Page 1

G586IPV
G586IPVF
Rev. A+
System Board
User's Manual
- D31060430 -
Page 2

FCC Statement on Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However,
there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio TV technician for help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with the
emission limits.
The manufacturer makes no warranties with respect to this documentation and disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability, quality, or
fitness for any particular purpose. The information in this document is
subject to change without notice. The manufacturer reserves the right to
make revisions to this publication and to make changes to any and/or
all parts of its content, at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such changes. Further, the manufacturer assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction............................................................ 5
Features and Specifications .................................................. 6
Package Checklist .............................................................. 8
Chapter 2: Hardware Installation ............................................... 9
Preparing the Area.............................................................. 9
Handling the System Board .................................................. 9
Installing the System Board .................................................10
Board Layout ....................................................................12
System Memory ................................................................14
DIMM ........................................................................14
SIMM ........................................................................15
Jumper settings for DIMM and SIMM ................................16
Cache Memory .................................................................17
Installing the Cache Module ...........................................18
CPU Installation ................................................................19
Jumper Settings for CPUs ..............................................19
Installing Upgrade CPUs................................................22
Installing A Fan/Heatsink for Cyrix CPUs ...........................24
Jumper Settings for Display Type...........................................26
Built-in Ports.....................................................................26
Serial Ports.................................................................27
PS/2 Mouse Port..........................................................28
Parallel Port ................................................................28
Floppy Disk Drive Controller ...........................................28
IDE Hard Disk Interface .................................................29
Installing Expansion Cards...................................................31
Chapter 3: Software Installation ...............................................32
Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility ...........................................32
Standard CMOS Setup..................................................33
BIOS Features Setup ....................................................35
Chipset Features Setup .................................................37
Power Management Setup .............................................38
PNP/PCI Configuration Setup..........................................38
Load BIOS Defaults ......................................................38
Load Setup Defaults .....................................................39
Integrated Peripherials...................................................39
Page 4

Supervisor Password ....................................................39
User Password ............................................................40
IDE HDD Auto Detection................................................41
HDD Low Level Detection ..............................................43
Save & Exit Setup ........................................................44
Exit Without Saving.......................................................44
System Error Report ..........................................................45
IDE Device Drivers.............................................................47
Chapter 4: Troubleshooting Checklist ............................................. 48
Appendix A: Types of Modules ......................................................49
Appendix B: Memory and I/O Maps................................................50
Appendix C: PCI I/O Pin Assignments ............................................52
Appendix D: ISA I/O Pin Assignments ............................................53
Appendix E: Connector Pin Assignments .......................................54
Appendix F: Row Address of the DRAM nad SDRAM........................61
Page 5

Chapter 1
Introduction
The G586IPV and G586IPVF, equipped with a 321-pin Zero Insertion
Force (ZIF) CPU socket, is a fast Pentium processor system board supporting Intel Pentium CPUs running at 75MHz, 90MHz, 100MHz,
120MHz, 133MHz, 150MHz, 166MHz frequencies. The G586IPV AND
G586IPVF also supports Cyrix P120+, P133+, P150+ and P166+, AMD
5K86, and future 200MHz CPUs.
The G586IPV and G586IPVF can support 8MB to 128MB of system
memory using EDO, fast page mode x32 DRAM, or fast page mode x64
SDRAM. This system board also supports pipeline burst SRAM and
SDRAM, and provides easy cache upgrades using 256KB or 512KB
cache modules.
The G586IPV and G586IPVF board has two bus master PCI IDE connectors. Bus mastering reduces CPU use during disk transfer. This system board is also equipped with two NS16C550A-compatible serial
ports, an SPP/ECP/EPP parallel port, a floppy disk drive controller, one
PS/2 mouse port and one PS/2 or AT keyboard connector.
The G586IPV and G586IPVF are similar, but they have four differences:
1. Expansion Slots: The G586IPV has 4 dedicated PCI slots and 3
dedicated 16-bit ISA slots, and the G586IPVF has 3 dedicated PCI
slots, 3 dediacted 16-bit ISA slots and 1 shared PCI/ISA slot.
2. PCB Size: The size of the G586IPV is 25cm (9.84") x 22cm (8.66"),
and that of the G586IPVF is 26cm (10.14") x 22cm (8.66")
3. Battery: The G586IPV uses the lithium battery adn the G586IPVF
uses the ODIN battery with 10 years guaranty.
4. CPU Voltage: The G586IPV supports three kinds of CPU voltages,
and the G586IPVF suooprts five kinds of CPU voltages.
Page 6

Features and Specifications
Processor
• Intel Pentium™ 75/90/100/120/133/150/166MHz
• Future Pentium™ OverDrive Processor
• Cyrix P120+/ P133+/ P150+/ P166+
• AMD 5K86 75/90MHz
• Future 200MHz CPUs
Chipset
• Intel 82430VX PCIset
Cache Memory
• Supports 0KB, 256KB or 512KB pipeline burst, direct map writeback cache
• One 160-pin cache module slot
• Two options:
- 0KB onboard: upgradeable with a 256KB or 512KB cache module
- 256KB onboard: upgradeable with a 256KB cache module for a
maximum of 512KB cache
System Memory
• 8MB to 128MB onboard memory
• One 168-pin DIMM socket using x64 EDO, fast page mode, or
SDRAM, 60ns or 70ns, 3.3V
• Four 72-pin SIMM sockets using EDO or fast page mode x32
DRAM, 60ns or 70ns, 5V
BIOS
• Award BIOS, Windows 95 Plug and Play compatible
• Flash EPROM for easy BIOS upgrades
Energy Efficient Design
• System power management supported
• CPU stopped clock control
• Hardware supports SMI green mode
• Microsoft/Intel APM 1.1 compliant
• External power management switch supported
6
Page 7

PCI IDE Interface
• PIO Mode 3 and Mode 4 Enhanced IDE (data transfer rate up to
16.6MB/sec.)
• DMA Mode 2 Bus Master IDE (data transfer rate up to 22.2MB/
sec.)
• Bus mastering reduces CPU utilization during disk transfer
• ATAPI IDE CD-ROM supported
Integrated I/O
• Winbond I/O controller
• Two NS16C550A-compatible high speed UARTS
• One SPP/ECP/EPP parallel port
• Supports 360KB, 720KB, 1.2MB, 1.44MB, and 2.88MB floppy
drives
• IrDA TX/RX header
• Supporta two universal serial bus connectors in future revision
CPU Socket
• 321-pin ZIF socket (Intel Socket 7)
• Supports future low-voltage CPUs
Connectors
• 2 serial ports
• 1 parallel port
• 2 IDE connectors
• 1 floppy connector
• 1 PS/2 mouse port
• 1 mini-DIN-6 PS/2 keyboard connector or AT keyboard connector
Expansion Slots
• 4 dedicated PCI slots (G586IPV only)
3 dedicated PCI Slots (G586IPVF only)
• 3 dedicated 16-bit ISA slots
• 1 shared PCI/ISA slot (G586IPVF only)
PCB
• 4 layers, Baby AT from factor
• 25cm (9.84") x 22cm (8.66") (G586IPV only)
26cm (10.14") x 22cm (8.66") (G586IPVF only)
7
Page 8

Package Checklist
The G586IPV and G586IPVF package contains the following items:
• The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board
• The G586IPV and G586IPVF user’s manual
• One 40-pin IDE hard disk cable
• One 34-pin floppy disk drive cable
• One 25-pin printer port cable for chassis mounting
• One card-edge bracket with serial and mouse port cables
• One set of IDE drivers
• Cache module (optional)
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your
dealer or sales representative for assistance.
8
Page 9

Chapter 2
Hardware Installation
This chapter summarizes the steps to install the G586IPV and
G586IPVF system board into your system unit. It also includes a description of the area in which you must work and directions for memory
installation. Before installing the system board, obtain the memory you
plan to install. Please refer to information on page 14 for the number
and type of SIM modules needed for the amount of memory you require.
Preparing the Area
Before unpacking the system board, make sure the location you have
selected is relatively free of dust and static electricity. Excessive exposure to dust, static electricity, direct sunlight, excessive humidity, extreme cold, and water can damage the operational capabilities of your
system board. Avoid placing the unit on surfaces such as carpeted
floors. These areas also attract static electricity which can damage
some circuits on your system board.
Make sure the power source has a properly grounded, three-pronged
socket. It is essential that the power connection be properly grounded
for correct functioning of your system board. For further protection, we
recommend that you use a surge suppressor. This will protect the system board from damage that may result from a power surge on the
electrical line.
Move items that generate magnetic fields away from your system board
since magnetic fields can also damage your system board. Once you
have selected the ideal location, unpack the G586IPV and G586IPVF
system board carefully.
Handling the System Board
It is quite easy to inadvertently damage your system board even before
installing it in your system unit. Static electrical discharge can damage
computer components without causing any signs of physical damage.
You must take extra care in handling the system board to ensure
against electrostatic build-up.
9
Page 10

