Page 1

XBee® Gateway
User Guide
Page 2

Revision history—90001399-13
Revision Date Description
D July 2017 Updated the Certificate Management section to specify that this feature is
available only for Wi-Fi devices.
E September
2017
F January
2020
G February
2020
H October
2020
Reorganized and edited the document.
Added information about the unique password for the web interface.
Added link to data sheet specifications.
Updated information for XBee network OTA firmware updates.
Trademarks and copyright
Digi, Digi International, and the Digi logo are trademarks or registered trademarks in the United
States and other countries worldwide. All other trademarks mentioned in this document are the
property of their respective owners.
© 2020 Digi International Inc. All rights reserved.
Disclaimers
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of Digi International. Digi provides this document “as is,” without warranty of
any kind, expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of fitness or
merchantability for a particular purpose. Digi may make improvements and/or changes in this manual
or in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this manual at any time.
Warranty
To view product warranty information, go to the following website:
www.digi.com/howtobuy/terms
Send comments
Documentation feedback: To provide feedback on this document, send your comments to
techcomm@digi.com.
Customer support
Digi Technical Support: Digi offers multiple technical support plans and service packages to help our
customers get the most out of their Digi product. For information on Technical Support plans and
pricing, contact us at +1 952.912.3444 or visit us at www.digi.com/support.
XBee Gateway User Guide
2
Page 3

Contents
About Digi XBee Gateway
Regulatory information and certifications 9
RF exposure statement 9
FCC certifications and regulatory information (USA only) 9
Declaration of Conformity (DoC) 10
CE mark (Europe) 10
Industry Canada (IC) certifications 11
Korea Communications Commission (KCC) certifications 11
Safety statements 11
Warnings for Use of Wireless Devices 12
International EMC (Electromagnetic Emissions/Immunity/Safety) standards 13
Maximum power and frequency bands 13
XBee Gateway: Cellular 14
XBee Gateway: Ethernet 14
XBee Gateway: Wi-Fi 14
XBee Gateway Python application 14
XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit 14
Hardware interfaces 15
Configuration and management interfaces 15
XBee Gateway web interface 15
Remote Manager interface 15
RFGateway and Python remote device management solutions 16
Programming interface applications 16
Product differences from predecessor ConnectPort® X products 17
Where to find more information 18
Get started
Set up the XBee Gateway Cellular hardware 19
Verify your components 19
Connect the cellular hardware 21
Connect XBee Gateway to the network 22
Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware 22
Verify your components 23
Connect the Wi-Fi hardware 24
Connect XBee Gateway to the network 25
Set up your XBee Gateway
Set up XBee Gateway summary 27
XBee Gateway User Guide
3
Page 4

Joining ZigBee networks 28
Join XBee Gateway to an existing ZigBee network 29
Configure XBee Gateway with a custom PAN ID 30
XBee Gateway and non-XBee ZigBee Devices 31
Administration and maintenance tasks
Logging in to the web interface 32
File management 32
File Management page in Remote Manager 32
File Management page in the XBee Gateway web interface 33
Certificate Management 34
Certificate Management page in the web interface 34
Back up or restore the configuration 35
Back up and restore files from Remote Manager 35
Back up and restore files from the XBee Gateway web interface 36
Update firmware 37
Update firmware from Remote Manager 37
Update firmware from the XBee Gateway web interface 39
About firmware files 40
Mobile device status 40
Display the mobile device status 41
Mobile Status page 41
Change the password for the web interface 49
Display the XBee Gateway End User License Agreement (EULA) 51
Restore XBee Gateway factory defaults 52
Reboot XBee Gateway 52
Display system information 52
Disconnect XBee Gateway from Remote Manager 52
About programming
Python 54
XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit web application source code 55
Programming calls through Server Command Interface (SCI) and Remote Command Interface
(RCI) 55
XBee Gateway file system 55
Important directories 55
Load applications onto XBee Gateway 56
Program XBee Gateway using Python
Find Python learning resources 58
Python support forum 58
Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference Manual 58
Digi-specific Python modules for programming 58
Sample programs 58
Button handling 59
LED control 59
Watchdog 60
RCI callback 61
XBee functions 62
XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager 62
XBee Gateway User Guide
4
Page 5

How does the XBee Gateway Python application work? 62
XBee Gateway Python application requirements 63
Key features and operations of the XBee Gateway Python application 64
Store status data for XBee lines in Remote Manager 64
Receive serial data from Remote Manager 68
Store serial data in Remote Manager 75
Manage XBee DIO lines though Remote Manager 78
XBee Gateway Python application configuration file 85
XBee Gateway Python application command errors 86
Configure a Python application in the web interface 86
Digi ESP for Python 87
Access the program samples in Digi ESP 87
Install the Digi ESP for Python Development Environment 88
DIA software 91
Linux command shell (command line interface) 91
User name and password for the Linux command shell 91
Connect and log in to the XBee Gateway device 91
Log in to XBee Gateway through the Digi ESP for Python command line interface 92
Configure XBee Gateway
Configure settings from Remote Manager 95
Basic configuration settings 95
Advanced configuration settings 95
Configure settings from the XBee Gateway web interface 96
Access the XBee Gateway web interface 96
Home page 97
Ethernet IP network settings 98
Default Ethernet settings 98
Configure Ethernet Settings 99
Ethernet Network Configuration page 99
Wireless (Wi-Fi) network settings 101
Default wireless (Wi-Fi) settings 101
Configure wireless settings 101
Wi-Fi network settings 101
Mobile connectivity settings 104
Default behavior with the cellular network 104
Set up and configure GSM-based devices 105
Provision a CDMA-based device 106
Configure mobile settings 107
Mobile Connectivity Configuration page 108
Short Message Service (SMS) 109
Digi Mobile SureLink™ settings 112
Configure Mobile SureLink settings 112
Mobile SureLink integrity monitoring settings 112
Link integrity test options 114
DNS settings 115
Configure Domain Name Server (DNS) 115
Domain Name Server (DNS) Configuration page 115
Mobile firewall settings 116
Configure mobile firewall settings 116
Enable or Disable Mobile firewall settings 116
Autostart settings for the Python Program 116
Configure Python settings 117
Python settings 117
XBee Gateway User Guide
5
Page 6

Button service assignments settings 117
Configure button service assignments 117
Button service assignments page 118
Restore XBee Gateway factory defaults 118
Use discovery tools to enable configuration changes 118
Use the button to enable special-purpose Wi-Fi configuration mode 119
Use the button to enable the web interface 120
Configure Remote Manager connectivity settings 120
Configure connectivity settings 121
Basic connectivity settings 121
Advanced connectivity settings 122
Advanced connectivity settings for the web interface 124
Device Cloud client initiated connection page 127
Device Cloud Configuration page 128
Device Cloud network type page 129
Connect to a different instance of Remote Manager 130
Configure a proxy server 130
Network services settings 131
Configure network services settings 131
Network Services Configuration page 131
GPS static position settings 133
Configure GPS Static Position settings 133
GPS Static Position page 134
Time settings 134
Configure time settings 134
Time Server Configuration page 135
Time Zone Configuration page 135
Time Configuration page 135
Configure XBee network settings
Configure XBee Networks page in Remote Manager 137
Configure XBee network settings in the web interface 138
XBee Configuration page 138
Device Details page 139
XBee network OTA firmware updates 141
Update the XBee network node firmware (OTA updates) from Remote Manager 141
Update the XBee node firmware (OTA updates) from the web interface 142
OTA firmware update troubleshooting 144
XBee Gateway network Python log file 145
XBee network troubleshooting resources 145
Learn more about XBee Gateway
Default startup and operation behaviors for XBee Gateway 146
Default behavior regarding NTP time server access 146
Default behavior regarding DNS 146
Firewalls and required open ports 147
Deploying devices over a network 147
Connect the XBee nodes to XBee Gateway 147
Configure XBee Gateway as a coordinator 147
Join nodes to the coordinator 148
Verify that XBee nodes are joined to the coordinator 149
Configure the ZigBee network addressing parameters for XBee nodes 150
XBee Gateway User Guide
6
Page 7

Key addressing parameters 150
Configure the network addressing parameters 151
Explore serial I/O 151
Understand the process for configuring the serial I/O 151
Example serial I/O configuration 152
Configure the serial I/O 152
Explore digital and analog I/O 153
Understand the process for digital and analog I/O 153
Example digital or analog I/O configuration 154
Configure the digital or analog I/O 155
View your device data 157
View device data from Remote Manager 158
View device data and events in the Python log file for XBee Gateway 158
Hardware
Ethernet and Wi-Fi hardware 161
Cellular hardware 162
Antennas 163
XBee Gateway button 163
XBee Gateway LEDs descriptions 164
Power LED 164
XBee LED 165
Network LED 165
Signal strength LED (cellular models only) 166
Troubleshoot your XBee Gateway
XBee Gateway system log 168
XBee Gateway log files and contents 168
Display the system log 169
Cellular connection issues 170
Common provisioning issues 170
Troubleshooting XBee Gateway GSM devices 171
Troubleshooting XBee Gateway CDMA devices 172
Device Discovery troubleshooting tips 172
Rebooting XBee Gateway 173
Troubleshooting LEDs 173
Firewalls and required open ports 174
Cannot connect to NTP time server to get correct time 175
Cannot connect to DNS server to resolve the Remote Manager server address 175
Need more help? 175
XBee Gateway User Guide
7
Page 8

About Digi XBee Gateway
Digi XBee® Gateway provides a low-cost, programmable solution to connect networks of XBeeenabled devices to IP networks. With a simple, open-source Python™ development environment, this
gateway enables custom applications to run locally while interfacing across existing Ethernet/WiFi/cellular networks for WAN connectivity to cloud-based software applications.
The XBee Gateway contains the XBeeZigBee product.
You can manage XBee Gateway products remotely via Digi Remote Manager®. Remote Manager
allows users to remotely manage thousands of deployed devices, supporting features like remote
firmware upgrades and event alarms.
This guide describes how to get started with yourXBee Gateway. This guide is intended for a
developer or programmer. It covers the following information:
n Hardware
n Get started
n Set up your XBee Gateway
XBee Gateway User Guide
8
Page 9

About Digi XBee Gateway Regulatory information and certifications
n Administration and maintenance tasks
n About programming
n Program XBee Gateway using Python
n Configure XBee Gateway
n Configure XBee network settings
n Learn more about XBee Gateway
n Troubleshoot your XBee Gateway
Regulatory information and certifications
RF exposure statement
In order to comply with RF exposure limits established in the ANSI C95.1 standards, the distance
between the antenna or antennas and the user should not be less than 20 cm.
FCC certifications and regulatory information (USA only)
FCC Part 15 Class B
Radio Frequency Interface (RFI) (FCC 15.105)
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class B digital devices pursuant to
Part 15 Subpart B, of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try and correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
n Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
n Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
n Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
n Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Labeling Requirements (FCC 15.19)
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
If the FCC ID is not visible when installed inside another device, then the outside of the device into
which the module is installed must also display a label referring to the enclosed module FCC ID.
Modifications (FCC 15.21)
Changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved by Digi may void the user’s
authority to operate this equipment.
XBee Gateway User Guide
9
Page 10

About Digi XBee Gateway Regulatory information and certifications
Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
Digi has issued Declarations of Conformity for the XBee Gateway concerning emissions, EMC, and
safety. For more information, see www.digi.com/resources/certifications.
Important note
Digi customers assume full responsibility for learning and meeting the required guidelines for each
country in their distribution market. Refer to the radio regulatory agency in the desired countries of
operation for more information.
CE mark (Europe)
The XBee Gateway is certified for use in several European countries. For information, visit
www.digi.com/resources/certifications.
If the XBee Gateway is incorporated into a product, the manufacturer must ensure compliance of the
final product with articles 3.1a and 3.1b of the RE Directive (Radio Equipment Directive). A Declaration
of Conformity must be issued for each of these standards and kept on file as described in the RE
Directive.
Furthermore, the manufacturer must maintain a copy of the XBee Gateway user manual
documentation and ensure the final product does not exceed the specified power ratings, antenna
specifications, and/or installation requirements as specified in the user manual. If any of these
specifications are exceeded in the final product, a submission must be made to a notified body for
compliance testing to all required standards.
OEM labeling requirements
The CE marking must be affixed to a visible location on the OEM product.
CE labeling requirements
The CE mark shall consist of the initials “CE” taking the following form:
n If the CE marking is reduced or enlarged, the proportions given in the above graduated
drawing must be respected.
XBee Gateway User Guide
10
Page 11

About Digi XBee Gateway Safety statements
n The CE marking must have a height of at least 5 mm except where this is not possible on
account of the nature of the apparatus.
n The CE marking must be affixed visibly, legibly, and indelibly.
Industry Canada (IC) certifications
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
This device complies with Industry Canada’s licence-exempt RSSs. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause interference; and
(2) This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
Le présent appareil numerique n’emet pas de bruits radioelectriques depassant les limites applicables
aux appareils numeriques de la class B prescrites dans le Reglement sur le brouillage radioelectrique
edicte par le ministere des Communications du Canada.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts
de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes:
(1) l'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et
(2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage
est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Korea Communications Commission (KCC) certifications
We, Digi International, in agreement with Powermat gateway, as per The Radio Research Agency
(RRA), division of the Korea Communications Commission (KCC), consider this device Industrial Class A
Equipment (Industrial Broadcasting & Communication Equipment) and therefore electromagnetic
wave-suitable.
For Class A Equipment (Business Broadcasting and Communications Equipment)
The equipment is for business use (Class A), and has acquired electromagnetic conformity
registration, so sellers and users are required to take caution in this regard.
Safety statements
Important Safety Information
CAUTION! To avoid contact with electrical current, follow all safety items listed below.
XBee Gateway User Guide
11
Page 12

About Digi XBee Gateway Safety statements
n Never install electrical wiring during an electrical storm.
n Never install an Ethernet connection in wet locations unless that connector is specifically
designed for wet locations.
n Use caution when installing or modifying lines.
n Use a screwdriver and other tools with insulated handles.
n Wear safety glasses or goggles.
n Do not place Ethernet wiring or connections in any conduit, outlet or junction box containing
electrical wiring.
n Installation of inside wire may bring you close to electrical wire, conduit, terminals and other
electrical facilities. Extreme caution must be used to avoid electrical shock from such facilities.
Avoid contact with all such facilities.
n Ethernet wiring must be at least 6 feet from bare power wiring or lightning rods and
associated wires, and at least 6 inches from other wire (antenna wires, doorbell wires, wires
from transformers to neon signs), steam or hot water pipes, and heating ducts.
n Do not place an Ethernet connection where it would allow a person to use an Ethernet device
while in a bathtub, shower, swimming pool, or similar hazardous location.
n Protectors and grounding wire placed by the service provider must not be connected to,
removed, or modified by the customer.
n Do not touch uninsulated Ethernet wiring if lightning is likely.
n External Wiring: Any external communications wiring installed needs to be constructed to all
relevant electrical codes. In the United States this is the National Electrical Code Article 800.
Contact a licensed electrician for details.
Warnings for Use of Wireless Devices
CAUTION! Observe all warning notices regarding use of wireless devices.
Potentially Hazardous Atmospheres
Observe restrictions on the use of radio devices in fuel depots, chemical plants, etc. and areas where
the air contains chemicals or particles, such as grain, dust, or metal powders, and any other area
where you would normally be advised to turn off your vehicle engine.
Safety in Aircraft
Switch off the wireless device when instructed to do so by airport or airline staff. If the device offers a
‘flight mode’ or similar feature, consult airline staff about its use in flight.
XBee Gateway User Guide
12
Page 13

About Digi XBee Gateway Maximum power and frequency bands
Safety in Hospitals
Wireless devices transmit radio frequency energy and may affect medical electrical equipment. Switch
off wireless devices wherever requested to do so in hospitals, clinics, or health care facilities. These
requests are designed to prevent possible interference with sensitive medical equipment.
Pacemakers
Pacemaker manufacturers recommended that a minimum of 15 cm (6 inches) be maintained between
a handheld wireless device and a pacemaker to avoid potential interference with the pacemaker.
These recommendations are consistent with independent research and recommendations by Wireless
Technology Research.
Persons with Pacemakers
n Should ALWAYS keep the device more than 15 cm (6 inches) from their pacemaker when turned
ON.
n Should not carry the device in a breast pocket.
n If you have any reason to suspect that the interference is taking place, turn OFF your device.
International EMC (Electromagnetic Emissions/Immunity/Safety) standards
This product complies with the requirements of following Electromagnetic Emissions/Immunity/Safety
standards.
There are no user-serviceable parts inside the product. Contact your Digi representative for repair
information.
Emissions Immunity Safety
AS/NZS 4268:2008 (Amended by A1:2010) Class
B (Wi-Fi only)
AS/NZS CISPR 22:2009 Class B
EN 301 489-17 V2.1.1:2009 Class B (Wi-Fi only)
EN 55022:2010 Class B
EN 61000-3-2:2006
EN 61000-3-3:2008
FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class B
FCC Part 15 Subpart C (Wi-Fi only)
ICES-003:2004 Class B
RSS-Gen:2010 (Wi-Fi only)
RSS-210:2010 (Wi-Fi only)
EN 301 489-17 V2.1.1:2009
(Wi-Fi only)
EN 55024:2010
EN 301 489-24 V1.5.1 (Cellular
only)
Maximum power and frequency bands
This section contains the maximum power and frequency bands for the XBee Gateway.
IEC 60950-1:2005
EN 60950-1:2006
UL 60950-1
CSA C22.2 No.
60950-1
XBee Gateway User Guide
13
Page 14

