Delta Electronics 10DKDG3S Operation Manual

AH500
Industrial Automation Headquarters
Delta Electronics, Inc.
Taoyuan Technology Center
No.18, Xinglong Rd., Taoyuan City,
Taoyuan County 33068, Taiwan
TEL: 886-3-362-6301 / FAX: 886-3-371-6301
Asia
Delta Electronics (Jiangsu) Ltd.
Wujiang Plant 3
1688 Jiangxing East Road,
Wujiang Economic Development Zone
Wujiang City, Jiang Su Province, P.R.C. 215200
TEL: 86-512-6340-3008 / FAX: 86-769-6340-7290
Delta Greentech (China) Co., Ltd.
238 Min-Xia Road, Pudong District,
ShangHai, P.R.C. 201209
TEL: 86-21-58635678 / FAX: 86-21-58630003
Delta Electronics (Japan), Inc.
Tokyo Ofce
2-1-14 Minato-ku Shibadaimon,
Tokyo 105-0012, Japan
TEL: 81-3-5733-1111 / FAX: 81-3-5733-1211
Delta Electronics (Korea), Inc.
1511, Byucksan Digital Valley 6-cha, Gasan-dong,
Geumcheon-gu, Seoul, Korea, 153-704
TEL: 82-2-515-5303 / FAX: 82-2-515-5302
Operation Manual
Delta Electronics Int’l (S) Pte Ltd.
4 Kaki Bukit Ave 1, #05-05, Singapore 417939
TEL: 65-6747-5155 / FAX: 65-6744-9228
Delta Electronics (India) Pvt. Ltd.
Plot No 43 Sector 35, HSIIDC
Gurgaon, PIN 122001, Haryana, India
TEL : 91-124-4874900 / FAX : 91-124-4874945
Americas
Delta Products Corporation (USA)
Raleigh Ofce
P.O. Box 12173,5101 Davis Drive,
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, U.S.A.
TEL: 1-919-767-3800 / FAX: 1-919-767-8080
Delta Greentech (Brasil) S.A.
Sao Paulo Ofce
Rua Itapeva, 26 - 3° andar Edicio Itapeva One-Bela Vista
01332-000-São Paulo-SP-Brazil
TEL: 55 11 3568-3855 / FAX: 55 11 3568-3865
Europe
Deltronics (The Netherlands) B.V.
Eindhoven Ofce
De Witbogt 20, 5652 AG Eindhoven, The Netherlands
TEL: 31-40-2592850 / FAX: 31-40-2592851
AH-0109420-05
AH500
Operation Manual
*We reserve the right to change the information in this manual without prior notice.
2018-05-15
www.deltaww.com
Version
Revision
Date
1st
1. The first version was published.
2013/03/28
2nd
2. The information about AHPS15-5A, AH32AM10N-5A,
addresses of the C devices in Appendix B are updated.
4. Information concerning latched area in the device
AH500 Operation Manual
Revision His tory
AH32AM10N-5C, AH16AR10N-5A, AH32AN02T-5A,
AH32AN02T-5C, AH32AN02P-5A, AH32AN02P-5C,
AH08AD-5C, AH08DA-5C, AH08PTG-5A, AH15PM-5A,
AH10PFBM-5A, AH10PFBS-5A, AH10COPM-5A,
AHRTU-PFBS-5A, AHAADP01/02EF-5A, and
DVPAETB-IO34C is added to all chapters.
3. The storage temperature, the program capacity of
AHCPU500, the specifications for the input/output
relays, the functional specifications for the analog
input/output modules, the electrical specifications for
the temperature measurement modules, the response
characteristics of the input terminals on
AH05PM-5A/AH10PM-5A in Chapter 2 are updated.
4. The specifications for AH16AR10N-5A, and, the
specifications for AH15PM-5A, and the specifications
for AHPS15-5A are added to Chapter 2.
5. Section 4.2.1 is updated.
6. Section 5.1.1 is updated.
7. Point (6) is added to section 6.6.1.
8. Section 9.3.2.1 is updated.
9. Section 11.2.3 is updated, and section 11.3 is added to
Chapter 11.
10. The troubleshooting for new models is added to
Chapter 12.
11. The AH500 addresses of the T devices and the AH500
2014/06/13
1. Information concerning AHCPU511-RS2,
AHCPU511-EN, AHCPU521-EN, AHCPU531-EN,
3rd
AH08AD-5A and AH08DA-5A is added.
2. Information concerning larger program capacity and
memory, Serial control interface with multiple
functions and high-speed Ethernet communication
interface is updated to section 1.3.
3. Instruction execution speed, maximum number of
Information concerning backplanes which can be
connected is updated in section 2.2.1. Information
concerning AH500 advanced CPU modules is added to
section 2.2.2. Information concerning arrangement of
AH32AN02P-5 input/output terminals is updated in
section 2.4.4. Information concerning Interrupt input
terminals of AH05PM-5A and input signals as well as
terminal X1.2~X1.5 of AH15PM-5A and AH20MC-5A is
updated in section 2.8.1. Informaiton concering the
applicable input/output module is updated in section
2.11.1.
2016/08/15
Version
Revision
Date
4th
1. New contents concerning AH15SCM-5A,
Windows 7 and Windows 10 are added in Appendix A.
settings.
range is updated in section 5.1.4.
5. Information concerning specifications for SD card is
updated in section 7.1.2.
6. Information concerning address is updated in section
8.3.2.
7. Information concerning AHCPU5X0 is added in chapter
9.
8. Information concerning AHCPU5X0 is added to section
11.1, 11.1.4, 11.2, 11.3, and 11.4.
9. Section 12.2.1, 12.2.2, 12.2.3, 12.2.5, 12.3.2, 12.4.1
are updated.
10. Information concerning installation in Windows 8 is
added in Appendix A.
11. Section B.2 is removed from Appendix B.
AHRTU-ETHN-5A are added in chapter 1.
2. New contents concerning module weights are added in
chapter 2 and I/O connection cable models
input/output terminals of AH series are also updated.
3. New information about EtherNet/IP is added in section
11.5.
4. New contents concerning EtherNet/IP troubleshooting
are added in section 12.2.5 and delete the error codes
16#9B01~16#9B20.
5. New contents concerning installing the USB driver in
2017/03/31
1. New contents concerning AH15EN-5A, AHCPU501-RS2,
AHCPU521-RS2, AHCPU531-RS2, and AHCPU501-EN
are added.
2. New contents concerning AHCPU501-RS2,
AHCPU521-RS2, AHCPU531-RS2, AHCPU501-EN,
AH04HC-5A and redundancy system are added in
Chapter 2.
5th
3. Update contents concerning ISPSoft in Chapter 6, 7 8
and 9.
4. Update contents concerning applicable memory cards.
5. Update the maximum characters can be input for the
CPU naming. Update the software supported and its
versions for the network I/O module.
6. Update parameters for network communication
20180515

AH500 Operation Manual
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Introduction ............................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.1 Related Manuals ............................................................................... 1-2
1.1.2 Description of Models ........................................................................ 1-2
1.2 Overview .................................................................................................. 1-8
1.3 Characteristics .........................................................................................1-10
Chapter 2 Specifications and System Configuration
2.1 General Specifications.............................................................................. 2-3
2.2 Specifications for CPU Modules ............................................................... 2-3
2.2.1 Performance Specifications ............................................................... 2-3
2.2.2 Profiles .............................................................................................. 2-6
2.3 Basic System Configuration ..................................................................... 2-8
2.3.1 Introduction ....................................................................................... 2-8
2.3.2 Configuring a Main Backplane .......................................................... 2-9
2.3.3 Configuring an Extension Backplane ................................................2-10
2.3.4 Maximum Extension .........................................................................2-10
2.4 Specifications for Digital Input/Output Modules ....................................... 2-11
2.4.1 General Specificati ons ...................................................................... 2-11
2.4.2 Profiles .............................................................................................2-14
2.4.3 Dimensions ......................................................................................2-22
2.4.4 Arrangement of Input/Output Terminals ............................................2-27
2.5 Specifications for Analog Input/Output Modules ......................................2-35
2.5.1 General Specificati ons ......................................................................2-35
2.5.2 Profiles .............................................................................................2-39
2.5.3 Dimensions ......................................................................................2-41
2.5.4 Arrangement of Input/Output Terminals ............................................2-41
2.5.5 Setting Parameters ...........................................................................2-43
2.6 Specifications for Temperature Measurement Modules ...........................2-46
2.6.1 General Specificati ons ......................................................................2-46
2.6.2 Profiles .............................................................................................2-48
2.6.3 Dimensions ......................................................................................2-50
2.6.4 Arrangement of Input/Output Terminals ............................................2-51
2.6.5 Setting Parameters ...........................................................................2-52
i

2.7 Specifications for Network Modules ........................................................ 2-53
2.7.1 General Specificati ons ..................................................................... 2-53
2.7.2 Profiles ............................................................................................. 2-56
2.7.3 Dimensions ...................................................................................... 2-65
2.7.4 Arrangement of Input/Output Terminals ........................................... 2-68
2.7.5 Setting Parameters .......................................................................... 2-69
2.8 Specifications for Motion Control Modules .............................................. 2-72
2.8.1 General Specificati ons ..................................................................... 2-72
2.8.2 Profiles ............................................................................................. 2-83
2.8.3 Dimensions ...................................................................................... 2-89
2.8.4 Arrangement of Input/Output Terminals ........................................... 2-92
2.8.5 Setting Parameters .......................................................................... 2-97
2.9 Specifications for Remote Input/Output Modules .................................... 2-99
2.9.1 General Specificati ons ..................................................................... 2-99
2.9.2 Profiles ........................................................................................... 2-100
2.9.3 Dimensions .................................................................................... 2-104
2.10 Specifications for Power Supply Modules .......................................... 2-106
2.10.1 General Specifications ................................................................ 2-106
2.10.2 Profiles ....................................................................................... 2-107
2.10.3 Dimensions ................................................................................. 2-108
2.10.4 Arrangement of Terminals .......................................................... 2-109
2.11 Space Module, Backplanes, and Extension Cables ........................... 2-110
2.11.1 General Specifications ................................................................ 2-110
2.11.2 Profiles ....................................................................................... 2-111
2.11.3 Dimensions ................................................................................. 2-114
Chapter 3 Installing Software
3.1 Installing and Uninstalling ISPSoft ............................................................ 3-2
3.1.1 Installing ISPSoft ................................................................................ 3-2
3.1.2 Uninstalling ISPSoft ........................................................................... 3-6
3.2 Installing and Uninstalling COMMGR ........................................................ 3-7
3.2.1 Installing COMMGR ........................................................................... 3-7
3.2.2 Uninstalling COMMGR ....................................................................... 3-9
Chapter 4 Installing Hardware
4.1 Installation ................................................................................................. 4-2
4.1.1 Mounting a Backplane ....................................................................... 4-2
4.1.2 Installing a Module ............................................................................. 4-4
ii

