DeVilbiss GFG-517 Service Manual

SERVICE MANUAL
GFGTM GRAVITY PROTM MODEL GFG-517
CONVENTIONAL SPRAY GUN
EN
IMPORTANT: Before using this
equipment, read all safety precautions
and instructions. Keep for future use.
DESCRIPTION
The GFG-517 is a general purpose, heavy
duty, high production spray gun suitable for
use with most types of materials. The fluid
tip and needle and internal fluid passages
are stainless steel.
Note
This gun includes 300 series
stainless steel fluid passages and
400/300 S.S. series tip and needle.
Guns may be used with chlorinated
solvent materials. The gravity cup
must also be compatible for use
with chlorinated solvent materials
(GFC-501 Acetal).
IMPORTANT: This gun is designed for use
with mildly corrosive and non-abrasive
materials. If used with other high corrosive
or abrasive materials, it must be expected
that frequent and thorough cleaning will be
required and the necessity for replacement
of parts will be increased.
Note
The GFC gravity feed cups are
included with the gun as part of
the GFG-618 gun and cup kits. See
Accessories on page 6 for more
information.
2. Attach the gravity feed cup to the
material inlet.
Note
Protective coating and rust inhibitors have been used to keep the
gun in good condition prior to
shipment. Before using the gun,
flush it with solvents so that these
materials will be removed from
fluid passages.
OPERATION
Mix, prepare and strain the material to be
sprayed according to the paint manufacturer's instructions.
Strain material through a 60 or 90 mesh
screen.
1. Fill the gravity feed cup with the material. Do not overfill. Make sure that
the cup lid vent hole is clear.
2. Turn on the air at the source of supply.
Adjust the atomization air pressure to
35 psi.
3. Open the spreader adjustment valve
(19) (Fan) by turning the valve stem
counter-clockwise.
4. Close the fluid needle adjusting screw
(25) by turning clockwise.
5. Spray a test area by turning the fluid
needle adjusting screw (25) counterclockwise until a full coat is obtained.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
To clean air cap and fluid tip, brush exterior
with a stiff bristle brush. If necessary to clean
cap holes, use a broom straw or toothpick.
Never use a wire or hard instrument. This
may scratch or burr holes causing a distorted spray pattern.
To clean fluid passages, remove excess
material from cup, then flush with a suitable
solvent. Wipe gun exterior with a solvent
dampened cloth. Never completely immerse in solvent as this is detrimental to
the lubricants and packings.
Note
When replacing the fluid tip or fluid
needle, replace both at the same
time. Using worn parts can cause
fluid leakage. Tip and needle sets
are available. See Chart 2. Also,
replace the needle packing at this
time. Lightly lubricate the threads
of the fluid tip before reassembling.
Torque to 12-15 ft. lbs. Do not
overtighten the fluid tip.
To prevent damage to the fluid tip (2)
or fluid needle (2), be sure to either
1) pull the trigger and hold while
tightening or loosening the fluid tip
or 2) remove fluid needle adjusting
screw (25) to relieve spring pressure
against needle collar.
INSTALLATION
1. Attach the air supply line to the air
inlet (18). An air transformer installed
as close as possible to the gun will
provide filtered and regulated air.
Note
When larger diameter air hoses
are used, it is advisable to use an
8' or 10' "whip end" or a smaller diameter hose at the gun for greater
flexibility or movement.
SB-2-179-G (8/2015) 1 / 8
If the finish is too sandy and dry, the material flow may be too low for the atomization
air pressure being used.
If the finish sags, there is too much material
flowing for the atomization air pressure
being used.
Both of the above can be corrected by increasing or decreasing the atomization air
pressure or the material flow. Pattern width
can be altered by turning the spreader
adjustment valve (19), either clockwise to
decrease the width or counter-clockwise
to increase the width.
SPRAY GUN LUBRICATION
Daily, apply a drop of SSL-10* spray gun
lube at trigger bearing stud (15) and the
stem of the air valve (10) where it enters
the air valve assembly (13). The shank of
the fluid needle (2) where it enters the packing nut (6) should also be oiled. The fluid
needle packing (5) should be lubricated
periodically. Make sure the baffle (4) and
retaining ring (1) threads are clean and
free of foreign matter. Before assembling
retaining ring to baffle, clean the threads
thoroughly, then add two drops of SSL-10
spray gun lube to threads. The fluid needle
spring (22) and air valve spring (11) should
be coated with a very light grease, making
(Continued on page 3)
EN
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This manual contains information that is important for you to know and understand. This information relates to USER SAFETY and
PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we use the following symbols. Please pay particular
attention to these sections.
NOTE
Important information that tells how to
Important safety information - A hazard
that may cause serious injury or loss of life.
The following hazards may occur during the normal use of this equipment.
Please read the following chart before using this equipment.
