Page 1

AK75-EC
Rev. A+
System Board Users Manual
Carte Mère Manuel Pour Utilisateur
System-Platine Benutzerhandbuch
Manual del Usuario de Placas Base
47800108
Page 2

Copyright
This publication contains information that is protected by
copyright. No part of it may be reproduced in any form or by
any means or used to make any transformation/adaptation
without the prior written permission from the copyright holders.
This publication is provided for informational purposes only. The
manufacturer makes no representations or warranties with respect to
the contents or use of this manual and specifically disclaims any
express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any
particular purpose. The user will assume the entire risk of the use or
the results of the use of this document. Fur ther, the manufacturer
reserves the right to revise this publication and make changes to its
contents at any time, without obligation to notify any person or
entity of such revisions or changes.
© 2001. All Rights Reserved.
Trademarks
Microsoft® MS-DOS®, WindowsTM, Windows® 95, Windows® 98,
Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME, Windows® 2000 and Windows
NT® 4.0 are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
AMD, AthlonTM and DuronTM are registered trademarks of
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. VIA is a registered trademark of
VIA Technologies, Inc. Award is a registered trademark of Award
Software, Inc. Other trademarks and registered trademarks of
products appearing in this manual are the properties of their
respective holders.
Caution
To avoid damage to the system:
Use the correct AC input voltage range.
To reduce the risk of electric shock:
Unplug the power cord before removing the system chassis
cover for installation or ser vicing. After installation or servicing,
cover the system chassis before plugging the power cord.
Page 3

Battery:
Danger of explosion if battery incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommend by
the manufacturer.
Dispose of used batteries according to the battery
manufacturers instructions.
Joystick or MIDI port:
Do not use any joystick or MIDI device that requires more than
10A current at 5V DC . There is a risk of fire for devices that
exceed this limit.
FCC and DOC Statement on Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to tr y to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio TV technician for
help.
Notice:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority
to operate the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with
the emission limits.
Page 4

