Dell FC San Owner's Manual

53-1001964-01
October 1, 2010
8/4Gbps FC SAN Module
Administrator’s Guide
53-1001964-01
*53-1001964-01*

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE
CAUTION
DANGER
A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
A CAUTION indicates potential damage to hardware or loss of data if instructions are not followed.
A DANGER indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2010 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, Inspiron, Dell Precision, Dimension, OptiPlex, Latitude, PowerEdge, PowerVault, PowerApp,
PowerConnect, and Dell OpenManage are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel, Pentium, and Celeron are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in
the U.S. and other countries; Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, MS-DOS and Windows Vista are either trademarks or registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
ii Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001964-01

Contents
About this Document
How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Command syntax conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Notes, cautions, and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Key terms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
Industry resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
Chapter 1 NPIV Basic Concepts
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
NPIV overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
FC SAN Module port types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
FC SAN Module limitations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Chapter 2 Configuring Ports on the FC SAN Module
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Port state description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Default port mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Remapping ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Removing internal ports (F_Ports) from external ports (N_Ports)6
Chapter 3 Managing Policies and Features
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Policies overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Displaying current policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
FC SAN Module policy enforcement matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide iii
53-1001345-01

Advanced Device Security policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How the ADS policy works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Enabling and disabling the Advanced Device Security policy. . . 8
Setting the list of devices allowed to log in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Setting the list of devices not allowed to log in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Removing devices from the list of allowed devices . . . . . . . . . . 9
Adding new devices to the list of allowed devices. . . . . . . . . . .10
Displaying the list of allowed devices on the FC SAN Module .10
ADS policy considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Automatic Port Configuration policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
How the APC policy works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Enabling and disabling the APC policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Automatic Port Configuration policy considerations . . . . . . . . .12
Port Grouping policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
How port groups work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Adding an external port (N_Port) to a port group. . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Deleting an external port (N_Port) from a port group . . . . . . . . 14
Removing a port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Renaming a port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Disabling the Port Grouping policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Port Grouping policy modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Creating a port group and enabling login balancing mode. . . . 15
Rebalancing internal ports (F_Ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Enabling Managed Fabric Name Monitoring mode. . . . . . . . . . 17
Disabling Managed Fabric Name Monitoring mode . . . . . . . . . 17
Displaying the current fabric name monitoring timeout value . 17
Setting the current fabric name monitoring timeout value. . . . 17
Port Grouping policy considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Failover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Failover configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Enabling and disabling Failover on an external port (N_Port) .20
Enabling and disabling Failover for a port group . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Adding a preferred secondary external port (N_Port) . . . . . . . . 21
Deleting internal ports from a preferred secondary external port21
Failback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Failback configurations in the FC SAN Module . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Enabling and disabling Failback on an external port (N_Port) 23
Enabling and disabling Failback for a port group . . . . . . . . . . . 24
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 4 Fabric Configuration with the Dell FC SAN Module
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Connectivity of multiple devices overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Fabric and Edge switch configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Verifying the switch mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Enabling NPIV on M-EOS switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Connectivity to Cisco Fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Enabling NPIV on a Cisco switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
iv Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

Appendix A Troubleshooting
Appendix B Command Reference
Understanding role-based access control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Understanding Virtual Fabric restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Understanding Admin Domain restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Using the command line interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Index
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide v
53-1001345-01

vi Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

Tables
Tab l e 1 Port state description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Tab l e 2 Description of port mapping in preceding figure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Tab l e 3 FC SAN Module default F_Port-to-N_Port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tab l e 4 Policy enforcement matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Tab l e 5 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Tab l e 6 Role definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Tab l e 7 Virtual Fabric contexts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tab l e 8 Switch Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tab l e 9 AD types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide vii
53-1001345-01

