Page 1

SOFTWARE SUITE
Preliminary User’s Manual
Page 2

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
2
Contents
Introduction
Overview
Bluetooth Neighborhood
Bluetooth Configuration Tool
Bluetooth Network Manager
Bluetooth Control Center
Main window
Profiles and services
List view
Basic functions
Device discovery
Service discovery
Link establishment
Disconnecting
Status information
Device groups
Windows Explorer
Online Help
Managing COM ports
Establishing COM port links
Object transfer
Making your business card available
Business card transfer
Sending objects directly from MS Outlook
File transfer
Sending files
Receiving files
Audio links
Networking
Settings
Bluetooth Radio settings
Profile properties
Local device properties
Properties (Bluetooth Neighborhood options)
Remote device properties
Appendices
Profiles
Regulatory statements
Page 3

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
3
Introduction
With the Bluetooth Software Suite, you can
establish wireless links between your computer
and other Bluetooth enabled devices. Without
using any cables, you can transfer sound, objects
and files; connect to serial devices like a mouse,
modem, printer etc.; and network.
This user’s manual is a comprehensive guide to
the Bluetooth™ Software Suite version 1.0. It
contains all the descriptions and instructions you
need to be able to make the most of the program.
We will start by providing an overview of the
applications of the Bluetooth Software Suite. We
will then look closer into the Bluetooth
Neighborhood main window, which is where most
of the action takes place. Next, we will account for
the basic principles of operating the Bluetooth
Neighborhood. We will then turn to each of the
services (applications) currently facilitated by your
Bluetooth Software Suite. Finally, we will deal with
the various settings of the program.
In addition to this user’s manual, the
documentation for the Bluetooth Software Suite
comprises a Beginner’s Guide providing a general
introduction to the Bluetooth technology. Both the
User’s Manual and the Beginner’s Guide are
included on the CD-ROM for the Bluetooth
Software Suite. Furthermore, when you have
installed the Bluetooth Software Suite, the two
documents are available from the Windows Start
menu. Finally, the Bluetooth Software Suite is
accompanied by a printed installation guide.
The Bluetooth Software Suite and Microsoft
Windows are highly integrated. However, it is
beyond the scope of this manual to explain the
basics of using Windows. If you need
information on that topic, please refer to the
Windows user’s manual or online help.
Disclaimer
Any responsibility or liability for loss or damage in
connection with the use of this product and the
accompanying documentation is disclaimed. The
information in this document is furnished for
informational use only, is subject to change
without notice, may contain errors or inaccuracies,
and represents no commitment whatsoever. This
agreement is governed by the laws of Denmark.
Document issue: Draft TR 00-04-19
Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its proprietor and used by
this manufacturer under license.
Page 4

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
4
Overview
In this section, we will introduce the four
applications making up the Bluetooth Software
Suit: The Bluetooth Neighborhood, Configuration
Utility, Network Manager, and Control Center.
Bluetooth Neighborhood
The Bluetooth Neighborhood is where most
operations of the Bluetooth Software Suite are
carried out. From this application you can:
• Carry out device discovery, i.e. find out which
remote Bluetooth devices are active within
your range;
• Carry out service discovery, i.e. find out
which services (applications) a remote device
facilitates;
• Establish links to remote devices.
The Bluetooth Neighborhood is the main
application of the Bluetooth Software Suite, and
there is, of course, much more to be said about it.
Indeed, most of the descriptions and instructions
given in this manual concern the Bluetooth
Neighborhood.
Bluetooth Configuration Tool
The Bluetooth Configuration Tool is used for
managing virtual communications (COM) ports,
e.g. when you want to establish links to serial
devices like printers or modems. Furthermore, the
Bluetooth Configuration Tool allows you to test if
the system has been set up and works properly.
Bluetooth Network Manager
The Bluetooth Network Manager eliminates the
need to make new network settings every time
you want to switch between a Windows NT
domain and an ad-hoc Bluetooth network. With
the Bluetooth Network Manager, you can make
the settings once and for all and then, when you
want to change from one network to another,
simply select the desired profile from a list.
Page 5

