Page 1

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Module
This manual describes the operation of the XBee® Wi-Fi RF module, which consists of 802.11 bgn firmware loaded
onto XBee® hardware. The XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules are designed to operate within the 802.11 protocol and
support the unique needs of low-cost, low-power wireless sensor networks. The modules require minimal power
and provide reliable delivery of data between remote devices and wireless 802.11 b, g or n access points and
routers. The modules operate within the ISM 2.4 GHz frequency band.
Digi International Inc.
11001 Bren Road East
Minnetonka, MN 55343 877 912-3444 or 952 912-3444
http://www.digi.com
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. All rights reserved
No part of the contents of this manual may be transmitted or reproduced in
any form or by any means without the written permission of Digi
International, Inc.
XBee® is a registered trademark of Digi International, Inc.
Technical Support Phone: (866) 765-9885 toll-free U.S.A. & Canada
(801) 765-9885 Worldwide
8:00 am - 5:00 pm [U.S. Mountain Time]
Online Support: http://www.digi.com/support/eservice/login.jsp
Email: rf-experts@digi.com
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 1
Page 2
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Contents
1. Overview ............................................................................................................................................. 5
Specifications ...................................................................................................................................... 6
General Specifications .................................................................................................................... 6
RF Specifications ............................................................................................................................. 7
Electrical Specifications ................................................................................................................ 11
Environmental Specifications ....................................................................................................... 11
Serial Communications Specifications .......................................................................................... 12
UART ............................................................................................................................................. 12
SPI ................................................................................................................................................. 12
GPIO Specifications ........................................................................................................................... 13
Agency Approvals ............................................................................................................................. 14
Pin Signals ......................................................................................................................................... 14
Design Notes ..................................................................................................................................... 15
Power Supply ................................................................................................................................ 15
Recommended Pin Connections .................................................................................................. 15
Board Layout ................................................................................................................................ 16
Mounting Considerations ............................................................................................................. 18
2. RF Module Operation ....................................................................................................................... 19
Serial Communications ..................................................................................................................... 19
UART Communications ................................................................................................................. 19
SPI Communications ..................................................................................................................... 20
Serial Buffers .................................................................................................................................... 21
Serial Receive Buffer ..................................................................................................................... 21
Serial Transmit Buffer ................................................................................................................... 21
UART Flow Control ....................................................................................................................... 21
Serial Interface Protocols ................................................................................................................. 22
Transparent Operation ................................................................................................................. 22
API Operation ............................................................................................................................... 23
A Comparison of Transparent and API Operation ........................................................................ 23
Modes of Operation ......................................................................................................................... 24
Idle Mode ..................................................................................................................................... 24
Transmit Mode ............................................................................................................................. 24
Receive Mode ............................................................................................................................... 24
Command Mode ........................................................................................................................... 24
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 2
Page 3

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Sleep Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 26
3. 802.11 bgn Networks ....................................................................................................................... 27
Infrastructure Networks ................................................................................................................... 27
Ad Hoc Networks .............................................................................................................................. 27
Network Basics ................................................................................................................................. 28
XBee® Wi-Fi Standards ..................................................................................................................... 28
Encryption ........................................................................................................................................ 28
CHANNELS ........................................................................................................................................ 29
4. XBee IP Services ................................................................................................................................ 29
XBee Application Service .................................................................................................................. 30
Local Host ..................................................................................................................................... 30
Network Client .............................................................................................................................. 31
Serial Communication Service .......................................................................................................... 34
Transparent mode ........................................................................................................................ 34
API mode ...................................................................................................................................... 34
5. Sleep ................................................................................................................................................. 35
Sleeping with the UART .................................................................................................................... 35
Sleeping with the SPI ........................................................................................................................ 35
Sleep Options ................................................................................................................................... 36
AP Associated sleep ...................................................................................................................... 36
Deep sleep (non-associated sleep) ............................................................................................... 36
Sampling data using sleep modes .................................................................................................... 37
Sample Rate (ATIR) ....................................................................................................................... 37
Wake Host .................................................................................................................................... 37
6. XBee Analog and Digital IO Lines ...................................................................................................... 38
IO Sampling ....................................................................................................................................... 38
Queried Sampling ......................................................................................................................... 40
Periodic IO Sampling ..................................................................................................................... 40
I/O Examples ................................................................................................................................. 41
7. API Operation ................................................................................................................................... 42
API Frame Specifications .................................................................................................................. 42
API UART and SPI Exchanges ............................................................................................................ 45
AT Commands ............................................................................................................................... 45
Transmitting and Receiving RF Data ............................................................................................. 45
Remote AT commands ................................................................................................................. 46
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 3
Page 4

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Supporting the API ........................................................................................................................ 46
API Frames ........................................................................................................................................ 47
TX (Transmit) request: 64-Bit ....................................................................................................... 47
AT Command ................................................................................................................................ 47
AT Command-Queue Parameter Value ........................................................................................ 48
Remote AT Command Request .................................................................................................... 49
Transmit (TX) request: IPv4 .......................................................................................................... 51
AT Command Response ................................................................................................................ 52
Modem Status .............................................................................................................................. 53
Transmission Status ...................................................................................................................... 54
IO Data Sample RX Indicator ........................................................................................................ 55
Remote Command Response ....................................................................................................... 57
RX (Receive) Packet: IPv4 ............................................................................................................. 58
8. XBee Command Reference Tables.................................................................................................... 59
Addressing ........................................................................................................................................ 59
Networking Commands .................................................................................................................... 60
Security Commands .......................................................................................................................... 60
RF Interfacing Commands ................................................................................................................ 60
Serial Interfacing ............................................................................................................................... 61
I/O Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 62
Diagnostics Interfacing ..................................................................................................................... 65
AT Command Options ...................................................................................................................... 66
Sleep Commands .............................................................................................................................. 66
Execution Commands ....................................................................................................................... 67
9. Module Support ................................................................................................................................ 68
X-CTU Configuration Tool ................................................................................................................ 68
Serial Firmware Updates ............................................................................................................. 68
Regulatory Compliance ................................................................................................................ 68
Agency Certifications ................................................................................................................... 68
United States FCC ............................................................................................................................. 68
OEM Labeling Requirements ....................................................................................................... 69
FCC Notices ................................................................................................................................... 69
FCC-Approved Antennas (2.4 GHz) .............................................................................................. 70
RF Exposure .................................................................................................................................. 73
Europe (ETSI) .................................................................................................................................... 74
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 4
Page 5
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
OEM Labeling Requirements ....................................................................................................... 74
Restrictions .................................................................................................................................. 74
Declarations of Conformity ......................................................................................................... 74
Approved Antennas ..................................................................................................................... 75
XBee RF Module ........................................................................................................................... 75
Canada (IC) ....................................................................................................................................... 76
Transmitters with Detachable Antennas .................................................................................... 76
Detachable Antenna .................................................................................................................... 76
Australia (C-Tick) .............................................................................................................................. 77
10. Warranty Information .................................................................................................................... 78
1-Year Warranty............................................................................................................................... 78
Appendix A: Definitions ...................................................................................................................... 79
1. Overview
The XBee® Wi-Fi RF module provides wireless connectivity to end-point devices in 802.11 bgn
networks. Utilizing the 802.11 feature set, these modules are interoperable with other 802.11
bgn devices, including devices from other vendors. With XBee, users can have their 802.11 bgn
network up-and running in a matter of minutes.
The XBee® Wi-Fi modules are compatible with other devices that use 802.11 bgn technology.
These include Digi external 802.11x devices like the ConnectPort and the Digi Connect Wi-SP, as
well as embedded products like the ConnectCore series and Digi Connect series of products.
More information on these Digi products can be found at:
http://www.digi.com/products/wireless/wifisolutions/
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 5
Page 6

Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
Dimensions
0.960 x 1.297 (2.438cm x 3.294cm)
Operating Temperature
-40 to 85° C (Industrial)
Antenna Options
PCB Antenna, U.FL Connector, RPSMA Connector, or
Integrated Wire
Specifications
General Specifications
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 6
Page 7
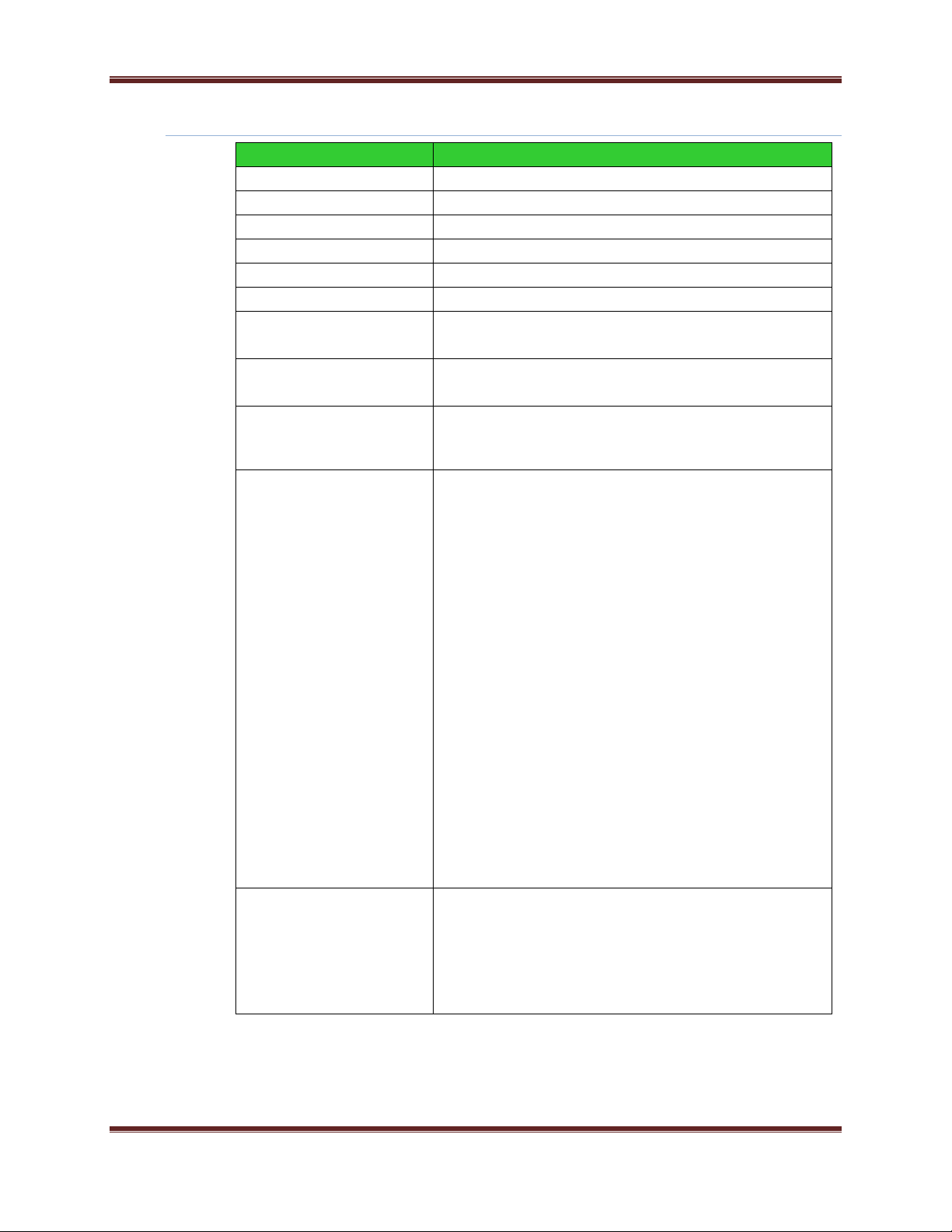
Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
Frequency
ISM 2.4-2.5GHz
Number of Channels
14
Channels
1 to 14
Adjustable Power
Yes
Interface immunity
802.11 b, g, and n
Indoor/Urban Range
TBD
Outdoor RF line-of-sight
Range
TBD
Transmit Power Output
>15dBm
RF Data Rate
802.11 b 1, 2, 5.5, and 11Mbps
802.11 g 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 Mbps
802.11 n 6.5, 13, 19.5, 26, 39, 52, 58.5, and 65 Mbps
EVM
802.11 b 1Mbps 8%
802.11 b 2Mbps 17%
802.11 b 5.5Mbps 10%
802.11 b 11Mbps 12%
802.11 g 6Mbps -13dB
802.11 g 9Mbps -15dB
802.11 g 12Mbps -16dB
802.11 g 18Mbps -18dB
802.11 g 24Mbps -19dB
802.11 g 36Mbps -21dB
802.11 g 48Mbps -24dB
802.11 g 54 Mbps -25dB
802.11 n MCS0 6.5Mbps -15dB
802.11 n MCS1 13Mbps -16dB
802.11 n MCS2 19.5Mbps -17dB
802.11 n MCS3 26Mbps -19dB
802.11 n MCS4 39Mbps -20dB
802.11 n MCS5 52Mbps -21dB
802.11 n MCS6 58Mbps -23dB
802.11 n MCS7 65Mbps -24dB
Receiver Sensitivity
802.11 b 1Mbps -97dBm (<8% PER)
802.11 b 2Mbps -93dBm (<8% PER)
802.11 b 11Mbps -89dBm (<8% PER)
802.11 g 6Mbps -91dBm (<10% PER)
802.11 g 54 Mbps -75dBm (<10% PER)
802.11 n 65Mbps -72dBm (<10% PER)
RF Specifications
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 7
Page 8
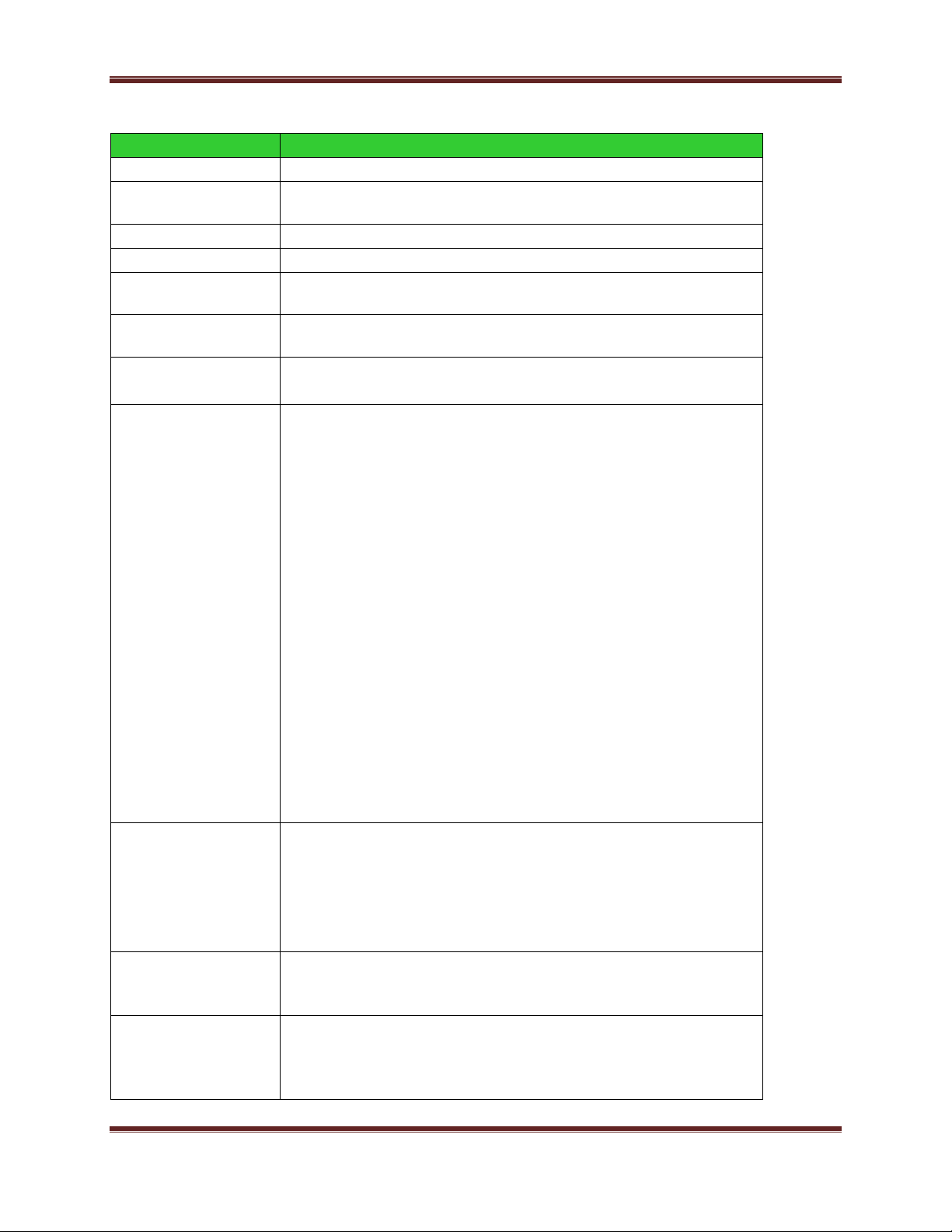
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
Frequency
ISM 2.4-2.5GHz
Number of
Channels
14
Channels
1 to 14
Adjustable Power
Yes
Interface
immunity
802.11 b, g, and n
Indoor/Urban
Range
TBD
Outdoor RF line-
of-sight Range
TBD
Transmit Power
(Average)
802.11 b 1Mbps 16dBm
802.11 b 2Mbps 16dBm
802.11 b 5.5Mbps 16dBm
802.11 b 11Mbps 16dBm
802.11 g 6Mbps 16dBm
802.11 g 9Mbps 16dBm
802.11 g 12Mbps 16dBm
802.11 g 18Mbps 16dBm
802.11 g 24Mbps 15dBm
802.11 g 36Mbps 15dBm
802.11 g 48Mbps 14dBm
802.11 g 54 Mbps 14dBm
802.11 n MCS0 6.5Mbps 16dBm
802.11 n MCS1 13Mbps 16dBm
802.11 n MCS2 19.5Mbps 16dBm
802.11 n MCS3 26Mbps 16dBm
802.11 n MCS4 39Mbps 15dBm
802.11 n MCS5 52Mbps 15dBm
802.11 n MCS6 58Mbps 14dBm
802.11 n MCS7 65Mbps 14dBm
Transmit Power
Range (Peak)
802.11b: 11.16 dBm to 19.21 dBm (13.06 mW to 83.37 mW)
802.11g: 13.89 dBm to 20.70 dBm (24.49 mW to 117.49 mW)
802.11n: 14.17dBm to 20.46 dBm (26.12 mW to 111.17 mW)
Overall: 11.16 dBm to 20.70 dBm (13.06 mW to 117.49 mW)
RF Data Rate
802.11 b 1, 2, 5.5, and 11Mbps
802.11 g 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 Mbps
802.11 n 6.5, 13, 19.5, 26, 39, 52, 58.5, and 65 Mbps
EVM
802.11 b 1Mbps 8%
802.11 b 2Mbps 17%
802.11 b 5.5Mbps 10%
802.11 b 11Mbps 12%
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 8
Page 9
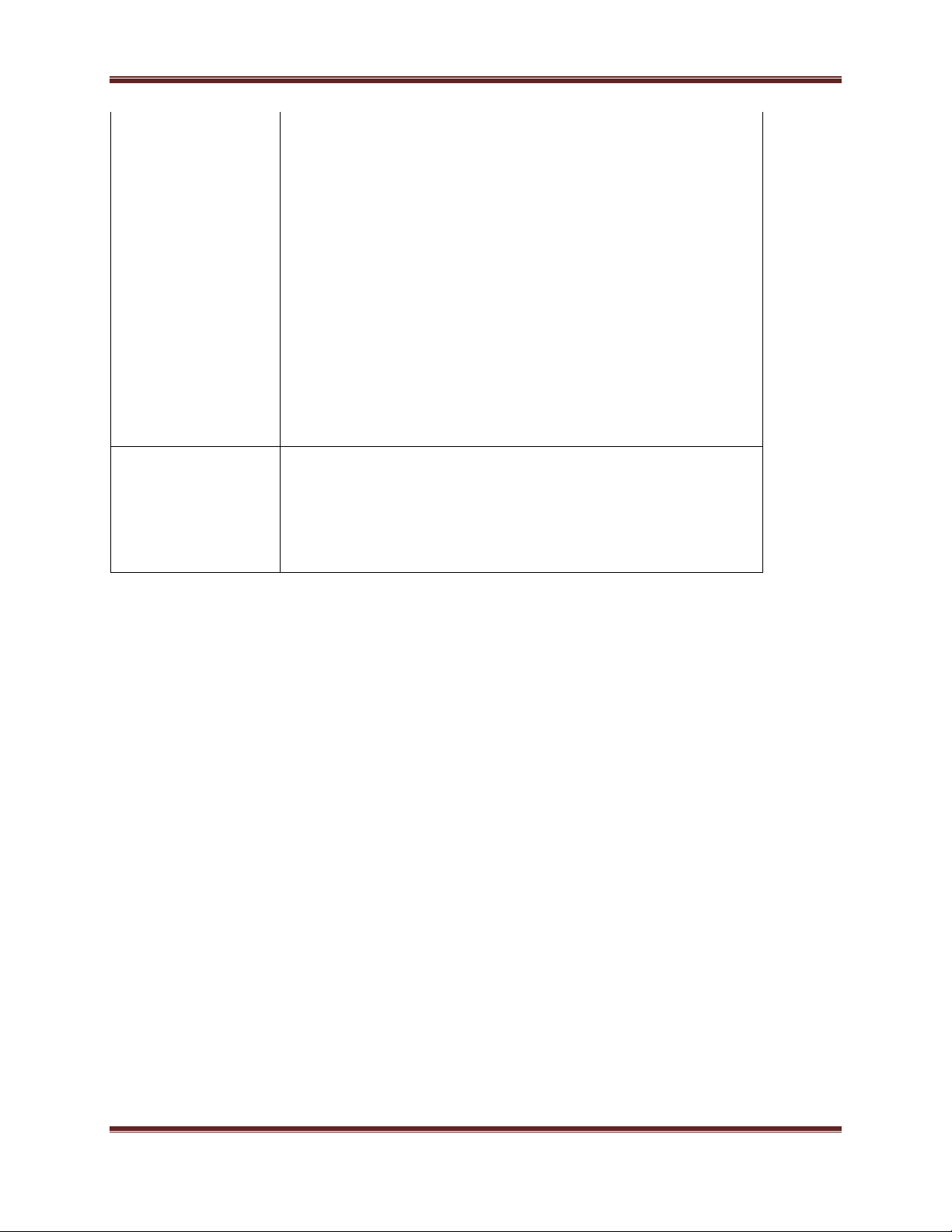
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
802.11 g 6Mbps -13dB
802.11 g 9Mbps -15dB
802.11 g 12Mbps -16dB
802.11 g 18Mbps -18dB
802.11 g 24Mbps -19dB
802.11 g 36Mbps -21dB
802.11 g 48Mbps -24dB
802.11 g 54 Mbps -25dB
802.11 n MCS0 6.5Mbps -15dB
802.11 n MCS1 13Mbps -16dB
802.11 n MCS2 19.5Mbps -17dB
802.11 n MCS3 26Mbps -19dB
802.11 n MCS4 39Mbps -20dB
802.11 n MCS5 52Mbps -21dB
802.11 n MCS6 58Mbps -23dB
802.11 n MCS7 65Mbps -24dB
Receiver
Sensitivity
802.11 b 1Mbps -97dBm (<8% PER)
802.11 b 2Mbps -93dBm (<8% PER)
802.11 b 11Mbps -89dBm (<8% PER)
802.11 g 6Mbps -91dBm (<10% PER)
802.11 g 54 Mbps -75dBm (<10% PER)
802.11 n 65Mbps -72dBm (<10% PER)
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 9
Page 10
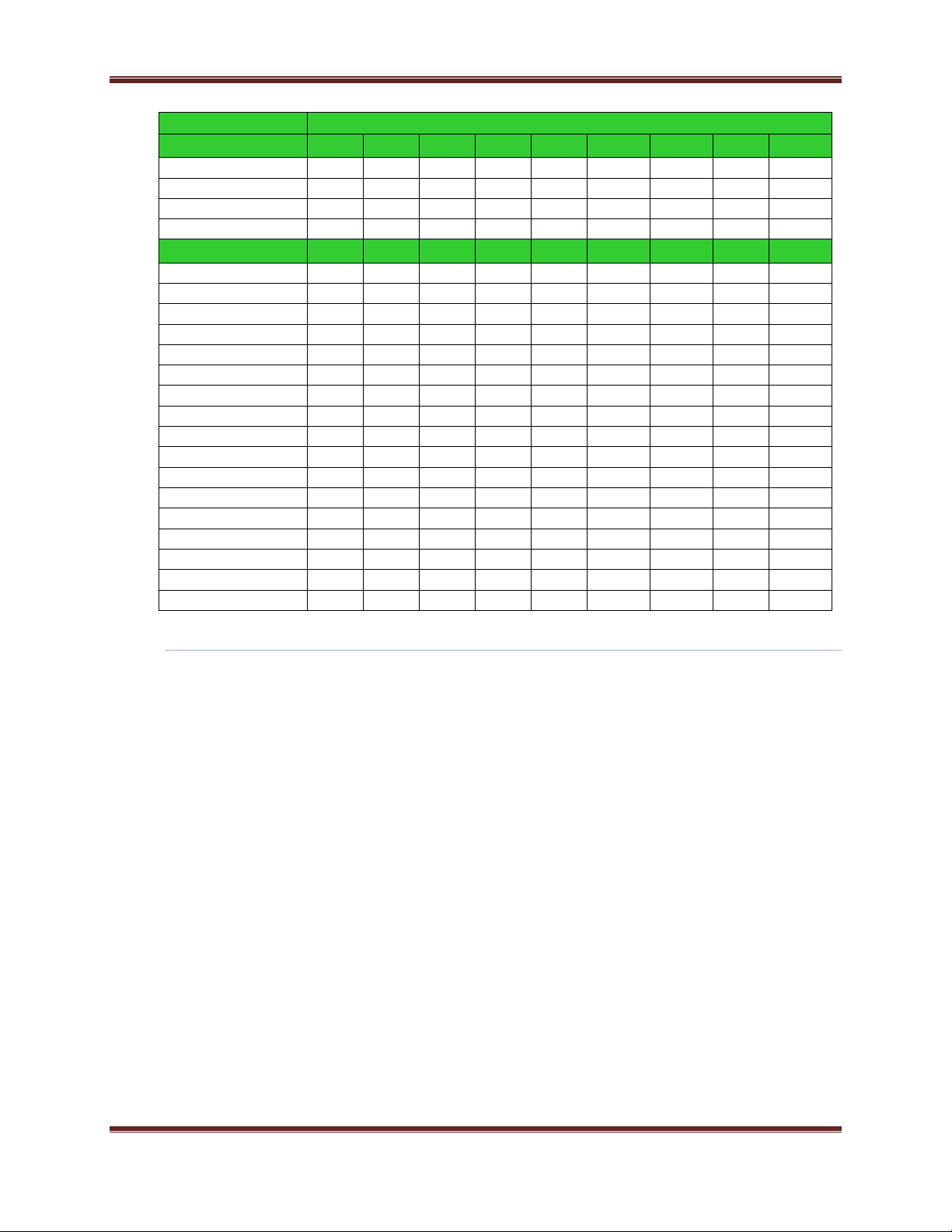
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Spectral Mask
XBee Wi-Fi
Data Rate
-50 to 22
MHz
-22 to -11
MHz
11 To 22
Mhz
22 to 50
MHz
Units
802.11 b 1Mbps
-52
-39
-39
-52
dBc
802.11 b 2Mbps
-52
-38
-38
-54
dBc
802.11 b 5.5Mbps
-56
-43
-48
-54
dBc
802.11 b 11Mbps
-54
-39
-37
-55
dBc
Data Rate
-50 to -30
MHz
-30 to -20
MHz
-20 to -11
MHz
-11 to -9
MHz
9 to 11
MHz
11 to 20
MHz
20 to 30
MHz
30 to 50
MHz
Units
802.11 g 6Mbps
-46
-43.5
-28.5
-16.5
-16.5
-27.5
-42.5
-47
dBc
802.11 g 9Mbps
-46
-42.5
-27.5
-17.5
-16.5
-27.5
-42.5
-46
dBc
802.11 g 12Mbps
-46
-42.5
-28.5
-17.5
-17.5
-27.5
-41.5
-47
dBc
802.11 g 18Mbps
-46
-42.5
-27.5
-17.5
-17.5
-27.5
-41.5
-45
dBc
802.11 g 24Mbps
-47
-44.5
-30.5
-19.5
-19.5
-30.5
-43.5
-47
dBc
802.11 g 36Mbps
-47
-44.5
-30.5
-21.5
-21.5
-30.5
-46.5
-49
dBc
802.11 g 48Mbps
-47
-48.5
-36.5
-23.5
-24.5
-36.5
-48.5
-52
dBc
802.11 g 54Mbps
-47
-48.5
-33.5
-24.5
-23.5
-33.5
-49.5
-49
dBc
802.11 n MCS0 6.5Mbps
-45
-39.5
-26.5
-16.5
-16.5
-26.5
-39.5
-45
dBc
802.11 n MCS1 13Mbps
-44
-40.5
-26.5
-16.5
-15.5
-25.5
-39.5
-45
dBc
802.11 n MCS2 19.5Mbps
-44
-41.5
-27.5
-16.5
-16.5
-27.5
-40.5
-45
dBc
802.11 n MCS3 26Mbps
-44
-40.5
-27.5
-16.5
-16.5
-25.5
-38.5
-45
dBc
802.11 n MCS4 39Mbps
-45
-42.5
-30.5
-19.5
-19.5
-29.5
-42.5
-47
dBc
802.11 n MCS5 52Mbps
-46
-43.5
-30.5
-18.5
-18.5
-29.5
-43.5
-46
dBc
802.11 n MCS6 58Mbps
-47
-45.5
-34.5
-22.5
-22.5
-33.5
-46.5
-48
dBc
802.11 n MCS7 65Mbps
-47
-46.5
-34.5
-22.5
-22.5
-33.5
-46.5
-49
dBc
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 10
Page 11

Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
Supply Voltage
3.1 - 3.6 V
Operating Current
(transmit, max output
power)
802.11 b 1Mbps 260mA
802.11 b 2Mbps 260mA
802.11 b 5.5Mbps 260mA
802.11 b 11Mbps 260mA
802.11 g 6Mbps 240mA
802.11 g 9Mbps 220mA
802.11 g 12Mbps 210mA
802.11 g 18Mbps 200mA
802.11 g 24Mbps 190mA
802.11 g 36Mbps 180mA
802.11 g 48Mbps 170mA
802.11 g 54 Mbps 170mA
802.11 n MCS0 6.5Mbps 230mA
802.11 n MCS1 13Mbps 210mA
802.11 n MCS2 19.5Mbps 200mA
802.11 n MCS3 26Mbps 200mA
802.11 n MCS4 39Mbps 190mA
802.11 n MCS5 52Mbps 180mA
802.11 n MCS6 58Mbps 180mA
802.11 n MCS7 65Mbps 180mA
Operating Current
(Receive)
140mA
Deep Sleep
Current
<2uA @25C
Electrical Specifications
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Environmental Specifications
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 11
Page 12

Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
UART Pins
Module Pin Number
DOUT/DIO13
2
DIN/DIO14
3
nCTS/DIO7
12
nRTS/DIO6
16
Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
SPI Pins
Module Pin Number
SPI_SCLK/DIO2
18
SPI_SSEL/DIO3
17
SPI_MOSI/DIO4
11
SPI_MISO/DIO12
4
SPI_ATTN/DIO9
13
Serial Communications Specifications
The XBee Wi-Fi RF modules support both UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter)
and SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface, in master or slave mode) serial connections.
UART
More information on UART operation is found in the UART section in chapter 2.
SPI
The SC2 (Serial Communication Port 2) of the module is connected to the SPI port.
SPI Pin Assignments
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
For more information on SPI operation see the SPI section in chapter 2.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 12
Page 13
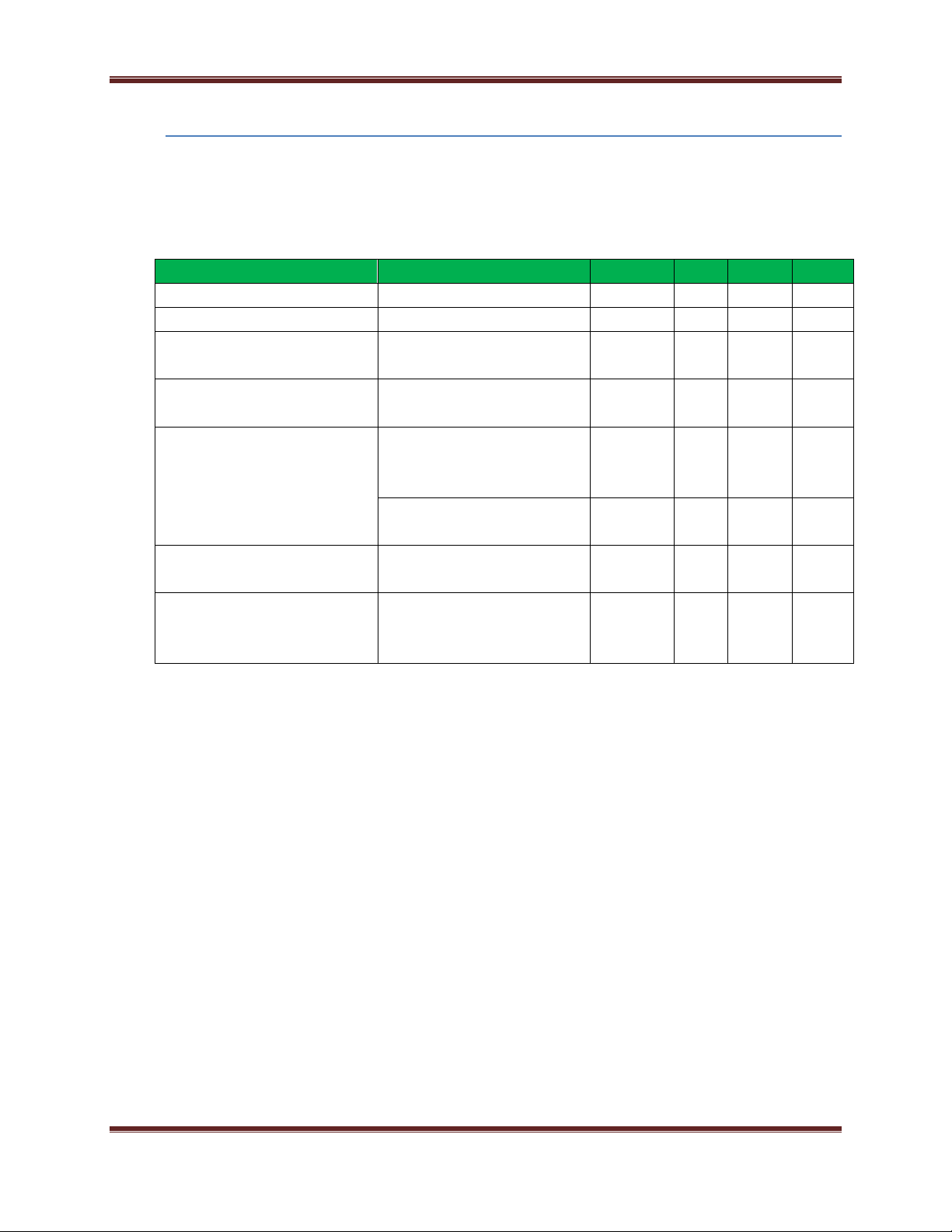
Parameter
Condition
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Input Low Voltage
0.3VDD
V
Input High Voltage
0.7VDD
V
Output high Voltage relative to
VDD
Sourcing 6mA, VDD=3.0V
95 %
Output low voltage relative to
VDD
Sourcing 6mA, VDD=3.0V
5 %
Output fall time
0.5 mA drive strength and load
capacitance CL=12.5-25pF.
20+0.1CL
250
ns
2 mA drive strength and load
capacitance CL=350-600pF.
20+0.1CL
250
ns
I/O pin hysteresis (VIOTHR+ Viothr-)
VDD=3 to 3.6V
0.1VDD
V
Pulse width of pulses to be
removed by the glitch
suppression filter
10 50
ns
GPIO Specifications
The XBee Wi-Fi modules have 14 GPIO (General Purpose Input Output) ports available. Those
available will depend on the module configuration as some GPIO’s are consumed by serial
communication, etc.
See GPIO section for more information on configuring and using GPIO ports
Electrical Specification for GPIO pads
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 13
Page 14
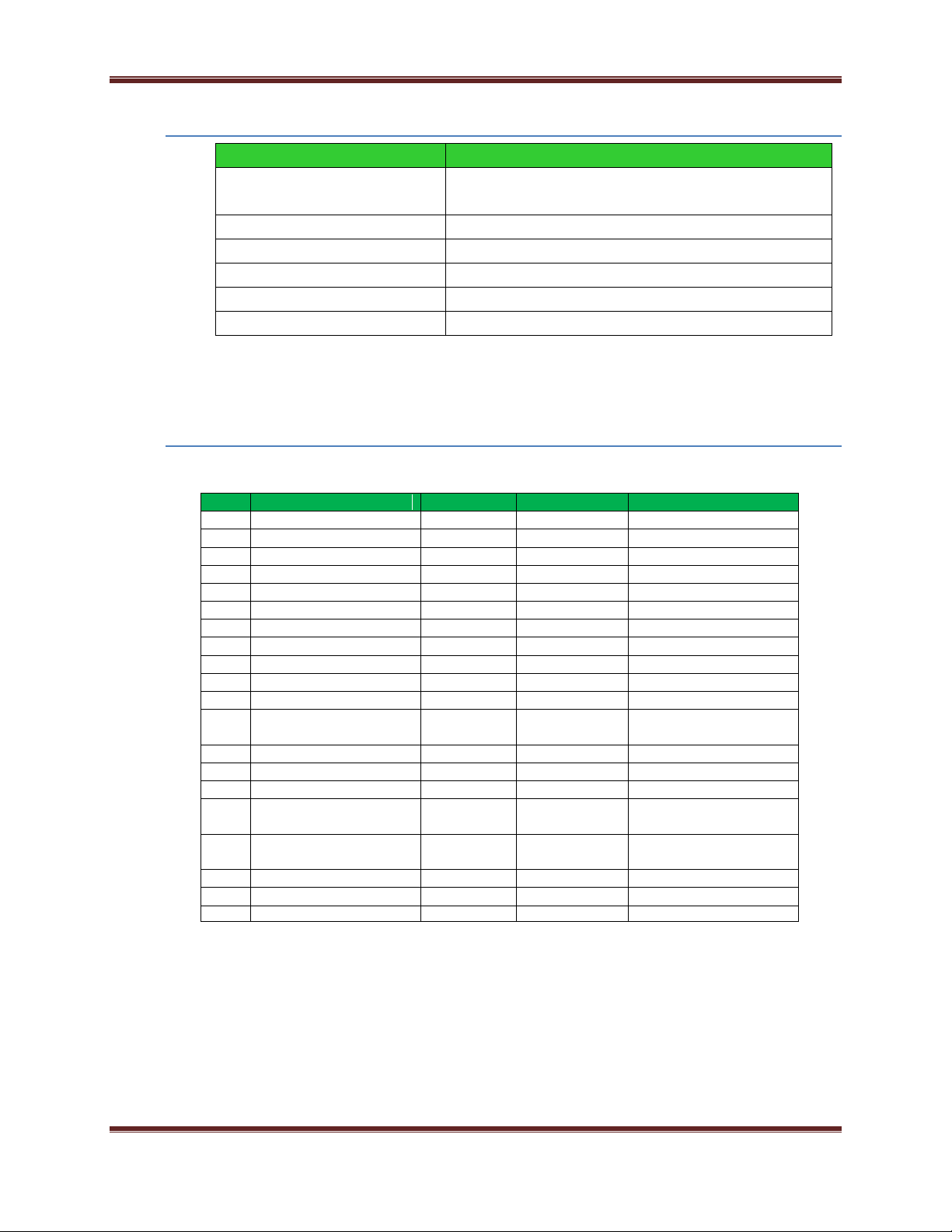
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Specification
XBee Wi-Fi
United States (FCC Part 15.247)
FCC ID: MCQ-XBS6
Industry Canada (IC)
IC: 1846A-XBS6
Europe (DC)
ETSI
Australia
Pending
Brazil
Pending
Japan
Pending
Pin #
Name
Direction
Default State
Description
1
VCC
- - Power Supply
2
DOUT/DIO13
Both
Output
UART Data out
3
Din/nConfig/DIO14
Both
Input
UART Data In
4
DIO12/SPI_MISO
Both
Output
GPIO/ SPI slave out
5
nRESET
Input
Module Reset
6
DIO10
Both
GPIO
7
DIO11
Both
GPIO
8
reserved
-
Disabled
Do Not Connect
9
nDTR/SLEEP_RQ/DIO8
Both
Input
Pin Sleep Control line /GPIO
10
GND
- - Ground
11
DIO4/AD4/SPI_MOSI
Both
GPIO/SPI slave In
12
nCTS/DIO7
Both
Output
Clear-to-Send Flow
Control/GPIO
13
On_nSLEEP/DIO9/SPI_nATTN
Output
Output
Module Status Indicator/GPIO
14
VREF
Input - NC
15
Associate/DIO5
Both
Output
Associate Indicator/GPIO
16
nRTS/DIO6
Both
Input
Request-to-Send Flow
Control/GPIO
17
AD3/DIO3/SPI_nSSEL
Both
Analog Input/GPIO/SPI Select
18
AD2/DIO2/SPI_CLK
Both
Analog Input/GPIO/SPI Clock
19
AD0/DIO0
Both
Analog Input/GPIO
20
AD1/DIO1
Both
Analog Input/GPIO
Agency Approvals
FCC Approval (USA) Refer to Chapter 12 FCC Requirements. Systems that contain XBee Wi-Fi modules inherit Digi
Certifications.
Pin Signals
Pin Assignment for the XBee Wi-Fi module
(Low‐asserted signals are distinguished with a lower case n before the signal name.)
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 14
Page 15
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Design Notes
The XBee modules do not specifically require any external circuitry or specific connections for
proper operation. However, there are some general design guidelines that are recommended
for help in troubleshooting and building a robust design.
Power Supply
Poor power supply can lead to poor radio performance especially if the supply voltage is not
kept within tolerance or is excessively noisy. To help reduce noise a 1uF and 8.2pF capacitor
are recommended to be placed as near to pin 1 on the PCB as possible. If using a switching
regulator for your power supply, switching frequencies above 500 kHz are preferred. Power
supply ripple should be limited to a maximum 50mV peak to peak.
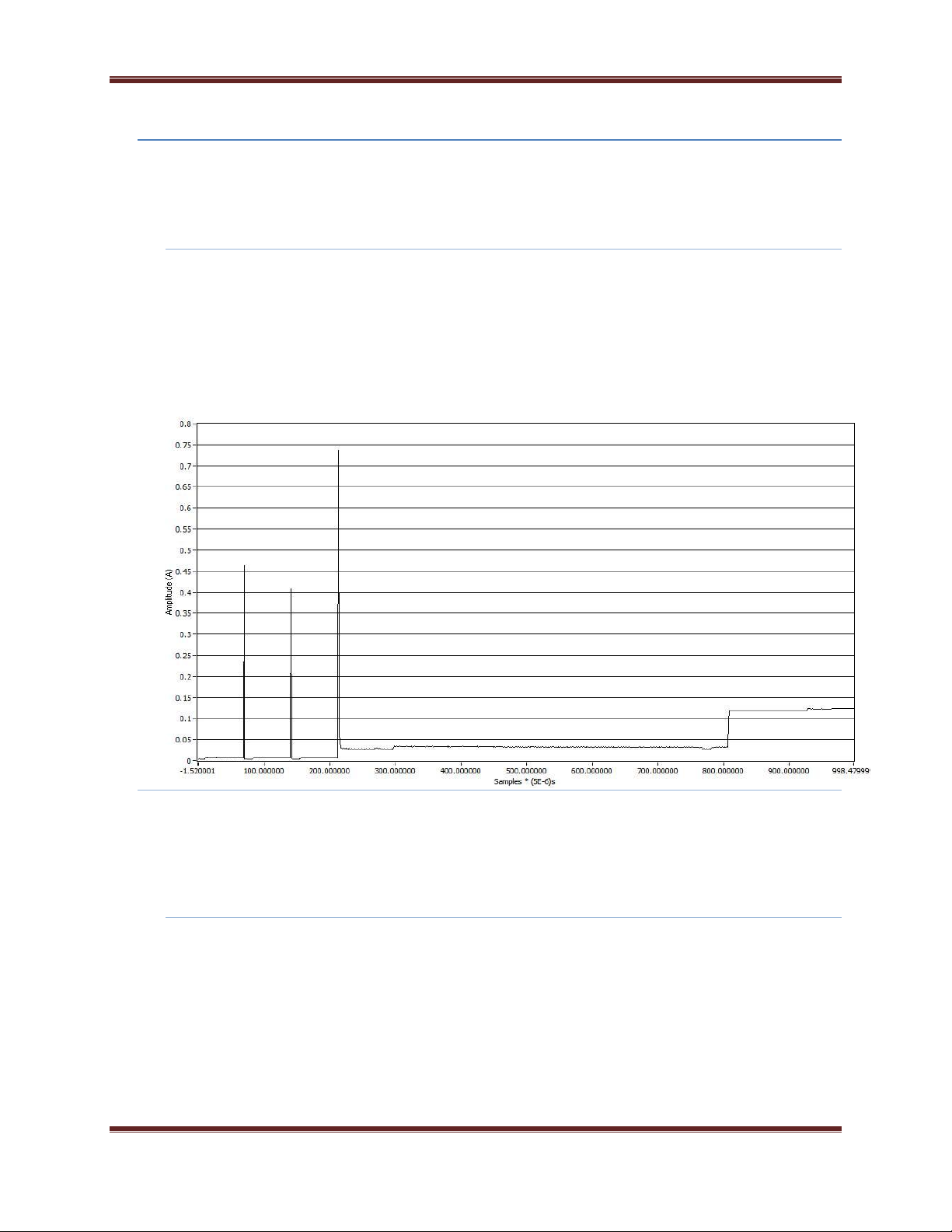
Typical start up current for the module is shown in the graph below:
Due to the fast nature of the current peaks, it is recommended that at least a 500uF capacitor
be placed on the VCC line. This will enable the XBee to start up with an acceptable voltage
slump in the power supply.
Recommended Pin Connections
The only required pin connections are VCC, GND, and either DOUT and DIN or SPI_CLK,
SPI_SSEL, SPI_MOSI, and SPI MISO. To support serial firmware updates, VCC, GND,
DOUT, DIN, RTS, and DTR should be connected.
All unused pins should be left disconnected. All inputs on the radio can be pulled high
with 30k internal pull-up resistors using the PR software command. No specific
treatment is needed for unused outputs.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 15
Page 16

Board Layout
The radios are also designed to be self sufficient and work with the integrated and
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
For applications that need to ensure the lowest sleep current, inputs should never be
left floating. Use internal or external pull-up or pull-down resistors, or set the unused
I/O lines to outputs.
Other pins may be connected to external circuitry for convenience of operation
including the Associate pin (pin 15) and the On_nSLEEP pin (pin 13) will change level or
behavior based on the state of the module.
XBee modules do not have any specific sensitivity to nearby processors, crystals or other
PCB components. Other than mechanical considerations, no special PCB placement is
required for integrating XBee radios except for those with integral antennas. In general,
Power and GND traces should be thicker than signal traces and be able to comfortably
support the maximum currents.
external antennas without the need for additional ground planes on the host PCB.
However, considerations should be taken on the choice of antenna and antenna
location. Metal objects that are near an antenna cause reflections and may reduce the
ability for an antenna to efficiently radiate. Using an integral antenna in an enclosed
metal box will greatly reduce the range of a radio. For this type of application an
external antenna would be a better choice.
External antennas should be positioned away from metal objects as much as possible.
Metal objects next to the antenna or between transmitting and receiving antennas can
often block or reduce the transmission distance. Some objects that are often overlooked
are metal poles, metal studs or beams in structures, concrete (it is usually reinforced
with metal rods), metal enclosures, vehicles, elevators, ventilation ducts, refrigerators
and microwave ovens.
Antennas should reside above or away from any metal objects like batteries, tall
electrolytic capacitors or metal enclosures. Antenna elements radiate perpendicular to
the direction they point. Thus a vertical antenna emits across the horizon.
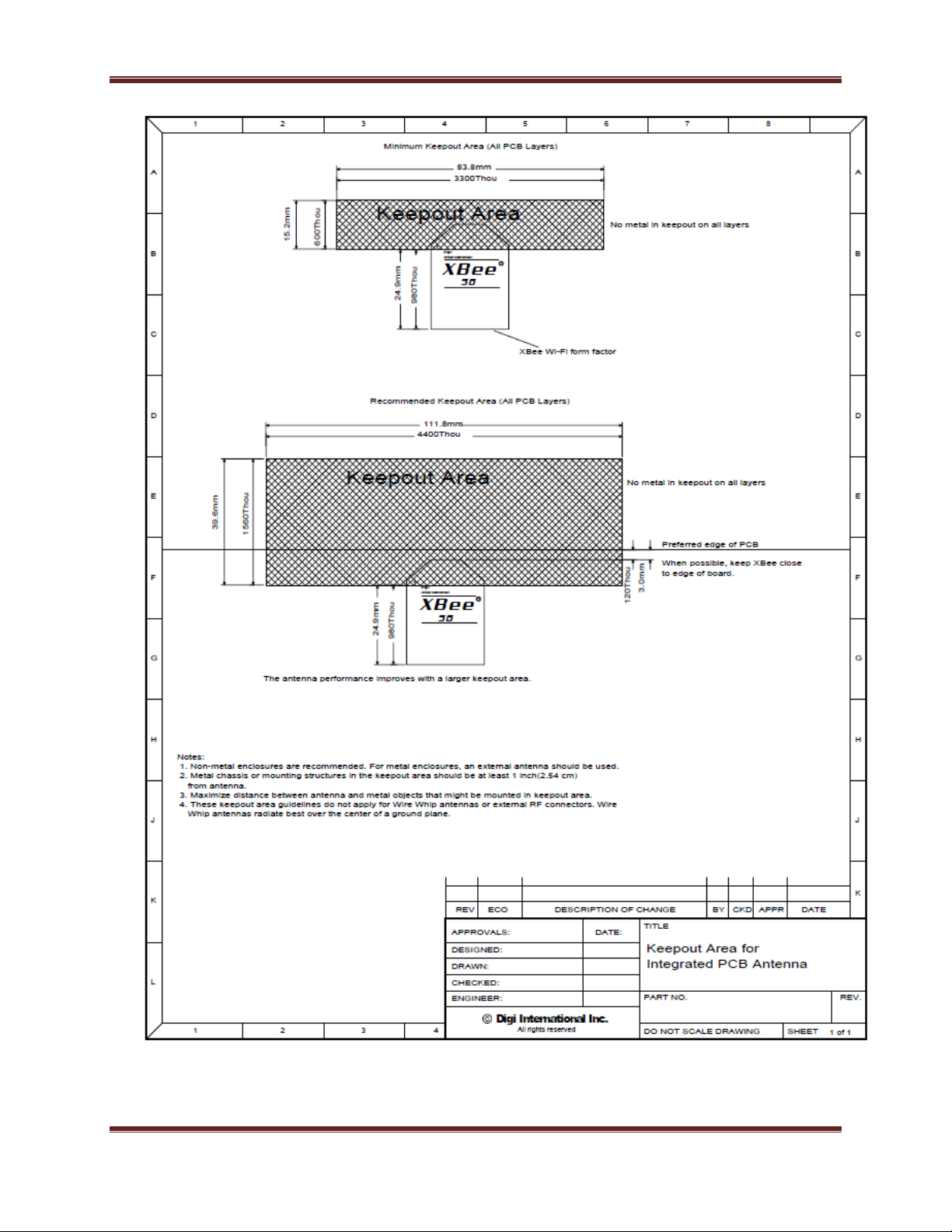
PCB Antennas should not have any ground planes or metal objects above or below the
module at the antenna location. For best results the module should be in a plastic
enclosure, instead of metal one. It should be placed at the edge of the PCB to which it is
mounted. The ground, power and signal planes should be vacant immediately below the
antenna section (See drawing for recommended keep out area).
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 16
Page 17
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 17
Page 18

Mounting Considerations
XBee modules were designed to mount into a receptacle (socket) and therefore do not require
any soldering when mounting to a board. The XBee Wi-Fi Development Kits contain 2 USB
interface boards which use two 10-pin receptacles to receive modules.
The receptacles used on Digi development boards are manufactured by Century Interconnect.
Several other manufacturers provide comparable mounting solutions; however, Digi currently
uses the following receptacles:
Through-hole single-row receptacles - Samtec P/N: MMS-110-01-L-SV (or equivalent)
Through-hole single-row receptacles - Mill-Max P/N: 831-43-0101-10-001000
Surface-mount double-row receptacles - Century Interconnect P/N: CPRMSL20-D-0-1 (or
equivalent)
Surface-mount single-row receptacles - Samtec P/N: SMM-110-02-SM-S
Digi also recommends printing an outline of the module on the board to indicate the
orientation the module should be mounted.
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 18
Page 19
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
2. RF Module Operation
Serial Communications
The XBee RF Modules interface to a host device through a logic-level asynchronous serial port, or
a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) port. Through its serial ports, the module can communicate
with any logic and voltage compatible UART or SPI; or through a level translator to any serial
device (for example: through a RS-232 or USB interface board).
UART Communications
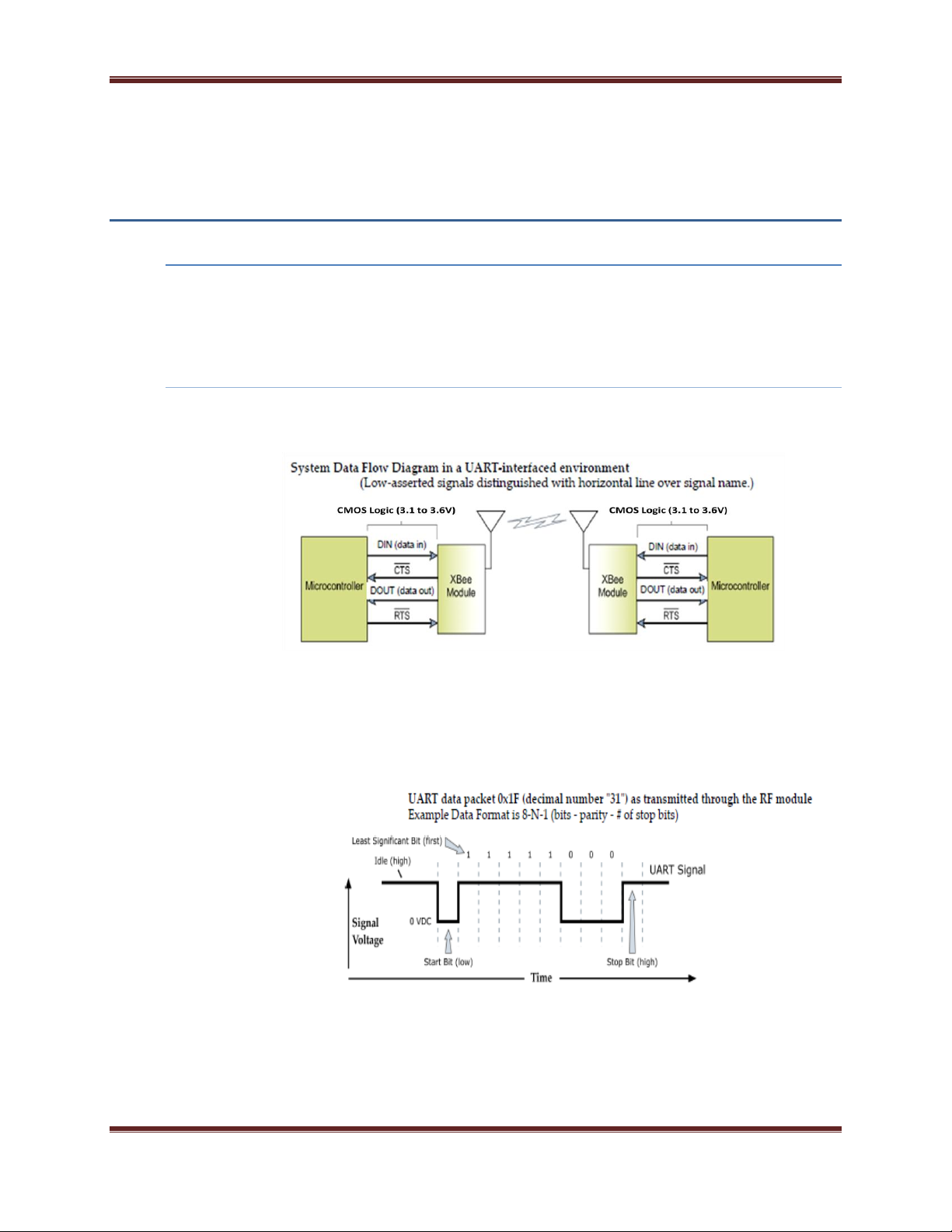
UART Data Flow
Devices that have a UART interface can connect directly to the pins of the RF module as shown in
the figure below.
UART Serial Data
Data enters the module UART through the DIN (pin 3) as an asynchronous serial signal. The signal
should idle high when no data is being transmitted.
Each data byte consists of a start bit (low), 8 data bits (least significant bit first) and a stop bit
(high). The following figure illustrates the serial bit pattern of data passing through the module.
Serial communications depend on the two UARTs (the microcontroller's and the RF module's) to
be configured with compatible settings (baud rate, parity, start bits, stop bits, data bits).
The UART baud rate, parity, and stop bits settings on the XBee module can be configured with
the BD, NB, and SB commands respectively. See the command table in chapter 10 for details.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 19
Page 20

