DeVilbiss FLG4 Service Bulletin

FLG4 PRESSURE FEED SPRAY GUN
SERVICE BULLETIN
SB-2-784-A
Replaces SB-2-784
Spray gun repair kit
FLG4-488-K
ENGLISH
GUN DESCRIPTION
The FinishLine® series are general purpose spray guns for
HVLP spraying applications suitable for use with a wide variety
of common coating materials.
SPECIFICATIONS
Maximum Air Pressure: 100 psi
Maximum Fluid Pressure: 100 psi
Gun Body: Forged Aluminum
Fluid Path: Anodized Aluminum and Stainless
Fluid Inlet: 3/8" NPS male
Air Inlet: 1/4" NPS male
Gun Weight
Pressure Feed: 19.43 oz / 551 g
Steel
IMPORTANT!
DO NOT DESTROY
It is the customer's responsibility to
have all operators and service personnel
read and understand this manual.
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE OPERATING THIS DEVILBISS PRODUCT
Contact DeVilbiss for additional copies
of this manual.
Page 2 SB-2-784-A
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This manual contains information that is important for you to know and understand. This information relates to USER SAFETY and
ENGLISH
PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we use the following symbols. Please pay particular
attention to these sections.
NOTE
Important information that tells how
Important safety information – A hazard
that may cause serious injury or loss
of life.
to prevent damage to equipment,
or how to avoid a situation that may
cause minor injury.
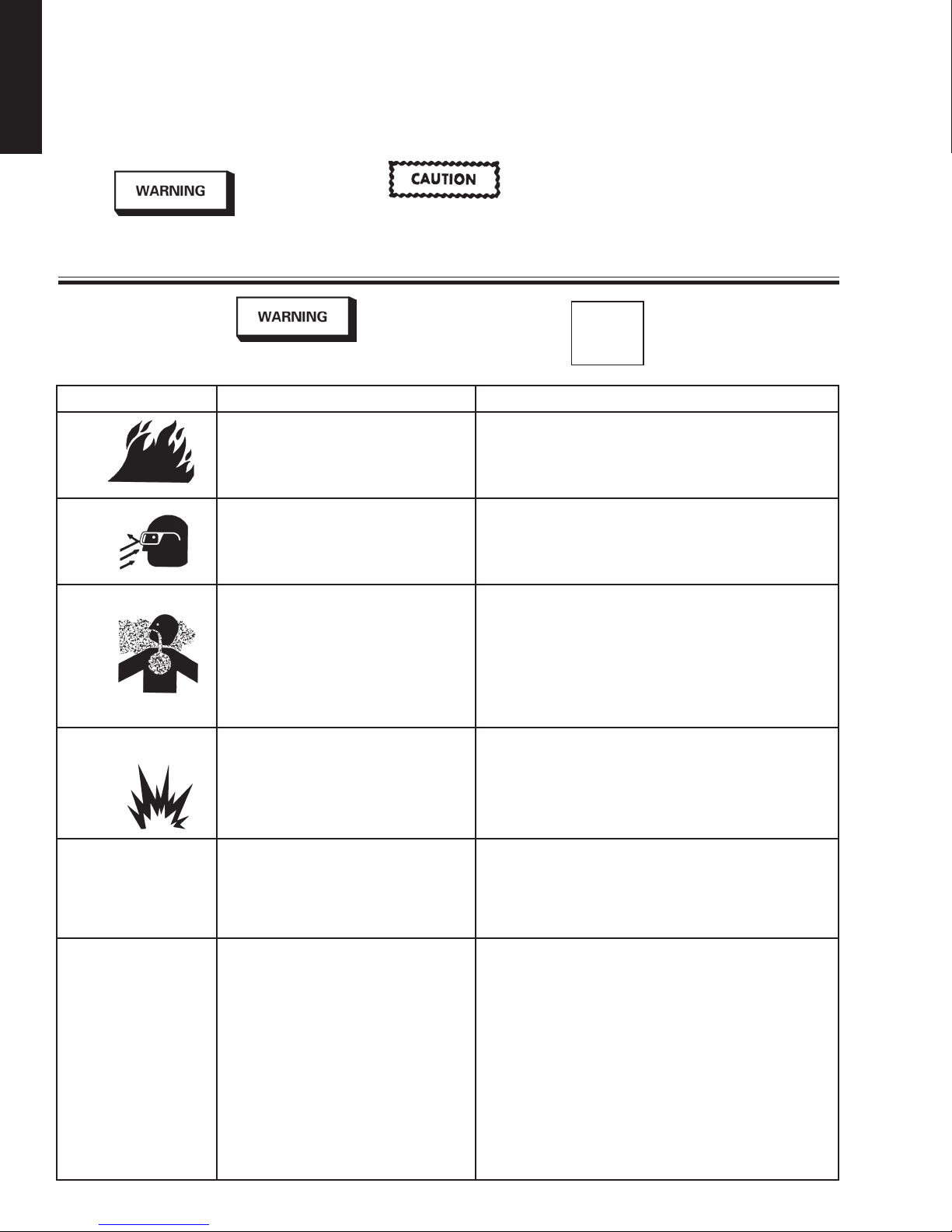
The following hazards may occur during the normal use of this equipment.
