Page 1

UM-19985-E
DT9834 Series
User’s Manual
Page 2

Fifth Edition
March, 2006
Copyright © 2004-2006 by Data Translation,
Inc.
All rights reserved.
Information furnished by Data Translation, Inc.
is believed to be accurate and reliable; however,
no responsibility is assumed by Data Translation,
Inc. for its use; nor for any infringements of
patents or other rights of third parties which
may result from its use. No license is granted by
implication or otherwise under any patent rights
of Data Translation, Inc.
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United
States Government is subject to restrictions as set
forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in
Technical Data and Computer software clause at
48 C.F.R, 252.227-7013, or in subparagraph (c)(2)
of the Commercial computer Software Registered Rights clause at 48 C.F.R., 52-227-19 as
applicable. Data Translation, Inc., 100 Locke
Drive, Marlboro, MA 01752
Data Translation, Inc.
100 Locke Drive
Marlboro, MA 01752-1192
(508) 481-3700
www.datatranslation.com
Fax: (508) 481-8620
E-mail: info@datx.com
Data Translation® is a registered trademark of
Data Translation, Inc. DT-Open Layers
DataAcq SDK
TM
Link
, DTx-EZTM, and DT VPITM are trademarks
TM
, DataAcq OMNI CDTM, DT-LV
TM
,
of Data Translation, Inc.
All other brand and product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
Page 3

Radio and Television Interference
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with CISPR
EN55022 Class A, and EN50082-1 (CE) requirements and also with
the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in
a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case
the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
Changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved
by Data Translation could void your authority to operate the
equipment under Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Note: This product was verified to meet FCC requirements under
test conditions that included use of shielded cables and connectors
between system components. It is important that you use shielded
cables and connectors to reduce the possibility of causing
interference to radio, television, and other electronic devices.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio
noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the Radio
Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques
dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de la class
A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique
édicté par le Ministère des Communications du Canada.
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
About this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Intended Audience. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How this Manual is Organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Conventions Used in this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Related Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Where To Get Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Chapter 1: Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
DT9834 Hardware Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Supported Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chapter 2: Principles of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Analog Input Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Input Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Analog Input Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Specifying a Single Analog Input Channel . . . . . . . . . . 27
Specifying One or More Analog Input Channels . . . . . 27
Specifying the Digital Input Port in the Analog Input
Channel-Gain List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Specifying Counter/Timers in the Analog Input
Channel-Gain List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Performing Dynamic Digital Output Operations . . . . 32
Input Ranges and Gains. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Specifying the Gain for a Single Channel . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Specifying the Gain for One or More Channels . . . . . . 34
Input Sample Clock Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Analog Input Conversion Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5
Page 6

Contents
Continuous Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Triggered Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Internally Retriggered Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Externally Retriggered Scan Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Input Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Data Format and Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Analog Output Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Output Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Analog Output Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Specifying a Single Analog Output Channel . . . . . . . . 45
Specifying Multiple Analog Output Channels and/or the
Digital Output Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Output Ranges and Gains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Output Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Output Clocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Output Conversion Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Continuously Paced Analog Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Waveform Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Data Format and Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Digital I/O Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Digital I/O Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Operation Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Counter/Timer Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
C/T Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
C/T Clock Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Gate Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Pulse Output Types and Duty Cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Counter/Timer Operation Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
6
Page 7

Event Counting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Up/Down Counting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Frequency Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Edge-to-Edge Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Rate Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
One-Shot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Repetitive One-Shot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Chapter 3: Supported Device Driver Capabilities. . . . . . . . 69
Data Flow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Buffering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
DMA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Triggered Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Synchronous Digital I/O. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Clocks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Counter/Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Miscellaneous . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Contents
Chapter 4: Programming Flowcharts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Single-Value Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Continuous A/D Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Continuous D/A Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Continuous Digital Input Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Continuous Digital Output Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Event Counting Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
7
Page 8

Contents
Up/Down Counting Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Frequency Measurement Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Edge-to-Edge Measurement Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Pulse Output Operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Simultaneous Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
General Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
If Your Module Needs Factory Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Chapter 6: Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Using the Calibration Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Calibrating the Analog Input Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Connecting a Precision Voltage Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Using the Auto-Calibration Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Using the Manual Calibration Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Calibrating the Analog Output Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Appendix A: Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Appendix B: Connector Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
OEM Version Connector Pin Assignments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
BNC Connection Box Connector Pin Assignments. . . . . . . . . . 152
Analog Input Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Digital I/O Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Analog Output, Counter/Timer, Clock, and Trigger
Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
STP Connection Box Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Screw Terminal Block TB1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Screw Terminal Block TB2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Screw Terminal Block TB3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8
Page 9

Screw Terminal Block TB4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Screw Terminal Block TB5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Screw Terminal Block TB6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Screw Terminal Block TB7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
EP353 Accessory Panel Connector Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . 168
Connector J1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Connector J2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
EP356 Accessory Panel Connector Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . 172
Connector J1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Connector J2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
EP355 Screw Terminal Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Attached to Connector J2 on the OEM Module . . . . . . . . . 175
Attached to Connector J3 on the OEM Module . . . . . . . . . 175
Contents
9
Page 10

Contents
10
Page 11

This manual describes the features of the DT9834 Series modules, the
capabilities of the DT9834 Series Device Driver, and how to program
the DT9834 Series modules using DT-Open Layers™ software.
Troubleshooting information is also provided.
Note: The DT9834 Series module is available either installed in a
metal BNC connection box, an STP (screw terminal panel)
connection box (for the 32-analog input channel version only), or as
a board-level OEM version that you can install in your own custom
application. If the information in this manual applies to all versions
of the DT9834 Series module, the manual uses the product name
"DT9834 Series module." Otherwise, the specific product name is
mentioned.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for engineers, scientists, technicians, or
others responsible for using and/or programming the DT9834 Series
modules for data acquisition operations in the Microsoft®
Windows® 2000 or Windows XP operating system. It is assumed that
you have some familiarity with data acquisition principles and that
you understand your application.
About this Manual
11
Page 12

About this Manual
How this Manual is Organized
This manual is organized as follows:
• Chapter 1, “Overview,” describes the major features of the
DT9834 Series module, as well as the supported software and
accessories for the modules.
• Chapter 2, “Principles of Operation,” describes all of the features
of the DT9834 Series module and how to use them in your
application.
• Chapter 3, “Supported Device Driver Capabilities,” lists the data
acquisition subsystems and the associated features accessible
using the DT9834 Series Device Driver.
• Chapter 4, “Programming Flowcharts,” describes the processes
you must follow to program the subsystems of the DT9834 Series
module using DT-Open Layers-compliant software.
• Chapter 5, “Troubleshooting,” provides information that you can
use to resolve problems with the DT9834 Series module and
device driver, should they occur.
12
• Chapter 6, “Calibration,” describes how to calibrate the analog
I/O circuitry of the DT9834 Series modules.
• Appendix A, “Specifications,” lists the specifications of the
DT9834 Series module.
• Appendix B, “Connector Pin Assignments,” shows the pin
assignments for the connectors and the screw terminal
assignments for the screw terminals on the DT9834 Series
module.
• An index completes this manual.
Page 13

Conventions Used in this Manual
The following conventions are used in this manual:
• Notes provide useful information or information that requires
special emphasis, cautions provide information to help you avoid
losing data or damaging your equipment, and warnings provide
information to help you avoid catastrophic damage to yourself or
your equipment.
• Items that you select or type are shown in bold.
Related Information
Refer to the following documents for more information on using the
DT9834 Series modules:
• Benefits of the Universal Serial Bus for Data Acquisition. This white
paper describes why USB is an attractive alternative for data
acquisition. It is available on the Data Translation web site
(www.datatranslation.com).
About this Manual
• DT9834 Series Getting Started Manual (UM-19983). This manual,
included on the Data Acquisition OMNI CD™, describes the how
to install the DT9834 Series modules and related software.
• DT Measure Foundry Getting Started Manual (UM-19298) and
online help. These documents describe how to use DT Measure
Foundry™ to build drag-and-drop test and measurement
applications for Data Translation® data acquisition devices
without programming.
• DataAcq SDK User’s Manual (UM-18326). For programmers who
are developing their own application programs using the
Microsoft C compiler, this manual describes how to use the
DT-Open Layers DataAcq SDK™ to access the capabilities of
Data Translation data acquisition devices.
13
Page 14

About this Manual
Where To Get Help
• DTx-EZ Getting Started Manual (UM-15428). This manual
describes how to use the ActiveX controls provided in DTx-EZ™
to access the capabilities of Data Translation data acquisition
devices in Microsoft Visual Basic® or Visual C++®.
• DT-LV Link Getting Started Manual (UM-15790). This manual
describes how to use DT-LV Link™ with the LabVIEW™
graphical programming language to access the capabilities of
Data Translation data acquisition devices.
• DAQ Adaptor for MATLAB (UM-22024). This document describes
how to use Data Translation’s DAQ Adaptor to provide an
interface between the MATLAB Data Acquisition subsystem
from The MathWorks and Data Translation’s DT-Open Layers
architecture.
• Microsoft Windows 2000 or Windows XP documentation.
• USB web site (http://www.usb.org).
14
Should you run into problems installing or using a DT9834 Series
module, the Data Translation Technical Support Department is
available to provide technical assistance. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. If you are outside the United States or Canada, call your
local distributor, whose number is listed on our web site
(www.datatranslation.com).
Page 15

1
Overview
DT9834 Hardware Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Supported Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
15
Page 16

Chapter 1
DT9834 Hardware Features
The DT9834 Series is a family of high-performance, multifunction
data acquisition modules for the USB (Ver. 2.0 or Ver. 1.1) bus. The
key hardware features of the DT9834 Series modules are as follows:
• Available either installed in a metal BNC connection box, STP
connection box (for the 32-analog input channel version only) or
as a board-level OEM version that you can install in your own
custom application.
• Simultaneous operation of analog input, analog output, digital
I/O, and counter/timer subsystems.
• Analog input subsystem:
− 12-bit or 16-bit A/D converter. The resolution depends on the
model you purchase.
− Throughput rate up to 500 kSamples/s.
− Up to 32 single-ended or 16 differential analog input channels.
The channel type and the number of channels provided
depend on the model you purchase. If you do not intend to
perform analog input operations, you can also purchase a
DT9834 Series module that contains no analog input channels.
16
− Programmable gain of 1, 2, 4, or 8 provides input ranges of
±10, ±5, ±2.5, and ±1.25 V.
− 1024-location channel-gain list. You can cycle through the
channel-gain list using continuous scan mode or triggered
scan mode. The maximum sampling rate when using the
channel-gain list is 500 kSamples/s.
• Analog output subsystem:
− Four 12-bit or 16-bit D/A converters. The resolution depends
on the model you purchase. If you do not intend to perform
analog output operations, you can also purchase a DT9834
Series module that contains no D/A converters.
− Output rate up to 500 kSamples/s.
Page 17