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
5
Bluetooth Control Center
The Bluetooth Control Center is a small tray icon
application located in the lower right corner of the
screen. The Bluetooth Control Center shows the
state of the Bluetooth radio, and allows you to
enable/ disable the Bluetooth radio manually.
Also, the Bluetooth Control Center is where you
open the Bluetooth Network Manager.
Page 6
Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
6
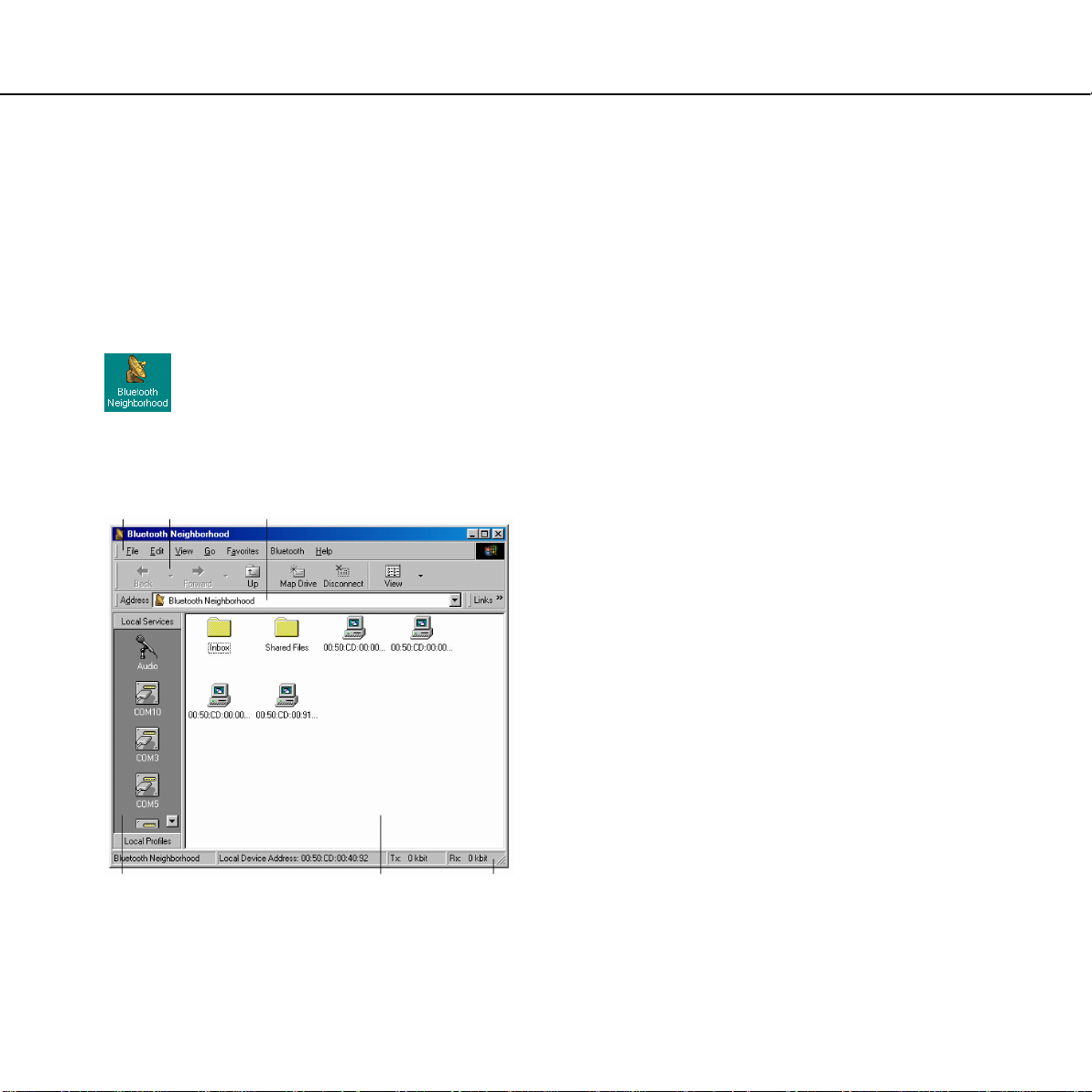
Main window
When you have installed the Bluetooth Software
Suite on your computer, the Bluetooth
Neighborhood icon will appear on your desktop.
To open the Bluetooth Neighborhood, click the
icon:
You will now see the Bluetooth Neighborhood
main window:
j k l
The six elements making up the Bluetooth
Neighborhood main window are:
j Menu bar
k Tool bar
l Address bar
m Local Profiles/Local Services bar
n List view
o Status bar
Some of these elements are standard Windows
items. In this manual we will mainly focus on the
elements that are specifically related to operating
the Bluetooth Software Suite. Accordingly, we will
start out by looking into two elements that play a
key role in operating the Bluetooth Neighborhood:
The Local Profiles/Local Services bar and the list
view. In later sections, we will account for the
items of the Bluetooth pull-down menu on the
menu bar.
m n o
Page 7
Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
7
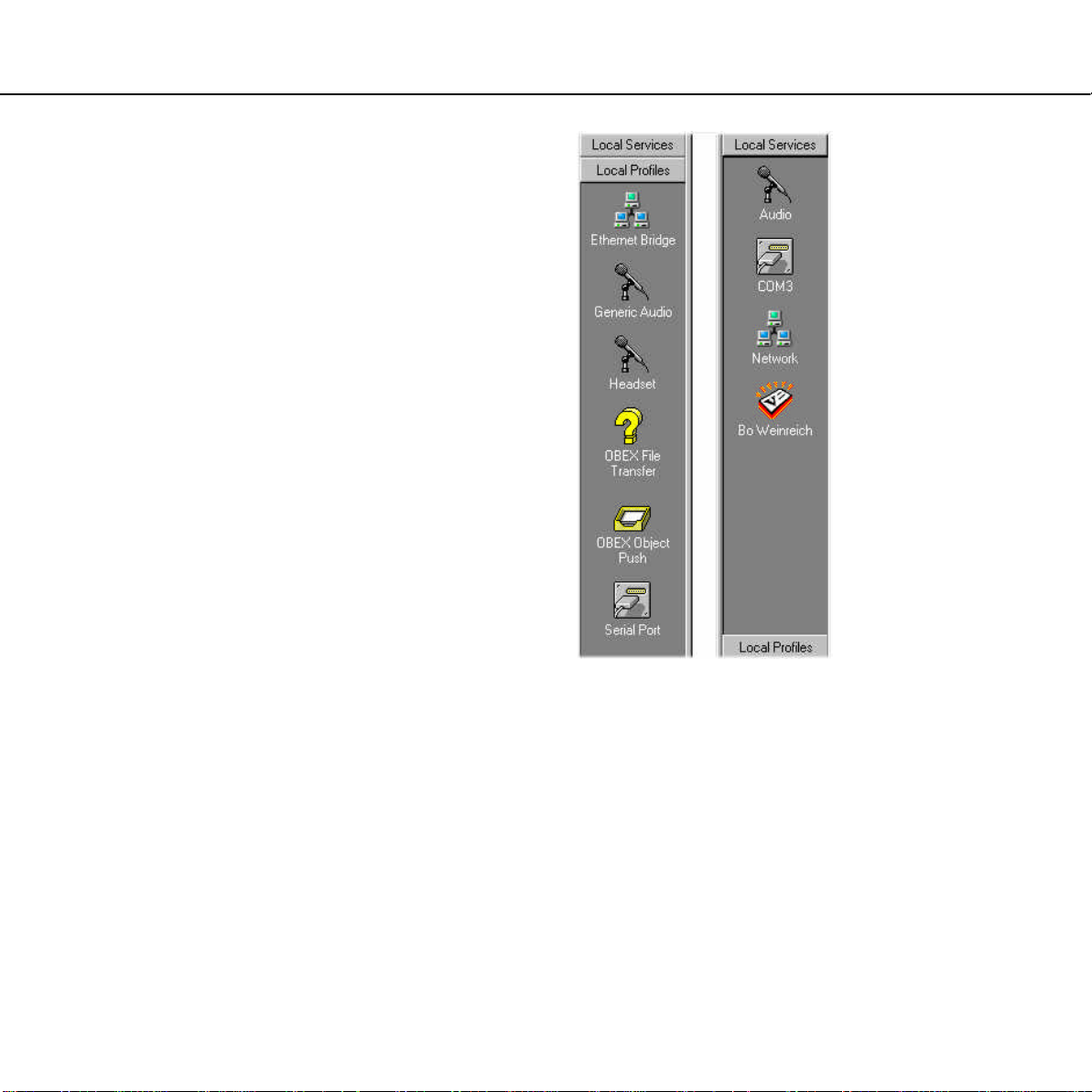
Profiles and services
The local profiles are the applications that you can
use your device for. When two devices are to
interoperate, i.e. communicate with each other,
they must have a shared profile. If, for instance,
you want to transfer a file from one computer to
another, both computers must support the profile
OBEX File Transfer.
While the function of the Local Profiles bar is to
