Page 1

Digi XBee® Cellular LTE Cat 1
Embedded Modem
User Guide
Page 2

Revision history—90001525
Revision Date Description
W March 2020
X September 2020
Y October 2020
Z November 2020
AA January 2021
Added cellular firmware update information.
Added information about XBee header connectors.
Added new CLI commands:
n ER (Remote Manager TCP Port Override)
n ES (Remote Manager UDP Port Override)
n MT (Remote Manager Idle Timeout)
n PG (Ping)
Updated existing CLI commands:
n AI (Association Indication)
n P# (Destination Phone Number)
n TP (Temperature)
n VR (Firmware Version)
Updated Transmit (TX) Status - 0x89.
Added information for File system APIframes.
Updated Software libraries.
Updated Socket Connect - 0x42.
Updated Socket Connect Response - 0xC2.
Added design recommendations for SIM cards.
Trademarks and copyright
Digi, Digi International, and the Digi logo are trademarks or registered trademarks in the United
States and other countries worldwide. All other trademarks mentioned in this document are the
property of their respective owners.
© 2021 Digi International Inc. All rights reserved.
Disclaimers
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of Digi International. Digi provides this document “as is,” without warranty of
any kind, expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of fitness or
merchantability for a particular purpose. Digi may make improvements and/or changes in this manual
or in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this manual at any time.
Warranty
To view product warranty information, go to the following website:
www.digi.com/howtobuy/terms
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
2
Page 3

Customer support
Gather support information: Before contacting Digi technical support for help, gather the following
information:
Product name and model
Product serial number (s)
Firmware version
Operating system/browser (if applicable)
Logs (from time of reported issue)
Trace (if possible)
Description of issue
Steps to reproduce
Contact Digi technical support: Digi offers multiple technical support plans and service packages.
Contact us at +1 952.912.3444 or visit us at www.digi.com/support.
Feedback
To provide feedback on this document, email your comments to
techcomm@digi.com
Include the document title and part number (Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User
Guide, 90001525 X) in the subject line of your email.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
3
Page 4

Contents
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
Applicable firmware and hardware 15
SIM cards 15
Cellular service 16
Get started with the XBee Cellular Modem
Identify the kit contents 18
Connect the hardware 19
Install and upgrade XCTU 20
Add a device to XCTU 20
Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU 21
Check for cellular registration and connection 21
XBee connection examples
Connect to the Echo server 23
Connect to the ELIZA server 25
Connect to the Daytime server 27
Send an SMS message to a phone 29
Perform a (GET) HTTP request 31
Connect to a TCP/IP address 33
Software libraries 33
Debugging 34
Get started with MicroPython
About MicroPython 36
Why use MicroPython 36
MicroPython on the XBee Cellular Modem 36
Use XCTU to enter the MicroPython environment 36
Use the MicroPython Terminal in XCTU 37
Troubleshooting 37
Example: hello world 37
Example: turn on an LED 37
Example: code a request help button 38
Enter MicroPython paste mode 39
Catch a button press 39
Send a text (SMS) when the button is pressed 41
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
4
Page 5

Add the time the button was pressed 42
Example: debug the secondary UART 43
Exit MicroPython mode 43
Other terminal programs 44
Tera Term for Windows 44
Use picocom in Linux 45
Get started with Digi Remote Manager
Create a Remote Manager account and add devices 47
Create a Remote Manager account 48
Add an XBee Cellular Modem to Remote Manager 48
Verify the connection between a device and Remote Manager 49
Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks 49
Overview: Create a schedule for a set of tasks 49
Examples 50
Example: Read settings and state using Remote Manager 50
Example: Configure a device from Remote Manager using XML 51
Example: Schedule a task to update the device firmware using Remote Manager 52
Example: Update MicroPython from Remote Manager using XML 53
Manage data in Remote Manager 57
Review device status information from Remote Manager 57
Manage secure files in Remote Manager 58
Remote Manager reference 59
Enable SM/UDP 59
TCP connection 59
Disconnect 61
Configure XBee settings within Remote Manager 61
Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode
Get started with CoAP 64
CoAP terms 64
CoAP quick start example 64
Configure the device 65
Example: manually perform a CoAPrequest 65
Example: use Python to generate a CoAP message 66
Get started with MQTT 68
Example: MQTT connect 68
Send a connect packet 70
Example: send messages (publish) with MQTT 71
Example: receive messages (subscribe) with MQTT 72
Use MQTT over the XBee Cellular Modem with a PC 73
Update the firmware
Create a plan for device and cellular component firmware updates 78
Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU 79
Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU 79
Update the device firmware 81
Update the firmware from the Devices page in Remote Manager 81
Update the firmware using web services in Remote Manager 82
Use a host processor to update the modem firmware for XBee devices over UART 84
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
5
Page 6

Update the cellular firmware 87
Update the cellular component firmware using Remote Manager 87
Update the cellular firmware using the API 90
Technical specifications
Interface and hardware specifications 94
RF characteristics 94
Networking specifications 95
Power requirements 96
Power consumption 96
Electrical specifications 96
Regulatory approvals 97
Hardware
Mechanical drawings 100
Pin signals 100
Pin connection recommendations 102
XBee header connector requirements 102
RSSI PWM 102
SIM card 102
Associate LED functionality 102
Development boards 104
XBIB-U-DEV reference 104
XBIB-CU-TH reference 106
XBIB-C-GPS reference 109
Interface with the XBIB-C-GPS module 110
Antenna recommendations
Antenna specifications 112
Antenna connections 112
Antenna placement 113
RF exposure 113
Design recommendations
Power supply considerations 115
Add a capacitor to the RESET line 115
Heat considerations and testing 115
Heat sink guidelines 117
Bolt-down style 117
Adhesive style heat sink 117
Add a fan to provide active cooling 118
Custom configuration: Create a new factory default 118
Set a custom configuration 119
Clear all custom configurations on a device 119
Clean shutdown 119
SD (Shutdown) command 119
Sleep feature 120
Airplane mode 120
SIMcards 120
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
6
Page 7

Cellular connection process
Connecting 122
Cellular network 122
Data network connection 122
Data communication with remote servers (TCP/UDP) 122
Disconnecting 122
Modes
Select an operating mode 125
Transparent operating mode 126
API operating mode 126
Bypass operating mode (DEPRECATED) 126
Enter Bypass operating mode 127
Leave Bypass operating mode 127
Restore cellular settings to default in Bypass operating mode 127
Command mode 127
Enter Command mode 127
Troubleshooting 128
Send AT commands 128
Response to AT commands 129
Apply command changes 129
Make command changes permanent 129
Exit Command mode 129
MicroPython mode 129
Sleep modes
About sleep modes 132
Normal mode 132
Pin sleep mode 132
Cyclic sleep mode 132
Cyclic sleep with pin wake up mode 132
Airplane mode 132
Connected sleep mode 132
The sleep timer 133
MicroPython sleep behavior 133
Serial communication
Serial interface 135
Serial data 135
UART data flow 135
Serial buffers 136
CTS flow control 136
RTS flow control 136
SPI operation
SPI communications 138
Full duplex operation 139
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
7
Page 8

Low power operation 140
Select the SPI port 140
Force UART operation 141
Data format 141
File system
Overview of the file system 143
Directory structure 143
Paths 143
Secure files 143
XCTU interface 144
Encrypt files 144
SMS behaviors
SMS encoding 145
Socket behavior
Supported sockets 147
Best practices when using sockets 147
Sockets and Remote Manager 147
Sockets and API mode 147
Socket timeouts 147
Socket limits in API mode 147
Enable incoming TCP connections 148
API mode behavior for outgoing TCP and TLS connections 148
API mode behavior for outgoing UDP data 149
API mode behavior for incoming TCP connections 149
API mode behavior for incoming UDP data 150
Transparent mode behavior for outgoing TCP and TLS connections 150
Transparent mode behavior for outgoing UDP data 150
Transparent mode behavior for incoming TCP connections 150
Transparent mode behavior for incoming UDP connections 151
Extended Socket frames
Examples 152
Available Extended Socket frames 153
Extended Socket example: Single HTTP Connection 153
Send a Socket Create frame 153
Receive a Socket Create response 154
Send Socket Connect 154
Receive a Socket Connect Response 154
Receive a Socket Status 155
Send HTTP Request using Socket Send frame 155
Receive TX Status 156
Receive one or more Receive Data frames 156
Receive Socket Status indicating closed connection 157
Extended Socket example: UDP 157
Send a Socket Create frame 157
Receive a Socket Create response 158
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
8
Page 9

Bind local source addres 158
Receive Bind/Listen Response 158
Send to Digi echo server 159
Receive TX Status 159
Receive echoed data 159
Send to Digi time server 160
Receive TX Status 160
Receive daytime value 160
Close the socket 161
Receive close response 161
Extended Socket example: TCPListener 162
Send a Socket Create frame 162
Receive a Socket Create response 162
Designate the socket as a listener 162
Receive a Socket Bind/Listen Response 163
Making a connection to the listener socket 163
Receiving Data from the new socket 164
Receive a Socket Status indicating closed connection 164
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Specifying TLS keys and certificates 167
Transparent mode and TLS 168
API mode and TLS 168
Key formats 168
Certificate limitations 168
Cipher suites 168
Server Name Indication (SNI) 169
Secure the connection between an XBee and Remote Manager with server authentication 169
Step 1: Get the certificate 169
Step 2: Configure device 169
Step 3: Verify that authentication is being performed 169
AT commands
Special commands 172
AC (Apply Changes) 172
FR (Force Reset) 172
RE command 172
SD (Shutdown) 173
WR (Write) 173
HI (Hardware Identity) 173
Cellular commands 175
PH (Phone Number) 175
S# (ICCID) 175
IM (IMEI) 175
II (Subscriber identity) 175
MN (Operator) 175
MV (Modem Firmware Version) 176
MU (Modem firmware revision number) 176
DB (Cellular Signal Strength) 176
DT (Cellular Network Time) 176
AN (Access Point Name) 177
AM (Airplane Mode) 177
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
9
Page 10

OA (Operating APN) 178
DV (Secondary Antenna Function Switch) 178
SQ (Reference Signal Received Quality) 178
SW (Reference Signal Received POWER) 179
PN (SIMPIN) 179
PK (SIMPUK) 179
CU (Cellular user name) 180
CW (Cellular password) 180
Network commands 181
IP (IP Protocol) 181
TL (TLS Protocol Version) 181
$0 (TLS Profile 0) 181
$1 (TLS Profile 1) 182
$2 (TLS Profile 2) 182
TM (IP Client Connection Timeout) 182
TS (IP Server Connection Timeout) 183
DO (Device Options) 183
PG (Ping) 183
Addressing commands 185
SH (Serial Number High) 185
SL (Serial Number Low) 185
MY (Module IP Address) 185
P# (Destination Phone Number) 185
N1 (DNS Address) 186
N2 (DNS Address) 186
DL (Destination Address) 186
OD (Operating Destination Address) 186
DE (Destination port) 187
C0 (Source Port) 187
LA (Lookup IP Address of FQDN) 187
Serial interfacing commands 189
BD (Baud Rate) 189
NB (Parity) 189
SB (Stop Bits) 190
RO (Packetization Timeout) 190
TD (Text Delimiter) 190
FT (Flow Control Threshold) 190
AP (API Enable) 191
I/O settings commands 192
D0 (DIO0/AD0) 192
D1 (DIO1/AD1) 192
D2 (DIO2/AD2) 193
D3 (DIO3/AD3) 193
D4 (DIO4) 193
D5 (DIO5/ASSOCIATED_INDICATOR) 194
D6 (DIO6/RTS) 194
D7 (DIO7/CTS) 195
D8 (DIO8/SLEEP_REQUEST) 195
D9 (DIO9/ON_SLEEP) 196
P0 (DIO10/PWM0 Configuration) 196
P1 (DIO11/PWM1 Configuration) 196
P2 (DIO12 Configuration) 197
PD (Pull Direction) 197
PR (Pull-up/down Resistor Enable) 198
M0 (PWM0 Duty Cycle) 199
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
10
Page 11

I/O sampling commands 200
TP (Temperature) 200
IS (Force Sample) 200
Sleep commands 202
SM (Sleep Mode) 202
SP (Sleep Period) 202
ST (Wake Time) 202
SO (Sleep Options) 203
Command mode options 204
CC (Command Sequence Character) 204
CT (Command Mode Timeout) 204
CN (Exit Command mode) 204
GT (Guard Times) 204
MicroPython commands 206
PS (Python Startup) 206
PY (MicroPython Command) 206
Firmware version/information commands 208
VR (Firmware Version) 208
VL (Verbose Firmware Version) 208
HV (Hardware Version) 208
HS (Hardware Series) 208
CK (Configuration CRC) 208
AI (Association Indication) 209
FI(FTP OTA Update Indication) 209
FO (FTP OTA command) 210
Diagnostic interface commands 212
DI (Remote Manager Indicator) 212
CI (Protocol/Connection Indication) 212
AS (Active scan for network environment data) 214
Execution commands 216
NR (Network Reset) 216
!R (Modem Reset) 216
File system commands 217
Error responses 217
ATFS (File System) 217
ATFS PWD 217
ATFS CDdirectory 217
ATFS MDdirectory 217
ATFS LS [directory] 217
ATFS PUTfilename 218
ATFS XPUTfilename 218
ATFS HASHfilename 218
ATFS GETfilename 218
ATFS MVsource_pathdest_path 218
ATFS RMfile_or_directory 218
ATFS INFO 218
ATFSFORMAT confirm 219
Remote Manager commands 220
MO (Remote Manager Options) 220
DF (Remote Manager Status Check Interval) 220
EQ (Remote Manager FQDN) 220
K1 (Remote Manager Server Send Keepalive) 220
K2 (Remote Manager Device Send Keepalive) 221
$D (Remote Manager certificate) 221
ER (Remote Manager TCP Port Override) 221
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
11
Page 12

ES (Remote Manager UDP Port Override) 222
MT (Remote Manager Idle Timeout) 222
System commands 223
KL (Device Location) 223
KC (Contact Information) 223
KP (Device Description) 223
Socket commands 224
SI (Socket Info) 224
Operate in API mode
API mode overview 227
Use the AP command to set the operation mode 227
API frame format 227
API operation (AP parameter = 1) 227
API operation with escaped characters (AP parameter = 2) 228
API frames
AT Command - 0x08 232
AT Command: Queue Parameter Value - 0x09 233
Transmit (TX) SMS - 0x1F 234
Transmit (TX) Request: IPv4 - 0x20 235
Tx Request with TLS Profile - 0x23 237
AT Command Response - 0x88 239
Transmit (TX) Status - 0x89 240
Modem Status - 0x8A 242
Receive (RX) Packet: SMS - 0x9F 243
Receive (RX) Packet: IPv4 - 0xB0 244
User Data Relay - 0x2D 245
Example use cases 245
User Data Relay Output - 0xAD 246
FW Update - 0x2B 247
FW Update Response - 0xAB 248
Socket Create - 0x40 249
Socket Create Response - 0xC0 250
Socket Option Request - 0x41 251
Socket Option Response - 0xC1 252
Socket Connect - 0x42 253
Socket Connect Response - 0xC2 254
Socket Close - 0x43 255
Socket Close Response - 0xC3 256
Socket Send (Transmit) - 0x44 257
Socket SendTo (Transmit Explicit Data): IPv4 - 0x45 258
Socket Bind/Listen - 0x46 259
Socket Listen Response - 0xC6 260
Socket New IPv4 Client - 0xCC 261
Socket Receive - 0xCD 262
Socket Receive From: IPv4 - 0xCE 263
Socket Status - 0xCF 264
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
12
Page 13

File system APIframes
Local File System Request - 0x3B 266
File Open - 0x01 268
File Close - 0x02 269
File Read - 0x03 270
File Write - 0x04 271
File Hash - 0x08 272
Directory Create - 0x10 273
Directory Open - 0x11 274
Directory Close - 0x12 276
Directory Read - 0x13 277
Get Path ID - 0x1C 278
Rename - 0x21 280
Delete - 0x2F 281
Volume Info - 0x40 282
Volume Format - 0x4F 283
Local File System Response - 0xBB 284
Troubleshooting
Cannot find the serial port for the device 287
Condition 287
Solution 287
Other possible issues 288
Enable Virtual COM port (VCP) on the driver 288
Correct a macOS Java error 289
Condition 289
Solution 289
Unresponsive cellular component in Bypass mode 290
Condition 290
Solution 290
Not on expected network after APN change 291
Condition 291
Solution 291
Syntax error at line 1 291
Solution 291
Error Failed to send SMS 291
Solution 291
Regulatory information
Modification statement 293
Interference statement 293
FCC notices 293
FCC Class B digital device notice 293
Labeling requirements for the host device 294
FCC publication 996369 related information 294
2.1 General 294
2.2 List of applicable FCC rules 294
2.3 Summarize the specific operational use conditions 295
2.4 Limited module procedures 295
2.5 Trace antenna designs 295
2.6 RF exposure considerations 295
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
13
Page 14

2.7 Antennas 295
2.8 Label and compliance information 295
2.9 Information on test modes and additional testing requirements 295
2.10 Additional testing, Part 15 Subpart B disclaimer 295
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
14
Page 15

Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
The XBee Cellular Modem is an embedded Long-Term Evolution (LTE) Category 1 cellular module that
provides original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) with a simple way to integrate cellular
connectivity into their devices.
The XBee Cellular Modem enables OEMs to quickly integrate cutting edge 4G cellular technology into
their devices and applications without dealing with the painful, time-consuming, and expensive FCC
and carrier end-device certifications.
With the full suite of standard XBee API frames and AT commands, existing XBee customers can
seamlessly transition to this new device with only minor software adjustments. When OEMs add the
XBee Cellular Modem to their product, they create a future-proof design with flexibility to switch
between wireless protocols or frequencies as needed.
You can read some frequently asked questions here.
Applicable firmware and hardware
This manual supports the following firmware:
n 100A and above
Note This manual uses the placeholder value "xx" in the firmware versions listed above, as the
manual documents the released features as of the time of its writing. Digi International periodically
releases new firmware containing bug fixes and new features. As new firmware is released and
distributor stock is refreshed, the new firmware will gradually become available without the need to
update. However, no guarantees can be made that a specific version of the firmware will be populated
on any given XBee as delivered. If a specific revision is desired, it is the user's responsibility to ensure
that version is loaded onto all XBees purchased.
Note You must upgrade your device to the latest firmware for all features to be available. See Update
the firmware.
It supports the following hardware:
n XBC-V1-UT-xxx
SIM cards
If you order the wrong type of SIM card it will not work with the XBee Cellular Modem.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
15
Page 16

Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide Cellular service
Verizon recommends SIM SKU: M2MTRI-NONRUG-GT-A or an equivalent that must include a 4FF
punch out. This SKU is in triple punch, so devices with 2FF/3FF or 4FF can use this SIM SKU.
Bulk SIMs for M2M/IoT are available from:
Phone
National distributor Network Contact
number Email
Reliance
Communications
Ingram Micro - Sales
Ingram Micro - Sales
Ice Mobility
KORE
KORE
Cellular service
Digi now offers Cellular Bundled Service plans. This service includes pre-configured cellular data
options that are ideal for IoT applications, bundled together with Digi Remote Manager for customers
who want to remotely monitor and manage their devices.
To learn more, or obtain the plan that is right for your needs, contact us:
n By phone: 1-877-890-4014 (USA/toll free) or +1-952-912-3456 (International). Select the
Wireless Plan Support or Activation option in the menu.
n By email: Data.Plan.QuoteDesk@digi.com.
Verizon
direct
Verizon
direct
Verizon
direct
Verizon
direct
Verizon
MVNO
Verizon
MVNO
Raja Ali 917-517-
7282
Lesli Reeves 317-707-
2371
Steve Kreiger 317-707-
2474
Tom Puchala 847-876-
1768
Genesis
Crowder
Mike Basso 877-710-
877-7105673
5673
raja.ali@reliance.us
lesli.reeves@ingrammicro.com
steve.kreiger@ingrammicro.com
tom.puchala@icemobility.com
gcrowder@korewireless.com
mbasso@korewireless.com
The XBee Cellular kit includes six months of free cellular service. Six months of free cellular service
assumes a rate of 5 MB/month. If you exceed a limit of 30 MB during the six month period your SIM will
be deactivated.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
16
Page 17

Get started with the XBee Cellular Modem
This section describes how to connect the hardware in the XBee, and provides some examples you can
use to communicate with the device.
You should perform all of the steps below in the order shown.
1. Identify the kit contents
2. Connect the hardware
3. Install and upgrade XCTU
4. Use one of the following methods to verify your cellular connection:
n Connect to the Echo server
n Connect to the ELIZA server
n Connect to the Daytime server
Optional steps
You can review the information in these steps for more XBee connection examples and examples of
how to use MicroPython.
1. Review additional connection examples to help you learn how to use the device. See XBee
connection examples.
2. Review introductory MicroPython examples. You can use MicroPython to enhance the
intelligence of the XBee to enable you to do edge-computing by adding business logic in
MicroPython, rather than using external components.
n Example: hello world
n Example: turn on an LED
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
17
Page 18
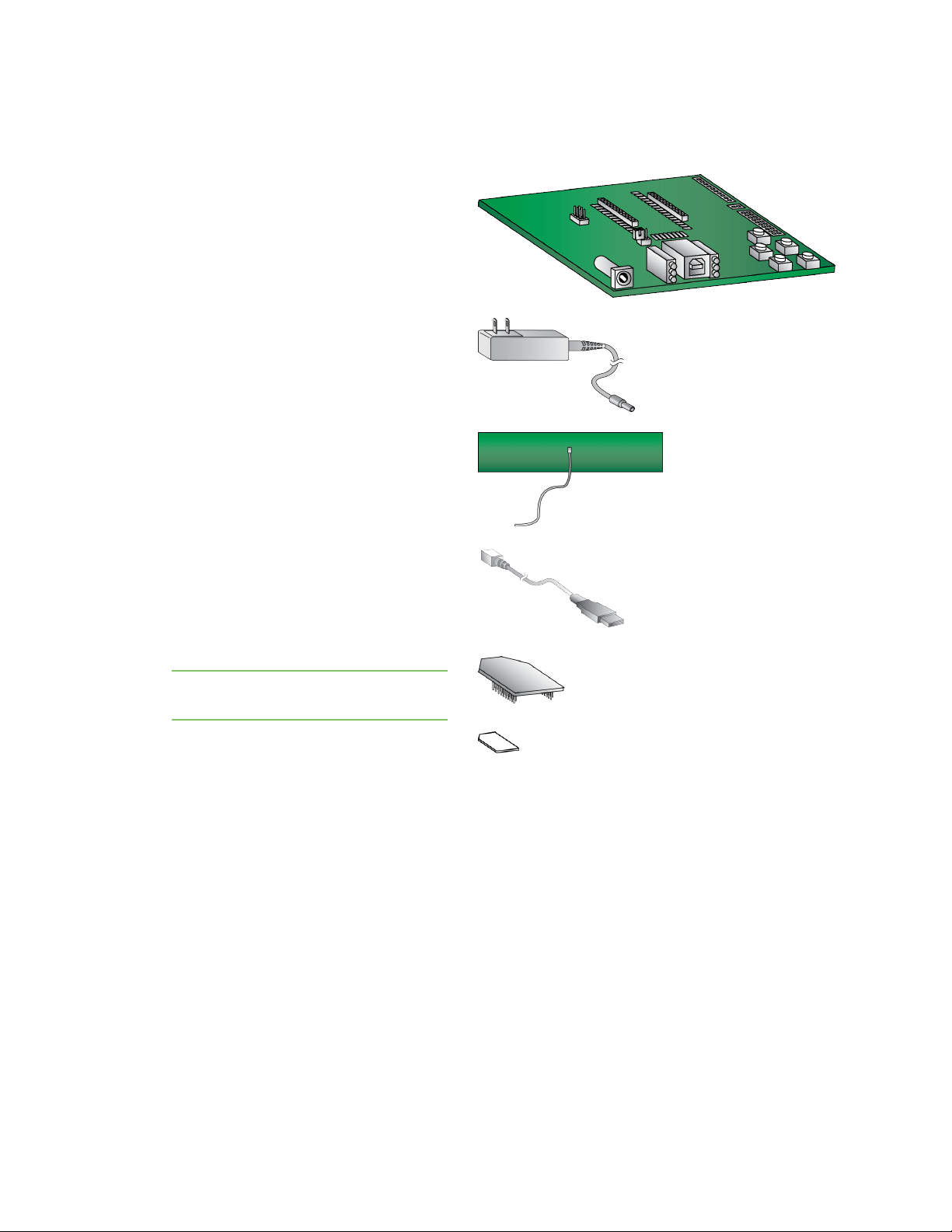
Get started with the XBee Cellular Modem Identify the kit contents
Identify the kit contents
The Developer's kit includes the following:
One XBIB-U-DEV board
One 12 V power supply
Two cellular antennas with U.FL
connectors
One USB cable
One XBee Cellular Modem
Note The XBee Cellular Modem comes
attached to the board in ESDwrap.
One SIMcard
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
18
Page 19
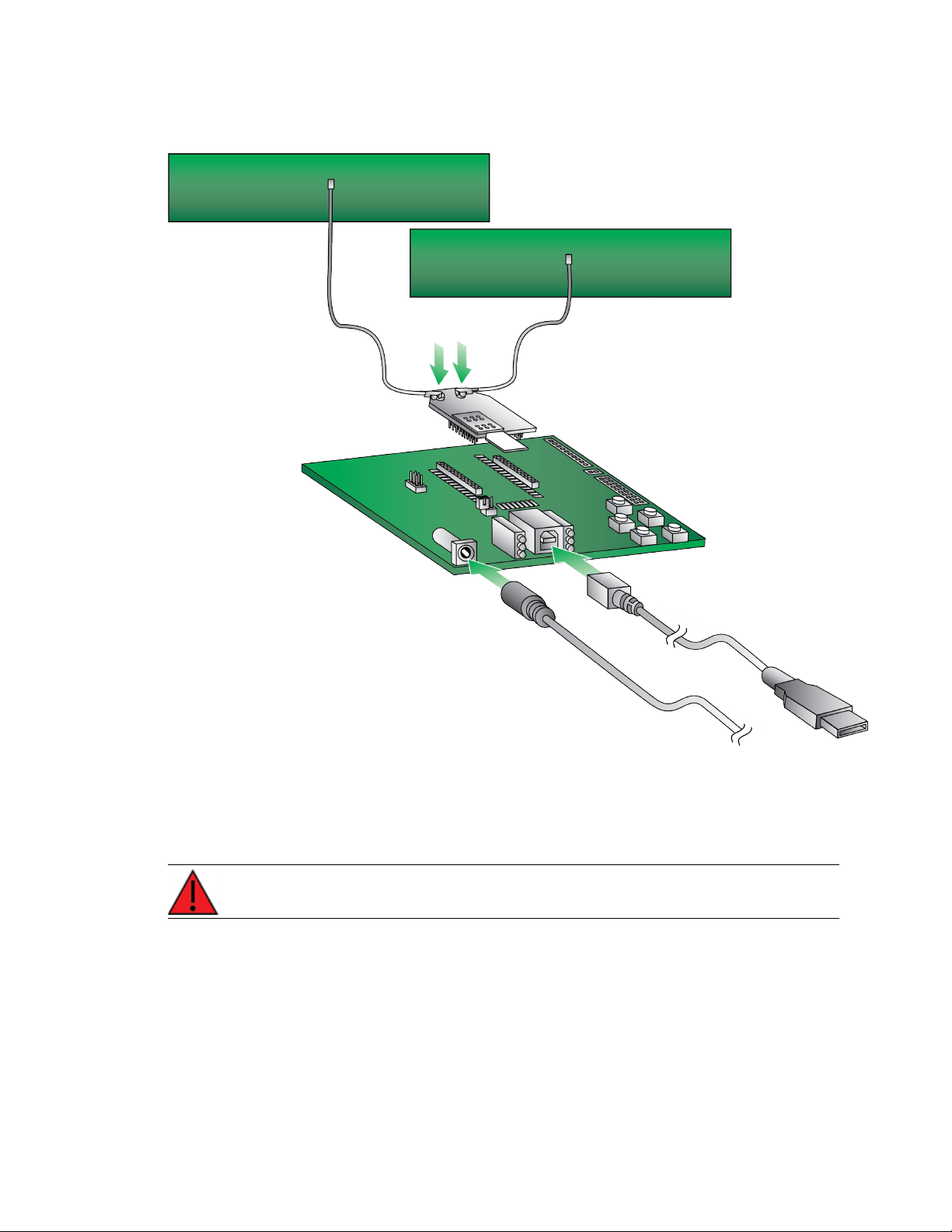
Get started with the XBee Cellular Modem Connect the hardware
Connect the hardware
1. The XBee Cellular Modem should already be plugged into the XBIB-U-DEV board. For more
information about development boards, see Development boards.
2. The SIMcard should be already be inserted into the XBee Cellular Modem. If not, install the
SIMcard into the XBee Cellular Modem.
WARNING! Never insert or remove the SIM card while the device is powered!
3. Connect the antennas to the XBee Cellular Modem. Align the U.FL connectors carefully, then
firmly press straight down to seat the connector. You should hear a snap when the antenna
attaches correctly. U.FL is fragile and is not designed for multiple insertions, so exercise
caution when connecting or removing the antennas. We recommend using a U.FL removal tool.
4. Plug the 12 V power supply to the power jack on the development board.
5. Connect the USB cable from a PC to the USB port on the development board. The computer
searches for a driver, which can take a few minutes to install.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
19
Page 20
Get started with the XBee Cellular Modem Install and upgrade XCTU
Install and upgrade XCTU
XBee Configuration and Test Utility (XCTU) is a multi-platform program developed by Digi that enables
users to interact with Digi radio frequency (RF) devices through a graphical interface. The application
includes built-in tools that make it easy to set up, configure, and test Digi RF devices.
XCTU does not work directly over an SPI interface.
You can use XCTU to update the device firmware, and if needed, XCTU will attempt to update your
cellular firmware. Firmware is the program code stored in the device's persistent memory that
provides the control program for the device.
For instructions on downloading and using XCTU, see the XCTU User Guide.
Note If you are on a macOS computer and encounter problems installing XCTU, see Correct a macOS
Java error.
Step 1: Install and upgrade XCTU
You can use XCTU to update the device firmware.
1. To use XCTU, you may need to install FTDI Virtual COMport (VCP)drivers onto your computer.
Click here to download the drivers for your operating system.
2. Upgrade XCTU to the latest version. This step is required.
Step 2: Add a device to XCTU
You must add a device to XCTU before you can update the device's firmware or configure the device
from XCTU.
Add a device to XCTU
These instructions show you how to add the XBee to XCTU.
If XCTU does not find your serial port, see Cannot find the serial port for the device and Enable Virtual
COM port (VCP) on the driver.
1.
Launch XCTU .
Note XCTU's Update the radio module firmware dialog box may open and will not allow you
to continue until you click Update or Cancel on the dialog.
2. Click Help > Check for XCTUUpdates to ensure you are using the latest version of XCTU.
3.
Click the Discover radio modules button in the upper left side of the XCTU screen.
4. In the Discover radio devices dialog, select the serial ports where you want to look for XBee
modules, and click Next.
5. In the Set port parameters window, maintain the default values and click Finish.
6. As XCTU locates radio modules, they appear in the Discovering radio modules dialog box.
7. Select the device(s) you want to add and click Add selected devices.
If your module could not be found, XCTU displays the Could not find any radio module dialog
providing possible reasons why the module could not be added.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
20
Page 21
Get started with the XBee Cellular Modem Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU
Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU
You should use XCTU to update the device firmware on your XBee to the most recent version. This
ensures that you can take advantage of all the latest fixes and features. XCTU will update the device
firmware, and if needed, XCTU will attempt to update your cellular firmware.
Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU.
Check for cellular registration and connection
The cellular network registration and address assignment must occur successfully. To verify the
network connection, you can view the LED on the development board or check the status of the
relevant commands in XCTU.
Registration can take several minutes.
Before you begin
n Make sure you have added the device to XCTU. See Add a device to XCTU.
n Make sure you are in an area with adequate cellular network reception.
n Verify that the antennas are connected properly to the device.
View LED action
The LED on the development board blinks when the XBee is registered to the cellular network; see
Associate LED functionality. If the LEDremains solid, registration has not occurred properly.
View commands in SCTU
1.
Launch XCTU .
2.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
3. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
4. Verify the status of your network connection using the following commands:
n AI (Association Indication) reads 0 when the device successfully registers to the
cellular network and the LED is blinking. If it reads 23 it is connecting to the Internet; 22
means it is registering to the cellular network.
n MY (Module IP Address) should display a valid IPaddress. If it reads 0.0.0.0, it has not
registered yet.
Hints
n
To search for an ATcommand in XCTU, use the search box .
n
To read a command's value, click the Read button next to the command.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
21
Page 22

XBee connection examples
The following examples provide some additional scenarios you can try to get familiar with the XBee.
These examples are focused on inter-operating with a host processor to drive the XBee.
If you are interested in using the intelligence built into the XBee, see Get started with MicroPython.
Note Some carriers restrict your internet access. If access is restricted, running some of these
examples may not be possible. Check with your carrier provider to determine whether internet access
is restricted.
Connect to the Echo server 23
Connect to the ELIZA server 25
Connect to the Daytime server 27
Send an SMS message to a phone 29
Perform a (GET) HTTP request 31
Connect to a TCP/IP address 33
Software libraries 33
Debugging 34
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
22
Page 23
XBee connection examples Connect to the Echo server
Connect to the Echo server
This server echoes back the messages you type.
Note For help with debugging, see Debugging.
The following table explains the AT commands that you use in this example.
At
command Value Description
IP (IP
Protocol)
TD
(Text
Delimiter)
DL
(Destination
Address)
DE
(Destination
Port)
1 Set the expected
transmission mode to
TCP communications.
D (0x0D)
52.43.121.77 The target IPaddress of
2329 (0x2329) The target port number of
The text delimiter to be
used for Transparent
mode, as an ASCII hex
code. No information is
sent until this character is
entered, unless the
maximum number of
characters has been
reached. Set to 0 to
disable text delimiter
checking. Set to D for a
carriage return.
the echo server.
the echo server.
To communicate with the Echo server:
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2. Open XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
3.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5.
To switch to TCP communication, in the IP field, select 1 and click the Write button .
6. To enable the XBee to recognize carriage return as a message delimiter, in the TD field, type D
and click the Write button.
7. To enter the destination address of the echo server, in the DL field, type 52.43.121.77 and click
the Write button.
8. To enter the destination IP port number, in the DE field, type 2329 and click the Write button.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
23
Page 24
XBee connection examples Connect to the Echo server
Note XCTU does not follow the standard hexadecimal numbering convention. The leading 0x is
not needed in XCTU.
9.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar to open a serial console to the
device. For instructions on using the Console, see the AT console topic in the XCTU User Guide.
10.
Click the Open button to open a serial connection to the device.
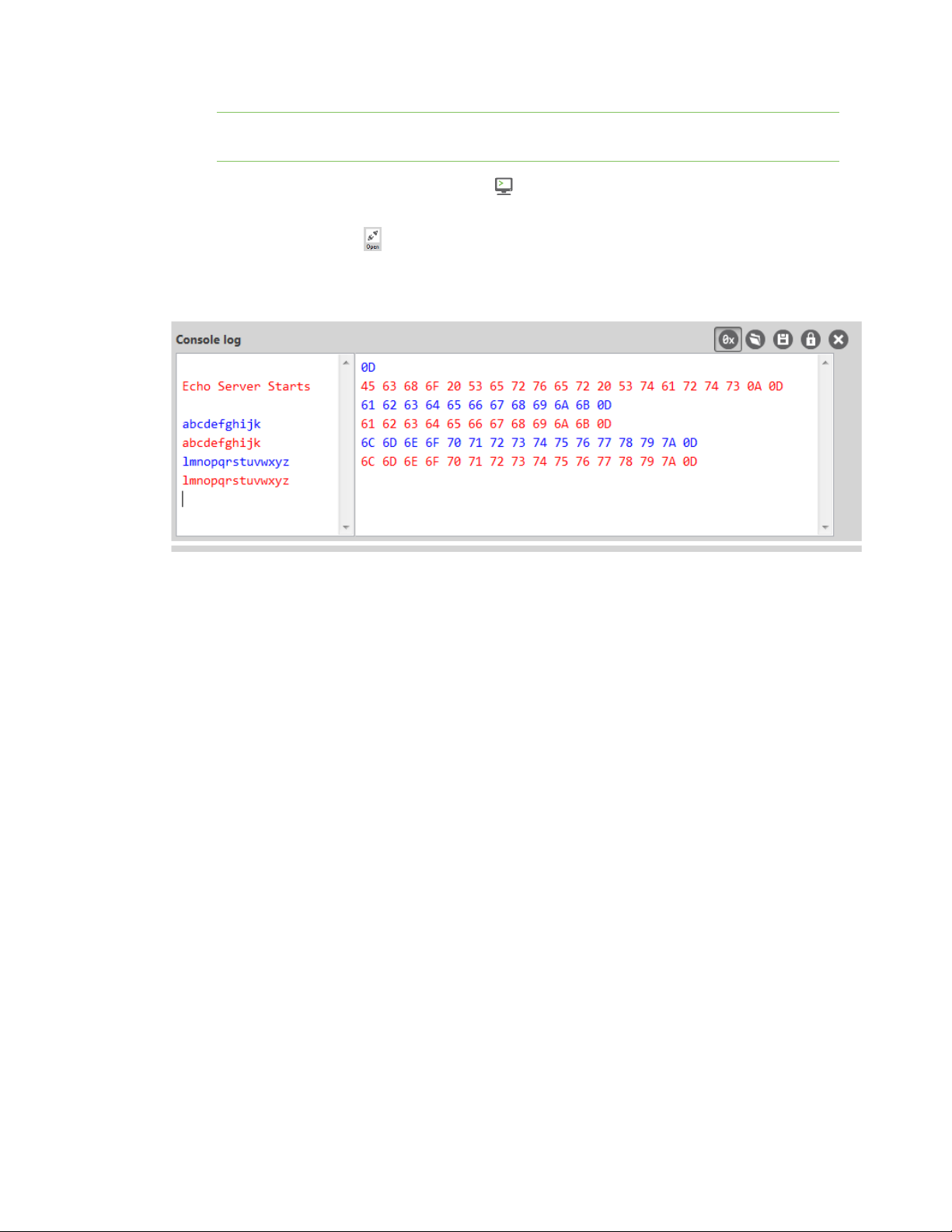
11. Click in the left pane of the Console log, then type in the Console to talk to the echo server.
The following screenshot provides an example of this chat.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
24
Page 25

