Page 1

Product Preview
MC13192/D
Rev. 2.4, 06/2004
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.4 GHz, Low Power
Transceiver for 802.15.4
nc...
, I
or
Contents
1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2 Block Diagrams . . . . . . . 3
3 Data Transfer Modes . . 3
4Electrical
emiconduct
Characteristics . . . . . . . 5
5Functional
Description . . . . . . . . . . 8
6 Contact
Connections . . . . . . . . 11
7 Applications
Information . . . . . . . . . . 15
8 Packaging
Information . . . . . . . . . . 18
eescale S
MC13192
(Scale 1:1)
Package Information
Plastic Package
Case 1311-03
(QFN-32)
Ordering Information
Device Device Marking Package
MC13192 13192 QFN-32
The MC13192 is a short range, low power, 2.4 GHz ISM band transceiver which contains a
complete 802.15.4 physical layer (PHY) modem designed for the IEEE 802.15.4 wireless
standard supporting star and mesh networking.
When combined with an appropriate microcontroller (MCU), the MC13192 provides a cost
effective solution for short-range data links and networks. In terface with t he MCU is
accomplished utilizing a four wire serial peripheral interface (SPI) connection which allows
for the use of a variety of processors. The software and processor can be scaled to fit
applications ranging from simple point-to-point systems, through complete ZigBee™
networking.
For more detailed information on MC13192 operation, refer to the MC13192 Reference
Manual, part number MC13192RM/D.
Applications include, but are not limited to, the following:
Fr
This document contains information on a product under development.
Motorola reserves the right to change or discontinue this product without notice. © Motorola,Inc.,2004.All rights
• Remote control and wire replacement in industrial systems such as wireless sensor
networks
• Factory automation and motor cont rol
• Heating and cooling
• Inventory management and RF ID tagging
Potential consumer applications include:
• Home automation and control
• Human interface devices
• Remote entertainment control
Page 2

Features
• Wireless toys
The transceiver includes a low noise amplifier, 1.0 mW PA, VCO, full spread-spectrum encoding and
decoding. The device supports 250 kbps O-QPSK data in 5.0 MHz channels, per the IEEE 802.15.4
specification. A Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is used for RX and TX data transfer and control.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
1 Features
• Recommended power supply range: 2.0 to 3.4 V
• 16 Channels
• 0 dBm (Typical), up to 3.6 dBm maximum output power
• Buffered Transmit and Receive D ata Packets for Simplified Use with Low Cost Microcontrollers
• Supports 250 kbps O-QPSK Data in 5.0 MHz Channels and Full Spread-Spectrum Encode and
Decode (Compatible with IEEE Standard 802.15.4)
• Three Power Down Modes for Power Conservation:
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
— < 1 µA Off Current
— 3.0 µ A Typical Hibernate Current
— 40 µA Typical Doze Current
• RX sensitivity of -92 dBm (Typical) at 1.0% Packet Error Rate
• Four internal timer comparators are available to reduce MCU resource requirements
• Clock output is available for use by MCU
• Seven General Purpose Input/Output ports (GPIO) are available
• Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to 85°C
• Small form factor QFN-3 2 Package
— Meets Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) 3
— 260°C Peak Reflow temperature
— Meets lead-free requir ements
2 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 3