viii Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

About this Document
•How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
•Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
•Key terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
•Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xii
How this document is organized
This document is a procedural guide to help SAN administrators configure and manage the Dell
8/4Gbps FC SAN Module, hereafter identified as the FC SAN Module.
This preface contains the following components:
• Chapter 1, “NPIV Basic Concepts” describes NPIV function and an overview of key the FC SAN
Module key features.
• Chapter 2, “Configuring Ports on the FC SAN Module” describes how to configure ports in FC
SAN Module mode.
• Chapter 3, “Managing Policies and Features” describes how to enable policies on the FC SAN
Module. It also provides information on how to set up Failover and Failback.
• Chapter 4, “Fabric Configuration with the Dell FC SAN Module” describes how to connect
multiple devices using the FC SAN Module.
• Appendix A, “Troubleshooting” provides symptoms and troubleshooting tips to resolve issues.
• Appendix B, “Command Reference” provides a reference for CLI commands used for module
configuration and information.
Document conventions
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notices formats.
Text formatting
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used in this document are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords and operands
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide ix
53-1001345-01

italic text Provides emphasis
NOTE
ATTENTION
Identifies variables
Identifies paths and Internet addresses
Identifies document titles
code text Identifies CLI output
Identifies syntax examples
For readability, command names in the narrative portions of this guide are presented in mixed
lettercase: for example, switchShow. In actual examples, command lettercase is often all
lowercase. Otherwise, this manual specifically notes those cases in which a command is case
sensitive. The ficonCupSet and ficonCupShow commands are an exception to this convention.
Command syntax conventions
Command syntax in this manual follows these conventions:
command Commands are printed in bold.
--option, option Command options are printed in bold.
-argument, arg Arguments.
[ ] Optional element.
variable Variables are printed in italics. In the help pages, values are underlined
enclosed in angled brackets < >.
... Repeat the previous element, for example “member[;member...]”
value Fixed values following arguments are printed in plain font. For example,
--show WWN
| Boolean. Elements are exclusive. Example:
--show -mode egress | ingress
Notes, cautions, and warnings
The following notices appear in this document.
A note provides a tip, emphasizes important information, or provides a reference to related
information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
or
x Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01
CAUTION
A Caution statement alerts you to situations that can be potentially hazardous to you or cause
DANGER
damage to hardware, firmware, software, or data.
A Danger statement indicates conditions or situations that can be potentially lethal or extremely
hazardous to you. Safety labels are also attached directly to products to warn of these conditions
or situations.
Notice to the reader
This document may contain references to the trademarks of the following corporations. These
trademarks are the properties of their respective companies and corporations.
These references are made for informational purposes only.
Corporation Referenced Trademarks and Products
Brocade Corporation Brocade
Dell Corporation Dell, 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module
Cisco Systems, Inc. Cisco
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Sun, Solaris
Netscape Communications Corporation Netscape
Red Hat, Inc. Red Hat, Red Hat Network, Maximum RPM, Linux Undercover
Emulex Corporation Emulex
QLogic Corporation QLogic
Key terms
For definitions of SAN-specific terms, visit the Storage Networking Industry Association online
dictionary at: http://www.snia.org/education/dictionary.
The following terms are used in this manual.
FC SAN Module
Port aggregation I/O module that reduces SAN (storage area network)
deployment complexity by leveraging NPIV (N_Port ID Virtualization).
Edge switch A fabric switch that connects host, storage, or other devices, such as the FC
SAN Module, to the fabric.
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide xi
53-1001345-01

F_Port A fabric port. A switch port that connects a host, HBA (host bus adaptor), or
Mapping On the FC SAN Module, the configuration of internal port (F_Port) to external
N_Port A node port. A Fibre Channel host or storage port in a fabric or point-to-point
NPIV N_Port ID Virtualization. Allows a single Fibre Channel port to appear as
Preferred Secondary N_Port
Additional information
This section lists additional industry-specific documentation that you might find helpful.
storage device to the SAN. On the FC SAN Module, the internal port (F_Port)
connects to an HBA on an individual blade server.
port (N_Port) routes.
connection. On the FC SAN Module, the external port (N_Port connects to the
Edge switch.
multiple, distinct ports providing separate port identification and security
zoning within the fabric for each operating system image as if each operating
system image had its own unique physical port.
On the FC SAN Module, the preferred secondary external port (N_Port) refers
to the secondary path to which an internal port (F_Port) fails over if the
primary external port goes offline.
Industry resources
For additional information, visit the Technical Committee T11 Web site. This Web site provides
interface standards for high-performance and mass storage applications for Fibre Channel, storage
management, and other applications:
http://www.t11.org
For information about the Fibre Channel industry, visit the Fibre Channel Industry Association Web
site:
http://www.fibrechannel.org
Getting technical help
Contact your switch support supplier for hardware, firmware, and software support, including
product repairs and part ordering. To expedite your call, have the following information available:
1. General Information
• Dell Service Tag
• Technical Support contract number, if applicable
• FC SAN Module model
• FC SAN Module operating system version
• Error numbers and messages received
xii Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