XBee connection examples Connect to the ELIZA server
Connect to the ELIZA server
You can use the XBee to chat with the ELIZA Therapist Bot. ELIZAis an artificial intelligence (AI) bot
that emulates a therapist and can perform simple conversations.
Note For help with debugging, see Debugging.
The following table explains the AT commands that you use in this example.
At command Value Description
IP (IP Protocol) 1 Set the expected
transmission mode to TCP
communications.
DL (Destination
Address)
DE (Destination
Port)
To communicate with the ELIZA Therapist Bot:
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2. Open XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
3.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5.
To switch to TCP communication, in the IP field, select 1 and click the Write button .
6. To enter the destination address of the ELIZATherapist Bot, in the DL field, type 52.43.121.77
and click the Write button.
7. To enter the destination IP port number, in the DE field, type 2328 and click the Write button.
8.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar to open a serial console to the
device. For instructions on using the Console, see the AT console topic in the XCTU User Guide.
52.43.121.77 The target IP address of the
ELIZA server.
2328 (0x2328) The target port number of
the ELIZA server.
9.
Click the Open button to open a serial connection to the device.
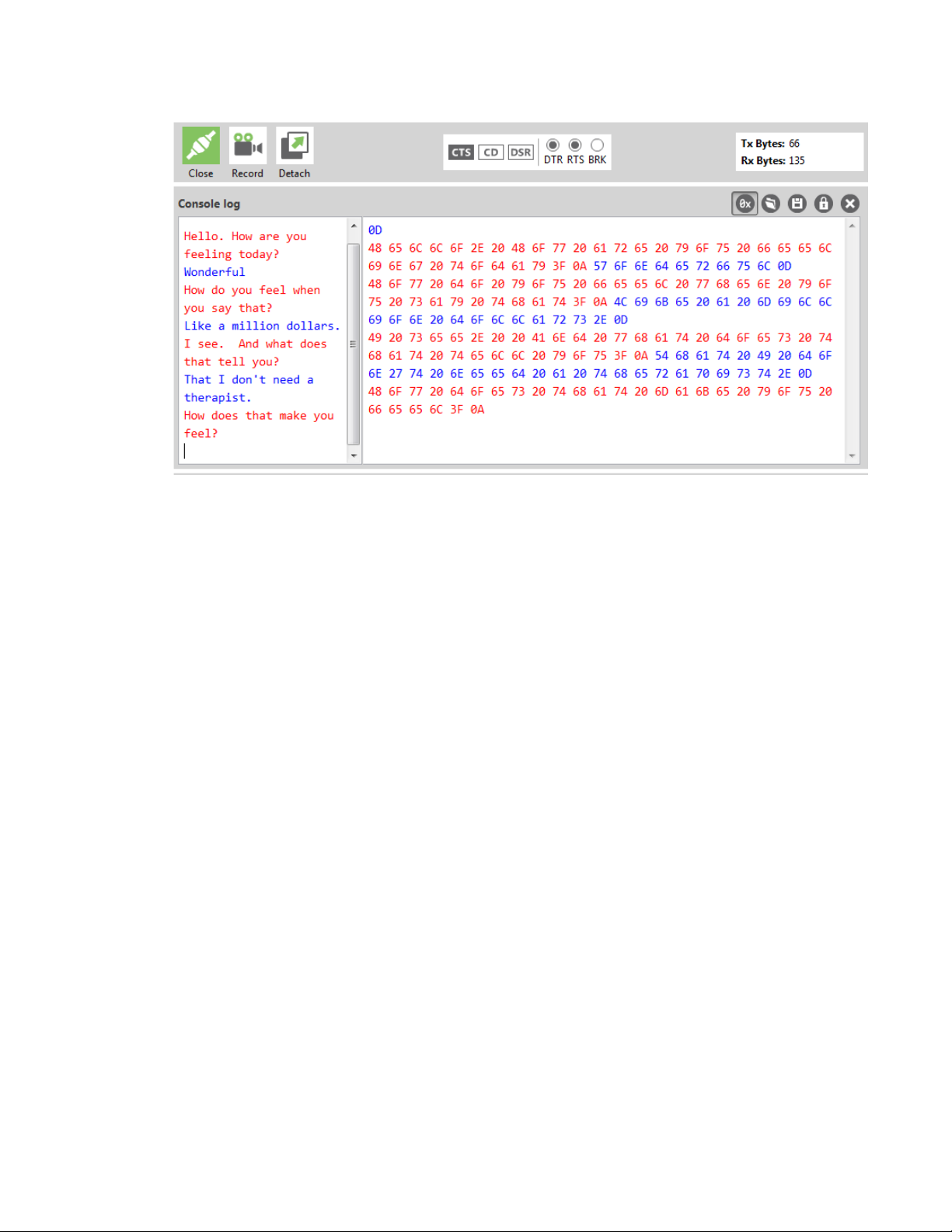
10. Click in the left pane of the Console log, then type in the Console to talk to the ELIZA Therapist
Bot. The following screenshot provides an example of this chat with the user's text in blue.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
25
Page 26
XBee connection examples Connect to the ELIZA server
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
26
Page 27

XBee connection examples Connect to the Daytime server
Connect to the Daytime server
The Daytime server reports the current Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) value responding to any
user input.
Note For help with debugging, see Debugging.
The following table explains the AT commands that you use in this example.
At command Value Description
IP (IP
Protocol)
DL
(Destination
Address)
DE
(Destination
Port)
TD (Text
Delimiter)
To communicate with the Daytime server:
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2. Open XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
1 Set the expected transmission
mode to TCP communications.
52.43.121.77 The target IP of the Daytime
server.
232A (0x232A) The target port number of the
Daytime server.
0
The text delimiter to be used for
Transparent mode, as an ASCII
hex code. No information is sent
until this character is entered,
unless the maximum number of
characters has been reached. Set
to zero to disable text delimiter
checking.
3.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5.
To switch to TCP communication, in the IP field, select 1 and click the Write button .
6. To enter the destination address of the daytime server, in the DL field, type 52.43.121.77 and
click the Write button.
7. To enter the destination IP port number, in the DE field, type 232A and click the Write button.
8. To disable text delimiter checking, in the TD field, type 0 and click the Write button.
9.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar to open a serial console to the
device. For instructions on using the Console, see the AT console topic in the XCTU User Guide.
10.
Click the Open button to open a serial connection to the device.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
27
Page 28
XBee connection examples Connect to the Daytime server
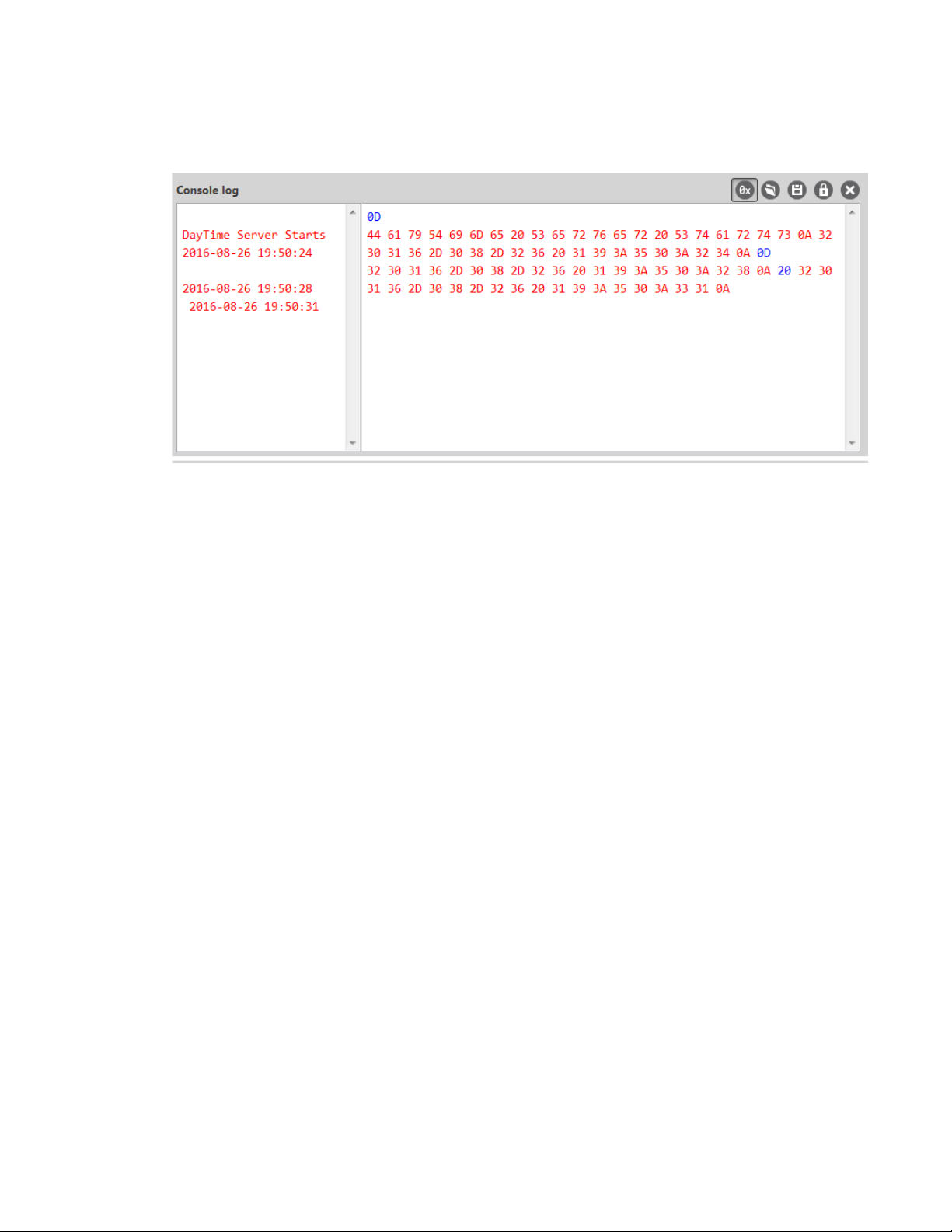
11. Click in the left pane of the Console log, then type in the Console to query the Daytime server.
The following screenshot provides an example of this chat.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
28
Page 29

XBee connection examples Send an SMS message to a phone
Send an SMS message to a phone
The XBee Cellular Modem can send and receive Short Message Service (SMS) transmissions (text
messages) while in Transparent mode. This allows you to send and receive text messages to and from
an SMS capable device such as a mobile phone.
Note For help with debugging, see Debugging.
The following table explains the AT commands that you use in this example.
Command Value Description
AP (APIEnable)
IP (IP Protocol)
P#
(DestinationPhone
Number)
TD (Text Delimiter)
PH (Module's SIM
phone number)
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2. Open XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
3.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
0 Set the device's API mode to Transparent mode.
2 Set the expected transmission mode to SMScommunication.
<Target
phone
number>
D (0x0D)
Read
only
The target phone number that you send to, for example, your
cellular phone. See P# (Destination Phone Number) for instructions
on using this command.
The text delimiter to be used for Transparent mode, as an ASCII hex
code. No information is sent until this character is entered, unless
the maximum number of characters has been reached. Set to 0 to
disable text delimiter checking. Set to D for a carriage return.
The value that represents your device's phone number as supplied
by the SIM card. This is used to send text messages to the device
from another cellular device.
5.
To switch to SMS communication, in the IP field, select 2 and click the Write button .
6. To enter your cell phone number, in the P# field, type the <target phone number> and click
the Write button. Type the phone number using only numbers, with no dashes. You can use the
+ prefix if necessary. The target phone number is the phone number you wish to send a text to.
7. In the TD field, type D and click the Write button.
8. Note the number in the PH field; it is the XBee Cellular Modem phone number, which you see
when it sends an SMS to your phone.
9.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar to open a serial console to the
device. For instructions on using the Console, see the AT console topic in the XCTU User Guide.
10.
Click the Open button to open a serial connection to the device.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
29
Page 30
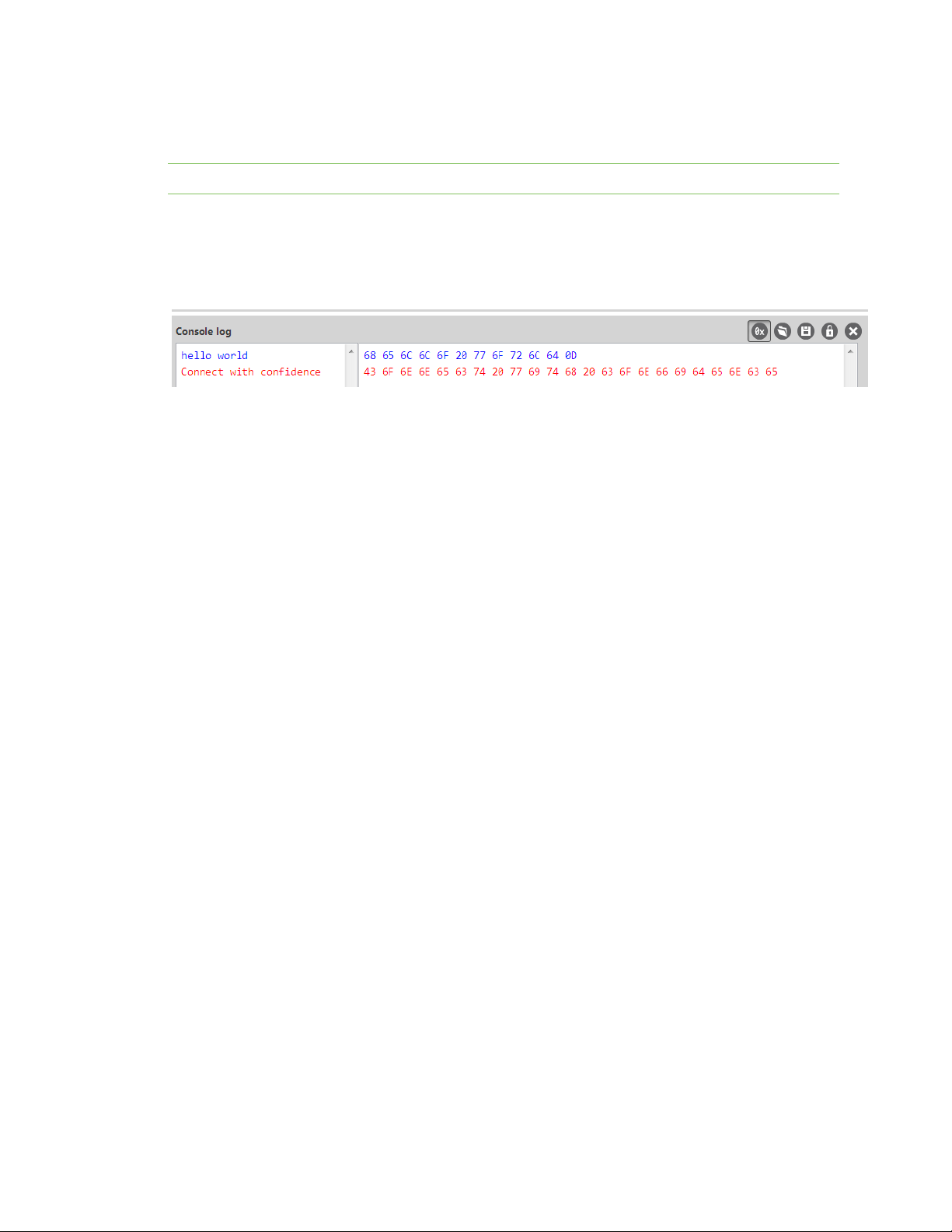
XBee connection examples Send an SMS message to a phone
11. Click in the left pane of the Console log, type hello world and press Enter. The XBee Cellular
Modem sends the message to the destination phone number set by the P# command.
Note If you are receiving individual characters, verify that you set TD correctly.
12. When the phone receives the text, you can see that the sender's phone number matches the
value reported by the XBee Cellular Modem with the PH command.
13. On the phone, reply with the text connect with confidence and the XBee Cellular Modem
outputs this reply from the UART.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
30
Page 31

XBee connection examples Perform a (GET) HTTP request
Perform a (GET) HTTP request
You can use the XBee to perform a GET Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) request using XCTU. HTTP
is an application-layer protocol that runs over TCP. This example uses httpbin.org/ as the target
website that responds to the HTTP request.
Note For help with debugging, see Debugging.
To perform a GETrequest:
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2. Open XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
3.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5. To enter the destination address of the target website, in the DL field, type httpbin.org and
click the Write button .
6. To enter the HTTP request port number, in the DE field, type 50 and click the Write button.
Hexadecimal 50 is 80 in decimal.
7. To switch to TCP communication, in the IP field, select 1 and click the Write button.
8. To move into Transparent mode, in the APfield, select 0 and click the Write button.
9. Wait for the AI (Association Indication) value to change to 0 (Connected to the Internet).
10.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar.
11.
From the AT console, click the Add new packet button in the Send packets dialog. The
Add new packet dialog appears.
12. Enter the name of the data packet.
13. Type the following data in the ASCII input tab:
GET /ip HTTP/1.1
Host: httpbin.org
14. Click the HEX input tab and add 0A (zero A) after each 0D (zero D), and add an additional 0D 0A
at the end of the message body. For example, copy and past the following text into the HEX
input tab:
47 45 54 20 2F 69 70 20 48 54 54 50 2F 31 2E 31 0D 0A 48 6F 73 74 3A 20 68 74 74 70 62 69 6E
2E 6F 72 67 0D 0A 0D 0A
Note The HTTP protocol requires an empty line (a line with nothing preceding the CRLF) to terminate
the request.
15. Click Add packet.
16.
Click the Open button .
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
31
Page 32

XBee connection examples Perform a (GET) HTTP request
17. Click Send selected packet.
18. A GETHTTP response from httpbin.org appears in the Console log.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
32
Page 33

XBee connection examples Connect to a TCP/IP address
Connect to a TCP/IP address
The XBee Cellular Modem can send and receive TCP messages while in Transparent mode; see
Transparent operating mode.
Note You can use this example as a template for sending and receiving data to or from any
TCP/IPserver.
Note For help with debugging, see Debugging.
The following table explains the AT commands that you use in this example.
Command Value Description
IP (IP
Protocol)
DL
(Destination
IPAddress)
DE
(Destination
Port)
To connect to a TCP/IP address:
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2. Open XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
3.
Click the Configuration working mode button.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5.
In the IP field, select 1 and click the Write button .
6. In the DL field, type the <target IP address> and click the Write button. The target IP address
is the IPaddress that you send and receive from.
7. In the DE field, type the <target port number>, converted to hexadecimal, and click the Write
button.
8. Exit Command mode.
1 Set the expected transmission mode to TCPcommunication.
<Target
IPaddress>
<Target
portnumber>
The target IP address that you send and receive from. For example, a
data logging server’s IP address that you want to send
measurements to.
The target port number that the device sends the transmission to.
This is represented as a hexadecimal value.
After exiting Command mode, any UART data sent to the device is sent to the destination IP address
and port number after the RO (Packetization Timeout) occurs.
Software libraries
One way to communicate with the XBee device is by using a software library. The libraries available
for use with the XBee Cellular Modem include:
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
33
Page 34

