Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
80C652/83C652
CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1996 Aug 15
IC20 Data Handbook
1997 Dec 05
Page 2
Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
DESCRIPTION
The P80C652/83C652 Single-Chip 8-Bit
Microcontroller is manufactured in an
advanced CMOS process and is a derivative
of the 80C51 microcontroller family. The
80C652/83C652 has the same instruction set
as the 80C51. Three versions of the
derivative exist:
83C652 — 8k bytes mask programmable
80C652 — ROMless version
87C652 — EPROM version (described in a
This device provides architectural
enhancements that make it applicable in a
variety of applications for general control
systems. The 8XC652 contains a non-volatile
8k × 8 read-only program memory, a volatile
256 × 8 read/write data memory, four 8-bit I/O
ports, two 16-bit timer/event counters
(identical to the timers of the 80C51), a
multi-source, two-priority-level, nested
interrupt structure, an I
and on-chip oscillator and timing circuits. For
systems that require extra capability, the
8XC652 can be expanded using standard
TTL compatible memories and logic.
The device also functions as an arithmetic
processor having facilities for both binary and
BCD arithmetic plus bit-handling capabilities.
The instruction set consists of over 100
instructions: 49 one-byte, 45 two-byte and 17
three-byte. With a 16(24)MHz crystal, 58% of
the instructions are executed in 0.75(0.5)µs
and 40% in 1.5(1)µs. Multiply and divide
instructions require 3(2)µs.
ROM
separate chapter)
2
C interface, UART
FEATURES
•80C51 central processing unit
•8k × 8 ROM expandable externally to
64k bytes
•256 × 8 RAM, expandable externally to
64k bytes
•Two standard 16-bit timer/counters
•Four 8-bit I/O ports
2
•I
C-bus serial I/O port with byte oriented
master and slave functions
•Full-duplex UART facilities
•Power control modes
– Idle mode
– Power-down mode
•ROM code protection
•Extended frequency range: 3.5 to 24 MHz
•Three operating ambient temperature
ranges:
0 to +70°C
–40 to +85°C
–40 to +125°C
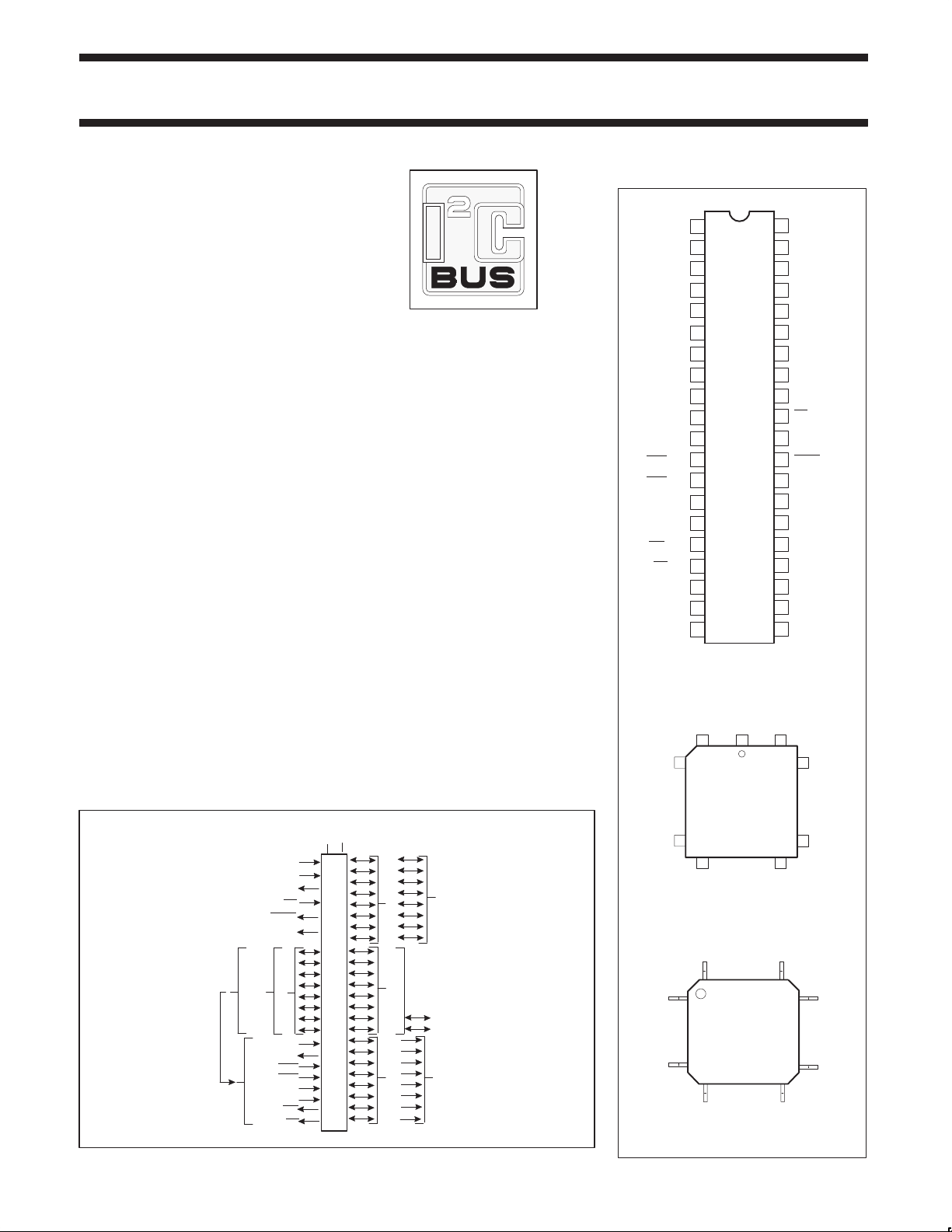