Quick Setup Guide
Table of Contents
Guide
Quick Setup
Chapter 1
Quick Setup Guide.............................................
Chapter 2
English......................................................................
Chapter 3
Français (French).................................................
Chapter 4
Deutsch (German)................................................
Chapter 5
Español (Spanish)..................................................
5
23
43
64
86
4
Page 5
Chapter 1 - Quick Setup Guide
Quick Setup Guide
Table of Contents
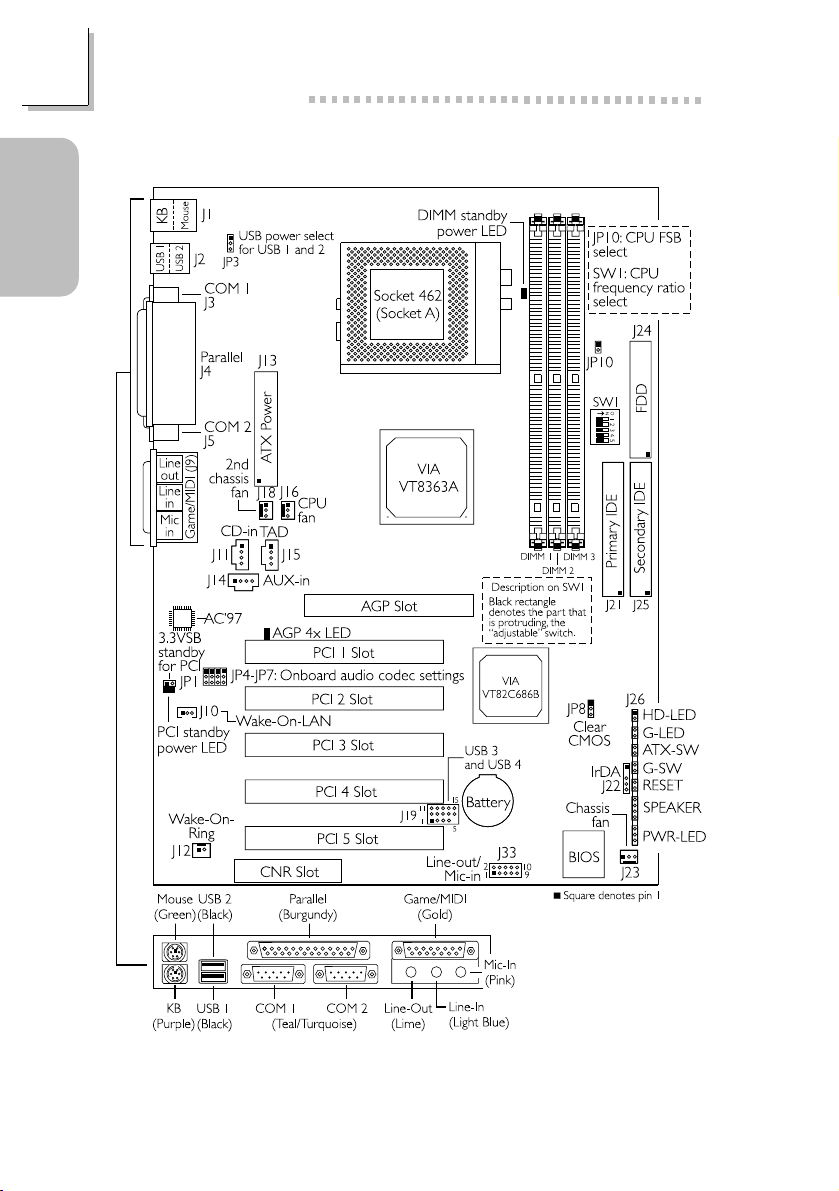
1.1 System Board Layout..................................................................................................
1.2 Jumpers.....................................................................................................................................
1.3 Ports and Connectors................................................................................................
1.4 Award BIOS Setup Utility.......................................................................................
10
18
Guide
6
7
Quick Setup
5
Page 6
Guide
Quick Setup
Quick Setup Guide
1.1 System Board Layout
6
Page 7
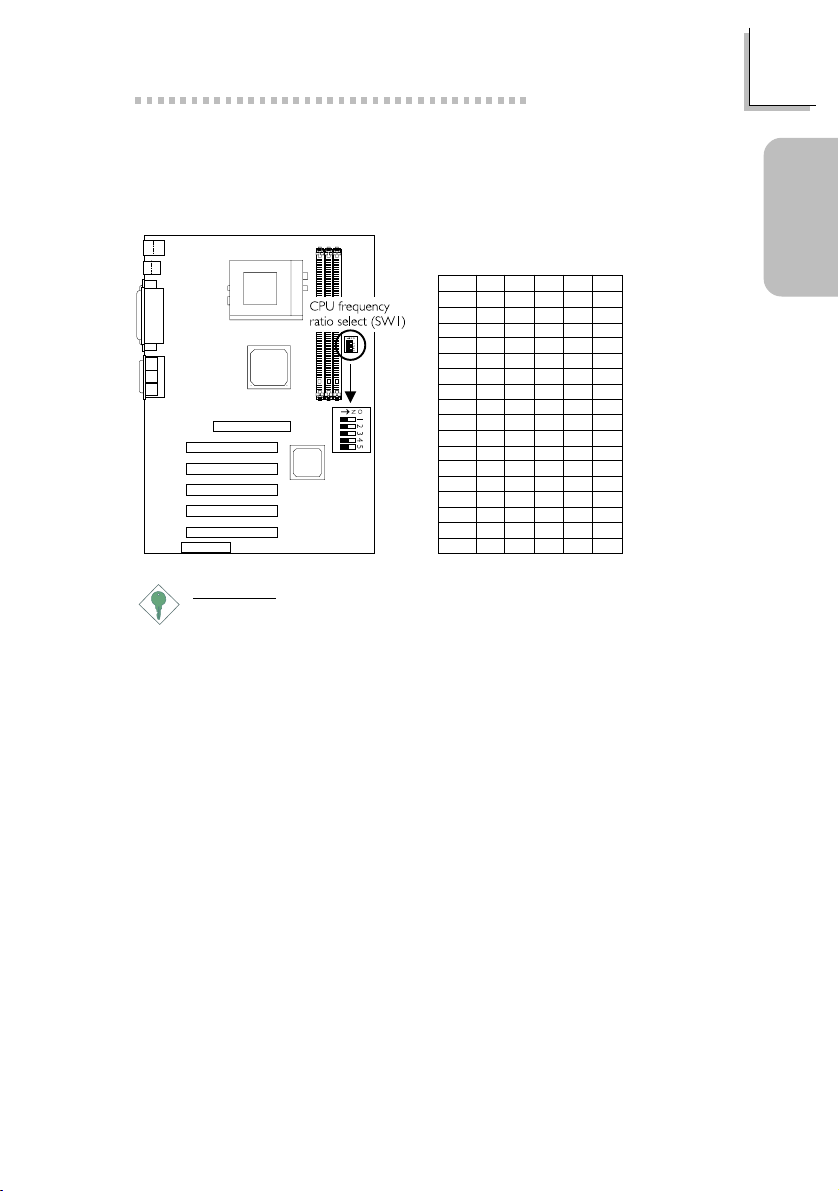
1.2 Jumpers
1.2.1 CPU Frequency Ratio - SW1
Quick Setup Guide
Guide
Ratio
Auto
5x
5.5x
6x
6.5x
7x
7.5x
8x
8.5x
9x
9.5x
10x
10.5x
11x
11.5x
12x
12.5x
Off
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
On
On
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
On
On
On
On
Off
On
On
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
Off
On
On
On
On
5
4
3
2
1
Important:
We do not recommend that you adjust the CPU to a higher
frequency ratio because it may result to the CPUs or systems
instability and are not guaranteed to provide better system
performance. If you are unable to boot up the system with the
frequency ratio you selected, please power off the system and
set SW1 pins 1-5 to Off (Auto).
Quick Setup
7
Page 8
Quick Setup Guide
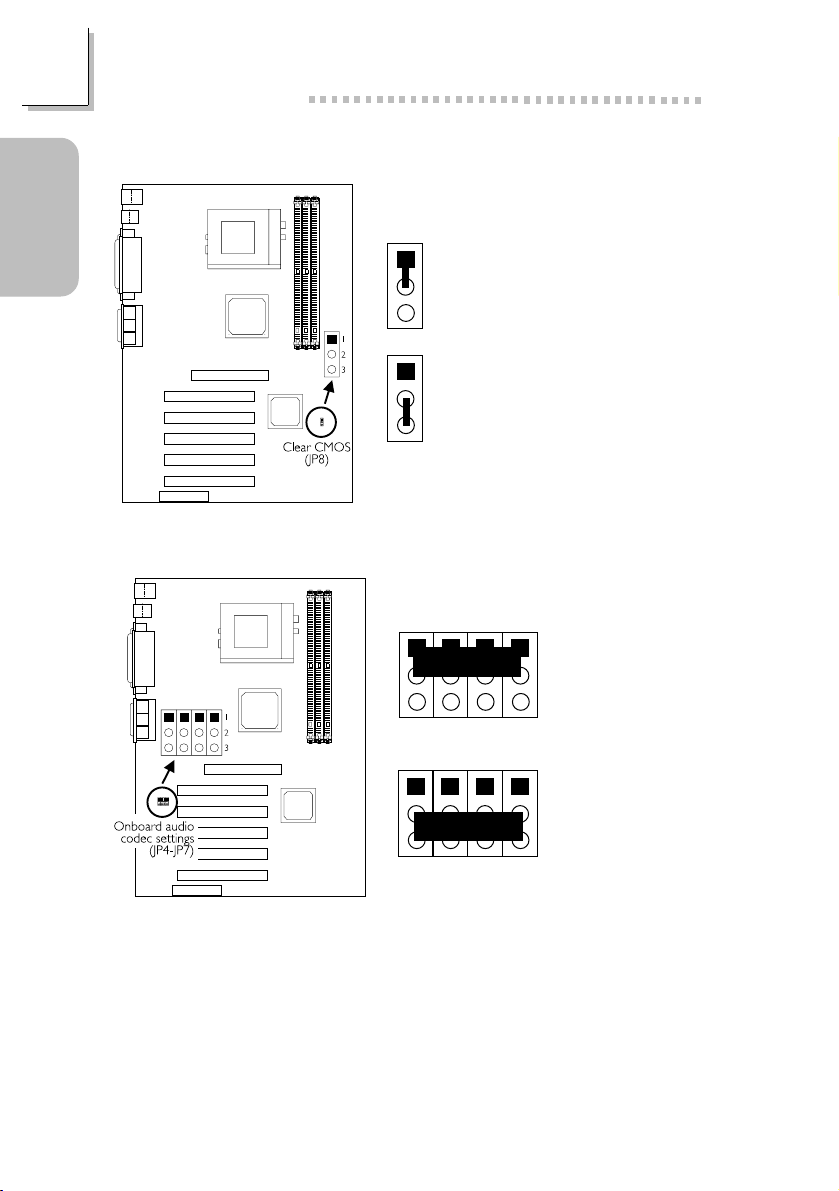
1.2.2 Clear CMOS Data - JP8
Guide
Quick Setup
1
1-2 On:
2
Normal (default)
3
1
2-3 On:
2
Clear CMOS Data
3
1.2.3 Onboard Audio Codec - JP4, JP5, JP6 and JP7
JP4 JP6JP5 JP7
1-2 On:
1
Enable the
2
Onboard Audio
3
Codec (default)
JP4 JP6JP5 JP7
1
2-3 On:
Disable the
2
Onboard Audio
3
Codec
8
Page 9
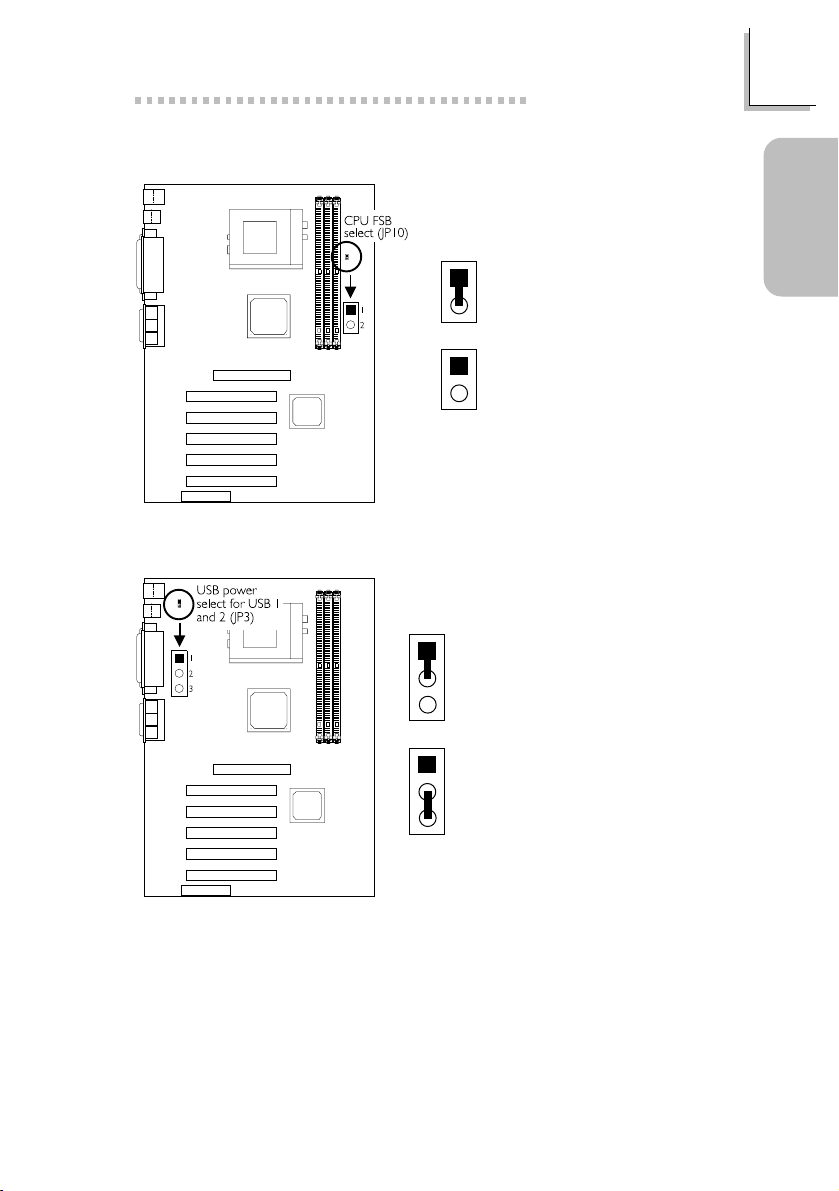
Quick Setup Guide
1.2.4 CPUs Front Side Bus - JP10
On: 100MHz
1
(200MHz DDR) CPU
2
(default)
1
Off: 133MHz
(266MHz DDR) CPU
2
1.2.5 USB Power for USB 1 and USB 2 - JP3
1
1-2 On:
2
5V (default)
3
Guide
Quick Setup
1
2-3 On:
2
5VSB
3
9
Page 10
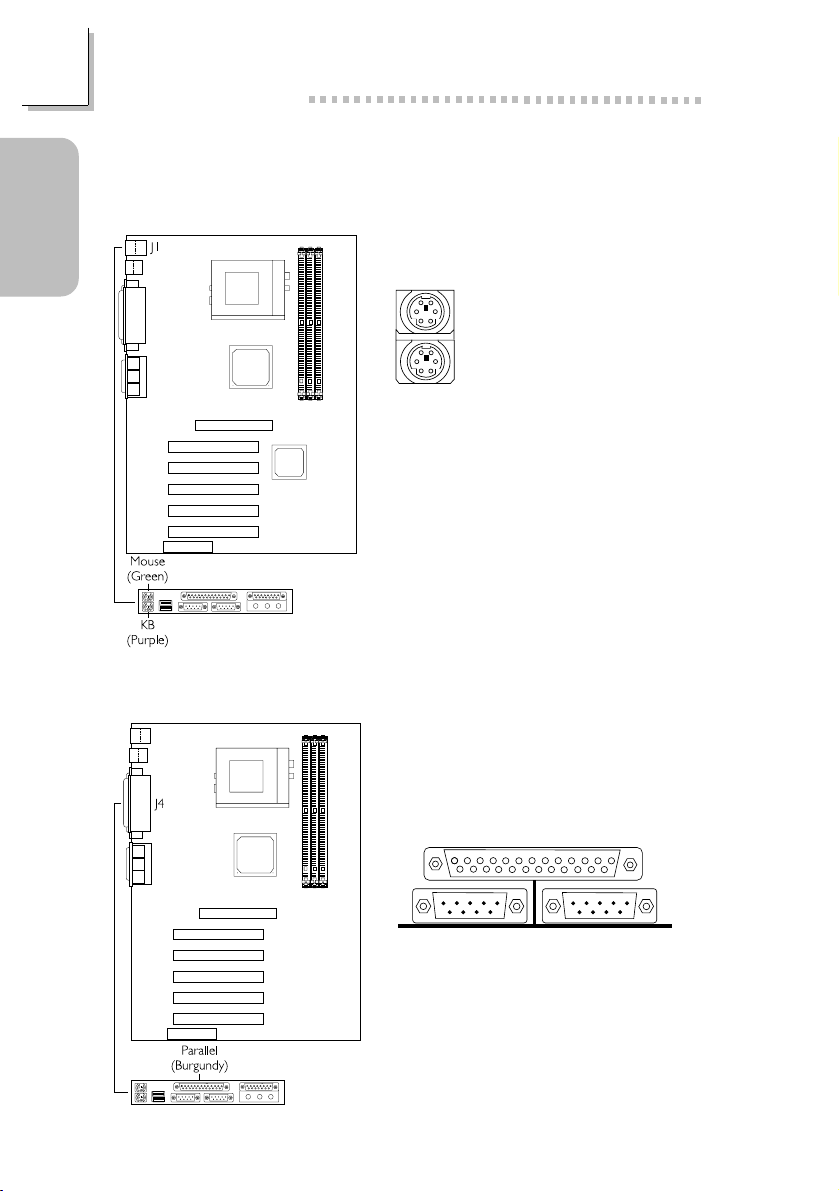
Guide
Quick Setup
Quick Setup Guide
1.3 Ports and Connectors
1.3.1 PS/2 Mouse and PS/2 Keyboard Ports
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 Keyboard
Make sure to turn off your computer
prior to connecting or disconnecting a
mouse or keyboard. Failure to do so
may damage the system board.
10
1.3.2 Parallel Port
Parallel Port
Page 11
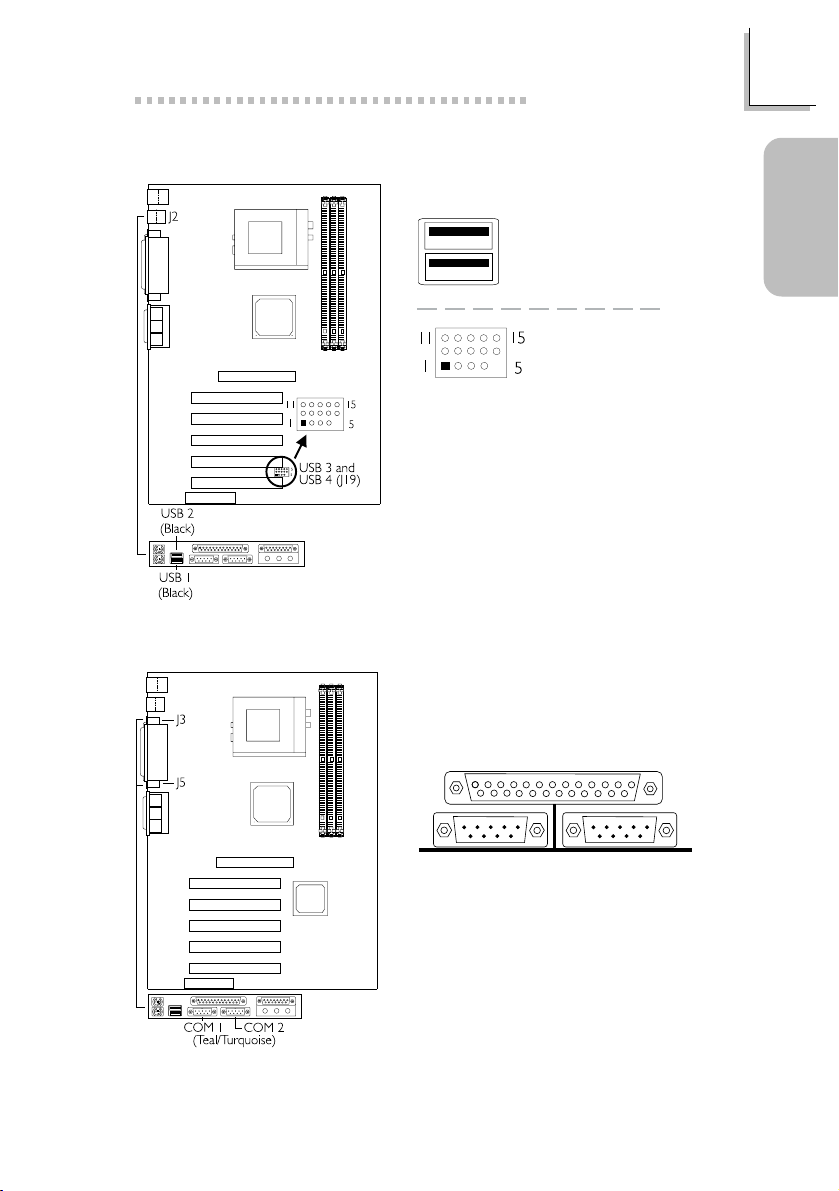
1.3.3 Universal Serial Bus Ports
Quick Setup Guide
1.3.4 Serial Ports
1 VCC
2 UP23 UP2+
4 Ground
5 Key
USB 2
USB 1
USB 3 and USB 4
(J19)
6 VCC
7 UP38 UP3+
9 Ground
10 Ground
Guide
Quick Setup
11 Ground
12 Ground
13 UP2+
14 UP215 VCC
COM 1
Serial Port
COM 2
Serial Port
11
Page 12
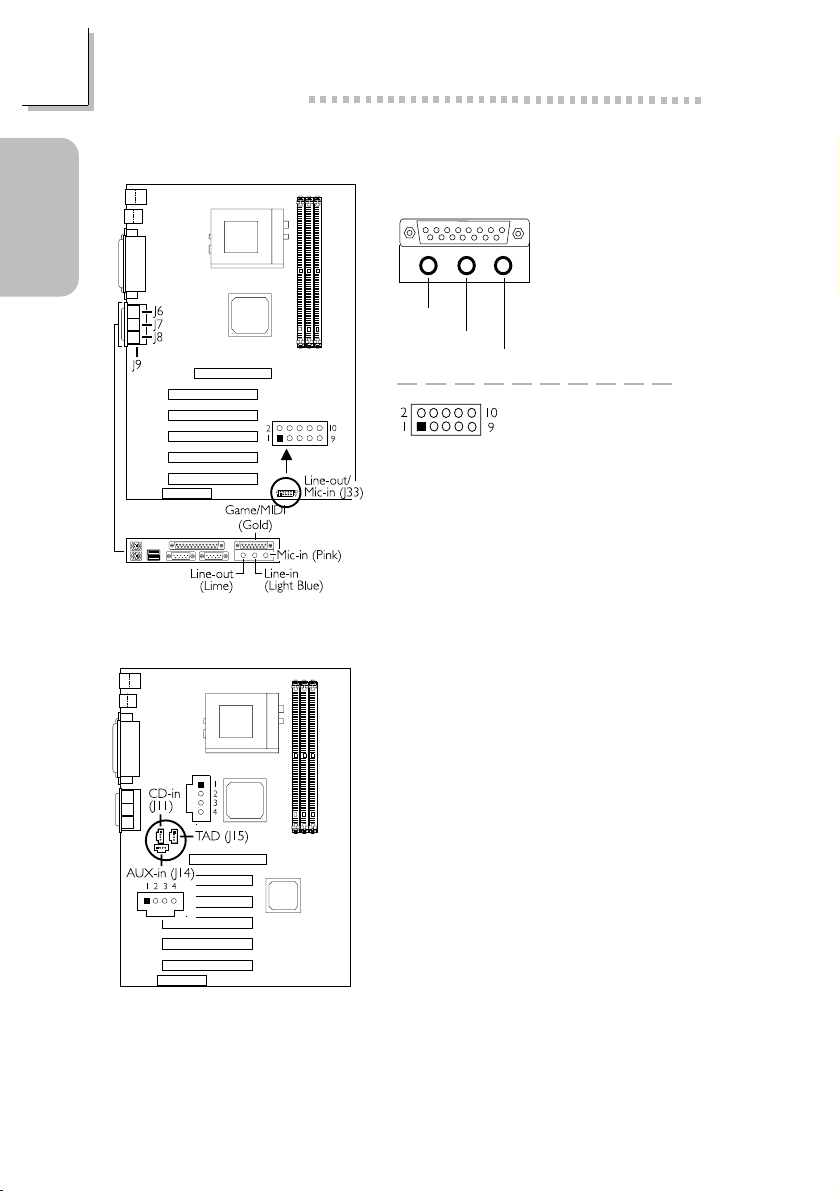
Quick Setup Guide
1.3.5 Game/MIDI Port and Audio Jacks
Guide
Quick Setup
Line-out
1 VCC
2 VCC
3 -Data
4 -Data
5 +Data
1.3.6 Internal Audio Connectors
AUX-in / CD-in
1 Left audio channel
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 Right audio channel
Game/MIDI Port
Audio Jacks
Line-in
Mic-in
Line-out/Mic-in
(J33)
6 +Data
7 Ground
8 Ground
9 Ground
10 Ground
12
TAD
1 Modem-out (from modem)
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 Modem-in (to modem)
Page 13
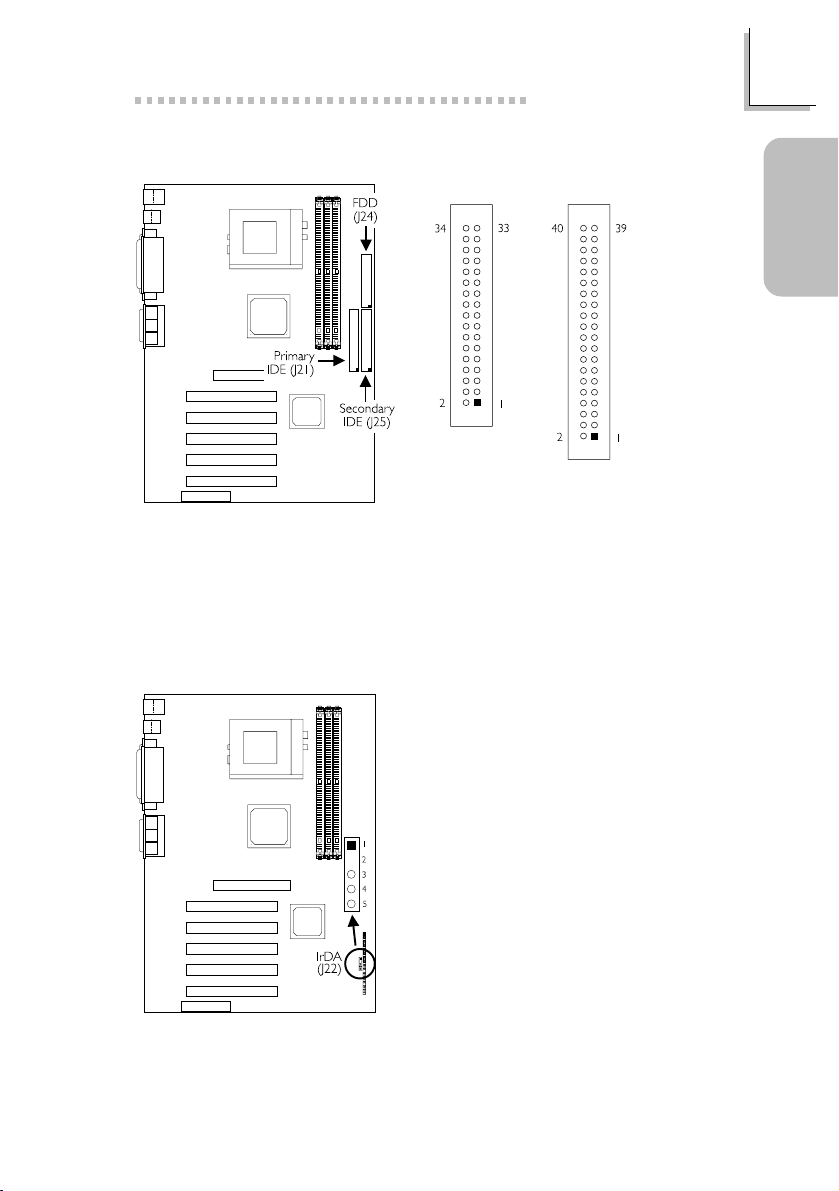
Quick Setup Guide
1.3.7 Floppy and IDE Disk Drive Connectors
FDD
IDE
If you encountered problems while using an ATAPI CD-ROM drive that is
set in Master mode, please set the CD-ROM drive to Slave mode. Some
ATAPI CD-ROMs may not be recognized and cannot be used if
incorrectly set in Master mode.
1.3.8 IrDA Connector
Guide
Quick Setup
1 VCC
2 N. C.
3 IRRX
4 Ground
5 IRTX
The sequence of the pin functions on
some IrDA cable may be reversed
from the pin function defined on the
system board. Make sure to connect
the cable to the IrDA connector
according to their pin functions.
13
Page 14
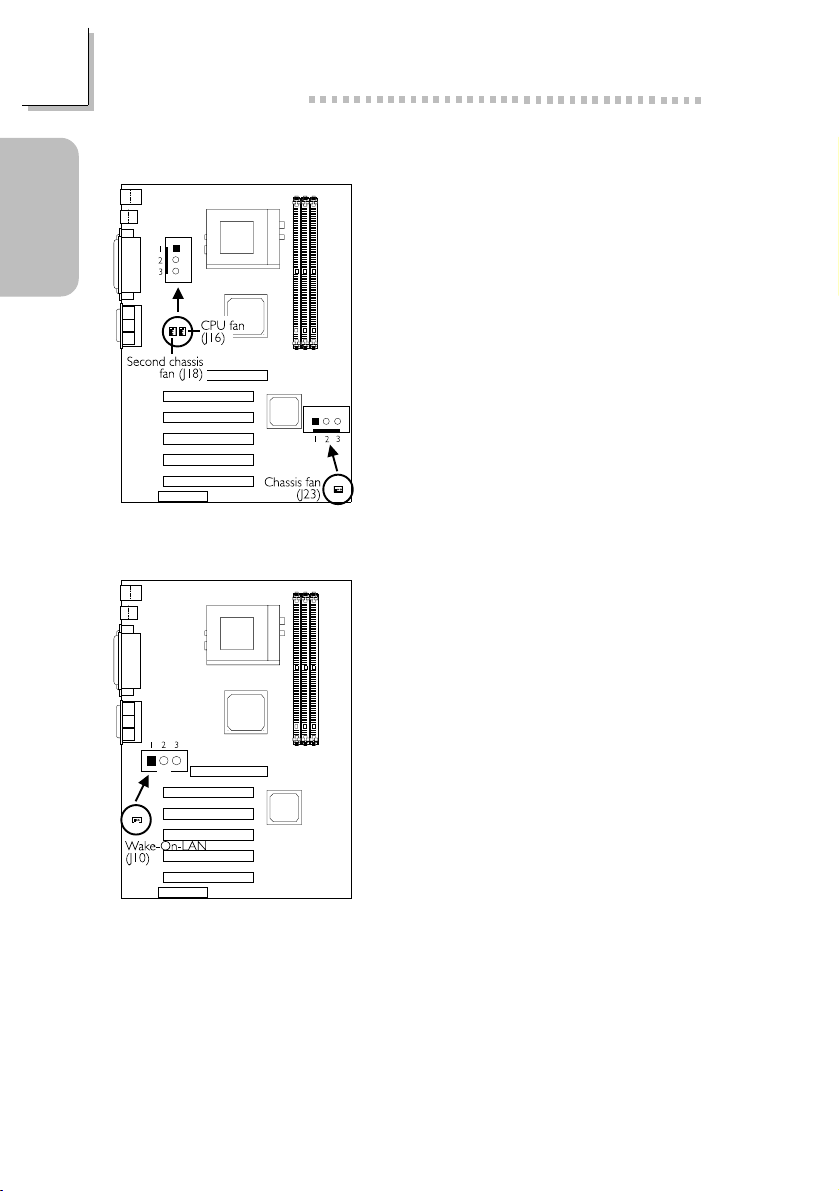
Guide
Quick Setup
Quick Setup Guide
1.3.9 Fan Connectors
CPU Fan
1On
2 +12V
3 Sense
Chassis Fan
1 On/Off
2 +12V
3 Sense
Second Chassis Fan
1 Ground
2 +12V
3N. C.
1.3.10 Wake-On-LAN Connector
14
1 +5VSB
2 Ground
3 WOL
The 5VSB power source of your power
supply must support ≥720mA.
Page 15
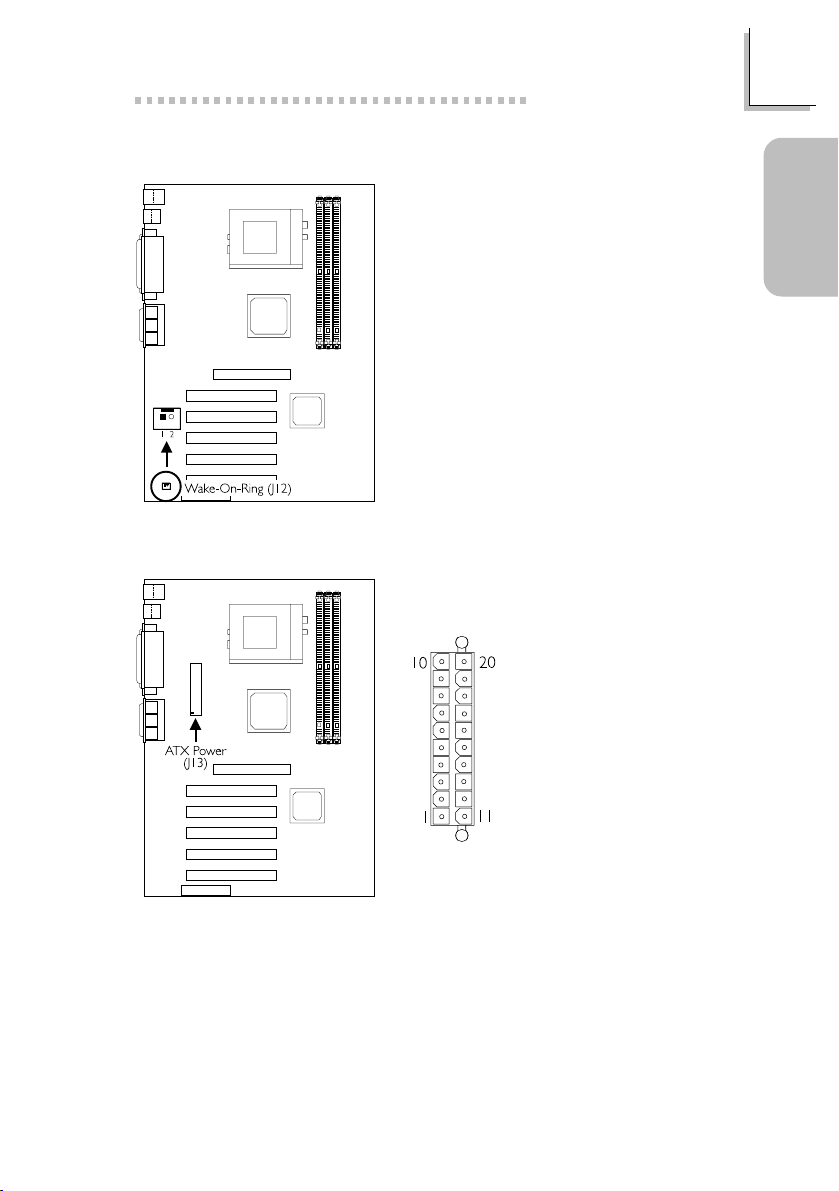
1.3.11 Wake-On-Ring Connector
Quick Setup Guide
Guide
1.3.12 Power Connector
1 Ground
2 RI#
If you are using a modem add-in card,
the 5VSB power source of your power
supply must support ≥720mA.
1 3.3V
2 3.3V
3 Ground
4 +5V
5 Ground
6 +5V
7 Ground
8 PW-OK
9 5VSB
10 +12V
11 3.3V
12 -12V
13 Ground
14 PS-ON
15 Ground
16 Ground
17 Ground
18 -5V
19 +5V
20 +5V
Quick Setup
The system board requires a minimum of 300W electric current.
15
Page 16
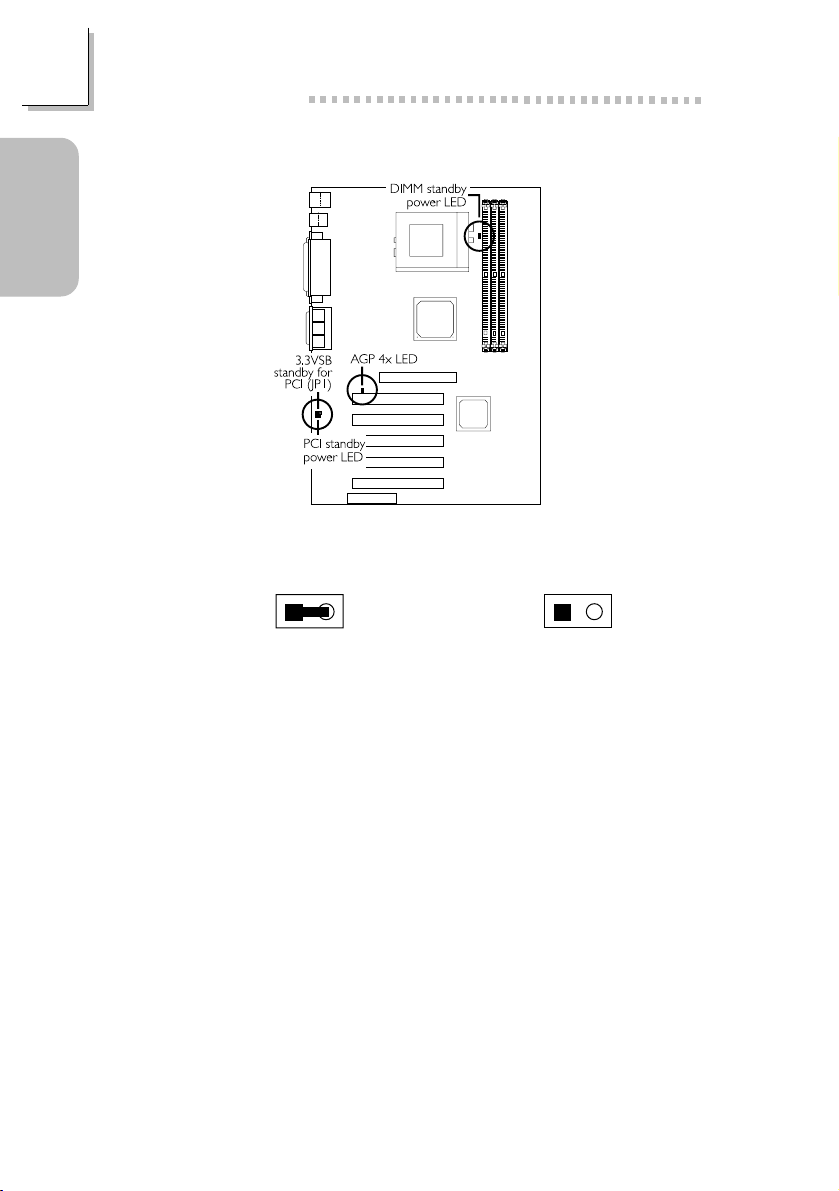
Guide
Quick Setup
Quick Setup Guide
1.3.13 AGP 4x LED / DIMM/PCI Standby Power LED
3.3VSB Standby for PCI - Jumper JP1
16
2
1
On: Default
3.3VSB Standby Power to PCI slots
(PCI 2.2 spec.)
The AGP 4x LED will light only when the AGP slot is installed with a 4x
add-in card.
The DIMM Standby Power LED will turn red when the systems power is
on or when it is in the Suspend state (Power On Suspend or Suspend to
RAM). It will not light when the system is in the Soft-Off state.
The PCI Standby Power LED will turn red when the system is in the
power-on, Soft-Off or Suspend (Power On Suspend or Suspend to RAM)
state.
Lighted LEDs serve as a reminder that you must power-off the system
then turn off the power supplys switch or unplug the power cord prior to
installing any memory modules or add-in cards.
Non-PCI 2.2 spec.
1
2
Off:
Page 17
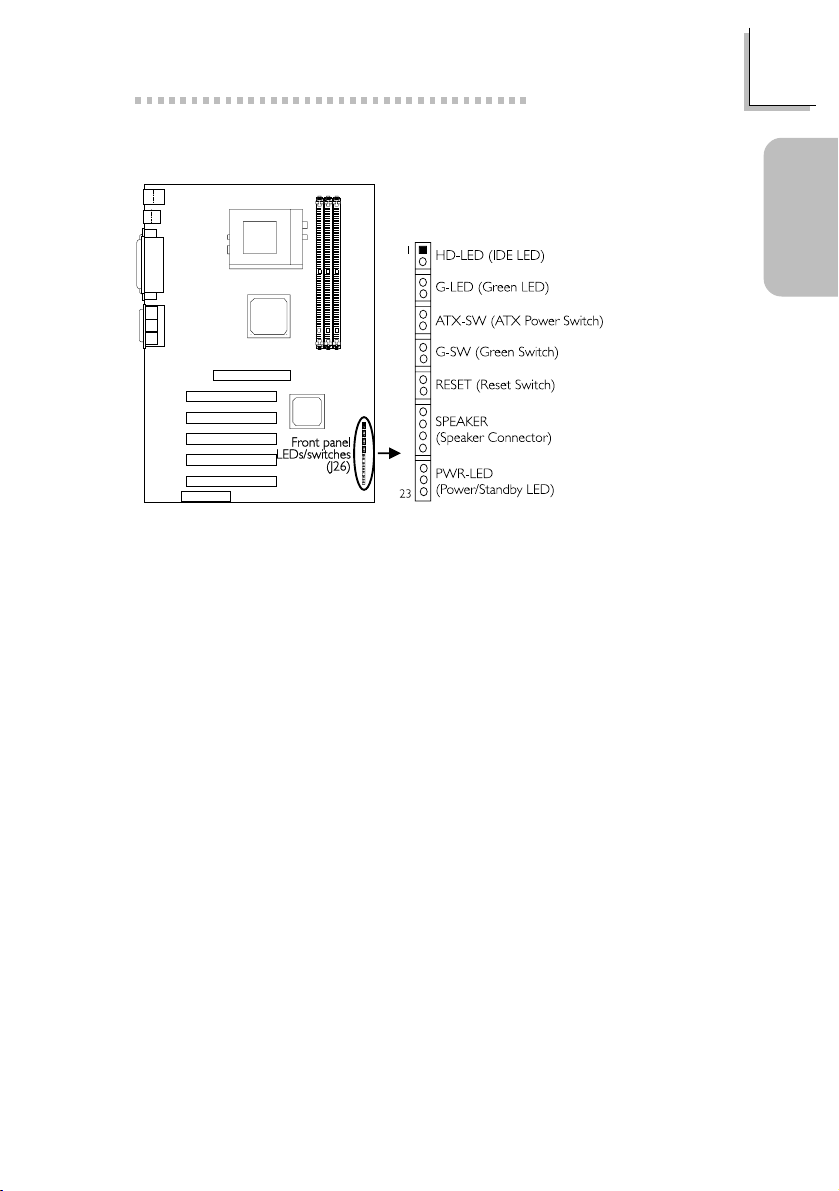
1.3.14 Front Panel LEDs and Switches
Quick Setup Guide
Guide
Quick Setup
1 HDD LED Power
2 HDD
3 N. C.
4 Green LED Power
5 Ground
6 N. C.
7 PWRBT+
8 PWRBT9 N. C.
10 SMI
11 Ground
12 N. C.
13 H/W Reset
14 Ground
15 N. C.
16 Speaker Data
17 N. C.
18 Ground
19 Speaker Power
20 N. C.
21 LED Power (+)
22 N.C.
23 LED Power (-) or
Standby Signal
17
Page 18