4.2 Wiring ....................................................................................................... 4-5
4.2.1 Wiring a Power Supply Module ......................................................... 4-5
4.2.2 Wiring I/O Modules ............................................................................ 4-7
Chapter 5 Devices
5.1 Introduction of Devices .................................................................................. 5-2
5.1.1 Devise Table ..................................................................................... 5-2
5.1.2 Basic Structure of I/O Storages ......................................................... 5-4
5.1.3 Relation Between the P LC Action and the Device Type .................... 5-4
5.1.4 Latched Areas in the Device Range .................................................. 5-5
5.2 Functions of Devices ................................................................................ 5-5
5.2.1 Values and Constants ............................................................................. 5-6
5.2.2 Floating-point Numbers .......................................................................... 5-6
5.2.3 Strings ............................................................................................... 5-6
5.2.4 Input Relays ...................................................................................... 5-6
5.2.5 Output Relays ................................................................................... 5-7
5.2.6 Auxiliary Relays ................................................................................. 5-7
5.2.7 S pecial Auxiliary Relays .................................................................... 5-7
5.2.8 Stepping Relays ................................................................................ 5-7
5.2.9 Timers ............................................................................................... 5-8
5.2.10 Counters ........................................................................................ 5-8
5.2.11 32-bit Counters .............................................................................. 5-9
5.2.12 Data Registers ..............................................................................5-10
5.2.13 Special Data Registers .................................................................5-10
5.2.14 Link Registers ...............................................................................5-10
5.2.15 Index Registers .............................................................................5-10
Chapter 6 Wri ti ng a Prog r am
6.1 Quick Start ................................................................................................ 6-2
6.1.1 Example ............................................................................................ 6-2
6.1.2 Hardware ........................................................................................... 6-2
6.1.3 Program ............................................................................................ 6-2
6.2 Procedure for Creating a Project in ISPSoft ............................................. 6-3
6.3 Creating a Project ..................................................................................... 6-3
6.4 Hardware Configuration............................................................................ 6-4
6.4.1 Configuring a Module ........................................................................ 6-5
6.4.2 Setting the Parameters in a CPU Module and a Module ................... 6-6
6.5 Creating a Program .................................................................................. 6-8
iii

6.5.1 Adding a Ladder Diagram .................................................................. 6-8
6.5.2 Basic Editing─Creating a Contact and a Coil ................................... 6-10
6.5.3 Basic Editing─Inserting a Network and Typing an Instruction .......... 6-13
6.5.4 Basic Editing─Selection of a Network and Operation ...................... 6-15
6.5.5 Basic Editing─Connecting a Contact in Parallel ............................... 6-16
6.5.6 Basic Editing─Editing a Comment ................................................... 6-17
6.5.7 Basic Editing─Inserting an Applied Instruction ................................. 6-18
6.5.8 Basic Editing—Creating a Comparison Contact and Typing a Constant
........................................................................................................ 6-20
6.5.9 Writing a Program ............................................................................ 6-21
6.5.10 Checking and Compiling a Program ............................................. 6-22
6.6 Testing and Debugging a Program ......................................................... 6-23
6.6.1 Creating a Connection ..................................................................... 6-23
6.6.2 Downloading a Program and Parameters ........................................ 6-25
6.6.3 Connection Test ............................................................................... 6-27
6.7 Setting a Real-time Clock ........................................................................ 6-33
Chapter 7 Memory Card
7.1 Overview of Memory Cards ....................................................................... 7-2
7.1.1 Appearances of Memory Cards ......................................................... 7-2
7.1.2 Specifications for SD Car ds ............................................................... 7-2
7.2 Using a Memory Card ............................................................................... 7-3
7.2.1 Formatting a Memory Card ................................................................ 7-3
7.2.2 Write Protect Function of a Memory Card .......................................... 7-4
7.3 Installing and Removing a Memory Card .................................................. 7-5
7.3.1 SD Slot in a CPU Module ................................................................... 7-5
7.3.2 Installing a Memory Card ................................................................... 7-5
7.3.3 Removing a Memory Card ................................................................. 7-5
7.4 Contents of a Memory Card ...................................................................... 7-6
7.4.1 Initializing a Memory Card ................................................................. 7-6
7.4.2 Folder Structure in a Memory Card .................................................... 7-6
7.5 Reading/Writing a Memory Card ............................................................... 7-7
7.5.1 Backing up the System ...................................................................... 7-7
7.5.2 Restoring the Sys tem ......................................................................... 7-7
7.6 Introduction of CARD Utility ...................................................................... 7-8
7.7 Backup .................................................................................................... 7-10
7.8 Restoration .............................................................................................. 7-13
iv

Chapter 8 Hardware Configuration
8.1 Hardware Configuration Tool for AH500 Series Modules─HWCONFIG ... 8-3
8.1.1 Introduction of the Environment of HWCONFIG ................................ 8-3
8.1.2 Configuring a Module ........................................................................ 8-5
8.1.2.1 Adding a Module ........................................................................ 8-5
8.1.2.2 Assigning Devices to a Module .................................................. 8-8
8.1.2.3 Editing a Comment ....................................................................8-12
8.1.2.4 Deleting a Module .....................................................................8-13
8.1.2.5 Replacing a Module ..................................................................8-13
8.1.2.6 Searching for/Replacing a Module ............................................8-14
8.1.2.7 Copying/Pasting a Module ........................................................8-18
8.1.2.8 Cutting/Pasting a Module ..........................................................8-20
8.1.2.9 Dragging a Module ....................................................................8-21
8.1.2.10 Adding an Extension Rack ........................................................8-22
8.1.2.11 Deleting a Rack .........................................................................8-23
8.1.2.12 Replacing a Rack ......................................................................8-24
8.1.2.13 Cutting/Copying/Pasting an Extension Rack .............................8-25
8.1.2.14 Dragging an Extension Rack .....................................................8-28
8.1.2.15 Rearranging the Input/Output Devices ......................................8-28
8.2 Setting the Parameters in an AH500 Series CPU Module .......................8-29
8.2.1 Opening the PLC Parameter Setting Window ..................................8-29
8.2.2 Setting the Basic CPU Parameters ..................................................8-30
8.2.2.1 CPU: Name ...............................................................................8-30
8.2.2.2 CPU: System .............................................................................8-31
8.2.2.3 CPU: Latched Device Range ....................................................8-34
8.2.3 COM Port .........................................................................................8-36
8.2.4 Ethernet─Basic ................................................................................8-37
8.2.5 Ethernet─Advance ...........................................................................8-38
8.2.5.1 Ethernet─Advance: Filter ..........................................................8-38
8.2.5.2 Ethernet─Advance: NTP ...........................................................8-40
8.2.5.3 Ethernet─Advance: Email .........................................................8-41
8.2.5.4 Ethernet─Advance: Email Trigger .............................................8-42
8.2.5.5 Ethernet─Advance: Email and Trigger Configuration ................8-46
8.2.5.6 Ethernet─Advance: Socket .......................................................8-47
8.2.5.7 Ethernet─Advance: Web ...........................................................8-49
8.2.6 Saving and Downloading/Uploading the PLC Parameters ...............8-50
8.3 Setting the Parameters in an AH500 Series Module ...............................8-51
8.3.1 Managing the Version of a Module ...................................................8-51
v

8.3.2 Setting the Parameters in a Module ................................................. 8-52
8.3.3 Exporting and Importing the Parameters in a Module ...................... 8-56
8.3.4 Setting the Parameters in an Intelligent Module............................... 8-57
8.4 Management o f the Par amet er s in AH500 Series Hardware and Onli ne
Diagnosis ................................................................................................ 8-58
8.4.1 Saving and Printing a Hardware Configuration ................................ 8-58
8.4.2 Purchase Order ................................................................................ 8-59
8.4.3 Rack Information Li st ....................................................................... 8-60
8.4.4 Downloading/Uploading the System Parameters ............................. 8-61
8.4.5 I/O Scan ........................................................................................... 8-62
8.4.6 Online Diagnosis .............................................................................. 8-63
8.4.6.1 Online Mode ............................................................................. 8-64
8.4.6.2 Module Information and Diagnosis ........................................... 8-65
8.4.6.3 Changing the Status of a Module Online ................................... 8-66
8.4.6.4 Monitoring Table........................................................................ 8-68
8.5 Setting Interrupts ..................................................................................... 8-69
8.5.1 Program Architectures ..................................................................... 8-69
8.5.2 Tasks Supported by AH500 Series CPU Modules ........................... 8-69
8.5.3 I/O Interrupts .................................................................................... 8-70
8.5.4 Low Voltage Detection Interrupt ....................................................... 8-71
8.5.5 Communication Interrupts ................................................................ 8-72
8.5.6 External Interrupts ............................................................................ 8-72
8.5.7 Timer Interrupts ................................................................................ 8-73
Chapter 9 Network Configuration
9.1 Network Configuration Tool─NWCONFIG ................................................ 9-2
9.1.1 Introduction of NWCONFIG ............................................................... 9-2
9.1.2 Basic Knowledge ............................................................................... 9-3
9.1.3 Communication Setting in NWCONFIG ............................................. 9-4
9.1.3.1 Connection Mechanism in NWCONFIG ...................................... 9-5
9.1.3.2 Setting Communication Parameters ........................................... 9-6
9.1.4 Workflow ............................................................................................ 9-7
9.2 Creating a Network Architecture ............................................................. 9-12
9.2.1 Deploying Nodes .............................................................................. 9-12
9.2.2 Connecting to a Network .................................................................. 9-15
9.2.3 Adjusting or Deleting Devices or Networks ...................................... 9-20
9.2.4 Setting the Attribut es o f a Node/N e t work ......................................... 9-23
9.2.5 Hiding/Displaying Devices or Ne tworks ........................................... 9-27
vi