− Output range of ±10 V.
Overview
− The DACs are deglitched to prevent noise from interfering
with the output signal.
− Output channel list. You can cycle through the output channel
list using continuous output mode or waveform generation
mode. For waveform generation mode, you can
simultaneously update all four DACs at 500 kS/s per channel;
for continuous output mode, you can simultaneously update
all four DACs at 250 kS/s per channel.
• Digital I/O subsystem:
− One digital input port, consisting of 16 digital input lines. You
can program any of the first eight digital input lines to
perform interrupt-on-change operations. You can read the
value of the digital input port using the analog input
channel-gain list.
− One digital output port, consisting of 16 digital output lines.
You can output the value of the digital output port using the
output channel list.
− An additional dynamic digital output line that changes state
whenever an analog input channel is read.
• Five 32-bit counter/timer (C/T) channels that perform event
counting, up/down counting, frequency measurement,
edge-to-edge measurement, continuous pulse output, one-shot,
and repetitive one-shot operations. You can read the value of one
or more of the C/T channels using the analog input channel-gain
list.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
• External or internal clock source.
• Trigger operations using a software command, an analog
threshold value, or an external digital trigger.
• 500 V galvanic isolation barrier that prevents ground loops to
maximize analog signal integrity and protect your computer.
1
1
17
Page 18
Chapter 1
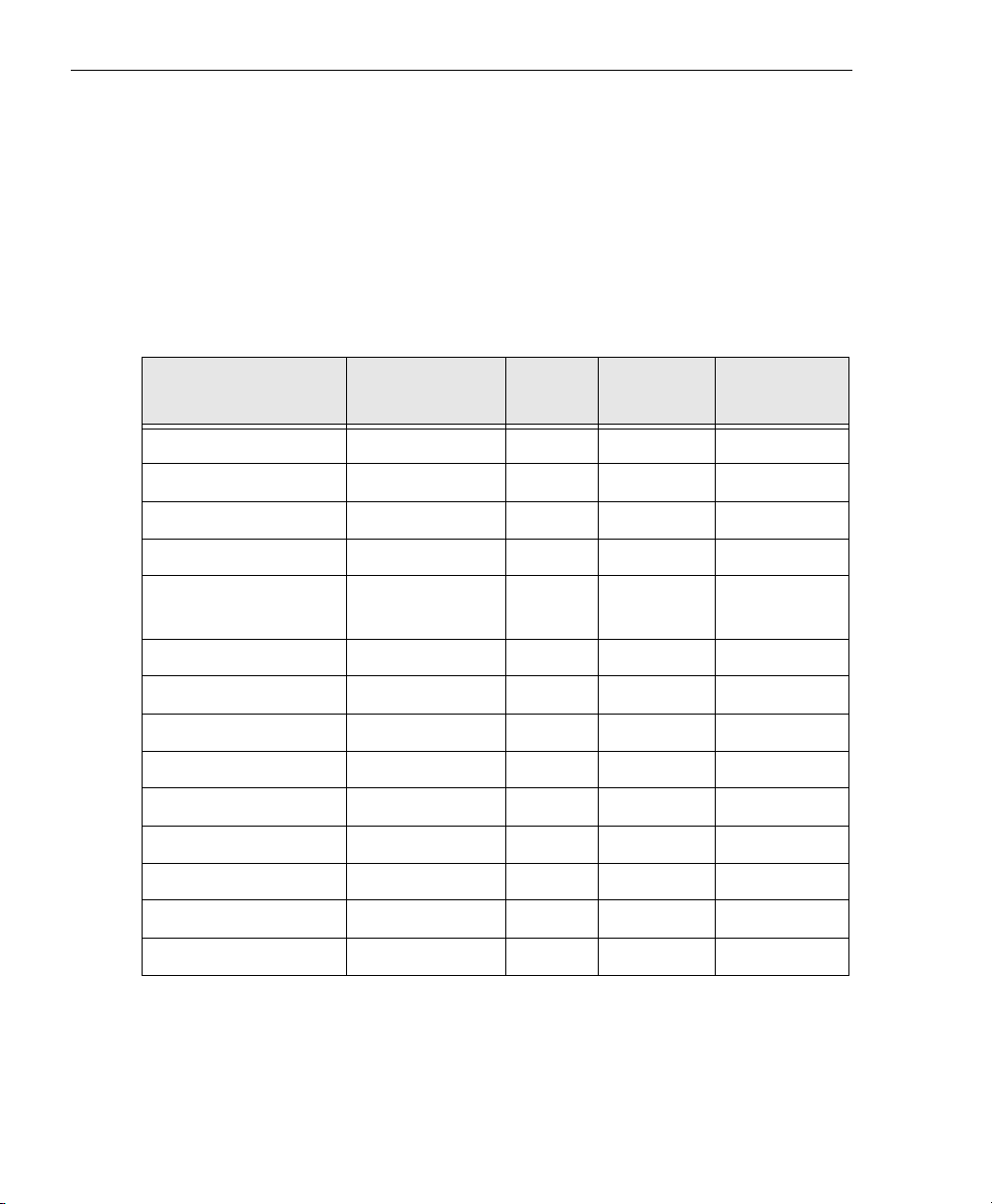
The key differences among the DT9834 Series modules are
summarized in Tabl e 1. Note that all modules provide 16 digital
input lines, 16 digital output lines, five counter/timers, and a
throughput rate of up to 500 kSamples/s.
OEM packaging refers to the board-level version; the power supply is
not included.
Table 1: Summary of DT9834 Series Modules
Analog
Module Analog Inputs
DT9834-00-4-12-OEM None 4 12 bits OEM
DT9834-00-4-12-BNC None 4 12 bits BNCa
DT9834-00-4-16-OEM None 4 16 bits OEM
DT9834-00-4-16-BNC None 4 16 bits BNC
Outputs
Resolution Packaging
a
18
DT9834-16-0-12-OEM 16 single-ended
or 8 differential
DT9834-16-0-12-BNC 16 single-ended
b
c
0 12 bits OEM
0 12 bits BNCd
DT9834-08-0-12-BNC 8 differential 0 12 bits BNC
DT9834-16-0-16-OEM 16 SE or 8 DI
DT9834-16-0-16-BNC 16 single-ended
b
0 16 bits OEM
c
0 16 bits BNCd
DT9834-08-0-16-BNC 8 differential 0 16 bits BNC
DT9834-16-4-12-OEM 16 SE or 8 DI
DT9834-16-4-12-BNC 16 single-ended
b
4 12 bits OEM
c
4 12 bits BNCf
DT9834-08-4-12-BNC 8 differential 4 12 bits BNC
DT9834-16-4-16-OEM 16 SE or 8 DI
b
4 16 bits OEM
e
e
g
Page 19
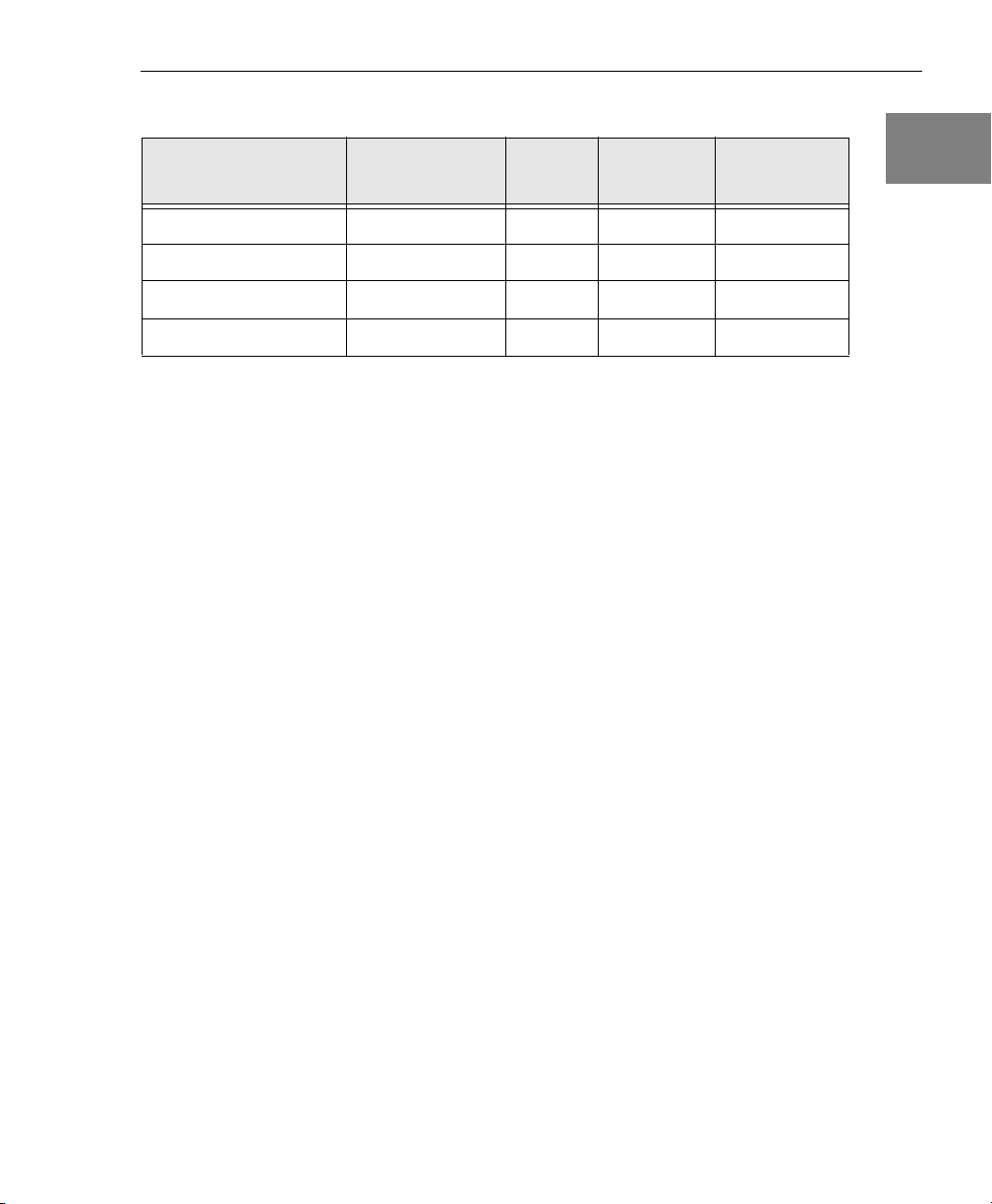
Table 1: Summary of DT9834 Series Modules (cont.)
Overview
Analog
Module Analog Inputs
DT9834-16-4-16-BNC 16 single-endedc 4 16 bits BNCf
DT9834-08-4-16-BNC 8 differential 4 16 bits BNC
DT9834-32-0-16-STP 32 SE or 16 DI
DT9834-32-0-16-OEM 32 SE or 16 DI
a. A BNC connection box with no BNCs for analog inputs, 4 BNCs for analog outputs, 1 BNC for
an external DAC clock, and 1 BNC for an external DAC trigger.
b. Software-selectable.
c. For single-ended-only BNC modules, you must specify the 16 single-ended channels through
software; eight differential channels is the default software configuration.
d. A BNC connection box with 16 BNCs for single-ended analog inputs, no BNCs for analog
outputs, 1 BNC for an external A/D clock, and 1 BNC for an external A/D trigger.
e. A BNC connection box with 8 BNCs for differential analog inputs, no BNCs for analog
outputs, 1 BNC for an external A/D clock, and 1 BNC for an external A/D trigger.
f. A BNC connection box with 16 BNCs for single-ended analog inputs, 4 BNCs for analog
outputs, 1 BNC for an external A/D clock, 1 BNC for an external DAC clock, 1 BNC for an
external A/D trigger, and 1 BNC for an external DAC trigger.
g. A BNC connection box with 8 BNCs for differential analog inputs, 4 BNCs for analog outputs,
1 BNC for an external A/D clock, 1 BNC for an external DAC clock, 1 BNC for an external
A/D trigger, and 1 BNC for an external DAC trigger.
h. You access single-ended channels 16 through 31 through the Analog Input connector on the
BNC connection box.
i. An STP connection box with screw terminals for connecting up to 32 single-ended or 16
differential analog inputs, 16 digital inputs, 16 digital outputs, 5 counter/timers, an external
A/D clock, and an external A/D trigger.
Outputs
h
0 16 bits STPi
b
0 16 bits OEM
Resolution Packaging
g
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
19
Page 20

Chapter 1
Supported Software
The following software is available for use with the DT9834 Series
modules and is on the Data Acquisition OMNI CD:
• DT9834 Series Device Driver – The device driver allows you to
use a DT9834 Series module with any of the supported software
packages or utilities. Refer to the DT9834 Series Getting Started
Manual (UM-19983) for more information on loading and
configuring the device driver.
• Quick Data Acq application – The Quick Data Acq application
provides a quick way to get up and running using a DT9834
Series module. Using this application, you can verify key features
of the modules, display data on the screen, and save data to disk.
Refer to the DT9834 Series Getting Started Manual (UM-19983) for
more information on using the Quick Data Acq application.
• DT Measure Foundry – An evaluation version of this software is
included or provided via a link on the Data Acquisition OMNI
CD. DT Measure Foundry is a drag-and-drop test and
measurement application builder designed to give you top
performance with ease-of-use development. Order the full
development version of this software package to develop your
own application using real hardware.
20
• DataAcq SDK – Use the DataAcq SDK if you want to develop
your own application software for the DT9834 Series modules
using the Microsoft C compiler; the DataAcq SDK complies with
the DT-Open Layers standard.
• DTx-EZ – DTx-EZ provides ActiveX controls, which allow you to
access the capabilities of the DT9834 Series modules using
Microsoft Visual Basic or Visual C++; DTx-EZ complies with the
DT-Open Layers
• DAQ Adaptor for MATLAB – Data Translation’s DAQ Adaptor
provides an interface between the MATLAB Data Acquisition
(DAQ) subsystem from The MathWorks and Data Translation’s
DT-Open Layers architecture.
standard.
Page 21

• DT-LV Link – Use DT-LV Link if you want to use the LabVIEW
graphical programming language to access the capabilities of the
DT9834 Series modules.
Refer to the Data Translation web site (www.datatranslation.com) for
information about selecting the right software package for your
needs.
Overview
1
1
Accessories
You can purchase the following optional items from Data Translation
for use with the OEM version of the DT9834 Series module:
• EP361 – +5V power supply and cable.
• EP353 – Accessory panel that provides one 37-pin, D-sub
connector for attaching analog input signals and one 26-pin
connector for attaching a 5B Series signal conditioning backplane.
• EP355 – Screw terminal panel that provides 14-position screw
terminal blocks for attaching analog input, analog output,
counter/timer, digital I/O, trigger, and clock signals.
• EP356 – Accessory panel that provides two 37-pin, D-sub
connectors for attaching digital I/O, analog output,
counter/timer, trigger, and clock signals.
• EP333 – 2-meter shielded cable with two 37-pin connectors that
connect an EP356 accessory panel to an STP37 screw terminal
panel.
• EP360 – 2-meter shielded cable with two 37-pin connectors that
connect either the Analog Input connector on the BNC
connection box or an EP353 accessory panel to an STP37 screw
terminal panel.
1
1
1
1
1
1
• STP37 – Screw terminal panel that provides 37 screw terminal
blocks for attaching analog output, counter/timer, digital I/O,
trigger, and clock signals.
1
21
Page 22

Chapter 1
• 5B01 – 16-channel backplane that accepts 5B Series signal
conditioning modules.
• 5B08 – 8-channel backplane that accepts 5B Series signal
conditioning modules.
• AC1315 – 2-foot, 26-pin female to 26-pin female cable that
connects a 5B Series backplane to the DT9834 Series module.
22
Page 23

