Page 1
VRE402
Precision
Dual Reference
DESCRIPTION
FEATURES
The VRE402 is a low cost, high precision, ±2.5V
reference. Packaged in 14 pin DIP or SMT
packages, the device is ideal for new designs that
need a high performance reference.
The device provides ultrastable ±2.500V output
with ±0.250 mV (.01%) initial accuracy and a
temperature coefficient of 0.6 ppm/°C. This
improvement in accuracy is made possible by a
unique, patented multipoint laser compensation
technique developed by Thaler Corporation.
Another key feature of this reference is the 0.3 mV
maximum tracking error between the positive and
negative output voltages over the operating
temperature range. This is extremely important in
high performance systems for reducing overall
system errors.
For designs which use the DIP package in a
socket, there is a reference ground pin to
eliminate reference ground errors.
The VRE402 is recommended for use as a
reference for high precision A/D and D/A
converters which require an external precision
reference. The device is ideal for calibrating
scale factor on high resolution A/D converters.
The VRE402 offers superior performance over
monolithic references.
• ±2.500 V OUTPUT ± 0.250 mV (.01%)
• TEMPERATURE DRIFT: 0.6 ppm/°C
• LOW NOISE: 1.5µVpp (0.1-10Hz)
• TRACKING ERROR: 0.2 mV max.
• EXCELLENT LINE REGULATION: 6ppm/V Typ.
• SURFACE MOUNT AND DIP PACKAGES
FIGURE 1
VRE402DS REV. A MAY 1996
SELECTION GUIDE
Model
Temp.
Range
°C
Temp.
Coeff.
ppm/
°C
VRE402A 0.25 0.6 0°C to +70°C
VRE402B 0.40 1.0 0°C to +70°C
VRE402C 0.50 2.0 0°C to +70°C
VRE402J 0.25 0.6 -40°C to +85°C
VRE402K 0.40 1.0 -40°C to +85°C
VRE402L 0.50 2.0 -40°C to +85°C
For package option add D for DIP or S for Surface
Mount to end of model number.
Initial
Error
mV
THALER CORPORATION • 2015 N. FORBES BOULEVARD • TUCSON, AZ. 85745 • (520) 882-4000
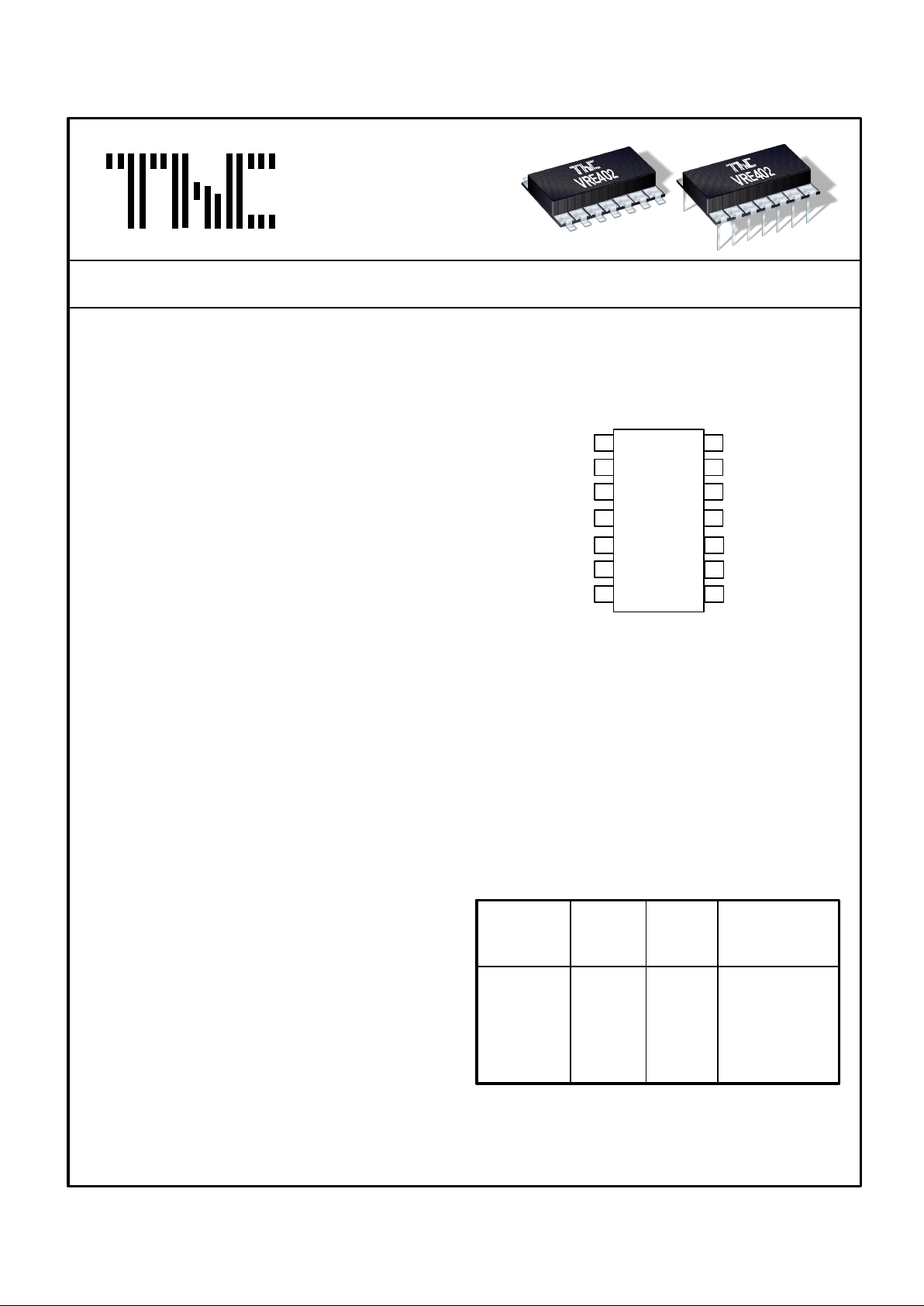
11
12
13
14
VRE402
TOP
VIEW
1
2
3
4
N/C
+V
IN
GND
REF. GND
+V
OUT
PIN CONFIGURATION
5
6
7
10
9
8
- V
OUT
N/C
- V
IN
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
Page 2
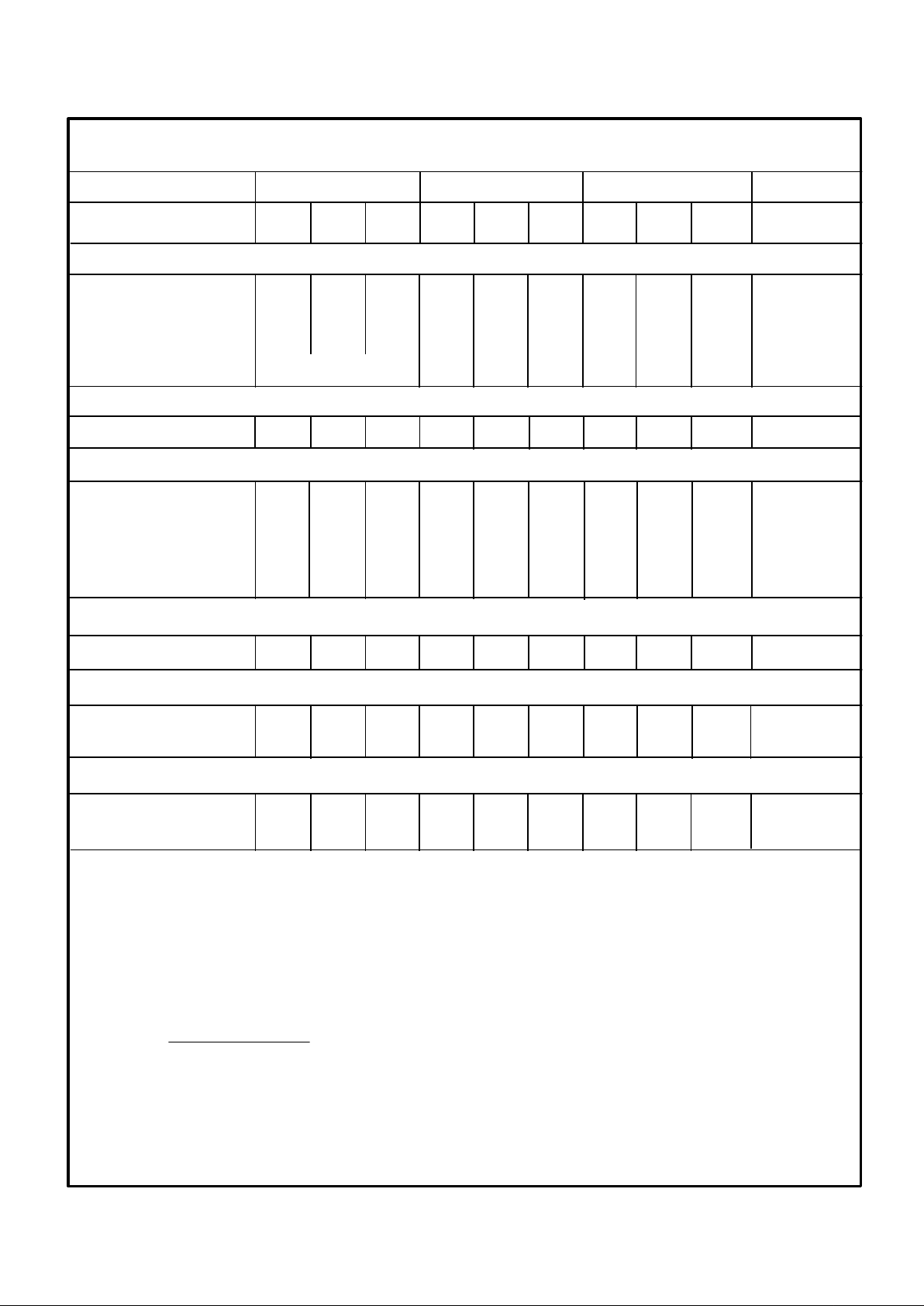
MODEL A/J B/K C/L
PARAMETER MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX UNITS
