Page 1

SPRAY GUN TROUBLESHOOTING AND
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE GUIDE
SERVICE BULLETIN
SB-2-001-F
Replaces SB-2-001-E
IMPORTANT: Before using this equipment, read all
safety precautions and instructions in this manual.
Keep for future use.
Page 2
Page 2 SB-2-001-F
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This manual contains information that is improtant for you to know and understand. This information relates
to USER SAFETY and PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we
use the following symbols. Please pay particular attention to these sections.
Note
Important safety information A hazard that may cause
serious injury or loss of life.
Important information that tells
how to prevent damage to equipment, or how to avoid a situation
that may cause minor inury.
Information that you should
pay special attention to.
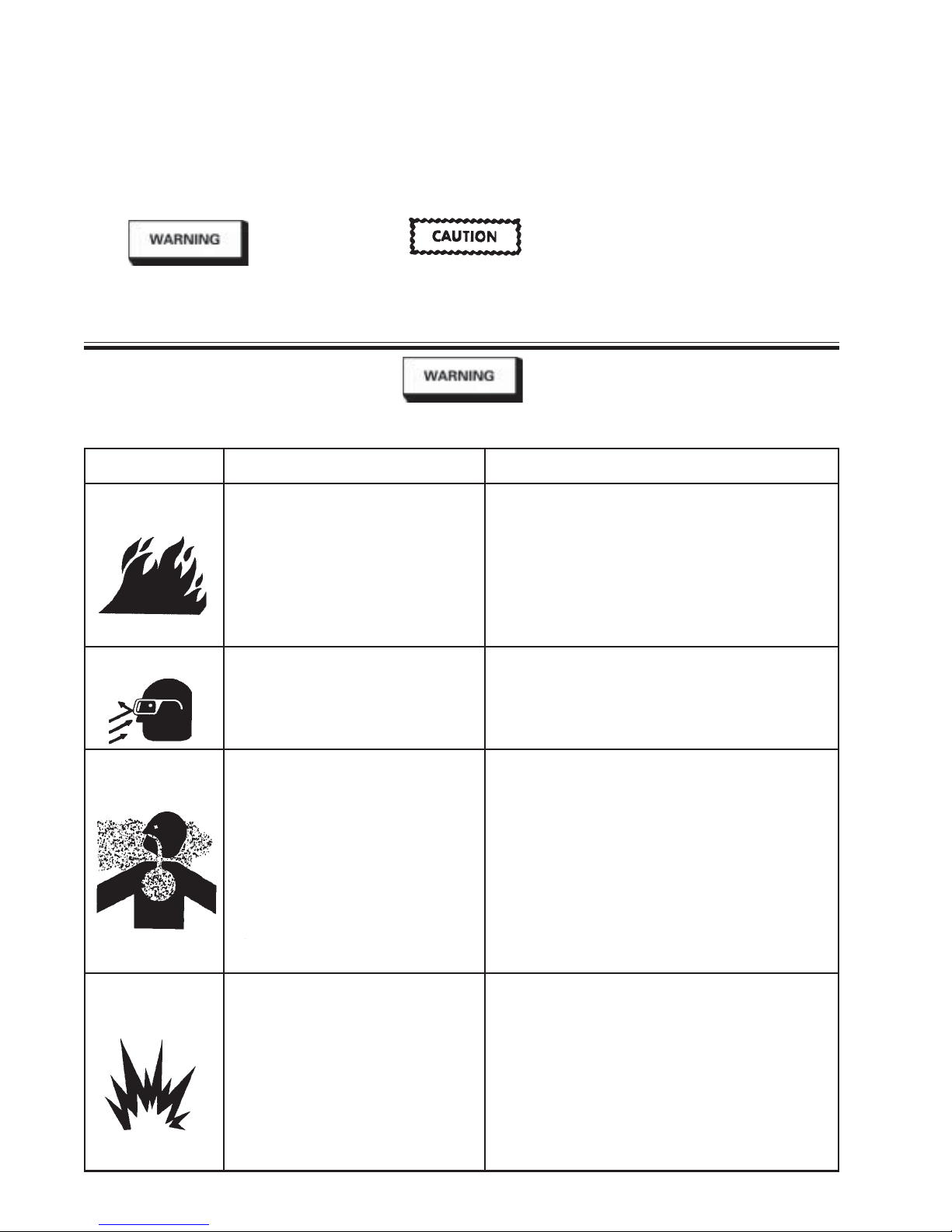
The following hazards may occur during the normal use of this equipment. Please read the following chart before using this equipment.
