Page 1

379 Campus Drive, Suite 100
TM
I
NSTALLATION AND ADMINISTRATION
G
FOR
UIDE
HP-UX®
Somerset, NJ 08873
fax: 732.667.1091
phone: 732.667.1080
email: sales@datatekcorp.com
http://www.datatekcorp.com
R
ELEASE
I
SSUE 2
1.0.22
Page 2
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................4
1.1
What is IP-CommKit? .....................................................................................4
2 DOCUMENTATION.........................................................................................5
3 INSTALLATION AND CONFIGURATION ......................................................6
3.1
Overview .........................................................................................................6
3.2
IP Addresses...................................................................................................6
3.3
UTM Installation..............................................................................................8
3.4
BNS Node Configuration..............................................................................10
3.5
Software Installation ....................................................................................14
3.5.1 Prerequisites............................................................................................................ 14
3.5.2 Removing CommKit Host Interface Software ...................................................... 14
3.5.3 Installing IP-CommKit Software............................................................................. 15
3.5.4 Registration ............................................................................................................. 18
3.6
Customize the Control Tables .....................................................................21
3.6.1 dkiptab...................................................................................................................... 21
3.6.2 dkitrc and dkitcfg .................................................................................................... 21
3.6.3 dksrvtab ................................................................................................................... 22
4 CONTROL TABLES .....................................................................................23
5 ADMINISTRATION .......................................................................................24
5.1
Files That Grow ............................................................................................ 24
5.2
dkitrc Script File ..........................................................................................24
5.3
Special Device Files .....................................................................................24
5.4
Printer Administration..................................................................................25
6 TROUBLESHOOTING ..................................................................................26
6.1
Overview .......................................................................................................26
6.2
Procedures....................................................................................................26
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
2
Page 3
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
6.2.1 Check that the UTM is in service ........................................................................... 26
6.2.2 Check that the CPM is in service........................................................................... 27
6.2.3 Check the Mode Switch on the UTM ..................................................................... 29
6.2.4 Ping the UTM from the host ................................................................................... 30
6.2.5 Check /var/opt/dk/dkipdlog .................................................................................... 30
6.2.6 Check /var/opt/dk/log/dkdaemonlog ..................................................................... 32
6.2.7 Check /var/opt/dk/dksrvlog .................................................................................... 34
6.3
Stopping and Starting ..................................................................................37
7 COMPATIBILITY...........................................................................................38
8 MANUAL PAGES .........................................................................................39
9 END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR SOFTWARE .............................40
9.1
SOFTWARE LICENSE ..................................................................................40
9.2
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS..........................................................40
9.3
SOFTWARE SUPPORT.................................................................................41
9.4
EXPORT RESTRICTIONS .............................................................................41
9.5
9.6
9.7
9.8
LIMITED WARRANTY ...................................................................................41
NO OTHER WARRANTIES ...........................................................................41
SPECIAL PROVISIONS.................................................................................42
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY ........................................................................... 42
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
3
Page 4
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
1 1
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
1 I N T R O D U C T I O N
1.1 W
HAT IS
IP-C
OMMKIT
?
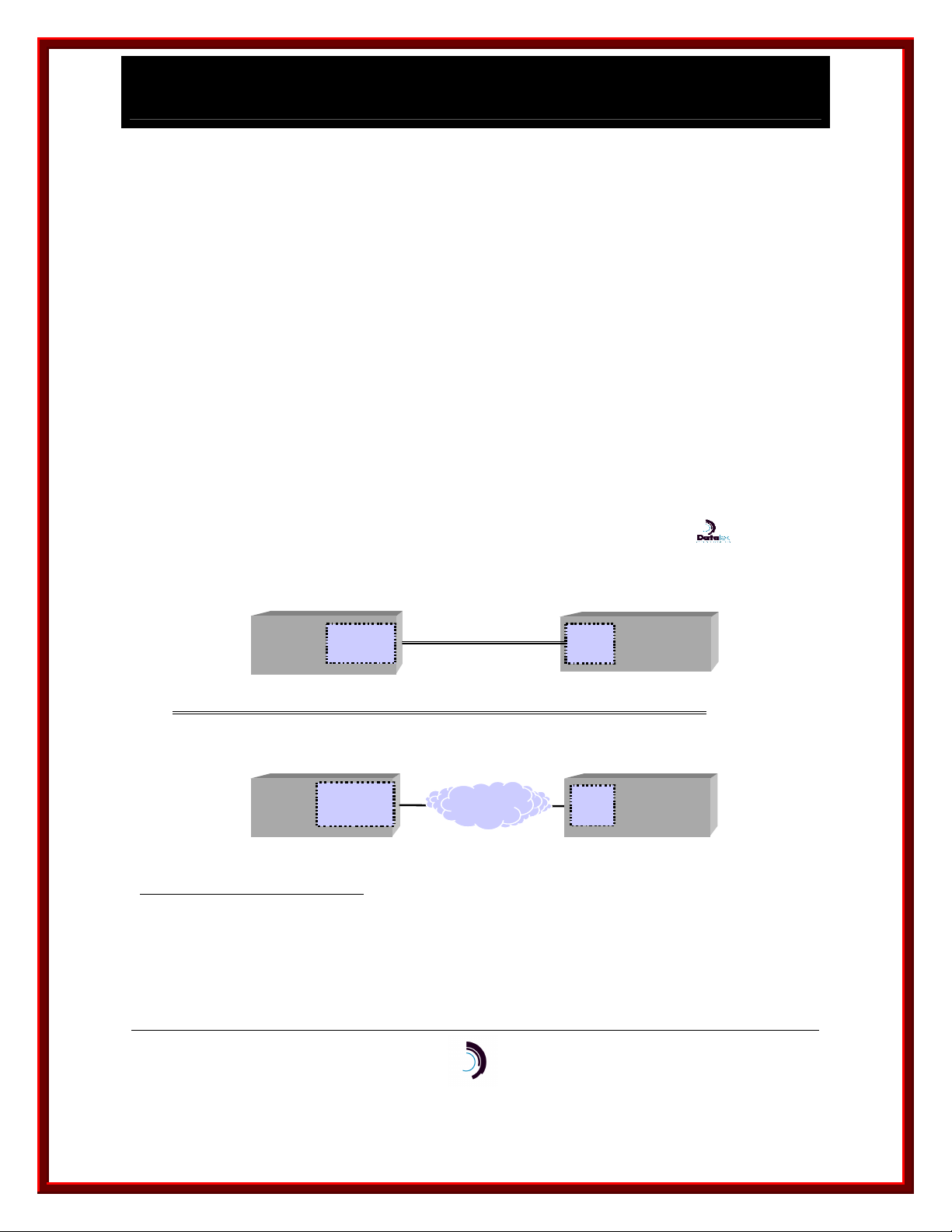
IP-CommKit is a new twist on the CommKit® Host Interface for BNS-2000 and BNS-2000 VCS
(a.k.a. Datakit II VCS). Where the CommKit Host Interface uses a fiber optic cable to connect
the host computer to the BNS node, IP-CommKit uses a 10Base-T LAN. Instead of a fiber
interface card in the host computer, IP-CommKit uses the host’s standard LAN interface card. In
the BNS node, use of IP-CommKit requires replacement of the CPM Module with a Universal
Trunk Module (UTM).
All of these changes are invisible to the host applications and the BNS network. Host
applications and CommKit features behave identically. No need to recompile your applications.
H o s t a n d N od e I n t e rfa c e s
C om m K i t
H os t In ter fa c e
BE FO RE ...
B EF O RE ...
O S H o s t
C om pu ter
F IBE R
M OD U L E
F I B E R O PT IC CA B L E
L I M IT E D DI S T A N C E
S E P AR AT ION
C PM H S
B NS - 2 00 0
o r
B NS - 2 00 0 V CS
IP -C o m m K it
H os t In ter fa c e
1 0 / 1 0 0 Ba s e TIP1 0 / 1 0 0 Ba s e T
AF TE R.. .
A FT E R.. .
O S H o s t
C om pu ter
S T AN D AR D
L AN
M OD U L E
U TM
A NY W H E RE
B NS - 2 00 0
o r
B NS - 2 00 0 V CS
IP-CommKit is a trademark of Alcatel-Lucent, Inc., licensed to Datatek Applications, Inc., a company
independent of Alcatel-Lucent, Inc.
Datakit is a registered trademark of Alcatel-Lucent, Inc., licensed to Datatek Applications, Inc., a company
independent of Alcatel-Lucent, Inc.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
4
Page 5
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
2 D O C U M E N T A T I O N
Since IP-CommKit behaves like a CommKit Host Interface, you can use the CommKit Host
Interface documentation to find answers to most questions. Specifically, use the CommKit Host
Interface for NCR PCI Computers Installation and Administration Guide. This document follows
the same general outline, i.e., it has the same major sections in the same order. Where there are
changes or additions for IP-CommKit, they are described in the appropriate section of this
document. While NCR computers running MP-RAS are very different from HP computers
running HP-UX, IP-CommKit is built from source code that was ported from the release of the
CommKit Host Interface that ran on NCR computers. As a result, much of the information in the
CommKit Host Interface for NCR PCI Computers Installation and Administration Guide applies to
IP-CommKit running on HP computers.
HP-UX and HP are registered trademarks of Hewlett Packard, Inc. Systems Division.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
5
Page 6