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
SPI Communications
The XBee Wi-Fi module supports SPI communications in the slave mode. Slave mode receives the clock signal
and data from the master and returns data to the master. The SPI port uses the following signals on the XBee:
SPI_MOSI (Master Out, Slave In) – inputs serial data from the master
SPI_MISO (Master In, Slave Out) – outputs serial data to the master
SPI_SCLK (Serial Clock) – clocks data transfers on MOSI and MISO
SPI_nSSEL (Slave Select) – enables serial communication with the slave
SPI_nATTN(Attention) – Alerts the master that slave has data queued to send. The XBee module will
assert this pin as soon as data is available to send to the SPI master and it will remain asserted until
the SPI master has clocked out all available data.
In this mode the following apply:
SPI Clock rates up to 3.5 MHz are possible.
Data is MSB first
Frame Format mode 0 is used. This means CPOL=0 (idle clock is low) and CPHA=0 (data is sampled on
the clock’s leading edge). Mode 0 is diagramed below.
SPI port is setup for API mode and is equivalent to AP=1.
Frame Format for SPI communications
SPI mode is chip to chip communication. Digi does not supply SPI communication option on the Device
Development Evaluation Boards.
SPI mode is enabled by holding DOUT/DIO13 (pin 2) low while resetting the module until SPI_nATTN
asserts. By this means, the XBee Wi-Fi module will disable the UART and go straight into SPI
communication mode. Once configuration is completed, a modem status frame is queued by the module
to the SPI port which will cause the SPI_nATTN line to assert. The host can use this to determine that the
SPI port has been configured properly. This method internally forces the configuration for the AP, D2, D3,
D4, D9, and P2 commands as needed for SPI operations. As long as a WR command is not issued, these
configuration values will revert back to previous values after a power on reset. If, on the other hand, a
WR command is issued while in SPI mode, these same parameters will be written to flash. It is then the
user’s responsibility to set these parameters as appropriate
When the slave select (SPI_nSSEL) signal is asserted by the master, SPI transmit data is driven to the
output pin SPI_MISO, and SPI data is received from the input pin SPI_MOSI. The SPI_nSSEL pin has to be
asserted to enable the transmit serializer to drive data to the output signal SPI_MISO. A falling edge on
SPI_nSSEL causes the SPI_MISO line to be tri-stated such that another slave device can drive it, if so
desired..
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 20
Page 21
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
If the output buffer is empty, the SPI serializer transmits the last valid bit repeatedly, which may be either
high or low. Otherwise, the module formats all output in API mode 1 format, as described in chapter 7.
The attached host is expected to ignore all data that is not part of a formatted API frame.
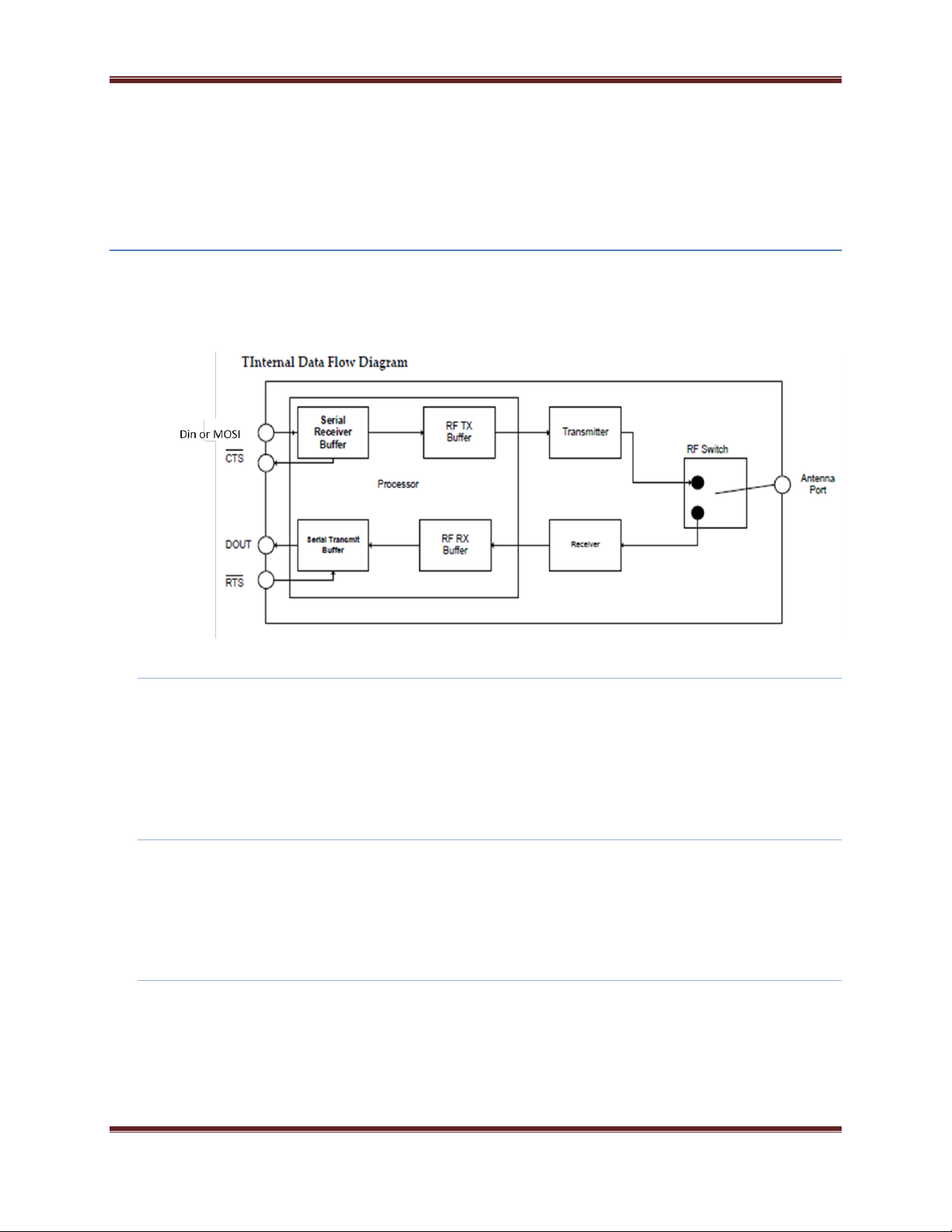
Serial Buffers
The XBee modules maintain buffers to collect received serial and RF data, which is illustrated in the figure
below. The serial receive buffer collects incoming serial characters and holds them until they can be
processed. The serial transmit buffer collects data that is received via the RF link that will be transmitted out
the UART or SPI port
Serial Receive Buffer
When serial data enters the RF module through the DIN Pin (or the MOSI pin), the data is stored in the
serial receive buffer until it can be processed. Under certain conditions, the module may not be able to
process data in the serial receive buffer immediately. If large amounts of serial data are sent to the
module such that the serial receive buffer would overflow, then the new data will be discarded. If the
UART is in use, this can be avoided by the host side honoring CTS flow control.
Serial Transmit Buffer
When RF data is received, the data is moved into the serial transmit buffer and sent out the UART or SPI
port. If the serial transmit buffer becomes full and system buffers are also full, then the entire RF data
packet is dropped. Whenever data is received faster than it can be processed and transmitted out the
serial port, there is a potential of dropping data, even in TCP mode.
UART Flow Control
The nRTS and nCTS module pins can be used to provide RTS and/or CTS flow control. CTS flow control
provides an indication to the host to stop sending serial data to the module. RTS flow control allows the
host to signal the module to not send data in the serial transmit buffer out the UAR. RTS and CTS flow
control are enabled using the D6 and D7 commands.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 21
Page 22
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
nCTS Flow Control
The FT command allows the user to specify how many bytes of data can be queued up in the serial
transmit buffer before the module asserts CTS low. The serial receive buffer can hold up the 2100 bytes,
but FT cannot be set any larger than 2083 bytes, leaving 17 bytes that can be sent by the host before the
data is dropped.
By default, FT is 2035 (0x7F3), which allows the host to send 65 bytes to the module after the module
asserts CTS before the data is dropped.
In either case, CTS will not be re-asserted until the serial receive buffer has FT-17 or less bytes in use.
nRTS Flow Control
If RTS flow control is enabled (D6 command), data in the serial transmit buffer will not be sent out the
DOUT pin as long as nRTS is de-asserted (set high). The host device should not de-assert nRTS for long
periods of time to avoid filling the serial transmit buffer. If an RF data packet is received, and the serial
transmit buffer does not have enough space for all of the data bytes, the entire RF data packet will be
discarded.
Note: If RTS flow control is enabled and the XBee is sending data out the UART when nRTS is de-asserted
(set high), the XBee could send up to 4 characters out the UART to clear its FIFO after nRTS is de-asserted.
This implies that the user needs to de-assert nRTS by the time its receive capacity is within 4 bytes of full.
Serial Interface Protocols
The XBee modules support both transparent and API (Application Programming Interface) serial
interfaces.
Transparent Operation
When operating in transparent mode, the modules act as a serial line replacement. All UART
data received is queued up for RF transmission. When RF data is received, the data is sent out
through the UART. The module configuration parameters are configured using the AT command
mode interface. Please note that transparent operation is not an option when using SPI.
Data is buffered in the serial receive buffer until one of the following causes the data to be
packetized and transmitted:
No serial characters are received for the amount of time determined by the RO
parameter. If RO is zero, data is packetized as soon as it is received, without delay.
If RO is non-zero, the data is packetized after RO character times of no transitions
on the DIN pin. However, if the time required for RO characters is less than 100
microseconds, then DIN must still be idle for at least 100 microseconds, which is the
minimal idle time required for packetizing packets at any baud rate.
The Command Mode Sequence (GT + CC + GT) is received. Any character buffered in
the serial receive buffer before the sequence is packetized and transmitted before
command mode is entered.
The maximum number of characters that will fit in an RF packet is received.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 22
Page 23

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Transparent Operation Features
Simple Interface
All received serial data is transmitted unless the module is in command mode.
Easy to support
It is easier for an application to support transparent operation and command mode.
API Operation Features
Easy to manage data
transmissions to multiple
destinations
Transmitting RF data to multiple remotes only requires changing the address in the
API frame. This Process is much faster than transparent operation where the
application must enter AT command mode, change the address, exit command mode,
and then transmit data. Each API transmission can return a transmit status frame
indicating the success or reason for failure
Received data frames
indicate the sender's
address
All received RF data API frames indicate the source address.
Advanced Networking
diagnostics
API frames can provide indication of IO samples from remote devices, transmission
status messages, and local radio status messages.
API Operation
API operation is an alternative to transparent operation. The frame-based API extends the level
to which a host application can interact with the networking capabilities of the module. When in
API mode, all data entering and leaving the UART or SPI is contained in frames that define
operations or events within the module.
Transmit Data Frames (received through the DIN pin (pin 3) or SPI_MOSI (pin 11 )) include:
RF Transmit Data Frame
Local commands (equivalent to AT commands)
Remote commands to be sent to another radio
Receive Data Frames (sent out the DOUT pin (pin 2) or SPI_MISO (pin 4 )) include:
RF-received data frames
Local command responses
Remote command responses
I/O samples from a remote radio
Event notifications such as transmission status, reset, associate, disassociate, etc.
The API provides an alternative means of configuring modules and of routing data at the local
host application layer. A local host application can send data frames to the module that contain
address and payload information instead of using command mode to modify addresses. The
module will send data frames to the application containing status packets; as well as source, and
payload information from received data packets. The API operation option facilitates many
operations such as the examples cited below:
Transmitting data to multiple destinations without entering Command Mode
Receive success/failure status of each transmitted RF packet
Identify the source address of each received packet
A Comparison of Transparent and API Operation
The following table compares the advantages of transparent and API modes of operation:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 23
Page 24

Remote Configuration
Set/read configuration commands can be sent to remote devices to configure them
as needed using the API.
As a general rule of thumb, API firmware is recommended when a device:
If the above conditions do not apply, (e.g. in a sensor node, or a simple application) then
transparent operation might be suitable. It is acceptable to use a mixture of devices
running API mode and transparent mode in a network.
Modes of Operation
Idle Mode
When not receiving or transmitting data, the RF module is in Idle Mode. The module
shifts into the other modes of operation under the following conditions:
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
sends RF data to multiple destinations
sends remote configuration commands to manage devices in the network
receives IO samples from remote devices
receives RF data packets from multiple devices, and the application needs to
know which device sent which packet
Transmit Mode (Serial data in the serial receive buffer is ready to be packetized)
Receive Mode (Valid RF data is received through the antenna)
Sleep Mode
Command Mode (Command Mode Sequence is issued)
Transmit Mode
When serial data is received and is ready to be packetized, the RF module will exit Idle
Mode and attempt to transmit the data. The destination address determines which
node(s) will receive the data.
Receive Mode
If a valid RF packet is received, the data is transferred to the serial transmit buffer.
Command Mode
To modify or read RF Module parameters, the module must first enter into Command
Mode - a state in which incoming serial characters are interpreted as commands. Refer
to the API Operation chapter for an alternate means of configuring modules, which is
the only method available for SPI mode. (Command mode is unavailable when using the
SPI interface.)
AT Command Mode
To Enter AT Command Mode:
Send the 3-character command sequence “+++” and observe guard times before and
after the command characters. [Refer to the “Default AT Command Mode Sequence”
below.]
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 24
Page 25

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Default AT Command Mode Sequence (for transition to Command Mode):
No characters sent for one second [GT (Guard Times) parameter = 0x3E8]
Input three plus characters (“+++”) within one second *CC (Command Sequence
Character) parameter = 0x2B.]
No characters sent for one second [GT (Guard Times) parameter = 0x3E8]
Once the AT command mode sequence has been issued, the module sends an "OK\r"
out the UART. The "OK\r" characters can be delayed if the module has not finished
transmitting received serial data.
When command mode has been entered, the command mode timer is started (CT
command), and the module is able to receive AT commands on the UART or SPI port.
All of the parameter values in the sequence can be modified to reflect user preferences.
NOTE: Failure to enter AT Command Mode is most commonly due to baud rate
mismatch. By default, the BD (Baud Rate) parameter = 3 (9600 bps).
To Send AT Commands, send AT commands and parameters using the syntax shown
below:
To read a parameter value stored in the RF module’s register, omit the parameter field.
The preceding example would change the RF module baud rate to 7, which would allow
operation at 115,200bps. To store the new value to non-volatile (long term) memory,
subsequently send the WR (Write) command.
For modified parameter values to persist in the module’s registry after a reset, changes
must be saved to non-volatile memory using the WR (Write) Command. Otherwise,
parameters are restored to previously saved values after the module is reset.
Command Response
When a command is sent to the module, the module will parse and execute the
command. Upon successful execution of a command, the module returns an “OK”
message. If execution of a command results in an error, the module returns an “ERROR”
message.
Applying Command Changes
Any changes made to the configuration command registers through AT commands will
not take effect until the changes are applied. For example, sending the BD command to
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 25
Page 26

Sleep Mode
Sleep modes allow the RF module to enter states of low power consumption when not in use.
The XBee Wi-Fi modules support both pin sleep (sleep mode entered on pin transition) and
cyclic sleep (module sleeps for a fixed time). XBee sleep modes are discussed in detail in chapter
5.
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
change the baud rate will not change the actual baud rate until changes are applied.
Changes can be applied in one of the following ways:
The AC (Apply Changes) command is issued.
AT command mode is exited.
To Exit AT Command Mode:
1. Send the ATCN (Exit Command Mode) command (followed by a carriage return).
[OR]
2. If no valid AT Commands are received within the time specified by CT (Command
Mode Timeout) Command, the RF module automatically returns to Idle Mode.
For an example of programming the RF module using AT Commands and descriptions
of each configurable parameter, please see the Command Reference Table chapter.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 26
Page 27

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
3. 802.11 bgn Networks
Infrastructure Networks
The main type of wireless network will involve a number of wireless devices (called
stations) talking through a master wireless device known as an Access Point (AP for
short). This type of setup is called an Infrastructure or BSS (Basic Service Set) network.
Most wireless networks are of this type. An example of an infrastructure wireless
network is shown below:
Infrastructure Wireless Network
Ad Hoc Networks
Wireless devices can get on a wireless network without an access point. This is called an
Ad Hoc or IBSS (Independent Basic Service Set) network. An example of an ad hoc
wireless network is shown below:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 27
Page 28