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
P1.0
1
P1.1
2
P1.2
3
P1.3
4
P1.4
5
P1.5
6
SCL/P1.6
SDA/P1.7
INT0
INT1
RST
RxD/P3.0
TxD/P3.1
/P3.2
/P3.3
T0/P3.4
T1/P3.5
WR
/P3.6
/P3.7
RD
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
7
7
8
PLASTIC
9
DUAL
IN-LINE
10
PACKAGE
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
6140
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
V
DD
P0.0/AD0
P0.1/AD1
P0.2/AD2
P0.3/AD3
P0.4/AD4
P0.5/AD5
P0.6/AD6
P0.7/AD7
EA
ALE
PSEN
P2.7/A15
P2.6/A14
P2.5/A13
P2.4/A12
P2.3/A11
P2.2/A10
P2.1/A9
P2.0/A8
39
LOGIC SYMBOL
1997 Dec 05
RST
XTAL1
XTAL2
PSEN
ALE
FUNCTIONS
ALTERNATE
INT0
INT1
EA
PORT 3
RxD
TxD
T0
T1
WR
RD
DD
PLASTIC
LEADED
CHIP
VSSV
PORT 0PORT 1PORT 2
DATA BUS
ADDRESS AND
SCL
SDA
ADDRESS BUS
17
1
11
CARRIER
18 28
44
PLASTIC
QUAD
FLAT
PACK
12 22
29
34
33
23
2
Page 3
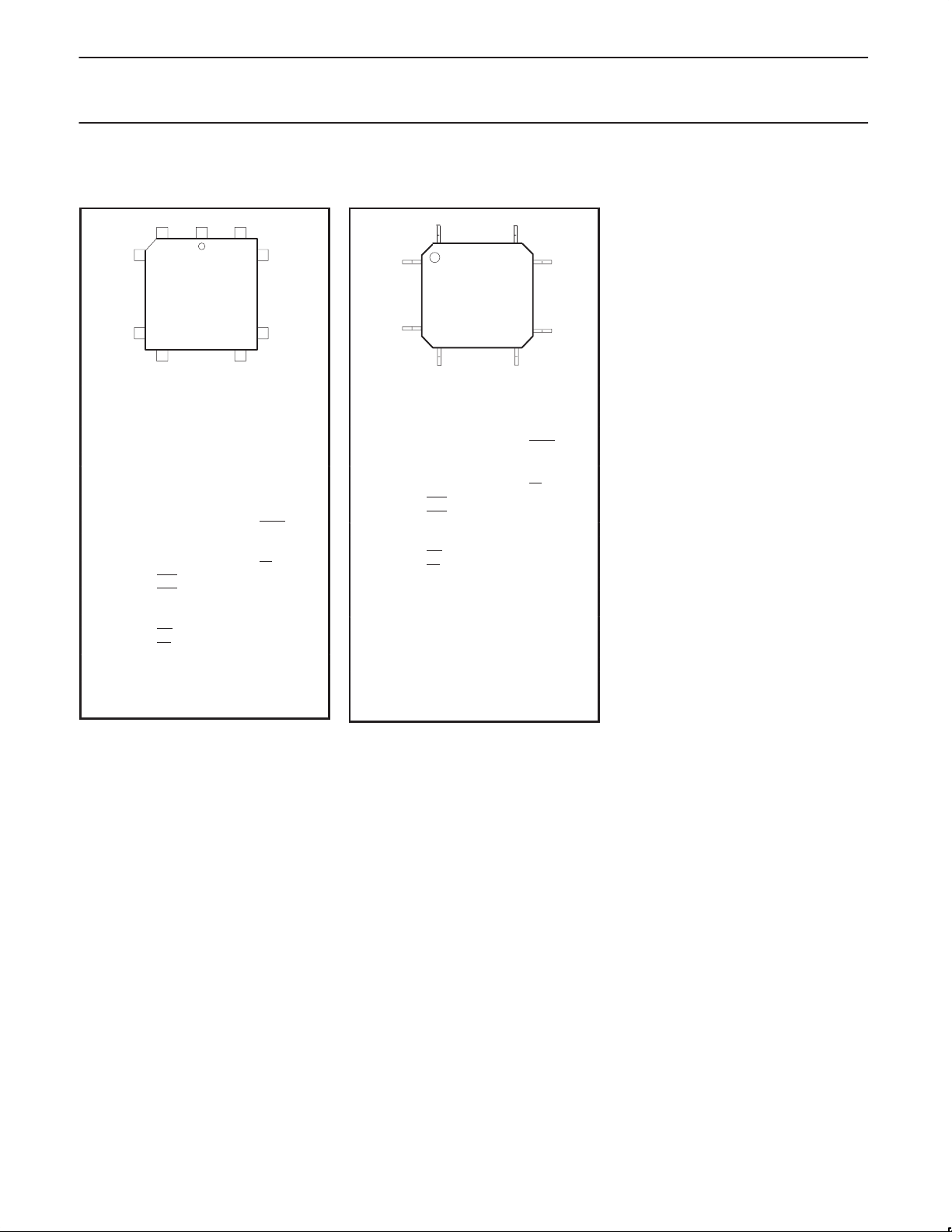
Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
PLASTIC LEADED CHIP CARRIER PIN FUNCTIONS
6140
7
PLASTIC
LEADED CHIP
CARRIER
17
18 28
Pin Function Pin Function
1 NC* 23 NC*
2 P1.0 24 P2.0/A8
3 P1.1 25 P2.1/A9
4 P1.2 26 P2.2/A10
5 P1.3 27 P2.3/A11
6 P1.4 28 P2.4/A12
7 P1.5 29 P2.5/A13
8 P1.6/SCL 30 P2.6/A14
9 P1.7/SDA 31 P2.7/A15
10 RST 32 PSEN
11 P3.0/RxD 33 ALE
12 NC* 34 NC*
13 P3.1/TxD 35 EA
14 P3.2/INT0 36 P0.7/AD7
15 P3.3/INT1 37 P0.6/AD6
16 P3.4/T0 38 P0.5/AD5
17 P3.5/T1 39 P0.4/AD4
18 P3.6/WR 40 P0.3/AD3
19 P3.7/RD 41 P0.2/AD2
20 XTAL2 42 P0.1/AD1
21 XTAL1 43 P0.0/AD0
22 V
SS
*DO NOT CONNECT
44 V
39
29
DD
PLASTIC QUAD FLAT PACK PIN FUNCTIONS
44 34
1
PLASTIC
QUAD
FLAT
PACK
11
12 22
Pin Function Pin Function
1 P1.5 23 P2.5/A13
2 P1.6/SCL 24 P2.6/A14
3 P1.7/SDA 25 P2.7/A15
4 RST 26 PSEN
5 P3.0/RxD 27 ALE
6 V
SS4
7 P3.1/TxD 29
8 P3.2/INT0 30 P0.7/AD7
9 P3.3/INT1 31 P0.6/AD6
10 P3.4/T0 32 P0.5/AD5
11 P3.5/T1 33 P0.4/AD4
12 P3.6/WR 34 P0.3/AD3
13 P3.7/RD 35 P0.2/AD2
14 XTAL2 36 P0.1/AD1
15 XTAL1 37 P0.0/AD0
16 V
SS1
17 NC* 39 V
18 P2.0/A8 40 P1.0
19 P2.1/A9 41 P1.1
20 P2.2/A10 42 P1.2
21 P2.3/A11 43 P1.3
22 P2.4/A12 44 P1.4
*DO NOT CONNECT
NOTES TO QFP ONLY:
1. Due to EMC improvements, all V
(6, 16, 28, 39) must be connected to V
on the 80C652/83C652.