2
Principles of Operation
Analog Input Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Analog Output Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Digital I/O Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Counter/Timer Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
23
Page 24
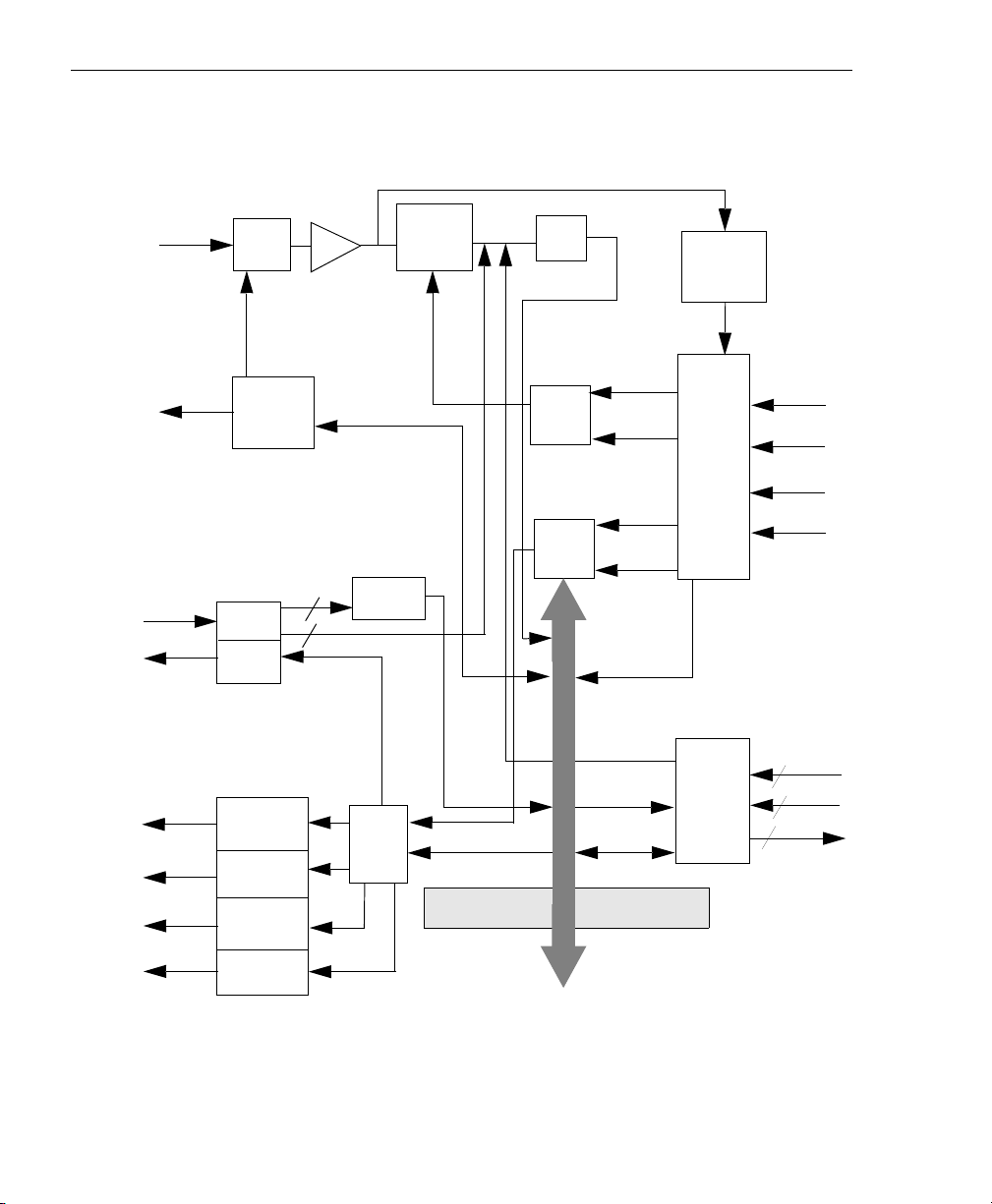
Chapter 2
Analog
Input
Channels
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the DT9834 Series modules.
Input
MUX
Programmable
Gain (1, 2, 4, 8)
12-Bit or
16-Bit
ADC
Input
FIFO
Analog
Threshold
Trigger
Dynamic
Digital
Output
4 Analog Output Channels
ChannelGain List
(1024)
Digital I/O
16 In
16 Out
12/16-Bit
D/A
12/16-Bit
D/A
12/16-Bit
D/A
12/16-Bit
D/A
8
16
Interrupt
Logic
Output
FIFO
Input
Control
Output
Control
500 V Isolation
Barrier
USB 1.1 or 2.0 Interface
Ext. A/D
Tr ig
Ext. A/D
Clk
Ext. D/A
Tr ig
Ext. D/A
Clk
Clock
and
Trigger
Logic
5 32-Bit
Counter/
Timers
Ext. A/D Trig
Ext. A/D Clk
Ext. D/A Trig
Ext. D/A Clk
5 Clock In
5 Gate In
5 Signal Out
24
Figure 1: Block Diagram of the DT9834 Series Modules
Page 25
Analog Input Features
This section describes the following features of analog input (A/D)
operations on the DT9834 Series module:
• Input resolution, described below
• Analog input channels, described on page 26
• Input ranges and gains, described on page 33
Principles of Operation
2
2
• Input sample clock sources, described on page 34
• Analog input conversion modes, described on page 35
• Input triggers, described on page 40
• Data format and transfer, described on page 41
• Error conditions, described on page 43
Input Resolution
Tabl e 2 lists the input resolution of the DT9834 Series modules that
support analog input operations. The resolution is fixed at either 12
bits or 16 bits, depending on the module you are using; you cannot
specify the resolution in software.
Module Resolution Module Resolution
DT9834-16-0-12-OEM
DT9834-16-0-12-BNC
DT9834-08-0-12-BNC
DT9834-16-4-12-OEM
DT9834-16-4-12-BNC
DT9834-08-4-12-BNC
Table 2: Input Resolution
12 bits DT9834-16-0-16-OEM
DT9834-16-0-16-BNC
DT9834-08-0-16-BNC
DT9834-16-4-16-OEM
DT9834-16-4-16-BNC
DT9834-08-4-16-BNC
DT9834-32-0-16-STP
DT9834-32-0-16-OEM
2
2
2
2
2
16 bits
2
2
25
Page 26

Chapter 2
Analog Input Channels
You can use the analog input channels in one of the following
configurations:
• Single-ended − Single-ended channels are useful when you are
measuring high-level signals, when noise is not significant, when
the source of the input is close to the module, and when all the
input signals are referred to the same common ground.
• Pseudo-Differential − Pseudo-differential channels are useful
when noise or common-mode voltage (the difference between the
ground potentials of the signal source and the ground of the
screw terminal panel or between the grounds of other signals)
exists and when the differential configuration is not suitable for
your application. This option provides less noise rejection than
the differential configuration; however, more analog input
channels are available.
• Differential − Differential channels are useful when you want to
measure low-level signals, when noise is a significant part of the
signal, or when common-mode voltage exists.
26
The BNC connection box is shipped in either a differential or
single-ended channel configuration. For the STP and OEM versions
of the module, you configure the channel type as single-ended or
differential through software.
Note: For pseudo-differential inputs, specify single-ended in
software; in this case, how you wire these signals determines the
configuration.
Page 27
Principles of Operation
Using the Open Layers Control Panel applet, you can also select
whether to use 10 kΩ termination resistance between the low side of
each differential channel and isolated analog ground. This feature is
particularly useful with floating signal sources. Refer to the DT9834
Series Getting Started Manual for more information about wiring to
inputs and configuring the driver to use bias return termination
resistance.
The DT9834 Series modules can acquire data from a single analog
input channel or from a group of analog input channels. Channels are
numbered 0 to 31 for single-ended and pseudo-differential inputs,
and 0 to 15 for differential inputs.
The following subsections describe how to specify the channels.
Specifying a Single Analog Input Channel
The simplest way to acquire data from a single analog input channel
is to specify the channel for a single-value analog input operation
using software; refer to page 35 for more information about
single-value operations.
2
2
2
2
2
You can also specify a single channel using the analog input
channel-gain list, described in the next section.
Specifying One or More Analog Input Channels
You can read data from one or more analog input channels using an
analog input channel-gain list. You can group the channels in the list
sequentially (starting either with 0 or with any other analog input
channel) or randomly. You can also specify a single channel or the
same channel more than once in the list.
2
2
2
2
27
Page 28

Chapter 2
Using software, specify the channels in the order you want to sample
them. You can enter up to 1,024 entries in the channel-gain list. The
channels are read in order (using continuously paced scan mode or
triggered scan mode) from the first entry in the list to the last entry in
the list. Refer to page 35 for more information about the supported
conversion modes.
You can also use software to set up a channel-inhibit list. This feature
is useful if you want to discard acquired values from specific entries
in the channel-gain list. Using the channel-inhibit list, you can enable
or disable inhibition for each entry in the channel-gain list. If enabled,
the value is discarded after the channel is read; if disabled, the value
is not discarded after the channel is read.
Notes: If you select an analog input channel as the analog threshold
trigger source, the channel used for this trigger source must be the
first channel specified in the channel-gain list; refer to page 40 for
more information about this trigger source.
28
The maximum rate at which the module can read the analog input
channels depends on the total number of analog input channels
and/or counter/timer channels (see page 30) in the list, and whether
or not you are reading the digital input port (see the next section).
For example, since the maximum throughput of the analog input
subsystem is 500 kSamples/s, the module can read two analog input
channels at a rate of 250 kSamples/s each or four analog input
channels at a rate of 125 kSamples/s each.
Page 29

Principles of Operation
Specifying the Digital Input Port in the Analog Input Channel-Gain List
The DT9834 Series modules allow you to read the digital input port
(all 16 digital input lines) using the analog input channel-gain list.
This feature is particularly useful when you want to correlate the
timing of analog and digital events.
To read the digital input port, specify channel 16 or channel 32 in the
analog input channel-gain list. Use channel 16 for modules with 16
single-ended channels or eight differential channels; use channel 32
for modules with 32 single-ended channels or 16 differential
channels. You can enter channel 16 or 32 anywhere in the list, and
you can enter it more than once, if desired.
The digital input port is treated like any other channel in the analog
input channel-gain list; therefore, all the clocking, triggering, and
conversion modes supported for analog input channels are
supported for the digital input port, if you specify them this way.
2
2
2
2
2
Note: The maximum rate at which the module can read the digital
input port depends on the total number of analog input channels
(see page 27) and counter/timer channels (see the next section) in
the channel-gain list. For example, since the maximum throughput
of the analog input subsystem is 500 kSamples/s, the module can
read one analog input channel and the digital input port (two
channels/ports) at a rate of 250 kSamples/s each or three analog
input channels and the digital input port (four channels/ports) at a
rate of 125 kSamples/s each.
2
2
2
2
29
Page 30
Chapter 2
Specifying Counter/Timers in the Analog Input Channel-Gain List
The DT9834 Series modules allow you to read the value of one or
more of the five counter/timer channels using the analog input
channel-gain list. This feature is particularly useful when you want to
correlate the timing of analog and counter/timer events.
To read a counter/timer channel, specify the appropriate channel
number in the analog input channel-gain list (refer to Table 3 on page
30). You can enter a channel number anywhere in the list, and you
can enter it more than once, if desired.
You need two channel-gain list entries to read one 32-bit counter
value. The first entry stores the lower 16-bit word, and the second
entry stores the upper 16-bit word. If you need only the lower 16-bit
word, you do not have to include the second entry. The entire 32-bit
count value is latched when the lower 16-bit word is stored. This
prevents the counter/timer from incrementing between samples.
Tabl e 3 lists the channel number(s) to use for each counter/timer.
30
Table 3: Using Counter/Timers in Analog Input Channel-Gain List
Channel to Specify in
Channel-Gain List for:
Modules with
Counter/Timer
Channel
C/T_0_LOW Lower 16 bits (0 to 15) of C/T 0 Channel 17 Channel 33
C/T_0_HI Upper 16 bits (16 to 31) of C/T 0 Channel 18 Channel 34
C/T_1_LOW Lower 16 bits (0 to 15) of C/T 1 Channel 19 Channel 35
C/T_1_HI Upper 16 bits (16 to 31) of C/T 1 Channel 20 Channel 36
C/T_2_LOW Lower 16 bits (0 to 15) of C/T 2 Channel 21 Channel 37
Description
16 SE or 8 DI
Channels
Modules with
32 SE or 16 DI
Channels
Page 31

Principles of Operation
Table 3: Using Counter/Timers in Analog Input Channel-Gain List (cont.)
Channel to Specify in
Channel-Gain List for:
Modules with
Counter/Timer
Channel
C/T_2_HI Upper 16 bits (16 to 31) of C/T 2 Channel 22 Channel 38
C/T_3_LOW Lower 16 bits (0 to 15) of C/T 3 Channel 23 Channel 39
C/T_3_HI Upper 16 bits (16 to 31) of C/T 3 Channel 24 Channel 40
C/T_4_LOW Lower 16 bits (0 to 15) of C/T 4 Channel 25 Channel 41
C/T_4_HI Upper 16 bits (16 to 31) of C/T 4 Channel 26 Channel 42
The counter/timer channel is treated like any other channel in the
analog input channel-gain list; therefore, all the clocking, triggering,
and conversion modes supported for analog input channels are
supported for the counter/timers, if you specify them this way.
Note: The maximum rate at which the module can read the
counter/timers depends on the total number of counter/timer
channels and analog input channels (see page 27) in the list and
whether or not you are reading the digital input port (see page 29).
For example, since the maximum throughput of the analog input
subsystem is 500 kSamples/s, the module can read one analog input
channel and one counter/timer channel (two channels) at a rate of
250 kSamples/s each or three analog input channels and one
counter/timer channel (four channels) at a rate of 125 kSamples/s
each.
Description
16 SE or 8 DI
Channels
Modules with
32 SE or 16 DI
Channels
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
31
Page 32