Please read the following chart before using this equipment.
HAZARD CAUSE SAFEGUARDS
Fire
Solvent Spray
Inhaling Toxic Substances
Explosion Hazard Incompatible Materials
General Safety
Cumulative Trauma
Disorders ("CTD's")
CTD's, or musculoskeletal
disorders, involve damage
to the hands, wrists,
elbows, shoulders, neck,
and back. Carpal tunnel
syndrome and tendonitis
(such as tennis elbow or
rotator cuff syndrome) are
examples of CTD's.
Solvent and coatings can be highly flammable
or combustible especially when sprayed.
During use and while cleaning and flushing,
solvents can be forcefully expelled from fluid
and air passages. Some solvents can cause
eye injury.
Certain materials may be harmful if inhaled, or
if there is contact with the skin.
Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents - for
example; methylene chloride and 1,1,1, Trichloroethane are not chemically compatible
with the aluminum that might be used in many
system components. The chemical reaction
caused by these solvents reacting with
aluminum can become violent and lead to an
equipment explosion.
Improper operation or maintenance of
equipment.
Use of hand tools may cause cumulative
trauma disorders ("CTD's").
CTD's, when using hand tools, tend to affect the
upper extremities. Factors which may increase
the risk of developing a CTD include:
1. High frequency of the activity.
2. Excessive force, such as gripping, pinching,
or pressing with the hands and fingers.
3. Extreme or awkward finger, wrist, or arm
positions.
4. Excessive duration of the activity.
5. Tool vibration.
6. Repeated pressure on a body part.
7. Working in cold temperatures.
CTD's can also be caused by such activities
as sewing, golf, tennis, and bowling, to name
a few.
Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep air free of
accumulations of flammable vapors.
Smoking must never be allowed in the spray area.
Fire extinguishing equipment must be present in the spray area.
Wear eye protection.
Follow the requirements of the Material Safety Data Sheet
supplied by your coating material manufacturer.
Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep the air free of
accumulations of toxic materials.
Use a mask or respirator whenever there is a chance of inhaling
sprayed materials. The mask must be compatible with the material being sprayed and its concentration. Equipment must be as
prescribed by an industrial hygienist or safety expert, and be
NIOSH approved.
Guns with stainless steel internal passageways may be used
with these solvents. However, aluminum is widely used in other
spray application equipment - such as material pumps, regulators, valves, and this gun and cup. Check all equipment items before use and make sure they can also be used safely with these
solvents. Read the label or data sheet for the material you intend
to spray. If in doubt as to whether or not a coating or cleaning
material is compatible, contact your material supplier.
Operators should be given adequate training in the safe use
and maintenance of the equipment (in accordance with the
requirements of NFPA-33, Chapter 15). Users must comply with
all local and national codes of practice and insurance company
requirements governing ventilation, fire precautions, operation,
maintenance, and housekeeping. These are OSHA Sections
1910.94 and 1910.107 and NFPA-33.
