DFI G586IPV, G586IPV/E User Manual

G586IPV
Rev. C
System Board
User’s Manual
+
- 31061108 -

FCC Statement on Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However,
there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio TV technician for help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with the
emission limits.
The manufacturer makes no warranties with respect to this documentation and disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability, quality, or
fitness for any particular purpose. The information in this document is
subject to change without notice. The manufacturer reserves the right to
make revisions to this publication and to make changes to any and/or
all parts of its content, at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such changes. Further, the manufacturer assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction............................................................ 5
Features and Specifications .................................................. 6
Package Checklist .............................................................. 8
Chapter 2: Hardware Installation ............................................... 9
Preparing the Area.............................................................. 9
Handling the System Board .................................................. 9
Installing the System Board .................................................10
Board Layout ....................................................................12
System Memory ................................................................13
DIMM ........................................................................13
SIMM ........................................................................14
Cache Memory .................................................................16
Installing the Cache Module ...........................................16
CPU Installation ................................................................17
Jumper Settings for Intel CPUs........................................18
Jumper Settings for Cyrix 6x86 CPUs ...............................19
Jumper Settings for AMD-K5 CPUs ..................................20
Installing Upgrade CPUs................................................21
Installing A Fan/Heatsink for Cyrix CPUs ...........................23
Jumper Settings for CMOS Clear ..........................................24
Jumper Settings for Display Type...........................................24
Built-in Ports.....................................................................25
Serial Ports.................................................................25
PS/2 Mouse Port..........................................................25
Parallel Port ................................................................26
Floppy Disk Drive Controller ...........................................26
IDE Hard Disk Interface .................................................27
Universal Serial Bus Connectors......................................29
Installing Expansion Cards...................................................29
Chapter 3: Software Installation ...............................................30
Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility ...........................................30
Standard CMOS Setup..................................................31
BIOS Features Setup ....................................................35
Chipset Features Setup .................................................39
Power Management Setup .............................................40
PNP/PCI Configuration Setup..........................................42

Load BIOS Defaults ......................................................44
Load Setup Defaults .....................................................44
Integrated Peripherials...................................................45
Supervisor Password ....................................................47
User Password ............................................................48
IDE HDD Auto Detection................................................48
HDD Low Level Format .................................................51
Save & Exit Setup ........................................................52
Exit Without Saving.......................................................52
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) ....................................52
System Error Report ..........................................................55
Driver Installation...............................................................57
Chapter 4: Troubleshooting Checklist .............................................58
Appendix A: Types of Modules ......................................................62
Appendix B: Memory and I/O Maps................................................63
Appendix C: Connectors ..............................................................65
Appendix D: Row Address Strobe of DRAM and SDRAM...................68
4

Chapter 1
Introduction
The G586IPV, equipped with a 321-pin Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) CPU
socket, is Pentium processor-class system board supporting Intel Pentium CPUs running at 75MHz, 90MHz, 100MHz, 120MHz, 133MHz,
150MHz, 166MHz and 200MHz frequencies. The G586IPV also supports Cyrix 6x86 P120+/P133+/P150+/P166+ and AMD-K5 PR75/PR90/
PR100/PR120/PR133 CPUs.
The G586IPV can support 8MB to 128MB of system memory. It is
equipped with 4 SIMM sockets using EDO or fast page mode x32
DRAM. Your system board may also come with a DIMM socket that
uses x64 EDO, fast page mode or SDRAM. The G586IPV also supports
256KB or 512KB pipeline burst SRAM and provides easy cache upgrades using a 256KB cache module.
The G586IPV design is based on the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) local bus and Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) standards. It is equipped with 4 dedicated PCI slots and 3 dedicated 16-bit
ISA slots.
The G586IPV board has two bus master PCI IDE connectors. Bus mastering reduces CPU use during disk transfer. This system board is also
equipped with two NS16C550A-compatible serial ports, an SPP/ECP/
EPP parallel port, a floppy disk drive controller, one PS/2 mouse port,
one PS/2 or AT keyboard connector, two connectors for external USB
ports and one IrDA header for wireless connectivity between your computer and peripheral devices.
5

Features and Specifications
Processor
• Intel Pentium 75/90/100/120/133/150/166/200MHz
• Future Pentium OverDrive processor
• Cyrix 6x86 P120+/P133+/P150+/P166+
• AMD-K5 PR75/PR90/PR100/PR120/PR133
Chipset
• Intel 82430VX PCIset
Cache Memory
• 256KB or 512KB pipeline burst, direct map write-back cache
installed on the system board
- Onboard 256KB: upgradeable with a 256KB cache module for a
maximum of 512KB cache
- Onboard 512KB: maximum cache memory (no cache module slot)
System Memory
• 8MB to 128MB onboard memory
• One 168-pin DIMM socket using x64 EDO, fast page mode, or
SDRAM, 60ns or 70ns, 3.3V (The G586IPV is also available without
this socket.)
• Four 72-pin SIMM sockets using EDO or fast page mode x32
DRAM, 60ns or 70ns, 5V
BIOS
• Award BIOS, Windows 95 Plug and Play compatible
• Flash EPROM for easy BIOS upgrades
• Supports DMI function
Energy Efficient Design
• System power management supported
• CPU stopped clock control
• Hardware supports SMI green mode
• Microsoft/Intel APM compliant
• External power management switch supported
6

PCI IDE Interface
• PIO Mode 3 and Mode 4 Enhanced IDE (data transfer rate up to
16.6MB/sec.)
• DMA Mode 2 Bus Master IDE (data transfer rate up to 22.2MB/sec.)