Chapter 2
Performing Dynamic Digital Output Operations
Using software, you can enable a synchronous dynamic digital
output operation for the analog input subsystem. This feature is
particularly useful when you want to synchronize and control
external equipment.
One dynamic digital output line is accessible through hardware. This
line is set to a value of 0 on power up; a reset does not affect the value
of the dynamic digital output line. Note that this line is provided in
addition to the other 16 digital output lines; see page 53 for more
information about the digital I/O features.
You specify the value (0 or 1) to write from the dynamic digital
output line using the analog input channel-gain list. A value of 0
indicates a low-level signal; a value of 1 indicates a high-level signal.
As each entry in the channel-gain list is read, the corresponding value
is output to the dynamic digital output line. For example, assume
that dynamic digital output operations are enabled; that the
channel-gain list contains analog input channels 0, 1, 2, and 3; and
that the channel-gain list contains the dynamic digital output values
1, 0, 0, 1. Figure 2 shows this configuration.
32
Analog Input Channel-Gain List
Analog Input
Channels
0
1
2
3
Dynamic Digital
Output Values
1
0
0
1
Values Output from
Dynamic Digital
Output Line
1
0
0
1
Figure 2: Example Using Dynamic Digital Outputs
Page 33

As analog input channel 0 is read, a high-level signal is output to the
dynamic digital output line. As analog input channels 1 and 2 are
read, a low-level signal is output to the dynamic digital output line.
As analog input channel 3 is read, a high-level signal is output to the
dynamic digital output line.
Input Ranges and Gains
Tabl e 4 lists the supported gains and effective bipolar input ranges
for each.
Table 4: Effective Input Range
Principles of Operation
2
2
2
Gain Input Range
1±10 V
2±5 V
4 ±2.5 V
8 ±1.25 V
Using software, specify a range of −10 V to +10 V. Note that this is the
range for the entire analog input subsystem, not the range per
channel.
For each channel, choose the gain that has the smallest effective range
that includes the signal you want to measure. For example, if the
range of your analog input signal is ±1.05 V, specify a range of −10 V
to +10 V for the module and use a gain of 8 for the channel; the
effective input range for this channel is then ±1.25 V, which provides
the best sampling accuracy for that channel.
The way you specify gain depends on how you specified the
channels, as described in the following subsections.
2
2
2
2
2
2
33
Page 34

Chapter 2
Specifying the Gain for a Single Channel
The simplest way to specify gain for a single channel is to specify the
gain for a single-value analog input operation using software; refer to
page 35 for more information about single-value operations.
You can also specify the gain for a single channel using an analog
input channel-gain list, described in the next section.
Specifying the Gain for One or More Channels
You can specify the gain for one or more analog input channels using
an analog input channel-gain list. Using software, set up the
channel-gain list by specifying the gain for each entry in the list.
For example, assume the analog input channel-gain list contains three
entries: channels 5, 6, and 7 and gains 2, 4, and 1. A gain of 2 is
applied to channel 5, a gain of 4 is applied to channel 6, and a gain of
1 is applied to channel 7.
34
Note: For channel 16 or 32 (the digital input port) and channels 17
through 26 or channels 33 through 42 (the counter/timer channels),
specify a gain of 1.
Input Sample Clock Sources
DT9834 Series modules allow you to use one of the following clock
sources to pace analog input operations:
• Internal A/D clock – Using software, specify the clock source as
internal and the clock frequency at which to pace the operation.
The minimum frequency supported is 0.75 Samples/s; the
maximum frequency supported is 500 kSamples/s.
Page 35

Principles of Operation
According to sampling theory (Nyquist Theorem), specify a
frequency that is at least twice as fast as the input’s highest
frequency component. For example, to accurately sample a
20 kHz signal, specify a sampling frequency of at least 40 kHz.
Doing so avoids an error condition called aliasing, in which high
frequency input components erroneously appear as lower
frequencies after sampling.
• External A/D clock – An external A/D clock is useful when you
want to pace acquisitions at rates not available with the internal
A/D clock or when you want to pace at uneven intervals.
Connect an external A/D clock to the External ADC Clock input
signal on the DT9834 Series module. Conversions start on the
falling edge of the external A/D clock input signal.
Using software, specify the clock source as external. The clock
frequency is always equal to the frequency of the external A/D
sample clock input signal that you connect to the module.
Note: If you specify channel 16 or 32 (the digital input port) and/or
channels 17 through 26 or channels 33 through 42 (the counter/timer
channels) in the channel-gain list, the input sample clock (internal or
external) also paces the acquisition of the digital input port and/or
counter/timer channels.
2
2
2
2
2
2
Analog Input Conversion Modes
DT9834 Series modules support the following conversion modes:
• Single-value operations are the simplest to use. Using software,
you specify the range, gain, and analog input channel. The
module acquires the data from the specified channel and returns
the data immediately. For a single-value operation, you cannot
specify a clock source, trigger source, scan mode, or buffer.
2
2
2
35
Page 36

Chapter 2
Single-value operations stop automatically when finished; you
cannot stop a single-value operation.
• Scan mode takes full advantage of the capabilities of the DT9834
Series modules. For a scan, you can specify a channel-gain list,
clock source, trigger source, scan mode, buffer, and buffer wrap
mode using software. Two scan modes are supported:
continuous scan mode and triggered scan mode (often called
burst mode). These modes are described in the following
subsections.
Using software, you can stop a scan by performing either an
orderly stop or an abrupt stop. In an orderly stop, the module
finishes acquiring the data, stops all subsequent acquisition, and
transfers the acquired data to host memory; any subsequent
triggers are ignored.
In an abrupt stop, the module stops acquiring samples
immediately; the acquired data is not transferred to host
memory, and any subsequent triggers are ignored.
Continuous Scan Mode
36
Use continuous scan mode if you want to accurately control the
period between conversions of individual channels in a scan.
When it detects an initial trigger, the module cycles through the
channel-gain list, acquiring and converting the value for each entry in
the list (this process is defined as the scan). The module then wraps to
the start of the channel-gain list and repeats the process continuously
until either the allocated buffers are filled or until you stop the
operation. Refer to page 41 for more information about buffers.
The conversion rate is determined by the frequency of the input
sample clock; refer to page 34 for more information about the input
sample clock. The sample rate, which is the rate at which a single
entry in the channel-gain list is sampled, is determined by the
frequency of the input sample clock divided by the number of entries
in the channel-gain list.
Page 37

Principles of Operation
To select continuous scan mode, use software to specify the data flow
as continuous and to specify the initial trigger (the trigger source that
starts the operation). You can select a software trigger, an external
TTL trigger, or an analog threshold trigger as the initial trigger. Refer
to page 40 for more information about the supported trigger sources.
2
Figure 3 illustrates continuous scan mode using a channel-gain list
with three entries: channel 0, channel 1, and channel 2. In this
example, analog input data is acquired on each clock pulse of the
input sample clock. When it reaches the end of the channel-gain list,
the module wraps to the beginning of the channel-gain list and
repeats this process. Data is acquired continuously.
Chan 0
Input
Sample
Clock
Initial trigger event occurs
Chan 2
Chan 1
Figure 3: Continuous Scan Mode
Chan 0
Chan 1
Chan 2
Data acquired continuously
Chan 0
Chan 2
Chan 1
Chan 0
Chan 1
Triggered Scan Mode
Use triggered scan mode if you want to accurately control both the
period between conversions of individual channels in a scan and the
period between each scan. This mode is useful in emulating
simultaneous sample-and-hold and trigger-per-buffer operations.
You can acquire up to 262,144 samples per trigger (256 times per
trigger x 1024-location channel-gain list).
Chan 2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
DT9834 Series modules support two triggered scan modes: internally
retriggered and externally retriggered. These modes are described in
the following subsections.
2
37
Page 38

Chapter 2
Internally Retriggered Scan Mode
In internally retriggered scan mode, the module waits for the initial
trigger to occur. When it detects an initial trigger, the module scans
the analog input channel-gain list a specified number of times (up to
256), and then waits for an internal retrigger to occur. When it detects
an internal retrigger, the module scans the channel-gain list the
specified number of times, and then waits for another internal
retrigger to occur. The process repeats continuously until either the
allocated buffers are filled or you stop the operation; refer to page 41
for more information about buffers.
The sample rate is determined by the frequency of the input sample
clock divided by the number of entries in the channel-gain list; refer
to page 34 for more information about the input sample clock. The
conversion rate of each scan is determined by the frequency of the
internal retrigger clock. The minimum frequency supported is 0.75
Samples/s; the maximum frequency supported is 500 kSamples/s.
Specify the retrigger frequency as follows:
38
Min. Retrigger = # of CGL entries x # of CGLs per trigger
Period A/D sample clock frequency
Max. Retrigger = 1
Frequency Min. Retrigger Period
For example, if you are using 512 channels in the channel-gain list,
scanning the channel-gain list 256 times every trigger or retrigger,
and using an A/D sample clock with a frequency of 100 kHz, set the
maximum retrigger frequency to 0.762 Hz, since
0.762 Hz = 1
( 512 * 256) +2 μs
100 kHz
+ 2 μs
Page 39

Principles of Operation
To select internally retriggered scan mode, use software to specify the
following parameters:
• Dataflow as continuous
• Triggered scan mode usage enabled
2
• The initial trigger (the trigger source that starts the acquisition)
• Retrigger mode as internal
• The number of times to scan per trigger or retrigger (also called
the multiscan count)
• The frequency of the retrigger clock
Externally Retriggered Scan Mode
In externally retriggered scan mode, the module waits for the initial
trigger to occur. When it detects an initial trigger, the module scans
the channel-gain list up to 256 times, and then waits for an external
retrigger to occur.
When the retrigger occurs, the module scans the channel-gain list the
specified number of times, and then waits for another external digital
(TTL) trigger to occur. The process repeats continuously until either
the allocated buffers are filled or you stop the operation; refer to page
41 for more information about buffers.
The conversion rate of each channel is determined by the frequency
of the input sample clock; refer to page 34 for more information about
the input sample clock. The conversion rate of each scan is
determined by the period between external retriggers; therefore, it
cannot be accurately controlled. The module ignores external triggers
that occur while it is acquiring data. Only external retrigger events
that occur when the module is waiting for a retrigger are detected
and acted on.
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
39
Page 40

Chapter 2
To select externally retriggered scan mode, use software to specify
the following parameters:
• Dataflow as continuous
• Triggered scan mode enabled
• The initial trigger (the trigger source that starts the operation) as
any of the supported trigger sources
• Retrigger mode as an external retrigger (retrigger extra)
• The number of times to scan per trigger or retrigger (also called
the multiscan count)
• The retrigger source as the external digital (TTL) trigger
Note: If you want to use the external digital (TTL) trigger source as
both the initial trigger and the retrigger source, specify the retrigger
mode as scan-per-trigger. In this case, you do not have to specify the
retrigger source.
40
Input Triggers
A trigger is an event that occurs based on a specified set of
conditions. Acquisition starts when the module detects the initial
trigger event and stops when the specified number of samples has
been acquired (if the buffer wrap mode is none, described on page
42), or when you stop the operation. Note that when you stop the
operation, the module finishes reading the channel-gain list.
If you are using triggered scan mode, the module continues to
acquire data using the specified retrigger source to clock the
operation. Refer to page 37 for more information about triggered scan
mode.
Page 41

Principles of Operation
The DT9834 Series module supports the following trigger sources:
• Software trigger − A software trigger event occurs when you
start the analog input operation (the computer issues a write to
the module to begin conversions). Using software, specify the
trigger source as a software trigger.
• External digital (TTL) trigger − An external digital (TTL) trigger
event occurs when the DT9834 Series module detects a transition
(high-to-low or low-to-high) on the External ADC Trigger input
signal connected to the module. Using software, specify the
trigger source as a rising-edge external digital trigger (external)
or a falling-edge external digital trigger (extra).
• Analog threshold trigger – An analog threshold trigger event
occurs when the signal on the first channel in the analog input
channel-gain list rises above (low-to-high transition) a
programmable threshold level. Using software, specify the
trigger source as a positive threshold trigger (threshpos).
You can use any one of the 16 analog input channels as the
analog trigger. The analog trigger channel must be the first entry
in the analog input channel-gain list.
You specify the threshold level in the olDaPutSingleValue
function, using D/A subsystem 1. Specify a value between 0 and
255, where 0 equals 0 V and 255 equals +10 V.
2
2
2
2
2
2
Data Format and Transfer
DT9834 Series modules use offset binary data encoding, such as 000
(for 12-bit modules) or 0000 (for 16-bit modules) to represent negative
full-scale, and FFFh (for 12-bit modules) or FFFFh (for 16-bit
modules) to represent positive full-scale. Use software to specify the
data encoding as binary.
The ADC outputs FFFh (for 12-bit modules) or FFFFh (for 16-bit
modules) for above-range signals, and 000 (for 12-bit modules) or
0000 (for 16-bit modules) for below-range signals.
2
2
2
41
Page 42

