Page 1

HD171/HD173-H81
Mini-ITX Industrial Motherboard
User’s Manual
A35120527
1
Page 2

Copyright
FCC and DOC Statement on Class B
This publication contains information that is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any transformation/adaptation without
the prior written permission from the copyright holders.
This publication is provided for informational purposes only. The manufacturer makes no
representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this manual and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular
purpose. The user will assume the entire risk of the use or the results of the use of this document. Further, the manufacturer reserves the right to revise this publication and make changes
to its contents at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions
or changes.
Changes after the publication’s first release will be based on the product’s revision. The website
will always provide the most updated information.
© 2015. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks
Product names or trademarks appearing in this manual are for identification purpose only and
are the properties of the respective owners.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorientorrelocatethereceivingantenna.
• Increasetheseparationbetweentheequipmentand thereceiver.
• Connectthe equipment intoanoutletonacircuitdifferentfromthattowhichthe receiver
is connected.
• Consultthedealeror anexperiencedradioTVtechnicianfor help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with the emission limits.
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Copyright .............................................................................................................2
Trademarks ........................................................................................................2
FCC and DOC Statement on Class B .....................................................2
About this Manual ..........................................................................................4
Warranty ............................................................................................................4
Static Electricity Precautions ......................................................................4
Safety Measures ..............................................................................................4
About the Package .........................................................................................5
Chapter 1 - Introduction .............................................................................6
Specifications ................................................................................................6
Features ..........................................................................................................7
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation ................................................9
Board Layout .................................................................................................9
System Memory ............................................................................................9
Installing the DIMM Module ........................................................................10
CPU ................................................................................................................11
Installing the CPU .......................................................................................12
Installing the Fan and Heat Sink.................................................................. 14
Jumper Settings .........................................................................................15
Clear CMOS Data ........................................................................................15
Auto Power-on Select ..................................................................................15
USB Power Select ....................................................................................... 16
COM 2 RS422/485 Select ............................................................................ 16
Digital I/O Power Select .............................................................................. 17
Digital I/O Output State ..............................................................................17
Mini PCIe/mSATA Signal Select ....................................................................18
Mini PCIe/mSATA Power Select .................................................................... 18
Rear Panel I/O Ports .................................................................................19
12V DC-in (HD171)/19~24V DC-in (HD173) ................................................. 19
COM (Serial) Ports ......................................................................................20
Graphics Interfaces ..................................................................................... 20
RJ45 LAN Ports ...........................................................................................21
USB Ports ................................................................................................... 21
Audio .........................................................................................................22
I/O Connectors ...........................................................................................23
SATA (Serial ATA) Connectors ...................................................................... 23
SATA (Serial ATA) Power Connectors ............................................................23
Digital I/O Connector ..................................................................................24
Cooling Fan Connectors............................................................................... 24
Chassis Intrusion Connector ........................................................................ 25
Front Panel Connector ................................................................................ 25
Expansion Slots .......................................................................................... 26
Standby Power LED ....................................................................................26
Battery .......................................................................................................27
Chapter 3 - BIOS Setup ............................................................... 28
Overview ..................................................................................................... 28
AMI BIOS Setup Utility .............................................................................29
Main ..........................................................................................................29
Advanced ...................................................................................................29
Chipset ......................................................................................................37
Boot...........................................................................................................43
Security ...................................................................................................... 44
Save & Exit ................................................................................................45
Updating the BIOS ....................................................................................45
Notice: BIOS SPI ROM .............................................................................46
Chapter 4 - Supported Software ...........................................................47
Chapter 5 - Digital I/O Programming Guide .................................... 65
Appendix A - Watchdog Sample Code................................................67
Appendix B - System Error Message ...................................................68
Appendix C - Troubleshooting ................................................................69
3
Page 4
About this Manual
Static Electricity Precautions
An electronic file of this manual is included in the CD. To view the user’s manual in the CD, in-
sertthe CD into a CD-ROM drive.Theautorunscreen(Main Board Utility CD) willappear.Click
“User’s Manual” on the main menu.
Warranty
1. Warranty does not cover damages or failures that arised from misuse of the product, inability to use the product, unauthorized replacement or alteration of components and product specifications.
2. The warranty is void if the product has been subjected to physical abuse, improper installation, modification, accidents or unauthorized repair of the product.
3. Unless otherwise instructed in this user’s manual, the user may not, under any circumstances, attempt to perform service, adjustments or repairs on the product, whether in or
out of warranty. It must be returned to the purchase point, factory or authorized service
agency for all such work.
4. We will not be liable for any indirect, special, incidental or consequencial damages to the
product that has been modified or altered.
It is quite easy to inadvertently damage your PC, system board, components or devices even
before installing them in your system unit. Static electrical discharge can damage computer
components without causing any signs of physical damage. You must take extra care in handling them to ensure against electrostatic build-up.
1. To prevent electrostatic build-up, leave the system board in its anti-static bag until you are
ready to install it.
2. Wear an antistatic wrist strap.
3. Do all preparation work on a static-free surface.
4. Hold the device only by its edges. Be careful not to touch any of the components, contacts
or connections.
5. Avoid touching the pins or contacts on all modules and connectors. Hold modules or connectors by their ends.
Important:
Electrostaticdischarge(ESD)candamage yourprocessor,diskdrive andothercomponents. Perform the upgrade instruction procedures described at an ESD workstation only. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD protection by
wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the system chassis. If a wrist strap is unavailable, establish and maintain contact with the system
chassis throughout any procedures requiring ESD protection.
Safety Measures
To avoid damage to the system:
• UsethecorrectAC inputvoltagerange.
To reduce the risk of electric shock:
• Unplugthe powercordbeforeremovingthesystemchassiscoverforinstallation or servicing. After installation or servicing, cover the system chassis before plugging the power
cord.
4
Page 5

About the Package
The package contains the following items. If any of these items are missing or damaged,
please contact your dealer or sales representative for assistance.
• OneHD171/HD173motherboard
• OneSerialATAdata withpowercable
• OneDVD
• OneQR(QuickReference)
• OneI/OShield
The board and accessories in the package may not come similar to the information listed
above. This may differ in accordance to the sales region or models in which it was sold. For
more information about the standard package in your region, please contact your dealer or
sales representative.
Optional Items
• USBportcable
• COMportcable
• SerialATAdatawithpowercable
• I/OShield
• Poweradapter(100W,12V)
• Poweradapter(120W,19V)
• Heatsinkwithfan
The board and accessories in the package may not come similar to the information listed
above. This may differ in accordance to the sales region or models in which it was sold. For
more information about the standard package in your region, please contact your dealer or
sales representative.
Before Using the System Board
Before using the system board, prepare basic system components.
If you are installing the system board in a new system, you will need at least the following
internal components.
• ACPU
• Memorymodule
• Storagedevicessuchashard diskdrive,CD-ROM, etc.
You will also need external system peripherals you intend to use which will normally include at
least a keyboard, a mouse and a video display monitor.
5
Page 6

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Specifications
Processor
Chipset
Super I/O
Address
System Memory
Expansion
Interfaces
Graphics
Audio
LAN
Serial ATA
Trusted
Platform
Module - TPM*
(optional)
Damage Free
Intelligence
BIOS
LGA 1150 socket for:
•
- 4th Generation Intel® CoreTM processors (22nm process technology)
: Intel® CoreTM i7-4770TE (8M Cache, up to 3.3 GHz); 45W
: Intel® CoreTM i5-4590T (6M Cache, up to 3.0 GHz); 35W
: Intel® CoreTM i5-4570TE (4M Cache, up to 3.3 GHz); 35W
: Intel® CoreTM i3-4350T (4M Cache, 3.1 GHz); 35W
: Intel® CoreTM i3-4340TE (4M Cache, 2.6 GHz); 35W
: Intel® CoreTM i3-4330TE (4M Cache, 2.4 GHz); 35W
: Intel® Pentium® G3320TE (3M Cache, 2.3 GHz); 35W
: Intel® Celeron® G1820TE (2M Cache, 2.2 GHz); 35W
• Intel® H81 Express Chipset
• NCT6106/4Eh
• Two 204-pin DDR3 SODIMM sockets
• Supports DDR3 1333/1600MHz
• Supports up to 16GB system memory
• Supports dual channel memory interface
• DRAM device technologies: 1Gb, 2Gb and 4Gb DDR3 DRAM technologies are
supported for x8 and x16 devices, unbuffered, non-ECC
• 1 PCIe x16 Gen 3 slot (PCIe 3.0)
• 1 Mini PCIe slot
- Supports USB and PCIe signals
- Supports mSATA
- Supports full size Mini PCIe card
• Intel® HD Graphics
• Display ports: 1 DP, 1 DVI-I (DVI-D signal), 1 VGA
• DP: supports DP++, resolution up to 3840x2160 @ 60Hz
• DVI-D, VGA: resolution up to 1920x1200 @ 60Hz
• Supports 6 Graphics Execution Units (EUs)
• Intel® Clear Video Technology
• DirectX Video Acceleration (DXVA) support for accelerating video processing
• Realtek ALC888 5.1-channel High Denition Audio
• Intel® I210 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet controller
• Intel® I217 Gigabit Ethernet Phy
• Integrated 10/100/1000 transceiver
• Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab
• 2 SATA 3.0 ports with data transfer rate up to 6Gb/s
• Provides a Trusted PC for secure transactions
• Provides software license protection, enforcement and password protection
• Monitors CPU/system temperature and overheat alarm
• Monitors Vcore/+5V/+12V/+3.3V/3VSB/VBAT
• Monitors CPU/system fan speed and failure alarm
• Read back capability that displays temperature, voltage and fan speed
• Watchdog timer function
• AMI BIOS
- 64Mbit SPI BIOS
Chapter 1
Rear Panel I/O
Ports
I/O Connectors
Energy Efcient
Design
Power
Consumption
OS Support
Temperature
Humidity
Dimensions
• 1 12V (HD171) or 19~24V (HD173) DC-in jack
or 4-pin power connector* (optional)
• 1 DB-9 RS232 serial port
• 1 VGA port
• 1 DP port (default) or 1 mini-DIN-6 PS/2 keyboard/mouse port* (optional)
• 1 DVI-D port
• 2 RJ45 LAN ports
• 2 USB 2.0 ports
• 2 USB 3.0 ports
• Mic-in, line-in and line-out jacks
• 2 connectors for 4 external USB 2.0 ports
• 1 connector for 1 external USB 2.0 port or
1 vertical USB 2.0/1.1 port* (optional)
• 3 connectors for 3 external serial ports (2.0mm pitch)
- 1 RS422/485
- 2 RS232
• 1 8-bit Digital I/O connector
• 1 front audio connector for line-out and mic-in jacks
• 1 LPC connector
• 2 Serial ATA connectors
• 2 Serial ATA power connectors
• 1 chassis intrusion connector
• 1 front panel connector
• 2 fan connectors
• Supports ErP Lot6 power saving* (optional)
• Supports ACPI
• System Power Management
• Wake-On-Events include:
- Wake-On-PS/2 KB/Mouse* (optional)
- Wake-On-USB KB/Mouse
- Wake-On-LAN
- RTC timer to power-on the system
• CPU stopped clock control
• AC power failure recovery
• HD171-H81N: 35.28W with i7-4770TE at 2.3GHz and 2x 8GB DDR3 SODIMM
• Windows XP Professional x86 & SP3 (32-bit) (limited function)
• Windows 7 Ultimate x86 & SP1 (32-bit)
• Windows 7 Ultimate x64 & SP1 (64-bit)
• Windows 8 Enterprise x86 (32-bit)
• Windows 8 Enterprise x64 (64-bit)
• Operating: 0oC to 60oC
• Storage: -20oC to 85oC
• 10% to 90%
• Mini-ITX form factor
• 170mm (6.7") x 170mm (6.7")
Note:
*Optional and is not supported in standard model. Please contact your sales representative for more information.
6
Chapter 1 Introduction www.d.com
Page 7