• Bus mastering reduces CPU utilization during disk transfer
• ATAPI IDE CD-ROM supported
Integrated I/O
• Super I/O controller
• Two NS16C550A-compatible high speed UARTs
• One SPP/ECP/EPP parallel port
• Supports 360KB, 720KB, 1.2MB, 1.44MB, and 2.88MB floppy drives
CPU Socket
• 321-pin ZIF socket (Intel Socket 7)
• Supports future multimedia CPUs
Connectors
• 2 connectors for external USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports
• 1 connector for IrDA interface
• 2 serial ports
• 1 parallel port
• 2 IDE connectors
• 1 floppy connector
• 1 PS/2 mouse port
• 1 PS/2 or AT keyboard connector
Expansion Slots
• 4 dedicated PCI slots
• 3 dedicated 16-bit ISA slots
PCB
• 4 layers, Baby AT form factor
• 25cm (9.84") x 22cm (8.66")
7

Package Checklist
The G586IPV package contains the following items:
• The G586IPV system board
• The G586IPV user’s manual
• Serial, mouse and printer port cables
Option 1:
- One card-edge bracket with a 9-pin and 25-pin serial port cables
- One card-edge bracket with a 25-pin printer port cable and a PS/2
mouse port cable
Option 2:
- One card-edge bracket with two 9-pin serial port cables and a
PS/2 mouse port cable
- One 25-pin printer port cable for chassis mounting
• One 40-pin IDE hard disk cable
• One 34-pin floppy disk drive cable
• One IDE driver diskette
• Five jumpers
• One card-edge bracket with two USB port cables (optional)
• Cache module (optional)
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your
dealer or sales representative for assistance.
8

Chapter 2
Hardware Installation
This chapter summarizes the steps to install the G586IPV system board
into your system unit. It also includes a description of the area in which
you must work and directions for memory installation. Before installing
the system board, obtain the memory you plan to install. Refer to the
System Memory section for the number and type of memory modules
needed for the amount of memory you require.
Preparing the Area
Before unpacking the system board, make sure the location you have
selected is relatively free of dust and static electricity. Excessive exposure to dust, static electricity, direct sunlight, excessive humidity, extreme cold, and water can damage the operational capabilities of your
system board. Avoid placing the unit on surfaces such as carpeted
floors. These areas also attract static electricity which can damage
some circuits on your system board.
Make sure the power source has a properly grounded, three-pronged
socket. It is essential that the power connection be properly grounded
for correct functioning of your system board. For further protection, we
recommend that you use a surge suppressor. This will protect the system board from damage that may result from a power surge on the
electrical line.
Move items that generate magnetic fields away from your system board
since magnetic fields can also damage your system board. Once you
have selected the ideal location, unpack the G586IPV system board
carefully.
Handling the System Board
It is quite easy to inadvertently damage your system board even before
installing it in your system unit. Static electrical discharge can damage
computer components without causing any signs of physical damage.
You must take extra care in handling the system board to ensure
against electrostatic build-up.
9

Static Electricity Precautions
1. To prevent electrostatic build-up, leave the board in its anti-static
bag until you are ready to install it.
2. Wear an antistatic wrist strap.
3. Do all preparation work on a static-free surface with the system
board components facing up.
4. Hold the system board only by its edges. Be careful not to touch
any of the components, contacts or connections, especially gold
contacts, on the board.
5. Avoid touching the pins or contacts on all modules and connectors.
Hold modules and connectors by their ends.
Warning:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your processor, disk drives,
add-in boards, and other components. Perform the upgrade instruction
procedures described at an ESD workstation only. If such a station is
not available, you can provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the system chassis.
If a wrist strap is unavailable, establish and maintain contact with the
system chassis throughout any procedures requiring ESD protection.
Installing the System Board
If you are installing the G586IPV system board, the following outlines
the basic installation steps. Before installing the system board into your
system unit, you should prepare the tools you will need.
You will need:
• One medium size, flat-bladed screwdriver
• One medium Phillips screwdriver
• One needle-nosed pliers
• One small nutdriver
1. Unlock your system unit. Turn off the power and disconnect all
power cords and cables.
10

2. Remove the system unit cover. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions if necessary.
3. Detach all connectors from the old system board and remove expansion cards seated in any expansion slots.
4. Loosen the screws holding the original system board and remove
the board from the system. Save the screws.
5. Remove the G586IPV from its original packing box. Be careful to
avoid touching all connectors and pins on the board. Please refer to
the handling instructions on pages 9-10 for proper handling techniques.
6. Insert the memory modules into the memory banks on the
G586IPV. The quantity and location of the memory modules depends on the memory configuration and type of modules you intend
to use.
7. Insert the cache module, if any, into the cache module slot on the
G586IPV. Refer to the Cache Memory section for upgrading your
cache memory.
8. Install the CPU. Be sure pin 1 of the CPU is aligned with pin 1 of
the socket.
9. Set the corresponding jumpers.
10. Install the prepared G586IPV system board into the case and replace the screws.
11. Reinstall all cards and connectors and replace the system unit
cover. Reconnect all power cords and cables.