Chapter 2
Before you begin acquiring data, you must allocate buffers to hold
the data. A Buffer Done message is returned whenever a buffer is
filled. This allows you to move and/or process the data as needed.
Note: We recommend that you allocate buffers of 1024 samples or
more to optimize the performance of your DT9834 Series module. If
you allocate smaller buffers, the software automatically adjusts the
buffer size to 256 samples/buffer, 512 samples/buffer, or
768 samples/buffer, whichever is closest. The rate at which Buffer
Done messages are returned depends on the buffer size.
We recommend that you allocate a minimum of three buffers for
analog input operations, specifying one of the following buffer wrap
modes in software:
• None – Data is written to multiple allocated input buffers
continuously; when no more empty buffers are available, the
operation stops. If wrap mode is none, the module guarantees
gap-free data.
42
• Multiple – Data is written to multiple allocated input buffers
continuously; if no more empty buffers are available, the module
overwrites the data in the current buffer, starting with the first
location in the buffer. This process continues indefinitely until
you stop it. If wrap mode is multiple, the module does not
guarantee gap-free data.
Page 43

Error Conditions
Principles of Operation
The DT9834 Series modules can report an error if one of the following
conditions occurs:
• A/D Over Sample – The A/D sample clock rate is too fast. This
error is reported if a new A/D sample clock pulse occurs while
the ADC is busy performing a conversion from the previous A/D
sample clock pulse. The host computer can clear this error. To
avoid this error, use a slower sampling rate.
• Input FIFO Overflow – The analog input data is not being
transferred fast enough to the host computer. The host computer
can clear this error, but the error will continue to be generated if
the Input FIFO is still full. To avoid this error, close other
applications that may be running while you are acquiring data. If
this has no effect, try using a computer with a faster processor or
reduce the sampling rate.
If one of these error conditions occurs, the module stops acquiring
and transferring data to the host computer.
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
43
Page 44

Chapter 2
Analog Output Features
This section describes the following features of analog output
operations:
• Output resolution, described below
• Analog output channels, described on page 45
• Output ranges and gains, described on page 47
• Output triggers, described on page 47
• Output clocks, described on page 47
• Data format and transfer, described on page 51
• Error conditions, described on page 52
Output Resolution
Tabl e 2 lists the output resolution of the DT9834 Series modules that
support analog output operations. The resolution is fixed at either 12
bits or 16 bits, depending on the module you are using; you cannot
specify the resolution in software.
44
Module Resolution Module Resolution
DT9834-00-4-12-OEM
DT9834-00-4-12-BNC
DT9834-16-4-12-OEM
DT9834-16-4-12-BNC
DT9834-08-4-12-BNC
Table 5: Output Resolution
12 bits DT9834-00-4-16-OEM
DT9834-00-4-16-BNC
DT9834-16-4-16-OEM
DT9834-16-4-16-BNC
DT9834-08-4-16-BNC
16 bits
Page 45

Analog Output Channels
Principles of Operation
The DT9834 Series modules support four DC-level analog output
channels (DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3). Refer to the DT9834
Series Getting Started Manual for information about how to wire
analog output signals to the module.
The DACs are deglitched to prevent noise from interfering with the
output signal. They power up to a value of 0 V ±10 mV. Unplugging
the module resets the DACs to 0 V.
The DT9834 Series modules can output data from a single DAC or
sequentially from one or more DACs and/or the digital output port.
The following subsections describe how to specify the DACs/port.
Specifying a Single Analog Output Channel
The simplest way to output data from a single DAC is to specify the
channel for a single-value analog output operation using software;
refer to page 48 for more information about single-value operations.
You can also specify a single DAC using the output channel list,
described in the next section.
2
2
2
2
2
2
Specifying Multiple Analog Output Channels and/or the Digital Output Port
You can output data from one or more DACs and/or the digital
output port using the output channel list. This feature is particularly
useful when you want to correlate the timing of analog and digital
output events.
2
2
2
45
Page 46

Chapter 2
Using software, specify the data flow mode as continuous for the
D/A subsystem (described on page 48) and specify the output
channels you want to update, where 0 is DAC0, 1 is DAC1, 2 is
DAC2, 3 is DAC3, and 4 is the digital output port. You can enter a
maximum of 5 entries in the output channel list and the channels
must be in order. Note that you can skip a channel in the list,
however, if you do not want to update it. For example, if you want to
update only DAC3 and the digital output port, specify channels 3 and
4 in the output channel list. If you want to update all the DACs and
the digital output ports, specify channels 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the output
channel list. The channels are output in order from the first entry in
the list to the last entry in the list.
The amount of data that you can output for each channel depends on
how many channels are in the output channel list. For example, if
only one channel is entered in the output channel list, you can output
up to 128K values; if all five channels are entered in the output
channel list, you an output up to 24K values per channel.
46
Notes: The maximum rate at which the module can update the
output channels depends on the total number of channels in the
output channel list. Since the maximum throughput for each output
channel is 500 kSamples/s, the module can update two output
channels at a rate of 1000 kSamples/s or all five output channels at a
rate of 2.5 MSamples/s.
The digital output port is treated like any other channel in the output
channel list; therefore, all the clocking, triggering, and conversion
modes supported for analog output channels are supported for the
digital output port, if you specify the digital output port in the
output channel list.
Page 47

Output Ranges and Gains
Principles of Operation
Each DAC on the DT9834 Series module can output bipolar analog
output signals in the range of ±10 V.
Through software, specify the range for the entire analog output
subsystem as −10 V to +10 V, and the gain for each DAC as 1.
Output Triggers
A trigger is an event that occurs based on a specified set of
conditions. The DT9834 Series modules support the following output
trigger sources:
• Software trigger – A software trigger event occurs when you
start the analog output operation. Using software, specify the
trigger source as a software trigger.
• External digital (TTL) trigger – An external digital (TTL) trigger
event occurs when the DT9834 Series module detects a transition
(high-to-low or low-to-high) on the External DAC Trigger input
signal connected to the module. Using software, specify the
trigger source as external and the polarity as high-to-low
transition or low-to-high transition.
2
2
2
2
2
2
Output Clocks
DT9834 Series modules allow you to use one of the following clock
sources to pace analog output operations:
• Internal DAC clock – Using software, specify the clock source as
internal and the clock frequency at which to pace the operation.
The minimum frequency supported is 0.75 Samples/s; the
maximum frequency supported is 500 kSamples/s.
• External DAC clock – An external DAC clock is useful when you
want to pace conversions at rates not available with the output
sample clock or when you want to pace at uneven intervals.
2
2
2
47
Page 48

Chapter 2
Connect an external DAC clock to the External DAC Clock input
signal on the DT9834 Series module. Analog output operations
start on the rising edge of the external DAC clock output signal.
Using software, specify the clock source as external. The clock
frequency is always equal to the frequency of the external DAC
clock output signal that you connect to the module.
Output Conversion Modes
DT9834 Series modules support the following conversion modes:
• Single-value operations are the simplest to use but offer the least
flexibility and efficiency. Use software to specify the analog
output channel that you want to update, and the value to output
from that channel. For a single-value operation, you cannot
specify a clock source, trigger source, or buffer. Single-value
operations stop automatically when finished; you cannot stop a
single-value operation.
• Continuous analog output operations take full advantage of the
capabilities of the DT9834 Series modules. In this mode, you can
specify an output channel list, clock source, trigger source, buffer,
and buffer wrap mode. Two continuous analog output modes are
supported: continuously paced and waveform generation mode.
These modes are described in the following subsections.
48
Note that in waveform mode, each channel in the output channel
list must write the same number of values, use the same output
clock (refer to page 47), and use the same output trigger (refer to
page 47).
Continuously Paced Analog Output
Use continuously paced analog output mode if you want to
accurately control the period between conversions of individual
channels in the output channel list (refer to page 45 for information
on specifying the output channel list).
Page 49

Principles of Operation
Use software to fill the output buffer with the values that you want to
write to the DACs and to the digital output port, if applicable. For
example, if your output channel list contains only DAC0 and the
digital output port, specify the values in the output buffer as follows:
the first output value for DAC0, the first output value for the digital
output port, the second output value for DAC0, the second output
value for the digital output port, and so on.
When it detects a trigger, the module starts writing the values from
the output buffer to the channels specified in the output channel list.
The operation repeats continuously until either all the data is output
from the buffers (if buffer wrap mode is none) or you stop the
operation (if buffer wrap mode is multiple). Refer to page 51 for more
information about buffer modes.
Make sure that the host computer transfers data to the output
channel list fast enough so that the list does not empty completely;
otherwise, an underrun error results.
To select continuously paced analog output mode, use software to
specify the data flow as continuous, the buffer wrap mode as
multiple or none, and the trigger source as any of the supported
trigger sources. Refer to page 47 for more information about the
supported trigger sources.
2
2
2
2
2
2
To stop a continuously paced analog output operation, you can stop
sending data to the module, letting the module stop when it runs out
of data, or you can perform either an orderly stop or an abrupt stop
using software. In an orderly stop, the module finishes outputting the
specified number of samples, and then stops; all subsequent triggers
are ignored. In an abrupt stop, the module stops outputting samples
immediately; all subsequent triggers are ignored.
2
2
2
49
Page 50

Chapter 2
Waveform Generation
Use waveform generation mode if you want to output a waveform
repetitively.
The waveform pattern can range from 2 to 120K (122,880) samples if
you specify one output channel, 2 to 60K (61,440) samples for two
output channels, 2 to 40K (40,960) samples for three output channels,
2 to 30K (30,720) samples for four output channels, or 2 to 24K
(24,576) samples for five output channels.
Note: The waveform pattern size must be the same for all output
channels, and the total number of samples must be a multiple of the
total number of output channels.
Use software to fill the output buffer with the values that you want to
write to the channels in the output channel list. For example, if your
output channel list contains only DAC0 and the digital output port,
specify the values in the output buffer as follows: the first output
value for DAC0, the first output value for the digital output port, the
second output value for DAC0, the second output value for the
digital output port, and so on.
50
When it detects a trigger, the host computer transfers the entire
waveform pattern to the module, and the module starts writing
output values to the output channels, as determined by the output
channel list. Use software to allocate the memory and specify the
waveform pattern.
To select waveform generation mode, use software to specify the data
flow as continuous, the buffer wrap mode as single (refer to page 52),
and the trigger source as any of the supported trigger sources (refer
to page 47).
Page 51

Data Format and Transfer
Principles of Operation
Data from the host computer must use offset binary data encoding
for analog output signals, such as 000 (for 12-bit modules) or 0000 (for
16-bit modules) to represent −10 V, and FFFh (for 12-bit modules) or
FFFFh (for 16-bit modules) to represent +10 V. Using software,
specify the data encoding as binary.
Before you begin writing data to the output channels, you must
allocate and fill buffers with the appropriate data. A Buffer Done
message is returned whenever a buffer is output. This allows you to
output additional data as needed.
Note: Allocate buffers of 1024 samples or more to optimize the
performance of your DT9834 Series module. If you allocate smaller
buffers, the software automatically adjusts the buffer size to 256
samples/buffer, 512 samples/buffer, or 768 samples/buffer,
whichever is closest. The rate at which Buffer Done messages are
returned depends on the buffer size.
Specify one of the following buffer wrap modes in software:
2
2
2
2
2
2
• None − Data is written from multiple output buffers
continuously; when no more buffers of data are available, the
operation stops. If wrap mode is none, the module guarantees
gap-free data; however, the data written may not be what you
expect.
• Multiple − Data is written from multiple output buffers
continuously; when no more buffers of data are available, the
module returns to the first location of the current buffer and
continues writing data. This process continues indefinitely until
you stop it. If wrap mode is multiple, the module does not
guarantee gap-free data.
2
2
2
51
Page 52

Chapter 2
• Single − Data is written from a single output buffer
continuously; when all the data in the buffer is written, the
module returns to the first location of the buffer and continues
writing data. This process continues indefinitely until you stop it.
If wrap mode is single and the allocated output buffer is equal to
or less than the size of the FIFO on the module, the data is written
once to the module. The module recycles the data, allowing you
to output the same pattern continuously without having to
reload the data from the output channel list.
Note: If the size of your buffers is less than 128K and you stop the
analog output operation, the operation stops after the current buffer
and the next buffer have been output.
Error Conditions
The DT9834 Series modules can report an error if one of the following
conditions occurs:
52
• Output FIFO Underflow – The output channel list data is not
being sent from the host fast enough. This error is reported if an
output sample clock pulse occurs while the output channel list is
empty. Note that if no new data is available to be output by either
the DACs or the digital output port, the last value placed in the
output channel list continues to be output by the DACs/port.
You can ignore this error when performing a single-value
operation.
• DAC Over Sample error – The output sample clock rate is too
fast. This error is reported if a new output sample clock occurs
while the module is busy loading the next values from the output
channel list into the DACs and/or digital output port. To avoid
this error, try slowing down the D/A clock, using a different
wrap mode, increasing the buffer sizes, or using more buffers.
Page 53

