Page 1
US1176
7.5A ULTRA LOW DROPOUT POSITIVE
ADJUSTABLE REGULATOR WITH SHUTDOWN INPUT
PRELIMINARY DATASHEET
FEATURESFEATURES
Guaranteed <TBDV Dropout at 7.5A
Fast Transient Response
1% Voltage Reference Initial Accuracy
Built-in Thermal Shutdown
APPLICATIONSAPPLICATIONS
3.3V to 2.7V Intel I740 chip set.
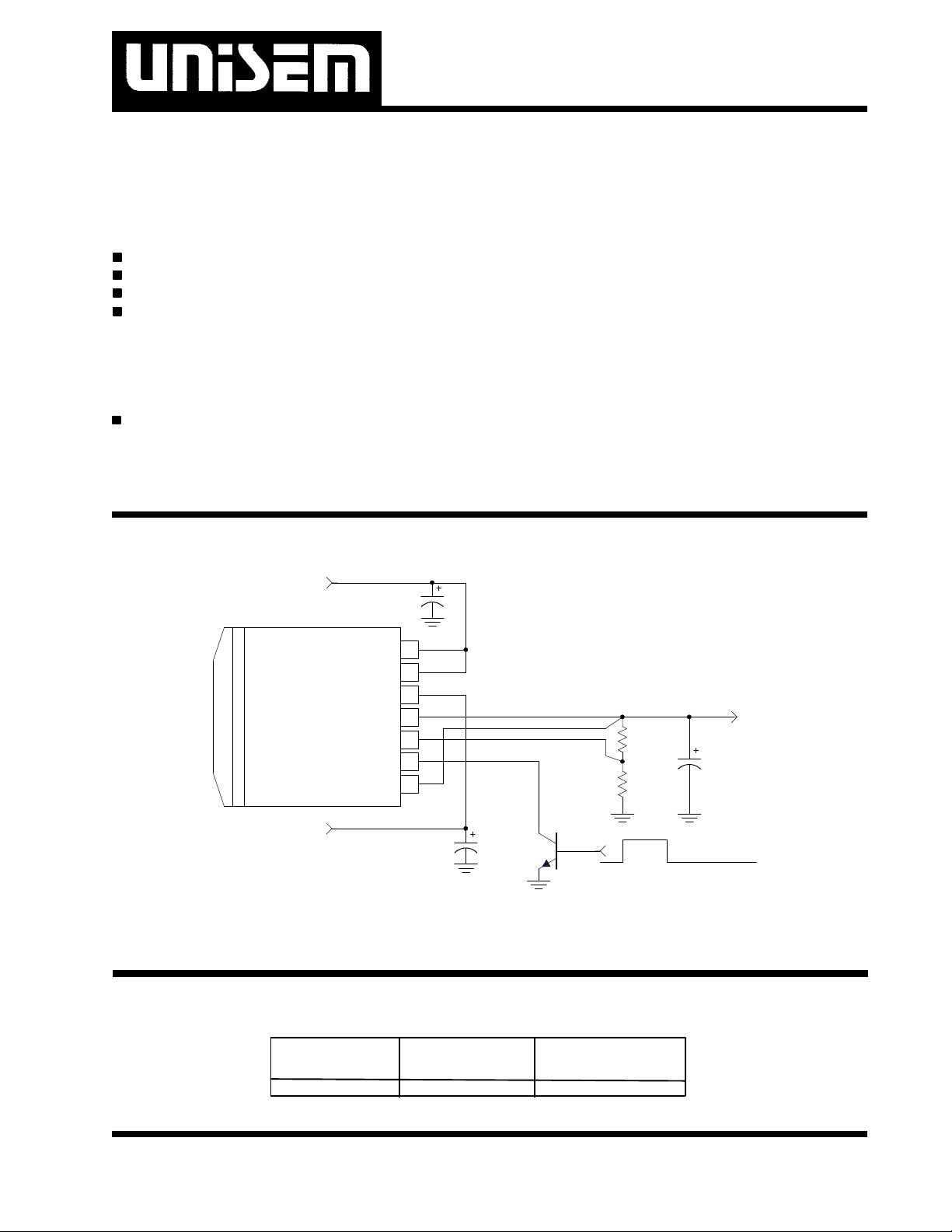
TYPICAL APPLICATIONTYPICAL APPLICATION
3.3V
US1176
Vin
Vin
Vctrl
Vout
Adj
SD
Vsense
C1
DESCRIPTIONDESCRIPTION
The US1176 product is a 7.5A regulator with extremely
low dropout voltage using a proprietary Bipolar process that achieves comparable equivalent on resistance to that of discrete MOSFETs. The US1176
also provides a convenient Shutdown pin that allows the
regulator to be shutdown and reduce the input current
consumption. Unlike the PNP type regulators this device does not have high quiecent current during the start
up mode making it ideal for applications where there is
limited current capability such operation from the 5V
Standby supply of the computer power supply.One application is the new generation of the RDRAM memory
that needs to provide 2.5V from 3.3V input and be able
to operate from 5VSB as well.
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
R1
R2
2.7V
C3
1176app1-1.1
5V
Typical application of US1176 .