28 V
38 V
EA
SS2
/V
DD
SS3
SS
33
23
PP
pins
SS
1997 Dec 05
3
Page 4
Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
( )
1,2
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
ORDER INFORMATION
PHILIPS
PART ORDER NUMBER
PART MARKING
ROMless ROM
P80C652EBP P83C652EBP/xxx SOT129-1 P80C652EBPN P83C652EBPN S87C652-4N40
P80C652EBA P83C652EBA/xxx SOT187-2 P80C652EBAA P83C652EBAA S87C652-4A44
P80C652EBB P83C652EBB/xxx SOT307-2 P80C652EBBB P83C652EBBB S87C652-4B44
P80C652EFP P83C652EFP/xxx SOT129-1 P80C652EFPN P83C652EFPN S87C652-5N40
P80C652EFA P83C652EFA/xxx SOT187-2 P80C652EFAA P83C652EFAA S87C652-5A44
P80C652EFB P83C652EFB/xxx SOT307-2 P80C652EFBB P83C652EFBB S87C652-5B44
P80C652EHP P83C652EHP/xxx SOT129-1 P80C652EHPN P83C652EHPN
P80C652EHA P83C652EHA/xxx SOT187-2 P80C652EHAA P83C652EHAA
P80C652EHB P83C652EHB/xxx SOT307-2 P80C652EHBB P83C652EHBB
P80C652IBP P83C652IBP/xxx SOT129-1 P80C652IBPN P83C652IBPN
P80C652IBA P83C652IBA/xxx SOT187-2 P80C652IBAA P83C652IBAA
P80C652IBB P83C652IBB/xxx SOT307-2 P80C652IBBB P83C652IBBB
P80C652IFP P83C652IFP/xxx SOT129-1 P80C652IFPN P83C652IFPN
P80C652IFA P83C652IFA/xxx SOT187-2 P80C652IFAA P83C652IFAA
P80C652IFB P83C652IFB/xxx SOT307-2 P80C652IFBB P83C652IFBB
NOTES:
1. 80C652 and 83C652 frequency range is 3.5MHz–16MHz or 3.5MHz–24MHz.
2. For specification of the EPROM version, see the 87C652 data sheet.
3. xxx denotes the ROM code number.
3
Drawing
Number
PHILIPS NORTH AMERICA
PART ORDER NUMBER
ROMless ROM EPROM
TEMPERATURE RANGE
2
Plastic Dual In-line Package
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
Plastic Quad Flat Pack
Plastic Dual In-line Package
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
Plastic Quad Flat Pack
Plastic Dual In-line Package
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
Plastic Quad Flat Pack
Plastic Dual In-line Package
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
Plastic Quad Flat Pack
Plastic Dual In-line Package
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
Plastic Quad Flat Pack
(°C)
AND PACKAGE
0 to +70,
0 to +70,
0 to +70,
–40 to +85,
–40 to +85,
–40 to +85,
–40 to +125,
–40 to +125,
–40 to +125,
0 to +70,
0 to +70,
0 to +70,
–40 to +85,
–40 to +85,
–40 to +85,
FREQ
MHz
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
24
24
24
24
24
24
1997 Dec 05
4
Page 5
Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
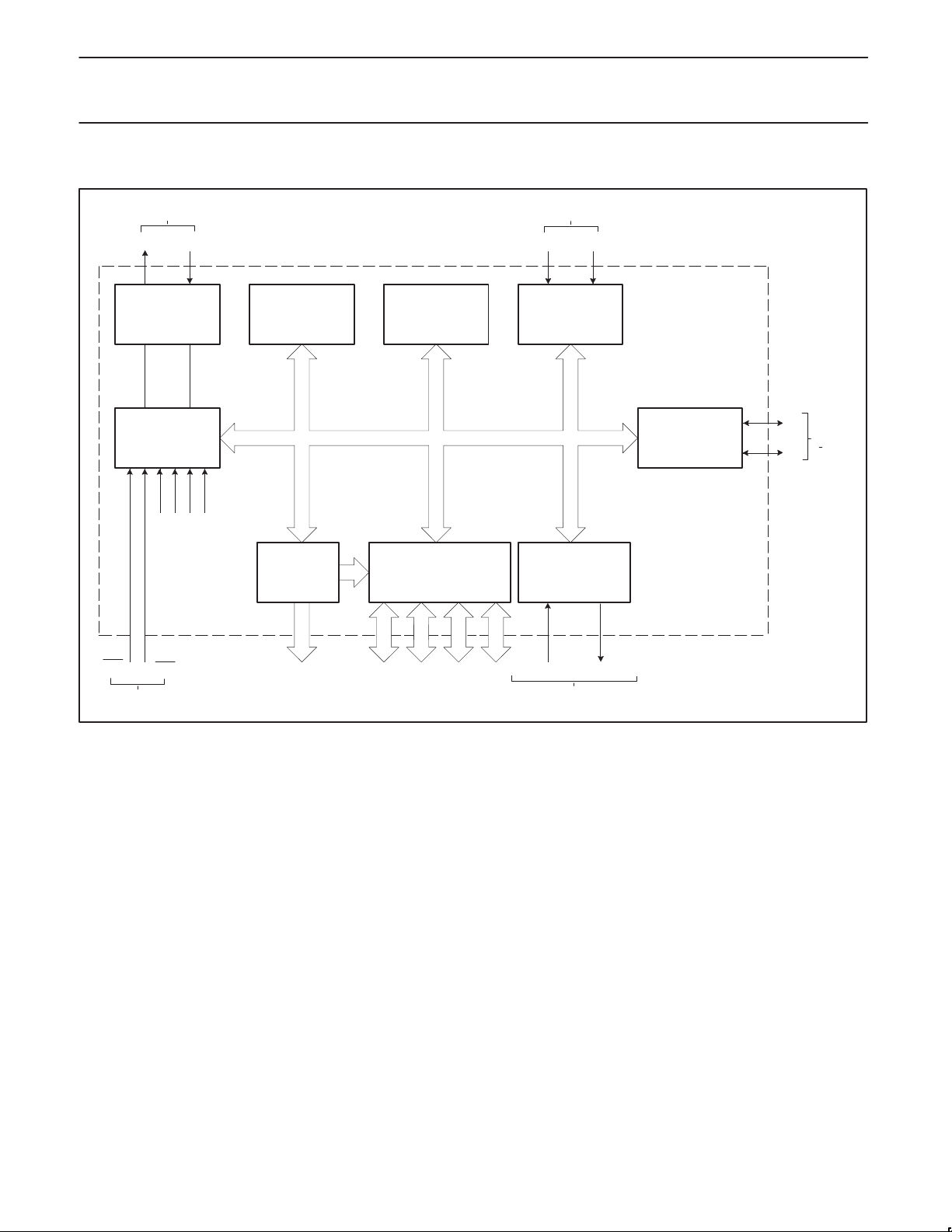
BLOCK DIAGRAM
FREQUENCY
REFERENCE
COUNTERS
XTAL2 XTAL1
OSCILLATOR
INT0
EXTERNAL
INTERRUPTS
AND
TIMING
CPU
INTERNAL
INTERRUPTS
INT1
PROGRAM
MEMORY
(8K x 8 ROM)
64K BYTE BUS
EXPANSION
CONTRTOL
CONTROL
DATA
MEMORY
(256 x 8 RAM)
PROGRAMMABLE I/O
PARALLEL PORTS,
ADDRESS/DATA BUS
AND I/O PINS
T0 T1
TWO 16-BIT
TIMER/EVENT
COUNTERS
PROG SERIAL PORT
FULL DUPLEX UART
SYNCHRONOUS SHIFT
SERIAL IN SERIAL OUT
SHARED WITH
PORT 3
2
I
C SERIAL I/O
SDA
SCL
SHARED
WITH
PORT 1
1997 Dec 05
5
Page 6

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN NUMBER
MNEMONIC DIP PLCC QFP TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
V
SS
V
DD
P0.0–0.7 39–32 43–36 37–30 I/O Port 0: Port 0 is an open-drain, bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to
P1.0–P1.7 1–8 2–9 40–44,
P1.6 7 8 2 I/O SCL: I2C-bus serial port clock line.