HAZARD CAUSE SAFEGUARDS
Fire
Solvent Spray
Solvent and coatings can be highly
flammable or combustible especially
when sprayed.
During use and while cleaning and
flushing, solvents can be forcefully
expelled from fluid and air passages.
Some solvents can cause eye injury.
prevent damage to equipment, or how
to avoid a situation that may cause
minor injury.
Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep air free of
accumulations of flammable vapors.
Smoking must never be allowed in the spray area.
Fire extinguishing equipment must be present in the spray
area.
Wear eye protection.
Information that you should pay
special attention to.
Inhaling Toxic Substances
Explosion Hazard Incompatible Materials
General Safety
Certain materials may be harmful if
inhaled, or if there is contact with the skin.
Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents - for
example; methylene chloride and 1,1,1,
- Trichloroethane are not chemically
compatible with the aluminum that might
be used in many system components.
The chemical reaction caused by these
solvents reacting with aluminum can
become violent and lead to an equipment
explosion.
Improper operation or maintenance of
equipment.
Follow the requirements of the Material Safety Data Sheet
supplied by your coating material manufacturer.
Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep the air free of
accumulations of toxic materials.
Use a mask or respirator whenever there is a chance of
inhaling sprayed materials. The mask must be compatible
with the material being sprayed and its concentration.
Equipment must be as prescribed by an industrial hygienst
or safety expert, and be NIOSH approved.
Guns with stainless steel internal passageways may be used
with these solvents. However, aluminum is widely used
in other spray application equipment - such as material
pumps, regulators, valves, and cups. Check all equipment
items before use and make sure they can also be used safely
with these solvents. Read the label or data sheet for the
material you intend to spray. If in doubt as to whether or
not a coating or cleaning material is compatible, contact
your material supplier.
Operators should be given adequate training in the safe
use and maintenance of the equipment (in accordance
with the requirements of NFPA-33, Chapter 15). Users must
comply with all local and national codes of practice and
insurance company requirements governing ventilation, fire
precautions, operation, maintenance, and housekeeping.
These are OSHA Sections 1910.94 and 1910.107 and NFPA-
33. Risk is reduced by avoiding or lessening factors 1-7.
SB-2-179-G (8/2015)2 / 8
HAZARD CAUSE SAFEGUARDS
EN
Cumulative Trauma
Disorders ("CTD's")
CTD's, or musculoskeletal
disorders, involve damage
to the hands, wrists,
elbows, shoulders, neck,
and back. Carpal tunnel
syndrome and tendonitis
(such as tennis elbow or
rotator cuff syndrome) are