9.2.6 Correct Network Ar chitecture ...........................................................9-30
9.2.7 Downloading Routing Tables ............................................................9-33
9.2.8 Testing Routing.................................................................................9-34
9.3 Managing and Applying NWCONFIG ......................................................9-36
9.3.1 Saving Parameters and Printing a Network Framework ...................9-36
9.3.2 Downloading Parameters .................................................................9-37
9.3.2.1 Introduction of Parameters ........................................................9-37
9.3.2.2 Description of Downloading Parameters ...................................9-38
9.3.3 Using Routing in ISPSoft ..................................................................9-39
Chapter 10 Operating Principle of the CPU Module
10.1 Operation of the CPU Module .................................................................10-2
10.1.1 Procedure .........................................................................................10-2
10.1.2 I/O Refreshing and Communication Ser vice ....................................10-3
10.2 Operating Modes of the CPU Module ......................................................10-3
10.2.1 Operating Modes ..............................................................................10-3
10.2.2 Statuses and Operation under Different Operating Modes ...............10-3
Chapter 11 Convenient Functions
11.1 PLC Link (for AHCPU5X0 models) .......................................................... 11-2
11.1.1 Introduction of a PLC Link ............................................................ 11-2
11.1.2 Constructing a PLC Link in NWCONFIG in ISPSoft ...................... 11-2
11.1.2.1 Opening the PLC Link Table Editor Window ............................. 11-3
11.1.2.2 Designating a Port as a Master Station (Step 1) ....................... 11-4
11.1.2.3 Setting Communication Parameters (Step 2) ............................ 11-6
11.1.2.4 Creating a Data Exchange Table (Step 3) ................................ 11-7
11.1.2.5 Monitoring a PLC Link ............................................................. 11-14
11.1.2.6 Important Points About Constructing a PLC Link .................... 11-18
11.1.3 Executing a PLC Link through the Program in ISPSoft ............... 11-20
11.1.3.1 Parameters Related to a PLC Link .......................................... 11-20
11.1.3.2 Setti ng a PLC Link .................................................................. 11-25
11.1.4 Related Special Auxiliary Relays and Special Data Registers .... 11-31
11.2 Ether Link (for AHCPU5X0 models)....................................................... 11-33
11.2.1 Introduction of an Ether Link ....................................................... 11-33
11.2.1.1 General Specifications and Functions ..................................... 11-34
11.2.1.2 Steps of Constructing an Ether Link ........................................ 11-35
11.2.2 Constructing an Ether Link in NWCONFIG in ISPSoft ................ 11-36
11.2.2.1 Constructing an Ether Link ...................................................... 11-36
vii

11.2.2.2 Opening the Ether Link Configuration Window ....................... 11-36
11.2.2.3 Creating and Managing a Data Exchange Table .................... 11-38
11.2.2.4 Node List and Display Area .................................................... 11-41
11.2.2.5 Start Mode of an Ether Link .................................................... 11-43
11.2.2.6 Downloading the Parameters Related to an Ether Link .......... 11-45
11.2.2.7 Uploading the Parameters Related to an Ether Link ............... 11-47
11.2.2.8 Deleting Asynchronous Device ............................................... 11-48
11.2.2.9 Enabling/Disabling the Online Monitoring Function ................ 11-49
11.2.2.10 Starting/Stopping the Execution of an Ether Link Online ......... 11-53
11.2.2.11 Monitoring Table and Error Log ............................................... 11-56
11.2.3 Related Special Auxiliary Relays and Special Data Registers .... 11-57
11.3 Data Exchange Func ti on ....................................................................... 11-60
11.3.1 MO DBUS Data Exchange .......................................................... 11-60
11.3.1.1 MODBUS Data Exchange ....................................................... 11-60
11.3.1.2 MODBUS Data Exchange - PLC Parameter Setti ng ............... 11-60
11.3.1.3 MODBUS Data Exchange - Downloading/Uploading Parameters ....
............................................................................................ 11-63
11.3.1.4 MODBUS Data Exchange – Special Auxiliary Relays ............. 11-64
11.3.2 MODBUS TCP Data Exchange .................................................. 11-81
11.3.2.1 MODBUS TCP Data Exchange ............................................... 11-81
11.3.2.2 MOD BUS TCP Dat a Ex change - PLC Parameter Setting ....... 11-82
11.3.2.3 MODBUS TCP Data Exchange - Downloading/Uploading
Parameters…… ...................................................................... 11-86
11.3.2.4 MODBUS TCP Data Exchange – Special Auxiliary Relays .... 11-88
11.4 Web ..................................................................................................... 11-116
11.4.1 Introduction ............................................................................... 11-116
11.4.2 Usage ....................................................................................... 11-116
11.4.3 Troubleshooting ........................................................................ 11-118
11.5 EtherNet/IP ......................................................................................... 11-121
Chapter 12 Troubleshooting
12.1 Troubleshooting ................................................................................... 12-2
12.1.1 Basic Inspection ........................................................................... 12-2
12.1.2 Eliminating Errors ......................................................................... 12-2
12.1.3 Troubleshooting Procedure .......................................................... 12-3
12.1.4 Viewing Error Logs ....................................................................... 12-4
12.2 Troubleshooting for CPU Modules ....................................................... 12-5
12.2.1 ERROR LED Indicator’s Being ON ............................................... 12-5
viii

12.2.2 ERROR LED Indicator’s Blinking ..................................................12-7
12.2.3 BUS FAULT LED Indicator’s Being ON ......................................12-12
12.2.4 BUS FAULT LED Indicator’s Blinking .........................................12-13
12.2.5 Troubleshooting for AH500 Redundancy System .......................12-14
12.2.6 Troubleshooting for Ether N et/IP .................................................12-24
12.2.7 Others .........................................................................................12-25
12.3 Troubleshooting for I/O Modules ........................................................12-41
12.3.1 Troubleshooting for Anal og I/O Modul es and Te mper at ure
Measurement Modules ...............................................................12-41
12.3.2 Troubleshooting for AH 02H C-5A/AH04HC-5A ...........................12-44
12.3.3 Troubleshooting for AH 05PM -5A/AH10PM-5A/AH15PM-5A ......12-45
12.3.4 Troubleshooting for AH 20M C-5A ................................................12-47
12.3.5 Troubleshooting for AH 10EN -5A/AH15EN-5A ............................12-48
12.3.6 Troubleshooting for AH 10SC M -5A/AH15SCM-5A ......................12-48
12.3.7 Troubleshooting for AH 10D NET-5A ............................................12-49
12.3.8 Troubleshooting for AH 10PF BM -5A ...........................................12-50
12.3.9 Troubleshooting for AH10PFBS-5A ............................................12-50
12.3.10 Troubleshooting for AH10COPM-5A ...........................................12-51
12.4 Error Codes and LED Indicators ........................................................12-52
12.4.1 CPU Modules..............................................................................12-53
12.4.2 Analog I/O Modules and Temperature Measurement Modules ..12-75
12.4.3 AH02HC-5A/AH04HC-5A ...........................................................12-76
12.4.4 AH05PM-5A/AH10PM-5A/AH15PM-5A ......................................12-77
12.4.5 AH20MC-5A................................................................................12-78
12.4.6 AH10EN-5A/AH15EN-5A ............................................................12-79
12.4.7 AH10SCM-5A/AH15SCM-5A ......................................................12-79
12.4.8 AH10DNET-5A............................................................................12-79
12.4.9 AH10PFBM-5A ...........................................................................12-80
12.4.10 AH10PFBS-5A ............................................................................12-81
12.4.11 AH10COPM-5A ..........................................................................12-81
Appendix A Installing a USB Driver
A.1 Installing the USB Driver for an AH500 Series CPU module in Windows XP
with SP3 ....................................................................................................... A-2
A.2 Installing the USB Driver for an AH500 Series CPU module in Windows 7 .. A-6
A.3 Installing the USB Driver for an AH500 Series CPU module in Windows 8 ........
................................................................................................................... A-10
ix

A.4 Installing the USB Driver for an AH500 Series CPU module in Windows 10
.......................................................................................................................... A-13
Appendix B Device Addresses
B.1 Device Addresses .................................................................................... B-2
x