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Network Basics
Clients will need to join the wireless network before they can send data across it. This is
called Association. In order for a device to associate it must know the following items about
the desired wireless network:
SSID: the name of the wireless network.
Encryption: if and how the network encrypts or scrambles its data.
Authentication: how and if the network requires its members to ―prove their identity.
Channel: what channel (frequency range) the wireless network uses.
Once a device is associated it can send and receive data from other associated devices on
the same network. When the client is done or needs to leave, it then can Dis-associate and
be removed from the wireless network.
XBee® Wi-Fi Standards
The XBee Wi-Fi module will operate in three of the available 802.11 standards.
802.11 b
The 802.11b standard was approved in July 1999 and can be considered the second
generation. 802.11b operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency ISM band. The data rate is from
1 to 11 Mbps.
802.11 g
The 802.11g standard was approved in 2003. It provides a maximum data rate of 54
Mbps. In addition, the standard is also fully backwards-compatible with existing 802.11b
wireless networks.
802.11 n
The 802.11n standard was approved in 2009. It provides for data rates up to 300Mbps.
The XBee® Wi-Fi module uses the single stream n mode with 20MHz bandwidth and is
capable of 65 Mbps over the air in n mode.
Encryption
Encryption is a method of scrambling a message that makes it unreadable to unwanted
parties, adding a degree of secure communications. There are different protocols for
providing encryption, and the XBee Wi-Fi module supports WPA, and WPA2.
AUTHENTICATION
Authentication deals with proving the identity of the wireless device attempting to
associate with the network. There are different methods of doing this. The XBee Wi-Fi
module supports Open and Shared Key.
Open
Open Authentication is when the access point simply accepts the wireless devices
identify without verifying or proving it. The benefits to this is simplicity and compatibility
(all devices can do it).
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 28
Page 29

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Shared Key
Shared Key is when the wireless devices must present the proper key to get on the
network. Although Shared Key has more security than Open Authentication it should
not be considered secure. One of the benefits of Shared Key Authentication is simplicity.
CHANNELS
The XBee® Wi-Fi modules operate in the 2.412-2.484 MHz range. The frequency range is
broken down into 14 channels. Data is transmitted on a channel by radio frequencies
over a certain frequency range. In order to avoid bad performance caused by the
overlapping (“collision”) of channel frequencies in a wireless LAN environment, it is very
important that the channels of neighboring access points are selected accordingly.
The center frequencies of the 14 possible channels range from 2.412 GHz to 2.484 GHz,
with each channel being 22 MHz wide and centered in 5 MHz intervals. This means that
only 3 channels (1, 6, and 11) in North America are not subject to overlapping.
4. XBee IP Services
The XBee provides services using IP (Internet Protocol) for XBee and other clients on the
network. IP services provide functionality to allow XBee configuration and direct serial port
access. There are two XBee services:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 29
Page 30

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
XBee Application Service
Serial Communication Service
XBee Application Service
This service primarily provides for XBee configuration. It also provides API compatibility
for customers who have designed around other XBee’s. It uses UDP to transfer packets
on port number 0xBEE. Packets are optionally acknowledged by the service but retries
are not available. An extra header is added to the packet data to define commands for
configuration and serial data transfer. The following sections describe how this service
can be accessed from a local host or network client.
Local Host
From a local host this functionality is accessed through XBee API frames. There are
remote AT command frames as well as transmission frames. The API frames are listed
as follows:
TX request: 64-bit (TX64)
RX indicator: 64-bit (RX64)(This frame is generated by the XBee module.)
Remote AT command
TX64 and RX64 API frames
The intent of the XBee transmit and receive 64-bit API frames is to provide a
standardized set of API frames to use for a point to multipoint network—a
closed network of XBee Wi-Fi modules. These frames are compatible with the
XBee 802.15.4 module.
Transmitting data
The local host uses the TX64 frame to send data to another XBee using this
service. When the frame is received through the serial port the XBee converts
the contents of the frame to a serial data transfer command as defined by the
XBee application service.
Receiving data
A received Serial data transfer command will go to the serial port. The mode of
the serial port will determine the format of the data. When in API mode the
data will be sent to the host using the RX 64-bit frame.
Note: It is not recommended to use this service to send data to a network client.
Use the serial communication service.
Remote AT command configuration
The Remote AT command frame is used to change configuration on a remote Xbee. See
Remote AT command frame in the API Operation chapter for more information.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 30
Page 31

Field
Name
Offset
Description
Command
ID
0
Serial Data:0x0
Remote AT command:0x2 Application acknowledgements are not supported
Serial Data Acknowledgement: 0x80 Sent in response to option bit 1 sent for the Serial Data
command
Serial Data Acknowledgement: 0x80
Remote AT command response:0x82
Command
options
1
Packet Fields
Offset
Example
Description
Client Packet Data
Command
ID
0 0x02
Command
options
1
0
Options are not available for this command
Command
Specific
Data
Frame ID 2 0x01
This is provided for application support and is not used by the
XBee. The value will be sent back as part of the response
packet.
Configuration
options
3
0x02
0 – Queue command parameter. Must send AC command or
use option 2 to apply changes.
2 – Apply changes to all changed commands
AT Command
MSB 4
0x49 (I)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify the AT
command
LSB 5
0x44(D)
Parameter Value
If present, indicates the requested parameter value to set the
given command. If no characters present, command is
queried.
Network Client
This port is accessed by sending a packet from the client using the UDP protocol on port 0xBEE.
Data sent to this port must have an additional header preceding the data. The header
description follows:
Sending configuration commands
AT commands can be sent to the XBee Wi-Fi module from a network client. The following packet
structure must used to send the command.
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
The response will be sent back to the host with the following bytes.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 31
Page 32

Packet Fields
Offset
Example
Description
Client Packet Data
Command ID
0
0x82
Command
Options
1
0x00
Options not available for this response
Command
Specific Data
Frame ID
3
0x01
Copied from the command
Configuration
command options
3
0x88
Options not available for this response
AT Command
MSB 5
0x49 (I)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify
the AT command
LSB 6
0x44 (D)
Status 0x00
0 = OK
1 = ERROR
2 = Invalid Command
3 = Invalid Parameter
Parameter Value
7
The first
byte of
the ID
value
would
start here
Register data in binary or ASCII format, based on the
command. For the ID command, the data is in ASCII
format. If the command was set, then this field is not
returned.
Packet Fields
Offset
Example
Description
Client Packet data
Command ID
0
0
Command
Options
1
0x2
bit 1 - Request acknowledgment be sent.
Command
Specific Data
Serial Data
3
0x01
Can be up to 1400 bytes. Data will be sent out the
XBee's serial port.
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Sending serial data command to XBee
Using this service to send data out the serial port is not required. Most users will choose to use
the Serial Communication Service (see below) for sending data from a network client. One
reason to use the XBee Application Service to send the serial data command from a network
client is to receive an acknowledgment when sending a UDP packet.
The client can request an acknowledgement from the XBee but must wait to receive the
acknowledgement before sending the next packet. The client is responsible for retransmissions
due to missed acknowledgments. When resending packets, duplicates can be received at the
destination due to a successful serial data command and a failed acknowledgment packet. The
host in this case must be able to handle duplicate packets.
Serial Data Command:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 32
Page 33

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Packet Fields
Offset
Example
Description
Client Packet Data
Command ID
0
0x80
Command
Options
1
0x0
Options not available for this response
Command
Specific Data
No command specific data
X
B
e
e
P
a
c
k
e
t
D
a
t
a
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
Command ID
0
0x04
Command
Options
1
0x00
Options not available for this response
Command
Specific Data
Number Samples
3
0x01
Will be set to one. DIO and ADC considered a sample. At
least one DIO or ADC must be enabled to get this packet
type.
Digital Mask
MSB 4
0x00
Bit Mask. Each bit represents an enabled DIO I/O line
starting with DIO0 at bit 0.
LSB 5
0x01
Analog Mask
6
0x02
Bit Mask. Each bit represents an enabled ADC starting
with ADC0 at bit 0.
Digital Sample
MSB 7
0x00
This field is only present if at least one DIO I/O is
enabled. Use the digital mask to determine if sample is
present. Each bit represents a DIO line start with bit 0 for
DIO0.
LSB 8
0x01
Analog Sample
MSB 9
0x01
Analog Samples start here and will be in order as
indicated in the Analog Mask. Only those lines enabled
will be sent. In the example this sample is for AD1.
LSB 10
0x00
Supply Voltage
11
0xC1C
Indicates that the supply voltage is 0xC1C = 3100
(decimal) mV = 3.1V on the radio that sent the I/O
sample
Serial Data command acknowledgment if requested:
Receiving I/O sampled data
Sample data generated by the module will be sent to the address configured by the DL
commands. This data can be sent to either XBee or a network client. It will be sent using UDP on
the 0xBEE port as with other XBee Application services. Sample data will be received by the
client as follows:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 33
Page 34

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Serial Communication Service
A client or XBee can send data directly to the serial port using this service. No additional header
or formatting is required. The port is configured using the C0 command. The behavior of this
service varies based on the mode of the serial port and is discussed in the following sections.
Transparent mode
Only one port is available and can be either UDP or TCP. It is configured through the IP
command. Data received by the service is sent to the serial port without any additional
processing.
UDP
When the IP command is configured for UDP, data received on the serial
port will be packetized and sent to the IP address specified by the DL
command and to the destination port specified by the DE command.
The source port is defined by the C0 command.
TCP
TCP provides for a connection based protocol. When in transparent
mode the module will only allow one connection at a time. A
connection can be initiated by a local host or by a network client.
A local host initiates a connection by sending data to the serial port. A
connection will be created based on the DL (IP address) and DE
(destination port) commands.
A network client establishing a TCP connection to the XBee will use the
port defined by the C0 command. When established any data sent by
the local host will not create a new connection based on DL and DE, but
rather the existing connection will be utilized.
API mode
Because API mode has more capabilities both UDP and TCP are supported at the
same time. The local host will utilize the TX IPv4 transmit frame to send data
from the module and will receive data through the RX IPv4 received frame.
These frames give greater IP control and visibility to the local host. See the API
section for more information.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 34
Page 35

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
5. Sleep
The XBee Wi-Fi module supports two different sleep modes.
Pin Sleep
Cyclic Sleep
In addition the sleep mode current draw can be modified with the following sleep options.
AP Associated Sleep
Deep Sleep
Pin sleep allows an external microcontroller to determine when the XBee should sleep and when it
should wake by controlling the Sleep_RQ pin when using the UART or SPI_nSSEL when using SPI. In
contrast, cyclic sleep allows the sleep period and wake times to be configured through the use of AT
commands or through the DTIM setting on the access point (associated sleep). The module can stay
associated to the access point or can enter a deeper sleep and associate to the access point for each
sleep/wake occurrence. The sleep mode is configurable with the SM and SO commands.
Besides the four sleep modes mentioned above, each of them operate a little differently based on
the serial interface (UART or SPI).
Sleeping with the UART
When the serial interface is UART, the On/nSleep pin is used to indicate that the module is entering
sleep mode, unless pin 13 is configured for a different usage. (See command reference table) If D9
is configured for On/nSleep, then it is driven low when asleep and high when awake, whether using
pin sleep or cyclic sleep.
If CTS hardware flow control is enabled (D7 command), the CTS pin (pin 12) is de-asserted (high)
when entering sleep to indicate that serial data should not be sent to the module. The module will
not respond to serial or RF data when it is sleeping. Applications that utilize the UART are
encouraged to observe CTS flow control in any of the sleep modes. When the XBee wakes from
sleep with flow control enabled, the CTS pin is asserted (low).
If using pin sleep, D8 (mapped to XBee pin 9) must be configured for SleepRq (See command
reference table) to put the module to sleep. Otherwise, there is no sleep at all, meaning the module
will always stay awake in full power mode. When D8 is configured for SleepRq, the host should
drive pin 9 high to wake the module up and the host should drive pin 9 low to wake the module up.
Sleeping with the SPI
When the serial interface is SPI, pin 13 is used as an attention indicator to tell the SPI master when it
has data to send. Since SPI only operates in API mode, it will assert SPI/nATTN and send out a
modem status indicator after initialization. The host can use this to know when the radio is ready to
operate as a SPI slave. Since the function of pin 13 is to indicate when the XBee has data to send to
the host, it may legitimately be driven high or low while the module is awake. Therefore, there is no
equivalent to the On/nSleep indicator when using the SPI.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 35
Page 36

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
SPI_SSEL (pin 17) is the equivalent of SleepRq for the SPI interface. The SPI master drives pin 17 low
not only to indicate that the XBee is selected as the active slave, but also to indicate that the XBee
should wake up. When the SPI master drives pin 17 high, that gives the XBee license to go back to
sleep, which it will do after data is clocked out.
Sleep Options
AP Associated sleep
This option allows the module to sync up with beacons sent from the AP which contains
the DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message). The DTIM indicates when broadcast and
multicast data will be sent on the network. This property is configured on the AP and is
typically configured as a number that sets up an interval of beacon sent between
beacons with DTIM.
The sleep modes are described as follows with this option enabled.
Pin sleep mode
The module remains associated to the AP and will wake based on the period of the
DTIM. This wake period will not be seen by the local host unless data has been sent to
the module. In this case the module will ‘wake’ by asserting the appropriate I/O lines.
The local UART host is then required to de-assert SleepRq to awaken the module. Note
that the module will be drawing more current when waiting for the host to de-assert
SleepRq. Once SleepRq is de-asserted the module will then send the data to the host.
SPI operation is similar except that the radio asserts nATTN when data becomes
available and then the local host is expected to assert SPI_SSEL and to provide a clock
until the data available is sent out.
When the local UART host needs to send data it de-asserts SleepRq. Once the
appropriate status I/O lines are asserted (CTS and/or On/nSleep) the module is ready to
accept data. However data will be queued and not sent until the next DTIM.
When the local SPI host needs to send data it asserts nATTN. This wakes up the module,
which will then accept the incoming data. However data will be queued and not sent
until the next DTIM.
Cyclic sleep mode
The module remains associated to the AP and will sleep based on the period of the
DTIM. After DTIM, the module will awaken for 30 milliseconds to check for data from
the AP and to allow the host to send data or commands. This time is factored in as part
of the overall ST time. When data is received or sent then the module will remain
awake for ST time and any further activity will not restart this time. The module will
draw the RX current during the wake period.
Deep sleep (non-associated sleep)
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 36
Page 37

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
This option allows the Wi-Fi circuitry to be power down resulting in the lowest sleep
current but at the expense of longer wake up times. This is due to the module
associating with the access point every time it wakes up. The intent of this option is to
allow for very long sleep times.
Pin sleep mode
In this mode when SleepRq _RQ is asserted the module will power down the Wi-Fi
circuitry. When SleepRq is de-asserted the Wi-Fi circuitry is powered up. This causes
the module to associate to the access point for each wake event. The module could
take many seconds to complete the association and longer if DHCP is used.
Cyclic sleep mode
In this mode the module will enter and exit sleep based on the SP and ST commands.
The module will control power to the Wi-Fi circuitry as it cycles through sleep and wake.
This causes the module to associate to the access point for each wake event. The
module could take many seconds to complete the association and longer if DHCP is
used. However to control battery usage, ST specifies and limits the wake time. If ST
expires before association is successful, sleeping is resumed without ever associating. It
is the user’s responsibility to configure ST as needed. Also, the user should wait for
association after waking up before sending data. When data is sent by the local host
then the module will remain awake for ST time and any further activity will not restart
this time. The module will draw RX current during the wake period.
Sampling data using sleep modes
Data can be sampled when waking from any sleep mode by enabling an ADC or digital input and
setting IR appropriately with respect to ST to obtain the desired number of samples.
Sample Rate (ATIR)
If multiple samples are wanted during the wake period then IR can be used. This will
provide ST/IR+1 samples. Each sample will be sent separately.
Wake Host
Wake host parameter (ATWH) delays UART and sample data from being initiated until
the timer has expired. This allows the host to wake up before receiving data or a sensor
to power up before an I/O sample is taken.
Digital outputs and special function outputs such as ON_SLEEP and CTS are not affected
by WH. This is to allow these signals to be used to wake up devices.
Note that for deep sleep, both WH must be expired and the module must be associated
before I/O samples are taken.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 37
Page 38

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Pin name(s)
Module pin
AT cmd
Command Range
DIO12/SPI_MISO
4
P2
0,1,3-5
DIO10
6
P0
0,3-5
DIO11
7
P1
0,3-5
DIO8/nDTR/SLEEP_RQ
9
D8
0-5
DIO4/AD4/SPI_MOSI
11
D4
0-5
DIO7/nCTS
12
D7
0,1,3-7
DIO9/ON_nSLEEP/SPI_nATTN
13
D9
0,1,3-6
DIO5/ASSOCIATE
15
D5
0,1,3-5
DIO6/nRTS
16
D6
0,1,3-5
DIO3/AD3/SPI_nSSEL
17
D3
0-5
DIO2/AD2/SPI_CLK
18
D2
0-5
DIO1/AD1
19
D1
0-5
DIO0/AD0
20
D0
0-5
Pin Command Parameter
Description
0
Disabled
1
Peripheral control
2
Analog
3
Data in monitored
4
Data out default low
5
Data out default High
6
RS485 enable low/SPI_nATTN
7
RS485 enable high
>7
Unsupported
6. XBee Analog and Digital IO Lines
XBee-PRO Wi-Fi firmware supports a number of analog and digital IO pins that are configured
through software commands. Analog and digital IO lines can be set or queried. The following
table lists the configurable IO pins and the corresponding configuration commands.
IO Configuration
To enable an analog or digital IO function on one or more XBee module pin(s), the appropriate
configuration command must be issued with the correct parameter. After issuing the configuration
command, changes must be applied on the module for the IO settings to take effect. Pull-up
resistors can be set for each digital input line using the PR command. The PR value updates the state
of all pull-up resistors.
IO Sampling
The XBee ZB modules have the ability to monitor and sample the analog and digital IO lines. IO
samples can be read locally or transmitted to a remote device to provide indication of the
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 38
Page 39

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Bytes
Name
Description
1
Sample Sets
Number of sample sets in the packet. (Always set to 1.)
2
Digital Channel mask
Digital IO line on the module.
bit 0 = DIO0
bit 1 = DIO1
bit 2 = DIO2
bit 3 = DIO3
bit 4 = DIO4
bit 5 = DIO5
bit 6 = DIO6
bit 7 = DIO7
bit 8 = DIO8
bit 9 = DIO9
bit 10 = DIO10
bit 11 = DIO11
bit 12 = DIO12
For example, a digital channel mask of 0x002F means
DIO0 1, 2, 3, and 5 are enabled as digital IO.
1
Analog Channel Mask
Indicates which lines have analog inputs enabled for
sampling. Each bit in the analog channel mask
corresponds to one analog input channel.
• bit 0 = AD0
• bit 1 = AD1
• bit 2 = AD2
• bit 3 = AD3
• bit 4 = AD4
Variable
Sampled Data Set
If any digital IO lines are enabled, the first two bytes of
the data set indicate the state of all enabled digital IO.
Only digital channels that are enabled in the Digital
Channel Mask bytes have any meaning in the sample
set. If no digital IO is enabled on the device, these 2
bytes will be omitted.
Following the digital IO data (if any), each enabled
analog channel will return 2 bytes. The data starts with
AD0 and continues sequentially for each enabled analog
input channel up to AD4, and the supply voltage at the
end.
current IO line states. (Only API firmware devices can send remote IO sample data out their
UART or SPI ports.)
There are three ways to obtain IO samples, either locally or remotely:
•Queried Sampling
•Periodic Sampling
•Change Detection Sampling.
IO sample data is formatted as shown in the table below
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 39
Page 40