Static Electricity Precautions
1. To prevent electrostatic build-up, leave the board in its anti-static
bag until you are ready to install it.
2. Wear an antistatic wrist strap.
3. Do all preparation work on a static-free surface with the system
board components facing up.
4. Hold the system board only by its edges. Be careful not to touch
any of the components, contacts or connections, especially gold
contacts, on the board.
5. Avoid touching the pins or contacts on all modules and connectors.
Hold modules and connectors by their ends.
Warning:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your processor, disk drives,
add-in boards, and other components. Perform the upgrade instruction
procedures described at an ESD workstation only. If such a station is
not available, you can provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the system chassis.
If a wrist strap is unavailable, establish and maintain contact with the
system chassis throughout any procedures requiring ESD protection.
Installing the System Board
If you are installing the G586IPV AND G586IPVF system board, the
following outlines the basic installation steps. Before installing the system board into your system unit, you should prepare the tools you will
need.
You will need:
• One medium size, flat-bladed screwdriver
• One medium Phillips screwdriver
• One needle-nosed pliers
• One small nutdriver
1. Unlock your system unit. Turn off the power and disconnect all
10
Page 11

power cords and cables.
2. Remove the system unit cover. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions if necessary.
3. Detach all connectors from the old system board and remove expansion cards seated in any expansion slots.
4. Loosen the screws holding the original system board and remove
the board from the system. Save the screws.
5. Remove the G586IPV and G586IPVF from its original packing box.
Be careful to avoid touching all connectors and pins on the board.
Please refer to the handling instructions on pages 9-10 for proper
handling techniques.
6. Insert the memory modules into the memory banks on the G586IPV
and G586IPVF. The quantity and location of the memory modules
depends on the memory configuration and type of modules you intend to use.
7. Insert the cache module, if any, into the cache module slot on the
G586IPV and G586IPVF. Refer to the Cache Memory section on
page 15 for upgrading your cache memory.
8. Install the CPU. Be sure pin 1 of the CPU is aligned with pin 1 of
the socket.
9. Set the corresponding jumpers.
10. Install the prepared G586IPV and G586IPVF system board into the
case and replace the screws.
11. Reinstall all cards and connectors and replace the system unit
cover. Reconnect all power cords and cables.
11
Page 12
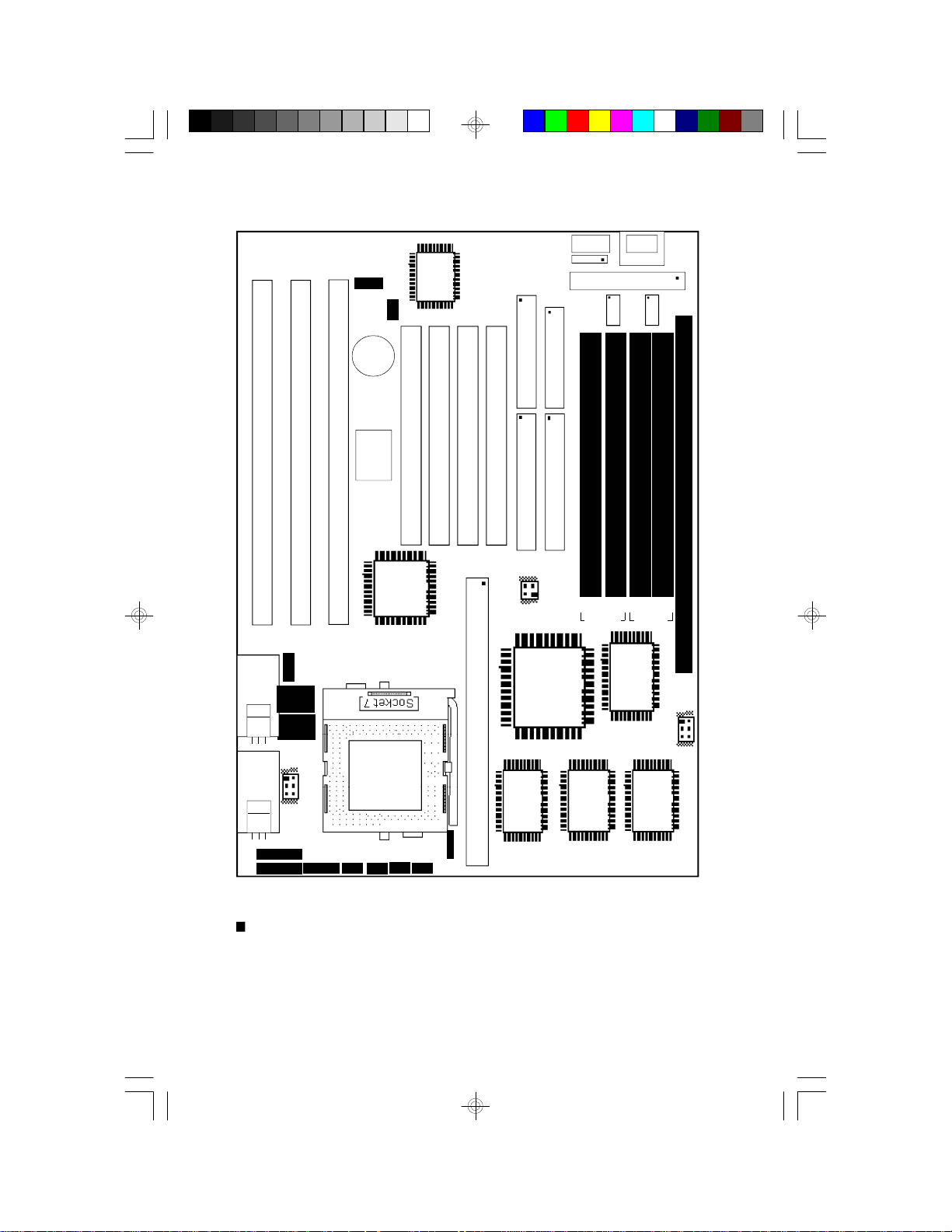
Board Layout
JP3
CN3
J3
Winbond
JP4
I/O
U3
J6:FDC
J7:Printer
CN1
CN2
PL1
J5
COM 2
DM1
J4
COM 1
Battery
PCI Slot 4
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 1
ISA Slot 1
ISA Slot 2
ISA Slot 3
BIOS
J9: Secondary IDE
J8: Primary IDE
U17
Intel
SB82371SB
J10
SSM1
JP8
Cache Module Slot
JP6
SM4
U21
Intel 82437VX
SM3
Bank 0
U20
SM2
Bank 1
Intel 82438VX
SM1
JP10
JP9
JP11
J11
J18
J16J17
J15
Pin 1 of the jumpers and connectors
PBSRAM = Pipeline Burst SRAM
12
U23
PBSRAM
32kx32
J13J14
Pin 1
The G586IPV system board
U22
U24
PBSRAM
32kx32
Intel 82438VX
Page 13