HAZARD CAUSE SAFEGUARDS
Fire Solvent and coatings can be highly Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep air
flammable or combustible free of accumulations of flammable vapors.
especially when sprayed.
Smoking must never be allowed in the spray area.
Fire extinguishing equipment must be present
in the spray area.
Solvent Spray During cleaning and flushing, Wear eye protection.
solvents can be forcefully expelled
from fluid fluid and air passages.
Some solvents can cause eye
injury.
Inhaling Toxic Certain materials may be harmful Follow the requirements of the Material Safety
Substances if inhaled, or if there is contact Data Sheet supplied by your coating material
with the skin. manufacturer.
Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep the
air free of accumulations of toxic materials.
Use a mask or respirator whenever there is a
chance of inhaling sprayed materials. The mask
must be compatible with the material being
sprayed and its concentration. Equipment must
be as prescribed by an industrial hygienst or
safety expert, and be NIOSH approved.
Explosion Hazard Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents Guns with stainless steel internal passageways
Incompatible - for example; methylene chloride may be used with these solvents. However,
Materials and 1, 1, 1 - Trichloroethane are aluminum is widely used in other spray
not chemically compatible with application equipment - such as material pumps,
the aluminum that might be used cups and regulators, valves, etc. Check all
in many system components. The equipment items before use and make sure
chemical reaction caused by these they can also be ued safely with these solvents.
solvents reacting with aluminum Read the label or data sheet for the material
can become violent and lead to an you intend to spray. If in doubt as to whether
equipment explosion. or not a coating or cleaning material is com-
patible, contact your material supplier.
Page 3
SB-2-001-F Page 3
PRINCIPLES OF AIR SPRAY
Spray application is perhaps the simplest method of