examples of CTD's.
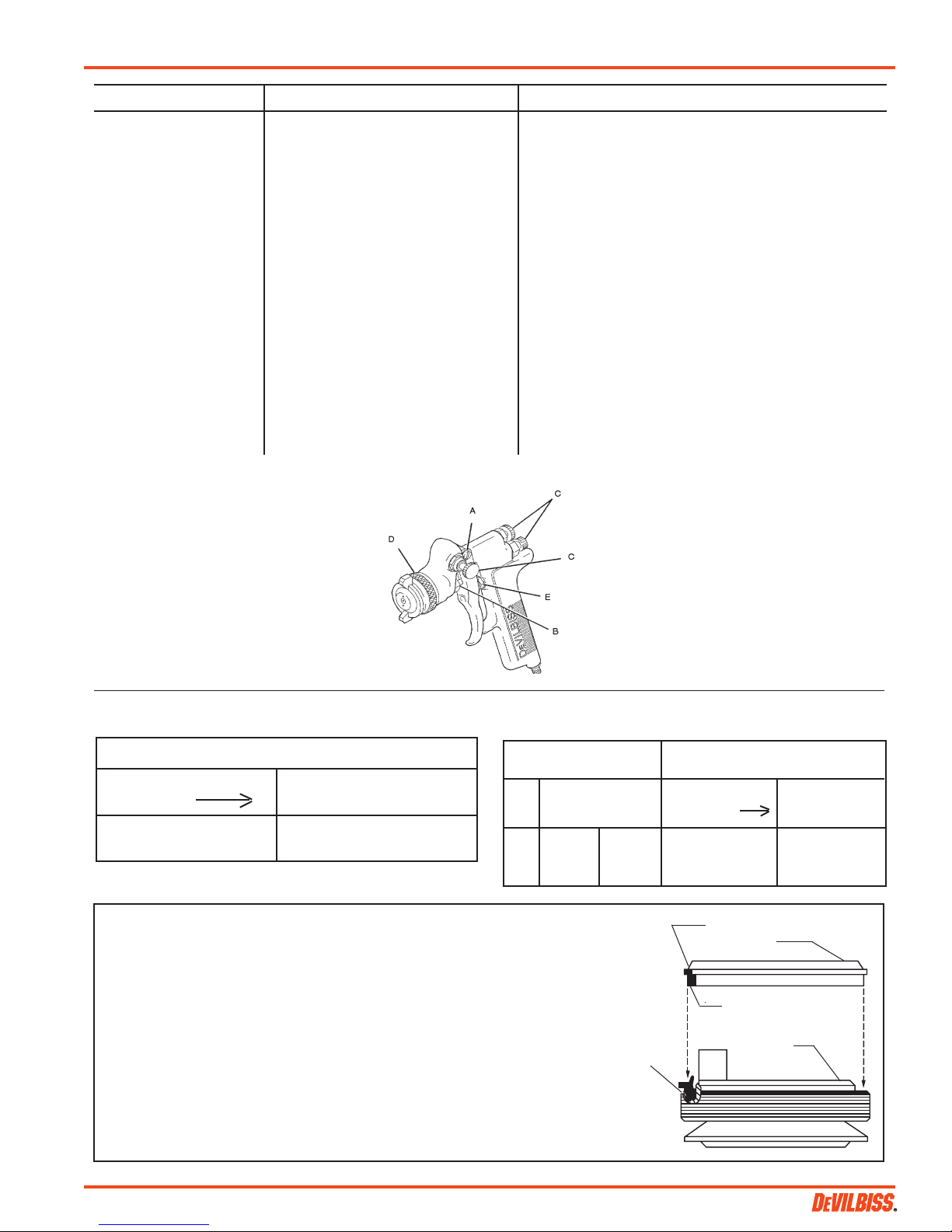
(Continued from page 1)
sure that any excess grease will not clog the
air passages. For best results, lubricate the
points indicated, daily.
*Not for air tools or high RPM equipment.
A. Trigger Points
B. Packing
C. Adjusting Valves
D. Baffle Threads
E. Air Valve Cartridge
Use of hand tools may casue cumulative
trauma disorders ("CTD's").
CTD's, when using hand tools, tend
to affect the upper extremities.
Factors which may increase the risk of
developing a CTD include:
1. High frequency of the activity.
2. Excessive force, such as gripping,
pinching, or pressing with the hands
and fingers.
3. Extreme or awkward finger, wrist, or
arm positions.
4. Excessive duration of the activity.
5. Tool vibration.
6. Repeated pressure on a body part.
7. Working in cold temperatures.
CTD's can also be caused by such
activities as sewing, golf, tennis, and
bowling, to name a few.
Pain, tingling, or numbness in the shoulder, forearm,
wrist, hands, or fingers, especially during the night, may
be early symptoms of a CTD. Do not ignore them. Should
you experience any such symptoms, see a physician
immediately. Other early symptoms may include vague
discomfort in the hand, loss of manual dexterity, and
nonspecific pain in the arm. Ignoring early symptoms and
continued repetitive use of the arm, wrist, and hand can
lead to serious disability.
PARTS REPLACEMENT
Replacement Instructions for O-ring on
Spreader Adjustment Valve
1. Remove retaining ring (20) on spreader
adjustment.
2. Remove valve stem and PTFE O-ring
(21) from valve body.
3. Insert new PTFE O-ring (21) in valve
body. Make sure it is pushed past the
threads.
4. Insert valve stem.
5. Reinstall retaining ring (20).
CHART 1
Air Caps
If This No. On Ref. No. 1 Air Cap
Cap, Order with Retaining Ring
No. 9000 AV-440-9000
No. 80 MB-4039-80
GTI-33 Baffle Seal Replacement (3)
1. Remove fluid tip (2).
2. Remove baffle (4).
3. Remove seal (3) from baffle.
4. Assemble seal to baffle with angled
side up as shown at right.
NOTE
The seal should be a tight fit
on the baffle. If it is a loose fit
on the baffle, assure that it is
assembled with the angled
side up.
5. Install baffle on gun.
6. Install fluid tip (2) and tighten to
12-15 ft-lbs.
The seal is designed to be a tight
fit on the baffle. The seal should
be able to be removed using your
fingers. If you are unable to remove the seal using your fingers,
insert a small screwdriver between the outer lip and the back
of the baffle and pry the seal off.
CHART 2
Fluid Tips and Needles
GFG-517 Ref. #2
Tip Fluid Tip Size If This No. On Tip and
Size I.D. Dimensions Tip, Order Needle Sets
EX 0.070" 1.75 mm AV-2115-EX JGA-4040-EX
FW 0.063" 1.6 mm AV-2115-FW JGA-4040-FW
FF 0.055" 1.4 mm AV-2115-FF JGA-4040-FF
ANGLED SIDE
SEAL
NOTE
Pry here if
necessary
THICK SIDE
BAFFLE
SB-2-179-G (8/2015) 3 / 8
 Loading...
Loading...