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Block Diagrams
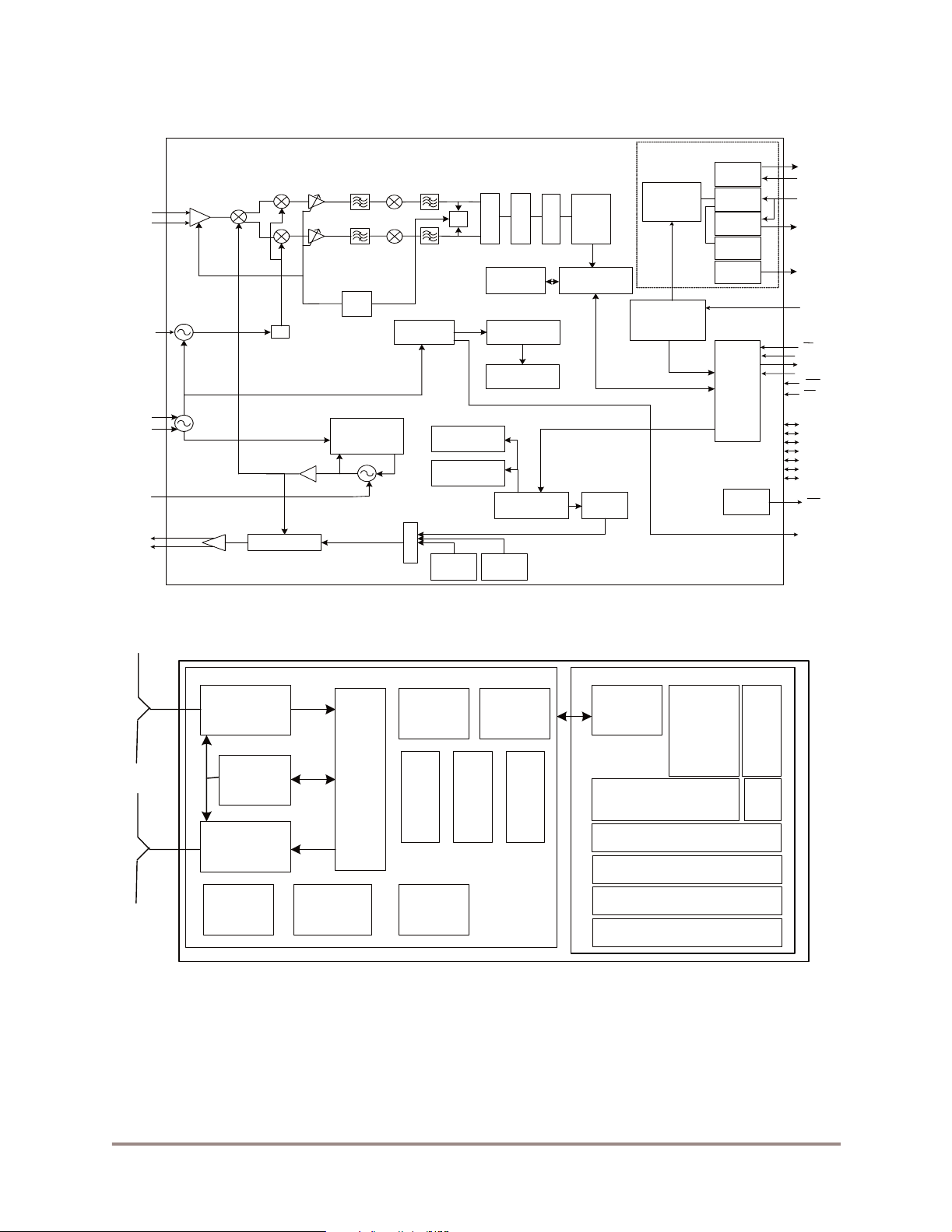
2 Block Diagrams
Figure 1 shows a simplified block diagram of the MC13192. The MC13192 is an IEEE 802.15.4
transceiver that provides most of the functions required in the Physical Layer (PHY) specification.
Figure 2 shows the basic sy stem bl ock dia gram for the MC1319 2 in an appl icat ion. I nterf ace wit h the I C is
accomplished through a 4-wire Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI). The Medium Access Control (MAC),
drivers, and Network and Application software as required reside on the host processor. The host can be
anything from a simple 8-bit device up to a sophisticated 32-bit processor depending on application
requirements.
3 Data Transfer Modes
The MC13192 has two data transfer modes:
1. Packet Mode — Data is buffered in on-chip RAM
2. Streaming Mode — Data is processed word by word
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
When using the Motorola 802.15.4 MAC, only the streaming mode can be used. For proprietary
applications, packet mode is used to conserve MCU resources.
3.1 Packet Structure
Figure 3 shows the packet structure of the MC13192. Payloads of up to 125 bytes are supported. The
MC13192 adds a four byte preamble, a one byte start of frame delimiter (SFD), and a one byte frame
length indicator before the data. A Frame Check Sequence (FCS) is calculated and appended to the end of
the data.
3.2 Receive Path Description
In the receive signal path, the RF input is converted to low IF In-phase and Quadrature (I & Q) signals
through two down conversion stages. A Clear Channel Assessment (CCA) can be performed based on the
baseband energy integrated over a specific time interval. The digital back end performs Differential Chip
Detection (DCD), the correlator “de spreads” the Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) Offset QPSK
(O-QPSK) signal, determines the symbols and packets, and detects the data.
The preamble, SFD, and frame length are parsed and used. A two-byte FCS is calculated and compar ed to
the FCS value appended to the transmitted data, generating a Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC) result.
Link Quality is measured over a 64 µs period after the packet preamble and stored in ROM.
If the MC13192 is in packet mode, the data is processed as an entire packet. The MCU is notified that an
entire packet has been received via an interrupt.
If the MC13192 is in streaming mode, the MCU is notified by an interrupt on a word by word basis.
3.3 Transmit Path Description
The transmit path is t he exact r everse of the recei ve path. The data stor ed in RAM is ret rieved or clocked i n
via the SPI, formed into packets per the 802.15.4 PHY, spread, and then up converted to the transmit
frequency.
If the MC13192 is in packet mode, data is processed as an entire packet. The data is loaded into the TX
buffer. The MCU then requests that the MC13192 transmit the data. The MCU is notified that the whole
packet has successfully been transmitted via an interrupt.
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 3
Page 4
Data Transfer Modes
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
In streaming mode, the data is fed to the MC13192 on a word by word basis with an interrupt serving as a
notification that the MC13192 is ready for more data. This continues until the whole packet is transmitted.
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
RFIN+
RFIN-
VDDLO2
Crystal1
Crystal2
VDDLO1
PAO+
PAO-
1st IF M ixe r
LNA
IF = 65 MHz
