
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA7110; SAA7110A
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1)
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC22
1995 Oct 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 APPLICATIONS
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
5 ORDERING INFORMATION
6 SYSTEM VIEW
7 BLOCK DIAGRAM
8 PINNING
9 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
9.1 Analog input processing (see Fig.5)
9.2 Analog control circuits
9.3 Chrominance processing (see Fig.6)
9.4 Luminance processing (see Fig.7)
9.5 YUV-bus (digital outputs)
9.6 Synchronization (see Fig.7)
9.7 Clock generation circuit
9.8 Power-on reset
9.9 RTCO output
10 GAIN CHARTS
11 LIMITING VALUES
12 CHARACTERISTICS
13 TIMING
14 OUTPUT FORMATS
15 CLOCK SYSTEM
15.1 Clock generation circuit
15.2 Power-on control
16 I2C-BUS DESCRIPTION
16.1 I2C-bus format
16.2 I2C-bus receiver/transmitter tables
16.3 I2C-bus detail
16.4 I2C-bus detail (continued)
17 SOURCE SELECTION MANAGEMENT
18 ANTI-ALIAS FILTER GRAPHS
19 CORING FUNCTION
19.1 Coring function adjustment by subaddress 06H
to affect band filter output adjustment
20 LUMINANCE FILTER GRAPHS
21 I2C-BUS START SET-UP
21.1 Remarks to Table 66
22 APPLICATION INFORMATION
23 START-UP, SOURCE SELECT AND
STANDARD DETECTION FLOW EXAMPLE
23.1 CODE 0 STARTUP and STANDARD
Procedure
23.2 MODE 0 Source Select Procedure
23.3 MODE 1 Source Select Procedure
23.4 MODE 2 Source Select Procedure
23.5 MODE 3 Source Select Procedure
23.6 MODE 4 Source Select Procedure
23.7 MODE 5 Source Select Procedure
23.8 MODE 6 Source Select Procedure
23.9 MODE 7 Source Select Procedure
23.10 MODE 8 Source Select Procedure
24 PACKAGE OUTLINE
25 SOLDERING
25.1 Introduction
25.2 Reflow soldering
25.3 Wave soldering
25.4 Repairing soldered joints
26 DEFINITIONS
27 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
28 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1995 Oct 18 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
1 FEATURES
• Six analog inputs (6 × CVBS or 3 × Y/C or
combinations)
• Three analog processing channels
• Three built-in analog anti-aliasing filters
• Analog signal adding of two channels
• Two 8-bit video CMOS analog-to-digital converters
• Fully programmable static gain for the main channels or
automatic gain control for the selected CVBS/Y channel
• Selectable white peak control signal
• Luminance and chrominance signal processing for
PAL B/G, NTSC M and SECAM
• Full range HUE control
• Automatic detection of 50/60 Hz field frequency, and
automatic switching between standards PAL and NTSC,
SECAM forceable
• Horizontal and vertical sync detection for all standards
• Cross-colour reduction by chrominance comb filtering
for NTSC or special cross-colour cancellation for
SECAM
• UV signal delay lines for PAL to correct chrominance
phase errors
• The YUV-bus supports a data rate of:
– 780 × fh= 12.2727 MHz for 60 Hz (NTSC)
– 944 × fh= 14.75 MHz for 50 Hz (PAL/SECAM)
• Square pixel format with 768/640 active samples per
line on the YUV-bus
• CCIR 601 level compatible
• 4:2:2 and 4:1:1 YUV output formats in 8-bit
resolution
• User programmable luminance peaking for aperture
correction
• Compatible with memory-based features
(line-locked clock, square pixel)
• Requires only one crystal (26.8 MHz) for all standards
• Real time status information output (RTCO)
• Brightness Contrast Saturation (BCS) control for the
YUV-bus
• Negation of picture possible
• One user programmable general purpose switch on an
output pin
• Switchable between on-chip Clock Generation Circuit
(CGC) and external CGC (SAA7197)
• Power-on control
2
• I
C-bus controlled.
2 APPLICATIONS
• Desktop video
• Multimedia
• Digital television
• Image processing
• Video phone
• Video picture grabbing.
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The one chip front-end SAA7110; SAA7110A is a digital
multistandard colour decoder (OCF1) on the basis of the
DIG-TV2 system with two integrated Analog-to-Digital
Converters (ADCs), a Clock Generation Circuit (CGC) and
Brightness Contrast Saturation (BCS) control.
The CMOS circuit SAA7110; SAA7110A, analog front-end
and digital video decoder, is a highly integrated circuit for
desktop video applications. The decoder is based on the
principle of line-locked clock decoding. It operates
square-pixel frequencies to achieve correct aspect ratio.
Monitor controls are provided to ensure best display. The
circuit is I2C-bus controlled.
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
V
DDD
T
amb
1995 Oct 18 3
analog supply voltage 4.75 5.25 V
digital supply voltage 4.5 5.5 V
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
5 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7110 PLCC68 plastic leaded chip carrier; 68 leads SOT188-2
SAA7110A PLCC68 plastic leaded chip carrier; 68 leads SOT188-2
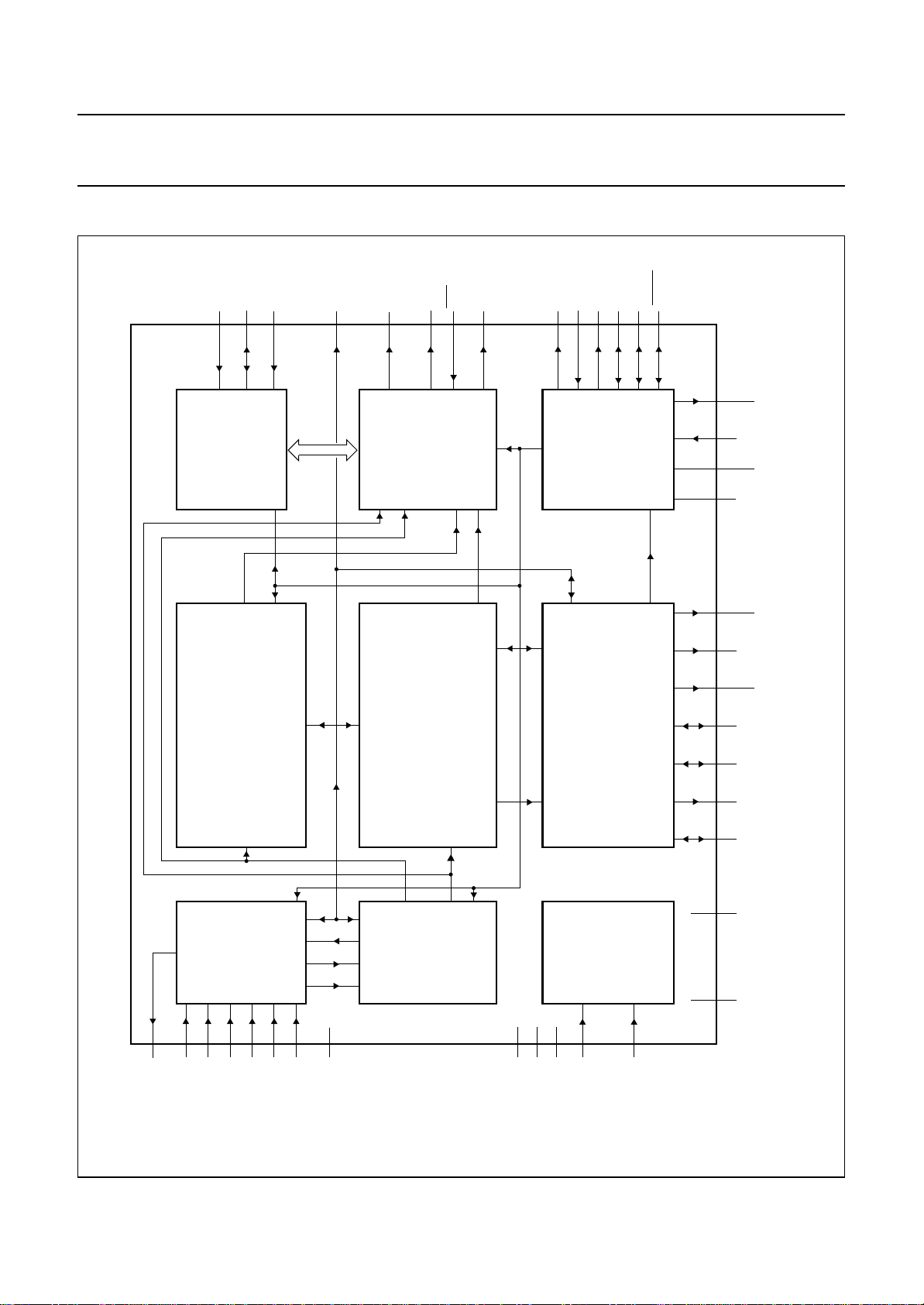
6 SYSTEM VIEW
PC ISA - BUS
handbook, full pagewidth
2
I
C
six
video inputs
ONE
CHIP
FRONT-END
OCF1
clock
VIDEO
MEMORY
CONTROLLER
VMC
VIDEO
FRAME
MEMORY
YUV - BUS
Fig.1 System diagram.
MGC821
1995 Oct 18 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
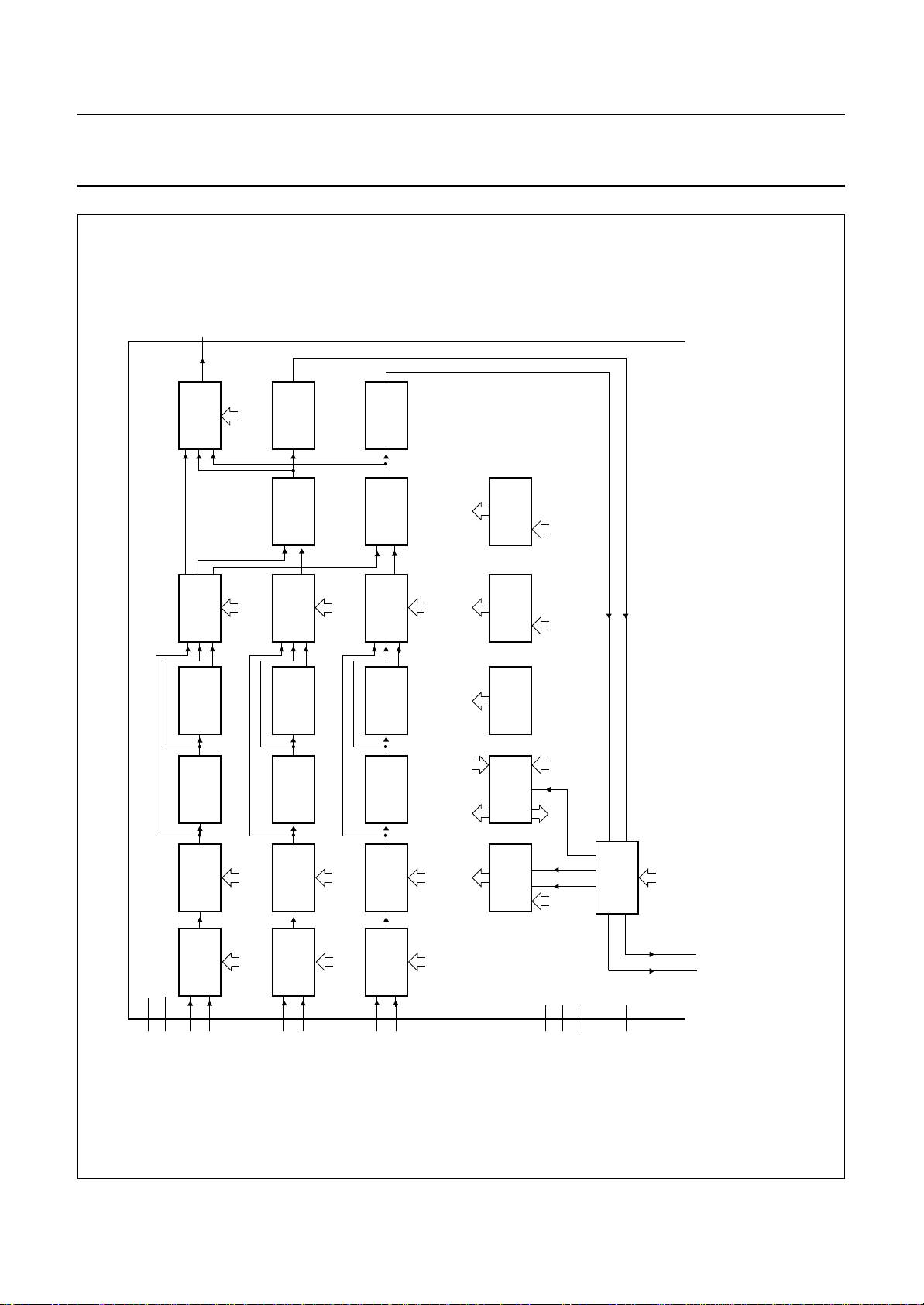
7 BLOCK DIAGRAM
LLC2
CREF
RESET
XTALO
65
XTALI
66
CLOCK
GENERATION
30
CIRCUIT
UV7
to
UV0
SA
6
5
4
C-BUS
2
I
INTERFACE
GPSW
(VBLK)
64
55 to 62
8
C-BUS
2
I
CONTROL
SCL
SDA
Y7 to Y0
53, 54
45 to 50,
AND
CONTROL
CONTRAST
SATURATION
BRIGHTNESS
FEIN
(MUXC)
63
OUTPUT
FORMATTER
Y
UV
HREF
42
CLOCKS
LLC
312932
POWER-ON
CONTROL
33
2524
MGC820
CGCE
DDA0
V
LFCO
SSA0
V
BYPASS
CIRCUIT
CHROMINANCE
C/CVBS
CON
ANALOG
PROCESSING
AD2 AD3
CIRCUIT
LUMINANCE
Y/CVBS
ANALOG
CONTROL
SAA7110
SAA7110A
3 26
RTCO
39
PLIN (HL)
40
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.2 Block diagram.
HSY HCLVS
HS
V
V
SS
DD
ODD (VL)
36
CIRCUIT
SYNCHRONIZATION
Y
Y
TEST
BLOCK
CONTROL
37
41 38
67, 51, 43,
35, 28
68, 52, 44,
34, 27
11
23
AOUT
13
AI42
1995 Oct 18 5
AI41
15
AI32
17
AI31
19
AI22
21
AI21
7, 8, 9
i.c.
18, 14, 10
20, 16, 12
SSA4
DDA4
to V
to V
SSA2
DDA2
V
V
22
V
SS(S)
2
AP
1
SP

