is touched,
the display shows the corresponding parameter value.
Lock Switch
The Lock switch is used to lock the focus of the EQ section on
the current plug-in. When the plug-in focus is locked, the current plug-in remains in the EQ section, even when a different
track is focused on D-Command. This switch lights when the
plug-in focus is locked.
Save and Save As Switches
The Save and Save As switches perform the Save and Save As
commands in the Plug-in settings menu. The Save command
saves current parameter settings to the current plug-in settings
file, and the Save As command saves the parameter settings to
a new plug-in settings file.
To save an EQ plug-in setting from D-Command:
1 Press the Save or Save As switch in the Channel Select con-
trols of the EQ section. The Save or Save As switch flashes
while the Save Settings dialog is open.
2 Type a name for the plug-in setting.
3 Do one of the following:
• Click OK to save the settings and close the dialog.
• Press the flashing Save or Save As switch to save the settings and close the dialog.
• Press the Escape switch to exit the dialog without saving
the settings.
Channel Select switches
Bypass indicator
Channel Select Switches
Multichannel Plug-ins
When you are working with a multichannel plug-in, all channels are controlled in tandem and the Channel Select switches
have no effect, except with multichannel plug-ins (such as
Focusrite d2) that directly support channel selection.
Multi-Mono Plug-ins
When you are working with a multi-mono plug-in, the controls for the channels are usually linked and edited together.
However, you can edit plug-in settings for individual channels
of a multi-mono plug-in by unlinking all of the channels, or
by using the Channel Select switches to link specific channels.
There are Channel Select switches for the following channels:
• L (Left)
• C (Center)
• R (Right)
• Ls (Left Surround)
• Rs (Right Surround)
• LFE
These choices can be used to support all possible channel configurations in Pro Tools. A maximum of six channels (5.1 surround) may be in use at any time.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 59
Page 66

Master Link Switch
Select/Link/Bypass Mode Switch
Multichannel Plug-ins
When you are working with a multichannel plug-in, all channels are controlled in tandem, so the Master Link switch has
no effect, except with multichannel plug-ins (such as
Focusrite d2) that directly support channel linking.
Multi-Mono Plug-ins
When you are working with a multi-mono plug-in, the Master
Link switch toggles the Master Link button in the plug-in window, which links or unlinks all channels of the plug-in. When
the Master Link button is enabled, the Link switch is lit.
The Select/Link/Bypass Mode switch determines the function
of the Channel Select switches with multi-mono plug-ins.
Select Mode In this mode, the Channel Select switches determine which channel of a multi-mono plug-in is the focus of
the plug-in controls. When a channel is selected, its switch is
lit. If any channels are linked, their switches follow linked behavior.
In Select mode, if the D-Command Channel Window Display
preference is set to Yes, the Channel Select switches also
change the channel display in the plug-in window.
Bypass Mode In this mode, the Channel Select switches determine which channels of a multi-mono plug-in are bypassed.
When a channel is bypassed, its switch is lit. If any channels
are linked, their switches follow linked behavior.
Link Mode In this mode, the Channel Select switches determine which individual channels of a multi-mono plug-in are
linked together. Linked channels are indicated by switches
that are lit.
D-Command Guide60
Page 67

EQ Edit and Display Controls
Automation switch
Window switch
Compare switch
Cycle switch
Edit and Display controls in the EQ section
Automation Safe switch
Master Bypass switch
Automation Switch
The Automation switch lets you enable EQ parameters for automation by touching or pressing their controls in the EQ section only.
In Automation mode, the Auto switch is lit. While in this
mode, the Auto indicator for any rotary encoder enabled for
automation is lit red, and the switch for any parameter enabled for automation is lit.
To toggle automation on and off for individual EQ parameters:
1 Press the Automation switch.
Clip indicator
Output meter
Page switch
Automation Safe Switch
The Automation Safe switch toggles the Safe button in the
plug-in window, which protects existing automation for that
plug-in from being overwritten.
Compare Switch
The Compare switch toggles the Compare button in the
plug-in window, which alternates between the currently
saved plug-in setting and any changes you have made.
Window Switch
2 Touch the rotary encoders or press the switches in the EQ
section for which you want to toggle automation.
3 Press the Automation switch again to exit Automation
mode.
To toggle automation on and off for all parameters of an EQ
plug-in:
1 Press the Automation switch.
2 Do one of the following:
• Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac).
– or –
• Hold Do to All.
3 Touch any rotary encoder or press any switches in the EQ
section.
4 Press the Automation switch again to exit Automation
mode.
The Window switch is used to open and close the on-screen window for the currently focused plug-in.
Output Meter and Clip Indicator
The Output meter shows the output levels for the current
plug-in. The Clip indicator lights when a clip is reported by
the plug-in, and can be cleared by pressing the Clear Clip
switch in the Session Management section.
Cycle Switch
The Cycle switch steps through all available EQ plug-ins on
the focused channel.
Master Bypass Switch
The Master Bypass switch bypasses the plug-in.
Page Switch
The Page switch steps through the pages for the currently displayed plug-in. The Page switch lights when plug-ins have
more than one page of controls. Active controls are shown in
the on-screen plug-in window by colored outlines.
Chapter 7: Plug-in Controls 61
Page 68

D-Command Guide62
Page 69

Chapter 8: Transport and Navigation Controls
Transport Section
The D-Command Transport section includes transport switches, switches for setting the transport mode, scrub/shuttle switches
and controls, and advanced audition and locate switches.
Master Record Mode
Pro Tools Transport
D-Command Transport Section
switch
Locate switches
switches
Transport Switches
Audition switches
MIDI Merge
indicator
Transport Modes switches
Scrub/Shuttle
controls
Play Switch Begins playback of the Pro Tools session from the
current cursor position.
Record Switch Arms Pro Tools for recording. The exact function of the Record switch depends on the current Pro Tools
record mode (QuickPunch, TrackPunch, Wait for Note,
Pause).
Stop
Rewind
Pro Tools Transport switches
Fast
Forward
Play
Record
Pro Tools Transport
The D-Command Pro Tools Transport switches correspond to
the controls in the Pro Tools Transport window.
Rewind Switch Moves backward through the Pro Tools session
beginning from the current cursor position.
Fast Forward Switch Moves forward through the Pro Tools session beginning from the current cursor position.
Stop Switch Stops playback of the Pro Tools session.
MIDI Merge Indicator Shows when MIDI Merge is activated.
Latching Behavior for Fast Forward and Rewind Switches
You can set Fast Forward or Rewind to follow latched behavior
from the D-Command Transport section.
To set Fast Forward to latch:
■ Hold the Fast Forward switch and momentarily press the Re-
wind switch.
To set Rewind to latch:
■ Hold the Rewind switch and momentarily press the Fast
Forward switch.
Chapter 8: Transport and Navigation Controls 63
Page 70

Playback of Timeline Selection and Edit Selection from the Transport
5 To trim to the cursor location, press the Trim switch again.
To cancel without trimming, press Escape.
When the Timeline and Edit selections in the Edit window are
unlinked, you can set the D-Command Transport to control
playback of either the Timeline selection or the Edit selection.
To focus the D-Command Transport on the Timeline selection:
■ Press the Edit/Timeline Selection switch in the Miscella-
neous Controls section so that the Timeline LED is lit.
To focus the D-Command Transport on the Edit selection:
■ Press the Edit/Timeline Selection switch in the Miscella-
neous Controls section so that the Edit LED is lit.
Scrub/Shuttle Controls
The Scrub/Shuttle controls are used for scrubbing, scrubbing
while trimming, shuttling, and making selections.
Scrub
Trim
switch
switch
Shuttle
switch
Scrub Switch
The Scrub switch places the transport in Scrub mode, which
lets you scrub from the cursor position or across a selection.
To use Scrub mode:
1 While Pro Tools is stopped, press the Scrub switch.
2 Rotate the Scrub/Shuttle wheel clockwise to scrub audio for-
ward, or counter-clockwise to scrub audio backward.
3 To exit, press the Scrub switch again.
Shuttle Switch
The Shuttle switch places the transport in Shuttle mode,
which lets you locate the cursor in the Edit window.
To use Shuttle mode:
1 While Pro Tools is stopped, press the Shuttle switch.
2 Rotate the Scrub/Shuttle wheel clockwise to shuttle forward,
or counter-clockwise to shuttle backward.
3 To exit, press the Shuttle switch again.
Scrub/Shuttle Wheel
Scrub/Shuttle controls
Scrub/Shuttle Wheel
The Scrub/Shuttle wheel is used to control cursor position in
Pro Tools and for locating external machines.
Trim Switch
The Trim switch places the transport in Trim/Scrub mode,
which lets you scrub to locate an edit point, then trim to that
point.
To use Trim/Scrub:
1 Navigate to a region or selection you want to trim.
2 Press the Trim switch.
To trim to the end of a selection, hold Alt (Windows) or
Option (Mac) while pressing the Trim switch.
Scrub, Trim/Scrub and Shuttle modes can be used to create selections and define regions in the Pro Tools Edit window.
Master Record Enable Switch
Master Record Enable switch
Master Record Mode switch
The Master Record Enable switch toggles record enable status
for all applicable audio tracks in a session. This switch flashes
when channels are record-enabled and the Pro Tools transport is stopped, and lights continuously during recording.
If any tracks in the session are record-enabled, pressing the
Master Record Enable switch takes them out of their enabled
state. If no channels are record-enabled, pressing the Master
Record Enable switch places all applicable audio tracks into
record-enabled state.
3 Press the Scrub switch.
4 Rotate the Scrub/Shuttle wheel to move the cursor to the
trim location.
D-Command Guide64
Page 71

Transport Mode Switches
Audition
switch
Pre-Roll
switch
Mark In
switch
Mark Out
switch
Post-Roll
switch
Audition Switches
The Transport Mode switches are used to put the Pro Tools
transport in the various playback and record modes.
switch
QuickPunch
switch
9-Pin Remote
switch
Pro Tools Online
switch
Transport Mode switches
Machine Online
switch
Loop Playback
switch
TrackPunch
Pro Tools Online Switch
The Pro Tools Online switch toggles the Pro Tools online
state. The online state is mirrored in the Online button in the
Pro Tools Transport window.
While Pro Tools is online and waiting for time code, this
switch flashes. When time code is received, this switch lights
continuously.
9-Pin Remote Switch
The 9-Pin Remote switch enables 9-pin Remote Deck Emulation mode with Digidesign MachineControl.
Machine Online Switch
This feature has not been implemented for D-Command.
Loop Playback Switch
The Loop Playback switch toggles Loop Playback mode in
Pro Tools. When Loop Playback mode is active, this switch
lights. The Loop Playback state is mirrored in the Play button
in the Pro Tools Transport window.
QuickPunch Switch
The QuickPunch switch toggles QuickPunch record mode in
Pro Tools. When QuickPunch mode is active, this switch
lights. The QuickPunch state is mirrored in the Record button
in the Pro Tools Transport window.
The Audition switches are used to activate pre-roll and
post-roll in playback, define selection in and out points, and
trigger automatic playback of ranges
Audition switches
Audition Switch
The Audition switch toggles Audition mode on and off. When
Audition mode is on, this switch lights.
When Audition mode is on, you can quickly listen to either
the start or end of a selection, with or without pre-roll or
post-roll, by pressing the following switches:
Pre-Roll Switch Plays audio starting at the pre-roll point up to
the beginning of the selection.
Mark In Switch Plays audio starting at the selection start
through the length of the post-roll amount.
Mark Out Switch Plays audio back-timed from the selection
end by the pre-roll amount.
Post-Roll Switch Plays audio starting at the end of a selection
through the post-roll amount.
Pre-Roll and Post-Roll Switches
When Audition mode is off, the Pre-Roll and Post-Roll
switches toggle pre-roll and post-roll playback on and off in
Pro Tools. When pre-roll or post-roll is active, the corresponding switch lights.
When Audition mode is on, the Pre-Roll and Post-Roll
switches play a range of audio around the current Edit selection.
TrackPunch Switch
The TrackPunch switch toggles TrackPunch record mode in
Pro Tools. When TrackPunch mode is active, this switch
lights. The TrackPunch state is mirrored in the Record button
in the Pro Tools Transport window.
Chapter 8: Transport and Navigation Controls 65
Page 72