Chapter 1
Features
• Watchdog Timer
The Watchdog Timer function allows your application to regularly “clear” the system at the set
time interval. If the system hangs or fails to function, it will reset at the set time interval so
that your system will continue to operate.
• DDR3
DDR3 delivers increased system bandwidth and improved performance. The advantages of
DDR3 are its higher bandwidth and its increase in performance at a lower power than DDR2.
• Graphics
The integrated Intel® HD graphics engine delivers an excellent blend of graphics performance
and features to meet business needs. It provides excellent video and 3D graphics with outstanding graphics responsiveness. These enhancements deliver the performance and compat-
ibilityneededfor today’s and tomorrow’s business applications. Supports 1DP,1DVI-I(DVI-D
signal)and1VGAinterfacesfordisplayoutputs.
• PCI Express
PCI Express is a high bandwidth I/O infrastructure that possesses the ability to scale speeds
by forming multiple lanes. The PCI Express architecture supports high performance graphics
infrastructure by enhancing the capability of a PCIe x16 Gen 3 at 16GB/s bandwidth.
• Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a storage interface that is compliant with SATA 1.0a specification. With speed of
up to 6Gb/s (SATA 3.0), it improves hard drive performance faster than the standard parallel
ATA whose data transfer rate is 100MB/s. The bandwidth of the SATA 3.0 will be limited by
carrier board design.
• Gigabit LAN
Intel® I210 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet and Intel® I217 Gigabit Ethernet Phy controllers support up to 1Gbps data transmission.
• Audio
The Realtek ALC888 audio codec provides 5.1-channel High Definition audio output.
• Wake-On-PS/2 (optional)
This function allows you to use the PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse to power-on the system.
• Wake-On-LAN
This feature allows the network to remotely wake up a Soft Power Down (Soft-Off) PC. It is
supported via the onboard LAN port or via a PCIe LAN card that uses the PCIe PME (Power
Management Event) signal. However,if your system is in the Suspend mode, you can poweronthe systemonlythrough anIRQor DMAinterrupt.
Important:
The5V_standbypowersourceof yourpowersupply mustsupport≥720mA.
• Wake-On-USB
This function allows you to use a USB keyboard or USB mouse to wake up a system from the
S3(STR -SuspendToRAM)state.
Important:
If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse function for 2 USB ports, the
5V_standbypower sourceofyourpowersupplymust support≥1.5A.For3ormore
USBports, the5V_standbypower sourceofyour powersupplymust support≥2A.
• RTC Timer
The RTC installed on the system board allows your system to automatically power-on on the
set date and time.
• ACPI STR
Thesystem board is designed to meettheACPI(AdvancedConfiguration and PowerInterface)
specification. ACPI has energy saving features that enables PCs to implement Power Management and Plug-and-Play with operating systems that support OS Direct Power Management.
ACPI when enabled in the Power Management Setup will allow you to use the Suspend to RAM
function�
With the Suspend to RAM function enabled, you can power-off the system at once by pressing
the power button or selecting “Standby” when you shut down Windows® without having to
go through the sometimes tiresome process of closing files, applications and operating system.
This is because the system is capable of storing all programs and data files during the entire
operating session into RAM (Random Access Memory) when it powers-off.The operating session will resume exactly where you left off the next time you power-on the system.
Important:
The5V_standbypowersourceof yourpowersupply mustsupport≥720mA.
Chapter 1 Introduction www.d.comChapter 1 Introduction
Important:
The5V_standbypowersourceof yourpowersupply mustsupport≥720mA.
7
Page 8

Chapter 1
• Power Failure Recovery
When power returns after an AC power failure, you may choose to either power-on the system
manually or let the system power-on automatically.
• USB
The system board supports the new USB 3.0. It is capable of running at a maximum transmis-
sion speed of up to 5 Gbit/s (625MB/s) and is faster than USB 2.0 (480 Mbit/s, or 60 MB/s)
and USB 1.1 (12Mb/s). USB 3.0 reduces the time required for data transmission, reduces
power consumption, and is backward compatible with USB 2.0. It is a marked improvement
in device transfer speeds between your computer and a wide range of simultaneously
accessible external Plug and Play peripherals.
8
Chapter 1 Introduction www.d.com
Page 9

Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
Board Layout
4-pin power (optional)
DC-in
LGA 1150
Chapter 2
Important:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your board, processor, disk drives, add-in
boards, and other components. Perform installation procedures at an ESD workstation
only. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the system chassis. If
a wrist strap is unavailable, establish and maintain contact with the system chassis
throughout any procedures requiring ESD protection.
LAN 1
USB 1-2
USB 3.0
LAN 2
USB 2-3
USB 2.0
Line-in
Line-out
Mic-in
DVI-I
(DVI-D signal)
DP
COM 1
VGA
COM 2 RS422/485
USB 3.0 1-2 Power
Select (JP3)
USB 2.0 2-3 Power
Select (JP2)
Intel
WGI210AT
2
1
Front Audio
ISL95820
ASMedia
ASM1442
CPU Fan
1
Select (JP6)
1
1
+3.3V Power LED
10
9
Realtek
ALC888
34
12
12
109
COM 2
1
2
1
LPC
12
12
109
COM 3 COM 4
Intel
H81
ME Disable
12
11
Clear CMOS
Data (JP7)
Mini PCIe/mSATA Signal Select (JP5)
13
109
1210
1
Mini PCIe/
mSATA
Power
Select (JP4)
USB 4-5 Power Select
USB 8-9/11 Power Select
1
SPI
Flash
BIOS
PCIe x16
Mini PCIe
Auto Power-on Select (JP11)
DIO 0-3 Output State
DIO Power Select
DIO 4-7 Output State
Chassis Intrusion
1
(JP9)
(JP8)
Standby
Power LED
USB 2.0
(JP9) (JP8)
1 1
21
10921109
USB 4-5
(JP10)
(JP13)
(JP12)
USB 8-9
USB 11
(JP11)
1
SATA 3.0
SATA 1
1
SATA 0
1
SATA Power 0
1
2
1
1
1 1
(JP10)
(JP13)
DIO
DDR3_1 SODIMM
Battery
System
Front
Panel
(JP12)
Buzzer
Fan
DDR3_2 SODIMM
SATA
Power 1
1
4
1
4
1
1112
12
System Memory
Important:
When the Standby Power LED lights red, it indicates that there is power on the system board. Power-off the PC then unplug the power cord prior to installing any devices. Failure to do so will cause severe damage to the motherboard and components.
Rear I/O
Onboard I/O
Storage
Expansion
Features
DDR3-2
DDR3-1
Standby
Power LED
• HD171-H81: 12V DC-in jack (default) or 4-pin power connector (optional).
HD173-H81: 19~24V DC-in jack (default) or 4-pin power connector (optional).
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
• Two 204-pin DDR3 SODIMM sockets
• Supports 1333/1600MHz DDR3 SDRAM
• Supports up to 16GB system memory
• Supports dual channel memory interface
9
www.dfi .com
Page 10