coating where a sizeable area or volume of material
is involved or when intricate shapes and irregular
surfaces require painting. Spray will give the most
uniform film thickness making it easy to obtain a
smooth finish.
The air spray gun is a tool which uses compressed
air to atomize paint, or other sprayable material, and
to apply it to a surface. Air and material enter the
gun through separate passages, and are mixed at
the air cap in a controlled pattern. Air spray guns
may be classified in various ways. Two ways of
classifying guns are by the location of the material
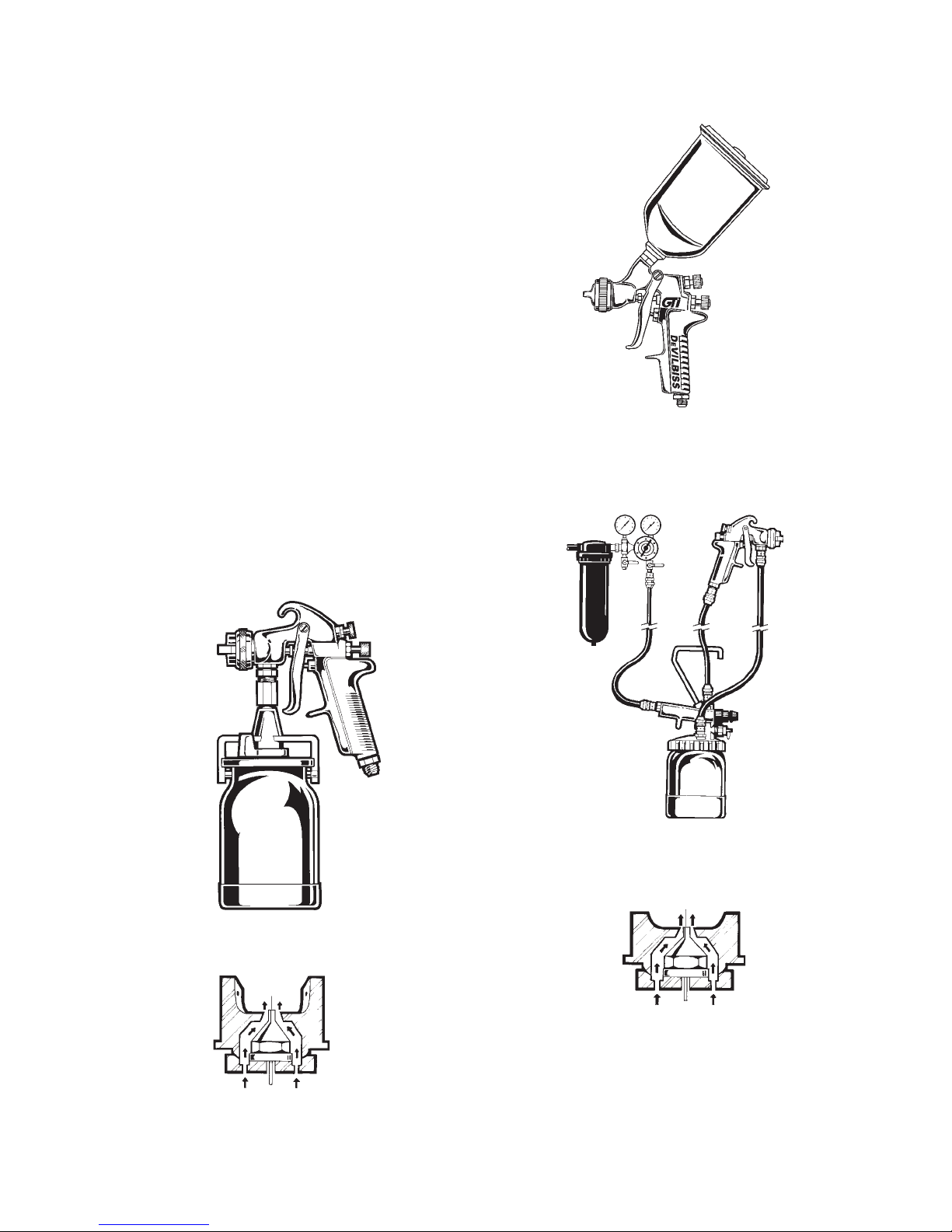
container and the material feed system. Figure 1
shows a gun with a cup attached below. This is
called Suction Feed which draws material to the
gun by suction. Figure 3 is a gun with a cup attached
above. This is called Gravity Feed - the material
travels down, carried by gravity. Figure 4 shows a
material container some distance away from the
spray gun. This is Pressure Feed - the material is
fed by positive pressure. Suction feed is easily
identified by the fluid tip extending slightly beyond
the face of the air cap, as shown in Figure 2. Suction
feed guns are suited to many color changes and to
small amounts of material, such as in touchup or
lower production operations.
Figure 3 Gravity Feed Gun With Cup on Top
Gravity feed guns are ideal for small applications
such as spot repair, detail finishing or for finishing in
a limited space. They require less air than a suction
feed gun and usually have less overspray.
Figure 1 Suction Feed Gun with Attached Cup
Fluid
Tip
Figure 2 Suction Feed Air Cap
Figure 4 Typical Pressure Feed Gun With Remote
Cup
Fluid
Tip
Air Cap
Air Cap
Figure 5 Pressure Feed Air Cap
A pressure feed system is normally used when large
quantities of material are to be applied, when the
material is too heavy to be siphoned from a container
or when fast application is required.
Page 4
Page 4 SB-2-001-F
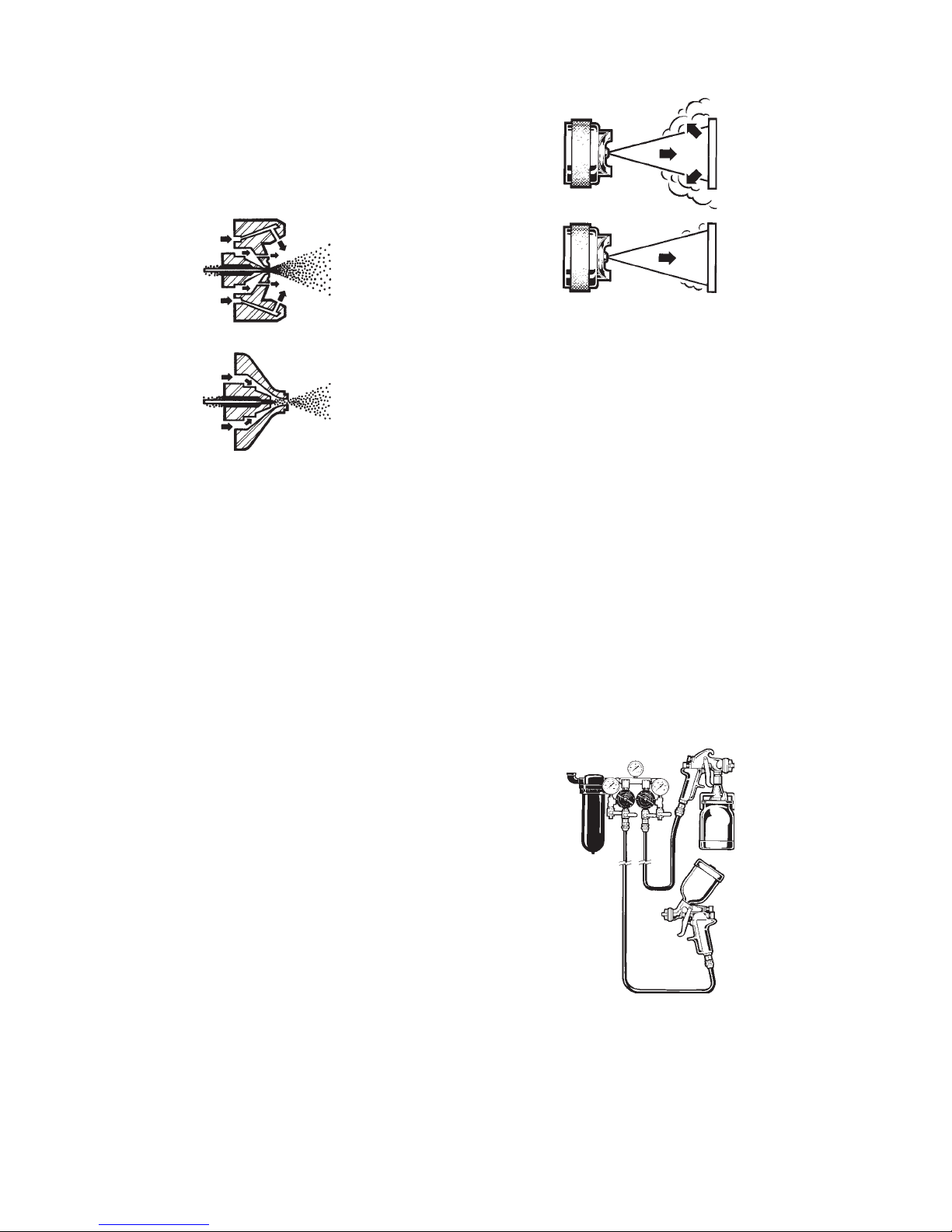
Internal and External Mix Guns