Quick Setup Guide
1.4 Award BIOS Setup Utility
1.4.1 Main Menu
Guide
Quick Setup
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced Chipset Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PnP/PCI Configurations
PC Health Status
Esc
: Quit
F10
: Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type...
1.4.2 Standard CMOS Features
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
Date (mm:dd:yy)
Time (hh:mm:ss)
K
IDE Primary Master
K
IDE Primary Slave
K
IDE Secondary Master
K
IDE Secondary Slave
Drive A
Drive B
Video
Halt On
Base Memory
Extended Memory
Total Memory
Standard CMOS Features
Wed, Feb 7 2001
4 : 35 : 5
Press Enter None
Press Enter None
Press Enter None
Press Enter None
1.44M, 3.5 in.
None
EGA/VGA
All, But Keyboard
640K
129024K
130048K
Frequency/Voltage Control
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
: Select Item
↑↓→←
Menu Level
Change the day, month,
year and century
Item Help
18
↑↓→← :Move
F5:Previous Values
Enter:Select
+/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
F1:General Help
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
Page 19
1.4.3 Advanced BIOS Features
Quick Setup Guide
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
Virus Warning
CPU L1 Cache
CPU L2 Cache
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking
Quick Power On Self Test
First Boot Device
Second Boot Device
Third Boot Device
Boot Other Device
Swap Floppy Drive
Boot Up Floppy Seek
Boot Up NumLock Status
Typematic Rate Setting
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
X
Typematic Delay (Msec)
X
Security Option
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability
↑↓→← Move F1:General HelpEnter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
Advanced BIOS Features
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Floppy
HDD-0
LS120
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
Off
Disabled
6
250
Setup
Non-OS2
Disabled
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized DefaultsF5:Previous Values
Menu Level
Allows you to choose
the VIRUS warning
feature for IDE Hard
Disk boot sector
protection. If this
function is enabled and
someone attempt to
write data into this
area, BIOS will show a
warning message on
screen and alarm beep
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
1.4.4 Advanced Chipset Features
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
DRAM Timing By SPD
SDRAM Cycle Length
DRAM Clock
System BIOS Cacheable
Video RAM Cacheable
AGP Aperture Size
AGP-4X Mode
AGP Driving Control
AGP Driving Value
X
OnChip USB
USB Keyboard Support
OnChip Sound
OnChip Modem
Advanced Chipset Features
Disabled
3
100MHz
Disabled
Disabled
64M
Enabled
Auto
DA
Enabled
Disabled
Auto
Auto
Menu Level
Item Help
Item Help
Guide
Quick Setup
↑↓→← Move
F5:Previous Values
+/-/PU/PD:Value
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
F10:Save
ESC:Exit
F1:General HelpEnter:Select
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
19
Page 20
Quick Setup Guide
1.4.5 Integrated Peripherals
Guide
Quick Setup
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
On-Chip Primary IDE
On-Chip Secondary IDE
IDE Prefetch Mode
IDE Primary Master PIO
IDE Primary Slave PIO
IDE Secondary Master PIO
IDE Secondary Slave PIO
IDE Primary Master UDMA
IDE Primary Slave UDMA
IDE Secondary Master UDMA
IDE Secondary Slave UDMA
Init Display First
IDE HDD Block Mode
Onboard FDD Controller
Onboard Serial Port 1
Onboard Serial Port 2
UART2 Mode Select
IR Function Duplex
X
TX,RX Inverting Enable
X
Onboard Parallel Port
Parallel Port Mode
ECP Mode Use DMA
↑↓→← Move
EPP Mode Select
Sound Blaster
SB I/O Base Address
SB IRQ Select
SB DMA Select
MPU-401
MPU-401 I/O Address
Game Port (200-207H)
F5:Previous Values
Integrated Peripherals
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
PCI Slot
Enabled
Enabled
3F8/IRQ4
2F8/IRQ3
Standard
Half
No, Yes
378/IRQ7
ECP/EPP
3
+/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
EPP1.7
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Disabled
220H
IRQ 5
DMA 1
Disabled
330-333H
Enabled
Menu Level
Item Help
F1:General HelpEnter:Select
The screen above list all the fields available in the Integrated Peripherals
submenu, for ease of reference in this manual. In the actual CMOS setup,
you have to use the scroll bar to view the fields. The settings on the screen
are for reference only. Your version may not be identical to this one.
20
Page 21
1.4.6 Power Management Setup
Quick Setup Guide
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
ACPI Function
Power Management
K
ACPI Suspend Type
PM Control by APM
Video Off Option
Video Off Method
MODEM Use IRQ
Soft-Off By PWRBTN
PWR Lost Resume State
K
Wake Up Events
↑↓→← Move
F5:Previous Values
Power Management Setup
Enabled
Press Enter
S1(POS)
Yes
Suspend -> Off
V/H SYNC+Blank
3
Instant-off
Keep Off
Press Enter
+/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Menu Level
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
1.4.7 PnP/PCI Configurations
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
Reset Configuration Data
Resources Controlled By
X
IRQ Resources
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
Assign IRQ For VGA
Assign IRQ For USB
PnP/PCI Configurations
Disabled
Auto(ESCD)
Press Enter
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Menu Level
Default is Disabled.
Select Enabled to
reset Extended System
Configuration Data
(ESCD) when you exit
Setup if you have
installed a new add-on
and the system
reconfiguration has
caused such a serious
conflict that the OS
cannot boot.
Item Help
F1:General HelpEnter:Select
Item Help
Guide
Quick Setup
↑↓→← Move
F5:Previous Values
+/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
F1:General HelpEnter:Select
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
21
Page 22

Quick Setup Guide
1.4.8 PC Health Status
Guide
Quick Setup
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
Current System Temp.
Current CPU Temperature
Current CPU Fan Speed
Current Chassis Fan Speed
Vcore
3.3V
5V
12V
CPU Fan Protection
CPU Temp. Prot. Function
CPU Temp. Prot. Alarm
↑↓→← Move
F5:Previous Values
PC Health Status
27C/80F
37C/98F
0 RPM
0 RPM
1.75 V
3.31 V
5.05 V
12.03 V
Disabled
Disabled
60
+/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Menu Level
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
1.4.9 Frequency/Voltage Control
CMOS Setup Utility - Copyright (C) 1984-2000 Award Software
CPU Vcore Select
Spread Spectrum Modulated
CPU Host/PCI Clock
Frequency/Voltage Control
Default
Disabled
Default
Menu Level
Item Help
F1:General HelpEnter:Select
Item Help
22
↑↓→← Move
F5:Previous Values
+/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
F1:General HelpEnter:Select
The settings on the screen are for reference only. Your version may not be
identical to this one.
Page 23
Chapter 2 - English
Table of Contents
English
2.1 Features and Specifications.....................................................................................
2.2 Identifying a CPU that Supports the Multiplier
Overclocking Function.................................................................................................
2.3 Using the CPU Fan Protection Function...................................................
2.4 Using the CPU Temperature Protection Function.............................
2.5 Using the Suspend to RAM Function..........................................................
2.6 Supported Softwares...................................................................................................
2.7 Troubleshooting.................................................................................................................
Package Checklist
The system board package contains the following items:
þ The system board
þ A users manual
þ One IDE cable for ATA/33, ATA/66 or ATA/100 IDE drives
þ One 34-pin floppy disk drive cable
þ One Main Board Utility CD
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your
dealer or sales representative for assistance.
24
30
31
32
33
35
38
English
23
Page 24

English
English
2.1 Features and Specifications
2.1.1 Features
Chipset
VIA® KT133A - VT8363A and VT82C686B
Processor
The system board is equipped with a switching voltage regulator
that automatically detects 1.100V to 1.850V.
AMD AthlonTM/DuronTM 100/133MHz (200/266MHz DDR) FSB
processor (600/650/700/750/800/850/900/950MHz, 1GHz,
1.3GHz or future processors)
System Memory
Supports up to 1.5GB using VCM (Virtual Channel Memory) or
PC SDRAM DIMM (unbuffered or registered)
- Registered DIMM - PC-100 only.
Three 168-pin DIMM sockets
Uses x64 PC SDRAM, 3.3V
- PC-100 SDRAM DIMM for 100MHz memory bus
- PC-133 SDRAM DIMM for 133MHz memory bus
L2 cache memory
- Duron
- Athlon
cache
cache
TM
processor: built-in 64KB Level 2 pipelined burst
TM
processor: built-in 256KB Level 2 pipelined burst
24
Note:
PC-100 SDRAM DIMM is supported when used with
100MHz FSB processor.
PC-133 SDRAM DIMM is supported when used with
100MHz FSB or 133MHz FSB processor.
If you are using more than one DIMM, make sure you
insert the same type of DIMMs into the DIMM sockets.
Using different types (VCM or PC SDRAM) of DIMMs may
cause problems.
Page 25

English
DIMMs
2MBx64
4MBx64
8MBx64
Memory Size
16MB
32MB
64MB
DIMMs
16MBx64
32MBx64
64MBx64
Memory Size
128MB
256MB
512MB
Expansion Slots
The system board is equipped with 1 universal AGP slot, 5
dedicated PCI slots and 1 CNR (Communication and Networking
Riser) slot for modem riser card only.
AGP is an interface designed to support high performance 3D
graphics cards. It utilizes a dedicated pipeline to access system
memory for texturing, z-buffering and alpha blending. The universal
AGP slot supports AGP 2x with up to 533MB/sec. bandwidth and
AGP 4x with up to 1066MB/sec. bandwidth for 3D graphics
applications. AGP in this system board will deliver faster and better
graphics to your PC.
Onboard Audio Features
Supports Microsoft® DirectSound/DirectSound 3D
AC97 supported with full duplex, independent sample rate con-
verter for audio recording and playback
ATX Double Deck Ports (PC 99 color-coded connectors)
English
Two USB ports
Two NS16C550A-compatible DB-9 serial por ts
One SPP/ECP/EPP DB-25 parallel port
One mini-DIN-6 PS/2 mouse port
One mini-DIN-6 PS/2 keyboard por t
One game/MIDI por t
Three audio jacks: line-out, line-in and mic-in
Connectors
One connector for 2 additional external USB por ts
One connector for IrDA interface
Two IDE connectors
One floppy drive interface supports up to two 2.88MB floppy
drives
One ATX power supply connector
25
Page 26

English
English
One Wake-On-LAN connector
One Wake-On-Ring connector
CPU, chassis and second chassis fan connectors
Three internal audio connectors (AUX-in, CD-in and TAD)
PCI Bus Master IDE Controller
Two PCI IDE interfaces suppor t up to four IDE devices
Supports ATA/33, ATA/66 and ATA/100 hard drives
PIO Mode 3 and Mode 4 Enhanced IDE (data transfer rate up
to 16.6MB/sec.)
Bus mastering reduces CPU utilization during disk transfer
Supports ATAPI CD-ROM, LS-120 and ZIP
IrDA Interface
The system board is equipped with an IrDA connector for wireless
connectivity between your computer and peripheral devices. It
supports peripheral devices that meet the HPSIR and ASKIR
standard.
USB Ports
The system board supports 4 USB por ts. Two onboard USB por ts
are located at the ATX double deck ports of the board. The J19
connector on the system board allows you to connect the optional
3rd and 4th USB ports. These optional USB ports, which are
mounted on a card-edge bracket, will be provided as an option.
USB allows data exchange between your computer and a wide
range of simultaneously accessible external Plug and Play peripherals.
26
BIOS
Award BIOS, Windows® 95/98/2000/ME Plug and Play compat-
ible
Supports SCSI sequential boot-up
Flash EPROM for easy BIOS upgrades
Supports DMI 2.0 function
2Mbit flash memory
Vcore and CPU external bus clock selectable in the BIOS
Page 27

Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
The system board comes with a DMI 2.0 built into the BIOS. The
DMI utility in the BIOS automatically records various information
about your system configuration and stores these information in the
DMI pool, which is a part of the system board's Plug and Play
BIOS. DMI, along with the appropriately networked software, is
designed to make inventory, maintenance and troubleshooting of
computer systems easier.
2.1.2 System Health Monitor Functions
The system board is capable of monitoring the following system
health conditions.
Monitors CPU/system temperature and overheat alarm
Monitors 12V/5V/3.3V/VCORE voltages and failure alarm
Monitors CPU/chassis fan speed and failure alarm
Automatic chassis fan on/off control
Read back capability that displays temperature, voltage and fan
speed
If you want a warning message to pop-up or a warning alarm to
sound when an abnormal condition occurs, you must install the VIA
Hardware Monitor utility. This utility is included in the CD that came
with the system board.
English
English
2.1.3 Intelligence
CPU Temperature Protection
The CPU Temperature Protection function has the capability of
monitoring the CPUs temperature during system boot-up. Once it
has detected that the CPUs temperature exceeded the CPU
temperature limit defined in the BIOS, the system will automatically
power-off after 5 warning beeps.
27
Page 28

English
English
CPU Fan Protection
The CPU Fan Protection function has the capability of monitoring the
CPU fan during system boot-up and will automatically power-off the
system once it has detected that the CPU fan did not rotate. This
preventive measure has been added to protect the CPU from
damage and insure a safe computing environment.
Over Voltage
The Over Voltage function allows you to manually adjust to a higher
core voltage that is supplied to the CPU. Although this function is
supported, we do not recommend that you use a higher voltage
because unstable current may be supplied to the system board
causing damage.
CPU Overclocking
The CPU Overclocking function allows you to adjust the processors
bus clock. However, overclocking may result to the processors or
systems instability and are not guaranteed to provide better system
performance.
Automatic Chassis Fan Off
28
The chassis fan will automatically turn off once the system enters the
Suspend mode.
Dual Function Power Button
Depending on the setting in the Soft-Off By PWRBTN field of the
Power Management Setup, this switch will allow the system to enter
the Soft-Off or Suspend mode.
Wake-On-Ring
This feature allows the system that is in the Suspend mode or Soft
Power Off mode to wake-up/power-on to respond to calls coming
through an internal or external modem.
Important:
If you are using a modem add-in card, the 5VSB power source
of your power supply must support a minimum of ≥720mA.
Page 29

English
RTC Timer to Power-on the System
The RTC installed on the system board allows your system to
automatically power-on on the set date and time.
Wake-On-LAN
The Wake-On-LAN function allows the network to remotely wake
up a Soft Power Down (Soft-Off) PC. Your LAN card must support
the remote wakeup function.
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support a
minimum of ≥720mA.
AC Power Failure Recove ry
When power returns after an AC power failure, you may choose to
either power-on the system manually, let the system power-on
automatically or return to the state where you left off before power
failure occurs.
ACPI STR
English
The system board is designed to meet the ACPI (Advanced
Configuration and Power Interface) specification. ACPI has energy
saving features that enables PCs to implement Power Management
and Plug-and-Play with operating systems that support OS Direct
Power Management. Currently, only Windows® 98/2000/ME suppor ts
the ACPI function allowing you to use the Suspend to RAM function.
With the Suspend to RAM function enabled, you can power-off the
system at once by pressing the power button or selecting Standby
when you shut down Windows® 98/2000/ME without having to go
through the sometimes tiresome process of closing files, applications
and operating system. This is because the system is capable of
storing all programs and data files during the entire operating session
into RAM (Random Access Memory) when it powers-off. The
operating session will resume exactly where you left off the next time
you power-on the system.
Important:
The 5VSB power source of your power supply must support
≥
1A.
29
Page 30
English
English
Virus Protection
Most viruses today destroy data stored in hard drives. The system
board is designed to protect the boot sector and partition table of
your hard disk drive.
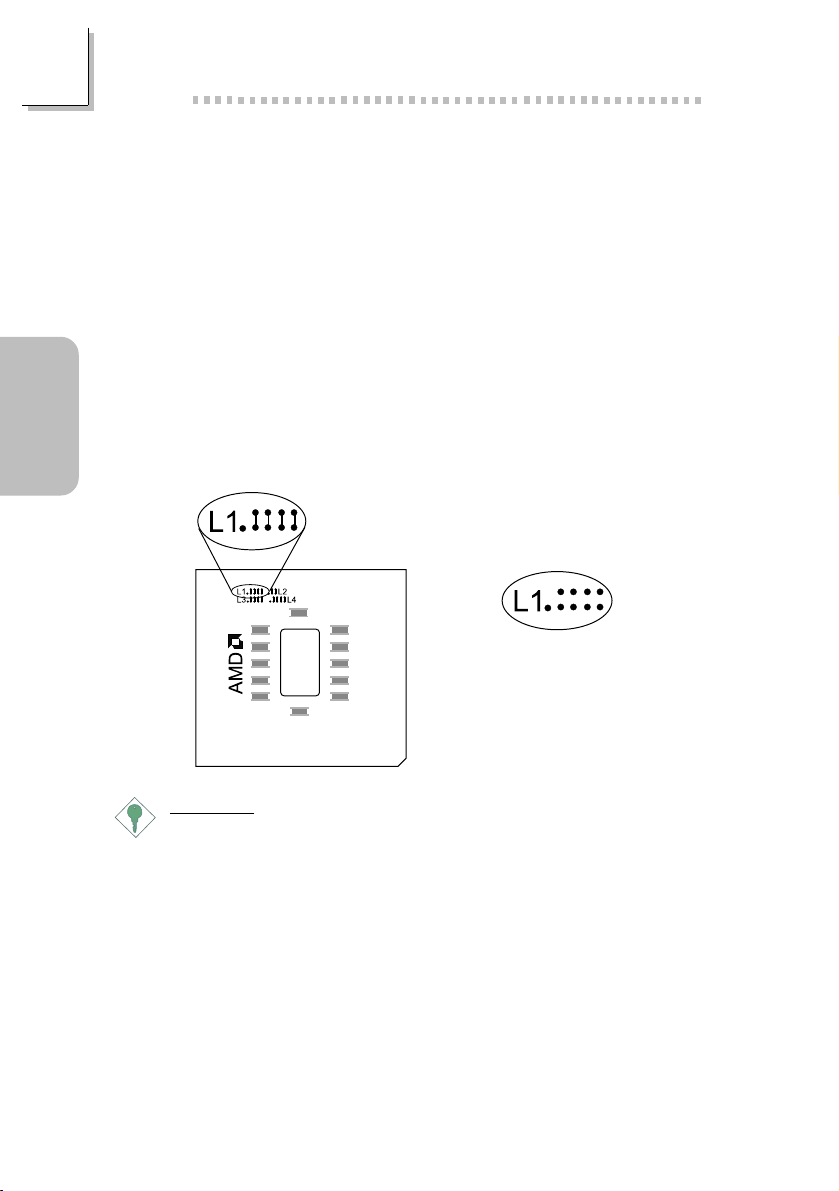
2.2 Identifying a CPU that Supports the
Multiplier Overclocking Function
Not all AMD CPUs support the multiplier overclocking function.
Please give special attention to L1 on the CPU. L1s four bridges
must be closed (short) in order for the frequency ratio selected on
SW1 to take effect. The figure below will help you identify the type
of CPU that would allow you to adjust its frequency ratio.
L1s four bridges closed (short).
L1s four bridges open.
30
Important:
We do not recommend that you adjust the CPU to a higher
frequency ratio because it may result to the CPUs or systems
instability and are not guaranteed to provide better system
performance. If you are unable to boot up the system with the
frequency ratio you selected, please power off the system and set
SW1 pins 1-5 to Off (Auto).
Page 31

