Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
DJ-30 12” Jointer
(Model 37-360, Three Phase)
(Model 37-361, Single Phase)
PART NO. 1349482 - 02-06-04
Copyright © 2004 Delta Machinery
To learn more about DELTA MACHINERY
visit our website at: www.deltamachinery.com.
For Parts, Service, Warranty or other Assistance,
please call
1-800-223-7278 (In Canada call 1-800-463-3582).
Page 2
2
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
Used without the safety alert symbol indicates potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in property damage.
This manual contains information that is important for you to know and understand. This information relates to protecting YOUR SAFETY and PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we use the
symbols below. Please read the manual and pay attention to these sections.
SAFETY GUIDELINES - DEFINITIONS
SOME DUST CREATED BY POWER SANDING, SAWING, GRINDING, DRILLING, AND OTHER
CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES contains chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
· lead from lead-based paints,
· crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
· arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to
these chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, always wear MSHA/NIOSH
approved, properly fitting face mask or respirator when using such tools.
GENERAL SAFETY RULES
READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL WARNINGS AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE
USING THIS EQUIPMENT. Failure to follow all instructions listed below, may result in electric shock,
fire, and/or serious personal injury or property damage.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Woodworking can be dangerous if safe and proper operating procedures are not followed. As with all machinery, there
are certain hazards involved with the operation of the product. Using the machine with respect and caution will
considerably lessen the possibility of personal injury. However, if normal safety precautions are overlooked or ignored,
personal injury to the operator may result. Safety equipment such as guards, push sticks, hold-downs, featherboards,
goggles, dust masks and hearing protection can reduce your potential for injury. But even the best guard won’t make
up for poor judgment, carelessness or inattention. Always use common sense
and exercise caution
in the workshop.
If a procedure feels dangerous, don’t try it. Figure out an alternative procedure that feels safer. REMEMBER: Your
personal safety is your responsibility. For additional information please visit our website www
.deltamachinery.com.
This machine was designed for certain applications only. Delta Machinery strongly recommends that this
machine not be modified and/or used for any application other than that for which it was designed. If you have any
questions relative to a particular application, DO NOT use the machine until you have first contacted Delta to determine
if it can or should be performed on the product.
Technical Service Manager
Delta Machinery
4825 Highway 45 North
Jackson, TN 38305
(IN CANADA: 505 SOUTHGATE DRIVE, GUELPH, ONTARIO N1H 6M7)
Page 3

3
GENERAL SAFETY RULES
1. FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY, READ THE INSTRUCTION
MANUAL BEFORE OPERATING THE MACHINE.
Learning the machine’s application, limitations, and
specific hazards will greatly minimize the possibility of
accidents and injury.
2. WEAR EYE PROTECTION. ALWAYS USE SAFETY
GLASSES. Also use face or dust mask if cutting
operation is dusty. Everyday eyeglasses are NOT safety
glasses. USE CERTIFIED SAFETY EQUIPMENT. Eye
protection equipment should comply with ANSI Z87.1
standards, hearing equipment should comply with
ANSI S3.19 standards, and dust mask protection
should comply with MSHA/NIOSH certified respirator
standards. Splinters, air-borne debris, and dust can
cause irritation, injury, and/or illness.
3. WEAR PROPER APPAREL. Do not wear loose
clothing, gloves, neckties, rings, bracelets, or other
jewelry which may get caught in moving parts. Nonslip
footwear is recommended. Wear protective hair
covering to contain long hair.
4. DO NOT USE THE MACHINE IN A DANGEROUS
ENVIRONMENT. The use of power tools in damp or
wet locations or in rain can cause shock or
electrocution. Keep your work area well-lit to prevent
tripping or placing arms, hands, and fingers in danger.
5. MAINTAIN ALL TOOLS AND MACHINES IN PEAK
CONDITION. Keep tools sharp and clean for best and safest
performance. Follow instructions for lubricating and changing
accessories. Poorly maintained tools and machines can further
damage the tool or machine and/or cause injury.
6. CHECK FOR DAMAGED PARTS. Before using the
machine, check for any damaged parts. Check for
alignment of moving parts, binding of moving parts,
breakage of parts, and any other conditions that may
affect its operation. A guard or any other part that is
damaged should be properly repaired or replaced.
Damaged parts can cause further damage to the
machine and/or injury.
7. KEEP THE WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents.
8. KEEP CHILDREN AND VISITORS AWAY. Your shop is a
potentially dangerous environment. Children and visitors can
be injured.
9. REDUCE THE RISK OF UNINTENTIONAL STARTING.
Make sure that the switch is in the “OFF” position
before plugging in the power cord. In the event of a
power failure, move the switch to the “OFF” position.
An accidental start-up can cause injury.
10. USE THE GUARDS. Check to see that all guards are in
place, secured, and working correctly to prevent injury.
11. REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES
BEFORE STARTING THE MACHINE. Tools, scrap
pieces, and other debris can be thrown at high speed,
causing injury.
12. USE THE RIGHT MACHINE. Don’t force a machine or
an attachment to do a job for which it was not
designed. Damage to the machine and/or injury may
result.
13. USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. The use of
accessories and attachments not recommended by
Delta may cause damage to the machine or injury to the
user.
14. USE THE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure
your extension cord is in good condition. When using
an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to
carry the current your product will draw. An undersized
cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in loss of
power and overheating. See the Extension Cord Chart
for the correct size depending on the cord length and
nameplate ampere rating. If in doubt, use the next
heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number, the
heavier the cord.
15. SECURE THE WORKPIECE. Use clamps or a vise to hold
the workpiece when practical. Loss of control of a
workpiece can cause injury.
16. FEED THE WORKPIECE AGAINST THE DIRECTION OF
THE ROTATION OF THE BLADE, CUTTER, OR ABRASIVE
SURFACE. Feeding it from the other direction will cause
the workpiece to be thrown out at high speed.
17. DON’T FORCE THE WORKPIECE ON THE MACHINE.
Damage to the machine and/or injury may result.
18. DON’T OVERREACH. Loss of balance can make you
fall into a working machine, causing injury.
19. NEVER STAND ON THE MACHINE. Injury could occur if the
tool tips, or if you accidentally contact the cutting tool.
20. NEVER LEAVE THE MACHINE RUNNING UNATTENDED.
TURN THE POWER OFF. Don’t leave the machine until it
comes to a complete stop. A child or visitor could be injured.
21. TURN THE MACHINE “OFF”, AND DISCONNECT THE
MACHINE FROM THE POWER SOURCE before installing
or removing accessories, before adjusting or changing
set-ups, or when making repairs. An accidental start-up
can cause injury.
22. MAKE YOUR WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF WITH
PADLOCKS, MASTER SWITCHES, OR BY
REMOVING STARTER KEYS. The accidental start-up
of a machine by a child or visitor could cause injury.
23. STAY ALERT, WATCH WHAT YOU ARE DOING, AND
USE COMMON SENSE. DO NOT USE THE
MACHINE WHEN YOU ARE TIRED OR UNDER THE
INFLUENCE OF DRUGS, ALCOHOL, OR MEDICATION. A moment of inattention while operating power
tools may result in injury.
24. THE DUST GENERATED by certain woods and wood
products can be injurious to your health. Always
operate machinery in well-ventilated areas, and provide
for proper dust removal. Use wood dust collection
systems whenever possible.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE RULES MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY.
10-27-03
Page 4