Chapter 1 Introduction
Table of Contents
1.1 Introduction ......................................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.1 Related Manuals ......................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.2 Description of Models .................................................................................. 1-2
1.2 Overview ............................................................................................................ 1-8
1.3 Characteristics .................................................................................................. 1-10
1-1
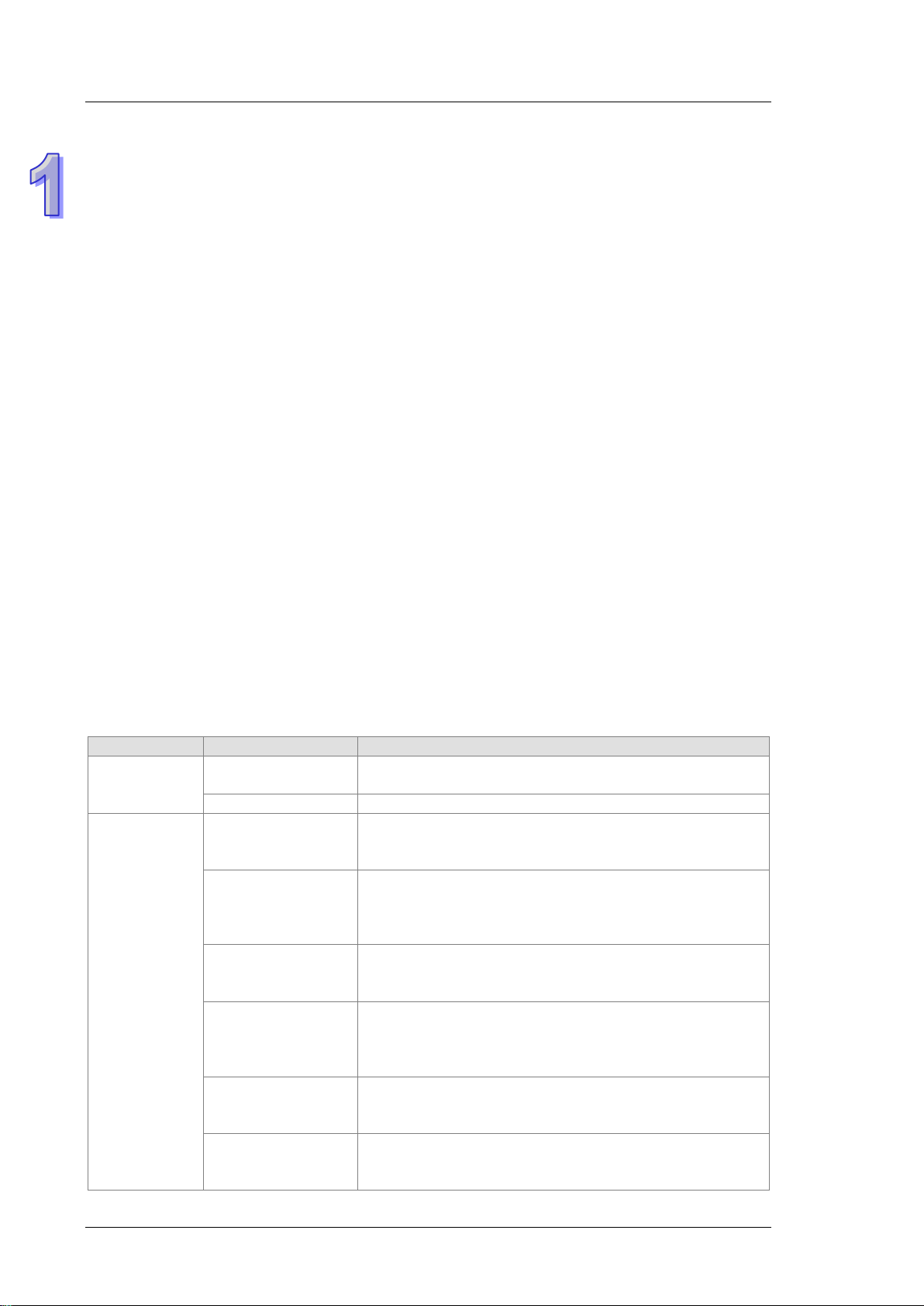
AH500 Operation Manual
Classification
Model Name
Description
50/60 Hz
AHPS15-5A
24 V DC
It is a basic CPU module with two built-in RS-485 port s, one
inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 32K steps.
It is a basic CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port, one
is 32K steps.
768 inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 48K steps.
It is an advanced CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port,
capacity is 48K steps.
It is a basic CPU module with two built-in RS-485 port s, one
inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 64K steps.
It is a basic CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port, one
interface. It supports 1280 inputs/outputs. The program capacity
1.1 Introduction
This manual introduces functions of CPUs, devices, module tables, troubleshooting, and etc.
1.1.1 Related Manuals
The related manuals of the AH500 series programmable logic controllers are composed of the following
AH500 Quick Start
It guides users to use the system before they read the related manuals.
AH500 Programming Manual
It introduces the progra mming of the AH50 0 ser ies progr amm able logi c contro ller s, the ba sic instruct ions,
and the applied instructions.
ISPSoft User Manual
It introduces the use of ISPSoft, the programming lan gua ge (Ladder , IL, SFC , FBD , an d S T ), the co nce pt
of POUs, and the concept of tasks.
AH500 Hardware Manual
It introduces electrical specifications, appearances, dimensions, and etc.
AH500 Operation Manual
It introduces functions of CPUs, devices, module tables, troubleshooting, and etc.
AH500 Module Manual
It introduces the use of special I/O modules. For example, network modules, analog I/O modules,
temperature measurement module s, moti on control modules, and etc.
AH500 Motion Control Module Manual
It introduces the specifications for the motion control modules, the wiring, the instructions, and the
functions.
PMSoft User Manual
It introduces the use of PMSoft, including the editing mode, the connection, and the pas sword setting.
AH500 Redundancy System Operation Manual
It introduces the AH500 redundancy structures, establishments, programming designs, and operations.
1.1.2 Description of Models
Power supply
module
CPU module
AHPS05-5A
AHCPU500-RS2
AHCPU500-EN
AHCPU501-RS2
AHCPU501-EN
AHCPU510-RS2
AHCPU510-EN
100~240 V AC
built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports 768
built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD
interface. It supports 768 inputs/outputs. The pr ogra m capacity
It is an advanced CPU module with two built-in RS-485 ports,
one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports
one built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in
SD interface. It supports 768 input s/out puts. The program
built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports 1280
built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD
1-2
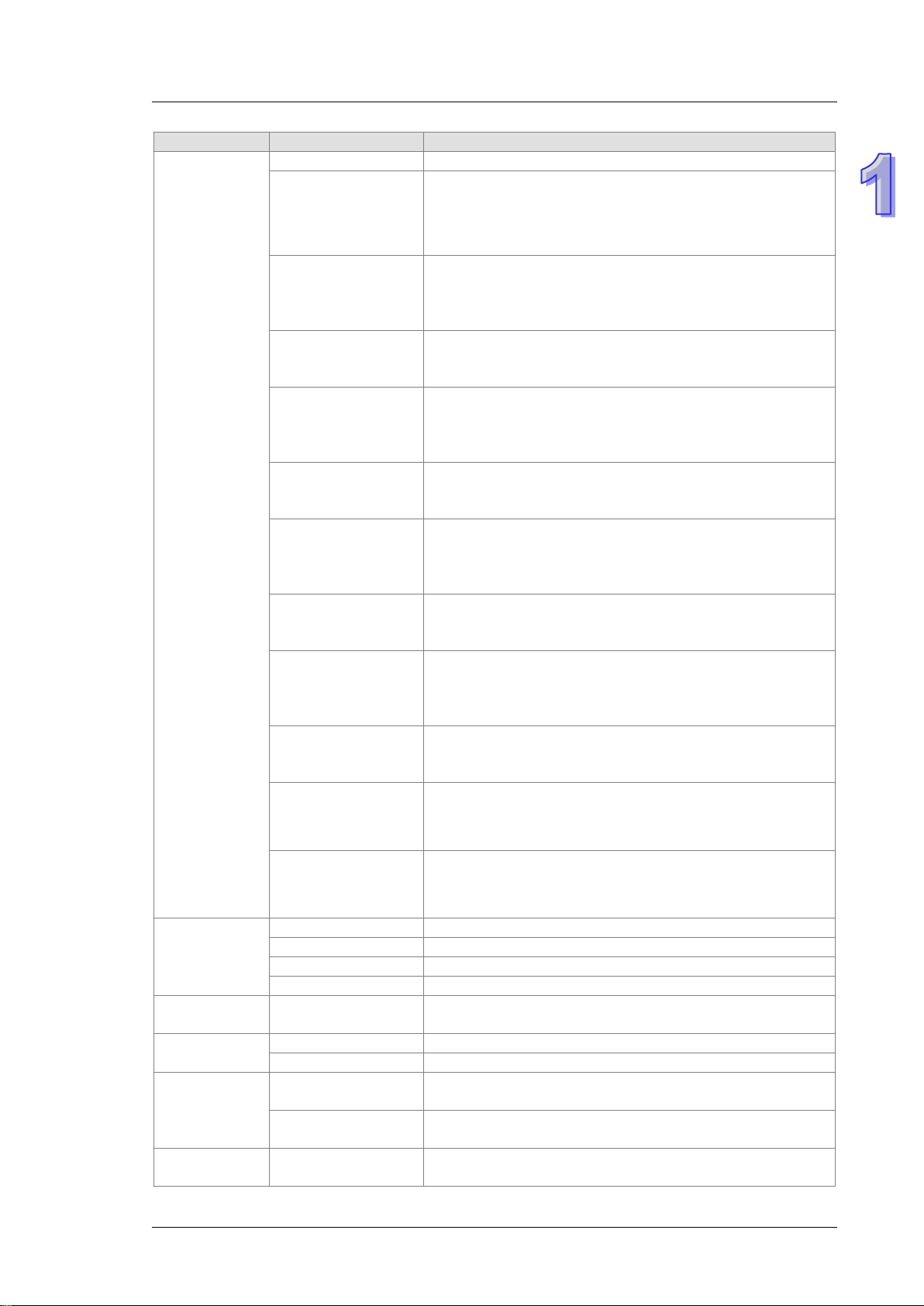
Chapter 1 Introduction
Classification
Model Name
Description
is 64K steps.
capacity is 96K steps.
It is a basic CPU module with two built-in RS-485 port s, one
inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 128K steps.
It is a basic CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port, one
is 128K steps.
It is an advanced CPU module with two built-in RS-485 ports,
2304 inputs/outputs . The program capacity is 192K steps.
It is an advanced CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port,
capacity is 192K steps.
It is a basic CPU module with two built-in RS-485 port s, one
inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 256K steps.
is 256K steps.
It is an advanced CPU module with two built-in RS-485 ports,
4352 inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 384K steps.
It is an advanced CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port,
It is a redundant CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port,
program c apacity is 1M steps.
AHBP04M1-5A
Four-slot main backplane for a CPU/RTU rack
AHBP06M1-5A
Six-slot main backplane for a CPU/RTU rack
AHBP08M1-5A
Eight-slot main backplane for a CPU/RTU rack
AHBP12M1-5A
Twelve-slot main backplane for a CPU/RTU rack
Redundant
backplane
backplane
AHBP06E1-5A
Six-slot extension backplane for a CPU/RTU extension rack
AHBP08E1-5A
Eight-slot extension backplane for a CPU/R T U ex tension rac k
CPU/RTU redundant extension rack
Eight-slot extension backplane with power redundancy for a
CPU/RTU redundant extension rack
input/output
5 mA
It is an advanced CPU module with two built-in RS-485 ports,
AHCPU511-RS2
AHCPU511-EN
AHCPU520-RS2
AHCPU520-EN
AHCPU521-RS2
AHCPU521-EN
AHCPU530-RS2
AHCPU530-EN
one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports
1280 inputs/outputs. The program capacity is 96K steps.
It is an advanced CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port,
one built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in
SD interface. It supports 1280 input s/o utpu ts. The program
built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports 2304
built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD
interface. It supports 2304 inputs/outputs. The program capacity
one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports
one built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in
SD interface. It supports 2304 input s/o utpu ts. The program
built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It supports 4352
It is a basic CPU module with one built-in Ethernet port, one
built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD
interface. It supports 4352 inputs/outputs. The program capacity
Main backplane
Extension
Redundant
extension
backplane
Digital
AHCPU531-RS2
AHCPU531-EN
AHCPU560-EN2
AHBP04MR1-5A Four-slot redundant backplane for a CPU/RTU rack
AHBP06ER1-5A
one built-in USB port, and one built-in SD interface. It support s
one built-in RS-485 port, one built-in USB port, and one built-in
SD interface. It supports 4352 inputs/outputs. The progr am
capacity is 384K steps.
one built-in RS-485/RS-232 port, one built-in USB port, and one
built-in SD interface. It support s 65536 inputs/outputs. The
Six-slot extension backplane with power redundancy for a
AHBP08ER1-5A
AH16AM10N-5A
24 V DC
1-3
AH500 Operation Manual
Classification
Model Name
Description
Terminal block
24 V DC
Terminal block
DB37 connector
24 V DC
Latch connector
24 V DC
Latch connector
100~240 V AC
Terminal block
24 V DC
(I/O interrupts are supported.)
240 V AC/24 V DC
Terminal block
Terminal block
12~24 V DC
Terminal block
12~24 V DC
Terminal block
12~24 V DC
DB37 connector
32 outputs
module 16 inputs
AH32AM10N-5A
AH32AM10N-5B
AH32AM10N-5C
AH64AM10N-5C
AH16AM30N-5A
AH16AR10N-5A
5 mA
32 inputs
24 V DC
5 mA
32 inputs
5 mA
32 inputs
3.2 mA
64 inputs
4.5 mA~9 mA (100 V, 50 Hz)
16 inputs
5 mA
16 inputs
Terminal block
Digital
input/output
module
AH16AN01R-5A
AH16AN01T-5A
AH16AN01P-5A
AH32AN02T-5A
AH32AN02T-5B
2 A
16 outputs
Relay
12~24 V DC
0.5 A
16 outputs
Sinking output
0.5 A
16 outputs
Sourcing output
0.1 A
32 outputs
Sinking output
0.1 A
32 outputs
Sinking output
1-4
AH32AN02T-5C
12~24 V DC
0.1 A