2.3 Using the CPU Fan Protection Function
The CPU must be kept cool by using a CPU fan with heatsink.
Without sufficient air circulation across the CPU and heatsink, the
CPU will overheat damaging both the CPU and system board.
The CPU Fan Protection function supported by the system board
has the capability of monitoring the CPU fan during system boot-up
and will automatically power-off the system once it has detected that
the CPU fan did not rotate. This preventive measure has been
added to protect the CPU from damage and insure a safe
computing environment.
English
To use the CPU Fan Protection function, please follow the steps
below.
1. Before you power-on the system, make sure the heatsink and
CPU fan are correctly installed onto the CPU. The system is
capable of monitoring the CPU fan, therefore you must use a fan
with sense pin to support this function. Connect the CPU fan to
the 3-pin fan connector at location J16 on the system board.
2. Make sure the CPU Fan Protection field in the PC Health
Status submenu of the BIOS is set to Enabled.
3. You may now power-on the system.
Two circumstances may occur causing the system to power-off
automatically. A beeping alarm will sound before the system will
power-off.
1. The CPU fan did not rotate because the CPU fan is damaged.
When you boot-up the system and the CPU fan did not rotate,
it may indicate that the fan is damaged. Replace it with a new
fan.
2. The CPU fan did not rotate immediately upon system boot-up
or it took some time before the CPU fan rotated.
English
If the CPU fan did not rotate immediately upon system boot-up
or it took some time before the fan rotated, check whether the
heatsink and fan are mounted properly onto the CPU then
31
Page 32

English
English
restart the system. If the same problem occurs, you must replace
it with a good quality fan - one that will rotate immediately once
power comes in and also one that can dissipate heat more
efficiently, otherwise, you have to disable this function in the CPU
Fan Protection field (PC Health Status submenu) of the BIOS.
2.4 Using the CPU Temperature Protection
Function
The CPU Temperature Protection function has the capability of
monitoring the CPUs temperature during system boot-up. To use this
function, set the CPU Temp. Prot. Function field to Enabled then
select the desired CPU temperature limit in the CPU Temp. Prot.
Alarm field (PC Health Status submenu of the BIOS). Once the
system has detected that the CPUs temperature exceeded the limit,
5 warning beeps will sound and at the same time, a warning
message will appear on the boot-up screen instructing you to press
<Del> in order to enter the main menu of the BIOS. If you did not
press <Del>, the system will automatically power-off after the 5
warning beeps. You may either:
1. Press <Del> then enter a new CPU temperature limit;
32
or
2. Allow the system to power-off after the 5 warning beeps then
check whether the heatsink and fan are mounted properly onto
the CPU because high CPU temperature may be due to
incorrect fan/heatsink installation. Now restart the system. If the
same problem persist, it may be that the CPU fan is damaged
or it is not rotating properly. Try replacing it with a new fan. If it
is due to other contributing factors that resulted to high CPU
temperature, you may need to set a lower CPU temperature
limit.
CPU Temperature References
When you power-up a system, the BIOS message appears on the
screen and the memory count begins. After the memor y test, the
CPU temperature range is normally between 32oC and 35oC. When
you run an operating system then tried to reboot the system, the
Page 33

CPU temperature range at this time is between 40oC and 45oC.
These temperature references serve as a guide when you select the
CPU temperature limit.
2.5 Using the Suspend to RAM Function
1. Select Power Management Setup in the main menu screen and
press <Enter>.
2. In the ACPI Function field, select Enabled.
3. In the ACPI Suspend Type field, select S3(STR).
English
4. Press <Esc> to return to the main menu.
5. Select Save & Exit Setup and press <Enter>. Type <Y> and
press <Enter>.
6. Install Windows® 98/2000/ME by typing the following
parameter. This is to ensure that the ACPI function is supported.
[drive]:>setup /p j
If you have previously installed Windows® 98/2000/ME, you
need to upgrade the system in order to support ACPI. Please
contact Microsoft for upgrade information.
7. Boot Windows® 98/2000/ME. In the Windows® 98/2000/ME
desktop, click the Start button. Move the cursor to Settings,
then click Control Panel.
To check whether ACPI was properly installed, double-click the
System icon. In the System Properties dialog box, click the
Device Manager tab. In View devices by type, click System
devices.
8. Double-click the System icon. In the System Proper ties dialog
box, click the Performance tab.
9. Click File System. In the Typical role of this computer field,
select Mobile or docking system. Click Apply, then click OK.
Restart the computer.
English
10. Repeat step 7 to open the Control Panel dialog box. Doubleclick the Power Management icon.
33
Page 34

English
11. Click the Advanced tab. In the When I press the power
button on my computer field, select Standby.
12. After completing the steps above and you want to power-off
the computer, you do not need to go through the process of
closing files, applications and operating system. You can poweroff the computer at once by pressing the power button or
selecting Standby when you shut down Windows® 98/2000/
ME.
To power-on the computer, just press the power button. The
operating session where you left off when you power-off the
computer will resume in not more than 8 seconds.
English
If you have changed the color or resolution (in the Display
Properties dialog box), do not apply the settings without
restarting. You must restart the computer.
34
Page 35

2.6 Supported Softwares
2.6.1 VIA Hardware Monitor
The system board comes with the VIA Hardware Monitor utility
contained in the provided CD. It is capable of monitoring the
systems hardware conditions such as the temperature of the CPU
and system, voltage, and speed of the CPU and chassis fans. It also
allows you to manually set a range to the items being monitored. If
the values are over or under the set range, a warning message will
pop-up. The utility can also be configured so that a beeping alarm
will sound whenever an error occurs. We recommend that you use
the Default Setting which is the ideal setting that would keep the
system in good working condition.
English
English
Note:
Use this utility only in Windows® 95, Windows® 98, Windows
98 SE, Windows® ME, Windows® 2000 or Windows NT® 4.0
operating system.
To install the utility, insert the CD into a CD-ROM drive. The autorun
screen (Main Board Utility CD) will appear. Click the VIA Hardware
Monitor button to install the utility. Refer to its readme file for
instructions on using the utility.
2.6.2 VIA® Service Pack
The CD in the system board package also comes with the VIA
Service Pack. The service pack includes the following drivers.
Bus Master PCI IDE Driver
AGP VxD Driver
VIA Chipset Functions Registry
VIA PCI IRQ Miniport Driver
To install the drivers, insert the CD into a CD-ROM drive. The
autorun screen (Main Board Utility CD) will appear. Click the VIA
Service Pack button. For installation instructions or information, click
the Read Me button in the autorun screen.
®
®
35
Page 36

English
English
VIA® Service Pack Installation Notes
The AGP VxD Driver and VIA Chipset Functions Registry drivers
in the VIA Ser vice Pack are supported in Windows® 95,
Windows® 98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME and Windows
2000.
You must first install VIA® Service Pack prior to installing any other
drivers. However, this may not be the case for some AGP cards.
Please read carefully the following information.
Important:
The VG A dr iver that came with some AGP cards is already
bundled with the AGP VxD driver. Since the version of the
bundled VxD driver may be older than the one provided in the
CD, installing the bundled VxD driver may cause problems . If
you are using this type of card, we recommend that you install
first the AGP cards VGA driver before installing the VIA Service
Pack.
To install the VIA Service pack, please follow the steps below.
1. Insert the CD that came with the system board package into a
CD-ROM drive. The autorun screen (Main Board Utility CD) will
appear.
®
36
2. Click VIA Service Pack.
3. The Welcome screen will appear. Click Next. Please read the
VIA Service Pack readme carefully before proceeding to step 4.
4. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete the installation.
5. Reboot the system for the drivers to take effect.
2.6.3 Audio Drivers and Software Application
The CD in the system board package also includes audio drivers
and audio playback software for Windows 95, Windows 98,
Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows NT 4.0 and Windows
2000 operating systems. For installation instructions or information
about their corresponding readme, click the Read Me button in
the autorun screen. The autorun screen normally appears after the
CD is inserted into a CD-ROM drive.
Page 37

2.6.4 Drivers and Utilities Installation Notes
1. "Autorun" ONLY supports the Windows 95, Windows 98,
Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows 2000 and Windows
NT 4.0 operating systems. If after inserting the CD, "Autorun"
did not automatically start (which is, the Main Board Utility CD
screen did not appear), please go directly to the root directory
of the CD and double-click "Setup".
2. Please go to DFI's web site at "http://www.dfi.com/suppor t/
download1.asp" for the latest version of the drivers or software
applications.
English
3. All steps or procedures to install software drivers are subject to
change without notice as the softwares are occassionally updated.
Please refer to the readme files, if available, for the latest
information.
English
37
Page 38

English
English
2.7 Troubleshooting
This section of the manual is designed to help you with problems
that you may encounter with your personal computer. To efficiently
troubleshoot your system, treat each problem individually. This is to
ensure an accurate diagnosis of the problem in case a problem has
multiple causes.
Some of the most common things to check when you encounter
problems while using your system are listed below.
1. The power switch of each peripheral device is turned on.
2. All cables and power cords are tightly connected.
3. The electrical outlet to which your peripheral devices are
connected is working. Test the outlet by plugging in a lamp or
other electrical device.
4. The monitor is turned on.
5. The displays brightness and contrast controls are adjusted
properly.
6. All add-in boards in the expansion slots are seated securely.
7. Any add-in board you have installed is designed for your system
and is set up correctly.
38
CPU Fan Protection
After booting up the system, a beeping alarm sounded then the
systems power was turned off:
1. The CPU fan did not rotate because the fan is damaged.
Replace it with a new one.
2. The CPU fan did not rotate immediately or it took some time
before the fan rotated. Check whether the heatsink and fan are
mounted properly onto the CPU then restart the system. If the
same problem occurs, you must replace it with a good quality
fan - one that will rotate immediately once power comes in and
also one that can dissipate heat more efficiently, otherwise, you
have to disable this function in the CPU Fan Protection field
(PC Health Status submenu) of the BIOS.
Page 39

CPU Frequency Ratio
The system did not boot up with the frequency ratio I selected.
Selecting a higher frequency ratio may result to the CPUs or
systems instability and are not guaranteed to provide better system
performance. Power off the system and set SW1 pins 1-5 to Off
(Auto).
Monitor/Display
If the display screen remains dark after the system is turned on:
English
1. Make sure that the monitors power switch is on.
2. Check that one end of the monitors power cord is properly
attached to the monitor and the other end is plugged into a
working AC outlet. If necessary, try another outlet.
3. Check that the video input cable is properly attached to the
monitor and the systems display adapter.
4. Adjust the brightness of the display by turning the monitors
brightness control knob.
The picture seems to be constantly moving.
1. The monitor has lost its vertical sync. Adjust the monitors vertical
sync.
2. Move away any objects, such as another monitor or fan, that
may be creating a magnetic field around the display.
3. Make sure your video cards output frequencies are supported
by this monitor.
The screen seems to be constantly wavering.
1. If the monitor is close to another monitor, the adjacent monitor
may need to be turned off. Fluorescent lights adjacent to the
monitor may also cause screen wavering.
Power Supply
English
When the computer is turned on, nothing happens.
1. Check that one end of the AC power cord is plugged into a live
outlet and the other end properly plugged into the back of the
system.
39
Page 40

English
English
2. Make sure that the voltage selection switch on the back panel is
set for the correct type of voltage you are using.
3. The power cord may have a short or open. Inspect the cord
and install a new one if necessar y.
Floppy Drive
The computer cannot access the floppy drive.
1. The floppy diskette may not be formatted. Format the diskette
and try again.
2. The diskette may be write-protected. Use a diskette that is not
write-protected.
3. You may be writing to the wrong drive. Check the path
statement to make sure you are writing to the targeted drive.
4. There is not enough space left on the diskette. Use another
diskette with adequate storage space.
Hard Drive
Hard disk failure.
1. Make sure the correct drive type for the hard disk drive has
been entered in the BIOS.
2. If the system is configured with two hard drives, make sure the
bootable (first) hard drive is configured as Master and the
second hard drive is configured as Slave. The master hard drive
must have an active/bootable partition.
40
Excessively long formatting period.
1. If your hard drive takes an excessively long period of time to
format, it is likely a cable connection problem. However, if your
hard drive has a large capacity, it will take a longer time to
format.
Parallel Port
The parallel printer doesnt respond when you try to print.
1. Make sure that your printer is turned on and that the printer is
on-line.
Page 41

2. Make sure your software is configured for the right type of
printer attached.
3. Verify that the onboard LPT ports I/O address and IRQ settings
are configured correctly.
4. Verify that the attached device works by attaching it to a parallel
port that is working and configured correctly. If it works, the
printer can be assumed to be in good condition. If the printer
remains inoperative, replace the printer cable and try again.
Serial Port
The serial device (modem, printer) doesnt output anything or is
outputting garbled characters.
1. Make sure that the serial devices power is turned on and that
the device is on-line.
2. Verify that the device is plugged into the correct serial port on
the rear of the computer.
3. Verify that the attached serial device works by attaching it to a
serial port that is working and configured correctly. If the serial
device does not work, either the cable or the serial device has a
problem. If the serial device works, the problem may be due to
the onboard I/O or the address setting.
4. Make sure the COM settings and I/O address are configured
correctly.
English
English
Keyboard
Nothing happens when a key on the keyboard was pressed.
1. Make sure the keyboard is properly connected.
2. Make sure there are no objects resting on the keyboard and
that no keys are pressed during the booting process.
System Board
1. Make sure the add-in card is seated securely in the expansion
slot. If the add-in card is loose, power off the system, re-install
the card and power up the system.
2. Check the jumper settings to ensure that the jumpers are
properly set.
3. Verify that all memory modules are seated securely into the
memory sockets.
41
Page 42

English
English
4. Make sure the memory modules are in the correct locations.
5. If the board fails to function, place the board on a flat surface
and seat all socketed components. Gently press each component
into the socket.
6. If you made changes to the BIOS settings, re-enter setup and
load the BIOS defaults.
42
Page 43

Chapter 3 - Français (French)
Table des Matières
Français (French)
!
3.1 Caractéristiques et Spécifications......................................................................
3.2 Identifier un CPU qui Supporte le Multiplier Overclocking
Fonction....................................................................................................................................
3.3 Utilisation de la Fonction de Protection de CPU par
Ventilateur...............................................................................................................................
3.4 Utilisation de la Fonction de Protection de Température du
CPU..............................................................................................................................................
3.5 Utilisation de la Fonction de Suspension sur RAM.........................
3.6 Logiciels Supportés........................................................................................................
3.7 Dépannage............................................................................................................................
Liste de Vérification de lEmballage
Lemballage de la carte système contient les éléments suivants:
þ La carte système
þ Un manuel utilisateur
þ Un câble IDE pour les lecteurs IDE ATA/33, ATA/66 ou
ATA/100
þ Un câble 34 broches pour lecteur de disquette
þ Un CD Main Board Utility
44
51
52
53
54
56
59
Français
(French)
Si lun de ces éléments nétait pas dans lemballage ou sil était
endommagé, veuillez contacter votre revendeur ou votre
représentant.
43
Page 44

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
3.1 Caractéristiques et Spécifications
3.1.1 Caractéristiques
Chipset
VIA® KT133A - VT8363A et VT82C686B
Processeur
La carte système est équipée dun régulateur de commutation de
voltage qui détecte automatiquement de 1.100V à 1.850V.
AMD AthlonTM/DuronTM 100/133MHz (200/266MHz DDR) FSB
processeur (600/650/700/750/800/850/900/950MHz, 1GHz,
1.3GHz ou futur processeur)
Mémoire Système
Supporte jusquà 1.5Go de mémoire utilisant VCM (Virtual
Channel Memory) ou PC SDRAM DIMM (tampon ou
enregistrées)
- DIMM de enregistrées - PC-100 seulement
3 sockets DIMM 168 broches
Utilisation de x64 PC SDRAM, 3.3V
- PC-100 SDRAM DIMM pour la mémoire bus de 100MHz
- PC-133 SDRAM DIMM pour la mémoire bus de 133MHz
L2 mémoire cache
- Processeur DuronTM: Cache de pipeline burst intégré 64Ko
Niveau 2
- Processeur AthlonTM: Cache de pipeline burst intégré 256Ko
Niveau 2
Français
44
Note:
PC-100 SDRAM DIMM est supporté quand il est utilisé
avec 100MHz FSB processeur.
PC-133 SDRAM DIMM est supporté quand il est utilisé
avec 100MHz FSB ou 133MHz FSB processeur.
Si vous utilisez plus dune DIMM, prenez soin dinsérer le
même type de DIMM dans les logements DIMM. Le fait
dutiliser des DIMM de type différents (VCM ou PC SDRAM)
peut engendrer des problèmes.
Page 45

Français (French)
!
DIMMs
2MBx64
4MBx64
8MBx64
Mémoire
16MB
32MB
64MB
DIMMs
16MBx64
32MBx64
64MBx64
Mémoire
128MB
256MB
512MB
Logements dExtension
La carte système est équipée dun slot AGP universel, 5 logements
PCI dédiés et 1 CNR (Communication et Mis en réseau Riser) prise
nutilise que pour la carte de modem riser.
AGP est une interface conçue pour supporter des car tes graphiques
3D de haute performance. Elle utilise un pipeline dédié pour accéder
à la mémoire système pour le texturage, le z-buffering et le mélange
alpha. Le slot AGP universel supporte 2x AGP avec une bande
passante allant jusquà 533Mo/sec et 4x AGP avec une bande
passante allant jusquà 1066Mo/sec pour les applications graphiques
3D. AGP sur cette car te système offrira des graphiques meilleurs et
plus rapide à votre PC.
Caractéristiques Audio sur Carte
Suppor te DirectSound de Microsoft®/DirectSound 3D de
Microsoft
®
AC97 supporté avec full duplex, convertisseur de vitesse
déchantillonnage indépendant pour enregistrement audio et
lecture.
Français
(French)
Ports Double Module ATX (Connecteurs PC 99 avec codes
couleur)
2 Ports USB
2 port série DB-9 compatible NS16C550A
1 port parallèle DB-25 SPP/ECP/EPP
1 por t souris PS/2 mini-DIN-6
1 por t clavier PS/2 mini-DIN-6
1 por t jeu/MIDI
3 prises audio: ligne de sortie, ligne dentrée et entrée micro
45
Page 46

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
Connecteurs
1 connecteur pour 2 ports USB supplémentaires
1 connecteur pour interface IrDA
2 connecteurs IDE
1 connecteur de lecteur de disquettes supportant jusquà deux
lecteurs de disquettes de 2.88Mo
1 connecteur dalimentation ATX
1 connecteur Wake-On-LAN
1 connecteur Wake-On-Ring
Connecteurs de ventilateurs de CPU, de châssis et de second
châssis ventilateur
3 connecteurs audio internes (AUX-in, CD-in et TAD)
Contrôleur IDE de BUS Maître PCI
Deux interfaces PCI IDE supportant jusquà quatre matériels IDE
Supporte des disques durs ATA/33, ATA/66 et ATA/100
IDE Améliorés Mode 3 et 4 PIO (vitesse de transfert de
données allant jusquà 16.6Mo/sec.)
La gestion de Bus réduit lutilisation du CPU pendant les
transferts sur disque
Supporte les CD-ROM ATAPI, LS-120 et ZIP
Français
46
Interface IrDA
La carte système est équipée dun connecteur IrDA pour les
connexions sans fil entre votre ordinateur et des périphériques. Il
supporte les périphériques qui sont conformes aux standards HPSIR
ou ASKIR.
Ports USB
La car te système supporte 4 ports USB. Deux ports USB sur car te
se trouvent sur les ports double deck ATX de la car te. Le
connecteur J19 situé sur la carte système vous permet de connecter
ème
les 3
qui sont montés sur un support latéral de carte, vous seront fournis
en option. USB permet léchange de données entre votre ordinateur
et un grande éventail de périphériques externes Plug and Play
accessibles simultanément.
et 4
ème
ports USB optionnels. Ces ports USB optionnels,
Page 47

Français (French)
BIOS
Compatible avec Award BIOS, Windows® 95/98/2000/ME Plug
and Play
Supporte lamorçage séquentiel SCSI
EPROM Flash pour une mise à niveau facile du BIOS
Supporte la fonction DMI 2.0
Mémoire Flash 2Mbit
Vcore et lhorloge du bus du processeur pouvant être
sélectionné dans le BIOS
Interface de Gestion de Bureau (DMI)
La carte système est livrée avec un DMI 2.0 intégré au BIOS.
Lutilitaire DMI dans le BIOS enregistre automatiquement diverses
informations concernant la configuration de votre système et stocke
ces informations dans la liste DMI, qui est une partie du BIOS Plug
and Play de la car te système. DMI, accompagné du logiciel en
réseau approprié, est conçu pour rendre linventaire, lentretien et le
dépannage du système de lordinateur plus facile.
3.1.2 System Health Monitor Fonctions
La carte système est capable de gérer les conditions de santé
système suivantes.
!
Français
(French)
Alarme de température et de surchauffe de CPU/système de
moniteurs
Alarme déchec et de voltage 12V/5V/3.3V/VCORE de
moniteurs
Alarme déchec et de vitesse de ventilateur de CPU/châssis de
moniteurs
Contrôle de marche/arrêt automatique de ventilateur de châssis
Capacité de relecture affichant la température, le voltage et la
vitesse de ventilateur
Si vous désirez quun message davertissement apparaisse ou quune
alarme retentisse lorsque quune condition anormale se produit, vous
devez installer VIA Hardware Monitor. Cet utilitaire est compris
dans le CD qui est livré avec la carte système.
47
Page 48