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
8 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
SP 1 test pin input; (shift pin) connect to ground for normal operation
AP 2 test pin input; (action pin) connect to ground for normal operation
RTCO 3 Real Time Control Output. This pin is used to fit serially the increments of the HPLL and
FSC-PLL and information of the PAL or SECAM sequence.
2
SA 4 I
SDA 5 I
SCL 6 I
i.c. 7 reserved pin; do not connect
i.c. 8 reserved pin; do not connect
i.c. 9 reserved pin; do not connect
V
SSA4
10 ground for analog input 4
AI42 11 analog input 42
V
DDA4
12 supply voltage (+5 V) for analog input 4
AI41 13 analog input 41
V
SSA3
14 ground for analog input 3
AI32 15 analog input 32
V
DDA3
16 supply voltage (+5 V) for analog input 3
AI31 17 analog input 31
V
SSA2
18 ground for analog input 2
AI22 19 analog input 22
V
DDA2
20 supply voltage (+5 V) for analog input 2
AI21 21 analog input 21
V
SS(S)
22 substrate ground
AOUT 23 analog test output; do not connect
V
V
DDA0
SSA0
24 supply voltage (+5 V) for internal CGC (Clock Generation Circuit)
25 ground for internal CGC
LFCO 26 Line Frequency Control output; this is the analog clock control signal driving the external
V
DD
V
SS
27 supply voltage (+5 V)
28 ground
LLC 29 Line-Locked Clock input/output (CGCE = 1, output; CGCE = 0, input). This is the system
LLC2 30 Line-Locked Clock
CREF 31 Clock reference input/output (CGCE = 1, output; CGCE = 0, input). This is a clock qualifier
C-bus slave address select input. LOW: slave address = 9CH for write, 9DH for read;
HIGH = 9DH for write, 9FH for read.
2
C-bus serial data input/output
2
C-bus serial clock input
CGC. The frequency is a multiple of the actual line frequency (nominally 7.375/6.13636 MHz).
The signal has a triangular form with 4-bit accuracy.
clock, its frequency is 1888 × f
for 50 Hz/625 lines per field systems and 1560 × fh for
h
60 Hz/525 lines per field systems; or variable input clock up to 32 MHz in input mode.
1
⁄2output; f
LLC2
= 0.5 × f
(CGCE = 1, output; CGCE = 0, high
LLC
impedance).
signal distributed by the internal or an external clock generator circuit (CGC). Using CREF all
interfaces on the YUV-bus are able to generate a bus timing with identical phase.
1995 Oct 18 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
RESET 32 Reset active LOW input/output (CGCE = 1, output; CGCE = 0, input); sets the device into a
defined state. All data outputs are in high impedance state. The I2C-bus is reset (waiting for
START condition). Using the external CGC, the LOW period must be maintained for at least
30 LLC clock cycles.
CGCE 33 CGC Enable active HIGH input (CGCE = 1, on-chip CGC active; CGCE = 0, external CGC
mode, use SAA7197).
V
DD
V
SS
HCL 36 Horizontal Clamping input/output pulse (programmable via I
HSY 37 Horizontal Synchronization input/output indicator (programmable via I
HS 38 Horizontal Synchronization output (programmable; the HIGH period is 128 LLC clock cycles).
PLIN (HL) 39 PAL Identifier Not output; marks for demodulated PAL signals the inverted line (PLIN = LOW)
ODD (VL) 40 ODD/EVEN field identification output; a HIGH state indicates the odd field. Select ODD
VS 41 Vertical Synchronization input/output (programmable via I
HREF 42 Horizontal Reference output; this signal is used to indicate data on the digital YUV-bus. The
V
SS
V
DD
34 supply voltage (+5 V)
35 ground
output; PULIO = 0, input). This signal is used to indicate the black level clamping period for
the analog input interface. The beginning and end of its HIGH period (only in the output mode)
can be programmed via the I2C-bus registers 03H, 04H in 50 Hz mode and registers 16H,
17H in 60 Hz mode, active HIGH.
PULIO = 1, output; PULIO = 0, input). This signal is fed to the analog interface. The beginning
and end of its HIGH period (only in the output mode) can be programmed via the I2C-bus
registers 01H, 02H in 50 Hz mode and registers 14H, 15H in 60 Hz mode, active HIGH.
The position of the positive slope is programmable in 8 LLC increments over a complete line
2
(64 µs) via the I
C-bus register 05H in 50 Hz mode or register 18H in 60 Hz mode.
and a non-inverted line (PLIN = HIGH) and for demodulated SECAM the DR line
(PLIN = LOW) and the DB line (PLIN = HIGH). Select PLIN function via I
(H-PLL locked output; a HIGH state indicates that the internal PLL has locked. Select HL
function via I2C-bus bit RTSE = 1).
2
function via I
C-bus bit RTSE = 0.
(Vertical Locked output; a HIGH state indicates that the internal Vertical Noise Limiter (VNL)
is in a locked state. Select VL function via I2C-bus bit RTSE = 1).
output; OEHV = 0, input). This signal indicates the vertical synchronization with respect to the
YUV output. The high period of this signal is approximately six lines if the VNL function is
active. The positive slope contains the phase information for a deflection controller, for
example the TDA9150. In input mode this signal is used to synchronize the vertical gain and
clamp blanking stage, active HIGH.
positive slope marks the beginning of a new active line. The HIGH period of HREF is either
768 Y samples or 640 Y samples long depending on the detected field frequency
(50/60 Hz mode). HREF is used to synchronize data multiplexer/demultiplexers. HREF is also
present during the vertical blanking interval.
43 ground
44 supply voltage (+5 V)
2
C-bus bit PULIO: PULIO = 1,
2
C-bus bit PULIO:
2
C-bus bit RTSE = 0.
2
C-bus bit OEHV: OEHV = 1,
1995 Oct 18 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
Y7 45
Y6 46
Y5 47
Y4 48
Y3 49
Y2 50
V
SS
V
DD
51 ground
52 supply voltage (+5 V)
Y1 53
Y0 54
UV7 55
UV6 56
UV5 57
UV4 58
UV3 59
UV2 60
UV1 61
UV0 62
FEIN
63 Fast Enable input (active LOW); this signal is used to control fast switching on the digital
(MUXC)
GPSW
64 General Purpose Switch output; the state of this signal is programmable via I
(VBLK)
XTALO 65 Crystal oscillator output (to 26.8 MHz crystal); not used if TTL clock is used.
XTALI 66 Crystal oscillator input (from 26.8 MHz crystal) or connection of external oscillator with TTL
V
SS
V
DD
67 ground
68 supply voltage (+5 V)
Upper 6 bits of the 8-bit luminance (Y) digital output. As part of the digital YUV-bus
(data rate LLC/2), or A/D2(3) output (data rate LLC/2) selectable via I
2
C-bus bit SQPB = 1.
Lower 2 bits of the 8-bit luminance (Y) digital output. As part of the digital YUV-bus
2
(data rate LLC/2), or A/D2(3) output (data rate LLC/2) selectable via I
C-bus bit SQPB = 1.
8-bit digital UV (colour difference) output; multiplexed colour difference signal for U and V
component of demodulated CVBS or chrominance signal. The format and multiplexing
2
scheme can be selected via I
C-bus control. These signals are part of the digital YUV-bus
(data rate LLC/2), or A/D3(2) output (data rate LLC/2) selectable via I2C-bus bit SQPB = 1.
YUV-bus. A high at this input forces the IC to set its Y and UV outputs to the high impedance
state. To use this function set I2C-bus bits MS24 and MS34 and MUYC to LOW.
(Multiplex Components input; control signal for the analog multiplexers for fast switching
between locked Y/C signals or locked CVBS signals. FEIN automatically fixed to LOW (digital
YUV-bus enabled), if one of the three MUXC functions are selected (MS24 or MS34 or
MUYC = HIGH).
2
C-bus register
0Dh, bit 1. Select GPSW function via I2C-bus bit VBLKA = 0. (Vertical Blank test output; select
VBLK via I2C-bus bit VBLKA = 1).
compatible square wave clock signal.
1995 Oct 18 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SS
handbook, full pagewidth
i.c.
9
i.c.
8
i.c.
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
SA
4
RTCO
3
AP
2
SP
1
VDDV
68
67
66 XTALI
XTALO
GPSW (VBLK)
65
64
FEIN (MUXC)
UV0
UV1
63
62
61
V
SSA4
V
DDA4
V
SSA3
V
DDA3
V
SSA2
V
DDA2
V
SS(S)
AOUT
V
DDA0
V
SSA0
LFCO
AI42
AI41
AI32
AI31
AI22
AI21
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
SAA7110
SAA7110A
60
UV2
59
UV3
58
UV4
57
UV5
56
UV6
55
UV7
54
Y0
53
Y1
52
V
DD
51
V
SS
50
Y2
49
Y3
48
Y4
47
Y5
46
Y6
45
Y7
44
V
DD
27
28
29LLC
30
31
32
33
34
SS
DD
V
V
LLC2
CREF
RESET
CGCE
DD
V
Fig.3 Pin configuration.
1995 Oct 18 9
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
MGC822
SS
V
HCL
HSY
HS
PLIN (HL)
VS
ODD (VL)
HREF
SS
V