Classification
Model Name
Description
Latch connector
AH32AN02P-5A
12~24 V DC
Terminal block
DB37 connector
12~24 V DC
Latch connector
12~24 V DC
Latch connector
12~24 V DC
Latch connector
100~240 V AC
Terminal block
24 V DC
Terminal block
Terminal block
24 V DC
Sourcing output
AH32AN02P-5B
AH32AN02P-5C
AH64AN02T-5C
Chapter 1 Introduction
Sinking output
0.1 A
32 outputs
Sourcing output
12~24 V DC
0.1 A
32 outputs
Sourcing output
0.1 A
32 outputs
Sourcing output
0.1 A
64 outputs
Sinking output
Digital
input/output
module
AH64AN02P-5C
AH16AN01S-5A
AH16AP11R-5A
AH16AP11T-5A
0.1 A
64 outputs
Sourcing output
0.5 A
16 outputs
TRIAC
5 mA
8 inputs
240 V AC/24 V DC
2 A
8 outputs
Relay
24 V DC
5 mA
8 inputs
12~24 V DC
0.5 A
8 outputs
Sinking output
AH16AP11P-5A
5 mA
8 inputs
12~24 V DC
0.5 A
8 outputs
1-5
AH500 Operation Manual
Classification
Model Name
Description
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Eight-channel analog input module
Eight-channel analog input module
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Eight-channel analog input module
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Four-channel analog output module
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Eight-channel analog input module
Eight-channel analog output module
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Four-channel analog input module
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Four-channel four-wire/three-wire RTD
Three-wire conversion time: 300 ms/channel
Eight-channel four-wire/three-wire/two-wire RTD
Conversion time: 20 ms/4 channels and 200 ms/8 channels
AH04AD-5A
AH08AD-5A
Terminal block
Four-channel analog input module
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, -10 V~10 V, 0/4 mA~20 mA, and
-20 mA~20 mA
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, -10 V~10 V, 0/4 mA~20 mA, and
-20 mA~20 mA
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Analog
input/output
module
AH08AD-5B
AH08AD-5C
AH04DA-5A
AH08DA-5A
AH08DA-5B
AH08DA-5C
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, and -10 V~10 V
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/4 mA~20 mA, and -20 mA~20 mA
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, -10 V~10 V, and 0/4 mA~20 mA
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, -10 V~10 V, 0/4 mA~20 mA
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, and -10 V~10 V
Eight-channel analog output module
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/4 mA~20 mA
Analog
input/output
module
Temperature
measurement
module
1-6
AH06XA-5A
AH04PT-5A
AH08PTG-5A
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, -10 V~10 V, 0/4 mA~20 mA, and
-20 mA~20 mA
Conversion time: 150 us/channel
Two-channel analog output module
Hardware resolution: 16 bits
0/1 V~5 V, -5 V~5 V, 0 V~10 V, -10 V~10 V, and 0/4 mA~20 mA
Sensor type: Pt100/Pt1000/Ni100/Ni1000 sensor, and 0~300 Ω
input impedance
Resolution: 0.1°C/0.1°F (16 bit s)
Four-wire conversion time: 150 ms/channel
Sensor type: Pt100/Pt1000/Ni100/Ni1000, and 0~300 Ω input
impedance
Resolution: 0.1°C/0.1°F (16 bit s)

Classification
Model Name
Description
AH04TC-5A
Conversion time: 200 ms/channel
Eight-channel thermocouple
Conversion time: 200 ms/channel
AH02HC-5A
Two-channel high-speed counter module (200 kHz)
AH04HC-5A
Four-channel high-speed counter module (200 kHz)
AH05PM-5A
Two-axis pulse train motion control module (1 MHz)
Six-axis pulse train motion control module
(Four axes: 1 MHz; Two axes: 200 kHz)
Twelve-axis DMCNET (Delta Motion Control Network) motion
control module (10 Mbps)
It is an Ethernet communication module. It can function as a
supports a Modbus TCP master and EtherNet/IP (V2.0).
supports a Modbus TCP master and IEC60870-5-104.
It is a serial communication module with two RS-485/RS-422
part of the power.
It is a serial communication module with two RS-232 ports, and
part of the power.
It is a DeviceNet communication module. It can function as a
Mbps.
AH10PFBM-5A
PROFIBUS-DP master module
AH10PFBS-5A
PROFIBUS-DP slave module
master or a slave.
AHRTU-DNET-5A
DeviceNet remote I/O module
AHRTU-PFBS-5A
PROFIBUS-DP remote I/O module
AHRTU-ETHN-5A
Ethernet remote I/O module
0.6 meter extension cable for connecting an extension
backplane
1.0 meter extension cable for connecting an ex tensi on
backplane
backplane
3.0 meter extension cable for connecting an ex tensi on
backplane
AHAADP01EF-5A/
AHAADP02EF-5A
I/O extension
cable
1.0 meter I/O extension cable (latch connector) for
AH32AM10N-5C and AH64AM10N-5C
Chapter 1 Introduction
Four-channel thermocouple
Sensor type: J, K, R, S, T, E, N, and -150~+150 mV
Resolution: 0.1°C/0.1°F
Motion control
module
Network
module
AH08TC-5A
AH10PM-5A
AH15PM-5A Four-axis pulse train motion control module (1 MHz )
AH20MC-5A
AH10EN-5A
AH15EN-5A
AH10SCM-5A
AH15SCM-5A
Sensor type: J, K, R, S, T, E, N, and -150~+150 mV
Resolution: 0.1°C/0.1°F
mater or a slave. It is equipped with two Ethernet ports, and
It is an Ethernet communication module. It can function as a
mater or a slave. It is equipped with two Ethernet ports, and
ports, and supports Modbus and UD Link protocols.
One part of communication is isolated from the other part of the
communication, and one part of power is isolated from the other
supports Modbus and UD Link protocols.
One part of communication is isolated from the other part of the
communication, and one part of power is isolated from the other
AH10DNET-5A
AH10COPM-5A
Remote I/O
module
AHACAB06-5A
AHACAB10-5A
Extension cable
AHACAB15-5A
AHACAB30-5A
UC-ET010-24A
master or a slave. The maximum communication speed is 1
It is a CANopen communication module. It can function as a
1.5 meter extension cable for connecting an ex tensi on
Fiber optics modules for extension backplanes
1-7