256MHz
Crystal
Osc illator
16MHz
PA
MC13192
Analog Receiver
Frequency
Generation
Analog
Transmitter
2nd IF Mixer
IF = 1 M H z
÷4
Phase Shift Modulator
PMA
Decimation
Filter
AGC
Synthesizer
Baseband
2.45GHz
VCO
Mixer
Programmable
Matched
Filter
Prescaler
MUX
CCA
Transmit
Packet RAM 2
Transmit
Packet RAM 1
FCS
Generation
DCD
Receive
Packet RAM
24 Bit Event Timer
4 Programmable
Timer Comparators
Transmit RAM
Header
Generation
Correlator
Arbiter
Symbol
Synch & Det
Packet
Processor
Receive RAM
Arbiter
Symbol
Generation
Figure 1. MC13192 Simplified Block Diagram
Microcontroller
Control
Logic
Digital Transceiver
IRQ Arbiter
and GPIO
RAM Arbiter
SPI
SPI
Timer
Analog
Power-Up
Control
Logic
Sequence
Manager
(Control Logic)
Regulator
Digital
Regulator L
Digital
Regulator H
Crystal
Regulator
VCO
Regulator
SERIAL
PERIPHERAL
IRQ
Arbiter
Rom (Flash)
RAM
CPU A/D
Application
Network
VDDA
VBATT
VDDINT
VDDD
VDDVCO
RXTXEN
CE
MOSI
MISO
SPICLK
(SPI)
INTERFACE
ATTN
RST
GPIO1
GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO4
GPIO5
GPIO6
GPIO7
IRQ
CLKO
Timer
Voltage
Regulators
Power Up
Management
Buffer RAM
MAC
PHY Driver
Figure 2. System Level Block Diagram
4 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 5
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Electrical Characteristics
nc...
, I
or
4 bytes
Preamble
1 byte 1 byte
Start of
Frame
Delimiter
Figure 3. MC13192 Packet Structure
Frame
Length
125 bytes Max
Payload FCS
4 Electrical Characteristics
4.1 Maximum Ratings
Table 1. Maximum Ratings
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Power Supply Voltage V
Junction Temperature T
Storage Temperature Range T
BATT, VDDINT
stg
2 bytes
3.6 Vdc
J
125 °C
-55 to 125 °C
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
Note: Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may occur.
Functional operation should be restricted to the limits in the Electrical Characteristics
or Recommended Operating Conditions tables.
Note: Meets Human Body Model (HBM) = 2 kV and Machine Model (MM) = 200 V except RFin = 100 V MM,
PAout = 50 V MM & 1 kV HBM, and VBATT = 100 V MM. RF pins have no ESD protection including PAO+
and PAO -.
4.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Table 2. Recommended Operating Conditions
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Power Supply Voltage V
Input Frequency f
Ambient Temperature Range T
Logic Input Voltage Low V
Logic Input Voltage High V
BATT,
V
DDINT
in
A
il
ih
2.0 2.7 3.4 Vdc
2.405 - 2.480 GHz
-40 25 85 °C
0-30%
V
DDINT
70%
V
DDINT
-V
DDINT
V
V
SPI Clock Rate f
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 5
SPI
--8.0MHz
Page 6
Electrical Characteristics
Table 2. Recommended Operating Conditions (Continued)
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
RF Input Power P
Crystal Reference Oscillator Frequency (±40 ppm over
everything to meet the 802.15.4 standard.)
4.3 DC Electrical Characteristics
Table 3. DC Electrical Characteristics
(VCC = 2.7 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted)
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Power Supply Current (V
Off
Hibernate
Doze (No CLKO)
Idle
Transmit Mode
Receive Mode
Input Current Low (V
Input Current High (Vin = V
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
in
+ V
BATT
= 0V) I
DDINT
)
DDINT
)I
max
f
ref
I
leakage
I
CCH
I
CCD
I
CCI
I
CCT
I
CCR
il
ih
oh
ol
--200dBm
16 MHz Only
-
-
-
-
-
-
- -1.0 - µA
-1.0-µA
80%
V
DDINT
0-20%
<1.0
3.0
40
500
34
37
-V
DDINT
V
DDINT
-
-
-
-
-
-
µA
µA
µA
µA
mA
mA
V
V
eescale S
Fr
6 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 7