P1.7 8 9 3 I/O SDA: I2C-bus serial port data line.
P2.0–P2.7 21–28 24–31 18–25 I/O Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s
P3.0–P3.7 10–17 11,
RST 9 10 4 I Reset: A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running, resets the
ALE 30 33 27 I/O Address Latch Enable: Output pulse for latching the low byte of the address during an
PSEN 29 32 26 O Program Store Enable: Read strobe to external program memory via Port 0 and Port 2. It
EA 31 35 29 I External Access: If during a RESET, EA is held at TTL, level HIGH, the CPU executes out
XTAL1 19 21 15 I Crystal 1: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock generator
XTAL2 18 20 14 O Crystal 2: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
NOTE:
To avoid “latch-up” effect at power-on, the voltage on any pin at any time must not be higher than V
20 22 6, 16,
28, 39
I Ground: 0V reference. With the QFP package all VSS pins (V
connected.
SS1
to V
) must be
SS4
40 44 38 I Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power-down
operation.
them float and can be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed
low-order address and data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In
this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
I/O Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups, except P1.6 and P1.7
1–3
which are open drain. Port 1 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 1 pins that are externally pulled
low will source current because of the internal pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics:
). Alternate functions include:
I
IL
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As
inputs, port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the
internal pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
address byte during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to
). Port 2 emits the high-order
IL
external data memory that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this application, it
uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory
that use 8-bit addresses (MOV @Ri), port 2 emits the contents of the P2 special function
register.
I/O Port 3: Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s
13–195,7–13
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As
inputs, port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the
pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
the 80C51 family , as listed below:
). Port 3 also serves the special features of
IL
10 11 5 I RxD (P3.0): Serial input port
11 13 7 O TxD (P3.1): Serial output port
12 14 8 I INT0 (P3.2): External interrupt
13 15 9 I INT1 (P3.3): External interrupt
14 16 10 I T0 (P3.4): Timer 0 external input
15 17 11 I T1 (P3.5): Timer 1 external input
16 18 12 O WR (P3.6): External data memory write strobe
17 19 13 O RD (P3.7): External data memory read strobe
device. An internal diffused resistor to V
capacitor to V
DD
.
permits a power-on reset using only an external
SS
access to external memory. In normal operation, ALE is emitted at a constant rate of 1/6
the oscillator frequency . Note that one ALE pulse is skipped during each access to external
data memory.
is activated twice each machine cycle during fetches from the external program memory.
When executing out of external program memory two activations of PSEN
during each access to external data memory. PSEN
no fetches from external program memory. PSEN
is not activated (remains HIGH) during
can sink/source 8 LSTTL inputs and can
are skipped
drive CMOS inputs without external pull–ups.
of the internal program memory ROM provided the Program Counter is less than 8192. If
during a RESET, EA
memory. EA
is held a TTL LOW level, the CPU executes out of external program
is not allowed to float.
circuits.
+ 0.5V or VSS – 0.5V, respectively.
DD
1997 Dec 05
6
Page 7

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
Table 1. 8XC652/654 Special Function Registers
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
ACC* Accumulator E0H E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0 00H
B* B register F0H F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0 00H
DPTR:
DPH
DPL
IE*# Interrupt enable A8H EA ES1 ES0 ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 0x000000B
IP*# Interrupt priority B8H – PS1 PS0 PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0 xx000000B
P0* Port 0 80H AD7 AD6 AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0 FFH
P1*# Port 1 90H SDA SCL FFH
P2* Port 2 A0H A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 FFH
P3* Port 3 B0H RD WR T1 T0 INT1 INT0 TXD RXD FFH
PCON Power control 87H SMOD – – – GF1 GF0 PD IDL 0xxx0000B
S0CON*# Serial 0 port control 98H SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI 00H
S0BUF# Serial 0 data buffer 99H xxxxxxxxB
PSW* Program status word D0H CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P 00H
S1DAT# Serial 1 data DAH 00H
SP Stack pointer 81H 07H
S1ADR# Serial 1 address DBH
Data pointer
(2 bytes)
Data pointer high
Data pointer low
DIRECT
ADDRESS
83H
82H
BIT ADDRESS, SYMBOL, OR ALTERNATIVE PORT FUNCTION
MSB LSB
AF AE AD AC AB AA A9 A8
BF BE BD BC BB BA B9 B8
87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
9F 9E 9D 9C 9B 9A 99 98
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SLAVE ADDRESS
GC 00H
RESET
VALUE
00H
00H
S1STA# Serial 1 status D9H SC4 SC3 SC2 SC1 SC0 0 0 0 F8H
DF DE DD DC DB DA D9 D8
S1CON*# Serial 1 control D8H CR2 ENS1 STA STO SI AA CR1 CR0 00000000B
8F 8E 8D 8C 8B 8A 89 88
TCON* Timer control 88H TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 00H
TH1 Timer high 1 8DH 00H
TH0 Timer high 0 8CH 00H
TL1 Timer low 1 8BH 00H
TL0 Timer low 0 8AH 00H
TMOD Timer mode 89H GATE C/T M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0 00H
* SFRs are bit addressable.
# SFRs are modified from or added to the 80C51 SFRs.
1997 Dec 05
7
Page 8

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
ROM CODE PROTECTION (83C652)
The 8XC652 has an additional security
feature. ROM code protection may be
selected by setting a mask–programmable
security bit (i.e., user dependent). This
feature may be requested during ROM code
submission. When selected, the ROM code is
protected and cannot be read out at any time
by any test mode or by any instruction in the
external program memory space.
The MOVC instructions are the only
instructions that have access to program
code in the internal or external program
memory. The EA
RESET and is “don’t care” after RESET
(also if the security bit is not set). This
implementation prevents reading internal
program code by switching from external
program memory to internal program memory
during a MOVC instruction or any other
instruction that uses immediate data.
input is latched during
OSCILLA T OR CHARACTERISTICS
XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output,
respectively, of an inverting amplifier. The
pins can be configured for use as an on-chip
oscillator, as shown in the Logic Symbol,
page 2.