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Example
Sample AT Response
0x01
[1 sample set]
0x0C0C
[Digital Inputs: DIO 2, 3, 10, 11 selected]
0x03
[Analog Inputs; A/D 0,1]
0x0408
[Digital input states: DIO 3,10 high, DIO 2,11 low]
0x03D0
[Analog input ADIO 0=0x3D0]
0x0124
[Analog input ADIO 1=0x120]
0x0CC9
Voltage source is 0xCC9mV = 3.273 volts
The sampled data set will include 2 bytes of digital IO data only if one or more IO lines on the
device are configured as digital IO. If no pins are configured as digital IO, these 2 bytes will be
omitted.
The digital IO data is only relevant if the same bit is enabled in the digital IO mask.
Analog samples are 10 bit values and aligned on a 16 bit boundary. The analog reading is scaled
such that 0x0000 represents 0V, and 0x3FF = 3.0V. The analog inputs on the module are capped
at 0x3FF. Analog samples are returned in order starting with AD0 and finishing with AD4, and
the supply voltage. Only enabled analog input channels return data as shown in the figure
below.
To convert the A/D reading to mV, do the following:
AD (mV) = (A/D reading (converted to decimal) * 3081) / 1023
The reading in the sample frame represents voltage inputs of 2939.4 mV (0x3D0) and 879.43
mV (0x124) for AD0 and AD1 respectively.
Queried Sampling
The IS command can be sent to a device locally, or to a remote device using the API remote
command frame (see chapter 8 for details). When the IS command is sent, the receiving device
samples all enabled digital IO and analog input channels and returns an IO sample. If IS is sent
locally, the IO sample is sent out the UART or SPI port. If the IS command was received as a
remote command, the IO sample is sent over-the-air to the device that sent the IS command.
If the IS command is issued in command mode, the module returns a carriage return-delimited
list containing the above-listed fields. If the IS command is issued in API mode, the module
returns an API command response packet with the IO data included in the command data
portion of the response frame.
The following table shows an example of the fields in an IS response.
Periodic IO Sampling
Periodic sampling allows the XBee module to take an IO sample and transmit it to a
remote device at a periodic rate. The periodic sample rate is set by the IR command. If
IR is set to 0, periodic sampling is disabled. For all other values of IR, data will be
sampled after IR milliseconds have elapsed and transmitted to a remote device. The DL
command determines the destination address of the IO samples. DL can be set to
transmit to a network client or another XBee Wi-Fi module. Only modules with API
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 40
Page 41

I/O Examples
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
mode enabled for the UART can send IO data samples out their UART. Network clients
will receive the IO data packet as described in the XBee IP Services chapter.
A module will transmit periodic IO samples at the IR rate until the ST timer expires and
the device can resume sleeping.
Change Detection Sampling
Modules can be configured to transmit a data sample immediately whenever a
monitored digital IO pin changes state. The IC command is a bitmask that can be used to
set which digital IO lines should be monitored for a state change. If one or more bits in
IC is set, an IO sample will be transmitted as soon as a state change is observed in one of
the monitored digital IO lines. Change detection samples are transmitted to the IPv4
address specified by DL.
Example 1: Configure the following IO settings on the XBee
Configure AD1/DIO1 as a digital input with pull-up resistor enabled
Configure AD2/DIO2 as an analog input
Configure DIO4 as a digital output, driving high.
To configure AD1/DIO1 as an input, issue the ATD1 command with a parameter of 3
("ATD13"). To enable pull-up resistors on the same pin, the PR command should be
issued with bit 3 set (e.g. ATPR8, ATPR1FFF, etc.). The ATD2 command should be issued
with a parameter of 2 to enable the analog input ("ATD22"). Finally, DIO4 can be set as
an output, driving high by issuing the ATD4 command with a parameter value of 5
("ATD45").
After issuing these commands, changes must be applied before the module IO pins will
be updated to the new states. The AC or CN commands can be issued to apply changes
(e.g. ATAC).
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 41
Page 42

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
7. API Operation
As an alternative to Transparent Operation, API (Application Programming Interface) Operations are
available. API operation requires that communication with the module be done through a structured
interface (data is communicated in frames in a defined order). The API specifies how commands,
command responses and module status messages are sent and received from the module using a
UART or SPI Data Frame.
Please note that Digi may add new API frames to future versions of firmware, so please build into
your software interface the ability to filter out additional API frames with unknown Frame Types.
API Frame Specifications
Two API modes are supported and both can be enabled using the AP (API Enable) command.
Use the following AP parameter values to configure the module to operate in a particular mode:
AP = 1: API Operation
AP = 2: API Operation (with escaped characters)
API Operation (AP parameter = 1)
When this API mode is enabled (AP = 1), the UART or SPI data frame structure is defined as
follows:
UART or SPI Data Frame Structure:
Any data received prior to the start delimiter is silently discarded. If the frame is not received
correctly or if the checksum fails, the module will reply with a module status frame indicating
the nature of the failure.
API Operation-with Escape Characters (AP parameter = 2)
When this API mode is enabled (AP = 2), SPI mode is not supported and the UART frame
structure is defined as follows:
UART Data Frame Structure ‐ with escape control characters:
Escape characters
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 42
Page 43

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
When sending or receiving a UART or SPI data frame, specific data values must be escaped
(flagged) so they do not interfere with the data frame sequencing. To escape an interfering data
byte, insert 0x7D and follow it with the byte to be escaped XOR’d with 0x20.
Data bytes that need to be escaped:
•0x7E – Frame Delimiter
•0x7D – Escape
•0x11 – XON
•0x13 – XOFF
Example - Raw UART Data Frame (before escaping interfering bytes):
0x7E 0x00 0x02 0x23 0x11 0xCB
0x11 needs to be escaped which results in the following frame:
0x7E 0x00 0x02 0x23 0x7D 0x31 0xCB
Note: In the above example, the length of the raw data (excluding the checksum) is 0x0002 and
the checksum of the non-escaped data (excluding frame delimiter and length) is calculated as:
0xFF - (0x23 + 0x11) = (0xFF - 0x34) = 0xCB.
Length
The length field has a two-byte value that specifies the number of bytes that will be contained in
the frame data field. It does not include the checksum field.
Framed Data
Frame data of the UART or SPI data frame forms an API-specific structure as follows:
UART or SPI Data Frame & API‐specific Structure:
The cmdID frame (API-identifier) indicates which API messages will be contained in the cmdData
frame (Identifier-specific data). Note that multi-byte values are sent big endian. The XBee
modules support the following API frames:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 43
Page 44

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
API Frame Names
API ID
Tx64 Request
0x00
AT Command
0x08
AT Command - Queue Parameter Value
0x09
Remote Command Request
0x07
TX IPv4
0x20
Rx64 Indicator
0x80
AT Command Response
0x88
TX Status
0x89
Modem Status
0x8A
IO Data Sample Rx Indicator
0x82
Remote Command Response
0x87
RX IPv4
0xB0
API Frame Names and Values
Checksum
To test data integrity, a checksum is calculated and verified on non-escaped data.
To calculate: Not including frame delimiters and length, add all bytes keeping only the lowest 8
bits of the result and subtract the result from 0xFF.
To verify: Add all bytes (include checksum, but not the delimiter and length). If the checksum is
correct, the sum will equal 0xFF.
API Examples
Example: Create an API AT command frame to configure an XBee baud rate to 230,400 (set BD
to 0x08). The frame should look like (in hex):
7E 00 05 08 01 42 44 08 68
Where:
0x0005 = length excluding checksum
0x08 = AT Command API frame type
0x01 = Frame ID (set to non-zero value for transmit status)
0x4244 = AT Command ('BD')
0x08 = value to set command to
0x68 = Checksum
The checksum is calculated as [0xFF - (0x08 + 0x01 + 0x42 + 0x44 + 0x08)]
Example: Send a remote command to a module who’s IP address is 192.168.0.103 (C0 A8 00 67)
to set AD1/DIO1 as a digital input (D1=3) and apply changes to force the IO update. The API
remote command frame should look like (in hex):
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 44
Page 45

7E 00 0E 07 01 00 00 00 00 C0 A8 01 64 02 44 31 03 B0
Where:
0x000E = length (14 bytes excluding checksum)
0x07 = Remote Command API frame type
0x01 = Frame ID
0x00000000 C0A80067 = Remote address (Pad first 4 bytes with 00)
0x02 = Apply Changes (Remote Command Options)
0x4431 = AT command ('D1')
0xB0 = Checksum
API UART and SPI Exchanges
AT Commands
The following image shows the API frame exchange that takes place at the UART or SPI
when sending an AT command request to read or set a module parameter. The
response can be disabled by setting the frame ID to 0 in the request.
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Transmitting and Receiving RF Data
The following image shows the API exchanges that take place at the UART or SPI when
sending RF data to another device. The transmit status frame is always sent at the end
of a data transmission unless the frame ID is set to 0 in the transmit request. If the
packet cannot be delivered to the destination, the transmit status frame will indicate
the cause of failure. The received data frame (0x80 or 0xB0) is set by the AP command.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 45
Page 46

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Remote AT commands
The following image shows the API frame exchanges that take place at the UART or SPI
when sending a remote AT command. A remote command response frame is not sent
out the UART or SPI if the remote device does not receive the remote command.
Supporting the API
Applications that support the API should make provisions to deal with new API frames
that may be introduced in future releases. For example, a section of code on a host
microprocessor that handles received serial API frames (sent out the module's DOUT
pin) might look like this:
void XBee_HandleRxAPIFrame(_apiFrameUnion *papiFrame){
switch(papiFrame->api_id){
case RX_RF_DATA_FRAME:
//process received RF data frame break;
case RX_IO_SAMPLE_FRAME:
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 46
Page 47

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the
checksum
LSB 2
0x0D
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x00
Frame ID
4
0x01
64-Bit
Destination
Address
5
0x00
Align IP address to low 32-bits of the field. The
other bytes set to 0. IP address is in hex. The
address in this example is 192.168.0.100
0x00
0x00
0x00
0xC0
0xA8
0x00
0x64
TX Options
13
0x00
0x01 – Disable ACK
All other bits must be set to 0.
Data
14
0x1516
Max is 1398 bytes. Data will be sent to the XBee
application service port.
Checksum
0xD9
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to
this byte.
//process IO sample frame break;
default:
//Discard any other API frame types that are not being used break;
}
}
API Frames
The following sections illustrate the types of frames encountered while using the API.
TX (Transmit) request: 64-Bit
Frame Type: 0x0
This frame type uses the XBee Application Service. This command allows for software
compatibility with other XBee module such as the 802.15.4 module.
AT Command
Frame Type: 0x08
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 47
Page 48

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the
checksum
LSB 2
0x05
API Frame
Specific
Data
API Frame Identifier
3
0x08
Frame ID
4
0x01
AT Command
MSB 5
0x4E(N)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify
the AT command
LSB 6
0x49(I)
Parameter Value
-
-
If present, indicates the requested parameter value
to set the given register. If no characters present,
register is queried.
Checksum 7
0x5E
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to
this byte.
Used to query or set module parameters on the local device. This API command applies
changes after executing the command. (Changes made to module parameters take
effect once changes are applied.) The API example below illustrates an API frame when
modifying the NI parameter value of the module.
AT Command-Queue Parameter Value
Frame Type: 0x09
This API type allows module parameters to be queried or set. In contrast to the “AT Command”
API type, new parameter values are queued and not applied until either the “AT Command”
(0x08) API type or the AC (Apply Changes) command is issued. Register queries (reading
parameter values) are returned immediately.
Example: Send a command to change the baud rate (BD) to 115200 baud, but don't apply
changes yet. (Module will continue to operate at the previous baud rate until changes are
applied.)
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 48
Page 49

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x05
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x09
Frame ID
4
0x01
AT Command
MSB 5
0x42 (B)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify the
AT command
LSB 6
0x44 (D)
Parameter Value
7
0x07
If present, indicates the requested parameter value to set
the given register. If no characters present, register is
queried.
Checksum 8
0x68
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this
byte.
Note: In this example, the parameter could have been sent as a zero-padded 2-byte or 4-byte
value.
Remote AT Command Request
Frame Type: 0x07
Used to query or set module parameters on a remote device. For parameter changes on the remote
device to take effect, changes must be applied, either by setting the apply changes options bit, or by
sending an AC command to the remote.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 49
Page 50

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x0D
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x07
Frame ID
4
0x01
64-Bit
Destination
Address
5
0x00
Align IP address to low 32-bits of the field. The other bytes
set to 0. IP address is in hex. The address in this example is
192.168.0.100
6
0x00
7
0x00
8
0x00
9
0xC0
10
0xA8
11
0x00
12
0x64
Command
Options
13
0x02
0x02 – Apply changes on the remote. If not set then the AC
command must be sent or the last remote command sent
must set this option.
AT
Command
MSB 14
0x44(D)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify the
AT command
LSB 15
0x4C(L)
Parameter
Value -
If present, indicates the requested parameter value to set
the given register. If no characters present, register is
queried.
Checksum 16
0x99
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this
byte.
Example: Send a remote command to query the DL register on a remote device. In this example,
the IP address of the remote is 192.168.0.100.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 50
Page 51

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x11
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x20
Frame ID
4
0x01
Set to a value that will be passed back in the Tx Status frame.
0 disables the Tx Status frame.
IPv4 32 bit
Destination
Address
MSB 5
0xC0
Use 0xFFFFFFFF for broadcast when protocol is UDP. The
address in the example is for a destination of 192.168.0.100
6
0xA8
7
0x00 8 0x64
16 Bit
Destination
Port
MSB 9
0x26
UDP or TCP port number
LSB 10
0x16
16 bit Source
Port
MSB 11
0x26
UDP or TCP port number
LSB 12
0x16
Protocol
13
0x00
0 = UDP, 1= TCP - Protocol use for the transmitted data
Transmit
Options
Bitfield
14
0x00
Bit field: BIT 1 =
1 - Terminate socket after tx complete
0 - Leave socket open (use TCP timeout).
Ignore bit for UDP packets. All other bits are reserved and
should be 0.
RF Data
15
0x48(‘H’)
Up to 1400 bytes of data
16
0x65(‘e’)
17
0x6C(‘l’)
18
0x6C('l’)
19
0x6F('o')
Checksum 20
0xA6
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this byte.
Transmit (TX) request: IPv4
Frame Type: 0x20
This frame type utilizes the serial data service. The frame gives greater control to the application
over the IP setting for the data.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 51
Page 52

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x05
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x88
Frame ID
4
0x01
AT
Command
MSB 5
0x42 (B)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify the
AT command
LSB 6
0x44 (D)
Status 0x00
0 = OK
1 = ERROR
2 = Invalid Command
3 = Invalid Parameter
Parameter
Value
7
Register data in binary format. If the register was set, then
this field is not returned, as in this example.
Checksum 8
0xF0
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this
byte.
AT Command Response
Frame Type: 0x88
In response to an AT Command message, the module will send an AT Command Response
message. Some commands will send back multiple frames (for example, the AS (Active Scan)
command).
Example: Suppose the BD parameter is changed on the local device with a frame ID of 0x01. If
successful (parameter was valid), the response below would be received.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 52
Page 53

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x02
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x8A
Status 4 0x00
0 = Hardware reset or power up
1 = Watchdog timer reset
2 = Joined
3 = No longer joined to access point
4 = IP configuration error
Checksum 5
0x75
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this
byte.
Modem Status
Frame Type: (0x8A)
RF module status messages are sent from the module in response to specific conditions.
Example: The following API frame is returned when a module is powered on in API mode.
Note: New modem status codes may be added in future firmware releases.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 53
Page 54

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x03
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x89
Frame ID
4
0x01
Identifies the frame for which status is being reported.
This number corresponds with the Frame ID provided in
the transmission. If that frame ID was 0, then this frame
will not be generated.
Status 5 0x00
0x00 = Success
0x03 = Transmission was purged because it was
attempted before stack was completely up.
0x04 = Physical error occurred on the interface with the
WiFi transceiver.
0x21 = TX64 transmission timed out awaiting an
acknowledgement from the remote device.
0x32 = Resource Error; Either buffers or sockets were
depleted, preventing a transmission from occurring.
0x74 = Message not sent because it was too long
0x76 = Attempt to create a client socket failed
Checksum 6
0x75
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this
byte.
Transmission Status
Frame Type: (0x89)
RF transmission status messages are sent from the module in response to transmission attempts.
Example: The following API frame is returned when a successful transmission occurs on an API
transmission using frame ID 01.
Note: New transmission status codes may be added in future firmware releases.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 54
Page 55

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the
checksum
LSB 2
0x15
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x82
64-Bit
Source
Address
4
0x00
Align IP address to low 32-bits of the field. The other
bytes set to 0. IP address is in hex. The example uses
address 192.168.0.103
5
0x00
6
0x00
7
0x00 8 0xC0 9 0xA8
10
0x00
11
0x67
RSSI at
time of
join
12
0x2E
Receive
Options
13
0x00
0x01 - Packet Acknowledged
Number of
samples
14
0x01
Number of sample sets included in the payload.
(Always set to 1)
Digital
Channel
Mask*
MSB
15
0x01
Bitmask field that indicates which digital IO lines on
the remote have sampling enabled (if any). In this
example DIO8 is active.
LSB 16
0x00
Analog
Channel
Mask**
17
0x81
Bitmask field that indicates which analog IO lines on
the remote have sampling enabled (if any). The most
significant bit signals that the Vcc value is included in
the frame. In this example Analog input 1 and Vcc are
active.
Digital
Samples (if
included)
MSB
18
0x00
If the sample set includes any digital IO lines (Digital
Channel Mask > 0), these two bytes contain samples
for all enabled digital IO lines. DIO lines that do not
have sampling enabled return 0. The bits in these 2
bytes map the same as they do in the Digital Channels
Mask field. In this example, DIO8 has value 0.
LSB 19
0x00
Analog
Sample
MSB
20
0x03
If the sample set includes any analog input lines
(Analog Channel Mask > 0), each enabled analog input
returns a 2-byte value indicating the A/D
measurement of that input. Analog samples are
ordered sequentially from AD0/DIO0 to AD4/DIO4, to
the supply voltage.
LSB 21
0xB5
IO Data Sample RX Indicator
Frame Type: 0x82
When the module receives an IO sample frame from a remote device, it sends the sample out
the UART or SPI using this frame type. Only modules running API mode will be able to receive IO
samples.
Example: The following is the IO sample response from a radio at IP address 192.168.0.103
reporting one active DIO (DIO8) and one active analog input (AN1).
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 55
Page 56

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Vcc
MSB
22
0x0C
Vcc in mV (hex). In this example Vcc is 3231 mV.
LSB 23
0x9F
Checksum
24
0x9A
0xFF - the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this byte.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 56
Page 57