4
ADDITIONAL SAFETY RULES FOR JOINTERS
1. DO NOT OPERATE THIS MACHINE until it is
completely assembled and installed according to the
instructions. A machine incorrectly assembled can
cause serious injury.
2. OBTAIN ADVICE from your supervisor, instructor, or
another qualified person if you are not thoroughly
familiar with the operation of this machine.
Knowledge is safety.
3. FOLLOW ALL WIRING CODES and recommended
electrical connections to prevent shock or
electrocution.
4. KEEP KNIVES SHARP and free from rust and pitch.
Dull or rusted knives work harder and can cause
kickback.
5. TIGHTEN THE INFEED/OUTFEED TABLES before
starting the machine. Loss of control of the workpiece can cause serious injury.
6. PROPERLY SECURE THE BLADES IN THE CUTTERHEAD
before turning the power “ON”. Loose blades may be
thrown out at high speeds.
7. NEVER TURN THE MACHINE “ON” before clearing the
table of all objects (tools, scraps of wood, etc.). Flying
debris can cause serious injury.
8. NEVER TURN THE MACHINE “ON” with the workpiece
contacting the cutterhead. Kickback can occur.
9. AVOID AWKWARD OPERATIONS AND HAND
POSITIONS. A sudden slip could cause a hand to
move into the cutterhead.
10. KEEP ARMS, HANDS, AND FINGERS away from
the cutterhead to prevent severe injury.
11. NEVER MAKE CUTS deeper than 1/8" (3.2mm) to
prevent kickback.
12. NEVER JOINT OR PLANE A WORKPIECE that is
shorter than 10" (254mm), narrower than 3/4"
(19.0MM), or less than 1/2" (12.7mm) thick. Jointing
smaller workpieces can allow your hand to contact
the cutterhead causing severe injury.
13. USE HOLD-DOWN/PUSH BLOCKS for jointing or
planing any workpiece lower than the fence. Jointing
or planing small workpieces can result in kickback
and severe injury.
14. HOLD THE WORKPIECE FIRMLY against the table
and fence. Loss of control of the workpiece can
cause kickback and result in serious injury.
15. NEVER PERFORM “FREE-HAND” OPERATIONS. Use
the fence to position and guide the workpiece. Loss
of control of the workpiece can cause serious injury.
16. DO NOT attempt to perform an abnormal or little-
used operation without study and the use of
adequate hold-down/push blocks, jigs, fixtures,
stops, etc.
17. DO NOT FEED A WORKPIECE from the outfeed
end of the machine.The workpiece will be thrown out
of the opposite end at high speeds.
18. DO NOT ATTEMPT to back out a workpiece while
the cutters are still rotating.
18. DO NOT FEED A WORKPIECE that is warped,
contains knots, or is embedded with foreign objects
(nails, staples, etc.) to prevent kickback.
19. MAINTAIN THE PROPER RELATIONSHIP OF
INFEED AND OUTFEED TABLE SURFACES and
cutterhead knife path. Loss of control of the workpiece can cause serious injury.
20. PROPERLY SUPPORT LONG OR WIDE WORKPIECES.
Loss of control of the workpiece can cause injury.
21.
NEVER PERFORM LAYOUT, ASSEMBLY, OR SETUP WORK on the table/work area when the
machine is running. A sudden slip could cause a
hand to move into the cutterhead. Severe injury
can result.
22. TURN THE MACHINE “OFF”, disconnect the
machine from the power source, and clean the
table/work area before leaving the machine. LOCK
THE SWITCH IN THE “OFF” POSITION to prevent
unauthorized use. Someone else might accidentally
start the machine and cause injury to themselves.
23. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION regarding the safe
and proper operation of power tools (i.e. a safety
video) is available from the Power Tool Institute,
1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851
(www.powertoolinstitute.com). Information is also
available from the National Safety Council, 1121
Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201. Please
refer to the American National Standards Institute
ANSI 01.1 Safety Requirements for Woodworking
Machines and the U.S. Department of Labor OSHA
1910.213 Regulations.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE RULES MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Refer to them often
and use them to instruct others.
04-24-03
Page 5
5
A separate electrical circuit should be used for your machines. This circuit should not be less than #12 wire and should
be protected with a 20 Amp time lag fuse. If an extension cord is used, use only 3-wire extension cords which have 3prong grounding type plugs and matching receptacle which will accept the machine’s plug. Before connecting the
machine to the power line, make sure the switch (s) is in the “OFF” position and be sure that the electric current is of
the same characteristics as indicated on the machine. All line connections should make good contact. Running on low
voltage will damage the machine.
DO NOT EXPOSE THE MACHINE TO RAIN OR OPERATE THE MACHINE IN DAMP LOCATIONS.
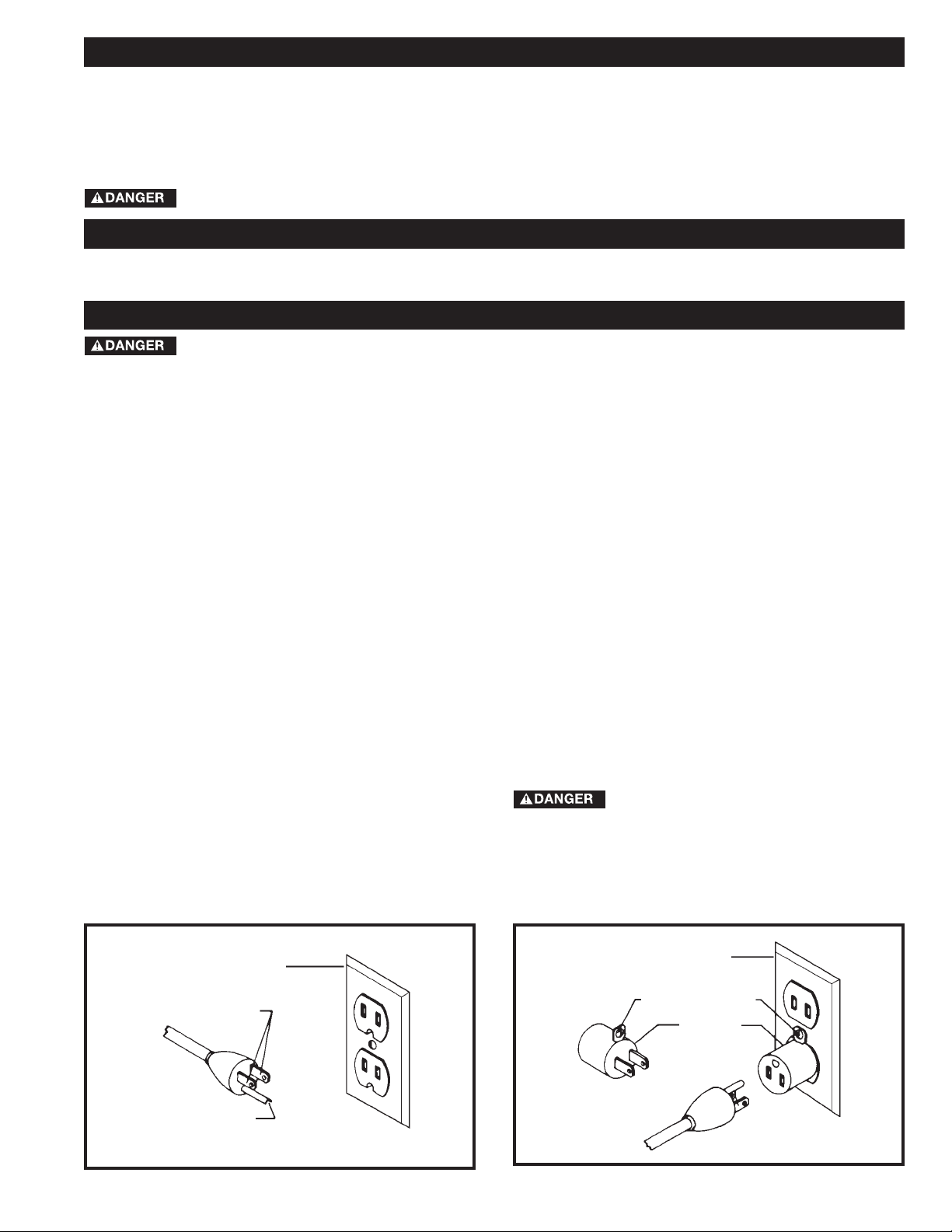
Fig. A Fig. B
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
GROUNDING
MEANS
ADAPTER
2. Grounded, cord-connected machines intended for use
on a supply circuit having a nominal rating less than 150
volts:
If the machine is intended for use on a circuit that has an
outlet that looks like the one illustrated in Fig. A, the
machine will have a grounding plug that looks like the plug
illustrated in Fig. A. A temporary adapter, which looks like
the adapter illustrated in Fig. B, may be used to connect
this plug to a matching 2-conductor receptacle as shown
in Fig. B if a properly grounded outlet is not available. The
temporary adapter should be used only until a properly
grounded outlet can be installed by a qualified electrician.
The green-colored rigid ear, lug, and the like, extending
from the adapter must be connected to a permanent
ground such as a properly grounded outlet box. Whenever
the adapter is used, it must be held in place with a metal
screw.
NOTE: In Canada, the use of a temporary adapter is not
permitted by the Canadian Electric Code.
IN ALL CASES, MAKE CERTAIN THE
RECEPTACLE IN QUESTION IS PROPERLY
GROUNDED. IF YOU ARE NOT SURE HAVE A
QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN CHECK THE RECEPTACLE.
1. All grounded, cord-connected machines:
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding
provides a path of least resistance for electric current to
reduce the risk of electric shock. This machine is