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.4 AC Electrical Characteristics
Table 4. Receiver AC Electrical Characteristics
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Electrical Characteristics
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
Sensitivity for 1% Packet Error Rate (PER) SENS
Saturation (maximum input level) SENS
Adjacent Channel Interference for 1% PER (desired
signal -82 dBm)
Alternate Channel Interference for 1% PER (desired
signal -82 dBm)
Frequency Error Tolerance - - 200 kHz
Symbol Rate Error Tolerance - 80 ppm
In-band Spurious Reception - 28 - dB
Table 5. Transmitter AC Electrical Characteristics
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Nominal Output Power P
Error Vector Magnitude EVM 27 %
Power Control Range - 20 - dB
Over the Air Data Rate T
per
max
out
bit
--92-dBm
0dBm
-23-dB
-35-dB
-0-dBm
- 250 - kbps
eescale S
Fr
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 7
Page 8

Functional Description
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
5 Functional Description
5.1 MC13192 Operational States
The MC13192 has a number of operational states that allow for low-current operation. Entry from the Off
to Idle state occurs when RST
to Off, Hibernate, and Doze is controlled through the SPI. These states are summarized, along with the
transition times, in Tab le 6. Current drain in the various states is listed in Table 3, DC Electrical
Characteristics.
Table 6. MC13192 Mode Definitions and Transition Times
is de-asserted. Once in Idle, the SPI is active and controls the IC. Transition
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
Mode Definition
Off All IC functions Off, Leakage only. RST asserted. 23.332 ms to Idle
Hibernate Crystal Reference Oscillator Off. (SPI not functional.) IC Responds to
.
ATTN
Doze Crystal Reference Oscillator On but CLKO output available only if
Register 7, Bit 9 = 1 for frequencies of 1 MHz or less. (SPI not
functional.) Responds to ATTN and can be programmed to enter Idle
State through an internal timer comparator.
Idle Crystal Reference Oscillator On with CLKO output available. SPI active.
Receive Crystal Reference Oscillator On. Receiver On. SPI should not be
accessed.
Transmit Crystal Reference Oscillator On. Transmitter On. SPI should not be
accessed.
Transition Time
To or From Idle
18.332 ms to Idle
332 µs to Idle
144 µs from Idle
144 µs from Idle
eescale S
Fr
8 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 9