Digital I/O Features
This section describes the following features of digital I/O
operations:
• Digital I/O lines, described below
• Operation modes, described on page 54
Digital I/O Lines
DT9834 Series modules support one digital input port, consisting of
16 digital input lines (lines 0 to 15) and one digital output port,
consisting of 16 digital output lines (lines 0 to 15).
You can specify the digital I/O line that you want to read or write in
a single-value digital I/O operation. Refer to page 54 for more
information about single-value operations.
In addition, you can specify the entire digital input port in an analog
input channel-gain list to perform a continuous digital input
operation, or you can specify the entire digital output port in an
output channel list to perform a continuous digital output operation.
Refer to page 54 for more information about continuous digital I/O
operations.
Principles of Operation
2
2
2
2
2
2
A digital line is high if its value is 1; a digital line is low if its value is
0. On power up or reset, a low value (0) is output from each of the
digital output lines.
The DT9834 Series modules allow you to program the first eight
digital input lines to perform interrupt-on-change operations. Refer
to page 54 for more information.
The DT9834 Series modules provide a dynamic digital output line
that you can update whenever an analog input channel is read. The
dynamic digital output line is in addition to the 16 digital output
lines. Refer to page 55 for more information.
2
2
2
53
Page 54

Chapter 2
Operation Modes
The DT9834 Series modules support the following digital I/O
operation modes:
• Single-value operations are the simplest to use but offer the least
flexibility and efficiency. You use software to specify the digital
I/O port and a gain of 1 (the gain is ignored). Data is then read
from or written to all the digital I/O lines. For a single-value
operation, you cannot specify a clock or trigger source.
Single-value operations stop automatically when finished; you
cannot stop a single-value operation.
• Continuous digital I/O takes full advantage of the capabilities of
the DT9834 Series modules. You can specify a clock source, scan
mode, trigger source, buffer, and buffer wrap mode for the
operation.
− Digital input – For digital input operations, enter the digital
input port (all 16 digital input lines) as channel 16 or 32 in the
analog input channel-gain list; refer to page 29 for more
information. The input sample clock (internal or external)
paces the reading of the digital input port (as well as the
acquisition of the analog input and counter/timer channels);
refer to page 34 for more information.
54
− Digital output – For digital output operations, enter the
digital output port (all 16 digital output lines) as channel 4 in
the output channel list; refer to page 45 for more information.
The output clock (internal or external) paces the update of the
digital output port (as well as the update of the analog output
channels); refer to page 47 for more information.
• Interrupt-on-change operations – You can use the Open Layers
Control Panel applet to select any of the first eight digital input
lines to perform interrupt-on-change operations. When any one
of the specified bits changes state, the module reads the entire
16-bit digital input value and generates an interrupt.
Page 55

• Dynamic digital output is useful for synchronizing and
controlling external equipment and allows you to output data to
the dynamic digital output line each time an analog input value
is acquired. This mode is programmed through the analog input
subsystem; refer to page 32 for more information.
Counter/Timer Features
Principles of Operation
2
2
This section describes the following features of counter/timer (C/T)
operations:
• C/T channels, described below
• C/T clock sources, described on page 57
• Gate types, described on page 58
• Pulse types and duty cycles, described on page 59
• C/T operation modes, described on page 60
C/T Channels
The DT9834 Series modules provide five 32-bit counter/timers. The
counters are numbered 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4. Each counter accepts a clock
input signal and gate input signal and outputs a pulse (pulse output
signal), as shown in Figure 4.
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
55
Page 56

Chapter 2
Clock Input SIgnal
(internal or external)
To specify the counter/timer to use in software, specify the
appropriate C/T subsystem. For example, counter/timer 0
corresponds to C/T subsystem element 0; counter/timer 3
corresponds to C/T subsystem element 3.
Using software, you can also specify one or more of the
counter/timers in the analog input channel-gain list. You need two
channel-gain list entries to read a 32-bit counter value. The first entry
stores the lower 16-bit word, and the second entry stores the upper
16-bit word.
Counter
Gate Input Signal
(software or external
input)
Figure 4: Counter/Timer Channel
Pulse Output Signal
56
If you need only the lower 16-bit word, you do not have to include
the second entry. The entire 32-bit count value is latched when the
lower 16-bit word is stored. This prevents the counter/timer from
incrementing between samples. Refer to page 30 for more
information about using C/Ts in the channel-gain list.
Page 57

C/T Clock Sources
Principles of Operation
The following clock sources are available for the counter/timers:
• Internal C/T clock – The internal C/T clock always uses an
18 MHz time base. Through software, specify the clock source as
internal, and specify the frequency at which to pace the operation
(this is the frequency of the Counter n Out signal).
• External C/T clock – An external C/T clock is useful when you
want to pace counter/timer operations at rates not available with
the internal C/T clock or if you want to pace at uneven intervals.
The frequency of the external C/T clock can range from .004 Hz
to 9 MHz.
Connect the external clock to the Counter n Clock input signal on
the DT9834 Series module. Counter/timer operations start on the
rising edge of the clock input signal.
Using software, specify the clock source as external and specify a
clock divider between 2 and 2,147,483,647.
Note: The external C/T clock (the clock connected to the Counter n
Clock input signal) determines how often you want to count events,
measure frequency, or measure the time interval between edges.
2
2
2
2
2
2
If you specify a counter/timer in the analog input channel-gain list,
the external A/D clock (the clock connected to the External ADC
Clock input signal) determines how often you want to read the
counter value. Refer to page 34 for more information about the
external A/D clock.
2
2
2
57
Page 58

Chapter 2
Gate Types
The edge or level of the Counter n Gate signal determines when a
counter/timer operation is enabled. DT9834 Series modules provide
the following gate types:
• None − A software command enables any counter/timer
operation immediately after execution.
• Logic-low level external gate input − Enables a counter/timer
operation when the Counter n Gate signal is low, and disables the
counter/timer operation when the Counter n Gate signal is high.
Note that this gate type is used for event counting and rate
generation modes; refer to page 60 for more information about
these modes.
• Logic-high level external gate input − Enables a counter/timer
operation when the Counter n Gate signal is high, and disables a
counter/timer operation when the Counter n Gate signal is low.
Note that this gate type is used for event counting and rate
generation modes; refer to page 60 for more information about
these modes.
58
• Falling-edge external gate input − Enables a counter/timer
operation when a high-to-low transition is detected on the
Counter n Gate signal. In software, this is called a low-edge gate
type. Note that this gate type is used for edge-to-edge
measurement, one-shot, and repetitive one-shot mode; refer to
page 60 for more information about these modes.
• Rising-edge external gate input − Enables a counter/timer
operation when a low-to-high transition is detected on the
Counter n Gate signal. In software, this is called a high-edge gate
type. Note that this gate type is used for edge-to-edge
measurement, one-shot, and repetitive one-shot mode; refer to
page 60 for more information about these modes.
Specify the gate type in software.
Page 59

Pulse Output Types and Duty Cycles
Principles of Operation
The DT9834 Series modules can output the following types of pulses
from each counter/timer:
• High-to-low transitions – The low portion of the total pulse
output period is the active portion of the counter/timer clock
output signal.
• Low-to-high transitions – The high portion of the total pulse
output period is the active portion of the counter/timer pulse
output signal.
You specify the pulse output type in software.
The duty cycle (or pulse width) indicates the percentage of the total
pulse output period that is active. For example, a duty cycle of 50
indicates that half of the total pulse output is low and half of the total
pulse output is high. You specify the duty cycle in software.
Figure 5 illustrates a low-to-high pulse with a duty cycle of
approximately 30%.
Active Pulse Width
2
2
2
2
2
2
high pulse
Total Pulse Period
Figure 5: Example of a Low-to-High Pulse Output Type
2
low pulse
2
2
59
Page 60

Chapter 2
Counter/Timer Operation Modes
DT9834 Series modules support the following counter/timer
operation modes:
• Event counting
•Up/down counting
• Frequency measurement
• Edge-to-edge measurement
• Rate generation
• One-shot
• Repetitive one-shot
Note: The active polarity for each counter/timer operation mode is
software-selectable.
60
The following subsections describe these modes in more detail.
Event Counting
Use event counting mode if you want to count the number of rising
edges that occur on the Counter n Clock input when the Counter n
Gate signal is active (low-level or high-level). Refer to page 58 for
information about specifying the active gate type.
You can count a maximum of 4,294,967,296 events before the counter
rolls over to 0 and starts counting again.
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as event counting
(count), the C/T clock source as external, and the active gate type as
low-level or high-level.
Page 61

Principles of Operation
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. Refer to the
DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting an event
counting application.
Up/Down Counting
Use up/down counting mode if you want to increment or decrement
the number of rising edges that occur on the Counter n Clock input,
depending on the level of the Counter n Gate signal.
2
2
If the Counter n Gate signal is high, the C/T increments; if the
specified gate signal is low, the C/T decrements.
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as up/down
counting (up/down), and the C/T clock source as external. Note that
you do not specify the gate type in software.
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. Refer to the
DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting an
up/down counting application.
Note: Initialize the counter/timer so that the C/T never increments
above FFFFFFFFh or decrements below 0.
Frequency Measurement
Use frequency measurement mode if you want to measure the
number of rising edges that occur on the Counter n Clock input over
a specified duration.
2
2
2
2
2
2
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as frequency
measurement (count) or event counting (count), the clock source as
external, and the time over which to measure the frequency.
2
61
Page 62

Chapter 2
You can use the Windows timer (which uses a resolution of 1 ms), or
if you need more accuracy than the Windows timer provides, you can
connect a pulse of a known duration (such as a one-shot output of
another user counter) to the Counter n Gate input signal.
If you use a known pulse, use software to set up the counter/timers
as follows:
1. Set up one of the counter/timers for one-shot mode, specifying
the clock source as internal, the clock frequency, the gate type
that enables the operation as rising edge or falling edge, the
polarity of the output pulse as high-to-low transition or
low-to-high transition, the pulse width, and the duty cycle of the
output pulse.
2. Set up the counter/timer that will measure the frequency for
event counting mode, specifying the type of clock pulses to count
and the gate type (this should match the pulse output type of the
counter/timer set up for one-shot mode).
3. Start both counters (pulses are not counted until the active period
of the one-shot pulse is generated).
62
4. Read the number of pulses counted. (Allow enough time to
ensure that the active period of the one-shot occurred and that
events have been counted.)
5. Determine the measurement period using the following
equation:
Measurement period = 1
Clock Frequency
6. Determine the frequency of the clock input signal using the
following equation:
Frequency Measurement = Number of Events
Measurement Period
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. One way to wire
a frequency measurement operation is to use the same wiring as an
* Active Pulse Width
Page 63

Principles of Operation
event counting application, but not use an external gate signal. Refer
to the DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting a
frequency measurement application.
Edge-to-Edge Measurement
Use edge-to-edge measurement mode if you want to measure the
time interval between a specified start edge and a specified stop edge.
2
2
The start edge and the stop edge can occur on the rising edge of the
Counter n Gate input, the falling edge of the Counter n Gate input,
the rising edge of the Counter n Clock input, or the falling edge of the
Counter n Clock input. When the start edge is detected, the
counter/timer starts incrementing, and continues incrementing until
the stop edge is detected. The C/T then stops incrementing until it is
enabled to start another measurement.
You can use edge-to-edge measurement to measure the following:
•Pulse width of a signal pulse (the amount of time that a signal
pulse is in a high or a low state, or the amount of time between a
rising edge and a falling edge or between a falling edge and a
rising edge). You can calculate the pulse width as follows:
− Pulse width = Number of counts/18 MHz
• Period of a signal pulse (the time between two occurrences of the
same edge - rising edge to rising edge or falling edge to falling
edge). You can calculate the period as follows:
− Period = 1/Frequency
− Period = Number of counts/18 MHz
• Frequency of a signal pulse (the number of periods per second).
You can calculate the frequency as follows:
2
2
2
2
2
2
− Frequency = 18 MHz/Number of Counts
When the operation is complete, you can read the value of the
counter.
2
63
Page 64

Chapter 2
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as edge-to-edge
measurement mode (measure), the C/T clock source as internal, the
start edge type, and the stop edge type.
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. Refer to the
DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting an
edge-to-edge measurement application.
Rate Generation
Use rate generation mode to generate a continuous pulse output
signal from the Counter n Out line; this mode is sometimes referred
to as continuous pulse output or pulse train output. You can use this
pulse output signal as an external clock to pace other operations, such
as analog input, analog output, or other counter/timer operations.
The pulse output operation is enabled whenever the Counter n Gate
signal is at the specified level. While the pulse output operation is
enabled, the counter outputs a pulse of the specified type and
frequency continuously. As soon as the operation is disabled, rate
generation stops.
64
The period of the output pulse is determined by the C/T clock source
(either internal using a clock divider, or external). You can output
pulses using a maximum frequency of 9 MHz (this is the frequency of
the Counter n Out signal). Refer to page 57 for more information
about the C/T clock sources.
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as rate generation
(rate), the C/T clock source as either internal or external, the clock
divider (for an internal clock), the polarity of the output pulses
(high-to-low transition or low-to-high transition), the duty cycle of
the output pulses, and the active gate type (low-level or high-level).
Refer to page 59 for more information about pulse output signals and
to page 58 for more information about gate types.
Page 65