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start
Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the checksum
LSB 2
0x0D
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0x87
Frame ID
4
0x01
64-Bit
Responder
Address
5
0x00
Align IP address to low 32-bits of the field. The other bytes
set to 0. Value is in hex. In this example the IP address is
192.168.0.103
6
0x00
7
0x00
8
0x00
9
0xC0
10
0xA8
11
0x00
12
0x67
AT
Command
MSB
13
0x44 (D)
Command Name - Two ASCII characters that identify the
AT command
LSB 14
0x31 (1)
Status
15
0x00
0 = OK
1 = ERROR
2 = Invalid Command
3 = Invalid Parameter
4 = Tx Failure
Parameter
Value
-
If present, indicates the requested parameter value to set
the given register. If no characters present, register is
queried.
Checksum
16
0x33
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset 3 to this
byte.
Remote Command Response
Frame Type: 0x87
If a module receives a remote command response RF data frame in response to a Remote AT
Command Request, the module will send a Remote AT Command Response message out the
UART or SPI.
Example: If a remote command is sent to a remote device with an IP address of 192.168.0.103
to set the D1 parameter to 3 (digital input), the response is shown in the example API frame in
the table below.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 57
Page 58

Frame Fields
Offset
Example
Description
API Packet
Start Delimiter
0
0x7E
Length
MSB 1
0x00
Number of bytes between the length and the
checksum
LSB 2
0x10
API Frame
Specific Data
API Frame
Identifier
3
0xB0
IPv4 32 bit
Source
Address
MSB 4
0xC0
The address in the example is for a source
address of 192.168.0.104
5
0xA8 6 0x00
7
0x68
16 Bit
Destination
Port
MSB 8
0x26
Same value as the C0 command.
LSB 9
0x16
16 bit
Source Port
MSB
10
0x26
LSB 11
0x16
Protocol
MSB
12
0x00
0 = UDP, 1= TCP - Protocol use for the
transmitted data
Status
13
0x00
Reserved
RF Data
14
0x48 'H'
Up to 1400 bytes of data
15
0x65 'e'
16
0x6C 'l'
17
0x6C 'l'
18
0x6F 'o'
Checksum 19
0x13
0xFF minus the 8 bit sum of bytes from offset
3 to this byte.
RX (Receive) Packet: IPv4
Frame Type: 0xB0
This frame is used by XBee when RF data is received using the Serial Data service on the
port defined by the C0 command.
Example: When a module in API mode receives an IPv4 transmission, it will produce an
RX notification (0xB0) and send it out the UART or SPI. This example is the response to a
UDP transmission to IP address 192.168.0.103 with data ‘Hello’ from the source address
192.168.0.104.
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 58
Page 59

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
AT Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
DL
Destination Address Low. Set/Get the 32 bits of the IPv4 destination
address. Using AT command mode this value is entered using dotted
notation (example 192.168.0.100).
0.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
255.255.255.255
MY
IP Network Address. Read the 32-bit network address of the module when
using DHCP. Set/Read values when using static IP address.
0.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
0.0.0.0
MK
IP Address Mask. This command is read only when DHCP is enabled.
0.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
0.0.0.0
GW
Gateway IP address. This command is read only when DHCP is enabled.
0.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
0.0.0.0
SH
Serial Number High. Read the high 16 bits of the module's unique 48-bit
address.
0 - 0xFFFFFFFF [read-only]
factory-set
SL
Serial Number Low. Read the low 32 bits of the module's unique 48-bit
address.
0 - 0xFFFFFFFF [read-only]
factory-set
NI
Node Identifier. Stores a string identifier. The register only accepts printable
ASCII data. In AT Command Mode, a string cannot start with a space. A
carriage return ends the command. Command will automatically end when
maximum bytes for the string have been entered.
20-Byte printable ASCII
string
ASCII space
character (0x20)
DE
Destination Port. Set/Get destination UDP/TCP port value.
0 - 0xFFFF
0x2616
C0
Serial Communication Service Port. Set/Get port number used to provide the
serial communication service. Data sent to this port will come out of the
serial port of the module. The protocol used is set by the IP command when
UART is in transparent mode.
0 – 0xFFFF
0x2616
DD
Device Type Identifier. Stores a device type value. This value can be used to
differentiate different XBee-based devices. Digi reserves the range 0 0xFFFFFF.
0-0xFFFFFFFF
0x50000
NP
Maximum RF Payload Bytes. This value returns the maximum number of RF
payload bytes that can be sent in a transmission Note: NP returns a
hexadecimal value. (e.g. if NP returns 0x54, this is equivalent to 84 bytes)
0 - 0xFFFF
[read-only]
8. XBee Command Reference Tables
Addressing
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 59
Page 60

AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
ID
SSID. Set/read the SSID of the access point, which may be up to 31 ASCII characters
Up to 31 bytes of
printable ASCII
NULL
AH
Network Type. Set/read network type. Network types supported are Infrastructure
(using an access point) and Adhoc (IBSS).
0-IBSS Joiner
1-IBSS Creator
2 - Infrastructure
2
IP
IP Protocol. Set/Read the protocol used for the serial communication service. This is
the port used by the C0 command.
0 – UDP
1 - TCP
0
MA
IP Addressing Mode. Set / read the IP addressing mode.
0 – DHCP
1 – Static
0
TM
TCP timeout. Set/Read the timeout for connection on TCP socket. If 0, socket closes
immediately after data sent.
0-0xFF [x 100 msec]
0x0A
AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
EE
Encryption Enable. Set/Read the encryption enable setting.
0 – No security
1 – WPA
2 – WPA2
0
PK
Security Key. Set the security key used for WPA and WPA2 security. This command is
write only; PK cannot be read.
0 -31-ASCII
characters
AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
PL
Power Level. Select/Read the power level at which the RF module transmits
conducted power.
0– 7 dBm
1-7 dBm
2- 7 dBm
3- 10 dBm
4- 15 dBm
4
CH
Channel. Read the channel number of the access point or 0xFF if not associated.
Channel can be set when AH is configured for Adhoc creator mode. Note when using
Adhoc mode note all channels are available in all countries. It is the responsibility of
the installer to use the appropriate channels.
1-0xE
[read only]
BR
Bit Rate of IBSS Creator. Data rates MCS0-7 are 802.11n data rates from 6.5 Mbps to
65Mbps. If not IBSS creator, 0 (auto-rate) is the only valid rate.
0- Auto-rate
1- 1 Mbps
2 – 2 Mbps
3 – 5.5 Mbps
4 – 11 Mbps
5 – 6 Mbps
6 – 9 Mbps
7 – 12 Mbps
8 – 18 Mbps
9 – 24 Mbps
0x0A – 36 Mbps
0x0B – 48 Mbps
0x0C – 54 Mbps
0x0D – MCS0
0x0E – MCS1
0x0F – MCS2
0x10 – MCS3
0x11 – MCS4
0x12 – MCS5
0x13 – MCS6
0x14 – MCS7
0
Networking Commands
Security Commands
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
RF Interfacing Commands
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 60
Page 61

AT Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
AP
API Enable. Enable API Mode.
0 = Transparent
mode
1 = API-enabled
2 = API-enabled
(w/escaped control
characters)
1
BD
Interface Data Rate. Set/Read the serial interface data rate for communication
between the module serial port and host. Any value above 0x08 will be interpreted as
an actual baud rate. When a value above 0x08 is sent, the closest interface data rate
represented by the number is stored in the BD register.
0 - 7
(standard baud
rates)
0 = 1200 bps
1 = 2400
2 = 4800
3 = 9600
4 = 19200
5 = 38400
6 = 57600
7 = 115200
8= 230400
0x100 - 0xE1000
(non-standard rates
up to 921kbps)
3
NB
Serial Parity. Set/Read the serial parity setting on the module.
0 = No parity
1 = Even parity
2 = Odd parity
0
SB
Stop Bits. Set/read the number of stop bits for the UART. (Two stop bits are not
supported if mark parity is enabled.)
0 = 1 stop bit
1 = 2 stop bits
0
RO
Packetization Timeout. Set/Read number of character times of inter-character
silence required before packetization. Set (RO=0) to transmit characters as they
arrive instead of buffering them into one RF packet . Regardless of how small RO is,
the inter-character silence required to trigger a transmission of the data is 100 usec.
0 - 0xFF
[x character times]
3
FT
Flow Control Threshold. De-assert CTS when FT bytes are in the UART receive buffer
0x11 – 0x823
0x7F3
D7
DIO7 Configuration. Select/Read options for the DIO7 line of the RF module.
0 = Disabled
1 = CTS Flow
Control
3 = Digital input
4 = Digital output,
low
5 = Digital output,
high
6 = RS-485 transmit
enable (low enable)
7 = RS-485 transmit
enable (high enable)
1
D6
DIO6 Configuration. Configure options for the DIO6 line of the RF module.
0 = Disabled
1 = RTS flow control
3 = Digital input
4 = Digital output,
low
5 = Digital output,
high
0
Serial Interfacing
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 61
Page 62

AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
IR
IO Sample Rate. Set/Read the IO sample rate to enable periodic sampling. For
periodic sampling to be enabled, IR must be set to a non-zero value, and at least one
module pin must have analog or digital IO functionality enabled (see D0-D8, P0-P2
commands). The sample rate is measured in milliseconds.
0-0xFFFF (x 1 ms)
0 – no sampling
IC
IO Digital Change Detection. Set/Read the digital IO pins to monitor for changes in
the IO state. IC works with the individual pin configuration commands (D0-D9, P0-P2).
If a pin is enabled as a digital input/output, the IC command can be used to force an
immediate IO sample transmission when the DIO state changes. IC is a bitmask that
can be used to enable or disable edge detection on individual channels. Unused bits
should be set to 0.
0 - 0xFFFF
0
IF
Sample from Sleep Rate. The number of sleep cycles that must elapse between
periodic I/O samples. This allows I/O samples to be taken only during some wake
cycles. During those cycles I/O samples are taken at the rate specified by IR. IR can be
0 which will cause only one sample to be taken.
1-0xFF
(1 gives you a
sample every sleep
cycle)
1
P0
DIO10 Configuration. Select/Read function for the DIO10 line of the RF module.
0 = Disabled,
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
P1
DIO11 Configuration. Select/Read function for the DIO11 line of the RF module.
0 = Disabled
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
P2
DIO12 Configuration. Select/Read function for the DIO12 line of the RF module.
0 = Disabled
1 = SPI_MISO
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
I/O Settings
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 62
Page 63

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
D0
AD0/DIO0 Configuration. Select/Read function for AD0/DIO0.
0 = Disabled
2 = Analog input
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
D1
AD1/DIO1 Configuration. Select/Read function for AD1/DIO1
0 - Disabled
2 = Analog input
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
D2
AD2/DIO2 Configuration. Select/Read function for AD2/DIO2
0 = Disabled
1 = SPI_MOSI
2 = Analog input
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
D3
AD3/DIO3 Configuration. Select/Read function for AD3/DIO3.
0 = Disabled
1 = SPI_SSEL
2 = Analog input
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
D4
DIO4 Configuration. Select/Read function for DIO4.
0 = Disabled
1 = SPI_MOSI
2 = Analog input
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
0
D5
DIO5 Configuration. Select/Read function for DIO5.
0 = Disabled
1 = Associated LED
3 = Digital input
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
1
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 63
Page 64

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
D8
DIO8 Configuration. Select/Read function for DIO8.
0 = Disabled
1 = SleepRq
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
1
D9
DIO9 Configuration. Select/Read function for DIO9
0 = Disabled
1 = On/Sleep
indicator
3 = Digital input,
monitored
4 = Digital output,
default low
5 = Digital output,
default high
6 = SPI_ATTN
1
LT
Assoc LED Blink Time. Set/Read the Associate LED blink time. If the Associate LED
functionality is enabled (D5 command), this value determines the on and off blink
times for the LED when the module has joined a network. If LT=0, the default blink
rate of 250ms will be used. For all other LT values, LT is measured in 10ms.
0, 0x14 - 0xFF (200 2550 ms)
0
PR
Pull-up Resistor. Set/read the bit field that configures the internal pull-up resistor
status for the I/O lines. "1" specifies the pull-up resistor is enabled. "0" specifies no
pullup.(30k pull-up resistors)
Bits:*
0 - DIO4 (Pin 11)
1 - AD3 / DIO3 (Pin 17)
2 - AD2 / DIO2 (Pin 18)
3 - AD1 / DIO1 (Pin 19)
4 - AD0 / DIO0 (Pin 20)
5 - RTS / DIO6 (Pin 16)
6 - DTR / Sleep Request / DIO8 (Pin 9)
7 - DIN / Config (Pin 3)
8 - Associate / DIO5 (Pin 15)
9 - On/Sleep / DIO9 (Pin 13)
10 - DIO12 (Pin 4)
11 - DIO10 (Pin 6)
12 - DIO11 (Pin 7)
13 - CTS / DIO7 (Pin 12)
0 - 0x7FFF
0 - 0x7F7F
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 64
Page 65

AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
VR
Firmware Version. Read firmware version of the module.
The firmware version returns 4 hexadecimal values (2 bytes) "ABCD". Digits ABC are
the main release number and D is the revision number from the main release. "B" is a
variant designator where 0 means standard release.
0 - 0xFFFF [read-
only]
Factory-set
HV
Hardware Version. Read the hardware version of the module.
This command can be used to distinguish among different hardware platforms. The
upper byte returns a value that is unique to each module type. The lower byte
indicates the hardware revision.
XBee WiFi modules return 0x1Fxx for the HV command.
0 - 0xFFFF [read-
only]
Factory-set
AI
Association Indication. Read information regarding last node join request:
0x00 - Successfully joined an access point, established IP addresses and IP listening
sockets.
0x01 – WiFi initialization in progress. This status should only be seen for a few
milliseconds.
0x22 – Selected SSID not found
0x23 – SSID not configured. (An active scan can occur in this state.
0x27 – SSID was found, but join failed
0xff – Module is currently scanning for the configured SSID
0x41 – Module joined a network and is waiting for IP configuration to complete,
which usually means it is waiting for a DHCP provided address
0x42 – Module is joined, IP is configured, and listening sockets are being set up
Note: New non-zero AI values may be added in later firmware versions. Applications
should read AI until it returns 0x00, indicating a successful startup (coordinator) or
join (routers and end devices)
0 - -
only]
-
AS
Active Scan. Scan for access points in the vicinity. This command can only be issued
when SSID is NULL, which can be forced by first issuing the NR command. If SSID is
not NULL, then the active scan command returns an error.
This command may be issued in command mode or in API mode. In either case, the
following information is returned for each access point found:
01 – Indicates scan type of 802.11
FF – Place holder for future use
ST – Security type where: 00=open, 01=WPA, 02=WPA2, and 03=WPA
RS – RSSI of access point (negated hex value
ID = SSID of access point found.
When this command is issued in command mode, the above record is displayed, one
per line for each access point found. Readable ASCII characters are output with
commas between fields and carriage returns between records.
When it is issued in API mode, each record (i.e. each access point) outputs a separate
AT command response of type 0x88 with the above fields in binary format.
Note that this command is not available as a remote command.
-
-
TP
Temperature. Read temperature of module in degrees Celsius.
-40 to 85C
-
CK
Configuration Code. Read the configuration code associated with the current AT
command configuration
2 bytes
-
%V
Supply Voltage. Read supply voltage in millivolt units.
3.1 to 3.6V
-
Diagnostics Interfacing
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 65
Page 66

AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
CT
Command Mode Timeout. Set/Read the period of inactivity (no valid commands
received) after which the RF module automatically exits AT Command Mode and
returns to Idle Mode. This time can be up to ten minutes.
2 - 0x1770 [x 100
ms]
0x64 (100d)
CN
Exit Command Mode. Explicitly exit the module from AT Command Mode. (Whether
command mode is left by the CN command or by CT timing out, changes will be
applied upon exit.
-
-
GT
Guard Times. Set required period of silence before and after the Command Sequence
Characters of the AT Command Mode Sequence (GT + CC + GT). The period of silence
is used to prevent inadvertent entrance into AT Command Mode.
2 (max of 3.3 decimal
sec)
0x3E8
(1000d)
CC
Command Mode Character Set/read the command mode character used between
guard times of the AT Command Mode Sequence (GT + CC + CC + CC + GT). This
sequence allows the module to enter into AT Command Mode.
0 - 0xFF
0x2B
(‘+’ ASCII)
AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter Range
Default
SM
Sleep Mode Sets the sleep mode on the RF module. Sleep mode is also affected by
the SO command, option bit 6. See the “Sleep” chapter for a full explanation of the
various sleep modes.
0 = No sleep
1 = Pin sleep
4 = Cyclic sleep
5 = Cyclic sleep, pin
wake
0
SP
Sleep Period. This value determines how long the device will sleep at a time, up to 24
hours or 86,400 seconds. This corresponds to 0x83d600 in 10ms units.
1 - 0x83D600 x
10ms
0xC8 (2 seconds)
SO
Command
Sleep Options. Configure options for sleep. Unused option bits should be set to 0.
Sleep options include:
0x40 – Stay associated with AP during sleep. Draw more current during sleep with
this option enabled, but also awake from sleep more rapidly.
0x100 – For cyclic sleep, ST specifies the time before returning to sleep. With this bit
set, new receptions from either the serial or the RF port will NOT restart the ST timer.
Current implementation does not support this bit being turned off.
0 - 0xFF
0x100
WH
Wake Host. Set/Read the wake host timer value. If the wake host timer is set to a
non-zero value, this timer specifies a time (in millisecond units) that the device
should allow after waking from sleep before sending data out the UART or
transmitting an IO sample. If serial characters are received, the WH timer is stopped
immediately.
0 - 0xFFFF (x 1ms)
0
ST
Wake Time. Wake time for cyclic modes. New data will not refresh the timer.
However, if there is data to transmit or receive after ST expires, those actions will
occur before the module goes to sleep. Max wake time is 3600 seconds.
0x1 – 0x36EE80 (x 1
ms)
0x7D0
AT Command Options
Sleep Commands
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 66
Page 67

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
AT
Command
Name and Description
Parameter
Range
Default
AC
Apply Changes. Applies changes to all command registers causing queued command
register values to be applied. For example, changing the serial interface rate with the
BD command will not change the UART interface rate until changes are applied with
the AC command. The CN command and 0x08 API command frame also apply
changes.
-
-
WR
Write. Write parameter values to non-volatile memory so that parameter
modifications persist through subsequent resets. Note: Once WR is issued, no
additional characters should be sent to the module until after the "OK\r" response is
received. The WR command should be used sparingly to preserve flash.
-
-
RE
Restore Defaults. Restore module parameters to factory defaults.
-
-
FR
Software Reset. Reset module. Responds immediately with an OK status, and then
performs a software reset about 2 seconds later.
-
-
NR
Network Reset. Reset network layer. For WiFi, this means to disassociate from the
access point and set SSID to NULL, thereby preventing the node from immediately
establishing the same connection with the same access point. This also allows the
active scan command to be executed so that access point candidates can be selected
from the resultant list.
Note that NR and NR0 both do the same thing and may be used interchangeably.
0
-
IS
Force Sample Forces a read of all enabled digital and analog input lines.
-
-
Execution Commands
Where most AT commands set or query register values, execution commands cause an action to be executed on
the module. Execution commands are executed immediately and do not require changes to be applied.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 67
Page 68