• supportSave command output
• Detailed description of the problem and specific questions
• Description of any troubleshooting steps already performed and results
• Serial console and Telnet session logs
• syslog message logs
2. 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Serial Number
The FC SAN Module serial number and corresponding bar code are provided on the serial
number label attached to the module. Following is an example of a serial number and barcode:
:
*FT00X0054E9*
FT00X0054E9
3. World Wide Name (WWN). Use the CLI wwn or switchShow commands to display the WWN.
4. Software licenses. Use the CLI licenseShow command to display the list of licenses available
on the unit.
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide xiii
53-1001345-01

xiv Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

Chapter
NPIV Basic Concepts
In this chapter
•NPIV overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•FC SAN Module port types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•FC SAN Module limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
NPIV overview
With the FC SAN Module, your Enterprise fabric can handle additional external ports (N_Ports)
instead of domains. You do this by configuring internal ports (F_Ports) to connect to the fabric as
external ports, which increases the number of device ports you can connect to a single fabric.
Because the Dell (Fibre Channel) FC SAN Module functions as an NPIV port aggregator, it is
compatible with Brocade Fabric OS, M-EOS v9.1 or v9.6 and later, and Cisco-based fabrics v3.0 (1)
or later and v3.1 (1) and later. This document describes configurations using the CLI commands.
1
Since the FC SAN Module operates using NPIV it is logically transparent to the host and the fabric.
You can increase the number of blade servers that have access to the fabric without increasing the
number of switches. This simplifies configuration and management in a large fabric by reducing the
number of domain IDs and ports. Figure 1 shows how the FC SAN Module connects to blade
servers (Hosts) and fabrics.
FIGURE 1 FC SAN Module connection
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide 1
53-1001345-01

FC SAN Module port types
1
FC SAN Module port types
The Dell NPIV Switch FC SAN Module differs from a typical fabric switch because it is a port
aggregator rather than a switch; instead, it connects to the fabric using node ports (N_Ports).
Typically fabric switches connect to the fabric using ISL (InterSwitch Link) ports, such as E_Ports.
Following are the Fibre Channel (FC) ports that the FC SAN Module uses:
• F_Port - internal fabric port that connects a blade server (HBA).
• N_Port - external node port that connects to a switch.
FC SAN Module limitations
The limitations of the FC SAN Module are as follows:
• The maximum number of devices that can be connected to a fabric switch through the FC SAN
Module depends on the maximum number of local devices supported by the fabric.
• Loop devices are not supported.
• Port groups cannot be overlapped. This means that an N_Port cannot belong to two different
groups.
• Direct connections to SAN target devices are not supported.
• Management Platform Services is not supported.
• Name Services is not supported.
• Zoning is not supported; security enforcement is done using the ADS policy.
2 Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

Chapter
Configuring Ports on the FC SAN Module
In this chapter
•Port state description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
•Port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Port state description
The following table describes the possible port states.
TABLE 1 Port state description
State Description
No _Card No interface card present
No _Module No module (GBIC or other) present
Mod_Val Module validation in process
Mod_Inv Invalid module
No_Light The module is not receiving light
No_Sync Receiving light but out of sync
In_Sync Receiving light and in sync
Laser_Flt Module is signaling a laser fault
Port_Flt Port marked faulty
Diag_Flt Port failed diagnostics
Lock_Ref Locking to the reference signal
Testing Running diagnostics
Offline Connection not established (only for virtual ports)
Online The port is up and running
2
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide 3
53-1001345-01