JP3
Winbond
JP4
I/O
COM 1
J4
J5
COM 2
J3
CN1
CN2
PL1
DM1
U3
J6:FDC
J7:Printer
PCI Slot 4
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 1
ISA Slot 2
ISA Slot 3
ISA Slot 4
J9: Secondary IDE
J8: Primary IDE
U17
SSM1
Intel
SB82371SB
J10
Battery
BIOS
SM4
U21
SM3
Bank 0
Intel 82437VX
SM2
Bank 1
SM1
JP8
JP9
JP11
J11
J16J17
J15
J14
J18
The G586IPVF system board
Pin 1 of the jumpers and connectors
PBSRAM = Pipeline Burst SRAM
J13
Pin 1
Cache Module Slot
U22
JP6
32kx32
U23
32kx32
U20
PBSRAM
U24
PBSRAM
JP10
Intel 82438VX
Intel 82438VX
13
Page 14
System Memory
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board supports two kinds of
memory modules: DIMM and SIMM. DIMM which uses SDRAM, performs better than SIMMs, which use DRAM.
DIMM
The DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) sockets can support 3.3V
SDRAM, FPM and EDO DRAM.
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board can support 8MB to 16MB
memory of using a 1MBx64 or 2MBx64 168-pin DIMM. The G586IPV
and G586IPVF is equipped with one DIMM socket at location DM1 on
your system board.
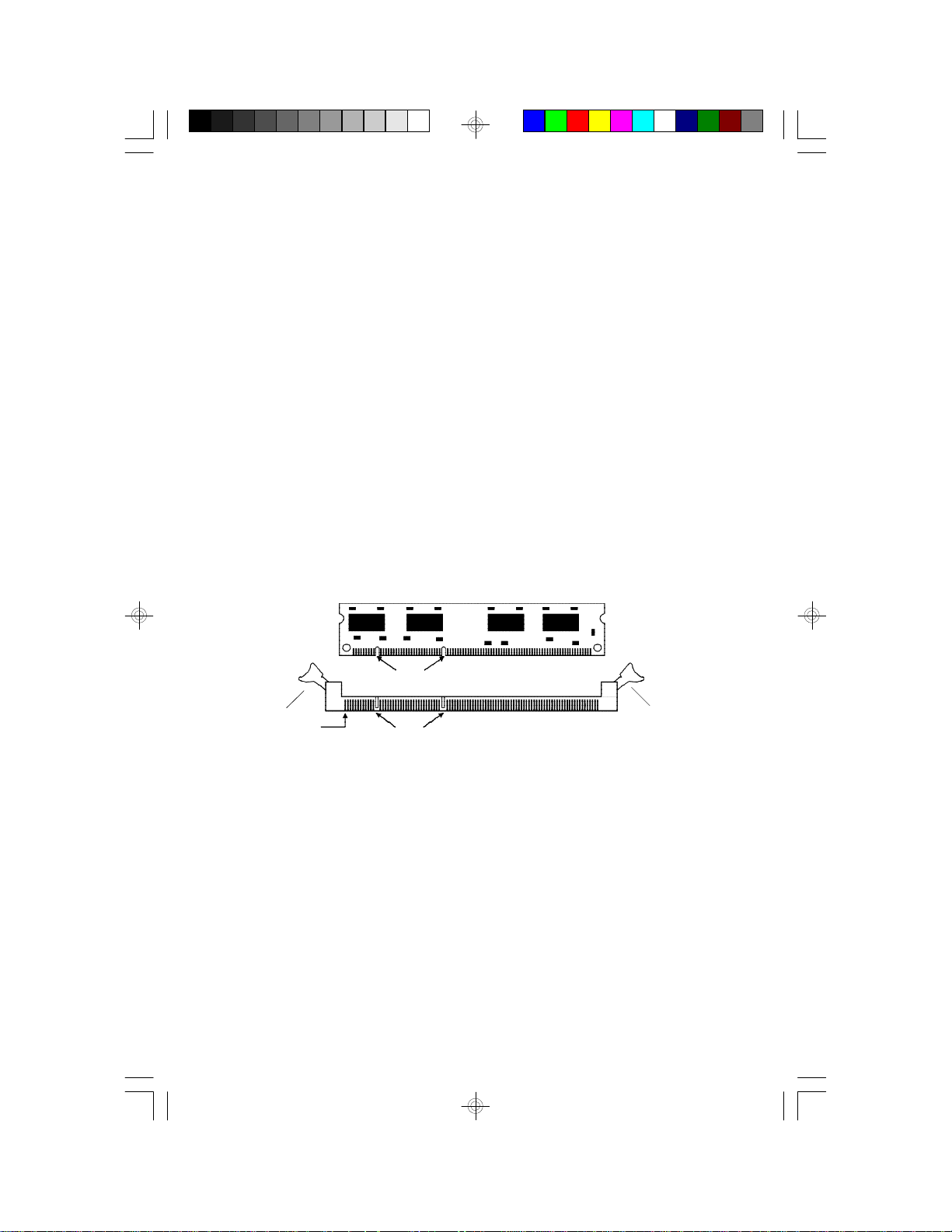
Installing the DIM Module
A DIM module simply snaps into a socket on the system board. Pin 1 of
the DIM module must correspond with Pin 1 of the socket.
Notch
Tab
Pin 1
Key
1. Pull the "tabs" which are at the ends of the socket to the side.
2. Position the DIMM above the socket with the "notches" in the module aligned with the "keys" on the socket.
3. Seat the module vertically into the socket. Make sure it is completely
seated. The tabs will hold the DIMM in place.
14
Tab
Page 15
SIMM
The SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module) sockets are divided into two
banks on the system board, Bank 0 and Bank 1. Each bank consists of
2 SIMM sockets.
You will need either 2 or 4 pieces of SIM modules, depending on the
amount of memory you intend to install. The system board will not work
if you install 1 or 3 pieces. Make sure you insert the same type of
SIMMs in one bank. You can install SIMMs in either of the banks, Bank
0 or Bank 1, but you must populate a bank first before going to the next
bank.
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board can support 8MB to 128MB
of memory using 1MBx32, 2MBx32, 4MBx32, or 8MBx32 72-pin SIMMs.
The table below shows the supported SIM modules and their corresponding memory sizes.
SIMMs
1MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
Memory Size
4MB
8MB
16MB
32MB
Examples:
If you are installing 8MB of memory, you must insert two 1MBx32
SIMMs in Bank 0 or Bank 1. Inserting one 2MBx32 module will not
work.
If you are installing 24MB of memory, you must insert two 1MBx32
SIMMs in Bank 0 and two 2MBx32 SIMMs in Bank 1. You may also
install it vice versa by inserting two 1MBx32 SIMMs in Bank 1 and two
2MBx32 SIMMs in Bank 0.
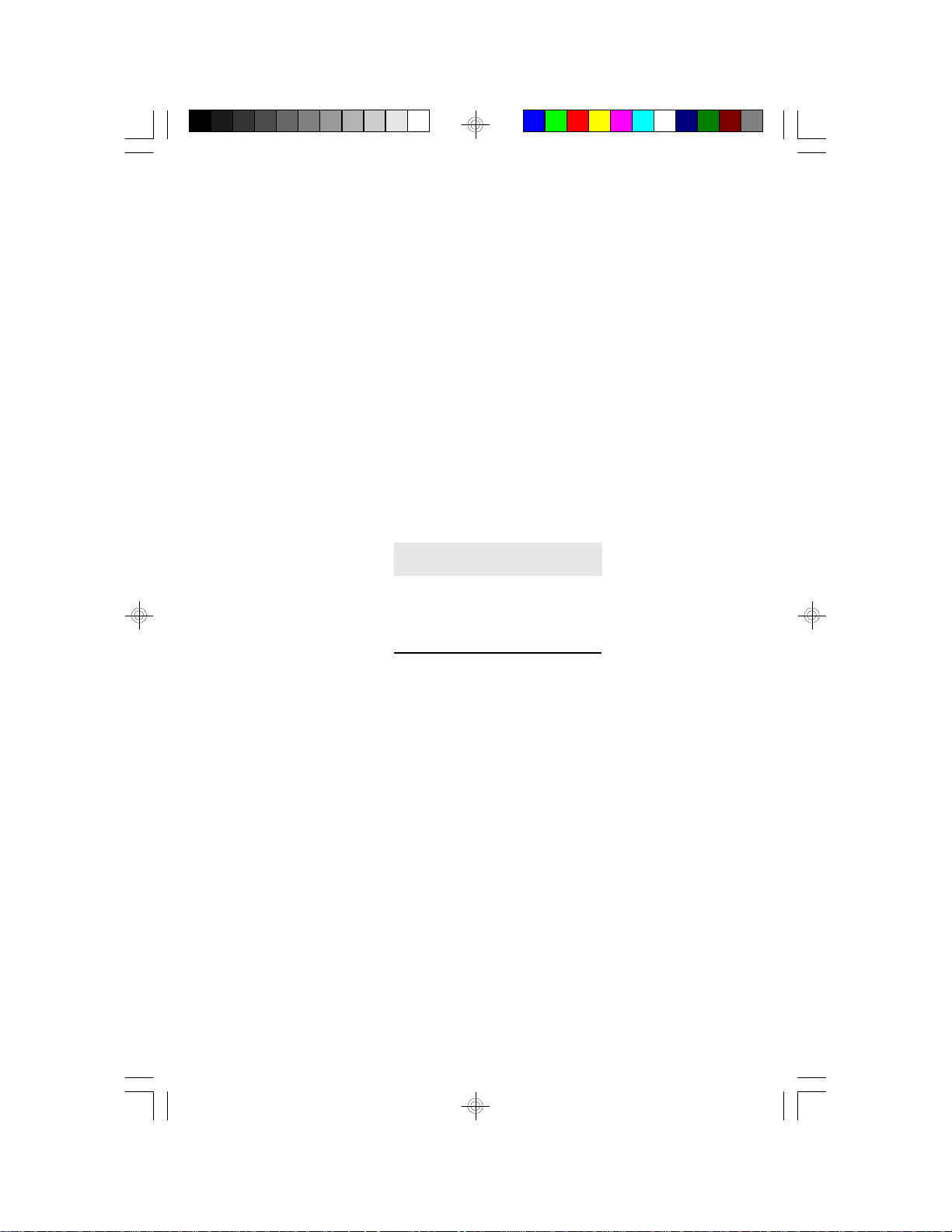
Installing a SIM Module
A SIM module simply snaps into a socket on the system board. Pin 1 of
the SIM module must correspond with Pin 1 of the socket .
15
Page 16

notch
key
1. Position the SIMM above the socket with the “notch” in the module
aligned with the “key” on the socket.
2. Seat the module at a 45° angle into the bank. Make sure it is com-
pletely seated. Tilt the module upright until it locks in place in the
socket.
Warning:
The DIMM and SIMM can not exist on the G586IPV AND G586IPVF
system board at the same time. You must choose either a DIMM or
SIMMs on your system board.
Jumper Settings for DIMM & SIMM
Jumper JP10
DIMM and SIMM Select
Jumper JP10 must match the type of module installed on the G586IPV
and G586IPVF system board. If you change your memory module,
make sure this jumper is changed accordingly.
16
2
1
6
5
3
JP10: 3-5, 4-6 On
DIMM
2
1
64
4
5
3
JP10: 1-3, 2-4 On
SIMM
(Default)
Page 17

Cache Memory
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board can support 256KB or
512KB pipeline burst, direct map write-back cache SRAM. Your system
board may come with 0KB or 256KB cache mounted onboard. The 160pin cache module slot lets you upgrade your cache memory by installing a 256KB or 512KB cache module.
Note:
You do not need to set any jumpers or modify the Award BIOS Setup
utility when you install the cache module.
If your system board comes with 0KB cache, you can install a 256KB or
512KB cache module in the cache module slot. If your system board
comes with 256KB cache at locations U22 and U23, you can upgrade
your cache memory to 512KB by installing a 256KB cache module in
the cache module slot. Please refer to page 12 for the locations of the
cache module slot (SSM1), U22 and U23.
Onboard Cache Upgradeable Cache Module
0KB
256KB
upgradeable with a 256KB or 512KB cache module
upgradeable with a 256KB cache module for a
maximum of 512KB cache
Warning:
We highly recommend that you use T2BSM32-256 or T2BSM32-512
cache modules. If you are using cache modules other than the ones
recommended above, make sure your cache module(s) meets the Intel
COAST 2.x specification. Severe damage might occur on the cache
module or system board if you insert modules other than those specified above.
17
Page 18

Installing the Cache Module
Locate the 160-pin cache module slot on the system board (SSM1).
See pages 12 and 13 for the location. Position the cache module above
the slot. Make sure pin 1 of the cache module is aligned with pin 1 of
the slot. Carefully slide the module into the slot. Press firmly on the top
of it to seat it properly.
Note:
With the cache module installed in the cache module slot, the components on the solder side of the add-in card in PCI Slot 1 and 2 must not
protrude more than 5mm. There is no limit to the length of the add-in
card installed in PCI Slot 3.
18
Page 19

CPU Installation
The G586IPV and G586IPVF allows for easy installation of CPUs. Make
sure all jumpers are set correctly before applying power or you may damage the CPU or system board. Please see the jumper settings on the following pages. Use the needle-nosed pliers to move the jumpers if necessary.
Jumper Settings for CPUs
Intel CPUs
Intel CPUs
75MHz
90/100/120/150/
166MHz
Intel CPUs
75/90/100MHz
120/133MHz
150/166MHz
3
4
3
4
1
5 6
1
5 6
Voltage
2.8V
3.3V*
3.52V
PCI CLK
↓
2
2
1-2On
1-2On
3-4On
For the G586IPV only
50MHz
2x
JP8
JP9
JP4
Off
On
Pin 1-2
Off
On
On
JP4
↓
Pin 3-4
Off
Off
On
1
2
CPU CLK
60/66MHz
1.5x
2.5x
1
2
1
2
JP11
JP30 (For the G586IPVF only)
JP9
JP11
1-3On, 2-4On
3-5On, 4-6On
3-5On, 4-6On
Voltage
2.5V
2.8V
2.9V
3.3V*
3.52V
For the G586IPVF only
Intel CPUs
75MHz
90/120/150MHz
100/133/166MHz
JP9
1-2On
1-2On
1-2On
1-2On
3-4On
JP11
1-3On, 2-4On
1-3On, 2-4On
1-3On, 2-4On
3-5On, 4-6On
3-5On, 4-6On
CPU CLK
50MHz
60MHz
66MHz
↓
4
2
1-2On
3-4On
5-6On
3-4On
3-4On
3
1
JP30
Pin 1-2
JP6
On
Off
On
*Default
Pin 3-4
On
On
Off
19
Page 20

