Page 1

› 4, 12, or 16 Universal Isolated Inputs
T/C, RTD, mA, mV, V, Potentiometer and more
› Compact design, optimizing DIN rail space
› Modbus RTU or TCP connection options, for simple
connection to SCADAs and PLCs
› Optional WiFi connectivity, cutting the cost of cabling
› Compact DIN rail mount design
› 4 Digital inputs
› Easy USB programming via your PC:
defineinstruments.com/workbench
General Description
The Zen RTU Mini is a Remote Terminal Unit
made for harsh industrial environments. Each
channel is isolated and EMC hardened. The
universal input is one of the most exible on
the market, making it a breeze to interface to
a wide range of sensors.
The basic Zen RTU Mini unit has four isolated
universal input channels, and comes in a
compact 1.38" (35mm) case. This can be expanded to 12 inputs (2.36" [60mm] case) or
16 inputs (3.35" [85mm] case).
This expanding design enables you to collate
a large number of signals and simply and efciently route them to your PLC or SCADA
system, while optimizing your DIN rail space.
Our free WorkBench conguration soware
is designed to assist and even teach you how
to congure the unit, and provides a range of
easy-to-use presets and exible controls. The
intuitive help panel follows you during setup
and updates automatically with relevant tips,
wiring diagrams, and application examples.
1
Zen RTU Mini
Remote Terminal Unit
Symbol Denitions
CAUTION
Risk of electric shock
Please refer to user manual.
CAUTION
Risk of danger
Please refer to user manual.
Direct current.
Equipment protected throughout by
DOUBLE INSULATION or REINFORCED
INSULATION.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 2

2
CONTENTS
Contents ................................................. 2
Order Codes ............................................ 3
Safety Notices ......................................... 3
1 - Specications ................................... 4
2 - WiFi Operating Modes .................... 5
2.1 - Station Mode .......................... 5
2.2 - Access Point Mode .................. 5
3 - Dimensions & Installation .............. 6
3.1 - Case Dimensions ..................... 6
3.2 - Installation Environment ........ 6
3.3 - Installation Instructions .......... 7
3.4 - EMC Installation Guidelines .... 8
4 - Installing Dene WorkBench .......... 9
5 - Soware Conguration ................ 11
5.1 - Connecting ............................ 11
5.2 - WorkBench Interface
Overview ............................... 12
5.3 - Main Navigation ................... 13
6 - Wiring & LED's ............................... 14
6.1 - Zen RTU Mini Terminals ........ 14
6.2 - Analog Input ......................... 15
6.3 - Serial Port (RS232 / RS485) .. 15
6.4 - Digital Input .......................... 15
6.5 - Power Supply ........................ 17
6.6 - Front Panel & LED's ............... 17
7 - Input Wiring & Specications ....... 18
7.1 - Current Input ........................ 18
7.2 - Voltage Input ........................ 20
7.3 - RTD Input .............................. 22
7.4 - Thermocouple Input ............. 23
7.5 - Digital Pulse .......................... 24
7.6 - Potentiometer Input ............. 25
7.7 - AC Current Sensor ................ 26
7.8 - Attenuator ............................ 26
8 - Connecting To A PLC ..................... 27
8.1 - Zen RTU Mini Registers ......... 27
9 - Maintenance .................................. 29
9.1 - Calibration ............................ 29
9.2 - Troubleshooting ................... 29
A - Appendix A - EMC Test Results .... 30
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 3

ORDER CODES
ZEN–RTU–MINI – –
3
Zen RTU Mini Channel Conguration
Channel Conguration 4
12
16
Comms
EMOD
WIFI
4 universal inputs, standard 1.38" (35mm) case
12 universal inputs, expanded 2.36" (60mm) case
16 universal inputs, expanded 3.35" (85mm) case
Built in RS485/232 only
Built in RS485/232 + Additional Ethernet Modbus/TCP
Built in RS485/232 + Additional WiFi
Comm Port(s)
Accessories
Bridge Key BRIDGE-KEY USB Bridge Key, required for PC programming us-
ing our free WorkBench soware
SAFETY NOTICES
For your safety and the prevention of damage to the Zen RTU Mini and other equipment connected to it, please read complete instructions prior to installation and
operation of the Zen RTU Mini and carefully observe all safety regulations and
instructions. Consult this manual carefully in all cases where hazard symbols are
marked on the Zen RTU Mini.
Use of this instrument in a manner not specied by the manufacturer may compromise the protection provided by the instrument. This instrument should not be used
to directly drive valves, motors, or other actuators, unless equipped with appropriate safeguards.
It is the responsibility of the user to identify potential hazards that may arise in
the event of a fault to unit, and implement safeguards for the prevention of harm
to persons or equipment. The safety of any system incorporating this unit is the
responsibility of the assembler of the system.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 4

4
1
SPECIFICATIONS
Power
Power supply Low Voltage (10–32V DC)
Isolation test voltage 2500V AC 50Hz for
1min to analog inputs
Isolation to digital inputs None
General specications
Linearity & repeatability <±0.1% FSO
Channel separation 125db minimum
RF immunity <±1% eect FSO typical
Noise immunity (CMRR) 160dB tested at
300V RMS 50Hz
Permanent memory (E
writes per input parameter
2
ROM) 100,000
Analog input
Universal isolated analog inputs
Zen RTU Mini4: 4 Input channels
Zen RTU Mini12: 12 Input channels
Zen RTU Mini16: 16 Input channels
See Section 7 for input specications and wiring
Input isolation 2,500V AC 1 minute
between all input channels
Isolation test voltage 1000V DC for 1min
(Analog input to analog input)
Input resolution 16 bits
Accurate to <±0.1% FSO (unless otherwise
stated in Section 7)
Digital input
4 x Digital inputs
Functions Status, up counter, up/down
counter with direction, debounced counter,
frequency, gated frequency
Counter register output 32 bit
Frequency range 0–10,000Hz
Input types NPN, Clean Contact, Voltage
2–30V DC
Threshold 1.2V typical
Debounce counter range 0–100Hz
Isolation Not isolated to power supply
Programming
USB programmable Via 'PC Setup' port
using Bridge Key USB programmer (sold
separately)
Dene WorkBench Free download at:
deneinstruments.com/workbench
Comms
Protocols Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP
Default comm port RS485 / RS232 auto-
select. Selectable baud rate 2400–230000
baud. Format 8 bit, no parity, 1 stop
Optional additional comm (front panel)
Select WiFi or Ethernet Modbus/TCP
Isolation test voltage 1000V DC for 1min
(Comm to analog input, Comm to digital
input)
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 5