About Digi XBee Gateway XBee Gateway Python application
XBee Gateway: Cellular
Maximum power Associated frequencies
6.3 mW 5 MHz channel spacing, beginning at 2405 MHz and ending at
2480 MHz
2 W Cellular 850 and 900 MHz bands
1 W Cellular 1800 and 1900 MHz bands
XBee Gateway: Ethernet
Maximum power Associated frequencies
6.3 mW 5 MHz channel spacing, beginning at 2405 MHz and ending at
2480 MHz
XBee Gateway: Wi-Fi
Maximum power Associated frequencies
6.3 mW 5 MHz channel spacing, beginning at 2405 MHz and ending at
2480 MHz
88 mW 13 overlapping channels each 22 MHz wide and spaced at 5
MHz. Centered at 2.412 to 2.472 MHz.
XBee Gateway Python application
The XBee Gateway Python application resides on XBee Gateway. Its key functions include connecting
your XBee modules to Remote Manager, enabling uploads of data to Remote Manager, and receiving
remote text and commands. The XBee Gateway Python application is installed by default in your XBee
Gateway device and automatically starts when the gateway is initialized.
For more information on the XBee Gateway Python application, see XBee Gateway Python application
and Remote Manager.
XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit
Digi offers a development kit called the XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit.
The XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit is designed to make it easy to set up your XBee ZigBee hardware and
configure its sample web application. You can see sensor data from your development board on the
web, as well as send data and commands from the web to your device. The components in this kit
allow you to create highly customized solutions for connected devices.
To order this kit, go to the XBee Gateway product page for ordering information. For setup
instructions, see the XBeeZigBeeCloudKit Getting Started Guide.
XBee Gateway User Guide
14
Page 15

About Digi XBee Gateway Hardware interfaces
Hardware interfaces
XBee Gateway hardware interfaces include a button for controlling various device operations, LEDs
that indicate device state and status of connections, and activity for Ethernet, Wi-Fi, cellular, and XBee
network connections. You can control some of these hardware features through programming.
For detailed information about hardware interfaces, see Hardware.
Configuration and management interfaces
To establish network connectivity with an XBee Gateway device, minimal configuration is required in
many environments. This means that you may not need to set or change configuration settings from
their factory defaults to begin developing with the device. There are several user interfaces for
interacting with XBee Gateway, for example to view or change configuration settings or perform
important administrative tasks such as updating firmware or rebooting the device. These include:
n XBee Gateway web interface: A web-based interface for configuring, monitoring, and
administering Digi devices.
n Remote Manager interface: A web-based, remote-management interface.
n RFGateway and Python remote device management solutions
n Programming interface applications
XBee Gateway web interface
The XBee Gateway web interface, available via a local network connection to XBee Gateway, provides
an easy way to configure device settings and perform administrative tasks. Device information
displayed varies by model.
You are required to log in to the web interface. The default user name and password are described
below:
n User name: python
n Password: The unique password printed on the device label. If the password is not on the
device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work, the password may
have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
For more information, see Configure settings from the XBee Gateway web interface.
Remote Manager interface
Remote Manager is a software-as-a-service that empowers IT, network operations and customer
support organizations to conquer the challenges of managing the vast array of equipment in their
device networks. As a network grows, the complexity of effectively managing the network assets
grows exponentially.
When XBee Gateway powers up, the device automatically connects to Remote Manager. Remote
Manager provides the capabilities you need to manage a dynamic device network, including:
n Centralized control over large numbers of devices
n Reducing service complexity
n Maintaining high levels of security
XBee Gateway User Guide
15
Page 16

About Digi XBee Gateway Configuration and management interfaces
n Configuring and decommissioning of equipment
n Adding functionality to device networks
In addition, you can use the Remote Manager Web Services (API) to provide seamless integration from
Digi gateways into customer back-office applications. You can access these Web Services via the API
Explorer tab of the Documentation tab of the Remote Manager interface. See Digi Remote Manager
Programmer Guide for more information.
Some things to note about using Remote Manager:
n You must register devices on Remote Manager before you can access them from Remote
Manager.
n To minimize network traffic, Remote Manager uses caching. As a result, device settings can be
out-of-sync between the device and the settings viewed on the Remote Manager console.
n You can refresh device information on demand when the device is connected. The device
information refreshes automatically when a device connects.
For more information about configuring settings from Remote Manager, see Configure settings from
Remote Manager.
For more information on Remote Manager as a remote device network management solution, see
these resources:
n Digi Remote Manager User Guide
n Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide
n Remote Manager tutorials and other documents available on the Digi Remote Manager
product page
Note To serve our customers most effectively, Digi International Inc. is consolidating its cloud
services, Digi Device Cloud and Digi Remote Manager®, under the Remote Manager name. This phased
process does not affect device functionality or the functionality of the web services and other
features. However, you will find instances of both Device Cloud and Digi Remote Manager in some
documentation, firmware, and user interfaces.
RFGateway and Python remote device management solutions
XBee Gateway includes Remote Manager functionality by default. This functionality allows you to see
your data in the cloud quickly and with minimal effort.
However, you can extend the system through the Python interpreter and customize the gateway to
connect directly to the environment of your choice. See the Digi XBee, RFGateway and Python
Resource page for more information.
Programming interface applications
XBee Gateway offers a variety of interfaces that produce and/or consume data. Developing software
programs for XBee Gateway products allows Digi customers to provide custom logic to control the
information to and from these interfaces.
For more information, see About programming.
XBee Gateway User Guide
16
Page 17

About Digi XBee Gateway Product differences from predecessor ConnectPort® X products
Product differences from predecessor ConnectPort® X products
XBee Gateway differs from predecessor ConnectPort X products. These differences are important to
programmers and integrators who are familiar with the predecessor devices and need to develop
applications and install or manage the gateway. These differences include the following.
n Operating system: XBee Gateway is built on the industry-standard Linux operating system,
versus a Digi-proprietary embedded operating system.
n Memory: XBee Gateway has 64 MB of RAM and 128 MB of flash memory. Users have access to
up to 20 MB of RAM and up to 20 MB of flash memory. Predecessor devices had less RAM and
flash memory available for custom Python applications.
n System date and time: XBee Gateway, for reasons of improved security, has a greater
dependence on time synchronization than predecessor products. In so doing, XBee Gateway
uses standard Network Time Protocol (NTP) and requires connectivity with an external NTP
time server. Without NTP, the device cannot:
l Correctly validate security certificate
l Disable the ability to connect to Remote Manager
l Disable the ability to update the firmware
n Button: XBee Gateway features a programmable button. You can configure this button to
activate some Digi native features (such as returning a device to its factory defaults), and you
can also use this button for custom applications. For more information on the button, see XBee
Gateway button. This button behavior differs from the Reset button behavior on other gateway
products.
n User interfaces:
l XBee Gateway has a web user interface for both network configuration and access to the
log file for troubleshooting the initial connection to Remote Manager. For more information
on the web interface, see Configure XBee Gateway.
l Command-line interface differences: XBee Gateway allows access to the Linux shell
using SSH. For more information about the shell, see Linux command shell (command line
interface). Access to a command-line interface through Telnet is not supported for network
security reasons. Commands in the command-line interface for predecessor ConnectPort X
products are not supported. However, some ConnectPort X2 command-line interface
commands have equivalents in the Remote Command Interface (RCI).
n Firmware updates: Due to the complexity of the Linux-based system, you cannot use standard
firmware updates to downgrade a system.
n Logging: XBee Gateway supports continuous logging for troubleshooting. You can browse the
log files from the web interface or pull the log files from the device file system in Remote
Manager. They are stored in the Linux file system in the /WEB/logging directory and persist
across reboots and power cycles. For more information, see View the Python log file.
XBee Gateway User Guide
17
Page 18

About Digi XBee Gateway Where to find more information
n Supported Python version: XBee Gateway uses Python interpreter version 2.7. Many
predecessor ConnectPort X products use Python 2.4.
Any custom-compiled Python code must be recompiled for Python interpreter 2.7. Custom
Python modules are not 100% compatible with XBee Gateway. Therefore, in addition to
recompiling, you may need to port.
Where to find more information
See the following topics in this guide for more information:
n Learn more about XBee Gateway
n About programming
The following documents are available on www.digi.com unless otherwise noted:
n For more information about features and operation of the XBee RF module mounted inside the
gateway, see XBee/XBee-PRO ZigBee RF Module User Guide.
n You can refer to the ConnectPort X2e section in the Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference Manual
for additional programming content for ConnectPort X2e products. Information in this section
also applies to XBee Gateway.
n DIA section in the Digi Python Reference Manual for Developers guide
n Digi Remote Manager User Guide
n Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide
n Datasheets and other documents on the Digi Remote Manager product page
XBee Gateway User Guide
18
Page 19

Get started
Based on the XBee Gateway model that you have, choose one of the following options:
n Set up the XBee Gateway Cellular hardware
n Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
Set up the XBee Gateway Cellular hardware
This section walks you through the steps required to set up your XBee Gateway Cellular hardware and
provides additional reference information.
Verify your components
Included equipment
Equipment Description
XBee Gateway
(Cellular model)
XBee Gateway User Guide
19
Page 20

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Cellular hardware
Equipment Description
Ethernet cable
Power supply
Note A loose label sticker that includes the unique device password may be included in the box. Retain
this label sticker with your hardware records. This default password will be needed to log into the
device's web UI if the device is factory reset.
XBee Gateway User Guide
20
Page 21

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Cellular hardware
Connect the cellular hardware
1. Install a SIM card. See Set up and configure GSM-based devices for instructions.
2. Optional: If you are using an Ethernet connection in addition to the cellular, connect one end of
the Ethernet cable to your gateway and the other to a live Ethernet jack.
XBee Gateway User Guide
21
Page 22

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
3. Connect the power supply.
4. Startup Sequence - After power is applied:
a. The Power LEDturns solid green.
b. The XBee LEDturns blinking green when XBee Gateway
creates a ZigBee network.
c. The Network LEDgradually turns solid green when XBee
Gateway connects to Remote Manager.
d. For the Cellular model, the Signal Strength LEDturns
either yellow or green, depending on the cellular signal
strength.
Connect XBee Gateway to the network
Choose one of the following options:
Connect to an Ethernet network
Your XBee gateway automatically connects to the Ethernet network when a DHCP server is available
to assign an IP address to it and no firewalls block outgoing traffic to ports 3197 and 3199. If the
Ethernet network does not come up, see Cannot connect to DNS server to resolve the Remote
Manager server address.
Note XBee Gateway requires a DHCP server to assign its IP address. If you do not have a DHCP
server, see Ethernet IP network settings for information on configuring your IP parameters.
Connect to a Cellular network
Register the modem in the XBee Gateway cellular device and set it up in your mobile service provider's
network. Registration and setup differs among models. See Default behavior with the cellular network
for information on configuring the XBeeGateway cellular model (GSM or CDMA). Disconnect the
Ethernet cable when the configuration steps are complete.
Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
This section walks you through the steps required to set up your XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware and
provides additional reference information.
XBee Gateway User Guide
22
Page 23

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
Verify your components
Included equipment
Equipment Description
XBee Gateway
(Wi-Fi model)
Ethernet cable
Power supply
Note A loose label sticker that includes the unique device password may be included in the box. Retain
this label sticker with your hardware records. This default password will be needed to log into the
device's web UI if the device is factory reset.
XBee Gateway User Guide
23
Page 24

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
Connect the Wi-Fi hardware
1. Optional: If using an Ethernet connection in addition to the Wi-Fi, connect one end of the
Ethernet cable to your gateway and the other to a live Ethernet jack.
XBee Gateway User Guide
24
Page 25

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
2. Connect the power supply.
3. Startup Sequence - After power is applied:
a. The Power LEDturns solid green.
b. The XBee LEDturns blinking green when XBee Gateway creates a
ZigBee network.
c. The Network LEDgradually turns solid green when XBee Gateway
connects to Remote Manager.
Note For more information on these LEDstates, see XBee Gateway LEDs descriptions.
Connect XBee Gateway to the network
Choose one of the following options:
Connect to a Wi-Fi network
1. Get the following Wi-Fi security information from your network administrator. You will need this
to connect to your Wi-Fi access point in step 6.
SSID: ____________________
Wi-Fi security mode: ____________________
Passphrase or key: ____________________
Other parameters: ____________________
2. Press the button on your XBee Gateway once to enable Access Point mode. This Access Point
mode is active for five minutes.
XBee Gateway User Guide
25
Page 26

Get started Set up the XBee Gateway Wi-Fi hardware
3. From the list of Wi-Fi network connections on your computer, connect your computerto the Wi-
Fi network named xbgw-xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx, where xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx is the serial number of
the gateway.
4. Once you connect to the Wi-Fi network on your computer, open a web browser and type the
URL of XBee Gateway: http://192.168.100.1. This will open the XBee Gateway web interface.
5. Log in to the web interface.
n User name: The default user name is python. If that user name does not work, it may
have been changed by your system administrator. Contact your system administrator
for help.
n Password: The unique, default password is printed on the device label. If the password
is not on the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work,
the password may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
6. From the XBeeGateway web interface, go to Configuration > Wireless Network.
7. On the Wireless Network Configuration page, click Run Wizard under Interface Configuration
and follow the prompts to configure your device. See Wi-Fi network settings for more
information.
8. Restore the Wi-Fi network on your computer to its previous connection.
Connect to an Ethernet network
Your XBee gateway automatically connects to the Ethernet network, when a DHCP server is available
to assign an IP address to it and no firewalls block outgoing traffic to ports 3197 and 3199. If the
Ethernet network does not come up, see Cannot connect to DNS server to resolve the Remote
Manager server address.
Note XBee Gateway requires a DHCP server to assign its IP address. If you do not have a DHCP
server, see Ethernet IP network settings for information on configuring your IP parameters.
XBee Gateway User Guide
26
Page 27

Set up your XBee Gateway
This section walks you through the steps required to set up your XBee Gateway and provides
additional reference information.
Set up XBee Gateway summary
These instructions give an overview of how to set up XBee Gateway.
1. Configure the network settings. These settings include IP networking parameters and Remote
Manager connectivity.For more information, see:
n Wireless (Wi-Fi) network settings
n Ethernet IP network settings
n Mobile connectivity settings
2. Connect the XBee nodes to XBee Gateway. This step involves configuring the parameters for
forming XBee networks on both XBee Gateway and XBee nodes. There are three substeps:
a. Configure XBee Gateway as a coordinator.
b. Join XBee nodes to the coordinator.
c. Verify that the XBee nodes are joined to the coordinator.
See Connect the XBee nodes to XBee Gateway for more information.
3. Configure XBee ZigBee network addressing settings. See Configure the ZigBee network
addressing parameters for XBee nodes for more information.
4. Explore configuring XBee nodes for input/output.
a. If using serial I/O, configure XBee nodes for serial I/O. See Explore serial I/O for
b. If using digital or analog I/O, configure the XBee nodes for digital or analog I/O. See
5. Look at your device data on Remote Manager. See View your device data for more information.
The following image shows the layout of a fully set up XBee Gateway.
XBee Gateway User Guide
more information.
Explore digital and analog I/O for more information.
27
Page 28

Set up your XBee Gateway Joining ZigBee networks
Joining ZigBee networks
ZigBee networks are called Personal Area Networks or PANs. In the ZigBee protocol, the only node
that can start a new network is the coordinator. For that reason, each ZigBee network must have one
coordinator.
XBee Gateway includes a built-in XBee ZigBee node already configured as coordinator. Therefore, as
soon as you power on the XBee Gateway device, your ZigBee network is initialized.
To start a network, the coordinator must automatically choose a PAN identifier (PAN ID) and the
operating channel for that network. Once those parameters are established and the network is
XBee Gateway User Guide
28
Page 29