11
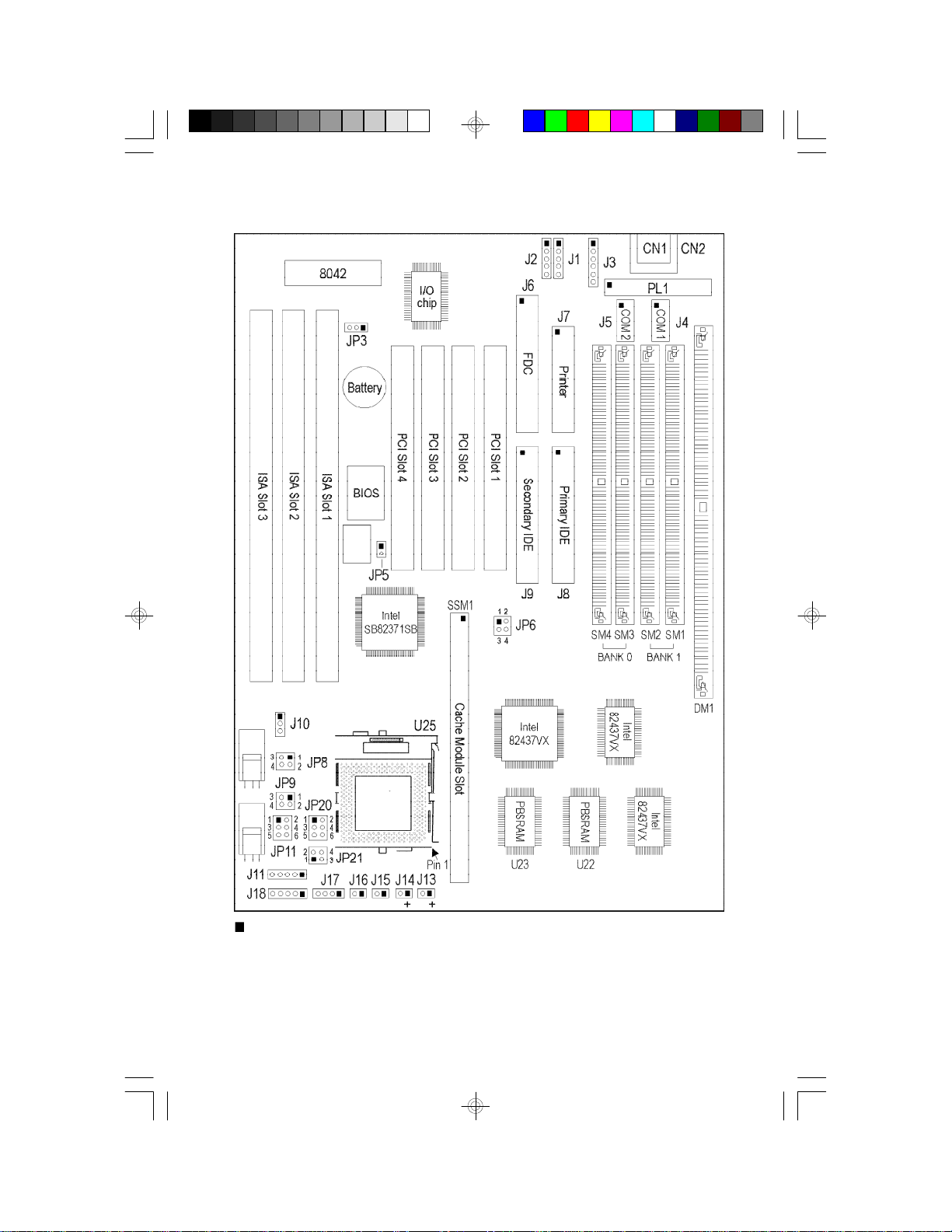
Board Layout
square denotes pin 1
PBSRAM = Pipeline Burst SRAM
12
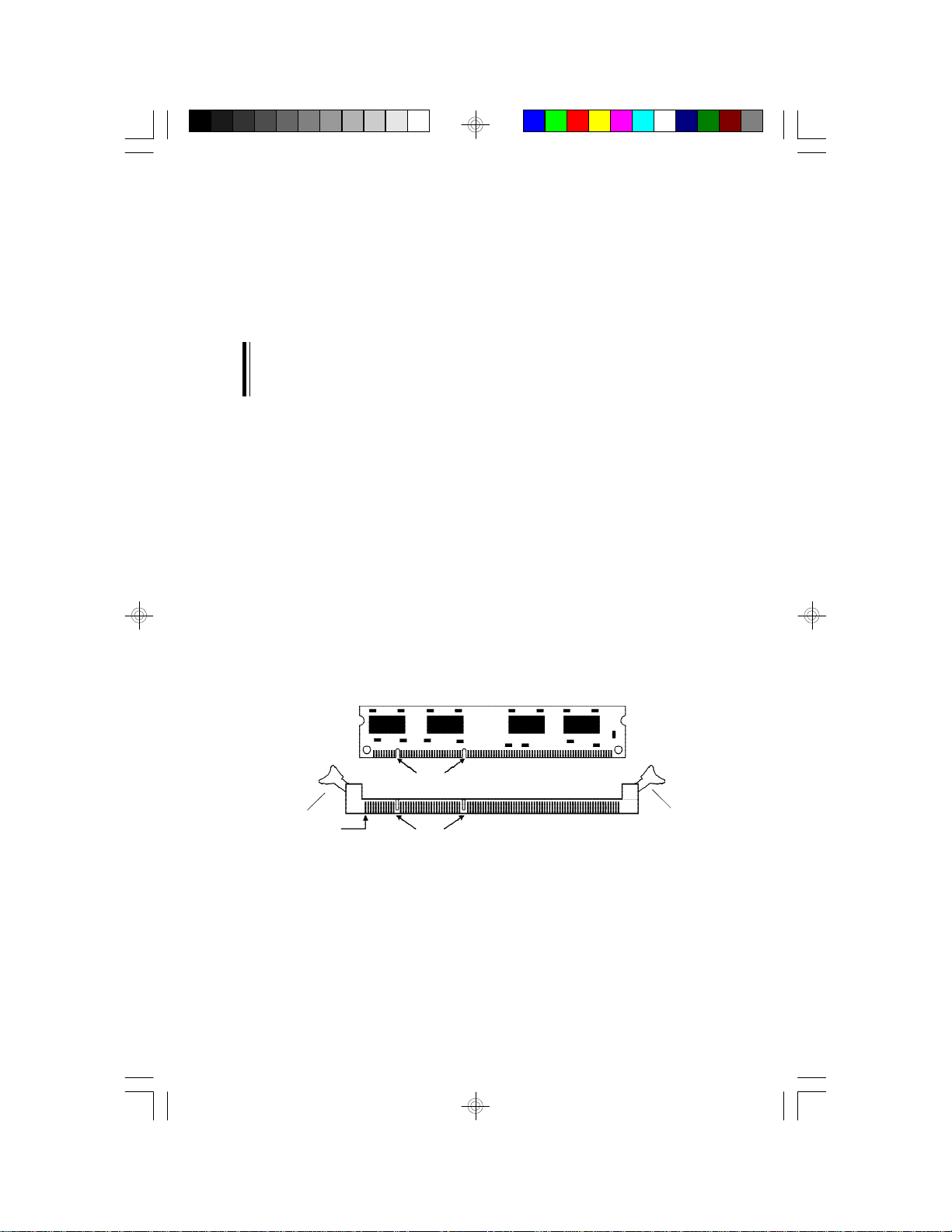
System Memory
The G586IPV system board supports two kinds of memory modules:
DIMM and SIMM. DIMM, which uses SDRAM, performs better than
SIMM, which uses DRAM. Refer to page 12 for the locations of the DIM
and SIM sockets.