Pain, tingling, or numbness in the shoulder, forearm, wrist,
hands, or fingers, especially during the night, may be early
symptoms of a CTD. Do not ignore them. Should you experience
any such symptoms, see a physician immediately. Other early
symptoms may include vague discomfort in the hand, loss of
manual dexterity, and nonspecific pain in the arm. Ignoring early
symptoms and continued repetitive use of the arm, wrist, and
hand can lead to serious disability. Risk is reduced by avoiding
or lessening factors 1-7.
Information that you should pay special
attention to.
CA PROP
65
PROP 65 WARNING
WARNING: This product contains
chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer and birth
defects or other reproductive harm.
SB-2-784-A Page 3
IMPORTANT: Before using this equipment, read all safety
precautions on page 2 and instructions. Keep for future use.
Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents - for example; 1, 1,
1- trichloroethane and methylene chloride - can chemically react with the aluminum in this gun and cause an
explosion hazard. Read the label or data sheet for the
material you intend to spray. Do not use spray materials
containing these solvents with this spray gun.
IMPORTANT: This gun may be used with most common coating
and finishing materials. It is designed for use with mildly corrosive
and non-abrasive materials. If used with other high corrosive or
abrasive materials, it must be expected that frequent and thorough cleaning will be required and the necessity for replacement
of parts will be increased.
OPERATION
Strain material thru 60 or 90 mesh screen.
HVLP Models:
The No. 4 (HVLP) air cap requires an air supply at the gun inlet of
26 psi max., measured with the trigger pulled.
This gun was manufactured to provide maximum transfer efficiency
by limiting air cap pressure to 10 psi (complies with rules issued
by SCAQMD and other air quality authorities).
This gun will produce approximately 10 psi cap pressure at 26 psi
inlet pressure, as measured at the gun inlet.
Adjust fluid pressure to deliver the desired paint volume. Adjust
air pressure and fluid flow to provide a uniform dispersion of atomized paint throughout the pattern. Keep air pressure as low as
possible to minimize bounce - back and overspray. Excessive air
pressure will result in split patterns. Low air pressure will result in
heavy centered patterns and poor atomization. Excessive fluid flow
will result in heavy center spray patterns. Inadequate fluid flows
may cause the pattern to split. See "TROUBLESHOOTING" section.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
To clean air cap and fluid tip, brush exterior with a stiff bristle brush.
If necessary to clean cap holes, use a broom straw or toothpick if
possible. If a wire or hard instrument is used, extreme care must
be used to prevent scratching or burring of the holes which will
cause a distorted spray pattern.
To clean fluid passages, remove excess material at source, then
flush with a suitable solvent. Wipe gun exterior with a solvent
dampened cloth. Never completely immerse in solvent as this
is detrimental to the lubricants and packings.
Note
When replacing the fluid tip or fluid needle, replace both at
the same time. Using worn parts can cause fluid leakage.
To prevent damage to the fluid tip (3) or fluid needle (8),
be sure to either:
• Pull the trigger and hold while tightening or loosening
the fluid tip, or
• Remove fluid needle adjusting knob (7) to relieve spring
pressure against needle collar.
Spray Gun Lubrication
Daily, apply a drop of SSL-10 spray gun lube at trigger bearing
stud and the stem of the air valve. The shank of the fluid needle
where it enters the packing nut should also be oiled. The fluid
needle packing (8) should be kept soft and pliable by periodic
lubrication. Make sure the baffle (5) and retaining ring (1) threads
are clean and free of foreign matter. Before assembling retaining
ring to baffle, clean the threads thoroughly, then add two drops
of SSL-10 spray gun lube to threads. The fluid needle spring (7)
and air valve spring (9) should be coated with a very light grease,
making sure that any excess grease will not clog the air passages.
For best results, lubricate daily.
ENGLISH
Chart 1 – Fluid Tips
Fluid Tip (Ref. No. 5)
Part No. Computer No.
FLG-332-13K 803051 0.051 1.3 General purpose, light to medium viscosity material.