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Functional Description
5.2 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Control of the MC13192 and data transfers are accomplished by means of a 4-wire Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI). This section details the operatio n of the SPI.
5.2.1 General
The MC13192 operates as a slave device only. Data to be written into the IC is presented on the Master
Out/Slave In (MOSI) pin of the device, while data read from the device is presented to the master device
on the Master In/Sla ve Out (MISO) pin. Synchronization of t h e d ata is accomplished by the retur n-t o-zero
Serial Clock (SPICLK) input and is fr amed by the Chi p Enable (CE
into the IC on the l eading edge of SPICLK and da ta is clo cked out of the IC at MIS O on the f alli ng edge o f
SPICLK. The master device should transfer MISO data to its internal registers on the trailing edge of
SPICLK. A typical interconnection to a microprocessor is shown in Figure 4.
MCU MC13192
) pin. Data on MOSI is always clocked
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
Shift Register
Baud Rate
Generator
RxD
TxD MOSI
Sclk SPICLK
Chip Enable (CE)
MISO
Shift Register
CE
Figure 4. SPI Interface
MISO is an active output and as such, does not enter a high impedance state at any time regardless of the
state of CE
.
Although the SPI is fully static, internal memory, timer and interrupt arbiters require an internal clock,
CLK
, derived from the crystal reference oscillator, to communicate from the SPI registers to internal
core
registers and memory.
Figure 5 and Table 7 show the SPI timing diagram and timing specifications.
CE
SPICLK
t
CE_SU
t
CLKH
t
PER
t
CLKL
t
CE_H
MOSI Addr 1R/W
t
SU
MISO
t
H
t
SU
t
H
Read 1
Write 0
t
t
P1
SU
t
H
Read 0
t
P1
Figure 5. SPI Parametric Timing Diagram.
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 9
Page 10

Functional Description
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 7. SPI Parametric Timing Specifications
nc...
, I
or
1/t
PER
t
CLKH
t
CLKL
t
CE_SU
t
CE_H
t
SU
t
H
t
P1
t
P2
SPICLK frequency 8.0 MHz
Pulse Width, SPICLK high 0.5 * t
Pulse Width, SPICLK low 0.5 * t
Setup Time, CE low to rising SPICLK 0.5 * t
Hold Time, rising SPICLK to CE high 1.0 * t
Setup Time, MOSI to rising SPICLK 0.5 * t
Hold Time, MOSI to rising SPICLK 0.5 * t
Propagation Delay, MISO to rising SPICLK 0 µs
Propagation Delay, MISO to rising CE 0 µs
NOTE:
PER
PER
PER
PER
PER
PER
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
The minimum duration of a si ngular SPI acc ess, at the maximu m SPICLK
rate of 8 MHz is 3.0 µs.
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
10 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 11

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Contact Connections
6 Contact Connections
Table 8. Contact Function Description
Contact # Contact Name Type Description Functionality
1 RFIN- RF Input LNA negative differential input 2.4 to 2.5 GHz
2 RFIN+ RF Input LNA positive differential input 2.4 to 2.5 GHz
3 Not Used Tie to Ground
4 Not Used Tie to Ground
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
5 PAO+ RF Output /DC
Input
6 PAO- RF Output/DC
Input
7 Not used Tie to Ground
8 GPIO4 Digital Input/
Output
9 GPIO3 Digital Input/
Output
Power Amplifier Positive Output.
Open drain. Connect to V
Power Amplifier Negative Output.
Open drain. Connect to V
General Purpose Input/Output 4. When digital
General Purpose Input/Output 3 When digital
DDA
DDA
2.4 to 2.5 GHz
.
2.4 to 2.5 GHz
.
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
eescale S
Fr
10 GPIO2 Digital Input/
Output
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 11
General Purpose Input/Output 2.
When gpio_alt, Register 9, Bit 7, = 1,
GPIO2 functions as a “CRC Valid”
indicator.
When digital
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
Page 12