Chapter 2
The system board supports the following memory interface.
Single Channel (SC)
Data will be accessed in chunks of 64 bits (8B) from the memory channels.
Dual Channel (DC)
Data will be accessed in chunks of 128 bits from the memory channels. Dual channel provides
better system performance because it doubles the data transfer rate.
DIMMs are on the same channel.
Single Channel
Dual Channel
DIMMs in a channel can be identical or
completely different. However, we highly
recommend using identical DIMMs.
Not all slots need to be populated.
DIMMs of the same memory configuration
are on different channels.
Installing the DIMM Module
Note:
The system board used in the following illustrations may not resemble the actual
board. These illustrations are for reference only.
1. Make sure the PC and all other peripheral devices connected to it has been powered down.
2. Disconnect all power cords and cables.
3. Locate the DIMM socket on the system board.
4. Push the “ejector tabs” which are at the ends of the socket to the side.
Ejector tab
5. Note how the module is keyed to the socket.
Ejector tab
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Notch
Key
10
www.dfi .com
Page 11
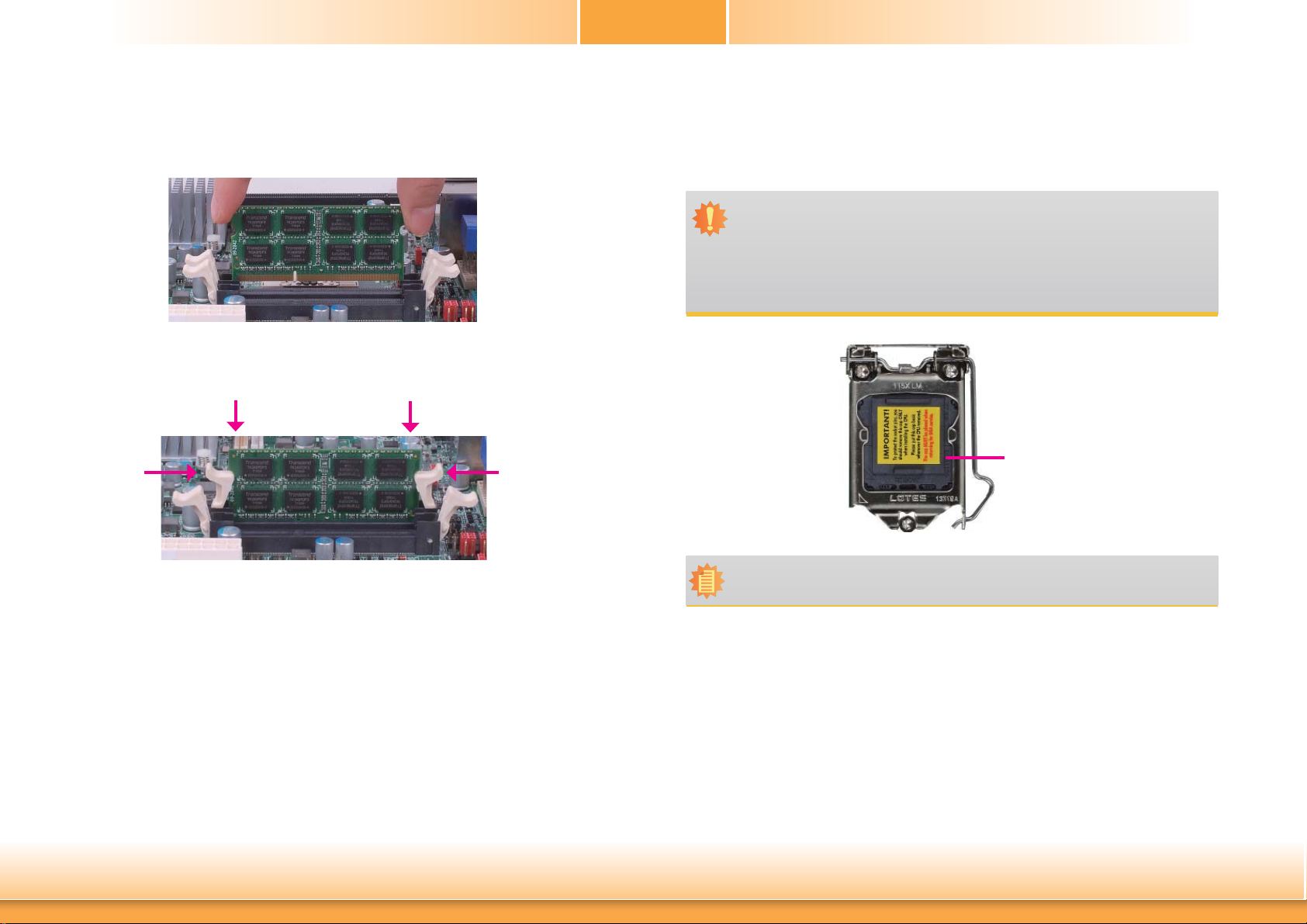
Chapter 2
6. Grasping the module by its edges, position the module above the socket with the “notch”
in the module aligned with the “key” on the socket. The keying mechanism ensures the
module can be plugged into the socket in only one way.
7. Seat the module vertically, pressing it down firmly until it is completely seated in the
socket. The ejector tabs at the ends of the socket will automatically snap into the locked
position to hold the module in place.
CPU
The system board is equipped with a surface mount LGA 1150 socket. This socket is exclusively designed for installing a LGA 1150 packaged Intel CPU.
Important:
1. Before you proceed, make sure (1) the LGA 1150 socket comes with a protective
cap, (2) the cap is not damaged and (3) the socket’s contact pins are not bent.
If the cap is missing or the cap and/or contact pins are damaged, contact your
dealer immediately.
2. Make sure to keep the protective cap. RMA requests will be accepted and processed only if the LGA 1150 socket comes with the protective cap.
Protective
cap
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Note:
The system board used in the following illustrations may not resemble the actual
board. These illustrations are for reference only.
11
www.dfi .com
Page 12
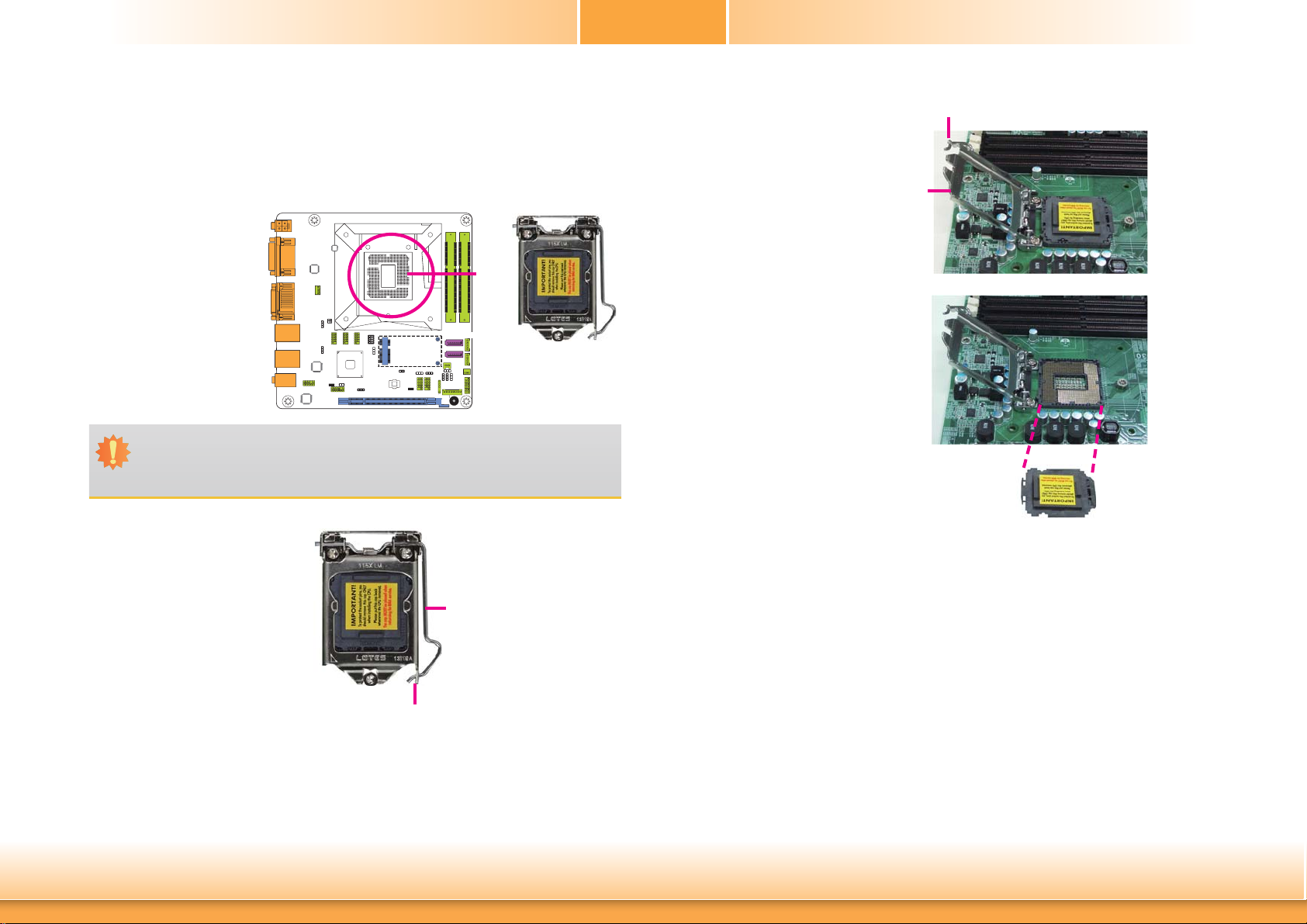
Chapter 2
Installing the CPU
1. Make sure the PC and all other peripheral devices connected to it has been powered down.
2. Disconnect all power cords and cables.
3. Locate the LGA 1150 CPU
socket on the system
board.
Important:
The CPU socket must not come in contact with anything other than the CPU. Avoid
unnecessary exposure. Remove the protective cap only when you are about to install
the CPU.
4. Unlock the socket by pushing the load lever down,
moving it sideways until it
is released from the retention tab; then lift the load
lever up.
Load lever
5. Lifting the load lever will at
the same time lift the load
plate.
Lift the load lever up to
the angle shown on the
photo.
6. Remove the protective cap
from the CPU socket. The
cap is used to protect the
CPU socket against dust
and harmful particles.
Remove the protective cap
only when you are about
to install the CPU.
Load
plate
Load lever
Protective cap
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Retention tab
12
www.dfi .com
Page 13

Chapter 2
7. Insert the CPU into the
socket. The gold triangular
mark on the CPU must
align with the corner of
the CPU socket shown on
the photo.
The CPU’s notch will at
the same time fit into the
socket’s alignment key.
Important:
The CPU will fit in only one orientation and can easily be inserted without exerting
any force.
Alignment key
Alignment key
Gold triangular mark
8. Close the load plate then
push the load lever down.
While closing the load
plate, make sure the front
edge of the load plate
slides under the retention
knob.
9. Hook the load lever under
the retention tab.
Retention knob
Load lever
Retention tab
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
13
www.dfi .com
Page 14

Chapter 2
Installing the Fan and Heat Sink
The CPU must be kept cool by using a CPU fan with heat sink. Without sufficient air circulation across the CPU and heat sink, the CPU will overheat damaging both the CPU and system
board.
Note:
A boxed Intel
CPU was purchased separately, make sure to only use Intel
sink.
1. Before you install the fan / heat sink, you must apply a thermal paste onto the top of the
CPU. The thermal paste is usually supplied when you purchase the fan / heat sink assembly. Do not spread the paste all over the surface. When you later place the heat sink on
top of the CPU, the compound will disperse evenly.
Some heat sinks come with a patch of pre-applied thermal paste. Do not apply thermal
paste if the fan / heat sink already has a patch of thermal paste on its underside. Peel the
strip that covers the paste before you place the fan / heat sink on top of the CPU.
2. Place the heat sink on top
of the CPU. The 4 pushpins around the heat sink,
which are used to secure
the heat sink onto the system board, must match the
4 mounting holes around
the socket.
®
processor already includes the CPU fan and heat sink assembly. If your
®
-certified fan and heat
Mounting hole
4. Rotate each push-pin according to the direction of
the arrow shown on top of
the pin.
Push down two pushpins
that are diagonally across
the heat sink. Perform the
same procedure for the
other two push-pins.
5. Connect the CPU fan’s
cable to the CPU fan
connector on the system
board.
Heat sink
“Locked” position of
push-pin
“Unlocked” position
of push-pin
3. Orient the heat sink such
that the CPU fan’s cable is
nearest the CPU fan connector.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
CPU Fan connector
CPU Fan connector
14
www.dfi .com
Page 15

Chapter 2
Jumper Settings
Clear CMOS Data
132
1-2 On:
Normal (default)
If you encounter the following,
JP7
132
2-3 On:
Clear CMOS Data
Auto Power-on Select
132
1-2 On:
Power-on via Power Button
(default)
JP11
JP11 is used to select the method of powering on the system. If you want the system to
power-on whenever AC power comes in, set JP11 pins 2 and 3 to On. If you want to use the
power button, set pins 1 and 2 to On.
When using the JP11 “Power On” feature to power the system back on after a power failure
occurs, the system may not power on if the power lost is resumed within 5 seconds (power
flicker).
132
2-3 On:
Power-on via AC power
a) CMOS data becomes corrupted.
b) You forgot the supervisor or user password.
you can reconfigure the system with the default values stored in the ROM BIOS.
To load the default values stored in the ROM BIOS, please follow the steps below.
1. Power-off the system and unplug the power cord.
2. Set JP7 pins 2 and 3 to On. Wait for a few seconds and set JP7 back to its default setting,
pins 1 and 2 On.
3. Now plug the power cord and power-on the system.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
15
www.dfi .com
Page 16

Chapter 2
USB Power Select
3
2
1
1-2 On: +5V
(default)
3
2
1
2-3 On:
+5V_standby
JP2, JP3, JP8 and JP9 are used to select the power of the USB ports. Selecting +5V_standby
will allow you to use a USB device to wake up the system.
Important:
If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse function for 2 USB ports, the
+5V_standby power source of your power supply must support ≥1.5A. For 3 or more
USB ports, the +5V_standby power source of your power supply must support ≥2A.
USB 3.0 1-2
(JP3)
USB 2.0 2-3
(JP2)
USB 4-5
(JP9)
132
1-2 On: +5V
(default)
USB 8-9/11
(JP8)
132
2-3 On:
+5V_standby
COM 2 RS422/485 Select
4
2
JP6
COM 2:
RS422/485
21
9
JP6 is used to configure the COM port 2 to RS422 or RS485. The pin functions of the COM
port will vary according to the jumper’s setting.
3
1
4
2
1-2 On: RS422
(default)
21
TXD+
NC.
NC.
NC.
9
3
1
RXD-RXD+
TXDNC.
NC.
JP6
COM 2
4
3
2
1
3-4 On: RS485
21
DATA-DATA+
TXD NC.
NC.
NC.
NC.
NC.
NC.
9
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
16
www.dfi .com
Page 17

Chapter 2
Digital I/O Power Select
3
2
1
1-2 On: +5V_standby
(default)
JP13
3
2
1
2-3 On: +5V
Digital I/O Output State
DIO 0-3
3
2
1
1-2 On: +5V or
+5V_standby
(JP10)
DIO 4-7
(JP12)
2-3 On: GND
(default)
3
2
1
JP13 is used to select the power of DIO (Digital I/O) signal.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Based on the power level of DIO (Digital I/O) selected on JP13, JP10 (DIO pin 0-3) and JP12
(DIO pin 4-7) are used to select the state of DIO output: pull high or pull low. When selecting
pull high, the power selection will be the same as JP13’s setting.
17
www.dfi .com
Page 18

Chapter 2
Mini PCIe/mSATA Signal Select
JP5
JP5 is used to select the Mini PCIe signal: PCIe (default) or mSATA.
1
3
12 10
1-4-7-10, 2-5-8-11 On:
PCIe (default)
1
3
12 10
2-5-8-11, 3-6-9-12 On:
mSATA
Mini PCIe/mSATA Power Select
JP4 is used to select the power supplied with the Mini PCIe.
JP4
3
2
1
1-2 On: +3.3V
(default)
3
2
1
2-3 On:
+3.3V_standby
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
18
www.dfi .com
Page 19