FLG-332-15K 803052 0.059 1.5
FLG-332-22K 803054 0.086 2.2
Chart 2 – HVLP Air Flows (#4 Cap)
Inlet Pressure
(PSI)
17 11.5 6
21 13 8
26 15 10
Air Flow
(SCFM)
Fluid Tip
Size
(in.)
Cap Presure
(PSI)
Fluid Tip
Size
(mm)
Applications
Latex or heavy bodied materials.FLG-332-18K 803053 0.070 1.8
Page 4 SB-2-784-A
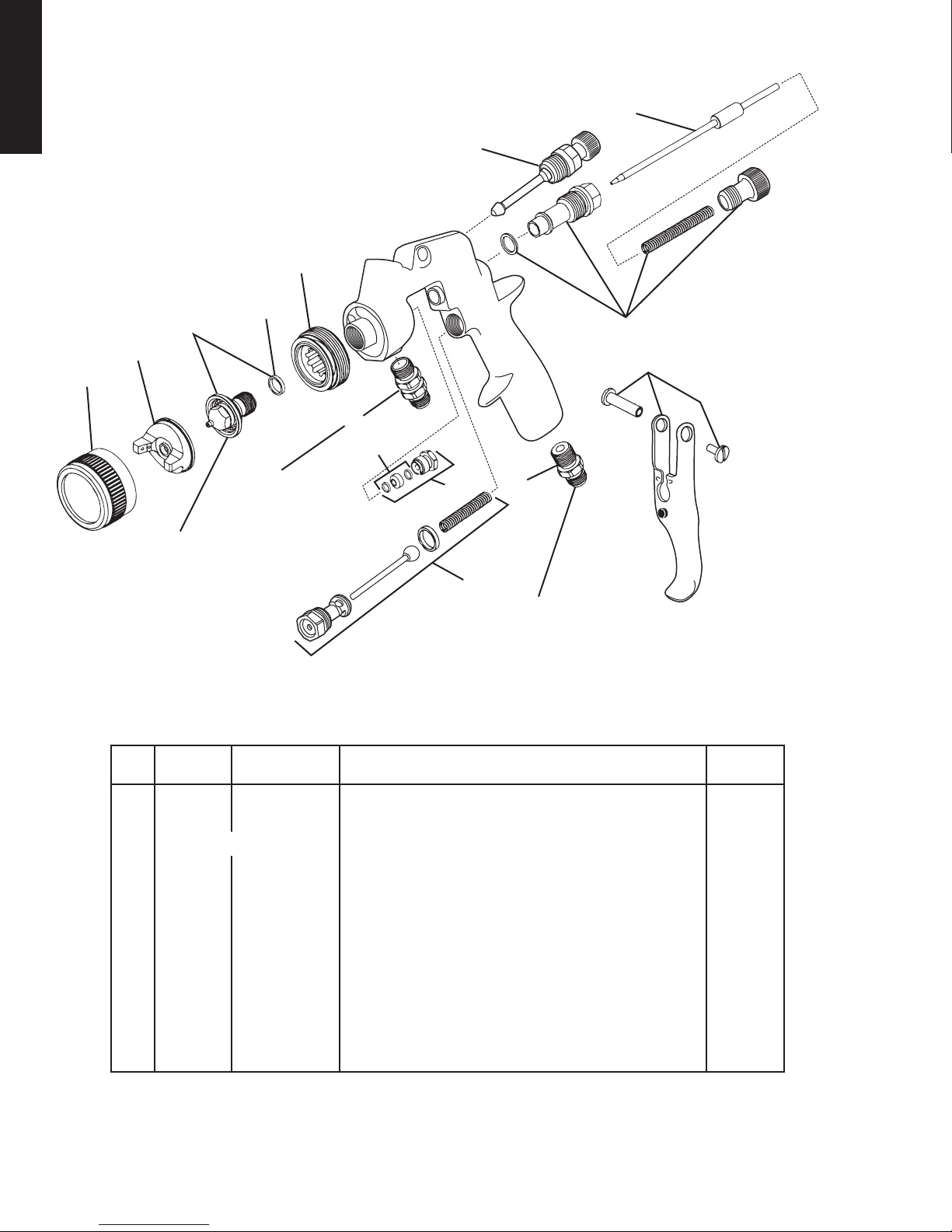
Gun Drawing
ENGLISH
1
3
2
Fluid Tip
Torque to 15–20 ft-lbs
5
4
t
Fluid Inlet Nipple
3/8" NPS(m)
Torque to 20–25 ft-lbs
12
t
t
8
6
t
7
11
t
t
8
10
9
Air Inlet Nipple 1/4" NPS(m)
Torque to 15 ft-lbs
Use medium strength thread sealant
(ie. Devcon #2242 Blue or equivalent)
on threads
PARTS LIST
Ref.