5
Environmental conditions
Operating temp –40 to 176°F (–40 to 80°C)
Storage temp –40 to 176°F (–40 to 80°C)
Operating humidity 5–85% RH max,
non-condensing
Compliances
EN-61326-1:2006
EMC Emissions EN 558022-A;
Immunity EN 50082-1; Safety EN 60950
2
WIFI OPERATING MODES
Construction
Casing DIN 35 rail mounting; Material: ABS
inammability V0 (UL94)
Dimensions (H x W x D)
Zen RTU Mini4 = 3.98 x 1.38 x 4.72"
(101 x 35 x 120mm)
Zen RTU Mini12 = 3.98 x 2.36 x 4.72"
(101 x 60 x 120mm)
Zen RTU Mini16 = 3.98 x 3.35 x 4.72"
(101 x 85 x 120mm)
Height with antenna
4.65" (118mm), WiFi model only
2.1 - Station Mode
The most common operating mode for a WiFi enabled Zen RTU Mini is the Station (or Client)
Mode. This mode is used when the unit is required to connect to an access point of an existing
WiFi network as a client.
Depending on the plugin, it can be set up to work with a DHCP server (default setting), or to
have a xed (or Static) IP address. The user must enter the SSID and passphrase of the WiFi
network that it is attempting to connect to.
2.2 - Access Point Mode
Some WorkBench plugins also allow a WiFi enabled Zen RTU Mini to be run as an access point
which is totally independent of any other networks. This can be useful if there are no WiFi
networks available, or if they are not accessible for security reasons.
When running in Access Point Mode, the Zen RTU Mini will function as a DHCP server and can
work with up to 5 Clients. The user can set the SSID, passphrase, and also which WiFi channel
to use.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 6

6
5.75" (146mm)
4.65" (11 8mm)
Mini16: 3.35"
3
DIMENSIONS & INSTALLATION
3.1 - Case Dimensions
Mini4: 1.38"
(35mm)
Mini12: 2.36" (60mm)
Mini16: 3.35" (85mm)
4.72" (120mm)
DIN 35 Rail
4.45" (113 mm)
3.98" (101mm)
(35mm)
Mini4: 1.38"
(85mm)
Mini12: 2.36" (60mm)
3.2 - Installation Environment
The Zen RTU Mini should be installed in a
location that does not exceed the maximum operating temperature, and at a safe
distance from other devices that generate
excessive heat. The installation environment
should provide good air circulation to the
unit.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
The plastic casing and product label may be
cleaned, if required, using a so, damp cloth
and neutral soap product. Caution should
be exercised when cleaning the unit to
avoid water dripping inside, as this will
damage the internal circuits.
Page 7
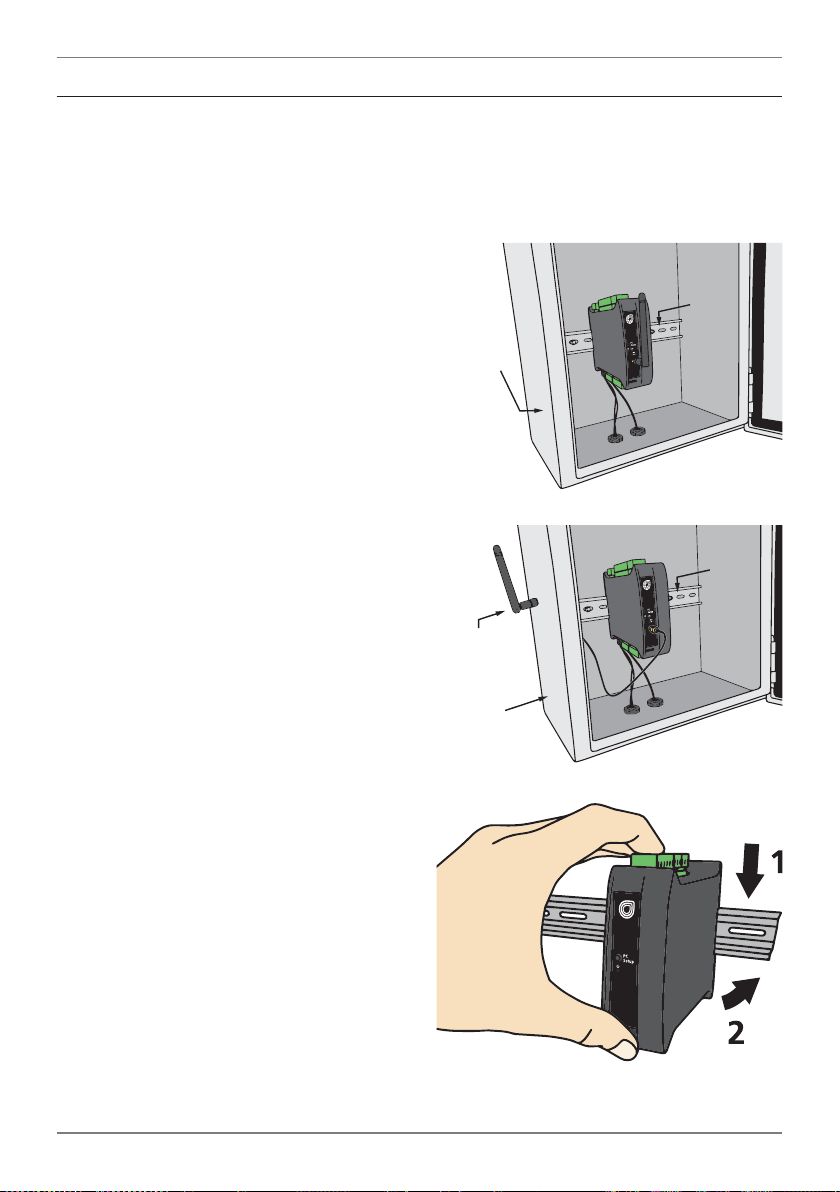
3.3 - Installation Instructions
Antenna mounted
outside enclosure
using antenna
extension cable
The Zen RTU Mini is rated IP20, and should be mounted in a protective enclosure to protect
the unit from weather conditions and dust. If using the Zen RTU Mini with WiFi, the unit must
be located within range of a WiFi network. The maximum distance is 1476 (450m) L.O.S.
A - Plastic Enclosure (Fig 1)
Prepare the Plastic Enclosure (not supplied)
as illustrated by mounting a DIN 35 rail, cable
glands, and any other required components.
If you are using the WiFi model, the antenna
may be mounted directly on the Zen RTU
Mini (inside the Plastic Enclosure).
B - Metal Enclosure (Fig 2)
Prepare the Metal Enclosure (not supplied)
as illustrated by mounting a DIN 35 rail, cable
glands, and any other required components.
This enclosure type should be earthed.
If you are using the WiFi model or a cellular
modem, a Metal Enclosure will impede your
signal strength. In these cases, the antenna
should be installed on the outside of the enclosure using a compatible Antenna Exten-
sion Cable.
C - DIN Rail Mounting (Fig 3)
To clip the unit onto the DIN rail:
(1) Hook the upper part of the unit onto the
rail, and then (2) Press down towards the rail
until the red hook clicks into place.
Leave at least 0.79" (2cm) clear on either
side of the unit, and at least 1.97" (5cm)
clear above and below the unit, to allow
room for airow and wiring.
Plastic
enclosure
Metal
enclosure
35mm
DIN rail
35mm
DIN rail
Fig 1
Fig 2
7
D - Wiring
Refer to Sections 6–7 in this manual.
Fig 3
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 8