ABSOLUTE RATINGS
Power Supply ±13.5 ±15 ±22 * * * * * * V
Operating Temp. (A,B,C) 0 +70 * * * * °C
Operating Temp. (J,K,L) -40 +85 * * * * °C
Storage Temperature -65 +150 * * * * °C
Short Circuit Protection Continuous * *
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
VRE402 ±2.5 * * V
OUTPUT VOLTAGE ERRORS
Initial Error 0.25 0.40 0.50 mV
Warmup Drift 1 2 3 ppm
T
min
- T
max
0.6 1.0 2.0 ppm/ °C
Tracking Error 0.2 0.3 0.4 mV
Long-Term Stability 6 * * ppm/1000hrs
Noise (.1-10Hz) 1.5 * * µVpp
OUTPUT CURRENT
Range ±10 * * mA
REGULATION
Line 3 10 * * * * ppm/V
Load 3 * * ppm/mA
POWER SUPPLY CURRENTS
+PS 7 9 * * * * mA
-PS 4 6 * * * * mA
VRE402
NOTES: *Same as A/J Models.
1. The specified values are without external trim.
2. The temperature coefficient (tc) is determined by the
box method using the following formula:
V
max
- V
min
tc = x 10
6
V
nominal
x (T
max-Tmin
)
3. The tracking error is the deviation between the
positive and negative output over the operating temp.
range.
(1)
(4)
(2)
(3)
VRE402DS REV. A MAY 1996
Vps =±15V, T = 25°C, RL = 10KΩ unless otherwise noted.