equipped with an electric cord having an equipmentgrounding conductor and a grounding plug. The plug must
be plugged into a matching outlet that is properly installed
and grounded in accordance with all local codes and
ordinances.
Do not modify the plug provided - if it will not fit the outlet,
have the proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding
conductor can result in risk of electric shock. The
conductor with insulation having an outer surface that is
green with or without yellow stripes is the equipmentgrounding conductor. If repair or replacement of the
electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the
equipment-grounding conductor to a live terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if
the grounding instructions are not completely
understood, or if in doubt as to whether the machine is
properly grounded.
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3-prong
grounding type plugs and matching 3-conductor
receptacles that accept the machine’s plug, as shown in
Fig. A.
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord immediately.
POWER CONNECTIONS
MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS
Your machine is wired for (see SPEC PLATE VOLTAGE), 60 HZ alternating current. Before connecting the machine to
the power source, make sure the switch is in the “OFF” position.
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
THIS MACHINE MUST BE GROUNDED WHILE IN USE TO PROTECT THE OPERATOR FROM
ELECTRIC SHOCK.
Page 6
6
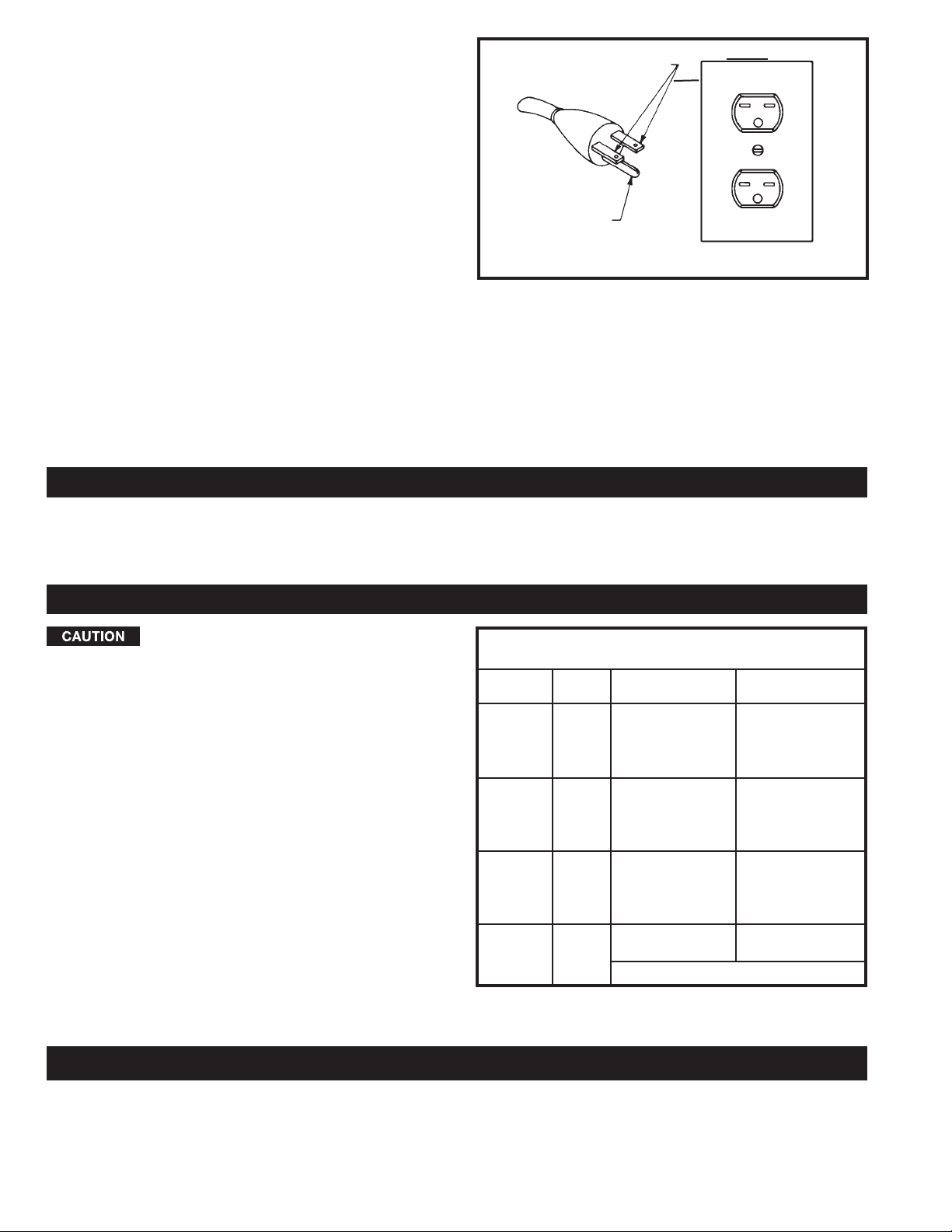
3. Grounded, cord-connected machines intended for
use on a supply circuit having a nominal rating between
150 - 250 volts, inclusive:
If the machine is intended for use on a circuit that has an
outlet that looks like the one illustrated in Fig. C, the
machine will have a grounding plug that looks like the
plug illustrated in Fig. C. Make sure the machine is
connected to an outlet having the same configuration as
the plug. No adapter is available or should be used with
this machine. If the machine must be re-connected for
use on a different type of electric circuit, the reconnection should be made by qualified service
personnel; and after re-connection, the machine should
comply with all local codes and ordinances.
4. Permanently connected machines:
If the machine is intended to be permanently connected,
the machine should be connected to a grounded metal
permanent wiring system, or to a system having an
equipment-grounding conductor.
Fig. C
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES
EXTENSION CORDS
Use proper extension cords. Make sure
your extension cord is in good condition and is a 3-wire
extension cord which has a 3-prong grounding type
plug and matching receptacle which will accept the
machine’s plug. When using an extension cord, be sure
to use one heavy enough to carry the current of the
machine. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line
voltage, resulting in loss of power and overheating. Fig.
D-1 shows the correct gauge to use depending on the
cord length. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. The
smaller the gauge number, the heavier the cord.
Fig. D-2
MINIMUM GAUGE EXTENSION CORD
RECOMMENDED SIZES FOR USE WITH STATIONARY ELECTRIC MACHINES
Ampere Total Length Gauge of
Rating Volts of Cord in Feet Extension Cord
0-6 240
up to
50 18 AWG
0-6 240 50-100 16 AWG
0-6 240 100-200 16 AWG
0-6 240 200-300 14 AWG
6-10 240
up to
50 18 AWG
6-10 240 50-100 16 AWG
6-10 240 100-200 14 AWG
6-10 240 200-300 12 AWG
10-12 240
up to
50 16 AWG
10-12 240 50-100 16 AWG
10-12 240 100-200 14 AWG
10-12 240 200-300 12 AWG
12-16 240
up to
50 14 AWG
12-16 240 50-100 12 AWG
12-16 240
GREATER THAN 100 FEET NOT RECOMMENDED
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Delta Model 37-360 and 37-361 (DJ-30) are 12" Precision Jointers with a cutting capacity of 12" (304mm) wide, 3/4"
deep (19mm max.) and 3/4" (19mm) rabbeting. Model 37-360 includes a three-phase 3 HP motor that is wired for 220V
(can be wired at 460V). Model 37-361 includes a single phase 3 HP motor wired for 230V. Both include a fence, threeknife cutterhead, cutterhead guard, and push blocks.
FOREWORD
THREE PHASE OPERATION
Three phase jointers are not supplied with a power cord. They must be permanently connected to the building electrical
system and grounded according to the National Electrical Code. Since they must be permanently connected to the
building electrical system, extension cords cannot be used with three phase jointers.
Page 7
7
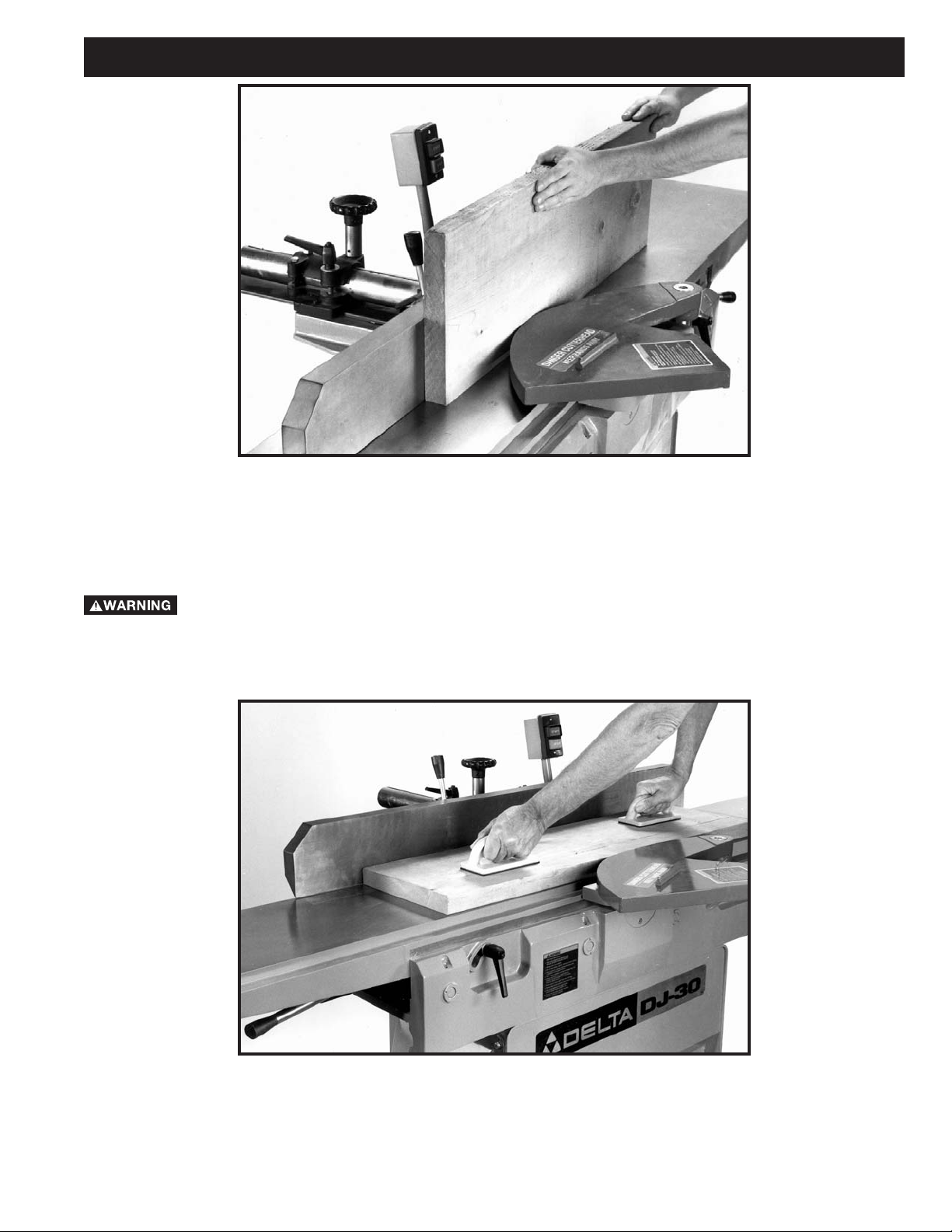
DEFINITIONS OF JOINTING AND PLANING OPERATIONS
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
JOINTING OPERATIONS – Jointing cuts or edge jointing is the simplest and most common operation which can be
done on the jointer and these cuts are made to square an edge of a workpiece. The fence is square with the table and
the depth of cut is approximately 1/8 inch. The workpiece is positioned on the jointer with the narrow edge of the
workpiece on the infeed table and the major flat surface of the workpiece against the fence, as shown in Fig. 2. The
workpiece is moved from the infeed table, across the cutterhead to the outfeed table.
PLANING OPERATIONS – Planing or surfacing is identical to the jointing operation except for the position of the
workpiece. For planing, the major flat surface of the workpiece is placed on the infeed table of the jointer with the narrow
edge of the workpiece against the fence, as shown in Fig. 3. The workpiece is moved from the infeed table, across the
cutterhead to the outfeed table establishing a flat surface on the workpiece. Always use push blocks when performing
planing operations and NEVER pass your hands directly over the cutterhead.
Never pass your hands directly over the cutterhea. Use push blocks to feed the workpiece
whenever possible.
The hand over the outfeed table presses the work down so that the newly-formed surface will make perfect contact with
the table. The hand over the infeed table (usually the right hand) exerts no downward pressure, but simply advances
the work to the cutterhead. Both hands exert pressure to keep the work in contact with the fence.
Page 8