Chapter 2
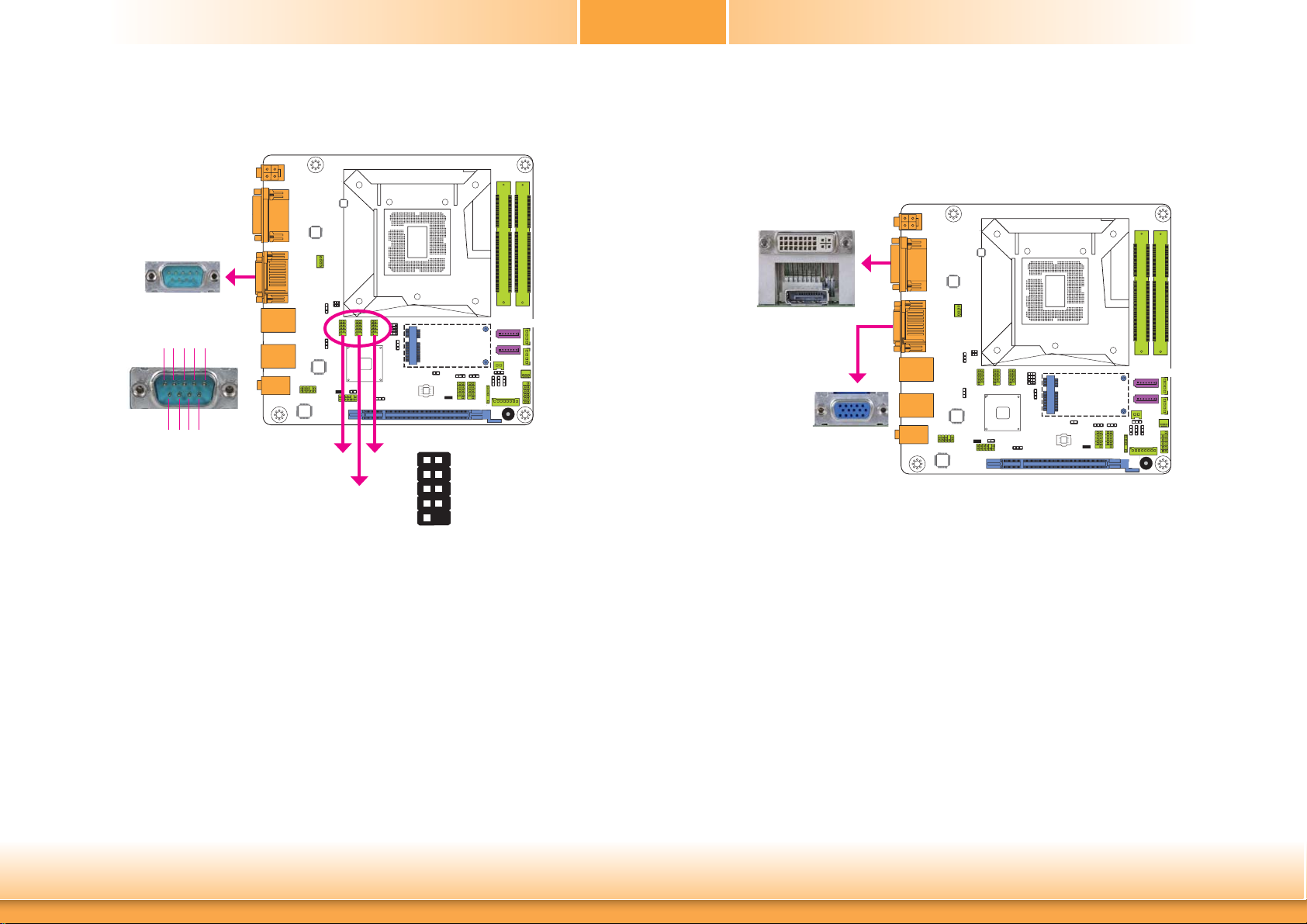
Rear Panel I/O Ports
DVI-I
(DVI-D signal)
DC-in
DP USB 3.0
The rear panel I/O ports consist of the following:
• 1 12V (HD171) or 19~24V (HD173) DC-in jack or 4-pin power connector* (optional)
• 1 COM port
• 1 VGA port
• 1 DP port (default) or 1 mini-DIN-6 PS/2 keyboard/mouse port* (optional)
• 1 DVI-D port
• 2 RJ45 LAN ports
• 2 USB 2.0 ports
• 2 USB 3.0 ports
• 1 Line-in jack
• 1 Line-out jack
• 1 Mic-in jack
COM 1
VGA
LAN 1
LAN 2
USB 2.0
Line-in
Line-out
Mic-in
12V DC-in (HD171)/19~24V DC-in (HD173)
DC-in
This jack provides maximum of 100W/120W power and is considered a low power solution.
Connect a DC power cord to this jack. We only provide 12V/19V DC output in the package
contents. Using a voltage more than the recommended range may fail to boot the system or
cause damage to the system board.
The DC-in jack on the system board co-lays with a 4-pin power connector (optional) as the
photo displayed below.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
4-pin power
DC-in jack
19
www.dfi .com
Page 20
Chapter 2
COM (Serial) Ports
COM 1
COM 1: RS232
DCD-TDRD
DTR-
12345
6789
COM 1, COM 3 and COM 4 are fixed at RS232.
The pin functions of COM port 2 will vary according to JP6’s setting. JP6 allows you to configure the Serial COM port 2 to RS422 or RS485. Refer to “COM 2 RS422/485 Select” in this
chapter for more information.
The serial ports are asynchronous communication ports with 16C550A-compatible UARTs that
can be used with modems, serial printers, remote display terminals, and other serial devices.
Connecting External Serial Ports
Your COM port may come mounted on a card-edge bracket. Install the card-edge bracket to
an available slot at the rear of the system chassis then insert the serial port cable to the COM
connector. Make sure the colored stripe on the ribbon cable is aligned with pin 1 of the COM
connector.
BIOS Setting
Configure the serial COM ports in the Advanced menu (“Super IO Configuration” submenu) of
the BIOS. Refer to the chapter 3 for more information.
GND
RI-
CTS-
RTS-
DSR-
21
COM 2 COM 4
COM 2: RS422/485
COM 3
COM 3/COM 4: RS232
9
Graphics Interfaces
The display ports consist of the following:
• 1 VGA port
• 1 DP port
• 1 DVI-D port
DVI-D
DP
VGA
VGA Port
The VGA port is used for connecting a VGA monitor. Connect the monitor’s 15-pin D-shell cable
connector to the VGA port. After you plug the monitor’s cable connector into the VGA port,
gently tighten the cable screws to hold the connector in place.
DP Port
The DisplayPort is a digital display interface used to connect a display device such as a computer monitor. It is used to transmit audio and video simultaneously. The interface, which is
developed by VESA, delivers higher performance features than any other digital interface.
DVI-D Port
The DVI-I port is used to connect an LCD monitor. This port supports DVI-D signal only.
Connect the display device’s cable connector to the DVI-I port. After plugging the cable connector into the port, gently tighten the cable screws to hold the connector in place.
BIOS Setting
Configure the display devices in the Chipset menu (“System Agent Configuration” submenu) of
the BIOS. Refer to the chapter 3 for more information.
Driver Installation
Install the graphics driver. Refer to chapter 4 for more information.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
20
www.dfi .com
Page 21

Chapter 2
RJ45 LAN Ports USB Ports
LAN 1
Features
• Intel® I210 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet controller
• Intel
The two LAN ports allow the system board to connect to a local area network by means of a
network hub.
BIOS Setting
Configure the onboard LAN ports in the Chipset menu (“PCH-IO Configuration” submenu) of
the BIOS. Refer to the chapter 3 for more information.
Driver Installation
Install the LAN drivers. Refer to the chapter 4 for more information.
®
LAN 2
LAN 1
LAN 2
I217 Gigabit Ethernet Phy
USB 2
USB 1
USB 3.0
USB 3
USB 2
USB 2.0
USB 2.0
12
9
10
USB 8-9
VCC
-Data
+Data
GND
N. C.
USB 4-5
VCC
-Data
+Data
GND
Key
The USB device allows data exchange between your computer and a wide range of simultaneously accessible external Plug and Play peripherals.
The system board is equipped with two onboard USB 3.0 ports (USB 1-2) and two onboard
USB 2.0 ports (USB 2-3). The 10-pin connectors allow you to connect 4 additional USB 2.0/1.1
ports (USB 4-5/8-9). The 5-pin connector allows you to connect 1 additional USB 2.0/1.1 port
(USB 11) or co-lays with 1 vertical USB 2.0/1.1 port. The additional USB ports may be mounted on a card-edge bracket. Install the card-edge bracket to an available slot at the rear of the
system chassis and then insert the USB port cables to a connector.
USB 11
VCC
DataData+
GND
1
USB 2.0
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
BIOS Setting
Configure these onboard USB devices in the Advanced menu (“USB Configuration” submenu)
of the BIOS. Refer to the chapter 3 for more information.
Driver Installation
You may need to install the proper drivers in your system operation to use the USB device.
Refer to your operating system’s manual or documentation for more information.
21
www.dfi .com
Page 22

Chapter 2
Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse
The Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse function allows you to use a USB keyboard or USB mouse
to wake up a system from the S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state. To use this function:
• Jumper Setting
JP2, JP3, JP8 and JP9 must be set to “2-3 On: +5V_standby”. Refer to “USB Power Select” in
this chapter for more information.
Important:
If you are using the Wake-On-USB Keyboard/Mouse function for 2 USB ports, the
+5V_standby power source of your power supply must support ≥1.5A. For 3 or more
USB ports, the +5V_standby power source of your power supply must support ≥2A.
Audio
Rear audio
Line-in
Line-out
Mic-in
Front audio
Rear Audio
The system board is equipped with 3 audio jacks. A jack is a one-hole connecting interface for
inserting a plug.
Presence Signal
Mic2-JD
GND
2
1
Mic2-R
Mic2-L
Line2-R
Line2-JD
Key
Front_IO_Sense
Line2-L
10
9
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
• Line-in Jack (Light Blue)
This jack is used to connect any audio devices such as Hi-fi set, CD player, tape player,
AM/FM radio tuner, synthesizer, etc.
• Line-out Jack (Lime)
This jack is used to connect a headphone or external speakers.
• Mic-in Jack (Pink)
This jack is used to connect an external microphone.
Front Audio
The front audio connector allows you to connect to the second line-out and mic-in jacks that
are at the front panel of your system.
Driver Installation
Install the audio driver. Refer to the chapter 4 for more information.
22
www.dfi .com
Page 23

Chapter 2
I/O Connectors
SATA (Serial ATA) Connectors
Features
GND
RXP
RXN
TXN
GND
TXP
GND
1
SATA 3.0 6Gb/s
SATA 1
SATA 0
SATA (Serial ATA) Power Connectors
7
These SATA power connectors supply power to the SATA drive. Connect one end of the provided power cable to the SATA power connector and the other end to your storage device.
SATA
Power 1
SATA
Power 0
1
4
+12V
Ground
Ground
+5V
• 2 Serial ATA 3.0 ports with data transfer rate up to 6Gb/s (SATA 0 and SATA 1)
The Serial ATA connectors are used to connect Serial ATA devices. Connect one end of the Serial ATA data cable to a SATA connector and the other end to your Serial ATA device.
BIOS Setting
Configure the Serial ATA drives in the Advanced menu (“SATA Configuration” submenu) of the
BIOS. Refer to the chapter 3 for more information.
Note:
Some 3rd party SATA Gen 2 speed device controllers used on the system board paired
with the Intel
or mSATA SSD devices, please check whether the device and the cable which are
used on the system board conform to Intel's official regulations.
®
8 series chipset are intermittently detected. Before using SSD devices
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
23
www.dfi .com
Page 24

Chapter 2
Digital I/O Connector
Digital I/O
The 8-bit Digital I/O connector provides powering-on function to external devices that are connected to these connectors.
Digital I/O Connector
Cooling Fan Connectors
CPU Fan
Speed Control
4
Sense
Power
Ground
1
System Fan
Sense
Power
Ground
1
3
The fan connectors are used to connect cooling fans. The cooling fans will provide adequate
airflow throughout the chassis to prevent overheating the CPU and system board components.
Pins Function
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
DIO7
DIO6
DIO5
DIO4
DIO3
DIO2
DIO1
DIO0
BIOS Setting
The Advanced menu (“PC Health Status” submenu) of the BIOS will display the current speed
of the cooling fans. Refer to the chapter 3 for more information.
24
www.dfi .com
Page 25