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
9 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
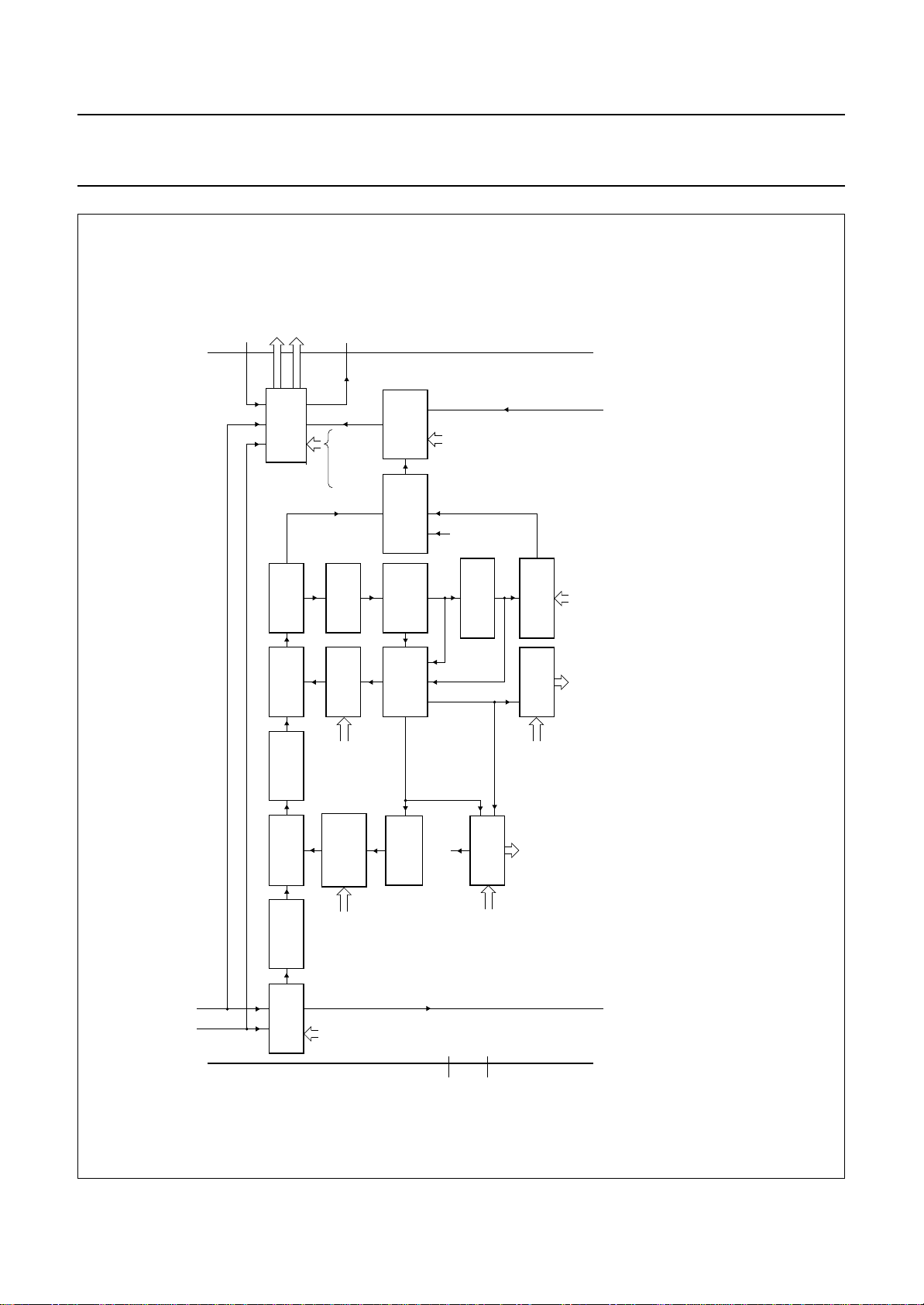
9.1 Analog input processing (see Fig.5)
The SAA7110; SAA7110A offers six analog signal inputs,
two analog main channels with clamping circuit, analog
amplifier, anti-alias filter and video CMOS ADC. A third
analog channel also with clamping circuit, analog amplifier
and anti-alias filter can be added or switched to both main
channels directly before the ADCs.
9.2 Analog control circuits
The clamping control circuit controls the correct clamping
of the analog input signals. The coupling capacitor is also
used to store and filter the clamping voltage. The normal
digital clamping level for luminance or CVBS signals is 64
and for chrominance signals is128.
2
The gain control circuits generate via I
C-bus the static
gain levels for the three analog amplifiers or controls one
of these amplifiers automatically via a built-in Automatic
Gain Control (AGC). The AGC is used to amplify a
CVBS or Y signal to the required signal amplitude,
matched to the ADCs input voltage range.
The anti-alias filters are adapted to the clock frequency.
The vertical blanking control circuit generates an I2C-bus
programmable vertical blanking pulse. During the vertical
blanking time gain and clamping control are frozen.
The fast switch control circuit is used for special
applications.
9.2.1 C
LAMPING
The coupling capacitor is used as clamp capacitance for
each input. An internal digital clamp comparator generates
the information concerning clamp-up or clamp-down. The
clamping levels for the two ADC channels are adjustable
over the 8-bit range (1 to 254). Clamping time in normal
use is set with the HCL pulse at the back porch of the video
signal. The clamping pulse HCL is user adjustable.
9.2.2 G
AIN CONTROL (see Fig.4)
The luminance AGC can be used for every channel were
luminance or CVBS is being received. AGC active time is
the sync tip of the video signal. The sync tip pulse HSY is
user adjustable. The AGC can be switched off and the gain
for the three main input channels can be adjusted
independently. Signal (white) peak control limits the gain
at signal overshoots. The flow charts (see Figs 8 and 9)
show more details of the AGC. The influence of supply
voltage variation within the specified range is automatically
eliminated by clamp and automatic gain control.
handbook, halfpage
analog input level
+2.8 dB
−6 dB
maximum
0 dB
minimum
range 8.8 dB
Fig.4 Automatic gain control range.
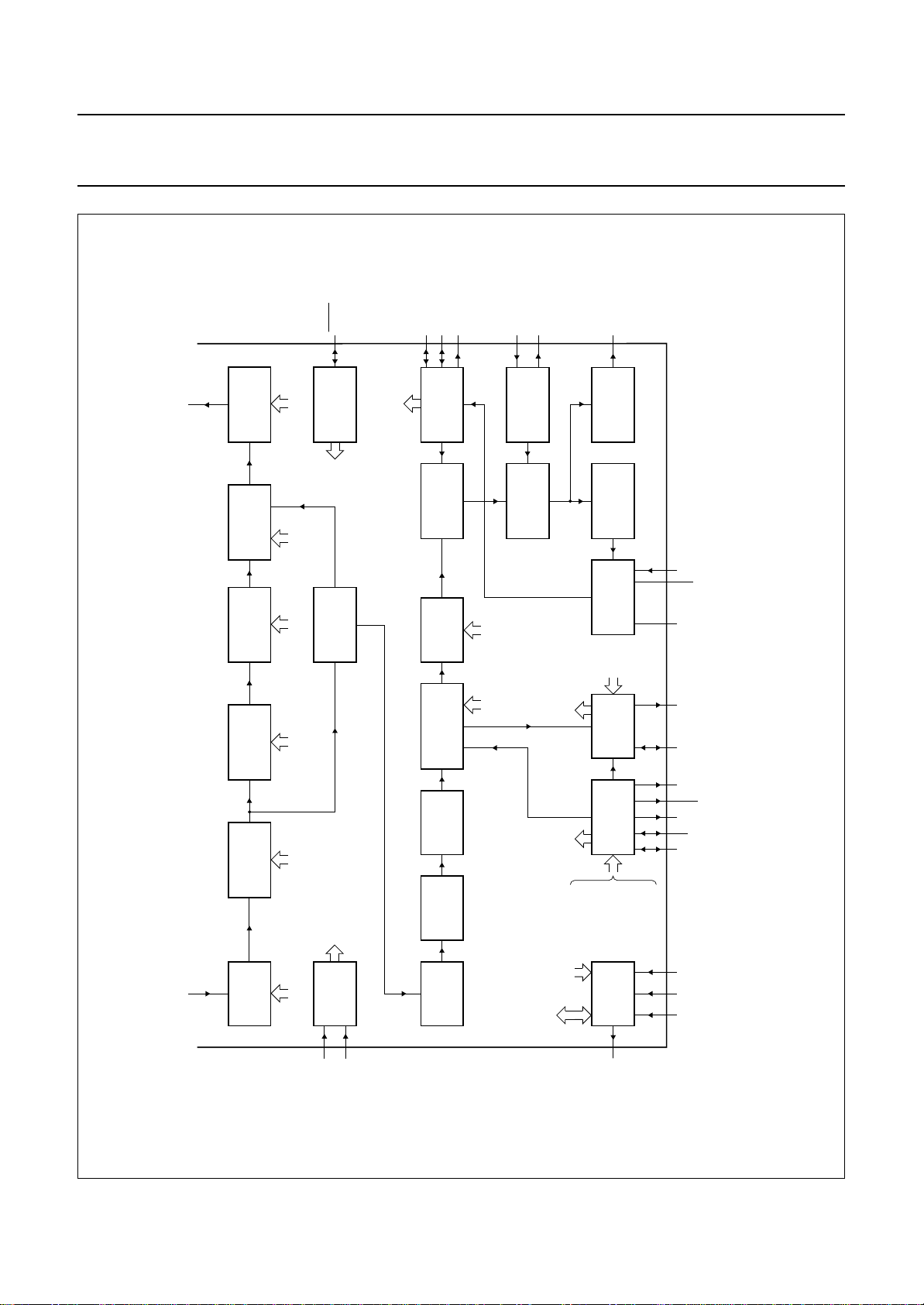
9.3 Chrominance processing (see Fig.6)
The 8-bit chrominance signal passes the input interface,
the chrominance bandpass filter to eliminate DC
components, and is finally fed to the multiplication inputs
of a quadrature demodulator, where two subcarrier signals
from the local oscillator DTO1 with 90 degrees phase shift
are applied. The frequency is dependent on the present
colour standard.
The multiplier operates as a quadrature demodulator for all
PAL and NTSC signals; it operates as a frequency down
mixer for SECAM signals.
The two multiplier output signals are converted to a serial
UV data stream and applied to two low-pass filter stages,
then to a gain controlled amplifier. A final multiplexed
low-pass filter achieves, together with the preceding
stages, the required bandwidth performance.
The PAL and NTSC originated signals are applied to a
comb filter.
The signal originated from SECAM is fed through a Cloche
filter (0 Hz centre frequency), a phase demodulator and a
differentiator to obtain frequency demodulated colour
difference signals. The SECAM signal is fed after
de-emphasis to a cross-over switch, to provide both the
serial transmitted colour difference signals. These signals
are fed to the BCS control and finally to the output fomatter
stage and to the output interface.
controlled
ADC input level
0 dB
MGC823
1995 Oct 18 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
9.4 Luminance processing (see Fig.7)
The 8-bit luminance signal, a digital CVBS format or a
luminance format (S-VHS, HI8), is fed through a
switchable prefilter. High frequency components are
emphasized to compensate for loss. The following
chrominance trap filter (fc= 4.43 or 3.58 MHz centre
frequency selectable) eliminates most of the colour carrier
signal, therefore, it must be bypassed for S-Video (S-VHS,
HI8) signals.
The high frequency components of the luminance signal
can be peaked (control for sharpness improvement via
I2C-bus) in two bandpass filters with selectable transfer
characteristics.
A coring circuit with selectable characteristics improves
the signal once more. This signal is then added to the
original (unpeaked) signal. A switchable amplifier achieves
common DC amplification, because the DC gains are
different in both chrominance trap modes.
The improved luminance signal is fed via the variable
delay to the BCS control and the output interface.
9.5 YUV-bus (digital outputs)
The 16-bit YUV-bus transfers digital data from the output
interfaces to a feature box, or a field memory, a digital
colour space converter (SAA 7192 DCSC) or a video
enhancement and digital-to-analog processor (SAA7165
VEDA2). The outputs are controlled by an output enable
FEIN on pin 63).
chain (
The YUV data rate equals LLC2. Timing is achieved by
marking each second positive rising edge of the clock LLC
in conjunction with CREF (clock reference).
The synchronization pulses are sliced and fed to the phase
detectors where they are compared with the sub-divided
clock frequency. The resulting output signal is applied to
the loop filter to accumulate all phase deviations.
Adjustable output signals HCL and HSY are generated in
accordance with analog front end requirements. The
output signals HS, VS, and PLIN are locked to the timing
reference, guaranteed between the input signal and the
HREF signal, as further improvements to the circuit may
change the total processing delay. It is therefore not
recommended to use them for applications which require
absolute timing accuracy to the input signals. The loop
filter signal drives an oscillator to generate the line
frequency control signal LFCO.
9.7 Clock generation circuit
The internal CGC generates all clock signals required for
the one chip front-end. The output signal LFCO is a
digital-to-analog converted signal provided by the
horizontal PLL. It is the multiple of the line frequency
(7.38 MHz = 472 × f
6.14 MHz = 360 × fh in 60 Hz systems). Internally the
LFCO signal is multiplied by a factor of 2 or 4 in the PLL
circuit (including phase detector, loop filtering, VCO and
frequency divider) to obtain the LLC and LLC2 output clock
signals. The rectangular output clocks have a 50% duty
factor.
It is also possible to operate the OCF1 with an external
CGC (SAA7197) providing the signals LLC and CREF.
The selection of the internal/external CGC will be
controlled by the CGCE input signal.
9.8 Power-on reset
in 50 Hz systems and
h
The output signals Y7 to Y0 are the bits of the digital
luminance signal. The output signals UV7 to UV0 are the
bits of multiplexed colour difference signals (B−Y) and
(R−Y). The frame in the format tables is the time, required
to transfer a full set of samples. In the event of 4 :2:2
format two luminance samples are transmitted in
comparison to one U and one V sample within the frame.
The time frames are controlled by the HREF signal.
Fast enable is achieved by setting inputFEIN to LOW. The
signal is used to control fast switching on the digital
YUV-bus. HIGH on this pin forces the Y and UV outputs to
a high-impedance state.
9.6 Synchronization (see Fig.7)
The pre-filtered luminance signal is fed to the
synchronization stage. It's bandwidth is reduced to 1 MHz
in a low-pass filter.
1995 Oct 18 11
Power-on reset is activated at power-on (using only
internal CGC), when the supply voltage decreases below
3.5 V. The indicator output
RESET signal can be applied to reset other circuits of the
digital TV system.
9.9 RTCO output
The real time control and status output signal contains
serial information about actual system clock, subcarrier
frequency and PAL/SECAM sequence. The signal can be
used for various applications in external circuits, for
example, in a digital encoder to achieve clean encoding.
RESET is LOW for a time. The
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
AOUT
23
MGC824
TEST
SELECTOR
SWITCH
BYPASS
FILTER
ANTI-ALIAS
ANALOG
AMPLIFIER
CLAMP
CIRCUIT
AOSL
FUSE
REFS4AINS4
ADC
FAST
ADDER
SWITCH
SWITCH
BYPASS
FILTER
ANTI-ALIAS
ANALOG
AMPLIFIER
CLAMP
CIRCUIT
FUSE
REFS3
ADC
FAST
ADDER
SWITCH
SWITCH
BYPASS
FILTER
ANTI-ALIAS
ANALOG
AMPLIFIER
CLAMP
CIRCUIT
FUSE
GAS2
GAS3
IVAL
WISL
GAD2
WVAL
REFS2
GAD3
WRSE
WIRS
GUDL
FAST
SWITCH
CONTROL
VERTICAL
CONTROL
BLANKING
CONTROL
ANTI-ALIAS
GAIN
CONTROL
CLAMP
CONTROL
GAI2
GACO
HOLD
GLIM
WIPA
CLL2n
MX24
MX34
MS24
MUYC
VBPS
VBPR
GAI3
WIPE
CLL3n
MUD1
MS34
VBCO
IWIP
GAI4
SBOT
MUD2
IGAI
GASL
CROSS
TWO2
TWO3
YSEL
CSEL
MULTIPLEXER
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.5 Analog input processing and analog control part.
SWITCH
SOURCE
20, 16, 12
11
18, 14, 10
13
AI42
SSA4
DDA4
to V
to V
SSA2
DDA2
V
V
1995 Oct 18 12
AI41
AIND4
SOURCE
15
17
AI32
SWITCH
AI31
AINS3
AIND3
SWITCH
SOURCE
19
21
AI22
AI21
AINS2
AIND2
ANALOG
CONTROL
CLS2
CLTS
987
i.c.
CLS3
CLS4
i.c.
22
i.c.
SS(S)
V
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
Y7 to Y0
UV7 to UV0
FEIN
63
(MUXC)
62
55 to
53, 54
45 to 50,
HREF
42
MGC825
OUTPUT
FORMATTER
AND INTERFACE
GAIN
CONTROL
LOW-PASS LOW-PASS
QUADRATURE
DEMODULATOR
HRFS
SQPB
HRMV
OFTS
CHSB
OEYC
OEHV
CLOCH FILTER
PI2
LOOPFILTER
LFIS
CKTS
CKTQ
CHCV
(DTO1)
OSCILLATOR
AND DIVIDER
DISCRETE TIME
CONTROL
CONTRAST
SATURATION
BRIGHTNESS
AND SECAM
COMB FILTERS
RECOMBINATION
PHASE
DETECTOR
AMPLITUDE
DEMODULATOR
BURST GATE
ACCUMULATOR
PI1
LOOP FILTER
BRIG
SEQA
SEQA
SATN
CONT
DIFFERENTIATOR
SEQUENCE
DE-EMPHASIS
STANDARD
COLO
ALTD
PROCESSOR
SXCRCODE
handbook, full pagewidth
CONTROL
SECS
Fig.6 Multi-standard decoder part.
1995 Oct 18 13
BANDPASS
CHROMINANCE
INPUT
INTERFACE
BYPS
HUEC
CHRS
34, 27
68, 52, 44,
DD
V
PLSE
SESE
35, 28
67, 51, 43,
SS
V
CHROMINANCE CIRCUIT
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
DELAY
VARIABLE
AND
WEIGHTING
ADDING STAGE
CORING
FILTER
VARIABLE
BANDPASS
BFBY
PREF
RESET
32
CONTROL
POWER-ON
AMPLIFIER
MATCHING
BPSS
CREF
LLC
29
31
CLOCK
CLOCK(3 to 0)
LINE-LOCKED
DELAY
LOOP FILTER
PHASE
DETECTOR
LLC2
30
GENERATOR
ADJUSTMENT
2
HPLL
HLCK
COARSE
XTALI
65
66
CLOCK
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
DISCRETE TIME
HLCK
VTRC
XTALO
GENERATOR
(DTO2)
FIDT
LFCO
26
DAC4
DAC6
CLOCK
CIRCUIT
GENERATION
VNOI
FSEI
AUFD
VERTICAL
PROCESSOR
4137 38 39 40 25 24 333
MGC826
CGCEODD (VL)
SSA0
V
DDA0
V
handbook, full pagewidth
FINE
PHASE
DETECTOR
TRAP
CHROMINANCE
SYNC
SLICER
LUMINANCE CIRCUIT
PREFILTER
PREF BYPS CORI APER YDEL
2
AP
BLOCK
CONTROL
1
SP
SYNC
PREFILTER
TEST
1995 Oct 18 14
COUNTER
STTC
HLCK
IDEL
HSYB
HSYS
HCLB
HCLS
HPHI
HS6B
HS6S
HC6B
HC6S
PULIO
OEHV
SYNCHRONIZATION CIRCUIT
VBLKA
C-BUS
2
I
CONTROL
SSTB
GPSW
C-BUS
2
I
INTERFACE
64
GPSW
(VBLK)
HP6I
SCEN
36
456
RTCO
HSY
HCL HS VS
SA SCL SDA
PLIN (HL)
Fig.7 Luminance and synchronization part.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
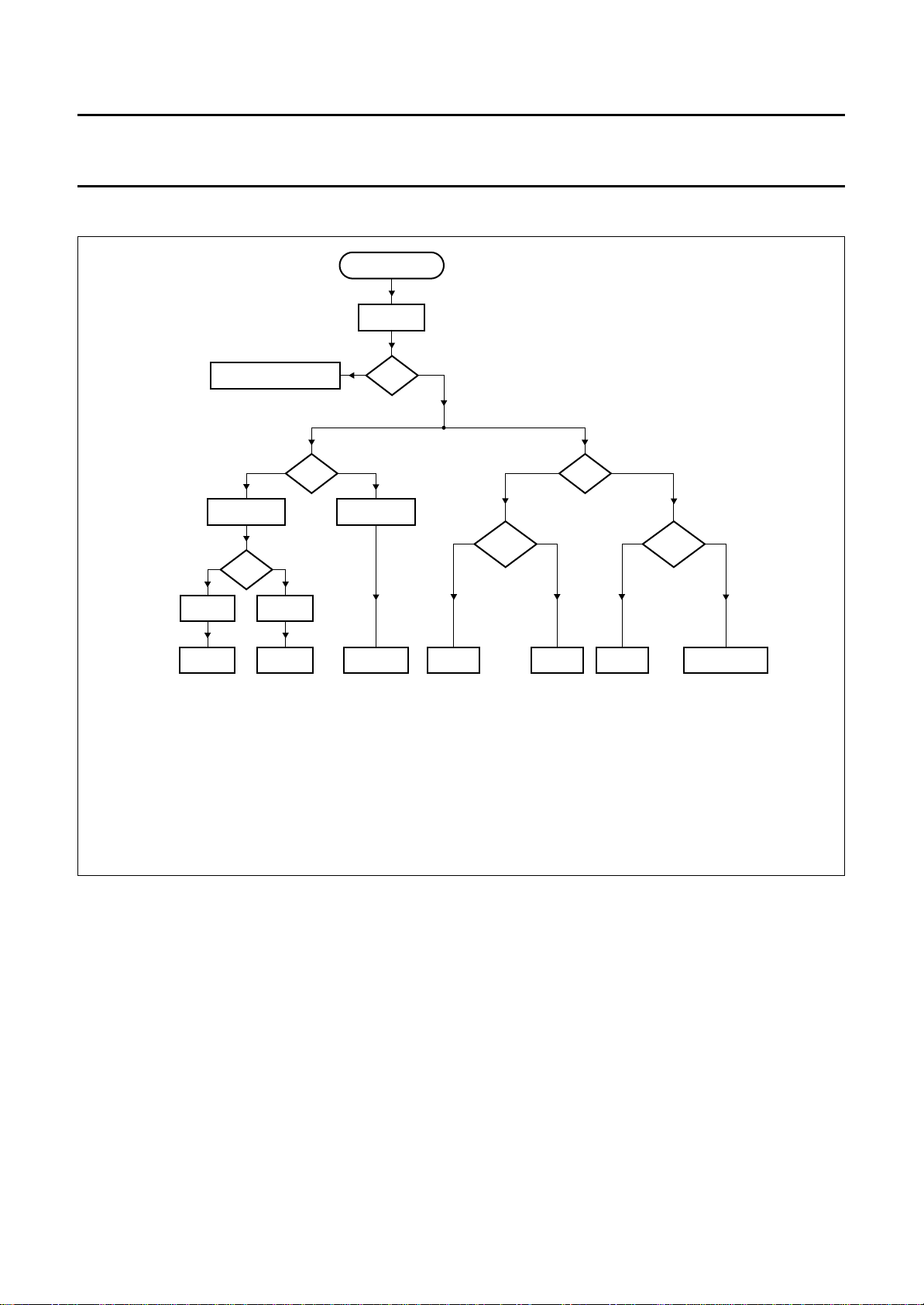
10 GAIN CHARTS
handbook, full pagewidth
NO BLANKING ACTIVE
CLAA = 1
10
<
CCL
CLAU = 1 CLAU = 0
+ CLAMP − CLAMP + GAIN − GAIN − GAIN SLOW + GAINNO CLAMP
CLAU = clamp up.
VBLK = vertical blanking pulse.
WIPE = white peak level (adjustable).
SBOT = sync bottom level (adjustable).
CLL = clamp level (adjustable).
CLAA = clamp active.
HSY = horizontal sync pulse.
HCL = horizontal clamp pulse.
10
HCL
ANALOG IN
ADC
10
VBLK
<− CLAMP GAIN −>
10
CLAA = 0
10 10
>
SBOT
HSY
> WIPE
MGC827
1995 Oct 18 15
Fig.8 Clamp and gain flow chart.
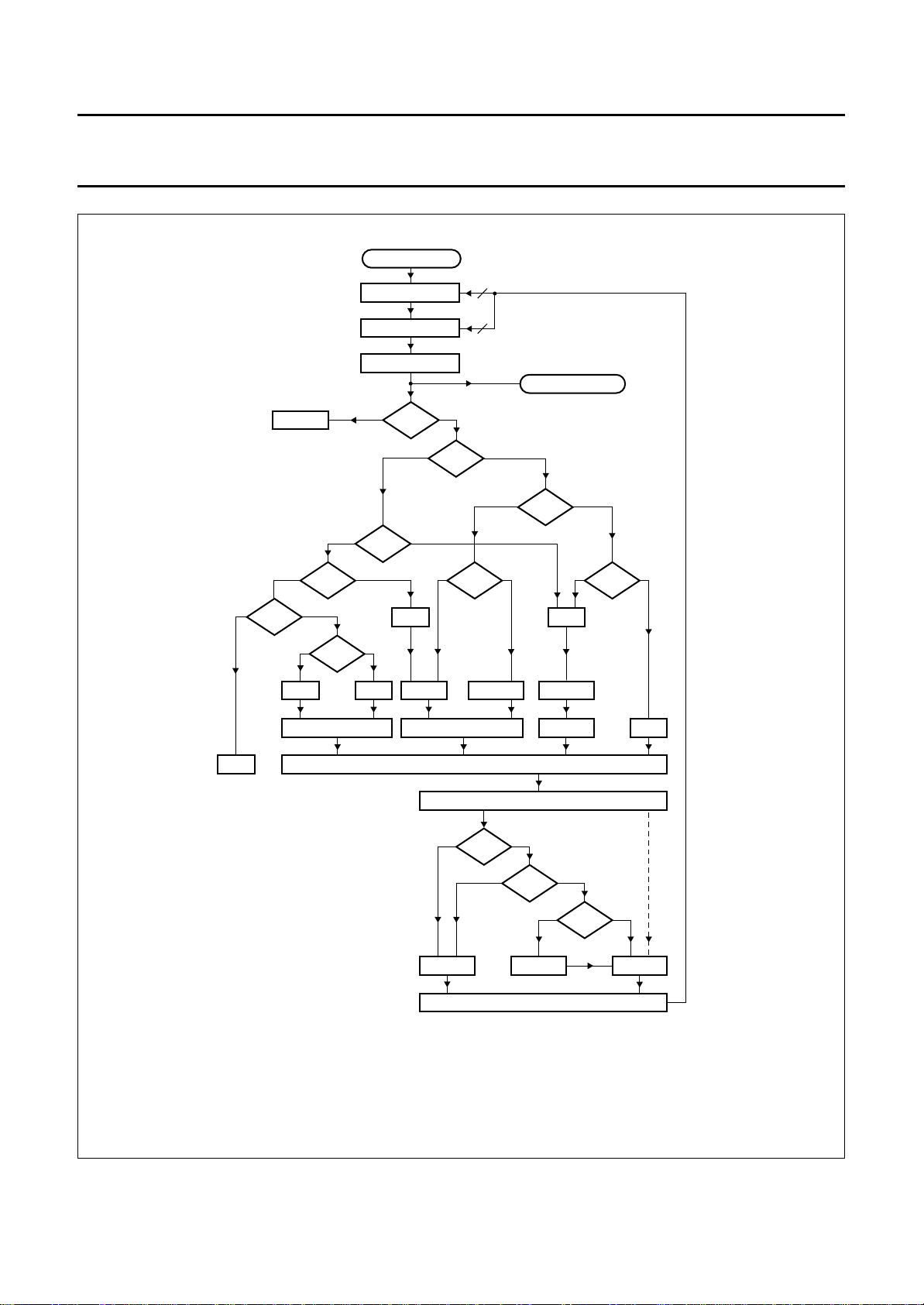
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
0
no action
WRSE
0
+4/F
analog input
amplifier
anti-alias amplifier
ADC8
1
VBLK
1
>WIPE
0
1
−
IVAL
0
1
1
1
WIRS
+4/L
MSB
2
LSB
0
X
1
<SBOT<SBOT
+IVAL −WVAL
6
decoder input
0
1
0
HSY
0
1
>WIPE
X = 1X = 0
0
STOP
X = system variable (start with logic 0).
Y = IAGV-FGVI > GUDL.
VBLK = vertical blanking pulse.
HSY = horizontal sync pulse.
SBOT = sync bottom level (adjustable).
WIPE = white peak level (adjustable).
IVAL = integration value gain (adjustable).
WVAL = integration value WIPE (adjustable).
IGAI = integration factor gain (adjustable).
IWIP = integration factor WIPE (adjustable).
AGV = actual gain value.
FGV = frozen gain value.
GUDL = gain update level (adjustable).
WRSE = white peak reset enable.
WIRS = white peak reset select.
L = line.
F = field.
*IWIP *IGAI *IWIP
gain accumulator (20 bits)
actual gain value 8-bit (AGV) [−3/+6 dB]
1
AGV
0
X
1
gain value 8-bit
HSY
update
0
1
Fig.9 Luminance AGC flow chart.
+/− 0
0
Y
FGV
MGC828
1995 Oct 18 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
11 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134); all ground pins and all supply pins connected
together.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
V
DDD
V
I(A)
V
I(D)
V
diff
T
stg
T
amb
T
amb(bias)
P
tot
V
esd
analog supply voltage −0.5 +7.0 V
digital supply voltage −0.5 +7.0 V
analog input voltage −0.5 +7.0 V
digital input voltage −0.5 +7.0 V
voltage difference between V
SSAall
and V
SSall
− 100 mV
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
operating ambient temperature under bias −10 +80 °C
total power dissipation V
DDA=VDDD
= 7 V; note 1 − 2.5 W
electrostatic discharge all pins note 2 −2000 +2000 V
Note
1. Compare with typical total power consumption in Chapter “Characteristics”.
2. Equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor through a 1.5 kΩ series resistor.
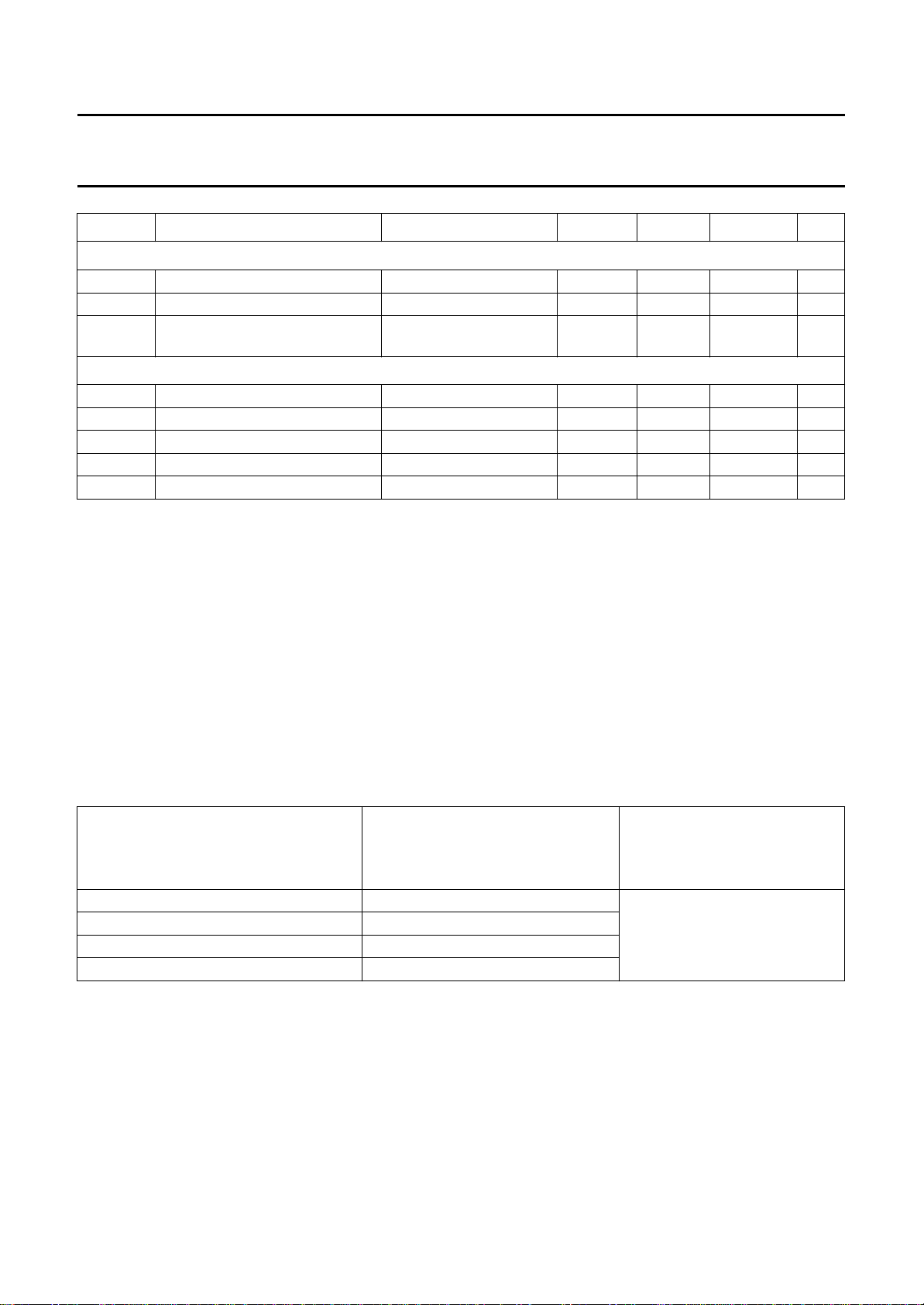
12 CHARACTERISTICS
V
DDD
=5V; V
DDA
=5V; T
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
DDA
V
DDD
I
DDA(tot)
I
DDD(tot)
P
tot
analog supply voltage 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
digital supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
total analog supply current −−150 mA
total digital supply current −−250 mA
total power dissipation − 1.2 1.7 W
Analog part
I
clamp
V
i(p-p)
clamping current VI= 1.25 V DC −2 − +2 µA
input voltage (peak-to-peak
C
= 10 nF 0.5 1.0 1.38 V
couple
value), AC coupling required
input impedance clamping current off 200 −− kΩ
Z
i
C
i
α
ct
input capacitance −−10 pF
channel crosstalk fi< 5 MHz −−50 − dB
Analog-to-digital converters
B analog bandwidth at −3dB − 15 − MHz
φ
diff
G
diff
f
LLC
DLE DC differential linearity error −
differential phase amplifier + AAF = bypass − 2 − deg
differential gain amplifier + AAF = bypass − 2 − %
ADC clock rate 11 − 16 MHz
1
⁄
2
− LSB
ILE DC integral linearity error − 1 − LSB
1995 Oct 18 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Digital inputs
V
IL
LOW level input voltage
SDA and SCL
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage
SDA and SCL
V
IL(clk)
LOW level input voltage for
clocks
V
IH(clk)
HIGH level input voltage for
clocks
V
IH(XTALI)
V
IL(n)
HIGH level input voltage XTALI 3.0 − VDD+ 0.5 V
LOW level input voltage all other
inputs
V
IH(n)
HIGH level input voltage all other
inputs
I
LI
C
i(clk)
C
i(I/O)
C
i(n)
input leakage current −−10 µA
input capacitance for clocks −−10 pF
input capacitance I/Os at high impedance −−8pF
input capacitance all other inputs −−8pF
Digital outputs
V
LFCO
LFCO output voltage
(peak-to-peak value)
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL(clk)
LOW level output voltage note 2 0 − 0.6 V
HIGH level output voltage note 2 2.4 − V
LOW level output voltage for
clocks
V
OH(clk)
HIGH level output voltage for
clocks
note 1 1.4 − 2.6 V
−0.5 − +1.5 V
3.0 − VDD+ 0.5 V
−0.5 − +0.6 V
2.4 − VDD+ 0.5 V
−0.5 − +0.8 V
2.0 − VDD+ 0.5 V
DD
−0.5 − +0.6 V
2.6 − VDD+ 0.5 V
V
Clock input timing (LLC)
T
cy
δ duty factor for t
t
r
t
f
cycle time 31 − 45 ns
LLCH/Tcy
rise time Vi= 0.6 to 2.4 V −−5ns
fall time Vi= 2.4 to 0.6 V −−5ns
Control and CREF input timing (note 3)
t
SU;DAT
t
HD;DAT
t
HD;FEIN
t
HD;OTHER
input data set-up time 11 −− ns
input data hold time 3 −− ns
input data hold time for FEIN 3 −− ns
input data hold time all other
note 3 6 −− ns
inputs
1995 Oct 18 18
40 − 60 %