Note:
If a DIM module is installed in the DIMM socket, you can install SIM
modules in Bank 0 only. Do not install any SIM modules in Bank 1.
DIMM
If your system board is not equipped with the DIMM socket, please
ignore this section.
The 168-pin DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) socket uses x64 EDO,
FPM and SDRAM. The G586IPV system board can support 8MB to
16MB memory using 1MBx64 or 2MBx64 DIMM.
Installing the DIM Module
A DIM module simply snaps into a socket on the system board. Pin 1 of
the DIM module must correspond with Pin 1 of the socket.
Notch
Tab
Pin 1
Key
Tab
1. Pull the “tabs” which are at the ends of the socket to the side.
2. Position the DIMM above the socket with the “notches” in the module aligned with the “keys” on the socket.
3. Seat the module vertically into the socket. Make sure it is completely seated. The tabs will hold the DIMM in place.
13
SIMM
The SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module) sockets are divided into two
banks on the system board, Bank 0 and Bank 1. Each bank consists of
2 SIMM sockets.
You will need either 2 or 4 pieces of SIM modules, depending on the
amount of memory you intend to install. The system board will not work
if you install 1 or 3 pieces. Make sure you insert the same type of
SIMMs in one bank. You can install SIMMs in either of the banks, Bank
0 or Bank 1, but you must populate one bank first before going to the
next bank.
The G586IPV system board can support 8MB to 128MB of memory using 1MBx32, 2MBx32, 4MBx32, or 8MBx32 72-pin SIMMs. The table
below shows the supported SIM modules and their corresponding
memory sizes.
SIMMs
1MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
Memory Size
4MB
8MB
16MB
32MB
The table below summarizes the bank locations and modules needed
for the corresponding memory sizes.
Memory Size
8MB
8MB
16MB
16MB
16MB
SIMM3
1MBx32
—
2MBx32
—
1MBx32
Bank 0
SIMM4
1MBx32
—
2MBx32
—
1MBx32
1MBx32
2MBx32
1MBx32
SIMM1
—
—
Bank 1
SIMM2
—
1MBx32
—
2MBx32
1MBx32
14
Bank 0
Bank 1
Memory Size
24MB
24MB
32MB
32MB
40MB
40MB
48MB
48MB
64MB
64MB
64MB
72MB
72MB
80MB
80MB
96MB
96MB
128MB
SIMM3
1MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
2MBx32
1MBx32
4MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
—
4MBx32
1MBx32
8MBx32
2MBx32
8MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
8MBx32
SIMM4
1MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
2MBx32
1MBx32
4MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
—
4MBx32
1MBx32
8MBx32
2MBx32
8MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
8MBx32
SIMM1
2MBx32
1MBx32
—
2MBx32
4MBx32
1MBx32
4MBx32
2MBx32
—
8MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
1MBx32
8MBx32
2MBx32
8MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
SIMM2
2MBx32
1MBx32
—
2MBx32
4MBx32
1MBx32
4MBx32
2MBx32
—
8MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
1MBx32
8MBx32
2MBx32
8MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
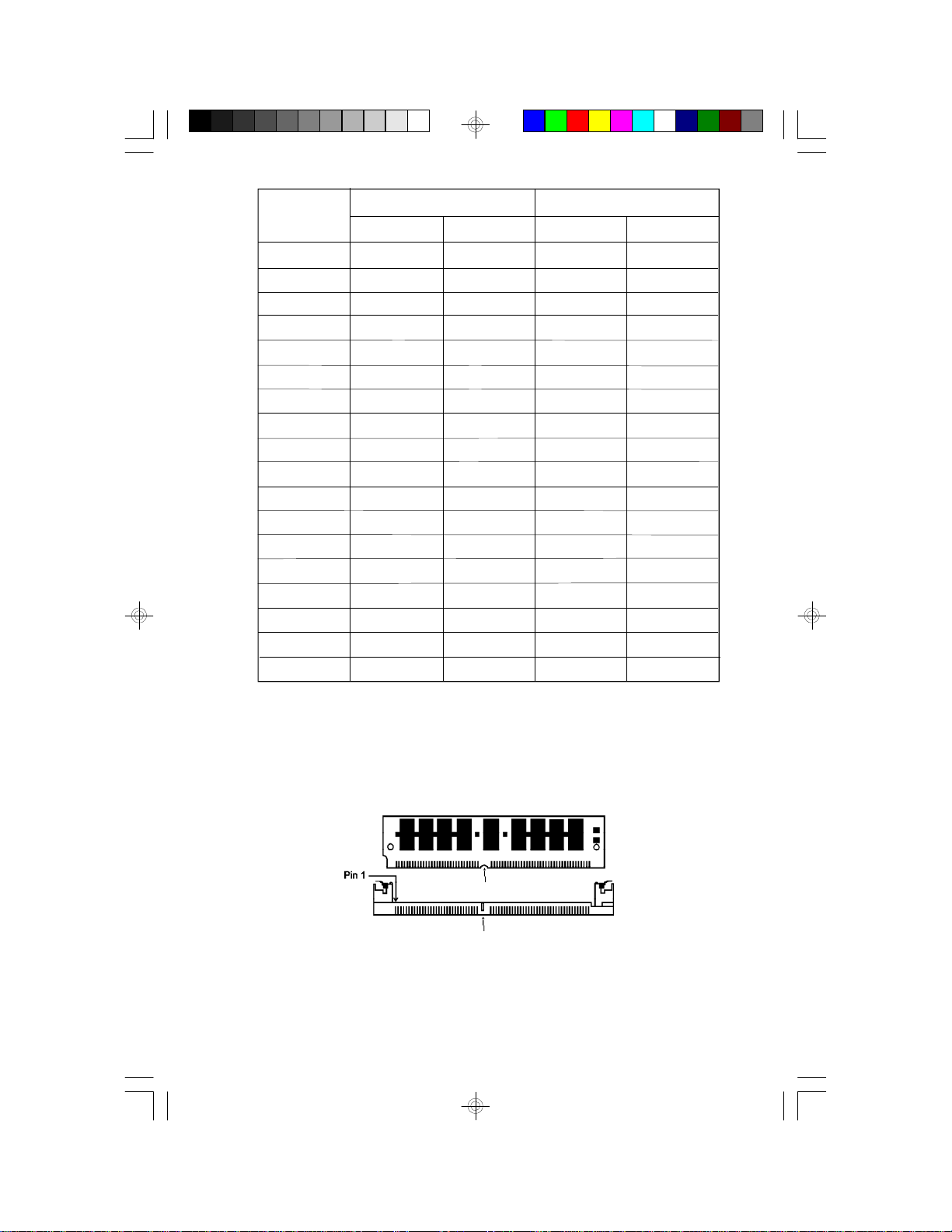
Installing a SIM Module
A SIM module simply snaps into a socket on the system board. Pin 1 of
the SIM module must correspond with Pin 1 of the socket.