Computer
No.
Part No.
1 803055 FLG-333 Retaining Ring 1
2 803693 FLG-1-4 Air Cap 1
3 See Chart 1, p.3 Fluid Tip & Seal Kit 1
4 690020 FLG-304-K5 Fluid Tip Seal (Kit of 5) 1
5 690021 FLG-305 Baffle 1
6 803528 FLG-465 Spreader Air Adjustment Valve 1
7 803525 FLG4-364-K Needle Knob, Spring, Bushing & Gasket Kit 1
8 803526 FLG4-366-K FLG4 Needle, Needle Packing & Nut Kit 1
9 190780 JGS-449-1 Air Valve & Gasket Kit 1
10 190287 P-MB-51 Air Inlet Nipple 1
11 191943 JGS-477-1 Trigger, Trigger Stud & Screw 1
12 191942 JGA-4044 Fluid Inlet & Nut Kit 1
Additional Spray Gun Accessories on page 6.
Replacement
Part No. Description
FLG4-488-K
FLG4 Gun Repair Kit (Contains 1 each: Fluid Tip Seal, Needle Packing,
t
Trigger Stud, Trigger Screw, and Gasket for Air Valve & Needle Bushing.)
Ind. Parts
Required
TROUBLESHOOTING
CONDITION CAUSE CORRECTION
Heavy top or
bottom pattern
Horn holes plugged.
Obstruction on top or bottom of fluid tip.
Cap and/or tip seat dirty.
Clean. Ream with non-metallic point.
Clean.
Clean.
SB-2-784-A Page 5
ENGLISH
Heavy right or left
side pattern
Heavy center pattern
Split spray pattern
Jerky or fluttering spray
Unable to get round spray
Will not spray
Paint bubbles in cup
Left or right side horn holes plugged.
Dirt on left or right side of fluid tip.
Remedies for the top-heavy, bottom-heavy, right-heavy, and left-heavy patterns:
1. Determine if the obstruction is on the air cap or the fluid tip. Do this by making a test spray
pattern. Then, rotate the cap one-half turn and spray another pattern. If the defect is inverted,
obstruction is on the air cap. Clean the air cap as previously instructed.
2. If the defect is not inverted, it is on the fluid tip. Check for a fine burr on the edge of the fluid tip.
Remove with #600 wet or dry sand paper.
3. Check for dried paint just inside the opening; remove by washing with solvent.
Fluid flow too high for atomization air.
Material flow exceeds air cap's capacity.
Spreader adjustment valve set too low.
Atomizing pressure too low.
Material too thick.
Atomization air pressure too high.
Fluid flow too low.
Spreader adjusting valve set too high.
*Loose or damaged fluid tip/seat.
Material level too low.
Container tipped too far.
Obstruction in fluid passage.
Dry or loose fluid needle packing nut.
Spreader adjustment screw not seating
properly.
Air cap retaining ring loose.
No air pressure at gun.
Fluid needle adjusting screw not open
enough.
Fluid tip not tight. Tighten tip.
Clean. Ream with non-metallic point.
Clean.
Balance air pressure and fluid flow. Increase spray
pattern width with spreader adjustment valve.
Thin or lower fluid flow.
Adjust.
Increase pressure.
Thin to proper consistency.
Reduce at transformer or gun.
Increase fluid flow (increases gun handling speed).
Adjust.
Tighten or replace.
Refill.
Hold more upright.
Backflush with solvent.
Lubricate or tighten.