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
4. The specified values are unloaded.
Page 3

TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
VRE402DS REV. A MAY 1996
QUIESCENT CURRENT VS. TEMP
Temperature oC
JUNCTION TEMP. RISE VS. OUTPUT CURRENT
Output Current (mA)
PSRR VS. FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
QUIESCENT CURRENT VS. TEMP
Temperature oC
JUNCTION TEMP. RISE VS. OUTPUT CURRENT
Output Current (mA)
PSRR VS. FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
Temperature oC
VRE402A
V
OUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
Temperature oC
VRE402B
V
OUT
vs. TEMPERATUREV
OUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
Temperature oC
VRE402C
Temperature oC
VRE402J
V
OUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
Temperature oC
VRE402K
V
OUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
Temperature oC
VRE402L
V
OUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
POSITIVE OUTPUT (TYP)
NEGATIVE OUTPUT (TYP)
Page 4

DISCUSSION OF PERFORMANCE
VRE402DS REV. A MAY 1996
VRE402
FIGURE 2
THEORY OF OPERATION
The following discussion refers to the schematic in
figure 2 below. A FET current source is used to bias
a 6.3V zener diode. The zener voltage is divided by
the resistor network R1 and R2. This voltage is then
applied to the noninverting input of the operational
amplifier which amplifies the voltage to produce a
2.500V output. The gain is determined by the
resistor networks R3 and R4: G=1 + R4/R3. The
6.3V zener diode is used because it is the most
stable diode over time and temperature.
The current source provides a closely regulated
zener current, which determines the slope of the
references’ voltage vs. temperature function. By
trimming the zener current a lower drift over
temperature can be achieved. But since the voltage
vs. temperature function is nonlinear this
compensation technique is not well suited for wide
temperature ranges.
Thaler Corporation has developed a nonlinear
compensation network of thermistors and resistors
that is used in the VRE series voltage references.
This proprietary network eliminates most of the
nonlinearity in the voltage vs. temperature function.
By adjusting the slope, Thaler Corporation produces
a very stable voltage over wide temperature ranges.
This network is less than 2% of the overall network
resistance so it has a negligible effect on long term
stability.
The VRE402 reference has it’s ground brought out
on two pins (pin 6 and 7) which are connected
internally. This allows the user to achieve greater
accuracy when using a socket. Voltage references
have a voltage drop across their power supply
ground pin due to quiescent current flowing through
the contact resistance. If the contact resistance was
constant with time and temperature, this voltage
drop could be trimmed out. When the reference is
plugged into a socket, this source of error can be as
high as 20ppm. By connecting pin 7 to the power
supply ground and pin 6 to a high impedance
ground point in the measurement circuit, the error
due to the contact resistance can be eliminated. If
the unit is soldered into place, the contact
resistance is sufficiently small that it does not effect
performance.
Page 5

DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A .114 .136 2.90 3.45 E .410 .435 10.4 11.0
B .018 .027 .460 .690 E1 .390 .415 9.91 10.5
B1 .047 .056 1.19 1.42 E2 .265 .270 6.73 6.86
B2 .097 .103 2.46 2.62 G1 .285 .315 7.24 8.00
C .009 .020 0.22 0.51 L .195 .225 4.95 5.72
D .690 .715 17.5 18.1 P .090 .110 2.29 2.79
D 1 .666 .680 16.9 17.2 Q .050 .070 1.27 1.79
S .040 .060 1.02 1.52
INCHES MILLIMETER
INCHES MILLIMETER
VRE402DS REV. A MAY 1996
MECHANICAL
FIGURE 4
FIGURE 3
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A .114 .136 2.90 3.45 E .495 .526 12.5 13.3
B .098 .103 2.48 2.62 E1 .390 .415 9.91 10.5
B1 .047 .056 1.19 1.42 E2 .265 .270 6.73 6.86
C .103 .118 2.62 3.00 P .090 .110 2.29 2.79
C1 .009 .020 0.22 0.51 Q .024 .035 0.61 .890
C2 .054 .062 1.37 1.57 S .040 .060 1.02 1.52
D .690 .715 17.5 18.1
D1 .666 .680 16.9 17.2
INCHES MILLIMETER
INCHES MILLIMETER
 Loading...
Loading...