notch
key
15

1. Position the SIMM above the socket with the “notch” in the module
aligned with the “key” on the socket.
2. Seat the module at a 45° angle into the bank. Make sure it is completely seated. Tilt the module upright until it locks in place in the
socket.
Cache Memory
The G586IPV system board can support 256KB or 512KB pipeline
burst, direct map write-back cache SRAM. Your system board may
come with 256KB or 512KB cache mounted at locations U22 and U23
of the system board.
If your system board is mounted with 256KB cache, you may upgrade
your cache memory to 512KB by installing a 256KB cache module in
the 160-pin cache module slot (SSM1). Refer to page 12 for the locations of the SRAMs and cache module slot. If your system board is
mounted with 512KB cache, which is the maximum cache memory supported by the system board, the cache module slot will not be installed
on the system board.
Warning:
We highly recommend that you use the T2BSM32-256 or T3BSM256
cache module. If you are using a cache module other than the ones
recommended above, make sure your cache module meets the Intel
COAST 2.x or 3.x specification. Severe damage might occur on the
cache module or system board if you insert modules other than those
specified above.
Installing the Cache Module
Locate the 160-pin cache module slot on the system board (SSM1).
See page 12 for the location. Position the cache module above the slot.
Make sure pin 1 of the cache module is aligned with pin 1 of the slot.
Carefully slide the module into the slot. Press firmly on the top of it to
seat it properly.
16
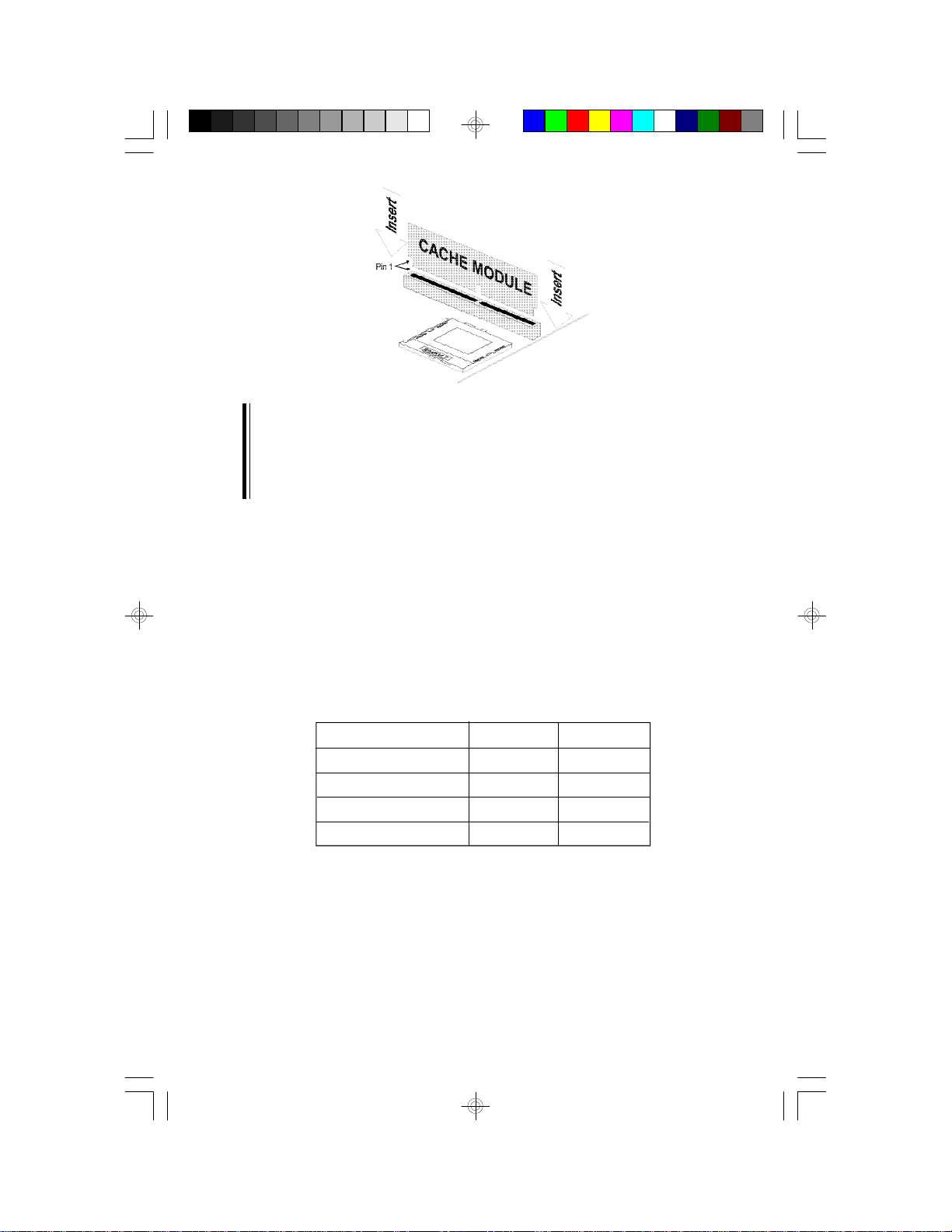
Note:
With the cache module installed in the cache module slot, the components on the solder side of the add-in card in PCI Slot 3 and the components on the component side of the add-in card in PCI Slot 2 must
not protrude more than 5mm.