Cyrix CPUs
Cyrix CPUs
P120+/P133+
P150+/P166+
Cyrix CPUs
P120+/P133+/
P150+/P166+
3
4
3
4
1
5 6
CPU CLK
50/55MHz
60/66MHz
PCI CLK
↓
1
2
1
2
2
JP11
2x
JP8
JP9
JP4
↓
Off
JP4
On
Pin 1-2OnPin 3-4
Off
1
2
Cyrix CPUs
P120+
P133+
P150+
P166+
CPU CLK
50MHz
55MHz
60MHz
66MHz
↓
4
2
3
1
Pin 1-2
On
Off
On
Off
JP6
Pin 3-4
On
Off
Off
On
1
5 6
Voltage
2.8V
3.3V*
3.52V
For the G586IPV only
20
2
JP30 (For the G586IPVF only)
JP9
1-2On
1-2On
3-4On
JP11
1-3On, 2-4On
3-5On, 4-6On
3-5On, 4-6On
Voltage
2.5V
2.8V
2.9V
3.3V*
3.52V
JP9
1-2On
1-2On
1-2On
1-2On
3-4On
JP11
1-3On, 2-4On
1-3On, 2-4On
1-3On, 2-4On
3-5On, 4-6On
3-5On, 4-6On
For the G586IPVF only
JP30
1-2On
3-4On
5-6On
3-4On
3-4On
Page 21

AMD 5K86 and future 200MHz CPUs
AMD 5K86 CPUs
75MHz
90MHz
Future CPUs
200MHz
AMD 5K86 CPUs
75/90MHz
Future CPUs
200MHz
CPU CLK
50MHz
60MHz
CPU CLK
66MHz
PCI CLK
1.5x
PCI CLK
3x
JP4
Off
On
JP4
On
Pin 1-2
Off
Pin 1-2
Off
↓
JP4
Pin 3-4
Off
Pin 3-4
On
↓
1
3
4
3
4
JP8
2
1
JP9
2
AMD 5K86 CPUs
1
2
75MHz
90MHz
Future CPUs
200MHz
CPU CLK
50MHz
60MHz
CPU CLK
66MHz
↓
4
2
Pin 1-2
Pin 1-2
3
JP6
1
On
On
Off
Pin 3-4
On
Off
Pin 3-4
On
2
1
JP11
5
6
2
1
JP30 (For the G586IPVF only)
5 6
Voltage
2.8V
3.3V*
3.52V
JP9
1-2On
1-2On
3-4On
JP11
1-3On, 2-4On
3-5On, 4-6On
3-5On, 4-6On
For the G586IPV only
Voltage
2.5V
2.8V
2.9V
3.3V*
3.52V
JP9
1-2On
1-2On
1-2On
1-2On
3-4On
JP11
1-3On, 2-4On
1-3On, 2-4On
1-3On, 2-4On
3-5On, 4-6On
3-5On, 4-6On
For the G586IPVF only
JP30
1-2On
3-4On
5-6On
3-4On
3-4On
21
Page 22

Installing Upgrade CPUs
The G586IPV AND G586IPVF is equipped with a 321-pin Zero Insertion
Force (ZIF) socket at location U25 of the system board. Refer to page
12 for the location of the ZIF socket. This socket is designed for easy
removal of an old CPU and easy insertion of an upgrade CPU. The
socket allows you to carefully place the new CPU into its position. If you
need to apply excessive force to insert the CPU, you are not installing
the CPU correctly.
Warning:
Open the socket only if you are actually installing a CPU. The warranty
on the original CPU will be voided if the S/N seal is broken.
Before proceeding with the upgrade, take note of the following. The microprocessor and heat sink may be hot if the system has been running.
To avoid the possibility of a burn, power the system off and let the
processor and heat sink cool for 10 minutes.
The 321-pin ZIF socket consists of five rows of pin holes on each side.
To prevent improper CPU installation, the ZIF socket has a Plug/Keying
mechanism. Several holes in the socket are plugged so that the CPU
will go in only one way. If you cannot easily insert the CPU, verify that
pin 1 of the CPU is aligned with pin 1 of the socket.
22
Zero Insetion Force (ZIF) Socket
Page 23

To install an upgrade CPU, do the following.
1. Make sure the handle on the side of the ZIF socket is up. To raise
the handle, push it down, slightly pull it out to the side, then raise it
as far as it will go. It may be necessary to initially apply a small
amount of sideways force to free the handle from its retaining “tab.”
Once clear of the “tab,” the handle will open relatively easily. The
top plate will slide back. Do not use screwdrivers or other tools to
open the socket, or you may damage the system or socket.
Lifting the Handle
2. Once the lever is completely up, remove the old CPU carefully by
lifting it straight out of the socket. You are now ready to insert the
new CPU.
23
Page 24

3. Position the CPU above the ZIF socket. Make sure pin 1 of the
CPU is aligned with pin 1 of the socket. Lower the chip until the
pins are inserted properly in their corresponding holes. Remember
that very little force is needed to install the CPU. If the CPU is not
easily inserted, verify whether or not pin 1 of the CPU is aligned
with pin 1 of the socket. Applying too much pressure can damage
the CPU or the socket.
Positioning the CPU Above the ZIF Socket
4. Push the handle down until the handle locks into place. The top
plate will slide forward. You will feel some resistance as the pressure starts to secure the CPU in the socket. This is normal and will
not damage the CPU. However, if the handle is not completely
closed, damage to the CPU and/or system board may result.
Installing A Fan/Heatsink for Cyrix CPUs
If you use a Cyrix CPU, you must choose a fan/heatsink which is made
for Cyrix processors. Position the fan/heatsink on the CPU such that the
air from the side of the fan/heatsink will flow across the heat regulators
on the system board. See the figure on the next page.
24
Page 25

Clearnance Requirements
Your CPU comes with a heatsink mounted on top. To maintain proper
airflow once the upgrade is installed on the system board, the CPU and
heatsink require certain space clearances.
The clearance above the CPU's fan/heatsink must be at least 0.4
inches. The clearance on at least 3 of 4 sides of the processor and
heatsink must be at least 0.2 inches. All cables (for floppy drive, hard
drive, CD-ROM, etc.) must be routed clear of the CPU and its airspace.
Fan Exhaust
The CPU must be kept cool by using a fan with heatsink. The temperature of the air entering the fan/heatsink cannot exceed 45oC (113oF).
The ambient or room temperature must be below 37oC (99oF).
25
Page 26

Jumper Setting for Display
Jumper JP3
Display Type Select
Jumper JP3 sets the display adapter to color or mono. This jumper
must match the type of display adapter installed. If you change your
video adapter, make sure this jumper is changed accordingly.
1
2
3
1-2 On: Color
2-3 On: Mono
1
2
3
(default)
Built-in Ports
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board is equipped with two serial
ports, one parallel printer port, one FDD connector, two IDE hard disk
shrouded headers and one PS/2 mouse connector. Refer to pages 12
and 13 for the locations of the built-in connectors and pin 1 of those
connectors.
26
The location of the G586IPV built-in connectors
Page 27

The location of the G586IPVF built-in connectors
Serial Ports
The built-in serial ports are RS-232C asynchronous communication
ports with 16C550A-compatible UARTs that can be used with modems,
serial printers, remote display terminals, and other serial devices. They
use the following system I/O addresses:
Port Configuration
Serial Port 1
Serial Port 2
* Default
COM1
3F8h*
3F8h
COM2
2F8h
2F8h*
COM3
3E8h
3E8h
COM4
2E8h
2E8h
Connecting the Serial Ports
Two DB-9P serial port cables are provided with the system board. They
are mounted on a card-edge bracket along with the PS/2 mouse cable.
The upper serial port cable should be used for the COM 1 primary serial port; connect it to connector J4 on the system board. The lower
serial port cable should be used for the COM 2 secondary serial port;
connect it to connector J5 on the system board. Make sure the colored
stripes on the ribbon cables are aligned with pin 1 of connectors J4 and
J5. Mount the card-edge bracket to the system chassis.
27
Page 28

PS/2 Mouse Port
The PS/2 mouse port is a 6-pin connector on the system board. Attach
the 6-pin mouse port cable, which came with the G586IPV and
G586IPVF, to connector J3 or CN3 (for the G586IPV only). Make sure
the brown wire on the PS/2 mouse connector is aligned with pin 1 of
connector J3 or CN3 (for the G586IPV only).
Parallel Port
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board has a standard connector
for interfacing your PC to a parallel printer. The parallel port on your
system board can be set to any of the following system I/O addresses:
I/O Address: 3BC-3BE Hex
378-37A Hex (default)
278-27A Hex
Connecting the Parallel Printer Port
Attach the DB-25S printer port cable, which came with the system
board, to connector J7 on the G586IPV and G586IPVF system board.
Make sure the colored stripe on the ribbon cable aligns with pin 1 of
connector J7. Use a small nutdriver to mount the cable into a DB-25
cutout in the system chassis.
Floppy Disk Drive Controller
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board has a built-in floppy disk
controller that supports two standard floppy disk drives. You can install
any 360KB, 720KB, 1.2MB, 1.44MB, or 2.88MB floppy disk drives.
Connecting the Floppy Disk Cable
1. Install the 34-pin header connector into the floppy disk connector
(J6) on the system board. The colored edge of the ribbon should be
aligned with pin 1 of connector J6.
2. Install the other 34-pin header connector(s) into the disk drive(s).
Align the colored edge of the daisy chained ribbon cable with pin 1
of the drive edge connector(s). The end-most connector should be
attached to the drive you want to designate as Drive A.
28
Page 29

IDE Hard Disk Interface
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board is equipped with two PCI
IDE shrouded headers that will interface four Enhanced IDE (Integrated
Drive Electronics) hard disk drives.
Note:
Only Enhanced IDE hard drives or ATAPI CD-ROMs can be connected
to the IDE interface.
Connecting the IDE Hard Disk Interface
To prevent improper IDE cable installation, each PCI IDE shrouded
header has a keying mechanism. The 40-pin connector on the IDE
cable can be placed into the header only if pin 1 of the connector is
aligned with pin 1 of the header.
Header
Note:
The IDE cable with a standard 40-pin connector (without the keying
mechanism) can be installed in the PCI IDE shrouded header. Be extremely careful to match the colored edge of the ribbon with pin 1 of the
header.
29
Page 30