To drive the device from an external clock
source, XTAL1 should be driven while XTAL2
is left unconnected. There are no
requirements on the duty cycle of the
external clock signal, because the input to
the internal clock circuitry is through a
divide-by-two flip-flop. However, minimum
and maximum high and low times specified in
the data sheet must be observed.
Reset
A reset is accomplished by holding the RST
pin high for at least two machine cycles (24
oscillator periods), while the oscillator is
running. To insure a good power-on reset, the
RST pin must be high long enough to allow
the oscillator time to start up (normally a few
milliseconds) plus two machine cycles. At
power-on, the voltage on V
come up at the same time for a proper
start-up.
and RST must
DD
Idle Mode
In the idle mode, the CPU puts itself to sleep
while all of the on-chip peripherals stay
active. The instruction to invoke the idle
mode is the last instruction executed in the
normal operating mode before the idle mode
is activated. The CPU contents, the on-chip
RAM, and all of the special function registers
remain intact during this mode. The idle
mode can be terminated either by any
enabled interrupt (at which time the process
is picked up at the interrupt service routine
and continued), or by a hardware reset which
starts the processor in the same manner as a
power-on reset.
Power-Down Mode
In the power-down mode, the oscillator is
stopped and the instruction to invoke
power-down is the last instruction executed.
Only the contents of the on-chip RAM are
preserved. A hardware reset is the only way
to terminate the power-down mode. The
control bits for the reduced power modes are
in the special function register PCON. Table 2
shows the state of the I/O ports during low
current operating modes.
I2C Serial Communication—SIO1
The I2C serial port is identical to the I2C
serial port on the 8XC552. The operation of
this subsystem is described in detail in the
8XC552 section of this manual.
Note that in both the 8XC652/4 and the
8XC552 the I
to port pins P1.6 and P1.7. Because of this,
P1.6 and P1.7 on these parts do not have a
pull-up structure as found on the 80C51.
Therefore P1.6 and P1.7 have open drain
outputs on the 8XC652/4.
2
C pins are alternate functions
Table 2. External Pin Status During Idle and Power-Down Mode
MODE
Idle Internal 1 1 Data Data Data Data
Idle External 1 1 Float Data Address Data
Power-down Internal 0 0 Data Data Data Data
Power-down External 0 0 Float Data Data Data
Serial Control Register (S1CON) – See Table 3
S1CON (D8H)
Bits CR0, CR1 and CR2 determine the serial clock frequency that is generated in the master mode of operation.
CR2 ENS1 STA STO SI AA CR1 CR0
PROGRAM
MEMORY
ALE PSEN PORT 0 PORT 1 PORT 2 PORT 3
Table 3. Serial Clock Rates
BIT FREQUENCY (kHz) AT f
CR2 CR1 CR0
0 0 0 23 47 62.5 94 256
0 0 1 27 54 71 107
0 1 0 31.25 62.5 83.3 125
0 1 1 37 75 100 150
1 0 0 6.25 12.5 17 25 960
1 0 1 50 100 133
1 1 0 100 200
1 1 1 0.24 < 62.5
NOTES:
1. These frequencies exceed the upper limit of 100kHz of the I
6MHz 12MHz 16MHz 24MHz f
1
0 to 255
0.49 < 62.5
0 to 254
2
OSC
DIVIDED BY
OSC
1
1
1
1
1
267
0.65 < 55.6
0 to 253
C-bus specification and cannot be used in an I2C-bus application.
1
200
1
400
0.98 < 50.0
0 to 251
96 × (256 – (reload value Timer 1))
reload value range Timer 1 (in mode 2)
224
192
160
120
60
1997 Dec 05
8
Page 9

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
PARAMETER
Storage temperature range –65 to +150 °C
Voltage on any other pin to V
Input, output current on any single pin
Power dissipation (based on package heat transfer
limitations, not device power consumption)
NOTES:
1. Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent
damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
these or any conditions other than those described in the AC and DC Electrical
Characteristics section of this specification is not implied.
2. This product includes circuitry specifically designed for the protection of its internal devices
from the damaging effects of excessive static charge. Nonetheless, it is suggested that
conventional precautions be taken to avoid applying greater than the rated maxima.
3. Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified. All
voltages are with respect to V
SS
SS
1, 2, 3
unless otherwise noted.
RATING UNIT
–0.5 to + 6.0 V
±5
1 W
mA
DEVICE SPECIFICATIONS
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
TYPE
P8XC652EBx 4.5 5.5 3.5 16 0 to +70
P8XC652EFx 4.5 5.5 3.5 16 –40 to +85
P8XC652EHx 4.5 5.5 3.5 16 –40 to +125
P8XC652IBx 4.5 5.5 3.5 24 0 to +70
P83X652IFx 4.5 5.5 3.5 24 –40 to +85
(V)
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
(°C)
1997 Dec 05
9
Page 10

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VSS = 0V; VDD = 5V ± 10%
TEST LIMITS
SYMBOL PARAMETER PART TYPE CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
IL
V
IL1
V
IL2
V
IH
V
IH1
V
IH2
V
OL
V
OL1
V
OL2
V
OH
V
OH1
I
IL
I
TL
I
L1
I
L2
I
DD
R
RST
C
IO
NOTES ON NEXT PAGE.