Clean or replace.
Tighten.
Check air supply and air lines, blow out gun air
passages.
Open fluid needle adjusting screw.
Starved spray pattern
Excessive overspray
Excessive fog
Dry spray
Fluid leaking from packing nut
Fluid leaking or dripping from
front of gun
*Most common problem.
Inadequate material flow.
Low atomization air pressure.
Too much atomization air pressure.
Gun too far from work surface.
Improper stroking (arcing, gun motion too
fast).
Too much or too fast-drying thinner.
Too much atomization (air pressure.)
Air pressure too high.
Gun tip too far from work surface.
Gun motion too fast.
Gun out of adjustment.
Packing nut loose.
Packing worn or dry.
Packing nut too tight.
Dry packing.
Fluid tip or needle worn or damaged.
Foreign matter in tip.
Fluid needle spring broken.
Wrong size needle or tip.
Back fluid adjusting screw out to first thread, or
change to larger tip size.
Increase air pressure and rebalance gun.
Reduce pressure.
Adjust to proper distance.
Move at moderate pace, parallel to work surface.
Remix properly.
Reduce air pressure.
Reduce air pressure.
Adjust to proper distance.
Slow down.
Adjust.
Tighten, do not bind needle.
Replace or lubricate.
Adjust.
Lubricate.
Replace tip and needle.
Clean.
Replace.
Replace.

Page 6 SB-2-784-A
TROUBLESHOOTING (Continued)
CONDITION CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGLISH
Runs and sags
Thin, sandy coarse finish drying
before it flows out
Thick, dimpled finish "orange
peel"
ACCESSORIES
Too much material flow.
Material too thin.
Gun tilted on an angle, or gun motion too
slow.
Gun too far from surface.
Too much air pressure.
Improper thinner being used.
Gun too close to surface.
Too much material coarsely atomized.
Air pressure too low.
Improper thinner being used.
Material not properly mixed.
Surface rough, oily, dirty.
Adjust gun or reduce fluid flow.
Mix properly or apply light coats.
Hold gun at right angle to work and adapt to proper
gun technique.
Check distance. Normally approximately 8".
Reduce air pressure and check spray pattern.
Follow paint manufacturer's mixing instructions.
Check distance. Normally approximately 8".
Follow paint manufacturer's mixing instructions.
Increase air pressure or reduce fluid flow.
Follow paint manufacturer's mixing instructions.
Follow paint manufacturer's mixing instructions.
Properly clean and prepare.
HAF-507
Whirlwind™ In-Line Air Filter
Removes water, oil, and debris from the air line.
WR-103 Wrench
Contains all necessary
tip, hose and nut sizes
used on or with gun.
Automotive Quick Connects
For HVLP Guns (Air)
High Flow Type.
HC-4419 Stem
1/4" NPT(F)
HC-4719 Coupler
1/4" NPT(M) /NPS(M)
HARG-510 Air Regulator
Use to maintain nearly constant outlet
pressure despite changes in inlet pressure and downstream flow.
Millennium 3000
Twin Cartridge
Paint Spray Respirator
NIOSH-Certified, for respiratory protection in atmospheres not immediately
dangerous to life.
Small Medium Large
40-141 40-128 40-143
Spray Gun
Lube
SSL-10-12
(Twelve
2 oz.
Air Adjusting Valves
HAV-500 No Gauge
HAV-512 w/0-100 psi
HAV-555 w/0-160 psi
bottles)
Compatible with all
paint materials; contains no silicone or
petroleum distillates
to contaminate paint.
MSDS available upon
request.
Use to control air usage
at gun.
192212 Professional Spray Gun
Cleaning Kit
Contains six precision tools designed to
effectively clean all DeVilbiss, Binks, Finishline
and other brand spray guns.
Dial Gauge
Digital Gauge
HC-1166 Stem
1/4" NPT(M)
HC-4720 Coupler
1/4" NPT(F)
192218 Scrubs®
Hand Cleaner Towels
Scrubs® are a premoistened
hand cleaner towel for painters,
body men and mechanics that
go where you go and no water
is needed.
 Loading...
Loading...