Set up your XBee Gateway Joining ZigBee networks
initialized, the coordinator and routers can allow other devices (other routers or end devices) to join
the network and route data.
Each network is defined with a unique PAN identifier (PAN ID). This identifier is common among all
devices of the same network. That is, devices on the same ZigBee network must share the same PAN
ID in order to communicate with each other. When you power on a coordinator, it automatically
establishes the PAN ID or uses a pre-configured one when it creates the new network.
n If the PANID of the coordinator is 0, it performs a PAN scan to identify nearby ZigBee networks
and uses a random unused PAN ID to start the new network. By default, an XBee Gateway
coordinator is configured to generate a random PAN ID.
n If the PANID for a router or end device is 0, it performs a PAN scan and tries to join any
available ZigBee network it finds.
You can connect to an XBee ZigBee module that is configured as a router node to the network
initialized by XBee Gateway. By default, the PAN ID of this ZigBee module is configured to 0. Therefore,
if you power on the XBee ZigBee module and there is no other ZigBee network around, the module
joins the ZigBee network initialized by XBee Gateway automatically. The joining operation occurs
when the Association LED of the board on which the XBee ZigBee module is mounted starts blinking.
The 802.15.4 PHY (physical layer) protocol description defines 16 operating channels in the 2.4 GHz
frequency band. Before starting the network, the coordinator automatically performs a channel scan
to select a good channel to use for the network.
You can configure all the ZigBee nodes in a network with the channel or channels on which they
operate.
Join XBee Gateway to an existing ZigBee network
Although this is not a common task, you can configure your XBee Gateway device to operate as a
router and join an existing ZigBee network.
To join XBee Gateway to an existing ZigBee network:
1. Open a web browser and type the URL of XBee Gateway: http://192.168.100.1. The XBee
Gateway web interface appears.
2. Log in to the web interface:
n User name: The default user name is python. If that user name does not work, it may
have been changed by your system administrator. Contact your system administrator
for help.
n Password: The unique, default password is printed on the device label. If the password
is not on the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work,
the password may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
3. Click XBee Network in the left menu.
4. Select the XBee Gateway ZigBee local XBee device. The XBeeConfiguration page appears.
5. From the XBee Configuration page, click Network Settings.
XBee Gateway User Guide
29
Page 30

Set up your XBee Gateway Joining ZigBee networks
6. Configure the Extended PAN ID (ID) option with the PAN ID of the network to which XBee
Gateway should join.
7. Clear the Coordinator Enable(CE) check box. This allows XBee Gateway to behave as a router
node within the ZigBee network.
8. Click Apply to save the changes to the device. After you apply the changes, XBee Gateway
behaves as a router node and tries to connect to the ZigBee network with the PAN ID that you
configured.
To join your XBee ZigBee module from the kit to an existing network, follow the steps described in
Configure XBee Gateway with a custom PAN ID.
Configure XBee Gateway with a custom PAN ID
In some cases, you want control of the PAN ID used to create your ZigBee network. Use a custom
PANIDand configure the coordinator, routers, and end devices to use it when there are other
networks around and you do not want your router or end device nodes to join them.
To configure XBee Gateway with a custom PANID:
1. Open a web browser and type the URL of XBee Gateway: http://192.168.100.1. The XBee
Gateway web interface appears.
XBee Gateway User Guide
30
Page 31

Set up your XBee Gateway XBee Gateway and non-XBee ZigBee Devices
2. Log in to the web interface:
n User name: The default user name is python. If that user name does not work, it may
have been changed by your system administrator. Contact your system administrator
for help.
n Password: The unique, default password is printed on the device label. If the password
is not on the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work,
the password may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
3. Under Configuration, click XBee Network.
4. Select the XBee Gateway local XBee device that you want to configure. The XBee
Configuration page appears.
5. From the XBee Configuration page, click Network Settings.
6. Configure the Extended PAN ID (ID) option with your custom PAN ID value.
7. Click Apply to save the changes to the device. After applying the changes, the coordinator
initializes the ZigBee network with the new PAN ID. If you had any other ZigBee nodes
connected to the network, you must update their PAN IDs so they will join the new one.
XBee Gateway and non-XBee ZigBee Devices
You can refer to additional resources to learn about using XBee Gateway with non-XBee ZigBee
devices. Digi provides support and resources for your use of the product.
Resources include:
n Digi forum
n Digi Knowledge Base
n XBee/XBee-PRO ZB RF Modules User Guide for more information about features and operation of
the XBee RF module mounted inside the gateway
n XBee ZigBee information on the Digi XBee ZigBee product page
XBee Gateway User Guide
31
Page 32

Administration and maintenance tasks
There are several administrative and maintenance tasks that you need to perform periodically on
XBee Gateway. This topic covers common administrative tasks and how to perform them through
Remote Manager and the web interface.
Logging in to the web interface
When you access the web interface, a log in screen displays. You must enter a user name and
password specified for the device.
n User name: The default user name is python. If that user name does not work, it may have
been changed by your system administrator. Contact your system administrator for help.
n Password: The unique, default password is printed on the device label. If the password is not
on the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work, the password
may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
File management
The XBee Gateway file management feature lets you manage custom applications, their associated
data files, and other files. The File Management page is available in Remote Manager and in the web
interface.
You can also push firmware update files to the device file system, and pull log files from the device file
system. See XBee Gateway file system for information about the file system.
File Management page in Remote Manager
You can use the File Management page in Remote Manager to load files, such as custom application
files, onto XBee Gateway and display current information about loaded files.
You can also use this page to download system log files from XBee Gateway to view for
troubleshooting or other purposes. These log files are in the /WEB/logging folder. For a description of
the XBee Gateway file system layout, see XBee Gateway file system.
Note Digi recommends using no more than 20 MB for custom applications, as XBee Gateway requires
a portion of the same space to be capable of managing persistent system logs and firmware updates.
Access the File Management page
Follow this process to access the File Management page in Remote Manager:
XBee Gateway User Guide
32
Page 33
Administration and maintenance tasks File management
1. Access Remote Manager and log in. If you do not yet have a Remote Manager account, click the
Sign up link on the Remote Manager log in page.
2. Click the Device Management tab.
3. From the list of devices, double-click on the device you want to review.
4. Click the File Management link in the left-hand pane. The File Management screen displays.
File Management toolbar
The File Management toolbar provides quick access to file management tasks.
Button/Field
Name Description
Upload file Opens a dialog for uploading files to the current folder (directory).
Download file Downloads the selected file to a computer. You can choose to open
the downloaded file with a specified tool or save it.
Delete Deletes the selected items.
Refresh Refreshes the list of folders and files displayed.
Back Move to the previous folder in folder history.
Forward Move to the next folder in folder history.
Home Returns to the root folder.
Current or
destination
folder
Go Goes to the directory specified in
An editable field that displays the current folder. You can use this
field to type a different destination directory.
Current or destination folder
field.
File Management page in the XBee Gateway web interface
You can use the File Management page to load files onto XBee Gateway and display current
information about loaded files. For a description of the XBee Gateway file system layout, see XBee
Gateway file system.
Access the File Management page
Follow this process to access the File Management page in the web interface:
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Click File Management under Administration to launch the File Management page.
XBee Gateway User Guide
33
Page 34

Administration and maintenance tasks Certificate Management
File Management page
The following fields and buttons appear on the File Management page:
Volume Information section: Displays the current directory for loading files and free space remaining.
Note Digi recommends using no more than 20 MB for custom applications, as XBee Gateway requires
a portion of the same space to be capable of managing persistent system logs and firmware updates.
Upload to Current Directory section: Uploads files to the current directory.
n Choose File: To find a file on your computer, click Choose File and go to the file.
n Update file: Click Update file to begin the file upload process.
File List: A listing of the current directory (as noted in the Volume Information section) on the device.
n Open: Opens a directory after it is selected in the file list. The current directory changes and
the list is updated.
n Make Directory: Creates a new, empty directory in the current directory.
n Save As: Downloads a regular file from the file system to your local computer.
n Remove: Deletes files or empty directories. If there are one or more files in a directory, the
directory cannot be deleted.
Refresh button: Reloads the information on the page.
Certificate Management
The Certificate Management feature allows you to load and manage entries in a database that
contains certificate and private key data.
Note A link to the Certificate Management page is available in the web interface only if the XBee
Gateway device is the Ethernet + Wi-Fi version. A link to this page is not available in the web interface
for the Ethernet or Ethernet + Cellular device versions.
This feature supports:
n Displaying certificate database entries
n Loading certificate database entries
n Saving certificate database entries
n Removing certificate database entries
n Importing a private key for the Digi device into the database
Certificates and public/private host key pairs are an integral part of public key infrastructure (PKI)
based security.
Certificate Management page in the web interface
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Click Administration > Certificate Management.
XBee Gateway User Guide
34
Page 35
Administration and maintenance tasks Back up or restore the configuration
Note The link to the Certificate Management page is available in the web interface only if the XBee
Gateway device is the Ethernet + Wi-Fi version.
The following fields and buttons appear on the Certificate Management page:
n Volume Information: Displays information about the user file system, /userfs.
n Current Directory: Certificates are saved in this directory on the device. Note that navigating
to the file system is not possible on this page. To go to the file system, click File Management
under Administration and then go to the file system.
n Free Space: The amount of free space on the user file system. The typical size of a backup file
is about 8 KB.
n Upload Certificate: Uploads a certificate to XBee Gateway.
n Current Certificates: Lists all the certificates currently loaded on XBee Gateway.
n Refresh button: Refreshes the list of certificates.
n Activate button: Activates the loaded certificates.
Back up or restore the configuration
After you configure XBee Gateway device, back up the configuration settings. You can back up the
settings from the Remote Manager or the web interface.
Having a backup of the configuration settings is recommended if you run into one of the following
situations:
n You need to restore the configuration settings because a problem occurred.
n You upgraded or added the firmware and you need to restore your configuration settings.
n You added new devices that need to be configured and want to use the same configuration
settings as the original device. In this instance, you can load the backup configuration settings
from the original device onto other devices.
Back up and restore files from Remote Manager
1. Access Remote Manager and log in.
2. From the Devices page, click the devices in the Device list that you want to back up.
3. Click the More button within the toolbar and then select the Export Properties option from
under the Devices category.
4. Choose one of the following options from the Export Properties dialog and then click OK:
n Export all: Exports the device’s entire configuration. The option allows you to export
the entire configuration, including IP address information, and provides you with a
complete backup configuration for the device.
n Export all except unique network and device identity properties: Exports the
non-networking portion of the configuration. Choose this option if you want to use this
device's configuration as a template to apply to a group of devices in the future.
XBee Gateway User Guide
35
Page 36

Administration and maintenance tasks Back up or restore the configuration
Back up and restore files from the XBee Gateway web interface
The Backup/Restore page allows you to back up and restore the following device configuration
settings to a file:
n XBee Gateway
n (Optional) XBee RF module
Back up files
To back up files from the XBee Gateway web interface:
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Click Administration > Backup/Restore.
3. In the Volume Information section, review the amount of free space available.
4. If you want to save the configuration settings for the XBee RF module along with the device
configuration settings, select the Include XBee gateway radio settings in the backup file
option.
5. In the Backup field, enter the name of the back up file.
6. Click OK to start the process.
Restore files
To restore files from the XBee Gateway web interface:
1. Access the XBee Gateway web interface. You are required to log in to the web interface.
2. Click Backup/Restore under Administration.
3. Click Choose File in the Restore Configuration section.
4. Select the configuration file you want to restore.
5. Click OK.
6. Click Restore to restore the configuration from the selected file.
Backup/Restore page
The following fields and buttons appear on the Backup/Restore page:
Volume Information section: Displays information about the user file system, /userfs.
n Current Directory: The backup file is temporarily saved in this directory on the device. Note
that navigating to the file system is not possible on this page. To go to the file system, click File
Management under Administration and then go to the file system.
n Free Space: The amount of free space on the user file system. The typical size of a backup file
is about 8 KB.
Backup Configuration section: Downloads the gateway configuration file through the web browser
and allows you to save the file on your computer.
n Include XBee gateway radio settings in the backup file: If enabled, the configuration
settings for the XBee RF module are saved along with the device configuration settings.
XBee Gateway User Guide
36
Page 37

Administration and maintenance tasks Update firmware
n Backup: The name of the backup file. The default file name is backup.cfg. You can change the
file name from the save file dialog box. Any name is allowed.
Restore Configuration section: Restores configuration settings from a backup file on your computer
or a server.
n Choose File: Opens a browse dialog for locating and selecting the appropriate configuration
file.
n Restore: Click Restore to restore the configuration from the selected file.
Errors
Any errors that occur during the restore process appear in a red banner at the top of the
Backup/Restore page. Typically, the only reason an error occurs is if a user has modified the backup
file. The following list provides some of the possible error messages.
n Invalid file contents: The file contents are not a valid backup format. This may be caused by
invalid XML syntax.
n Element set_setting has extra content (name): The settings group name is not recognized.
n Element set_setting failed to validate content (name): Incorrect value for setting name.
n Other RCI errors are possible, but are less common.
Update firmware
There are several types of firmware updates for XBee Gateway:
n XBee Gateway operating system: You can download Gateway operating system firmware
updates for XBee Gateway from the Digi Support site. You can then load the firmware through
the web interface or Remote Manager.
You can only upgrade the gateway operating system, not downgrade it, through the web
interface or Remote Manager. The firmware image contains a certificate that is verified before
XBee Gateway accepts an upgrade.
n XBee RF module on the gateway: See Update the local XBee Gateway firmware.
n XBee RF modules on your local network to be delivered Over the Air (OTA): As XBee
networks can involve a large number of nodes, Digi provides a way to schedule automatic XBee
Gateway firmware updates and manage firmware files. In the XBee Gateway web interface,
OTA firmware updates are performed from a page linked from the XBee Configuration page.
These firmware updates are supported for XBee ZigBee modules only. For information on
these updates, see XBee network OTA firmware updates.
Update firmware from Remote Manager
You can update the firmware from Remote Manager:
n Update the XBee Gateway device operating system firmware
n Update the local XBee Gateway firmware
n Update the XBee network node firmware (OTA updates) from Remote Manager
You can also schedule firmware updates from Remote Manager.
XBee Gateway User Guide
37
Page 38

Administration and maintenance tasks Update firmware
Update the XBee Gateway device operating system firmware
To update the XBee Gateway device operating system firmware:
1. Download the appropriate firmware from XBee Gateway product support page. For more
details on firmware filename conventions, see About firmware files.
2. Log in to Remote Manager.
3. Click the Device Management tab.
4. Select one or more devices from the device list to which you want to apply firmware updates,
right-click, and select Update Firmware.
5. Type or browse to the .bin filename containing the firmware update.
6. Click Update Firmware.
Update the local XBee Gateway firmware
To update the local XBee Gateway firmware:
1. Download the appropriate firmware from the XBee Gateway product support page. For more
details on firmware file name conventions, see About firmware files.
2. Log in to Remote Manager.
3. Click the Device Management tab.
4. Go to the device list.
5. Select one or more devices to which you want to apply firmware updates, right-click, and then
select Update Gateway XBee Radio Firmware.
6. Type or browse to the .ebl filename containing the firmware update.
7. Click Update Firmware.
The XBee Gateway firmware is updated. If the gateway is enabled, most XBee Gateway module
settings will be preserved when the firmware update completes. Some settings, such as
encryption keys, may not be preserved and must be entered again.
8. If required, type your encryption keys.
Schedule firmware updates
You can schedule firmware updates from Remote Manager. See the Digi Remote Manager User Guide
for more information on scheduling firmware updates.
1. Log in to Remote Manager.
2. Click the Device Management tab.
3. From the list, select the device for which you want to schedule a firmware update.
4. Right-click on the device, and choose Firmware > Update Firmware. The Update Firmware
dialog appears.
5. In the File field, enter or browse for the file containing the firmware update.
XBee Gateway User Guide
38
Page 39

Administration and maintenance tasks Update firmware
6. From the Schedule Options drop-down in the upper right corner of the dialog, select the
appropriate scheduling option.
7. Click Update Firmware to schedule the update.
Update firmware from the XBee Gateway web interface
Firmware updates are available from the Administration > Firmware Update page in the XBee
Gateway web interface.
n Update the XBee Gateway device operating system firmware
n Update the local XBee Gateway firmware
Update the XBee Gateway device operating system firmware
To update the XBee Gateway device operating system firmware:
1. Download the appropriate firmware from the XBee Gateway product support page. For more
details on firmware filename conventions, see About firmware files.
2. Access and log into the web interface.
3. Click Administration > Firmware Update. The Firmware Update page appears.
4. Select the Upgrade device operating system check box.
5. Click Next.
Status information for the firmware update appears, including the following information:
n Target Firmware: The device operating system firmware to be loaded on XBee
Gateway.
n Status: The current status of the firmware update operation.
For the XBee Gateway device operating system, the firmware update operation moves
through several states:
a. The web browser uploads the firmware file.
b. The firmware update is applied to the XBee Gateway operating system. If
the firmware update is successful, the message Firmware Upgrades
Completed Successfully appears. If errors occur during the update, the
message Completed with errors appears. If you need help understanding
the errors and viewing the log file containing the errors, contact Digi
Support.
c. XBee Gateway automatically reboots.
d. XBee Gateway returns to an operating state (run). All these states are
shown on the Firmware Update page.
Update the local XBee Gateway firmware
To update the local XBee Gateway firmware:
XBee Gateway User Guide
39
Page 40