Chapter 2
Chassis Intrusion Connector
Chassis
12
Signal
Ground
The board supports the chassis intrusion detection function. Connect the chassis intrusion
sensor cable from the chassis to this connector. When the system’s power is on and a chassis
intrusion occurred, an alarm will sound. When the system’s power is off and a chassis intrusion
occurred, the alarm will sound only when the system restarts.
Intrusion
Front Panel Connector
Front
Panel
HDD-LED - HDD LED
This LED will light when the hard drive is being accessed.
RESET-SW - Reset Switch
This switch allows you to reboot without having to power off the system.
ATX-SW - ATX Power Switch
This switch is used to power on or off the system.
ATX- SW
PWR-LED
12 11
RESET-SW
HDD-LED
21
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
PWR-LED - Power/Standby LED
When the system’s power is on, this LED will light. When the system is in the S1 (POS - Power
On Suspend) state, it will blink every second. When the system is in the S3 (STR - Suspend To
RAM) state, it will blink every 4 seconds.
Pin Pin Assignment Pin Pin Assignment
HDD-LED
RESET SW
25
3 HDD Power
5 Signal 4 LED Power
7 Ground 6 Signal
9 RST Signal
11 N.C. 10 Signal
PWR-LED
ATX-SW
2 LED Power
8 Ground
www.dfi .com
Page 26

Chapter 2
Expansion Slots
Mini PCI Express
PCI Express x16
Mini PCI Express Slot
The Mini PCIe socket is used to install a Mini PCIe card. Mini PCIe card is a small form factor
PCI card with the same signal protocol, electrical definitions, and configuration definitions as
the conventional PCI.
Standby Power LED
Standby Power LED
This LED will light red when the system is in the standby mode. It indicates that there is power on the system board. Power-off the PC and then unplug the power cord prior to installing
any devices. Failure to do so will cause severe damage to the motherboard and components.
PCI Express x16 Slot
Install PCI Express x16 graphics card, that comply to the PCI Express specifications, into the
PCI Express x16 slot. To install a graphics card into the x16 slot, align the graphics card above
the slot then press it down firmly until it is completely seated in the slot. The retaining clip of
the slot will automatically hold the graphics card in place.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
26
www.dfi .com
Page 27

Battery
GND
Chapter 2
+3.3V
Battery
The lithium ion battery powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. It is an auxiliary source
of power when the main power is shut off.
Safety Measures
• Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced.
• Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommend by the manufacturer.
• Dispose of used batteries according to local ordinance
.
1
2
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
27
www.dfi .com
Page 28

Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - BIOS Setup
Overview
The BIOS is a program that takes care of the basic level of communication between the CPU
and peripherals. It contains codes for various advanced features found in this system board.
The BIOS allows you to configure the system and save the configuration in a battery-backed
CMOS so that the data retains even when the power is off. In general, the information stored
in the CMOS RAM of the EEPROM will stay unchanged unless a configuration change has been
made such as a hard drive replaced or a device added.
It is possible that the CMOS battery will fail causing CMOS data loss. If this happens, you need
to install a new CMOS battery and reconfigure the BIOS settings.
Note:
The BIOS is constantly updated to improve the performance of the system board;
therefore the BIOS screens in this chapter may not appear the same as the actual
one. These screens are for reference purpose only.
Default Configuration
Most of the configuration settings are either predefined according to the Load Optimal Defaults
settings which are stored in the BIOS or are automatically detected and configured without
requiring any actions. There are a few settings that you may need to change depending on
your system configuration.
Legends
Keys Function
Right and Left arrows
Up and Down arrows
<Esc>
+ (plus key)
- (minus key)
Tab
<F1>
<F2>
<F3>
<F4>
<Enter>
Moves the highlight left or right to select a menu.
Moves the hightlight up or down between submenu or fi elds.
Exit to the BIOS Setup Utility.
Scrolls forward through the values or options of the highlighted fi eld.
Scrolls backward through the values or options of the highlighted fi eld.
Select a fi eld.
Displays general help
Pervious values
Optimized defaults
Saves and resets the setup program.
Press <Enter> to enter the highlighted submenu.
Entering the BIOS Setup Utility
The BIOS Setup Utility can only be operated from the keyboard and all commands are keyboard commands. The commands are available at the right side of each setup screen.
The BIOS Setup Utility does not require an operating system to run. After you power up the
system, the BIOS message appears on the screen and the memory count begins. After the
memory test, the message “Press DEL to run setup” will appear on the screen. If the message
disappears before you respond, restart the system or press the “Reset” button. You may also
restart the system by pressing the <Ctrl> <Alt> and <Del> keys simultaneously.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Scroll Bar
When a scroll bar appears to the right of the setup screen, it indicates that there are more
available fields not shown on the screen. Use the up and down arrow keys to scroll through all
the available fields.
Submenu
When ““ appears on the left of a particular field, it indicates that a submenu which contains
additional options are available for that field. To display the submenu, move the highlight to
that field and press <Enter>.
28
www.dfi .com
Page 29

Chapter 3
AMI BIOS Setup Utility Advanced
Main
The Main menu is the first screen that you will see when you enter the BIOS Setup Utility.
Main
BIOS Information
BIOS Vendor
Core Version
Compliancy
Project Version
Build Date and Time
System Language
System Date
System Time
Access Level
System Date
The date format is <day>, <month>, <date>, <year>. Day displays a day, from Sunday to Saturday. Month displays the month, from January to December. Date displays
the date, from 1 to 31. Year displays the year, from 1980 to 2099.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Boot Security
American Megatrends
4.6.5.4
UEFI 2.3.1; PI 1.2
1AQQW 0.25 x64
11/17/2014 13:15:02
[English]
[Mon 12/29/2014]
[14:20:59]
Administrator
Save & ExitChipset
Choose the system default
language
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
The Advanced menu allows you to configure your system for basic operation. Some entries are
defaults required by the system board, while others, if enabled, will improve the performance
of your system or let you set some features according to your preference.
Important:
Setting incorrect field values may cause the system to malfunction.
Main
ACPI Power Management Confi guration
Trusted Computing
CPU Confi guration
SATA Confi guration
PCH-FW Confi guration
USB Confi guration
Super IO Confi guration
PC Health Status
Network Stack
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Save & ExitChipset Boot Security
ACPI Power Management
Confi guration
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
System Time
The time format is <hour>, <minute>, <second>. The time is based on the 24-hour
military-time clock. For example, 1 p.m. is 13:00:00. Hour displays hours from 00 to
23. Minute displays minutes from 00 to 59. Second displays seconds from 00 to 59.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
29
www.dfi .com
Page 30

Chapter 3
ACPI Power Management Configuration
This section is used to configure the ACPI Power Management.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
ACPI Power Management Confi guration
Resume by PME
Resume by Ring
Resume by RTC Alarm
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
Resume by PME
Enable this field to use the PME signal to wake up the system.
Resume by Ring
Enable this field to use the Ring signal to wake up the system.
About Resume by PME
(PCI, PCIE, LAN). If
PME is enabled, then PCH
After-G3 function is enabled, too. But Auto Power
On function is fail.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Trusted Computing
This section configures settings relevant to Trusted Computing innovations.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Confi guration
Security Device Support
Current Status Information
No Security Device Found
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Disable]
Enables or Disables
BIOS support for security
device. O.S will not show
Security Device. TCG
EFI protocol and INT1A
interface will not be
available.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Security Device Support
This field is used to enable or disable BIOS supporting for the security device. O.S will
not show the security device. TCG EFI protocol and INT1A interface will not be
available.
Resume by RTC Alarm
When Enabled, the system uses the RTC to generate a wakeup event.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
30
www.dfi .com
Page 31

Chapter 3
CPU Configuration
This section is used to configure the CPU. It will also display the detected CPU information.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Enabled for Windows XP
CPU Confi guration
Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4570TE CPU @ 2.70GHz
CPU Signature
Processor Family
Microcode Patch
FSB Speed
Max CPU Speed
Min CPU Speed
CPU Speed
Processor Cores
Intel HT Technology
Intel VT-X Technology
Intel SMX Technology
64-bit
EIST Technology
CPU C3 State
CPU C6 State
CPU C7 State
L1 Data Cache
L1 Code Cache
L2 Cache
L3 Cache
Hyper-threading
Active Processor Cores
Intel Virtualization Technology
EIST
Intel TXT(LT) Support
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
306c3
6
1a
100 MHz
2700 MHz
800 MHz
2700 MHz
2
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
32 KB x2
32 KB x2
256 KB x2
4096 KB
[Enabled]
[All]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
and Linux (OS optimized
for Hyper-Threading
Technology) and Disabled
for other OS (OS not
optimized for
Hyper-Threading
Technology). When
Disabled only one thread
per enabled core is
enabled.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Hyper-threading
Enable this field for Windows XP and Linux which are optimized for Hyper-Threading
technology. Select disabled for other OSes not optimized for Hyper-Threading technology. When disabled, only one thread per enabled core is enabled.
Active Processor Cores
Number of cores to enable in each processor package.
SATA Configuration
This section is used to configure the settings of SATA device.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
SATA Controller(s)
SATA Mode Selection
Serial ATA Port 0
Software Preserve
Serial ATA Port 1
Software Preserve
mSATA Port
Software Preserve
[Enabled]
[IDE]
Empty
Unknown
Empty
Unknown
Empty
Unknown
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Enable or disable SATA
Device.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
SATA Controller(s)
This field is used to enable or disable the Serial ATA devices.
SATA Mode Selection
The mode selection determines how the SATA controller(s) operates.
IDE Mode
This option configures the Serial ATA drives as Parallel ATA storage devices.
AHCI Mode
This option allows the Serial ATA devices to use AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface).
Intel Virtualization Technology
When this field is set to Enabled, the VMM can utilize the additional hardware capabilities provided by Vanderpool Technology.
EIST
This field is used to enable or disable the Intel Enhanced SpeedStep Technology.
Intel TXT(LT) Support
Enables or disables the support of the Intel Trusted Execution Technology.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
31
www.dfi .com
Page 32

Chapter 3
When IDE mode is selected in the SATA Mode Selection, it will display the following
information:
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
SATA Controller(s)
SATA Mode Selection
Serial ATA Port 0
Software Preserve
Serial ATA Port 1
Software Preserve
mSATA Port
Software Preserve
[Enabled]
[IDE]
Empty
Unknown
Empty
Unknown
Empty
Unknown
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Determines how SATA
controller(s) operate.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter:
Select
+/-:
Change Opt.
F1:
General Help
F2:
Previous Values
F3:
Optimized Defaults
F4:
Save & Reset
ESC:
Exit
When AHCI mode is selected in the SATA Mode Selection, it will display the following
information:
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
SATA Controller(s)
SATA Mode Selection
SATA Controller Speed
Serial ATA Port 0
Software Preserve
Port 0
Hot Plug
Serial ATA Port 1
Software Preserve
Port 1
Hot Plug
mSATA Port
Software Preserve
mSATA Port
Hot Plug
[Enabled]
[AHCI]
[Default]
Empty
Unknown
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
Empty
Unknown
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
Empty
Unknown
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
Determines how SATA
controller(s) operate.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter:
Select
+/-:
Change Opt.
F1:
General Help
F2:
Previous Values
F3:
Optimized Defaults
F4:
Save & Reset
ESC:
Exit
SATA Controller Speed
Indicates the maximum speed that the SATA controller can support.
Port 0, Port 1 and mSATA Port
Enables or disables the SATA port.
Hot Plug
Designates the SATA port as hot pluggable.
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
32
www.dfi .com
Page 33

Chapter 3
PCH-FW Configuration
This section is used to configure the parameters of Management Engine Technology.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Confi gure Management
ME FW Version
ME Firmware Mode
ME Firmware Type
ME Firmware SKU
Firmware Update Confi guration
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
9.1.2.1010
Normal Mode
Full Sku Firmware
1.5MB
Engine Technology
Parameters
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Firmware Update Configuration
Enables or disables Me FW Image Re-Flash function.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Enable/Disable Me FW
Me FW Image Re-Flash
[Disabled]
Image Re-Flash function.
USB Configuration
This section is used to configure the parameters of the USB device.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
USB Confi guration
USB Module Version
USB Devices:
1 keyboard, 1 Mouse, 2 Hubs
Legacy USB Support
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
8.10.27
[Enabled]
Enables Legacy USB
support. AUTO option
disables legacy support if
no USB devices are
connected. DISABLE
option will keep USB
devices available only for
EFI applications.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Legacy USB Support
Enabled
Enables legacy USB.
Auto
Disables support for legacy when no USB devices are connected.
Disabled
Keeps USB devices available only for EFI applications.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
33
www.dfi .com
Page 34