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
3 I N S T A L L A T I O N A N D C O N F I G U R A T I O N
3.1 O
This section describes the procedures for connecting a host computer to a Lucent Technologies
BNS-2000 or BNS-2000 VCS network using IP-CommKit.
This section supercedes the Installation and Configuration section of the CommKit Host Interface
for NCR PCI Computers Installation and Administration Guide.
This section references procedures in the UTM User’s Manual. Have it handy before you begin.
This section assumes that your host computer is already connected to a LAN. If it’s not, you
should follow the procedures supplied with your computer for connecting it to a LAN.
Installation and configuration of IP-CommKit consists of the following steps:
• Obtain an IP address for the UTM and determine the appropriate subnet mask. Also
• Install the UTM and I/O distribution board in the BNS node.
• Configure the UTM through its console port.
• Configure the UTM in the BNS node’s controller database.
VERVIEW
determine the host IP address and, if needed, a gateway IP address.
• Install the IP-CommKit software on the host computer
• Customize the dkiptab and, if needed, dkitcfg and the other control tables.
The following sections describe each step in detail.
3.2 IP A
This section assumes a basic knowledge of IP networks. If you don’t have this knowledge, we
recommend that you learn a little about them. We recommend Internetworking with TCP/IP, by
Douglas E. Comer. Otherwise, enlist the help of your IP network administrator.
10/13/11
DDRESSES
Datatek Applications Inc.
6
Page 7
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
Each UTM requires an IP address, as does the host computer. You should obtain IP addresses
for UTMs from your IP network administrator. This document assumes that the host computer is
already connected to a LAN, and thus already has an IP address assigned to it. If your host
connects to several LANs, it will have several IP addresses assigned to it, one for each LAN.
You should find out the addresses assigned to the LAN that the host will use for communicating
with the UTM. You need the host’s IP addresses in numeric form for configuring the UTM. To
obtain this, take a look at the file /etc/rc.config.d/netconf with pg, vi, or whatever you like to use to
look at text files. It is a shell script provided by HP that configures the LAN interfaces on your
machine at boot time. This file contains good comments from the HP developers, but the
important lines are the assignments to array variables with the name IP_ADDRESS and
SUBNET_MASK. Here is a sample of the relevant lines:
INTERFACE_NAME[0]=lan0
IP_ADDRESS[0]=135.17.59.216
SUBNET_MASK[0]=255.255.255.0
This host has one LAN interface named lan0, and its assigned IP address is 135.17.59.216.
To configure the UTM, you also need the subnet mask for the IP subnet to which it attaches.
Most often, an IP subnet corresponds to a LAN segment. For example, all interfaces attached to
the same 10Base-T hub are on the same LAN segment, and almost always have the same
subnet mask. If the host and UTM connect to the same subnet, you can find out the subnet
mask from the /etc/rc.config.d/netconf file. In the previous example, the subnet mask is
255.255.255.0.
If the host and UTM do not attach to the same subnet, your IP network administrator must provide
you with an appropriate subnet mask for the UTM. In addition, the administrator must provide
you with the IP address of a gateway router. This gateway must reside on the same subnet as
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
7
Page 8
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
the UTM, and must know how to route packets from the UTM to the host computer. Again, you
need the gateway address in numeric form.
3.3 UTM I
Consult the UTM User’s Manual, Section 3, for instructions on how to install the UTM and I/O
distribution board in the BNS node.
After you have installed the UTM and I/O distribution board in the BNS node, you must configure
the UTM. The initial configuration of the UTM must be done through its console port. You can
access the UTM console port in a variety of ways. For example, you can connect a “dumb”
terminal directly to the console port on the I/O distribution board. You can also connect the
console port into the BNS network through a SAM or TY module, and then access the console
through a terminal or host that is connected to the network. Section 3 of the UTM User’s Manual
shows how to make connections to the UTM’s console port.
To configure the UTM, you need an IP address and subnet mask that you will assign to the UTM,
as well as the IP address assigned to the host LAN interface. If the UTM and host are not on the
same subnet, you will also need the IP address of a gateway that can forward packets from the
NSTALLATION
UTM to the host.
Enter the following commands on the UTM console port.
<TRK-UNIV> login passwd=initial
<TRK-UNIV> rm
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
8
Page 9
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
<TRK-UNIV> trk type=IPDSU
<TRK-UNIV> trk modtype=CPM
<TRK-UNIV> lo ipaddr=utm_ip_address submask=utm_subnet_mask
<TRK-UNIV> ga ipaddr=gateway_ip_address
<TRK-UNIV> trk dest=host_ip_address
Here the IP addresses and subnet mask are shown in bold Italics. You would replace these
names with numbers when you enter the commands.
Enter the following command to check the configuration:
<TRK-UNIV> vfy mod
The output should be similar to the report below.
Current Configuration:
DK Board Type ==> TN1009 (CPM-HS) w/Serial# 136.
Service State ==> Out of Service.
Operating Mode ==> Simplex.
Trunk Type ==> IP-DSU Compatible Trunk on 10BaseT Network Port.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
9
Page 10
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
IP-DSU Loopback Status ==> Loopbacks are not enabled.
IP-DSU Data Encryption Status ==> Disabled.
Actual IP-DSU Service State ==> Not Connected.
Local MAC Address ==> 0.19.5.84.49.56
Local IP Address ==> utm_ip_address
Subnet Mask ==> subnet_mask
Gateway IP Address ==> gateway_ip_address
IP-DSU Destination IP Address ==> host_ip_address
SNMP Trap Manager ==> Not defined.
Check the address and subnet mask fields that you entered. If they are correct, enter the
following command to restore the UTM to service.
<TRK-UNIV> rs
The UTM has many useful console commands that are not described here. See section 4 of the
UTM User’s Manual for a complete description. Once you have done the initial configuration of
the UTM through the console port, you can access all console commands through the LAN port
via telnet. For example, you should be able to telnet to the UTM from the host on which you
installed the IP-CommKit software.
3.4 BNS N
If you are upgrading a CPM-HS module to a UTM, you don’t need to make any changes to the
BNS node configuration. You can simply remove the CPM-HS module and its I/O distribution
board, and install the UTM and its I/O distribution board in the same slot. The UTM appears as a
CPM-HS module to the controller in the BNS node.
ODE CONFIGURATION
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
10
Page 11
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
If this is a new installation, you must configure the UTM in the BNS node’s controller database.
The following procedure describes a simple configuration. It consists of entering a group, an
address and a cpm in the controller database.
Before you begin, pick a name that you will use as this host’s address in the BNS network. In
configurations using a single dkserver, it’s convenient to make this address and the group name
the same as the host’s nodename. By default, dkserver announces itself to the BNS node by the
host’s nodename. To determine this name, enter the following command on the host:
uname -n
This prints the host’s nodename. Note that the uname(1M) command with no flags is equivalent
to uname -s. This prints the system name, which can be different from the nodename. If you find
this confusing, you can use the setuname(1M) command to make the system name and node
name the same.
If you want to use a name that’s different from the host’s nodename, you must modify the dkitcfg
file. See section 3.6.2.
Now, enter a group. A group binds together a collection of like modules under one name. In this
simple example, there is only one UTM, so the group has only one member. In more complex
configurations, you can put up to eight UTMs in one group and distribute incoming calls between
these modules using round robin service.
The following dialogue shows the procedure for entering a group on the BNS node console. Text
that you type exactly is shown in bold, and text that you modify for your installation is shown in
bold italics. <Enter> and <Delete> refer to the enter and delete keys on your keyboard.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
11
Page 12
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
CC0> enter group
GROUP [up to 8 chars]: nodename
TYPE [local, trunk: +(local)]: local
DIRECTION [originate, receive, 2way]: 2way
DEVICE OR HOST [up to 8 chars: +(standard)]: <Enter>
PASSWORD [up to 8 chars, none: +(none)]: <Enter>
ROUND ROBIN SERVICE [per_port, per_module, none: +(none)]: <Enter>
GROUP [up to 8 chars]: <Delete>
Next, enter an address. An address is bound to one or more groups. In this simple example,
there is one group, with one UTM in the group. We use the same name for the group and
address in this example, although it’s not required.
CC0> enter address
LEVEL [network, area, exchange, local, speedcall: +(local)]: <Enter>
TYPE [numeric, mnemonic, both: +(mnemonic)]: <Enter>
MNEMONIC ADDRESS [up to 8 chars]: nodename
PAD SUPPORT [yes, no: +(no)]: <Enter>
DIRECTORY ENTRY [up to 30 chars double quoted, none: +(none)]:
"appropriate description of host"
GROUP(S) [up to 4 groups separated by commas, none: +(none)]:
nodename
ORIGINATING GROUP NAME SECURITY PATTERN(S)
[comma-separated pattern list, same_as, none: +(none)]:
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
12
Page 13
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
<Enter>
INITIAL SERVICE STATE [in, out: +(out)]: in
LEVEL [network, area, exchange, local, speedcall: +(local)]: <Delete>
Next, enter the cpm. In reality, the cpm is a UTM, but the BNS controller can’t tell the difference.
In the dialog below, you must use values for mod_address and num_channels that are correct
for your configuration. Use the slot number where you installed the UTM for the mod_address.
By default, dkdaemon(1M) sets the number of channels per UTM to 64, so use this value for
num_channels. If you want to use more channels, you must modify the dkitcfg file. See section
3.6.2
CC0> enter cpm
MODULE ADDRESS: mod_address
COMMENT [up to 60 chars double quoted, or none: +(none)]:
"appropriate comment"
HARDWARE TYPE [422, hs: +(hs)]: <Enter>
NUMBER OF CHANNELS [3-512: +(32)]: num_channels
CALL SCREENING PROFILE ID [up to 8 chars, none: +(none)]: <Enter>
CONNECT-TIME BILLING [on, off: +(off)]: <Enter>
SINGLE OR MULTIPLE GROUPS [single, multiple: +(single)]: <Enter>
GROUP [up to 8 chars]: nodename
ENDPOINT NUMBER OR RANGE [0000-9999, none: +(none)]: <Enter>
MODULE ADDRESS: <Delete>
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
13
Page 14