display the profiles your device supports, Local
Services bar is what you will actually be using
when operating the Bluetooth Neighborhood.
Facilitated by a profile, each of the services
represents a specific operation that your device
can carry out. An example of a service is business
card transfer, which is facilitated by the profile
OBEX Object Push. Business card transfer can
take place between your computer and other
Bluetooth devices supporting OBEX Object Push.
In later sections, we will show you how to make
use of each of the services that your device
features.
For the Local Profiles tab, click Local Profiles.
For the Local Services tab, click Local Services.
In addition to the items shown on the Local
Profiles bar, the Bluetooth Software Suite
supports a number of other profiles. For a
complete list of the supported profiles, including
which services each profile facilitates, please see
the appendix “Profiles”.
Page 8
Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
8
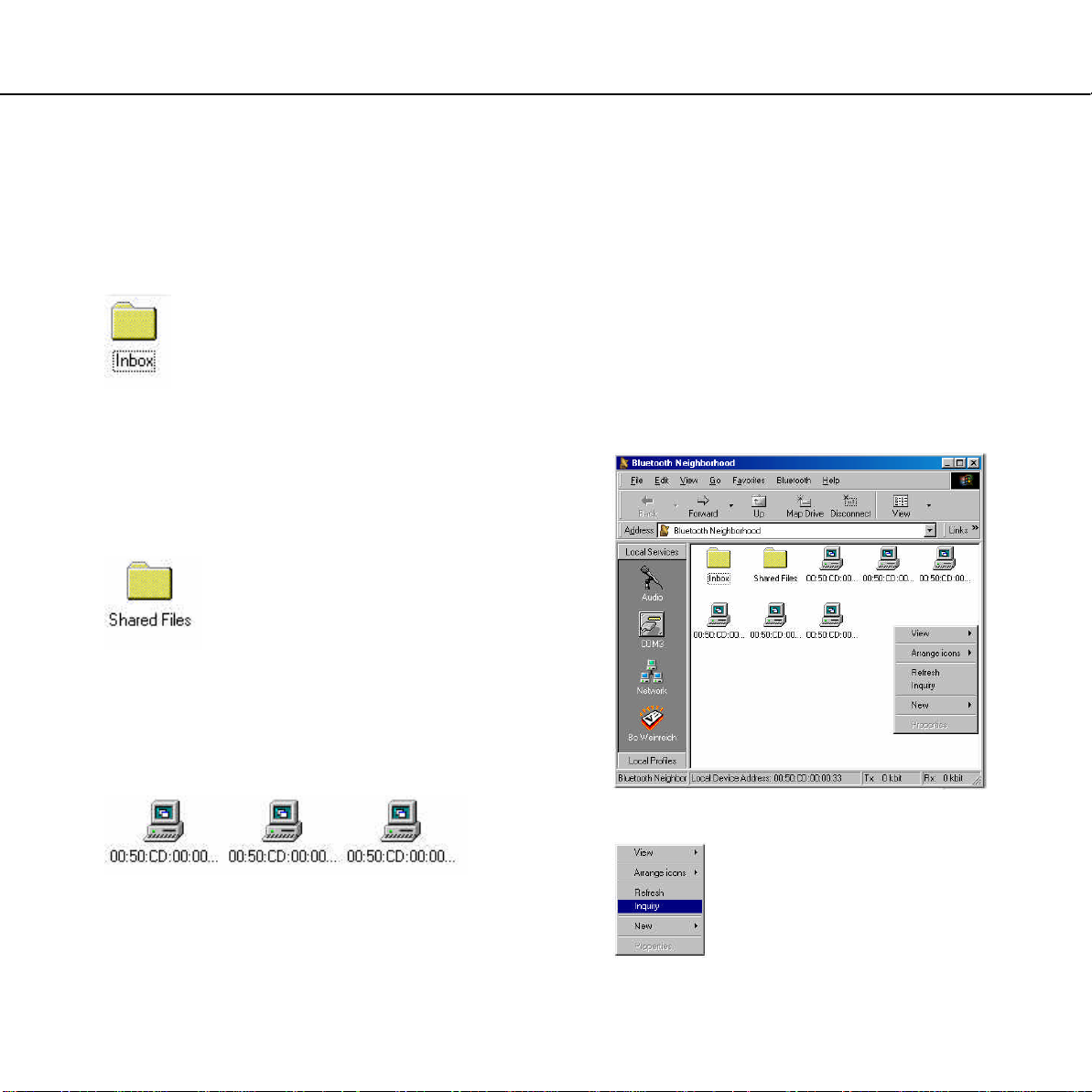
List view
The list view in the main window contains three
elements: the Inbox, the Shared Files folder, and
a list of the discovered devices:
Inbox:
This is where your device receives Microsoft
Outlook objects like electronic business cards, email messages etc. sent from other devices. You
can edit the Inbox in all the ways you are used to
from Windows, i.e. you can copy, rename, drag
and drop etc.
Shared Files:
Basic functions
Device discovery
Before your device can communicate with a
remote Bluetooth device, it needs to discover the
remote devices that are active within range. This
operation is called device discovery.
1. Right-click an empty part of the window:
This folder contains the computer files that your
device receives from other devices. Like the
Inbox, you can manipulate the Shared Files folder
in all the ways you are used to from Windows.
Discovered devices:
These are the remote Bluetooth devices that are
active within range, and that your device has
discovered during device discovery (see next
section).
2. Click Inquiry:
Page 9
Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
9
The window now shows an updated list of active
remote devices within range.
Alternatively, you can carry out device discovery
from the Bluetooth pull-down menu on the menu
bar by selecting the item Device Discovery.
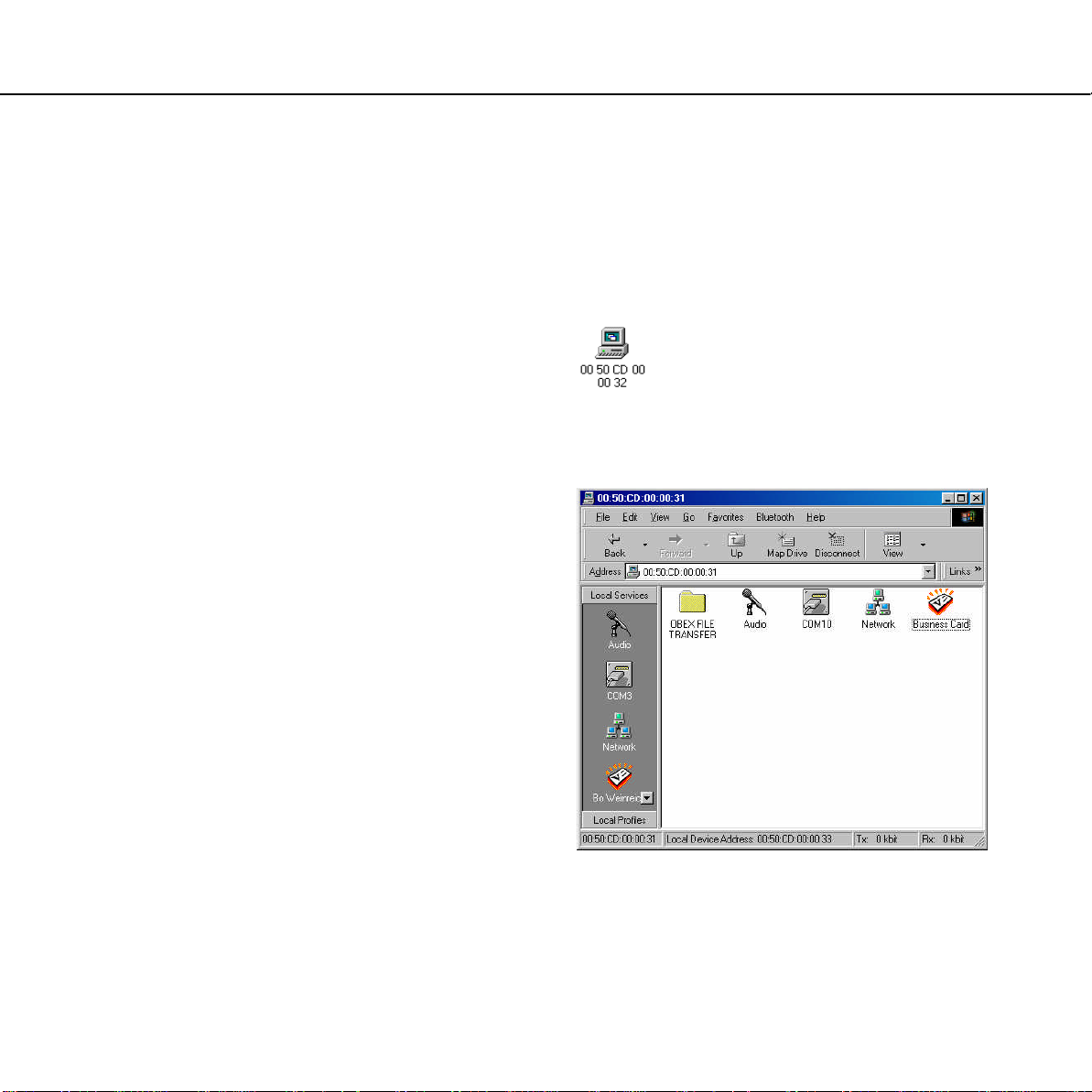
Service discovery
Before trying to establish a link to a remote
device, it may be useful to know which services
the device facilitates. To find out, you can carry
out service discovery.
Double-click the remote device:
Instead of your local Inbox, Shared Files folder,
and discovered devices, you will now see a list of
the services that the remote device supports:
(To return to the Bluetooth main window, click
^ Back.)
Page 10
Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
10
Link establishment
When you have carried out service discovery, you
can establish a link to the remote device. You can
make use of any service that both your device and
the remote device support: Drag the local
service to the corresponding remote service:
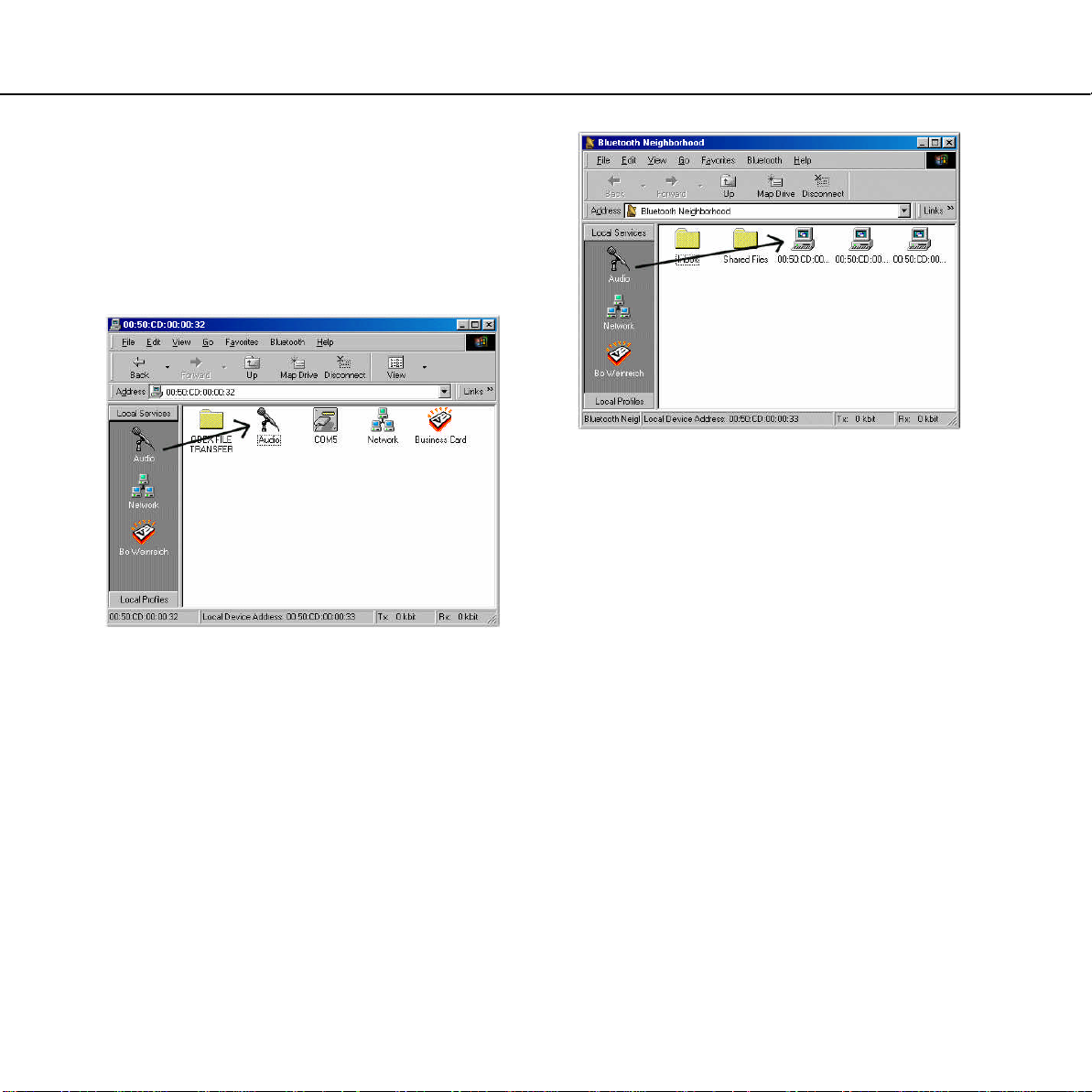
In the above example, an audio link is being
established by dragging the local Audio service to
the remote Audio service.
If the link is established successfully, the icons for
both the local and the remote Audio services will
flash.
If you know in advance that a remote device
supports a particular service, you can skip service
discovery. Just drag the local service to the
remote device:
In this example, an audio link is being established
by dragging the local Audio service to the remote
device.
If the link is established successfully, the icons for
both the local service and the remote device will
flash.
Page 11