8
E - Removal from DIN Rail (Fig 4)
To unclip the unit from the DIN rail, power
the unit down and remove the power
connector.
Then insert a small screwdriver into the slot
on the red hook (just visible when the power
connector is removed), and lever it down.
This will release the hook, allowing the unit
to be detached from the DIN rail.
3.4 - EMC Installation Guidelines
Fig 4
The Zen RTU Mini has been designed to
cope with large EMC disturbances. This
has been achieved by continual testing
and improvement of ltering and layout
techniques.
The Zen RTU Mini meets CE noise requirements, and even surpasses them in many
tests. (For full details and test results, see
Appendix A.) However in some applications
with less than optimum installations and
large power switching, the EMC performance of the unit can be further improved
by:
A Installing the unit in an earthed Metal
Enclosure (as in Fig 2). This is particular-
ly useful if the control box is mounted
close to large power switching devices
like contactors. Every switching cycle
there is a possibility of generating a
large amount of near eld radiated
noise. The Metal Enclosure, acting as
a faraday cage, will shunt this radiation
to ground and away from the unit.
B Increasing the physical distance from
the power devices. For example, increasing the control box distance from
6" to 12" from the noise source will reduce the noise seen by the control box
by a factor of 4. (Probably the cheapest
and best results in this situation could
be obtained by adding RC snubbers to
the contactors or power switches.)
C Using shielded cable on sensitive input
and control signal lines. Good results
can be obtained by grounding the
shields to the metal enclosure close to
the entry point. All cables act as aerials and pick up unwanted R.F. radiated
signals and noise; the earthed shield
acts as a faraday cage around the cables, shunting the unwanted energy to
ground.
Shields can also help with capacitively
coupled noise typically found in circumstances when signal cable is laid on top
of noisy switching power cables. Of
course in this case you are better o to
keep separate signal and power lines.
D Laying cable on earthed cable trays can
also help reduce noise seen by the Zen
RTU Mini. This is particularly useful if
there are long cable runs, or the unit is
close to radiating sources such as two
way radios.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 9

9
4
Dene WorkBench oers a comprehensive and yet simple-to-use setup tool for your Zen RTU
Mini, complete with data log extraction and visualization.
You must install WorkBench before connecting the Zen RTU Mini to your computer. If you
have already connected using the Bridge Key, please disconnect before continuing.
A Download the latest version of WorkBench from
www.deneinstruments.com/workbench
B Extract the install le from the zip folder. Right-click on the zip folder and choose
'Extract All', (or extract the le using another extraction utility of your choice).
INSTALLING DEFINE WORKBENCH
C Double-click on the extracted .msi
install le. This will launch the
WorkBench installer.
Depending on your security settings,
a 'Security Warning' dialog may
appear. If you see the security
message, click 'Run'.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 10
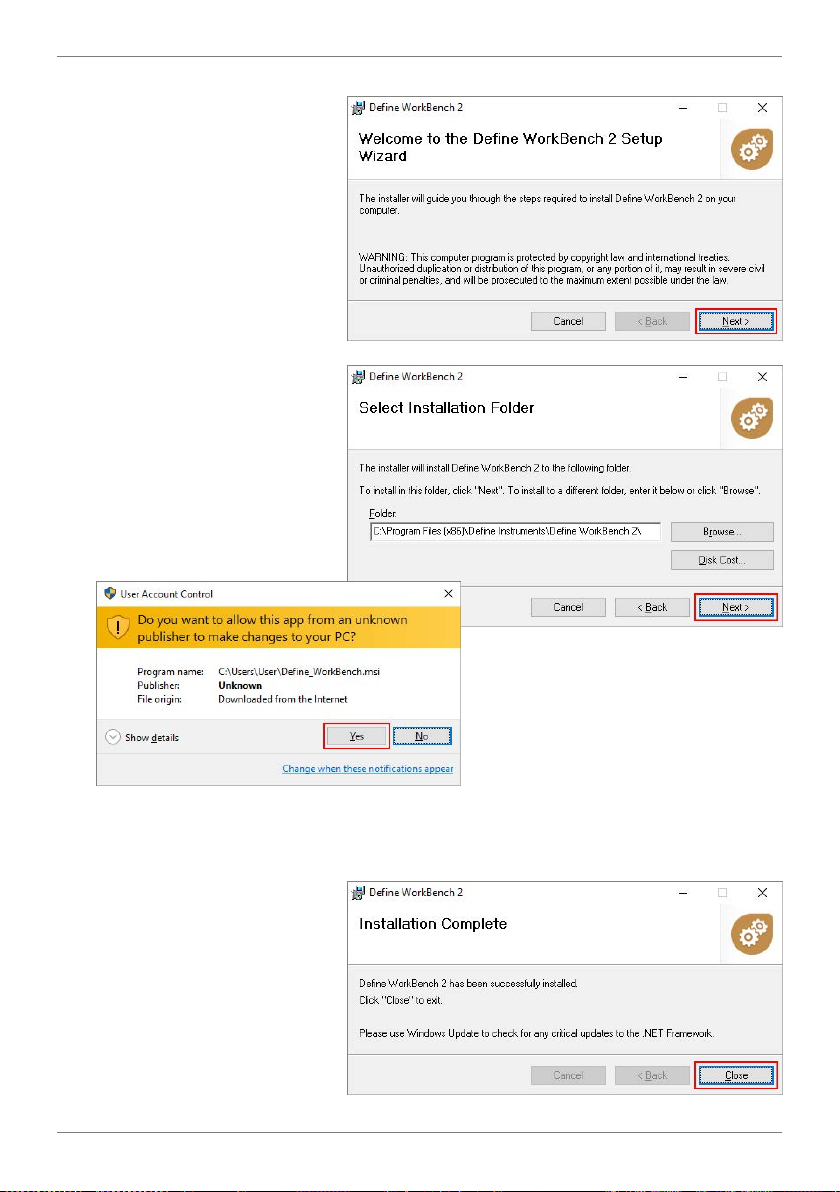
10
D The WorkBench setup
wizard will launch.
Click 'Next' to get started.
E The wizard will also ask for
conrmation that you wish
to begin the installation.
Click 'Next' to continue.
F The wizard will then prompt
you to select an installation
folder.
You may accept the default
installation folder, or select
an alternative location by
clicking 'Browse'.
Click 'Next' to continue.
G Depending on your security
settings, the 'User Account
Control' dialog may appear.
If it does, simply click 'Yes ' to allow the program to be installed
on your computer.
H The install wizard will now install Dene WorkBench. Please wait. This process usually
takes 2–3 minutes, but may take longer in some situations.
I When the installation has
successfully completed, the
following dialog will appear.
Click 'Close' to exit.
The installer will place an
icon on your desktop for
easy access to WorkBench.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 11