Port mapping
N_2
F_A2
Blade Servers
FC SAN Module
Edge Switch
Fabric
(Switch_A)
enabled
NPIV
F_4
F_3
F_2
F_1
N_1
F_A1
enabled
NPIV
N_3
F_B1
enabled
NPIV
Blade_1
Blade_2
Blade_3
Blade_4
F_5
Blade_5
F_6
Blade_6
F_7
Blade_7
F_8
Blade_8
Edge Switch
(Switch_B)
N_4
F_B2
enabled
NPIV
2
Port mapping
The FC SAN Module uses port-mapped pre-provisioned routes to direct traffic from the blade server
(HBAs) to the fabric. When you first turn on the module, by default, the internal ports (F_Ports) are
mapped to a set of predefined external ports (N_Ports). For the default port mapping, see Tabl e 3
on page 5. See t “Remapping ports” on page 5 if you want to change the default mapping. Figure 2
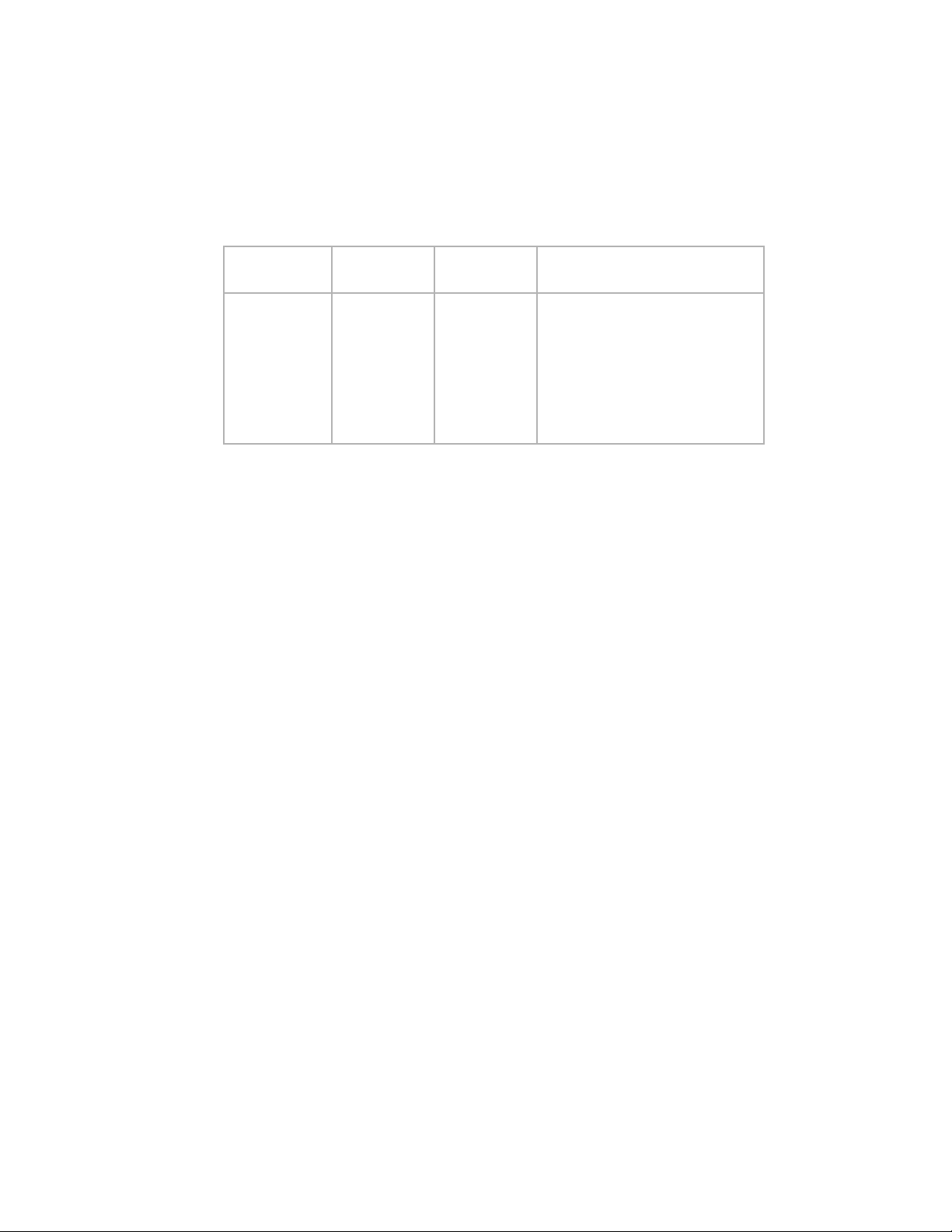
shows a mapping with eight internal ports (F_Ports) evenly mapped to four external ports (N_Ports).
External ports connect to the same fabric through different Edge switches.
FIGURE 2 Example NPIV port mapping
Tab le 2 provides a description of the port mapping in Figure 2.
TABLE 2 Description of port mapping in preceding figure
NPIV Switch Fabric
F_Port N_Port Edge switch F_Port
F_1, F_2 N_1 Switch_A F_A1
F_3, F_4 N_2 Switch_A F_A2
F_5, F_6 N_3 Switch_B F_B1
F_7, F_8 N_4 Switch_B F_B2
4 Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01
Port mapping
2
Default port mapping
Tab le 3 shows the default port mapping. By default, Failover and Failback policy are enabled on all
external ports (N_Ports).
TABLE 3 FC SAN Module default F_Port-to-N_Port mapping
Total Ports Server Ports
(F_Ports)
24 1-16 0, 17-23 1, 2 mapped to 17
The FC SAN Module ships with 12 active ports and two installed SFP+ optical transceivers. A port
upgrade license is available to activate 12 additional ports and includes two additional SFP+
transceivers. Additional single SFP+ transceivers are also available for maximum bandwidth and
redundancy.
External Ports
(N_Ports)
Default F_ to N_Port Mapping
3, 4 mapped to 18
5, 6 mapped to 19
7, 8 mapped to 20
9, 10 mapped to 21
11, 12 mapped to 22
13, 14 mapped to 23
15, 16 mapped to 0
By default, port licensing on the FC SAN Module is dynamic, so port licenses are flexibly assigned
from the pool of available licenses. Ports 17 and 18 are licensed at the factory (and align with the
two included SFP+ transceivers). The remaining ten licenses are assigned to active ports as
required, making port licensing more flexible.
If no additional SFP+ transceivers are used to enable additional external ports on the FC SAN
Module and your M1000e blade chassis contains more than four blade servers, you should make
modifications to the default port mapping to ensure connectivity for all servers to the SAN.
Remapping ports
extern
You can modify the default port mapping by adding internal ports (F_Ports) to an external port
(N_Port). Doing so, routes that traffic to and from the fabric through the specified external port.
You can assign an internal port to only one primary external port at a time. If the internal is already
assigned to an external port, you must remove it from the external port before you can add it to a
different port.
Use the following steps to add an internal port (F_Port) to an external port (N_Port).
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the command with the
list of internal to the external port.
The f_portlist can contain multiple internal ports (F_Ports) numbers separated by semicolons,
for example “17;18”.
--mapadd n_portnumber “f_port1;f_port2;... “operand to add the
switch:admin> ag --mapadd 13 "6;7"
F-Port to N-Port mapping has been updated successfully
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide 5
53-1001345-01