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Data and control output timing (note 4)
C
L(data)
output load capacitance
(data, HREF and VS)
C
L(control)
t
HD;DAT
t
PD(data)
output load capacitance (control) 7.5 − 25 pF
output data hold time CL=15pF 13 −− ns
propagation delay from negative
edge of LLC (data, HREF and
VS)
t
PD(control)
propagation delay from negative
edge of LLC (control)
t
PD(Z))
propagation delay from negative
edge of LLC (to 3-state)
Clock output timing (LLC and LLC2)
C
L(LLC)
T
cy
δ duty factors for t
t
r
t
f
t
d
output load capacitance 15 − 40 pF
cycle time LLC 31.5 − 45 ns
LLCH/tLLC
t
LLC2H/tLLC2
rise time 0.6 to 2.6 V −−5ns
fall time 2.6 to 0.6 V −−5ns
delay time LLC output to LLC2
output
Data qualifier output timing (CREF)
t
HD;CREF
t
PD;CREF
output hold time CL=15pF 4 −− ns
propagation delay from positive
edge of LLC
and
CL=50pF −−29 ns
CL=25pF −−29 ns
note 5 −−15 ns
LLC2 63 − 90 ns
Vi= 1.5 V;
C
LLC/LLC2
= 40 pF; note 6
CL=40pF −−20 ns
15 − 50 pF
40 − 60 %
−−8ns
Horizontal PLL
f
Hnom
nominal line frequency 50 Hz field − 15625 − Hz
60 Hz field − 15734 − Hz
∆f
H/fHnom
permissible static deviation 50 Hz field −−5.6 %
60 Hz field −−6.7 %
Subcarrier PLL
f
Hnom
nominal subcarrier frequency PAL − 4433618 − Hz
NTSC − 3579545 − Hz
∆fH/f
Hnom
lock-in range 400 −− Hz
1995 Oct 18 19
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Crystal oscillator
f
n
∆f/f
n
∆T/f
n
CRYSTAL SPECIFICATION (X1); note 7
T
amb
C
L
R
s
C1 motional capacitance − 1.1 ±20% − fF
C0 parallel capacitance − 3.5 ±20% − pF
Notes
1. The LFCO output level must be measured with a load circuit of 10 kΩ in parallel with 15 pF.
2. The levels must be measured with load circuits, the loads depend on the type of output stage. Control outputs (except
HREF and VS); 1.2 kΩ at 3 V (TTL load); CL= 25 pF: data outputs (plus HREF and VS); 1.2 kΩ at 3 V (TTL load);
CL=50pF.
3. Other control input signals are CGCE, VS, SA, HCL and HSY.
4. Data output signals are YUV (15 to 0). Control output signals are HREF, VS, HS, HSY, HCL, RTCO, PLIN (HL),
ODD (VL) and GPSW0 (VBLK). The effects of rise and fall times are included in the calculation of t
t
PDZ
5. The minimum propagation delay from 3-state to data active related to falling edge of LLC is 0 ns.
6. LLC2 is not active while CGCE = 0.
7. Philips catalogue number 9922 520 30004.
nominal frequency 3rd harmonic − 26.8 − MHz
permissible frequency deviation −50 × 10−6− +50 × 10
permissible frequency deviation
−20 × 10−6− +20 × 10
with temperature
operating ambient temperature 0 − 70 °C
load capacitance 8 −− pF
series resonance resistance − 50 80 Ω
HD;DAT
. Timings and levels refer to drawings and conditions illustrated in Fig.10.
−6
−6
, tPD and
Table 1 Processing delay
FUNCTION
TYPICAL ANALOG DELAY
AI21 TO ADCIN (AOUT) (ns)
Without amplifier or anti-alias filter 10
With amplifier, without anti-alias filter 30
With amplifier plus anti-alias filter (50 Hz) 30 + 40
With amplifier plus anti-alias filter (60 Hz) 30 + 50
1995 Oct 18 20
DIGITAL DELAY
ADCIN (AOUT) TO YUVOUT
(1/LLC)
(YDEL = 0; CAD2/3 = 1)
248
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
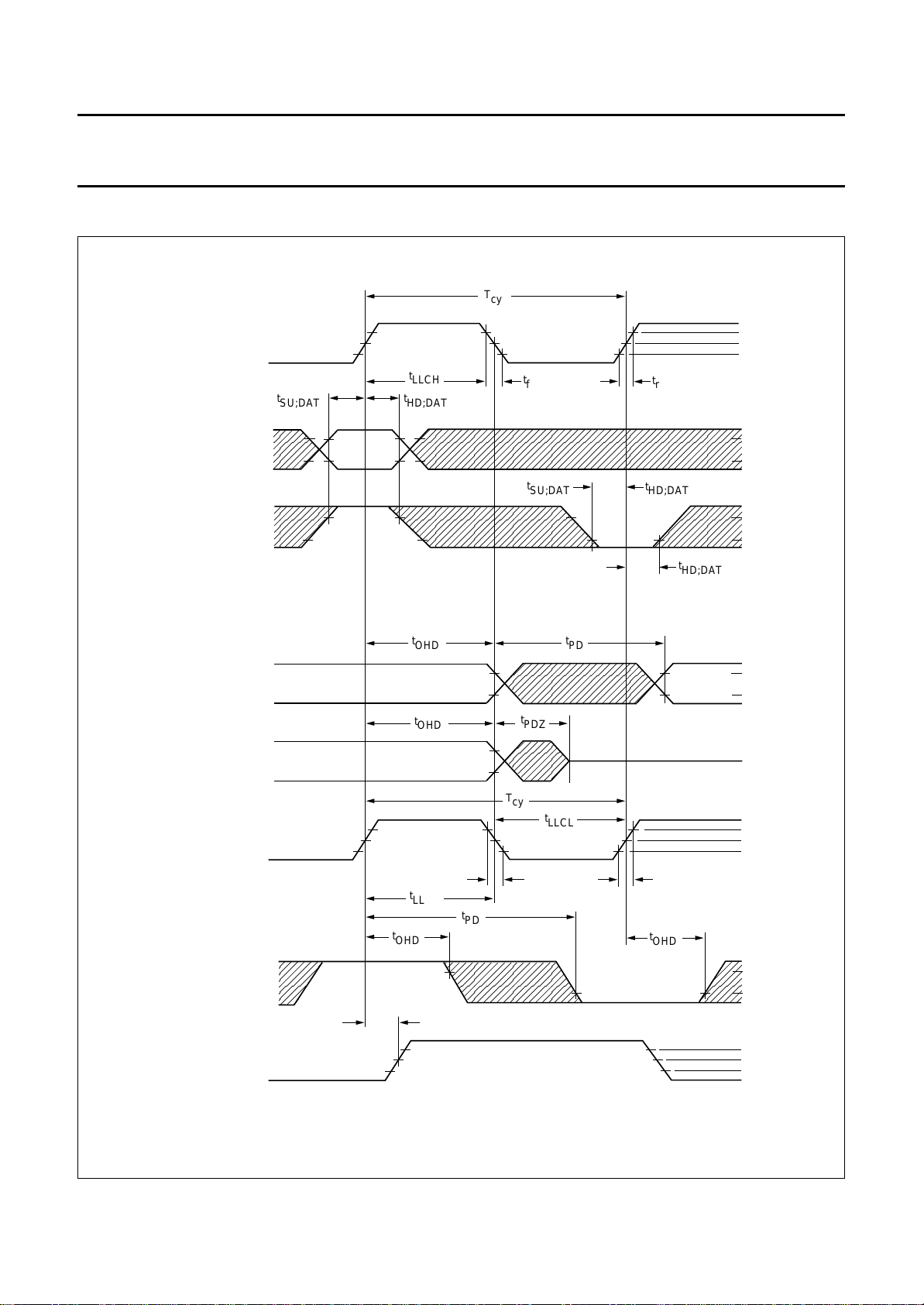
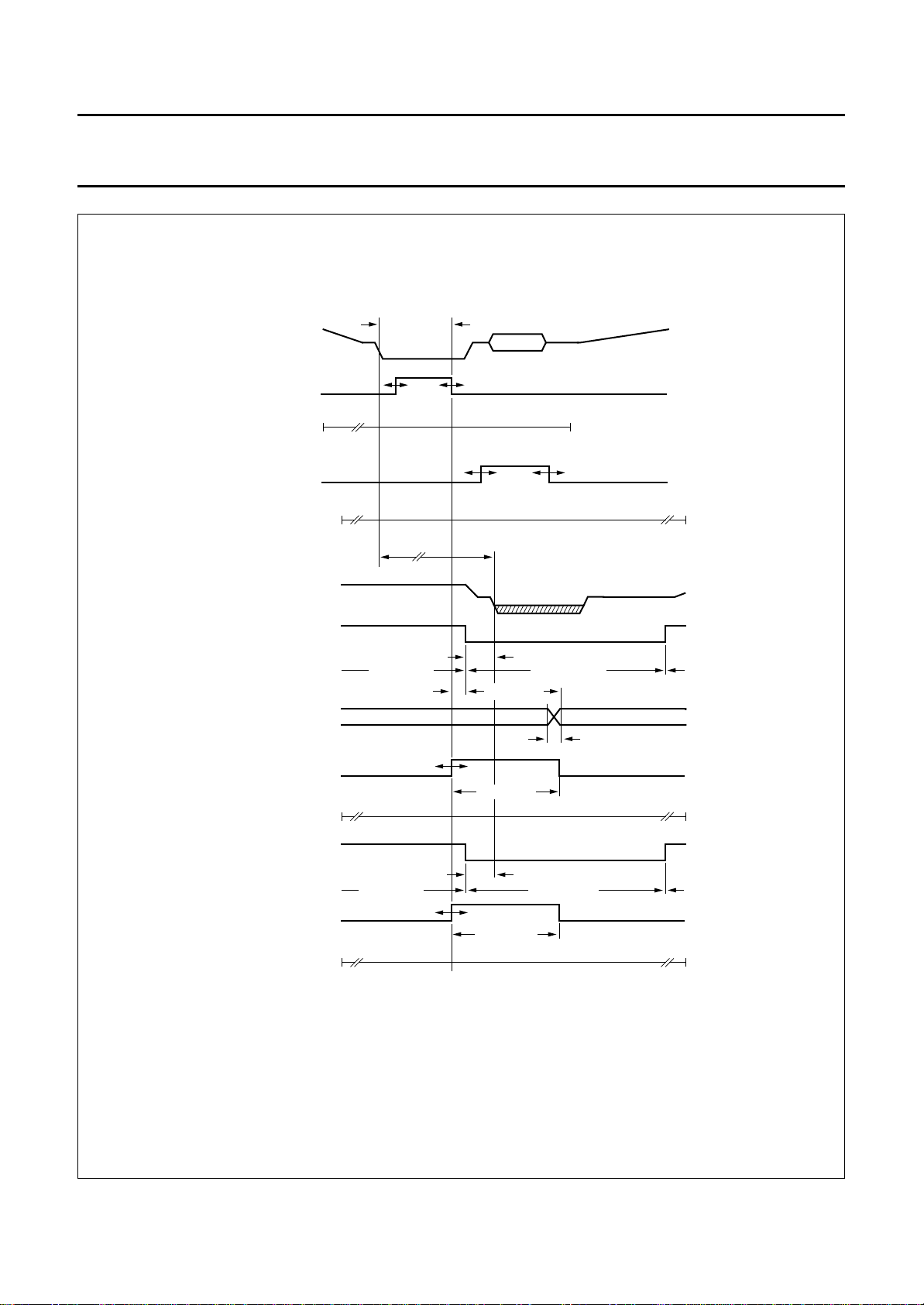
13 TIMING
T
handbook, full pagewidth
CLOCK INPUT LLC
t
SU;DAT
t
LLCH
t
HD;DAT
cy
2.4 V
1.5 V
0.6 V
t
f
t
r
INPUTS CONTROL
INPUT CREF
OUTPUTS YUV, HREF, VS AND HS
OUTPUTS YUV (to 3-state)
CLOCK OUTPUT LLC
t
OHD
t
OHD
t
OHD
t
LLCH
2.0 V
0.8 V
t
SU;DAT
t
PD
t
PDZ
T
cy
t
LLCL
t
f
t
PD
t
HD;DAT
t
r
t
OHD
t
HD;DAT
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.4 V
0.6 V
2.6 V
1.5 V
0.6 V
OUTPUT CREF
CLOCK OUTPUT LLC2
1995 Oct 18 21
t
dLLC2
Fig.10 Clock/data timing.
MGC829
2.4 V
0.6 V
2.6 V
1.5 V
0.6 V
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
CVBS
HSY
HSY
programming range
(step size: 2/LLC)
HCL
HCL
programming range
(step size: 2/LLC)
Y output
HREF (50 Hz)
PLIN (50 Hz)
HS (50 Hz)
+191
+127
62 × 2/LLC
768 × 2/LLC
30 × 2/LLC
0
burst
−64
processing delay CVBS−>YUV
18 × 2/LLC
176 × 2/LLC
94 × 2/LLC
4/LLC
−128
(1)
HS (50 Hz)
programming range
(step size: 8/LLC)
HREF (60 Hz)
HS (60 Hz)
HS (60 Hz)
programming range
(step size: 8/LLC)
(1) See Table 1.
HRMV = 1 and HRFS = 0.
+117
+97
0
640 × 2/LLC
0
Fig.11 Horizontal timing.
1995 Oct 18 22
64 × 2/LLC
−118
18 × 2/LLC
140 × 2/LLC
64 × 2/LLC
−97
MGC830
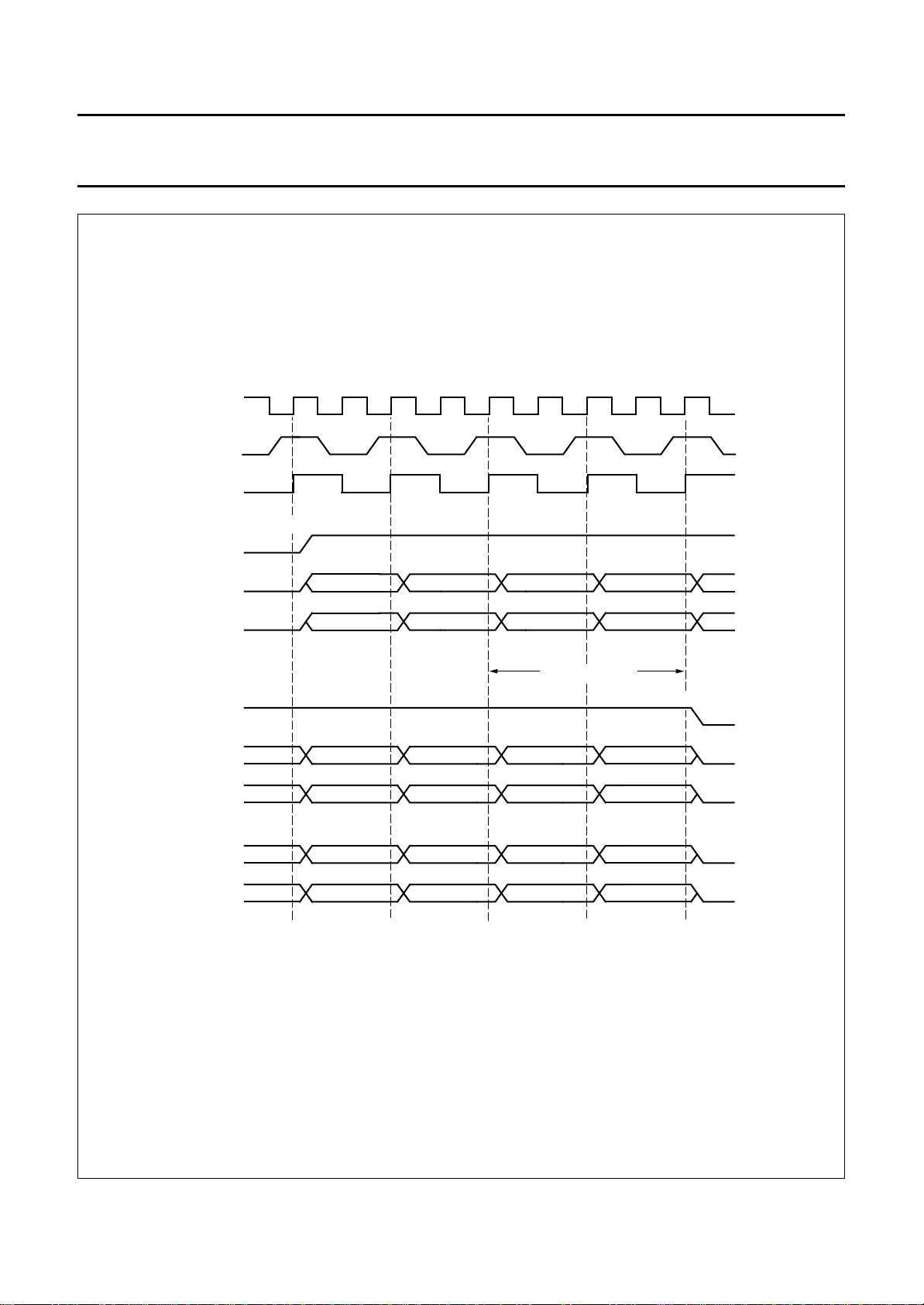
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
LL27
CREF
INTERNAL
BUS CLOCK
HREF
Yn
UVn
HREF
Yn
(50 Hz)
UVn
START OF ACTIVE LINE
01234
U0 V0 U1 V1 U2
ONE BUS CYCLE
END OF ACTIVE LINE
767766765764763
U766 V766V764U764V762
Yn
(60 Hz)
UVn
1995 Oct 18 23
V636U636V634
Fig.12 HREF timing.
639638637636635
U638 V638
MGC831