11
5
SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION
5.1 - Connecting
Connect the Bridge Key
To program your Zen RTU Mini, connect
one end of the Interface Cable to the 'PC
Setup' port on the unit's front panel, and
the other end to your Bridge Key.
Then plug the Bridge Key into your computer's USB port (see Fig 5).
Supply Power
Supply power to the Zen RTU Mini, referring
to 6.1 for wiring.
Connect to your Zen RTU Mini
in Dene WorkBench
Launch Dene WorkBench (see Section 4
for installation instructions), and select the
'Prog Port' tab.
If your Zen RTU Mini is powered up and connected via the Bridge Key, then the COM
Port will be detected automatically. Click
'Connect'.
Fig 5
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 12
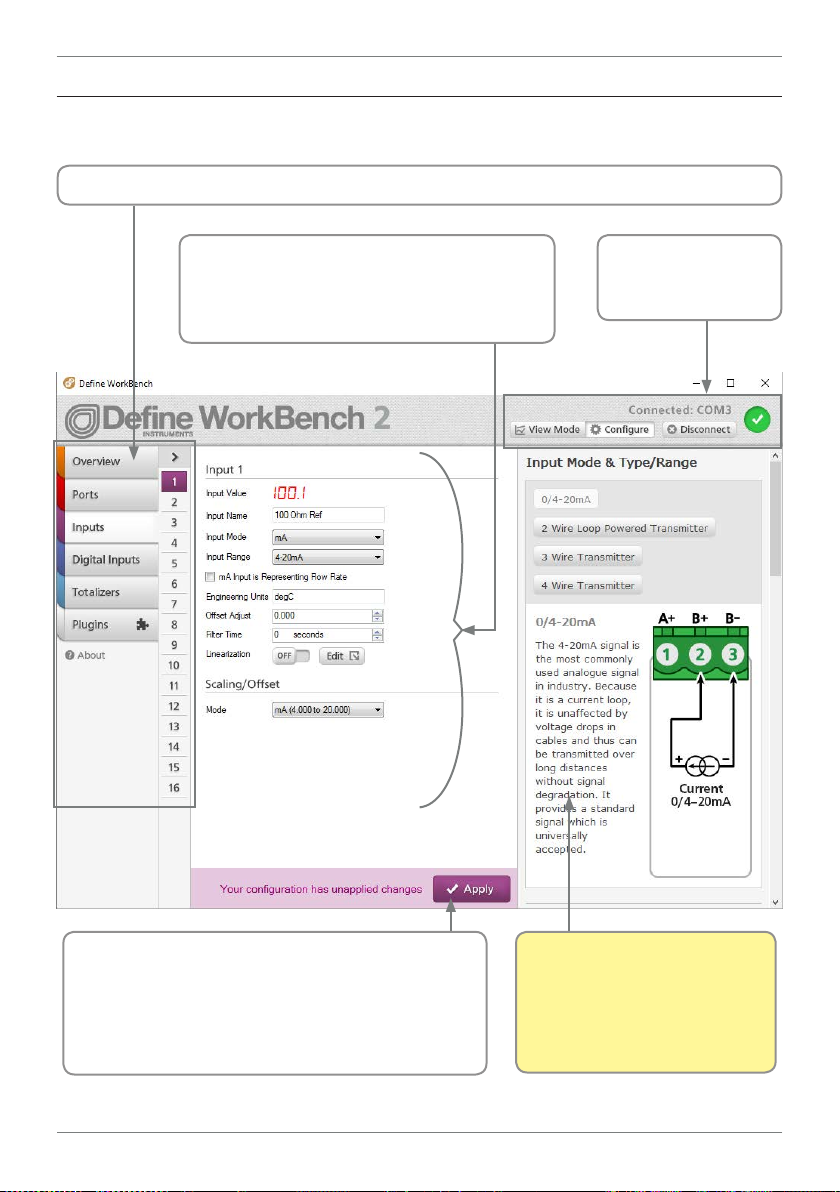
12
5.2 - WorkBench Interface Overview
Main Navigation, including channel sub-navigation. See 5.3 for more information.
Control Area
Main control area for conguring your
system. Any changes made in this area will
bring up the Apply Button (see below)
Connection Panel
Disconnect button
Connection status
Apply Button
Appears if you have made any changes in the
Control Area. WorkBench will not allow you to
browse to a new tab in the Main Navigation with
unapplied changes to your conguration.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Help Panel
Wiring diagrams, explanations
and helpful tips will automatically appear in this panel as
you congure the unit.
Page 13