!
Français (French)
3.1.3 Intelligence
Protection de Température du CPU
La fonction de Protection de Température du CPU possède la
capacité de contrôler la température du CPU pendant lamorçage du
système. Une fois quelle aura détecté que la température du CPU
dépasse la température de sécurité du CPU définie dans le BIOS, le
système séteindra automatiquement après avoir émis les 5 signaux
sonores dalerte.
Français
(French)
Protection du CPU par Ventilateur
La fonctionnalité de protection du CPU par Ventilateur a la possibilité
de contrôler le ventilateur du CPU pendant lamorçage du système
et éteindra automatiquement le système si elle détecte que le
ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas. Cette fonctionnalité a été ajoutée
pour protéger le CPU contre tout dommage et assurer un
environnement informatique sûr.
Sur-Voltage
La fonction de Sur-Voltage vous permet dajuster manuellement dans
un voltage interne plus faible appliqué au CPU. Bien que cette
fonction soit supportée, nous ne vous conseillons pas dutiliser un
voltage plus élevé parce quun courant instable pourrait être appliqué
à la carte système ce qui entraînerait des détériorations.
Daccélération dhorloge de CPU
La fonction daccélération dhorloge de CPU vous permet dajuster
lhorloge du bus du processeur. Cependant, laccélération dhorloge
peut entraîner linstabilité du processeur ou du système et ne garantit
pas de meilleures performances du système.
Arrêt Automatique de Ventilateur de Châssis
Les ventilateurs de châssis sarrêteront automatiquement une fois
que le système est entré en mode Suspension.
Français
48
Page 49

Français (French)
Bouton dAlimentation à Fonction Double
En fonction du paramétrage dans le champ Soft-Off By PWRBTN
du Programme dInstallation de la Power Management Setup, ce
commutateur permettra à votre système dentrer en mode Soft-Off
ou Suspension.
Wake-On-Ring
Cette caractéristique permet au système qui se trouve en mode
Suspension ou en mode Arrêt Alimentation par Logiciel de se
réveiller/sallumer pour répondre à des appels provenant dun
modem interne ou externe.
Important:
Si vous utilisez une carte complémentaire de modem, la source
dalimentation de 5VSB de votre boîtier dalimentation doit
supporter un minimum de ≥720mA.
Minuterie RTC pour Allumer le Système
Le RTC installé sur la carte système permet à votre système de
sallumer automatiquement à une date et heure présélectionnée.
Wake-On-LAN
!
Français
(French)
La fonction Wake-On-LAN permet au réseau de réveiller à distance
un PC Mis Hors Tension par Logiciel (Soft Power Down ou SoftOff). Votre carte LAN doit suppor ter la fonction de réveil à distance.
Important:
La source dalimentation 5VSB de votre boîtier dalimentation
doit supporter ≥720mA (minimum).
Récupération après Défaillance dAlimentation CA
Quand lalimentation revient après une défaillance dalimentation CA,
vous pouvez choisir dallumer le système manuellement, de laisser le
système sallumer automatiquement ou de retourner à létat que
vous aviez quitté avant que la défaillance dalimentation se produise.
49
Page 50

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
ACPI STR
La carte système est conçue de façon à être conforme aux
spécifications ACPI (Configuration Avancée et Interface
dAlimentation). ACPI compor te une fonction déconomie dénergie
qui permet aux PC de mettre en uvre la Gestion dAlimentation
et Plug and Play avec des systèmes dexploitation qui supportent
la Gestion dAlimentation Directe de Système dExploitation.
Actuellement, seulement Windows® 98/2000/ME supporte la
fonction ACPI. Quand ACPI est activé dans le Programme de Power
Management Setup, cela vous permet dutiliser la fonction de
Suspension sur RAM.
Quand la fonction de Suspension sur RAM est activée, vous pouvez
éteindre le système immédiatement en appuyant sur le bouton
dalimentation ou en sélectionnant Veille quand vous éteignez
Windows® 98/2000/ME sans avoir à passer par le processus
quelquefois ennuyeux de fermeture des fichiers, des applications et
du système dexploitation. Ceci est du au fait que le système est
capable de stocker tous les fichiers programmes et de données
pendant toute la session dutilisation dans la RAM (Mémoire à Accès
Aléatoire) lorsque quil séteint. La session dutilisation reprendra
exactement où vous lavez laissée la prochaine fois que vous
allumerez le système.
Français
50
Important:
La source dalimentation 5VSB de votre boîtier dalimentation
doit supporter ≥1A.
Protection contre les Virus
La plupart des virus détruisent les données stockées sur les disques
durs. La carte système est conçue pour protéger le secteur
damorçage et la table de partition de votre disque dur.
Page 51

Français (French)
3.2 Identifier un CPU qui Supporte le Multiplier
Overclocking Fonction
Ce nest pas que tous les AMD CPUs suppor tent le multiplier
overclocking fonction. Veuillez faire très attention à L1 sur le CPU. Il
faut que les quatre ponts de L1 soient fermés (shor t) pour que la
fréquence proportion choisie sur le SW1 soit opérée. Le figure cidessous vous aide didentifier le type de CPU qui vous permet de
régler ses fréquence proportion.
Les quatre ponts du L1 ferment (short).
Les quatre ponts du L1
ouvrent.
!
Français
(French)
Important:
Nous ne vous recommender de régler le CPU à plus haut fréquence
proportion car il peut résulter du CPU ou du système instable et ne
vous garantit de fournir mieux performance du système. Si vous ne
pouvez pas mettre en marcher le système avec le fréquence
proportion vous avez choisi, veuillez mettre le système à Off et le
SW1 pins 1-5 à Off (Auto).
51
Page 52

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
3.3 Utilisation de la Fonction de Protection de
CPU par Ventilateur
Le CPU doit être refroidi à laide dun ventilateur de CPU et dun
radiateur. Sans une circulation dair suffisante à travers le CPU et le
radiateur, le CPU se mettrait à trop chauffer ce qui endommagerait
le CPU et la carte système.
La fonction de Protection Ventilateur du CPU supportée par la carte
système a la possibilité de contrôler le ventilateur de CPU pendant
lamorçage du système et éteindra automatiquement le système sil
détecte que le ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas. Cette
fonctionnalité a été ajoutée pour protéger le CPU contre tout
dommage et assurer un environnement informatique sûr.
Pour utiliser la fonction de Protection Ventilateur du CPU, veuillez
suivre les étapes ci-dessous.
1. Avant de mettre le système sous tension, assurez vous que le
radiateur et le ventilateur du CPU sont installés correctement sur
le CPU. Le système est peut contrôler le ventilateur de CPU,
cependant vous devez utiliser une broche de détection de
ventilateur pour supporter cette fonction. Connectez le ventilateur
du CPU au connecteur de ventilateur à 3 broches à
lemplacement J16 de la carte système.
Français
52
2. Assurez vous que la CPU Fan Protection enregistrée dans le
sous-menu PC Health Status du BIOS est positionnée sur
Enabled.
3. Vous pouvez maintenant mettre le système sous-tension
Deux situations peuvent se présenter forçant le système à séteindre
automatiquement. Un bip dalarme se fera entendre avant que le
système ne séteigne.
1. Le ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas, cela peut indiquer que le
ventilateur est endommagé. Remplacez-le par un nouveau
ventilateur.
Page 53

Français (French)
2. Le ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas immédiatement lors de
lamorçage du système ou il se passe un moment avant que le
ventilateur du CPU ne se mette à tourner.
Si le ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas immédiatement lors de
lamorçage du système ou sil se passe un moment avant que le
ventilateur ne se mette à tourner, vérifiez si le radiateur et le
ventilateur sont montés correctement sur le CPU puis
redémarrez le système. Si le même problème se produit, vous
devez remplacer le ventilateur avec un ventilateur de bonne
qualité un qui se mettra à tourner dès la mise sous tension et
qui de plus peut dissiper la chaleur avec plus defficacité, sinon,
vous devrez désactiver cette fonction dans le champ CPU Fan
Protection (Sous-menu PC Health Status) du BIOS.
3.4 Utilisation de la Fonction de Protection de
Température du CPU
La fonction de Protection de Température du CPU possède la
capacité de contrôler la température du CPU pendant lamorçage du
système. Pour utiliser la fonction, paramétrez le champ CPU Temp.
Prot. Function sur Enabled et sélectionnez de Température du CPU
dan le champ CPU Temp. Prot. Alarm (sous-menu PC Health
Status du BIOS). Une fois quelle a détecté que la température du
CPU dépasse la température de sécurité du CPU définie dans ce
champ, 5 signaux sonores dalerte se feront entendre et un message
davertissement apparaîtra sur lécran damorçage vous invitant à
appuyer sur la touche <Suppr> afin dentrer dans le menu principal
du BIOS. Vous pouvez aussi:
!
Français
(French)
1. Appuyer sur <Suppr> puis entrer un nouveau paramètre
(sécurité de température du CPU) dans ce champ;
or
2. Permet au système de séteindre après les 5 signaux sonores
davertissement. La température trop élevée du CPU peut être
dûe à un ventilateur endommagé de CPU ou à une mauvaise
installation du ventilateur/radiateur. Vérifiez tout dabord si le
radiateur et le ventilateur sont montés correctement sur le CPU.
Puis redémarrez le système. Si le même problème persiste, cela
53
Page 54

!
Français (French)
peut venir du fait que le ventilateur du CPU est endommagé ou
quil ne tourne pas correctement. Essayez de le remplacer par un
nouveau ventilateur. Si cela est dû à dautres facteurs, résultant en
une température trop élevée du CPU, vous devrez peut-être
paramétrer ce champ sur une valeur plus faible de température
de sécurité de CPU.
Référence de Température du CPU
Quand vous mettez un système sous tension, le message du BIOS
apparaît à lécran et le comptage de mémoire commence. Après le
test mémoire, la température du CPU sera comprise entre 32oC et
35oC. Mais quand vous lancez un système dexploitation et ensuite
que vous essayez de réamorcer le système, la température du CPU,
à ce moment-là, se situe entre 40oC et 45oC. Cette référence de
température vous guide quand vous paramétrez ce champ en
fonction du niveau de protection désirée pour votre CPU.
Français
3.5 Utilisation de la Fonction de Suspension sur
RAM
Français
(French)
54
1. Sélectionnez Power Management Setup dans lécran de
programme principal et appuyez sur <Enter>.
2. Dans le champ ACPI Function, sélectionnez Enabled.
3. Dans le champ ACPI Suspend Type, sélectionnez S3(STR).
4. Appuyez sur <Esc> pour retourner au menu principal.
5. Sélectionnez Save & Exit Setup et appuyez sur <Enter>, Tapez
<Y> et appuyez sur <Enter>.
6. Installez Windows® 98/2000/ME en tapant les paramètres
suivants. Ceci ser t à vous assurer que la fonction ACPI est
supportée.
[lecteur]:>setup /p j
Si vous avez installé Windows® 98/2000/ME préalablement,
vous avez besoin de mettre le système à niveau de façon à
supporter ACPI. Veuillez contacter Microsoft pour les
informations de mise à niveau.
Page 55

Français (French)
!
7. Démarrez Windows® 98/2000/ME. Sur le bureau de Windows
98/2000/ME, cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer. Déplacez le
curseur sur Paramètres, puis cliquez sur Panneau de
Configuration.
8. Double cliquez sur licône Système. Dans la boîte de Propriétés
Système, cliquez sur longlet Performances.
9. Cliquez sur le Fichier Système. Dans le champ Rôle Typique de
cet Ordinateur, sélectionnez Système Portable ou Station
dAccueil. Cliquez sur Appliquer, puis cliquer sur OK.
Redémarrez lordinateur.
10. Répétez létape 7 pour ouvrir la boîte de dialogue du Panneau
de Configuration. Double cliquez sur licône Gestion
dAlimentation.
11. Cliquez sur longlet Avancé. Dans le champ Quand jappuie sur
le bouton dalimentation de mon ordinateur, sélectionnez Mise
en Veille.
12. Après avoir réalisé les étapes ci-dessus et si vous voulez
éteindre lordinateur, vous navez pas besoin de passer par le
processus de fermeture des fichiers, des applications et du
système dexploitation. Vous pouvez éteindre lordinateur
directement en appuyant sur le bouton dalimentation ou en
sélectionnant Mise en Veille quand vous fermez Windows® 98/
2000/ME.
®
Français
(French)
Pour allumer lordinateur, appuyez simplement sur le bouton
dalimentation. La session que vous avez laissée quand vous
avez éteint lordinateur reprendra en moins de 8 secondes.
Si vous avez changé la couleur ou la résolution (dans la boîte
de dialogue de Propriétés dAffichage), nappliquez pas les
paramètres sans redémarrer. Vous devez redémarrer lordinateur.
55
Page 56

!
Français (French)
3.6 Logiciels Supportés
3.6.1 Utilitaire VIA Hardware Monitor
La carte système est livrée avec un utilitaire de VIA Hardware
Monitor contenu dans le CD fourni. Il peut gérer les conditions du
système du matériel telle que la température du CPU et du système,
le voltage et la vitesse des ventilateurs de CPU et de châssis. Il
vous permet aussi de positionner manuellement un éventail de
matériels pouvant être gérés. Si les valeurs sont situées au-dessus ou
en dessous de léventail présélectionné, un message davertissement
apparaîtra. Lutilitaire peut aussi être configuré de sorte que lalarme
sonore retentisse chaque fois quune erreur se produit. Nous vous
recommandons dutiliser les Default Setting qui sont les paramètres
idéaux pour maintenir le système en bon état de fonctionnement.
Note:
Utilisez cet utilitaire seulement dans les systèmes dexploitation
Windows® 95, Windows® 98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME,
Windows® 2000 ou Windows NT® 4.0.
Français
Français
(French)
56
Pour installer lutilitaire, insérez le CD dans le lecteur CD-ROM.
Lécran autorun (CD Main Board Utility) apparaîtra. Cliquez sur le
bouton VIA Hardware Monitor pour installer lutilitaire. Reportez
vous à son fichier readme pour les instructions sur lutilisation de
lutilitaire.
3.6.2 VIA Service Pack
Le CD contenu dans lemballage de la carte système est aussi
accompagné du VIA Service Pack. Le Service Pack comprend les
pilotes suivants:
Bus Master PCI IDE Driver
AGP VxD Driver
VIA Chipset Functions Registry
VIA PCI IRQ Miniport Driver
Pour installer les pilotes, insérez le CD dans le lecteur CD-ROM.
Lécran autorun (Main Board Utility CD) apparaîtra. Cliquez sur le
bouton VIA Service Pack. Pour les instructions dinstallation ou
pour les informations concernant leur fichier readme correspondant,
cliquez sur le bouton Read Me situé dans lécran autorun.
Page 57

Français (French)
Notes dInstallation de VIA® Service Pack
VIA Service Pack qui se trouve dans le CD fourni comprend les
pilotes AGP VxD Driver et VIA Chipset Functions Registry. Ces
pilotes sont suppor tés sous Windows® 95, Windows® 98, Windows
98 SE, Windows® ME et Windows® 2000. Vous devez tout dabord
installer VIA Service Pack avant dinstaller tout autre pilote.
Cependant, ceci peut ne pas être le cas pour certains car tes AGP.
Veuillez lire soigneusement les informations ci-dessous.
Important:
Le pilote VGA qui accompagne les cartes AGP est déjà groupé
avec le pilote AGP VxD. Etant donné que la version du pilote
groupé VxD est peut-être plus ancienne que celle fournie dans
le CD, linstallation du groupe VxD peut poser des problèmes. Si
vous utilisez ce type de carte, nous vous conseillons dinstaller
tout dabord le pilote VGA de la carte AGP avant dinstaller le
VIA Ser vice Pack.
Pour installer le VIA Service Pack, veuillez suivre les étapes ci-dessous.
1. Insérez le CD qui accompagne lensemble carte système dans le
lecteur CD-ROM. Lécran dexécution automatique (Main Board
Utility CD) apparaîtra.
!
®
Français
(French)
2. Cliquez sur VIA Service Pack.
3. Lécran de Welcome apparaîtra. Cliquez sur Next. Veuillez lire
soigneusement le fichier VIA Service Pack readme avant de
passer à létape 4.
4. Suivez les invites décran pour réaliser linstallation.
5. Réamorcez le système pour que les pilotes soient opérationnels.
57
Page 58

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
3.6.3 Pilotes Audio et Logiciels dApplications
Le CD contenu dans lemballage de la car te système comprend
aussi des pilotes audio et des logiciels de lecture audio pour
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, Windows® ME,
Windows NT 4.0 et Windows 2000. Pour les instructions
dinstallation ou pour les informations concernant leur fichier readme
correspondant, cliquez sur le bouton Read Me situé dans lécran
autorun. Lécran autorun apparaît normalement une fois que le CD
est inséré dans le lecteur CD-ROM.
3.6.4 Notes pour lInstallation des Pilotes et des Utilitaires
1. Autorun SEULEMENT supporte les systèmes dexploitation
Windows® 95, Windows® 98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME,
Windows® 2000 et Windows NT® 4.0. Si, après avoir inséré le
CD, Autorun ne démarre pas automatiquement (Dans ce cas,
lécran de CD Main Board Utility napparaîtra pas), veuillez aller
directement au répertoire racine du CD et double cliquez sur
Setup.
2. Veuillez vous rendre sur le site web de DFI à "http://
www.dfi.com/support/download1.asp" pour trouver la dernière
version des pilotes ou logiciel dapplications.
Français
58
3. Toutes les étapes ou procédures pour installer les pilotes sont
susceptibles dêtre modifiées sans notice préalable étant donné
que les logiciels sont mis à jour occasionnellement. Veuillez vous
reporter aux fichiers LisezMoi, sils sont disponibles, pour obtenir
les dernières informations.
Page 59

Français (French)
3.7 Dépannage
Ce chapitre du manuel est destiné à vous aider résoudre les
problèmes éventuels que vous pourriez rencontrer avec votre
ordinateur. Pour dépanner efficacement votre système, traitez chaque
problème individuellement. Ceci permettra de faire un diagnostique
exact du problème dans le cas ou celui-ci aurait des causes multiples.
Certains des points les plus courants, à vérifier lorsque vous
rencontrez des problèmes lors de lutilisation de votre système sont
énumérés ci-dessous.
1. Linterrupteur dalimentation de chaque périphérique est sur la
position marche.
2. Tous les câbles et cordons dalimentation sont bien connectés.
3. La prise secteur sur laquelle vos périphériques sont branchés
fonctionne correctement. Testez la prise en branchant une lampe
ou tout autre appareil électrique.
4. Le moniteur est allumé.
5. Les contrôles de luminosité et de contraste daffichage sont
correctement réglés.
6. Toutes les cartes dextension situées dans les logements
dextension sont correctement enfichées.
7. Chaque carte dextension installée est conçue pour votre
système et paramétrée correctement.
!
Français
(French)
Protection CPU par Ventilateur
Après avoir amorcé le système, une alarme sonore retentit puis
lalimentation du système est mise hors tension.
1. Le ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas car le ventilateur est
endommagé. Remplacez-le par un neuf.
2. Le ventilateur du CPU ne tourne pas immédiatement ou il faut
attendre un moment avant que le ventilateur ne tourne. Vérifiez
que le radiateur et le ventilateur sont montés correctement sur le
CPU, puis redémarrez le système. Si le problème persiste, vous
devez le remplacer le ventilateur par un ventilateur de bonne
qualité un ventilateur qui se mettra immédiatement à tourner à
la mise sous tension et qui pourra dissiper la chaleur plus
efficacement, sinon, vous devrez désactiver cette fonction dans le
59
Page 60

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
champ CPU Fan Protection (Sous-menu PC Health Status) du
BIOS.
Taux de la Fréquence de Processeurs
Ne pouvez pas mettre en marcher le système avec le fréquence
proportion vous avez choisi.
Nous ne vous recommender de régler le CPU à plus haut fréquence
proportion car il peut résulter du CPU ou du système instable et ne
vous garantit de fournir mieux performance du système. Veuillez
mettre le système à Off et le SW1 pins 1-5 à Off (Auto).
Français
Moniteur/Affichage
Si lécran daffichage reste éteint après la mise sous tension du
système.
1. Assurez vous que le bouton dalimentation est sur la position
marche.
2. Vérifiez que lune des extrémités du cordon dalimentation du
moniteur est correctement connectée au moniteur et que lautre
extrémité est branchée à une prise de courant CA en état de
marche. Si nécessaire, essayez une autre prise.
3. Vérifiez que le câble dentrée vidéo est correctement connecté au
moniteur et à ladaptateur daffichage du système.
4. Ajustez la luminosité de laffichage en tournant le bouton de
contrôle de luminosité du moniteur.
60
Limage bouge constamment.
1. Le moniteur a perdu sa synchronisation verticale. Ajustez la
synchronisation verticale du moniteur.
2. Eloignez tous les objets, tel quun autre moniteur ou un
ventilateur, qui pourrait créer un champ magnétique autour de
laffichage.
3. Assurez vous que les fréquences de sortie de votre carte vidéo
sont supportées par ce moniteur.
Page 61

Français (French)
Lécran ondule constamment.
1. Si le moniteur est proche dun autre moniteur, il est peut-être
nécessaire déteindre ce dernier. Les lampes fluorescentes situées
à proximité du moniteur peuvent aussi faire onduler limage à
lécran.
Alimentation
A la mise sous tension de lordinateur rien ne se passe.
1. Vérifiez que lune des extrémités du cordon dalimentation CA
est branchée dans une prise de courant en état de marche et
que lautre extrémité est correctement branchée au dos du
système.
2. Assurez vous que linterrupteur de sélection de voltage situé sur
le panneau arrière est positionné pour le type correct de voltage
que vous utilisez.
3. Le cordon dalimentation présente peut-être un court circuit ou
une coupure. Inspectez le cordon et installez-en un nouveau si
nécessaire.
!
Lecteur de Disquettes
Lordinateur ne peut pas accéder au lecteur de disquettes.
1. La disquette nest peut-être pas formatée. Formatez la disquette
et réessayez.
2. La disquette est peut-être protégée en écriture. Utilisez une
disquette qui nest pas protégée en écriture.
3. Vous êtes peut-être en train décrire sur le mauvais lecteur.
Vérifiez le chemin daccès pour vous assurer que vous écrivez
bien sur le lecteur visé.
4. Lespace est insuffisant sur la disquette. Utilisez une autre
disquette compor tant un espace de stockage adéquat.
Disque Dur
Défaillance du disque dur.
1. Assurez vous que le type correct de lecteur pour le disque dur a
été entré dans le BIOS.
Français
(French)
61
Page 62