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
1. Download the appropriate firmware from the XBee Gateway product support page. For more
details on firmware filename conventions, see About firmware files.
2. Access and log into the web interface.
3. Click Administration > Firmware Update. The Firmware Update page appears.
4. Select the Upgrade local (gateway) XBee’s firmware check box.
5. Click Next.
6. Type or browse to the filename containing the firmware update.
7. Click Next.
Status information for the firmware update appears, including the following information:
n Target Firmware: The device operating system firmware to be loaded on XBee
Gateway.
n Status: The current status of the firmware update operation.
The XBee firmware is updated. If the gateway is enabled, most XBee module settings will be
preserved when the firmware update completes. Some settings, such as encryption keys, may
not be preserved and must be entered again.
8. If required, type your encryption keys.
About firmware files
Firmware files for the operating system and XBee module on XBee Gateway are available through Digi
Technical Support on the XBee Gateway Support page. Click the Firmware Updates link.
Gateway operating system firmware files
Gateway operating system firmware files have a .bin extension.
XBee RF module firmware files
XBee RF module firmware files have an .ebl extension. From the Digi XBee Gateway - Zigbee support
page, click the Firmware Updates option. You can select the product and then download the
firmware.
There is only one firmware file for the XBee RF module in XBee Gateway products. It is named XBP24-
S2C_40XX.ebl, where XX is the firmware version.
There are other possible file types for OTA firmware updates. See XBee network OTA firmware
updates.
Mobile device status
The items on Mobile Status page are specific to a cellular modem or service provider account. These
items vary in the information reported from modem to modem and also differ between CDMA and
GSM services. A value that appears here depends on the modem type and connection state; if there is
no value for a status field, it does not appear. Use this information when troubleshooting issues and
communicating with technical support.
XBee Gateway User Guide
40
Page 41

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Display the mobile device status
To display the status of mobile device, choose one of the following options:
From Remote Manager
1. Click the Device Management tab.
2. From the device list, double-click the device to display the device properties menu.
3. Select System Information >Mobile Information. The Mobile Information page appears.
From the XBee Gateway web interface
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Click Administration > Mobile Status. The Mobile Status page appears.
Mobile Status page
The following table describes the fields on the Mobile Status or Mobile Information page.
Cellular
Status field
Device type Both The type of cellular modem. The possible values are
Manufacturer Both The manufacturer of the cellular modem.
Model Both The manufacturer’s model number for the cellular
Revision Both The manufacturer’s version number for the software
Serial number Both The manufacturer’s serial number for the cellular
Phone number Both
SIM IMSI GSM The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) for
SIM ICCID GSM The Integrated Circuit Card Identifier (ICCID) for the SIM
modem type
Description
CDMA
and GSM.
modem.
running on the cellular modem.
modem.
The phone number stored on the SIM (for GSM) or cellular
modem (for CDMA). The SIM may not have a number
stored, or it may not be correct.
the SIM card. This value is the account number for the
mobile subscriber.
card. This value is the serial number of the SIM card.
XBee Gateway User Guide
41
Page 42
Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
SIM PIN status GSM
SIM slot index GSM
Indicates the lock status of the SIM. There area many
possible status values. The most common status values
are:
n READY: SIM is ready. The PIN was entered or no
PIN is required.
n SIM PIN: A PIN is required to unlock the SIM. You
can enter the PIN from the Mobile Configuration
page.
n SIM PUK, SIM PIN2, SIM PUK2, and similar codes:
The SIM is locked and cannot be unlocked by the
XBee Gateway cellular device. It must be placed in
another device or phone to be unlocked.
n Error: Either the SIM was not inserted or there
was another SIM problem.
This status only appears for products that support
multiple SIMs. Indicates which SIM slot is currently in use
by the device.
n 0 means the first slot.
n 1 means the second slot.
MEID CDMA Mobile equipment identifier (MEID). A globally unique
number identifying a physical piece of CDMA mobile
station equipment.
PRL version CDMA Preferred Roaming List version number. Updates are
done at the same time as provisioning. Note that this
may change with new modems.
XBee Gateway User Guide
42
Page 43

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
Provisioning status CDMA
Signal strength Both
Specifies the status of the provisioning process for the
cellular modem, Provisioning is the process by which the
cellular modem is configured with the information
required to access the cellular network.
n Not provisioned: The modem is not provisioned.
Contact your mobile service provider to make
sure your device is registered to your mobile
account.
n Provisioned: The modem is configured and ready
to use.
n In progress: The modem is in the process of being
provisioned.
n Failed: Provisioning was unsuccessful. This may
be caused by a poor signal, or the cellular modem
was not activated with the carrier.
Received cellular signal strength indicator (RSSI) for GSM
and CDMA. A measure of the signal level of the network.
Different RSSI levels are used by GSM and CDMA to
determine the number of bars.
n For GSM: -108 or more is 1 bar, -93 is 2, -77 is 3
bars.
Signal level Both
Signal quality Both
n For CDMA: -105 or more is 1 bar, -90 is 2, -75 is 3
bars.
The number of bars indicates the strength of the
received cellular signal.
n 0: No signal
n 1: Poor signal
n 2: Adequate signal
n 3: Good signal
An indicator of the quality of the received cellular signal,
measured in dB. This value is also known as Ec/Io.
XBee Gateway User Guide
43
Page 44

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
Registration status Both
The status of the cellular modem’s connection to a
cellular network.
n Not registered
n Registered (Home network)
n Searching for Network
n Not Registered (Access Denied)
n Not Available (Reason not Known)
n Registered (Roaming)
Cell ID GSM Identifier of the cellular base station with which the
cellular modem is registered.
System ID CDMA The system identification number of the cellular network
with which the cellular modem is registered.
Network ID CDMA The network identification number of the cellular
network with which the cellular modem is registered.
Location area code GSM Identifier of the location of a group of cellular base
stations with which the cellular modem is registered, in
hexadecimal format.
Mobile country code
GSM Identifies a mobile phone operator/carrier with which the
cellular modem is registered.
Mobile network code GSM Identifies a mobile phone operator/carrier with which the
cellular modem is registered.
Operator name GSM The name of the mobile operator with which the modem
is registered. This corresponds to the mobile country and
network codes.
Band GSM 2G
service only
The radio frequency band used by the modem. GSMcan
use one of the following bands:
n GSM 850
n GSM 900
n DCS 1800
n PCS 1900
Future modems may have different values.
XBee Gateway User Guide
44
Page 45

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
Service CDMA
The type of data service provided by the cellular network.
For CDMA, the data service is one of the following:
n None
n 1xRTT
n EVDO Rev 0
n EVDO Rev A
Future cellular modems may have other values.
Channel Both Radio channel being used by the cellular modem.
Profile Both
The current set of mobile configuration settings used to
configure the cellular modem. XBee Gateway cellular
products always use profile 0.
XBee Gateway User Guide
45
Page 46

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
Connection state Both
The operating state of the cellular modem. The possible
states are as follows:
n Initializing: Resetting and configuring the
modem.
n Registering: Searching for the modem's cellular
network.
n Delay before connecting: The modem delays
after an unsuccessful connection (Verizon only).
n Connecting: Establishing a mobile data
connection.
n Connected: Established an active mobile data
connection .
n Disconnecting: Ending the mobile data
connection.
n Disconnected: Ended the mobile data connection.
See Disconnect reason for the cause.
n Disabled: The mobile data connection is disabled
in the configuration settings.
n Provisioning: Configuring the modem to access
the mobile carrier (CDMA only).
n PRL update: Updating the preferred roaming list
(CDMA only).
n Operator scan: Searching the modem for
available mobile operators (GSM only).
n No device found: The modem is not available or
is malfunctioning.
Connection duration Both Amount of time the current mobile data connection has
been active. The format is N days HH:MM:SS.
XBee Gateway User Guide
46
Page 47

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
Connection error Both
This status appears only after a connection error occurs.
The possible reasons the previous connection attempt
failed are as follows:
n SIM PIN required: The SIM PIN must be entered
on the Mobile Configuration page.
n SIM PIN incorrect: The SIM PIN entered does not
match the actual one for the SIM.
n SIM not ready: No SIM inserted or other SIM
problem.
n Not registered: The modem did not register with
a cellular network.
n Dial failed: Error starting data connection.
n Authentication failed: Incorrect login or
password entered on the Mobile Configuration
page.
n Connection timeout: Connection did not
complete.
n Device reset error: The modem could not be
reset.
n Device open error: The modem is malfunctioning.
n Device config error: The modem could not be
configured.
n PPP error: Internal system error.
XBee Gateway User Guide
47
Page 48

Administration and maintenance tasks Mobile device status
Cellular
Status field
modem type
Description
Disconnect reason Both
This status appears after a previous connection ends.
The possible reasons the previous connection ended are
as follows:
n User requested: Initiated by user action.
n Network disconnect: Initiated by cellular network
or carrier.
n Carrier loss: Poor signal or disconnected by
network.
n Connection timer: Connection did not complete.
n Receive idle timer: No data received for
configured receive idle time.
n Device monitoring error: Error while monitoring
the modem status. May indicate a malfunctioning
modem.
IP address Both Internet protocol address of the mobile data interface.
You can contact the device at this IP address if permitted
by the carrier.
Peer address Both Internet protocol address of the mobile data server. This
IP address is typically provided as background
information, and not normally used to communicate with
the device.
DNS primary address Both
IP address of the primary Domain Name System (DNS)
server assigned by the mobile carrier. This server
resolves domain names to IP addresses.
See Default behavior regarding DNS for more information
on how XBee Gateway uses the DNS primary and
secondary address.
DNS secondary address Both IP address of the backup DNS server assigned by the
mobile carrier.
Receive idle time Both The amount of time since the cellular modem last
received data.
Transmit idle time Both The amount of time since the cellular modem last
transmitted data.
Connections Both The number of mobile data connection attempts since
the XBee Gateway cellular device was started.
XBee Gateway User Guide
48
Page 49

Administration and maintenance tasks Change the password for the web interface
Cellular
Status field
Connection errors Both The number of unsuccessful mobile data connection
Carrier loss Both The number of times the connection was lost because of
LCP echo failed Both The number of failed Link Control Protocol (LCP) echo
Idle timeout Both The number of connection resets that occurred because
User disconnect Both The number of disconnects of the cellular connection
modem type
Description
attempts since the XBee Gateway cellular device was
started.
poor signal or being disconnected by the network.
requests that were sent after a “quiet” interval to test
the cellular link and/or keep it alive. Not used by XBee
Gateway cellular products.
the idle timeout reached/exceeded the maximum
allowed for transmitted and received data.
performed by device users.
occurs when a user provisions the cellular modem.
This type of user disconnect
Monitoring errors Both Number of errors encountered while monitoring the
cellular modem status. May indicate a malfunctioning
modem.
Device resets Both Number of cellular modem resets caused by errors, failed
connection attempts, or user requests.
Received bytes Both Number of bytes received by the cellular modem during
the current data session.
Transmitted bytes Both Number of bytes transmitted by the cellular modem
during the current data session.
Total received bytes Both Total number of bytes received by the modem since the
XBee Gateway cellular device was started.
Total transmitted bytes Both Total number of bytes transmitted by the modem since
the XBee Gateway cellular device was started.
Change the password for the web interface
You can change the current password for the python user account, which is used to access the web
interface. You can use any of the methods described below. The password must have a minimum of
eight valid, printable, ASCIIcharacters.
Note Each device has a unique, default password printed on the device label. If the password is not on
the device label, the default password is dbps. If neither these defaults work, the password may have
already been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
XBee Gateway User Guide
49
Page 50

Administration and maintenance tasks Change the password for the web interface
Linux command shell
1. Connect and log in to the XBee Gateway device.
2. At the prompt type: passwd
3. At the Old Password prompt, enter the current password.
4. At the New Password prompt, enter the new password.
Web interface
1. Access the XBee Gateway web interface.
2. Select Configuration > Authentication.
3. In the Current Password field, enter the current password.
4. In the New Password field, enter the new password.
5. In the Confirm Password field, re-enter the new password.
6. Click Apply.
RCIfrom the Linux command shell
1. Connect and log in to the XBee Gateway device.
2. Type the following, replacing NEW_PASSWORD with the new password you wish to use and
CURRENT_PASSWORD with your existing password:
rci_request '<do_command target="set_password"><login>python</login><password>NEW_
PASSWORD</password><current_password>CURRENT_PASSWORD</current_
password></do_command>'
Note If the password contains the following characters, you will need to escape those
characters following standard Linux shell conventions: ' (apostrophe), < (less than sign), >
(greater than sign).
3. If successful, the following message appears:
<rci_reply version="1.1"><do_command target="set_password"></do_command></rci_reply>
If an error is encountered, the following message appears:
<rci_reply version="1.1"><do_command target="set_password"><error id="4"><desc>Update
failed</desc><hint>password</hint></error></do_command></rci_reply>
You can check the system logs for more information on the error.
RCIfrom Python
The rci module in Python can process RCI using the process_request method. It accepts as a
single argument an RCI request, and returns the response. The set_password request matches the
request used in RCI from the Linux command shell (as described above), but wrapped in the rci_
request tag.
XBee Gateway User Guide
50
Page 51

Administration and maintenance tasks Display the XBee Gateway End User License Agreement (EULA)
Copy and enter the code below, replacing NEW_PASSWORD with the new password you wish to use
and CURRENT_PASSWORD with the existing password.
<rci_request>
<do_command target="set_password">
<login>python</login>
<password>NEW_PASSWORD</password>
<current_password>CURRENT_PASSWORD</current_password>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
Note The set_password do_command to change the python password is only available in XBee
Gateway firmware versions 3.2.30.x and newer.
RCIfrom Digi Remote Manager
1. From a web browser, log in to Remote Manager.
2. Select Documentation > APIExplorer. The APIconsole appears.
3. From the API console, select POST HTTP Method and write the following SCI request, as
follows:
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="{device_id}"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="set_password">
<login>python</login>
<password>NEW_PASSWORD</password>
<current_password>CURRENT_PASSWORD</current_password>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
Where:
n {device_id} is the ID of your XBee Gateway device.
n NEW_PASSWORD is the new password you want to use.
n CURRENT_PASSWORD is the existing password.
4. Click Send.
Display the XBee Gateway End User License Agreement (EULA)
You can access the End User License Agreement (EULA) for XBee Gateway from the web interface.
XBee Gateway User Guide
51
Page 52
Administration and maintenance tasks Restore XBee Gateway factory defaults
Note The XBee Gateway EULA is not available through Remote Manager.
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Click Legal Notices under Administration.The EULA for XBee Gateway appears.
Restore XBee Gateway factory defaults
You can restore the device to its factory default configuration. This action clears any configuration
settings you may have entered through the supported device interfaces. This feature is assigned to
the button by default.
On the XBee Gateway device, press and hold the button for ten seconds to return the device settings
to factory defaults.
Reboot XBee Gateway
You can reboot XBee Gateway as needed. Note that XBee Gateway reboots itself if you make changes
to the configuration that require a reboot to activate those changes.
To reboot XBee Gateway, choose one of the following options:
n From Remote Manager, right-click the XBee Gateway device and select More > Reboot.
n From the web interface, click Administration > Reboot.
Wait approximately one minute for the reboot to complete.
Display system information
To display system information, choose one of the following options:
From Remote Manager
1. Click the Device Management tab.
2. From the device list, double-click the device to display the device properties menu.
3. Click System Information. The System Information page appears.
From the XBee Gateway web interface
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. View general system information and system statistics from the Home page.
Disconnect XBee Gateway from Remote Manager
You can disconnect XBee Gateway from Remote Manager.
1. Log in to Remote Manager.
2. Click the Device Management tab.
3. From the device list, select the XBee Gateway device that you want to disconnect.
4. Select More > Disconnect. A confirmation dialog displays.
5. Click Yes to complete the disconnect process.
XBee Gateway User Guide
52
Page 53