5.3 - Main Navigation
13
Overview
View basic device information including Serial Number and rmware version. Password
protect, export a conguration certicate,
and save/upload conguration settings.
Ports
This tab is only visible if you are connected to
your Zen RTU Mini via the USB Programming
Port. It enables you to congure a range of
settings for the default RS232 / RS485 port.
Inputs
Set up and scale the universal isolated input
channels. Includes integrated wiring diagrams and examples.
Digital Inputs
Set up the four digital inputs and view their
live status.
Totalizers
Congure up to 10 totalizers using either an
input channel or a digital input as the source.
Plugins
Plugins are small programs which are loaded
into the Zen RTU Mini to expand its functionality or simplify its use. Available plugins
include:
Ĝ WiFi (requires WiFi hardware)
Enables your Zen RTU Mini to wirelessly
connect to a LAN or the internet
via a local WiFi network, allowing
it to become a Modbus TCP server
for configuration or data viewing
applications.
Ĝ Ethernet (requires Ethernet hardware)
This plugin enables your Zen RTU Mini
to connect to a LAN or the internet via
wired Ethernet connection, allowing
it to become a Modbus TCP server
for configuration or data viewing
applications.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 14

14
6
WIRING & LED'S
6.1 - Zen RTU Mini Terminals
Upper Terminals
Lower Terminals
Zen RTU Mini16
(Channels 13−16)
Zen RTU Mini12
(Channels 5−12)
Zen RTU Mini4
(Channels 1−4)
Zen RTU Mini4
(Channels 1−4)
Zen RTU Mini12
(Channels 5−12)
Zen RTU Mini16
(Channels 13−16)
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 15

15
6.2 - Analog Input See 6.1A (also 6.1E–G for Zen RTU Mini12/16)
The four primary analog input channels (included for all Zen RTU Mini models) are shown in
6.1A. For Zen RTU Mini models with expanded input channels, please also refer to 6.1E (for
channels 5–8), 6.1F (for channels 9–12), and 6.1G (for channels 13–16).
All input terminals are universal and can be wired for a range of input types, as detailed in
Section 7. Please also refer to the product label for input terminal pinouts.
6.3 - Serial Port (RS232 / RS485) See 6.1B
The auto-detecting serial terminal on
the top side of the unit can be wired for
either RS232 or RS485, as shown.
RX
NC
COM
NC
TX
NC
NC
TX+
TX–
COM
RS232
RS485
NOTE
Pins marked 'NC' MUST be le disconnected to ensure correct auto-detection of
your comm type.
6.4 - Digital Input
See 6.1C
The Zen RTU Mini has four Digital Inputs (A–D) which can be
congured and scaled using Dene WorkBench from the "Digi-
tal Inputs" tab, as per the list below:
› Status (active/inactive - can be read by a SCADA system as
a general digital input)
› Counter (up to 10KHz, or 100Hz Debounced)
› Frequency (up to 10KHz)
› Flow count (up to 10KHz)
› Flow rate (up to 10KHz)
› RPM (up to 10KHz)
External
+24V
Supply
COM
D A
3 Wire Proximity
Transducer,
Paddle Wheel etc.
Output
Selected
digital
input
channel
D D
D B
D C
+5V
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 16

16
30
29
28
27
26
Reed Switch or
Relay Contact
COM
D A
D B
D C
Selected digital
input channel
D D
+5V
Open Collector O/P
Selected digital
input channel
COM
D A
D D
D B
D C
+5V
Digital Output
(5–30V DC)
COM
D A
D B
NOTE
The Digital Inputs can be congured in soware to be either Sinking (active low
input) or Sourcing (active high input). The diagrams in this manual are for Sinking
wiring, which is the default conguration. To view Sourcing wiring, please refer to
the help information provided in Dene WorkBench.
Connection example for digital inputs (A–D)
Reed Switch or
Relay Contact
3-wire Proximity
Transducer,
Paddle Wheel etc.
–
OP
+
Com
A
B
Selected digital
input channel
D D
D C
+5V
Digital Output
5-30V DC
Open
Collector
–
+
+
–
+
–
C
D
+24V Supply
Note 1 All cables must be screened, with screen earthed at one end only.
NOTE
The universal analog inputs can also be wired as digital pulse inputs (see 7.5).
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 17

6.5 - Power Supply
See 6.1D
Wire your power supply for 10–32V DC supply, as shown.
(If the supply voltage is less than 10V at power up, the power LED (see
6.6B) will ash very quickly every 2–3 seconds until the supply voltage
reaches an acceptable level.)
CAUTION
Low voltage (10–32V DC) only. Higher voltages will damage the
Zen RTU Mini.
6.6 - Front Panel & LED's
A - Programming port
See 5.1
B - Additional comm port and LED status area
17
10–32V DC
EMOD
LED
Description
Flashing between Green & Red= Normal operation.
Red for 2–3 seconds following power up= Unit is booting up
and checking for errors.
Intermittent rapid ashing Red= Supply voltage is too low.
Red continually= Error (contact your distributor).
Flashing= Data is being transmitted, or a connection is being
established.
Link LED's indicate the status of the wireless link.
Green O, Red On= Not connected (idle).
Green/Red Toggling= Trying to connect in Station Mode.
Green/Red Flashing= Trying to connect in Access Point Mode.
Green On, Red O= Station Connected.
Green On, Red On= Access Point Connected.
Note: See Section 2 for more information on WiFi operating modes.
WIFI
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 18

18
7
INPUT WIRING & SPECIFICATIONS
CAUTION
Risk of electric shock. Dangerous and lethal voltages may be present on the input termi-
nals. Please take appropriate precautions to ensure safety.
CAUTION
Risk of danger. The sensor input can potentially oat to dangerous and unexpected volt-
ages depending on what external circuit it is connected to. Appropriate considerations
must be given to the potential of the sensor input with respect to earth common.
7.1 - Current Input
Range 0–20mA, 4–20mA
Input impedance 45Ω
Maximum over-range protected by PTC
to 24V DC
Accuracy 0.1% FSO max
0/4–20mA DC is the most commonly used analog signal in industry, and is universally accepted.
As a current loop, it is unaected by voltage drops in cables, and can be transmitted over long
distances without signal degradation.
Linearity & repeatability 0.1% FSO max
Channel separation 0.001% max
Ambient dri 0.003%/°C FSO typical
RF immunity 1% eect FSO typical
Output
Output
External
+24V
Current
0/4–20mA
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Supply
2 Wire Loop
Powered
Transmitter
4–20mA
Output
External
+24V
Supply
3 Wire
Transmitter
0/4–20mA
+24V Supply
4 Wire
Transmitter
0/4–20mA
Output
External
Page 19