Input low voltage,
except EA, P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA 0 to +70°C –0.5 0.2VDD–0.1 V
–40 to +85°C –0.5 0.2VDD–0.15 V
–40 to +125°C –0.5 0.2VDD–0.25 V
Input low voltage to EA 0 to +70°C –0.5 0.2VDD–0.3 V
–40 to +85°C –0.5 0.2VDD–0.35 V
–40 to +125°C –0.5 0.2VDD–0.45 V
Input low voltage to P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA
6
–0.5 0.3V
DD
Input high voltage, except XTAL1, RST,
P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA 0 to +70°C 0.2VDD+0.9 VDD+0.5 V
–40 to +85°C 0.2VDD+1.0 VDD+0.5 V
–40 to +125°C 0.2VDD+1.0 VDD+0.5 V
Input high voltage, XTAL1, RST 0 to +70°C 0.7V
DD
VDD+0.5 V
–40 to +85°C 0.7VDD+0.1 VDD+0.5 V
–40 to +125°C 0.7VDD+0.1 VDD+0.5 V
Input high voltage, P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA
Output low voltage, ports 1, 2, 3,
6
IOL = 1.6mA
8, 9
0.7V
DD
6.0 V
0.45 V
except P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA
Output low voltage, port 0, ALE, PSEN IOL = 3.2mA
8, 9
0.45 V
Output low voltage, P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA IOL = 3.0mA 0.4 V
Output high voltage, ports 1, 2, 3, ALE, PSEN
10
IOH = –60µA 2.4 V
IOH = –25µA 0.75V
IOH = –10µA 0.9V
DD
DD
Output high voltage; port 0 in external bus mode IOH = –800µA 2.4 V
IOH = –300µA 0.75V
IOH = –80µA 0.9V
DD
DD
Logical 0 input current, ports 1, 2, 3,
except P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA 0 to +70°C VIN = 0.45V –50 µA
–40 to +85°C –75 µA
–40 to +125°C –75 µA
Logical 1-to-0 transition current, ports 1, 2, 3,
except P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA 0 to +70°C See note 7 –650 µA
–40 to +85°C –750 µA
–40 to +125°C –750 µA
< 6.0V
I
DD
< V
I
< 6.0V
DD
±10 µA
±10 µA
µA
Input leakage current, port 0, EA 0.45V < V
Input leakage current, P1.6/SCL, P1.7/SDA 0V < V
0V < V
Power supply current: See note 1
4, 5
4, 5
3, 11
3, 11
2, 11
2, 11
VDD=5.5V 26.5 mA
VDD=5.5V 33.8 mA
6 mA
7 mA
50 µA
–40 to +125°C 100 µA
Active mode @ 16MHz
Active mode @ 24MHz
Idle mode @ 16MHz
Idle mode @ 24MHz
Power down mode
Power down mode
Internal reset pull-down resistor 50 150 kΩ
Pin capacitance Freq.=1MHz 10 pF
V
V
V
V
V
1997 Dec 05
10
Page 11

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
NOTES FOR DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
1. See Figures 9 through 11 for I
2. The operating supply current is measured with all output pins disconnected; XTAL1 driven with t
= VSS + 0.5V; VIH = V
V
IL
3. The idle mode supply current is measured with all output pins disconnected; XTAL1 driven with t
V
4. The power-down current is measured with all output pins disconnected; XTAL2 not connected; Port 0 = P1.6 = P1.7 = V
EA
5. 2V
6. The input threshold voltage of P1.6 and P1.7 (SIO1) meets the I
= V
IH
–0.5V; XTAL2 not connected; Port 0 = P1.6 = P1.7 = VDD; EA = RST = VSS. See Figure 10.
DD
= RST = VSS. See Figure 11.
≤ V
≤ VDDmax.
PD
logic 0 while an input voltage above 0.7V
7. Pins of ports 1 , 2, and 3 source a transition current when they are being externally driven from 1 to 0. The transition current reaches its
maximum value when V
8. Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause spurious noise to be superimposed on the V
IN
to external bus capacitance discharging into the port 0 and port 2 pins when these pins make 1-to-0 transitions during bus operations. In the
test conditions.
DD
–0.5V; XTAL2 not connected; EA = RST = Port 0 = P1.6 = P1.7 = VDD. See Figure 9.
DD
2
will be recognized as a logic 1.
DD
C specification, so an input voltage below 0.3VDD will be recognized as a
= tf = 5ns;
r
= tf = 5ns; VIL = VSS + 0.5V;
r
is approximately 2V .
s of ALE and ports 1 and 3. The noise is due
OL
DD
;
worst cases (capacitive loading > 100pF), the noise pulse on the ALE pin may exceed 0.8V . In such cases, it may be desirable to qualify
ALE with a Schmitt Trigger, or use an address latch with a Schmitt Trigger STROBE input.
9. Under steady state (non-transient) conditions, I
I
= 26mA total for Port 0; Maximum IOL = 15mA total for Ports 1, 2, and 3; Maximum IOL = 71mA total for all output pins. If IOL exceeds the
OL
test conditions, V
10.Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause the V
may exceed the related specification. Pins are not guaranteed to sink current greater than the listed test conditions.
OL
address bits are stabilizing.
11. I
for other frequencies can be derived from Figure 1, where FREQ is the external oscillator frequency in MHz. I
DDMAX
40
I
DD
(mA)
30
must be externally limited as follows: Maximum IOL = 10mA per port pin; Maximum
OL
on ALE and PSEN to momentarily fall below the 0.9VDD specification when the
OH
is given in mA.
DDMAX
50
I
DD
(mA)
40
(1)
20
10
(2)
0
0481216
(1) MAXIMUM OPERATING MODE: V
(2) MAXIMUM IDLE MODE: VDD = V
These values are valid within the specified
frequency range.
= V
DD
DDmax
DDmax
f
XTAL1
(MHz)
Figure 1. IDD vs. Frequency
30
20
10
0
0
(1) MAXIMUM OPERATING MODE: V
(2) MAXIMUM IDLE MODE: VDD = V
These values are valid within the specified
frequency range.
4
81216
(1)
(2)
= V
DD
DDmax
DDmax
f
XTAL1
24
(MHz)
1997 Dec 05
11
Page 12

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1, 2
(16 MHz type)
16MHz CLOCK VARIABLE CLOCK
SYMBOL FIGURE PARAMETER MIN MAX MIN MAX UNIT
1/t
t
LHLL
t
AVLL
t
LLAX
t
LLIV
t
LLPL
t
PLPH
t
PLIV
t
PXIX
t
PXIZ
t
AVIV
t
PLAZ
CLCL
2 Oscillator frequency 3.5 16 MHz
2 ALE pulse width 85 2t
2 Address valid to ALE low 8 t
2 Address hold after ALE low 28 t
2 ALE low to valid instruction in 150 4t
2 ALE low to PSEN low 23 t
2 PSEN pulse width 143 3t
2 PSEN low to valid instruction in 83 3t
–40 ns
CLCL
–55 ns
CLCL
–35 ns
CLCL
–100 ns
CLCL
–40 ns
CLCL
–45 ns
CLCL
–105 ns
CLCL
2 Input instruction hold after PSEN 0 0 ns
2 Input instruction float after PSEN 38 t
2 Address to valid instruction in 208 5t
–25 ns
CLCL
–105 ns
CLCL
2 PSEN low to address float 10 10 ns
Data Memory
t
RLRH
t
WLWH
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
LLDV
t
AVDV
t
LLWL
t
AVWL
t
QVWX
t
DW
t
WHQX
t
RLAZ
t
WHLH
3, 4 RD pulse width 275 6t
3, 4 WR pulse width 275 6t
3, 4 RD low to valid data in 148 5t
–100 ns
CLCL
–100 ns
CLCL
–165 ns
CLCL
3, 4 Data hold after RD 0 0 ns
3, 4 Data float after RD 55 2t
3, 4 ALE low to valid data in 350 8t
3, 4 Address to valid data in 398 9t
3, 4 ALE low to RD or WR low 138 238 3t
3, 4 Address valid to WR low or RD low 120 4t
3, 4 Data valid to WR transition 3 t
3, 4 Data setup time before WR 288 7t
3, 4 Data hold after WR 13 t
–50 3t
CLCL
–130 ns
CLCL
–60 ns
CLCL
–150 ns
CLCL
–50 ns
CLCL
–70 ns
CLCL
–150 ns
CLCL
–165 ns
CLCL
+50 ns
CLCL
3, 4 RD low to address float 0 0 ns
3, 4 RD or WR high to ALE high 23 103 t
–40 t
CLCL
+40 ns
CLCL
Shift Register
t
XLXL
t
QVXH
t
XHQX
t
XHDX
t
XHDV
5 Serial port clock cycle time
5 Output data setup to clock rising edge
5 Output data hold after clock rising edge
5 Input data hold after clock rising edge
5 Clock rising edge to input data valid
3
3
3
3
3
0.75 12t
492 10t
80 2t
CLCL
–133 ns
CLCL
–117 ns
CLCL
0 0 ns
492 10t
–133 ns
CLCL
External Clock
t
CHCX
t
CLCX
t
CLCH
t
CHCL
6 High time
6 Low time
6 Rise time
6 Fall time
3
3
3
3
20 20 t
20 20 t
20 20 ns
20 20 ns
CLCL –
CLCL –
t
CLCX
t
CHCX
NOTES:
1. Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified.