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
a: 1st field
input CVBS
HREF
ODD
b: 2nd field
input CVBS
HREF
ODD
a: 1st field
input CVBS
HREF
ODD
VS
VS
VS
(1)
(1)
(2)
123456789625
533 × 2/LLC
2 × 2/LLC
314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321313
61 × 2/LLC
2 × 2/LLC
123456789525
441 × 2/LLC
2 × 2/LLC
(1) Nominal input signal 50 Hz.
(2) Nominal input signal 60 Hz.
HRMV = 1 and HRFS = 0.
1995 Oct 18 24
b: 2nd field
input CVBS
HREF
ODD
VS
(2)
264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271263
51 × 2/LLC
2 × 2/LLC
MGC832
Fig.13 Vertical timing.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
LLC
CREF
HREF
t
SU;DAT
FEIN
t
OHD
YUV
Fig.14 FEIN timing.
Table 2 Digital output control
OEYC FEIN YUV (15 : 0)
00 Z
1 0 active
X1 Z
t
HD;DAT
from 3-stateto 3-state
t
PD
MGC833
handbook, full pagewidth
BIT NO.:
TIME SLOT:
RTCO sequence is generated in LLC/4.
For transmission LLC/2 timing is required.
1995 Oct 18 25
HIGH
128
transmitted once per line
LOW
HPLL-INCR.
FSCPLL-INCR.
RESERVED
14
13
1
0 67
4
0
21
22
19
14
1617
1920
15
18
45
9
13
14
11 1012
6
8
7
3
452
3
0
1
63
Fig.15 Real time control output timing.
SEQUENCE
RESERVED
(50 Hz SYSTEMS)
RESERVED
1
(60 Hz SYSTEMS)
276
188
MGC834

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
14 OUTPUT FORMATS
Table 3 Output formats
BUS
SIGNAL
Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7 Y7
Y6 Y6 Y7 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6 Y6
Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5 Y5
Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4 Y4
Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3 Y3
Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2 Y2
Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1 Y1
Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0 Y0
UV7 U7 U5 U3 U1 U7 U5 U3 U1 U7 V7 U7 V7 U7 V7
UV6 U6 U4 U2 U0 U6 U4 U2 U0 U6 V6 U6 V6 U6 V6
UV5 V7 V5 V3 V1 V7 V5 V3 V1 U5 V5 U5 V5 U5 V5
UV4 V6 V4 V2 V0 V6 V4 V2 V0 U4 V4 U4 V4 U4 V4
UV3 00000000U3V3U3V3U3V3
UV2 00000000U2V2U2V2U2V2
UV1 00000000U1V1U1V1U1V1
UV0 00000000U0V0U0V0U0V0
Y frame 01234567 0 1 2345
UV frame 0 4 0 2 4
Y
U LLC4 LLC8
V LLC4 LLC8
PIXEL BYTE SEQUENCE 4 :1:1 FORMAT PIXEL BYTE SEQUENCE 4 :2:2 FORMAT
data rate sample frequency data rate sample frequency
LLC2
LLC2
LLC2
LLC2
1995 Oct 18 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
CCIR 601 digital levels.
+255
+235
LUMINANCE 100%
+128
+16
0
+255
+240
+212 +212
+128
U-COMPONENT
+44
+16
0
blue 100%
blue 75%
yellow 75%
yellow 100%
+255
+240
+128
+44
+16
V-COMPONENT
0
red 100%
red 75%
cyan 75%
cyan 100%
MGC835
a. Y output range. b. U output range (B−Y). c. Y output range (R−Y).
Fig.16 YUV output signal range.
handbook, full pagewidth
quartz (3rd harmonic)
26.8 MHz
C =
10 pF
C =
10 pF
XTALO
XTALI
L = 10 µH +/-20%
C =
1 nF
65
SAA7110
SAA7110A
66
a. with quartz crystal. b. with external clock.
Fig.17 Oscillator application.
1995 Oct 18 27
XTALO
XTALI
65
SAA7110
SAA7110A
66
MGC836

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
15 CLOCK SYSTEM
15.1 Clock generation circuit
The internal CGC generates the system clocks LLC, LLC2
and the clock reference signal CREF. The internally
generated LFCO (triangular waveform) is multiplied by
four via the analog PLL (including phase detector, loop
filter, VCO and frequency divider). The rectangular output
signals have a 50% duty factor.
handbook, full pagewidth
LFCO
BAND PASS
FC = LLC/4
ZERO
CROSS
DETECTION
DETECTION
Table 4 System clock frequencies
CLOCK
50 Hz 60 Hz
XTAL 26.8 26.8
LLC 29.5 24.545454
LLC2 14.75 12.272727
LLC4 7.375 6.136136
LLC8 3.6875 3.068181
PHASE
LOOP
FILTER
DIVIDER
1/2
FREQUENCY (MHz)
OSCILLATOR
DIVIDER
1/2
LLC
LLC2
Fig.18 Clock generation circuit.
DELAY CREF
MGC837
1995 Oct 18 28

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
15.2 Power-on control
Power-on reset is activated at power-on (using only internal CGC) and if the supply voltage falls below 3.5 V. TheRESET
signal can be applied to reset other circuits of the digital TV system.
handbook, full pagewidth
Table 5 Power-on control sequence
INTERNAL POWER-ON
CONTROL SEQUENCE
Directly after power-on
asynchronous reset
Y7 to Y0, UV7 to UV0, RTCO, PLIN, ODD,
GPSW, SDA, HREF, HS, VS, HCL and HSY
in high impedance state
CGCE
LLC
POC V
DD
ANALOG
POC
LOGIC
CLOCK I/O
CONTROL
POC V
DD
DIGITAL
DELAY
CONTROL
CLOCK
OUTPUT
ACTIVE
CONTROL
RESET
MGC838
Fig.19 Power-on control circuit.
PIN OUTPUT STATUS FUNCTION
direct switching to high impedance (outputs)
or input mode (I/Os) for 20 to 200 ms
Start synchronous
2
C-bus reset sequence
I
Status after I
2
C-bus reset Y7 to Y0, UV7 to UV0, HREF and HS held
Status after power-on
control sequence
1995 Oct 18 29
LLC, LLC2 and CREF in HIGH state
LLC, LLC2 and CREF active starting I2C-bus reset sequence
SA0DH = 7DH (VTRC = 0, RTSE = 1,
in high impedance state
VS, HCL and HSY held in input function
mode
HRMV = 1, SSTB = 0, SECS = 1)
SA0EH = 00H (HPLL = 0, OEHV = 0,
OEYC = 0, CHRS = 0, GPSW = 0)
SA31H = 00H (AOSL1:0=00, WIRS = 0,
WRSE = 0, SQPB = 0, VBLKA = 0,
PULIO = 0)
RTCO, PLIN, ODD, GPSW and SDA active after power-on (reset sequence) a complete
2
C-bus transmission is required
I

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16 I2C-BUS DESCRIPTION
2
16.1 I
Table 6 Description of I
S START condition
Slave address 1001 110Xb (SA = LOW) or 1001 111Xb (SA = HIGH)
ACK acknowledge generated by the slave
Subaddress subaddress byte, see Table 7
Data data byte, see Table 7; note 1
P STOP condition
X read/write control bit:
Slave address 9CH for write, 9DH for read (SA = 0)
Subaddress 00H to 19H decoder part
C-bus format
S SLAVE ADDRESS ACK SUBADDRESS ACK DATA (n bytes) ACK P
2
C-bus format
CODE DESCRIPTION
X = 0, order to write (the circuit is slave receiver)
X = 1, order to read (the circuit is slave transmitter)
9EH for write, 9FH for read (SA = 1
1AH to 1FH reserved
20H to 34H front-end part
Note
1. If more than one byte DATA is transmitted then the auto-increment of the subaddress is performed.
1995 Oct 18 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.2 I2C-bus receiver/transmitter tables
Table 7 OCF1
RECEIVER
Slave address 10011100b, 9CH (SA = 0) and 10011110b, 9EH (SA = 1)
REGISTER FUNCTION
SUB
ADD
(1)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DMSD-SQP + BSC slave receiver (SU 00H to 19H)
Increment delay 00 007
IDEL7
HSY begin 50 Hz 01 015
HSYB7
HSY stop 50 Hz 02 023
HSYS7
HCL begin 50 Hz 03 031
HCLB7
HCL stop 50 Hz 04 039
HCLS7
HSY after PHI1 50 Hz 05 047
HPHI7
Luminance control 06 055
BYPS
Hue control 07 063
HUEC7
Colour killer threshold
QUAM (PAL/NTSC)
Colour killer threshold
SECAM
08 071
CKTQ4
09 079
CKTS4
PAL switch sensitivity 0A 087
PLSE7
SECAM switch sensitivity 0B 095
SESE7
Gain control chrominance 0C 103
COLO
Standard/mode control 0D 111
VTRC
I/O and clock control 0E 119
HPLL
Control #1 0F 127
AUFD
Control #2 10 135
XXX
Chrominance gain reference 11 143
CHCV7
Chrominance saturation 12 151
SATN7
006
IDEL6
014
HSYB6
022
HSYS6
030
HCLB6
038
HCLS6
046
HPHI6
054
PREF
062
HUEC6
070
CKTQ3
078
CKTS3
086
PLSE6
094
SESE6
102
LFIS1
110
XXX
118
XXX
126
FSEL
134
XXX
142
CHCV6
150
SATN6
005
IDEL5
013
HSYB5
021
HSYS5
029
HCLB5
037
HCLS5
045
HPHI5
053
BPSS1
061
HUEC5
069
CKTQ2
077
CKTS2
085
PLSE5
093
SESE5
101
LFIS0
109
XXX
117
XXX
125
SXCR
133
XXX
141
CHCV5
149
SATN5
DATA BYTE
004
IDEL4
012
HSYB4
020
HSYS4
028
HCLB4
036
HCLS4
044
HPHI4
052
BPSS0
060
HUEC4
068
CKTQ1
076
CKTS1
084
PLSE4
092
SESE4
100
XXX
108
XXX
116
OEHV
124
SCEN
132
XXX
140
CHCV4
148
SATN4
(2)
003
IDEL3
011
HSYB3
019
HSYS3
027
HCLB3
035
HCLS3
043
HPHI3
051
CORI1
059
HUEC3
067
CKTQ0
075
CKTS0
083
PLSE3
091
SESE3
099
XXX
107
RTSE
115
OEYC
123
XXX
131
XXX
139
CHCV3
147
SATN3
002
IDEL2
010
HSYB2
018
HSYS2
026
HCLB2
034
HCLS2
042
HPHI2
050
CORI0
058
HUEC2
066
XXX
074
XXX
082
PLSE2
090
SESE2
098
XXX
106
HRMV
114
CHRS
122
YDEL2
130
HRFS
138
CHCV2
146
SATN2
001
IDEL1
009
HSYB1
017
HSYS1
025
HCLB1
033
HCLS1
041
HPHI1
049
APER1
057
HUEC1
065
XXX
073
XXX
081
PLSE1
089
SESE1
097
XXX
105
SSTB
113
XXX
121
YDEL1
129
VNOI1
137
CHCV1
145
SATN1
000
IDEL0
008
HSYB0
016
HSYS0
024
HCLB0
032
HCLS0
040
HPHI0
048
APER0
056
HUEC0
064
XXX
072
XXX
080
PLSE0
088
SESE0
096
XXX
104
SECS
112
GPSW
120
YDEL0
128
VNOI0
136
CHCV0
144
SATN0
1995 Oct 18 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
REGISTER FUNCTION
Luminance contrast 13 159
HSY begin 60 Hz 14 167
HSY stop 60 Hz 15 175
HCL begin 60 Hz 16 183
HCL stop 60 Hz 17 191
HSY after PHI1 60 Hz 18 199
Luminance brightness 19 207
DUAD slave receiver (SU 20H to 32H)
Analog control #1 20 007
Analog control #2 21 015
Mixer control #1 22 023
Clamping level control 21 23 031
Clamping level control 22 24 039
Clamping level control 31 25 047
Clamping level control 32 26 055
Gain control analog #1 27 063
White peak control 28 071
Sync bottom control 29 079
Gain control analog #2 2A 087
Gain control analog #3 2B 095
Mixer control #2 2C 103
Integration value gain 2D 111
SUB
ADD
(1)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CONT7
HS6B7
HS6S7
HC6B7
HC6S7
HP6I7
BRIG7
AIND4
VBCO
GACO1
CLL217
CLL227
CLL317
CLL327
HOLD
WIPE7
SBOT7
IWIP1
IGAI1
CLS4
IVAL7
158
CONT6
166
HS6B6
174
HS6S6
182
HC6B6
190
HC6S6
198
HP6I6
206
BRIG6
006
AIND3
014
MS34
022
GACO0
030
CLL216
038
CLL226
046
CLL316
054
CLL326
062
GASL
070
WIPE6
078
SBOT6
086
IWIP0
094
IGAI0
102
XXX
110
IVAL6
157
CONT5
165
HS6B5
173
HS6S5
181
HC6B5
189
HC6S5
197
HP6I5
205
BRIG5
005
AIND2
013
MX241
021
CSEL
029
CLL215
037
CLL225
045
CLL315
053
CLL325
061
GAI25
069
WIPE5
077
SBOT5
085
GAI35
093
GAI45
101
CLS3
109
IVAL5
DATA BYTE
156
CONT4
164
HS6B4
172
HS6S4
180
HCLB4
188
HC6S4
196
HP6I4
204
BRIG4
004
FUSE1
012
MX240
020
YSEL
028
CLL214
036
CLL224
044
CLL314
052
CLL324
060
GAI24
068
WIPE4
076
SBOT4
084
GAI34
092
GAI44
100
CLS2
108
IVAL4
(2)
155
CONT3
163
HS6B3
171
HS6B3
179
HC6B3
187
HC6S3
195
HP6I3
203
BRIG3
003
FUSE0
011
MS24
019
MUYC
027
CLL213
035
CLL223
043
CLL313
051
CLL323
059
GAI23
067
WIPE3
075
SBOT3
083
GAI33
091
GAI43
099
XXX
107
IVAL3
154
CONT2
162
HS6B2
170
HS6S2
178
HC6B2
186
HC6S2
194
HP6I2
202
BRIG2
002
AINS4
010
REFS4
018
CLTS
026
CLL212
034
CLL222
042
CLL312
050
CLL322
058
GAI22
066
WIPE2
074
SBOT2
082
GAI32
090
GAI42
098
XXX
106
IVAL2
153
CONT1
161
HS6B1
169
HS6S1
177
HC6B1
185
HC6S1
193
HP6I1
201
BRIG1
001
AINS3
009
REFS3
017
MX341
025
CLL211
033
CLL221
041
CLL311
049
CLL321
057
GAI21
065
WIPE1
073
SBOT1
081
GAI31
089
GAI41
097
TWO3
105
IVAL1
152
CONT0
160
HS6B0
168
HS6S0
176
HC6B0
184
HC6S0
192
HP6I0
200
BRIG0
000
AINS2
008
REFS2
016
MX340
024
CLL210
032
CLL220
040
CLL310
048
CLL320
056
GAI20
064
WIPE0
072
SBOT0
080
GAI30
088
GAI40
096
TWO2
104
IVAL0
1995 Oct 18 32

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
REGISTER FUNCTION
SUB
ADD
(1)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Vertical blanking pulse set 2E 119
VBPS7
Vertical blanking pulse reset 2F 127
VBPR7
ADCs gain control 30 135
XXX
Mixer control #3 31 143
AOSL1
Integration value white peak 32 151
WVAL7
Mixer control #4 33 159
OFTS
Gain update level 34 167
MUD2
118
VBPS6
126
VBPR6
134
WISL
142
AOSL0
150
WVAL6
158
XXX
166
MUD1
117
VBPS5
125
VBPR5
133
GAS3
141
WIRS
149
WVAL5
157
CHSB
165
GUDL5
DATA BYTE
116
VBPS4
124
VBPR4
132
GAD31
140
WRSE
148
WVAL4
156
XXX
164
GUDL4
(2)
115
VBPS3
123
VBPR3
131
GAD30
139
SQPB
147
WVAL3
155
CAD3
163
GUDL3
114
VBPS2
122
VBPR2
130
GAS2
(3)
138
AFCCS
146
WVAL2
154
CAD2
162
GUDL2
113
VBPS1
121
VBPR1
129
GAD21
137
VBLKA
145
WVAL1
153
XXX
161
GUDL1
112
VBPS0
120
VBPR0
128
GAD20
136
PULIO
144
WVAL0
152
XXX
160
GUDL0
Notes
1. Subaddresses to be reset: 0D to 7DH, 0E and 31 to 00H after RESET = 0 (CGCE = 0) or power-on (CGCE = 1).
2. All reserved XXX-bits must be set to LOW, XX-bit is don’t care.
3. AFCCS bit does not exist in SAA7110A due to advanced anti-alias filter characteristic, don’t care (XX).
Table 8 OCF1
TRANSMITTER: Byte number 0 (transmitted if SSTB = 0 or after RESET has been 0)
Slave address 10011101b, 9DH (SA = 0) and 10011111b, 9FH (SA = 1
VERSION STATUS BYTE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
ID7 to ID0; note 1 ID7 ID6 ID5 ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
Note
1. ID7 to ID0 indicates the version number of the IC, for example SAA7110A V1 = 01H.
Table 9 OCF1 TRANSMITTER: Byte number 1 (transmitted if SSTB = 1)
Slave address 10011101b, 9DH (SA = 0) and 10011111b, 9FH (SA = 1)
STATUS BYTE FUNCTION D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
See Table 10 for explanation of bits STTC HLCK FIDT GLIM XXX WIPA ALTD CODE
1995 Oct 18 33