Connection example for 2, 3 & 4 wire mA output transmitters
+24V Supply
2-Wire
Transmitter
B+
B–
19
Input
Channel
Output +
Output −
Output +
Output −
Power
Supply
3-Wire
Transmitter
4-Wire
Transmitter
Note 1 All analog inputs are isolated to
other channels and all other voltages.
They also have built in over voltage protection to 24V, protecting the unit if the
24V supply is inadvertently connected to
the unit when congured for mA input.
Note 2 All cables must be screened, with
screen earthed at one end only.
B+
Input
Channel
B–
B+
Input
Channel
B–
Note 3 Do not run input cables in close
vicinity to noisy power supplies, contactors or motor cables. The best practice is
to run input cables on a separate earthed
cable tray. This will minimize RFI eects,
of which magnitude cannot be easily
predicted.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 20

20
7.2 - Voltage Input
Ranges ±200mV, –200mV to 1V,
0–10V, 0–18V
Input impedance >500KΩ on all ranges
Maximum over-voltage 24V DC
Linearity & repeatability 0.1% FSO max
Channel separation 0.001% max
Ambient dri 0.003%/°C FSO typical
RF immunity 1% eect FSO typical
Accuracy 0.1% FSO max
The Zen RTU Mini accepts both voltage and millivolt inputs. Along with the standard 0–10V
DC range, a variety of other ranges are provided to suit a various applications. These can all be
selected using the WorkBench soware and easily scaled into engineering units.
The ±200mV DC and -200mV to 1V DC ranges are ideal for low signal applications, such as
measuring large DC currents using external current shunts, or interfacing to sensors with low
voltage output. A 0–18V general purpose voltage range is also provided.
0–10V, ±200mV
–200mV to 1V,
0–18V DC
Output
External
+24V Supply
2 Wire
Transmitter
0–10V DC
Output
Output
External
+24V
Supply
3 Wire
Transmitter
0–10V DC
Output
External
+24V Supply
4 Wire
Transmitter
0–10V DC
Output
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 21

Connection Example for Millivolt & Voltage Inputs for 2, 3 & 4 Wire
Transmitters
+24V Supply
2-Wire
Transmitter
B+
B–
21
Input
Channel
Output +
Output −
Output +
Output −
Power
Supply
3-Wire
Transmitter
4-Wire
Transmitter
Note 1 Each voltage input must not see
more than 18V peak between the negative and the input, otherwise permanent
damage may occur.
Note 2 All cables must be screened, with
screen earthed at one end only.
B+
Input
Channel
B–
B+
Input
Channel
B–
Note 3 Do not run input cables in close
vicinity to noisy power supplies, contactors or motor cables. The best practice is
to run input cables on a separate earthed
cable tray. This will minimize RFI eects,
of which magnitude cannot be easily
predicted.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 22

22
3-Wire
Field RTD
3-Wire
Field RTD
3-Wire
Field RTD
7.3 - RTD Input
RTD Pt100 3 wire RTD DIN 43760: 1980
RTD Pt1000 3 wire RTD standard
Resolution
-328–572°F (-200–300°C) = 0.02°F (0.01°C)
-328–1472°F (-200–800°C) = 0.1°F (0.1°C)
Lead resistance 10Ω/lead max
Sensor current 0.6mA continuous
Sensor fail upscale
Accuracy
-328–572°F (-200–300°C) = ±0.1°C
-328–1472°F (-200–800°C) = ±0.3°C
Ambient dri 0.003°C/°C typical
recommended
The RTD (standing for Resistance Temperature Device) is highly stable
and accurate, and is fast becoming the most popular temperature
sensor in industry. Oen referred to as Pt100 and Pt1000, the Pt represents platinum (the dominant metal in its construction), and 100/1000
is the resistance in ohms at 0°C.
Supported RTD types/ranges
Pt100/Pt1000 (0.02°F/0.01°C res) -328 to 572°F (-200 to 300°C)
Pt100/Pt1000 (0.1°F/0.1°C res) -328 to 1472°F (-200 to 800°C)
Note 1 All RTD inputs are isolated from
each other.
Note 2 All RTD cables must be screened,
with screen earthed at one end only. All
three wires must be the same resistance
(i.e. the same type and size).
Note 3 To minimize lead resistance errors,
3-wire RTD’s should be used. Oset errors
for 2-wire RTD’s may be compensated for
in the soware.
Note 4 Do not run input cables in close
vicinity to noisy power supplies, contactors or motor cables. The best practice is
to run input cables on a separate earthed
cable tray. This will minimize RFI eects,
of which magnitude cannot be easily
predicted.
Connection Example for 3-Wire RTD
Inputs
A
Input
B
Channel
B
A
Input
B
Channel
B
A
Input
B
Channel
B
RTD 3 Wire
Pt100/1000
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 23

7.4 - Thermocouple Input
T/C
T/C
T/C
23
Thermocouple types B, E, J, K, N, R, S or
T type (see table below for ranges)
Cold junction compensation 14 to 140°F
(–10 to 60°C)
CJC dri <0.02°C/°C typical for all inputs
The thermocouple
is one of the most
common temperature sensors used in
industry. It relies on
the Seebeck coecient
between dissimilar
metals. The thermocouple type is selected
with reference to the
application temperature range and environment, with J and K
type being the most common.
Connection Example for
Thermocouple Inputs
B+
B–
B+
B–
B+
B–
Note 1 All thermocouple inputs are isolated from each other. There is no need to
buy expensive isolated thermocouples.
Thermocouple
Input
Channel
Input
Channel
Input
Channel
Sensor open Upscale
TC lead resistance 100Ω max
Input impedance >500KΩ
Accuracy 0.1% of FSO ±1°C typical
Supported thermocouple types/ranges
B 32 to 3272°F (0 to 1800°C)
E -328 to 1292°F (-200 to 700°C)
J -328 to 1832°F (-200 to 1000°C)
K -328 to 2300°F (-200 to 1260°C)
N -328 to 2372°F (-200 to 1300°C)
R 32 to 3092°F (0 to 1700°C)
S 32 to 3092°F (0 to 1700°C)
T -328 to 752°F (-200 to 400°C)
Note 2 For accurate thermocouple mea-
surements (especially at low temperatures) the top cover must always be tted.
Avoid dras and temperature dierences
across terminals. Once installation is complete, close the cabinet door and allow
the cabinet to reach equilibrium. This may
take several hours. Place all thermocouple
probes into a calibrated thermal bath at
temperature of interest. Any osets can
be zeroed out in the soware.
Note 3 All thermocouples are referenced
to a combination of four CJC temperature sensors on the main Zen board. This
minimizes errors caused by the mounting
orientation of the Zen unit, and temperature dierences in enclosures. However,
for high accuracy applications it is still
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 24