2. Load capacitance for port 0, ALE, and PSEN
= 100pF, load capacitance for all other outputs = 80pF.
3. These values are characterized but not 100% production tested.
µs
ns
ns
1997 Dec 05
12
Page 13

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1, 2
(24 MHz type)
24MHz CLOCK VARIABLE CLOCK
SYMBOL FIGURE PARAMETER MIN MAX MIN MAX UNIT
1/t
t
LHLL
t
AVLL
t
LLAX
t
LLIV
t
LLPL
t
PLPH
t
PLIV
t
PXIX
t
PXIZ
t
AVIV
t
PLAZ
CLCL
2 Oscillator frequency 3.5 24 MHz
2 ALE pulse width 43 2t
2 Address valid to ALE low 17 t
2 Address hold after ALE low 17 t
2 ALE low to valid instruction in 102 4t
2 ALE low to PSEN low 17 t
2 PSEN pulse width 80 3t
2 PSEN low to valid instruction in 65 3t
–40 ns
CLCL
–25 ns
CLCL
–25 ns
CLCL
–65 ns
CLCL
–25 ns
CLCL
–45 ns
CLCL
–60 ns
CLCL
2 Input instruction hold after PSEN 0 0 ns
2 Input instruction float after PSEN 17 t
2 Address to valid instruction in 128 5t
–25 ns
CLCL
–80 ns
CLCL
2 PSEN low to address float 10 10 ns
Data Memory
t
RLRH
t
WLWH
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
LLDV
t
AVDV
t
LLWL
t
AVWL
t
QVWX
t
DW
t
WHQX
t
RLAZ
t
WHLH
3, 4 RD pulse width 150 6t
3, 4 WR pulse width 150 6t
3, 4 RD low to valid data in 118 5t
–100 ns
CLCL
–100 ns
CLCL
–90 ns
CLCL
3, 4 Data hold after RD 0 0 ns
3, 4 Data float after RD 55 2t
3, 4 ALE low to valid data in 180 8t
3, 4 Address to valid data in 210 9t
3, 4 ALE low to RD or WR low 75 175 3t
3, 4 Address valid to WR low or RD low 92 4t
3, 4 Data valid to WR transition 12 t
3, 4 Data setup time before WR 162 7t
3, 4 Data hold after WR 17 t
–50 3t
CLCL
–75 ns
CLCL
–30 ns
CLCL
–130 ns
CLCL
–25 ns
CLCL
–28 ns
CLCL
–150 ns
CLCL
–165 ns
CLCL
+50 ns
CLCL
3, 4 RD low to address float 0 0 ns
3, 4 RD or WR high to ALE high 17 67 t
–25 t
CLCL
+25 ns
CLCL
Shift Register
t
XLXL
t
QVXH
t
XHQX
t
XHDX
t
XHDV
5 Serial port clock cycle time
5 Output data setup to clock rising edge
5 Output data hold after clock rising edge
5 Input data hold after clock rising edge
5 Clock rising edge to input data valid
3
3
3
3
3
0.5 12t
283 10t
23 2t
CLCL
–133 ns
CLCL
–60 ns
CLCL
0 0 ns
283 10t
–133 ns
CLCL
External Clock
t
CHCX
t
CLCX
t
CLCH
t
CHCL
6 High time
6 Low time
6 Rise time
6 Fall time
3
3
3
3
17 17 t
17 17 t
5 5 ns
5 5 ns
CLCL –
CLCL –
t
CLCX
t
CHCX
NOTES:
1. Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified.
2. Load capacitance for port 0, ALE, and PSEN
= 100pF, load capacitance for all other outputs = 80pF.
3. These values are characterized but not 100% production tested.
µs
ns
ns
1997 Dec 05
13
Page 14

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS – I2C INTERFACE
SYMBOL PARAMETER INPUT OUTPUT
SCL TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
t
HD;STA
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
RC
t
FC
STAR T condition hold time ≥ 14 t
SCL LOW time ≥ 16 t
SCL HIGH time ≥ 14 t
CLCL
CLCL
CLCL
SCL rise time ≤ 1µs –
SCL fall time ≤ 0.3µs < 0.3µs
SDA TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
t
SU;DAT1
t
SU;DAT2
t
SU;DAT3
t
HD;DAT
t
SU;STA
t
SU;STO
t
BUF
t
RD
t
FD
Data set-up time ≥ 250ns > 20 t
SDA set-up time (before rep. STAR T cond.) ≥ 250ns > 1µs
SDA set-up time (before STOP cond.) ≥ 250ns > 8 t
Data hold time ≥ 0ns > 8 t
Repeated START set-up time ≥ 14 t
STOP condition set-up time ≥ 14 t
Bus free time ≥ 14 t
CLCL
CLCL
CLCL
SDA rise time ≤ 1µs –
SDA fall time ≤ 0.3µs < 0.3µs
NOTES:
1. At 100 kbit/s. At other bit rates this value is inversely proportional to the bit-rate of 100 kbit/s.
2. Determined by the external bus-line capacitance and the external bus-line pull-resistor, this must be < 1µs.
3. Spikes on the SDA and SCL lines with a duration of less than 3 t
SCL = 400pF.