8
UNPACKING AND CLEANING
Carefully unpack the machine and all loose items from the shipping container(s). Remove the protective coating from
all unpainted surfaces. This coating may be removed with a soft cloth moistened with kerosene (do not use acetone,
gasoline or lacquer thinner for this purpose). After cleaning, cover the unpainted surfaces with a good quality household
floor paste wax.
NOTICE: THE PHOTO ON THE MANUAL COVER ILLUSTRATES THE
CURRENT PRODUCTION MODEL. ALL OTHER ILLUSTRATIONS CONTAINED
IN THE MANUAL ARE REPRESENTATIVE ONLY AND MAY NOT DEPICT THE
ACTUAL COLOR, LABELING OR ACCESSORIES AND ARE INTENDED TO
ILLUSTRATE TECHNIQUE ONLY.
REMOVING SHIPPING CRATE
1 - Dust Hood
2 - 8mm Hex wrench
3 - 12 and 14mm open end wrench
4 - 10 and 12mm open end wrench
5-5/8″ long Button Head
Screws (7)
6 - Push Blocks (2)
7 - 1-1/8″ long
Socket Head Screws (2)
8 - Flat Washers (2)
9 - Fence Assembly
10 - 4mm T-Handle wrench
(not shown)
11 - 3mm and 10mm Hex wrench
(not shown)
12 - 17mm and 19mm Open end
wrench (not shown)
Fig. 4
1
2
3
4
5
8
7
6
Your new 12″ Jointer is shipped complete in one wooden shipping crate. Remove the crate from around the machine
leaving the bottom of the machine fastened to the shipping skid at this time. Remove the fence assembly, dust hood
and all loose items from the shipping crate. Figure 4 illustrates all the loose items supplied with your machine.
Page 9