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
11
Disconnecting
To interrupt a link established to a remote device:
1. Right-click the remote service or remote
device (which is flashing because a link has
been established).
2. Click Disconnect:
The link will now be interrupted.
Status information
When you attempt to carry out a specific operation
in the Bluetooth Neighborhood, the program will
always let you know whether or not the operation
is carried out successfully. In addition to flashing
icons indicating that a link has been established,
the status bar and messages boxes keep you
informed of the progress of any operation.
Device groups
A device group is a folder containing a number of
remote devices. You can communicate with the
device group as with any single remote device.
This feature makes it possible to distribute objects
and files to more than one device at a time,
establish multiple audio links to be used for
conferencing, etc. To create a user group:
1. Open the Bluetooth Neighborhood main
window.
2. Right-click the first device to be included
in the group.
3. Click Add to New Device Group:
The device has now been copied into a new
folder:
Page 12

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
12
The default name of the folder is New Group.
However, you can rename and edit the folder
in all the ways you are used to from
Windows.
4. Finally, drag each of the other devices to
be included in the group into the folder:
Windows Explorer
While using the Bluetooth Neighborhood, you may
find it convenient to open Windows Explorer. One
of the ways of doing that is from the Bluetooth
Neighborhood main window:
1. Right-click the Inbox or the Shared Files
folder:
2. Click Explore:
You will now see a new active window, containing
both Windows Explorer and the Bluetooth
Neighborhood:
Page 13