XBee connection examples Debugging
n XBee Java library
n XBee Python library
n XBee ANSI C library
The XBee Java Library is a Java API. The package includes the XBee library, its source code and a
collection of samples that help you develop Java applications to communicate with your XBee devices.
The XBee Python Library is a Python API that dramatically reduces the time to market of XBee
projects developed in Python and facilitates the development of these types of applications, making it
an easy process.
The XBee ANSI C Library project is a collection of portable ANSI C code for communicating with the
devices in API mode.
Debugging
If you experience problems with the settings in the examples, you can load the default settings in
XCTU.
Note If you load the default settings, you will need to reapply any configuration settings that you have
previously made.
1.
On the Configuration toolbar, click the Default button to load the default values
established by the firmware, and click Yes to confirm.
2. Factory settings are loaded but not written to the device. To write them, click the Write button
on the toolbar.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
34
Page 35

Get started with MicroPython
This section provides an overview and simple examples of how to use MicroPython with the XBee
Cellular Modem. You can use MicroPython to enhance the intelligence of the XBee to enable you to do
edge-computing by adding business logic in MicroPython, rather than using external components.
Note For in-depth information and more complex code examples, refer to the Digi MicroPython
Programming Guide.
About MicroPython 36
MicroPython on the XBee Cellular Modem 36
Use XCTU to enter the MicroPython environment 36
Use the MicroPython Terminal in XCTU 37
Example: hello world 37
Example: turn on an LED 37
Example: code a request help button 38
Example: debug the secondary UART 43
Exit MicroPython mode 43
Other terminal programs 44
Use picocom in Linux 45
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
35
Page 36

Get started with MicroPython About MicroPython
About MicroPython
MicroPython is an open-source programming language based on Python 3, with much of the same
syntax and functionality, but modified to fit on small devices with limited hardware resources, such as
microcontrollers, or in this case, a cellular modem.
Why use MicroPython
MicroPython enables on-board intelligence for simple sensor or actuator applications using digital and
analog I/O. MicroPython can help manage battery life. Cryptic readings can be transformed into useful
data, excess transmissions can be intelligently filtered out, modern sensors and actuators can be
employed directly, and logic can glue inputs and outputs together in an intelligent way.
For more information about MicroPython, see www.micropython.org.
For more information about Python, see www.python.org.
MicroPython on the XBee Cellular Modem
The XBee Cellular Modem has MicroPython running on the device itself. You can access a MicroPython
prompt from the XBee Cellular Modem when you install it in an appropriate development board (XBDB
or XBIB), and connect it to a computer via a USB cable.
Note MicroPython does not work with SPI.
The examples in this guide assume:
n You have XCTU on your computer. See Install and upgrade XCTU.
n You have a terminal program installed on your computer. We recommend using the Use the
MicroPython Terminal in XCTU. This requires XCTU 6.3.7 or higher.
n You have an XBee Cellular Modem installed in an appropriate development board, such as an
XBIB-U-DEV.
Note Most examples in this guide require the XBIB-U-DEV board.
n The XBee Cellular Modem is connected to the computer via a USB cable and XCTU recognizes
it.
n The board is powered by an appropriate power supply, 12 VDC and at least 1.1 A.
Use XCTU to enter the MicroPython environment
To use the XBee Cellular Modem in the MicroPython environment:
1. Use XCTU to add the device(s); see Install and upgrade XCTU and Add a device to XCTU.
2. The XBee Cellular Modem appears as a box in the Radio Modules information panel. Each
module displays identifying information about itself.
3. Click this box to select the device and load its current settings.
4. Set the device's baud rate to 115200 b/s, in the BD field select 115200 [7] or higher and click
the Write button . We recommend using flow control to avoid data loss, especially when
pasting large amounts of code/text.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
36
Page 37

Get started with MicroPython Use the MicroPython Terminal in XCTU
5. Put the XBee Cellular Modem into MicroPython mode, in the APfield select MicroPython REPL
[4] and click the Write button .
6. Note what COM port(s) the XBee Cellular Modem is using, because you will need this
information when you use terminal communication. The Radio Modules information panel lists
the COM port in use.
Use the MicroPython Terminal in XCTU
You can use the MicroPython Terminal to communicate with the XBee Cellular Modem when it is in
MicroPython mode.1This requires XCTU 6.3.7 or higher. To enter MicroPython mode, follow the steps
in Use XCTU to enter the MicroPython environment. To use the MicroPython Terminal:
1.
Click the Tools drop-down menu and select MicroPython Terminal. The terminal opens.
2. Click Open. If you have not already added devices to XCTU:
a. In the Select the Serial/USB port area, click the COM port that the device uses.
b. Verify that the baud rate and other settings are correct.
3.
Click OK. The Open icon changes to Close , indicating that the device is properly connected.
4. Press Ctrl+B to get the MicroPython version banner and prompt.
You can now type or paste MicroPython commands at the >>> prompt.
Troubleshooting
If you receive No such port: 'Port is already in use by other applications.' in the MicroPython
Terminal close any other console sessions open inside XCTU and close any other serial terminal
programs connected to the device, then retry the MicroPython connection in XCTU.
If the device seems unresponsive, try pressing Ctrl+C to end any running programs.
You can use the +++ escape sequence and look for an OK for confirmation that you have the correct
baud rate.
Example: hello world
Before you begin, you must have previously added a device in XCTU. See Add a device to XCTU.
1. At the MicroPython >>> prompt, type the Python command: print("Hello, World!")
2. Press Enter to execute the command. The terminal echos back Hello, World!.
Example: turn on an LED
1. Note the DS4 LED on the XBIB board. The following image highlights it in a red box. The LED is
normally off.
1
See Other terminal programs if you do not use the MicroPython Terminal in XCTU.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
37
Page 38

Get started with MicroPython Example: code a request help button
2. At the MicroPython >>> prompt, type the commands below, pressing Enter after each one.
After entering the last line of code, the LED illuminates. Anything after a # symbol is a
comment, and you do not need to type it.
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
import machine
from machine import Pin
led = Pin("D4", Pin.OUT, value=0) # Makes a pin object set to output 0.
# One might expect 0 to mean OFF and 1 to mean ON, and this is normally the
case.
# But the LED we are turning on and off is setup as what is# known as
"active low".
# This means setting the pin to 0 allows current to flow through the LED and
then through the pin, to ground.
3. To turn it off, type the following and press Enter:
led.value(1)
You have successfully controlled an LED on the board using basic I/O.
Example: code a request help button
This example provides a fast, deep dive into MicroPython designed to let you see some of the powerful
things it can do with minimal code. It is not meant as a tutorial; for in-depth examples refer to the Digi
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
38
Page 39

Get started with MicroPython Example: code a request help button
MicroPython Programming Guide.
Many stores have help buttons in their aisles that a customer can press to alert the store staff that
assistance is required in that aisle. You can implement this type of system using the Digi XBee Cellular
Modem, and this example provides the building blocks for such a system. This example, based on SMS
paging, can have many other uses such as alerting someone with a text to their phone if a water
sensor in a building detects water on the floor, or if a temperature sensor reports a value that is too
hot or cold relative to normal operation.
Enter MicroPython paste mode
In the following examples it is helpful to know that MicroPython supports paste mode, where you can
copy a large block of code from this user guide and paste it instead of typing it character by character.
To use paste mode:
1. Copy the code you want to run. For this example, copy the following code that is the code from
the previous LED (Example: turn on an LED) example:
from machine import Pin
led = Pin("D4", Pin.OUT, value=0)
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
2. Paste the copied code. Press CTRL + Shift + V or right-click in the Terminal and select Paste.
3. In the terminal, at the MicroPython >>> prompt type Ctrl+E to enter paste mode. The terminal
displays paste mode; Ctrl-C to cancel, Ctrl-D to finish.
4. The code appears in the terminal occupying multiple lines, where each line starts with its line
number and three = symbols. For example line 1 starts with 1===.
5. If the code is correct, press Ctrl+D to run the code and you should once again see the DS4 LED
turn on. If you get a Line 1 SyntaxError: invalid syntax error, see Syntax error at line 1.
Additionally, if you want to exit paste mode without running the code, for example, or if the
code did not copy correctly, press Ctrl+C to cancel and return to the normal MicroPython >>>
prompt.
6. Next turn the LED off. Copy the code below:
from machine import Pin
led = Pin("D4", Pin.OUT, value=1)
print("DS4 LED now OFF!")
print("Paste Mode Successful!")
7. Press Ctrl+E to enter paste mode.
8. Press Ctrl + Shift + V or right-click in the Terminal and select Paste to paste the copied code.
9. If the code is correct, press Ctrl+D to run it. The LED should turn off and you should see two
confirmation messages print to the screen.
Catch a button press
For this part of the example, you write code that responds to a button press on the XBIB-U-DEV board
that comes with the XBee Cellular Modem Development Kit. The code monitors the pin connected to
the button on the board labeled SW2.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
39
Page 40

Get started with MicroPython Example: code a request help button
For this part of the example, you write code that responds to a button press on the XBIB-U-DEV board
that comes with the XBee Cellular Modem Development Kit. The code monitors the pin connected to
the button on the board labeled SW2.
On the board you see DIO0 written below SW2, to the left of the button. This represents the pin that
the button is connected to.
In MicroPython, you will create a pin object for the pin that is connected to the SW2 button. When you
create the pin object, the DIO0 pin is called D0 for short.
The loop continuously checks the value on that pin and once it goes to 0 (meaning the button has been
pressed) a print() call prints the message Button pressed! to the screen.
At the MicroPython >>> prompt, copy the following code and enter it into MicroPython using paste
mode (Ctrl+E), right-click in the Terminal, select Paste to paste the copied code, and press Ctrl+D to
run the code.
# Import the Pin module from machine, for simpler syntax.
from machine import Pin
# Create a pin object for the pin that the button "SW2" is connected to.
dio0 = Pin("D0", Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
# Give feedback to inform user a button press is needed.
print("Waiting for SW2 press...")
# Create a WHILE loop that checks for a button press.
while (True):
if (dio0.value() == 0): # Once pressed.
print("Button pressed!") # Print message once pressed.
break # Exit the WHILE loop.
# When you press SW2, you should see "Button pressed!" printed to the
screen.
# You have successfully performed an action in response to a button press!
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
40
Page 41

Get started with MicroPython Example: code a request help button
Note If you have problems pasting the code, see Syntax error at line 1. For SMS failures, see Error
Failed to send SMS.
Send a text (SMS) when the button is pressed
After creating a while loop that checks for a button press, add sending an SMS to your code. Instead of
printing Button pressed! to the screen, this code sends Button pressed to a cell phone as a text
(SMS) message.
To accomplish this, use the sms_send() method, which sends a string to a given phone number. It
takes the arguments in the following order:
1. <phone number>
2. <message-to-be-sent>
Before you run this part of the example, you must create a variable that holds the phone number of
the cell phone or mobile device you want to receive the SMS.
1. To do this, at the MicroPython >>> prompt, type the following command, replacing 1123456789
with the full phone number (no dashes, spaces, or other symbols) and press Enter:
ph = 1123456789
2. After you create this ph variable with your phone number, copy the code below and enter it
into MicroPython using paste mode (Ctrl+E) and then run it.
from machine import Pin
import network # Import network module
import time
c = network.Cellular() # initialize cellular network parameter
dio0 = Pin("D0", Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
while not c.isconnected(): # While no network connection.
print("Waiting for connection to cell network...")
time.sleep(5)
print("Connected.")
# Give feedback to inform user a button press is needed.
print("Waiting for SW2 press...")
while (True):
if (dio0.value() == 0):
# When SW2 is pressed, the module will send an SMS
# message saying "Button pressed" to the given target cell phone
number.
try:
c.sms_send(ph, 'Button Pressed')
print("Sent SMS successfully.")
except OSError:
print("ERROR- failed to send SMS.")
# Exit the WHILE loop.
break
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
41
Page 42

Get started with MicroPython Example: code a request help button
Note If you have problems pasting the code, see Syntax error at line 1. For SMS failures, see Error
Failed to send SMS.
Add the time the button was pressed
After you add the ability to send an SMS to the code, add functionality to insert the time at which the
button was pressed into the SMS that is sent. To accomplish this:
1. Create a UDP socket with the socket() method.
2. Save the IP address and port of the time server in the addr variable.
3. Connect to the time server with the connect() method.
4. Send hello to the server to prompt it to respond with the current date and time.
5. Receive and store the date/time response in the buf variable.
6. Send an SMSin the same manner as before using the sms_send() method, except that you add
the time into the SMS message, such that the message reads: [Button pressed at: YYYY-MM-
DD HH:MM:SS]
To verify that your phone number is still in the memory, at the MicroPython >>> prompt, type ph and
press Enter.
If MicroPython responds with your number, copy the following code and enter it into MicroPython
using paste mode and then run it. If it returns an error, enter your number again as shown in Send a
text (SMS) when the button is pressed. With your phone number in memory in the ph variable, copy
the code below and enter it into MicroPython using paste mode (Ctrl+E) and then run it.
from machine import Pin
import network
import usocket
import time
c = network.Cellular()
dio0 = Pin("D0", Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
while not c.isconnected(): # While no network connection.
print("Waiting for connection to cell network...")
time.sleep(5)
print("Connected.")
# Give feedback to inform user a button press is needed.
print("Waiting for SW2 press...")
while (1):
if (dio0.value() == 0):
# When button pressed, now the module will send "Button Press" AND
# the time at which it was pressed in an SMS message to the given
# target cell phone number.
socketObject = usocket.socket(usocket.AF_INET, usocket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Connect the socket object to the web server specified in
"address".
addr = ("52.43.121.77", 10002)
socketObject.connect(addr)
bytessent = socketObject.send("hello")
print("Sent %d bytes on socket" % bytessent)
buf = socketObject.recv(1024)
# Send message to the given number. Handle error if it occurs.
try:
c.sms_send(ph, 'Button Pressed at: ' + str(buf))
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
42
Page 43

Get started with MicroPython Example: debug the secondary UART
print("Sent SMS successfully.")
except OSError:
print("ERROR- failed to send SMS.")
# Exit the WHILE loop.
break
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
Now you have a system based on the XBee Cellular Modem that sends an SMS in response to a certain
input, in this case a simple button press.
Note If you have problems pasting the code, see Syntax error at line 1. For SMS failures, see Error
Failed to send SMS.
Example: debug the secondary UART
This sample code is handy for debugging the secondary UART. It simply relays data between the
primary and secondary UARTs.
from machine import UART
import sys, time
def uart_init():
u = UART(1)
u.write('Testing from XBee\n')
return u
def uart_relay(u):
while True:
uart_data = u.read(-1)
if uart_data:
sys.stdout.buffer.write(uart_data)
stdin_data = sys.stdin.buffer.read(-1)
if stdin_data:
u.write(stdin_data)
time.sleep_ms(5)
u = uart_init()
uart_relay(u)
You only need to call uart_init() once.
Call uart_relay() to pass data between the UARTs.
Send Ctrl-C to exit relay mode.
When done, call u.close() to close the secondary UART.
Exit MicroPython mode
To exit MicroPython mode:
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
43
Page 44

Get started with MicroPython Other terminal programs
1.
In the XCTU MicroPython Terminal, click the green Close button .
2. Click Close at the bottom of the terminal to exit the terminal.
3.
In XCTU's Configuration working mode , change AP API Enable to another mode and click
the Write button . We recommend changing to Transparent mode [0], as most of the
examples use this mode.
Other terminal programs
If you do not use the MicroPython Terminal in XCTU, you can use other terminal programs to
communicate with the XBee Cellular Modem. If you use Microsoft Windows, follow the instructions for
Tera Term, if you use Linux, follow the instructions for picocom. To download these programs:
n Tera Term for Windows; see https://ttssh2.osdn.jp/index.html.en.
n Picocom for Linux; see https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php/Setting_up_Picocom_-_
Ubuntu and for the source code and in-depth information https://github.com/npat-
efault/picocom.
Tera Term for Windows
With the XBee Cellular Modem in MicroPython mode (AP = 4), you can access the MicroPython prompt
using a terminal.
1. Open Tera Term. The Tera Term: New connection window appears.
2. Click the Serial radio button to select a serial connection.
3. From the Port: drop-down menu, select the COM port that the XBee Cellular Modem is
connected to.
4. Click OK. The COMxx - Tera Term VT terminal window appears and Tera Term attempts to
connect to the device at a baud rate of 9600 b/s. The terminal will not allow communication
with the device since the baud rate setting is incorrect. You must change this rate as it was
previously set to 115200 b/s.
5. Click Setup and Serial Port. The Tera Term: Serial port setup window appears.
6. In the Tera Term: Serial port setup window, set the parameters to the following values:
n Port: Shows the port that the XBee Cellular Modem is connected on.
n Baud rate:115200
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
44
Page 45

Get started with MicroPython Use picocom in Linux
n Data: 8 bit
n Parity: none
n Stop: 1 bit
n Flow control: hardware
n Transmit delay: N/A
7. Click OK to apply the changes to the serial port settings. The settings should go into effect
right away.
8. To verify that local echo is not enabled and that extra line-feeds are not enabled:
a. In Tera Term, click Setup and select Terminal.
b. In the New-line area of the Tera Term: Serial port setup window, click the Receive drop-
down menu and select CR if it does not already show that value.
c. Make sure the Local echo box is not checked.
9. Click OK.
10. Press Ctrl+B to get the MicroPython version banner and prompt.
Now you can type MicroPython commands at the >>> prompt.
Use picocom in Linux
With the XBee Cellular Modem in MicroPython mode (AP = 4), you can access the MicroPython prompt
using a terminal.
Note The user must have read and write permission for the serial port the XBee Cellular Modem is
connected to in order to communicate with the device.
1. Open a terminal in Linux and type picocom -b 115200 /dev/ttyUSB0. This assumes you have
no other USB-to-serial devices attached to the system.
2. Press Ctrl+B to get the MicroPython version banner and prompt. You can also press Enter to
bring up the prompt.
If you do have other USB-to-serial devices attached:
1. Before attaching the XBee Cellular Modem, check the directory /dev/ for any devices named
ttyUSBx, where x is a number. An easy way to list these is to type: ls /dev/ttyUSB*. This
produces a list of any device with a name that starts with ttyUSB.
2. Take note of the devices present with that name, and then connect the XBee Cellular Modem.
3. Check the directory again and you should see one additional device, which is the XBee Cellular
Modem.
4. In this case, replace /dev/ttyUSB0 at the top with /dev/ttyUSB<number>, where <number>
is the new number that appeared.
5. It should connect and show Terminal ready.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
45
Page 46