2
Port mapping
3. Enter the ag --mapshow command and specify the port number to display the list of mapped
internal ports (F_Ports). Verify that the added internal ports (F_Ports) appear in the list.
switch:admin> ag --mapshow 13
N_Port : 13
Failover(1=enabled/0=disabled) : 1
Failback(1=enabled/0=disabled) : 1
Current F_Ports : None
Configured F_Ports : 6;7
PG_ID : 0
PG_Name : pg0
Removing internal ports (F_Ports) from external ports (N_Ports)
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag
--mapdel command to remove the internal port from the external port.
The f_portlist can contain multiple internal port numbers separated by semicolons, for
example “17;18”.
switch:admin> ag --mapdel 17;18
F-Port to N-Port mapping has been updated successfully
3. Enter the switchshow command to verify that the internal port is free (unassigned).
Unassigned F_Port status is Disabled (No mapping for internal port). See port 6 in the following
example.
switch:admin> switchshow
switchName: fsw534_4016
switchType: 45.0
switchState: Online
switchMode: Access Gateway Mode
switchWwn: 10:00:00:05:1e:02:1d:b0
switchBeacon: OFF
Area Port Media Speed State Proto
=====================================
0 0 cu AN No_Sync
1 1 cu AN No_Sync Disabled (N-Port Offline for F-Port)
2 2 cu AN No_Sync Disabled (N-Port Offline for F-Port)
3 3 cu AN No_Sync Disabled (N-Port Offline for F-Port)
4 4 cu AN No_Sync Disabled (N-Port Offline for F-Port)
5 5 cu AN No_Sync Disabled (N-Port Offline for F-Port)
6 6 cu AN No_Sync Disabled (No mapping for F-Port)
7 7 cu AN No_Sync
8 8 cu AN No_Sync
9 9 cu AN No_Sync
10 10 -- N4 No_Module
11 11 -- N4 No_Module
12 12 -- N4 No_Module
13 13 id N4 Online N-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:35:10:1e 0x5a0a00
14 14 id N4 Online N-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:35:10:1e 0x5a0900
15 15 id N4 Online N-Port 10:00:00:05:1e:35:10:1e 0x5a0800
6 Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