CPU Installation
The G586IPV allows for easy installation of CPUs. Make sure all jumpers
are set correctly before applying power or you may damage the CPU or
system board. Please see the jumper settings on the following pages. Use
the needle-nosed pliers to move the jumpers if necessary. The table below
shows the External Bus Clock of the CPUs supported by the system board
and their corresponding PCI Clock and Bus Clock.
External Bus Clock
50MHz
55MHz
60MHz
66MHz
PCI CLK
25MHz
27.5MHz
30MHz
33MHz
Bus CLK
8.333MHz
9.1666MHz
7.5MHz
8.25MHz
17

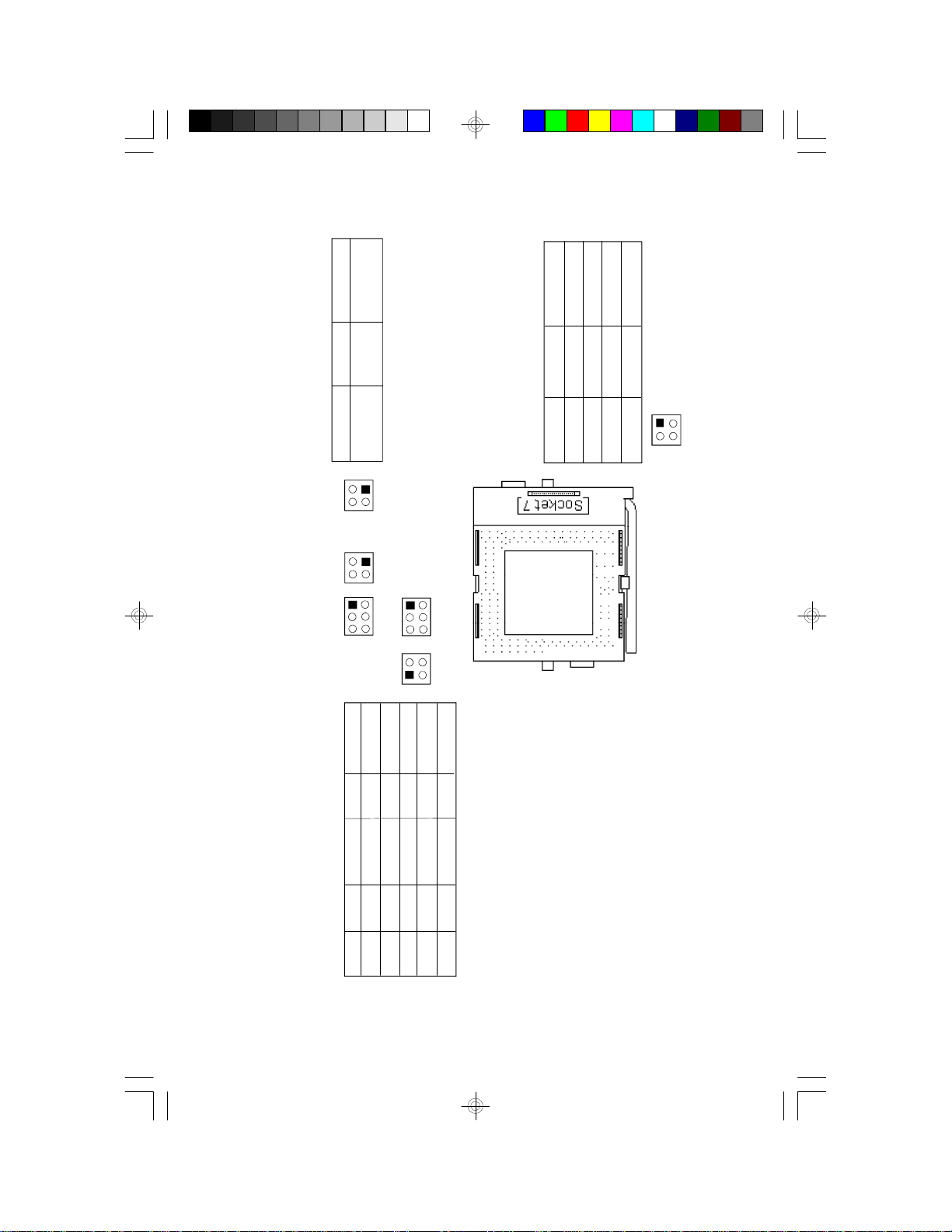
Jumper Settings for Intel CPUs
JP8
Freq. Ratio
Intel CPUs
JP11
1-2 Off, 3-4 Off
1.5x2x2.5x
75/90/100MHz
3
JP8
4
3
JP9
4
1
3
5
JP6
1-2 On, 3-4 Off
1-2 Off, 3-4 On
1-2 On, 3-4 Off
1-2 Off, 3-4 On
1-2 On, 3-4 On
3x
120/133MHz
150/166MHz
200MHz
1
2
1
2
1
4
3
6 2
4
5
2
1
JP20
6 2
4
JP21
3
1-2 On, 3-4 On
50MHz
60MHz
66MHz
Ext. Bus Clk
2
1
Intel CPUs
75MHz
90/120/150MHz
100/133/166/
200MHz
JP6
3
4
18
JP21
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 On
1-2, 3-4 On
JP20
5-6 On
3-4 On
1-2 On
3-4 On
3-4 On
JP11
1-3, 2-4 On
1-3, 2-4 On
1-3, 2-4 On
3-5, 4-6 On
3-5, 4-6 On
JP9
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
3-4 On
2.5V
2.8V
2.9V
3.3V*
Voltage
3.5V
* Default
Warning:
The default setting of JP9, JP11, JP20 and JP21 is
3.3V. If the voltage of your CPU is not 3.3V, make
sure you set JP9, JP11, JP20 and JP21 according to
the voltage of your CPU, otherwise, your system will
hang.