Get started with MicroPython Use picocom in Linux
Now you can type MicroPython commands at the >>> prompt.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
46
Page 47

Get started with Digi Remote Manager
Digi Remote Manager® is a cloud-based device and data management platform that you can use to
configure and update a device, and view and manage device data.
The sections below describe how to create a Remote Manager account, upgrading your device,
configure your device, and manage data in Remote Manager.
1. Create a Remote Manager account and add devices
2. To ensure that all Remote Manager features are available, you should upgrade your device to
the latest firmware. See Update the firmware from the Devices page in Remote Manager or
Update the firmware using web services in Remote Manager.
3. Configure your device in Remote Manager
To be able to configure your device in Remote Manager, the device must be connected to
Remote Manager. You can connect to and configure your device in Remote Manager using one
of the following methods:
o
Scheduled connection: In this method, you create a list of tasks that you want to
perform on the device, and then start the operation. This is the recommended method,
and is the best choice for low data usage. See Configure Remote Manager features by
scheduling tasks.
o
Always connected: This method can be used for initial configuration, or when you are
not concerned with low data usage. See Configure XBee settings within Remote
Manager.
4. Secure the connection between an XBee and Remote Manager with server authentication.
5. Manage data in Remote Manager
6. Remote Manager reference
Create a Remote Manager account and add devices
To be able to use Remote Manager, you must create a Remote Manager account and add your XBee
devices to the device list. You should also verify that the device is enabled to connect to Remote
Manager.
1. Create a Remote Manager account.
2. Add an XBee Cellular Modem to Remote Manager.
3. Verify the connection between a device and Remote Manager
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
47
Page 48

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Create a Remote Manager account and add devices
Create a Remote Manager account
Digi Remote Manager is an on-demand service with no infrastructure requirements. Remote devices
and enterprise business applications connect to Remote Manager through standards-based web
services. This section describes how to configure and manage an XBee using Remote Manager. For
detailed information on using Remote Manager, refer to the Remote Manager User Guide, available via
the Documentation tab in Remote Manager.
Before you can manage an XBee with Remote Manager, you must create a Remote Manager account.
To create a Remote Manager account:
1. Go to https://www.digi.com/products/cloud/digi-remote-manager.
2. Click 30 DAYFREETRIAL/LOGIN.
3. Follow the online instructions to complete account registration. You can upgrade your
Developer account to a paid account at any time.
When you are ready to deploy multiple XBee Cellular Modems in the field, upgrade your account to
access additional Remote Manager features.
Add an XBee Cellular Modem to Remote Manager
Each XBee Cellular Modem must be added to the Remote Manager account inventory list.
Before adding an XBee to your Remote Manager account inventory, you need to determine the
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number for the device. Use XCTUto view the IMEI
number by querying the IM parameter.
To add an XBee to your Remote Manager account inventory, follow these steps:
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Device Management > Devices.
3. Click Add Devices. The Add Devices dialog appears.
4. Select IMEI#, and type or paste the IMEI number of the XBee you want to add. The IM
(IMEI)command provides this number.
5. Click Add to add the device. The XBee is added to your inventory.
6. Click OK to close the Add Devices dialog and return to the Devices view.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
48
Page 49

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
Verify the connection between a device and Remote Manager
By default, the XBee is configured to enable communication with Remote Manager. The
communication between XBee and Remote Manager is achieved using periodic UDP operations.
You should verify the default settings to ensure that communcation will work as desired.
1.
Launch XCTU .
2. Verify that the MO command is set to 6, which is the default.
3. Configure the frequency of polls for Remote Manager activity using the DF command. The
default is 1440 minutes (24 hours).
4. Enable the SM/UDP feature in Remote Manager for each device. See Enable SM/UDP.
Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
Remote Manager provides tools to perform common management and maintenance tasks on your
XBee device. A Remote Manager task is a sequence of commands that can be performed on one or
more XBee Cellular devices. Tasks can then be assigned to a schedule. When a scheduled task is run it
becomes an active operation and can be monitored for status and completion.
Note You must upgrade your device to the latest firmware for all features to be available. See Update
the firmware.
Some typical examples of useful things that can be done with scheduled tasks include:
n Change configuration
n Update your MicroPython application and libraries to add features and capabilities
n Update your security certificates
n Perform a data service device request
n Send an SMS message to your device
Scheduled tasks can be created and performed through the following methods:
n Remote Manager Schedules user interface.
n Remote Manager API Explorer user interface
n Programming web service calls
Note For any of these methods to work properly, you must have SM/UDP enabled. See Enable
SM/UDP.
Overview: Create a schedule for a set of tasks
When using the most current firmware version, the XBee Cellular devices are designed to poll Remote
Manager once per day over the SM/UDP protocol to check for any active operations. In order to
perform a set of tasks, the device needs to be told to connect to Remote Manager, perform the
sequence of tasks, and then told to disconnect.
The following provides a template of how to create a schedule for an XBee to connect, perform a set
of tasks and then disconnect:
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
49
Page 50

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
1. Make sure that SM/UDPis enabled. See Enable SM/UDP.
2. Log into Remote Manager.
3. Click Device Management > Schedules.
4. Click New Schedule. The New Schedule page displays.
Note The Steps to schedule a task wizard may display. Click the x in the upper left corner to
close the wizard. See Schedule walk-through feature in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for
more information.
5. In the Description field, enter a name for the schedule, such "Read Settings."
6. Add the following tasks:
a. Click SM/UDP > SM/UDP Request Connect. A task is added to the dialog.
b. Add other tasks as needed. For examples, refer to the Examples section.
c. Click Device > Disconnect. A task is added to the dialog.
7. Click Schedule in the lower right corner of the dialog to schedule the tasks to run. The
schedule screen displays.
Note You can also click Save as to save this schedule for future use.
8. Select the device(s) on which you want to run this schedule. You can add more than one device.
9. Click Run Now.
Examples
The examples in the following sections assume you are using the Digi Remote Manager Schedule
wizard. However, you should be aware that operations can be created and performed
programmatically via web service calls or via the API explorer. The XML web service calls provide more
options than are available in the GUI dashboard for some tasks.
Example: Read settings and state using Remote Manager
In order to configure devices you will need to know the structure of the XML for your XBee's settings.
The easiest way to obtain this is to perform a query_setting RCI request against your device.
Note You must upgrade your device to the latest firmware for all features to be available. See Update
the firmware.
Note To obtain the state of the device, you can perform the same operations in the example below,
but replace query_setting with query_state.
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Device Management > Schedules.
3. Click New Schedule. The New Schedule page displays.
Note The Steps to schedule a task wizard may display. Click the x in the upper left corner to
close the wizard. See Schedule walk-through feature in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for
more information.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
50
Page 51

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
4. In the Description field, enter a name for the schedule, such "Read Settings."
5. Add the following tasks:
a. Click SM/UDP > SM/UPD Request Connect. A task is added to the dialog.
b. Click Device > RCI Command. A task is added to the dialog.
Change the RCI command to the following:
<rci_request>
<query_setting/>
</rci_request>
c. Click Device > Disconnect. A task is added to the dialog.
6. Click Schedule in the lower right corner of the dialog to schedule the tasks to run. The
schedule screen displays.
Note You can also click Save as to save this schedule for future use.
7. Select the device(s) on which you want to run this schedule. You can add more than one device.
8. Click Run Now.
9. Click Device Management > Operations to view information about the operation. See
Operations in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for more information about this page.
After your operation completes you can click Response to view the XML for all of the settings that
your XBee reports. This XML structure has the same settings that you will use in the set_setting
command to configure your XBee as shown in this example: Example: Configure a device from Remote
Manager using XML.
Example: Configure a device from Remote Manager using XML
You can configure each XBee device from Remote Manager, using XML. The devices must be in the
Remote Manager inventory device list and be active.
Note You must upgrade your device to the latest firmware for all features to be available. See Update
the firmware.
In this configuration example, you are changing the device to poll four times a day instead of just once.
In this case, you should change the DF parameter to 360 minutes.
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Device Management > Schedules.
3. Click New Schedule. The New Schedule page displays.
Note The Steps to schedule a task wizard may display. Click the x in the upper left corner to
close the wizard. See Schedule walk-through feature in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for
more information.
4. In the Description field, enter a name for the schedule, such as "Configure Reporting
Frequency."
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
51
Page 52

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
5. Add the following tasks:
a. Click SM/UDP > SM/UPD Request Connect. A task is added to the dialog.
b. Click Device > RCI Command. A task is added to the dialog.
Change the RCI command to the following:
<rci_request>
<set_setting>
<remote_manager>
<DF>360</DF>
</remote_manager>
</set_setting>
</rci_request>
c. Click Device > Disconnect. A task is added to the dialog.
6. Click Schedule in the lower right corner of the dialog to schedule the tasks to run. The
schedule screen displays.
Note You can also click Save as to save this schedule for future use.
7. Select the device(s) on which you want to run this schedule. You can add more than one device.
8. Click Run Now.
9. Click Device Management > Operations to view information about the operation. See
Operations in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for more information about this page.
Example: Schedule a task to update the device firmware using Remote Manager
You can use a scheduled task to update the XBee Cellular firmware. Since the device is configured by
default to poll Remote Manager once a day, you need to be able to set up a scheduled task to update
the device's firmware to take advantage of new features and fixes. To update the firmware to a new
version you will need to obtain the .ebin file for the new firmware from our support site. This file is one
of the files in the .zip (for example, XBXC-31011.zip) archive that you can download for the product.
Note You must upgrade your device to the latest firmware for all features to be available. See Update
the firmware.
To upgrade using a scheduled task perform the following steps:
1. Download the updated firmware file for your device from Digi's support site.
a. Go to the Digi XBee Cellular LTECAT 1 support page.
b. Scroll down to the Firmware Updates section.
c. Locate and click XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Verizon Firmware to download the zip file.
d. Unzip the file.
2. Log into Remote Manager.
3. Make sure that you have enabled SM/UDP. See Enable SM/UDP.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
52
Page 53

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
4. Click Device Management > Schedules.
5. Click New Schedule. The New Schedule page displays.
Note The Steps to schedule a task wizard may display. Click the x in the upper left corner to
close the wizard. See Schedule walk-through feature in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for
more information.
6. In the Description field, enter a name for the schedule, such as "Update XBee Firmware."
7. Add the following tasks:
a. Click SM/UDP > SM/UDP Request Connect. A task is added to the dialog.
b. Click Device > Gateway Firmware Update.
c. Click Browse and select the .ebin file (for example, XBXC-1011.ebin) for the new firmware
to update.
d. Click Device > Disconnect. A task is added to the dialog.
8. Click Schedule in the lower right corner of the dialog to schedule the tasks to run. The
schedule screen displays.
Note You can also click Save as to save this schedule for future use.
9. Select the device(s) on which you want to run this schedule. You can add more than one device.
10. Click Run Now.
11. Click Device Management > Operations to view information about the operation. See
Operations in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for more information about this page.
Example: Update MicroPython from Remote Manager using XML
You can use the API Explorer in Remote Manager to create a schedule that enables you to update the
MicroPython application. In this example, you want to add FTP client capability to the MicroPython
application. You will need to add the library uftp.py and then update the main.py application.
This example is done following these steps: upload the MicroPython files to Remote Manager, create
an XML file with the tasks that you want to perform, upload the XML file, and then schedule an
operation to upload the files onto your device.
Note You must upgrade your device to the latest firmware for all features to be available. See Update
the firmware.
Step 1: Upload the MicroPython files
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Data Services > Data Files.
3. Upload the MicroPython application main.py file.
a. Click New Folder. The New Folder dialog displays.
b. In the Folder name field, enter a descriptive name, such as "MicroPython."
c. Click Create. The new file is added to the list of files.
d. Find the "MicroPython" folder in the folder list.
e. Click Upload Files. The Upload Files dialog displays.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
53
Page 54

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
f. Browse for the main.py file. Check with your system administrator for the location of the
application file.
g. Click OK.
4. Upload the MicroPython library uftp.py file.
a. Find the "MicroPython" folder in the folder list.
b. Click Upload Files. The Upload Files dialog displays.
c. Browse for the uftp.py file. The library uftp.py file is found on the GitHub repository:
https://github.com/digidotcom/xbee-micropython
d. Click OK.
Step 2: Create an XML file with the tasks that you want to perform
This XML file will contain a list of commands for the operation that you will schedule in Step 3.
Note The RCI commands to set_settings in the task may fail to execute because of disconnects after
changing the value for MO.
1. Open the editor of your choice.
2. Create a new file named updatemicropython.xml.
3. Copy the XML below and paste it into the new file.
4. Save the file.
<task>
<description>Update MicroPython</description>
<command>
<name>SM/UDP Request Connect</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<end_task/>
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<send_message reply="none" >
<sm_udp>
<request_connect/>
</sm_udp>
</send_message>
</sci>
</command>
<command>
<name>RCI Command</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<continue/>
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<send_message cache="false" allowOffline="true" >
<!-- Disable Python Auto-start and enable TCP connection for remainder of commands-->
<rci_request>
<set_setting>
<micropython>
<PS>0</PS>
</micropython>
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
54
Page 55

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
<remote_manager>
<MO>7</MO>
</remote_manager>
</set_setting>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci>
</command>
<command>
<!-- Reboot to stop MicroPython -->
<name>Reboot</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<continue/>
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<reboot allowOffline="true" waitForReconnect="true"/>
</sci>
</command>
<!-- Update MicroPython application-->
<command>
<name>Upload Files</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<continue/>
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<file_system allowOffline="true" >
<commands>
<put_file path="/flash/main.py">
<file>~/MicroPython/main.py</file>
</put_file>
</commands>
</file_system>
</sci>
</command>
<command>
<name>Upload Files</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<continue/>
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<file_system allowOffline="true" >
<commands>
<put_file path="/flash/lib/uftp.py">
<file>~/MicroPython/uftp.py</file>
</put_file>
</commands>
</file_system>
</sci>
</command>
<command>
<name>RCI Command</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<continue/>
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
55
Page 56

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Configure Remote Manager features by scheduling tasks
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<send_message cache="false" allowOffline="true">
<!-- Enable Python Auto-start -->
<rci_request>
<set_setting>
<micropython>
<PS>1</PS>
</micropython>
<remote_manager>
<MO>6</MO>
</remote_manager>
</set_setting>
</rci_request>
</send_message>
</sci>
</command>
<!-- Reboot to start the program -->
<command>
<name>Reboot</name>
<event>
<on_error>
<end_task/>
</on_error>
</event>
<sci>
<reboot allowOffline="true" waitForReconnect="false"/>
</sci>
</command>
</task>
Step 3: Upload the XML to Remote Manager
In this step you will upload the file you just created (updatemicropython.xml) to Remote Manager.
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Data Services > Data Files.
3. Upload the XML file you just created: updatemicropython.xml
a. Find the "~/my_tasks" folder in the folder list.
b. Click Upload Files. The Upload Files dialog displays.
c. Browse for the updatemicropython.xml file.
d. Click OK.
Step 4: Schedule an operation to upload the files
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Documentation > API Explorer.
3. Click SCI Targets. The Select devices to be used in examples dialog appears.
a. From the Add Targets list box, search for the IMEI (device ID) of the device that you want
to update.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
56
Page 57

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Manage data in Remote Manager
b. Click Add. The device is added to the device list.
c. Click OK.
4. Click the Examples drop-down list button.
5. Click Scheduled Operation > Create immediate running schedule.
6. Update the XML to refer to the updatemicropython.xml file you created previously.
<!-- Runs immediately -->
<Schedule on="IMMEDIATE">
<targets>
<device id="00010000-00000000-03588320-70372440"/>
</targets>
<task path="~/my_tasks/updatemicropython.xml"/>
</Schedule>
7. Click Send to schedule the task.
8. Click Device Management > Operations to view information about the operation. See
Operations in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for more information about this page.
Manage data in Remote Manager
You can view and manage XBee data in Remote Manager.
You can also update your device firmware from Remote Manager. See Update the device firmware.
Review device status information from Remote Manager
You can view address, BLE, cellular, firmware, and I/O sampling status information for a XBee device in
Remote Manager. The device must be in the Remote Manager inventory device list and be active.
1. Set up a persistent connection to connect the device to Remote Manager using one of the
following methods:
n Remote Manager: A persistent connection can be set up in Remote Manager. This
option should be used when you have many deployed devices and no local access. See
Restore persistent connection to a remote XBee.
n XCTU: This option allows immediate access, and should be used when you have local
access, such as when using a development kit or in a lab environment.
2. Log into Remote Manager.
3. Click Device Management > Devices.
4. Select the device that you want to configure.
5. Click Properties in the toolbar. As an alternative, click Properties > Edit Device
Configuration. The configuration Home page appears.
6. Click Status in the toolbar to display the status sub-menus.
7. Click on the status group that has information you want to display. The status information is
related to ATcommands. For information about each ATcommand in the categories, click on
the appropriate link below.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
57
Page 58

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Manage data in Remote Manager
n Addressing
n Cellular
n Firmware Version/Information
n I/O
8. Click Home to return to the configuration Home page.
9. When all changes are complete, disconnect the device from Remote Manager.
Manage secure files in Remote Manager
You can interact with files on the XBee device from Remote Manager, using either the SCI (Server
command interface) or in the File Management view.
You can securely upload files by appending a hash sign (#) to the end of the file name. After the upload,
the hash sign (#) is not retained as part of the file name. For example, you could upload a file named
my-cert.crt appended with a hash sign (#): my-cert.crt#. After the upload is complete, the file is named
my-cert.crt.
Note Uploading secure files in Remote Manager has the same result as doing an ATFS XPUT locally.
See Secure files for more information.
SCI(Server command interface)
You can use the SCI (Server command interface) file_system command to securely upload a file.
For more information, see the file_system section in the Digi Remote Manager Programming Guide.
File Management view
You can upload and manage files in the Remote Manager File Management view.
1. Prepare the file that you want to upload.
a. Find the file on your hard drive.
b. Rename the file and append a hash sign (#) to the end of the file name.
2. Set up a persistent connection to connect the device to Remote Manager using one of the
following methods:
n Remote Manager: A persistent connection can be set up in Remote Manager. This
option should be used when you have many deployed devices and no local access. See
Restore persistent connection to a remote XBee.
n XCTU: This option allows immediate access, and should be used when you have local
access, such as when using a development kit or in a lab environment. See DO (Device
Options) and MO (Remote Manager Options). Both must be enabled.
3. Log into Remote Manager.
4. Click Device Management > Devices.
5. Select the device that you want to configure.
6. Click Properties in the toolbar. As an alternative, double-click on the device name. The
Properties page appears.
7. Click File Management. The File Management view appears.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
58
Page 59