Mark In and Mark Out Switches
Back Switch
When Audition mode is off, the Mark In and Mark Out
switches are used to define selection start and end during
playback, or when using the Scrub/Shuttle wheel.
When Audition mode is on, the Mark In and Mark Out
switches play a range of audio around the current Edit selection.
To move the selection start:
With the transport stopped, hold the Mark In switch and turn
the Scrub/Shuttle wheel.
To move the selection end:
With the transport stopped, hold the Mark In switch and turn
the Scrub/Shuttle wheel.
To move the entire selection:
With the transport stopped, hold both the Mark In and Mark
Out switches and turn the Scrub/Shuttle wheel.
Locate Switches
The Locate switches move the Pro Tools transport to the designated location.
Go To Start
switch
Go To End
switch
Back
switch
Back & Play
switch
Instant
Playback
switch
The Back switch stops the Transport (if it is moving) and
moves the playback cursor back (earlier in time) by the
amount of time selected in Back settings pop-up in Pro Tools.
You can also click repeatedly to move back multiple times.
Forward Mode
Forward mode can be invoked by pressing Alt (Windows) or
Option (Mac), and pressing the Back switch.
Back & Play Switch
The Back and Play switch combines the function of the Back
switch and the Transport Play switch. The playback cursor
moves back by the amount of time selected in the Back settings preference in Pro Tools.
If pre-roll is enabled, the pre-roll time will be observed in addition to the Back time if pre-roll is enabled.
Forward & Play Mode
Forward & Play mode can be invoked by doing the following:
To move the playback location forward and begin playback:
■ Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) and press the Back and
Play switch in the Transport section.
Instant Playback
The Instant Playback switch primes Pro Tools for playback, so
that pressing Play will begin playback instantaneously. This
switch can also be used during recording to put Pro Tools in
Record Pause mode.
Locate switches
Go To Start Switch
The Go To Start switch returns the playback cursor to the beginning of the session.
Go to End Switch
The Go To End switch moves the playback cursor to the end of
the session.
D-Command Guide66
Page 73

Zoom/Navigate Section
Nudge Left and Right switches
Bank Left and Right switches
The Zoom/Navigate section is used to control navigation, display, and selections in the Pro Tools Edit window.
Zoom Mode
switch
Arrow
switches
Zoom Preset switches
D-Command Zoom/Navigate Section
Zoom Mode Switch
The Zoom Mode switch puts the arrow switches in Zoom
mode.
Navigate Mode switch
Zoom Preset Switches
The Zoom Preset switches recall the five horizontal Zoom presets in Pro Tools.
To store a Zoom Preset:
1 Using either the Horizontal Zoom buttons or the Zoomer
tool, set the zoom level that you want to store.
2 While pressing Control (Windows) or Command (Mac),
press a Zoom Preset switch.
To recall a Zoom Preset:
■ Press the corresponding Zoom preset switch.
Nudge/Bank Section
The Nudge/Bank section controls the display of any channels
in Normal mode on the D-Command surface. If any channels
are in any of the Custom Fader modes, they are not affected by
Bank or Nudge commands, and the other channels move
around them.
Navigate Mode Switch
The Navigate Mode switch puts the arrow switches in Navigate mode.
Arrow Switches (Up, Down, Previous, Next)
The function of the Arrow switches depends on the current
mode.
Zoom Mode When set to Zoom Mode, the Up and Down Arrow switches change the vertical zoom and the Previous (Left)
and Next (Right) Arrow switches change the horizontal zoom.
Navigate Mode In Navigate mode, the Up and Down Arrow
switches move the edit cursor up and down among tracks, and
the Previous (Left) and Next (Right) Arrow switches move the
edit cursor left and right among region boundaries or transients (according to the Tab to Transients setting).
Text Entry In both Zoom or Navigate modes, the Arrow
switches can be also used to navigate on-screen text fields and
enter numerical values in the on-screen Main and Sub
Counters, Start/End/Length fields, and Pre/Post Roll fields in
the Edit and Transport windows. The Previous (Left) and Next
(Right) Arrow switches move between fields, and the Up and
Down Arrow switches change the value.
D-Command Nudge/Bank Section
Nudge Switches
The Nudge switches move the display of tracks on the control
surface to the left or right, one channel at a time.
To nudge the track focus forward or backward by one channel:
■ With a track focused in the Focus Channel Strip, hold Con-
trol (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the left or right
Nudge switch.
Bank Switches
The Bank switches move the display of tracks on the controls
surface to the left or right by the number of available channels
on the control surface.
To nudge the track focus forward or backward by eight channels:
■ With a track focused in the Focus Channel Strip, hold Con-
trol (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the left or right
Bank switch.
Chapter 8: Transport and Navigation Controls 67
Page 74

D-Command Guide68
Page 75
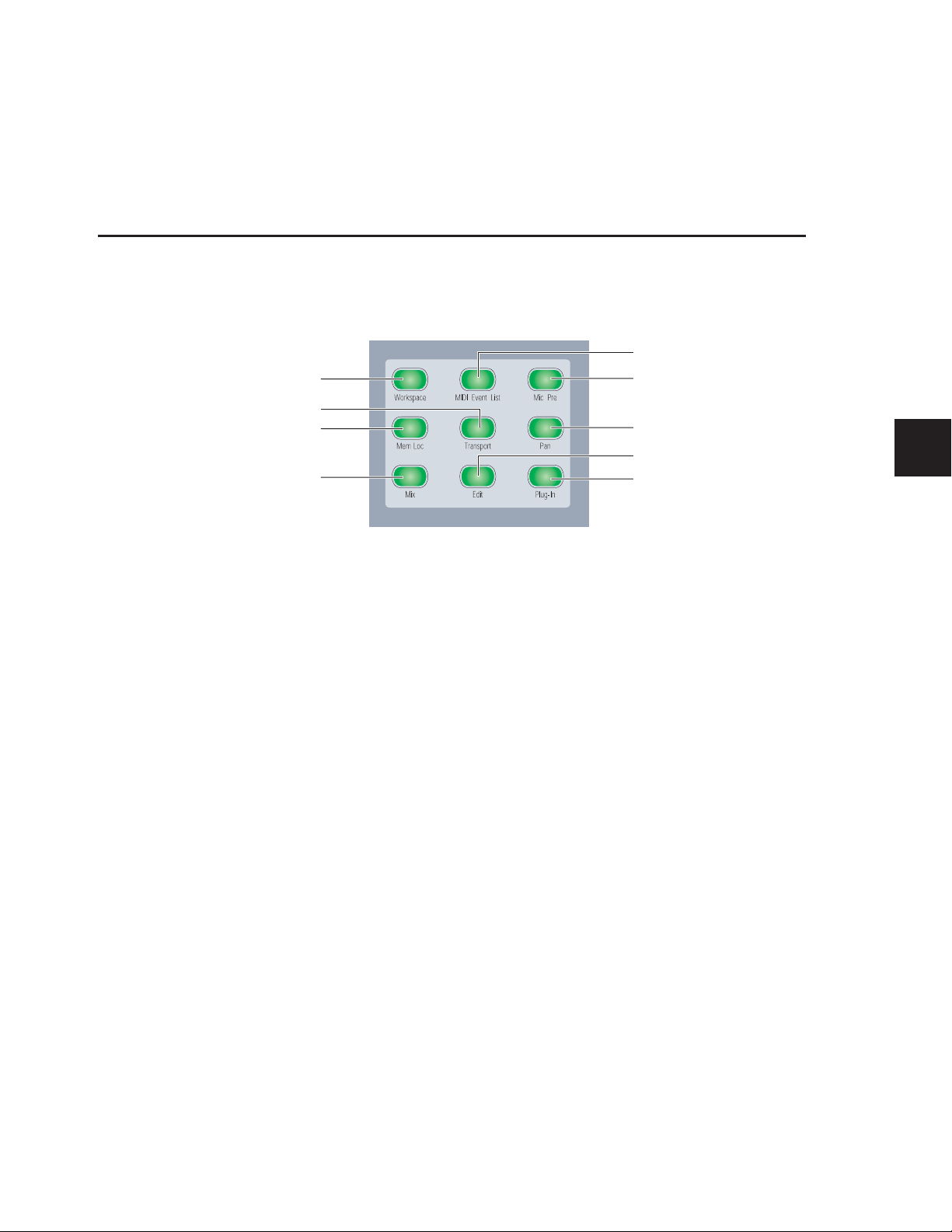
Chapter 9: Management Sections
Window Management Section
The Window Management section includes controls for opening and closing Pro Tools windows on-screen. When a window is
open, its corresponding switch is lit.
MIDI Event List switch
Workspace Browser switch
Transport switch
Memory Locations switch
Mix switch
D-Command Window Management section
Mic Pre switch
Pan switch
Edit switch
Plug-in switch
Workspace Browser Switch
The Workspace Browser switch opens and closes the DigiBase
Workspace Browser. Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) and
press this switch to close all DigiBase windows.
MIDI Event List Switch
The MIDI Event List switch opens and closes the MIDI Event
List or brings it to the front.
Mic Pre Switch
The Mic Pre switch opens and closes the Mic Pre window for
the focused track.
Memory Locations Switch
The Memory Locations Switch opens and closes the Memory
Locations window
Transport Switch
The Transport switch opens and closes the Transport window
Pan Switch
The Pan switch opens and closes the Pan window for the focused track. Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) to close all
Pan windows.
Mix Switch
The Mix switch opens the Mix Window or brings it to the
front.
Edit Switch
The Edit switch opens the Edit Window or brings it to the
front.
Plug-in Switch
The Plug-in switch opens and closes windows for any currently targeted plug-ins in the session. Hold Alt (Windows) or
Option (Mac) to close all plug-in windows.
Chapter 9: Management Sections 69
Page 76