Administration and maintenance tasks Disconnect XBee Gateway from Remote Manager
If XBee Gateway is configured to automatically reconnect to Remote Manager, the device reestablishes the connection to Remote Manager after its reconnection timeout period has
expired.
XBee Gateway User Guide
53
Page 54

About programming
XBee Gateway offers a variety of interfaces that produce and/or consume data. Developing software
programs for XBee Gateway products allows Digi customers to provide custom logic to control the
information to and from these interfaces.
This section introduces the Digi programming tools and resources available to you. You can also see
Program XBee Gateway using Python to learn about programming elements and operations available
for XBee Gateway using annotated example programs.
Python
XBee Gateway features a standard Python 2.7.1 distribution, allowing you to develop and test
applications that are not dependent on Digi-proprietary interface modules. Python is a dynamic,
object-oriented language for developing software applications, from simple programs to complex
embedded applications.
The standard Python 2.7.1 distribution has a more complete library set than the versions supported in
predecessor gateway products, and integrates well with standard Python. You can typically transfer
scripts developed in this manner to the device for final testing at the end of the development cycle,
with a computer serving as a device proxy during the bulk of development.
For detailed information about programming with Python, see Program XBee Gateway using Python.
The sections below describe the basic Python applications that you may use:
n Python: XBee Gateway features a standard Python 2.7.1 distribution, allowing you to develop
and test applications that are not dependent on Digi-proprietary interface modules. Python is a
dynamic, object-oriented language for developing software applications, from simple programs
to complex embedded applications.
For more information, see Program XBee Gateway using Python.
n XBee Gateway Python application: The XBee Gateway Python application resides on XBee
Gateway. Its key functions include connecting your XBee modules to Remote Manager,
enabling uploads of data to Remote Manager, and receiving remote text and commands.
Python application is installed by default in your XBee Gateway device and automatically starts
when the gateway is initialized.
For more information on the XBee Gateway Python application, see XBee Gateway Python
application and Remote Manager.
n Digi ESP: Digi ESP is an IDE featuring device detection, debugging, compiling, and downloading
of Device Integration Application (DIA)/Python code to Digi gateways.
For more information, see Digi ESP for Python.
XBee Gateway User Guide
54
Page 55

About programming XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit web application source code
n DIA: Device Integration Application (DIA) is an application software platform for Digi gateways.
DIA makes it easy to connect remote devices and sensors to Digi gateway products.
For more information, see DIA software.
n Linux command shell: The Linux command shell interface that is available on XBee Gateway is
useful for some programming and device management tasks. With the Linux command shell,
you can experiment with the Python interpreter interactively, create scripts, launch scripts,
and control the script operation.
For more information, see Linux command shell (command line interface).
XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit web application source code
You can use the XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit web application source code and other tools available on
Github to build your own custom applications.
The source code for the XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit web application is located at
https://github.com/digidotcom/XBeeZigBeeCloudKit.
For more information on the XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit, see the XBee ZigBee Cloud Kit support page.
Programming calls through Server Command Interface (SCI) and
Remote Command Interface (RCI)
You can use the Web Services Server Command Interface (SCI) and the Remote Command Interface
(RCI) as an alternative means of getting settings and state data from the device. For more
information, see:
n SCI (Server Command Interface) chapter of the Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide
n Remote Command Interface (RCI) Specification document
XBee Gateway file system
XBee Gateway supports standard Linux shell file operations for managing directories and files.
You can access the file system resident on XBee Gateway through the following interfaces:
n Web interface
n Command line interface
n Remote Manager
Important directories
/WEB/python
The /WEB/python/ directory contains user-specific files, such as custom Python applications. You can
create subdirectories in this area for the customer's applications. This area is read-write.
/WEB/logging
The /WEB/logging directory contains system log files, including eventlog.txt, python.log, digi.log,
xbee.log, and sef.log. These files are read-only. For more information on these files, see XBee Gateway
system log.
XBee Gateway User Guide
55
Page 56

About programming Load applications onto XBee Gateway
Load applications onto XBee Gateway
To load an application onto XBee Gateway, use the File Management function in Remote Manager or
the XBee Gateway web interface. For instructions, see File management.
XBee Gateway User Guide
56
Page 57

Program XBee Gateway using Python
XBee Gateway features a standard Python 2.7.1 distribution, allowing you to develop and test
applications that are not dependent on Digi-proprietary interface modules. Python is a dynamic,
object-oriented language for developing software applications, from simple programs to complex
embedded applications.
The standard Python 2.7.1 distribution has a more complete library set than the versions supported in
predecessor gateway products, and integrates well with standard Python. You can typically transfer
scripts developed in this manner to the device for final testing at the end of the development cycle,
with a computer serving as a device proxy during the bulk of development.
The following sections contain information about programming XBee Gateway with Python:
Find Python learning resources 58
Digi-specific Python modules for programming 58
Sample programs 58
XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager 62
Configure a Python application in the web interface 86
Digi ESP for Python 87
DIA software 91
Linux command shell (command line interface) 91
XBee Gateway User Guide
57
Page 58

Program XBee Gateway using Python Find Python learning resources
Find Python learning resources
You can learn more about programming with Python by referring to the following sections.
Python support forum
You can find answers to common questions and exchange ideas and examples with other members of
the Digi Python development community at the Digi Forum.
Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference Manual
The Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference Manual provides references for developing solutions using the
Digi communications portfolio, software and services, including Python, Remote Manager, DIA, and
more. This manual includes how-to's, example code, and M2M information to speed application
development.
Digi-specific Python modules for programming
Several Digi-provided built-in modules apply to functionality in XBee Gateway and are documented in
the ConnectPort X2e section in the Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference Manual. From that section, you
can go to the information pages on these modules:
n digihw: Provides an interface to local hardware.
n idigimsg: This is an internal module with functions used by DIA and Smart Energy Framework.
n rci: Provides a mechanism for processing arbitrary RCI request strings, as well as a means to
set up callbacks to allow Python scripts to respond to remote requests made via specialized
RCI commands.
n uptime: Allows access to the Linux gettime function for various clocks.
n watchdog: A safeguard that an application can use for critical operations, in which, if the
application threads do not service their watchdog within the promised interval, the entire
system reboots.
n xbee: A collection of utility methods for programming the XBee RF module on XBee Gateway. It
also includes the Python XBee socket interface support.
n digisms: For low-level, generic SMS message handling.
n idigisms: For communicating using Remote Manager SMS protocol to or from Remote
Manager.
Sample programs
These simple annotated samples introduce several programmable features for XBee Gateway,
including:
n Button handling
n LED control
n Watchdog
XBee Gateway User Guide
58
Page 59

Program XBee Gateway using Python Sample programs
n RCI callback
n XBee functions
Button handling
The following sample program demonstrates functions for handling the button on XBee Gateway.
import select
fd=open('/var/run/reset_button')(1)
p=select.poll()
p.register(fd, select.POLLPRI) (2)
fd.read() (3)
while True:
p.poll() (4)
fd.seek(0) (5)
val = int(fd.read()[0]) (6)
if val: (7)
print "Button pressed!"
else:
print "Button released!"
Program notes
1. The reset button is exposed as a Linux file. It can be read to determine the state of the button,
and it is possible to block waiting for the button state to change.
2. To block waiting for the button, the standard Python select module is used. This line, and the
line above, demonstrate how to create a polling object that can wait for button state changes.
3. Read the current value of the button, but forget it. This is done to “clear” the button and
prepare to wait for its state changes.
4. Rather than reading the button in a loop, the system waits for button state changes using the
polling object created earlier.
5. To read the current value, the system first “rewinds” to the beginning of the “file.”
6. fd.read() gets pending data from the button file. fd.read()[0] returns the first character of that
data. int(fd.read()[0]) makes explicit the fact that the system expects the character it reads to
be an integer.
7. If the system reads a non-zero value, the button is currently pressed.
LED control
Controlling the LEDs on XBee Gateway is handled through the user_led_set function. This sample
program controls the Network LED.
Note that if native features are still assigned to the LED, those behaviors will mix with the behaviors in
the sample program.
Note The highlighted numbers in the sample code correspond to the items in the Program Notes,
below.
XBee Gateway User Guide
59
Page 60

Program XBee Gateway using Python Sample programs
import digihw (1)
import time
while True:
digihw.user_led_set(True,1) (2)
time.sleep(1.0)
digihw.user_led_set(False,1) (3)
digihw.user_led_set(True, 2) (4)
time.sleep(1.0)
digihw.user_led_set(False,2) (5)
Program notes
1. The digihw module includes the user_led_set function needed by the program. The user_led_
set has two are two parameters: value and led. The user controlled LED is made to match the
logic state of the “value” parameter. A value of “True” turns on the LED, and a value of “False”
turns it off. The “led” parameter indicates which user LED to blink, with LED 1 being the default.
2. Turn on the “yellow” Network LED.
3. Turn off the “yellow” Network LED.
4. Turn on the “green” Network LED.
5. Turn off the “green” Network LED.
Watchdog
The watchdog feature, provided through the watchdog module, exists as a safeguard. If there are
critical operations that “must” happen periodically, or else the system will be irretrievably broken, an
application can request that a “watchdog” be established. If the application threads do not service
their watchdog within the promised interval, the entire system reboots. You can change or, if
necessary, delete the intervals for these software watchdogs. Using a software watchdog exists as a
measure of last resort. Appropriate error detection and handling with Python scripts is certainly
recommended.
The following sample program demonstrates the watchdog feature.
Note The highlighted numbers in the sample code correspond to the items in the Program Notes,
below.
import watchdog (1)
import time
w=watchdog.Watchdog('test',20) (2)
for x in xrange(1,6): (3)
print "Step ", x (4)
time.sleep(10.0) (5)
w.heartbeat() (6)
print "Step just before the end..." (7)
time.sleep(60.0) (8)
print "Step after the end." (9)
Program notes
1. The watchdog module includes the Watchdog class needed by the program.
2. Create a watchdog object named “test” that will expire in 20 seconds.
XBee Gateway User Guide
60
Page 61

Program XBee Gateway using Python Sample programs
3. Loop five times (1-5).
4. Indicate our iteration...
5. ... sleeping less than the timeout on each iteration, but more time than the timeout in total.
6. Reset the watchdog timer to 20 seconds each iteration, allowing all of the loops to complete.
7. Indicate that small loops are complete.
8. Sleep for an interval much longer than the timeout.
9. This print statement never executes, because the system will reboot when the watchdog
timeout expires.
RCI callback
An RCI callback involves two types of actions, demonstrated in the following programs:
n Making RCI requests from Python applications.
n Extending RCI to allow Remote Manager to make requests of Python applications. This is
known as an RCI callback.
The following example shows an RCI request.
Note The highlighted numbers in the sample code correspond to the items in the Program Notes,
below.
import rci (1)
request_string=""" (2)
<rci_request version="1.1">
<query_state>
<interface_info name="eth0">
<ip/>
</interface_info>
</query_state>
</rci_request>
"""
print rci.process_request(request_string) (3)
Program notes
1. The rci module includes the process_request function needed by the program.
2. A string representing the RCI request is needed. This sample uses the Python multi-line string
syntax to make it clear that the XML represents a request for the current IP address of the
Ethernet interface. Combining the lines into a single string on one line would work in the same
way.
3. The RCI XML is submitted for parsing, and the resulting string is returned. In this sample, the
result is simply printed.
Following example shows a simple RCI callback:
import rci (1)
def cb(req): (2)
XBee Gateway User Guide
61
Page 62

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
print "Received request: " + req (3)
r=rci.RciCallback() (4)
r.register_callback('test', cb) (5)
rci.process_request('<rci_request version="1.1"><do_command target="test"><customxml/></do_
command></rci_request>')(6)
Program notes
1. The RCI module includes the RciCallback class needed by the program.
2. Create a function to be called whenever a remote entity wants to communicate with this
script.
3. This simple function will simply demonstrate that it received a request that could be parsed
and handled however the application saw fit.
4. Create a callback object.
5. Assign the target “test” to the new callback object. If a remote entity issues a “do_command”
with the target “test”, the supplied callback function will be called.
6. This is simply an example that causes the callback to be called. This example could also have
been a remote SCI query through Remote Manager.
XBee functions
For a description of the XBee module and program samples, see the ZigBee module information
section in the Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference Manual.
XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
The XBee Gateway Python application is an application that resides on XBee Gateway. It allows you to
connect your XBee modules to Remote Manager, enabling them to upload data to Remote Manager
and receive remote text and commands. The XBee Gateway Python application is already installed in
your XBee Gateway device and automatically starts when the gateway is initialized.
For a complete description of Remote Manager, see the Digi Remote Manager User Guide on the
Remote Manager support page.
How does the XBee Gateway Python application work?
XBee Gateway and XBee Gateway Python application software combination acts as a bridge between
your XBee network and Remote Manager. This means that using the capabilities provided by Remote
Manager, you can communicate with and manage not just XBee Gateway, but also all the XBee
modules of the network individually. Similarly, all the XBee modules can report data to Remote
Manager and store the data there to be retrieved later.
Consumer applications, such as web apps, mobile apps, and so on, can use Remote Manager web
services to retrieve data stored by the XBee modules and represent it in different ways, or talk
directly with any of the XBee modules to configure them, activate Digital Input/Output (DIO) lines, etc.
The following figure illustrates the role of XBee Gateway and XBee Gateway Python application in such
a scenario.
XBee Gateway User Guide
62
Page 63

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
XBee Gateway Python application requirements
You must complete the following requirements before you can use the XBee Gateway Python
application and Remote Manager capabilities:
1. A Remote Manager account. If you do not have a Remote Manager account, follow the
instructions in the create a Remote Manager account section in the Digi Remote Manager User
Guide.
2. Your XBee Gateway device must be registered in your Remote Manager account. Follow the
instructions in the register a device section in the Digi Remote Manager User Guide.
3. The XBee Gateway Python application must be running in your XBee Gateway device. By
default, the XBee Gateway Python application is already installed and running on the XBee
Gateway devices; that is, the application executes automatically when the device is initialized.
Therefore, you do not have to start the application. If you uninstalled the application, use the
File Management function in Remote Manager or the XBee Gateway web interface to install
the XBee Gateway Python application again.
XBee Gateway User Guide
63
Page 64

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
Key features and operations of the XBee Gateway Python application
The XBee Gateway Python application provides the following features:
n Automatically store status information for DIO and Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) lines
reported by the XBee nodes of the network in Remote Manager.
n Receive serial data from Remote Manager and send it to the corresponding XBee module of
the network.
n Receive serial data from an XBee node of the network and store it in Remote Manager
automatically.
n Set the value of the DIO lines of any XBee module in the network through Remote Manager.
Store status data for XBee lines in Remote Manager
You can configure XBee nodes in a network to report information about the status of the DIO lines and
ADC values to the coordinator or other nodes in the network. This scenario is very common when the
XBee node is attached to one or more sensors to monitor a process or some environment values. In
such a case, you may want to report the data from the sensor(s) to the coordinator every time a line
changes its status or every period of time. Using the XBee Gateway Python application, you can
automatically upload those values to Remote Manager, store them there, and retrieve the values
later for use by other user applications.
Whenever an XBee module in the network reports the status of the DIO lines and ADC values to XBee
Gateway, the XBee Gateway Python application automatically handles the XBee frame containing
those values, processes it, and uploads the reported values to Remote Manager. This process
generates a data stream for each of the different measures reported by the XBee module. For more
information about data streams are, see the Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide. The following
figure demonstrates the process of storing status data on Remote Manager.
Using the Remote Manager Web Services API, you can retrieve the data stream values from Remote
Manager to be used in end user applications with different purposes, for example, to display a
histogram or generate a database. To learn more about the Remote Manager Web Services API, see
the Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide.
XBee Gateway User Guide
64
Page 65