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
Table 10 Explanation of bits shown in Table 9
BIT DESCRIPTION
STTC Status bit for horizontal time constant: LOW = TV time constant; HIGH = VCR time constant.
HLCK Status bit for locked horizontal frequency: LOW = locked; HIGH = unlocked.
FIDT Identification bit for detected field frequency: LOW = 50 Hz; HIGH = 60 Hz.
GLIM Gain value for active luminance is limited (maximum or minimum), active HIGH.
XXX reserved
WIPA White peak loop is activated, active HIGH.
ALTD Status HIGH: line alternating colour burst has been detected (PAL or SECAM).
CODE Status HIGH: any colour signal has been detected.
2
16.3 I
The I2C-bus receiver slave address is 9CH/9EH.
DMSD-SQP slave receiver (SU 00H to 19H).
C-bus detail
16.3.1 S
UBADDRESS 00 (DATA BYTE 007 to 000)
Table 11 Increment delay IDEL
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
DELAY TIME
(STEP SIZE = 4/LLC)
CONTROL BITS
IDEL7 IDEL6 IDEL5 IDEL4 IDEL3 IDEL2 IDEL1 IDEL0
(1)
−1 −4 11111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−195 −780
00111101
max. value for 60 Hz
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−236 −944
00010100
max. value for 50 Hz
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−256 −1024
outside central counter
00000000
(2)
Notes
1. A sign bit, designated A08 and internally set to HIGH, indicates values are always negative.
2. The horizontal PLL does not operate in this condition. The system clock frequency is set to a value fixed by the last
update and is within ±7.1% of the nominal frequency.
1995 Oct 18 34

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.2 SUBADDRESS 01 (DATA BYTE 015 to 008)
Table 12 Horizontal synchronization begin 50 Hz (HSYB)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
+191 −382 10111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−64 +128 11000000
16.3.3 S
Table 13 Horizontal synchronization stop 50 Hz (HSYS)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
16.3.4 S
Table 14 Horizontal clamping begin 50 Hz (HCLB)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
UBADDRESS 02 (DATA BYTE 023 to 016)
+191 −382 10111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−64 +128 11000000
UBADDRESS 03 (DATA BYTE 031 to 024)
+127 −254 01111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−128 +256 10000000
DELAY TIME
(STEP SIZE = 2/LLC)
DELAY TIME
(STEP SIZE = 2/LLC)
DELAY TIME
(STEP SIZE = 2/LLC)
HSYB7 HSYB6 HSYB5 HSYB4 HSYB3 HSYB2 HSYB1 HSYB0
HSYS7 HSYS6 HSYS5 HSYS4 HSYS3 HSYS2 HSYS1 HSYS0
HCLB7 HCLB6 HCLB5 HCLB4 HCLB3 HCLB2 HCLB1 HCLB0
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
16.3.5 S
Table 15 Horizontal clamping stop 50 Hz (HCLS)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
1995 Oct 18 35
UBADDRESS 04 (DATA BYTE 039 to 032)
DELAY TIME
(STEP SIZE = 2/LLC)
+127 −254 01111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−128 +256 10000000
HCLS7 HCLS6 HCLS5 HCLS4 HCLS3 HCLS2 HCLS1 HCLS0
CONTROL BITS

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.6 SUBADDRESS 05 (DATA BYTE 047 to 040)
Table 16 Horizontal synchronization start after PHI1 50 Hz (HPHI)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
+127 forbidden;
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
+118 01110110
+117 −32 µs
−118 +31.7 µs
−119 forbidden;
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−128 10000000
DELAY TIME
(STEP SIZE = 8/LLC)
outside available central
counter range
(max. negative value)
(max. positive value)
outside available central
counter range
HPHI7 HPHI6 HPHI5 HPHI4 HPHI3 HPHI2 HPHI1 HPHI0
01111111
01110101
10001010
10001001
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 36

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.7 SUBADDRESS 06 (DATA BYTE 055 to 048)
Table 17 Luminance control
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Aperture factor (APER); data bits D1 and D0
0 0 APER1 = 0; APER0 = 0
1 0.25 APER1 = 0; APER0 = 1
2 0.5 APER1 = 1; APER0 = 0
3 1.0 APER1 = 1; APER0 = 1
Corner correction (CORI) ±LSBs in 8-bit; data bits D3 and D2
0 0 (OFF) CORI1 = 0; CORI0 = 0
1 1 CORI1 = 0; CORI0 = 1
2 2 CORI1 = 1; CORI0 = 0
3 3 CORI1 = 1; CORI0 = 1
Aperture bandpass; centre frequency (BPSS); data bits D4 and D5
4.6 MHz (50 Hz) 3.8 MHz (60 Hz) BPSS1 = 0; BPSS0 = 0
4.3 MHz (50 Hz) 3.4 MHz (60 Hz) BPSS1 = 0; BPSS0 = 1
3.0 MHz (50 Hz) 2.5 MHz (60 Hz) BPSS1 = 1; BPSS0 = 0
3.2 MHz (50 Hz) 2.7 MHz (60 Hz) BPSS1 = 1; BPSS0 = 1
Prefilter active (PREF); data bit D6
Bypassed PREF = 0
Active PREF = 1
Chrominance trap bypass (BYPS); data bit D7
Active CVBS mode BYPS = 0
Bypassed S-Video mode BYPS = 1
16.3.8 S
Table 18 Hue phase control HUEC
HUE PHASE (DEGREES)
UBADDRESS 07 (DATA BYTE 063 to 056)
HUEC7 HUEC6 HUEC5 HUEC4 HUEC3 HUEC2 HUEC1 HUEC0
+178.6 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
0 00000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−180 10000000
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 37

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.9 SUBADDRESS 08 CONTROL NUMBER 1(DATA BYTE 071 to 064)
Table 19 Colour killer threshold QUAM (PAL/NTSC)
THRESHOLD
(reference is nominal burst amplitude=0dB)
−30 dB 1 1 1 1 1
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓
−24 dB 1 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓
−18 dB 0 0 0 0 0
16.3.10 S
UBADDRESS 09 CONTROL NUMBER 2(DATA BYTE 079 to 072)
Table 20 Colour killer threshold SECAM
THRESHOLD
(reference is nominal burst amplitude=0dB)
−30 dB 1 1 1 1 1
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓
−24 dB 1 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓
−18 dB 0 0 0 0 0
16.3.11 S
UBADDRESS 0A (DATA BYTE 087 to 080)
CONTROL BITS
CKTQ4 CKTQ3 CKTQ2 CKTQ1 CKTQ0
CONTROL BITS
CKTS4 CKTS3 CKTS2 CKTS1 CKTS0
Table 21 PAL switch sensitivity
SENSITIVITY
PLSE7 PLSE6 PLSE5 PLSE4 PLSE3 PLSE2 PLSE1 PLSE0
Low 11111111
Medium 1 0 000000
High
(1)
00000000
Note
1. Sensitivity HIGH means immediate sequence correction.
16.3.12 S
UBADDRESS 0B (DATA BYTE 095 to 088)
Table 22 SECAM switch sensitivity
SENSITIVITY
SESE7 SESE6 SESE5 SESE4 SESE3 SESE2 SESE1 SESE0
Low 11111111
Medium 1 0 000000
High
(1)
00000000
Note
1. Sensitivity HIGH means immediate sequence correction.
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 38

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.13 SUBADDRESS 0C (DATA BYTE 103 to 096)
Table 23 Gain control chrominance
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
AGC loop filter (LFIS); data bits D6 and D5
Slow time constant LFIS1 = 0; LFIS0 = 0
Medium time constant LFIS1 = 0; LFIS0 = 1
Fast time constant LFIS1 = 1; LFIS0 = 0
Actual chrominance gain frozen LFIS1 = 1; LFIS0 = 1
Colour on (COLO); data bit D7
Automatic colour killer COLO = 0
Colour forced on COLO = 1
16.3.14 S
Table 24 Standard/mode control
SECAM mode bit (SECS); data bit D0
Status byte select (SSTB); data bit D1
HREF position select (HRMV); data bit D2
Real time outputs mode select (RTSE); data bit D3
HL switched to output pin 39 VL switched to output pin 40 RTSE = 1
TV/VCR mode select (VTRC); data bit D7
UBADDRESS 0D (DATA BYTE 111 to 104)
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Other standards SECS =0
SECAM mode SECS = 1
Status byte = 0 (see transmitter) SSTB 0
Status byte = 1 (see transmitter) SSTB = 1
HREF position as SAA7191 (8 LLC2 later) HRMV = 0
HREF normal position HRMV = 1
PLIN switched to output pin 39
ODD switched to output pin 40
TV mode VTRC = 0
VTR mode VTRC = 1
RTSE = 0
1995 Oct 18 39

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.15 SUBADDRESS 0E (DATA BYTE 119 to 112)
Table 25 I/O and clock control
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
General purpose switch (GPSW); data bit D0
Switches directly pin 64 GPSW (application dependent);
VBLKA = 0
Select chrominance input (CHRS); data bit D2
Controlled by BYPS (subaddress 06) normal position CHRS = 0
Digital chrominance input switched to
second input channel (see Fig.20)
Output enable YUV-data (OEYC); data bit D3
YUV bus high impedance/input OEYC = 0
Output YUV-bus active OEYC = 1
GPSW = 0
GPSW = 1
CHRS = 1
Output enable horizontal/vertical synchronization (OEHV); data bit D4
HS, HREF and VS high impedance/inputs OEHV = 0
Output HS, HREF and VS active OEHV = 1
Horizontal PLL clock (HPLL); data bit D7
PLL closed HPLL = 0
PLL open, horizontal frequency fixed HPLL = 1
16.3.16 S
Table 26 Control number 1
Luminance delay compensation; steps in 2/LLC (YDEL); data bits D2, D1 and D0
Enable or disable of sync and clamp pulses; HSY and HCL (SCEN); data bit D4
SECAM cross colour reduction (SXCR); data bit D5
UBADDRESS 0F (DATA BYTE 127 to 120)
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
0 steps YDEL2 = 0; YDEL1 = 0; YDEL0 = 0
3 steps YDEL2 = 0; YDEL1 = 1; YDEL0 = 1
−4 steps YDEL2= 1; YDEL1 = 0 YDEL1 = 0
Disable sync and clamp (set to HIGH) SCEN = 0
Enable sync and clamp SCEN = 1
Reduction off SXCR = 0
Reduction on SXCR = 1
Field selection (FSEL); data bit D6
Automatic field detection(AUFD); data bit D7
Field state directly controlled via FSEL AUFD = 0
Automatic field detection AUFD = 1
1995 Oct 18 40
50 Hz, 625 lines FSEL = 0
60 Hz, 525 lines FSEL = 1

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.17 SUBADDRESS 10 (DATA BYTE 135 to 128)
Table 27 Control number 2
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Vertical noise reduction (VNOI); data bits D1 and D0
Normal mode VNOI1 = 0; VNOI0 = 0
Search mode VNOI1 = 0; VNOI0 = 1
Free running mode VNOI1= 1; VNOI0 = 0
Vertical noise reduction bypassed VNOI1 = 1; VNOI0 = 1
HREF select HRFS (HRFS); data bit D2
HREF matched to YUV output HRFS = 0
HREF matched to CVBS input HRFS= 1
16.3.18 S
Table 28 Chrominance gain reference value
16.3.19 S
Table 29 Chrominance saturation control
−1 inverse chrominance 1 1 000000
−2 inverse chrominance 1 0 000000
UBADDRESS 11 (DATA BYTE 143 to 136)
CONTROL BITS
REFERENCE VALUE
CHCV7 CHCV6 CHCV5 CHCV4 CHCV3 CHCV2 CHCV1 CHCV0
Maximum 1 1 111111
CCIR-level for PAL 0 1 011001
CCIR-level for NTSC 0 0 101100
Minimum 0 0 000000
UBADDRESS 12 (DATA BYTE 150 to 144)
CONTROL BITS
GAIN
SATN7 SATN6 SATN5 SATN4 SATN3 SATN2 SATN1 SATN0
1.999 Maximum 0 1 111111
1 CCIR-level 0 1 000000
0 colour off 0 0 000000
1995 Oct 18 41

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.20 SUBADDRESS 13 (DATA BYTE 158 to 152)
Table 30 Luminance contrast control
GAIN
1.999 Maximum 0 1 111111
70 CCIR-level 0 1 000110
1 01000000
0 luminance off 0 0 000000
−1 inverse luminance 1 1 000000
−2 inverse luminance 1 0 000000
16.3.21 S
Table 31 Horizontal synchronization begin 60 Hz (HS6B)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
16.3.22 S
Table 32 Horizontal synchronization stop 60 Hz (HS6S)
UBADDRESS 14 (DATA BYTE 167 to 160)
DELAY TIME
(step size = 2/LLC)
+191 −382 10111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−64 +128 11000000
UBADDRESS 15 (DATA BYTE 175 to 168)
CONT7 CONT6 CONT5 CONT4 CONT3 CONT2 CONT1 CONT0
HS6B7 HS6B6 HS6B5 HS6B4 HS6B3 HS6B2 HS6B1 HS6B0
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
+191 −382 10111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−64 +128 11000000
16.3.23 S
Table 33 Horizontal clamping begin 60 Hz (HC6B)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
UBADDRESS 16 (DATA BYTE 183 to 176)
+127 −254 01111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−128 +256 10000000
DELAY TIME
(step size = 2/LLC)
DELAY TIME
(step size = 2/LLC)
HS6S7 HS6S6 HS6S5 HS6S4 HS6S3 HS6S2 HS6S1 HS6S0
HC6B7 HC6B6 HC6B5 HC6B4 HC6B3 HC6B2 HC6B1 HC6B0
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 42

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.3.24 SUBADDRESS 17 (DATA BYTE 191 to 184)
Table 34 Horizontal clamping stop 60 Hz (HC6S)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
+127 −254 01111111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−128 +256 10000000
16.3.25 S
Table 35 Horizontal synchronization start after PHI1 60 Hz (HP6I)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
UBADDRESS 18 (DATA BYTE 199 to 192)
+127 forbidden;
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
+98 01100010
+97 −32 µs
−97 +31.7 µs
−98 forbidden;
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
−128 10000000
DELAY TIME
(step size = 2/LLC)
DELAY TIME
(step size = 8/LLC)
outside available central
counter range
(max. negative value)
(max. positive value)
outside available central
counter range
HC6S7 HC6S6 HC6S5 HC6S4 HC6S3 HC6S2 HC6S1 HC6S0
HP6I7 HP6I6 HP6I5 HP6I4 HP6I3 HP6I2 HP6I1 HP6I0
01111111
01100001
10011111
10011110
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
16.3.26 S
Table 36 Luminance brightness control
1995 Oct 18 43
UBADDRESS 19 (DATA BYTE 207 to 200)
OFFSET
BRIG7 BRIG6 BRIG5 BRIG4 BRIG3 BRIG2 BRIG1 BRIG0
255 (bright) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
139 (CCIR-level) 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1
128 10000000
0 (dark) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CONTROL BITS

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4 I2C-bus detail (continued)
DUAD slave receiver (SU 20H to 32H).
16.4.1 S
Table 37 Analog control #1
Analog input select 2 (AINS2); data bit D0
Analog input select 3 (AINS3); data bit D1
Analog input select 4 (AINS4); data bit D2
Analog function select (FUSE); data bits D4 and D3
Analog input disable 2 (AIND2); data bit D5
UBADDRESS 20 (DATA BYTE 007 to 000)
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Analog input AI22 selected AINS2 = 0
Analog input AI21 selected AINS2 = 1
Analog input AI32 selected AINS3 = 0
Analog input AI31 selected AINS3 = 1
Analog input AI42 selected AINS4 = 0
Analog input AI41 selected AIND4 = 1
Amplifier plus anti-alias filter bypassed
Amplifier active FUSE1 = 1; FUSE0 = 0
Amplifier plus anti-alias filter active FUSE1 = 1; FUSE0 = 1
Analog inputs 2 enabled AIND2 = 0
Analog inputs 2 disabled AIND2 = 1
FUSE1 = 0; FUSE0 = 0
FUSE1 = 0; FUSE0 = 1
Analog input disable 3 (AIND3); data bit D6
Analog inputs 3 enabled AIND3 = 0
Analog inputs 3 disabled AIND3 = 1
Analog input disable 4 (AIND4); data bit D7
Analog inputs 4 enabled AIND4 = 0
Analog inputs 4 disabled AIND4 = 1
1995 Oct 18 44

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.2 SUBADDRESS 21 (DATA BYTE 015 to 008)
Table 38 Analog control #2
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Reference select channel 2 (REFS2); data bit D0
Automatic clamping active REFS2 = 0
Reference level selected REFS2 = 1
Reference select channel 3 (REFS3); data bit D1
Automatic clamping active REFS3 = 0
Reference level selected REFS3 = 1
Reference select channel 4 (REFS4); data bit D2
Automatic clamping active REFS4 = 0
Reference level selected REFS4 = 1
MUXC select channel 24 (MS24); data bit D3
Analog MUX2 controlled by MX24 MS24 = 0
Analog MUX2 controlled by MUXC MS24 = 1
Analog MUX2 control (MX24); data bits D5 and D4
Adder mode MX241 = 0; MX240 = 0
Channel 2 on; channel 4 off MX241 = 0; MX240 = 1
Channel 2 off; channel 4 on MX241 = 1; MX240 = 0
Both channels off MX241 = 1; MX240 = 1
MUXC select channel 34 (MS34); data bit D6
Analog MUX3 controlled by MX34 MS34 = 0
Analog MUX3 controlled by MUXC MS34 = 1
Vertical blanking control off (VBCO); data bit D7
Vertical blanking on VBCO = 0
Vertical blanking off VBCO = 1
1995 Oct 18 45