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
9. Module Support
This chapter provides customization information for the XBee Wi-Fi module. In addition to providing
an extremely flexible and powerful API, the XBee module is a robust development platform that has
passed FCC and ETSI testing.
X-CTU Configuration Tool
Digi provides a Windows X-CTU configuration tool for configuring module parameters and updating
firmware. The XCTU has the capability to do the following:
Update firmware on a local module (requires USB or serial connection)
Read or write module configuration parameters on a local
Save and load configuration profiles containing customized settings.
Contact Digi support for more information about the X-CTU.
Serial Firmware Updates
Serial firmware updates make use of the XBee custom bootloader which ships in all units. This
modified bootloader is based on Ember's standalone bootloader, but with a modified entry
mechanism. The modified entry mechanism uses module pins 4, 10, and 30 (DIN, DTR, and RTS
respectively).
The X-CTU program can update firmware serially on the XBee module. Contact Digi support for
details.
Regulatory Compliance
XBee modules are certified for FCC and IC operation on all 11 channels (1-11) allowable, and ESTI certified for
all 13 channels (1-13) allowable.
Agency Certifications
United States FCC
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 68
Page 69

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
The XBee RF Module complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules and regulations. Compliance with the
labeling requirements, FCC notices and antenna usage guidelines is required.
To fulfill FCC Certification, the OEM must comply with the following regulations:
1. The system integrator must ensure that the text on back side of the module is placed on
the outside of the final product.
2. XBee RF Module may only be used with antennas that have been tested and approved for
use with this module [refer to the antenna tables in this section].
OEM Labeling Requirements
WARNING: The Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) must ensure that FCC labeling
requirements are met. This includes a clearly visible label on the outside of the final product
enclosure.
Required FCC Label for OEM products containing the XBee S6 RF Module
Contains FCC ID: MCQ-XBS6
The integrator is responsible for its product to comply with FCC Part 15, Sub. B - Unintentional
Radiators.
FCC Notices
IMPORTANT: The XBee Module have been certified by the FCC for use with other products without any
further certification (as per FCC section 2.1091). Modifications not expressly approved by Digi could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.
IMPORTANT: OEMs must test final product to comply with unintentional radiators (FCC section 15.107 &
15.109) before declaring compliance of their final product to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
IMPORTANT: The RF module has been certified for remote and base radio applications. If the module will be
used for portable applications, the device must undergo SAR testing.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more
of the following measures: Re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna, Increase the separation between the
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 69
Page 70

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Integrated Antennas
Minimum Cable Loss/Power
Reduction/Attenuation Required
Part Number
Type (Description)
Gain
Application
Min
Separation
b mode
g mode
n mode
Integrated PCB antenna
0 dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A
N/A
N/A
29000294
Integral PCB antenna
-0.5
dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A N/A N/A
A24-QI
Monopole (Integrated Whip)
1.5
dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A N/A N/A Dipole Antennas
Minimum Cable Loss/Power
Reduction/Attenuation Required
Part Number
Type (Description)
Gain
Application
Min
Separation
b mode
g mode
n mode
A24-HASM-450
Dipole (Half-wave articulated
RPSMA-4.5")
2.1
dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A N/A N/A
A24-HABSM
Dipole (Articulated RPSMA)
2.1
dBi
Fixed
20 cm
N/A N/A N/A
A24-HABUF-P5I
Dipole (Half-wave bulkhead
mount U.FL s/ 5" pigtail)
2.1
dBi
Fixed
20 cm
N/A N/A N/A
A24-HASM-525
Dipole (Half-wave articulated
RPSMA-5.25")
2.1
dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A N/A N/A
equipment and receiver, Connect equipment and receiver to outlets on different circuits, or Consult the dealer
or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC-Approved Antennas (2.4 GHz)
The XBee Wi-Fi Module can be installed utilizing antennas and cables constructed with non-standard
connectors (RPSMA, RPTNC, etc.).
The modules are FCC approved for fixed base station and mobile applications for the channels indicated in the
tables below. If the antenna is mounted at least 20cm (8 in.) from nearby persons, the application is
considered a mobile application. Antennas not listed in the table must be tested to comply with FCC Section
15.203 (Unique Antenna Connectors) and Section 15.247 (Emissions).
XBee Wi-Fi Module: XBee RF Modules have been tested and approved for use with all the antennas listed in
the tables below. (Cable-loss is required when using gain antennas as shown below.)
The antennas in the tables below have been approved for use with this module. Digi does not carry all of these
antenna variants. Contact Digi Sales for available antennas.
Antennas approved for use with the XBee Wi-Fi Module
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 70
Page 71

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Omi-Directional Antennas
Minimum Cable Loss/Power
Reduction/Attenuation Required
Part Number
Type (Description)
Gain
Application
Min
Separation
b mode
g mode
n mode
A24-F2NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
2.1
dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A
N/A N/A
A24-F3NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
3.0
dBi
Fixed/Mobile
20 cm
N/A
N/A N/A
A24-F5NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
5.0
dBi
Fixed
20 cm
N/A N/A 0.12dB
A24-F8NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
8.0
dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A N/A 3.12dB
A24-F9NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
9.5
dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A 1.0dB
4.62dB
A24-F10NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
10
dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A 1.5dB
5.12dB
A24-F12NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
12
dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A 3.5dB
7.12dB
A24-F15NF
Omin-Directional (Fiberglass
base station)
15
dBi
Fixed
2 m
0.56dB
6.5dB
10.12dB
A24-W7NF
Omin-Directional ( base station)
7.2
dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A N/A 2.32dB
A24-M7NF
Omin-directional (Mag-mount
base station)
7.2
dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
N/A
2.32dB
PANEL CLASS ANTENNAS
Minimum Cable Loss/Power
Reduction/Attenuation
Required
Part Number
Type (Description)
Gain
Application
Min Separation
b
mode
g mode
n mode
A24-P8SF
Flat Panel
8.5 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
5.96dB
10.04dB
A24-P8NF
Flat Panel
8.5 dBi
Fixed
3 m
N/A
5.96dB
10.04dB
A24-P13NF
Flat Panel
13 dBi
Fixed
4 m
N/A
10.46dB
14.54dB
A24-P14NF
Flat Panel
14 dBi
Fixed
5 m
N/A
11.46dB
15.54dB
A24-P15NF
Flat Panel
15.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
0.12dB
12.46dB
16.54dB
A24-P16NF
Flat Panel
16.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
1.12dB
13.46dB
17.54dB
A24-19NF
Flat Panel
19.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
4.12dB
16.46dB
20.54dB
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 71
Page 72

YAGI CLASS ANTENNAS for Channel 11-25
Minimum Cable Loss/Power
Reduction/Attenuation
Required
Part Number
Type (Description)
Gain
Application
Min
Separation
b
mode
g mode
n mode
A24-Y6NF
Yagi (6 element)
8.8dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
5.58dB
7.52dB
A24-Y7NF
Yagi (7 element)
9.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
5.78dB
7.72dB
A24-Y9NF
Yagi (9 element)
10.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
6.78dB
8.72dB
A24-Y10NF
Yagi (10 element)
11.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
7.78dB
9.72dB
A24-Y12NF
Yagi (12element)
12.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
8.78dB
10.72dB
A24-Y13NF
Yagi (13 element)
12.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
8.78dB
10.72dB
A24-Y15NF
Yagi (15 element)
12.5 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
9.28dB
11.22dB
A24-Y16NF
Yagi (16 element)
13.5 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
10.28dB
12.22dB
A24-Y16RM
Yagi (16 element, RPSMA connector)
13.5 dBi
Fixed
2 m
N/A
10.28dB
12.22dB
A24-Y18NF
Yagi (18 element)
15.0 dBi
Fixed
2 m
0.56dB
11.78dB
13.72dB
XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 72
Page 73

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
* If using the RF module in a portable application (for example - if the module is used in a handheld device and
the antenna is less than 20cm from the human body when the device is in operation): The integrator is responsible
for passing additional SAR (Specific Absorption Rate) testing based on FCC rules 2.1091 and FCC Guidelines for
Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, OET Bulletin and Supplement C. The testing results
will be submitted to the FCC for approval prior to selling the integrated unit. The required SAR testing measures
emissions from the module and how they affect the person.
RF Exposure
WARNING: To satisfy FCC RF exposure requirements for mobile transmitting devices, a
separation distance of 20 cm or more should be maintained between the antenna of this device
and persons during device operation. To ensure compliance, operations at closer than this
distance are not recommended. The antenna used for this transmitter must not be co-located
in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
The preceding statement must be included as a CAUTION statement in OEM product manuals in order to alert
users of FCC RF Exposure compliance.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 73
Page 74

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Europe (ETSI)
The XBee RF Module has been certified for use in several European countries. For a complete list, refer to
www.digi.com
If the XBee RF Modules are incorporated into a product, the manufacturer must ensure compliance of the final
product to the European harmonized EMC and low-voltage/safety standards. A Declaration of Conformity
must be issued for each of these standards and kept on file as described in Annex II of the R&TTE Directive.
Furthermore, the manufacturer must maintain a copy of the XBee user manual documentation and ensure the
final product does not exceed the specified power ratings, antenna specifications, and/or installation
requirements as specified in the user manual. If any of these specifications are exceeded in the final product, a
submission must be made to a notified body for compliance testing to all required standards.
OEM Labeling Requirements
The 'CE' marking must be affixed to a visible location on the OEM product.
CE Labeling Requirements
The CE mark shall consist of the initials "CE" taking the following form:
If the CE marking is reduced or enlarged, the proportions given in the above graduated
drawing must be respected.
The CE marking must have a height of at least 5mm except where this is not possible on
account of the nature of the apparatus.
The CE marking must be affixed visibly, legibly, and indelibly.
Restrictions
Declarations of Conformity
Digi has issued Declarations of Conformity for the XBee RF Modules concerning emissions, EMC and safety.
Files can be obtained by contacting Digi Support.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 74
Page 75

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Important Note:
Digi does not list the entire set of standards that must be met for each country. Digi customers assume full
responsibility for learning and meeting the required guidelines for each country in their distribution market.
For more information relating to European compliance of an OEM product incorporating the XBee RF Module,
contact Digi, or refer to the following web sites:
CEPT ERC 70-03E - Technical Requirements, European restrictions and general requirements: Available at
www.ero.dk/.
R&TTE Directive - Equipment requirements, placement on market: Available at www.ero.dk/.
Approved Antennas
When integrating high-gain antennas, European regulations stipulate EIRP power maximums. Use the
following guidelines to determine which antennas to design into an application.
XBee Wi-Fi RF Module
The following antennas types have been tested and approved for use with the XBee Module: XBee® Wi-FI RF
Modules © 2010 Digi International, Inc. 151
Antenna Type: Yagi
RF module was tested and approved with 15 dBi antenna gain with 1 dB cable-loss (EIRP Maximum of 14
dBm). Any Yagi type antenna with 14 dBi gain or less can be used with no cable-loss.
Antenna Type: Omni-Directional
RF module was tested and approved with 15 dBi antenna gain with 1 dB cable-loss (EIRP Maximum of 14
dBm). Any Omni-Directional type antenna with 14 dBi gain or less can be used with no cable-loss.
Antenna Type: Flat Panel
RF module was tested and approved with 19 dBi antenna gain with 4.8 dB cable-loss (EIRP Maximum of 14.2
dBm). Any Flat Panel type antenna with 14.2 dBi gain or less can be used with no cable-loss.
XBee RF Module
The following antennas have been tested and approved for use with the embedded XBee RF Module:
- Dipole (2.1 dBi, Omni-directional, Articulated RPSMA, Digi part number A24-HABSM)
- PCB Antenna (0 dBi)
-Wire Whip Antenna (1.5 dBi)
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 75
Page 76

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Canada (IC)
This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit
pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage
radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement
Labeling Requirements
Labeling requirements for Industry Canada are similar to those of the FCC. A clearly visible label on
the outside of the final product enclosure must display the following text:
Contains IC: 1846A-XBS6
The integrator is responsible for its product to comply with IC ICES-003 & FCC Part 15, Sub. B Unintentional Radiators. ICES-003 is the same as FCC Part 15 Sub. B and Industry Canada accepts
FCC test report or CISPR 22 test report for compliance with ICES-003.
Transmitters with Detachable Antennas
This radio transmitter (IC: 1846A-XBS6) has been approved by Industry Canada to operate with the
antenna types listed in the table above with the maximum permissible gain and required antenna
impedance for each antenna type indicated. Antenna types not included in this list, having a gain
greater than the maximum gain indicated for that type, are strictly prohibited for use with this
device.
Le présent émetteur radio (IC: 1846A-XBS6) a été approuvé par Industrie Canada pour fonctionner
avec les types d'antenne énumérés ci-dessous et ayant un gain admissible maximal et l'impédance
requise pour chaque type d'antenne. Les types d'antenne non inclus dans cette liste, ou dont le gain
est supérieur au gain maximal indiqué, sont strictement interdits pour l'exploitation de l'émetteur.
Detachable Antenna
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter may only operate using an antenna of a
type and maximum (or lesser) gain approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce
potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that
the equivalent isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that necessary for successful
communication.
Conformément à la réglementation d'Industrie Canada, le présent émetteur radio peut fonctionner
avec une antenne d'un type et d'un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par
Industrie Canada. Dans le but de réduire les risques de brouillage radioélectrique à l'intention des
autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir le type d'antenne et son gain de sorte que la puissance isotrope
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 76
Page 77

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
rayonnée équivalente (p.i.r.e.) ne dépasse pas l'intensité nécessaire àl'établissement d'une
communication satisfaisante.
Australia (C-Tick)
These modules comply with requirements to be used in end products in Australia. All products with
EMC and radio communications must have a registered C-Tick mark. Registration to use the
compliance mark will only be accepted from Australian manufacturers or importers, or their agent,
in Australia.
In order to have a C-Tick mark on an end product, a company must comply with a or b below.
a. have a company presence in Australia.
b. have a company/distributor/agent in Australia that will sponsor the importing of the end
product.
Contact Digi for questions related to locating a contact in Australia.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 77
Page 78

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
10. Warranty Information
1-Year Warranty
XBee RF Modules from Digi International, Inc. (the "Product") are warranted against defects in
materials and workmanship under normal use, for a period of 1-year from the date of purchase. In
the event of a product failure due to materials or workmanship, Digi will repair or replace the
defective product. For warranty service, return the defective product to Digi International, shipping
prepaid, for prompt repair or replacement.
The foregoing sets forth the full extent of Digi International's warranties regarding the Product.
Repair or replacement at Digi International's option is the exclusive remedy. THIS WARRANTY IS
GIVEN IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AND DIGI SPECIFICALLY
DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN
NO EVENT SHALL DIGI, ITS SUPPLIERS OR LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES IN EXCESS OF THE
PURCHASE PRICE OF THE PRODUCT, FOR ANY LOSS OF USE, LOSS OF TIME, INCONVENIENCE,
COMMERCIAL LOSS, LOST PROFITS OR SAVINGS, OR OTHER INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT, TO THE
FULL EXTENT SUCH MAY BE DISCLAIMED BY LAW. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR
LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. THEREFORE, THE FOREGOING
EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY IN ALL CASES. This warranty provides specific legal rights. Other rights
which vary from state to state may also apply.
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 78
Page 79

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Appendix A: Definitions
Definitions
Local Host
A device which is electrically connected to an XBee. Typically this is a microcontroller connected to
the serial pins of the module.
MAC address
A unique network identifier. All network devices are required to have their own unique
MAC address. The MAC address is on a sticker on your Digi device server. The number
is displayed as 12 hexadecimal digits, usually starting with 00:40:9D.
Network Client
A device which communicates with an XBee through the 802.11 network.
Static IP address assignment
The process of assigning a specific IP address to a device. Contrast with assigning a
device through Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), or Automatic Private IP
Addressing (APIPA or Auto-IP).
TCP
See Transmission Control Protocol.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
Part of the IEEE 802.11i encryption standard for wireless LANs. TKIP is the next
generation of the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), which is used to secure 802.11 wireless LANs.
TKIP provides per-packet key mixing, a message integrity check and a
re-keying mechanism, and addresses several design shortcomings of the original WEP.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
A set of rules (protocol) used along with the Internet Protocol (IP) to send data in the
form of message units between computers over the Internet. While IP handles the actual
delivery of the data, TCP handles keeping track of the individual units of data (called
packets) that a message is divided into for efficient routing through the Internet.
For example, when an HTML file is sent to you from a Web server, the Transmission
Control Protocol (TCP) program layer in that server divides the file into one or more
packets, numbers the packets, and then forwards them individually to the IP program
layer. Although each packet has the same destination IP address, it may get routed
differently through the network. At the other end (the client program in your computer),
TCP reassembles the individual packets and waits until they have arrived to forward
them to you as a single file.
TCP is known as a connection-oriented protocol, which means that a connection is
established and maintained until such time as the message or messages to be exchanged
by the application programs at each end have been exchanged. TCP is responsible for
ensuring that a message is divided into the packets that IP manages and for
reassembling the packets back into the complete message at the other end. In the Open
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 79
Page 80

XBee® Wi-Fi RF Modules
Systems Interconnection (OSI) communication model, TCP is in layer 4, the Transport
Layer.
UDP
See User Datagram Protocol.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
A communications protocol that offers a limited amount of service when messages are
exchanged between computers in a network that uses the Internet Protocol (IP). UDP is
an alternative to the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and, together with IP, is
sometimes referred to as UDP/IP. Like the Transmission Control Protocol, UDP uses
the Internet Protocol to actually get a data unit (called a datagram) from one computer
to another. Unlike TCP, however, UDP does not provide the service of dividing a
message into packets (datagrams) and reassembling it at the other end. Specifically,
UDP does not provide sequencing of the packets in which the data arrives, nor does it
guarantee delivery of data. This means that the application program that uses UDP must
be able to make sure that the entire message has arrived and is in the right order.
Network applications that want to save processing time because they have very small
data units to exchange (and therefore very little message reassembling to do) may prefer
UDP to TCP. The Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) uses UDP instead of TCP.
UDP provides two services not provided by the IP layer. It provides port numbers to
help distinguish different user requests and, optionally, a checksum capability to verify
that the data arrived intact.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
A data encryption/ user authentication method for 802.11 wireless LANs. WPA uses the
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
WPA
See Wi-Fi Protected Access.
WPA2/802.11i
WPA with AES-based encryption (CCMP)
© 2011 Digi International, Inc. Page 80
 Loading...
Loading...