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Remote Manager reference
8. Click the upload icon. The Upload File dialog appears.
a. Click Browse to browse for the file you want to upload. The selected file displays in the File
field. Make sure that the file name is appended by a hash sign (#).
b. Click OK. The uploaded file displays in the File Management view. Note that the file name
is no longer appended by a hash sign (#).
9. When all changes are complete, disconnect the device from Remote Manager.
Remote Manager reference
Enable SM/UDP
You can use the SM/UDP feature to leverage the very small data footprint of Remote Manager SM
protocol over UDP.
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Click Device Management > Devices.
3. Select the device that you want to configure.
4. Click More >SM/UDP > Configure. The SM/UDP dialog appears.
5. Verify that the Battery Operated Mode is not selected.
This mode is not supported with Remote Manager and if enabled, the connectivity between
XBee and Remote Manager may not work as expected.
6. Select SM/UDP Service Enabled to enable SM/UDP.
7. Click Save.
TCP connection
The TCP connection between an XBee and Remote Manager is dependent on the device's firmware
version. Options are to query Remote Manager once a day or to maintain a persistent TCP connection.
To determine which connection method is being used, refer to the version listed below.
Module Upgrade firmware version
XBee CAT 1 Verizon 1011
n At or above the listed version: If your firmware version is at or above the listed version, your
device queries Remote Manager only once a day. The device connects to Remote Manager,
queries Remote Manager for updates and then receives updates. When the update is complete,
the device disconnects from Remote Manager.
If you upgrade to the new firmware version, it is recommended that you keep the polling
frequency low to reduce data usage. In order to upgrade firmware in the future, refer to
Example: Schedule a task to update the device firmware using Remote Manager.
Note If you wish to restore the persistent connection behavior that was the default in prior
firmware versions, see Restore persistent connection to a remote XBee.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
59
Page 60

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Remote Manager reference
n Below the listed version: If your firmware version is below the listed version, a persistent
TCPconnection is used by default. The device is continually connected to Remote Manager
using TCP.
Restore persistent connection to a remote XBee
The default connectivity to Remote Manager in the most recent firmware polls once a day using
SM/UDP, which means that your XBee will always appear in a disconnected state and will use
significantly less data.
If needed, you can restore the default connectivity to use the former behavior, where the device is
continually connected using TCP. To do this, you will need to set bit 0 of the MO setting. The suggested
value for MO is 7 to connect securely over TLS, or you can use 1 for no security, which is the legacy
value.
You can make the change using one of the following methods:
n Local access: If you have local access to the device you can use XCTU to change the MO setting
back to the former default value.
n Remote access: If you only have remote access to your XBee you can change the device to
maintain a persistent connection to Remote Manager. To do this you can set up a scheduled
operation in Remote Manger for your device, as shown below.
To set up a scheduled operation to maintain a persistent connection:
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Make sure that you have enabled SM/UDP. See Enable SM/UDP.
3. Click Device Management > Schedules.
4. Click New Schedule. The New Schedule page displays.
Note The Steps to schedule a task wizard may display. Click the x in the upper left corner to
close the wizard. See Schedule walk-through feature in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for
more information.
5. In the Description field, enter a name for the schedule, such as "Restore Persistent."
6. Add the following tasks:
a. Click SM/UDP > SM/UPD Request Connect. A task is added to the dialog.
b. Click Device > RCI Command. A task is added to the dialog.
Change the RCI command to the following:
<rci_request>
<set_setting>
<remote_manager>
<MO>7</MO>
</remote_manager>
</set_setting>
</rci_request>
7. Click Schedule in the lower right corner of the dialog to schedule the tasks to run. The
schedule screen displays.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
60
Page 61

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Remote Manager reference
Note You can also click Save as to save this schedule for future use. The XML for your task is
saved in the ~\my_tasks directory on Data Services > Data Files in Remote Manager.
8. Select the device(s) on which you want to run this schedule. You can add more than one device.
9. Click Run Now. Within the next 24 hours, which is the default polling period for querying
Remote Manager, your device will connect and will remain connected, as specified by the
change to the MO setting.
10. Click Device Management > Operations to view information about the operation. See
Operations in the Digi Remote Manager® User Guide for more information about this page.
Disconnect
The TCP connection remains open and periodic polling occurs until you manually disconnect the
TCPconnection. After you have disconnected the TCP connection, Remote Manager is no longer
updated.
You can disconnect the TCP connection using either of the following methods:
n From the Devices page in Remote Manager: See Disconnect a device in the Digi Remote
Manager® User Guide.
n Using web services in Remote Manager: See Request connect SM/UDP support in the Digi
Remote Manager® Programming Guide.
Configure XBee settings within Remote Manager
You can configure the device settings to use features with Remote Manager. For more information,
see Example: Read settings and state using Remote Manager.
Configure device settings in Remote Manager
You can configure each XBee device from Remote Manager. The devices must be in the Remote
Manager inventory device list and be active.
1. Set up a persistent connection to connect the device to Remote Manager using one of the
following methods:
n Remote Manager: A persistent connection can be set up in Remote Manager. This
option should be used when you have many deployed devices and no local access. See
Restore persistent connection to a remote XBee.
n XCTU: This option allows immediate access, and should be used when you have local
access, such as when using a development kit or in a lab environment. See DO (Device
Options) and MO (Remote Manager Options). Both must be enabled.
2. Log into Remote Manager.
3. Click Device Management > Devices.
4. Select the device that you want to configure.
5. Click Properties in the toolbar. As an alternative, click Properties > Edit Device
Configuration. The configuration Home page appears.
6. Click Config in the toolbar to display the settings sub-menus.
7. Click on the settings category that you want to configure. The settings in that category appear.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
61
Page 62

Get started with Digi Remote Manager Remote Manager reference
8. Makethe desired configuration changes. See AT commands for information about each setting
in the categories.
9. As you finish configuring in each setting category, click Apply to save the changes. If the
changes are valid, Remote Manager writes them to non-volatile memory and applies them.
10. When all changes are complete, disconnect the device from Remote Manager.
Configure Remote Manager keepalive interval
Managing the data usage and the keepalive interval is important if you have the MO (Remote Manager
Options) command bit 0 set to 1 or if you have enabled the Request connect feature in Remote
Manager.
Digi Remote Manager is enabled on the XBee by default and has a 60 second keepalive interval, which
can result in excessive cellular data usage, depending on your plan. The K1 and K2 commands can be
used to tune the keepalive interval. Your carrier will disconnect an inactive socket automatically if
there is no activity, so you need to tune this value based on your carrier’s disconnect timeout.
You can further reduce your data usage by periodically duty cycling your Remote Manager connection,
either from MicroPython or your host processor. For example, you could enable the Remote Manager
connection for 2 hours a day and then disable the connection for 22 hours. Your host processor or
MicroPython program would need to keep track of the time to ensure the time interval.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
62
Page 63

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode
The following examples provide some additional scenarios you can use to get familiar with the XBee.
If you are interested in using the intelligence built into the XBee, see Get started with MicroPython.
Get started with CoAP 64
Get started with MQTT 68
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
63
Page 64

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with CoAP
Get started with CoAP
Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) is based on UDP connection and consumes low power to
deliver similar functionality to HTTP. This guide contains information about sending GET, POST, PUT
and DELETE operations by using the Coap Protocol with XCTU and Python code working with the XBee
Cellular Modem and Coapthon library (Python 2.7 only).
The Internet Engineering Task Force describes CoAP as:
The protocol is designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications such as smart energy and
building automation. CoAP provides a request/response interaction model between application
endpoints, supports built-in discovery of services and resources, and includes key concepts of
the Web such as URIs and Internet media types. CoAP is designed to easily interface with HTTP
for integration with the Web while meeting specialized requirements such as multicast
support, very low overhead, and simplicity for constrained environments (source).
CoAP terms
When describing CoAP, we use the following terms:
Term Meaning
Method COAP's method action is similar to the HTTP method. This guide discusses the GET,
POST, PUT and DELETE methods. With these methods, the XBee Cellular Modem can
transport data and requests.
URI URI is a string of characters that identifies a resource served at the server.
Token Atoken is an identifier of a message. The client uses the token to verify if the received
message is the correct response to its query.
Payload The message payload is associated with the POST and PUT methods. It specifies the
data to be posted or put to the URI resource.
MessageID The message ID is also an identifier of a message. The client matches the message ID
between the response and query.
CoAP quick start example
The following diagram shows the message format for the CoAP protocol; see ISSN: 2070-1721 for
details:
This is an example GET request:
44 01 C4 09 74 65 73 74 B7 65 78 61 6D 70 6C 65
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
64
Page 65

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with CoAP
The following table describes the fields in the GETrequest.
Field HEX Bits Meaning
Ver 44 01 Version 01, which is mandatory here.
T 00 Type 0: confirmable.
TKL 0100 Token length: 4.
Code 01 000 00001 Code: 0.01, which indicates the GET method.
Message ID C4 09 2 Bytes equal
to hex at left
Token 74 65 73 74 4 Bytes equal
to hex at left
Option delta B7 1011 Delta option: 11 indicates the option data is Uri-Path.
Optionlength 0111 Delta length: 7 indicates there are 7 bytes of data
Option value 65 78 61 6D
70 6C 65
7 Bytes equal
to hex at left
Message ID. The response message will have the
same ID. This can help out identification.
Token. The response message will have the same
token. This can help out identification.
following as a part of this delta option.
Example.
Configure the device
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2.
Open XCTU and click the Configuration working mode button.
3. Add the XBee Cellular Modem to XCTU; see Add a device to XCTU.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5.
To switch to UDPcommunication, in the IP field, select 0 and click the Write button .
6. To set the target IP address that the XBee Cellular Modem will talk to, in the DL field type
52.43.121.77and click the Write button . A CoAP server is publicly available at address
52.43.121.77.
7. To set the XBee Cellular Modem to send data to port 5683 in decimal, in the DEfield, type 1633
and click the Write button.
8. To move into Transparent mode, in the APfield, select 0 and click the Write button.
9. Wait for the AI (Association Indication) value to change to 0 (Connected to the Internet). You
can click Read to get an update on the AI value.
Example: manually perform a CoAPrequest
Follow the steps in Configure the device prior to this example. This example performs the CoAP
GETrequest:
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
65
Page 66

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with CoAP
n Method: GET
n URI: example
n Given message token: test
1.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar to add a customized packet.
2.
From the AT console, click the Add new packet button in the Send packets dialog. The
Add new packet dialog appears.
3. Click the HEX tab and type the name of the data packet: GET_EXAMPLE.
4. Copy and past the following text into the HEX input tab:
44 01 C4 09 74 65 73 74 B7 65 78 61 6D 70 6C 65
This is the CoAP protocol message decomposed by bytes to perform a GET request on an
example URI with a token test.
5. Click Add packet.
6.
Click the Open button .
7. Click Send selected packet. The message is sent to the public CoAP server configured in
Configure the device. A response appears in the Console log. Blue text is the query, red text is
the response.
The payload is Get to uri: example, which specifies that this is a successful CoAP GET to URI end
example, which was specified in the query.
Click the Close button to terminate the serial connection.
Example: use Python to generate a CoAP message
This example illustrates how the CoAP protocol can perform GET/POST/PUT/DELETE requests
similarly to the HTTP protocol and how to do this using the XBee Cellular Modem. In this example, the
XBee Cellular Modem talks to a CoAP Digi Server. You can use this client code to provide an abstract
wrapper to generate a CoAP message that commands the XBee Cellular Modem to talk to the remote
CoAP server.
Note It is crucial to configure the XBee Cellular Modem settings. See Configure the device and follow
the steps. You can target the IP address to a different CoAP public server.
1. Install Python 2.7. The Installation guide is located at: python.org/downloads/.
2. Download and install the CoAPthon library in the python environment from
pypi.python.org/pypi/CoAPthon.
3. Download these two .txt files: Coap.txt and CoapParser.txt. After you download them, open the
files in a text editor and save them as .py files.
4. In the folder that you place the Coap.py and CoapParser.py files, press Shift + right-click and
then click Open command window.
5. At the command prompt, type python Coap.py and press Enter to run the program.
6. Type the USB port number that the XBee Cellular Modem is connected to and press Enter. Only
the port number is required, so if the port is COM19, type 19.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
66
Page 67

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with CoAP
Note If you do not know the port number, open XCTU and look at the XBee Cellular Modem in the
Radio Modules list. This view provides the port number and baud rate, as in the figure below where
the baud rate is 9600 b/s.
7. Type the baud rate and press Enter. You must match the device's current baud rate.
XCTUprovides the current baud rate in the BD Baud Rate field. In this example you would type
9600.
8. Press Y if you want an auto-generated example. Press Enter to build your own CoAP request.
9. If you press Y it generates a message with:
n Method: POST
n URI: example
n payload:hello world
n token: test
The send and receive message must match the same token and message id. Otherwise, the client reattempts the connection by sending out the request.
In the following figure, the payload contains the server response to the query. It shows the results for
when you press Enter rather than Y.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
67
Page 68

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
Get started with MQTT
MQ Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a messaging protocol that is ideal for the Internet of Things (IoT)
due to a light footprint and its use of the publish-subscribe model. In this model, a client connects to a
broker, a server machine responsible for receiving all messages, filtering them, and then sending
messages to the appropriate clients.
The first two MQTTexamples do not involve the XBee Cellular Modem. They demonstrate using the
MQTTlibraries because those libraries are required for Use MQTT over the XBee Cellular Modem with
a PC.
The examples in this guide assume:
n Some knowledge of Python.
n An integrated development environment (IDE)such as PyCharm, IDLE or something similar.
The examples require:
n An XBee Cellular Modem.
n A compatible development board.
n XCTU. See Install and upgrade XCTU.
n That you install Python on your computer. You can download Python from:
https://www.python.org/downloads/.
n That you install the pyserial and paho-mqtt libraries to the Python environment. If you use
Python 2, install these libraries from the command line with pip install pyserial and pip
install paho-mqtt. If you use Python 3, use pip3 install pyserial and pip3 install paho-mqtt.
n The full MQTT library source code, which includes examples and tests, which is available in the
paho-mqtt github repository at https://github.com/eclipse/paho.mqtt.python. To download this
repository you must have Git installed.
Example: MQTT connect
This example provides insight into the structure of packets in MQTT as well as the interaction
between the client and broker. MQTT uses different packets to accomplish tasks such as connecting,
subscribing, and publishing. You can use XCTU to perform a basic example of sending a broker a
connect packet and receiving the response from the server, without requiring any coding. This is a
good way to see how the client interacts with the broker and what a packet looks like. The following
table is an example connect packet:
Description Hex value
CONNECT packet fixed header
byte 1 Control packet type 0x10
byte 2 Remaining length 0x10
CONNECT packet variable header
Protocol name
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
68
Page 69

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
Description Hex value
byte 1 Length MSB (0) 0x00
byte 2 Length LSB (4) 0x04
byte 3 (M) 0x4D
byte 4 (Q) 0x51
byte 5 (T) 0x54
byte 6 (T) 0x54
Protocol level
byte 7 Level (4) 0x04
Connect flags
byte 8
Keep alive
byte 9 Keep Alive MSB (0) 0x00
byte 10 Keep Alive LSB (60) 0x3C
Client ID
byte 11 Length MSB (0) 0x00
byte 12 Length LSB (4) 0x04
byte 13 (D) 0x44
byte 14 (I) 0x49
byte 15 (G) 0x47
byte 16 (I) 0x49
The following table describes the fields in the packet:
Fieldname Description
ProtocolName The connect packet starts with the protocol name, which is MQTT. The length of
CONNECT flags byte, see the table below for the bits.
the protocol name (in bytes) is immediately before the name itself.
0x02
ProtocolLevel Refers to the version of MQTT in use, in this case a value of 4 indicates MQTT
version 3.1.1.
Connect Flags Indicate certain aspects of the packet. For simplicity, this example only sets the
Clean Session flag, which indicates to the client and broker to discard any previous
session and start a new one.
Keep Alive How often the client pings the broker to keep the connection alive; in this example
it is set to 60 seconds.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
69
Page 70

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
Fieldname Description
Client ID The length of the ID (in bytes) precedes the ID itself. Each client connecting to a
broker must have a unique client ID. In the example, the ID is DIGI. When using the
Paho MQTT Python libraries, a random alphanumeric ID is generated if you do not
specify an ID.
The following table provides the CONNECT flag bits from byte 8, the CONNECT flags byte.
CONNECT Flag Bit(s) Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
User name flag 0
Password flag 0
Will retain 0
Will QoS 0 0
Will flag 0
Clean session 1
Reserved 0
Send a connect packet
Now that you know what a connect packet looks like, you can send a connect packet to a broker and
view the response. Open XCTU and click the Configuration working mode button.
1. Ensure that the device is set up correctly with the SIM card installed and the antennas
connected as described in Connect the hardware.
2.
Open XCTU and click the Configuration working mode button.
3. Add the XBee Cellular Modem to XCTU. See Add a device to XCTU.
4. Select a device from the Radio Modules list. XCTU displays the current firmware settings for
that device.
5. In the APfield, set Transparent Mode to [0] if it is not already and click the Write button.
6. In the DL field, type the IP address or the fully qualified domain name of the broker you wish to
use. This example uses test.mosquitto.org.
7. In the DE field, type 75B and set the port that the broker uses. This example uses 75B, because
the default MQTT port is 1883 (0x75B).
8. Once you have entered the required values, click the Write button to write the changes to the
XBee Cellular Modem.
9.
Click the Consoles working mode button on the toolbar to open a serial console to the
device. For instructions on using the Console, see the AT console topic in the XCTU User Guide.
10.
Click the Open button to open a serial connection to the device.
11.
From the AT console, click the Add new packet button in the Send packets dialog. The
Add new packet dialog appears.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
70
Page 71

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
12. Enter the name of the data packet. Name the packet connect_frame or something similar.
13. Click the HEX input tab and type the following (these values are the same values from the
table in Example: MQTT connect):
10 10 00 04 4D 51 54 54 04 02 00 3C 00 04 44 49 47 49
14. Click Add packet. The new packet appears in the Send packets list.
15. Click the packet in the Send packets list.
16. Click Send selected packet.
17. A CONNACK packet response from the broker appears in the Console log. This is a connection
acknowledgment; a successful response should look like this:
You can verify the response from the broker as a CONNACK by comparing it to the structure of a
CONNACK packet in the MQTT documentation, which is available at http://docs.oasis-
open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v3.1.1/os/mqtt-v3.1.1-os.html#_Toc398718081).
Example: send messages (publish) with MQTT
A basic Python example of a node publishing (sending) a message is:
mqttc = mqtt.Client("digitest") # Create instance of client with client ID
“digitest”
mqttc.connect("m2m.eclipse.org", 1883) # Connect to (broker, port,
keepalive-time)
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
71
Page 72