Session Management Section
The Session Management section includes controls for session-wide management and save operations.
All Notes Off Switch
The All Notes Off switch can be used to silence stuck notes
with MIDI devices. It sends an All Notes Off message to each
channel for all connected MIDI devices.
Plug-in Clip
indicator
Go To switch
D-Command Session Management section
Clear Clip
switch
All Notes Off
switch
Publish
switch
Save
switch
Redo
switch
Undo
switch
Go To Switch
The Go To switch is used to focus a specific track onto the Focus Channel section on the Main Unit.
To go to a specific track:
1 Press the Go To switch.
2 Enter the track position number for the track and press En-
ter.
Clear Clip Switch and Plug-in Clip Indicator
D-Command indicates occurrences of signal clipping on audio tracks, sends, and plug-ins. (Clip indication on D-Command follows the clip settings in the Pro Tools Display preferences.)
The Clear Clip switch lights if a clip occurs on an audio track
or on a send anywhere in the session. The Plug-in Clip indicator lights if a clip occurs on a plug-in anywhere in the session.
In addition, D-Command shows clipping with the following
indicators:
• If an audio track clips, the meter clip LED for the clipping
channel’s lights red.
• If a send clips, the Send switch flashes in the Channel Strip
Mode controls section. In addition, if one of the encoders
on the channel strip is controlling the clipping send, the
corresponding encoder clip LED lights red.
• If a plug-in clips, the Insert switch flashes in the Channel
Strip Mode controls section. In addition, if one of the encoders on the channel strip is displaying the clipping
plug-in, the corresponding encoder clip LED lights red.
Publish Switch
The Publish switch executes the Send Session Via DigiDelivery
command in Pro Tools, opening the Send To DigiDelivery dialog on-screen.
Save Switch
The Save switch executes the Save Session command in
Pro Tools. Whenever a change is made in a session and the
Save command is available, this switch lights.
To save the current session:
1 Press the Save switch. The switch flashes, prompting confir-
mation of the Save command.
2 Do one of the following:
• To confirm the Save command, press the Save switch
again.
– or –
• To cancel the Save command, press Escape.
Redo Switch
The Redo switch executes the Redo command in Pro Tools.
Undo Switch
The Undo switch executes the Undo command in Pro Tools.
Pressing the Clear Clip switch clears all clip indicators on
D-Command, and in the Pro Tools session.
D-Command Guide70
Page 77
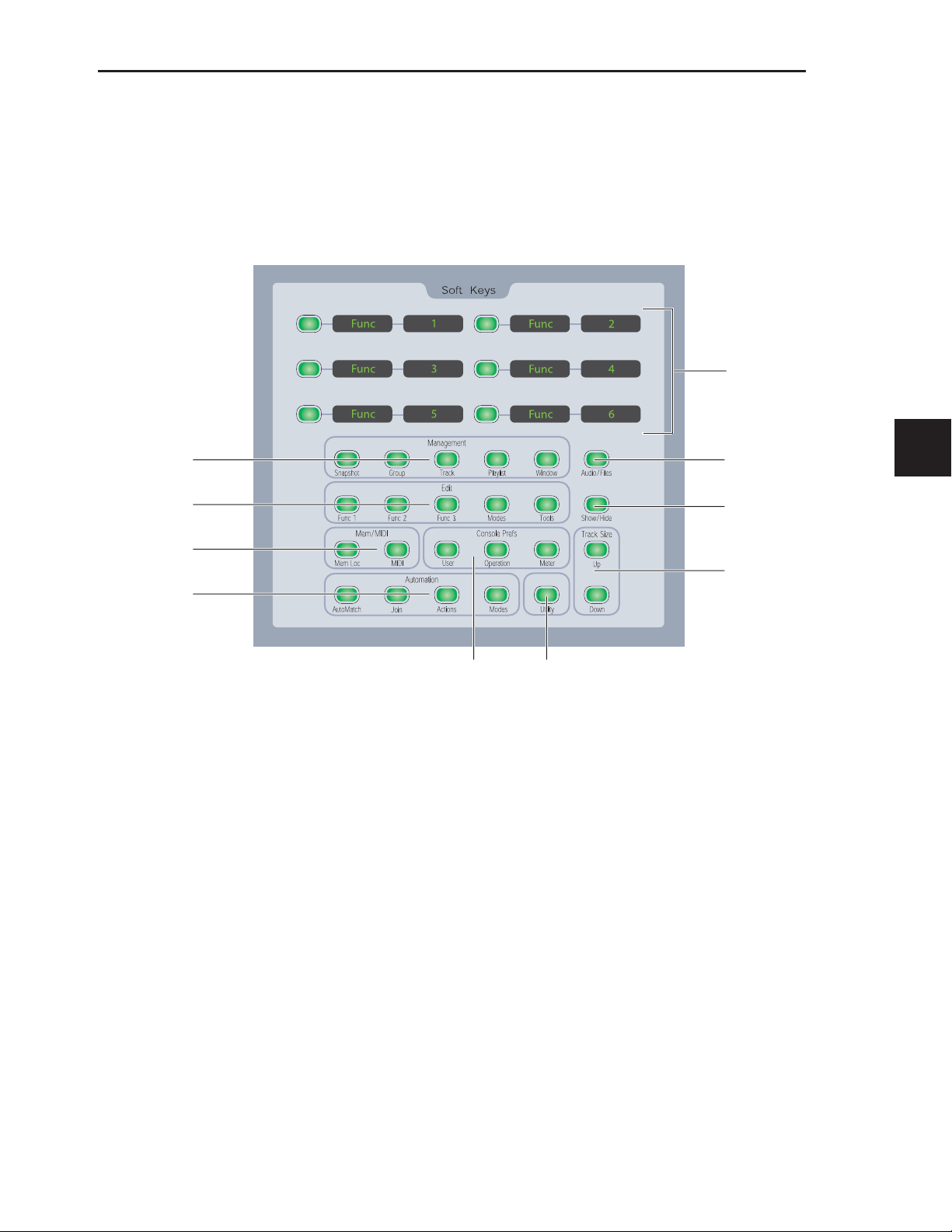
Soft Keys Section
The Soft Keys section provides access to a wide range of Pro Tools commands directly from the control surface. It also provides
access to preferences and settings specific to D-Command. The section consists of six variable-function soft keys and displays,
along with a matrix of mode switches that change the functions shown in the displays. When a function is shown in a Soft Key
display, pressing the corresponding Soft Key switch activates that function.
Some controls invoke multiple pages of Soft Key functions. To cycle through multiple pages of the same control, repeatedly press
the control switch.
Soft Key switches
and
displays
Management
controls
Edit
controls
Memory/MIDI
controls
Automation
controls
Console Preference
controls
D-Command Soft Keys section
Default Soft Key Display
When a session is first opened, the Soft Key displays show basic information about the session:
• Session Name
• Bit: Session Bit Depth
• Sampl: Session Sample Rate
• File: Session File Type
• Tcode: Session Time Code Rate
• Delay Compensation On/Off Status
Audio Files
switch
Show/Hide
switch
Track Size
switches
Utility
switch
Soft Keys Display with Pro Tools Dialogs
When Pro Tools has a dialog on-screen, the two lower Soft
Keys temporarily display “Escape” and “Enter,” letting you
cancel or confirm the dialog from the control surface.
Exiting from Soft Key Modes
You can exit a Soft Key mode and return to the default Soft
Key display by holding Control (Windows) or Command
(Mac) and pressing the currently lit Soft Key switch.
Delay Compensation can be toggled on and off from this display. The other settings shown above cannot be changed from
the Soft Keys section.
Chapter 9: Management Sections 71
Page 78
Management Controls
Snapshot
switch
Management controls
Snapshot Switch
This function is currently not implemented for D-Command.
Group Switch
The Group switch displays the following commands:
• Create Edit: Create Edit Groups
• Suspnd: Suspend Groups
• Create Mix: Create Mix Groups
• Create Both: Create Mix and Edit Groups
Track Switch
The Track switch displays the following commands:
• New Track: Track > New
• Dup Track: Track > Duplicate
• Delete Selectd: Track > Delete
• Make Act/In: Track > Make Active/Inactive
• Bounce: File > Bounce To > Disk
Playlist Switch
Group
switch
Track
switch
Playlist
switch
Window
switch
• Video Window: Window > Video
• System Usage: Window > System Usage
Page 3
• I/O Setup: Setup > I/O
• HW Setup: Setup > Hardware
• PB Engine: Setup > Playback Engine
• Disk Alloc: Setup > Disk Allocation
• Preferences: Setup > Preferences
• Peripherals: Setup > Peripherals
Edit Controls
Function 1
Edit controls
Edit Function 1 Switch (Basic Edit Commands)
The Edit Function 1 switch displays the following commands:
Page 1
• Cut: Edit > Cut
• Copy: Edit > Copy
• Paste: Edit > Paste
• Clear: Edit > Clear
• TCE To TLSel: Edit > TCE Edit to Timeline Selection
switch
Function 2
switch
Function 3
switch
Modes
switch
Tools
switch
The Playlist switch displays the following playlist commands:
• New: New Playlist
• Duplicate: Duplicate Playlist
• Delete Audio: Delete Unused Audio Playlists
• Delete MIDI: Delete Unused MIDI Playlists
Window Switch
The Window switch displays the following commands:
Page 1
• Auto Enabls: Window > Automation Enable
• Beat Det: Event > Beat Detective
• Strip Silence: Edit > Strip Silence
• Session Setup: Setup > Session
• Tasks: Window > Task Manager
• Projct Browser: Window > Project Browser
Page 2
• Color Pallet: Window > Color Palette
• Big Countr: Window > Big Counter
• Undo Histry: Window > Undo History
• Disk Space: Window > Disk Space
Page 2
• CutSP AllAut: Edit > Cut Special > All Automation
• CopySP AllAut: Edit > Copy Special > All Automation
• CutSP PanAut: Edit > Cut Special > Pan Automation
• CopySP PanAut: Edit > Copy Special > Pan Automation
• CutSP PI Aut: Edit > Cut Special > Plug-in Automation
• CopySP PI Aut: Edit > Copy Special > Plug-in Automation
Page 3
• PsteSP Merge: Edit > Paste Special > Merge
• ClrSP AllAut: Edit > Clear Special > All Automation
• PsteSP RepFil: Edit > Paste Special > Repeat to Fill Selection
• ClrSP PanAut: Edit > Clear Special > Pan Automation
• PsteSP ToCurr: Edit > Paste Special > To Current Automation Type
• ClrSP PI Aut: Edit > Clear Special > Plug-in Automation
D-Command Guide72
Page 79