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
13
In this new window, you can operate the Bluetooth
Neighborhood as usual; Windows Explorer will
stay open until you close the window again.
Furthermore, you can access Windows Explorer
from the Address bar:
Finally, you can of course open Windows Explorer
first, and then open the Bluetooth Neighborhood
by selecting it among the folders in Windows.
Online Help
The last of the topics we will deal with in this
section of the user’s manual is how to get online
help from Bluetooth Neighborhood. On the menu
bar at the top of the main window, click Help:
Page 14

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
14
Managing COM ports
Virtual communications (COM) ports are used
when you need to transfer serial data between
your computer and another Bluetooth enabled
device like a headset, modem, mouse etc.
For serial data, you need no physical port at the
back of the computer; however, you do need a
virtual one. The virtual COM port functions as an
address, so to speak, needed by your computer to
establish a link to a serial device.
Or carry out service discovery, then drag the
local COM port icon to a remote COM port
icon:
Establishing virtual COM port
links
When you have added a virtual COM port to the
Local Services bar, you can establish a link. Drag
the COM port icon to the remote device:
When the link has been established, you can
make use of the serial device to which you have
connected – whether a headset, modem, mouse
or the like.
Page 15

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
15
Transferring objects
With the Bluetooth Neighborhood, you can
transfer such objects related to Microsoft Outlook
as business cards, e-mails, and notes.
In this section, we will first show you how to store
your business card in the Bluetooth Neighborhood
for easy distribution to others. Also, we will look
into a number of different ways to transfer objects.
3. Drag the item containing your own contact
information into the Local Services bar:
Making your business card
available
1. Open both the Bluetooth Neighborhood
and Microsoft Outlook.
2. Arrange the Bluetooth Neighborhood and
Microsoft Outlook windows so that both
are visible on the screen:
A new icon among the local services shows that
your business card is now available in the
Bluetooth Neighborhood:
Page 16

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
16
Business cards transfer
To send your business card to a remote device,
drag the card icon to the remote device:
For the choice of sending, receiving, or
exchanging business cards with another user,
right-click the remote device:
You can now choose:
• To transfer your business card (included on
the Local Services bar) to the remote device:
Click Push business card.
• To transfer the remote user’s business
card to your device: Click Pull business
card.
• To exchange business cards with the
remote user: Click Exchange business
cards.
Page 17

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
17
Sending objects directly from
Microsoft Outlook
To send an object directly from Microsoft Outlook,
drag the object to the remote device:
File transfer
Sending files
There are two ways of transferring a file from one
Bluetooth device to another. One is to drag the
file from where it is stored to the remote
device:
In the example above, an e-mail message is being
transferred from the Microsoft Outlook inbox to the
remote device.
In the above example, a file is being dragged from
My Documents to the remote device.
Page 18