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
Finally, restore the cpm to service.
CC0> restore cpm
MODULE ADDRESS: mod_address
3.5 S
3.5.1 P
Before ordering and installing any software on your computer, verify that it is running a release of
its operating system that supports IP-CommKit. See the IP-CommKit Release Notes for a list of
supported operating system releases. Do not attempt to install the IP-CommKit software if your
computer is running an operating system release that is not supported. Also verify the kernel size:
32 or 64-bit and whether the libraries that are used are 32-bit or 64-bit. Also we need to know the
number of CPU’s/processors in the host. To determine this count, run the following command
which is usually in /usr/sbin:
$ sar -M –u 1 2
Contact us with the output of the command at ipcommkit@datatekcorp.com .
3.5.2 R
If you are upgrading a computer from the CommKit Host Interface to IP-CommKit, you must
remove the CommKit Host Interface software before installing the IP-CommKit. There are
several different versions of the CommKit Host Interface hardware and software for HP
OFTWARE INSTALLATION
REREQUISITES
EMOVING COMMKIT HOST INTERFACE SOFTWARE
computers, so you will need to consult the documentation provided by HP. As an example, for a
machine that uses the EISA bus fiber interface board, HP calls the CommKit Host Interface
software package for this board EisaDatakit. You would use the following procedure to remove it:
First, login as root. Now, enter the following command:
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
14
Page 15