9
REMOVING MACHINE FROM SHIPPING SKID
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
1. Open door (A) Fig. 5, under infeed table and remove mounting hardware that fastens infeed end of machine
to skid
2. Remove three screws (B) Fig. 6, and remove cover (C) from dust chute located under outfeed table. Remove
mounting hardware located inside cover (C) that fastens outfeed end of machine to skid and replace cover (C).
3. Remove machine
from shipping skid and
position in permanent
location.
THE
JOINTER IS VERY
HEAVY AND A
FORKLIFT OR HOIST
WITH STRAPS UNDER
THE TABLE
BRACKETS SHOULD
BE USED TO MOVE
THE MACHINE.
Figure 7 illustrates the
machine removed from
the shipping skid.
A
C
B
SELECTING FLOOR SPACE
It is important that the machine be set on a solid, level foundation. If rocking occurs, place metal shims at the corners
between the base and the floor. Lag screws or bolts may be used if desired to secure the machine to the floor using
the same holes that fastened the machine to the shipping skid.
Page 10

10
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLING DUST HOOD
1. Assemble the dust hood (A) Fig. 8, to the outfeed
end of the jointer base using the seven 5/8″ long button
head screws (B) as shown.
Fig. 11
Fig. 8
Fig. 9 Fig. 10
ASSEMBLING
JOINTER FENCE
1. Assemble the jointer fence assembly (A) Fig. 11, to
the machine cabinet, as shown, using the two 1-1/8″ long
screws (B) and flat washers supplied.
MOVING START-STOP
SWITCH TO THE UP POSITION
1. For shipping purposes, the start-stop switch and
switch arm (A) is shipped in the down position, as shown
in Fig. 9. Simply remove the two screws (B) Fig. 9, rotate
switch and switch arm (A) 180 degrees, as shown in
Fig. 10, and replace the two screws (B).
A
B
B
B
A
B
A
B
B
B
A
Page 11

11
SINGLE PHASE INSTALLATION
Fig. 12
A
B
Fig. 13 Fig. 14
1. Remove screw (A) Fig. 12, and terminal strip cover (B).
2. Remove plastic covering (C) Fig. 13, that snaps into
terminal strip.
3. Bring power line through access hole in bottom of
terminal strip box and connect the two power lines to
terminals (D) Fig. 14, and the green ground wire to ground
screw (E).
4. Replace plastic covering (C) Fig. 13, and terminal
strip cover removed in STEP 1.
C
E
D
IMPORTANT: The jointer cutterhead is a high inertia load which causes the motor to draw a high inrush
current during starting. The jointer must be connected to an electrical circuit protected by a properly sized
fuse or circuit breaker to handle this high inrush of current. We recommend either a 30 Amp time lag fuse, or
a 40 Amp motor start circuit breaker.
If your machine is supplied with single phase electricals, proceed as follows when connecting your machine to
an electrical power system:
Page 12

12
Fig. 16
Fig. 17
THREE PHASE INSTALLATION
If the motor on your machine is wired for 200, 230 or 460 Volts, Three Phase, proceed as follows when connecting
your machine to an electrical power system.
1. Remove screw (A) Fig. 15, and terminal strip cover
(B).
2. Remove plastic covering (C) Fig. 16, that snaps into
terminal strip.
3. Bring three phase power line through access hole in
bottom of terminal strip box and connect the three power
lines to terminals (D) Fig. 17, and the green ground wire
to ground screw (E).
C
E
D
Fig. 15
A
B
The rotation of the cutterhead must be in a
clockwise direction when viewed from the
left side of the machine; that is, the knives
must be rotating toward the infeed table
from the top. If the cutterhead rotation is
incorrect, disconnect the machine from the
power source and interchange any two of
the three incoming power lines connected to
terminals (D) Fig. 17.
Page 13

13
OPERATING CONTROLS AND ADJUSTMENTS
Fig. 18
Fig. 19
Fig. 20
Fig. 21
START-STOP SWITCH
The start-stop switch is conveniently located on a post,
behind the jointer fence, for easy accessibility. To start
the machine, simply press the start button (A) Fig. 18,
and to stop the machine, press the stop button (B).
FENCE OPERATION
1. The fence (A) Fig. 19, can be moved across the table
by loosening lock lever (B) and rotating handwheel (C).
After the fence is moved to its desired position, retighten
lock lever (B) securely. NOTE: Lock lever (B) can be repositioned by pulling out the handle and repositioning it
on the serrated nut located underneath the hub of the
handle. As the fence (A) is moved across the table, the
sliding portion of the column (D) guards the cutterhead in
back of the fence as shown.
2. To tilt the fence (A) to the right, as shown in Fig. 20,
or to the left, as shown in Fig. 21, loosen lock handle (E)
move the fence to the desired angle and tighten handle
(E) securely. NOTE: Handle (E) Figs. 20 and 21, is
spring-loaded and can be repositioned by pulling out the
handle and repositioning it on the serrated nut located
underneath the hub of the handle. Also, when tilting the
fence to the right (outward) as shown in Fig. 20, the stop
(F) Fig. 20, must be rotated to the up position as shown.
IMPORTANT: When cutting a bevel, we suggest that
whenever possible the fence (A) be tilted toward the
table, as shown in Fig. 21. The fence will then form a
V-shape with the tables, and the work is easily pressed
into the pocket while passing it across the knives.
A
B
A
C
D
B
A
F
E
E
A
Page 14

14
ADJUSTING FENCE
POSITIVE STOPS
The fence on your jointer is equipped with positive stops at
the most used fence positions of 90 degrees and 45
degrees right and left. To check and adjust the positive
stops, proceed as follows:
1. Position the fence 90 degrees to the table making sure
end of stop screw (A) is against stop (B) as shown in
Fig. 22.Then tighten lock handle (C).
2. Using a square (D) Fig. 23, check to see if the fence is
at 90 degrees to the table as shown.
3. If the fence is not at 90 degrees to the table, loosen
lock handle (C) Fig. 22, and lock nut (E). Turn stop screw
(A) until end of screw (A) contacts stop (B) when fence is
90 degrees to the table and lock handle (C) is tightened.
Fig. 22
Fig. 23
Fig. 24
Fig. 25
4. Tilt the fence inward as far as possible and using a
combination square (F) Fig. 24, check to see if the fence is
tilted inward 45 degrees to the table, as shown. If an
adjustment is necessary, loosen nuts (G) Fig. 25, and
adjust screws (H) until ends of screws (H) contact brackets
(J) when the fence is at 45 degrees to the table.
Always make certain the fence locking
handle (E) is tightened before operating machine.
C
B
A
E
D
F
J
H
G
E
J
H
G
Page 15

15
Fig. 26
Fig. 27
Fig. 28
5. Tilt the fence outward as far as possible and using a
combination square (F) Fig. 26, check to see if the fence is
tilted outward 45 degrees to the table, as shown. NOTE:
90 degree stop (B) must be rotated up in order to tilt the
fence outward. If an adjustment is necessary, loosen lock
nut (K) Fig. 27, and adjust screw (L) until head of screw (L)
contacts back of fence (M) when the fence is at 45 degrees
to the table.
Always make sure fence locking handle (E)
is tightened before operating machine.
INFEED TABLE
ADJUSTMENTS
To raise or lower the infeed table, loosen table lock handle
(A) Fig. 28, and move the table raising and lowering hand
lever (B) up or down until the table is at the desired position
and tighten table lock handle (A). NOTE: The table lock
handle (A) can be repositioned by pulling out the handle
and repositioning it on the serrated nut located under the
handle.
The depth of cut of the infeed table (position of table in
relationship with the cutting circle) can be read with the
English/Metric scale and pointer (G) Fig. 28.
Positive stops are provided on the jointer to limit the height
and depth of the infeed table. To adjust the stops, simply
loosen two locknuts (C) and (D) Fig. 29, and turn the two
adjustment screws (E) and (F) as necessary. Retighten
locknuts (C) and (D). We recommend that the height of the
infeed table be adjusted so the table at its highest point will
be 1/2mm below the highest point of the knives. This is an
important feature of your jointer which enables you to
rapidly position the infeed table for a finish or a final cut.
B
F
M
K
L
E
A
B
G
Fig. 29
E
C
D
F
Page 16