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.3 SUBADDRESS 22 (DATA BYTE 023 to 016)
Table 39 Mixer control #1
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Analog MUX3 control (MX34); data bits D1 and D0
Adder mode MX341 = 0; MX340 = 0
Channel 3 on; channel 4 off MX341 = 0; MX340 = 1
Channel 3 off; channel 4 on MX341 = 1; MX340 = 0
Both channels off MX341 = 1; MX340 = 1
Clamping function test (CLTS); data bit D2
Normal clamping mode CLTS = 0
CLAAn and CLAUn adjusted via CLL32 value for testing
(do not use)
Fast digital multiplexing channel 2/3 active (MUYC); data bit D3
Normal mode on CHR channel MUYC = 0
Multiplex mode on CHR channel for test purposes only
(do not use)
CLTS = 1
MUYC = 1
Luminance select (YSEL); data bit D4
ADC 2 to CVBS YSEL = 0
ADC 3 to CVBS YSEL = 1
Chrominance select (CSEL); data bit D5
ADC 3 to CHR (MUXC not inverse; MUYC = 1) CSEL = 0
ADC 2 to CHR (MUXC inverse; MUYC = 1) CSEL = 1
Automatic gain control (GACO); data bits D7 and D6
Automatic gain control off GACO1 = 0; GACO0 = 0
Automatic gain control channel 2 GACO1 = 0; GACO0 = 1
Automatic gain control channel 3 GACO1 = 1; GACO0 = 0
Automatic gain control channel 4 GACO1 = 1; GACO0 = 1
16.4.4 S
Table 40 Clamping level control 21 CLL21
DECIMAL CLAMP LEVEL
UBADDRESS 23 (DATA BYTE 031 to 024)
CONTROL BITS
CLL217 CLL216 CLL215 CLL214 CLL213 CLL212 CLL211 CLL210
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
64 01000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
128 10000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
254 11111110
1995 Oct 18 46

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.5 SUBADDRESS 24 (DATA BYTE 039 to 032)
Table 41 Clamping level control 22 CLL22
DECIMAL CLAMP LEVEL
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
64 01000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
128 10000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
254 11111110
16.4.6 S
Table 42 Clamping level control 31 CLL31
DECIMAL CLAMP LEVEL
UBADDRESS 25 (DATA BYTE 047 to 040)
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
64 01000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
128 10000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
254 11111110
CLL227 CLL226 CLL225 CLL224 CLL223 CLL222 CLL221 CLL220
CLL317 CLL316 CLL315 CLL314 CLL313 CLL312 CLL311 CLL310
CONTROL BITS
CONTROL BITS
16.4.7 S
Table 43 Clamping level control 32 CLL32
DECIMAL CLAMP LEVEL
1995 Oct 18 47
UBADDRESS 26 (DATA BYTE 055 to 048)
CLL327 CLL326 CLL325 CLL324 CLL323 CLL322 CLL321 CLL320
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
64 01000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
128 10000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
254 11111110
CONTROL BITS

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.8 SUBADDRESS 27 (DATA BYTE 063 to 056); GAIN CONTROL ANALOG #1
Table 44 Static gain control channel 2 (GAI2); data bits D5 to D0
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
0 −2.82 dB 0 0 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
15 0dB 001111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
31 3dB 011111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
47 6dB 101111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
63 9dB 111111
Table 45 Gain mode select (GASL); data bit D6
Difference value integration 0
Table 46 Automatic control integration (HOLD); data bit D7
AGC integration hold (freeze) 1
(step size = 0.19 dB)
FUNCTION CONTROL BIT GASL
Fix value integration 1
FUNCTION CONTROL BIT HOLD
AGC active 0
GAIN
GAI25 GAI24 GAI23 GAI22 GAI21 GAI20
CONTROL BITS
16.4.9 S
Table 47 White peak control WIPE
DECIMAL WHITE PEAK LEVEL
16.4.10 SUBADDRESS 29 (DATA BYTE 079 to 072)
Table 48 Sync bottom control SBOT
DECIMAL SYNC BOTTOM LEVEL
1995 Oct 18 48
UBADDRESS 28 (DATA BYTE 071 to 064)
CONTROL BITS
WIPE7 WIPE6 WIPE5 WIPE4 WIPE3 WIPE2 WIPE1 WIPE0
128 10000000
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
254 11111110
255 (white peak control off) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
CONTROL BITS
SBOT7 SBOT6 SBOT5 SBOT4 SBOT3 SBOT2 SBOT1 SBOT0
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
254 11111110

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.11 SUBADDRESS 2A (DATA BYTE 087 to 080); GAIN CONTROL ANALOG #2
Table 49 Static gain control channel 3 (GAI3); data bits D5 to D0
DECIMAL MUL TIPLIER
0 −2.82 dB 0 0 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
15 0dB 001111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
31 3dB 011111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
47 6dB 101111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
63 9dB 111111
Table 50 Integration factor white peak (IWIP); data bits D7 and D6
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Fast selection IWIP1 = 0; IWIP0 = 0
Slow selection IWIP1 = 1; IWIP0 = 1
16.4.12 SUBADDRESS 2B (DATA BYTE 095 to 088); GAIN CONTROL ANALOG #3
(step size = 0.19 dB)
| IWIP1 = 0; IWIP0 = 1
| IWIP1 = 1; IWIP0 = 0
GAIN
GAI35 GAI34 GAI33 GAI32 GAI31 GAI30
CONTROL BITS
Table 51 Static gain control channel 4 (GAI4); data bits D5 to D0
DECIMAL MUL TIPLIER
0 −2.82 dB 0 0 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
15 0dB 001111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
31 3dB 011111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
47 6dB 101111
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
63 9dB 111111
Table 52 Integration factor normal gain (IGAI); data bits D7 and D6
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Slow selection IGAI1 = 0; IGAI0 = 0
Fast selection IGAI1 = 1; IGAI0 = 1
(step size = 0.19 dB)
| IGAI1 = 0; IGAI0 = 1
| IGAI1 = 1; IGAI0 = 0
GAIN
GAI45 GAI44 GAI43 GAI42 GAI41 GAI40
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 49

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.13 SUBADDRESS 2C (DATA BYTE 103 to 096)
Table 53 Mixer control #2
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Two’s complement channel 2 (TWO2); data bit D0
Unipolar TWO2 = 0
Two’s complement (normal mode) TWO2 = 1
Two’s complement channel 3 (TWO3); data bit D1
Unipolar TWO3 = 0
Two’s complement (normal mode) TWO3 = 1
Clamping level select channel 2 (CLS2); data bit D4
CLL21 active CLS2 = 0
CLL22 active CLS2 = 1
Clamping level select channel 3 (CLS3); data bit D5
CLL31 active CLS3 = 0
CLL32 active CLS3 = 1
Clamping level select channel 4 (CLS4); data bit D7
CLL2n active CLS4 = 0
CLL3n active CLS4 = 1
16.4.14 S
UBADDRESS 2D (DATA BYTE 111 to 104)
Table 54 Integration value gain (IVAL)
CONTROL BITS
DECIMAL INTEGRATION VALUE GAIN
IVAL7 IVAL6 IVAL5 IVAL4 IVAL3 IVAL2 IVAL1 IVAL0
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
255 11111111
16.4.15 S
UBADDRESS 2E (DATA BYTE 119 to 112)
Table 55 Blanking pulse VBLK-set (VBPS)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
SET LINE NUMBER
(step size = 2)
VBPS7 VBPS6 VBPS5 VBPS4 VBPS3 VBPS2 VBPS1 VBPS0
CONTROL BITS
0 0 after rising edge of VS 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
131
(1)
262 after rising edge of VS 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
156
(2)
312 after rising edge of VS 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
Notes
1. Maximum for 60 Hz.
2. Maximum for 50 Hz.
1995 Oct 18 50

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.16 SUBADDRESS 2F (DATA BYTE 127 to 120)
Table 56 Blanking pulse VBLK-reset (VBPR)
DECIMAL
MULTIPLIER
RESET LINE NUMBER
(step size = 2)
VBPR7 VBPR6 VBPR5 VBPR4 VBPR3 VBPR2 VBPR1 VBPR0
CONTROL BITS
0 0 after rising edge of VS 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
131
(1)
262 after rising edge of VS 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
156
(2)
312 after rising edge of VS 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
Notes
1. Maximum for 60 Hz.
2. Maximum for 50 Hz.
16.4.17 S
UBADDRESS 30 (DATA BYTE 135 to 128)
Table 57 ADCs gain control
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Fix gain ADC channel 2 (GAD2); data bits D1 and D0
0 dB GAD21 = 0; GAD20 = 0
0.05 dB GAD21 = 0; GAD20 = 1
0.10 dB GAD21 = 1; GAD20 = 0
0.15 dB GAD21 = 1; GAD20 = 1
Gain ADC select channel 2 (GAS2); data bit D2
2
Fix gain via I
C-bus GAD2 GAS2 = 0
Automatic gain via loop GAS2 = 1
Fix gain ADC channel 3 (GAD3); data bits D4 and D3
0 dB GAD31 = 0; GAD30 = 0
0.05 dB GAD31 = 0; GAD30 = 1
0.10 dB GAD31 = 1; GAD30 = 0
0.15 dB GAD31 = 1; GAD30 = 1
Gain ADC select channel 3 (GAS3); data bit D5
2
Fix gain via I
C-bus GAD3 GAS3 = 0
Automatic gain via loop GAS3 = 1
White peak mode select (WISL); data bit D6
Difference value integration WISL = 0
Fix value integration WISL = 1
1995 Oct 18 51

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.18 SUBADDRESS 31 (DATA BYTE 143 to 136)
Table 58 Mixer control #3
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Pulses I/O control (PULIO); data bit D0
HCL and HSY to input pins PULIO = 0
HCL and HSY to output pins PULIO = 1
Pin function switch (VBLKA); data bit D1
GPSW active (normal) VBLKA = 0
VBLK test output active VBLKA = 1
DMSD-SQP bypassed (SQPB); data bit D3
DMSD data to YUV output SQPB = 0
A/D data to YUV output
for test purposes only (do not use)
SQPB = 1
White peak slow up integration enable (WRSE); data bit D4
Hold in white peak mode WRSE = 0
Slow up integration with 1 value in H or
V (dependent on WIRS)
White peak slow up integration select (WIRS); data bit D5
Slow up integration with 1 value per line WRIS = 0
Slow up integration with 1 value per field WRIS = 1
Analog test select (AOSL); data bits D7 and D6
AOUT connected to ground AOSL1= 0; AOSL0 = 0
AOUT connected to input AD2 AOSL1 = 0; AOSL0 = 0
AOUT connected to input AD3 AOSL1 = 1; AOSL0 = 1
AOUT connected to channel 4 AOSL1 = 1; AOSL0 = 1
16.4.19 S
Table 59 Integration value white peak (WVAL)
UBADDRESS 32 (DATA BYTE 151 to 144)
DECIMAL INTEGRATION VALUE
WHITE PEAK
1 00000001
↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
127 (max.) 01111111
WVAL7 WVAL6 WVAL5 WVAL4 WVAL3 WVAL2 WVAL1 WVAL0
WRSE = 1
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 52

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
16.4.20 SUBADDRESS 33 (DATA BYTE 159 to 152)
Table 60 Mixer control #4
FUNCTION CONTROL BITS
Clock select AD2 (CAD2); data bit D2
LLC for test purposes only (do not use) CAD2 = 0
LLC/2 CAD2 = 1
Clock select AD3 (CAD3); data bit D3
LLC for test purposes only (do not use) CAD3 = 0
LLC/2 CAD3 = 1
Change sign bit UV data (CHSB); data bit D5
UV output unipolar CHSB = 0
UV output two’s complement CHSB = 1
Output format select (OFTS); data bit D7
4 : 1 : 1 format OFTS = 0
4 : 2 : 2 format OFTS = 1
16.4.21 S
Table 61 Gain update level (GUDL; data bits D5 to D0
DECIMAL
Table 62 MUXC phase delay (MUD2); data bits D7 and D6
UBADDRESS 34 (DATA BYTE 167 to 160)
HYSTERESIS
FOR 8-BIT GAIN
0 0LSB >0 000000
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
7 ±7LSB >7 000111
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓↓↓↓↓
>31 off always 1 XXXXX
FUNCTION CONTROL BIT MUD
No phase delay MUD2 = 0; MUD1 = 0
1 LLC cycle phase delay for CLAA path MUD2 = 0; MUD1 = 1
2 LLC cycle phase delay for CLAA path MUD2 = 1; MUD1 = 0
3 LLC cycle phase delay for CLAA path MUD2 = 1; MUD1 = 1
NEW GAIN - OLD GAIN
UPDATE
GUDL5 GUDL4 GUDL3 GUDL2 GUDL1 GUDL0
CONTROL BITS
1995 Oct 18 53

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
17 SOURCE SELECTION MANAGEMENT
AIND4
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AINS4
AINS3
REFS4
AIND3
REFS3
GAIN4 AAF4
CLAMP
GAIN3 AAF3
CLAMP
CLS4
clamp up/down
MX340
MX341
ADC3
CLAMP
CON3
CLS3
CLL32
CLL31
CHRS v BYPS
CHROMA
CSEL
AI21
AI22
AINS2
AIND2
REFS2
REF128
GAIN2 AAF2
CLAMP
MX240
ADC2
MX241
clamp up/down
GAI4
GAI3
GAI2
GACO
CLAMP
CON2
GAIN
CON
YSEL
CLS2
All switch control bits set to LOW.
Fig.20 Source selection overview.
ll pagewidth
Table 63 Source selection management examples
EXAMPLE 1 EXAMPLE 2 EXAMPLE 3 EXAMPLE 4
INPUT
SIGNAL MODE SIGNAL MODE SIGNAL MODE SIGNAL MODE
AIN21 CVBS1 0 CVBS1 0 Y1 6 Y1 6
AIN22 CVBS2 1 C2 7 C2 7 CVBS2 1
AIN31 CVBS3 2 Y2 7 Y2 7 CVBS3 2
AIN32 CVBS4 3 C3 8 C3 8 CVBS4 3
AIN41 CVBS5 4 Y3 8 Y3 8 CVBS5 4
AIN42 CVBS6 5 CVBS6 5 C1 6 C1 6
LUMA
CLL22
CLL21
MGC839
handbook, full pagewidth
1995 Oct 18 54
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.21 Mode 0; CVBS1.
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC840

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.22 Mode 1; CVBS2.
AD3
AD2
Fig.23 Mode 2; CVBS3.
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC841
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC842
handbook, full pagewidth
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.24 Mode 3; CVBS4.
handbook, full pagewidth
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.25 Mode 4; CVBS5.
1995 Oct 18 55
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC843
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC844

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.26 Mode 5; CVBS6.
AD3
AD2
Fig.27 Mode 6; Y1 + C1.
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC845
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC846
handbook, full pagewidth
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.28 Mode 7; Y2 + C2.
handbook, full pagewidth
AI41
AI42
AI31
AI32
AI21
AI22
AD3
AD2
Fig.29 Mode 8; Y3 + C3.
1995 Oct 18 56
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC847
CHROMA
LUMA
MGC848

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
Table 64 I2C-bus control
CONTROL
Subaddress 20
Subaddress 21
(1)
INPUT
AIND4 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 −
AIND3 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 −
AIND2 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 −
FUSE1 1 −−−− − − −−−
FUSE0 1 −−−− − − −−−
AINS4 X X X X 1 0 0 X 1 −
AINS3 X X 1 0 X X 0 1 0 −
AINS2 1 0 X X X X 1 0 X −
VBCO 0 −−−−−−−−−
MS34 0 −−−−−−−−−
MX241 0 0 X X X X 0 0 1 −
MX240 0 0 X X X X 0 0 1 −
MS24 0 −−−−−−−−−
REFS4 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 −
REFS3 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 −
REFS2 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 −
012345 6789
MODE
Subaddress 22
GACO1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 −
GACO0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 −
CSEL X X X X X X 0 1 0 −
YSEL 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 −
MUYC 0 −−−− − −−−0
CLTS 0 −−−− −−− −0
MX341 X X 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 −
MX340 X X 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 −
Subaddress 2C
CLS4 X X X X 1 1 1 X 0 −
GABL 0 −−−−−−−−−
CLS3 X X 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 −
CLS2 0 0 X X X X 0 1 X −
4LSB 0011 −−−− − −−−0011
BYPS 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 −
Subaddresses SU
20H D9H D8H BAH B8H 7CH 78H 59H 9AH 3CH −
21H 16H 16H 05H 05H 03H 03H 12H 14H 21H −
1995 Oct 18 57

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
CONTROL
(1)
INPUT
012345 6789
MODE
22H 40H 40H 91H 91H D2H D2H 42H B1H C1H −
2CH 03H 03H 03H 03H 83H 83H A3H 13H 23H −
06H 0XXXXXXX 1XXXXXXX −
30H
(2)
44H 44H 60H 60H 60H 60H 44H 60H 44H −
Notes
1. CLL21 = 65d, CLL22 = 128d, CLL31 = 65d, CLL32 = 128d, GAI4 = 15d, GAI3 = 15dGAI2 = 15d; X set 0.
2. Optional: values for AD gain (+2 LSB’s gain resolution) active [not active: for all modes 40H].
18 ANTI-ALIAS FILTER GRAPHS
+3
handbook, full pagewidth
A
(dB)
−3
−9
−15
(1)
MGC849
−21
−27
−33
−39
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
(1) 50 Hz.
(2) 60 Hz.
(2)
Fig.30 Anti-alias filter graph for SAA7110A.
f (MHz)
1995 Oct 18 58

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
+3
handbook, full pagewidth
A
(dB)
−3
−9
−15
−21
−27
−33
−39
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
(1) 50 HZ, AFCCS = 0, LLC = 29.50 MHz.
(2) 50 HZ, AFCCS = 1, LLC = 29.50 MHz.
(3) 60 HZ, AFCCS = 0, LLC = 24.54 MHz.
(3) 60 HZ, AFCCS = 1, LLC = 24.54 MHz.
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1)
Fig.31 Anti-alias filter graph for SAA7110.
MGC850
f (MHz)
19 CORING FUNCTION
19.1 Coring function adjustment by subaddress 06H
to affect band filter output adjustment
The thresholds are related to the 13-bit word width in the
luminance processing part and influence the 1 to 3 LSB
(Yo to Y2) with respect to the 8-bit luminance output.
Table 65 CORI control settings a, b and c of Fig.32
CONTROL BITS
CORI1 CORI0
a0 1
b1 0
c1 1
+64
handbook, halfpage
+32
0
−32
−64
−64 −32 0 +64
MGC851
c
b
a
a
b
c
+32
Fig.32 Coring function.
1995 Oct 18 59

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
20 LUMINANCE FILTER GRAPHS
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
Fig.33 Luminance control: SU06H, 50 Hz/CVBS mode, prefilter on and coring off (40 to 63H).
63H
73H
53H
43H
40H
43H
53H
73H
63H
40H
f
Y (MHz)
MGC852
8
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
Fig.34 Luminance control: SU06H, 50 Hz/CVBS mode, prefilter on and coring off (40 to 43H).
43H
42H
41H
40H
43H
42H
41H
40H
f
Y (MHz)
MGC853
8
1995 Oct 18 60

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
23H
33H
13H
03H
00H
03H
13H
33H
23H
00H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.35 Luminance control: SU06H, 50 Hz/CVBS mode, prefilter off and coring off.
MGC854
8
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
83H
82H
81H
80H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.36 Luminance control: SU06H, 50 Hz/Y + C mode, prefilter off and coring off.
MGC855
8
1995 Oct 18 61