24
recommended to zero errors (see Note 2).
Note 4 All cables must be screened, with
screen earthed at one end only.
Note 5 When thermocouple inputs are selected, an upscale resistor is automatically
connected to the T/C + input, resulting in
an overow condition for open or broken
sensors.
7.5 - Digital Pulse
Frequency range 0–2500.0Hz
Fast counter range 0–2500.0Hz
Sensors Open collector (NPN, PNP), TTL
or Clean Contact
The Zen RTU Mini's universal input terminals
accept digital inputs from NPN, PNP or TTL
sensors as well as Clean Contacts. Pulses up
to 2.5kHz can be counted (except for the
debounced counter, which has a range of
0–50Hz).
A variety of operating modes are soware
programmable to suit your application.
Note 4 Do not run input cables in close
vicinity to noisy power supplies, contactors or motor cables. The best practice is
to run input cables on a separate earthed
cable tray. This will minimize RFI eects,
of which magnitude cannot be easily
predicted.
Frequency resolution 0.1Hz
Debounce counter range 0–50Hz max
Counter register output 32 bit
Accuracy ±0.5%
Soware programmable modes include:
› General counter
› General debounced counter (ideal for
mechanical relay contacts which are
subject to bouncing)
› General frequency
› Flow count (uses K-factor)
› Flow rate (uses K-factor)
› RPM (uses pulses per revolution)
NPN Open
Collector
Output
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
PNP Open
Collector
Output
TTL Input
Reed Switch or
Relay Contact
Page 25

25
NPN
Collector
Reed Switch
or
Contact
PNP
Collector
TTL
(0-5V max)
Connection Example for
Digital Pulse Inputs
A+
Relay
Input
Channel
B–
A+
Open
Input
Channel
B–
A+
Open
Input
Channel
B–
Input
5V
0
Input
Channel
A+
B–
7.6 - Potentiometer Input
Potentiometer input 3-wire
Excitation voltage Variable
Potentiometer resistance <2kΩ low pot;
>2kΩ high pot
Field prog zero 0–90% of span
Note 1 All digital inputs are isolated from
each other. Inputs from various sources
can be connected without fear of crating unwanted and troublesome ground
loops.
Note 2 Soware selectable functions
include: frequency to 2kHz, debounced
counter for contact closures to 100Hz
maximum, fast counter to 20KHz.
Note 3 All cables must be screened, with
screen earthed at one end only.
Note 4 Do not run input cables in close
vicinity to noisy power supplies, contactors or motor cables. The best practice is
to run input cables on a separate earthed
cable tray. This will minimize RFI eects,
of which magnitude cannot be easily
predicted.
Field prog span 0.1–100%
Linearity and repeatability
<±0.05% FSO typical
Response time 100msec
Temperature dri <50ppm/°C
A 3 wire potentiometer is typically used to measure position. A low or
high potentiometer range can be programmed to your unit using the
WorkBench soware.
These ranges must be calibrated using the two point calibration method.
Potentiometer
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 26

26
ACCS Jump Ranges
200A
010/420:
420-L:
7.7 - AC Current Sensor
Sensor type Current transformer
ACCS-420, ACCS-420-L and ACCS-010
Header selectable amperage range
ACCS-420/010 = 100/150/200A
ACCS-420-L = 10/20/50A
Output (Representing 0–100% of full scale
input range)
ACCS-420(-L) = 4–20mA DC loop powered
ACCS-010 = 0–10V DC
Isolation voltage 2,000V
Power supply
ACCS-420(-L) = Loop powered, 15–36V DC
ACCS-010 = Self powered
Overload (continuous)
ACCS-420/010 = 175/300/400A respectively
ACCS-420-L = 80/120/200A respectively
Accuracy 1% of full scale
Response time 250ms (10–90%)
Frequency 50–60Hz
The Zen RTU Mini accepts input from a Dene
Instruments AC current sensor.
Set the jumper on the top of the current sensor to
the desired current range, as shown below.
0–100A
0–10A
0–150A
0–20A
0–
0–50A
AC
Current
Sensor
External
AC Current
Sensor
4–20mA
24V DC
Supply
AC Current
Sensor
AC Current
Sensor
0–10V
7.8 - Attenuator
Max input voltage 1000V DC
Attenuation factor 1000
±0.1%
Input impedance 3.8MΩ
This unit accepts input from a high voltage attenuator (HVA-1000).
Wire the attenuator as shown.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Output impedance 3.8kΩ
Attenuator type Dierential
resistive
Ambient dri 50ppm/°C max
In
Attenuator
Out
0–100.00V or
0–1000.0V
Page 27