Edit Function 2 Switch
Memory Location
switch
MIDI
switch
Edit Tools Switch
The Edit Function 2 switch displays the following commands:
Page 1
• Trim to Sel: Edit > Trim > To Selection
• Cpture Region: Edit > Capture Region
• Seprte Region: Edit > Separate Region
• Heal Seprtn: Edit > Heal Separation
• Consolidate: Edit > Consolidate Selection
• Time Stamp: Audio Regions List > Time Stamp Selected
Page 2
• SendTo Back: Region > Send to Back
• SendTo Front: Region > Bring to Front
• Group Region: Region > Group
• Ungrp Region: Region > Ungroup
• Ungrp All: Region > Ungroup All
• Regrp Region: Region > Regroup
Edit Function 3 Switch (Manipulation Commands)
The Edit Function 3 switch displays the following commands:
Page 1
• Duplicate: Edit > Duplicate
• Repeat: Edit > Repeat
• Shift: Edit > Shift
• Insert Silnce: Edit > Insert Silence
• Lock Region: Region > Lock/Unlock
• Mute Region: Region > Mute/Unmute
The Edit Tool Tools switch displays the Pro Tools Edit Tools.
To cycle through multiple versions of the same tool, repeatedly press the corresponding Soft Key.
• Zoom: Normal/Single Zoomer tools
• Trim: Standard/Scrub/TCE Trimmer tools
• Select: Selector tool
• Grabbr: Time/Separation/Object Grabber tools
• Scrubber tool
• Pencil: Square, Random, Free, Line, Triangle, Arc, S-Curve
To select the Smart Tool, press any two buttons for the Trimmer, Selector or Grabber simultaneously.
Memory/MIDI Controls
Memory/MIDI controls
Memory Location Switch
The Memory Location switch (“Mem Loc”) displays the
names of Memory Locations in pages of six. The Soft Key display is paged by repeatedly pressing the Memory Location
switch in the Soft Keys section. To page backwards, hold Shift
while pressing the Memory Location switch.
Page 2
• Loop Region: Region > Loop Region
• Unloop Region: Region > Unloop Region
• ID/Rem SyncPT: Region > Identify/Remove Sync Point
• Rename Rgns: Region > Rename Regions
• Quantz ToGrid: Region > Quantize to Grid
• RgnDrop: Region List > Timeline Drop Order >
L to R/Top to Bottom
Edit Modes Switch
The Edit Modes switch displays the Pro Tools Edit modes:
• Shuffl: Shuffle Mode
• Spot: Spot Mode
• Slip: Slip Mode
• Grid Rel: Relative Grid Mode
• Grid Abs: Absolute Grid Mode
MIDI Switch
The MIDI switch displays the following commands:
Page 1
• Wait Note: Transport Window > Wait for Note button
• Count Off: Transport Window > Countoff button
• Merge Record: Transport Window > MIDI Merge button
• Transpose: Event > MIDI > Transpose
• Veloc: Event > MIDI > Change Velocity
• Click On/Off: Options > Click
Page 2
• Change Tempo: Change Tempo window
• Change Meter: Change Meter window
• Split Notes: Event > MIDI > Split Notes
• Select Notes: Event > MIDI > Select Notes
• Quantz: Event > MIDI > Grid/Groove Quantize
• Input Quantz: Event > MIDI > Input Quantize
Page 3
• Write PTProp: Track > Write MIDI Real Time Properties
• Remove DpNote: Event > Remove Duplicate Notes
Chapter 9: Management Sections 73
Page 80

Audio Files Switch
The Audio Files switch displays the following commands for
importing and exporting data into Pro Tools:
• Import Audio: File > Import > Audio
• Import MIDI: File > Import > MIDI
• Audio To Trk: File > Import > Audio To Track
• MIDI To Trk: File > Import > MIDI To Track
• Import SesDat: File > Import > Session Data
• Export Selctd: Regions List > Export Selected As Files
Show/Hide Switch
The Show/Hide switch displays commands from the
Show/Hide Tracks List menu.
The Show/Hide switch has two pages of Soft Key functions.
Show/Hide Switch (Page 1)
• Show All: Show All Tracks
• Hide All: Hide All Tracks
• Show Selctd: Show Only Selected Tracks
• Hide Selctd: Hide Only Selected Tracks
• Show Inactv: Show Only Inactive Tracks
• Hide Inactv: Hide Only Inactive Tracks
Console Preferences
User
switch
Console Preferences
Operation
switch
The Console Preference switches control D-Command preferences only, and do not affect the Pro Tools on-screen display.
User Switch
The User switch displays a user-configurable, custom set of
Soft Keys, chosen from any of the other Soft Key displays. To
cycle through both pages of User Soft Key selections, repeatedly press the User switch.
To add a Soft Key command to a User Soft Key selection:
1 In the Soft Keys section, press the User switch repeatedly to
display the page (Page 1 or Page 2) where you want to add the
operation.
2 Press the Soft Keys to display the page containing the oper-
ation you want to add.
Meter
switch
Show/Hide Switch (Page 2)
• Show Audio: Show Only Audio Tracks
• Hide Audio: Hide Only Audio Tracks
• Show Aux: Show Only Auxiliary Inputs
• Hide Aux: Hide Only Auxiliary Inputs
• Show MIDI: Show Only MIDI Tracks
• Hide MIDI: Hide Only MIDI Tracks
Show/Hide Switch (Page 3)
• Show Instmt: Show Only Instrument Tracks
• Hide Instmt: Hide Only Instrument Tracks
You can select multiple Show/Hide categories by holding Shift
while pressing the corresponding Soft Key.
3 Hold Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the
Soft Key for the operation.
To remove a Soft Key command from the User Soft Key selection:
1 Press the User switch repeatedly to display the operation
you want to remove.
2 Hold Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the
Soft Key for the User operation.
Meter Switch
The Meter switch displays the following D-Command meter
preferences:
SndMtr (Send Meters) Toggles send metering on channel rotary encoders on and off.
InsMtr (Insert Meters) Toggles plug-in metering on channel
rotary encoders on and off.
Meters Toggles channel metering between pre- and post-fader
modes.
CtrMtr (Center Meters) Toggles the 8-channel meter display
on the Main Unit meter bridge between main output levels
and the focused track.
RefLvl (Reference Level) Lets you change the D-Command
meter display to help monitor program material with respect
to different reference levels.
D-Command Guide74
Page 81
Operation Switch
The Operation switch controls operations specific to D-Command, and does not affect the Pro Tools on-screen display. For
details on setting preferences, see “Setting D-Command Preferences” on page 22.
The Operation switch has three pages of Soft Key functions.
Operation Switch (Page 1)
◆ When this preference is set to “No,” the on-screen display of
plug-in and send windows does not change to reflect the state
of the control surface.
TchVal (Touch Display of Parameter Values On/Off) Turns off
the display of parameter values when faders or encoders are
touched.
Import PIMaps (Impor t Plug-in Maps) Opens “Choose a mapping file” dialog in Pro Tools.
BnkJus (Bank Justification) Determines whether banks of
channels in Normal mode are justified at the left, left center
(to the left of the Main Unit), right center, (to the right of the
Main Unit) or right side of the control surface.
CF Jus (Custom Fader Justification) Determines whether channels in Custom Fader mode are placed at the left, center-left,
center-right, or right side of the control surface.
MaxCF (Maximum Custom Fader Bank Size) Determines the
number of channels to be used when displaying channels in
the Custom Fader modes. The bank size can be set to 4 and 8
faders for a Main Unit, and 4, 8, 16 and 24 faders for an expanded system.
Rotary (Rotar y Encoder Mode) Determines responsiveness of
rotary encoder knobs. Fixed mode is at normal resolution. The
velocity modes set different rates of encoder acceleration. In
Fine mode, response is fixed and at fine resolution.
Select (Select Switch Latch Mode) Determines whether channel Select buttons follow latching or exclusive-or (non-latching) behavior when in Select mode.
Encod (Encoder Order) Determines whether inserts, sends, and
pan controls will be displayed in order from top-to-bottom or
bottom-to-top on D-Command rotary encoders.
Export PIMaps (Expor t Plug-in Maps) Opens “Save Plug-in
Mapping As” dialog in Pro Tools.
For more information about importing and exporting
plug-in maps, see “Exporting and Importing .pim Files” on
page 99.
Operation Switch (Page 3)
CFTrks (Custom Faders Display Hidden Tracks) Determines
whether tracks that are hidden in Pro Tools are displayed or
hidden in Custom Fader modes. Tracks that are hidden in
Pro Tools but shown in Custom Faders cannot be Selected or
Record enabled.
Brdcst (Broadcast) Determines whether the XMON monitoring system is in Broadcast mode, which prevents AFL and PFL
solo modes from changing the XMON Control Room Input
source.
Match Time (AutoMatch Time) Lets you use the Scrub/Shuttle
wheel to set AutoMatch time for automated panning functions.
Glide Time (AutoGlide Time) Lets you use the Scrub/Shuttle
wheel to set AutoGlide time for automated panning functions.
Operation Switch (Page 2)
ApTrgt (Target Track from Application) Determines whether se-
lecting an Insert or Send on-screen focuses its track on the
D-Command Main Unit.
Faders (Faders On/Off) Turns off D-Command faders to prevent fader movement when monitoring a mix.
ChanWn (Channel Window Display) Determines whether displaying plug-in or send pan parameters (by pressing an encoder Select switch) on D-Command opens the corresponding
plug-in or send window on-screen in Pro Tools. Also determines whether the Channel Select switches (in the Dynamics
or EQ sections) change the channel display of multi-mono
plug-ins.
◆ When this preference is set to “Yes,” the on-screen display
of plug-in and send windows changes to reflect the state of the
control surface.
FCStrp (Focus Channel Strip) Determines whether focusing a
channel in the Focus Channel section also places a duplicate
of the focused channel in the channel strip to the immediate
left of the Global Controls section.
When Focus Channel Strip is enabled, all controls and modes
are linked. You can, however, use four encoders simultaneously by using the Page Up or Page Down switches to bring
a different set of sends or inserts to the duplicate channel’s encoders.
Trk/Ed (Link Track and Edit Selection) Toggles the Options >
Link Track and Edit Selection option, which automatically selects a track or range of tracks when a selection is made in the
track’s timeline.
The duplicate Focus Channel strip is not available when
D-Command is in a Custom Fader mode.
Chapter 9: Management Sections 75
Page 82

Automation Controls
AutoMatch
switch
Automation controls
AutoMatch Switch
The AutoMatch switch enables AutoMatch command in Latch
or Write automation modes.
Join Switch
The Join switch resumes writing automation in Latch mode,
on all channels that were previously writing automation, after
an interrupted automation pass.
Actions Switch
The Actions switch displays the following commands:
Actions Switch (Page 1)
WrtTo Start (Write To Start) Writes current automation values
from the insertion point backward to the beginning of a selection or track while performing an automation pass.
WrtTo All (Write to All) Writes current automation values to
an entire selection or track while performing an automation
pass.
WrtTo End (Write to End) Writes current automation values
from the insertion point forward to the end of a selection or
track while performing an automation pass.
WrtTo Next (Write to Next Breakpoint) Writes current automation values from the insertion point forward to the next automation breakpoint while performing an automation pass.
Snap Back Causes all Latch or Write enabled tracks to exit
their current automation pass and return instantly to the previously written automation levels. During playback, stops
writing of automation without applying any AutoMatch
ramping.
Join
switch
Actions
switch
Modes switch
Modes Switch
The Modes switch displays the following D-Command Modes:
AWrtTo Start (Auto Write to Start on Stop) Automatically
writes current automation values from the insertion point
backward to the beginning of a selection or track when the
transport is stopped after an automation pass.
By default, Automatic Write to Start on Stop mode is enabled
for a single automation pass only. Hold Start+Alt (Windows)
or Control+Option (Mac) while pressing the Auto ToStrt
switch to configure the mode to remain enabled after an automation pass.
AWrtTo All (Auto Write to All on Stop) Writes current automation values to an entire selection or track when the transport
is stopped after an automation pass.
By default, Automatic Write to All on Stop mode is enabled for
a single automation pass only. Hold Start+Alt (Windows) or
Control+Option (Mac) while pressing the Auto ToAll switch
to configure the mode to remain enabled after an
automation pass.
AWrtTo End (Auto Write to End on Stop) Writes current automation values from the insertion point forward to the end of
a selection or track when the transport is stopped after an automation pass.
By default, Automatic Write to End on Stop mode is enabled
for a single automation pass only. Hold Start+Alt (Windows)
or Control+Option (Mac) while pressing the Auto ToEnd
switch to configure the mode to remain enabled after an automation pass.
AWrtTo Next (Auto Write to Next Breakpoint on Stop) Writes
current automation values from the insertion point forward
to the next automation breakpoint when the transport is
stopped after an automation pass.
AutoJoin AutoJoin is used in Latch mode to automatically resume writing of automation after the transport is stopped and
started again during an automation pass.
Actions Switch (Page 2)
Copy To Send Opens the Copy To Send dialog to allow copy-
ing of track control values to each selected track’s send (Edit >
Automation > Copy To Send).
Thin Auto (Thin Automation) Performs the Thin Automation
command. (Edt > Automation > Thin).
D-Command Guide76
Page 83