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
Example: Configure the XBee node to report line and upload status
You can configure an XBee node from the network to report the status of the DIO1 each time it
changes and verify that the values are uploaded to Remote Manager.
To configure XBee node to report line and upload status:
1. Ensure the XBee device you are going to configure is attached to an XBee Interface Board
(XBIB). You will use the User Button 3 (SW3) of the XBIB to change the status of DIO1 as it is
directly connected to the DIO1 of the module.
2. From a web browser, go to the Home page of your XBee Gateway web interface.
3. Under Configuration, click XBee Network. The XBee Configuration page appears.
XBee Gateway User Guide
65
Page 66
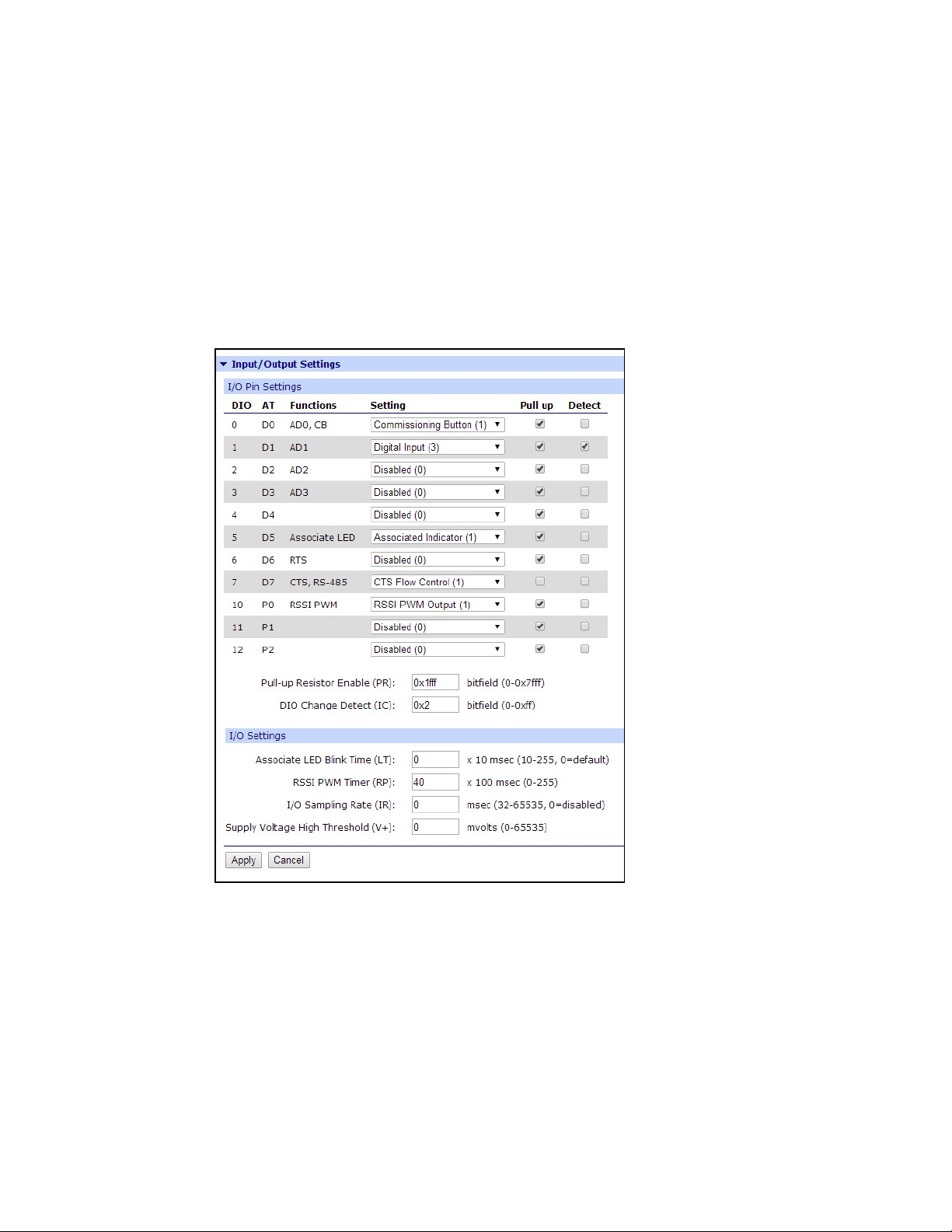
Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
4. Click the DiscoverXBee Devices button to locate the remote XBee devices that are in the
same network as XBee Gateway.
5. Click the XBee device that you want to configure.
6. From the XBee Configuration page, click Input/Output Settings.
7. Under I/O Pin Settings, configure I/O Pin 1 (AT setting D1) to Digital Input (3) and change
the value of the DIO Change Detect (IC) setting to 0x2. These settings configure DIO1 as
input. Each time the value of DIO1 changes, the XBee device sends an XBee packet to XBee
Gateway with the new value of the DIO. In addition, the XBee Gateway Python application
uploads the new value to Remote Manager.
8. On the XBIB, press the User Button 3 (SW3) several times. This action causes the XBee
module report the status of DIO1.
9. From a web browser, log in to Remote Manager.
10. From Remote Manager, click Data Services. The Data Services page appears.
XBee Gateway User Guide
66
Page 67

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
11. Click Data Streams. The Data Streams view contains all the data streams, or data channels, of
the devices that you have registered in your account.
There you will find the streams generated by any XBee node from your network that reported
any data. The data streams follow this pattern:
[device_id]/[source]/[xbee_mac]{/[dio_number]}
Where:
n [device_id] Is the ID of your XBee Gateway.
n [source] Is the source of the data. Legal values are:
l xbee.digitalIn
l xbee.analog
l xbee.serialIn
n [xbee_mac] Is the MAC Address of the XBee node that reported the data in the
following format:
[XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX]!
n [dio_number] Is the name of the DIO that generated the data. This is only present if
the [SOURCE] is xbee.digitalIn or xbee.analog.
One of those streams should correspond to the DIO1 of your XBee device. For example:
00000000-00000000-00409DFF-FF5C388D/xbee.digitalIn/[00:13:A2:00:40:31:A8:E1]!/DIO1
12. Click the serial data stream that correspond to the DIO1 of your XBee device. Note how the
values stored have been changed between 0 and 1. For example:
Each stream contains a historical view of the values of the data channel it represents. To
display the historical values, switch from the Table to Chart view.
XBee Gateway User Guide
67
Page 68

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
Receive serial data from Remote Manager
In some scenarios, you can attach an XBee module to a microcontroller that can manage the radio
module, configure it, process data reported by the module, and execute actions. In those cases, the
combination of XBee module and microcontroller can use a custom communications protocol
transmitted wirelessly from an XBee network node to the target XBee node, and via serial from the
target XBee node to the microcontroller to which it is attached.
The XBee Gateway Python application allows sending a serial data packet through Remote Manager,
using the Web Services API, to a specific XBee module or all XBee modules in the network that will be
transmitted through its serial interface. That serial packet can contain any data, including the custom
protocol that your XBee module and microcontroller use to communicate between them. The
following figure demonstrates the process for receiving serial data from Remote Manager.
To send serial data to one of the XBee nodes on your network through Remote Manager, you need to
use the Remote Manager Web Services API. In this case, you need to send a POST command
containing a Server Command Interface (SCI) request to Remote Manager. The SCI request in turn
contains a Remote Command Interface (RCI) do_command element, with xbgw as target attribute
and the send_serial command as content. To learn more about SCI requests, the RCI protocol, and
the Web Services API, see the Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide.
XBee Gateway User Guide
68
Page 69
Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
send_serial command definition
The send_serial command sends serial data to a specific XBee node in your network. To use this
command, add it to an SCI request inside the RCI do_command element.
Command syntax
The send_serial command must follow this syntax:
<send_serial addr=”{address|broadcast}” encoding={“base64”|”utf-8”}”>value</send_serial>
Command attributes
XBee Gateway User Guide
69
Page 70

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
n addr
l Usage: Required.
l Description: This attribute indicates the destination address of the node to which the
content indicated by the command body should be transmitted.
l Value: Legal values for this attribute include:
The 64-bit IEEE address of the node following one of these patterns:
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
[XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX]!
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX
The string broadcast, which transmits the string to all nodes using a broadcast packet.
n encoding
l Usage: Optional.
l Description: Specifies how the character data in the command elements is processed.
l Value: The following encoding types are allowed:
o
base64: Use Base64 encoding. Character data is decoded during command processing
prior to transmit on the RF network.
o
utf-8: Use UTF-8 variable-width encoding. While you can specify this encoding type,
current limitations in RCI/SCI processing through Remote Manager mean that true UTF-
8 encoding is not passed cleanly through all systems and end-to-end. It is only safe to
use ASCII. Specifying 'utf-8' is primarily useful for evaluation only.
o
Default value: base64.
Command body (value)
The command body contains the data to be transmitted to the specified XBee node of the network.
The command body content depends on the value of the encoding attribute:
n base64: The command body value must be encoded in base64. The XBee Gateway Python
application will receive the encoded content but, prior to transmission to the corresponding
XBee node, the application will decode the command body to its original content and that will
be transmitted.
n utf-8: The command body value must be the serial data that you want to send to the XBee
node. The entire content of the command body as received by the gateway Python application
will be transmitted subject to whitespace handling rules of XML and the limitations of Remote
Manager to represent individual code points. For best results, base64 encoding is preferred for
production code and evaluation is best when limited to the ASCII subset.
Note Whitespace is not significant when the XBee Gateway Python application processes base64.
However, whitespace in UTF-8 is significant, because it is impossible to determine whether the
XBee Gateway User Guide
70
Page 71

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
whitespace should be considered as such and thus take the conservative approach of keeping it
significant and passing it on.
Request and reply examples
n Request
This SCI request sends a serial data command with the text Hello, World! encoded in base64
to the XBee node of our network corresponding to the MAC address 00:11:22:33:44:55:65:77.
Note The request is using a dummy device ID and XBee MAC address. You will need to use your
own XBee Gateway device ID and XBee MAC address if you want to test this example.
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="00000000-00000000-001122FF-FF334455"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<send_serial addr="00:11:22:33:44:55:66:77"
encoding="base64"> SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==
</send_serial>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
XBee Gateway User Guide
71
Page 72

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
n Reply
If the SCI request succeeds, you will receive a SCI reply containing the send_serial command
response element. As it was successful, the response will be empty.
<sci_reply version="1.0">
<send_message>
<device id="00000000-00000000-001122FF-FF334455">
<rci_reply version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<responses command="send_serial">
<response/>
</responses>
</do_command>
</rci_reply>
</device>
</send_message>
</sci_reply>
If the SCI request fails, you will receive an SCI reply containing the send_serial command
response element that includes an error element indicating the cause of the error. For
example:
<sci_reply version="1.0">
<send_message>
<device id="00000000-00000000-001122FF-FF334455">
<rci_reply version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<responses command="send_serial">
<response>
<error id="encoding">
<desc>Unrecognized encoding</desc>
<hint>basd64</hint>
</error>
</response>
</responses>
</do_command>
</rci_reply>
</device>
</send_message>
</sci_reply>
The error element contains an id attribute indicating the error identifier. For more information
regarding the possible XBee Gateway Python application error identifiers, see XBee Gateway Python
application command errors.
XBee Gateway User Guide
72
Page 73

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
The desc element displays the meaning of the error identifier, and the hint element provides an
explanation of what caused the received error.
Example: Sending text to an XBee node through Remote Manager
The following example assumes the microcontroller attached to the XBee device is a computer.
You must install XCTU on your computer. If you do not have XCTU installed, go to www.digi.com/xctu
to download and install XCTU.
To send a Hello, World! text to an XBee node on your network through Remote Manager:
1. Attach the XBee node from your network to an XBIB device and connect it to your computer
using a serial or USB cable. This is the node that will receive the serial data.
2. Open XCTU and add the XBee node that is connected to your computer to the list of radio
modules.
3. Once XCTU has started and your XBee node is added to the list, select the node and click the
Consoles working mode tab. The Console log window appears and displays the XBee
node’s serial console.
4. Connect the console.
5. From a web browser, log in to Remote Manager.
6. Click Documentation and then click APIExplorer. The APIconsole appears.
XBee Gateway User Guide
73
Page 74

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
7. From the API console, select POSTHTTPMethod and write the following SCI request that
includes the send_serial command.The send_serial command will be sent to the remote
XBee node within the RCI do_command element, as follows:
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="{device_id}"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<send_serial addr="{xbee_mac}"
encoding="base64">SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==
</send_serial>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
Where:
n {device_id} is the ID of your XBee Gateway device.
{xbee_mac} is the MAC address of the XBee node that you attached to your computer.
For example:
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="00000000-00000000-00409dff-ff5c3BBd"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<send_serial addr="0013A2004031A8E1"
encoding="base64">SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==
</send_serial>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
The content of the send_serial command is the text Hello, World! encoded in base64 as it is
specified in the encoding attribute.
8. Click Send.
XBee Gateway User Guide
74
Page 75

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
9. Verify in XCTU that the serial console for the XBee node that you added received the data.
Depending on the operating mode (API or AT) of the XBee device, you will receive the data in
one of the following modes:
n AT mode: You will see the text Hello, World! in the console.
n API mode: You will receive a Receive Packet API frame with the Hello World! text (HEX
values of the ASCII characters) in the Received data field of the frame.
Store serial data in Remote Manager
As explained in Receive serial data from Remote Manager, when your XBee device is connected to a
microcontroller and you want to send serial data to it, you can do so through Remote Manager by
using the Web Services API and the send_serial command. The XBee Gateway Python application
stores serial data sent from the microcontroller to the XBee Gateway device and from the XBee
Gateway device to XBee Gateway running the XBee Gateway Python application.
Store serial data in Remote Manager when you want to:
n Track an event that happened in the microcontroller.
n Track the measurements that are managed by the microcontroller.
n Store commands or serial data generated by the microcontroller in Remote Manager.
End-user applications can retrieve the serial data from Remote Manager later to perform some tasks.
Whenever an XBee module on the network sends any kind of serial data to XBee Gateway, the XBee
Gateway Python application automatically processes the frame containing the serial data and uploads
it to Remote Manager, thereby generating a data stream. To learn more about data streams, see the
Digi Remote Manager User Guide and Digi Remote Manager Programmer Guide.
XBee Gateway User Guide
75
Page 76

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
Using the Remote Manager Web Services API, you can retrieve the serial data values from Remote
Manager. End user applications can use the serial data for different purposes. For example:
n Display a list of events
n Perform a specific task
To learn more about the Remote Manager Web Services API, see the Digi Remote Manager
Programmer Guide.
By default, the serial data is stored in Remote Manager and encoded in base64 format. The reason
behind this is that white spaces are not correctly handled by Remote Manager at the moment. The
XBee Gateway Python application has a configuration file containing the settings of the application.
One of those settings is the encoding of the serial data prior to store it in Remote Manager.
To change the setting to store the data in UTF-8 format:
1. Open /WEB/python/xbgw_settings.json in an editor.
2. Change "encode serial": true to "encode serial": false.
See XBee Gateway Python application configuration file for more information on the configuration file.
XBee Gateway User Guide
76
Page 77
Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
Example: Send serial data from an XBee node to XBee Gateway
The following example assumes the microcontroller attached to the XBee device is a computer.
To send a serial data package from an XBee node on your network to XBee Gateway and verify that it
has been automatically uploaded to Remote Manager:
1. Attach one XBee node from your network to an XBIB device and connect it to your computer
using a serial or USB cable. This is the node that will send the serial data to XBee Gateway.
2. Open XCTU. Add the XBee node that is connected to your computer to the list of radio modules.
3. Once XCTU has started and your XBee node is added to the list, select the node and click the
Consoles working mode tab. The Console log window appears and displays the XBee
node’s serial console.
4. Connect the console.
5. Depending on the working mode (API or AT) of the XBee device, choose one of the following
options.
n AT mode:
a. Click the Add new packet button and paste the following text in the dialog:
Hello, World!
b. Once the packet is added to the list of packets, select it and click the Send
selected packet button.
n API mode:
Click the Add new frame button.
a.
b. Paste the following text in the dialog:
7E 00 1B 10 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FE 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20
57 6F 72 6C 64 21 88
The previous text is a Transmit Request frame. You can also generate it by
yourself by clicking the Edit frame using the Frames Generator tool button:
c. After adding the frame to the list of frames, select the frame and click the
Send selected frame button.
6. From a web browser, log in to Remote Manager.
XBee Gateway User Guide
77
Page 78