!
Français
(French)
Français (French)
2. Si le système est configuré avec deux disques durs, assurez vous
que le disque dur amorçable (premier) est configuré en Maître et
le second disque dur est configuré en Esclave. Le disque dur
maître doit avoir une partition active/amorçable.
Durée de formatage trop longue.
1. Si votre disque dur met trop de temps à se formater, cela
provient sûrement dun problème de connexion de câble.
Cependant, si votre disque dur a une grande capacité, il mettra
plus de temps à se formater.
Français
Port Parallèle
Limprimante parallèle ne répond pas quand vous essayez
dimprimer.
1. Assurez vous que votre imprimante est allumée et que
limprimante est en ligne.
2. Assurez vous que votre logiciel est configuré pour le type
dimprimante connectée.
3. Vérifiez que ladresse dE/S et les paramètres IRQ du port LPT
sur carte sont configurés correctement.
4. Vérifiez que le périphérique connecté fonctionne en le connectant
à un port parallèle qui fonctionne et configuré correctement. Sil
fonctionne, limprimante peut être considérée comme étant en
bon état de marche. Si limprimante ne fonctionne toujours pas,
remplacez le câble dimprimante et essayez à nouveau.
62
Port Série
Le périphérique série (modem, imprimante) német aucun
caractère ou émet des caractères incohérents.
1. Assurez vous que le périphérique série est allumé et quil est en
ligne.
2. Vérifiez que le périphérique est branché sur le port série correct
au dos de lordinateur.
3. Vérifiez que le périphérique série connecté fonctionne, en le
branchant à un port série qui fonctionne et configuré
correctement. Si le périphérique série ne fonctionne pas, cela
signifie que le câble ou le périphérique série a un problème. Si le
Page 63

Français (French)
périphérique fonctionne, le problème est peut-être dû à la car te
dE/S ou au paramétrage dadressage.
4. Assurez vous que les paramètres COM et dadressage dE/S
sont configurés correctement.
Clavier
Rien ne se passe quand une touche du clavier est enfoncée.
1. Assurez vous que le clavier est connecté correctement.
2. Assurez vous quaucun objet nappuie sur le clavier et quaucune
touche nest enfoncée pendant le processus damorçage.
Carte Système
1. Assurez vous que la carte dextension est correctement placée
dans le logement dextension. Si la carte dextension a du jeu,
éteignez le système, réinstallez la car te et allumez le système.
2. Vérifiez les paramétrages de cavaliers pour vous assurer que les
cavaliers sont positionnés correctement.
3. Vérifiez que tous les modules mémoire sont correctement
installés dans les sockets mémoire.
4. Assurez vous que les modules mémoire se trouvent dans les
emplacements appropriés.
5. Si la carte ne fonctionne pas, placez la carte sur une surface
plane et vérifiez tous les composants sur socket. Appuyez
doucement sur chaque composant pour lenfoncer dans le socket.
6. Si vous avez apporté des modifications aux paramètres du BIOS,
ré entrez dans le programme dinstallation et chargez les
paramètres par défaut du BIOS.
!
Français
(French)
63
Page 64

"
Deutsch (German)
Chapter 4 - Deutsch (German)
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Deutsch
(German)
4.1 Leistungsmerkmale und Technische Daten...............................................
4.2 Eine CPU Identifizieren, die Overclocking-Funktion des
Vervielfachers Unterstützt.......................................................................................
4.3 Anwendung der Funktion Schutz des CPU-Ventilators..............
4.4 Anwendung der Funktion Schutz des CPU-Temperatur.............
4.5 Anwendung der Funktion Suspendieren auf RAM......................
4.6 Unterstützte Software.................................................................................................
4.7 Fehlersuche............................................................................................................................
Français
Verpackungsliste
In der Verpackung der Systemplatine sind folgende Artikel enthalten:
þ Eine Systemplatine
þ Ein Benutzerhandbuch
þ Ein IDE-Kabel für ATA/33-IDE-Laufwerke, ATA/66-IDE-Laufwerke
oder ATA/100-IDE-Laufwerke
þ Ein Floppylaufwerkskabel mit 34poligen Anschlußstecker
þ Eine CD mit Main Board Utility
Fehlt einer dieser Artikel oder weist einer dieser Artikel
Beschädigungen auf, wenden Sie sich an Ihren Händler oder Vertreter.
65
72
73
74
76
78
81
64
Page 65

Deutsch (German)
4.1 Leistungsmerkmale und Technische Daten
4.1.1 Leistungsmerkmale
Chipset
VIA® KT133A - VT8363A und VT82C686B
Prozessor
Die Systemplatine ist mit einem Spannungsregler ausgestattet, durch
welchen automatisch Spannungen von 1,100V bis 1,850V festgestellt
werden.
AMD AthlonTM/DuronTM 100/133MHz (200/266MHz DDR) FSB
prozessor (600/650/700/750/800/850/900/950MHz, 1GHz,
1.3GHz oder Zukünftige prozessor)
Systemspeicher
Unterstützt einen Speicher von bis zu 1.5GB mit ohne VCM
(Virtual Channel Memory) oder PC SDRAM DIMM
(Pufferspeicher oder registriert)
- Registriert-DIMM - nur für PC-100
3 DIMM-Fassungen mit 168poligem Anschlußstecker.
Anwendung des x64 PC SDRAM, 3,3 V
- PC-100-SDRAM-DIMM für 100-MHz-Speicher-Bus
- PC-133-SDRAM-DIMM für 133-MHz-Speicher-Bus
L2-Cache-Speicher
- DuronTM-Prozessor: eingebauter 64-KB-Burst-Cache der Stufe
2 und mit Pipeline
- AthlonTM-Prozessor: eingebauter 256-KB-Burst-Cache der
Stufe 2 und mit Pipeline
"
Deutsch
(German)
Hinweis:
PC-100 SDRAM DIMM wird unterstützt ¡A wenn er mit
100MHz FSB(Frequenz systembus) verwendet wird.
PC-133 SDRAM DIMM wird unterstützt¡A wenn er mit
100MHz FSB oder 133MHz FSB-verwendet wird.
Falls mehr als ein DIMM verwendet wird, darf nur derselbe
Typ der DIMMs in die DIMM-Steckfassungen eingesetzt
werden, da andere DIMM-Typen (VCM oder PC SDRAM) zu
Konflikten führen können.
65
Page 66

"
Deutsch (German)
DIMMs
2MBx64
4MBx64
8MBx64
Erweiterungssteckfasssungen
Die Systemplatine ist mit einer universellen AGP-Steckfassung
ausgerüstet, 5 dedizierten PCI-Steckfassungen und ein Einbaupltz von
CNR (Communication and Networking Riser : Kommunikation- und
Netzwerk-Steigleitung) nur für Modem-Steigleitungskarte.
Speicher
16MB
32MB
64MB
DIMMs
16MBx64
32MBx64
64MBx64
Speicher
128MB
256MB
512MB
Français
AGP ist eine Schnittstelle, die zum Unterstützen der Hochleistungs3D-Grafikkarten bestimmt ist und die für den Zugriff zum Speicher
für die Textur, das Z-Puffern und Alpha-Mischen eine dedizierte
Leitung verwendet. Für die 3D-Grafikanwendungen unterstützt die
universelle AGP-Steckfassung einen AGP 2x mit einer Bandweite von
bis zu 533MB/Sek. sowie einen AGP 4x mit einer Bandweite von bis
zu 1066MB/Sek. Durch den AGP in diesem System werden bessere
Grafiken schneller an Ihren PC übertragen.
Audiomerkmale auf Platine
Unterstützung des Microsoft® DirectSound/DirectSound 3D
AC97 mit Unterstützung des Vollduplexbetriebs, unabhängigem
Abtastratenumwandler für die Aufnahme und Wiedergabe
Deutsch
(German)
66
ATX-Zweietagen-Anschlüsse (PC 99 mit farbkodierten
Steckverbindungen)
2 USB-Anschlüsse
2 serieller DB-9-Anschluß, kompatibel mit NS16C550A
1 DB-25-Parallelanschluß SPP/ECP/EPP
1 Mini-DIN-6-Anschluß für eine PS/2-Maus
1 Mini-DIN-6-Anschluß für eine PS/2-Tastatur
1 Spiel-/MIDI-Anschluß
3 Audio-Anschlußbuchsen: Ausgangsleitung, Eingangsleitung und
Mikrofon-Eingang
Page 67

Deutsch (German)
Anschlußstecker
1 Anschlußfassung für 2 zusätzliche externe USB-Anschlüsse
1 Anschluß für die IrDA-Schnittstelle
2 IDE-Anschlüsse
Unterstützung von bis zu zwei 2,88MB-Floppylaufwerken durch
einen Floppylaufwerksanschluß
1 Anschlußstecker für das ATX-Netzgerät
1 Anschlußstecker für Wecken durch LAN
1 Anschlußstecker für Wecken durch Ring
CPU-, Chassis- und zweiter-chassis-ventilator-Anschlüsse
3 interne Audioanschlüsse (AUX-in, CD-in und TAD)
PCI-Bus-Master-IDE-Controller
Unterstützung von bis zu vier IDE-Geräten durch zwei PCI-IDE-
Schnittstellen.
Unterstützung der Festplatten ATA/33, ATA/66 und ATA/100
Erweitertes IDE des PIO-Modus 3 und 4 (Datenüber-
tragungsgeschwindigkeit von bis zu 16.6MB/Sek.).
Verminderte CPU-Benutzung während Diskettenübertragung
dank dem Bus-Master.
Unterstützung des ATAPI CD-ROMs, LS-120 und ZIP
"
IrDA-Schnittstelle
Die Systemplatine ist mit einem IrDA-Anschluß versehen, durch
welche eine kabellose Verbindung zwischen Ihrem Computer und
Peripheriegeräten hergestellt werden kann. Diese Schnittstelle
unterstützt Peripheriegeräte, die der HPSIR und ASKIR-Norm
entsprechen.
USB-Anschlüsse
Die Systemplatine Unterstützung der 4 USB-Anschlüsse. Zwei USBPorts auf der Hauptplatine befinden sich auf den ATX-DoppeldeckPorts der Platine. Der J19-Anschluß auf der Systemplatine ermöglicht
es dem Benutzer, die optionalen 3. und 4. USB-Ports anzuschließen.
Diese auf der Halterung an der Kartenkante montierten optionalen
USB-Ports können als Option verwendet werden. Durch USB
können Daten zwischen Ihrem Computer und einer großen Auswahl
an gleichzeitig zugänglichen externen Plug and Play Peripheriegeräten
ausgetauscht werden.
Deutsch
(German)
67
Page 68

"
Deutsch (German)
BIOS
Kompatibilität mit Award BIOS, Windows® 95/98/2000/ME Plug
and Play
Unterstützung des sequentiellen SCSI-Ladens
Flash EPROM für ein einfaches Aktualisieren des BIOS
Unterstützung der DMI-2.0-Funktion
Flash-Speicher (2Mbit)
Wählbarer Vcore und Bus-Taktgeber des Prozessors im BIOS
Desktop-Management-Schnittstelle (DMI)
Français
Die Systemplatine ist mit einem DMI 2.0 ausgestattet, die im BIOS
integriert ist. Durch das DMI-Dienstprogramm im BIOS werden
automatisch verschiedene Informationen über die Konfiguration Ihres
Systems registriert, wonach diese Informationen im DMI-Speicher
gespeichert werden. Dieser DMI-Speicher bildet einen Teil des Plug
and Play BIOS und des DMI der Systemplatine, zusammen mit der
richtig mit dem Netzwerk verbundenen Software. Auf diese Weise
soll der Unterhalt und die Fehlersuche des PC-Systems erleichtert
werden.
4.1.2 System Health Monitor Funktions
Deutsch
(German)
68
Durch die Systemplatine können die folgenden gesundheitlichen
Bedingungen Ihres Systems überwacht werden.
Überwachung der Temperatur des CPU/Systems und Warnsignal
bei Überhitzung
Überwachung der 12V/5V/3.3V/VCORE-Spannungen und
Warnsignal bei Ausfall
Überwachung der Geschwindigkeit des CPU-/Chassisventilators
sowie Warnsignal bei Ausfall
Automatisches Ein-/Ausschalten der des Chassisventilator
Anzeige der Temperatur, Spannung und der Geschwindigkeit des
Ventilators
Soll bei Auftreten einer abnormalen Situation eine Warnmeldung
erscheinen oder ein akustisches Warnsignal abgegeben werden, muß
das VIA Hardware Monitor installiert werden. Dieses
Dienstprogramm ist auf der CD enthalten, welche mit der
Systemplatine geliefert wurde.
Page 69

Deutsch (German)
4.1.3 Intelligente Ausstattungsteile
Schutz des CPU-Temperatur
Die Funktion des CPU-Temperaturschutzes ist imstande, die
Temperatur des CPUs während dem Starten des Systems zu
überwachen. Nachdem diese Funktion festgestellt hat, daß die
Temperatur des CPUs die im BIOS festgelegte sichere CPUTemperatur über steigt, ertönen 5 akustische Warnsignale und das
System wird automatisch heruntergefahren.
Schutz des CPU-Ventilators
Mit der CPU-Ventilator-Schutzfunktion kann der CPU-Ventilator beim
Starten des Systems überwacht werden. Das System wird durch
diese Funktion automatisch ausgeschaltet, nachdem das System
festgestellt hat, daß der CPU-Ventilator nicht rotiert. Durch diese
zusätzliche Vorbeugungsmaßnahme kann der CPU vor
Beschädigungen geschützt sowie eine sichere Betriebsumgebung
gewährleistet werden.
Überspannung
Mit der Überspannungsfunktion können Sie eine niedrigere
Kernspannung, mit der der CPU versorgt wird, von Hand einstellen.
Trotz der Unterstützung dieser Funktion wird von der Verwendung
einer höheren Spannung abgeraten, da die Systemplatine mit einer
unstabilen Spannung versorgt und dadurch beschädigt werden kann.
"
Mit der Funktion zum Einstellen des CPU-Taktgebers Können
Sie den Bus-Taktgeber des Prozessors von Hand und schrittweise.
Eine zu hohe Einstellung des Taktgebers kann jedoch zu einer
Unstabilität des Prozessors oder des Systems führen und
gewährleistet keine bessere Betriebsleistung des Systems.
Automatisches Ausschalten des Chassis-Ventilators
Die Chassisventilatoren werden automatisch ausgeschaltet, wenn das
System in den Suspendier-Modus geschaltet wird.
Deutsch
(German)
69
Page 70

"
Deutsch (German)
Netzschalter mit doppelter Funktion
Je nach der Einstellung im Feld Soft-Off By PWRBTN im Power
Management Setup kann das System durch diesen Schalter
ausgeschaltet oder in den Suspendier-Modus geschaltet werden.
Aufwachen bei Klingeln (Wake-On-Ring)
Mit diesem Merkmal kann das System, welches in den Suspendoder Soft-Power-Off-Modus geschaltet ist, aufgeweckt/eingeschaltet
werden, um eingehende Anrufe zu beantworten, die über ein internes
oder externes Modem geleitet werden.
Wichtig:
Falls Sie eine interne Modemkarte verwenden muß die 5VSBStromquelle des Netzgerätes in Ihrem PC mindestens ≥720mA
unterstützen.
RTC-Taktgeber zum Einschalten des Systems
Durch den auf der Systemplatine installier ten RTC kann Ihr System
automatisch am eingestellten Datum und zur eingestellten Uhrzeit
eingeschaltet werden.
Français
Deutsch
(German)
70
Wecken bei LAN (Wake-On-LAN)
Durch die Funktion Wecken bei LAN-Bereitschaft kann ein
ausgeschalteter PC ferngesteuert durch das Netzwerk eingeschaltet
werden. Ihre LAN-Kar te muß dazu jedoch die Weckfunktion durch
Fernsteuerung unterstützen.
Wichtig:
Die 5VSB-Stromversorgung Ihres Netzgerätes muß
(mindestens) ≥720mA unterstützen.
Wiederherstellung der Wechselstromversorgung nach einem
Ausfall
Bei der Wiederherstellung der Stromversorgung nach einem Ausfall
kann das System entweder manuell oder automatisch eingeschaltet
werden, oder Sie können den Betrieb des Systems an der Stelle
fortsetzen, wo der Betrieb durch den Stromausfall unterbrochen
wurde.
Page 71

Deutsch (German)
ACPI STR
Diese Systemplatine entspricht der ACPI-Vorschrift (Erweiterte
Konfiguration und Leitsungsschnittstelle). ACPI besitzt
Energiesparfunktionen, die es dem PC ermöglichen, das PowerManagement und Plug and Play mit Betriebssystemen anzuwenden,
durch welche das direkte OS-Power-Management unterstützt wird.
Gegenwärtig wird die ACPI-Funktion nur durch Windows® 98/2000/
ME unterstützt. Die Suspendieren-auf-RAM-Funktion kann
angewendet werden, wenn ACPI im Powe r-Management-Setup
aktiviert ist.
Wurde die Suspendieren-auf-RAM-Funktion aktiviert, kann das
System umgehend durch Drücken des Netzschalters oder durch
Auswählen von Standby beim Herunterfahren des Windows® 98/
2000/ME ausgeschaltet werden, ohne daß Sie dabei den manchmal
mühsamen Vo r gang zum Schließen aller Dateien,
Anwendungsprogramme und des Betriebssystems durchmachen
müssen, da das System imstande ist, sämtliche Programme und
Dateien während dem ganzen Arbeitsabschnitt beim Ausschalten in
den RAM (Direktzugriffspeicher) zu speichern. Beim nächsten
Einschalten des Systems wird der Arbeitsabschnitt genau an der
Stelle fortgesetzt, wo Sie ihn unterbrochen haben.
"
Wichtig:
Die 5VSB-Stromquelle Ihres Netzgerätes muß eine Leistung von
≥
1A unterstützen.
Virusschutz
Durch die meisten Viren werden heutzutage Daten auf Festplatten
zerstört. Diese Systemplatine wurde so entworfen, um dem BootSektor und der Partitionstabelle Ihres Festplattenlaufwerkes einen
entsprechenden Schutz zu bieten.
Deutsch
(German)
71
Page 72

"
Deutsch (German)
4.2 Eine CPU Identifizieren, die OverclockingFunktion des Vervielfachers Unterstützt
Nicht alle AMD-CPUs unterstützen die Overclocking-Funktion von
Vervielfacher. Beachten Sie besonders L1 auf der CPU. Die vier
Brücken von L1 müssen geschossen werden (kurz), damit die an
Schalter 1 gewählte Relative Häufigkeit wirken kann. Die Abbildung
unten wird Ihnen helfen, um den Typus der CPU zu identifizieren, die
Ihnen gestattet, ihre Relative Häufigkeit anzupassen.
Deutsch
(German)
Die vier Brücken von L1
geschlossen (kurz).
Wichtig:
Wir empfehlen nicht, daß Sie die CPU auf eine höhere Relative
Häufigkeit anpassen, weil es zur Instabilität der CPU oder des
Systems führen kann und es nicht garantiert wird, eine bessere
Systemleistung zu bieten. Wenn Sie mit der Relativen Häufigkeit, die
Sie gewählt haben, das System nicht booten können, schalten Sie bitte
das System ab und stellen Sie Stifter 1-5 von Schalter 1 auf Aus
(Auto) ein.
Français
Die vier Brücken von
L1 öffnen.
72
Page 73

Deutsch (German)
4.3 Anwendung der Funktion Schutz des CPUVentilators
Der CPU muß durch einen CPU-Ventilator mit Kühlkörper stets kühl
gehalten werden. Ohne eine angemessene Luftzirkulation um den
CPU und den Kühlkörper kann eine Überhitzung des CPUs
entstehen, wodurch der CPU und die Systemplatine beschädigt
werden.
Mit der durch die Systemplatine unterstützten CPU-VentilatorSchutzfunktion kann der CPU-Ventilator beim Starten des Systems
überwacht werden. Das System wird durch diese Funktion
automatisch ausgeschaltet, nachdem das System festgestellt hat, daß
der CPU-Ventilator nicht rotiert. Durch diese zusätzliche
Vorbeugungsmaßnahme kann der CPU vor Beschädigungen
geschützt sowie eine sichere Betriebsumgebung gewährleistet werden.
Zur Anwendung der Schutzfunktion für den CPU-Ventilator gehen Sie
wie folgt vor:
1. Stellen Sie vor dem Einschalten des Systems sicher, daß der
Kühlkörper und der CPU-Ventilator richtig im CPU installiert
wurden. Der System kann den CPU-Ventilator überwachen.
Verwenden Sie daher einen Ventilator mit einem Fühlerstift, um
diese Funktion zu unterstützen. Schließen Sie den CPU-Ventilator
an den 3poligen Ventilatoranschluß an der Stelle J16 auf der
Systemplatine an.
"
2. Stellen Sie sicher, daß CPU Fan Protection im PC Health
Status-Submenü des BIOS auf Enabled eingestellt ist.
3. Schalten Sie das System nun ein.
Durch die zwei folgenden Umstände, die auftreten können, wird das
System automatisch ausgeschaltet. Vor einem solchen automatischen
Ausschalten des Systems ertönt ein akustisches Warnsignal.
1. Der CPU-Ventilator wird nicht rotier t, was darauf hindeutet, daß
der Ventilator beschädigt ist. Ersetzen Sie ihn durch einen neuen
Ventilator.
Deutsch
(German)
73
Page 74