16
Fig. 30
OUTFEED TABLE
ADJUSTMENTS
For most jointing operations the outfeed table must be
exactly level with the knives at their highest point of
revolution. To move the outfeed table, loosen lock handle
(A)
Fig. 30, and move the table raising and lowering hand lever
(B) up or down until the table is level with the knives.
It may be necessary to adjust the positive stops. Loosen
the two locknuts (D) and (E) Fig. 31, and the two adjusting
screws (F) and (G) when moving the table up or down.
When the table is exactly level with the knives at the
highest point of revolution, tighten lock handle (A) Fig. 30,
and turn adjusting screw (F) Fig. 31, until it bottoms; then
tighten locknut (D). Screw (G) is also a positive stop for the
lower limit of the outfeed table. We suggest that this stop
also be tightened when the outfeed table is set level with
the knives. This will prevent the outfeed table from
accidently being lowered.
ADJUSTING BELT TENSION
The jointer is shipped with two V-belts assembled and
properly tensioned to the cutterhead and motor pulley. If
it becomes necessary to adjust belt tension, proceed as
follows:
B
A
Fig. 31
D
F
E
G
Fig. 32
Fig. 33
B
A
1. DISCONNECT THE MACHINE FROM THE POWER
SOURCE.
2. Pull outward on latch handle (A) Fig. 33, and open
hinged access door (B).
3. Fig. 31, illustrates the V-belts (C), motor pulley (D) and
cutterhead pulley (E). There should be approximately 1/2
inch deflection in the center span of the belts (C) using light
finger pressure. To adjust belt tension refer to STEP 4.
E
C
D
Page 17

Before operating jointer, check guard to
make sure it functions properly and
quickly returns to the closed position.
17
Fig. 34
Fig. 35
4. To adjust belt tension, turn nuts (F) and (G) Fig. 34, to
move motor plate (H) up or down until there is
approximately 1/2 inch deflection at the center span of the
belts, as explained in STEP 3.
ADJUSTING
SPRING TENSION OF
CUTTERHEAD GUARD
The cutterhead guard (A) Fig. 35, completely covers the
cutterhead. During operation the material being jointed or
planed pushes the guard (A) out of the way and at the
completion of the cut, the guard (A) springs back over the
cutterhead providing full coverage. If it ever becomes
necessary to adjust the spring tension of the cutterhead
guard (A), loosen two screws (B) and turn screw (C)
clockwise to increase or counterclockwise to decrease the
spring tension. Then tighten the two screws (B).
A
C
B
H
G
F
Page 18

18
The following directions will give the beginner a start on jointer operations. Use scrap pieces of lumber to check
settings and to get the feel of the operations before attempting regular work.
THE KNIVES ON THE JOINTER WILL NOT WEAR EVENLY BY FEEDING THE WOOD THROUGH THE
SAME SPOT ON THE TABLE EVERY TIME. FEED THE WOOD THROUGH THE JOINTER AT DIFFERENT SPOTS
ON THE TABLE WHEN POSSIBLE, TO HELP ELIMINATE UNEVEN WEAR OF THE KNIVES.
ALWAYS USE CUTTERHEAD GUARD AND KEEP HANDS AWAY FROM CUTTERHEAD. ALWAYS
USE PUSH BLOCKS WHENEVER POSSIBLE. NEVER MAKE JOINTING AND PLANING CUTS DEEPER THAN 1/8"
IN ONE PASS.
CUTTERHEAD ROTATION
The rotation of the cutterhead must be in a clockwise direction when viewed from the left side of the
machine; that is, the knives must be rotating toward the infeed table from the top. If the cutterhead rotation is incorrect,
disconnect the machine from the power source and proceed as follows:
Single Phase Machines – Interchange leads T5 and T8 in the motor junction box.
Three Phase Machines – Interchange any two of the three incoming power lines.
OPERATION
Fig. 36
PLACEMENT OF HANDS
DURING FEEDING
At the start of the cut, the left hand holds the work firmly
against the infeed table and fence, while the right hand
pushes the work toward the knives. After the cut is
underway, the new surface rests firmly on the outfeed table
as shown in Fig. 36. The left hand should then be moved to
the work on the outfeed table, at the same time maintaining
flat contact with the fence.The right hand presses the work
forward, and before the right hand reaches the cutter-head,
it should be moved to the work on the outfeed table.
NEVER PASS HANDS DIRECTLY OVER
THE CUTTERHEAD AND USE PUSH BLOCKS
WHENEVER POSSIBLE.
WORK
INFEED TABLE
OUT-FEED
TABLE
CUTTER
18
Page 19

19
Fig. 37
Fig. 38
Fig. 39
JOINTING AN EDGE
This is the most common operation for the jointer. Set the
guide fence square with the table. Depth of cut should be
the minimum required to obtain a straight edge. Hold the
best face of the piece firmly against the fence throughout
the feed as shown in Fig. 37.
DO NOT perform jointing operations on material shorter
than 10 inches, narrower than 3/4 inch or less than 1/2 inch
thick.
NEVER pass your hands directly over the cutterhead and
use push blocks to feed the workpiece whenever possible.
PLANING OR SURFACING
Planing or surfacing is identical to the jointing operation
except for the position of the workpiece. For planing, the
major flat surface of the workpiece is placed on the infeed
table of the jointer with the narrow edge of the workpiece
against the fence, as shown in Fig. 38. The workpiece is
moved from the infeed table, across the cutterhead to the
outfeed table establishing a flat surface on the workpiece.
Always use push blocks when performing planing
operations and NEVER pass your hands directly over the
cutterhead.
DO NOT perform planing
or surfacing operations on material shorter than 10 inches, narrower than 3/4 inch, wider
than 12 inches or less than 1/2 inch thick.
BEVELING
To cut a bevel, lock the fence at the required angle and run
the work across the knives while keeping the work firmly
against the fence and tables. Several passes may be
necessary to arrive at the desired result. When the angle is
small, there is little difference whether the fence is tilted to
the right or left. However, at greater angles approaching 45
degrees, it is increasingly difficult to hold the work properly
when the fence is tilted to the right. The advantage of the
double-tilting fence is appreciated under such conditions.
When tilted to the left, the fence forms a V-shape with the
tables, and the work is easily pressed into the pocket while
passing it across the knives as shown in Fig. 39. If the bevel
is laid out on the piece in such direction that this involves
cutting against the grain, it will be better to tilt the fence to
the right.
Page 20

20
TAPER CUTS
One of the most useful jointer operations is cutting an edge to a taper. The method can be used on a wide variety of work.
Tapered legs of furniture are a common example.
Instead of laying the piece on the infeed table, lower the forward end of the work onto the outfeed table. Do this very carefully,
as the piece will span the knives and they will take a “bite’” from the work, with a tendency to kickback unless the piece is
firmly held. Now push the work forward as in ordinary jointing. The effect is to plane off all the stock in front of the knives to
increasing depth, leaving a tapered surface.
The ridge left by the knives when starting the taper may be removed by taking a very light cut according to the regular method
for jointing, with the infeed table raised to its usual position.
Practice is required in this operation, and the beginner is advised to make trial cuts on waste material. Taper cuts over part
of the length and a number of other special operations can easily be done by the experienced craftsman.
Fig. 40
CUTTING A RABBET
When making a rabbet cut, as shown in Fig. 40, the
cutterhead guard must be removed. AFTER THE RAB-BET
CUT IS COMPLETED, BE CERTAIN GUARD IS REPLACED.
Use pushblocks whenever possible, as
shown.
1. Adjust the fence so that the distance between the end of
the knives and the fence is equal to the width of the
rabbet.
2. Lower the infeed table an amount equal to the depth of
the rabbet. If the rabbet is quite deep, it may be necessary to
cut it in two or more passes. In that event, the table
is lowered an amount equal to about half the depth of the
rabbet for the first pass, then lowered again to proper depth
to complete the cut.
Fig. 41 Fig. 42
JOINTING OR PLANING WARPED WOOD
If the wood to be jointed is dished or warped, take light cuts until the surface is flat. Avoid forcing such material down
against the table; excessive pressure will spring it while passing the knives, and it will spring back and remain curved after
the cut is completed.
DIRECTION OF GRAIN
Avoid feeding the wood into the jointer against the grain as shown in Fig. 41.The result will be chipped and splintered
edges. Feed with the grain as in Fig. 42, to obtain a smooth surface.
FRONT TABLE
FRONT TABLE
REAR
TABLE
REAR
TABLE
CUTTER
CUTTER
WRONG FEED - AGAINST THE GRAIN CORRECT FEED - WITH THE GRAIN
Page 21