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
# swremove EisaDatakit
However, the software package installed on your machine may have a different name. If you
don’t have your HP documentation, run the swlist(1M) command and look for Datakit or CommKit
in the description fields.
When you remove the software, you may see the following warning:
WARNING: The software specified contains a kernel fileset. It will be
necessary to reconfigure the kernel and reboot the system to
remove the functionality from the kernel.
If you plan to proceed immediately with the installation of IP-CommKit, you can ignore the notice
about rebooting the machine.
3.5.3 I
If a version of IP-CommKit was previously installed and the directory /tmp/ipcommkit is not empty,
remove its contents, logged in as root:
# cd /tmp/ipcommkit
# pwd (Verify that you are in the current directory)
# rm –rf *
Use the following procedure to install the IP-CommKit software.
NSTALLING
IP-C
OMMKIT SOFTWARE
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
15
Page 16

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
The IP-CommKit software is delivered as a .tar file, either on a Compact Disc or electronically.
First, login as root, then follow the appropriate procedure.
3 . 5 . 3 . 1 C
O M P AC T D I S C
Prepare for retrieving the .tar file from the CD:
# mkdir /cdrom
# mount –F cdfs –o cdcase,ro /dev/dsk/c1t2d0 /cdrom
Make a directory in which to expand the .tar file and go to that directory:
# mkdir /tmp/ipcommkit
# cd /tmp/ipcommkit
Retrieve the .tar file from the CD:
For HPUX R11_00 32 bit hosts:
# tar xf /cdrom/hp_11_00/ipckhp32.tar
For HPUX R11_00 64 bit hosts:
# tar xf /cdrom/hp_11_00/ipckhp64.tar
For HPUX R11_11 32 bit hosts:
# tar xf /cdrom/hp_11i/ipckhp32.tar
For HPUX R11_11 64 bit hosts:
# tar xf /cdrom/hp_11i/ipckhp64.tar
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
16
Page 17

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
For HPUX R10_20 hosts:
# tar xf /cdrom/hp_10_20/ipckhp.tar
Unmount the CD:
# umount /cdrom
To install the IP-CommKit software, enter the following command:
# swinstall –s /tmp/ipcommkit IPCOMMKIT
3 . 5 . 3 . 2 .
T AR FI L E
Instead of receiving a CD, the tar file may have been sent to you electronically. In that case,
make a directory in which to expand the tar file.
# mkdir /tmp/ipcommkit
The name of the .tar file will vary with the release. For example, for HPUX R10_20, the .tar file is
named ipckhp.tar.
Move this file to the /tmp/ipcommkit directory that you just created, then run the following
commands.
# cd /tmp/ipcommkit
# tar xf ipckhp.tar
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
17
Page 18

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
# swinstall -s /tmp/ipcommkit IPCOMMKIT
Your host is now configured to start the IP-CommKit software automatically at boot time. You can
reboot your host now, but you will need to register your copy of the software and configure your
control tables before you can use IP-CommKit. To reboot your host, enter the following
commands:
# cd /
# shutdown –y –r now
3.5.4 R
Starting with revision 1.0.12, the IP-CommKit software is copy-protected. You must obtain a
software key and register your copy of the software before you can use IP-CommKit.
Here is how the registration process works: When you purchase IP-CommKit, we provide you
with a software certificate number. For example, here is the software certificate number for the
IP-CommKit software running on one of my development machines:
20HP11113-000670-U6CU
If you received your software on a CD, the software certificate number is included in the package.
If the software was delivered electronically, the software certificate number is included in the e-
mail message. In either case, you must save the software certificate number since it serves as
your proof of purchase.
After installing the IP-CommKit software on your host computer, contact us to obtain a software
key. To generate your software key, we need your software certificate number and the
EGISTRATION
nodename of the host on which the software is installed. To determine the nodename, enter the
following command on the host:
$ uname -n
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
18
Page 19