An external mix gun mixes and atomizes air and fluid
outside the air cap. It can be used for applying all
types of materials, and it is particularly desirable
when spraying fast-drying paints such as lacquer. It
is also used when a high quality finish is desired.
Figure 6 External Mix Gun
Figure 7 Internal Mix Gun
This gun mixes air and material inside the air cap,
before expelling them. It is normally used where low
air pressures and volumes are available, or where
slow-drying materials are being sprayed. A typical
example is spraying flat wall paint, or outside house
paint, with a small compressor. Internal mix guns
are rarely used for finishing when a fast-drying
material is being sprayed, or when a high quality
finish is required.
HVLP (High-Volume/Low-Pressure)
HVLP uses a high volume of air (typically between
15-22 CFM) delivered at low pressure (10 psi or
less) to atomize paint into a soft, low-velocity spray
pattern.
Conventional
HVLP
Figure 8 Air Cap Overspray, Conventional/HVLP
The HVLP spray gun resembles a standard spray gun
in shape and operation.
HVLP is growing in popularity and it has also been
judged environmentally acceptable due to its high
transfer efficiency.
HVLP can be used with low to-medium solid materials, including two-component paints, urethanes,
acrylics, epoxies, enamels, lacquers, stains, primers, etc. More recently developed HVLP air caps can
also satisfactorily atomize even high solid coatings.
OPERATION
Suction and Gravity Feed Equipment Hook-Up
Connect the air supply from the compressor outlet
to the air filter regulator inlet. Connect the air
supply hose from the regulator outlet to the air inlet
on the spray gun. After the material has been
reduced to proper consistency, thoroughly mixed
and strained into the cup, attach the gun to the cup.
As a result, far less material is lost in overspray,
bounce-back than with conventional air spray. This
is why HVLP delivers a dramatically higher transfer
efficiency (the amount of material that is actually
applied to the part) than higher pressure spray
systems.