Utility Switch
Utility switch
The Utility switch places the D-Command in Utility mode.
When D-Command is in Utility mode, this switch flashes.
Utility mode lets you view D-Command system information,
name D-Command units, run D-Command diagnostic tests,
and set certain D-Command hardware preferences. For complete information on Utility mode, see Appendix A, “Utility
Mode”
Track Size Switches
Track Size Up
switch
Track Size Down
switch
Track Size controls
The Track Size Up and Down switches increase and decrease
the track height of all tracks where a selection or edit cursor is
present.
Chapter 9: Management Sections 77
Page 84

D-Command Guide78
Page 85

Chapter 10: Monitor and Meter Sections
Monitor Section Controls
The Monitor section includes a full set of controls for the control room monitoring, headphone/cue, and talkback/listenback
sections of D-Command. All input and output connections to the D-Command monitoring system are made on the XMON interface, which is connected to the D-Command console with the XMON cable, and remotely controlled from this section.
D-Command Monitor section
Input source switches
and Output controls
Cue
controls
Output Channel Select
and Mode switches
Monitor
Mode
controls
Talkback/Listenback
controls
Chapter 10: Monitor and Meter Sections 79
Page 86

Input Source Switches and Output Controls
Sum switch
Input source
switches
Surround
switch
Main switch
Stereo Input
switches
Sum Switch
In normal operation, the Input Source switches follow exclusive-or (non-latching) behavior, allowing only one source to
be monitored at a time.
However, D-Command has a Sum mode that allows multiple
input sources to be monitored at the same time. When Sum
mode is on, multiple input source switches can be active.
Sum mode ignores any input trim values when it is active.
Output Level control
Output
controls
Input source switches and Output controls
Alt Output
On/Off switch
Mini Output
On/Off switch
Main Output
On/Off switch
Input Source Switches
The monitor system has five input sources:
• Main Inputs (6 channels)
• Surround Inputs (6 channels)
• Stereo 1 Inputs (2 channels)
• Stereo 2 Inputs (2 channels)
• Stereo 3 Inputs (2 channels)
These sources are selected by pressing their corresponding Input switches, which light when the source is activated.
Input Level Trim Mode
Each input source can be trimmed independently, to allow for
setting of different reference levels or to compensate for differences in gain structure. Available trim values range from
–20 dB to +10 dB in 0.5 dB steps.
To trim input levels:
1 Press and hold the Input Source Selector switch for the input
you want to trim, until the switch flashes.
2 Turn the Main Output Level encoder knob to set the trim
value. The monitor section display shows “Trim” and the trim
value in dB.
3 Press the flashing Input Source Selector switch to exit Trim
mode.
To add or remove inputs in Sum mode:
1 Press the Sum switch. The switch lights to indicate Sum
mode is on.
2 Press any number of Input Source switches to toggle their
corresponding inputs on or off. It is possible to turn all inputs
off in this mode.
To exit Sum mode:
■ Press the Sum switch again. Monitoring reverts to the input
that was selected when you entered Sum mode.
Output On/Off Switches
The monitor system has three outputs:
• Main Control Room Outputs (6 channels)
• Alt Control Room Outputs (6 channels)
• Mini Control Room Outputs (2 channels)
Only one output can be active at a time. The Output On/Off
switches follow exclusive-or (non-latching) behavior. When
you activate an output, its name and gain value (in dB) are
shown in the monitor section display.
Output Level Control
The monitor system output section has a touch-sensitive rotary encoder for control of output level. When the encoder
knob is touched, the monitor section display shows the current level in dB. Gain ranges from a minimum of –INF to a
maximum of +10 dB, in 1 dB steps.
Output Level Trim Mode
Each output level control can be trimmed independently, to
allow for setting of different reference levels or to compensate
for differences in gain structure. Available trim values range
from –20 dB to +10 dB, in 0.5 dB steps.
To trim output levels:
1 Press and hold the On/Off switch for the output you want to
trim, until the switch flashes.
2 Turn the encoder knob to set the trim value. The monitor
display shows the trim value in dB.
3 Press the flashing On/Off switch to exit Trim mode.
D-Command Guide80
Page 87

Headphone/Cue Controls
Headphones
switch
Studio Loudspeaker
switch
The following table shows possible outputs for each input
source. (Talkback can be added to each of the outputs.)
Input Possible Outputs
Cue 1 Cue 1, Headphone, Studio LS
Cue Input Source
switches
Cue Output
Level control
Set Source
switch
AFL/PFL Level
switch
Assign Talkback switch
Cue Output
On/Off switch
Cue controls
Cue Input Source Switches
The Headphone/Cue monitor system has three input sources:
• Cue 1 Input (2 channels)
• Cue 2 Input (2 channels)
• Main Monitor Input (2 channels)
Cue Output On/Off Switches
Cue 2 Cue 2, Headphone, Studio LS
Main Monitor Cue 1, Cue 2, Headphone, Studio LS
To assign an input source to an output:
1 Press the switch for the output for which you want to assign
an input. The switch will light, and the Monitor LED display
will show the currently selected source.
2 Press the Set Source switch repeatedly to cycle through the
available source choices.
Assign Talkback Switch
The Assign Talkback switch lets you add the talkback signal to
any of the Headphone/Cue system outputs. The Assign Talkback switch lights to indicate that talkback is active for a given
output.
The Cue system has four available outputs:
• Cue 1 (2 channels)
• Cue 2 (2 channels)
• Headphone (2 channels)
• Studio Loudspeaker (2 channels)
The two Cue Outputs, Headphone Output, and Studio Loudspeaker Output can be active in any combination, including
all on or all off.
Chapter 10: Monitor and Meter Sections 81
Page 88

Output Channel Select Controls
Channel Select switches
Set Up switch
AFL and PFL
switches
Individual Output Trim Mode
Each output channel can be trimmed individually for each of
the three control room outputs (Main, Alt, and Mini), allowing you adjust the channel balance for each set of control
room speakers. Trim values are stored for each of the three
outputs. Available trim values range from –30 dB to +10 dB, in
0.5 dB steps.
Solo/Mute switch and indicators
Output Channel Select controls
Set Up Switch
The Set Up switch resets output trim levels to their default values.
Channel Select Switches
The Channel Select switches let you solo or mute individual
channels of the Control Room outputs. The function of the
Channel Select switches depends on the mode of the
Solo/Mute switch.
• When the mode is set to Solo, each Channel Select switch
solos the corresponding output channel.
• When the mode is set to Mute, each Channel Select switch
mutes the corresponding output channel.
In both modes, the Channel Select switches follow latched behavior, allowing multiple outputs to be soloed or muted. The
Channel Select switches light to indicate that they are active.
There are Channel Select switches for the following channels:
• L (Left)
• C (Center)
• R (Right)
• Ls (Left Surround)
• Rs (Right Surround)
• LFE
To trim the output level for an individual output channel:
1 Activate the control room output (Main, Alt, or Mini) whose
channel levels you want to trim.
2 Press and hold the Channel Select switch for the output
channel you want to trim, until the switch flashes.
3 Turn the Output Level encoder to set the trim value for the
channel. The monitor display shows “Trim” and the trim
value in dB.
4 Press the flashing Channel Select switch to exit Trim mode.
5 Repeat the above steps for each output channel and each set
of outputs (Main, Alt, or Mini) you want to trim.
Solo/Mute Switch and Indicators
The Solo/Mute switch toggles the function of the Channel Select switches between Solo and Mute modes. The indicators
light to indicate which mode is active.
These choices support all possible channel configurations in
Pro Tools. A maximum of six channels (5.1 surround) may be
in use at any time.
D-Command Guide82
Page 89