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
This prints the host's nodename.
The best way to contact us is to send an e-mail message to the following address:
ipcommkit@datatekcorp.com
In addition to your software certificate number and your host's nodename, please include your
name, company's name, e-mail address and telephone number. Also include the revision
number of the IP-CommKit software. This will help us to contact you when maintenance releases
are available. To check the revision number of the IP-CommKit software, enter the following
command:
$ /usr/sbin/swlist -l product IPCOMMKIT
# Initializing...
# Contacting target "spleen"...
#
# Target: spleen:/
#
# IPCOMMKIT 1.0.22 IP-CommKit for HP-UX
In this example, my development host's name is spleen and the revision number is 1.0.22
We will send you a reply with a software key that we generate from your software certificate
number and your host's nodename. For example, here is the software key for my development
machine:
AK422-2222-2ZBR-5BXP
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
19
Page 20

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
While e-mail is the best way to obtain a software key, we can also give you one over the
telephone. Here are our names and numbers:
Dan Conklin Sue Stultz
Senior Project Manager Chief Operating Officer
732 667-1080 X162 732 667-1080 X131
With the software certificate number and software key, you can register the IP-CommKit software
on your host. Log in as root. If IP-CommKit is running, stop it first (see details in section 6.3) and
run the following command:
$ /opt/dk/sbin/dkregister
The command will prompt you for the software certificate number and the software key, then
validate the values that you enter. If they are correct, it will save the registration information on
the host's disk. You will need to re-register your IP-CommKit software on this host again when
you install subsequent maintenance releases.
It is now a good time to customize your control tables. (If you had just re-registered your IP-
CommKit software and do not need to customize your control tables, start IP-CommKit again.
See section 6.3 for details.)
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
20
Page 21

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
3.6 C
3.6.1
(IP-CommKit must be stopped before you update this table. See 6.3 for details.)
The dkiptab is a new control file for IP-CommKit that tells the IP-CommKit software the IP
addresses assigned to the UTM and the host LAN interfaces. Even if you are upgrading a
computer from the CommKit Host Interface to IP-CommKit, you still must enter the dkiptab
before IP-CommKit will operate. While the installation scripts create a dkiptab file in the
appropriate directory, it contains only comments. Fortunately, the dkiptab is very easy to enter
with your favorite text editor. See the manual page (dkiptab(4)) for the file format and examples.
3.6.2
/sbin/init.d/dkitrc is a shell script that starts and stops the IP-CommKit software on the host
computer. It is linked into several /sbin /rc?.d directories so that it runs automatically when the
init state of the host computer changes, i.e., at startup and shutdown. The operation of dkitrc is
controlled by /etc/rc.config.d/dkitcfg.
USTOMIZE THE CONTROL TABLES
DKIPTAB
DKITRC AND DKITCFG
The dkitrc and dkitcfg scripts for IP-CommKit are different from the /sbin/dkit and
/etc/rc.config.d/dkit scripts used in some versions of HP’s CommKit Host Interface software. If
you are upgrading a computer from the CommKit Host Interface to IP-CommKit, and you
customized the configuration in /etc/rc.config.d/dkit script, you will need to customize the
dkitcfg script supplied with the IP-CommKit software. The most common reasons for
customizing the dkitcfg script are to change the number of channels available per interface from
the default value of 64, and to change the number of logical interfaces from the default value of 1.
The dkitcfg script itself contains instructions for making modifications. It should not be necessary
to make any modifications to the dkitrc script.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
21
Page 22

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
3.6.3
If you are upgrading your computer from the CommKit Host Interface to IP-CommKit, it’s likely
that the tables used by dkserver [see srvtab(4)] have already been customized. No changes to
these tables are needed to use IP-CommKit.
If you are installing IP-CommKit on a computer that has never run the CommKit Host Interface
software, the installation script installs a default set of server tables. /opt/dk/sbin/dkcust is a
script that can automatically customize these default tables. To use dkcust, you should know the
area and exchange assigned to the BNS node in which you install the UTM. This information can
be obtained by entering the verify node command on the BNS node console. Ask your BNS node
administrator, if you need assistance.
To use dkcust, simply run it and answer the questions.
DKSRVTAB
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
22
Page 23

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
4 C O N T R O L TA B L E S
The control tables used for the CommKit Host Interface are identical to those used for IP-
CommKit. Refer to Control Tables section of the CommKit Host Interface for NCR PCI
Computers Installation and Administration Guide for a detailed description of the control tables.
IP-CommKit has one additional control table, dkiptab. This file is read by dkipd when it starts to
find the IP addresses assigned to the UTM and host LAN interfaces. See the manual page
(dkiptab(4)) for the file format and examples.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
23
Page 24

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
5 A D M I N I S T R AT I O N
All of the topics discussed in the Administration section of the CommKit Host Interface for NCR
PCI Computers Installation and Administration Guide apply to IP-CommKit as well. There are few
minor changes and additions that are noted below:
5.1 F
dkipd creates a log file in /var/opt/dk/log/dkipdlog. This file will grow continuously, although at a
very slow rate compared to other log files, and should be cleaned out periodically by the system
administrator.
5.2
In addition to starting dkdaemon and dkserver, dkitrc starts dkipd.
5.3 S
The minor devices for the diagnostic channels, /dev/dk/diag0, etc., are not created for IP-
CommKit. These devices were used for managing hardware diagnostics for the fiber interface
board that is part of the CommKit Host Interface. IP-CommKit uses the LAN interface on your
host computer, and thus relies on the hardware diagnostics supplied with the LAN interface.
ILES THAT GROW
DKITRC SCRIPT FILE
PECIAL DEVICE FILES
IP-CommKit has one additional special device file, /dev/dk/dkip, tied to minor device number
16384. This device is used exclusively by dkipd to initialize the driver when it starts up.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
24
Page 25

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
5.4 P
There are several figures in this section that show fibers connecting hosts to CPM-HS boards in
the switches. With IP-CommKit, the hosts are connected to UTMs in the switches through IP
networks.
RINTER ADMINISTRATION
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
25
Page 26