Chapter
Managing Policies and Features
In this chapter
•Policies overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
•Advanced Device Security policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
•Automatic Port Configuration policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
•Port Grouping policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
•Failover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
•Failback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Policies overview
This chapter provides detailed information on the following policies.
• Advanced Device Security policy (ADS)
• Automatic Port Configuration policy (APC)
• Port Grouping policy (PG)
• Persistent ALPA policy
These policies can be used to control various advanced features, such as Failover, and Failback.
3
Displaying current policies
You can run the following command to display policies that are currently enabled or disabled on a
FC SAN Module.
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag
switch:admin> ag --policyshow
Policy_Description Policy_Name State
-------------------------------------------------Port Grouping pg Enabled
Auto Port Configuration auto Disabled
Advanced Device Security ads Enabled
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide 7
53-1001345-01
--policyshow command.

Advanced Device Security policy
NOTE
3
FC SAN Module policy enforcement matrix
The following table shows which combinations of policies can co-exist with each other.
TABLE 4 Policy enforcement matrix
Policies Auto Port Configuration Port Grouping ADS Policy
Auto Port Configuration
N_Port Grouping
ADS Policy
N/A Cannot co-exist Can co-exist
Mutually exclusive N/A Can co-exist
Can co-exist Can co-exist N/A
Advanced Device Security policy
The Advanced Device Security (ADS) is disabled by default for the FC SAN Module. ADS is a security
policy that restricts access to the fabric at the to a set of authorized devices. Unauthorized access
is rejected and the system logs a RASLOG message. You can configure the list of allowed devices
for each internal port (F_Port) by specifying their Port WWN (PWWN). The ADS policy secures virtual
and physical connections to the SAN.
How the ADS policy works
When you enable this policy, it applies to all internal ports (F_Ports) on the FC SAN Module. By
default, all devices have access to the fabric on all ports. You can restrict the fabric connectivity to
a particular set of devices where FC SAN Module maintains a per-port allow list for the set of
devices whose PWWN you define to log in through an internal port. You can view the devices with
active connections to an internal port using the ag --show command.
The ag --show command only displays the Core FC SAN Module, such as the modules that are
directly connected to fabric. The agshow
the Core and Edge modules.
--name name command displays the internal ports of both
Enabling and disabling the Advanced Device Security policy
By default, the ADS policy is disabled. When you manually disable the ADS policy, all of the allow
lists (global and per-port) are cleared. Before disabling the ADS policy, you should save the
configuration using the configupload command in case you need this configuration again.
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag
switch:admin> ag --policyenable ads
The policy ADS is enabled
3. Enter the ag --policydisable ads command to disable the ADS policy.
switch:admin> ag --policydisable ads
The policy ADS is disabled
8 Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
--policyenable ads command to enable the ADS policy.
53-1001345-01