Figure 9 Suction Feed & Gravity Feed System
Components
Spray a horizontal test pattern (air cap horns in a
vertical position). Hold the trigger open until the
paint begins to run. There should be even distribution of the paint across the full width of the pattern
(see Figure 11). Adjust with fan pattern adjustment.
Page 5

If distribution is not even, there is a problem with
either the air cap or the fluid tip. Refer to the
TROUBLESHOOTING section for examples of faulty
patterns to help diagnose the problem.
Figure 10 Horizontal Test Pattern with Even Material Distribution
If the pattern produced by the above test appears
normal, rotate the air cap back to a normal spraying
position and begin spraying (Example - a normal
pattern with a #9000 air cap will be about 9" long
when the gun is held 8" from the surface.) With the
fluid adjusting screw open to the first thread and
the air pressure set at approximately 30 psi, make
a few test passes with the gun on some clean paper.
Move the gun faster than usual when spraying the
test passes. If there are variations in particle size specks and/or large globs, the paint is not atomizing properly (See Figure 12). If the paint is not
atomizing properly, increase the air pressure slightly
and make another test pass. Continue this sequence until the paint particle size is uniform.
SB-2-001-F Page 5
To avoid hazardous bursting or equipment
damage, do not exceed the container's maximum working pressure.
Connect the fluid hose from the fluid outlet on the
tank or pump to the fluid inlet on the gun.
Open spreader adjustment valve for maximum pattern size. Open fluid adjustment screw until the first
thread is visible.
Shut off atomization air to the gun. Set the fluid
flow rate by adjusting the air pressure in the material container. Use about 6 psi for a remote cup and
about 15 psi for a 2-gallon, or larger, container.
Adjust the fluid flow in the following ways:
Remove the air cap. With atomization air off, pull
the trigger, flowing material into a clean, graduated
container for 10 seconds. Measure the amount of
material which flowed in that time and multiply
times 6 (or flow for 30 seconds and multiply time 2).
This is the fluid flow rate in ounces per minute. For
standard finishing, it should be about 14 to 16
ounces per minute. If the flow rate is less than this,
increase the air pressure in the container and repeat.
If the pattern seems starved for material and the
fluid adjusting screw is open wide (to the first
thread), the atomization air pressure may be too
high, or the material may be too heavy. Recheck the
viscosity or reduce the air pressure.
If the material is spraying too heavily and sagging,
reduce the material flow by turning in the fluid
adjusting screw (clockwise).
Figure 11 Pattern with Uneven Particle Size
Pressure Feed Components
A pressure feed system consists of a pressure feed
spray gun, pressure feed tank, cup or pump, an air
filter/regulator, appropriate air and fluid hoses and
an air compressor.
Connect the air hose from the air regulator to the air
inlet on the gun. Connect the mainline air hose to
the air inlet on the tank, cup or pump.
When the flow rate is correct, reinstall the air cap.
If fluid pressure at the tank, cup or pump exceeds 20
psi, the next larger fluid tip size should be used.
Turn the atomizaton air to about 30 psi at the gun.
Spray a fast test pattern on a clean sheet of paper
and check the consistency of the particle size.
Increase or decrease the air pressure until even
particle size is achieved.
Spray a horizontal test pattern holding the trigger
open until the material begins to run. Paint distribution across the full width of the pattern should be the
same (adjust with fan pattern adjustment). If it
cannot be adjusted, there may be a problem with
either the air cap or the fluid tip which must be
corrected. Refer to the Troubleshooting Section.
Hints for good spray technique.
Hold gun perpendicular 6" to 8" (HVLP guns) or 8"10" (suction, gravity or pressure conventional feed
guns) to surface being sprayed.
Don't tilt the gun in any direction. This will result in
uneven paint build causing runs and sags.
Trigger gun just before the edge of the surface to be
sprayed. The trigger should be held fully depressed
and the gun moved in one continuous motion, until
the other edge of the object is reached. Release the
trigger but continue the motion for a few inches until
it is reversed for the return stroke.
Page 6

Page 6 SB-2-001-F
Overlap each stroke 50%. Less than 50% will result
in streaks on the finished surface. Move the gun at
a constant speed while triggering since the material
flows at a constant rate.
Another technique of triggering is referred to as
"feathering". Feathering allows the operator to limit
fluid flow by applying only partial trigger travel.
Spray edges and corners first. This is called banding. Banding reduces overspray yet provides good
coverage on corners.
mended to replace both at the same time. Lapped
sets are available for most guns on pressure feed
combinations.