21
REMOVING, REPLACING AND SETTING KNIVES
If the knives are removed from the cutterhead for replacement or regrinding, care must be used in removing, replacing
and resetting them as follows:
1. DISCONNECT THE MACHINE FROM THE POWER SOURCE.
2. Move the fence to the right until it is clear of the cutterhead.
Fig. 43
Fig. 44
Fig. 45
MAINTENANCE
3. Loosen two screws (A) Fig. 43, and remove
cutterhead guard assembly.
BE EXTREMELY CAREFUL THAT
YOUR HANDS DO NOT COME IN CONTACT WITH
THE KNIVES. WEAR PROTECTIVE GLOVES WHEN
HANDLING THE KNIVES.
4. Using wrench (C) Fig. 44, slightly loosen the six knife
locking screws (D) in each knife slot by turning the
screws (D) clockwise. This relieves stress in the
cutterhead.
5. Loosen screws (D) Fig. 44, further, and remove the
knife, knife locking bar and lifter springs located under
the knives. Remove the remaining two knives in the same
manner.
6. Before replacing the knives, make certain the knife
locking bars are thoroughly clean and free of gum and
pitch and adjust the height of the outfeed table to be
.015” above the cutterhead body as follows:
A. Using a straight edge (E) Fig. 45, and feeler
gages (F) that equal .015” adjust the height of
the outfeed table to be .015” above the
cutterhead body (G). Then lock the outfeed table
in place.
A
B
C
D
D
G
E
F
Page 22

2222
Fig. 46
Fig. 48
7. IMPORTANT: For ease in rotating the cutterhead
during the knife setting operation, pull outward on latch
(H) Fig. 46, and open hinged access door (J). This
provides access to the cutterhead pulley (K) Fig. 47, and
belt (L) allowing you to rotate the cutterhead.
After knives are adjusted, make certain the
access door (J) is in the closed and locked
position.
8. Replace the knife locking bars, lifter springs and
knives into each slot in the cutterhead.
CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHEN
INSERTING THE KNIVES
AS THE CUTTING EDGES ARE VERY SHARP. Push
the knives down as far as possible and snug up the knife
locking screws by turning them counterclockwise just
enough to hold the knives in position.
9. Construct a “U” shaped block out of hardwood similar
to the one shown at (M) Fig. 48, and place this block on
the rear table over the cutterhead, as shown. Using
wrench (C), loosen knife locking screws by turning them
clockwise. The knife (O) will lift up and contact the ends
of the gage block (M). The knives are adjusted correctly
when the cutting edge of the knife contacts the gage
block when the knife is at its highest point. When you are
certain the knife is adjusted properly, tighten the knife
locking screws by turning them counterclockwise.
10. Adjust the remaining two knives in the same manner.
MAKE CERTAIN THAT ALL KNIVES
ARE SECURELY FASTENED IN
CUTTERHEAD BEFORE TURNING ON POWER.
11. Replace cutterhead guard.
M
O
C
J
H
Fig. 47
K
L
Page 23

23
MAINTENANCE
KEEP MACHINE CLEAN
Periodically blow out all air passages with dry compressed
air. All plastic parts should be cleaned with a soft damp
cloth. NEVER use solvents to clean plastic parts. They could
possibly dissolve or otherwise damage the material.
Wear ANSI Z87.1 safety glasses while
using compressed air.
FAILURE TO START
Should your machine fail to start, check to make sure the
prongs on the cord plug are making good contact in the
outlet. Also, check for blown fuses or open circuit breakers
in the line.
PARTS, SERVICE OR WARRANTY ASSISTANCE
All Delta Machines and accessories are manufactured to high quality standards and are serviced by a network
of Porter-Cable • Delta Factory Service Centers and Delta Authorized Service Stations. To obtain additional
information regarding your Delta quality product or to obtain parts, service, warranty assistance, or the location
of the nearest service outlet, please call 1-800-223-7278 (In Canada call 1-800-463-3582).
A complete line of accessories is available from your Delta Supplier, Porter-Cable • Delta Factory Service Centers,
and Delta Authorized Service Stations. Please visit our Web Site
www.deltamachinery.com for a catalog or
for the name of your nearest supplier.
Since accessories other than those offered by Delta have not been tested
with this product, use of such accessories could be hazardous. For
safest operation, only
Delta recommended accessories should be used with this product.
ACCESSORIES
Two Year Limited New Product Warranty
Delta will repair or replace, at its expense and at its option, any new Delta machine, machine part, or machine accessory
which in normal use has proven to be defective in workmanship or material, provided that the customer returns the product
prepaid to a Delta factory service center or authorized service station with proof of purchase of the product within two
years and provides Delta with reasonable opportunity to verify the alleged defect by inspection. For all refurbished Delta
product, the warranty period is 180 days. Delta may require that electric motors be returned prepaid to a motor
manufacturer’s authorized station for inspection and repair or replacement. Delta will not be responsible for any asserted
defect which has resulted from normal wear, misuse, abuse or repair or alteration made or specifically authorized by
anyone other than an authorized Delta service facility or representative. Under no circumstances will Delta be liable for
incidental or consequential damages resulting from defective products. This warranty is Delta’s sole warranty and sets
forth the customer’s exclusive remedy, with respect to defective products; all other warranties, express or implied, whether
of merchantability, fitness for purpose, or otherwise, are expressly disclaimed by Delta.
LUBRICATION
Apply household floor paste wax to the machine table and
extension table or other work surface weekly.
PROTECTING CAST IRON FROM RUST
To clean and protect cast iron tables from rust, you will
need the following materials: 1 pushblock from a jointer,
1 sheet of medium Scotch-Brite™ Blending Hand Pad, 1
can of WD-40®, 1 can of degreaser, 1 can of TopCote
®
Aerosol. Apply the WD-40 and polish the table surface
with the Scotch-Brite pad using the pushblock as a
holddown. Degrease the table, then apply the TopCote
®
accordingly.
Page 24