AFL and PFL Switches
Broadcast Mode for AFL and PFL Monitoring
The AFL and PFL switches invokes After Fader Listen and Pre
Fader Listen Solo modes.
AFL and PFL modes send signal to a separate output path with
independently adjustable levels for each mode. The XMON
Control Room Input source is automatically changed to monitor the AFL/PFL input, unless you put D-Control in Broadcast
mode (see “Broadcast Mode for AFL and PFL Monitoring” on
page 83). This lets you monitor the soloed channels in the
Main control room monitors (with Broadcast mode off) or in
a dedicated solo monitoring system (with Broadcast mode
on).
AFL and PFL Solo modes require the use of the Surround
Mixer plug-in.
To select the Solo mode:
1 Press the AFL or PFL switch in the D-Command Monitor sec-
tion to select the corresponding Solo mode.
Setting AFL and PFL Levels
Levels can be set separately for AFL and PFL modes from the
D-Command Monitor section.
You can put the D-Command monitoring system in Broadcast
mode, which prevents AFL and PFL solo modes from changing
the XMON Control Room Input source. This lets you solo
channels while preserving the main monitor mix.
You can then use the AFL/PFL path selector in the I/O Setup
dialog to route the AFL/PFL solo signal directly from the HD
Audio Interface to a separate set of speakers or headphones.
To put the XMON monitoring system in Broadcast mode:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Soft Key section.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “Broadcast”
While in Broadcast mode, any channels soloed while in AFL
or PFL are still sent to the AFL/PFL path, but XMON does not
switch the Control Room Input source to monitor that path.
While in Broadcast mode, any channels soloed while in SIP
mode will still cause all other tracks to be muted.
To set the AFL or PFL level:
1 Press the AFL or PFL switch in the D-Command Monitor sec-
tion.
2 Turn the Cue output level control. The AFL/PFL level is
shown in the Monitor displays.
To set the AFL or PFL level to its default setting:
1 Press the AFL or PFL switch in the D-Command Monitor sec-
tion.
2 Hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) and touch the Cue
output level control.
Chapter 10: Monitor and Meter Sections 83
Page 90
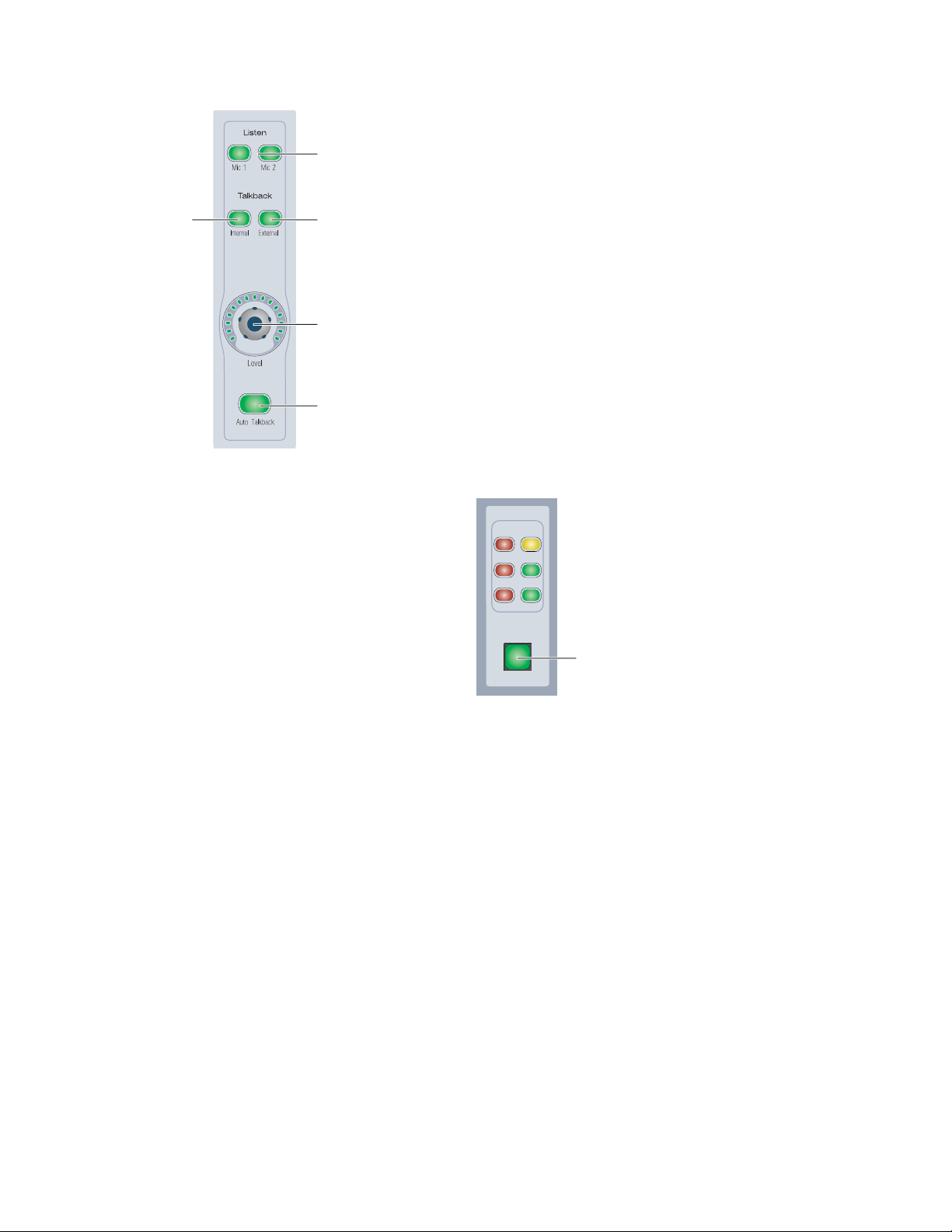
Talkback/Listen System
Listen Mic
Select switches
Auto Talkback Switch
The Auto Talkback switch activates a mode in which the talkback and listen microphones are automatically turned on
whenever the Pro Tools transport is not in Play or Record.
When Auto Talkback is active, the Auto Talkback switch
lights, and the Talkback switches flash.
Internal Talkback
switch
External Talkback
switch
Talkback/Listen
Level control
Auto Talkback
switch
Control Room Output controls
Talkback Controls
The Talkback system has two talkback microphone inputs
(one external, one built-in) both using the touch-sensitive rotary encoder for control of output volume. When either
switch is lit, the monitor section display show the corresponding volume level in dB. Level control on each ranges from a
minimum level of –INF to a maximum level of +30 dB.
Talkback Level Control
When the External Talkback switch is lit, the Level control adjusts the volume for the external talkback microphone. When
the encoder knob is touched, the monitor section display
shows the level in dB.
The Talkback Level control also adjusts the volume of the
built-in (Internal) microphone, located on the meter bridge of
the D-Command Main Unit.
While in Auto Talkback mode, you can temporarily disable
and re-enable talkback, while staying in Auto Talkback mode.
To temporarily disable Talkback while in Auto Talkback mode:
■ Press either of the flashing Talkback switches.
To re-enable talkback while in Auto Talkback mode:
■ Double-press either Talkback switch so it flashes again.
Talkback Switch
The Talkback switch, located at the bottom of the Channel
Strip Master section on the Main Unit, controls the D-Command Talkback function.
Auto Mode
Write Trim
Read
Touch
Latch Off
Talkback switch
Talkback
Dbl Press to Latch
Talkback switch
The Talkback switch can follow momentary or latched behavior. If held, the switch is active only when pressed down.
If rapidly double-pressed, the switch latches on and flashes to
indicate that talkback is active. Press the switch again to turn
off talkback.
Talkback Dim Function
When Talkback is engaged, the Dim switch lights and the Dim
function is automatically applied to the Main outputs. Any
adjustment of the Dim level affects both the Talkback Dim
function and the Control Room Output Dim function.
To set the Dim level:
1 Press and hold the Assign Talkback switch until the switch
flashes.
2 Turn the Cue Output Level encoder to set the Dim value.
The monitor section shows the Dim value in dB.
D-Command Guide84
Page 91

Listen Control
The Listen system has two selectable microphone inputs, both
using the touch-sensitive rotary encoder for level control.
To calibrate Control Room outputs to display SPL:
1 Send the reference material to the Main Control Room Out-
puts, and set the output level in Pro Tools to your studio reference level (for example, –18 dBFS).
Listen Mic Select Switches
There are two Listen Mic Select switches for the external listen
microphone inputs:
• Mic 1
• Mic 2
Either or both of these inputs can be active at any time. When
one input is active, the encoder controls the level of that input
independently. When both inputs are active, the encoder
controls both levels simultaneously, maintaining any relative
offset between the two.
Level control ranges from a minimum level of –INF to a maximum level of +30 dB.
Dim Level Control
The Dim Level control lets you adjust the amount of level reduction applied by the Dim switch, located at the bottom of
the Monitor section. Level reduction ranges from –30 dB to
0 dB, in 1 dB steps.
When the Dim encoder knob is touched, the monitor section
display shows “Dim” and the gain reduction in dB.
Monitor Output Mode Controls
Calibration Mode
switch
Mono switch
2 Pan the signal to center (so that equal level is sent to all
Main Control Room Output speakers).
3 Set the speaker-to-speaker balance for all speakers in the sys-
tem using Output Trim mode for each channel, using the
sound pressure level meter to measure SPL at the mix position.
See “Individual Output Trim Mode” on page 82.
4 Solo the Center speaker, and adjust the Main Control Room
Output level encoder until the sound pressure level meter
measures the target reference level (for example, 85 dB) at the
mix position.
5 Press and hold the Calibration Mode switch until it flashes.
6 Adjust the Main Control Room Output level encoder until
the target reference level is displayed in the Monitor Section
display.
7 Press the flashing Cal switch.
8 Repeat steps 4–7 for the Alt and Mini outputs.
To toggle the output display between dB and dB SPL:
1 Select the output whose display you want to toggle (Main,
Alt, or Mini).
2 Press the Calibration Mode switch.
◆ When the Calibration Mode switch is lit, output is dis-
played in dB SPL.
◆ When the Calibration Mode switch is unlit, output is dis-
played in dB.
Dim switch
Monitor Output Mode controls
Mute switch
Calibration Mode Switch
The Calibration Mode switch invokes a mode that changes
the output value displayed by the Monitor section display
from gain (expressed in dB) to sound pressure level (expressed in
dB SPL) for each of the control room outputs. This switch
lights when an SPL value is shown for the active output.
To display output levels in dB SPL, you must first calibrate
each output. This SPL calibration requires the use of a pink
noise source (or other reference material) and a sound pressure level meter to measure the output of individual control
room speakers.
Mono Switch
The Mono switch mixes the Left and Right signals of any of
the output modes (any surround channels are not affected) to
provide mono output, useful for checking phase and balance
relationships. The Mono switch lights to indicate that it is active.
Mono Trim Mode
Mono output can be trimmed to adjust its reference level in
comparison to other outputs. Available trim values range
from –12 dB to 0 dB, in 0.5 dB steps.
To trim mono output:
1 Press and hold the Mono switch until it flashes.
2 Turn Alt Output encoder knob to set the Mono trim value.
The monitor display shows “Trim” and the trim value in dB.
3 Press the flashing Mono switch to exit Trim mode.
Chapter 10: Monitor and Meter Sections 85
Page 92

Dim Switch
The Dim function applies an adjustable gain reduction to the
Control Room outputs. This function affects all three output
destinations. The Dim switch toggles the dim function on and
off, and lights to indicate that it is active.
Mute Switch
The Mute switch toggles the mute state for all Control Room
outputs. Mute operates globally on all three output destinations. The Mute switch lights to indicate that it is active.
If the Mute switch on the XMON interface front panel is activated, the Mute switch on D-Command must be used to unmute the monitor system. (Outputs cannot be unmuted from
XMON front panel.)
D-Command Guide86
Page 93
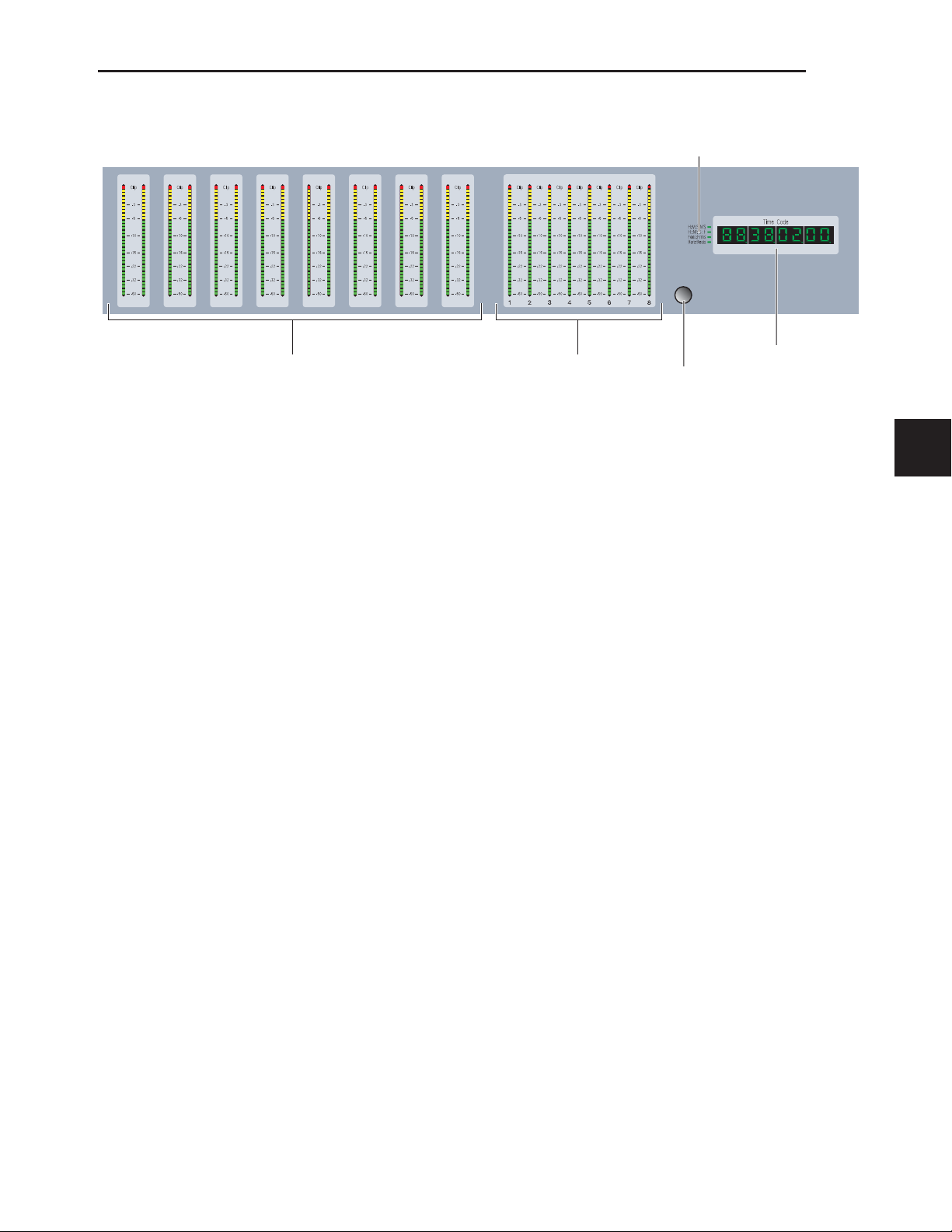
Meter and Time Code Displays (Main Unit)
Time Scale display format indicators
Channel Strip Meter displays
Meter and Time Scale displays (Main Unit)
Output Meter displays
Talkback Microphone
Time Scale display
Meters
The Channel Strip Meter display features dual 32-segment LED bar graphs for each channel, and can display pre- or post-fader
levels depending on the D-Command Meter Preferences setting. In Custom Fader mode, these meter displays can show plug-in
input and output meters, gain reduction meters for dynamics plug-ins, and other parameters. The top LED is red and indicates
clipping on the corresponding channel or parameter.
The Output Meter display includes eight 32-segment LED bar graphs with clip indication for displaying output levels or the level
of the track focused in the Focus Channel Strip, depending on the D-Command Meter Preferences setting.
For details on setting meter preferences, see “Meter Preferences” on page 24.
Time Scale Displays
The Time Scale displays on the Main Unit mirrors the Main Time Scales in Pro Tools.
Time Scale Display Format Indicators
The indicators to the left of the Time Scale displays show the currently displayed format for both the Main Time Scale and the
Sub Time Scale. Formats include:
• Hours:Minutes:Seconds:Milliseconds
• Hours:Minutes:Seconds:Frames
• Feet+Frames
• Bars|Beats
Talkback Microphone
The built-in D-Command talkback microphone is located between the Meters and the Time Scale display.
Chapter 10: Monitor and Meter Sections 87
Page 94