MAINTENANCE
AIR CAP - Remove the air cap from the gun and
immerse it in clean solvent. Blow it dry with compressed air.
If the small holes become clogged, soak the cap in
clean solvent. If reaming the holes is necessary, use
a toothpick, a broomstraw or some other soft
implement.
Incorrect
Correct
Figure 12 Spray Techniques
REPLACEMENT OF PARTS
Follow specific gun Service Bulletin exploded view
for replacing parts. There are areas requiring proper
sequence.
Do not clean holes with a wire, a nail or a similar
hard object. Doing so could permanently damage
the cap by enlarging the jets, resulting in a defective spray pattern.
Figure 13 Cleaning Air Cap
Suction or Pressure Feed Cleaning - A suction or
pressure feed gun with attached cup should be
cleaned as follows:
Turn off the air to the gun, loosen the cup cover and
remove the fluid tube from the paint. Holding the
tube over the cup, pull the trigger to allow the paint
to drain back into the cup.
The fan adjustment assembly should only be installed after turning the knob out. If left in, the stem
or needle could jam against the seat.
Pull trigger or remove fluid adjusting screw prior to
tip tightening. Tip and needle damage can occur.
Spray guns have some combination of plastic,
copper, leather and soft packings and gaskets. It is
recommended that these be replaced if the assembly is removed or when doing an overall repair. The
fluid needle packing must be replaced when the
packing nut bottoms out.
It is recommended to oil a new packing or needle
before assembly. Packing nuts should be tightened
just enough to seal (fluid leakage on pressure feed,
suction of air on suction feed). Too tight will bind
the needle as well as shorten life of packing. When
replacing the fluid tip or fluid needle, it is recom-
Page 7

Empty the cup and wash it with clean solvent and a
clean cloth. Clean off the outside of the tube. Fill
halfway with clean solvent and spray it through the
gun to flush out the fluid passages. Be sure to
comply with local codes regarding solvent disposal.
Then remove the air cap, clean it as previously
explained and replace it on the gun.
Wipe off the gun with a solvent soaked cloth, or if
necessary, brush the air cap and gun with a fiber
brush using clean-up liquid or thinner.
Cleaning a pressure feed gun with remote cup or
tank - Turn off air supply to cup or tank. Release
material pressure from the system by opening relief
valve. Material in hoses may be blown back. Lid
must be loose and all air pressure off. Keep gun
higher than container, loosen air cap approximately
2-3 turns, hold rag over air cap, and trigger gun until
atomizing air forces all material back into the pressure vessel.
SB-2-001-F Page 7
This device incorporates a highly efficient fluid
header, which meters a precise solvent/air mixture.
The cleaner operates with compressed air and
sends a finely atomized blast of solvent through the
fluid passages of the hose, the spray gun, etc.
This simple, easy to use cleaner speeds up equipment cleaning and saves solvent. It also reduces
VOC emissions. Be sure that both the hose cleaner
and gun are properly grounded.
Where local codes prohibit the use of a hose cleaner,
manually backflush the hose into the cup or tank
with solvent and dry with compressed air.
Clean the container and add clean solvent. Pressurize the system and run the solvent through until
clean. Atomization air should be turned off during
this procedure. Be sure to comply with local codes
regarding solvent dispersion and disposal.
Clean the air cap, fluid tip and tank. Reassemble for
future use.
A gun cleaner may be used for either type of gun.
This is an enclosed boxlike structure (vented) with
an array of cleaning nozzles inside.
Guns and cups are placed over the nozzles, the lid
is closed, the valve is energized, and the pneumatically controlled solvent sprays through the nozzles
to clean the quipment. The solvent is contained,
and must be disposed of properly.
Some states' codes require the use of a gun cleaner
and it is unlawful to discharge solvent into the
atmosphere. Another efficient method of cleaning
the hose and gun passages is with a "Gun & Hose
Cleaner" device, such as the "SolventSaver".
Note
Never soak the entire gun in cleaning solvent. This
will dry out the packings and remove lubrication.
LUBRICATION
Lubricate the fluid needle packing (A), the air valve
packing (B) the trigger bearing screw (C) and the
adjusting screw threads (D) with Spray Gun Lube,
*SSL-10, daily.
The fluid needle spring (E) should be lightly coated
with petroleum jelly.
Thoroughly clean the air cap and baffle threads (F),
and lubricate with spray gun lube, SSL-10, daily.