"
Deutsch
(German)
Deutsch (German)
2. Der CPU-Ventilator wurde unmittelbar nach dem Starten des
Systems nicht rotiert oder wurde erst nach einer Weile nach dem
Starten rotiert.
Falls der CPU-Ventilator nach dem Starten des Systems nicht
unmittelbar rotiert oder es eine Weile gedauert hat, bevor der
CPU-Ventilator rotiert wurde, prüfen Sie nach, ob der Kühlkörper
und der Ventilator richtig im CPU installiert worden sind. Starten
Sie danach das System erneut. Besteht das Problem weiterhin,
ersetzen Sie den Ventilator durch einen Ventilator einer guten
Qualität, der nach dem Einschalten sofort rotiert und welcher die
Abwärme wirksamer verteilt, da Sie sonst diese Funktion im Feld
CPU Fan Protection (im PC Health Status-Submenü des
BIOS) deaktivieren müssen.
Français
4.4 Anwendung der Funktion Schutz des CPUTemperatur
Die Funktion des CPU-Temperaturschutzes ist imstande, die
Temperatur des CPUs während dem Starten des Systems zu
überwachen. Zur Anwendung der Schutzfunktion für den CPUTemperatur, muß das CPU Temp. Prot. Function auf Enabled
eingestellt werden und im Feld CPU Temp. Prot. Alarm wählen Sie
CPU-Temperatur aus (im PC Health Status-Submenü des BIOS).
Nachdem diese Funktion festgestellt hat, daß die Temperatur des
CPUs die in diesem Feld eingegebene sichere CPU-Temperatur
übersteigt, ertönen 5 akustische Warnsignale und gleichzeitig erscheint
eine Warnmeldung auf dem Boot-Up-Schirm, auf dem Sie
aufgefordert werden, die <Del>-Taste zu drücken, um ins
Hauptmenü des BIOS zu gelangen. Sie können entweder:
1. Die Taste <Del>, dann eine neue Einstellung (sichere CPUTemperatur) in dieses Feld eingeben;
74
oder
2. Lassen Sie das System nach den 5 akustischen Warnsignalen
ausschalten. Die hohe Temperatur des CPUs kann durch einen
beschädigten CPU-Ventilator oder einer fehlerhaften Installation
des Ventilators oder des Kühlkörpers verursacht werden. Prüfen
Sie zuerst nach, ob der Kühlkörper und der Ventilator richtig in
Page 75

Deutsch (German)
den CPU installiert wurden. Star ten Sie nun das System erneut.
Tritt das Problem weiter auf, kann dies an einem Schaden des
CPU-Ventilators liegen oder daran, daß der CPU-Ventilator nicht
richtig gedreht werden kann. Versuchen Sie, den Ventilator durch
einen neuen zu ersetzen. Liegt der Defekt an anderen Ursachen,
die zu einer hohen Temperatur des CPU führten, müssen Sie
einen niedrigeren Wert für eine sichere CPU-Temperatur in dieses
Feld eingeben.
CPU-Temperaturbezugnahme
Beim Einschalten des Systems erscheint eine BIOS-Nachricht auf dem
Schirm und die Speicherkapazität wird gezählt. Nach dem
Speichertest wird die Temperatur des CPUs zwischen 32oC und
35oC betragen. Falls Sie aber ein Betriebssystem starten und danach
versuchen, das System neuzustar ten, wird die Temperatur des CPUs
zwischen 40oC und 45oC betragen. Diese Temperaturbezugnahme
hilft Ihnen beim Eingeben eines Wertes gemäß dem Schutzniveau, das
Sie für Ihren CPU vorsehen.
"
Deutsch
(German)
75
Page 76

"
Deutsch (German)
4.5 Anwendung der Funktion Suspendieren auf
RAM
1. Power Management Setup in dem Hauptbildschirm auswählen,
und die <Enter> drücken.
2. Im Feld ACPI Function wählen Sie Enabled aus.
3. Im Feld ACPI Suspend Type wählen Sie S3(STR) aus.
Deutsch
(German)
4. Die <Esc>-Taste drücken, um zum Hauptmenü zurückzukehren.
Français
5. Save & Exit Setup auswählen und die <Enter> drücken. Dann
<Y> eingeben und die <Enter> drücken.
6. Installieren Sie Windows® 98/2000/ME, indem Sie den folgenden
Parameter eingeben. Hiermit wird sichergestellt, daß die ACPIFunktion unterstützt wird.
[drive]:>setup /p j
Falls Windows® 98/2000/ME bereits installiert wurde, muß das
System aktualisiert werden, damit ACPI unterstützt werden
kann. Für weitere Informationen über die Aktualisierung wenden
Sie sich an Microsoft.
7. Windows® 98/2000/ME starten. Auf dem Windows® 98/2000/
ME-Desktop klicken Sie auf Start. Dann den Cursor auf
Einstellungen bewegen und auf Systemsteuerung klicken.
8. Auf das Symbol System doppelklicken. Im Dialogfenster
Systemeigenschaften klicken Sie auf das Register Leistung.
9. Auf Dateisystem klicken. Im Feld Standardnutzung dieses
Computers wählen Sie Mobiles oder Docksystem aus. Auf
Applizieren und dann auf OK klicken. Den PC neustarten.
76
10. Zum Öffnen des Dialogfensters Systemsteuerung wiederholen
Sie Schritt 7. Auf das Symbol Power-Management
doppelklicken.
11. Auf das Register Erweitert klicken. Im Feld Beim Drücken der
Netztaste des PCs wählen Sie Standby aus.
Page 77

Deutsch (German)
12. Nachdem Sie die obigen Schritte ausgeführt haben und den PC
ausschalten möchten, muß der Vorgang zum Schließen der
Dateien, Anwendungen und des Betriebssystems nicht
ausgeführt werden. Der PC kann direkt durch Drücken der
Netztaste oder durch Auswählen von Standby beim
Abschalten des Windows® 98/2000/ME ausgeschaltet werden.
Zum Einschalten des PCs einfach die Netztaste drücken. Der
Betrieb wird in weniger als 8 Sekunden an der Stelle wieder
aufgenommen, wo Sie den PC ausgeschaltet haben.
Falls die Farbe oder die Auflösung abgeändert wurde (im
Dialogfenster Bildschirmeigenschaften), dürfen die Einstellungen
ohne Neustarten nicht angewendet werden. Der PC muß
neugestartet werden.
"
Deutsch
(German)
77
Page 78

"
Deutsch (German)
4.6 Unterstützte Software
4.6.1 VIA Hardware Monitor-Dienstprogramm
Die Systemplatine wurde mit dem Dienstprogramm für das VIA
Hardware Monitor geliefer t. Dieses Dienstprogramm ist auf der
mitgelieferten CD enthalten. Mit diesem Dienstprogramm kann der
Zustand der Systemhardware, wie beispielsweise die Temperatur des
CPU und des Systems, die Spannung, die Geschwindigkeit der CPUund Chassisventilatoren, überwacht werden. Sie können damit
ebenfalls selbst einen Kontrollbereich der zu überwachenden Elemente
manuell bestimmen. Sind die Werte höher oder niedriger als der
eingestellte Bereich, erscheint ein Warnhinweis. Dieses
Dienstprogramm kann auch so eingestellt werden, daß bei Auftreten
eines Fehlers ein akustisches Warnsignal abgegeben wird. Es wird
empfohlen, daß Sie die Default Setting benutzen, da dies die ideale
Einstellung ist, mit der das System stets in gutem Funktionszustand
gehalten wird.
Hinweis:
Dieses Dienstprogramm darf nur unter dem Dienstprogramm
Windows® 95, Windows® 98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME,
Windows® 2000 oder Windows NT® 4.0 benutzt werden.
Français
Deutsch
(German)
78
Zum Installieren dieses Dienstprogramms legen Sie die CD in Ihr
CD-ROM-Laufwerk. Der Autorun-Schirm (CD mit Main Board
Utility) erscheint. Zum Installieren des Dienstprogramms klicken Sie
nun auf die VIA Hardware Monitor. Angaben zur Anwendung
dieses Dienstprogramms finden Sie in dessen readme-Datei
(Liesmich-Datei).
4.6.2 VIA-Servicepackung
Die VIA Service Pack ist auf der mit der Systemplatine mitgelieferten
CD enthalten. In dieser Servicepackung sind die folgenden Treiber
enthalten.
Bus Master PCI IDE Driver
AGP VxD Driver
VIA Chipset Functions Registry
VIA PCI IRQ Miniport Driver
Page 79

Deutsch (German)
Zum Installieren dieser Treiber legen Sie die CD in Ihr CD-ROMLaufwerk. Der Autorun-Schirm (Main Board Utility CD) erscheint. Auf
die VIA Ser vice Pack klicken. Angaben zur und Informationen über
die Installation finden Sie in der entsprechenden readme-Datei
(Liesmich-Datei). Auf die Read Me-Schaltfläche auf dem AutorunSchirm klicken.
Anleitung zur Installierung des VIA®-Service-Pakets
Das auf der geliefer ten CD enthaltene VIA Service Pack umfaßt
den AGP VxD Driver sowie die Treiber VIA Chipset Functions
Registry. Diese Treiber werden unter Windows® 95, Windows® 98,
Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME und Windows® 2000. Vor dem
Installieren irgendwelcher anderer Treiber muß jedoch zuerst das VIAService-Paket installiert werden. Dies kann für einige AGP-Karten
jedoch nicht zutreffen. Lesen Sie die untenstehenden Informationen
bitte gut durch.
Wichtig:
Der mit einigen AGP-Karten mitgelieferte VGA-Treiber ist bereits
mit dem AGP-VxD-Treiber gebündelt. Da die Version des
gebündelten VxD-Treibers eventuell älter als jene auf der CD
sein kann, können beim Installieren des gebündelten VxDTreibers Konflikte auftreten. Falls Sie diesen Kartentyp
verwenden wird empfohlen, vor dem VIA-Service-Paket zuerst
den VGA-Treiber der AGP-Karte zu installieren.
"
Gehen Sie zum Installieren des VIA-Service-Pakets wie folgt vor:
1. Legen Sie die mit dem Hauptplatinen-Paket mitgelieferte CD in
Ihr CD-ROM-Laufwerk ein. Der Autorun-Schirm (Main Board
Utility CD) erscheint.
2. Auf VIA Service Pack (VIA-Service-Paket) klicken.
3. Der Welcome-Schirm erscheint. Auf Next klicken. Lesen Sie die
Datei VIA Service Pack readme gut durch, bevor Sie zu Schritt
4 gehen.
4. Zum Abschließen des Installierungsvorgangs die Anleitung auf
dem Schirm befolgen.
5. Das System muß nun neugestartet werden, damit die Treiber
wirksam werden können.
Deutsch
(German)
79
Page 80

"
Deutsch (German)
4.6.3 Audiotreiber und Software-Anwendungsprogramm
Auf der mit der Systemplatine gelieferten CD sind ebenfalls
Audiotreiber und die Software für die Audiowiedergabe enthalten für
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, Windows® ME,
Windows NT 4.0 und Windows 2000. Angaben zur und
Informationen über die Installation finden Sie in der entsprechenden
readme-Datei (Liesmich-Datei). Auf die Read Me-Schaltfläche
auf dem Autorun-Schirm klicken. Der Autorun-Schirm erscheint
normalerweise automatisch nach dem Einlegen der CD in Ihr CDROM-Laufwerk.
Français
4.6.4 Hinweise zum Installieren der Treiber und der
Dienstprogramme
Deutsch
(German)
1. Durch Autorun werden NUR die Betriebssysteme Windows
95, Windows® 98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME, Windows
2000 und Windows NT® 4.0 unterstützt. Wurde nach Einlegen
der CD das Autorun nicht automatisch gestartet (d.h. der
Schirm mit der CD mit Main Board Utility für die Hauptplatine
erscheint nicht), gehen Sie direkt zum Stammverzeichnis der CD
und doppelklicken Sie auf Setup.
2. Auf der DFI-Webseite "http://www.dfi.com/support/
download1.asp" finden Sie die neuste Version der Treiber oder
Software-Anwendungsprogramme.
3. Änderungen sämtlicher Schritte oder Vorgänge zur Installation der
Softwaretreiber sind ohne Vorbenachrichtigung vorbehalten, da die
Softwareprogramme gelegentlich aktualisiert werden. Die neusten
Informationen finden Sie in den Readme-Dateien (LiesmichDateien), falls vorhanden.
®
®
80
Page 81

Deutsch (German)
4.7 Fehlersuche
In diesem Kapitel finden Sie Hinweise zum Lösen von Problemen, die
bei der Benutzung Ihres PCs auftreten können. Für eine erfolgreiche
Fehlersuche in Ihrem System behandeln Sie jede Störung einzeln, um
eine genaue Diagnose der Störung sicherzustellen, falls eine Störung
mehrere Ursachen hat.
Einige der geläufigsten Dinge zum Überprüfen bei einem Auftreten
eines Problems werden nachstehend aufgeführ t.
1. Jedes Peripheriegerät ist mit dessen Netzschalter eingeschaltet
worden.
2. Sämtliche Kabel und Netzkabel sind gut angeschlossen worden.
3. Die Netzsteckdose, an welche die Peripheriegeräte angeschlossen
sind, ist in gutem Betriebszustand. Prüfen Sie dies nach, indem Sie
eine Lampe oder ein anderes elektrisches Gerät daran
anschließen.
4. Der Monitor wurde eingeschaltet.
5. Die Regler zum Einstellen der Helligkeit und des Kontrasts sind
ordnungsgemäß eingestellt.
6. Sämtliche Zusatzkarten in den Erweiterungssteckfassungen sind
richtig und fest eingesetzt worden.
7. Sämtliche Zusatzkar ten, die installiert wurden, sind für Ihr System
bestimmt und wurden richtig eingesetzt.
"
Schutz des CPU-Ventilators
Nach dem Einschalten des Systems ertönt ein akustisches
Warnsignal und das System wird wieder ausgeschaltet.
1. Der CPU-Ventilator wird nicht gedreht, da der Ventilator
beschädigt ist. Ersetzen Sie ihn durch einen neuen.
2. Der CPU-Ventilator wurde nicht sofort gedreht oder erst nach
einer geraumen Zeit. Prüfen Sie nach, ob der Kühlkörper und der
Ventilator ordnungsgemäß auf den CPU montiert wurden und
starten Sie danach das System erneut. Tritt die Störung weiter auf
muß der Ventilator durch einen neuen ersetzt werden und zwar
durch einen, der nach dem Einschalten sofort gedreht wird und
durch welchen die Abwärme ebenfalls wirksamer abgeführt wird,
da Sie sonst die Funktion im Feld CPU Fan Protection
Deutsch
(German)
81
Page 82

"
Deutsch (German)
(Submenü mit dem PC Health Status) im BIOS deaktivieren
müssen.
Frequenzrate von Prozessoren
Sie mit der Relativen Häufigkeit, die Sie gewählt haben, das
System nicht booten können.
Wir empfehlen nicht, daß Sie die CPU auf eine höhere Relative
Häufigkeit anpassen, weil es zur Instabilität der CPU oder des
Systems führen kann und es nicht garantiert wird, eine bessere
Systemleistung zu bieten. Schalten sie bitte das System ab und stellen
Sie Stifter 1-5 von Schalter 1 auf Aus (Auto) ein.
Français
Monitor/Bildschirm
Falls der Bildschirm nach dem Einschalten des Systems leer
bleibt.
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß der Monitor mit dessen Netzschalter
eingeschaltet wurde.
2. Stellen Sie sicher, daß ein Ende des Netzkabels des Monitors
richtig am Monitor und das andere Ende an eine WSNetzsteckdose in gutem Betriebszustand angeschlossen ist.
Schließen Sie das Kabel an eine andere Steckdose an, falls
notwendig.
3. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das Videoeingangskabel richtig am Monitor
und an der Bildschirmkarte angeschlossen ist.
4. Stellen Sie die Helligkeit des Bildschirms mit dem entsprechenden
Regler ein.
Deutsch
(German)
82
Das Bild scheint sich ständig zu bewegen.
1. Der Monitor hat seine vertikale Synchronisation verloren. Stellen
Sie diese ein.
2. Entfernen Sie sämtliche Gegenstände, wie z.B. einen anderen
Monitor oder einen Ventilator, die ein Magnetfeld um den
Bildschirm erzeugen können.
3. Stellen Sie sicher, daß die Ausgangsfrequenzen der Videokarte
durch diesen Monitor unterstützt werden.
Page 83

Deutsch (German)
Der Schirm scheint ständig zu flimmern.
1. Falls der Monitor neben einen anderen Monitor aufgestellt wurde,
muß der danebenstehende Monitor möglicherweise ausgeschaltet
werden. Neonlampen neben dem Monitor können ebenfalls ein
Zittern des Bildes auf dem Bildschirm verursachen.
Stromversorgung
Nichts geschieht nach dem Einschalten des Computers.
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß ein Ende des WS-Netzkabels an eine
Netzsteckdose in gutem Betriebszustand und das andere Ende
richtig an die Rückseite des Systems angeschlossen wurden.
2. Stellen Sie sicher, daß der Spannungswählschalter auf der
Geräterückseite auf die richtige Spannung, die Sie benutzen,
eingestellt ist.
3. Das Netzkabel ist möglicherweise kurzgeschlossen oder
beschädigt. Prüfen Sie das Kabel nach oder verwenden Sie ein
neues, falls notwendig.
Floppylaufwerk
"
Der Computer hat keinen Zugriff zum Floppylaufwerk.
1. Die Floppydiskette wurde möglicherweise nicht formatiert.
Formatieren Sie die Diskette und versuchen Sie es erneut.
2. Die Diskette ist möglicherweise schreibgeschützt. Benutzen Sie
eine Diskette, die nicht schreibgeschützt ist.
3. Möglicherweise schreiben Sie auf das falsche Laufwerk. Prüfen Sie
die Pfadbezeichnung nach und stellen Sie sicher, daß Sie auf das
Ziellaufwerk schreiben.
4. Nicht genügend Speicherplatz auf der Diskette. Benutzen Sie eine
andere Diskette, auf der genügend Speicherplatz vorhanden ist.
Festplattenlaufwerk
Ausbleiben der Funktion des Festplattenlaufwerks.
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß der richtige Laufwerktyp für das
Festplattenlaufwerk im BIOS eingegeben wurde.
2. Falls das System für zwei Festplattenlaufwerke konfiguriert wurde,
stellen Sie sicher, daß das ladbare (erste) Festplattenlaufwerk als
Deutsch
(German)
83
Page 84

"
Deutsch (German)
Master und das zweite Festplattenlaufwerk als Slave konfiguriert
wurde. Das Master-Festplattenlaufwerk muß eine aktive/ladbare
Partition besitzen.
Ungewöhnlich lange Formatierdauer.
1. Falls das Festplattenlaufwerk eine ungewöhnlich lange Dauer zum
Formatieren benötigt liegt dieses Problem wahrscheinlich an einer
Kabelverbindung. Besitzt das Festplattenlaufwerk jedoch eine
große Kapazität wird das Formatieren eine längere Zeit dauern.
Deutsch
(German)
Parallelanschluß
Der Paralleldrucker reagiert nicht, wenn Sie ausdrucken wollen.
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß der Drucker eingeschaltet und online ist.
2. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das Softwareprogramm für den richtigen
Typ des angeschlossenen Druckers konfiguriert wurde.
3. Stellen Sie sicher, daß die E/A-Adresse des LPT-Anschlusses auf
der Platine und de IRQ-Einstellungen richtig konfiguriert wurden.
4. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das angeschlossene Gerät funktioniert,
indem Sie es an einen Parallelanschluß anschließen, der
funktioniert und richtig konfiguriert wurde. Funktionier t es, kann
angenommen werden, daß der Drucker in gutem Betriebszustand
ist. Reagiert der Drucker noch immer nicht, ersetzen Sie das
Druckerkabel und versuchen Sie es danach erneut.
Français
Serieller Anschluß
Das serielle Gerät (Modem, Drucker) reagiert nicht oder gibt
unleserliche Zeichen wieder.
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das serielle Gerät eingeschaltet und es
online ist.
2. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das Gerät an den richtigen seriellen
Anschluß auf der Rückseite des Computers angeschlossen ist.
3. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das angeschlossene serielle Gerät
funktioniert, indem Sie es an einen funktionierenden und richtig
konfigurierten seriellen Anschluß anschließen. Funktioniert das
serielle Gerät nicht, liegt das Problem entweder am Kabel oder
am seriellen Gerät. Funktioniert das serielle Gerät, kann das
Problem an der Einstellung des E/A auf der Platine oder an der
Adreßeinstellung liegen.
84
Page 85

Deutsch (German)
4. Stellen Sie sicher, daß die COM-Einstellungen und die E/AAdresse richtig konfiguriert sind.
Tas tatu r
Beim Drücken einer Taste auf der Tastatur geschieht nichts.
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß die Tastatur ordnungsgemäß angeschlossen
ist.
2. Achten Sie darauf, daß sich keine Gegenstände auf der Tastatur
befinden und daß während dem Startvorgang keine Tasten
gedrückt werden.
Systemplatine
1. Stellen Sie sicher, daß die Zusatzkarte gut und fest in die
Erweiterungssteckfassung eingesetzt wurde. Ist die Zusatzkarte
locker, schalten Sie das System aus, installieren die Karte erneut
und schalten das System danach erneut ein.
2. Die Einstellungen der Steckbrücke überprüfen, um deren richtige
Einstellung sicherzustellen.
3. Stellen Sie sicher, daß sämtliche Speichermodule gut in den
Speichersteckplätzen eingesetzt wurden.
4. Stellen Sie sicher, daß sich die Speichermodule an der richtigen
Stelle befinden.
5. Falls die Funktion der Platine ausbleibt, legen Sie diese auf eine
ebene Oberfläche und lokalisieren sämtliche eingesteckte
Komponente. Drücken Sie jede Komponente behutsam in den
Steckplatz.
6. Falls Sie die BIOS-Einstellungen abgeändert haben, gehen Sie
erneut zum Setup und laden die BIOS-Standardeinstellungen.
"
Deutsch
(German)
85
Page 86

#
Español (Spanish)
Chapter 5 - Español (Spanish)
Tabla de los Contenidos
5.1 Características y Especificaciones.......................................................................
5.2 Identificando una CPU que sea Compatible con la Función
del Multiplicador................................................................................................................
5.3 Utilizando la Función de Procteccion del Ventilador de CPU.....
5.4 Utilizando la Función Protección de Temperatura de CPU.....
5.5 Utilizando la Función de Suspender a RAM..........................................
5.6 Softwares Soportados................................................................................................
5.7 Investigación de Conflictos.....................................................................................
Lista de Chequeo del Paquete
El paquete del tablero de sistema contiene los siguientes ar tículos:
þ El tablero de sistema
þ Un manual de usuario
þ Un cable de IDE para las unidades de ATA/33, ATA/66 o
ATA/100 IDE
þ Un cable de unidad de disquete de 34-terminales
þ Un CD de Main Board Utility
Si cualquieres de estos artículos están perdidos o dañados, favor de
ponerse en contacto con su tratante o representantes de venta
para la asistencia.
87
94
95
96
97
99
102
Español
(Spanish)
86
Page 87