27
8
CONNECTING TO A PLC
8.1 - Zen RTU Mini Registers
Below is a list of the commonly used Zen RTU Mini registers, displayed rst in Modicon addressing format, and then as a direct address (brackets).
For a full register list, please see the Zen Registers document, available at:
deneinstruments.com/zen-registers
Analog inputs 32 bit signed registers
Ch1= 40645 (644) / 40646 (645) Ch9= 40661 (660) / 40662 (661)
Ch2= 40647 (646) / 40648 (647) Ch10= 40663 (662) / 40664 (663)
Ch3= 40649 (648) / 40650 (649) Ch11= 40665 (664) / 40666 (665)
Ch4= 40651 (650) / 40652 (651) Ch12= 40667 (666) / 40668 (667)
Ch5= 40653 (652) / 40654 (653) Ch13= 40669 (668) / 40670 (669)
Ch6= 40655 (654) / 40656 (655) Ch14= 40671 (670) / 40672 (671)
Ch7= 40657 (656) / 40658 (657) Ch15= 40673 (672) / 40674 (673)
Ch8= 40659 (658) / 40660 (659) Ch16= 40675 (674) / 40676 (675)
Analog inputs 32 bit oating point
Ch1= 41193 (1192) / 41194 (1193) Ch9= 41209 (1208) / 41210 (1209)
Ch2= 41195 (1194) / 41196 (1195) Ch10= 41211 (1210) / 41212 (1211)
Ch3= 41197 (1196) / 41198 (1197) Ch11= 41213 (1212) / 41214 (1213)
Ch4= 41199 (1198) / 41200 (1199) Ch12= 41215 (1214) / 41216 (1215)
Ch5= 41201 (1200) / 41202 (1201) Ch13= 41217 (1216) / 41218 (1217)
Ch6= 41203 (1202) / 41204 (1203) Ch14= 41219 (1218) / 41220 (1219)
Ch7= 41205 (1204) / 41206 (1205) Ch15= 41221 (1220) / 41222 (1221)
Ch8= 41207 (1206) / 41208 (1207) Ch16= 41223 (1222) / 41224 (1223)
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 28

28
Counter/frequency inputs 32 bit signed integers
Counter1= 40525 (524) / 40526 (525) Counter3= 40529 (528) / 40530 (529)
Counter2= 40527 (526) / 40528 (527) Counter4= 40531 (530) / 40532 (531)
Totalizers 32 bit signed integers
Total1= 40289 (288) / 40290 (289) Total6= 40299 (298) / 40300 (299)
Total2= 40291 (290) / 40292 (291) Total7= 40301 (300) / 40302 (301)
Total3= 40293 (292) / 40294 (293) Total8= 40303 (302) / 40304 (303)
Total4= 40295 (294) / 40296 (295) Total9= 40305 (304) / 40306 (305)
Total5= 40297 (296) / 40298 (297) Total10= 40307 (306) / 40308 (307)
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 29

29
9
MAINTENANCE
9.1 - Calibration
Your Zen RTU Mini has been fully calibrated at the factory, and can be recalibrated in soware
using Dene WorkBench (see Section 5). Scaling to convert the input signal to a desired display value is also done using WorkBench
If your Zen RTU Mini appears to be behaving incorrectly or inaccurately, refer to troubleshooting before attempting to calibrate it. When recalibration is required (generally every 2 years),
it should only be performed by qualied technicians using appropriate equipment.
Calibration does not change any user programmed parameters. However, it may aect the
accuracy of the input signal values previously stored.
9.2 - Troubleshooting
Issue Resolution
Auto-detecting RS Port is
not working
Power LED stays red
continuously
Cannot power up unit Check the power supply connections and supply range. (The
Ethernet device does not
appear on the network
when trying to connect in
WorkBench
Ensure that any terminal connections marked 'NC' are le
open - otherwise the Zen RTU Mini will not be able to autodetect your serial type.
Indicates an internal error which will need to be assessed
by the manufacturer. Please return the Zen RTU Mini to the
manufacturer for analysis and repair.
polarity on the power input is irrelevant.)
Repower the device aer you plug in the ethernet cable to
ensure that it appears on the network.
For further assistance, please contact technical support using the contact details listed at the
end of this document.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 30

30
A
APPENDIX A - EMC TEST RESULTS
Statement of Compliance
Products in the Dene Instruments 'Zen' series comply with EN 61326-1:2006.
Results Summary
The results from testing carried out in March 2014 are summarized in the following tables.
Immunity - Enclosure Ports
Phenomenon Basic Standard Test Value Performance Criteria
EM Field IEC 61000-4-3 10Vm (80MHz to 1GHz)
Electrostatic
Discharge (ESD)
IEC 61000-4-2 4kV/8kV contact/air Meets Criterion A (Note 1)
3V/m (1.4–2.7GHz)
Immunity - Signal Ports
Phenomenon Basic Standard Test Value Performance Criteria
Conducted RF IEC 61000-4-6 3V (150kHz to 80MHz) Meets Criterion A
Burst IEC 61000-4-4 1kV (5/50ns, 5kHz)
Surge IEC 61000-4-5 1kV L-E Meets Criterion A (Note 1)
1kV (5/50ns, 100kHz)
Meets Criterion A
Meets NAMUR NE 21
recommendation
Meets Criterion A (Note 1)
Meets NAMUR NE 21
recommendation
Immunity - AC Power
Phenomenon Basic Standard Test Value Performance Criteria
Conducted RF IEC 61000-4-6 3V(150Khz to 80Mhz) Meets Criterion A
Burst IEC 61000-4-4 2kV (5/50ns, 5kHz) L-N
1kV (5/50ns, 5kHz) L-L
Surge IEC 61000-4-5 2kV L-E
1KV L-L
Voltage Dips IEC 61000-4-11 0% during 1 cycle
40% during 10/12 cycles
70% during 25/30 cycles
Short Interruptions IEC 61000-4-11 0% during 250/300 cycles Meets Criterion A (Note 1)
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Meets Criterion A
Meets Criterion A
Meets Criterion A
Meets Criterion A (Note 1)
Meets Criterion A
Meets Criterion A
Meets Criterion A
Page 31

31
Performance Criteria
Performance Criterion A
During the test, normal performance within the specication limits.
Performance Criterion B
During testing, temporary degradation, or loss of performance or function which is
self-recovering.
Performance Criterion C
During testing, temporary degradation, or loss of function or performance which requires
operator intervention or system reset occurs.
*Note 1: EN61326-1 calls for a Criterion B pass; unit exceeds this by meeting Criterion A.
ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 (0202) Copyright © 2017 Dene Instruments
Page 32

De ne Instruments
New Zealand
(Head O ce)
Auckland 0632, New Zealand
Auckland 0661, New Zealand
Ph
Fax
www.de neinstruments.co.nz
10B Vega Place, Rosedale,
PO Box 245 Westpark Village,
: +64 (9) 835 1550
: +64 (9) 835 1250
sales@de neinstruments.co.nz
Zen RTU Mini Document Revision Code: ZEN-RTU-MINI-MAN-17V01 Date Code: 170202
United States (Dallas, TX)
Ph: (214) 926 4950
sales@de neinstruments.com
www.de neinstruments.com
South Africa (Pretoria)
sales@de neinstruments.co.za
www.de neinstruments.co.za
 Loading...
Loading...