Lubricate each of these points after every cleaning
in a gun washer.
*A Material Safety Data Sheet is available from
DeVilbiss upon request.
C
D
A
F
D
Figure 14 Using a Hose Cleaner
E
B
Figure 15 Lubrications Points
Page 8

Page 8 SB-2-001-F
TROUBLESHOOTING
CONDITION CAUSE CORRECTION
Heavy top or bottom pattern Horn holes plugged. Clean. Ream with non-metallic
point.
Obstruction on top or bottom of Clean.
fluid tip.
Cap and/or tip seat dirty. Clean.
Heavy right or left Left or right side horn holes plugged. Clean. Ream with non-metallic
side pattern point.
Dirt on left or right side of fluid tip. Clean.
Remedies for the top-heavy, bottom-heavy, right-heavy and left-heavy patterns:
1) Determine if the obstruction is on the air cap or the fluid tip. Do this by making
a test spray pattern. Then, rotate the cap one-half turn and spray another
pattern. If the defect is inverted, obstruction is on the air cap. Clean the air cap
as previously instructed.
2) If the defect is not inverted, it is on the fluid tip. Check for a fine burr on the
edge of the fluid tip. Remove with #600 wet or dry sand paper.
3) Check for dried paint just inside the opening. Remove paint by washing with
solvent.
Heavy center pattern Fluid pressure too high for atomization Balance air and fluid pressure.
air (pressure feed)). Increase spray pattern width with
spreader adjustment valve.
Material flow exceeds air cap's capacity. Thin or lower fluid flow.
Atomizing pressure too low. Increase pressure.
Material too thick. Thin to proper consistency.
Split spray pattern Fluid adjusting knob turned in too far. Back out counterclockwise to
achieve proper pattern.
Atomization air pressure too high. Reduce at transformer.
Fluid pressure too low (pressure feed only). Increase fluid pressure.
Spreader adjusting valve set too high. Adjust.
Suction And Pressure Feed
Jerky or fluttering spray
*Loose or damaged fluid tip/seat. Tighten or replace.
Material level too low. Refill.
Container tipped too far. Hold more upright.
Obstruction in fluid passage. Backflush with solvent.
Loose or broken fluid tube or fluid Tighten or replace.
inlet nipple.
Dry or loose fluid needle packing nut. Lubricate or tighten.
*Most common problem.
Page 9

SB-2-001-F Page 9
CONDITION CAUSE CORRECTION
Jerky or fluttering spray Suction Feed Only
(continued)
Material too heavy. Thin or replace.
Container tipped too far. Hold more upright.
Air vent in cup lid clogged. Clear vent passage.
Loose, damaged or dirty lid. Tighten, replace or clean coupling
nut.
Dry or loose fluid needle packing. Lubricate or tighten packing nut.
Fluid tube resting on cup bottom. Tighten or shorten.
Damaged gasket behind fluid tip. Replace gasket.
Unable to get round spray Fan adjustment screw not seating Clean or replace.
properly.
Air cap retaining ring loose. Tighten.
Will not spray No air pressure at gun. Check air supply and air lines.
Internal mix or pressure feed air cap Change to proper suction feed air
and tip used with suction feed. cap and tip.
Fluid pressure too low with internal Increase fluid pressure at tank.
mix cap and pressure tank.
Fluid needle adjusting screw not open Open fluid needle adjusting screw.
enough.
Fluid too heavy for suction feed. Thin material or change to pressure
feed.
Starved spray pattern Inadequate material flow. Back fluid adjusting screw out to
first thread, or increase fluid
pressure at tank.
Low atomization air pressure Increase air pressure and re-
(suction feed). balance gun.
Excessive overspray Too much atomization air pressure Reduce pressure.
Gun too far from work surface. Adjust to proper distance.
Improper stroking (arcing, gun motion Move at moderate pace, parallel
too fast). to work surface.
Excessive fog Too much, or too fast-drying thinner. Remix properly.
Too much atomization air pressure. Reduce pressure.
Page 10

Page 10 SB-2-001-F
CONDITION CAUSE CORRECTION
Dry Spray Air pressure too high. Decrease air pressure.
Material not properly reduced Reduce to proper consistency.
(suction feed).
Gun tip too far from work surface. Adjust to proper distance.
Gun motion too fast. Slow down.
Gun out of adjustment Adjust.