Chapter 3
Super IO Configuration
This section is used to configure the I/O functions supported by the onboard Super I/O chip.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Super IO Confi guration
Super IO Chip
Restore AC Power Loss
WatchDog Timer Unit
Super IO Watchdog Timer
Serial Port 1 Confi guration
Serial Port 2 Confi guration
Serial Port 3 Confi guration
Serial Port 4 Confi guration
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
NCT6102D
[Power Off]
[Second]
0
Restore AC Power Loss
Help.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Restore AC Power Loss
Power Off
When power returns after an AC power failure, the system’s power is off. You must
press the Power button to power-on the system.
Power On
When power returns after an AC power failure, the system will automatically power-on.
Serial Port 1 Configuration to Serial Port 4 Configuration
Sets the parameters of serial port 1 (COM A) to serial port 4 (COM D).
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Serial Port 1 Confi guration
Serial Port
Device Settings
Change Settings
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Serial Port 2 Confi guration
Serial Port
Device Settings
Change Settings
RS485 Auto Flow
[Enabled]
IO=3F8h; IRQ=4;
[Auto]
[Enabled]
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3;
[Auto]
[Enabled]
Enable or Disable Serial
Port (COM)
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Enable or Disable Serial
Port (COM)
Last State
When power returns after an AC power failure, the system will return to the state
where you left off before power failure occurs. If the system’s power is off when AC
power failure occurs, it will remain off when power returns. If the system’s power is on
when AC power failure occurs, the system will power-on when power returns.
Watchdog Timer Unit
Selects the watchdog timer unit: second or minute.
Super IO Watchdog Timer
Sets the timeout value of the super IO watchdog timer. 0 means disabled.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
34
www.dfi .com
Page 35

Chapter 3
PC Health Status
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Serial Port 3 Confi guration
Serial Port
Device Settings
Change Settings
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Serial Port 4 Confi guration
Serial Port
Device Settings
Change Settings
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Enabled]
IO=3E8h; IRQ=5;
[Auto]
[Enabled]
IO=2E8h; IRQ=7;
[Auto]
Enable or Disable Serial
Port (COM)
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Enable or Disable Serial
Port (COM)
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Serial Port
Enables or disables the serial port (COM).
Change Settings
Selects the IO/IRQ setting of the I/O device.
RS485 Auto Flow
Enables or disables the RS485 auto flow for the serial port 2.
This section displays the hardware health monitor.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
PC Health Status
Smart Fan Function
Case Open
CPU Temperature
System Temperature
CPU Fan Speed
System Fan Speed
VCORE
+5V
+12V
+1.5V
+3.3V
3VSB
VBAT
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Disabled]
: +32.5 C
: +33.5 C
: 1314 RPM
: N/A
: +1.728 V
: +4.998 V
: +12.232 V
: +1.520 V
: +3.296 V
: +3.312 V
: +3.040 V
Smart Fan Function Setting
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Smart Fan Function
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Smart Fan Function
CPU Smart Fan Control
Boundary 4
Boundary 3
Boundary 2
Boundary 1
Speed Count 5
Speed Count 4
Speed Count 3
Speed Count 2
Speed Count 1
System Smart Fan Control
Boundary 4
Boundary 3
Boundary 2
Boundary 1
Speed Count 5
Speed Count 4
Speed Count 3
Speed Count 2
Speed Count 1
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Enabled]
60
50
40
30
100
75
50
40
30
[Enabled]
60
50
40
30
100
75
50
40
30
Enable CPU Smart Fan
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
CPU Smart Fan Control
When this feature is set to Automatic, the CPU’s fan speed will rotate according to the
CPU’s temperature. The higher the temperature, the faster the speed of rotation.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
35
www.dfi .com
Page 36

Chapter 3
System Smart Fan Control
When this feature is set to Automatic, the System’s fan speed will rotate according to
the System’s temperature. The higher the temperature, the faster the speed of rotation.
Boundary 1 to Boundary 4
The range is 0-127.
Speed Count 1 to Speed Count 5
The range is 1-100%.
Case Open
Sets this field to Enabled to allow the system to alert you of a chassis intrusion event.
Network Stack
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Network Stack
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Network Stack
Enables or disables UEFI network stack.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Network Stack
Ipv4 PXE Support
Ipv6 PXE Support
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
Enable or disable UEFI
network stack.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Enable or disable UEFI
network stack.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
36
www.dfi .com
Page 37

Chapter 3
Ipv4 PXE Support
When enabled, Ipv4 PXE boot supports. When disabled, Ipv4 PXE boot option will not
be created.
Ipv6 PXE Support
When enabled, Ipv6 PXE boot supports. When disabled, Ipv6 PXE boot option will not
be created.
Chipset
This section configures relevant chipset functions.
Main
System Agent (SA) Confi guration
PCH-IO Confi guration
System Agent (SA) Configuration
This section is used to configure the parameters of System Agent.
System Agent Bridge Name
System Agent RC Version
VT-d Capability
VT-d
Graphics Confi guration
NB PCIe Confi guration
Memory Confi guration
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Chipset
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
Boot Security
Haswell
1.5.0.0
Supported
[Enabled]
Save & Exit
System Agent (SA)
Parameters
Check to enable VT-d
function on MCH.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
VT-d
Enables or disables the VT-d function on MCH.
37
www.dfi .com
Page 38

Chapter 3
Graphics Configuration
This field configures the graphics settings.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
Graphics Confi guration
IGFX VBIOS Version
IGfx Frequency
Primary Display
Internal Graphics
DVMT Pre-Allocated
LCD Control
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
2166
700 MHz
[Auto]
[Auto]
[32M]
Select which of IGFX/
PEG/PCI Graphics
device should be Primary
Display.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Primary Display
Auto When the system boots, it will auto detects the display device.
IGFX When the system boots, it will first initialize the onboard VGA.
PEG When the system boots, it will first initialize the PCI Express x16 graphics card.
Internal Graphics
Keeps IGD enabled based on the setup options
.
DVMT Pre-Allocated
Selects DVMT 5.0 Pre-Allocated (Fixed) Graphics Memory size used by the Internal
Graphics Device. Please refer to the screen shown below.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
Graphics Confi guration
IGFX VBIOS Version
IGfx Frequency
Primary Display
Internal Graphics
DVMT Pre-Allocated
LCD Control
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
2166
700 MHz
DVMT Pre-Allocated
32M
64M
96M
128M
160M
192M
224M
256M
288M
320M
352M
384M
416M
448M
480M
512M
1024M
Select DVMT5.0 PreAllocated (Fixed) Graphics Memory size used
by the Internal Graphics
Device.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
38
www.dfi .com
Page 39

Chapter 3
LCD Control
This field configures the LCD control.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
LCD Control
Primary IGFX Boot Display
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[VBIOS Default]
Select the Video Device
which will be activated
during POST. This has no
effect if external graphics
present.
Secondary boot display
selection will appear based
on your selection.
VGA modes will be supported only on primary
display.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
When any device is selected in the Primary IGFX Boot Display, it will display the
following information:
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
LCD Control
Primary IGFX Boot Display
Secondary IGFX Boot Display
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[CRT]
[None]
Select the Video Device
which will be activated
during POST. This has no
effect if external graphics
present.
Secondary boot display
selection will appear based
on your selection.
VGA modes will be supported only on primary
display.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
NB PCIe Configuration
This field is used to configure the settings of NB PCI Express.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
NB PCIe Confi guration
PEG0 - Gen X
Enable PEG
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Auto]
[Enabled]
Enable PEG
Enables or disables the PEG.
Confi gure PEG0
B0:D1:F0 Gen1-Gen2.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Secondary IGFX Boot Display
Selects secondary display device.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
39
www.dfi .com
Page 40

Chapter 3
Memory Configuration
This field only displays the memory configuration.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
Memory Information
Memory RC Version
Memory Frequency
Total Memory
Memory Voltage
DIMM#1
DIMM#2
CAS Latency (tCL)
Minimum delay time
CAS to RAS (tRCDmin)
Row Precharge (tRPmin)
Active to Precharge (tRASmin)
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
1.5.0.0
1333 Mhz
2048 MB (DDR3)
1.50V
2048 MB (DDR3)
Not Present
9
9
9
24
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
PCH-IO Configuration
This section illustrates the PCH parameters.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
Intel PCH RC Version
Intel PCH SKU Name
Intel PCH Rev ID
PCI Express Confi guration
USB Confi guration
PCH Azalia Confi guration
Onboard I217 LAN Controller
Onboard I210 LAN Controller
High Precision Event Timer Confi guration
High Precision Timer
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
1.5.0.0
H81
05/C2
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
Onboard I217 LAN Controller
Enables or disables the onboard I217 LAN controller.
Onboard I210 LAN Controller
Enables or disables onboard I210 LAN controller
High Precision Timer
PCI Express Confi guration
settings.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Enables or disables the the High Precision Event Timer.
40
www.dfi .com
Page 41

Chapter 3
PCI Express Configuration
This field is used to configure the PCI Express settings.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
PCI Express Confi guration
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
USB Configuration
This field is used to configure the USB settings.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
USB Confi guration
XHCI Mode
USB Ports Per-Port Disable Control
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Auto]
[Disabled]
Mode of operation of
xHCI controller.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
USB Precondition
Precondition works on USB host controller and root ports for faster enumeration.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
41
www.dfi .com
Page 42

Chapter 3
XHCI Mode
Selects the operation mode of XHCI controller. These options are Auto, Enabled, and
Disabled. When Disabled, it will display the following information:
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
USB Confi guration
XHCI Mode
EHCI1
EHCI2
USB Ports Per-Port Disable Control
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Disabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
Mode of operation of
xHCI controller.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
EHCI 1 and EHCI 2
These fields are used to control the functions of USB EHCI (USB 2.0) controllers
One EHCI controller must always be enabled.
.
USB Ports Per-Port Disable Control
This field is used to control each of the USB ports (0~13) disabling. When enabled,
it will display the following information:
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
USB Confi guration
XHCI Mode
USB Ports Per-Port Disable Control
USB Port #0
USB Port #1
USB Port #2
USB Port #3
USB Port #4
USB Port #5
USB Port #8
USB Port #9
USB Port #10
USB Port #11
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Auto]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
Control each of the USB
ports (0~13) disabling.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
USB Port #0/1/2/3/4/5/8/9/10/11
Enables or disables these USB ports.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
42
www.dfi .com
Page 43

Chapter 3
PCH Azalia Configuration
This field is used to configure the PCH Azalia settings.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Chipset
PCH Azalia Confi guration
Azalia
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
[Auto]
Control detection of the
Azalia device.
Disable= Azalia will be
unconditionally disabled
Enabled= Azalia will be
unconditionally enabled
Auto=Azalia will be ena-
bled if present, disabled
otherwise.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Boot
Main
Boot Confi guration
Setup Prompt Timeout
Bootup NumLock State
Quiet Boot
Boot Option Priorities
CSM Parameters
Setup Prompt Timeout
Selects the number of seconds to wait for the setup activation key. 65535(0xFFFF)
denotes indefinite waiting.
Bootup NumLock State
This allows you to determine the default state of the numeric keypad. By default, the
system boots up with NumLock on wherein the function of the numeric keypad is the
number keys. When set to Off, the function of the numeric keypad is the arrow keys.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Boot
1
[On]
[Disabled]
Security
Save & ExitChipset
Number of seconds to
wait for setup activation
key.
65535(0xFFFF) means
indefi nite waiting.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
Quiet Boot
Enables or disables the quiet boot function.
43
www.dfi .com
Page 44