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
mqttc.loop_start() # Start networking daemon
mqttc.publish("digitest/test1", "Hello, World!") # Publish message to
“digitest /test1” topic
mqttc.loop_stop() # Kill networking daemon
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
This example imports the MQTT library, allowing you to use the MQTT protocol via APIs in the library,
such as the connect(), subscribe(), and publish() methods.
The second line creates an instance of the client, named mqttc. The client ID is the argument you
passed in: digitest (this is optional).
In line 3, the client connects to a public broker, in this case m2m.eclipse.org, on port 1883 (the default
MQTT port, or 8883 for MQTT over TLS). There are many publicly available brokers available, you can
find a list of them here: https://github.com/mqtt/mqtt.github.io/wiki/brokers.
Line 4 starts the networking daemon with client.loop_start() to handle the background
network/data tasks.
Finally, the client publishes its message Hello, World! to the broker under the topic
digitest/backlog/test1. Any nodes (devices, phones, computers, even microcontrollers) subscribed to
that same topic on the same broker receive the message.
Once no more messages need to be published, the last line stops the network daemon with
client.loop_stop().
Example: receive messages (subscribe) with MQTT
This example describes how a client would receive messages from within a specific topic on the
broker:
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc): # The callback for when the
client connects to the broker
print("Connected with result code {0}".format(str(rc))) # Print result
of connection attempt
client.subscribe("digitest/test1") # Subscribe to the topic
“digitest/test1”, receive any messages published on it
def on_message(client, userdata, msg): # The callback for when a PUBLISH
message is received from the server.
print("Message received-> " + msg.topic + " " + str(msg.payload)) #
Print a received msg
client = mqtt.Client("digi_mqtt_test") # Create instance of client with
client ID “digi_mqtt_test”
client.on_connect = on_connect # Define callback function for successful
connection
client.on_message = on_message # Define callback function for receipt of a
message
# client.connect("m2m.eclipse.org", 1883, 60) # Connect to (broker, port,
keepalive-time)
client.connect('127.0.0.1', 17300)
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
72
Page 73

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
client.loop_forever() # Start networking daemon
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
The first line imports the library functions for MQTT.
The functions on_connect and on_message are callback functions which are automatically called by
the client upon connection to the broker and upon receiving a message, respectively.
The on_connect function prints the result of the connection attempt, and performs the subscription.
It is wise to do this in the callback function as it guarantees the attempt to subscribe happens only
after the client is connected to the broker.
The on_message function prints the received message when it comes in, as well as the topic it was
published under.
In the body of the code, we:
n Instantiate a client object with the client ID digi_mqtt_test.
n Define the callback functions to use upon connection and upon message receipt.
n Connect to an MQTT broker at m2m.eclipse.org, on port 1883 (the default MQTT port, or 8883
for MQTT over TLS) with a keepalive of 60 seconds (this is how often the client pings the broker
to keep the connection alive).
The last line starts a network daemon that runs in the background and handles data transactions and
messages, as well as keeping the socket open, until the script ends.
Use MQTT over the XBee Cellular Modem with a PC
To use this MQTT library over an XBee Cellular Modem, you need a basic proxy that transfers a payload
received via the MQTT client’s socket to the serial or COM port that the XBee Cellular Modem is active
on, as well as the reverse; transfer of a payload received on the XBee Cellular Modem’s serial or COM
port to the socket of the MQTT client. This is simplest with the XBee Cellular Modem in Transparent
mode, as it does not require code to parse or create API frames, and not using API frames means
there is no need for them to be queued for processing.
1. To put the XBee Cellular Modem in Transparent mode, set AP to 0.
2. Set DL to the IP address of the broker you want to use.
3. Set DE to the port to use, the default is 1883 (0x75B). This sets the XBee Cellular Modem to
communicate directly with the broker, and can be performed in XCTU as described in Example:
MQTT connect.
4. You can make the proxy with a dual-threaded Python script, a simple version follows:
import threading
import serial
import socket
def setup():
"""
This function sets up the variables needed, including the serial port,
and it's speed/port settings, listening socket, and localhost adddress.
"""
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
73
Page 74

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
global clisock, cliaddr, svrsock, ser
# Change this to the COM port your XBee Cellular module is using. On
# Linux, this will be /dev/ttyUSB#
comport = 'COM44'
# This is the default serial communication speed of the XBee Cellular
# module
comspeed = 115200
buffer_size = 4096 # Default receive size in bytes
debug_on = 0 # Enables printing of debug messages
toval = None # Timeout value for serial port below
# Serial port object for XBCell modem
ser = serial.Serial(comport,comspeed,timeout=toval)
# Listening socket (accepts incoming connection)
svrsock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Allow address reuse on socket (eliminates some restart errors)
svrsock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
clisock = None
cliaddr = None # These are first defined before thread creation
addrtuple = ('127.0.0.1', 17300) # Address tuple for localhost
# Binds server socket to localhost (allows client program connection)
svrsock.bind(addrtuple)
svrsock.listen(1) # Allow (1) connection
def ComReaderThread():
"""
This thread listens on the defined serial port object ('ser') for data
from the modem, and upon receipt, sends it out to the client over the
client socket ('clisock').
"""
global clisock
while (1):
resp = ser.read() ## Read any available data from serial port
print("Received {} bytes from modem.".format(len(resp)))
clisock.sendall(resp) # Send RXd data out on client socket
print("Sent {} byte payload out socket to client.".format(len
(resp)))
def SockReaderThread():
"""
This thread listens to the MQTT client's socket and upon receiving a
payload, it sends this data out on the defined serial port ('ser') to
the
modem for transmission.
"""
global clisock
while (1):
data = clisock.recv(4096) # RX data from client socket
# If the RECV call returns 0 bytes, the socket has closed
if (len(data) == 0):
print("ERROR - socket has closed. Exiting socket reader
thread.")
return 1 # Exit the thread to avoid a loop of 0-byte receptions
else:
print("Received {} bytes from client via socket.".format(len
(data)))
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
74
Page 75

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
print("Sending payload to modem...")
bytes_wr = ser.write(data) # Write payload to modem via
UART/serial
print("Wrote {} bytes to modem".format(bytes_wr))
def main():
setup() # Setup the serial port and socket
global clisock, svrsock
if (not clisock): # Accept a connection on 'svrsock' to open 'clisock'
print("Awaiting ACCEPT on server sock...")
(clisock,cliaddr) = svrsock.accept() # Accept an incoming
connection
print("Connection accepted on socket")
# Make thread for ComReader
comthread = threading.Thread(target=ComReaderThread)
comthread.start() # Start the thread
# Make thread for SockReader
sockthread = threading.Thread(target=SockReaderThread)
sockthread.start() # Start the thread
main()
Note This script is a general TCP-UART proxy, and can be used for other applications or scripts that
use the TCP protocol. Its functionality is not limited to MQTT.
Note You can easily copy and paste code from the online version of this guide. Use caution with the
PDF version, as it may not maintain essential indentations.
This proxy script waits for an incoming connection on localhost (127.0.0.1), on port 17300. After
accepting a connection, and creating a socket for that connection (clisock), it creates two threads,
one that reads the serial or COM port that the XBee Cellular Modem is connected to, and one that
reads the socket (clisock), that the MQTT client is connected to.
With:
n The proxy script running
n The MQTT client connected to the proxy script via localhost (127.0.0.1)
n The XBee Cellular Modem connected to the machine via USB and properly powered
n AP, DL, and DE set correctly
the proxy acts as an intermediary between the MQTT client and the XBee Cellular Modem, allowing
the MQTT client to use the data connection provided by the device.
Think of the proxy script as a translator between the MQTT client and the XBee Cellular Modem. The
following figure shows the basic operation.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
75
Page 76

Examples: IOT protocols with transparent mode Get started with MQTT
The thread that reads the serial port forwards any data received onward to the client socket, and the
thread reading the client socket forwards any data received onward to the serial port. This is
represented in the figure above.
The proxy script needs to be running before running an MQTT publish or subscribe script.
1. With the proxy script running, run the subscribe example from Example: receive messages
(subscribe) with MQTT, but change the connect line from client.connect("m2m.eclipse.org",
1883, 60) to client.connect("127.0.0.1", port=17300, keepalive=20). This connects the
MQTT client to the proxy script, which in turn connects to a broker via the XBee Cellular
Modem’s internet connection.
2. Run the publish example from Example: send messages (publish) with MQTT in a third Python
instance (while the publish script is running you will have three Python scripts running at the
same time).
The publish script runs over your computer’s normal Internet connection, and does not use the XBee
Cellular Modem. You are able to see your published message appear in the subscribe script’s output
once it is received from the broker via the XBee Cellular Modem. If you watch the output of the proxy
script during this process you can see the receptions and transmissions taking place.
The proxy script must be running before you run the subscribe and publish scripts. If you stop the
subscribe script, the socket closes, and the proxy script shows an error. If you try to start the proxy
script after starting the subscribe script, you may also see a socket error. To avoid these errors, it is
best to start the scripts in the correct order: proxy, then subscribe, then publish.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
76
Page 77

Update the firmware
You should update your XBee to the latest firmware to take advantage of all the latest fixes and
features. Refer to the topics below for information about the available update methods.
Digi strongly recommends that you devise a plan to update the firmware after initial deployment. For
more information, see Create a plan for device and cellular component firmware updates.
Create a plan for device and cellular component firmware updates 78
Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU 79
Update the device firmware 81
Update the cellular firmware 87
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
77
Page 78

Update the firmware Create a plan for device and cellular component firmware updates
Create a plan for device and cellular component firmware updates
You should update your XBee to the latest firmware to take advantage of all the latest fixes and
features. Changes to the cellular network, security issues, or software bugs may be identified which
require firmware updates to resolve. In addition, Digi periodically releases new device firmware which
includes new features and improves reliability and performance of existing features. You should
evaluate and test the new releases and update your firmware to take advantage of the
improvements and new features.
Note Digi will not accept responsibility for customers who have not planned to update their units.
Please review the information provided below.
Please review the suggestions below:
n Always test device and any cellular component firmware updates before deploying these
updates to units in the field.
n If updates will be performed using a PC, XCTU is able to perform complete firmware updates
on all device cellular modems, including updating the cellular component firmware.
n If updates will be performed using a host processor, see Use a host processor to update the
modem firmware for XBee devices over UART.
n If updates will be performed over-the-air (OTA):
l If your XBee application is using API mode, monitor for Modem Status (0x8A) API frames
with status codes 0x38 through 0x3A. These modem status frames inform the XBee's host
application about ongoing and completed or failed firmware updates.
l If your XBee application is using Transparent mode, test your application to determine
whether it is tolerant to over-the-air firmware updates of the cellular component and XBee
firmware. If your application cannot tolerate the network connection being non-functional
for up to 30 minutes (for example, if the XBee will be reset in a shorter time than that), do
not use over-the-air updates, and be aware that firmware updates to the XBee require
user intervention.
o
If the XBee firmware is updated over-the-air using Digi Remote Manager: After the new
firmware image has been downloaded and validated, the XBee modem reboots
automatically to install the firmware. The XBee then resets into the new firmware once
the update is complete, which may take up to 60 seconds.
o
If the cellular component firmware is being updated: After the cellular firmware update
image has been downloaded, the XBee modem disconnects from the network and the
cellular component will be updated. This update will take up to 30 minutes. After the
update completes (or fails), the XBee will reconnect to the cellular network
automatically.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
78
Page 79

Update the firmware Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU
Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU
Use XCTU to update the device firmware, and if needed, XCTU will attempt to update your cellular
firmware.
Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU
Note Before you begin, make sure you have XCTU installed and the device is added to the utility. See
Install and upgrade XCTU.
Update the device and cellular firmware using XCTU
You can use XCTU to update the device and cellular firmware. XCTU updates the device firmware to
the version you select, and then, if needed, XCTU will attempt to update your cellular firmware.
Prerequisites
n Windows PC
n Digi XCTU version 6.5.0 or newer. You should upgrade XCTU to the latest version.
n The device is added to XCTU. See Add a device to XCTU.
n Digi XBIB-CU-TH development board
To update the device and cellular firmware:
1.
Launch XCTU .
2.
Click the Configuration working modes button .
3. From the Radio Modules list, select the device that you want to update.
4. Verify the following configuration. The cellular component firmware update may not work if any
of these settings are enabled. Ensure the following:
n Airplane mode is disabled: ATAM set to 0
n Bypass mode is disabled: ATAP not 5
5. Click Update firmware. The Update the radio module firmware dialog appears and displays
the available and compatible device firmware for the selected XBee module.
6. Select the product family of the XBee module, the function set, and the latest firmware version
for the device.
7. Make sure you check the Force the module to maintain its current configuration to ensure
you do not lose any changes to your configuration.
8. If desired, you can select the Force the Cellular modem update option. When selected, the
cellular component is updated even if it is already on the newest firmware version. This step is
optional.
9. Click Update to update the device firmware.
10. If the cellular component firmware requires an update or if you selected the Force the
Cellular modem update option, a prompt displays.
11. Click OK to continue with the update process. XCTUperforms the following:
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
79
Page 80

Update the firmware Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU
n XCTU applies and updates the device firmware.
n If the cellular firmware is being updated, XCTU applies and updates the new cellular
firmware on the device.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
80
Page 81

Update the firmware Update the device firmware
Update the device firmware
You should update the device firmware on your XBee to the latest version to take advantage of all the
latest fixes and features. Security issues or software bugs may be identified which require firmware
updates to resolve. In addition, Digi periodically releases new firmware which includes new features
and improves reliability and performance of existing features.
n For information about updating the cellular firmware, see Update the cellular firmware.
n For information about using XCTU to update both the device firmware and, if needed, the
cellular firmware, see Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU.
The table below lists update methods you can use and the instructions for each method.
Method
FOTA (DRM)
Instructions
n Update the firmware from the Devices page in
Remote Manager
n Update the firmware using web services in Remote
Manager
n Schedule a task to update the device firmware
using Remote Manager
API
Use a host processor to update the modem firmware for
XBee devices over UART
Update the firmware from the Devices page in Remote Manager
You can update the device firmware for one or multiple devices from the Devices page in Remote
Manager.
Before you begin, verify the TCP connection method your device uses to connect to Remote Manager:
query once a day or use a persistent TCPconnection. See TCP connection.
To perform a firmware update:
1. Download the updated firmware file for your device from Digi's support site.
a. Go to the Digi XBee Cellular LTECAT 1 support page.
b. Scroll down to the Firmware Updates section.
c. Locate and click XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Verizon Firmware to download the zip file.
d. Unzip the file.
2. Set up a persistent connection to connect the device to Remote Manager. See Restore
persistent connection to a remote XBee.
3. Log into Remote Manager.
4. In your Remote Manager account, click Device Management > Devices.
5. Select the first device you want to update. To select multiple devices (must be of the same
type), press the Control key and select additional devices.
6. Click More in the Devices toolbar and select More > Update > Update Firmware. The Update
Firmware dialog appears.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
81
Page 82

Update the firmware Update the device firmware
7. Click Browse to select the .ebin file that you unzipped earlier.
8. Click Update Firmware. The updated devices automatically reboot when the updates are
complete.
Note The update is immediately rejected and an error is returned if the device is going into
sleep mode or is being shut down. See Clean shutdown.
9. When all changes are complete, disconnect the device from Remote Manager.
Update the firmware using web services in Remote Manager
Remote Manager supports both synchronous and asynchronous firmware update using web services.
The following examples show how to perform an asynchronous firmware update. See the Remote
Manager documentation for more details on firmware updates.
Before you begin, verify the TCP connection method your device uses to connect to Remote Manager:
query once a day or use a persistent TCPconnection. See TCP connection.
Note You must use XCTU to update the cellular component's firmware.
1. Download the updated firmware file for your device from Digi's support site.
a. Go to the Digi XBee Cellular LTECAT 1 support page.
b. Scroll down to the Firmware Updates section.
c. Locate and click XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Verizon Firmware to download the zip file.
d. Unzip the file and locate the .ebin file in the unzipped directory.
2. Send an HTTP SCI request to Remote Manager with the contents of the downloaded .ebin file
converted to base64 data. Refer to the the following examples:
Examples for .ebin:
n Example: Update the XBee firmware synchronously using a local file
n Example: Update the XBee firmware synchronously using a Remote Manager Data File
Example: Update the XBee firmware synchronously using a local file
import base64
import requests
# Location of firmware image
firmware_path = 'XBXC.ebin'
# Remote Manager device ID of the device being updated
device_id = '00010000-00000000-03526130-70153378'
# Remote Manager username and password
username = "my_Remote_manager_username"
password = "my_remote_manager_password"
url = 'https://remotemanager.digi.com/ws/sci'
# Get firmware image
fw_file = open(firmware_path, 'rb')
fw_data = fw_file.read()
fw_data = base64.encodebytes(fw_data).decode('utf-8')
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
82
Page 83

Update the firmware Update the device firmware
# Form update_firmware request
data = """
<sci_request version="1.0">
<update_firmware filename="firmware.ebin">
<targets>
<device id="{}"/>
</targets>
<data>{}</data>
</update_firmware>
</sci_request>
""".format(device_id, fw_data)
# Post request
r = requests.post(url, auth=(username, password), data=data)
if (r.status_code != 200) or ("error" in r.content.decode('utf-8')):
print("firmware update failed")
else:
print("firmware update success")
Example: Update the XBee firmware synchronously using a Remote Manager Data
File
To update the XBee firmware synchronously with Python 3.0, but using the device firmware image
already uploaded to Remote Manager, upload the device's *.ebin firmware to Remote Manager:
1. Download the updated firmware file for your device from Digi's support site. This is a zip file
containing .ebin and .mxi files for import.
2. Unzip the file and locate the .ebin inside the unzipped directory.
3. Log in to Remote Manager.
4. Click the Data Services tab.
5. Click Data Files.
6. Click Upload Files; browse and select the *.ebin firmware file to upload it.
7. Send an HTTP SCI request to Remote manager with the path of the .ebin file; see the example
below.
import base64
import requests
# Location of firmware image on Remote Manager
firmware_path = '~/XBXC.ebin'
# Remote Manager device ID of the device being updated
device_id = '00010000-00000000-03526130-70153378'
# Remote Manager username and password
username = "my_remote_manager_username"
password = "my_remote_manager_password"
url = 'https://remotemanager.digi.com/ws/sci'
# Form update_firmware request
data = """
<sci_request version="1.0">
<update_firmware filename="firmware.ebin">
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
83
Page 84

Update the firmware Update the device firmware
<targets>
<device id="{}"/>
</targets>
<file>{}</file>
</update_firmware>
</sci_request>
""".format(device_id, firmware_path)
# Post request
r = requests.post(url, auth=(username, password), data=data)
if (r.status_code != 200) or ("error" in r.content.decode('utf-8')):
print("firmware update failed")
else:
print("firmware update success")
Use a host processor to update the modem firmware for XBee devices over UART
This process explains how to update the modem firmware for XBee Cellular devices.
Update the modem firmware
1. Make sure you have the correct version of the modem firmware for your XBee device.
2. Enter programming (bootloader) mode. Use one of the following methods: ATcommands or
hardware signaling.
n ATcommands
a. Send the %P command. The %P command must be sent an argument derived from
the SL parameter of the module being updated. The argument is the value of SL
added to the value 0xDB8A and then masked by performing a bitwise-AND with
0x3FFF.
i. Run ATSL to get the address value, which is in hex.
ATSL
123456
ii. Add bitwise-AND with 0x3FFF.
(0xDB8A + 0x123456) & 0x3FFF= 0x0FE0
iii. Send the command AT%PFE0.
AT%PFE0
b. You will receive an error, which is expected.
c. Send the FRcommand to reboot and enter into bootloader.
n Invoke the bootloader with hardware signaling
a. De-Assert RTS (pin 16).
b. Assert DTR (pin 9).
c. Put DIN in a low state (break) (pin 3).
d. Reset the module (pin 5).
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
84
Page 85