Fluid leaking from Packing nut loose. Tighten, do not bind needle.
packing nut
Packing worn or dry Replace or lubricate.
Fluid leaking or dripping Packing nut too tight Adjust
from front of pressure
feed gun Dry packing. Lubricate.
Fluid tip or needle worn or Replace tip & needle with lapped
damaged sets.
Foreign matter in tip. Clean.
Fluid needle spring missing or Replace.
broken.
Wrong size needle or tip. Replace.
Needle bound by misaligned Tap sprayhead perimeter with a
sprayhead, (MBC guns only). wooden mallet. Retighten lock bolt.
Runs and sags Too much material flow. Adjust gun or reduce fluid pressure.
Material too thin. Mix properly or apply light coats.
Gun tilted on an angle. Hold gun at right angle to work and
adapt to proper gun technique.
Thin, sandy coarse finish Gun too far from surface. Check distance. Normally 6-8" - HVLP,
drying before it flows out 8-10" - conventional.
Too much air pressure. Reduce air pressure and check
spray pattern.
Improper thinner being used. Follow paint manufacturer's
mixing instructions.
Thick, dimpled finish Gun too close to surface. Check distance. Normally 6-8" - HVLP,
"orange peel". Too much 8-10" - conventional.
material coarsely
atomized Air pressure too low. Increase air pressure or reduce
fluid pressure.
Improper thinner being used. Follow paint manufacturer's
Material not properly mixed. Follow paint manufacturer's
Surface rough, oily, dirty. Properly clean and prepare.
mixing instructions.
mixing instructions.
Page 11

SB-2-001-F Page 11
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR SPRAY FINISHING NEEDS
More than just a spray gun manufacturer, DeVilbiss
is your single source for practical solutions to all
your spray finishing challenges.
To maximize your production output, you need
consistent, reliable performance, high-quality results and a responsive service partner who knows
the industry and your business. And with DeVilbiss,
you not only get the equipment, you also get the
expertise.
Since 1888, we've advanced the science of spray
finishing by introducing innovative products and
technological developments that set the standards
for the industry. These efforts help ensure that we
can deliver the best solution for your particular spray
finishing applications.
Spray Guns
• Conventional air spray and HVLP
• Standard-size, midsize, manual and automatic
• Waterborne compatible, stainless steel passages
• Shading and touch-up guns for precision control
• Decorative guns for textured finish
• Duster guns for tough cleaning applications
• Gravity feed, suction feed, pressure feed
• MAX™ the only true ergonomic spray gun
Cups and Tanks
• Pressure, gravity and suction feed cups
• Aluminum, stainless steel and polyethylene
• ASME-certified galvanized and stainless tanks
• Tank capacities from 2 gallon to 15 gallon
• Air motor drives
Air Control
• Regulators and gauges
• Adjusting valves
• Centrifugal, coalescing, in-line and desiccant filters
Hose
• Fluid and air hose
• Ball and air-adjusting valves
• Fittings and connections
Additional Accessories
• Thread Adapters
• SolventSaver™ gun and hose cleaners
• Gun-mounted fluid strainers
• Replacement parts kits
• Air cap test kits
• Fluid regulators
Page 12

Page 12 SB-2-001-F
DeVILBISS WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE LISTING - www.devilbiss.com
INDUSTRIAL FINISHING
DeVilbiss has authorized distributors throughout the world. FOR TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OR THE DISTRIBUTOR
NEAREST YOU, CALL TOLL FREE 1-888-992-4657 (U.S.A. AND CANADA ONLY). FOR LOCAL CALLS, SEE LISTING
BELOW.
U.S./Canada Sales & Customer Service Office Address Telephone No.
GLENDALE HEIGHTS, IL 60139 195 Internationale Blvd. (630) 237-5000
Toll Free Fax No. 1-877-790-6965
AUTOMOTIVE REFINISHING
DeVilbiss has authorized distributors throughout the world. For equipment, parts and service, check the Yellow Pages
under "Automobile Body Shop Equipment and Supplies". FOR TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE, CALL TOLL FREE
1-800-445-3988 (U.S.A. ONLY). FOR LOCAL CALLS, SEE LISTING BELOW.
U.S. Customer Service Office Address Telephone No.
MAUMEE, OH 43537 1724 Indian Wood Circle (419) 891-8100
Toll Free Fax No. 1-800-445-6643
3/01 ©Copyright 2001, DeVilbiss Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...