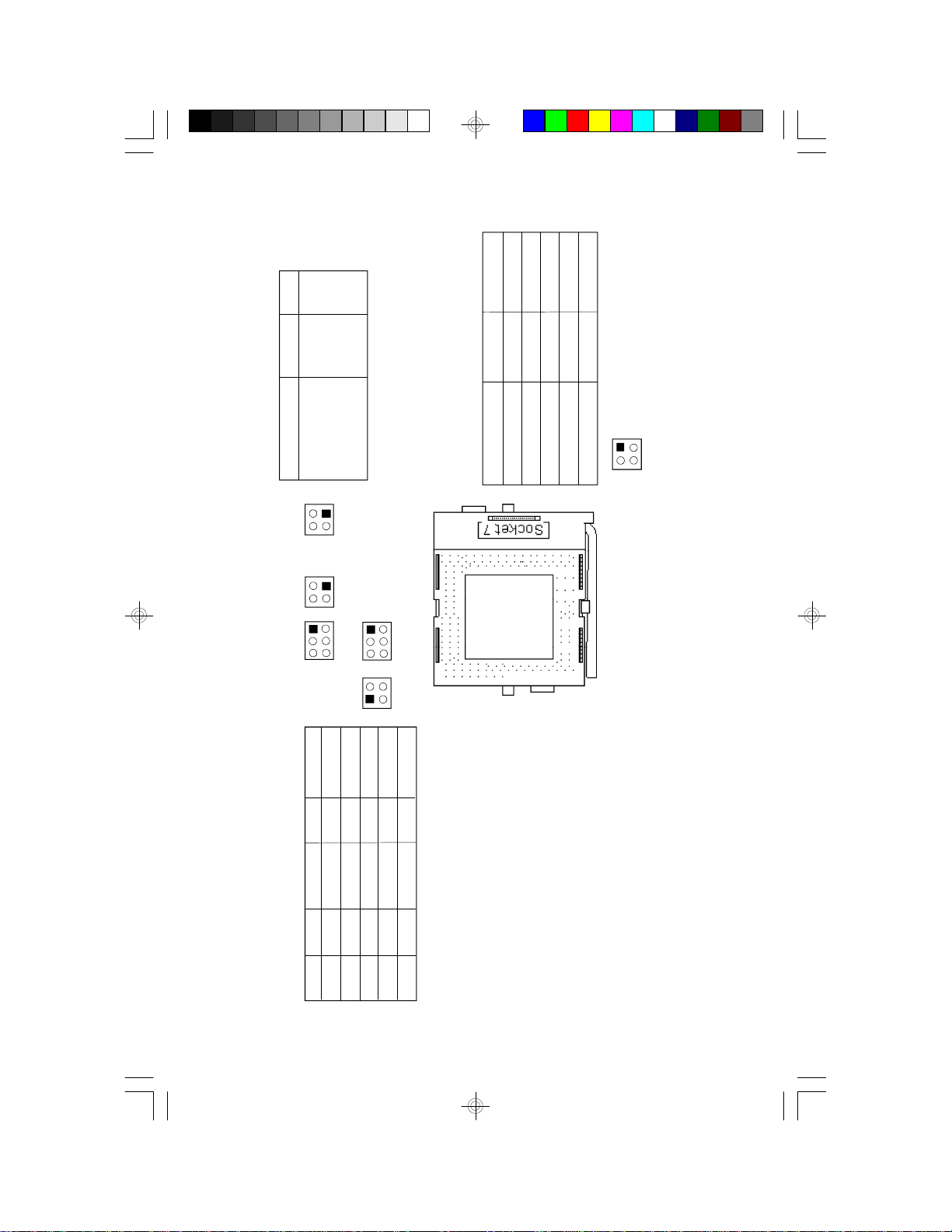
Jumper Settings for Cyrix 6x86 CPUs
JP8
1-2 On, 3-4 Off
JP6
1-2 Off, 3-4 Off
1-2 On, 3-4 Off
1-2 On, 3-4 On
1-2 Off, 3-4 On
2x
50MHz
55MHz
60MHz
Freq. Ratio
Cyrix CPUs
P120+/P133+/
P150+/P166+
1
3
JP8
2
4
1
3
JP9
2
4
1
3
5
JP11
1
4
3
6 2
4
5
2
1
JP20
6 2
4
JP21
3
Ext. Bus Clk
P120+
Cyrix CPUs
66MHz
2
1
JP6
3
P133+
P150+
4
P166+
JP21
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 On
1-2, 3-4 On
JP20
5-6 On
3-4 On
1-2 On
3-4 On
3-4 On
JP11
1-3, 2-4 On
1-3, 2-4 On
1-3, 2-4 On
3-5, 4-6 On
3-5, 4-6 On
JP9
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
3-4 On
2.5V
2.8V
2.9V
3.3V*
Voltage
3.5V
* Default
Warning:
The default setting of JP9, JP11, JP20 and JP21 is
3.3V. If the voltage of your CPU is not 3.3V, make
sure you set JP9, JP11, JP20 and JP21 according to
the voltage of your CPU, otherwise, your system will
hang.