Español (Spanish)
5.1 Características y Especificaciones
5.1.1 Características
Chipset
VIA® KT133A - VT8363A y VT82C686B
Procesador
El tablero de sistema es equipado con el regulador de voltaje de
cambio que detecta automáticamente 1.100V a 1.850V.
AMD AthlonTM/DuronTM 100/133MHz (200/266MHz DDR) FSB
processador (600/650/700/750/800/850/900/950MHz, 1GHz,
1.3GHz o futuros processador)
Memoria de Sistema
Soporta hasta la memoria de 1.5GB utilizando VCM (Virtual
Channel Memory) o PC SDRAM DIMM (intermedia o
registrado)
- Registrado de DIMM - sólo PC-100
3 enchufes de 168-terminales DIMM
Uso del x64 PC SDRAM, 3.3V
- PC-100 SDRAM DIMM por 100MHz (cien megaherz) de
memoria bus
- PC-133 SDRAMDIMM por 133MHz (ciento trenita y tres
megaherz) de memoria bus.
L2 Memoria Cache
- Procesor DuronTM: construido en 64KB nivel 2 pipeline burst
cache
- Procesor AthlonTM: construido en 256KB nivel 2 pipeline
burst cache
#
Nota:
PC-100 SDRAM DIMM apoya cuando usa con el proceso
de 100MHz FSB.
PC-133 SDRAM DIMM apoya cuando usa con el proceso
de 100MHz FSB o 133MHz FSB.
Si usted está utilizando más que un DIMM, asegura de
insertar el mismo tipo de DIMM dentro del encaje de
DIMM. Utilizando diferentes tipos (VCM o PC SDRAM) de
DIMM puede causar problemas.
Español
(Spanish)
87
Page 88

#
Español (Spanish)
DIMMs
2MBx64
4MBx64
8MBx64
Memoria
16MB
32MB
64MB
DIMMs
16MBx64
32MBx64
64MBx64
Memoria
128MB
256MB
512MB
Ranuras de Expansión
El tablero del sistema es equipado con 1 ranura de AGP universal, 5
ranuras de PCI dedicados y 1 ranura CNR (Communication and
Networking Riser) solamente para tarjeta de módem.
AGP es un interfaz diseñado para apoyar alta ejecución de tarjetas
de gráficas de 3D. Este utiliza conducto dedicado para acceder la
memoria de sistema para textuarizar, z-tampón y mezcla alfa. La
ranura de AGP universal apoya AGP 2x con hasta ancho de banda
de 533MB/seg. y AGP 4x hasta ancho de banda de 1066MB/seg.
Para las aplicaciones de gráficas de 3D. AGP en este tablero de
sistema transmitirá mejores y más rápidas gráficas a su PC.
Características de Audio En Tablero
Soporta DirectSound de Microsoft® / DirectSound 3D de
Microsoft
®
AC97 soportado con convertidor de tasa de muestra
independiente, doble completo para la grabación y playback del
audio
Español
(Spanish)
88
Puertos de Cubierta Doble de ATX (Conectores de PC 99 colorcifrado)
2 puertos de USB
2 puerto de serie DB-9 NS16C550A-compatible
1 puer to paralelo de SPP/ECP/EPP DB-25
1 puerto de ratón PS/2 mini-DIN-6
1 puerto de teclado mini-DIN-6 PS/2
1 puerto de juego/MIDI
3 enchufes de audio: línea de salida, línea de entrada y mic de
entrada
Page 89

Español (Spanish)
Conectores
1 conector para 2 puer tos de USB externo adicional
1 conector para interfaz de IrDA
2 conectores de IDE
1 conector de disquete sopor ta hasta dos disquetes de 2.88MB
1 conector de fuente de alimentación de ATX
1 conector de Wake-On-LAN
1 conector de Wake-On-Ring
Conectores de abanicos de CPU, chasis y secundario chasis
3 conectores de audio interno (AUX-in, CD-in y TAD)
Controlador de IDE Maestro de Bus PCI
Dos interfaces de PCI IDE soporta hasta 4 dispositivos de IDE
Soporta las unidades duras de ATA/33, ATA/66 y ATA/100
PIO Modo 3 y 4 Realzada IDE (tasa de transferencia de dato
hasta 16.6MB/seg.)
Controlación de Bus reduce la utilización de CPU durante la
trasferencia de disco
Soporta ATAPI CD-ROM, LS-120 y ZIP
Interfaz de IrDA
#
El tablero de sistema es equipado con el conector de IrDA para la
conexión de radiotelegráfico entre su computadora y dispositivos de
periferia. Soporta dispositivos de periferia que se encuentra con el
estándar de HPSIR o ASKIR.
Puertos de USB
El tablero de sistema soporta 4 puertos de USB. Dos puer tos de
USB en tablero son situados en el doble puerto de la cubier ta de
ATX del tablero. El conector J19 del tablero de sistema le permite
conectar a los puertos dobles de 3rd y 4th USB. Estos puertos
opcionales de USB, los cuales son montados en el soporte de
extremo de la tarjeta, será provisto como una opción. USB permite
el intercambio de dato entre su computadora y un inter valo amplio
de periferias de Enchufar y Usar externa accesible.
Español
(Spanish)
89
Page 90

#
Español (Spanish)
BIOS
Award BIOS, Windows® 95/98/2000/ME Enchufar y Usar
compatible
Soporta el incio de secuencia de SCSI
Parpadea EPROM para fácil actualización de BIOS
Soporta la función de DMI 2.0
Memoria Instante (2Mbitios)
Vcore y pulso de CPU selectible en el BIOS
Interfaz de Administración de Desktop (DMI)
El sistema de tablero viene con DMI 2.0 establecido en el BIOS. La
utilidad del DMI en el BIOS graba automáticamente varias
informaciones sobre la configuración de su sistema y almace estas
informaciones en la balsa de DMI, que es parte del tablero de
sistema Enchufar y Usar BIOS. DMI junto con software de red
apropiado, es diseñado para hacer más fácil el inventario,
mantenimiento y procedimiento para solucionar problema de los
sistemas de computadora.
5.1.2 Funciones de Monitor de Salud del Sistema
Español
(Spanish)
90
El tablero de sistema es capaz de vigilar las siguientes condiciones
de salud de sistema.
Monitores de temperatura de CPU/sistema y alarma de
acaloramiento.
Voltajes de monitores de 12V/5V/3.3V/VCORE y alarma de
fracaso
Vigila la velocidad del abanico del abanido del CPU/chasis; y
alarma de fracaso.
Control de encendido/apagado del abanico de chasis automático
Lea la capacidad de vuelta que presenta la temperatura, voltaje y
velocidad del abanico.
Si usted desea el mensaje de advertencia de extraerse o una alarma
de advertencia de sonar cuando ocurre una condición anormal, usted
debe instalar la VIA Hardware Monitor. Esta utilidad es incluido en
el CD que viene con su tablero de sistema.
Page 91

Español (Spanish)
5.1.3 Inteligencia
Protección de Temperatura de CPU
La función de Protección de Temperatura de CPU tiene la
capabilidad de alternar la temperatura de CPU durante el arranque
del sistema. Una vez que ha detectado que la temperatura de CPU
exceda a la temperatura de CPU de seguridad definida en el BIOS,
el sistema apagará automáticamente después de 5 pitidos de
advertencia.
Protecciones del Ventilador de CPU
La función de Procteccion del Ventilador de CPU monitorea el
ventilador durante el boot-up y también lo apaga automaticament
cuando se apaga la computadora. Estas medidas preventivas se ha
addicionado al sistema para proteger a la computadora.
Over Voltage o Sobre el Voltage
Esta función permite al usuario ajustar el Voltaje que es emitido al
CPU, Este sistema que ya esta implantado en la computadora no es
reconmendable ajustar el Voltaje mas alto de su limite. Esto puede
causar inestabilidad en la corriente causando daños en la tabla
principal.
#
CPU Overclocking o Ajuste del Pulso de CPU
Esta función permite ajusta el pulso del bus del procesor, Si se
ajusta el pulso mas de la cuenta sobre el limite, esto puede causar
inestabilidad y puede influenciar en la funtion del sistema.
Abanico Apagado de Chasis Automático
Los abanico de chasis apagarán automáticamente una vez que el
sistema entra al modo de Suspender.
Botón de Energía de Doble Función
Dependiendo en la configuración en el campo de Soft-Off By
PWRBTN de la Configuración de Power Management Setup, este
interruptor permite el sistema de entrar al modo de Soft-Off o
Suspender.
Español
(Spanish)
91
Page 92

#
Español (Spanish)
Campaneo de Despertar (Wake-On-Ring)
Esta característica permite el sistema que es en el modo de
Suspender o en el modo de Soft Power Off a despierto/encendido
para responder a llamadas que vienen desde un modem interno o
externo.
Importante:
Si usted está utilizando la tarjeta incorporada de modém, el
fuente de energía de 5VSB de su fuente de alimentación debe
soportar un mínimo de ≥720mA.
Temporizador de RTC para Encender el Sistema
El RTC instalado en el tablero de sistema permite su sistema de
encender automáticamente en la fecha y el tiempo configurado.
Listo el Wake-On-LAN
La función de Wake-On-LAN permite el red de despertar
remotamente el PC de Apagar de Soft (Soft-Off). Su tarjeta de
LAN debe soportar la función de desper tar remoto.
Importante:
El origen de energía de 5VSB de su fuente de alimentación
debe soportar >720mA.
Español
(Spanish)
92
Recuperación de Fracaso de Energía AC
Cuando la energía vuelve después del fracaso de energía AC, usted
puede elegir a encender su sistema manualmente, dejar el sistema de
encender automáticamente o volver al estado donde usted dejó
antes de ocurrir el fracaso de energía.
ACPI STR
El tablero de sistema es diseñado para encontrar con la
especificación de ACPI (Configuración Avanzada e Interfaz de
Energía). ACPI tiene las características de archivación de energía que
activa PC para ejecutar la Administración de Energía y Enchufar y
Usar con los sistemas operativos que soporta la Administración de
Energía Directa de OS. Corrientemente, sólo Windows® 98/2000/ME
soporta la función de ACPI. ACPI cuando activado en la Power
Page 93

Español (Spanish)
Management Setup le permitirá de utilizar la función de Suspender a
RAM.
Con la función de Suspender a RAM activada, usted puede apagar
el sistema una vez por presionando el botón de energía o
seleccionando Preparado cuando apaga el Windows® 98/2000/ME
sin tener que ir por el proceso de molesto algunas veces de los
archivos cerrados., aplicaciones y sistema operativo. Esto es porque
el sistema es capaz de almacenar todos los archivos de programas
y datos durante la sesión operativa entera dentro de RAM
(Memoria de Acceso Casual) cuando es apagado. La sesión
operativa resumirá exactamente donde usted dejará la próxima vez
que encienda la computadora.
Importante:
El origen de energía de 5VSB de su fuente de alimentación
debe soportar ≥1A.
Protección de Virus
La mayoría de los viruses de hoy destroye el dato almacenado en
los discos duros. El tablero de sistema es diseñado para proteger el
sector de inicio y tabla de partición de su unidad de disco duro.
#
Español
(Spanish)
93
Page 94

#
Español (Spanish)
5.2 Identificando una CPU que sea Compatible
con la Función del Multiplicador
No todas las CPU de tipo AMD son compatibles con la función del
multiplicador. Por favor preste especial atención a L1 en la CPU.
Los cuatro puentes de L1 deben ser cerrados en orden para que la
frecuencia seleccionada en SW1 tenga efecto. La figura de abajo le
ayudará a identificar el tipo de CPU que le permitiría ajustar su
frecuencia.
Los cuatro puentes L1 cerrados.
Los cuatro puentes
L1 abier tos.
Español
(Spanish)
94
Importante:
No le recomendamos que ajuste la CPU a una frecuencia más alta
porque esto puede resultar en una inestabilidad de la CPU o del
sistema y no garantiza un mejor rendimiento. Si no pueden butear el
sistema (cargar el sistema operativo) con la frecuencia que ha
seleccionado, por favor apague el sistema y configure los pins 1-5
SW1 en Off (Auto).
Page 95

Español (Spanish)
5.3 Utilizando la Función de Procteccion del
Ventilador de CPU
El CPU debe estar en temperatura adecuadas y no dejar que se
sobrecalienten para eso se usa el ventilador CPU, si no hay aire que
circule en el CPU esto sobrecaliente el CPU causando daños en el
CPU y en la tabla central.
El sistema de Ventilation CPU controla el ventilador automaticament
y lo prende y apaga cuando se apaga la computadora, este sistema
monitorea si el ventilado esta en rotacion. Este sistema evita daños
que se puedan producir en la computadora.
Para el uso de este sistem por favor siga los siguientes pasos;
1. Antes de ensender la computadora asegurese que el ventilador
este instalado apropiadamentesobre el CPU. El sistema es capaz
de detectar el ventilador entonces se debe conectar el ventilador
CPU en los 3 puntos localizados en J16 de la tabla.
2. Asegurese que el archivo de CPU Fan Protection (PC Health
Status submenu) este enprendido en el BIOS debe estar
Enabled.
#
3. Ahora puede encender la computadora.
Hay dos posibilidades que pueden causar que el sistema se apage.
EL alarma beep sonara antes que el sistema se apage
1. El ventilador no ha roteado, pude ser que este dañado el
ventilador, cambie el ventilador si es necesario.
2. El ventilador no ha roteado por que se ha tardado en rotear. Si
este es el caso entonces revise se el ventilador esta instalado
apropiadamente. Si este problema continua cambie el ventilador,
o puede ir a CPU Fan Protection (PC Health Status
submenu) este enprendido en el BIOS para disable apagar el
sistema de proctection del Fan.
Español
(Spanish)
95
Page 96

#
Español (Spanish)
5.4 Utilizando la Función Protección de
Temperatura de CPU
La función de Protección de Temperatura de CPU tiene la
capabilidad de alternar la temperatura de CPU durante el arranque
de sistema. Para usar la Funcion, coloca el CPU Temp. Prot.
Function campo a Enabled (capacitado) y selecciona de
temperatura de CPU en los campo CPU Temp. Prot. Alarm (PC
Health Status submenu) este enprendido en el BIOS. Una vez que
éste ha detectado que la temperatura de CPU exceda a la
temperatura de CPU de seguridad definida en este campo, sonará 5
pitidos de advertencias y en el mismo tiempo, un mensaje de
advertencia aparecerá en la pantalla de arranque instruyendole de
presionar <Del> parar entrar al menú principal de BIOS. Usted
puede:
1. Presionar <Del> luego introducir la nueva configuración en este
campo (temperatura de CPU segura);
o
2. Permite el sistema de apagar después de 5 pitidos de
advertencia. La alta temperatura de CPU puede ser ocacionada
por el abanico de CPU dañado o instalación de abanico/
disipador incorrecto. Examinar primero si disipador y el abanico
son montados propiamente en el CPU. Ahora reiniciar el sistema.
Si persiste el mismo problema, puede ser que es dañado el
abanico de CPU o no está girando propiamente. Tratar de
reemplazarlo con un nuevo abanico. Si es ocacionado por otros
factores de contribución que resulta la alta temperatura de CPU,
usted puede necesitar de configurar este campo a una
temperatura de CPU de seguridad más baja.
Español
(Spanish)
96
Referencia de Temperatura de CPU
Cuando enciende un sistema, aparece el mensaje de BIOS en la
pantalla e empieza la cuenta de memoria. Después de la prueba de
memoria, la temperatura de CPU estará entre 32oC y 35oC. Pero
cuando usted ejecutar un sistema de operación entonces trata de
rearrancar el sistema, la temperatura de CPU en este tiempo estará
Page 97

Español (Spanish)
entre 40oC y 45oC. Esta referencia de temperatura le guiará cuando
usted configura este campo según al nivel de protección que usted
desea para su CPU.
5.5 Utilizando la Función de Suspender a RAM
1. Selecciona Power Management Setup en la pantalla del menú
principal y presiona <Enter>.
2. En el campo de ACPI Function, selecciona Enabled.
3. En el campo de ACPI Suspend Type, selecciona S3(STR).
4. Presiona <Esc> para volver hacia el menú principal.
5. Selecciona Save & Exit Setup y presiona <Enter>. Teclea <Y>
y presiona <Enter>.
6. Instala Windows® 98/2000/ME por tecleando los siguientes
parámetros. Esto es para asegurar que la función de ACPI es
soportado.
[drive]:>setup /p j
#
Si ha instalado anteriormente Windows® 98/2000/ME, usted
necesita de actualizar el sistema para soportar ACPI. Favor
ponerse en contacto con Microsoft para la información de
actualizar.
7. Inicia el Windows® 98/2000/ME. En la pantalla del Windows
98/2000/ME, cliquea el botón de Inicio. Mueve el cursor a
Configuraciones, luego cliquea el Panel de Control.
8. Cliquea doblemente el ícono de Sistema. En la casilla de diálogo
de las Propiedades del Sistema, cliquea el tab de Ejecución.
9. Cliquea Sistema de Archivo. En el campo de Papel típico de
esta computadora, selecciona Móvil o sistema descolada:.
Cliquea Aplicar, luego cliquea OK. Reinicia su computadora.
10. Repite el paso 7 para abrir la casilla de diálogo del Panel de
Control. Cliquea doblemente el ícono de la Administración de
Energía.
®
Español
(Spanish)
97
Page 98

#
Español (Spanish)
11. Cliquea el tab de Avanzado. En el campo de Cuando presiono
el botón de energía en mí computadora, selecciona
Preparado.
12. Después de completar los pasos de arriba y usted desea
apagar la computadora, usted no necesita de ir por el proceso
de encerrar los archivos, aplicaciones y sistema operativo. Usted
puede apagar la computadora una vez por presionando el
botón de energía o seleccionando Preparado cuando cierra el
Windows® 98/2000/ME.
Para encender la computadora, sólo presiona el botón de
energía. La sesión operativa donde usted dejó cuando apaga la
computadora reanudará en no más que 8 segundos.
Si usted ha cambiado el color o la resolución (en la casilla del
diálogo de Propiedades de Visualización), no aplica las
configuraciones sin reiniciarse. Usted debe reiniciar la
computadora.
Español
(Spanish)
98
Page 99

Español (Spanish)
5.6 Softwares Soportados
5.6.1 Utilidad de VIA Hardware Monitor
El tablero de sistema viene con la utilidad de VIA Hardware
Monitor contenido en el CD provisto. Este es capaz de vigilar las
condiciones del hardware de sistema tal como la temperatura del
CPU y sistema, voltaje, y velocidad del CPU y abanicos de chasis.
También le permite de configurar manualmente un intervalo a los
artículos de ser vigilados. Si los valores son sobre o por debajo del
intervalo de configuración, extraerá un mensaje de advertencia. La
utilidad también puede ser configurado así que el alarma de pitido
sonará siempre que ocurra un error. Le recomendamos que utiliza la
Default Setting que es una configuración ideal que mantiene el
sistema en buena condición de funcionamiento.
Nota:
Utiliza esta utilidad sólo en el sistema de operación de
Windows® 95, Windows® 98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME,
Windows® 2000 o Windows NT® 4.0.
Para instalar la utilidad, inser ta el CD dentro de la unidad de CDROM. Aparecerá la pantalla del autocorrido (CD de Main Board
Utility). Cliquea el botón de VIA Hardware Monitor para instalar la
utilidad. Consultar a sus archivos de readme para instr ucciones en
utilizando la utilidad.
#
5.6.2 Paquete de Servicio VIA
El CD en el paquete de tablero del sistema también viene con el
VIA Service Pack. El paquete de servicio incluye los siguientes
programas instaladores.
Bus Master PCI IDE Driver
AGP VxD Driver
VIA Chipset Functions Registry
VIA PCI IRQ Miniport Driver
Para instalar los programas instaladores, inser ta el CD dentro de la
unidad de CD-ROM. Aparecerá la pantalla de autocorrido (Main
Board Utility CD). Cliquea el botón de VIA Service Pack. Para
instalación de instrucciones o información sobre sus correspodientes
Español
(Spanish)
99
Page 100

#
Español (Spanish)
readme, cliquea el botón de Read Me en la pantalla de
autocorrido.
Notas de Instalación de Paquete de Servicio VIA
VIA Service Pack en el CD provisto incluye los controladores de
AGP VxD Driver y VIA Chipset Functions Registry. Estos
controladores son soportados en Windows® 95, Windows® 98,
Windows® 98 SE, Windows® ME y Windows® 2000. Usted debe
primero instalar anteriormente el Paquete de Servicio de VIA para
instalar en cualquieres otros controladores. Sin embargo, este puede
que no sea el caso para algunas tarjetas de AGP. Favor de leer
cuidadosamente la información de abajo.
Importante:
El controlador de VGA que viene con algunas tarjetas de AGP
ya es manejado con el controlador de VxD de AGP. Desde que
la versión del controlador de VxD manejado puede ser más
viejo que el uno provisto en el CD, instalando el controlador de
VxD manejado puede causar problemas. Si usted está
utilizando este tipo de tarjeta, le recomendamos que instala
primero la tarjeta de AGP del controlador de AGA antes de
instalar el Paquete de Ser vico de VIA.
®
Español
(Spanish)
100
Para instalar el Pquete de Servicio de VIA, favor de seguir los pasos
debajos.
1. Insertar el CD que viene con el paquete del tablero de sistema
en la unidad de CD-ROM. Aparecerá la pantalla de autocorrido
(Main Board Utility CD).
2. Cliquea VIA Ser vice Pack.
3. Aparecerá la pantalla de Welcome. Cliquea Next. Favor de
leer cuidadosamente el VIA Service Pack readme antes de
proceder al paso 4.
4. Seguir las indicaciones de la pantalla para completar la instalación.
5. Reinicia el sistema para que los controladores toman efectos.
 Loading...
Loading...