4. t
= 1/f
CLCL
interface meets the I
= one oscillator clock period at pin XTAL1. For 63ns (42ns) < t
OSC
2
C-bus specification for bit-rates up to 100 kbit/s.
will be filtered out. Maximum capacitance on bus-lines SDA and
CLCL
< 285ns (16MHz (24MHz) > f
CLCL
> 3.5MHz) the SI01
OSC
> 4.0µs
> 4.7µs
> 4.0µs
2
CLCL
CLCL
CLCL
> 4.7µs
> 4.0µs
> 4.7µs
2
– t
1
– t
1
1
1
3
RD
FC
1
1
1
3
TIMING SIO1 (I2C) INTERFACE
START or repeated START condition
SDA
(INPUT/OUTPUT)
t
FDtRC
SCL
(INPUT/OUTPUT)
t
HD;STA
t
LOW
t
RD
t
HIGH
t
FC
t
SU;DAT1
t
HD;DAT
repeated START condition
STOP condition
t
t
SU;DAT2
SU;STA
t
SU; STO
0.7 V
0.3 V
t
SU;DAT3
DD
DD
t
BUF
START condition
0.7 V
DD
0.3 V
DD
1997 Dec 05
14
Page 15

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
EXPLANATION OF THE AC SYMBOLS
Each timing symbol has five characters. The
first character is always ‘t’ (= time). The other
characters, depending on their positions,
indicate the name of a signal or the logical
status of that signal. The designations are:
A – Address
C – Clock
D – Input data
H – Logic level high
I – Instruction (program memory contents)
L – Logic level low, or ALE
P – PSEN
t
ALE
LHLL
Q – Output data
R–RD
signal
t – Time
V – V alid
W– WR
signal
X – No longer a valid logic level
Z – Float
Examples: t
= Time for address valid
AVLL
to ALE low.
t
= Time for ALE low
LLPL
to PSEN
low.
ALE
PSEN
RD
PSEN
PORT 0
PORT 2
t
t
AVLL
LLPL
t
LLAX
A0–A7 A0–A7
t
AVIV
t
PLPH
t
LLIV
t
PLIV
t
t
PLAZ
t
PXIX
INSTR IN
A8–A15 A8–A15
PXIZ
Figure 2. External Program Memory Read Cycle
t
WHLH
t
LLDV
t
LLWL
t
RLRH
PORT 0
PORT 2
1997 Dec 05
t
AVLL
t
LLAX
A0–A7
FROM RI OR DPL
t
AVWL
t
t
t
RLAZ
t
AVDV
P2.0–P2.7 OR A8–A15 FROM DPH A8–A15 FROM PCH
RLDV
t
RHDX
DATA IN A0–A7 FROM PCL INSTR IN
RHDZ
Figure 3. External Data Memory Read Cycle
15
Page 16

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
ALE
t
WHLH
PSEN
WR
PORT 0
PORT 2
INSTRUCTION
ALE
CLOCK
OUTPUT DATA
t
WLWH
t
QVWX
t
DW
DATA OUT A0–A7 FROM PCL INSTR IN
WHQX
t
AVLL
t
t
LLAX
A0–A7
FROM RI OR DPL
t
AVWL
LLWL
t
P2.0–P2.7 OR A8–A15 FROM DPH A8–A15 FROM PCH
Figure 4. External Data Memory Write Cycle
012345678
t
XLXL
t
t
QVXH
XHQX
WRITE TO SBUF
INPUT DATA
CLEAR RI
1997 Dec 05
t
XHDV
VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID
t
XHDX
SET TI
SET RI
Figure 5. Shift Register Mode Timing
16
Page 17

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
V
IH1
0.8V
t
CHCL
t
CLCX
Figure 6. External Clock Drive at XTAL1
t
CLCL
t
CHCX
t
CLCH
VDD–0.5
0.45V
NOTE:
AC INPUTS DURING TESTING ARE DRIVEN AT V
0.45V FOR A LOGIC ‘0’. TIMING MEASUREMENTS ARE MADE AT V
LOGIC ‘1’ AND V
MAX FOR A LOGIC ‘0’.
IL
0.2V
0.2V
DD
DD
+0.9
–0.1
–0.5 FOR A LOGIC ‘1’ AND
DD
Figure 7. AC Testing Input/Output
MIN FOR A
IH
V
+0.1V
V
LOAD
LOAD
V
–0.1V
LOAD
NOTE:
FOR TIMING PURPOSES, A PORT IS NO LONGER FLOATING WHEN A 100MV
CHANGE FROM LOAD VOLTAGE OCCURS, AND BEGINS TO FLOAT WHEN A
100mV CHANGE FROM THE LOADED V
20mA.
TIMING
REFERENCE
POINTS
LEVEL OCCURS. IOH/IOL > +
OH/VOL
Figure 8. Float Waveform
–0.1V
V
OH
V
+0.1V
OL
1997 Dec 05
17
Page 18

Phlips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
(NC)
CLOCK SIGNAL
Figure 9. IDD Test Condition, Active Mode
V
V
DD
RST
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
DD
P0
EA
P1.6
P1.7
All other pins are disconnected
I
DD
V
DD
V
V
DD
*
*
CLOCK SIGNAL
(NC)
Figure 10. I
RST
EA
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
Test Condition, Idle Mode
DD
DD
P1.6
P1.7
V
DD
I
DD
V
DD
P0
*
*
All other pins are disconnected
V
DD
I
DD
V
RST
EA
DD
V
DD
P0
NOTE:
* Ports 1.6 and 1.7 should be connected to V
exceed the I
specification.
OL1
Purchase of Philips I2C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent
to use the components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the
I2C specifications defined by Philips. This specification can be ordered using the
code 9398 393 40011.
(NC)
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
P1.6
P1.7
*
*
Figure 11. IDD Test Condition, Power Down Mode
All other pins are disconnected. V
through resistors of sufficiently high value such that the sink current into these pins does not
CC
= 2V to 5.5V
DD
1997 Dec 05
18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
DIP40: plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil) SOT129-1
1997 Dec 05
19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
PLCC44: plastic leaded chip carrier; 44 leads SOT187-2
1997 Dec 05
20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
QFP44: plastic quad flat package; 44 leads (lead length 1.3 mm); body 10 x 10 x 1.75 mm SOT307-2
1997 Dec 05
21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
80C652/83C652CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers
Data sheet status
Data sheet
status
Objective
specification
Preliminary
specification
Product
specification
Product
status
Development
Qualification
Production
Definition
This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for product development.
Specification may change in any manner without notice.
This data sheet contains preliminary data, and supplementary data will be published at a later date.
Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make chages at any time without notice in order to
improve design and supply the best possible product.
This data sheet contains final specifications. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make
changes at any time without notice in order to improve design and supply the best possible product.
[1]
[1] Please consult the most recently issued datasheet before initiating or completing a design.
Definitions
Short-form specification — The data in a short-form specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the same type number and title. For
detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition — Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one
or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or
at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Application information — Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips
Semiconductors make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
Disclaimers
Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury . Philips Semiconductors customers using or selling these products for use in such applications
do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes — Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the products, including circuits, standard
cells, and/or software, described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or performance. Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, and makes no representations or warranties that these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work right infringement, unless
otherwise specified.
Philips Semiconductors
811 East Arques Avenue
P.O. Box 3409
Sunnyvale, California 94088–3409
Telephone 800-234-7381
Copyright Philips Electronics North America Corporation 1998
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
Date of release: 06-98
Document order number: 9397 750 04047
1997 Dec 05
22
 Loading...
Loading...