Connecting the Hard Disk Cable
1. If you are connecting two hard drives, install the 40-pin connector of
the IDE cable into the primary IDE shrouded header (connector J8).
If you are adding a third or fourth IDE device, install the 40-pin
connector of the other IDE cable into the secondary IDE shrouded
header (connector J9).
2. Install the other 40-pin header connector(s) into the device with the
colored edge of the ribbon cable aligned with pin 1 of the drive
edge connector(s).
Note:
Refer to your disk drive user’s manual for information about selecting
proper drive switch settings.
Adding a Second IDE Hard Drive
When using two IDE drives, one must be set as the master and the
other as the slave. Follow the instructions provided by the drive manufacturer for setting the jumpers and/or switches on the drives.
We recommend that the Enhanced IDE hard drives be from the same
manufacturer. In a few cases, drives from two different manufacturers
will not function properly when used together. The problem lies in the
hard drives, not the G586IPV and G586IPVF system board.
Preparing an IDE Drive for Use
IDE disk drives are already low-level formatted, with any bad-track errors entered, when shipped by the drive manufacturer. Do not attempt
to do a low-level format or you may cause serious damage to the drive.
To use an IDE drive, you need to enter the drive type (this information
is provided by the drive manufacturer) into the system’s CMOS setup
table. Then run FDISK and FORMAT provided with DOS.
Warning:
Do not run FDISK and FORMAT programs on a drive that has already
been formatted or you will lose all programs and data stored on the
drive.
30
Page 31

Installing Expansion Cards
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board is equipped with 4 dedicated PCI slots and 3 dedicated 16-bit ISA slots. All PCI slots are bus
masters.
Due to the size of the CPU with its accompanying heatsink/fan component, the length of the add-in cards in PCI slot 4 and ISA slot 1 is
limited to 18cm (7.07",measured from the bracket of the card). There is
no limit to the length of the add-in card installed in PCI Slot 4, but the
components on the solder side of the add-in card in PCI Slot 3 must not
protrude more than 5mm (0.2") to avoid interfering the cache module.
Refer to page 12 for the locations of the expansion slots.
Note:
The BIOS needs to be configured for the PCI add-in cards installed in
the PCI slots. Refer to the “PCI Configuration Setup” presented in the
“Software Installation” section of the manual.
31
Page 32

Chapter 3
Software Installation
After you power up your system, the BIOS message appears on your
screen and the memory count begins.
After the memory test, the following message will appear on the screen:
Press DEL to enter setup
If the message disappears before you respond, restart your system or
press the “Reset” button on the front of your computer. You may also
restart the system by pressing the <Ctrl> <Alt> and <Del> keys simultaneously. If you do not press these keys at the correct time and the
system does not boot, the following error message will appear:
Press Del to enter Setup
If you have set a password and selected “System” in the Security Option of the BIOS Features Setup menu, you will be prompted for the
password every time the system is rebooted or any time you try to enter
Setup. Type in the correct password and press <Enter>.
If you selected “Setup” in the Security Option, you will be prompted for
the password only when you try to enter Setup. Refer to the “BIOS
Features Setup” section for more information.
Award CMOS Setup Utility
Press <Ctrl> <Alt> <Esc> simultaneously or <Del> to enter the Setup
utility. A screen similar to the one on the next page will appear.
32
Page 33

ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION
LOAD BIOS DEFAULTS
LOAD SETUP DEFAULTS
:Quit
ESC
:Sve & Exit Setup
F10
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type...
INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS
SUPERVISOR PASSWORD
USER PASSWORD
IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION
HDD LOW LEVEL FORMAT
SAVE & EXIT SETUP
EXIT WITHOUT SAVING
↑↓→←
(Shift) F2
:Select Item
:Change Color
Use the arrow keys to highlight the option you want and press <Enter>.
The following describes each of these options.
Standard CMOS Setup
Use the arrow keys to highlight “Standard CMOS Setup” and press
<Enter>. A screen similar to the one below will appear.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Date (mm:dd:yy) : Mon, Apr 15 1996
Time (hh:mm:ss) : 9 : 5 : 55
HARD DISKS
Primary Master
Primary Slave
Secondary Master
Secondary Maste
DriveA :1.44M,3.5in.
DriveB :None
Video :EGA/VGA
Halt on :All Errors
ESCF1:Quit
:Help
TYPE
:Auto
:Auto
:Auto
:Auto
SIZE
0
0
0
0
CYLS
0
0
0
0
↑↓→←
(Shift)F2
HEAD
0
0
0
0
:Select Item
:Change
RECOMP
0
0
0
0
LANDZ
0
0
0
0
Base Memory : 640K
Extended Memory : 31744K
Other Memory : 384K
Total Memory : 32768K
PU/PD/+/- : Modify
SECTOR
0
0
0
0
MODE
AUTO
AUTO
AUTO
AUTO
Date and Time
This selection sets the time and date for the system. Press <F3> for the
calendar.
Hard Drive Type
This allows you to enter the appropriate specifications for the type of
hard disk drive(s) installed in your system. Under the “Type” category,
33
Page 34

you can select Auto, User, one of 46 predefined drive specifications or
None.
Auto: This option indicates that the parameters for your hard disk
drive(s) will be automatically detected and displayed when you boot
your system. By default, the LBA mode is selected for a hard disk drive
larger than 528 megabytes. If you decide not to accept the LBA mode,
you can either specify your selection in the “IDE HDD Auto Detection”
menu, or use the User option described below.
User: This type is user definable and allows you to enter the specifications yourself directly from the keyboard. Six categories of information
are required: Size, Cylinders, Heads, Precomp, LandZone, Sectors and
Mode. This information should be provided by your hard disk vendor or
system manufacturer. However, we recommend you use the “IDE HDD
Auto Detection” which provides a more efficient way to setup your hard
drive.
46 Predefined Drive Specifications: Any given hard drive must be set to
one specific drive type number. Please refer to your hard disk documentation for the appropriate type number.
None: If a hard drive is not installed, select <None> and press <Enter>.
Drive A and Drive B
These options are used to select the type of floppy disk drives installed
in your system. If neither drive is present, select “None”. Make sure you
choose the correct drive type; otherwise, your system might format the
device improperly.
Video
This is used to select the type of video adapter installed in your system.
Halt on
This category controls whether the system will halt in case an error is
detected during power up.
34
Page 35

No Errors: The system boot will not stop for any detected errors.
All Errors: The system will stop whenever the BIOS detects a non-fatal
error.
All, But Keyboard: The system will stop for any error except a keyboard
error.
All, But Diskette: The system will stop for any error except a disk error.
All, But Disk/Key: The system will stop for any error except a keyboard
or disk error.
Memory
The lower right hand corner shows the base memory size, extended
memory size, and the other memory size of your system. You cannot
alter these items; your computer automatically detects and displays
them.
The Other Memory size refers to the memory located in the 640K to
1024K address space. This is the memory used for different applications. DOS uses this area to load device drivers to free base memory
for application programs.
When you are through making changes in the Standard CMOS Setup,
press <Esc> to return to the main menu.
BIOS Features Setup
Use the arrow keys to highlight “BIOS Features Setup” and press
<Enter>, a screen similar to the one on the next page will appear.
35
Page 36

ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Virus Warning
CPU Internal Cache
External Cache
Quick Power On Self Test
Boot Sequence
Swap Floppy Drive
Boot Up Floopy Seek
Boot Up NumLock Status
Gate A20 Option
TypematicRate Setting
Typematic Rate (Char/Sec)
Typematic Delay (Msec)
Security Option
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
OS Select For DRAM>64MB
:Disabled
:Enabled
:Enabled
:Enabled
:A, C
:Disabled
:Enabled
:On
:Fast
:Disabled
:6
:250
:Setup
:Disabled
:Non-OS2
Video BIOS Shadow
C8000-CBFFF Shadow
CC000-CFFFF Shadow
D0000-D3FFF Shadow
D4000-D7FFF Shadow
D8000-DBFFF Shadow
DC000-DFFFF Shadow
ESC
:Quit
F1
:Help
F5
:Old Values
F6
:Load BIOS Defaults
F7
:Load Setup Defaults
↑↓→←
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
:Enabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Select Item
:Modify
:Color
The Virus Warning option may be set to “Enabled” or “Disabled”. If enabled, the BIOS issues a warning when any program or virus sends a
Disk Format command or attempts to write to the boot sector of the
hard disk drive.
Note:
If you are installing or running certain operating systems such as Windows 95, please disable the Virus Warning or the operating system may
not install nor work.
If you choose “System” in the Security Option, you will be prompted for
a password every time you cold boot your system or access setup. If
you choose “Setup”, you will be prompted for a password only when
trying to access setup.
Use the arrow keys to move the highlight bar to the option you wish to
change or modify. Use the <Page Up>, <Page Down>, <+> or <-> keys
to make the corresponding changes. Press <Esc> after making the
changes to return to the main menu.
Chipset Features Setup
The G586IPV AND G586IPVF uses the Intel 82430VX chipset. The
Chipset Features Setup allows you to modify some functions to optimize
system performance. If you press <Enter>, a screen similar to the one
on the next page will appear.
36
Page 37

ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Auto Configration
DRAM Timing
DRAM RAS# Precharge Time
DRAM R/W Leadoff Timing
Fast RAS To CAS Delay
DARM Read Burst (EDO/FP)
DRAM Write Burst Timing
Fast MA to RAS# Delay CLK
Fast EDO Path Select
Refresh RAS# Assertion
ISA Bus Clock
System BIOS Cacheable
Video BIOS Cacheable
8 Bit I/O Recovery Time
16 Bit I/O Recovery Time
Memory Hole At 15M-16M
Peer Concurrency
:Enabled
:60 ns
:3
:6
:3
:x222/x333
:x222
:1
:Disabled
:4 Clks
:PCICLK/4
:Enabled
:Enabled
:1
:1
:Disabled
:Enabled
ESC
:Quit
F1
:Help
F5
:Old Values
F6
:Load BIOS Defaults
F7
:Load Setup Defaults
↑↓→←
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
:Select Item
:Modify
:Color
Use the arrow keys to move the highlight bar to the option you wish to
change or modify. Use the <Page Up>, <Page Down>, <+> or <-> keys
to make the corresponding changes.
If the changes you made are incorrect or you change your mind, press
<F6> or <F7> to return to the default settings. Press <Esc> after making the changes to return to the main menu.
Power Management Setup
Use the arrow keys to highlight “Power Management Setup” and press
<Enter>. A screen similar to the one below will appear.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Power Management
PM Control by APM
Video Off Method
Doze Mode
Standby Mode
Suspend Mode
HDD Power Down
** Wake Up Events In Doze & Standby **
IRQ3 (Wake-Up Event)
IRQ4 (Wake-Up Event)
IRQ8 (Wake-Up Event)
IRQ12 (Wake-up Event)
:Disabled
:Yes
:V/H SYNC+Blank
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:Disabled
:On
:On
:On
:On
** Power Down & Resume Events **
IRQ3 (COM 2)
IRQ4 (COM 1)
IRQ5 (LPT 2)
IRQ6 (Floppy Disk)
IRQ7 (LPT 1)
IRQ8 (RTC Alarm)
IRQ9 (IRQ2 Redir)
IRQ10(Reserved)
IRQ11(Reserved)
IRQ12 (PS2 Mouse)
IRQ13 (Corpocessor)
IRQ14 (Hard Disk)
IRQ15 (Reserved)
ESC
:Quit
F1
:Help
F5
:Old Values
F6
:Load BIOS Defaults
F7
:Load Setup Defaults
:On
:On
:On
:On
:On
:On
:Off
:On
:On
:On
:On
:On
:On
:Off
↑↓→←
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
:Select Item
:Modify
:Color
Choosing “Enabled” in the Power Management option will allow you to
set Doze Mode, Standby Mode, Suspend Mode and HDD Power Down.
Choose “Disabled” if you do not want your system to enter the power
saving mode.
37
Page 38

PNP/PCI Configuration Setup
Use the arrow keys to highlight “PNP/PCI Configuration Setup” and
press <Enter>; a screen similar to the one below will appear.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Resources Control By
Reset Configuration Data
:Auto
:Disabled
PCI IRQ Active By : Level
PCI IDE IRQ Map To : PCI-AUTO
Primary IDE INT# : A
Secondary IDE INT# : B
ESC
:Quit
F1
:Help
F5
:Old Values
F6
:Load BIOS Defaults
F7
:Load Setup Defaults
↑↓→←
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
:Select Item
:Modify
:Color
The PNP/PCI Configuration Setup allows you to assign INT A, B, C or D
to the hard drives installed in your system. Each INT may then be assigned an IRQ value.
If the Resources Controlled By option is set to “Auto”, the system will
automatically detect the settings for you. IRQ 3 - IRQ 15 and DMA 0 DMA 7 options will not be shown in the PnP Configuration Setup
screen.
Load BIOS Defaults
The “Load BIOS Defaults” option loads the troubleshooting default values permanently stored in the ROM chips. These settings are not optimal and turn off all high performance features. You should use these
values only if you have hardware problems. Highlight this option on the
main menu and press <Enter>. The message below will appear.
Load BIOS Defaults (Y/N)? N
If you want to proceed, press <Y> and the default settings will be
loaded.
38
Page 39

Load Setup Defaults
The “Load Setup Defaults” option loads optimized settings from the
BIOS ROM. Use the Setup default values as standard values for your
system
Highlight this option on the main menu and press <Enter>. The message below will appear.
Load Setup Defaults (Y/N)? N
Type <Y> and press <Enter> to load the Setup default values.
Integrated Peripherials
Use the arrow keys to highlight “Integrated Peripherals” and press
<Enter>. A screen similar to the one below will appear.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
IDE HDD Block Mode
IDE Primary Master PIO
IDE Primary Slave PIO
IDE Secondary Master PIO
IDE Secondary Slave PIO
On-Chip Primary PCI IDE
On-Chip Secondary PCI IDE
PCI Slot IDE 2nd Channel
Onboard FDD Controller
Onboard Serial Port 1
Onboard Serial Port 2
UART 2 Mode
Onboard Parllel Port
Onboard Parllel Mode
:Enabled
:AUTO
:AUTO
:AUTO
:AUTO
:Enabled
:Enabled
:Disabled
:Enabled
:3F8/IRQ4
:2F8/IRQ3
:Standard
:378H/IRQ7
:SPP
ESC
:Quit
F1
:Help
F5
:Old Values
F6
:Load BIOS Defaults
F7
:Load Setup Defaults
↑↓→←
PU/PD/+/(Shift) F2
:Select Item
:Modify
:Color
The Integrated Peripherals allows you to enable, disable or select the
port address of the built-in serial ports, parallel port and floppy disk
controller.
Supervisor Password
If you want to protect your system and setup from unauthorized entry,
set a supervisor’s password with the “System” option selected in the
BIOS Features Setup.
39
Page 40

If you want to protect access to setup only, but not your system, set a
supervisor’s password with the “Setup” option selected in the BIOS
Features Setup. You will not be prompted for a password when you
cold boot the system.
Use the arrow keys to highlight the “Supervisor Password” option and
press <Enter>. The message below will appear.
Enter Password:
Type in the password. You are limited to eight characters. When done,
the message below will appear:
Confirm Password:
You are asked to verify the password. Type in exactly the same password. If you type in a wrong password, you will be prompted to enter
the correct password again.
To delete or disable the password function, highlight “Supervisor Password” and press <Enter>, instead of typing in a new password. Press
the <Esc> key to return to the main menu.
If you forget your password, you should clear any previously set password by setting Jumper JP3 to On for approximately two minutes.
Please refer to page 30 for more information.
User Password
If you want another user to have access only to your system but not to
setup, set a user’s password with the “System” option selected in the
BIOS Features Setup.
If you want a user to enter a password when trying to access setup, set
a user’s password with the “Setup” option selected in the BIOS Features Setup. Using user’s password to enter Setup allows a user to
access only the “User Password” option that appears on the main
screen. Access to all other options is denied.
40
Page 41

To set, confirm, verify, disable or delete a user’s password, follow the
procedures described in the section “Supervisor Password”. If you forget your password, refer to the procedure described in the same section.
IDE HDD Auto Detection
This option detects the hard disk parameters for the hard disk drives
installed in your system. Highlight this option and press <Enter>. A
screen similar to the one on the next page will appear.
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
HARD DISKS TYPE SIZE CYLS HEAD RECOMP LANDZ SECTOR MODE
Primary Master:
Select Primary Master Option (N=Skip): N
OPTIONS SIZE CYLS HEAD RECOMP LANDZ SECTOR MODE
2 (Y) 853 827 32 0 1653 63 LBA
1 853 1654 16 65535 1653 63 Normal
3 853 827 32 65536 1653 63 Large
Note: Some OSes (like SCO-UNIX) must be “NORMAL” for installation
ESC: Skip
Enter your choice, and press <Enter> to accept the parameters or press
<Esc> to abort. The parameters of the hard disk will be displayed in the
Standard CMOS Setup.
Hard Drive Mode
The G586IPV AND G586IPVF supports three HDD modes: Normal, LBA
and Large. If your hard disk drive does not support LBA mode, the
“LBA” option will not be displayed. If your HDD has 1024 or fewer cylinders, the “Large” option will not be displayed.
Normal Mode
The Normal mode is the generic access mode in which neither the
BIOS nor the IDE controller will make any transformations during harddrive access.
41
Page 42

The maximum number of cylinders, heads and sectors for Normal mode
are 1024, 16 and 63, respectively.
no. Cylinders (1024)
x no. Heads ( 16)
x no. Sectors ( 63)
x bytes per sector ( 512)
528 megabytes
If you set your HDD to Normal mode, the maximum accessible HDD will
be 528 megabytes even though the physical size of the HDD may be
greater than that.
LBA (Logical Block Addressing) Mode
The LBA mode is a HDD accessing method to overcome the 528 megabyte limitation. The number of cylinders, heads and sectors shown on
the screen may not be the actual number for the HDD.
During the HDD accessing, the IDE controller will transform the logical
address described by the sector, head and cylinder number into its own
physical address inside the HDD.
The maximum HDD size supported by the LBA mode is 8.4 gigabytes. It
is obtained by the following formula.
no. Cylinders (1024)
x no. Heads ( 225)
x no. Sectors ( 63)
x bytes per sector ( 512)
8.4 gigabytes
Large Mode
The Large mode is the extended HDD access mode supported by the
G586IPV AND G586IPVF system board. Some IDE HDDs have more
than 1024 cylinders without LBA support (in some cases, you may not
want the LBA mode). This system board provides another alternative to
support these
kinds of HDDs.
42
Page 43

The BIOS tells the operating system that the number of cylinders is half
of the actual number and that the number of heads is double the actual
number. During disk access, the reverse conversion is done by the
INT13h routine.
Example of Large mode:
CYLS. HEADS SECTORS MODE
1120 16 59 NORMAL
560 32 59 LARGE
Maximum HDD size:
no. Cylinders (1024)
x no. Heads ( 32)
x no. Sectors ( 63)
x bytes per sector ( 512)
1 gigabyte
Note:
To support LBA or Large mode, address translation software is included
in the Award BIOS HDD Service Routine (INT13h). If you are running
an operating system that bypasses the BIOS Int13 Service Routine,
LBA and Large Mode may fail.
HDD Low Level Format
This option will format, set the interleave mode and do a media analysis
of your hard drives. Highlight this option and press <Enter>. A screen
similar to the one below will appear.
43
Page 44

ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A59GD49)
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Hard Disk Low Level Format Utility
SELECT DRIVE
BAD TRACK LIST
PERFORMAT
Current select drive is : C
DRIVE: C CYLINDER: 0 HEAD: 0
CYLS
1654
HEAD
RECOMP
16
0
0
0
0
0
0
Primary Master:
Primary Slave:
Secondary Master:
Secondary Slave:
Up/Down-Select item ENTER-Accept ESC-Exit/Abort
SIZE
853
0
0
0
Copyright (C) Award Software, Inc. 1992-94 All Rights Reserved
65536
LANDZ
1653
0
0
0
0
0
0
No. CYLS HEAD
SECTOR
63
0
0
0
MODE
AUTO
AUTO
AUTO
AUTO
Warning:
Do not attempt to do a low-level format on an IDE drive, or you may
cause serious damage to the drive. IDE disk drives are already lowlevel formatted, with any bad-track errors entered, when shipped by the
drive manufacturer.
Save & Exit Setup
When all the changes have been made, highlight “Save & Exit Setup”
and press <Enter>. The message below will appear:
Save to CMOS and Exit (Y/N)? N
Type “Y” and press <Enter>. The following message will appear:
Reboot System (Y/N)? N
Type “Y” and press <Enter>. The modifications you have made will be
written into the CMOS memory, and the system will reboot. You will
once again see the initial diagnostics on the screen. If you wish to
make additional changes to the setup, press <Ctrl> <Alt> <Esc> simultaneously or <Del> after memory testing is done.
Exit Without Saving
When you do not want to save the changes you have made, highlight “Exit
Without Saving” and press <Enter>. The message below will appear:
44
Page 45

Quit Without Saving (Y/N)? N
Type “Y” and press <Enter>. The system will reboot and you will once
again see the initial diagnostics on the screen. If you wish to make any
changes to the setup, press <Ctrl> <Alt> <Esc> simultaneously or
<Del> after memory testing is done.
System Error Report
When the BIOS encounters an error that requires the user to correct
something, either a beep code will sound or a message will be displayed in a box in the middle of the screen and the message PRESS
F1 TO CONTINUE, CTRL-ALT-ESC or DEL TO ENTER SETUP, will be
shown in the information box at the bottom. Enter Setup to correct the
error.
POST Beep
There is one beep code in the BIOS. This code indicates that a video
error has occurred and the BIOS cannot initialize the video screen to
display any additional information. This beep code consists of a single
long beep followed by two short beeps. If you get this error, contact
your system board.
Error Messages
One or more of the following messages may be displayed if the BIOS
detects an error during the POST.
DISK BOOT FAILURE, INSERT SYSTEM DISK AND PRESS ENTER
No boot device was found. Insert a system disk into Drive A and press
<Enter>. If the system normally boots from the hard drive, make sure
the controller is inserted correctly and all cables are properly attached.
Also be sure the disk is formatted as a boot device. Reboot the system.
DISKETTE DRIVES OR TYPES MISMATCH ERROR - RUN SETUP
The type of diskette drive installed in the system is different from the
CMOS definition. Run setup to reconfigure the drive type correctly.
45
Page 46

DISPLAY SWITCH IS SET INCORRECTLY
The display switch on the system board can be set to either monochrome or color. This error indicates the switch is set to a different
setting than indicated in Setup. Determine which setting is correct and
either turn off the system and change the jumper or enter Setup and
change the VIDEO selection.
DISPLAY TYPE HAS CHANGED SINCE LAST BOOT
Since last powering off the system, the display adapter has been
changed. You must configure the system for the new display type.
ERROR ENCOUNTERED INITIALIZING HARD DRIVE
The hard drive cannot be initialized. Be sure the adapter is installed
correctly and all cables are correctly and firmly attached. Also, be sure
the correct hard drive type is selected in Setup.
ERROR INITIALIZING HARD DISK CONTROLLER
The system cannot initialize the controller. Make sure the card is correctly and firmly installed in the bus. Be sure the correct hard drive type
is selected in Setup. Also, check to see if any jumper needs to be set
correctly on the hard drive.
FLOPPY DISK CNTRLR ERROR OR NO CNTRLR PRESENT
The system cannot find or initialize the floppy drive controller. Make
sure the controller is installed correctly and firmly. If no floppy drive is
installed, be sure the Diskette Drive selection in Setup is set to NONE.
KEYBOARD ERROR OR NO KEYBOARD PRESENT
Cannot initialize the keyboard. Make sure the keyboard is attached correctly and no keys are being pressed during the boot.
If you are purposely configuring the system without a keyboard, set the
error halt condition in Setup to HALT ON ALL, BUT KEYBOARD. This
will cause the BIOS to ignore the missing keyboard and continue the
boot.
MEMORY ADDRESS ERROR AT...
Indicates a memory address error at a specific location. You can use
this location along with the memory map for your system to find and
replace the bad memory chips.
46
Page 47

MEMORY SIZE HAS CHANGED SINCE LAST BOOT
Memory has been added or removed since the last boot. Enter Setup
and enter the new memory size in the memory fields.
MEMORY VERIFY ERROR AT...
Indicates an error verifying a value already written to memory. Use the
location along with your system’s memory map to locate the bad chip.
OFFENDING ADDRESS NOT FOUND
This message is used in conjunction with the I/O CHANNEL CHECK
and RAM PARITY ERROR messages when the segment that has
caused the problem cannot be isolated.
OFFENDING SEGMENT
This message is used in conjunction with the I/O CHANNEL CHECK
and RAM PARITY ERROR messages when the segment that has
caused the problem has been isolated.
PRESS A KEY TO REBOOT
This will be displayed at the bottom screen when an error occurs that
requires a reboot. Press any key and the system will reboot.
SYSTEM HALTED, (CTRL-ALT-DEL) TO REBOOT...
Indicates the present boot attempt has been aborted and the system
must be rebooted. Press and hold down the CTRL, ALT and DEL keys
simultaneously.
IDE Device Drivers
To install the IDE device drivers supported by the G586IPV and
G586IPVF system board, please refer to the “Readme” file contained in
the provided diskette.
47
Page 48

Chapter 4
Troubleshooting Checklist
If you experience difficulty with the G586IPV and G586IPVF system
board, please refer to the checklist below. If you still cannot identify the
problem, please contact your dealer.
1. Check the jumper settings to ensure that the jumpers are properly
set. If in doubt, refer to the “Hardware Installation” section.
2. Verify that all SIMMs or DIMM are seated securely into the bank
sockets.
3. Make sure the SIMMs or DIMM are in the correct locations.
4. Check that all populated memory banks are filled with correctly
sized SIMMs.
5. If your board fails to function, place the board on a flat surface and
seat all socketed components (gently press each component into
the socket).
6. If you made changes to the BIOS settings, re-enter setup and
load the BIOS defaults.
48
Page 49

Appendix A
Types of Modules
The G586IPV and G586IPVF system board allows you to populate
memory with 1MBx64 or 2MBx64 DIMM, and 1MBx32, 2MBx32,
4MBx32 and 8MBx32 SIMMs. The following modules have been tested
with this board. Most untested brands will work but a few may fail to do
so.
DIMM
DIMM
Brand
Chip Number
SIMM
1MBx64
SIMM
1MBx32
2MBx32
4MBx32
8MBx32
NEC
Brand
Fujitsu
OKI
OKI
NEC
Micron
TI
Micron
Micron
NEC
Hitachi
Fujitsu
Mitsubishi
Hitachi
NEC
NEC
NEC
D4516161G5-7JF
(SDRAM)
Chip Number
81C1000A-70
M51440A-70
M511000B-70
424400-60
40447-60
TMS4400DJ-70
MT4C4007-70 (EDO)
MT4C4007-60 (EDO)
4218165-60 (EDO)
7400AS-70
8117400-70
422A06-70
5117400AS-70
4217400-60
4217405-70 (EDO)
4217405-60 (EDO)
49
Page 50

Appendix B
Memory and I/O Maps
Memory Address Map
Address Name Function
0000000 to 640KB System System Board Memory
009FFFF Board RAM
00A0000 to 128KB Video Reserved for Graphics
00BFFFF Display Memory Display Memory
00C0000 to 160KB I/O Reserved for ROM on
00E7FFF Expansion ROM I/O Adapter Card
00E8000 to 96KB ROM on System Board BIOS
00FFFFF the System Board
0100000 to Maximum System Board Memory
7FFFFFF Memory 128MB
50
Page 51

I/O Address Map
I/O Address Function
0000-001F DMA Controller 1, 8237A-5
0020-003F Interrupt Controller 1, 8259A, Master
0040-005F Timer, 8254-2
0060-006F 8742 (Keyboard Controller)
0070-007F Real-time Clock, NMI
0080-009F DMA Page Memory, 74LS612
00A0-00BF Interrupt Controller 2, 8259A
00C0-00DF DMA Controller 2, 8237A-5
00E8 Shadow RAM and Cache Control Bit
00F0 Clear Numeric Processor
00F1 Reset Numeric Processor Extension
00F8-00FF Numeric Processor Extension
01F0-01F8 Fixed Disk
0200-0207 Game I/O
0278-027F Parallel Printer Port 2
02F8-02FF Serial Port 2
0300-031F Prototype Card
0360-036F Reserved
0378-037F Parallel Printer Port 1
0380-038F SDLC, Bisynchronous 2
03A0-03AF Bisynchronous 1
03B0-03BF Monochrome Display and Printer Adapter
03C0-03CF Reserved
03D0-03DF Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter
03F0-03F7 Diskette Controller
03F8-03FF Serial Port 1
(Non-maskable Interrupt) Mask
Extension Busy
Note:
The I/O address hex 0000 to 00FF are reserved for the system board I/
O. Hex 0100 to 03FF are available on the I/O channels.
51
Page 52