AH500 Operation Manual
Classification
Model Name
Description
AH64AN02P-5C
1.0 meter I/O extension cable (DB37 connector) for
AH32AM10N-5B, AH32AN02T-5B, and AH32AN02P -5B
UC-ET010-13B
1.0 meter I/O extension cable for AH04HC-5A and AH20MC-5A
UC-ET010-15B
1.0 meter I/O extension cable for AH10PM-5A and AH15PM-5A
I/O external terminal module for AH32AM10N-5C and
32 inputs
I/O external terminal module for AH32AN02T-5C and
16 relay outputs
I/O external terminal module for AH32AN02P-5C and
16 relay outputs
I/O external terminal module for AH32AM10N-5B
32 inputs
32 relay outputs
I/O external terminal module for AH32AN02P-5B
32 relay outputs
I/O external terminal module for AH32AN02T-5C,
32 transistor outputs
I/O external terminal module for AH32AN02T-5B and
32 transistor outputs
UB-10-IO16C
I/O external terminal module for AH04HC-5A and AH20MC-5A
UB-10-IO24C
I/O external terminal module for AH10PM-5A
UB-10-IO34C
I/O external terminal module for AH15PM-5A
Space module
AHASP01-5A
Space module used for an empty I/O slot
UC-ET010-24C
UC-ET010-33B
1.0 meter I/O extension cable (latch connector) for
AH32AN02T-5C, AH32AN02P-5C, AH 64AN02T -5C and
External
terminal
module
UB-10-ID32A
UB-10-OR16A
UB-10-OR16B
UB-10-ID32B
UB-10-OR32A
UB-10-OR32B
UB-10-OT32A
UB-10-OT32B
AH64AM10N-5C
AH64AN02T-5C
AH64AN02P-5C
I/O external terminal module for AH32AN02T-5B
AH32AN02P-5C, AH64AN02T-5C, and AH64AN02P-5C
AH32AN02P-5B
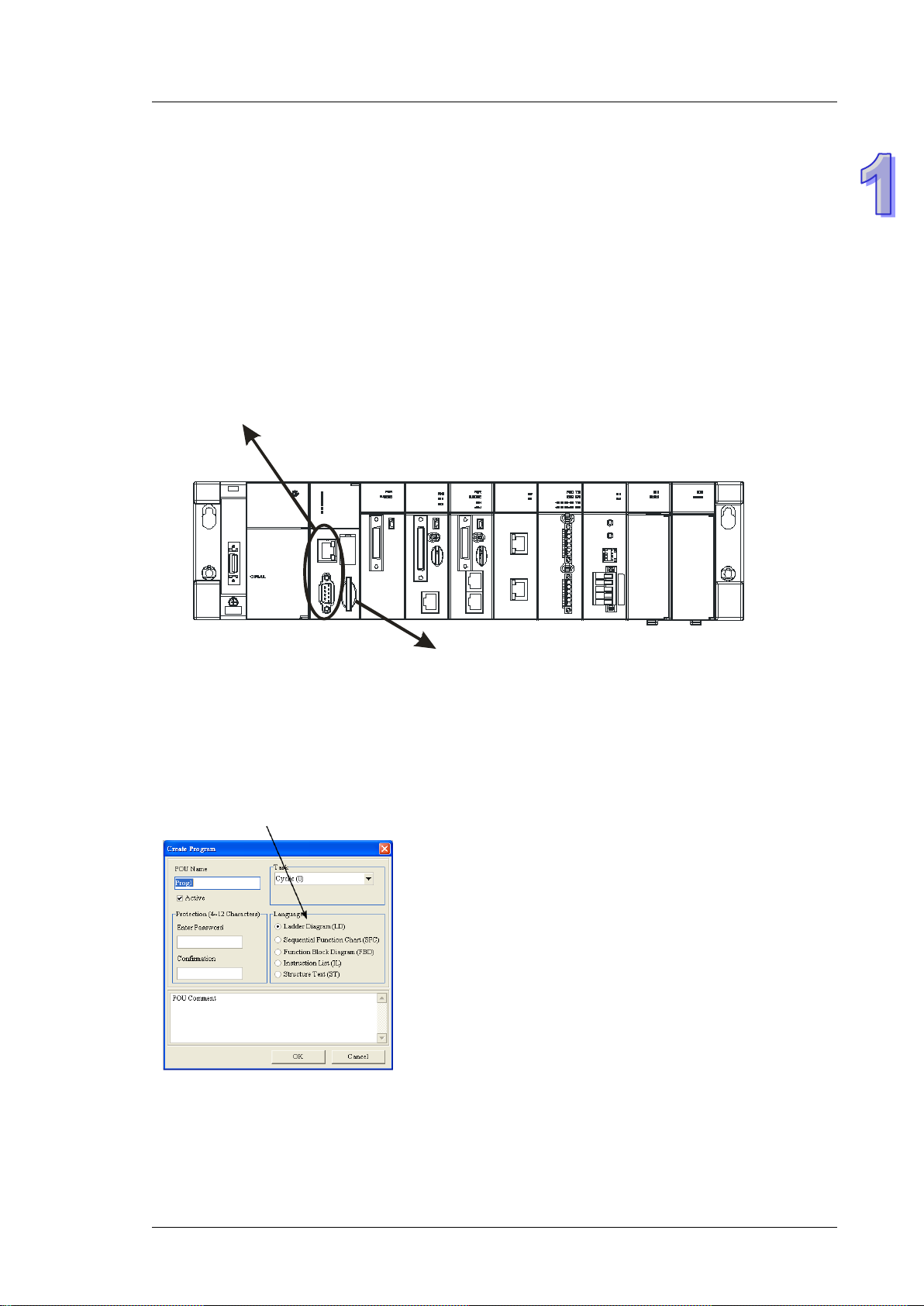
1.2 Overview
An AH500 series CPU module is a medium type of advanced controller with built-in communication ports. It
provides a strong network function for users, and users can create con nect ion among dev ic es on the network
through software. An AH500 series CPU module also provides structured programming. Users can assign
programs to different tasks, and write a program which is frequently executed in a function block. Besides,
users can choose different programmin g l anguages (instruction lists (IL), structured text s (S T ), ladder diagrams
(LD), sequential function charts (SFC), and function block diagrams (FBD)) dealt with by IEC 61131-3
according to their needs when writing programs. They can create the AH500 hardware co nfiguration by means
of hardware configuration sof t ware. They can also restore or back up a system rapidly through the built-in SD
interface in an AH500 series CPU module. This manual intr o duce s the basi c operat ion of an AH500 system,
and help users familiarize themselves with the AH500 system.
1-8
programs to different tasks, and write a program
create connection among devices in the network through software.
module.
according to their needs when writing program.
configuration software.
An AH500 series CPU module also provides
structured programming. Users can assign
which is frequently executed in a function block.
An AH500 series CPU module is a medium type of advanced controller with built-in
communication ports. It provides a strong network function for users, and users can
Chapter 1 Introduction
Users can re store or back up a system rapidly through the built-in SD interface in an AH500 series CPU
With ISPSoft, users can choose different programming
languages (instruction lists (IL), structured texts (ST), ladder
diagrams (LD), sequential function charts (SFC), and
function block diagrams (FBD) dealt with by IEC 61131-3
Users can create an AH500 hardware
configuration by means of the hardware
1-9
AH500 Operation Manual
7 backplanes
} }
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
...
Remote I/O
7 backplanes
Module
Description
Digital input/output
AH16AP11P-5A. and AH16AR10N-5A
Analog
module
Analog input/output
AH08DA-5B, AH08DA-5C, and AH06XA-5A
module
Motion
Controlling the motion
1.3 Characteristics
1. High efficiency
AH500 basic series CPU module: A 32-bit high-speed processor is used. The instructions ar e
executed at a speed of 3K steps/ms. (Fifty percent of the instructions are basic instructions, and fifty
percent of the instructions are applied instructions.)
AH500 advance series CPU module: A 32-bit high-speed processor is used. The instructions are
executed at a speed of 12K steps/ms. (Fifty percent of the instructions are basic instructions, and fifty
percent of the instructions are applied instructions.)
2. Supporting more inputs and outputs
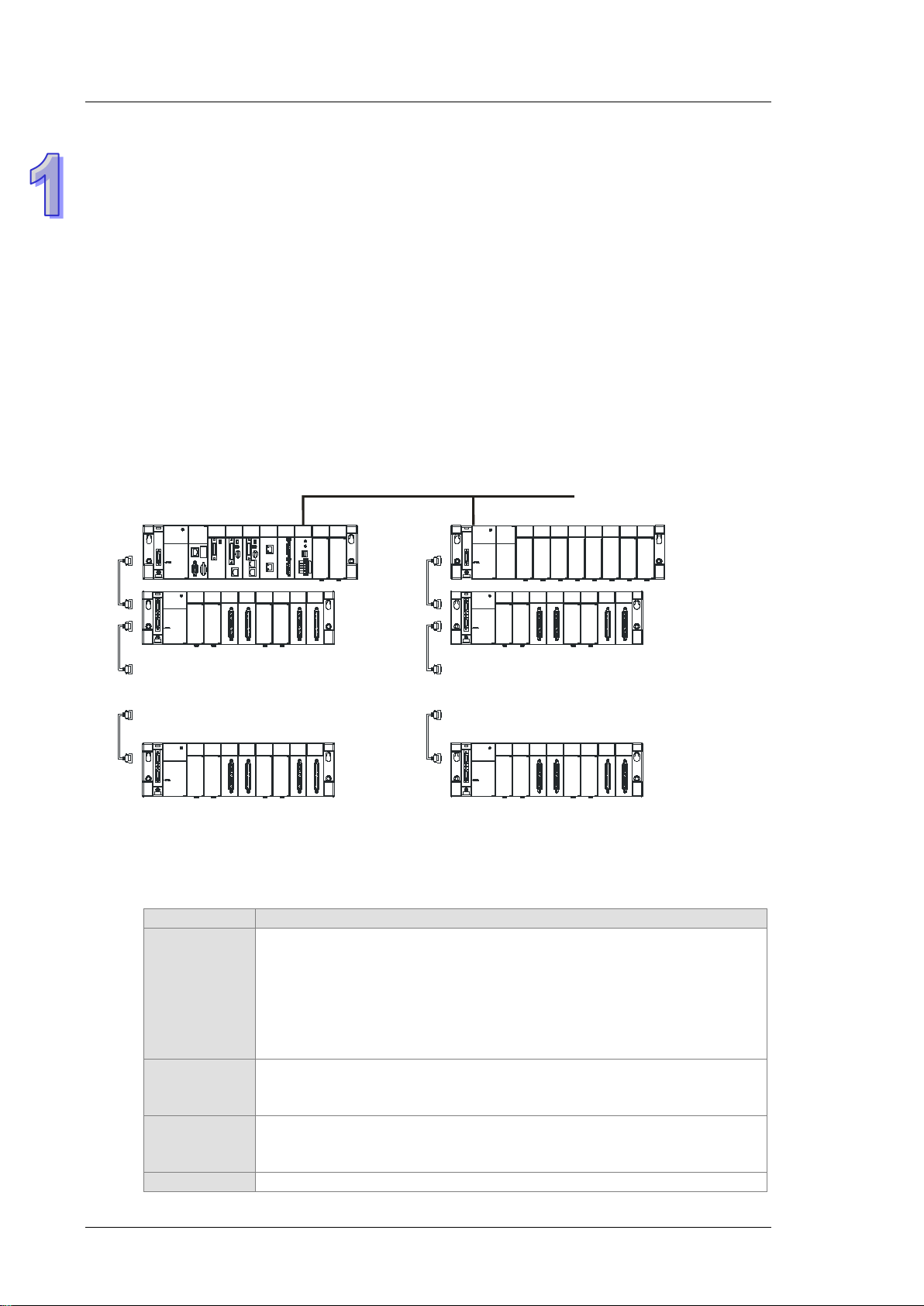
The AH500 series CPU module supports up to 4,352 local digital I/O or 544 analog I/O.
A complete AH500 system consists of eight backplanes at most, including a main backplane. Twelve
I/O modules at most can be installed on a main backplane, and eight I/O modules at most can be
installed on an ex tension backplane. Therefore, for the AH500 series CPU, sixty-eight digital
input/output modules at most or sixty-eight analog input/output modules at most can be inst alle d.
Eight RTU modules at most can be installed on the main backplane.
3. Multiple I/O modules
1-10
The I/O module s s upp ort ed by the AH500 seri es CP U module are digit al in put/output modules, a nal og
input/output modules, temperature measurement modules, network modules, mot ion c ontr o l m odul es,
and RTU modules.
AH16AM10N-5A, AH32AM10N-5A, AH32AM10N-5B, AH32AM10N-5C,
Digital
input/output
module
input/output
Temperature
measurement
AH64AM10N-5C, AH16AM30N-5A, AH16AN01R-5A, AH16AN01T-5A,
AH16AN01P-5A, AH32AN02T-5A, AH32AN02T-5B, AH32AN02T-5C,
AH32AN02P-5A, AH32AN02P-5B, AH32AN02P-5C, AH64AN02T-5C,
AH64AN02P-5C, AH16AN01S-5A, AH16AP11R-5A, AH16AP11T-5A,
AH04AD-5A, AH08AD-5A , AH08AD-5B, AH08AD-5C, AH04DA-5A, AH08DA-5A
Measuring the temperature
AH04PT-5A, AH08PTG-5A, AH04TC-5A, and AH08TC-5A
Chapter 1 Introduction
Module
Description
module
AH20MC-5A
Extending the communication interface (*There are multiple interfaces. All
AH10PFBS-5A, AH10PFBM-5A, and AH10COPM-5A
AHRTU-DNET-5A , AHRTU-PFBS-5A, and AHR TU-ETHN-5A.
b0b5b10
D0
b15
b0b5b10
X0
b15
control
Network
module
Remote I/O
module
AH02HC-5A, AH04HC-5A, AH05PM-5A, AH10PM-5A, AH15PM-5A, and
network modules can be installed on the main backplane except AH10SCM-5A
and AH15SCM-5A.)
AH10EN-5A, AH15EN-5A, AH10SCM-5A, AH15SCM-5A, AH10DNET-5A,
It is installed on the main backplane as a remote terminal unit. (*It supports
multiple communication interfaces.)
4. Larger program capacity and memory
Program capacity
AH500 basic series CPU module (AHCPU500/510/520/530): 32/64/128/256K steps.