Setting D-Command Meters for Different Reference Levels
The Pro Tools Reference Level meter preference lets you change the D-Command meter display to help monitor program material
with respect to different reference levels.
At each setting except 0 dB, a single LED lights continuously across the meter bridge at a fixed point to indicate that reference
level. You can then compare the peaks of the program material to the indicated level.
The following reference level settings are available:
0 dB This is the normal setting used for referencing material to a 0 dB (full code) reference level.
–14 dB This reference level setting lights a single LED at –14 dB across the meter bridge.
–18 dB This reference level setting lights a single LED at –18 dB across the meter bridge.
–20 dB This reference level setting lights a single LED at –20 dB across the meter bridge.
To set a D-Command meter reference level:
1 In the Soft Keys section, press the Meter switch.
2 Press the Soft Key that corresponds to “RefLvl” to cycle among the meter reference level settings.
3 Press the Meter switch to exit.
D-Command Guide88
Page 95

Chapter 11: Operating Modes
The power and flexibility of D-Command lies in its different
operating modes, which let you customize the behavior of its
channel strip controls to fit your workflow.
The two types of D-Command operating modes are Normal
mode and the four Custom Fader modes. This section provides
an overview of each mode and its associated commands.
Normal Mode
In Normal mode, Pro Tools tracks are displayed on D-Command in a standard console format. In this mode, channel
strips correspond to a track in the session, and most of the
channel strip controls correspond directly to on-screen controls or views in Pro Tools:
◆ Channel Fader controls channel volume
◆ Channel Display shows track name, and track volume when
fader is touched
◆ Pan switch shows Pan values on encoders (this is the default
view when a new track is created)
◆ Inserts switch shows Insert name on encoders
◆ Sends switch shows name of Send on the encoder display,
and Send level on the encoder LED ring
Assigning Elements to Tracks
You can assign Inputs, Outputs, Inserts, and Sends to tracks
directly from D-Command by entering Assign mode.
To assign an input or output to a track:
1 Press the Assign Inputs switch or Assign Outputs switch to
enter the corresponding Assign mode. Input and output assignments are displayed and edited on the lower encoder.
2 If necessary, press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch repeatedly to
move up through to the top menu level.
3 Turn the encoder knob to choose between audio interface
channels and busses.
4 Press the encoder Select switch to confirm your selection.
5 Turn the encoder knob to choose the audio interface chan-
nel or bus assignment that you want.
7 Press the flashing encoder Select switch or press the flashing
Assign switch to confirm the assignments.
To assign a send or insert to a track (global assign mode):
1 Press the Assign Sends switch or the Assign Inserts switch to
enter the corresponding Assign mode. The first two send or insert positions will show on the encoder displays by default.
2 To display and edit other insert positions, press the Page Up
or Page Down switches on the channel where you want to
make the assignment.
3 Turn the encoder knob that corresponds to the insert posi-
tion that you want to edit to select from the first level of menu
choices.
4 Press the encoder Select switch to move down and the By-
pass/Mute/Pre switch to move up through menu levels.
5 Press the encoder Select switch to confirm each menu level
selection.
6 Repeat steps 2–5 to modify other send or insert assignments.
7 Press each flashing encoder Select switch or press the flash-
ing Assign switch to confirm the assignments.
To assign a send or insert to a track (temporary assign mode):
1 Press the Inserts or Sends switch on the channel where you
want to make the assignment.
2 To display and edit other insert positions on the channel,
press the channel’s Page Up or Page Down switches.
3 Do one of the following:
• If the send or insert position is empty, press the encoder
select switch. The encoder display shows the “>” sign indicating that you are editing the send or insert position.
– or –
• If the send or insert position is already assigned, press
and hold the encoder select switch until the encoder display shows the “>” sign indicating that you are editing
the send or insert position.
4 Turn the encoder knob that corresponds to the insert posi-
tion that you want to edit to select from the first level of menu
choices.
6 Repeat steps 2–5 for any other channels that you want to as-
sign an input or output.
Chapter 11: Operating Modes 89
Page 96

5 Press the encoder Select switch to move down and the By-
pass/Mute/Pre switch to move up through menu levels.
6 Press the encoder Select switch to confirm each menu level
selection.
7 Repeat steps 2–5 to modify other send or insert assignments.
8 Press the flashing encoder Select switch to confirm the as-
signment.
To remove an input, output, send or insert:
1 Press an Assign switch to enter the corresponding Assign
mode.
6 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing encoder Select switch or press the flashing Assign Inputs switch to confirm the assignment.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the assignment.
Making Elements Active or Inactive
You can make Inputs, Outputs, Inserts, Sends, and entire
tracks active or inactive directly from D-Command by entering a temporary Make Inactive mode.
2 For the assignment you want to remove, press the encoder
Bypass/Mute/Pre switch repeatedly until you reach the top
level menu for the assignment.
3 Turn the encoder knob counter-clockwise until no assign-
ment is visible.
4 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing encoder Select switch or press the flashing Assign switch to confirm the removal.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the removal
and restore the assignment.
Assigning Inputs in Sessions with Multiple
Plug-In Outputs
In sessions with plug-ins that have multiple outputs, the outputs of those plug-ins are available as inputs in other audio
and Auxiliary Input tracks. These appear as a third category of
inputs, labelled plug-ins, in the track input menu.
When assigning inputs from D-Control, this third category of
inputs appears as a top-level menu choice.
To assign an input from a plug-in output:
1 Press the Assign Inputs switch.
2 On the channel where you want to make the assignment,
turn an encoder knob to select Plug-In from the first level of
menu choices.
3 Press the encoder Select switch to move down to the indi-
vidual plug-in level.
4 Turn the encoder knob to select the plug-in whose auxiliary
output you want to select.
5 Press the encoder Select switch to move down to the list of
plug-in auxiliary outputs.
To toggle input paths active/inactive:
1 Press the Make Inactive Inputs switch to enter the Make In-
active mode.
2 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the appropriate en-
coder to deactivate or reactivate the input. Inactive inputs are
shown with an inverted text display.
3 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode.
To toggle output paths active/inactive:
1 Press the Make Inactive Outputs switch to enter the Make
Inactive mode.
2 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the appropriate en-
coder to deactivate or reactivate the combined outputs for
that channel.
3 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode.
To toggle individual outputs sub-paths active/inactive:
1 Press the Make Inactive Outputs switch to enter the Make
Inactive mode.
2 Press the Select switch on the appropriate encoder to view
the output sub-paths for the channel.
3 Press the Page Up or Page Down switches to step through
the possible output sub-paths.
4 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the appropriate en-
coder to deactivate or reactivate your choice of output
sub-paths. Inactive output sub-paths are shown with an inverted text display.
5 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode.
To toggle a send or plug-in active/inactive:
1 Press the Make Inactive Sends switch or the Make Inactive
Inserts switch to enter the corresponding Make Inactive
mode. The first two insert or send positions will show on the
encoder displays.
D-Command Guide90
Page 97

2 To display and edit other insert positions, press the Page Up
or Page Down switches on the channel where you want to
make the assignment.
3 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on the appropriate en-
coder to deactivate or reactivate the insert or send assignment.
Inactive assignments are shown with an inverted text display.
4 Repeat steps 2–3 to modify other send or insert assignments.
5 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode.
To toggle a track inactive/active:
1 Press any of the Make Inactive switches.
2 Press channel strip Select buttons to deactivate or reactivate
the corresponding tracks.
3 Press the flashing Make Inactive switch to exit Inactive
mode.
Selecting a Track
You can select tracks in Pro Tools directly from D-Command.
In Select mode, Select switches can follow latching or
non-latching behavior. For details on setting the latch mode
for the Select switch, see “Select Switch Latch Mode” on
page 23.
To select a track from D-Command:
1 Make sure the Select/Focus switch mode is set to Select.
2 Press the channel Select switch for the track you want to se-
lect.
To select a range of tracks:
1 Press the Select switch on the channel at the start of the
range you want to select.
2 Hold Shift and press the Select switch on channel at the end
range you want to select.
Focusing a Track
You can focus any track in a session in the Focus Channel section, and the Dynamics and EQ sections of D-Command. Focusing a track also makes it available for use with the Custom
Fader Plug-in mode. (See “Plug-In Mode” on page 97.)
To focus a track in the Focus Channel section from D-Command:
1 Make sure the Select/Focus switch mode is set to Focus.
2 Press the channel Select switch for the track you want to fo-
cus.
To focus a track on the Focus Channel section from Pro Tools:
1 Make sure the Target Track from Application preference is
set to Yes. For details on this preference, see “Target Track from
Application” on page 24.
2 On-screen in Pro Tools, click the plug-in state plate, send
window, panner window, or mic pre pane for the track you
want to focus.
To focus a specific track number:
1 Do one of the following;
• Press the Go To switch on D-Command.
– or –
• Choose Operations > Scroll to Track Number in
Pro Tools.
2 Enter the track position number for the track and press En-
ter.
To nudge the track focus left or right by one channel:
■ Hold Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the
Nudge Left or Nudge Right switch.
To bank the track focus left or right by eight channels:
■ Hold Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the
Bank Left or Bank Right switch.
All tracks between the first channel and last channel (inclusive) are selected.
To select or deselect multiple, non-contiguous tracks, do one of
the following:
■ If the Select Switch Latch Mode is set to latch, press addi-
tional Select switches.
– or –
■ Hold Control (Windows) or Command (Mac) and press the
Select switches on multiple channels.
Focus Channel Strip
If the D-Command Focus Channel Strip Operations preference is set to Yes, focusing a track also places a duplicate of the
focused track in the channel strip to the immediate left of the
Global Controls section. See “FCStrp (Focus Channel Strip)”
on page 75.
The duplicate Focus Channel strip is not available when
D-Command is in a Custom Fader mode.
Chapter 11: Operating Modes 91
Page 98