Advanced Device Security policy
NOTE
NOTE
Use the ag --policyshow command to determine the current status of the ADS policy.
3
Setting the list of devices allowed to log in
You can determine which devices are allowed to log in by internal (F_Port) by specifying the device’s
port WWN (PWWN). Lists must be enclosed in double quotation marks. List members must be
separated by semicolons. The maximum number of entries in the allowed device list is twice the
per port maximum log in count. Replace the WWN list with an asterisk (*) to indicate all access on
the specified internal port list. Replace the internal port list with an asterisk (*) to add the specified
WWNs to all the internal ports' allow lists. A blank WWN list (““) indicates no access. The ADS policy
must be enabled for this command to succeed.
Use an asterisk enclosed in quotation marks,“*”, to set the Allow list to “All Access” to all internal
ports; use a pair of double quotation marks (“”) to set the Allow list to “No Access”.
Note the following characteristics of the Allow List:
• The maximum device entries allowed in the Allow List is twice the per port max login count.
• Each port can be configured to “not allow any device” or “to allow all the devices” to log in.
• If the ADS policy is enabled, by default, every port is configured to allow all devices to log
in.
• The same Allow List can be specified for more than one internal port.
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag --adsset command with the appropriate operands to set the list of devices
allowed to log into specific ports. In the following example, ports 1, 10, and, 13 are set to “all
access.”
switch:admin> ag–-adsset“1;10;13”“*”
WWN list set successfully as the Allow Lists of the F_Port[s]
Setting the list of devices not allowed to log in
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag --adsset command with the appropriate operands to set the list of devices not
allowed to log into specific ports. In the following example, ports 11 and 12 are set to “no
access.”
switch:admin > ag –-adsset “11;12” “”
WWN list set successfully as the Allow Lists of the F_Port[s]
Removing devices from the list of allowed devices
Use the ag --adsdel command to delete the specified WWNs from the list of devices allowed to log
in to the specified internal ports (F_Ports). Lists must be enclosed in double quotation marks. List
members must be separated by semicolons. Replace the internal port list with an asterisk (*) to
remove the specified WWNs from all the internal ports' allow lists. The ADS policy must be enabled
for this command to succeed.
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide 9
53-1001345-01

Advanced Device Security policy
3
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag --adsdel command to remove one or more devices from the list of allowed
devices.
Use the following syntax:
ag--adsdel "F_Port [;F_Port2;...]" "WWN [;WWN2;...]"
In the following example, two devices are removed from the list of allowed devices (for ports 3
and 9).
switch:admin> ag --adsdel "3;9"
"22:03:08:00:88:35:a0:12;22:00:00:e0:8b:88:01:8b"
WWNs removed successfully from Allow Lists of the F_Port[s]Viewing F_Ports
allowed to login
Adding new devices to the list of allowed devices
You can add the specified WWNs to the list of devices allowed to log in to the specified internal
ports (F_Ports). Lists must be enclosed in double quotation marks. List members must be
separated by semicolons. Replace the internal port list with an asterisk (*) to add the specified
WWNs to all the internal ports' allow lists. The ADS policy must be enabled for this command to
succeed.
1. Connect to the switch and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag --adsadd command with appropriate operands to add one or more new devices to
the list of allowed devices.
Use the following syntax:
ag--adsadd "F_Port [;F_Port2;...]" "WWN [;WWN2;...]"
In the following example, two devices are added to the list of allowed devices (for ports 3 and
9).
switch:admin> ag --adsadd "3;9"
"20:03:08:00:88:35:a0:12;21:00:00:e0:8b:88:01:8b"
WWNs added successfully to Allow Lists of the F_Port[s]
Displaying the list of allowed devices on the FC SAN Module
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the ag --adsshow command.
switch:admin> ag --adsshow
F_Port WWNs Allowed
------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 ALL ACCESS
3 20:03:08:00:88:35:a0:12
21:00:00:e0:8b:88:01:8b
9 20:03:08:00:88:35:a0:12
21:00:00:e0:8b:88:01:8b
10 ALL ACCESS
11 NO ACCESS
12 NO ACCESS
13 ALL ACCESS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
10 Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01