Contact Connections
Contact # Contact Name Type Description Functionality
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 8. Contact Function Description (Continued)
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
11 GPIO1 Digital Input/
Output
12 RST Digital Input Active Low Reset Pin. While held
13 RXTXEN Digital Input Active High. Low to high transition
14 ATTN Digital Input Active Low Attention pin. Transitions
15 CLKO Digital Output Clock output to host MCU.
16 SPICLK Digital Clock
Input
General Purpose Input/Output1.
When gpio_lt_en, Register 9, Bit 7,
= 1, GPIO1 functions as an “Out of
Idle” indicator.
low, the IC is “off” and all internal
information is lost from RAM and SPI
registers. When high, IC goes to
IDLE State, with SPI in default state.
initiates RX or TX sequence
depending on SPI setting. If held
high (e.g., tied to VBATT), SPI
setting starts RX or TX sequence.
IC from either Hibernate or Doze
states to Idle.
Programmable frequencies of:
16, 8, 4, 2, 1 MHz, and 62.5 kHz,
32.786+ kHz (default),
and 16.393+ kHz
External clock input for the SPI
interface.
When digital
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
Vil=30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
freq=16MHz (20/80
DC) 20 pF. All
others (50/50 DC)
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
freq= 8 MHz (max)
eescale S
Fr
17 MOSI Digital Input Master Out/Slave In. Dedicated SPI
data input.
18 MISO Digital Output Master In/Slave Out. Dedicated SPI
data output.
19 CE Digital Input Active Low Chip Enable. Activates
SPI.
20 IRQ Digital Output Active Low Interrupt Request Open drain device.
12 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
freq=8 Mbps (max)
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
Ω internal pull-
40 k
up. Interrupt can
be serviced every
6 µs with <20 pF
load. External pullup must be >4 k
Ω.
Page 13

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 8. Contact Function Description (Continued)
Contact # Contact Name Type Description Functionality
21 VDDD Bypass Digital supply bypass Decouple 0.1 to
Contact Connections
0.47 µF to ground.
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
22 VDDINT Input Digital interface supply & digital
regulator input – Connect to Battery
23 GPIO5 Digital Input/
Output
24 GPIO6 Digital Input/
Output
25 GPIO7 Digital Input/
Output
26 Crystal1 Input Crystal Reference oscillator input Connect to 16 MHz
General Purpose Input/Output 5 When digital
General Purpose Input/Output 6 When digital
General Purpose Input/Output 7 When digital
2.0 to 3.4 V
Decouple 0.47 to 1
µF to ground.
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
output:
Vol= 20%VDDINT
Voh=80%VDDINT
When digital
input:
Vil= 30%VDDINT
Vih=70%VDDINT
1 mA max source/
sink.
crystal and load
capacitor
27 Crystal2 Input/Output Crystal Reference oscillator output
Note: Do not load this pin by using
it as a 16 MHz source. Measure 16
MHz output at Contact 15, CLKO,
programmed for 16 MHz. See the
MC13192 Reference Manual for
details.
28 VDDLO2 Input/Bypass LO2 VDD supply - Connect to VDDA
externally
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 13
Connect to 16 MHz
crystal and load
capacitor
Decouple 100 to
1000 pF to ground
Page 14

Contact Connections
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 8. Contact Function Description (Continued)
Contact # Contact Name Type Description Functionality
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
29 VDDLO1 Input/Bypass LO1 VDD supply pad - Connect to
VDDA externally
30 VDDVCO Bypass VCO regulated supply bypass Decouple 100 to
31 VBATT Input Analog voltage regulators Input -
Connect to Battery
32 VDDA Output Analog regulated supply Output –
Connect to VDDLO1 and VDDLO2
externally
EP Ground External paddle / flag ground Connect to ground
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VDDA
VBATT
RFINRFIN+
Not Used
Not Used
PAO+
PAONot Used
VDDVCO
VDDLO1
GND
MC13192
GPIO4
GPIO3
GPIO2
GPIO1
RST
910111213141516
VDDLO2
RXTXEN
XTAL1
XTAL2
ATTN
GPIO7
24
GPIO6
23
GPIO5
VDDD
IRQ
CE
MISO
MOSI
22
21
20
19
18
17
VDDINT
CLKO
SPICLK
Decouple 100 to
1000 pF to ground
1000 pF to ground
Decouple 1 µF and
100 pF ground
Decouple 100 to
1000 pF to ground
eescale S
Fr
Figure 6. Contact Connections (Top View)
14 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 15