Principles of Operation
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. Refer to the
DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting a rate
generation application.
One-Shot
Use one-shot mode to generate a single pulse output signal from the
Counter n Out line when the specified edge is detected on the
Counter n Gate signal. You can use this pulse output signal as an
external digital (TTL) trigger to start other operations, such as analog
input or analog output operations.
After the single pulse is output, the one-shot operation stops. All
subsequent clock input signals and gate input signals are ignored.
The period of the output pulse is determined by the C/T clock source
(either internal using a clock divider, or external). Note that in
one-shot mode, the internal C/T clock is more useful than an external
C/T clock; refer to page 57 for more information about the C/T clock
sources.
2
2
2
2
2
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as one-shot, the
clock source as internal (recommended), the clock divider, the
polarity of the output pulse (high-to-low transition or low-to-high
transition), the duty cycle of the output pulse, and the active gate
type (rising edge or falling edge). Refer to page 59 for more
information about pulse output types and to page 58 for more
information about gate types.
Note: In the case of a one-shot operation, use a duty cycle as close
to 100% as possible to output a pulse immediately. Using a duty
cycle closer to 0% acts as a pulse output delay.
2
2
2
2
65
Page 66

Chapter 2
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. Refer to the
DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting a
one-shot application.
Repetitive One-Shot
Use repetitive one-shot mode to generate a pulse output signal from
the Counter n Out line whenever the specified edge is detected on the
Counter n Gate signal. You can use this mode to clean up a poor clock
input signal by changing its pulse width, and then outputting it.
The module continues to output pulses until you stop the operation.
Note that any Counter n Gate signals that occur while the pulse is
being output are not detected by the module.
The period of the output pulse is determined by the C/T clock source
(either internal using a clock divider, or external). Note that in
repetitive one-shot mode, the internal C/T clock is more useful than
an external clock; refer to page 57 for more information about the
C/T clock sources.
66
Using software, specify the counter/timer mode as repetitive
one-shot (oneshot-rpt), the polarity of the output pulses (high-to-low
transition or low-to-high transition), the duty cycle of the output
pulses, the C/T clock source as internal (recommended), the clock
divider, and the active gate type (rising edge or falling edge). Refer to
page 59 for more information about pulse output types and to page
58 for more information about gates.
Note: In the case of a repetitive one-shot operation, use a duty cycle
as close to 100% as possible to output a pulse immediately. Using a
duty cycle closer to 0% acts as a pulse output delay.
Page 67

Principles of Operation
Make sure that the signals are wired appropriately. Refer to the
DT9834 Getting Started Manual for an example of connecting a
repetitive one-shot application.
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
67
Page 68

Chapter 2
68
Page 69

3
Supported Device Driver
Capabilities
Data Flow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Buffering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
DMA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Triggered Scan Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Synchronous Digital I/O. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Clocks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Counter/Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Miscellaneous . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
69
Page 70

Chapter 3
The DT9834 Series Device Driver provides support for the analog
input (A/D), analog output (D/A), digital input (DIN), digital output
(DOUT), and counter/timer (C/T) subsystems. For information on
how to configure the device driver, refer to the DT9834 Series Getting
Started Manual.
Table 6: DT9834 Series Subsystems
DT9834 Series A/D D/A
Total Subsystems on Module 1 2 1 1 5
a. The first D/A subsystem (Element 0) is used for the analog output voltage.
Element 0 is either 12-bits or 16-bits, depending on the model of the module
that you are using. The output range is
(Element 1) is used for the analog input threshold trigger (See “Input
Triggers” on page 40.) Element 1 has a resolution of 8-bits and a range of 0 to
255, where 0 equals 0V and 255 equals +10V.
b. The DIN subsystem contains 16 digital input lines.
c. The DOUT subsystem contains 16 digital output lines.
±10V. The second D/A subsystem
a
DIN
b
DOUT
c
C/T
The tables in this chapter summarize the features available for use
with the DataAcq SDK and the DT9834 Series modules. The DataAcq
SDK provides functions that return support information for specified
subsystem capabilities at run-time.
70
The first row in each table lists the subsystem types. The first column
in each table lists all possible subsystem capabilities. A description of
each capability is followed by the parameter used to describe that
capability in the DataAcq SDK.
Note: Blank fields represent unsupported options.
The DataAcq SDK uses the functions olDaGetSSCaps (for those
queries starting with OLSSC) and olDaGetSSCapsEx (for those
Page 71

queries starting with OLSSCE) to return the supported subsystem
capabilities for a device.
For more information, refer to the description of these functions in
the DataAcq SDK online help. See the DataAcq User’s Manual for
information on launching this help file.
Data Flow
Supported Device Driver Capabilities
3
3
Table 7: DT9834 Series Data Flow Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Single-Value Operation Support
OLSSC_SUP_SINGLEVALUE Yes Yes Yes Yes
Continuous Operation Support
OLSSC_SUP_CONTINUOUS Yes Yes Yes
Continuous Operation until Trigger Event Support
OLSSC_SUP_CONTINUOUS_PRETRIG
Continuous Operation before & after Trigger Event
OLSSC_SUP_CONTINUOUS_ABOUTTRIG
DT-Connect Support
OLSSC_SUP_DTCONNECT
Continuous DT-Connect Support
OLSSC_SUP_DTCONNECT_CONTINUOUS
Burst DT-Connect Support
OLSSC_SUP_DTCONNECT_BURST
a. The DIN subsystem supports continuous mode by allowing you to read the digital input port
(all 16 digital input lines) using the analog input channel-gain list.
b. The DOUT subsystem supports continuous mode by allowing you to output data from the
digital output port (all 16 digital output lines) using the output channel list.
c. The C/T subsystem supports continuous mode by allowing you to read the value of one or
more of the five counter/timer channels using the analog input channel-gain list.
a
Ye sb
Ye sc
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
71
Page 72

Chapter 3
Buffering
Table 8: DT9834 Series Buffering Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Buffer Support
OLSSC_SUP_BUFFERING Yes Yes
Single Buffer Wrap Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_WRPSINGLE Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Multiple Buffer Wrap Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_WRPMULTIPLE Yes Yes
Inprocess Buffer Flush Support
OLSSC_SUP_INPROCESSFLUSH Yes
Waveform Generation Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_WAVEFORM_MODE Yes
a. The data from the DT9834 module is transferred to the host in 4,096-byte (2,048-sample)
segments. If the application calls olDaFlushFromBufferInprocess before the module has
transferred 2,048 samples to the host, the buffer on the done queue will contain 0 samples.
Your application program must deal with these situations when flushing an inprocess buffer.
a
72
Page 73

Supported Device Driver Capabilities
DMA
Table 9: DT9834 Series DMA Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Number of DMA Channels
OLSSC_NUMDMACHANS 00000
Supports Gap Free Data with No DMA
OLSSC_SUP_GAPFREE_NODMA Yes Yes
Supports Gap Free Data with Single DMA
OLSSC_SUP_GAPFREE_SINGLEDMA
Supports Gap Free Data with Dual DMA
OLSSC_SUP_GAPFREE_DUALDMA
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
73
Page 74

Chapter 3
Triggered Scan Mode
Table 10: DT9834 Series Triggered Scan Mode Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Triggered Scan Support
OLSSC_SUP_TRIGSCAN Yes
Maximum Number of CGL Scans per Trigger
OLSSC_MAXMULTISCAN 256
Supports Scan per Trigger Event Triggered Scan
OLSSC_SUP_RETRIGGER_SCAN_PER_
TRIGGER Yes
Supports Internal Retriggered Triggered Scan
OLSSC_SUP_RETRIGGER_INTERNAL Yes
Extra Retrigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_RETRIGGER_EXTRA Yes
Maximum Retrigger Frequency
OLSSCE_MAXRETRIGGER 250 kHz 250 kHz 0 0 0
Minimum Retrigger Frequency
OLSSCE_MINRETRIGGER 0.75 Hz 0.75 Hz 0 0 0
a
0000
74
a. The channel-gain list depth of 1024 entries in conjunction with a multiscan of 256 provides an
effective channel-gain list depth of up to 256K entries.
Page 75

Supported Device Driver Capabilities
Gain
Table 11: DT9834 Series Gain Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Maximum Channel-Gain List Depth
OLSSC_CGLDEPTH 1024 5 1 1 0
Sequential Channel-Gain List Support
OLSSC_SUP_SEQUENTIAL_CGL Yes Yes
Zero Start Sequential Channel-Gain List Support
OLSSC_SUP_ZEROSEQUENTIAL_CGL Yes Yes
Random Channel-Gain List Support
OLSSC_SUP_RANDOM_CGL Yes
Simultaneous Sample-and-Hold Support
OLSSC_SUP_SIMULTANEOUS_SH
Channel List Inhibit Support
OLSSC_SUP_CHANNELLIST_INHIBIT Yes
Programmable Gain Support
OLSSC_SUP_PROGRAMGAIN Yes
Number of Gains
OLSSC_NUMGAINS 4 1110
Noncontiguous Channels in Channel-Gain List
OLSSC_NONCONTIGUOUS_CHANNELNUM
AutoRanging Support
OLSSC_SUP_SINGLEVALUE_AUTORANGE
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
75
Page 76

Chapter 3
Synchronous Digital I/O
Table 12: DT9834 Series Synchronous Digital I/O Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Synchronous Digital I/O Support
OLSSC_SUP_SYNCHRONOUS_DIGITALIO Yes
Maximum Synchronous Digital I/O Value
OLSSC_MAX_DIGITALIOLIST_VALUE 1 65,535 0 0 0
Channels
Table 13: DT9834 Series Channel Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
76
Number of Channels
OLSSC_NUMCHANNELS
SE Support
OLSSC_SUP_SINGLEENDED Yes
SE Channels
OLSSC_MAXSECHANS 16 0000
DI Support
OLSSC_SUP_DIFFERENTIAL Yes Yes Yes Yes
DI Channels
OLSSC_MAXDICHANS 84110
DT2896 Channel Expansion Support
OLSSC_SUP_EXP2896
DT727 Channel Expansion
OLSSC_SUP_EXP727
a. For modules with 16 SE or 8 DI channels, channels 0 to 15 read the analog input channels;
channel 16 reads all 16 bits from the DIN subsystem; channels 17 to 26 read the C/T channels.
For modules with 32 SE or 16 DI channels, channels 0 to 31 read the analog input channels;
channel 32 reads all 16 bits from the DIN subsystem; channels 33 to 42 read the C/T channels.
27 or
a
42
4 1 1 0
Page 77

Supported Device Driver Capabilities
Filters
Table 14: DT9834 Series Filter Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Filter/Channel Support
OLSSC_SUP_FILTERPERCHAN
Number of Filters
OLSSC_NUMFILTERS 11110
Ranges
3
3
3
Table 15: DT9834 Series Range Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Number of Voltage Ranges
OLSSC_NUMRANGES 11000
Range per Channel Support
OLSSC_SUP_RANGEPERCHANNEL
Resolution
Table 16: DT9834 Series Resolution Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Software Programmable Resolution
OLSSC_SUP_SWRESOLUTION
Number of Resolutions
OLSSC_NUMRESOLUTIONS 1
a. Depending on the module that you purchased, the resolution is either 12 bits or 16 bits.
a
1a 1 1 1
3
3
3
3
3
3
77
Page 78

Chapter 3
Triggers
Table 17: DT9834 Series Trigger Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Software Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_SOFTTRIG Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
External Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_EXTERNTRIG Yes
Positive Threshold Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_THRESHTRIGPOS Yes
Negative Threshold Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_THRESHTRIGNEG
Analog Event Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_ANALOGEVENTTRIG
Digital Event Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_DIGITALEVENTTRIG
Timer Event Trigger Support
OLSSC_SUP_TIMEREVENTTRIG
Number of Extra Triggers
OLSSC_NUMEXTRATRIGGERS 1 0 0 0 0
a
Ye s Yes
78
a. OL_TRG_EXTERN is the rising-edge external digital (TTL) trigger input; OL_TRG_EXTRA is
the falling-edge digital external (TTL) trigger input; OL_TRG_THRESHPOS is the
positive-edge analog threshold trigger from an analog input channel.
Page 79

Supported Device Driver Capabilities
Clocks
Table 18: DT9834 Series Clock Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Internal Clock Support
OLSSC_SUP_INTCLOCK Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
External Clock Support
OLSSC_SUP_EXTCLOCK Yes Yes Yes
Simultaneous Input/Output on a Single Clock
Signal
OLSSC_SIMULTANEOUS_CLOCKING No Yes
Number of Extra Clocks
OLSSC_NUMEXTRACLOCKS 00000
Base Clock Frequency
OLSSCE_BASECLOCK 18 MHz 18 MHz 0 0 18 MHz
Maximum External Clock Divider
OLSSCE_MAXCLOCKDIVIDER 1111
Minimum External Clock Divider
OLSSCE_MINCLOCKDIVIDER 11112
Maximum Throughput
OLSSCE_MAXTHROUGHPUT 500 kHz 500 kHz 0 0 9 MHz
Minimum Throughput
OLSSCE_MINTHROUGHPUT 0.75 Hz 0.75 Hz 0 0
2,147,
483,647
0.004
Hz
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
79
Page 80