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
7. Click Data Services and then click Data Streams. The Data Streams page appears and displays
all the data streams (data channels) by the XBee nodes that are registered to your account on
your network that reported data. The streams follow this pattern:
[device_id]/[source]/[xbee_mac]{/[dio_number]}
Where:
n [device_id] Is the ID of your XBee Gateway.
n [source] Is the source of the data. Legal values are:
l xbee.digitalIn
l xbee.analog
l xbee.serialIn
n [xbee_mac] Is the MAC Address of the XBee node that reported the data in the
following format:
[XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX]!
n [dio_number] Is the name of the DIO that generated the data. This is only present if
the [SOURCE] is xbee.digitalIn or xbee.analog.
One of the streams displayed should correspond to the serial data of your XBee device.
For example:
00000000-00000000-00409DFF-FF5C388D/xbee.serialIn/[00:13:A2:00:40:31:A8:E1]!
Click that serial data stream. Observe how the latest serial data value corresponds to
the following text:
SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==
This serial data value is Hello, World! encoded in base64.
Manage XBee DIO lines though Remote Manager
The XBee Gateway Python application allows you to remotely manage the DIO lines of any of the XBee
nodes on your network through Remote Manager. Use this application feature to turn on/off different
actuators.
The XBee Gateway Python application can receive digital output commands sent through Remote
Manager (using the Web Services API) and dispatch them to a specific XBee module in the network to
set its corresponding pin high or low.
The following figure demonstrates how this remote management mechanism works.
XBee Gateway User Guide
78
Page 79
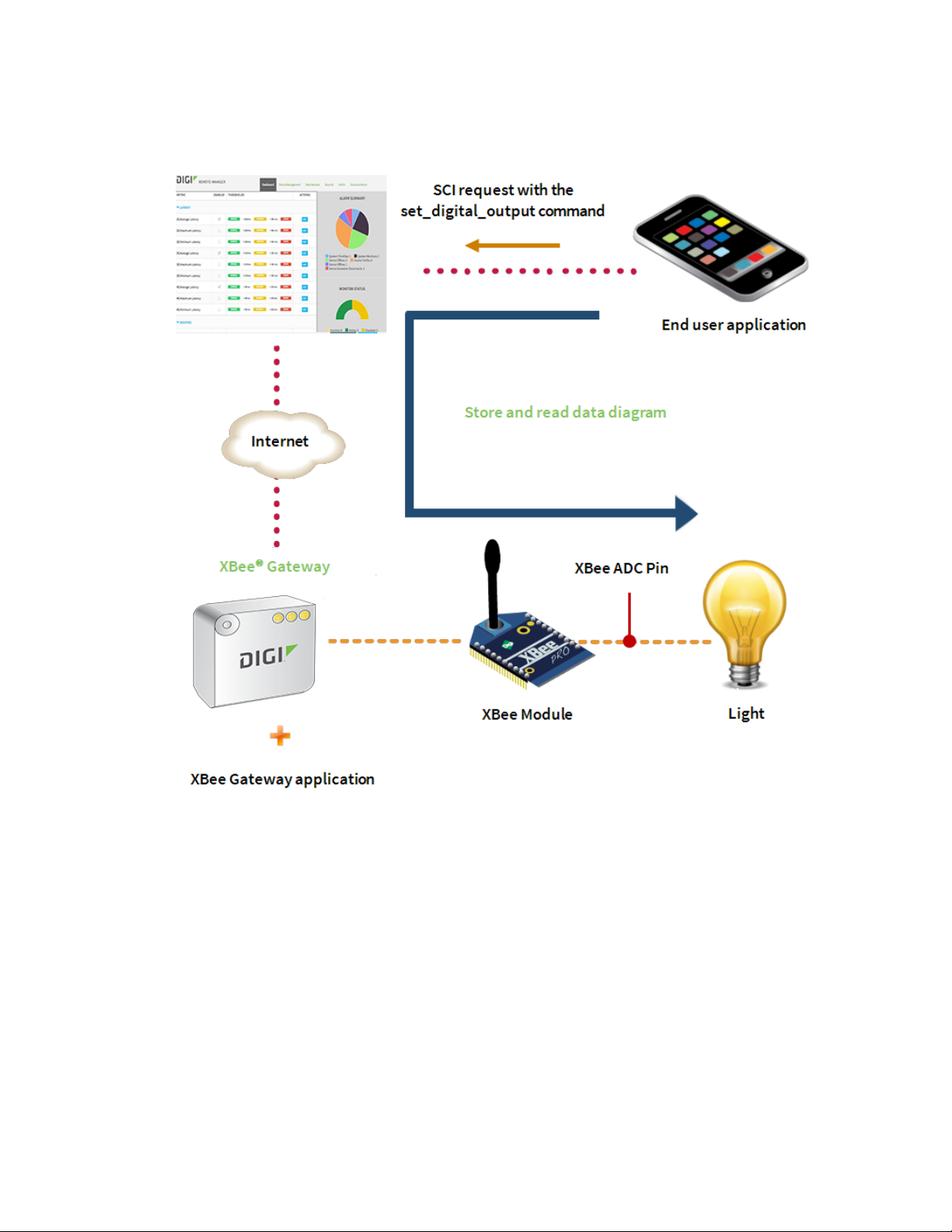
Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
To set the value of a DIO pin of one XBee node on your network through Remote Manager, you need to
use the Remote Manager Web Services API.
In this case, you will need to send a POST command, containing a Server Command Interface (SCI)
request to Remote Manager. The SCI command in turn contains a Remote Command Interface (RCI)
do_command element with xbgw as target attribute and the set_digital_output command as
content.
If you never worked with Remote Manager Web Services API before, see the Digi Remote Manager
Programmer Guide to learn more about SCI requests and RCI protocol.
set_digital_output command definition
The set_digital_output command configures the value of a DIO of a specific XBee node in your
network. Add this command to the SCI request inside the RCI do_command element.
Command syntax
XBee Gateway User Guide
79
Page 80

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
The set_digital_output command must follow this syntax:
<set_digital_output addr=”address” index=”index”>value</set_digital_output>
Command attributes
n addr
l Usage: Required.
l Description: This attribute indicates the destination address of the node to which the
content indicated by the command body should be transmitted. This address is expressed
as the 64-bit IEEE address of the node.
l Value: The 64-bit IEEE address of the node following one of these patterns:
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
[XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX]!
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX
n index
l Usage: Required if the name attribute is not specified.
l Description: This is the pin index for which settings are being changed.
l Value: The value for this attribute must represent a valid integer between 0 and 12.
Indices 0-9 map to DIO values. That is, they set the Dx AT parameter, where x is the index.
For example, index 8 is equivalent to setting D8; index 12 is equivalent to setting P2.
Indices 10-12 map to PWM values. That is, they set the Px AT parameter, where x is index-
10.
n name
l Usage: Required if index attribute is not specified.
l Description: The name of the pin for which settings are being changed.
l Value: Specify either the AT parameter corresponding to that pin (from D0 to D9) or the
functional name of the pin (from DIO0 to DIO12) as the value for this attribute.
Note Currently, set_digital_output supports setting pins on remote ZigBee nodes only. This means
that pin index 9 is invalid, because DIO9 is not user-configurable on such nodes. Future updates to this
command may open up the possibility to change this behavior; for example, for 802.15.4 nodes.
Command body (value)
The body of the set_digital_output command indicates whether to set the digital output pin low or
high. Legal values for the body to configure the pin are:
n high or true: Sets the pin high (ON). Other legal values include:
1, yes, y, on
XBee Gateway User Guide
80
Page 81

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
n low or false: Sets the pin low (OFF). Other legal values include:
0, no, n, off
Request and reply examples
n Request
This SCI request example configures DIO4 of the XBee node corresponding to the MAC address
00:13:a2:00:40:9f:6f:cb to high. The command uses the attribute index to indicate the pin to
be configured instead of the name one:
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="00000000-00000000-00409DFF-FF5C4C66"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<set_digital_output addr="00:13:a2:00:40:9f:6f:cb" index="4">1</set_digital_output>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
Note This example request uses a dummy device ID and XBee MAC address. You must use your
own XBee Gateway device ID and XBee MAC address to test this example.
XBee Gateway User Guide
81
Page 82

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
n Reply
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<device id="00000000-00000000-00409DFF-FF5C4C66"/>
<rci_reply version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<responses command="set_digit al_output">
<response/>
</responses>
</do_command>>
</rci_reply>
</device>
</send_message>
</sci_reply>
If the SCI request fails, you will receive an SCI reply containing the set_digital_output
command response element that includes an error element indicating the cause of the error.
For example:
<sci_reply version="1.0">
<send_message>
<device id="00000000-00000000-00409DFF-FF5C4C66">
<rci_reply version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<responses command="set _digital_output">
<response>
<error id="invalidattr">
<desc>Attribute value is incorrect</desc>
<hint>DIO9 cannot be configured for digital.</hint >
</error>
</response>
</responses>
</do_command>
</rci_reply>
</device>
</send_message>
</sci_reply>
The error element contains an id attribute indicating the error identifier. For more information
regarding the possible XBee Gateway Python application error identifiers, see XBee Gateway Python
application command errors.
The desc element displays the meaning of the error identifier. The hint element provides an
explanation with the cause of the received error.
XBee Gateway User Guide
82
Page 83

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
Example: Turn on an LED on the XBee interface board
To turn on the User LED 4 (DS4) of the XBee Interface Board (XBIB):
1. Ensure the XBee node you are going to configure is attached to an XBIB device. You will change
the status of the User LED 4 (DS4) of the board by modifying the value of the DIO4 of the XBee
node because they are connected each other.
2. From a web browser, go to the Home page of your XBee Gateway web interface.
3. Under Configuration, click XBee Network. The XBee Configuration page appears.
4. Click the DiscoverXBee Devices button to locate the remote XBee devices that are in the
same network as XBee Gateway.
5. Click the XBee device that you want to configure.
6. From the XBee Configuration page, click Input/Output Settings.
7. Under I/O Pin Settings, configure I/O Pin 4 (AT setting D1) to Digital Output High (5). This
way, the DIO4 is configured as output and its value is set to high turning the User LED 4 (DS4)
OFF because the LED in the board is using an inverted logic.
8. From a web browser, log in to Remote Manager.
9. Click Documentation and then click APIExplorer. APIconsole appears.
XBee Gateway User Guide
83
Page 84

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
10. From the API console, select POSTHTTPMethod and write the following SCI request that
includes the set_digital_output command.The set_digital_output command will be sent to
the remote XBee node within the RCI do_command element, as follows:
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="{device_id}"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<set_digital_output addr="{xbee_mac}" name="DIO4">low</set_digital_output>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
Where:
n {device_id} is the ID of your XBee Gateway device.
n {xbee_mac} is the MAC address of the XBee node that you attached to your computer.
For example:
<sci_request version="1.0">
<send_message>
<targets>
<device id="00000000-00000000-00409dff-ff5c3BBd"/>
</targets>
<rci_request version="1.1">
<do_command target="xbgw">
<set_digital_output addr="0013A2004031A8E1"
name="DIO4">low</set_digital_output>
</do_command>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci_request>
The set_digital_output command sets the value of the DIO4 to low, which will turn ON the
User LED 4 (DS4) of the board.
11. Click Send.
12. Verify that the User LED4 (DS4) on the XBIB board is now ON.
XBee Gateway User Guide
84
Page 85

Program XBee Gateway using Python XBee Gateway Python application and Remote Manager
13. Now try to turn the LED off by sending the same request, but changing the value of the set_
digital_output command to high.
XBee Gateway Python application configuration file
You can configure some of the XBee Gateway Python application features using a configuration file.
This configuration file is placed at the same level as the application itself within the file system and its
content is written in JSON format. The file has the following structure:
{
category 1: {
setting 1: value 1
setting 2: value 2
...
setting n: value n
}
category 2: {
setting 1: value 1
setting 2: value 2
...
setting n: value n
...
category n: {
setting 1: value 1
setting 2: value 2
...
setting n: value n
}
}
The first level of the settings structure in this configuration file is the name of the category to which
the settings contained inside belongs. The second level of the structure is the list of settings
contained in the category.
The contents of this configuration file are:
{
"devicecloud": {
"encode serial": true
}
}
The XBee Gateway Python application provides the following category, with one configurable setting:
n devicecloud
l encode serial:
o
Type: Boolean
o
Description: Indicates whether or not the serial data that is sent and stored in Remote
Manager is encoded in base64.
o
Default value: true
Change XBee Gateway Python application settings
To change any XBee Gateway Python application setting:
XBee Gateway User Guide
85
Page 86

Program XBee Gateway using Python Configure a Python application in the web interface
1. Open a web browser and access the Home page of your XBee Gateway web interface.
2. Click File Management under Administration.
3. Download the file xbgw_settings.json.
4. Using a text editor, open the xbgw_settings.json file and modify the settings that you want to
change.
5. Return to the File Management page for XBee Gateway and upload the xbgw_settings.json
file to XBee Gateway.
6. Reboot your XBee Gateway device. Your changes to the XBee Gateway Python application
settings go into effect when the XBee Gateway device is initialized.
XBee Gateway Python application command errors
When you use the Web Service API from Remote Manager to send the commands provided by the
XBee Gateway Python application, you may receive an error with an identifier. The following list
displays all possible errors that may appear when sending commands to XBee Gateway Python
application.
These errors do not generally appear during in normal operation. When setfailed, txfailed, or txfull
appears, the most likely cause is network issues. These errors typically appear when you issue a
command incorrectly.
ID Description
address Invalid address
encoding Unrecognized encoding
badoutput Invalid digital output value
base64 Unable to decode as base64
invalidattr Attribute value is incorrect
missingattr Missing required command attribute
toomanyattrs Too many attributes were given
setfailed Remote node rejected set command
txfailed Transmit operation failed
txfull Too many outstanding transmits
txstatus TX Status delivery failure
unexpected Unexpected/unclassified error
Configure a Python application in the web interface
The web interface of the XBee Gateway device includes a section that allows you to configure and
manage the Python processes or applications running in the device.
XBee Gateway User Guide
86
Page 87

Program XBee Gateway using Python Digi ESP for Python
Before you configure a Python application, the Python application must be loaded on the XBee
Gateway device. See File management for more information on loading files on an XBee Gateway
device.
To configure a Python application for an XBee Gateway device:
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Under Configuration, click Python.The Python Configuration page appears and displays the
list of Python processes or applications that are currently configured in XBee Gateway as well
as their status and the action that will be executed when the applications exit. Note that the
first time you load this page, the list will be empty.
3. Select the Enable check box associated with the Python application. When enabled, the Python
application starts immediately after your changes are saved. By selecting the Enable check
box, the Python application also automatically starts after a system starts up.
A green icon will appear in the Active column when a Python application is running. Note
that you can stop a configured Python application immediately by clearing the Enable check
box and clicking Apply.
4. Click Apply to save your changes.
Digi ESP for Python
Digi ESP™ for Python supports XBee Gateway. Digi ESP is an IDE featuring device detection, debugging,
compiling, and downloading of Device Integration Application (DIA)/Python code to Digi gateways. Digi
ESP includes example applications that can demonstrate the use of some of Digi’s proprietary Python
extensions, serving as templates for applications seeking to incorporate common functionality.
n For examples of how to use Digi ESP for Python with XBee Gateway, see Access the program
samples in Digi ESP.
n For Digi ESP for Python installation instructions, see Install the Digi ESP for Python
Development Environment.
Access the program samples in Digi ESP
Digi ESP for Python provides samples to use as a base for programming XBee Gateway, including
specific examples for exercising specific interfaces available on XBee Gateway. You can access these
program samples from the Python or DIA samples wizard.
To access the program samples in Digi ESP:
1. From Digi ESP, go to File > New > Digi Python Application Sample Project or File > New >
DIA Sample Project. The sample wizard for Python or DIA appears.
2. Select the Show only samples compatible with platform check box and then select XBee
Gateway from the combo box. The compatible samples appear in the Sample projects list.
3. Select the samples you want to display or click Select All to select all of the samples.
4. Click Next. The Remote device selection page appears.
XBee Gateway User Guide
87
Page 88

Program XBee Gateway using Python Digi ESP for Python
5. Specify the XBee Gateway device you want to use.
n Select Use Current Remote Device to use the device that is currently active in Remote
Manager.
n Select Select Specific Remote Device to display a list of devices and select a device
from the list.
6. Click Next to complete the process.
Install the Digi ESP for Python Development Environment
The Digi ESP for Python Development Environment is an Eclipse-based Integrated Development
Environment (IDE) that simplifies the process of creating Python applications for XBee Gateway. It
also provides many example projects.
To download and install the Digi ESP for Python Development Environment:
1. Navigate to the Digi XBee Gateway product support page.
2. Click the Product Support > Drivers link or scroll down the page to the Drivers section.
3. Click the Digi ESP for Python - Windows XP/Vista/Windows 7 installer link to download the
Digi ESPfor Python Development Environment.
Note While MACoperating systems are supported, this procedure shows how to install Digi
ESPfor Python on a Windows operating system. If you are using a MACoperator system, click
the Digi ESP for Python - MAC OS X (10.6) installer link.
4. Once the Digi ESP for Python framework has been downloaded, run the Digi ESP for Python
framework installation wizard.
a. Follow the steps in the wizard to complete the installation process.
b. In the Choose Components dialog, select Digi ESP for Python.
c. On the last page of the wizard, several prompts are displayed. Select Show Release
Notes to open and view the Release Notes for the Digi ESP for Python framework.
d. Click Finish to close the installation wizard. The installation process installs Digi
ESP in this program group:
Digi > Python > Dev Tools > Digi ESP for Python
5. The Digi ESP for Python framework will launch automatically. A prompt to select a workspace
directory is displayed. This 'workspace' is the directory where projects and configurations will
be stored. The default location is a sub-folder called workspace on the user home directory, for
example:
c:/Documents and Settings/[username]/workspace
Use the default workspace directory, or click Browse and navigate to your desired alternate
workspace location, select Use this as the default and do not ask again, and click OK.
XBee Gateway User Guide
88
Page 89
Program XBee Gateway using Python Digi ESP for Python
6. The first time you run Digi ESPfor Python, the Workbench displays.
Before the Workbench displays, the Welcome page displays for just a moment, and then
displays along the right side of the Workbench screen. Most of the time, the Welcome page is
minimized. When minimized, select Help > Welcome from the main menu to maximize the
Welcome page.
In the Welcome page, click the Workbench icon to display the Workbench screen.
XBee Gateway User Guide
89
Page 90