ADS policy considerations
The ADS policy can be enabled or disabled independent of status of other policies.
Automatic Port Configuration policy
The automatic Port Configuration (APC) policy is disabled by default. APC provides the ability to
automatically discover port types (host vs. fabric) and dynamically update the routing maps when a
new connection is detected. This policy is intended for a complete hands-off operation. APC
dynamically maps internal ports (F_Ports) to available external ports (N_Ports) so they are evenly
distributed. For example, when a port on the module is connected to a fabric switch, the module
configures the port as an external port. If a host is connected to a port on the FC SAN Module, then
it determines that it is connected and configures the port as an internal port and automatically
maps it to an existing external port with the least number of internal ports mapped to it.
How the APC policy works
When the APC policy is enabled, it applies to all ports on the switch. Enabling the APC policy is
disruptive and erases all existing port mappings. Therefore, before enabling the APC policy, you
must disable the FC SAN Module. When you disable the APC policy, the external port (N_Port)
configuration and the port mapping revert back to the default factory configurations for that
platform. It is recommended that you save the current configuration file using the configupload
command in case you might need this configuration again.
Automatic Port Configuration policy
3
Enabling and disabling the APC policy
Use the following steps to enable and disable Automatic Port Configuration policy.
Enabling APC policy
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the switchdisable command to ensure that the module is disabled.
3. Enter the configupload command to save the module’s current configuration.
4. Enter the ag --policyenable auto command to enable the APC policy.
switch:admin> ag --policyenable auto
All Port related Access Gateway configurations will be lost.
Please save the current configuration using configupload.
Do you want to continue? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
5. At the command prompt, type Y to enable the policy.
The switch is ready; a reboot is not required.
Disabling APC policy
1. Connect to the FC SAN Module and log in using an account assigned to the admin role.
2. Enter the switchdisable command to ensure that the module is disabled.
3. Enter the configupload command to save the module’s current configuration.
Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide 11
53-1001345-01

Port Grouping policy
3
4. Enter the command ag --policydisable auto to disable the APC policy.
5. At the command prompt, type Y to disable the policy.
switch:admin> ag --policydisable auto
Default factory settings will be restored.
Default mappings will come into effect.
Please save the current configuration using configupload.
Do you want to continue? (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Access Gateway configuration has been restored to factory default
6. Enter the switchenable command to enable the module.
Automatic Port Configuration policy considerations
Following are the considerations for the Automatic Port Configuration policy:
• The APC and the PG policies cannot be enabled at the same time.
• You cannot manually map ports with this policy enabled.
Port Grouping policy
The Port Grouping (PG) policy is enabled by default. Use the PG policy to partition the fabric and
host ports within a module into independently operated groups. Use the PG policy in the following
situations:
• When connecting the module to multiple physical or virtual fabrics.
• When you want to isolate specific hosts to specific fabric ports for performance, security, or
other reasons.
How port groups work
Create port groups using the ag --pgcreate command. This command groups external ports
(N_Ports) together as “port groups.” Any internal ports (F_Ports) mapped to the external ports
belonging to a port group will become members of that port group. Port grouping fundamentally
restricts failover of internal ports to the external ports that belong to that group. For this reason an
external ports cannot be member of two port groups. The default PG0 group contains all external
ports that do not belong to any other port groups.
Figure 3 on page 13 shows that.if you have created port groups and then an external port (N_Port)
goes offline, the internal ports (F_Ports) being routed through that port will fail over to any of the
external ports that are part of that port group and are currently active. For example, if external port
4 goes offline then internal ports 7 and 8 are routed through to external port 3 as long as external
port 3 is online because both external ports 3 and 4 belong to the same port group, PG2. If no
active external ports are available, the internal ports are disabled. The internal ports belonging to a
port group do not fail over to external ports belonging to another port group.
12 Dell 8/4Gbps FC SAN Module Administrator’s Guide
53-1001345-01
 Loading...
Loading...