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Applications Information
7 Applications Information
Figure 7 shows a basic application sc hema ti c for int er fa cin g the MC13192 with an MCU. Table 9 lists the
Bill of Materials.
The MC13192 has differential RF inputs and outputs. These are well suited to balanced PCB antenna
structures. Alternatively, chip antennas or other single-ended structures can be used with commercially
available chip bal uns or mi cro st ri p e qui valents. PAO+ and PAO- requ ir e c onnection to VDDA, the ana log
regulator output. This is best accomplished with microstrip lines which are decoupled to act as harmonic
traps. The 16 MHz crystal should be mounted close to the MC13192 because the crystal trim default
assumes the listed Toyoc om cryst al and the 9 pF capacit ors shown are used. I f a differe nt crysta l is used , it
should have a load capac itanc e of 9 pF or l ess. Byp assin g ca pacitor s a re crit ica l and should be pla ced close
to the device. Unused GPIOs and contacts should be grounded as shown.
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
The SPI connections to the MCU include IRQ
frequency of 8 MHz or less. Option ally, CLKO can provide a clock to the MCU. Th e CLKO frequency is
programmable via the SPI and has a default of 32.786+ kHz. The ATTN
from the MCU or can be negated by a swit ch or ot her har dware. The l atter app roach al lows th e MCU to be
put in a sleep mode a nd then awakene d by CLKO when th e ATTN
can be used to initiate receive or transmit sequences under MCU control. In this case, RXTXEN must be
controlled by an MCU GPIO with the optional connection shown. Otherwise, RXTXEN is held high and
receive or transmit sequences are initiated by an SPI command. Device reset (RST
through an optional connection to an MCU GPIO or by an external pull-down.
When used in Stream Mode, as wit h 802.15.4 MAC/PHY soft ware, MC13192 GPIO1 f unctions as a n “Out
of Idle” indicator and GPIO2 functions as a “CRC valid” indicator and are not available for general
purpose use.
, CE, MOSI, MISO and SPICLK. The SPI can run at any
line can be driven by a GPIO
line wakes up the MC13192 . RXTXEN
) can be controlled
eescale S
Fr
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 15
Page 16

Applications Information
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
MCU
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
GPIO (CE)
IRQ/INT
R4
10 kΩ
BATTERY
C2
Y1
9.0 pF
16.00 MHz
C7
100 pF
C1
C6
9.0 pF
100 pF
C5
100 pF
C3
0.1 µF
C10
100 pF
C11
R2
R3
Optional
1.0 µF
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
1 MΩ
100 kΩ
47 kΩ
GPIO7
XTAL1
XTAL2
VDDLO2
VDDLO1
VDDVCO
VBATT
VDDA
R1
L1
200 Ω
6.8 nH
MOSI
22
C4 0.1 µF
VDDINT
SPICLK
21
20
19
CE
IRQ
VDDD
MISO
24
23
GPIO5
GPIO6
U1
MC13192
RFIN-
RFIN+
1
2
3
PAO+
PAO-
Not Used
Not Used
4
5
6
GPIO
CLK
18
17
MOSI
MISO
SPICLK
CLKO
ATTN
RXTXEN
GPIO1
GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO4
Not Used
7
8
GPIO
RST
910111213141516
C8
100 pF
GPIO
are optional MCU
These three GPIO lines
GPIO
GPIO
connections.
Dedicated GPIO lines
used in Stream Mode.
Not used in Packet Mode.
ATTN
RESET
DDA
V
Traps
Microstip
Harmonic
Rx Antenna
Tx Antenna
C9
100 pF
Figure 7. MC13192 Applied With an MCU
16 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 17

nc...
, I
or
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 9. MC13192 to MCU Bill of Materials (BOM)
Item Number Label/Value Attributes Designation
19 pFSMD0201C1
29 pFSMD0201C2
3 0.1 uF SMD0201 C3
4 0.1 uF SMD0201 C4
5 100 pF SMD0201 C5
6 100 pF SMD0201 C6
7 100 pF SMD0201 C7
8 100 pF SMD0201 C8
9 100 pF SMD0201 C9
10 100 pF SMD0201 C10
11 1.0 uF SMD0201 C11
12 6.8 nH SMD0201 L1
Applications Information
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
13 200
14 1 M
15 100 k
16 10 k
17 MC13192 QFN U1
18 16.000 MHz TOYOCOM
Ω SMD0201 R1
Ω SMD0201 R2
Ω SMD0201 R3
Ω SMD0201 R4
Y1
TSX-10A, 9 pF
load
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 17
Page 18

nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
Packaging Information
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
8 Packaging Information
PIN 1
0.1
2X
EXPOSED DIE
ATTACH PAD
0.1 A B
32X
3.25
2.95
INDEX AREA
A
C
5
B
25
24
C
17
16 9
0.5
0.3
5
C
0.1 A B
3.25
2.95
VIEW M-M
5
(45 )
(1.73)
32
0.1
2X
DETAIL M
PIN 1 INDEX
1
0.5
8
N
0.30
32X
0.18
0.1
0.05
C
M
C
C0.1
C0.05
SEATING PLANE
0.217
0.137
(0.1)
5
G
1.00
1.0
0.75
0.8
0.05
0.00
M
NOTES:
1. ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS.
2. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ASME
Y14.5M, 1994.
3. THE COMPLETE JEDEC DESIGNATOR FOR THIS
PACKAGE IS: HF-PQFP-N.
4. CORNER CHAMFER MAY NOT BE PRESENT.
DIMENSIONS OF OPTIONAL FEATURES ARE FOR
REFERENCE ONLY.
5. COPLANARITY APPLIES TO LEADS, CORNER
LEADS, AND DIE ATTACH PAD.
0.25
28X
M
C
A B
M
C
6. FOR ANVIL SINGULATED QFN PACKAGES,
MAXIMUM DRAFT ANGLE IS 12°.
(0.25)
0.60
0.24
(0.5)
VIEW ROTATE D 90 ° CLOCKW ISE
0.217
0.137
PREFERRED BACKSIDE PIN 1 INDEX
(0.25)
DETAIL G
DETAIL S
DETAIL S
eescale S
Fr
0.065
32X
0.015
PREFERRED CORNER CONFIGURATION
BACKSIDE PIN 1 INDEX OPTION
DETAIL N
DETAIL M
(0.25)
4
DETAIL T
0.475
0.425
R
0.60
0.24
DETAIL N
CORNER CONFIGURATION OPTION
4
1.6
1.5
0.25
0.15
DETAIL M
BACKSIDE PIN 1 INDEX OPTION
BACKSIDE
PIN 1 INDEX
DETAIL M
PREFERRED BACKSIDE PIN 1 INDEX
0.39
2X
0.31
DETAIL T
BACKSIDE PIN 1 IN DEX OPTION
5
(90 )
0.1
2X
0.0
Figure 8. Outline Dimensions for QFN-32, 5x5 mm
(Case 1311-03, Issue E)
18 MC13192 Product Preview MOTOROLA
Page 19

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
NOTES
nc...
, I
or
emiconduct
eescale S
Fr
MOTOROLA MC13192 Product Preview 19
Page 20

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
HOW TO REACH US:
, I
USA/EUROPE/LOCATIONS NOT LISTED:
or
Motorola Literature Distribution;
P.O. Box 5405, Denver, Colorado 80217
1-303-675-2140 or 1-800-441-2447
JAPAN:
Motorola Japan Ltd.; SPS, Technical Information Center,
3-20-1, Minami-Azabu Minato-ku, Tokyo 106-8573 Japan
81-3-3440-3569
ASIA/PACIFIC:
emiconduct
Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; Silicon Harbour
Centre, 2 Dai King Street, Tai Po Industrial Estate,
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
852-26668334
TECHNICAL INFORMATION CENTER:
1-800-521-6274
eescale S
HOME PAGE:
Fr
http://www.motorola.com/semiconductors
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software implementers to
use Motorola products. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to
design or fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this
document.
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein.
Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products
for any particular pur pose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or
use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be provided in
Motorola data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual
performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated
for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any
license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed,
intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the
body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which
the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death may
occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized
application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries,
affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and
reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death
associated with such unintended or unauthor ized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola
was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Motorola and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. All other
product or service names are the proper ty of their respective owners. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
© Motorola, Inc. 2004
MC13192/D
 Loading...
Loading...