24
The following are trademarks of PORTER-CABLE •DELTA (Las siguientes son marcas registradas de PORTER-CABLE • DELTA S.A.) (Les marques
suivantes sont des marques de fabriquant de la PORTER-CABLE
•
DELTA): Auto-Set®, BAMMER®, B.O.S.S.®, Builder’s Saw®, Contractor’s Saw®,
Contractor’s Saw II™, Delta
®
, DELTACRAFT®, DELTAGRAM™, Delta Series 2000™, DURATRONIC™, Emc²™, FLEX®, Flying Chips™, FRAME SAW®,
Grip Vac™, Homecraft
®
, INNOVATION THAT WORKS®, Jet-Lock®, JETSTREAM®, ‘kickstand®, LASERLOC®, MICRO-SET®, Micro-Set®, MIDI LATHE®,
MORTEN™, NETWORK™, OMNIJIG
®
, POCKET CUTTER®, PORTA-BAND®, PORTA-PLANE®, PORTER-CABLE®&(design), PORTER-
CABLE
®
PROFESSIONAL POWER TOOLS, PORTER-CABLE REDEFINING PERFORMANCE™, Posi-Matic®, Q-3®&(design), QUICKSAND®&(design),
QUICKSET™, QUICKSET II
®
, QUICKSET PLUS™, RIPTIDE™&(design), SAFE GUARD II®, SAFE-LOC®, Sanding Center®, SANDTRAP®&(design), SAW
BOSS
®
, Sawbuck™, Sidekick®, SPEED-BLOC®, SPEEDMATIC®, SPEEDTRONIC®, STAIR EASE®, The American Woodshop®&(design), The Lumber
Company
®
&(design), THE PROFESSIONAL EDGE®, THE PROFESSIONAL SELECT®, THIN-LINE™, TIGER®, TIGER CUB®, TIGER SAW®,
TORQBUSTER
®
, TORQ-BUSTER®, TRU-MATCH™, TWIN-LITE®, UNIGUARD®, Unifence®, UNIFEEDER™, Unihead®, Uniplane™, Unirip®, Unisaw®,
Univise
®
, Versa-Feeder®, VERSA-PLANE®, WHISPER SERIES®, WOODWORKER’S CHOICE™.
Trademarks noted with ™ and ® are registered in the United States Patent and Trademark Office and may also be registered in other countries. Las
Marcas Registradas con el signo de ™ y ® son registradas por la Oficina de Registros y Patentes de los Estados Unidos y también pueden estar
registradas en otros países.
PORTER-CABLE • DELTA SERVICE CENTERS
(CENTROS DE SERVICIO DE PORTER-CABLE
• DELTA)
Parts and Repair Service for Porter-Cable •Delta Machinery are Available at These Locations
(Obtenga Refaccion de Partes o Servicio para su Herramienta en los Siguientes Centros de Porter-Cable
•
Delta)
Authorized Service Stations are located in many large cities. Telephone 800-438-2486 or 731-541-6042 for assistance locating one.
Parts and accessories for Porter-Cable
·
Delta products should be obtained by contacting any Porter-Cable·Delta Distributor, Authorized
Service Center, or Porter-Cable·Delta Factory Service Center. If you do not have access to any of these, call 800-223-7278 and you will
be directed to the nearest Porter-Cable
·
Delta Factory Service Center. Las Estaciones de Servicio Autorizadas están ubicadas en muchas
grandes ciudades. Llame al 800-438-2486 ó al 731-541-6042 para obtener asistencia a fin de localizar una. Las piezas y los accesorios
para los productos Porter-Cable
·
Delta deben obtenerse poniéndose en contacto con cualquier distribuidor Porter-Cable·Delta, Centro
de Servicio Autorizado o Centro de Servicio de Fábrica Porter-Cable
·
Delta. Si no tiene acceso a ninguna de estas opciones, llame al
800-223-7278 y le dirigirán al Centro de Servicio de Fábrica Porter-Cable
·
Delta más cercano.
ARIZONA
Tempe 85282 (Phoenix)
2400 West Southern Avenue
Suite 105
Phone: (602) 437-1200
Fax: (602) 437-2200
CALIFORNIA
Ontario 91761 (Los Angeles)
3949A East Guasti Road
Phone: (909) 390-5555
Fax: (909) 390-5554
San Diego 92111
7638 Clairemnot Blvd.
Phone: (858) 277-9595
Fax: (858) 277-9696
San Leandro 94577 (Oakland)
3039 Teagarden Street
Phone: (510) 357-9762
Fax: (510) 357-7939
COLORADO
Arvada 80003 (Denver)
8175 Sheridan Blvd., Unit S
Phone: (303) 487-1809
Fax: (303) 487-1868
FLORIDA
Davie 33314 (Miami)
4343 South State Rd. 7 (441)
Unit #107
Phone: (954) 321-6635
Fax: (954) 321-6638
Tampa 33609
4538 W. Kennedy Boulevard
Phone: (813) 877-9585
Fax: (813) 289-7948
GEORGIA
Forest Park 30297 (Atlanta)
5442 Frontage Road,
Suite 112
Phone: (404) 608-0006
Fax: (404) 608-1123
ILLINOIS
Addison 60101 (Chicago)
400 South Rohlwing Rd.
Phone: (630) 424-8805
Fax: (630) 424-8895
Woodridge 60517 (Chicago)
2033 West 75th Street
Phone: (630) 910-9200
Fax: (630) 910-0360
MARYLAND
Elkridge 21075 (Baltimore)
7397-102 Washington Blvd.
Phone: (410) 799-9394
Fax: (410) 799-9398
MASSACHUSETTS
Franklin 02038 (Boston)
Franklin Industrial Park
101E Constitution Blvd.
Phone: (508) 520-8802
Fax: (508) 528-8089
MICHIGAN
Madison Heights 48071 (Detroit)
30475 Stephenson Highway
Phone: (248) 597-5000
Fax: (248) 597-5004
MINNESOTA
Minneapolis 55429
5522 Lakeland Avenue North
Phone: (763) 561-9080
Fax: (763) 561-0653
MISSOURI
North Kansas City 64116
1141 Swift Avenue
Phone: (816) 221-2070
Fax: (816) 221-2897
St. Louis 63119
7574 Watson Road
Phone: (314) 968-8950
Fax: (314) 968-2790
NEW YORK
Flushing 11365-1595 (N.Y.C.)
175-25 Horace Harding Expwy.
Phone: (718) 225-2040
Fax: (718) 423-9619
NORTH CAROLINA
Charlotte 28270
9129 Monroe Road, Suite 115
Phone: (704) 841-1176
Fax: (704) 708-4625
OHIO
Columbus 43214
4560 Indianola Avenue
Phone: (614) 263-0929
Fax: (614) 263-1238
Cleveland 44125
8001 Sweet Valley Drive
Unit #19
Phone: (216) 447-9030
Fax: (216) 447-3097
OREGON
Portland 97230
4916 NE 122 nd Ave.
Phone: (503) 252-0107
Fax: (503) 252-2123
PENNSYLVANIA
Willow Grove 19090
(Philadelphia)
520 North York Road
Phone: (215) 658-1430
Fax: (215) 658-1433
TEXAS
Carrollton 75006 (Dallas)
1300 Interstate 35 N, Suite 112
Phone: (972) 446-2996
Fax: (972) 446-8157
Houston 77043
4321 Sam Houston Parkway,
West
Suite 180
Phone: (713) 983-9910
Fax: (713) 983-6645
WASHINGTON
Auburn 98001(Seattle)
3320 West Valley HWY, North
Building D, Suite 111
Phone: (253) 333-8353
Fax: (253) 333-9613
Printed in U.S.A. PC-0104-149
CANADIAN PORTER-CABLE • DELTA SERVICE CENTERS
ALBERTA
Bay 6, 2520-23rd St. N.E.
Calgary, Alberta
T2E 8L2
Phone: (403) 735-6166
Fax: (403) 735-6144
BRITISH COLUMBIA
8520 Baxter Place
Burnaby, B.C.
V5A 4T8
Phone: (604) 420-0102
Fax: (604) 420-3522
MANITOBA
1699 Dublin Avenue
Winnipeg, Manitoba
R3H 0H2
Phone: (204) 633-9259
Fax: (204) 632-1976
ONTARIO
505 Southgate Drive
Guelph, Ontario
N1H 6M7
Phone: (519) 767-4132
Fax: (519) 767-4131
QUÉBEC
1515 ave.
St-Jean Baptiste, Suite 160
Québec, Québec
G2E 5E2
Phone: (418) 877-7112
Fax: (418) 877-7123
1447, Begin
St-Laurent, (Montréal),
Québec
H4R 1V8
Phone: (514) 336-8772
Fax: (514) 336-3505
 Loading...
Loading...