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
18
Alternatively, first carry out service discovery on
the remote device. Then drag the file from
where it is stored into the remote service
OBEX FILE TRANSFER:
Receiving files
As already mentioned, when your Bluetooth
device receives a file sent from another device,
the file is placed in the Shared Files folder:
You can open a received file directly from the
Shared Files folder, or you can drag the file to
wherever you want to store it. In the following
example, a file is being dragged from the Shared
Files folder to My Documents:
Page 19

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
19
Audio links
An audio link makes it possible to transfer sound
from one Bluetooth device to another. With this
feature, you can e.g. connect your laptop to a
Bluetooth enabled modem and make telephone
calls, using the built-in microphone and speaker of
the laptop for the conversation. Or, with a headset
connected to your computer, you can establish an
audio link to one or more other computers, and
then use the computers as walkie-talkies. Other
examples of making use of audio links are for
NetMeeting Internet conferences, or for dictation
software based on voice recognition.
There are two ways of establishing an audio link:
Either drag the local service Audio to a remote
device:
Or carry out service discovery first, then drag the
local service Audio to the remote service
Audio:
When the link establishment has been carried out
successfully, you can put on your headset and
communicate, or make use of the audio link
otherwise.
Page 20

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
20
Networking
In this section, we will focus on setting up and
establishing Bluetooth networks. We will assume
that you have some previous experience with
ordinary, i.e. wired networks. If that is not the
case, please refer to the Microsoft Windows
user’s manual and online Help for basic
information on the topic.
Important information for
Windows 95 users
If your computer is set up with another Ethernet
adapter, e.g. a regular PCI network adapter, you
must enable this additional adapter before you
enable the Bluetooth based network.
To determine which adapters are
present in your computer
1. Open the Windows Control Panel.
2. Double-click System.
3. Click Device Manager.
4. Double-click Network adapters.
In the following example, the screen shows a
system with a 3Com Fast EtherLink network
adapter:
Before making use of TCP/IP across a Bluetooth
link, you must disable the 3Com network adapter.
To disable adapter
First of all, follow the instructions given above to
determine which adapters are present in your
computer. Then go through the following steps:
1. Click the adapter to be disabled.
2. Click the Properties button. You will now see
the 3Com Fast EtherLink XL 10/100Mb …
Properties dialog box:
Page 21

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
21
Setting up networks
The Network Manager deals with a problem in the
Windows operating system which afflicts users
who use their computer in more than one network.
Imagine e.g. that you want to use a regular
network adapter to connect to a wired local area
network (LAN) and your Bluetooth device to
connect to other computers in a wireless ad hoc
network. Every time you want to change between
the two setups, you would have to change IP
addresses, netmasks, gateways, host name, etc.
You can do all that from the Microsoft Network
Control Panel, but it is a manual, time consuming,
and error prone process.
The Bluetooth Network Manager solves this
3. In the section Device usage, check the
Disable in this hardware profile checkbox.
4. Click OK. You will return to the System
Properties dialog box.
5. Quit all programs, and restart the
computer.
problem; you can create network profiles that
memorize your networking setups and allow you
to restore them whenever you need to change
from one network to another. In other words, with
the Network Manager, switching between two
setups is reduced to choosing a network profile
from a menu.
Enabling or disabling the Bluetooth Network
Manager takes place from the Bluetooth Control
Center.
Page 22

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
22
Network link establishment
Establishing a network link is done in the same
way as you establish other Bluetooth links: In the
Bluetooth Neighborhood main window, drag the
local service Network to the remote device or
service:
You can now use the Bluetooth network in the
same way as if it were an ordinary local area
network.
Settings
In this part of the User’s Manual, we will focus on
the various settings of the Bluetooth Software
Suite. You will find information on the settings of
the Bluetooth radio, profile properties, local device
properties, properties (Bluetooth Neighborhood
options), and remote device properties.
Bluetooth radio settings
The settings of the Bluetooth radio are controlled
from the Bluetooth Control Center. From this
application, you can enable/disable the Bluetooth
radio. Furthermore, the Bluetooth Control Center
icon indicates the state of the Bluetooth radio
state.
Enabling/disabling the Bluetooth radio
From the Bluetooth Control Center, you can
enable or disable the Bluetooth radio:
1. Right-click the Bluetooth Control Center
icon.
2. Click Enable ... or Disable ...:
Indication of the Bluetooth radio state
Page 23

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
23
The Bluetooth Control Center displays one of
three icons to show the state of the Bluetooth
radio:
• Disabled:
In this state, your Bluetooth device cannot
communicate with, and is not discoverable by,
other devices.
• Enabled but not transmitting:
Profile properties
From the Bluetooth pull-down menu, accessible
from the menu bar, you can set the properties of
two of the local profiles: OBEX Object Push and
OBEX File Transfer.
Your device is ready to communicate with, and
is discoverable by, other devices.
• Enabled and transmitting:
Your device is communicating with one or
more remote devices. It is discoverable by
other devices.
Local device properties
From the Bluetooth menu, you can also set the
properties of your Bluetooth device.
There are three Local Device Properties dialogue
boxes: General, Modes, and Local Device Folder.
We will now take a look at each.
Page 24