Focusing a Plug-In
If the D-Command Focus Channel Strip Operations preference is set to Yes, focusing a track on D-Command brings the
name of the first active plug-in into the Focus Channel display.
To focus a plug-in in the Focus Channel display:
1 Make sure the Select/Focus switch mode is set to Focus.
2 Press the channel strips’s Select switch. The first plug-in that
is not a dynamics or EQ plug-in is automatically focused, and
its name appears in the Custom Faders display.
3 In the Custom Faders section, press the Bank/Cycle switch
to cycle through the plug-ins on the Custom Faders display.
The plug-in whose name appears in the Focus Channel display is then available for Custom Fader Plug-In mode. (See
“Plug-In Mode” on page 97.)
To focus a plug-in in the Dynamics or EQ section:
1 Focus the plug-in’s track in the Focus Channel section by
pressing the track’s Select switch. The first dynamics and EQ
plug-ins on that track are automatically focused in the corresponding D-Command section.
2 Press the Cycle switch in the Dynamics or EQ section to fo-
cus successive dynamics or EQ plug-ins on that channel. (The
No Insert option is always available.)
To focus a plug-in in the Custom Faders section (temporary
plug-in assign mode):
1 Press the Inserts switch on the plug-in’s channel strip to en-
ter Inserts mode.
2 Press the encoder Select switch for the plug-in that you want
to control.
The plug-in is focused in the Custom Fader section. (See
“Plug-In Mode” on page 97.)
Automation Safe Mode
The Automation Safe switch invokes a mode in which the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch for each encoder and the channel Select
switch become Automation Safe switches. While in this mode,
pressing a Bypass/Mute/Pre switch on a plug-in or send protects any automation on that plug-in or send from being overwritten. Pressing a channel Select switch protects any automated parameters on that track from being overwritten.
In Automation Safe mode, the Automation Safe switch is lit.
While in this mode, the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch for any protected insert or send is lit, and the channel Select switch for
any protected channel is lit.
To toggle Automation Safe mode on and off:
1 Press the Automation Safe switch.
2 Press the channel Select switch on the tracks for which you
want to toggle automation safe status.
3 Press the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch for the plug-ins or sends
for which you want to toggle automation safe status.
4 Press the Automation Safe switch again to exit Automation
Safe mode.
Bypassing Plug-ins
When a plug-in name is displayed on an encoder (in the top
level Inserts display), the encoder’s Bypass/Mute/Pre (B/M/P)
switch bypasses the corresponding plug-in. The B/M/P switch
lights when the insert or plug-in is bypassed.
To bypass a plug-in:
1 Press the Inserts switch on the plug-in’s channel to display
the first two Insert names on the channel’s encoders.
2 To display and edit other insert positions, press the Page Up
or Page Down switches.
3 Press the B/M/P switch that corresponds to the plug-in you
want to bypass. The B/M/P switch lights when the plug-in is
bypassed.
Making Plug-ins Active/Inactive
When a plug-in name is displayed on an encoder (in the top
level Inserts display), it can be made inactive without entering
Make Inactive mode.
To toggle a plug-in active/inactive:
1 Press the Inserts switch on a channel strip to display the
names of the plug-ins on the channel’s encoders.
2 If the insert location for the plug-in that you want to make
active/inactive is not showing, press the Page Up or Page
Down switches on the channel where you want to make the
assignment until the appropriate location is displayed.
3 Hold Control+Start (Windows) or Control+ Command
(Mac) and press the encoder Select switch for the plug-in.
Muting Sends
You can mute sends directly from D-Command by setting the
appropriate mode for the Bypass/Mute/Pre switch.
To mute sends:
1 Press the Sends switch on the track to display Send names in
the channel encoders.
2 To display and edit other send positions, press the Page Up
or Page Down switches.
D-Command Guide92
Page 99

3 Press the Switch Mode switch to set the mode to Mute.
4 Press the B/M/P switch for the send you want to mute. The
red Mute LED lights to indicate that the send is muted.
2 Press and hold the channel Select switch on the channel
where you want to assign the insert or send. The channel
scribble strip shows a right arrow (“>– –”) to indicate the channel is in assign mode.
Setting Send Pre-/Post-Fader Operation
You can set sends to pre-fader or post-fader operation directly
from D-Command, by setting the appropriate mode for the
Bypass/Mute/Pre switch.
To toggle sends between pre-fader and post-fader operation:
1 Press the Sends switch on the track to display Send names in
the channel encoders.
2 Press the Switch Mode switch to set the mode to Pre.
3 Press the B/M/P switch for the send you want to toggle. The
green Pre LED lights to indicate that the send is set for
pre-fader operation.
Flip Mode
Channels in Normal mode can use Flip Mode, which transfers
controls from a row of encoders to the channel faders.
In Flip mode, the Flip switch lights, the rotary encoder control
swaps with the channel fader; the encoder Select switch swaps
with the channel Select switch; the encoder Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch swaps with the channel Mute switch; and the encoder
display swaps with the channel display.
To transfer controls from a row of rotary encoders to the channel
faders:
■ Press the Flip switch that corresponds to the encoder row
that you want to transfer.
To exit Flip mode:
■ Press a lighted Flip switch.
Assigning Inserts and Sends While in Flip
Mode
You can assign Inserts or Sends directly to an encoder even
when its controls are flipped to the channel fader.
When an encoder’s controls are flipped to the channel fader,
the channel Select switch replaces the encoder Select switch,
the channel Mute switch replaces the Bypass/Mute/Pre
switch, and the channel Fader replaces the encoder knob.
To assign an individual insert or send to a flipped encoder:
1 On the channel where you want to make the assignment,
press the Inserts or Sends switch to display the corresponding
elements on the channel. The controls for the flipped encoder
appear on the channel fader.
3 Move the channel fader to select from the first level of menu
choices.
4 Press the channel Select switch to move down and the chan-
nel Mute switch to move up through menu levels.
5 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing channel Select switch to confirm the
assignment.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the assignment.
To change a previously assigned insert or send on a flipped
encoder:
1 On the channel where you want to change the assignment,
press the Inserts or Sends switch to display the corresponding
elements on the channel.
2 Press and hold the channel Select switch for the flipped in-
sert or send you want to change, until the channel scribble
strip shows a right arrow (“>”) next to the assignment to indicate the channel is in assign mode.
3 Do one of the following to select a new insert or send:
• Move the channel fader to select from the current level of
menu choices.
– or –
• Press the channel Select switch to move down and the
channel Mute switch to move up through menu levels.
4 When the new insert or send is displayed in the channel
scribble strip, do one of the following:
• Press the flashing channel Select switch to confirm the
assignment.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the assignment.
To remove an individual insert or send on a flipped encoder:
1 On the channel where you want to remove the assignment,
press the Inserts or Sends switch to display the corresponding
elements on the channel.
2 Press and hold the channel Select switch for the flipped in-
sert or send you want to remove, until the channel scribble
strip shows a right arrow (“>”) next to the assignment to indicate the channel is in assign mode.
3 Press the encoder Bypass/Mute/Pre switch repeatedly until
you reach the top level menu for the assignment.
4 Move the channel fader until no assignment is visible.
Chapter 11: Operating Modes 93
Page 100

5 Do one of the following:
• Press the flashing channel Select switch to confirm the
removal.
– or –
• Press the flashing Escape switch to cancel the removal
and restore the assignment.
Custom Fader Modes
With the Custom Faders feature, you can temporarily set aside
channel strips on D-Command and focus them on your own
customized groups of tracks, on Pro Tools Mix and Edit
groups, on specific track types, or on plug-in controls. Custom
Fader modes are only accessible on D-Command, and are not
displayed on-screen in Pro Tools.
On D-Command, Custom Fader channels are completely separate from the surrounding channels on the control surface.
All tracks in the session bank around the Custom Fader channels, and continue to behave normally in Pro Tools and on
D-Command.
When channels are in use by any of the Custom Fader modes,
the blue indicator marked “CF,” located to the left of the
channel fader, is lit.
The status of Custom Fader modes is saved with the Pro Tools
session. If you save and close a session with a Custom Fader
mode active, the session will reopen with the same mode active.
The three Custom Fader modes are covered in detail later in
this section:
Setting the Number of Custom Fader Channels
You can set the Custom Fader bank size, the maximum number of D-Command channels used by the Custom Fader
modes. The bank size can be set to 4 and 8 faders for a Main
Unit, and 4, 8, 16 and 24 faders for an expanded system.
To set the Custom Fader bank size:
1 Press the Operation switch in the Console Prefs Soft Keys
section.
2 Do one of the following:
• To increase the maximum number of faders used by the
Custom Fader modes, press the Soft Key that corresponds
to “Max CF.”
– or –
• To decrease the maximum number of faders used by the
Custom Fader modes, hold Shift and press the Soft Key
that corresponds to “Max CF.”
3 Press the Operation switch again to exit.
Custom Fader Controls
The Groups switch, Tracks switch, and Plug-In switch in the
Custom Faders section light when the corresponding Custom
Fader mode is active.
The Map switch works in combination with the Custom Fader
modes, and has no independent effect.
The Lock switch and Window switch function both in the
Custom Fader modes and independently. See “Lock Switch”
on page 40.
Groups Mode Lets you access Custom Groups or Mix/Edit
Groups functions.
The Custom Group functions let you create and recall up to
eight custom arrangements of tracks on D-Command that are
independent of the Mix or Edit groups in Pro Tools.
The Mix/Edit Group functions let you recall Pro Tools Mix or
Mix/Edit groups and display them on the Custom Fader channel strips. You can also activate and delete Mix or Mix/Edit
groups.
Tracks Mode Lets you bring all tracks of a particular type to
the Custom Fader channel strips. Track Types include Audio
tracks, Auxiliary Input tracks, MIDI tracks, Instrument tracks,
and Master Fader tracks.
Plug-In Mode Lets you focus the controls of a plug-in on the
Custom Fader channel strips, and any plug-in meters on the
channel strip’s meters.
A special expanded Plug-In mode focuses the plug-in header
controls (such as Bypass, Compare and Safe) on the channel
strip Mute switches.
D-Command Guide94
Focus Channel
display
Groups switch
Tracks switch
Plug-In switch
Custom Fader controls
Focus Channel
&
Custom Faders
Tracks
Bank / Cycle
Map switch
MapGroups
Lock switch
Lock
Window switch
WindowPlug-In
Bank/Cycle switch
 Loading...
Loading...