Appendix C
PCI I/O Pin Assignments
Component Side
B
PRSNT1#
PRSNT2#
DEVSEL#
-12V
TCK
Ground
TDO
+5V
+5V
INTB#
INTD#
Reserved
Ground
Ground
Reserved
Ground
CLK
Ground
REQ#
+5V (I/O)
AD[31]
AD[29]
Ground
AD[27]
AD[25]
N. C.
C/BE[3]#
AD[23]
Ground
AD[21]
AD[19]
N. C.
AD[17]
C/BE[2]#
Ground
IRDY#
N. C.
Ground
LOCK#
PERR#
N. C.
SERR#
N. C.
C/BE[1]#
AD[14]
Ground
AD[12]
AD[10]
Ground
- 01 -
- 02 -
- 03 -
- 04 -
- 05 -
- 06 -
- 07 -
- 08 -
- 09 -
- 10 -
- 11 -
- 12 -
- 13 -
- 14 -
- 15 -
- 16 -
- 17 -
- 18 -
- 19 -
- 20 -
- 21 -
- 22 -
- 23 -
- 24 -
- 25 -
- 26 -
- 27 -
- 28 -
- 29 -
- 30 -
- 31 -
- 32 -
- 33 -
- 34 -
- 35 -
- 36 -
- 37 -
- 38 -
- 39 -
- 40 -
- 41 -
- 42 -
- 43 -
- 44 -
- 45 -
- 46 -
- 47 -
- 48 -
- 49 -
A
TRST#
+12V
TMS
TDI
+5V
INTA#
INTC#
+5V
Reserved
+5V (I/O)
Reserved
Ground
Ground
Reserved
RST#
+5V (I/O)
GNT#
Ground
Reserved
AD[30]
N. C.
AD[28]
AD[26]
Ground
AD[24]
IDSEL
N. C.
AD[22]
AD[20]
Ground
AD[18]
AD[16]
N. C.
FRAME#
Ground
TRDY#
Ground
STOP#
N. C.
SDONE
SBO#
Ground
PAR
AD[15]
N. C.
AD[13]
AD[11]
Ground
AD[09]
Solder Side
52
AD[08]
AD[07]
N. C.
AD[05]
AD[03]
Ground
AD[01]
+5V (I/O)
ACK64#
+5V
+5V
- 52 -
- 53 -
- 54 -
- 55 -
- 56 -
- 57 -
- 58 -
- 59 -
- 60 -
- 61 -
- 62 -
C/BE[0]#
N. C.
AD[06]
AD[04]
Ground
AD[02]
AD[00]
+5V (I/O)
REQ64#
+5V
+5V
Page 53

Appendix D
ISA I/O Pin Assignments
B
Gnd
Reset Drv
+5V DC
IRQ9
-5V DC
DRQ2
-12V DC
OWS
+12V DC
Gnd
-SEMEMW
-SEMEMR
-IOW
-IOR
-Dack3
-DRQ3
-Dack1
DRQ1
-Refresh
CLK
IRQ7
IRQ6
IRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ3
-Dack2
Bale
+5V DC
OSC
Gnd
-Mem CS16
-I/O CS16
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12
IRQ13
IRQ14
-Dack0
DRQ0
-Dack5
DRQ5
-Dack6
DRQ6
-Dack7
DRQ7
+5V DC
-Master
Gnd
T/C
D
- 01 -
- 02 -
- 03 -
- 04 -
- 05 -
- 06 -
- 07 -
- 08 -
- 09 -
- 10 -
- 11 -
- 12 -
- 13 -
- 14 -
- 15 -
- 16 -
- 17 -
- 18 -
- 19 -
- 20 -
- 21 -
- 22 -
- 23 -
- 24 -
- 25 -
- 26 -
- 27 -
- 28 -
- 29 -
- 30 -
- 31 -
- 01 -
- 02 -
- 03 -
- 04 -
- 05 -
- 06 -
- 07 -
- 08 -
- 09 -
- 10 -
- 11 -
- 12 -
- 13 -
- 14 -
- 15 -
- 16 -
- 17 -
- 18 -
A
-I/O Chck
SD7
SD6
SD5
SD4
SD3
SD2
SD1
SD0
-I/O Chrdy
AEN
SA19
SA18
SA17
SA16
SA15
SA14
SA13
SA12
SA11
SA10
SA9
SA8
SA7
SA6
SA5
SA4
SA3
SA2
SA1
SA0
C
SBHE
LA23
LA22
LA21
LA20
LA19
LA18
LA17
-Memr
-Memw
SD08
SD09
SD10
SD11
SD12
SD13
SD14
SD15
53
Page 54

Appendix E
Connector Pin Assignments
Connector J3, CN3(for the G586IPV only)
PS/2 Mouse Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
Function
Mouse Data
Reserved
Ground
+5V
Mouse Clock
Reserved
J4 (COM1) and J5 (COM2)
COM 1 and COM 2 Serial Ports
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Function
DCD (Data Carrier Detect)
RX (Receive Data)
TX (Transmit Data)
DTR (Data Terminal Ready)
Ground (Signal Ground)
DSR (Data Set Ready)
RTS (Request to Send)
CTS (Clear to Send)
RI (Ring Indicator)
Connector J6
Floppy Disk Drive Connector
54
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Function
Ground
DENSEL
Ground
Reserved
Ground
Drate0
Ground
Index
Ground
MTR0
Ground
Pin
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
Function
DR1
Ground
DR0
Ground
MTR1
Drate1
Dir
Ground
Step
Ground
Write Data
Page 55

Pin
Functon
Pin
Function
23
24
25
26
27
28
Ground
Write Gate
Ground
Track 0
MSEN
Wr Protect
29
30
31
32
33
34
Ground
Read Data
Ground
Head Select
Ground
Disk Change
Connector J7
Parallel Printer Port
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Function
-Strobe
Data 0
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Data 6
Data 7
-Ack
Busy
Paper Empty
Select
Pin
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Function
-Autofd
-Error
-Init
-Slctin
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Connectors J8 and J9
Primary and Secondary IDE Hard Disk Drive Connectors
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Function
-Reset
Ground
D7
D8
D6
D9
D5
D10
D4
D11
D3
D12
D2
D13
D1
Pin
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Function
D14
D0
D15
Ground
Reserved
Reserved
Ground
-IOW
Ground
-IOR
Ground
Reserved
BALE
Reserved
Ground
55
Page 56

Pin
Function
Pin
Function
31
32
33
34
35
IRQ
IOCS16
SA1
Reserved
SA0
Connector J10
Fan Connector
Pin
1
2
3
Function
Ground
+12V
Ground
Connector J11
Power LED/Keylock Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
Function
IRTX
GND
IRRX
Reserve
VCC
36
37
38
39
40
SA2
HCS0
HCS1
LED
Ground
Connector J13
Infrared Connector
Pin
1
2
Connector J14
Green LED Connector
Pin
1
2
56
Function
VCC
Signal
Function
VCC
Signal
Page 57

Connector J15
Green Button Connector
Pin
1
2
Function
Ground
Signal
Connector J16
Reset Switch Connector
Pin
1
2
Function
Ground
Reset
Connector J17
Speaker Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
Function
Signal
Reserved
GND
VCC
Connector J18
Power LED/Keylock Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
Function
LED Signal
Reserved
Ground
Keylock Signal
Ground
57
Page 58

Connector CN1
PS/2 Keyboard Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
Function
Keyboard Data
Reserved
Ground
+5V
Keyboard Clock
Reserved
Connector CN2
AT Keyboard Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
Function
Keyboard Clock
Keyboard Data
Reserved
Ground
+5V
Connector PL1
Power Connector
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Function
Power Good
+5V
+12V
-12V
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
-5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
58
Page 59

Connector SSM1
Cache Module Slot
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
Function
Ground
TIO0
TIO2
TIO6
TIO4
RSVD
VCC3
TWE#
CADS#/CAA3
Ground
HBE4#
HBE6#
HBE0#
HBE2#
VCC3
CCS#/CAB4
GWE#
BWE#
Ground
A3
A7
A5
A11
A16
VCC3
A18
Ground
A12
A13
ADSP#
ECS1#/(CS#)
ECS2#
PD1
PD3
Ground
CLK1
Ground
D62
VCC3
D60
D58
D56
Ground
D54
D52
D50
Pin
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
Function
D48
Ground
D46
D44
D42
VCC3
D40
D38
D36
Ground
D34
D32
D30
VCC3
D28
D26
D24
Ground
D22
D20
D18
VCC3
D16
D14
D12
Ground
D10
D8
D6
VCC3
D4
D2
D0
Ground
Ground
TIO1
TIO7
TIO5
TIO3
RSVD
VCC5
RSVD
CADV#/CAA4
Ground
COE#
HBE5#
59
Page 60

Pin
Function
Pin
Function
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
HBE7#
HBE1#
VCC5
HBE3#
CAB3
CALE
Ground
RSVD
A4
A6
A8
A10
VCC5
A17
Ground
A9
A14
A15
RSVD
PD0
PD2
PD4
Ground
CLK0
Ground
F63
VCC5
D61
D59
D57
Ground
D55
D53
D51
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
D49
Ground
D47
D45
D43
VCC5
D41
D39
D37
Ground
D35
D33
D31
VCC5
D29
D27
D25
Ground
D23
D21
D19
VCC5
D17
D15
D13
Ground
D11
D9
D7
VCC5
D5
D3
D1
Ground
60
Page 61

Appendix F
Row Address Strobe of the DRAM and SDRAM
After you power up your system, the BIOS message appears on your
screen and the memory count begins.
After the memory test, the screen will appear as below:
Award Software, Inc.
System Configurations
CPU Type :6x86-P166+
Co-Processor :Installed
CPU Clock :133MHz
Diskette Drive A :1.44M, 3.5in.
Diskette Drive B :None
Pri. Master Disk :None
Pri. Slave Disk :None
Sec. Master Disk :None
Sec. Slave Disk :None
EDO DRAM at Row (s)
"Row (s)" refers to the Row Address Strobe of the DRAM or SDRAM.
The Row Address Strobe differs according to the location and type of
DRAM or SDRAM installed on the system board. The table below shows
the Row Address Strobe values with their corresponding type of SIM/
DIM modules and Bank locations.
Base Memory :640K
Extended Memory :15360K
Cache Memory :256K
Display Type :EGA/VGA
Serial Port(s) :3F8 2F8
Paraelle Port (s) :378
EDO DRAM at Row (s) : 0, 1
SDRAM at Row (s) :None
PB SRAM Presence :Yes
"Rows"
0
0, 1
0, 2
0, 1, 2, 3
2
2, 3
Number/Location of
SIM or DIM modules
2 SIMM / Bank 0
2 SIMM / Bank 0
4 SIMM / Bank 0, 1
4 SIMM / Bank 0, 1
1 DIMM / DM1
1 DIMM / DM1
Types of SIM/DIM module
( Single/Double Density)
Single density EDO DRAM
Double density EDO DRAM
Single density EDO DRAM
Double density EDO DRAM
Single density SDRAM
Double density SDRAM
61
 Loading...
Loading...