Chapter 3
Counter/Timers
Table 19: DT9834 Series Counter/Timer Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Cascading Support
OLSSC_SUP_CASCADING
Event Count Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_COUNT Yes
Generate Rate Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_RATE Yes
One-Shot Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_ONESHOT Yes
Repetitive One-Shot Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_ONESHOT_RPT Yes
Up/Down Counting Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_UP_DOWN Yes
Edge-to-Edge Measurement Mode Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_MEASURE 15
Continuous Edge-to-Edge Measurement Mode
Support
OLSSC_SUP_CTMODE_CONT_MEASURE
High to Low Output Pulse Support
OLSSC_SUP_PLS_HIGH2LOW Yes
Low to High Output Pulse Support
OLSSC_SUP_PLS_LOW2HIGH Yes
None (internal) Gate Type Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_NONE Yes
High Level Gate Type Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_HIGH_LEVEL Yes
Low Level Gate Type Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_LOW_LEVEL Yes
High Edge Gate Type Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_HIGH_EDGE Yes
a
b
b
b
80
Page 81

Supported Device Driver Capabilities
Table 19: DT9834 Series Counter/Timer Options (cont.)
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Low Edge Gate Type Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_LOW_EDGE Yes
Level Change Gate Type Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_LEVEL
High Level Gate Type with Input Debounce
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_HIGH_LEVEL_DEBOUNCE
Low Level Gate Type with Input Debounce Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_LOW_LEVEL_DEBOUNCE
High Edge Gate Type with Input Debounce
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_HIGH_EDGE_DEBOUNCE
Low Edge Gate Type with Input Debounce Support
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_LOW_EDGE_DEBOUNCE
Level Change Gate Type with Input Debounce
OLSSC_SUP_GATE_LEVEL_DEBOUNCE
Fixed Pulse Width Support
OLSSC_SUP_FIXED_PULSE_WIDTH
Quadrature Decoder
OLSSC_SUP_QUADRATURE_DECODER
a. Edge-to-edge measurement mode is supported on both the gate and clock signals; rising and
falling edges are both supported.
b. High-edge and low-edge are supported for one-shot and repetitive one-shot modes.
High-level and low-level are supported for event counting, up/down counting, frequency
measurement, edge-to-edge measurement, and rate generation modes.
3
b
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
81
Page 82

Chapter 3
Miscellaneous
Table 20: DT9834 Series Miscellaneous Options
DT9834 Series A/D D/A DIN DOUT C/T
Simultaneous Start List Support
OLSSC_SUP_SIMULTANEOUS_START Yes Yes
Pause Operation Support
OLSSC_SUP_PAUSE
Asynchronous Operation Support
OLSSC_SUP_POSTMESSAGE Yes Yes Yes
Binary Encoding Support
OLSSC_SUP_BINARY Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Twos Complement Support
OLSSC_SUP_2SCOMP
Interrupt Support
OLSSC_SUP_INTERRUPT Yes Yes
FIFO in Data Path Support
OLSSC_SUP_FIFO
Output FIFO Size
OLSSC_FIFO_SIZE_IN_K 128
Data Processing Capability
OLSSC_SUP_PROCESSOR Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Software Calibration Support
OLSSC_SUP_SWCAL Yes
c
Ye sc
b
a
Ye s
82
a. The DIN subsystem supports the posting of messages only if the digital input port is
configured for continuous mode and if you used the Open Layers Control Panel applet to
select any of the first eight digital input lines to perform interrupt-on-change operations. The
device driver posts the OLDA_WM_EVENTDONE_WITH_DATA message when a bit
changes state. The 16-bit value of the digital input port is also returned.
b. At the present time, this query is supported for the DT9834 Series modules only. For this
module, the output FIFO size is always 128 K.
c. DT9834 Series modules are calibrated at the factory. If you want to readjust the calibration of
the analog input or analog output circuitry, refer to Chapter 6 starting on page 125.
Page 83

4
Programming Flowcharts
Single-Value Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Continuous A/D Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Continuous D/A Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Continuous Digital Input Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Continuous Digital Output Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Event Counting Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Up/Down Counting Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Frequency Measurement Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Edge-to-Edge Measurement Operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Pulse Output Operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Simultaneous Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
83
Page 84

Chapter 4
The following flowcharts show the steps required to perform data
acquisition operations using DT-Open Layers. For illustration
purposes, the DataAcq SDK functions are shown; however, the
concepts apply to all DT-Open Layers software.
Note that many steps represent several substeps; if you are
unfamiliar with the detailed operations involved with any one step,
refer to the indicated page for detailed information. Optional steps
appear in shaded boxes.
84
Page 85

Single-Value Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Specify A/D subsystem 0 for an analog input
Get a handle to the subsystem with
olDaGetDASS.
Set the data flow to
OL_DF_SINGLEVALUE using
olDaSetDataFlow.
operation, D/A subsystem 0 for an analog output
operation, DIN subsystem 0 for a digital input
operation, or DOUT subsystem 0 for a digital
output operation.
Programming Flowcharts
4
4
4
For A/D subsystem 0 only,
set the range using olDaSetRange.
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Go to the next page.
4
4
4
4
4
4
85
Page 86

Chapter 4
Single-Value Operations (cont.)
Continued from previous page.
For the A/D subsystem, read a
single analog input value from
the specified channel (0 to 31 for
single-ended or
pseudo-differential mode or 0 to
15 for differential mode) using
the specified gain (1, 2, 4, or 8).
For the DIN subsystem, read the
value of the 16-bit digital input
port.
Acquiring
data?
No
Ye s
Acquire a single value using
olDaGetSingleValue.
Output a single value using
olDaPutSingleValue.
For the D/A subsystem, the value is
output to the specified channel
(DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, or DAC3)
using a gain of 1. For the DOUT
subsystem, the value is output to
the 16-bit digital output port.
Acquire/
output
Ye s
another
value?
No
Release the subsystem using
olDaReleaseDASS.
Release the driver and terminate the
session using olDaTerminate.
86
Page 87

Continuous A/D Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to the A/D subsystem
with olDaGetDASS.
Set the data flow using
olDaSetDataFlow.
Specify OL_DF_CONTINUOUS (the
default value).
Programming Flowcharts
4
4
4
Set up the analog input
channel-gain list (see page 105).
Set up the clocks and triggers
(see page 106).
Go to the next page.
4
4
4
4
4
4
87
Page 88

Chapter 4
Continuous A/D Operations (cont.)
Continued from previous page.
Set up triggered scan
(see page 107).
Set up buffering (see page 108).
After you configure the subsystem, you can
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Start the operation with olDaStart.
use olDaGetClockFrequency to return the
actual frequency of the internal clock; you
can use olDaGetRetriggerFrequency to
return the actual frequency of the internal
retrigger clock.
88
Deal with messages and buffers
(see page 110).
Stop the operation (see page 115).
Clean up the operation (see page 116).
Page 89

Continuous D/A Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to D/A subsystem 0
with olDaGetDASS.
Specify OL_DF_CONTINUOUS with
olDaSetDataFlow.
Continuous mode is the default setting.
Programming Flowcharts
4
4
4
Set up the output channel list
(see page 105).
Set up the clocks and triggers
(see page 106).
Go to the next page.
4
4
4
4
4
4
89
Page 90

Chapter 4
Continuous D/A Operations (cont.)
Continued from previous page.
Set up buffering (see page 109).
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Start the operation with olDaStart.
Deal with messages and buffers
(see page 110).
90
Stop the operation (see page 115).
Clean up the operation (see page 116).
Page 91

Programming Flowcharts
Continuous Digital Input Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to A/D subsystem 0
with olDaGetDASS.
Set up the analog input
channel-gain list (see page 105).
Set up the clocks and triggers
(see page 106).
Specify channel 16 or 32 as the digital
input port depending on how many
analog input channels your board
supports; specify a gain of 1.
4
4
4
4
Set up buffering (see page 108).
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Start the operation with olDaStart.
Deal with messages and buffers
(see page 110).
Stop the operation (see page 115).
Clean up the operation (see page 116).
4
4
4
4
4
91
Page 92

Chapter 4
Continuous Digital Output Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to the D/A subsystem with
olDaGetDASS.
Set up the analog output
channel list (see page 105).
Set up the clocks and triggers
(see page 106).
Set up buffering (see page 109).
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Start the operation with olDaStart.
Stop the operation (see page 115).
Clean up the operation (see page 116).
Specify channel 4 as the digital
output port; specify a gain of 1.
92
Page 93

Event Counting Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to the C/T subsystem with
olDaGetDASS.
Specify the clock source as
OL_CLK_EXTERNAL using
olDaSetClockSource.
Specify the clock divider using
olDaSetExternalClockDivider.
Specify the gate type as high-level
(OL_GATE_HIGH_LEVEL) or low-level
(OL_GATE_LOW_LEVEL) using
olDaSetGateType
Specify the appropriate C/T
subsystem/element. The DT9834 Series
supports five elements (0, 1, 2, 3, 4).
Specify a clock divider between 2 (the
default) and 2,147,483,647. The clock
divider determines the frequency at which
to pace the operation (this is the frequency
of the Counter n Out signal).
Programming Flowcharts
4
4
4
4
4
4
Specify the mode as OL_CTMODE_COUNT
using olDaSetCTMode.
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Go to the next page.
4
4
4
93
Page 94

Chapter 4
Event Counting Operations (cont.)
Continued from previous page.
Start the operation using olDaStart.
Read the events counted using
olDaReadEvents.
Get update
of events
total?
No
Stop the operation (see page 115).
Release each subsystem with
olDaReleaseDASS.
Release the device driver and terminate
the session with olDaTerminate.
Ye s
94
Page 95

Up/Down Counting Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to the C/T subsystem with
olDaGetDASS.
Specify the clock source as
OL_CLK_EXTERNAL using
olDaSetClockSource.
Specify the clock divider using
olDaSetExternalClockDivider.
Specify the mode as
OL_CTMODE_UP_DOWN
using olDaSetCTMode.
Specify the appropriate C/T
subsystem/element. The DT9834 Series
supports five elements (0, 1, 2, 3, 4).
Specify a clock divider between 2 (the
default) and 2,147,483,647. The clock
divider determines the frequency at which
to pace the operation (this is the frequency
of the Counter n Out signal).
Programming Flowcharts
4
4
4
4
4
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Go to the next page.
4
4
4
4
95
Page 96

Chapter 4
Up/Down Counting Operations (cont.)
Continued from previous page.
Start the operation using olDaStart.
Read the events counted using
olDaReadEvents.
Get update
of events
total?
No
Stop the operation (see page 115).
Release each subsystem with
olDaReleaseDASS.
Release the device driver and terminate
the session with olDaTerminate.
Ye s
96
Page 97

Programming Flowcharts
Frequency Measurement Operations
The following flowchart shows the steps required to perform a
frequency measurement operation using the Windows timer. If you
need more accuracy the Windows timer provides, refer to page 61 of
this manual or to your DataAcq SDK User’s Manual for more
information.
4
4
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to the C/T subsystem with
olDaGetDASS.
Specify the clock source as
OL_CLK_EXTERNAL using
olDaSetClockSource.
Specify the clock divider using
olDaSetExternalClockDivider.
Specify the mode as OL_CTMODE_COUNT
using olDaSetCTMode.
Go to the next page.
Specify the appropriate C/T
subsystem/element. The DT9834 Series
supports five elements (0, 1, 2, 3, 4).
Specify a clock divider between 2 (the
default) and 2,147,483,647. The clock
divider determines the frequency at which
to pace the operation (this is the frequency
of the Counter n Out signal).
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
97
Page 98

Chapter 4
Frequency Measurement Operations
(cont.)
Continued from previous page.
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Start the frequency measurement
operation using olDaMeasureFrequency.
Message is in the form
Measure
done
message
returned?
No
Ye s
OLDA_WM_MEASURE_DONE.
Use the LongtoFreq (IParam)
macro to get the measured
frequency value:
float = Freq;
Freq = LongtoFreq (IParam);
98
Release each subsystem with
olDaReleaseDASS.
Release the device driver and terminate
the session with olDaTerminate.
Page 99

Programming Flowcharts
Edge-to-Edge Measurement Operations
Initialize the device driver and get the
device handle with olDaInitialize.
Get a handle to the C/T subsystem with
olDaGetDASS.
Specify the mode as
OL_CTMODE_MEASURE
using olDaSetCTMode.
Specify the clock source as
OL_CLK_INTERNAL using
olDaSetClockSource.
Specify the appropriate C/T
subsystem/element. The DT9834 Series
supports five elements (0, 1, 2, 3, 4).
4
4
4
4
4
Specify the start edge
using olDaSetMeasureStartEdge.
Specify the stop edge
using olDaSetMeasureStopEdge.
Configure the subsystem using
olDaConfig.
Go to the next page.
Specify OL_GATE_RISING for a rising
edge on the Counter n Gate input,
OL_GATE_FALLING for a falling edge on
the Counter n Gate input,
OL_CLOCK_RISING for a rising edge on
the Counter n Clock input, or
OL_CLOCK_FALLING for a falling edge
on the Counter n Clock input.
4
4
4
4
99
Page 100

Chapter 4
Edge-to-Edge Measurement
Operations (cont.)
Continued from previous page.
Start the operation using olDaStart.
Message is in the form
Event
done
message
returned?
Ye s
No
OLDA_WM_EVENT_DONE. Note
that if you want to perform another
edge-to-edge measurement, you
can call olDaStart again or use the
OLDA_WM_EVENT_DONE handler
to call olDaStart again.
100
The LParam parameter of the
message contains the count.
Release each subsystem with
olDaReleaseDASS.
Release the device driver and terminate
the session with olDaTerminate.
 Loading...
Loading...