AH500 advanced series CPU module (AHCPU501/511/521/531): 48/96/192/384K steps.
Providing with a wider module selection for users to select a suitable CPU module according to their
program capacity needs.
Memory
AH500 basic series CPU module (AHCPU500/510/520/530): 16/32/64K words of memory and
64/256/512/1024 function blocks to be declared.
AH500 advanced series CPU module (AHCPU501/511/521/531): 24/48/96/128K words of memory
and 512/1024/2048/4096 function blocks to be declared.
5. Devices which can be used conveniently in a program
An AH500 series CPU module is equ ipped w ith devi ces which can be used convenie ntly in a program.
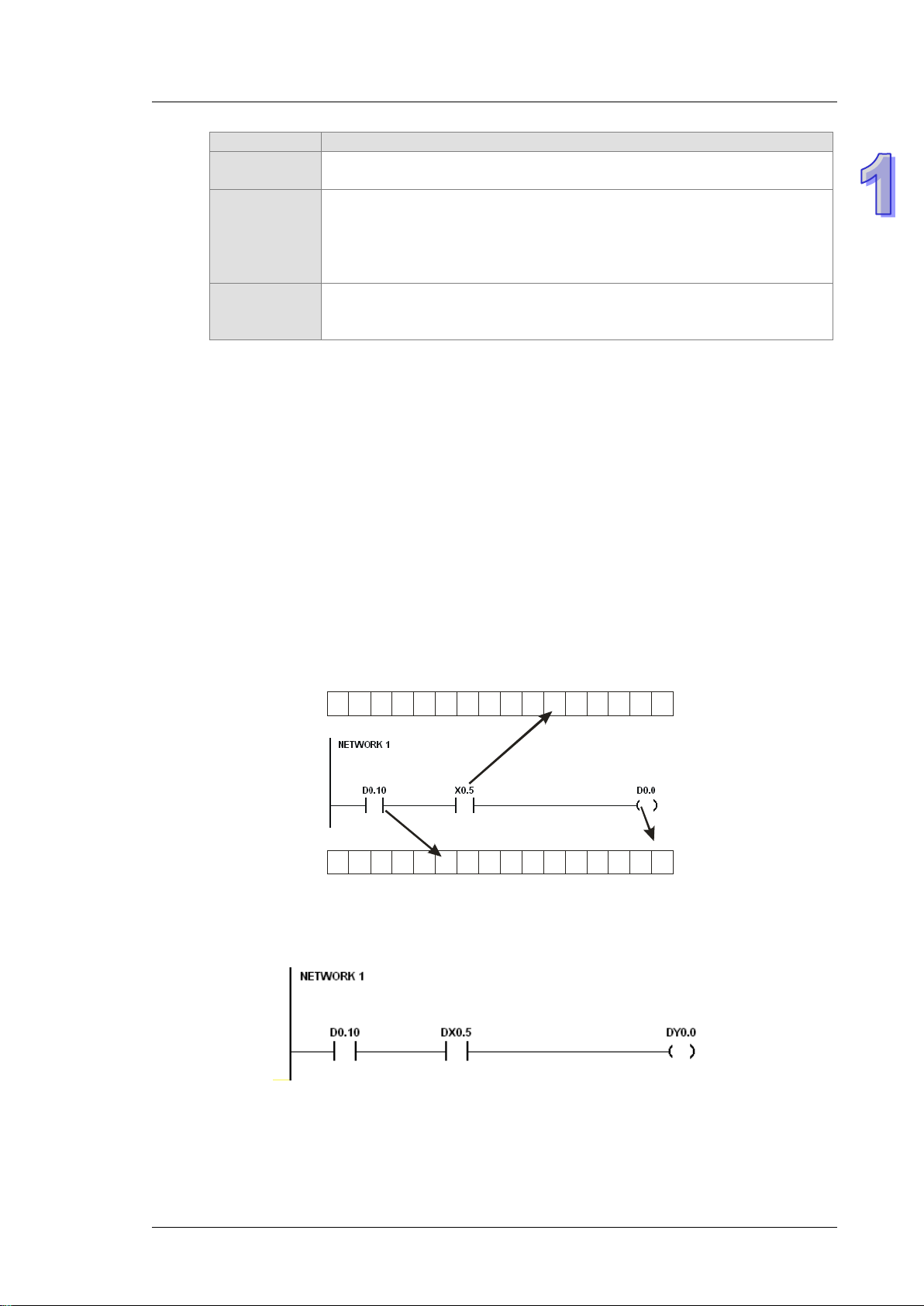
Users can flexibly specify a bit in a word dev ice, e. g. D0.0, X0.0, and Y0.0. Owing to that bit s in a w ord
device can be specified, these bits can function as cont act s and coils.
Users can access the state of DX0.0 and that of DY0.0 in a program. The state of DX0.0 and that of
DY0.0 are not limited by scan time. They are refreshed immediately in a program.
1-11
AH500 Operation Manual
6. Supporting IEC 61131-3
The AH500 series CPU module supports IEC 61131-3.
The programming languages which are supported are instruction lists (IL), structured texts (ST),
ladder diagrams (LD), sequential function charts (SFC), and function block diagrams (FBD).
Users can select a programming language according to their preference and the convenience. The
programming languages supp ort one another so that the pro gr am s writ ten by dif f er ent us er s are
related.
7. Strong function block
Not only the standard IEC61131-3 function blocks are supported, but also the convenient function
blocks provided by Delta Electronics, Inc. are supported. Users can write the program frequently
executed in a function blo ck so that t he program becomes more str u ctur ed a nd can be executed more
conveniently.
The symbol for a function block in a ladder diagram is like an Integrated circuit (IC) in a cir c uit d iagram.
Owing to the fact that the ladder diagram is based on the traditional circuit diagram, the operation of a
function block is quit e similar t o the fun ctio n of an i ntegr ated circuit. Users only need to send the signal
to the corresponding input of the function blo ck, and they ca n receive the signal or state which is
required. During the whole process, users do not need to consider the processing procedure inside
the function block.
1-12
Chapter 1 Introduction
A function block i s a progr am element equipp ed with the oper ation f unction . It is sim ilar to a subro utine,
and is a type of POU (Program Organization Unit). It can not operate by itself, and has to be called
through the program POU. After the related parameters are transmitted, the function defined by a
function block is executed. Besides, the final operation result can be sent to the device or variable
used in the superior POU after the execution of the function block is complete.
The setting of passwords by means of ISPSoft provides the secrecy of function blocks for speci al
businesses. The program inside a function block can not be learned, and the patent of a business will
not be infringed.
8. Task
The programs can be assigned to 283 tasks at most. Among the 288 tasks, 32 tasks are cyclic tasks,
32 tasks are I/O interrupts, 4 tasks are timer interrupts, 2 tasks are communication interrupts, 1 task is
an external 24 V low-voltage interrupt, and 212 tasks are user-defined tasks.
Users can enable and disable a task during the execution of a program by means of TKON and
TKOFF.
9. Increasing the efficiency of configuring the hardware through an USB cable and ISPSoft
The AH500 series CPU module provides a standard USB 2.0 interface. USB 2.0 increases the data
transfer rate, and decreases the time it takes to download the program, monitor the program and
configure the hardware. Besides, users do not need to buy a communication cable for the CPU
module. They can use a general USB cable to connect to the AH500 series CPU module.
1-13
AH500 Operation Manual
CPU530-RS2
RUN
ERROR
BUS FAULT
SYSTEM
COM1
COM2
C
O
M
C
O
M
2
1
USB
CPU530-EN
RUN
ERROR
BUS FAULT
SYSTEM
COM
Ethernet
COM
USB
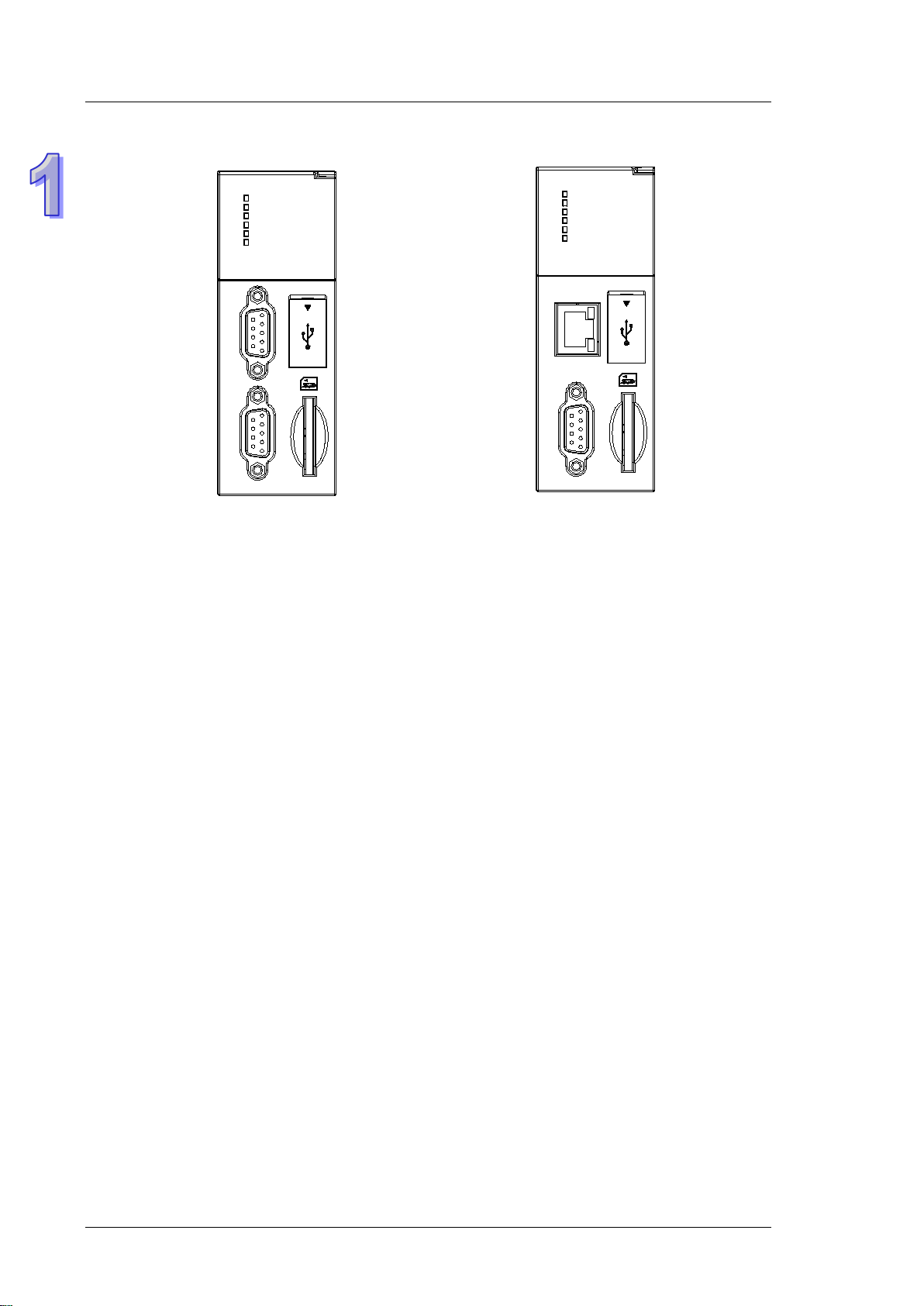
10. Serial control interface with multiple functions
AHCPU500/501/510/511/520/521/530/531-RS2 provides two DB9 serial control interfaces, i.e. COM1
and COM2.
AHCPU500/501/510/511/520/521/530/531-EN provides one DB9 serial control interface, i.e. COM.
Users can set the DB9 serial control interface to RS-232, RS-485, or RS-422 according to the
application environment. The data transfer rate can be increased from 9600 bps to 1 Mbps.
AH500 basic series CPU module (AHCPU500/510/520/530): After users set the PLC Link in
NWCONIFG in ISPSoft, they can exchange the data with a device through the RS-485 serial control
interface, and do not need to write any program.
AH500 advanced series CPU module (AHCPU501/511/521/531): After users set the PLC Link in
HWCONIFG in ISPSoft, they can exchange the data with a device through the RS-485 serial control
interface, and do not need to write any program.
11. High-speed Ethernet communication interface
AHCPU500/501/510/511/520/521/530/531-EN is equipped with a 10/100 M Ethernet communication
interface, and supports emails, webs, and socket services.
AH500 basic series CPU module (AHCPU500/510/520/530): After users set the PLC Link in
NWCONIFG in ISPSoft, they can exchange the data with a device network through the Ethernet
communication interface, and do not need to write any program.
AH500 advanced series CPU module (AHCPU501/511/521/531): After users set the PLC Link in
HWCONIFG in ISPSoft, they can exchange the data with a device through the Ethernet
communication interface, and do not need to write any program.
The statu s or the error messa ge rela ted t o the sy stem is se nt to us ers’ email box es immediately. Users
do not need to be on the spot to understand the problem.
12. Memory card
The memory card has the following functions.
System backup: The user program, the CPU parameters, the module table, the setting value in the
device
System recovery: The user program, the CPU parameters, the module table, and the setting value in
the device
Parameter storage: The value in the device
Log storage: The system error log and the system status log
1-14