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
6 T R O U B L E S H O O T I N G
6.1 O
This section describes troubleshooting procedures for IP-CommKit. It supercedes the
Troubleshooting section of the CommKit Host Interface for NCR PCI Computers Installation and
Administration Guide.
6.2 P
You are most likely to have difficulty with IP-CommKit right after installation. The following
sections describe procedures for troubleshooting the most common problems encountered after
installation. If you are having difficulty, start with the first procedure and work towards the end.
Resist the temptation to skip procedures that seem obvious.
6.2.1 C
Enter the following command on the UTM console port:
VERVIEW
ROCEDURES
HECK THAT THE
UTM
IS IN SERVICE
<TRK-UNIV> vfy mod
The output should be similar to the report below.
Current Configuration:
DK Board Type ==> TN1009 (CPM-HS) w/Serial# 136.
Service State ==> In Service.
Operating Mode ==> Simplex.
Trunk Type ==> IP-DSU Compatible Trunk on 10BaseT Network Port.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
26
Page 27

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
IP-DSU Loopback Status ==> Loopbacks are not enabled.
IP-DSU Data Encryption Status ==> Disabled.
Actual IP-DSU Service State ==> Not Connected.
Local MAC Address ==> 0.19.5.84.49.56
Local IP Address ==> utm_ip_address
Subnet Mask ==> subnet_mask
Gateway IP Address ==> gateway_ip_address
IP-DSU Destination IP Address ==> host_ip_address
SNMP Trap Manager ==> Not defined.
Specifically, check that the Service State is In Service. If it’s not, enter the following command
on the UTM console:
<TRK-UNIV> rs
6.2.2 C
Enter the following command on the BNS node console:
CC0> dstat mod mod_address
In this command, mod_address is the slot number where you installed the UTM. The output
should be similar to the report below:
HECK THAT THE
CPM
IS IN SERVICE
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
27
Page 28

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
00-12-18 13:43:46 NODE=node_name
M dstat module mod_address
****************************** MODULE 19 ******************************
MODULE TYPE SERVICE STATE HARDWARE ERROR COUNT SERIAL NUMBER
cpmhs in service 1 136
LAST HARDWARE ALARM
none
ONLINE ENABLED CABLE AVAIL
yes yes connected yes
Specifically, check that the SERVICE STATE is in service. If it’s not, enter the following
command on the node console:
CC0> rs cpm mod_address
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
28
Page 29

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
6.2.3 C
HECK THE MODE SWITCH ON THE
UTM
Verify the Mode switch on the faceplate of the UTM module is in the enabl position. The Mode
switch supports three positions: Enabl, Diag and Disab. The Mode switch must be in the Enabl
position for the UTM to function properly.
Reset
Mode
Switch
Red
Yellow
Green
Enabl
Diag
Disab
Fault
Off
Line
On
Line
Datatek
TN
2524
U T M
X
X
A
Y
O
O
Q
P
S
D
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
29
Page 30

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
6.2.4 P
On the host computer, enter the following command:
$ ping utm_ip_address
In this command, utm_ip_address is the IP address that you assigned to the UTM module. The
output should be similar to the report below:
utm_ip_address is alive
If you do not get this output, then the host and UTM cannot exchange packets. In this case, the
report would appear as follows:
ING THE
UTM
FROM THE HOST
no answer from utm_ip_address
If you get this output, check that you are using the correct UTM IP address. If you are, you
should enlist the aid of you IP network administrator. Don’t proceed until you can ping the UTM
from the host.
6.2.5 C
Enter the following command on the host computer:
$ tail /var/opt/dk/log/dkipdlog
10/13/11
HECK /VAR/OPT/DK/DKIPDLOG
Datatek Applications Inc.
30
Page 31

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
This displays the end of the log file created by dkipd(1M). The last two lines of the output should
be similar to the report below:
Dec 18 12:08:54 (8626) Connectivity from host_ip_address to utm_ip_address established
Dec 18 12:09:19 (8626) UTM module utm_ip_address restored to service
Here, the host_ip_address is the IP address assigned to the host computer, and the
utm_ip_address is the IP address assigned to the UTM. Note that dkipd will use the name
associated with the address, if possible. If your host connects to several UTMs, you should see
these two messages repeated for each UTM IP address.
If you see the first line, “Connectivity from …”, but not the second, “UTM module …”, it indicates
that the CPM is out of service. Go back to the procedure for checking that the CPM is in service.
If the output on your host is different, compare it to the following output examples that are
associated with common problems.
/opt/dk/sbin/dkipd: Error in configuration file "/etc/opt/dk/dkiptab"
Line 38: 0 dino 135.17..59.203
Can't resolve address: 135.17..59.203
This output is typical of an error in dkiptab, the configuration file for dkipd. You may have
forgotten to customize the file for you application, or you may have made a typing error. In the
output above, there was an error typing in the IP address of the UTM module. Note that the error
message indicates the line number where the error was detected.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
31
Page 32

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
Dec 18 14:26:38 (8810) Received keep-alive message from unknown address: 135.17.59.203
This output is typical when the UTM IP address you configured in dkiptab does not match the
UTM IP address you configured through the UTM console.
If the messages that you see don’t look similar to any of the examples above, consult the
dkipd(1M) manual page. This describes all messages that are written to the log file.
The primary responsibility for dkipd is to establish communications with the UTM. You can
confirm that dkipd and the UTM have established communications by issuing the vfy command
on the UTM console. The report should contain the following line:
Actual IP-DSU Service State ==> Peer Connectivity Established.
6.2.6 C
Enter the following command on the host computer:
# tail -17 /var/opt/dk/log/dkdaemonlog
This displays the log file created by dkdaemon(1M). The output should look similar to the
following report:
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8866) /opt/dk/sbin/dkdaemon : Started, Log Level = 5
HECK /VAR/OPT/DK/LOG/DKDAEMONLOG
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) acct_start: Accounting Disabled
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
32
Page 33