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
C3H
C2H
C1H
C0H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.37 Luminance control: SU06H, 50 Hz/Y + C mode, prefilter on and coring off.
MGC856
8
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
63H
73H
53H
43H
40H
43H
53H
73H
63H
40H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.38 Luminance control: SU06H, 60 Hz/CVBS mode, prefilter on and coring off.
MGC857
1995 Oct 18 62

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
43H
42H
41H
40H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.39 Luminance control: SU06H, 60 Hz/CVBS mode, prefilter on and coring off.
43H
42H
41H
40H
MGC858
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
23H
33H
13H
03H
00H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.40 Luminance control: SU06H, 60 Hz/CVBS mode, prefilter off and coring off.
03H
13H
33H
23H
00H
MGC859
1995 Oct 18 63

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
83H
82H
81H
80H
f
Y (MHz)
Fig.41 Luminance control: SU06H, 60 Hz/Y + C mode, prefilter off and coring off.
MGC860
8
18
handbook, full pagewidth
VY
(dB)
6
−6
−18
−30
0246
C3H
C2H
C1H
C0H
fY (MHz)
Fig.42 Luminance control: SU06H, 60 Hz/Y + C mode, prefilter on and coring off.
MGC861
8
1995 Oct 18 64

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
21 I2C-BUS START SET-UP
The values shown in Table 66 are optimized for the EBU colour bar (100% white and 75% chrominance amplitude)
signal. The decoder output signal level fulfils the CCIR 601 specification. The input of 100% colour bar level is possible,
but the signal (white) peak function reduces the digital luminance output. With a different set-up it is possible to proceed
100% colour bar signal without luminance colour bar reduction. The method is to modify the AD input range for this input
level by reducing the gain reference value (SBOT > 06h) and adjusting the digital Y output level with contrast and
brightness control.
2
Table 66 I
C-bus start set-up
SU NAME FUNCTION
00 IDEL7 to IDEL0 increment delay 01001100 4C
01 HSYB7 to HSYB0 horizontal sync (HSY) begin 50 Hz 00111100 3C
02 HSYS7 to HSYS0 horizontal sync (HSY) stop 50 Hz 00001101 0D
03 HCLB7 to HCLB0 horizontal clamp (HCL) begin 50 Hz 11101111 EF
04 HCLS7 to HCLS0 horizontal clamp (HCL) stop 50 Hz 10111101 BD
05 HPHI7 to HPHI0 horizontal sync after PHI1 50 Hz 11110000 F0
BYPS, PREF,
BPSS1 to BPSS0,
06
CORI1 to CORI0,
APER1 to APER0
07 HUEC7 to HUEC0 hue control 00000000 00
08 CKTQ4 to CKTQ0, XXX colour killer threshold PAL 11111XXX F8
09 CKTS4 to CKTS0, XXX colour killer threshold SECAM 11111XXX F8
0A PLSE7 to PLSE0 PAL switch sensitivity 01100000 60
0B SESE7 to SESE0 SECAM switch sensitivity 01100000 5B
COLO, LFIS1 to LFIS0,
0C
XXXXX
VTRC, XXX, RTSE, HRMV,
0D
SSTB, SECS
HPLL, XX, OEHV, OEYC,
0E
CHRS, X, GPSW
AUFD, FSEL, SXCR, SCEN,
0F
X, YDEL2 to YDEL0
XXXXX, HRFS,
10
VNOI1 to VNOI0
CHCV7 to CHCV0 PAL
11
CHCV7 to CHCV0 NTSC 00101100 2C
12 SATN7 to SATN0 chrominance saturation 01000000 40
13 CONT7 to CONT0 luminance contrast 01000110 46
14 HS6B7 to HS6B70 horizontal sync (HSY) begin 60 Hz 01000010 42
15 HS6S7 to HS6S0 horizontal sync (HSY) stop 60 Hz 00011010 1A
16 HC6B7 to HC6B0 horizontal clamp (HCL) begin 60 Hz 11111111 FF
17 HC6S7 to HC6S0 horizontal clamp (HCL) stop 60 Hz 11011010 DA
18 HP6I7 to HP6I0 horizontal sync after PHI1 60 Hz 11110000 F0
19 BRIGI7 to BRIG0 luminance brightness 10001011 8B
luminance control 00000000 00
gain control chrominance
standard/mode control 0 X X X 0110 06
I/O and clock control 0 X X 1 1 0 X 0 18
control #1 1001X000 90
control #2
chrominance gain reference
76543210start
000XXXXX 00
XXXXX000 00
01011001 59
BINARY HEX
1995 Oct 18 65

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
SU NAME FUNCTION
1A-1F reserved
AIND4, AIND3, AIND2,
20
FUSE1 to FUSE0, AINS4,
AINS3, AINS2
VBCO, MS34,
21
MX241 to MX240, MS24,
REFS4, REFS3, REFS2
GACO1 to GACO0, CSEL,
22
YSEL, MUYC, CLTS,
MX341 to MX340
23 CLL217 to CLL210 clamping level control channel 21 01000001 41
24 CLL227 to CLL220 clamping level control channel 22 10000000 80
25 CLL317 to CLL310 clamping level control channel 31 01000001 41
26 CLL327 to CLL320 clamping level control channel 32 10000000 80
HOLD, GASL,
27
GAI25 to GAI20
28 WIPE7 to WIPE0 white peak control 11111110 FE
29 SBOT7 to SBOT0 sync bottom control 00000001 01
IWIP1 to IWIP0,
2A
GAI35 to GAI30
IGAI1 to IGAI0,
2B
GAI45 to GAI40
CLS4, X, CLS3, CLS2,
2C
TWO3, TWO2
2D IVAL7 to IVAL0 integration value gain 00000001 01
VBPS7 to VBPS0; 50 Hz
2E
VBPS7 to VBPS0; 60 Hz 10000001 81
VBPR7 to VBPR0; 50 Hz
2F
VBPR7 to VBPR0; 60 Hz 00000011
X, WISL, GAS3,
30
GAD31 to GAD30, GAS2,
GAD21 to GAD20
AOSL1 to AOSL0, WIRS,
31
WRSE, SQPB, X, VBLKA,
PULIO
32 WVAL7 to WVAL0 integration value white peak 00000010 02
OFTS, X, CHSB, X, CAD3,
33
CAD2, XX
MUD2, MUD1,
34
GUDL5 to GUDL0
analog control #1 11011001 D9
analog control #2 00010110 16
mixer control #1 01000000 40
gain control analog #1
gain control analog #2
gain control analog #3
mixer control #2 0 X 0 0 X X 1 1 03
vertical blanking pulse SET
vertical blanking pulse RESET
ADCs gain control X 1000000 44
mixer control #3 01110X*01 71
mixer control #4 1 X 0 X 1 1 X X 8C
gain update level
76543210start
01001111 4F
11001111 CF
00001111 0F
10011010 9A
00000011
00000011 03
BINARY HEX
03
21.1 Remarks to Table 66
Values recommended for a CVBS (PAL or NTSC) signal, input AI21 via A/D channel 2 (MODE 0), and 4 : 2 : 2 CCIR
output signal level; all X values must be set LOW, X* value is don’t care; HPHI and HP6I are application dependent.
1995 Oct 18 66

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
22 APPLICATION INFORMATION
V
handbook, full pagewidth
Q1(26.8 MHz)
V
DDA
AI42
AI41
AI32
AI31
AI22
AI21
V
DD
SCL
SDA
FEIN (MUXC)
10
L1
µH
C16
1 nF
DD
V
SSA
R6
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R7
C17
10 pF
Unused analog inputs should not be connected.
R8
1 kΩ
C6
10 nF
75 Ω
V
SSA
C5
10 nF
75 Ω
V
SSA
C24
10 nF
75 Ω
V
SSA
C3
10 nF
75 Ω
V
SSA
C2
10 nF
75 Ω
V
SSA
C1
10 nF
75 Ω
V
SSA
1 kΩ
V
XTALO
XTALI
C18
10 pF
CGCE
SS
V
SS
C10
100 nF
C9
100 nF
C8
100 nF
C7
100 nF
20
24
16 12
11
13
15
17
19
SAA7110
SAA7110A
21
33
6
5
63
65
66
67
51
43
25
22
14 10
18
V
SSA
28
35
V
SS
Fig.43 Application diagram.
68
52
421
SA AP SP
C15
V
DD1
100 nF
C14
V
DD2
100 nF
C13
V
DD3
100 nF
V
C12
DD4
100 nF
V
C11
DD5
100 nF
27
3444
7
8
i.c.
V
SS
i.c.
V
SS
MGC862
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y7 to Y0
Y3
Y2
Y1
Y0
UV7
UV6
UV5
UV4
UV7 to UV0
UV3
UV2
UV1
UV0
HREF
HS
VS
RTCO
AOUT
GPSW (VBLK)
PLIN (HL)
ODD (VL)
LLC
LLC2
CREF
RESET
LFCO
HCL
HSY
45
46
47
48
49
50
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
42
38
41
3
23
64
39
40
29
30
31
32
26
36
37
9
i.c.
1995 Oct 18 67

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
LLC2A
LLC2B
0.1
µF
C20
LLCB
MGC863
n.c.
ODD (VL)
RESET
CREF
LLC2
LLC
4030293132
LFCO
26
HCL
36
HSY
37
SA AP SP
V
SS
i.c. i.c. i.c.
RESET
CREF
SS
V
LFCO2 LFCO RESN CREF LLCA
10 2014
SSD
6, 9
13, 18
34
16
LFCOSEL
V
SSA
V
ORD
P
198,17 5 11 12 15 7
SAA7197
1
2
CE
MS
1 kΩ
63
CGCE
R7
1 kΩ
FEIN (MUXC)
SAA7110
SAA7110A
33
65
XTALO
XTALI
(26.8 MHZ)
Q1
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
51 43 35 28 4 2 1789
SS
V
SS(S)
V
SSA4
V
SSA3
V
14 2210 67
SSA2
V
1825
SSA0
V
66
C16 C17 C18
10 µH
L1
10 pF 10 pF
1 nF
V
V
V
SS
SSA
SS
DDAVDDD
V
R10
C21 C22
100 nF 100 nF
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.44 Application diagram with external Clock Generator Circuit (CGC).
1995 Oct 18 68
The OCF1 supports for special applications the use of an external CGC (SAA7197). For normal operation the built-in CGC fulfils all requirements.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
23 START-UP, SOURCE SELECT AND STANDARD DETECTION FLOW EXAMPLE
handbook, full pagewidth
without standard routine
standard automatic
yes
B&W50?
power on
initializationstart source select
REFS active
mode select
REFS off
clamp active
?status byte?
no
mode 0 set-up
precharge clamping capacitor
mode 0 to 7
B&W50? yes = XX0XXX00
B&W60? yes = XX1XXX00
NTSC? yes = XX1XXXXX
SECAM? yes = XX0XXX01
yes
B&W60?
yes
NTSC set-upB&W50 set-up
B&W60 set-up
stop
Fig.45 Software flow example.
1995 Oct 18 69
no
NTSC?
no
no
PAL set-up
SECAM?
yes
SECAM set-up
MGC864

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
23.1 CODE 0 STARTUP and STANDARD Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1 NTSC-setup
SUB 00 WRITE
4C 3C 0D EF BD F0 00 00
F8 F8 60 60 00 06 18 90
00 2C 40 46 42 1A FF DA
F0 8B 00 00 00 00 00 00
D9 17 40 41 80 41 80 4F
FE 01 CF 0F 03 01 81 03
44 75 01 8C 03
SUB 21 WRITE 16 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
READ 1 !Status?
#STANDARD
IF 1 @XX0XXX00 !NO COLOR
THEN GOTO BW_50Hz
ENDIF
IF 1 @XX1XXX00 !NO COLOR
THEN GOTO BW_60Hz
ENDIF
SUB 06 WRITE 00
ENDIF
IF 1 @XX1XXXXX !60Hz
THEN GOTO NTSC
ENDIF
IF 1 @XX0XXXXX !50Hz
THEN GOTO PAL
ENDIF
#BW_50Hz
PRINT "BLACK&WHITE"
SUB 06 WRITE 80
SUB 2E WRITE 9A !VBPS
GOTO STOP
#BW_60Hz
PRINT "BLACK&WHITE"
SUB 06 WRITE 80
SUB 2E WRITE 81 !VBPS
GOTO STOP
#NTSC
SUB 0D WRITE 06 !SECS -> 0
SUB 11 WRITE 2C !CHCV
SUB 2E WRITE 81 !VBPS
PRINT "NTSC"
GOTO STOP
#PAL
SUB 0D WRITE 06 !SECS -> 0
SUB 11 WRITE 59 !CHCV
SUB 2E WRITE 9A !VBPS
PAUSE %150 !150ms
IF 1 @XX0XXX01
THEN GOTO SECAM
ELSE PRINT "PAL"
GOTO STOP
#SECAM
SUB 0D WRITE 07 !SECS -> 1
PRINT "SECAM"
GOTO STOP
#STOP
23.2 MODE 0 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 00 !CVBS MODE 0
SUB 20 WRITE D9 !AI21 ACTIVE
SUB 21 WRITE 17 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE 40 !AD2->LUMA and CHROMA
SUB 2C WRITE 03 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 44 !Gain AD2 active
SUB 31 WRITE 75 !AOSL -> 01b
SUB 21 WRITE 16 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.3 MODE 1 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 00 !CVBS MODE 1
SUB 20 WRITE D8 !AI22 ACTIVE
SUB 21 WRITE 17 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE 40 !AD2->LUMA and CHROMA
SUB 2C WRITE 03 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 44 !Gain AD2 active
SUB 31 WRITE 75 !AOSL -> 01b
SUB 21 WRITE 16 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.4 MODE 2 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 00 !CVBS MODE 2
SUB 20 WRITE BA !AI31 ACTIVE
SUB 21 WRITE 07 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE 91 !AD3->LUMA and CHROMA
SUB 2C WRITE 03 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 60 !Gain AD3 active
SUB 31 WRITE B5 !AOSL -> 10b
SUB 21 WRITE 05 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.5 MODE 3 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 00 !CVBS MODE 3
SUB 20 WRITE B8 !AI32 ACTIVE
SUB 21 WRITE 07 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE 91 !AD3->LUMA and CHROMA
SUB 2C WRITE 03 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 60 !Gain AD3 active
SUB 31 WRITE B5 !AOSL -> 10b
SUB 21 WRITE 05 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
1995 Oct 18 70

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
23.6 MODE 4 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 00 !CVBS MODE 4
SUB 20 WRITE 7C !AI41 ACTIVE
SUB 21 WRITE 07 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE D2 !AD3->LUMA and CHROMA
SUB 2C WRITE 83 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 60 !Gain AD3 active
SUB 31 WRITE B5 !AOSL -> 10b
SUB 21 WRITE 03 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.7 MODE 5 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 00 !CVBS MODE 5
SUB 20 WRITE 78 !AI41 ACTIVE
SUB 21 WRITE 07 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE D2 !AD3->LUMA and CHROMA
SUB 2C WRITE 83 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 60 !Gain AD3 active
SUB 31 WRITE B5 !AOSL -> 10b
SUB 21 WRITE 03 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.8 MODE 6 Source Select Procedure
SUB 2C WRITE 23 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 44 !Gain AD2 active
SUB 31 WRITE 75 !AOSL -> 01
SUB 21 WRITE 21 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 80 !Y+C MODE 6
SUB 20 WRITE 59 !AI21=Y, AI42=C
SUB 21 WRITE 17 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE 42 !AD2->LUMA, AD3->CHR
SUB 2C WRITE A3 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 44 !Gain AD2 active
SUB 31 WRITE 75 !AOSL -> 01
SUB 21 WRITE 12 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.9 MODE 7 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 80 !Y+C MODE 7
SUB 20 WRITE 9A !AI31=Y, AI22=C
SUB 21 WRITE 17 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE B1 !AD3->LUMA, AD2->CHR
SUB 2C WRITE 13 !CLAMP SELECT
SUB 30 WRITE 60 !Gain AD3 active
SUB 31 WRITE B5 !AOSL -> 10b
SUB 21 WRITE 14 !REFS OFF CLAMP AKTIV
23.10 MODE 8 Source Select Procedure
SLAVE 9C !OCF1
SUB 06 WRITE 80 !Y+C MODE 8
SUB 20 WRITE 3C !AI41=Y, AI32=C
SUB 21 WRITE 27 !REFS ON
SUB 22 WRITE C1 !AD2->LUMA, AD3->CHR
1995 Oct 18 71

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
24 PACKAGE OUTLINE
PLCC68: plastic leaded chip carrier; 68 leads
e
y
61
68
1
pin 1 index
D
X
SOT188-2
e
E
4460
43
A
Z
E
b
p
b
1
w M
H
E
E
e
A
A
1
A
4
(A )
3
k
9
β
1
27
k
10 26
e
Z
D
H
D
D
v M
A
B
v M
B
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (millimetre dimensions are derived from the original inch dimensions)
UNIT A
mm
inches
A
1
min. max. max. max. max.
4.57
0.51
4.19
0.180
0.020
0.165
A
0.25
0.01
A
4
3
3.30
0.13
b
p
0.53
0.33
0.021
0.013
b
0.81
0.66
0.032
0.026
1
D
24.33
24.13
0.958
0.950
(1)
(1)
E
eH
e
D
1.27
0.05
23.62
22.61
0.930
0.890
24.33
24.13
0.958
0.950
e
23.62
22.61
0.930
0.890
H
D
E
25.27
25.27
25.02
25.02
0.995
0.995
0.985
0.985
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.01 inches maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT188-2
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
112E10 MO-047AC
REFERENCES
k
1
k
E
1.22
1.07
0.048
0.042
0.51
0.020
L
1.44
1.02
0.057
0.040
detail X
p
0.007 0.0040.007
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
L
p
(1) (1)
Z
Z
E
D
ywv β
0.18 0.100.18
2.16
0.085
2.16
0.085
o
45
ISSUE DATE
92-11-17
95-03-11
1995 Oct 18 72

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
25 SOLDERING
25.1 Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
“IC Package Databook”
our
25.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all PLCC
packages.
The choice of heating method may be influenced by larger
PLCC packages (44 leads, or more). If infrared or vapour
phase heating is used and the large packages are not
absolutely dry (less than 0.1% moisture content by
weight), vaporization of the small amount of moisture in
them can cause cracking of the plastic body. For more
information, refer to the Drypack chapter in our
Reference Handbook”
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
“Quality
(order code 9398 510 63011).
25.3 Wave soldering
Wave soldering techniques can be used for all PLCC
packages if the following conditions are observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave) soldering
technique should be used.
• The longitudinal axis of the package footprint must be
parallel to the solder flow.
• The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves at
the downstream corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
25.4 Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
1995 Oct 18 73

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
One Chip Front-end 1 (OCF1) SAA7110; SAA7110A
26 DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
27 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
2
28 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
Purchase of Philips I
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
C COMPONENTS
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
1995 Oct 18 74
 Loading...
Loading...