Program XBee Gateway using Python Digi ESP for Python
7. You can display an overview for Digi ESPfor Python.
a. Select Help > Welcome from the main menu. The Welcome page appears.
b. In the Welcome tab, click the Overview icon. The Overview page appears.
c. On the overview page, click Getting Started. The Digi ESP for Python Getting Started
Guide is displayed in the Help - Digi ESPfor Python window.
8. Scroll to and click the XBee Gateway/ConnectPort X2e link.
9. Follow the XBee Gateway/ConnectPort X2e getting started instructions to build your first
application using Digi ESP for Python.
XBee Gateway User Guide
90
Page 91

Program XBee Gateway using Python DIA software
DIA software
The Digi ESP development environment includes Device Integration Application (DIA) software. DIA
software is another advanced programming tool for developing custom programs for XBee Gateway.
DIA software simplifies connecting remote devices and sensors to Digi gateway products by providing
ready-to-use software. DIA is targeted for applications that need to gather samples of data from a set
of devices, such as ZigBee sensors and wired industrial equipment. The Digi gateways can use the DIA
framework to gather data from XBee sensor networks, transform the data into a useful form, and
push the data to Remote Manager for consumption by a user.
DIA allows developers to focus efforts on proprietary logic, and includes a comprehensive library of
ready-to-use modules for common operations and abstractions for components like:
n Interface handling (drivers)
n Data management (channels)
n Data delivery (presentations)
Written in the Python programming language for use on Digi devices, you can extend it to meet unique
device connectivity requirements. When used with the Digi ESP for Python, DIA can shrink the
development cycle for complex data gathering and transformation applications.
For more information on DIA software, see the DIA section in the Digi Python Wiki Archive Reference
Manual.
Linux command shell (command line interface)
XBee Gateway has a Linux shell command line interface, which allows you to experiment with the
Python interpreter interactively, create scripts, launch scripts, and control the script operation. While
Digi ESP for Python is intended as the main programming interface, you may find this interface useful
for some programming and device management tasks.
A shell is a program that takes commands from the keyboard and gives them to the operating system
to perform. On XBee Gateway, a program called ash acts as the shell program. You can use this shell
in several useful instances, particularly in managing files, executing Python programs, and
programming and executing commands to the XBee RF module in the gateway.
Note For more information on the ash shell, go to the following website:
http://linux.die.net/man/1/ash. Note that the ash shell supported in XBee Gateway is similar, but not
identical, to the ash shell described in this website.
User name and password for the Linux command shell
The command line interface is accessed using SSH and is described in the Linux command shell
(command line interface). Access to XBee Gateway is at the user level.
n User name: python
n Password: The unique, default password is printed on the device label. If the password is not
on the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work, the password
may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
Connect and log in to the XBee Gateway device
To connect and log in to the XBee Gateway device through the command line interface:
XBee Gateway User Guide
91
Page 92

Program XBee Gateway using Python Linux command shell (command line interface)
1. Open a command prompt or terminal window, such as one provided by PuTTY. You can
download PuTTY from http://www.putty.org/.
2. Choose one of the following option:
n From Windows, type:
putty python@
n From Linux, type:
$ssh python@
Where my_ip_address is the IP address of XBee Gateway.
3. You are prompted for the password. The unique, default password is printed on the device
label. If the password is not on the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults
do not work, the password may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for
help.
my_ip_address
my_ip_address
Log in to XBee Gateway through the Digi ESP for Python command line interface
Within Digi ESP for Python, there is a separate login on the Device Manager LAN Connection tab in
Digi ESP for Python.
1. Access Digi ESP for Python.
2. Click the Device Manager icon in the toolbar.
3. Select Digi Device > New_configuration from the left pane.
4. Click the LAN Connection tab.
5. Perform authentication.
a. Select the User login information if required option.
b. In the Login field, enter the default user name: python
c. In the Password field, enter the unique, default password, which is printed on the
device label. If the password is not on the device label, the default password is
dbps. If these defaults do not work, the password may have been updated. Contact
your system administrator for help.
6. Click Apply to start the validation process.
XBee Gateway User Guide
92
Page 93
Program XBee Gateway using Python Linux command shell (command line interface)
XBee Gateway User Guide
93
Page 94

Configure XBee Gateway
XBee Gateway is designed to allow network communication with minimal configuration. However,
there are several configuration settings that you can adjust. This section covers the configuration of
these settings from Remote Manager and the XBee Gateway web interface.
After you configure XBee Gateway device, back up the configuration settings. See Back up or restore
the configuration for more information.
XBee Gateway uses the following configurable settings to start up the XBee Gateway device and
initiate communication.
Configure settings from Remote Manager 95
Configure settings from the XBee Gateway web interface 96
Ethernet IP network settings 98
Wireless (Wi-Fi) network settings 101
Mobile connectivity settings 104
Digi Mobile SureLink™ settings 112
DNS settings 115
Mobile firewall settings 116
Autostart settings for the Python Program 116
Button service assignments settings 117
Configure Remote Manager connectivity settings 120
Network services settings 131
GPS static position settings 133
Time settings 134
XBee Gateway User Guide
94
Page 95

Configure XBee Gateway Configure settings from Remote Manager
In addition to the methods described in this section, you can perform configuration programmatically,
through Web Services, and natively using Python modules. See About programming for more
information.
Configure settings from Remote Manager
In Remote Manager, you can configure XBee Gateway device settings, such as network connection,
failover, and time settings. You can also monitor and manage XBee Gateway device data.
Basic information about Remote Manager is in the Digi Remote Manager User Guide.
Before you can configure settings in Remote Manager, you must perform these prerequisites:
1. Set up a Remote Manager account. See Create a new account for instructions.
2. Log in to the Remote Manager account. See Log in to your Remote Manager account for
instructions.
3. Add XBee Gateway devices to the Remote Manager device list. See Add devices to your
inventory for instructions.
See Remote Manager interface for more basic information about Remote Manager.
Basic configuration settings
In Remote Manager, you can access basic configuration settings for XBee Gateway by double-clicking
on a device in the device list to display the Properties page. As an alternative, you can right-click on a
device and select the Properties option.
Some of the basic configuration settings located in this menu are:
n Ethernet IP network settings
n Mobile connectivity settings (for Cellular models only)
n Digi Mobile SureLink™ settings (for Cellular models only)
n DNS settings
n Mobile firewall settings (for Cellular models only)
n Autostart settings for the Python Program
n File Management page in Remote Manager
Advanced configuration settings
You can access advanced configuration settings for XBee Gateway by double-clicking on a device in the
device list to display the Properties page, and then selecting Advanced Configuration.
The settings available in this menu vary by model. Some of the settings are:
n Network services settings (for Cellular models only)
n Button service assignments settings
n Time settings
n Configure Remote Manager connectivity settings
n GPS static position settings
n Configure network failover
n Configure XBee network settings
XBee Gateway User Guide
95
Page 96

Configure XBee Gateway Configure settings from the XBee Gateway web interface
Configure settings from the XBee Gateway web interface
The XBee Gateway web interface allows you to configure critical network configuration settings and
other features. If you already know the IP address for the XBee Gateway device, you can open a web
browser and type the IP address in the address bar to open the XBee Gateway web interface. If you
do not know the IP address for the XBee Gateway device, you can use the Digi DeviceDiscovery utility
to locate XBee Gateway on your network.
The XBee Gateway web interface does not display every device setting. For more extensive access to
settings, use Remote Manager or a programmatic interface.
Access the XBee Gateway web interface
To access the XBee Gateway web interface, choose one of the following options:
If you know the XBee Gateway device's IP address
1. Open a web browser, type the IP address in the address bar, and press the Enter key. For
example: http://10.101.1.178.
2. The first time you attempt to access the XBee Gateway, a certificate management prompt
appears. Click Proceed Anyway or Advanced > Proceed Anyway.
3. A login screen appears. Enter the default user name and password:
n User name: python
n Password: The unique password printed on the device label. If the password is not on
the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work, the
password may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
4. The XBee Gateway web interface appears.
If you do not know the XBee Gateway device's IP address
If you already ran the Wireless Access Point wizard, you need the Digi Device Discovery Utility to
rediscover the device and open its web interface.
1. From a web browser, go to the Product Support Download page and click the Diagnostics,
Utilities & MIBs link from the Support Downloads section.
2. Select your product from the list, or a enter keywords to locate it.
3. Select your operating system from the drop-down list, then select the Device Discovery
Utility.
4. Follow the prompts to complete the installation of the Digi Device Discovery Utility.
5. To open the Digi Device Discovery on your computer, select Start >Digi >Digi Device
Discovery >Digi Device Discovery. The Digi Device Discovery window appears.
6. Locate your XBee Gateway in the list of devices by matching the Serial Number on the XBee
Gateway's label to the corresponding value in the MAC address column in the Digi Device
Discovery window.
XBee Gateway User Guide
96
Page 97

Configure XBee Gateway Configure settings from the XBee Gateway web interface
7. Double-click the device to open the XBee Gateway web interface, or select the device and click
Open web interface under Device tasks in the Digi Device Discovery window.
8. A login screen appears. Enter the default user name and password:
n User name: python
n Password: The unique password printed on the device label. If the password is not on
the device label, the default password is dbps. If these defaults do not work, the
password may have been updated. Contact your system administrator for help.
9. To change a subset of configuration settings through Digi Device Discovery, click the Configure
Network Settings button. When you change configuration settings, you are prompted for a
password. Leave the Password field blank and click OK.
Note If your firmware version is 3.2.30.x or later, the Digi Device Discovery tool is by default not
allowed to change configuration of the XBee Gateway device. ADDP must have the Read-Write
mode enabled in order for the button on the XBee Gateway device to control this feature. See
Network services settings.
Home page
The Home page appears by default when you access the web interface for a Digi device. The
information listed on this page may vary based on product and supported features.
Home page section Description
Device Information The Device Information section of the Home page
summarizes current system parameters and
network connectivity status.
Network Connectivity Status LED The Network Connectivity Status LED and
displayed information indicates the readiness of
XBee Gateway to communicate in a network and
with the Remote Manager server. See XBee Gateway
LEDs descriptions for descriptions of the status LEDs
and the various network connectivity status
conditions listed.
Refresh button Clicking Refresh to update the Home page. This
refresh operation is necessary because items like
system time and network connectivity status are not
dynamically updated when the state changes on the
device. This refresh operation also updates device
status information.
Left pane The left side of the Home page displays a menu
consisting of configuration and administration tasks.
XBee Gateway User Guide
97
Page 98

Configure XBee Gateway Ethernet IP network settings
Home page section Description
Configuration menu The options under Configuration in the menu allow
you to configure settings for various features. Some
of the configuration settings are organized on sets of
linked screens. The options in this menu may vary
based on product and supported features.
Administration menu The options under Administration in the menu allow
you to complete common device administration
tasks. See Administration and maintenance tasks for
more information.
Apply button The web interface runs locally on the device, which
means that the interface always maintains and
displays the latest settings in the Digi device. If you
make changes, click Apply to apply the changes to
the configuration settings to the Digi device.
Cancel changes to configuration settings
Restore configuration to default
Ethernet IP network settings
The Ethernet Network settings display the current IP address and DHCP settings for Ethernet
network communications. You can change the IP address from the default either by obtaining a new
one through DHCP or by entering a static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway, and Domain
Name System (DNS) servers.
Default Ethernet settings
For Ethernet networks, the default configuration for the Ethernet model of the XBee Gateway allows
you to power up the XBee device and join an Ethernet network without any additional configuration. In
this default configuration:
n XBee Gateway uses a DHCP server to obtain its IP address information. A DHCP server needs
to provide an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and Domain Name System (DNS)
server for the device. If you disable DHCP, you must set all of these IP address settings
yourself. In the absence of a DHCP server, you need to assign a static IP address using the Digi
Device Discovery Utility and changing the network settings through the web interface.
To cancel changes to configuration settings, click
Refresh or Reload on the web browser. This causes
the web browser to reload the page. Any changes
made since the last time the you clicked Apply are
reset to their original values.
You can restore the device configuration on a Digi
device to factory defaults. See Restore XBee
Gateway factory defaults for more information. Note
that you will have to reset the network configuration
settings after the restore operation is complete.
n The default behavior regarding NTP time server access, Configure Remote Manager
connectivity settings, and DNS server all proceed as described.
XBee Gateway User Guide
98
Page 99

Configure XBee Gateway Ethernet IP network settings
If your Ethernet network configuration does not match these default behaviors, you need to adjust
the Ethernet network configuration settings. See Configure Ethernet Settings for more information.
Configure Ethernet Settings
To configure Ethernet settings, choose one of the following options:
From Remote Manager
1. Click the Device Management tab.
2. From the device list, double-click the device to display the device properties menu.
3. Configure the Ethernet settings.
For a Cellular module:
a. Click the Ethernet Network properties. The Ethernet Network page appears.
b. Complete the fields and click Save to save your changes.
For a Wi-Fi module:
a. Click the Ethernet (eth)0 properties. The Ethernet (etho) page appears.
b. Complete the fields and click Save to save your changes.
From the XBee Gateway web interface
1. Access and log into the web interface.
2. Select Configuration > Ethernet Network to access the Ethernet IP network settings.
3. Complete the fields and click Apply to save your changes.
Ethernet Network Configuration page
The following list describes the Ethernet network settings the Ethernet Network page by section.
Note The Ethernet Network page is only available for Wi-Fi models.
Current IP Parameters
This section displays the active Ethernet IP parameters for XBee Gateway.
n IP Address: The IP address assigned to network devices.
n Subnet Mask: The subnet mask assigned to the device. The subnet mask is combined with the
IP address to determine which network this Digi device is part of.
n Default Gateway: The IP address of the computer that enables this Digi device to access other
networks, such as the Internet.
XBee Gateway User Guide
99
Page 100

Configure XBee Gateway Ethernet IP network settings
Interface Configuration
n Enable this network interface: Enables or disables the Ethernet network interface.
n Speed: The Ethernet speed that XBee Gateway uses on the Ethernet network.
l Automatic: The device senses the Ethernet speed of the network and adjusts
automatically. The default is Automatic. If one side of the Ethernet connection is using
auto (negotiating), the other side can set the Ethernet speed to whatever value is desired.
Or, if the other side is set for 100 Mbps, this side must use 100 Mbps.
10: The device operates at 10 megabits per second (Mbps) only.
l 100: The device operates at 100 Mbps only.
n Duplex Mode: The mode that XBee Gateway uses to communicate on the Ethernet network.
Specify one of the following options:
l Automatic: The device senses the mode used on the network and adjusts automatically.
The default is auto. If one side of the Ethernet connection is using auto, the other side can
set the duplex value to whatever is desired. If one side uses a fixed value (for example,
half-duplex), the other side has to use the same duplex mode.
Full Duplex: The device communicates in full-duplex mode.
Half Duplex: The device communicates in half-duplex mode.
Stored IP Configuration
You can set the IP address for XBee Gateway either automatically, using DHCP, or by assigning a
static IP address. You must enable either the DCHP or the Static IPoption.
n DHCP: Select On to enable DHCP to assign an IP address to the gateway. XBee Gateway uses a
DHCP server to obtain its IP address information, by default. A DHCP server needs to provide
an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and Domain Name System (DNS) server for the
device. If you disable DHCP, you must enable the Static IP option and configure these settings
manually.
In the absence of a DHCP server, you must assign a static IP address by accessing the Digi
Device Discovery tool and changing the network settings through that interface.
n AutoIP: Enables or disables use of AutoIP address assignment. When AutoIP is enabled, XBee
Gateway automatically self-configures an IP address when an address is not available from
other methods. For example, when the Digi device is configured for DHCP and a DHCP server is
not currently available. For more information on AutoIP, see RFC 3927, Dynamic Configuration
of IPv4 Link-Local Addresses.
n Static IP: Select ON to enable you to specify a static IP address for XBee Gateway. You must
specify the following:
l IP Address: The IP address assigned to network devices.
l Subnet Mask: The subnet mask assigned to the device. The subnet mask is combined with
the IP address to determine which network this Digi device is part of.
XBee Gateway User Guide
100
 Loading...
Loading...