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) /opt/dk/sbin/dkdaemon : Startup Complete
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) dkhsstart: Unit 0: 512 Chans, Ver 4, Rbuf 1024, NurpB 4
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 0 ACTIVE
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 1 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 2 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 3 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 4 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 5 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 6 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkhs Unit 7 Down, Retrying
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dknp Unit 0 ACTIVE
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) startstr: dkxmx Unit 0 ACTIVE
Dec 18 14:55:09 (8867) LOG: (0, 0) dkxqt mux driver is active
Dec 18 14:55:11 (8867) SERVER: (0, 2) "dino" Started by UID 0
By default, dkdaemon tries to start all eight logical interfaces. Only one logical interface is used
on the host computer where this log file was generated. This is Unit 0, and dkdaemon reports
that it is ACTIVE. dkdaemon reports that the remaining logical interfaces are Down. On your
host, you should check that all logical interfaces that you specified in the dkiptab are active.
If the messages that you see don’t look similar to any of the examples above, consult the
dkdaemon (1M) manual page. This describes all messages that are written to the log file.
Once dkdaemon starts, the host computer establishes communications with the BNS node
controller. You can confirm this by running the following command on the BNS node console:
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
33
Page 34

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
CC0> disp conn mod mod_address
Here, mod_address is the slot number where you installed the UTM. The output should look
similar to the report below:
00-12-19 17:46:20 NODE=node_name
M display connections mod mod_address
MODULE: 19
---------------
CH/PT CU/TM GROUP PKT CNT STATE TO MOD CH/PT CU/TM GROUP PKT CNT
BOARD (+ = PDD BOARD
CS/LCH or PVC, CS/LCH
PT/LCH # = RRC) PT/LCH
PT/DLCI PT/DLCI
1 **** 295 ACTIVE
Note that channel 1 is in the ACTIVE state.
6.2.7 C
Enter the following command on the host computer
HECK /VAR/OPT/DK/DKSRVLOG
$ tail /var/opt/dk/log/dksrvlog
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
34
Page 35

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
This displays the log file generated by dkserver(1M). The last few lines of the output should look
similar to the following report:
Dec 18 14:55:11 (8893) [0.000] SERVER dino is INITING files=(/etc/opt/dk/srvtab
/etc/opt/dk/dkuidtab) loglvl=6
Dec 18 14:55:11 (8893) [0.000] dkmgr : SERVER dino is ACTIVE and SERVING
The host file where this log file was generated is named dino, and it runs a single dkserver
process. The last line of the log file indicates that dkserver is ACTIVE and SERVING. Some
hosts run several dkserver processes. The last line should be repeated for each dkserver
process.
You might see an error message similar to the one below in the log file:
Dec 19 17:00:59 (515) [0.000] ERROR dkmgr: Unable to create server server_name dk_errno
= 3
The indicates that the address server_name has not been entered on the BNS node, or that the
address is not in service. Enter the following command on the BNS node to check the address:
CC0> ver addr all server_name
The report should be similar to the one below:
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
35
Page 36

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
00-12-19 17:16:42 NODE=node_name
M verify address all server_name
MNEMONIC ADDRESS: server_name X.121 NANP ADDRESS:
LEVEL: local SERVICE STATE: in
PAD SUPPORT: no
DIRECTORY: none
SECURITY: none
GROUP: group_name
If the report indicates that the address has not been entered, enter it using the instructions in the
BNS Node Configuration section of this document. If the report shows that the address is out of
service, restore the address with the following command:
CC0> res addr local server_name
When dkserver starts, it tells the BNS node that it is ready to accept incoming calls. You can
confirm this by entering the follow command on the BNS node console:
CC0> disp conn mod mod_address
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
36
Page 37
I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
The report should be similar to the one below:
00-12-19 17:46:20 NODE=node_name
M display connections mod mod_address
MODULE: 19
---------------
CH/PT CU/TM GROUP PKT CNT STATE TO MOD CH/PT CU/TM GROUP PKT CNT
BOARD (+ = PDD BOARD
CS/LCH or PVC, CS/LCH
PT/LCH # = RRC) PT/LCH
PT/DLCI PT/DLCI
1 **** 295 ACTIVE
2 group_name 89 SERVING
Note that channel 2 is in the SERVING state.
6.3 S
Some configuration changes require stopping and starting the IP-CommKit software to make the
changes effective. Specifically, changes to /etc/opt/dk/dkiptab require stopping and starting. You
can always do this by rebooting the host computer. However, this can be disruptive and time
consuming. A more convenient method is to log in as root, then enter the follow commands:
# sh /sbin/init.d/dkitrc stop
TOPPING AND STARTING
# sh /sbin/init.d/dkitrc start
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
37
Page 38

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
7 C O M P A T I B I L I T Y
This section of the CommKit Host Interface for NCR PCI Computers Installation and
Administration Guide describes the differences between UNIX System V Release 3 (SVR3) and
Release 4 (SVR4) versions. IP-CommKit for HP-UX was derived from the SRV4 version, so the
information in this section also applies to IP-CommKit. However, it’s only useful if you are porting
a CommKit Host Interface application that ran under SRV3 to IP-CommKit.
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
38
Page 39

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
8 M A N U A L P A G E S
Most of the manual pages for the CommKit Host Interface are identical to those for IP-CommKit.
The following man pages have been eliminated:
ATDIAG
DKCFG
DKDIAG
DKMAP
DKREGISTER
DKUNLOCK
DKVFY
PCDIAG
These pages described commands that were used for copy protection or fiber interface hardware
configuration and diagnostics. These commands are not needed for IP-CommKit.
The following manual pages have been added or revised for IP-CommKit
DKIPD
DKIPTAB
DKITRC
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
39
Page 40