Chapter 3
CSM Parameters
Main
Launch CSM
Boot option fi lter
Launch PXE OpROM policy
Launch Storage OpROM policy
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Boot
Security
[Enabled]
[UEFI and Legacy]
[Do not launch]
[Legacy only]
Save & ExitChipset
Launch CSM
This option controls if CSM will be launched.
Boot option filter
This option controls what devices system can boot to.
Launch PXE OpROM policy
This option controls if
CSM will be launched.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Security
Main
Password Description
If ONLY the Administrator’s password is set,
then this only limits access to Setup and is only
asked for when entering Setup.
If ONLY the User’s password is set, then this
is a power on password and must be entered to
boot or enter Setup. In Setup the User will have
Administrator rights.
The password length must be
in the following range:
Minimum length 3
Maximum length 20
Administrator Password
User Password
Administrator Password
Sets the administrator’s password.
User Password
Sets the user’s password.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Boot Security
Save & ExitChipset
Set Administrator
Password.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Controls the execution of UEFI and legacy PXE OpROM.
Launch Storage OpROM policy
Controls the execution of UEFI and legacy storage OpROM.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
44
www.dfi .com
Page 45

Chapter 3
Save & Exit
Main
Save Changes and Reset
Discard Changes and Reset
Restore Defaults
Boot Override
Launch EFI Shell from fi lesystem device
Save Changes and Reset
To save the changes, select this field and then press <Enter>. A dialog box will appear. Select Yes to reset the system after saving all changes made.
Discard Changes and Reset
To discard the changes, select this field and then press <Enter>. A dialog box will
appear. Select Yes to reset the system setup without saving any changes.
Aptio Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Advanced
Chipset
Version 2.15.1236. Copyright (C) 2012 American Megatrends, Inc.
Boot Security Save & Exit
Reset the system after
saving the changes.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter: Select
+/-: Change Opt.
F1: General Help
F2: Previous Values
F3: Optimized Defaults
F4: Save & Reset
ESC: Exit
Updating the BIOS
To update the BIOS, you will need the new BIOS file and a flash utility, AFUDOS.
EXE. Please contact technical support or your sales representative for the files.
To execute the utility, type:
A:> AFUDOS BIOS_File_Name /b /p /n /me
then press <Enter>.
C:\AFU\AFUDOS>afudos fi lename /B /P /N
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
|
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Reading fi le ..............................
Erasing fl ash .............................
Writing fl ash .............................
Verifying fl ash ..........................
Erasing BootBlock ....................
Writing BootBlock ....................
Verifying BootBlock .................
C:\AFU\AFUDOS>
AMI Firmware Update Utility(APTIO) v2.25
Copyright (C)2008 American Megatrends Inc. All Rights Reserved.
done
done
done
done
done
done
done
|
|
Restore Defaults
To restore and load the optimized default values, select this field and then press
<Enter>. A dialog box will appear. Select Yes to restore the default values of all the
setup options.
Launch EFI Shell from filesystem device
Attempts to launch EFI Shell application (Shell x64.efi) from one of the available
filesystem device.
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
45
www.dfi .com
Page 46

Chapter 3
Notice: BIOS SPI ROM
1. The Intel® Management Engine has already been integrated into this system board. Due to
the safety concerns, the BIOS (SPI ROM) chip cannot be removed from this system board
and used on another system board of the same model.
2. The BIOS (SPI ROM) on this system board must be the original equipment from the factory
and cannot be used to replace one which has been utilized on other system boards.
®
3. If you do not follow the methods above, the Intel
updated and will cease to be effective.
Note:
a. You can take advantage of flash tools to update the default configuration of the
BIOS (SPI ROM) to the latest version anytime.
b. When the BIOS IC needs to be replaced, you have to populate it properly onto the
system board after the EEPROM programmer has been burned and follow the
technical person's instructions to confirm that the MAC address should be burned
or not.
Management Engine will not be
Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
46
www.dfi .com
Page 47

Chapter 4
Chapter 4 - Supported Software
The CD that came with the system board contains drivers, utilities and software applications
required to enhance the performance of the system board.
Insert the CD into a CD-ROM drive. The autorun screen (Mainboard Utility CD) will appear. If
after inserting the CD, “Autorun” did not automatically start (which is, the Mainboard Utility
CD screen did not appear), please go directly to the root directory of the CD and double-click
“Setup”.
For Windows 8
For Windows 7
Chapter 4 Supported Software
47
www.dfi .com
Page 48

Chapter 4
For Windows XP Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 (For Windows XP)
Note:
Before installing Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5, make sure you have updated your
Windows XP operating system to Service Pack 3.
To install the driver, click “Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5” on the main menu.
1. Read the license agreement carefully.
Click “I have read and accept
the terms of the License Agree
ment” then click Install.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
2. Setup is now installing the
driver.
48
www.dfi .com
Page 49

Chapter 4
3. Click Exit.
Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility
The Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility is used for updating Windows® INF files so that
the Intel chipset can be recognized and configured properly in the system.
To install the utility, click “Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility” on the main menu.
1. Setup is ready to install the
utility. Click Next.
2. Read the license agreement
then click Yes.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
49
www.dfi .com
Page 50

Chapter 4
3. Go through the readme
document for more installation tips then click Next.
4. Click Finish to exit setup.
Microsoft DirectX 9.0C (For Windows XP)
To install the utility, click “Microsoft DirectX 9.0C Driver” on the main menu.
1. Click “I accept the
agreement” then click Next.
2. To start installation, click
Next.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
3. Click Finish. Reboot the
system for DirectX to take
effect.
50
www.dfi .com
Page 51

Chapter 4
Intel HD Graphics Drivers (For Windows XP)
To install the driver, click “Intel HD Graphics Drivers” on the main menu.
1. To start installation, click
Next.
2. Read the license agreement
then click Yes.
4. Setup is now installing the
driver. Click Next to continue.
5. Click “Yes, I want to restart
this computer now” then
click Finish.
Restarting the system will allow
the new software installation to
take effect.
3. Go through the readme
document for system requirements and installation tips then
click Next.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
51
www.dfi .com
Page 52

Chapter 4
Intel HD Graphics Drivers (For Windows 7 and Windows 8)
To install the driver, click “Intel HD Graphics Drivers” on the main menu.
1. Setup is now ready to
install the graphics driver.
Click Next.
By default, the “Automatically run WinSAT and enable the Windows Aero
desktop theme” is enabled. With this enabled, after installing the graphics
driver and the system rebooted, the screen will turn blank for 1 to 2 minutes
(while WinSAT is running) before the Windows Vista desktop appears. The
“blank screen” period is the time Windows is testing the graphics performance.
2. Read the license agreement
then click Yes.
3. Go through the readme
document for system requirements and installation
tips then click Next.
4. Setup is now installing the
driver. Click Next to continue.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
5. Click “Yes, I want to restart
this computer now” then
click Finish.
Restarting the system will
allow the new software
installation to take effect.
52
www.dfi .com
Page 53

Chapter 4
Intel Management Engine Drivers
To install the driver, click “Intel Management Engine Drivers” on the main menu.
1. Setup is ready to install the
driver. Click Next.
2. Read the license agreement
then click Yes.
3. Setup is currently installing
the driver. After installation
has completed, click Next.
4. After completing installation, click Finish.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
53
www.dfi .com
Page 54

Chapter 4
Audio Drivers
To install the driver, click “Audio Drivers” on the main menu.
1. Setup is ready to install the
driver. Click Next.
2. Click “Yes, I want to restart
my computer now” then
click Finish.
Restarting the system will
allow the new software
installation to take effect.
Intel LAN Drivers (For Windows XP)
The LAN drivers for Windows XP supporting on the HD631-Q87 system board has to be
installed manually. When you want to install the LAN driver for Windows XP, please follow the
steps below to accomplish the installation.
1. Launch the Hardware
Update Wizard for the
selected device. Select
"Update Driver."
2. Choose "Install from a list or
specific location (Advanced)"
and click "Next" to continue
the installation.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
54
www.dfi .com
Page 55

Chapter 4
3. Choose the option "Don't
search. I will choose the
driver to install" in order to
select the device driver from
a list, and click "Next."
4. Select a hardware type:
DVD/CD-ROM drives. Then,
click "Next."
6. Insert the installation disk
and make sure the selected
drive is correct.
(For 32-bit, the fi le name is “e1d5132.inf”.)
7. Select the device driver
you want to install for this
hardware and then click
"Next."
5. Select your hardware disk
and then click "Have Disk..."
Chapter 4 Supported Software
8. Check the software you
are installing, Then, click
"Continue Anyway" to start
the installation.
55
www.dfi .com
Page 56

Chapter 4
9. Click "Finish" to close the wizard.
10. After completing the instal-
lation, the Network adapters
"Intel(R) Ethernet Connection
I217LM" will appear on the
computer management list.
Intel LAN Drivers (For Windows 7 and Windows 8)
To install the driver, click “Intel LAN Drivers” on the main menu.
1. Setup is ready to install the
driver. Click Next.
2. Click “I accept the terms
in the license agreement”
then click “Next”.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
3. Select the program featuers
you want installed then
click Next.
56
www.dfi .com
Page 57

Chapter 4
4. Click Install to begin the
installation.
5. After completing installation, click Finish.
DFI Utility
DFI Utility provides information about the board, Watchdog,and DIO. To access the utility, click
“DFI Utility” on the main menu.
Note:
If you are using Windows 7, you need to access the operating system as an
administrator to be able to install the utility.
1. Setup is ready to instal
the DFI Utility driver
Click “Next”.
2. Click “I accept the terms in
the license agreement” then
click “Next”.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
57
www.dfi .com
Page 58

Chapter 4
3. Click “Install” to begin the
installation.
4. After completing installa
tion, click “Finish”.
The DFI Utility icon will appear on the desktop. Double-click the icon to open the utility.
Information
Chapter 4 Supported Software
HW Health
58
www.dfi .com
Page 59

Chapter 4
HW Health Set
WatchDog
DIO
Chapter 4 Supported Software
59
www.dfi .com
Page 60

Chapter 4
Intel USB 3.0 Drivers (For Windows 7)
To install the driver, click “Intel USB 3.0 Driver” on the main menu.
1. Setup is ready to install the driver.
Click Next.
2. Read the license agreement then
click Yes.
3. Go through the readme document for more installation tips
then click Next.
4. Setup is currently installing the
driver. After installation has completed, click Next.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
5. After completing installation, click
Finish.
60
www.dfi .com
Page 61

Chapter 4
Intel Rapid Storage Technology
(For Windows 7 and Windows 8)
The Intel Rapid Storage Technology is a utility that allows you to monitor the current status
of the SATA drives. It enables enhanced performance and power management for the storage
subsystem.
To install the driver, click “Intel Rapid Storage Technology” on the main menu.
1. Setup is now ready to install
2. Read the warning then click
the utility. Click Next.
Yes.
3. Read the license agreement then
click Yes.
4. Go through the readme document
for system requirements and installation tips then click Next.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
5. Setup is now installing the utility.
Click Next to continue.
61
www.dfi .com
Page 62

Chapter 4
6. Click “Yes, I want to restart my
computer now” then click Finish.
Restarting the system will allow the
new software installation to take
effect.
Infineon TPM Driver and Tool (optional)
To install the driver, click “Infineon TPM driver and tool (option)” on the main menu.
1. The setup program is preparing
to install the driver.
2. The setup program is now ready
to install the utility. Click Next.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
3. Click “I accept the terms in the
license agreement” and then
click “Next”.
62
www.dfi .com
Page 63

Chapter 4
4. Enter the necessary information
and then click Next.
5. Select a setup type and then click
Next.
7. TPM requires installing the Microsoft Visual C++ package prior to
installing the utility. Click Install.
8. The setup program is currently
installing the Microsoft Visual
C++ package.
6. Click Install.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
9. Click Finish.
63
www.dfi .com
Page 64

Chapter 4
10. Click “Yes“ to restart your system.
Adobe Acrobat Reader 9.3
To install the reader, click “Adobe Acrobat Reader 9.3” on the main menu.
1. Click Next to install or click
Change Destination Folder
to select another folder.
2. Click Install to begin installa-
tion.
Chapter 4 Supported Software
3. Click Finish to exit installation.
64
www.dfi .com
Page 65