Update the firmware Update the device firmware
e. Release the break on DIN (pin 3) The module should now be in bootloader at 38400
baud.
3. Once the module is in programming (bootloader) mode, configure the local serial port to
38400/8/N/1.
4. Get the hardware version of the radio module from the bootloader.
a. Send the V command. The response to that command has the following format:
XXXXYYYYZZAABBBBCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
n XXXX: The hardware version.
See ATHV, little endian.
n YYYY: The hardware revision.
See AT%R, little endian.
n ZZ: The hardware compatibility
number. See AT%C.
n AA: Unused and should be 0.
n BBBB: The hardware series. See
ATHS, little endian.
n CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC: The
serial number.
5. If possible, change the baud rate of the serial port to optimize the firmware update process.
Send the X command to the bootloader.
n The bootloader answers with the maximum supported baud rate (in ASCII) and, just
after that, the bootloader changes its baud rate to that value. Change your baud rate to
match the max supported rate.
n If the bootloader does not answer to this command, remain at the current rate.
6. Send the I command (initialization command). This command erases the current firmware from
the device.
7. Transfer the firmware to the device using the transfer protocol shown below.
Transfer the firmware to the device
1. You must split the file into 512 byte blocks.
2. Transfer each block using the following structure, with block index and CRC16 sent in little
endian byte:
P [2 bytes for block index] [block data with page size length] [2 bytes for CRC16]
Note CRC16 is calculated only with the bytes of the page to be sent, and is initialized with
0x0000. The polynomial used for the CRC16 is 0x8005.
3. After each block is transfered, wait for a response. Options are:
n 0x55 - ACK: This is the expected answer.
n 0x12: Checksum/CRC16 error.
n 0x13: Flash write/verify error.
Note If an error occurs, you may try to transfer each block up to three times.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
85
Page 86

Update the firmware Update the device firmware
4. Verify and write the firmware to flash.
a. Send the C command (verify) to verify and write the firmware to the flash.
b. Verify that the answer to this command is 0x55 (ACK). Any other result is an error.
5. Wait a couple of seconds for the firmware to be installed and start running.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
86
Page 87

Update the firmware Update the cellular firmware
Update the cellular firmware
You should update the cellular firmware on your device to take advantage of all the latest fixes and
features.
Note You should also create a plan to update the cellular component firmware on a regular basis,
after initial deployment. Security issues or software bugs may be identified which require firmware
updates to resolve.
n For information about updating the device firmware, see Update the device firmware.
n For information about using XCTU to update both the device firmware and, if needed, the
cellular firmware, see Update the device and the cellular firmware using XCTU.
Method
FOTA (DRM)
Instructions
Update the cellular component firmware using Remote Manager
API
Update the cellular firmware using the API
USB Not supported
Update the cellular component firmware using Remote Manager
You can update the firmware for a device's cellular component using Remote Manager.
Prerequisites
n Remote Manager account created and an XBee cellular device added.
n XBee cellular device must be connected to Remote Manager to initiate update.
n The device ID of the XBee cellular device that you want to update.
Applicable update files
The upgrade from 23.00.004 to 23.00.006 is a two-file upgrade:
n First upgrade: 23.00.004 to 23.00.004-B401
n Second upgrade: 23.00.004-B401 to 23.00.006
Note Customers must apply both upgrades. Applying only the first upgrade without the second will
result in a product that is on an intermediate version not intended for production use.
These upgrade files are hosted on ftp1.digi.com under the directory support/telit. See Determine
the location of the firmware version.
Current version Target version File for upgrade
23.00.004 23.00.004-B401 23.00.004__23.00.004-B401__LE866-SV1.ua
23.00.004-B401 23.00.006 23.00.004-B401__23.00.006__LE866-SV1.ua
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
87
Page 88

Update the firmware Update the cellular firmware
Determine the location of the firmware version
You must first determine the location of the firmware version to which you want to update. Digi
provides updates by hosting them on an FTP server: ftp1.digi.com. If the FTP location is not
accessible to your XBee Cellular, such as if you are using a VPN, the files may be retrieved and hosted
separately on a server that it can reach.
Firmware is provided in the form of delta images which will migrate the cellular component from a
known source to a given target version. You can verify the firmware version level of the cellular
component using the MV (Modem Version) AT command. Check documentation and release notes for
your XBee Cellular variant to determine the necessary upgrade path for your product.
You will need:
n The FTP hostname or IP address, which for Digi hosted files is: ftp1.digi.com
n The port running the FTP server, which is typically 21
n Username. For ftp1.digi.com, use: anonymous
n Password. For ftp1.digi.com, use your email address.
n Directory path containing update file.
n Update image filename.
Form the update request
A request to perform an update is communicated to the XBee Cellular through Remote Manager by
using the Data Services Device Request feature. The device request should be sent to the FTP_OTA
target and the payload of the request is the concatenation of the six fields identifying the full FTP
location of the update file using the NUL byte as a delimiter. We recommend using the base64
encoded binary transport option to avoid issues representing the request in XML.
For example, you want to update a module with the file sample.bin in the support/example directory
on Digi's FTP server.
The full body of the request:
The base64 encoded representation of the payload in turn:
ZnRwMS5kaWdpLmNvbQAyMQBhbm9ueW1vdXMAZXhhbXBsZUBkaWdpLmNvbQBzdXBwb3J0L2
V4YW1wbGUAc2FtcGxlLmJpbg==
The full Remote Manager device request is as shown below. Make sure to replace the Device ID
attribute with the ID for your device.
<sci_request version="1.0">
<data_service>
<targets>
<device id="Your device ID here"/>
</targets>
<requests>
<device_request target_name="FTP_OTA" format="base64">
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
88
Page 89

Update the firmware Update the cellular firmware
ZnRwMS5kaWdpLmNvbQAyMQBhbm9ueW1vdXMAZXhhbXBsZUBkaWdpLmNvbQBzdXBwb3J0L2V4Y
W1wbGUAc2FtcGxlLmJpbg==
</device_request>
</requests>
</data_service>
</sci_request>
Perform the update
Once the update details have been established and the device request body written, the update is
performed by doing an HTTP POST operation to the /ws/sci API endpoint of Remote Manager.
You can do this manually from the Remote Manager API Explorer.
1. Log into Remote Manager.
2. Select Documentation > API Explorer. The API Explorer page appears.
3. In the Path field, select or type: /ws/sci
4. Select the POST HTTPmethod option.
5. Copy the full Remote Manager device request you created in the previous step: Form the
update request.
6. Paste the copied SCI request into the window below the HTTP Method selection section.
7. Click Send to initiate the update.
Note Do not be alarmed if Remote Manager indicates that the device has disconnected. This is
normal, as performing the update requires a reboot, and the network connection is
temporarily disconnected during the reboot.
Validate the update
After the update has been triggered, it may take up to 30 minutes for the update to be applied and for
the module to be connected to the network once more. If the XBee is not configured to automatically
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
89
Page 90

Update the firmware Update the cellular firmware
connect to Digi Remote Manager, you will need to reconnect to Remote Manager to perform
validation.
You can check that the update process has succeeded by reading the MV parameter value. After the
update is complete, the version should reflect the desired target version.
Update the cellular firmware using the API
You can update the cellular component using the API.
In addition to knowing which cellular component firmware is required for a given release of the
module firmware, the host program needs to know which firmware versions for the module support a
cellular component firmware update. For example, if Release 3 is the first version of the module
firmware that supports cellular component firmware updates, you must update it before updating the
cellular component firmware. But to downgrade from Release 3 or greater to Release 2 or less, you
must downgrade the cellular component firmwarebeforedowngrading the module firmware.
Otherwise, the older firmware would not be able to downgrade the cellular component firmware.
Important notes
Consider the following before performing a cellular component firmware update.
Note Digi recommends that you perform a cellular firmware update using XCTU.
CAUTION! Avoid interrupting the process if possible. An interruption requires starting over. If
the interruption occurs while the bootloader is being updated (part number 82004156) the
device may not be recoverable.
n When downgrading the module firmware to version 1009 or earlier, Perform a cellular
component firmware update using API mode before the module firmware is updated.
n When updating to module firmware version 100A or later, Perform a cellular component
firmware update using API mode after the module firmware is updated.
n With the cellular component firmware updated, the APN is lost from the cellular component
configuration, even though it remains on the module configuration. To resolve this, re-enter AN
(Access Point Name) and re-apply it for the cellular component to connect to the cellular
network.
Perform a cellular component firmware update using API mode
This topic specifies how a host program can perform a cellular component firmware update without
XCTU.
Note Digi recommends that you perform a cellular firmware update using XCTU.
The cellular component firmware consists of two entities:
n Part number 82004156, which is the code for the bootloader on the Telit module
n Part number 82004015, which is the cellular code for the Telit module
Just as there is an association between module firmware releases and cellular component firmware
releases, there is also an association between bootloader and cellular code for the cellular
component. Once it is determined that a cellular component update is needed, the bootloader (part
number 82004156) should be updated followed by the cellular code (part number 82004015).
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
90
Page 91

Update the firmware Update the cellular firmware
1. Configure the module at a high baud rate. 460,800 (BD= 9) or 921,600 (BD = 0xA) is best to
optimize speed.
2. Configure the module in API mode (AP = 1).
3. Set up the host program to a matching baud rate and API mode.
4. Update the bootloader file (part number 82004156)
a. Send the first block of the file with ID set to 0 and bit 0 of the flags byte set to indicate the
first frame. The size of the block does not matter as long as it is less than maximum buffer
size (1500 bytes).
b. Wait for an ACK before proceeding. An ACK comes in a FW Update Response - 0xAB with a
status of 0. Under normal conditions, the ACK occurs within 100 ms. However, some
responses have been measured to take 80 seconds. To be safe it is best not to timeout on
the response for 90 seconds.
c. Send all but the last frame of the file with incrementing values for the ID and all bits in the
Flags field cleared. Wait for an ACK between each frame sent.
d. Send the last block of the file with the next ID and with bit 1 set to indicate last frame. Wait
for an ACK on the final case.
5. Update the cellular code file (part number 82004015) using the same steps as the bootloader
file.
After the final ACK is received for both the bootloader file and the cellular code file, the cellular
component firmware update is complete.
WARNING! With the cellular component firmware updated, the APN is lost from the cellular
component configuration, even though it remains on the module configuration. To resolve
this, re-enter AN (Access Point Name) and re-apply it for the cellular component to connect
to the cellular network.
As a verification, enterMV (Modem Firmware Version)to reveal the version of the cellular component
firmware.
Note The AIstatus must be 0x23 or 0 forMVto give a valid response.
About cellular firmware updates using the API
An XBee Cellular Modem contains two processors: a microcontroller that controls most operations of
the module, and a cellular component. Both processors contain firmware that you can update. For any
given release of the microcontroller firmware (after this referred to as the module firmware), there is
an associated release of the cellular component firmware. One or more releases of the module
firmware is associated with a given cellular component firmware. However, for a given module
firmware, there is only one associated release of the cellular component firmware. The following table
depicts an example of this with arbitrary release numbers:
Module firmware Cellular component firmware
Release 1 Release A
Release 2 Release A
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
91
Page 92

Update the firmware Update the cellular firmware
Module firmware Cellular component firmware
Release 3 Release B
Release 4 Release C
Release 5 Release C
Release 6 Release C
Release 7 Release D
Note The module version number keeps incrementing whether or not the cellular component
firmware version increases.
Error recovery
Several different types of errors can occur during an APIcellular firmware update.
Corrupted firmware on the cellular component
If something goes wrong during a firmware update, (such as a loss of power), the firmware on the
cellular component may be corrupted. This is indicated by an AI status of 0x24. If you see this status,
reset the module (you can use FR) and then follow the steps in Perform a cellular component
firmware update using API mode to redo the cellular component firmware update.
Error
An error occurs when FW Update Response - 0xAB returns a non-zero status code. This can be caused
by a programming error on the host side (such as out of order sequence numbers), a software error
on the module side (such as too short of a timeout waiting for responses from the cellular
component), or an invalid image of the cellular component firmware. When this occurs, the firmware
update is aborted such that it cannot be picked up from where it left off. The only reliable recovery is
to reset the module and then immediately Perform a cellular component firmware update using API
mode.
Host initiated cancellation
If the host sets bit 2 of the flags byte in FW Update - 0x2B, the update in progress is aborted. Recovery
is then equivalent to the recovery for negative acknowledgments, described above.
General case
Regardless of the reason for the error, a cellular component firmware update should always work
within ten seconds of a reset and after AI is 0x23 or 0.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
92
Page 93

Technical specifications
Interface and hardware specifications 94
RF characteristics 94
Networking specifications 95
Power requirements 96
Power consumption 96
Electrical specifications 96
Regulatory approvals 97
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
93
Page 94

Technical specifications Interface and hardware specifications
Interface and hardware specifications
The following table provides the interface and hardware specifications for the device.
Specification Value
Dimensions 24.38 mm x 32.94 mm (0.960 x 1.297 in)
Weight 5 g (0.18 oz)
Operating temperature
Antenna connector
Digital I/O 13 I/O lines, I2C
ADC 4 10-bit analog inputs
Analog input voltage range 0 - 2.5 V
Cellular chipset u-blox SARA-R410M-028
Form factor Digi XBee 20-pin through-hole
SIM size 4FF Nano
Specification Value
Dimensions 2.438 x 3.294 cm (0.960 x 1.297 in)
Weight 5 g (0.18 oz)
Operating temperature
Antenna connector U.FL for primary and secondary antennas
Digital I/O 13 I/O lines
-40 to +85 °C
Cellular: U.FL
Bluetooth: U.FL
-40 to +80 °C
ADC 4 12-bit analog inputs
RF characteristics
The following table provides the RF characteristics for the device.
Specification Value
Modulation LTE/4G – QPSK, 16 QAM
Transmit power 23 dBm
Receive sensitivity -102 dBm
Over-the-air maximum data rate 10 Mb/s
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
94
Page 95

Technical specifications Networking specifications
Networking specifications
The following table provides the networking and carrier specifications for the device.
Specification Value
Carrier and
technology
AT&T and Verizon LTE-M
T-Mobile NB-IoT in US
Vodafone and Deutsche Telekom NB-IoT in Europe
Compatible with other LTE-M carriers, see supported bands
Supported bands LTE FDD bands:
n Band 12 (700 Mhz)
n Band 28 (700 MHz)
n Band 13 (700 MHz)
n Band 20 (800 MHz)
n Band 26 (850 MHz)
n Band 18 (850 MHz)
n Band 5 (850 MHz)
n Band 19 (850 MHz)
n Band 8 (900 MHz)
n Band 4 (1700 MHz)
n Band 3 (1800 Mhz)
n Band 2 (1900 MHz)
n Band 25 (1900 MHz)
n Band 1 (2100 MHz)
1
LTE TDD bands:
n Band 39 (1900 MHz)
Security Digi Trustfence™
Downlink/uplink
LTE M1
speeds
n up to 300 kb/s DL
n up to 375 kb/s UL
LTE NB1
n up to 27.2 kb/s DL
n up to 62.5 kb/s UL
Duplex mode Half-duplex
Addressing
options
1
Band 25 is only supported by products containing SARA-R410M-02B-01 and newer. Band 25 is for LTE CATM1
only.
SMS and IP-based protocols may not be available. Check with your carrier's
specifications for LTE-M\NB-IoT.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
95
Page 96

Technical specifications Power requirements
Specification Value
Addressing options TCP/IPand SMS
Carrier and technology Verizon 4G LTE Cat 1
Supported bands 4 and 13
Security TLS
Power requirements
The following table provides the power requirements for the device.
Specification Value
Supply voltage 3.3 to 4.3 V
Specification Value
Supply voltage 3.0 to 5.5 V
Extended voltage range 2.7 to 5.5 VDC
Power consumption
The peak current was measured from multiple tested units.
Specification State Average current Measured peak current
Tx+RX current Active transmit, 23 dBm @ 3.3 V 860 mA 1020 mA
Tx+RX current Active transmit, 23 dBm @ 5.0 V 555 mA 630 mA
TX Only current Activetransmit,23dBm@3.3V 680 mA N/A
Rx + ACK current Active receive @ 3.3 V 530 mA N/A
Rx + ACK current Active receive @ 5 V 360 mA N/A
RX Only current Active receive @ 3.3 V 300 mA N/A
Idle current Idle/connected, listening @ 3.3 V 143 mA N/A
Idle current Idle/connected, listening @ 5 V 100 mA N/A
Sleep current Notconnected,Deep Sleep@3.3V 10 µA N/A
Electrical specifications
The following table provides the electrical specifications for the XBee Cellular Modem.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
96
Page 97

Technical specifications Regulatory approvals
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typical Max Units
VCCMAX Maximum limits
of VCC line
VDD_IO Internal supply
voltage for I/O
VDD_IO Internal supply
voltage for I/O
VI Voltage on any
pin
VIL Input low voltage 0.3*VDD_IOV
VIH Input high voltage 0.7*VDD_
VOL Voltage output
low
VOH Voltage output
high
I_IN Input leakage
current
While in deep sleep and
during initial power up
In normal running mode 3.3 V V
Sinking 6 mA VDD_IO = 3.3 V 0.2*VDD_IOV
Sourcing 6 mA VDD_IO = 3.3V0.75*VDD_
High Z state I/O connected
to Ground or VDD_IO
0 5.5 V
Min
(VCC-
0.3,3.3)
-0.3 VDD_IO +
IO
IO
0.1 100 nA
3.3 V
0.3
V
V
V
RPU Internal pull-up
resistor
RPD Internal pull-
down resistor
Regulatory approvals
The following table provides the regulatory and carrier approvals for the device.
Note The contains statement of FCC and IC IDs listed on the customer labels must match the ID
visible on the XBee device that is installed.
Specification Value Value
Model XBCEL XBCEL
Revision
United States Contains FCC ID: RI7LE866SV1 Contains FCC ID: RI7LE866SV1A
Innovation, Science and
Economic Development
Canada (ISED)
Enabled 40 kΩ
Enabled 40 kΩ
XBC-V1-UT-001 version M and prior
XBC-V1-UT-102 version F and prior
Contains IC: 5131A-LE866SV1 Contains IC: 5131A-LE866SV1A
XBC-V1-UT-001 version N and later
XBC-V1-UT-102 version G and later
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
97
Page 98

Technical specifications Regulatory approvals
Specification Value Value
Europe (CE) N/A N/A
RoHS Lead-free and RoHS compliant Lead-free and RoHS compliant
Australia N/A N/A
Verizon end-device
certified
Yes Yes
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
98
Page 99

Hardware
Mechanical drawings 100
Pin signals 100
XBee header connector requirements 102
RSSI PWM 102
SIM card 102
Associate LED functionality 102
Development boards 104
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
99
Page 100

Hardware Mechanical drawings
Mechanical drawings
The following figures show the mechanical drawings for the XBee Cellular Modem. All dimensions are
in inches.
For XBee header information, see XBee header connector requirements.
Pin signals
The pin locations are:
The following table shows the pin assignments for the through-hole device. In the table, low-asserted
signals have a horizontal line above signal name.
Digi XBee Cellular LTE Cat 1 Embedded Modem User Guide
100
 Loading...
Loading...