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
9 E N D - U S E R L I C E N S E A G R E E M E N T F O R
S O F T W A R E
This License Agreement ("License") is a legal contract between you and the manufacturer
("Manufacturer") of the software product(s) you acquired identified as ("SOFTWARE"). The
SOFTWARE may include printed materials that accompany the SOFTWARE. Any software
provided along with the SOFTWARE that is associated with a separate end-user license
agreement is licensed to you under the terms of that license agreement. By installing, copying,
downloading, accessing or otherwise using the SOFTWARE, you agree to be bound by the terms
of this LICENSE. If you do not agree to the terms of this LICENSE, Manufacturer is unwilling to
license the SOFTWARE to you. In such event, you may not use or copy the SOFTWARE, and
you should promptly contact Manufacturer for instructions on return of the unused product(s) for a
refund.
9.1 SOFTWARE LICENSE
You may only install and use one copy of the SOFTWARE on one host computer (unless
otherwise licensed by Manufacturer). The SOFTWARE may not be installed, accessed,
displayed, run, shared or used concurrently on or from different computers, including a
workstation, terminal or other digital electronic device (“Devices”). Notwithstanding the foregoing
and except as otherwise provided below, any number of Devices may access or otherwise utilize
the services of the SOFTWARE. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the
SOFTWARE, except and only to the extent that such activity is expressly permitted by applicable
law notwithstanding this limitation. The SOFTWARE is licensed as a single product. Its
component parts may not be separated for use on more than one host computer. You may not
rent, lease or lend the SOFTWARE in any manner. You may permanently transfer all of your
rights under this LICENSE provided you retain no copies, you transfer all of the SOFTWARE
(including all component parts, the media and printed materials, any upgrades, this LICENSE
and, if applicable, the Certificate(s) of Authenticity), and the recipient agrees to the terms of this
LICENSE. If the SOFTWARE is an upgrade, any transfer must also include all prior versions of
the SOFTWARE. Without prejudice to any other rights, Manufacturer may terminate this
LICENSE if you fail to comply with the terms and conditions of
must destroy all copies of the SOFTWARE and all of its component parts.
this LICENSE. In such event, you
9.2 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS
The SOFTWARE is licensed, not sold to you. The SOFTWARE is protected by copyright laws
and international copyright treaties, as well as other intellectual property laws and treaties. You
may not copy the printed materials accompanying the SOFTWARE. All title and intellectual
property rights in and to the content which may be accessed through use of the SOFTWARE is
the property of the respective content owner and may be protected by applicable copyright or
other intellectual property laws and treaties. This LICENSE grants you no rights to use such
content. All rights not expressly granted under this LICENSE are reserved Manufacturer and its
licensors (if any).
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
40
Page 41

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
9.3 SOFTWARE SUPPORT
SOFTWARE support is provided by Manufacturer, or its affiliates or subsidiaries separate from
the host computer on which it may be installed. SOFTWARE support is limited to the warranty
period stated below unless either a separate contract has been consummated between you and
the manufacturer or the manufacturer has agreed in writing at the time of purchase by you of the
software to an extension of the warranty. Should you have any questions concerning this
LICENSE, or if you desire to contact Manufacturer for any other reason, please refer to the
address provided in the documentation for the SOFTWARE.
9.4 EXPORT RESTRICTIONS
You agree that you will not export or re-export the SOFTWARE to any country, person, or entity
subject to U.S. export restrictions. You specifically agree not to export or re-export the
SOFTWARE: (i) to any country to which the U.S. has embargoed or restricted the export of goods
or services, which as of March 1998 include, but are not necessarily limited to Cuba, Iran, Iraq,
Libya, North Korea, Sudan and Syria, or to any national of any such country, wherever located,
who intends to transmit or transport the products back to such country; (ii) to any person or entity
who you know or have reason to know will utilize the SOFTWARE or portion thereof in the
design, development or production of nuclear, chemical or biological weapons; or (iii) to any
person or entity who has been prohibited from participating in U.S. export transactions by any
federal agency of the U.S. government.
9.5 LIMITED WARRANTY
Manufacturer warrants that (a) the SOFTWARE will perform substantially in accordance with the
accompanying written materials for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of shipment
Datatek Applications, Inc. Software support is limited to the hours of 9 AM to 5 PM ET Monday
through Friday excluding Datatek-observed holidays. Other coverage and extended warranty may
be purchased at additional cost. Any implied warranties on the SOFTWARE are limited to ninety
(90) days. Some states/jurisdictions do not allow limitations on duration of an implied warranty, so
the above limitation may not apply to you.
Manufacturer's and its suppliers' entire liability and your exclusive remedy shall be, at
Manufacturer's option, either (a) return of the price paid, or (b) repair or replacement of the
SOFTWARE that does not meet this Limited Warranty and which is returned to Manufacturer with
a copy of your receipt. This Limited Warranty is void if failure of the SOFTWARE has resulted
from accident, abuse, or misapplication. Any replacement SOFTWARE will be warranted for the
remainder of the original warranty period or thirty (30) days, whichever is longer.
from
9.6 NO OTHER WARRANTIES
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, MANUFACTURER AND ITS
SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT, WITH REGARD TO
THE SOFTWARE AND THE ACCOMPANYING WRITTEN MATERIALS. THIS LIMITED
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
41
Page 42

I P - C o m m K i t I n s t a l l a t i o n a n d A d m i n i s t r a t i o n G u i d e
f o r H P - U X – I s s u e 2 – R e l e a s e 1 . 0 . 2 2
WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS. YOU MAY HAVE OTHERS, WHICH
VARY FROM STATE/JURISDICTION TO STATE/JURISDICTION.
9.7 SPECIAL PROVISIONS
The SOFTWARE and documentation are provided with RESTRICTED RIGHTS. Use,
duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in
subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Software clause at DFARS 252.2277013 or subparagraphs (c)(1) and (2) of the Commercial Software-Restricted Rights at 48 CFR
52.227-19, as applicable. Manufacturer is Datatek Applications, Inc., 379 Campus Drive, Suite
100, Somerset, NJ 08873.
If you acquired the SOFTWARE in the United States of America, this Software License are
governed by the laws of the State of New Jersey, excluding its choice of laws provisions. If you
acquired the SOFTWARE outside the United States of America, local law may apply. This
LICENSE constitutes the entire understanding and agreement between you and the Manufacturer
in relation to the SOFTWARE and supersedes any and all prior or other communications,
statements, documents, agreements or other information between the parties with respect to the
subject matter hereof.
9.8 LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, in no event shall Manufacturer or its
suppliers be liable for any damages whatsoever (including without limitation, special,
incidental, consequential, or indirect damages for personal injury, loss of business profits,
business interruption, loss of business information, or any other pecuniary loss) arising
out of the use of or inability to use this product, even if Manufacturer has been advised of
the possibility of such damages. In any case, Manufacturer's and its suppliers' entire liability
under any provision of this License shall be limited to the amount actually paid by you for the
SOFTWARE. Because some states/jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability
for consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to you.
©Copyright 2001, 2012 Datatek Applications, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Printed in USA
10/13/11
Datatek Applications Inc.
42
 Loading...
Loading...