Chapter 5
Chapter 5 - Digital I/O Programming Guide
Register Description
The Input Port Register (register 0) reflects the incoming logic levels of the pins, regardless of whether the pin if defined as an input or output by the Configuration Register. They
act only on the red operation. Writes to this register have no effect. The default value (X) is
determined by the externally applied logic level. Before a red operation, a write transmission
is sent with the command byte to indicate to the I
accessed next.
Register 0 (Input Port Register)
BIT I-7 I-6 I-5 I-4 I-3 I-2 I-1 I-0
DEFAULT
The Onput Port Register (register 1) shows the outgoing logic levels of the pins defined as
outputs by the Configuration Register. Bit values in this register have no effect on pins defined
as inputs. In turns, reads from this register reflect the value that is in the flip-flop contolling
the output selection, not the actual pin value.
XXXXX XXX
2
C device that the Input Port Regiser will be
The Configuration Register (register 3) configures the direction of the I/O pins. If a bit in this
register is set to 1, the corresponding port pin is enabled as an input with a high-impedence
output driver. If a bit in this register is cleared to 0, the corresponding port is enabled as an
input.
Register 3 (Configuration Register)
BIT C-7 C-6 C-5 C-4 C-3 C-2 C-1 C-0
DEFAULT
11111 111
Register 1 (Onput Port Register)
BIT O-7 O-6 O-5 O-4 O-3 O-2 O-1 O-0
DEFAULT
The Polarity Inversion Register (register 2) allows polarity inversion of the pins defined as
inputs by the Configuration Register. If a bit in this register is set (written with 1), the corresponding port pin’s polarity is inverted. If a bit in this register is clear (written with a 0), the
corresponding port pin’s original polarity is retained.
BIT N-7 N-6 N-5 N-4 N-3 N-2 N-1 N-0
DEFAULT
11111 111
Register 2 (Polarity Inversion Register)
00000 000
Chapter 5 Digital I/O Programming Guide
65
www.dfi .com
Page 66

Chapter 5
Function Description
I2CWriteByte(SlaveAddr, SubAddr, Data):
Write a Byte data to a specified I2C Device.
I2CReadByte(SlaveAddr, SubAddr, *Data):
Read a Byte data from a specified I2C Device.
SetBit(*Data, Bit) :
Set Data bit n as “1”.
ClrBit(*Data, Bit) :
Set Data bit n as “0”.
GetBit(Data, Bit) :
Return the value of data bit n.
Sample Code
GPIO Configuration
#defi ne SLAVE_ADDR
#defi ne INPUT_PORT
#defi ne OUTPUT_PORT
#defi ne INVERSION_PORT
#defi ne COMFIG_PORT
GpioConfi g(int PinNum, int Mode)
{
BYTE Data;
BYTE TempPinNum = PinNum%8;
//Pin0-7 Input/Output Confi guration
I2C_ReadByte(SLAVE_ADDR, CONFIG_PORT, &Data);
if(Mode == 1){SetBit(&Data, TempPinNum);} //Input
else {ClrBit(&Data, TempPinNum);} //Output
I2C_WriteByte(SLAVE_ADDR, CONFIG_PORT, Data);
return 1;
0x42
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
GPIO Output Process
#defi ne SLAVE_ADDR
#defi ne INPUT_PORT
#defi ne OUTPUT_PORT
#defi ne INVERSION_PORT
#defi ne COMFIG_PORT
GpioOut(int PinNum, int Level)
{
BYTE Data;
BYTE TempPinNum = PinNum%8;
//Pin0-7
I2C_ReadByte(SLAVE_ADDR, OUTPUT_PORT, &Data);
if(Level == 0){ClrBit(&Data, TempPinNum);}
else {SetBit(&Data, TempPinNum);}
I2C_WriteByte(SLAVE_ADDR, OUTPUT_PORT, Data);
return 1;
0x42
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
GPIO Iutput Process
#defi ne SLAVE_ADDR
#defi ne INPUT_PORT
#defi ne OUTPUT_PORT
#defi ne INVERSION_PORT
#defi ne COMFIG_PORT
GpioIn(int PinNum, int *Status)
{
BYTE Data;
BYTE Group = PinNum/8;
BYTE TempPinNum = PinNum%8;
//Pin0-7
I2C_ReadByte(SLAVE_ADDR, INPUT_PORT, &Data);
*Status = GetBit(Data, TempPinNum);
return 1;
0x42
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
Chapter 5 Digital I/O Programming Guide
66
www.dfi .com
Page 67

Appendix A - Watchdog Sample Code
;Software programming example:
;---------------------------------------------
;(1) Enter Super IO Confi guration mode
;--------------------------------------------MOV DX,4EH
MOV AL,87H
OUT DX,AL
OUT DX,AL
;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------;(2) Confi guration Logical Device 8, register CRF0/CRF1 (WDT Control/WDT
timer)
;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------MOV DX,4EH
MOV AL,07H ;Ready to Program Logical Device
OUT DX,AL
MOV DX,4FH
MOV AL,08H ;Select Logical Device 8
OUT DX,AL
MOV DX,4EH
MOV AL, F1H ;Select watchdog timer register
OUT DX,AL
Appendix A
MOV DX,4FH
MOV AL,10H ;Set watchdog timer value
OUT DX,AL
MOV DX,4EH
MOV AL, F0H ;Select watchdog Control Register
OUT DX,AL
MOV DX,4FH
MOV AL,02H ;Set Watchdog Control Value
OUT DX,AL
;---------------------------------------------------------------;(1) Exit extended function mode
;---------------------------------------------------------------MOV DX,4EH
MOV AL,AAH
OUT DX,AL
Appendix A Watchdog Sample Code
67
www.dfi .com
Page 68

Appendix B
Appendix B - System Error Message
When the BIOS encounters an error that requires the user to correct something, either a beep
code will sound or a message will be displayed in a box in the middle of the screen and the
message, PRESS F1 TO CONTINUE, CTRL-ALT-ESC or DEL TO ENTER SETUP, will be shown in
the information box at the bottom. Enter Setup to correct the error.
Error Messages
One or more of the following messages may be displayed if the BIOS detects an error during
the POST. This list indicates the error messages for all Awards BIOSes:
CMOS BATTERY HAS FAILED
The CMOS battery is no longer functional. It should be replaced.
Hard Disk(s) fail (20)
HDD initialization error.
Hard Disk(s) fail (10)
Unable to recalibrate fixed disk.
Hard Disk(s) fail (08)
Sector Verify failed.
Keyboard is locked out - Unlock the key
The BIOS detects that the keyboard is locked. Keyboard controller is pulled low.
Important:
Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the battery manufacturer’s instructions.
CMOS CHECKSUM ERROR
Checksum of CMOS is incorrect. This can indicate that CMOS has become corrupt. This error
may have been caused by a weak battery. Check the battery and replace if necessary.
DISPLAY SWITCH IS SET INCORRECTLY
The display switch on the motherboard can be set to either monochrome or color. This indicates the switch is set to a different setting than indicated in Setup. Determine which setting
is correct, either turn off the system and change the jumper or enter Setup and change the
VIDEO selection.
FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (80)
Unable to reset floppy subsystem.
FLOPPY DISK(S) fail (40)
Floppy type mismatch.
Hard Disk(s) fail (80)
HDD reset failed.
Keyboard error or no keyboard present
Cannot initialize the keyboard. Make sure the keyboard is attached correctly and no keys are
being pressed during the boot.
Manufacturing POST loop
System will repeat POST procedure infinitely while the keyboard controller is pull low. This is
also used for the M/B burn in test at the factory.
BIOS ROM checksum error - System halted
The checksum of ROM address F0000H-FFFFFH is bad.
Memory test fail
The BIOS reports memory test fail if the memory has error(s).
Hard Disk(s) fail (40)
HDD controller diagnostics failed.
Appendix B System Error Message
68
www.dfi .com
Page 69

Appendix C - Troubleshooting Checklist
Appendix C
The picture seems to be constantly moving.
Troubleshooting Checklist
This chapter of the manual is designed to help you with problems that you may encounter
with your personal computer. To efficiently troubleshoot your system, treat each problem individually. This is to ensure an accurate diagnosis of the problem in case a problem has multiple
causes.
Some of the most common things to check when you encounter problems while using your
system are listed below.
1. The power switch of each peripheral device is turned on.
2. All cables and power cords are tightly connected.
3. The electrical outlet to which your peripheral devices are connected is working. Test the
outlet by plugging in a lamp or other electrical device.
4. The monitor is turned on.
5. The display’s brightness and contrast controls are adjusted properly.
6. All add-in boards in the expansion slots are seated securely.
7. Any add-in board you have installed is designed for your system and is set up correctly.
Monitor/Display
If the display screen remains dark after the system is turned on:
1. Make sure that the monitor’s power switch is on.
2. Check that one end of the monitor’s power cord is properly attached to the monitor and
the other end is plugged into a working AC outlet. If necessary, try another outlet.
3. Check that the video input cable is properly attached to the monitor and the system’s
display adapter.
4. Adjust the brightness of the display by turning the monitor’s brightness control knob.
1. The monitor has lost its vertical sync. Adjust the monitor’s vertical sync.
2. Move away any objects, such as another monitor or fan, that may be creating a magnetic
field around the display.
3. Make sure your video card’s output frequencies are supported by this monitor.
The screen seems to be constantly wavering.
1. If the monitor is close to another monitor, the adjacent monitor may need to be turned off.
Fluorescent lights adjacent to the monitor may also cause screen wavering.
Power Supply
When the computer is turned on, nothing happens.
1. Check that one end of the AC power cord is plugged into a live outlet and the other end
properly plugged into the back of the system.
2. Make sure that the voltage selection switch on the back panel is set for the correct type of
voltage you are using.
3. The power cord may have a “short” or “open”. Inspect the cord and install a new one if
necessary.
Floppy Drive
The computer cannot access the floppy drive.
1. The floppy diskette may not be formatted. Format the diskette and try again.
2. The diskette may be write-protected. Use a diskette that is not write-protected.
3. You may be writing to the wrong drive. Check the path statement to make sure you are
writing to the targeted drive.
4. There is not enough space left on the diskette. Use another diskette with adequate storage
space.
Appendix C Troubleshooting Checklist
69
www.dfi .com
Page 70

Appendix C
Hard Drive
Hard disk failure.
1. Make sure the correct drive type for the hard disk drive has been entered in the BIOS.
2. If the system is configured with two hard drives, make sure the bootable (first) hard drive
is configured as Master and the second hard drive is configured as Slave. The master hard
drive must have an active/bootable partition.
Excessively long formatting period.
If your hard drive takes an excessively long period of time to format, it is likely a cable connection problem. However, if your hard drive has a large capacity, it will take a longer time to
format.
Serial Port
The serial device (modem, printer) doesn’t output anything or is outputting garbled
characters.
1. Make sure that the serial device’s power is turned on and that the device is on-line.
2. Verify that the device is plugged into the correct serial port on the rear of the computer.
3. Verify that the attached serial device works by attaching it to a serial port that is working
and configured correctly. If the serial device does not work, either the cable or the serial
device has a problem. If the serial device works, the problem may be due to the onboard
I/O or the address setting.
4. Make sure the COM settings and I/O address are configured correctly.
System Board
1. Make sure the add-in card is seated securely in the expansion slot. If the add-in card is
loose, power off the system, re-install the card and power up the system.
2. Check the jumper settings to ensure that the jumpers are properly set.
3. Verify that all memory modules are seated securely into the memory sockets.
4. Make sure the memory modules are in the correct locations.
5. If the board fails to function, place the board on a flat surface and seat all socketed components. Gently press each component into the socket.
6. If you made changes to the BIOS settings, re-enter setup and load the BIOS defaults.
Keyboard
Nothing happens when a key on the keyboard was pressed.
1. Make sure the keyboard is properly connected.
2. Make sure there are no objects resting on the keyboard and that no keys are pressed during the booting process.
Appendix C Troubleshooting Checklist
70
www.dfi .com
 Loading...
Loading...