19
Jumper Settings for AMD-K5 CPUs
JP8
3-4 Off
1-2 Off,
JP6
1-2 On, 3-4 On
1-2 On, 3-4 Off
1-2 Off, 3-4 On
1-2 On, 3-4 Off
1-2 Off, 3-4 On
1.5x
Freq. Ratio
PR75/75MHz
PR90/90MHz
PR100/100MHz
PR120/90MHz
P-Rating/Core MHz
3
JP8
4
3
JP9
4
1
3
5
JP11
PR133/100MHz
1
2
1
2
1
4
35
6 2
4
JP20
6 2
2
4
JP21
3
1
50MHz
60MHz
66MHz
60MHz
66MHz
Ext. Bus Clk
2
1
PR75/75MHz
PR90/90MHz
PR100/100MHz
PR120/90MHz
P-Rating/Core MHz
PR133/100MHz
JP6
3
4
JP21
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 Off
1-2, 3-4 On
1-2, 3-4 On
20
JP20
5-6 On
3-4 On
1-2 On
3-4 On
3-4 On
JP11
1-3, 2-4 On
1-3, 2-4 On
1-3, 2-4 On
3-5, 4-6 On
3-5, 4-6 On
JP9
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
1-2 On
3-4 On
2.5V
2.8V
2.9V
3.3V*
Voltage
3.5V
* Default
Warning:
The default setting of JP9, JP11, JP20 and JP21 is
3.3V. If the voltage of your CPU is not 3.3V, make
sure you set JP9, JP11, JP20 and JP21 according to
the voltage of your CPU, otherwise, your system will
hang.
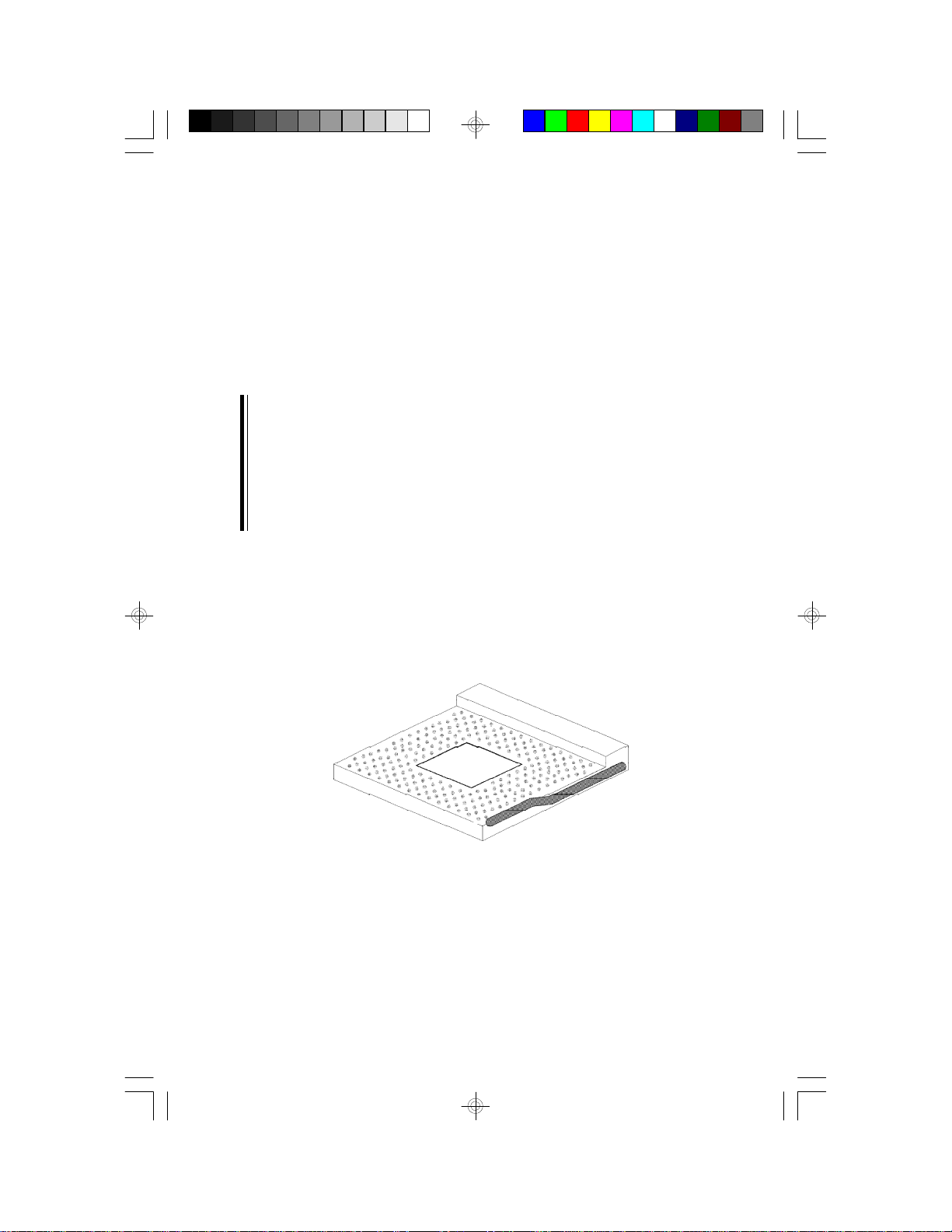
Installing Upgrade CPUs
The G586IPV is equipped with a 321-pin Zero Insertion Force (ZIF)
socket at location U25 of the system board. Refer to page 12 for the
location of the ZIF socket. This socket is designed for easy removal of
an old CPU and easy insertion of an upgrade CPU. The ZIF socket
allows you to carefully place the new CPU into its position. If you need
to apply excessive force to insert the CPU, you are not installing the
CPU correctly.
Warning:
Open the socket only if you are actually installing a CPU. The warranty
on the original CPU will be voided if the S/N seal is broken. Before
proceeding with the upgrade, take note of the following. The microprocessor and heatsink may be hot if the system has been running. To
avoid the possibility of a burn, power the system off and let the processor and heatsink cool for 20 minutes.
The 321-pin ZIF socket consists of five rows of pin holes on each side.
To prevent improper CPU installation, the ZIF socket has a Plug/Keying
mechanism. Several holes in the socket are plugged so that the CPU
will go in only one way. If you cannot easily insert the CPU, verify that
pin 1 of the CPU is aligned with pin 1 of the socket.
Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) Socket
To install an upgrade CPU, do the following:
1. Make sure the handle on the side of the ZIF socket is up. To raise
the handle, push it down, slightly pull it out to the side, then raise it
as far as it will go. It may be necessary to initially apply a small
21
 Loading...
Loading...