Chapter 1 Introduction
13. Hot swap
The AH500 series I/O modules support the on-line uninterruptible hot swap. When the system runs,
users can replace the module which breaks down without disconnecting the module. After the module
is replaced, the new module runs normally. Users do not need to set the module manually or switch
the state.
14. Supporting the on-line debugging mode
After a single instruction step has been complete, or after a breakpoint is specified, users can easily
find the bug in the program by means of the on-line debugging mode supported by the AH500 series
CPU module.
If users want to enter the debugging mode, the CPU module must run. After users enable the on-line
monitoring function, they have to click
language to programming language, but the same operat io n appl ies t o the se programming languages.
For the AH500 series PLC, structured texts do not support the debugging mode, and sequential
function charts support the de bugging mode during the action and the transiti on.
Step 1: Setting the PLC to RUN
. The debugging screen varies from programming
1-15

AH500 Operation Manual
Step 2: Entering the on-line mode
Step 3: Entering the debugging mode
15. Supporting the on-line editing mode
When the system runs, users can make use of the on-line ed iting m ode to u pdate the program w ithout
affecting the operation of the system.
When the system is in the on-line monitoring mode, users can enter the on-line editing mode by
clicking .
1-16

Chapter 1 Introduction
After the program is modified and compiled, users can update the program in the CPU module by
clicking .
1-17
 Loading...
Loading...