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
24
General
This dialog box concerns the identity information
of your device: The Bluetooth device name, and
the Bluetooth device address, device class, and
service class (which will all be explained in the
following.) Furthermore, the dialog box shows a
list of the remote devices that your device is
currently connected to, if any.
• Bluetooth device address, device class,
and service class: Unique factory-set
identity information sent to devices carrying
out device or service discovery on your
device. The information is transferred
automatically, and it will not appear on the
remote user’s screen.
Modes
The Local Device Properties item Modes
concerns various aspects of link establishment.
Here you can set such parameters as the
connectability, discoverability, pairing, and
security of your device:
• Bluetooth device name: Here you can insert
the name that you want your device to
present itself with when discovered by
another device.
Page 25

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
25
•• Connectability refers to whether or not other
devices having discovered your device will be
allowed to establish a link to it.
• Discoverability refers to whether or not other
devices will be allowed to discover your
device.
• Pairing refers to the creation of a link key – a
bond – between two devices. When the bond
has been created, future communication
between the two devices can take place
without any other devices being able to listen
in or interfere. You can decide whether or not
your device should be able to bond to other
devices.
• Security makes it possible to allow only
selected devices to communicate with your
device.
– No security means that no passkey will
be required from a device wanting to
communicate with your device.
– Service level security will require a
remote user to enter a password before
he can connect to a specific service of
yours. Consequently, you can protect
selected services by a passkey, while
other services require no passkey.
– Link level security will require a remote
user to enter a password before he is
allowed to establish a link (regardless of
which service he wants to connect to).
Page 26

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
26
Properties (Bluetooth
Neighborhood options)
For a number of options related to the Bluetooth
Neighborhood, select the Bluetooth menu item
Properties:
The dialog box Bluetooth Neighborhood Options
will appear. Here you can choose among General,
View, Device Discovery, and Link Policy.
General
View
The View dialog box contains two items related to
what is displayed on your screen in connection
with device discovery:
• Device Discovery: Here you can choose to
view the devices found during the last device
discovery that your device has carried out.
• Previously Discovered Devices: Here you
can choose to view devices that your device
has discovered previously: All devices ever
discovered, or devices discovered during a
specific period of time which you can set in
the dialog box.
Page 27

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
27
Device Discovery
This item contains four options related to device
discovery:
• Device Discovery: Here you can choose for
device discovery to take place only when you
activate the function manually (e.g. by
pressing F5), or automatically at specified
intervals.
• Expire Discovered Devices: Here you can
decide to have discovered devices removed
automatically from the main window after a
specified period of time.
• Device Discovery Length: Here you can set
the number of seconds that you want device
discovery to last.
• Device Discovery Period: This is where you
set the interval between device discoveries
when ”Automatic” has been selected above in
”Device Discovery”.
Page 28

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
28
Link Policy
The Link Policy settings concern the way your
device reacts when another device tries to
establish a link to it. Here you can decide whether
or not your device should reject link establishment
attempts, prompt you before accepting link
establishment or accept link establishment
automatically.
Remote device properties
To view the properties of a remote device, rightclick the device, and click Properties:
You will now see a dialog box displaying the
Bluetooth device name and other identity
information of the remote device:
Page 29

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
29
As appears, the dialog box also shows you when
you last saw, i.e. discovered, the remote device;
and when your device was last linked to the
remote device.
Finally, you can set link policy parameters for the
remote device, i.e. you can decide how your
device should react if the remote device attempts
to establish a link: Should you device reject link
establishment, prompt you before accepting link
establishment, or automatically accept link
establishment?
Page 30

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
30
Profiles
The following table shows a list of the profiles supported by the Bluetooth Software Suite
and the service/operation that each profile facilitates:
The profile:
Ethernet Bridge Ad-hoc networking
Generic Audio Audio
Headset Ultimate headset
OBEX File Transfer File transfer
OBEX Object Push Object transfer
Serial Port Managing virtual COM ports for serial device connection
Generic Access
Service Discovery Application Service discovery
Dial-up Networking (as data terminal)
FAX (as data terminal) Sending/receiving fax messages (using the fax software on your
LAN Access (as data terminal)
Generic Object Exchange Facilitates the other profiles File Transfer, Object Push, and
Synchronization Synchronization between two Bluetooth devices, e.g. of electronic
Supports the following service/operation:
computer).
Synchronization
calendar
Page 31

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
31
Regulatory statements
General
This product complies with any mandatory
product specification in any country where the
product is sold. In addition, the product
complies with the following.
European Union (EU) and EFTA
This equipment complies with the R&TTE
directive and has been provided with the CE mark
accordingly.
Note that the radio frequency band used by this
equipment has not been harmonized in all of the
EU.
United States of America and
Canada
Tested To Comply With FCC Standards FOR
HOME OR OFFICE USE. See FCC 47CFR part
15.19(b)(2).
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules
and with RSS-210 / RSS-139 of the Industry
Canada. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
Note that any changes or modifications to this
equipment not expressly approved by the
manufacturer may void the FCC authorization to
operate this equipment.
Page 32

Bluetooth Software Suite User’s Manual
32
Japan
Digianswer Japan office:
Address: BIA Inc.
No. 202 Gobancho House
4-22 Gobancho
Chiyoda-Ku, Tokyo 102-0076
Phone: 03 5276 5984
Fax: 03 5276 0625
E-mail: baisib@gol.com
Page 33

DK-9240 Nibe
Phone: +45 9671 0000
Fax: +45 9835 0052
E-mail: sales@digianswer.com
Web sites: www.digianswer.com / www.bluetooth.net
Skalhuse 5
 Loading...
Loading...