C2
Q1
SD Enable
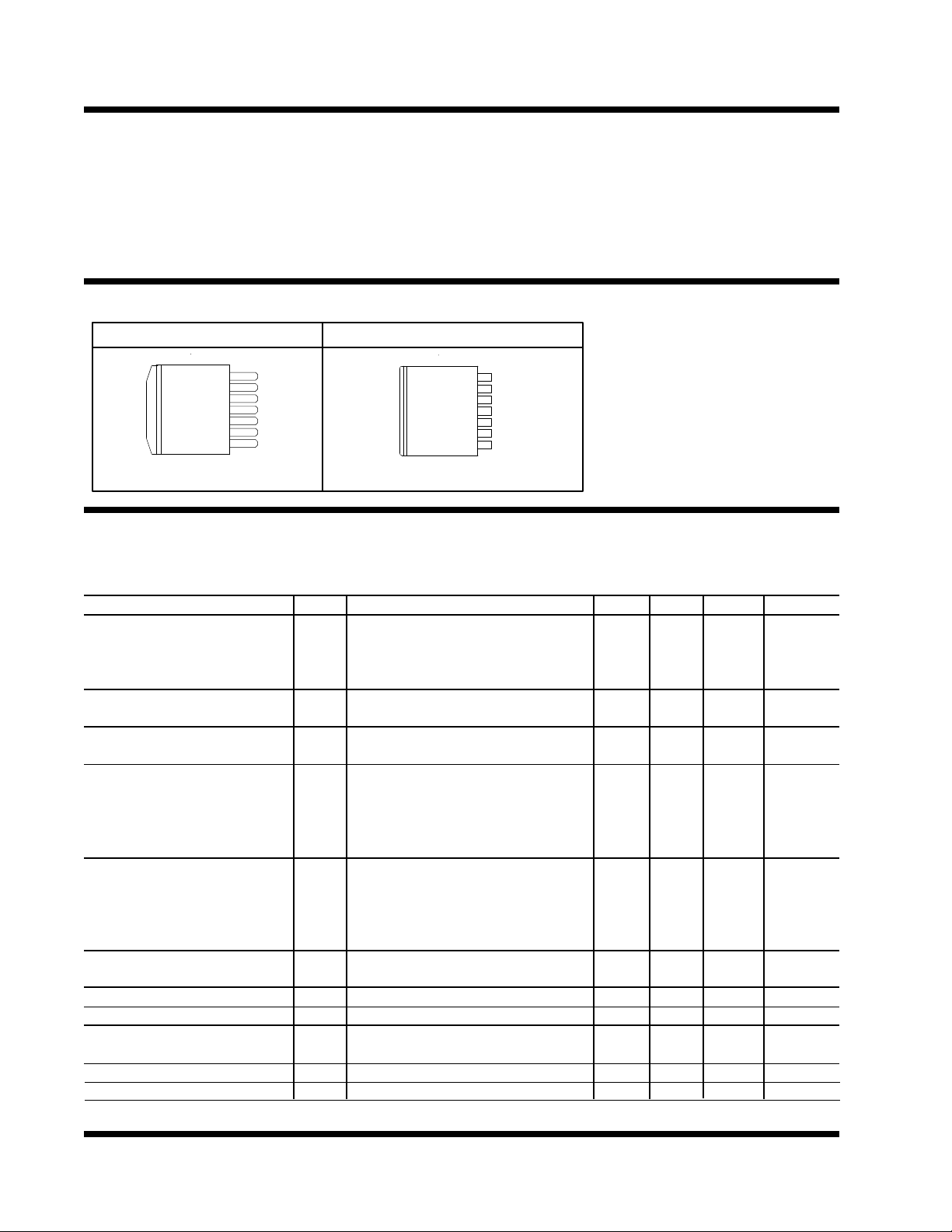
PACKAGE ORDER INFORMATIONPACKAGE ORDER INFORMATION
Tj (°C) 7 PIN PLASTIC 7 PIN PLASTIC
TO263 (M) POWER FLEX (P)
0 TO 125 US1176CM US1176CP
Rev. 1.1
9/24/99
2-1
Page 2
US1176
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGSABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Input Voltage (Vin) ........................................................... 7V
Control Input Voltage (Vctrl) .................................................. 14V
Power Dissipation............................................. Internally Limited
Storage Temperature Range ................................... -65°C TO 150°C
Operating Junction Temperature Range ..................... 0°C TO 150°C
PACKAGE INFORMATIONPACKAGE INFORMATION
7 PIN PLASTIC TO263 ( M ) 7 PIN PLASTIC POWER FLEX (P)
FRONT VIEW
7
Vin
6
Vin
5
Vctrl
4
Vout
3
Adj
2
SD
1
Vsense
θJA=35°C/W for 0.5" square pad θJA=35°C/W for 0.5" square pad
FRONT VIEW
7
Vin
6
Vin
5
Vctrl
4
Vout
3
Adj
2
SD
1
Vsense
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONSELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Unless otherwise specified ,these specifications apply over ,Cin=1uF,Cout=10uF, and Tj=0 to 125°C.Typical
values refer to Tj=25°C. Vout=Vsense.
PARAMETER SYM TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Reference Voltage Vref Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2V,Io=10mA 1.243 1.250 1.257 V
Tj=25,Vadj=0V
Vctrl=2.7to12V,Vin=2.05V to 5.5V, 1.237 1.250 1.263
Io=10mA to 7.5A,Vadj=0V
Line Regulation Vctrl=2.5Vto7V,Vin=1.75Vto5.5V
,Io=10mA ,Vadj=0V 0.5 mV
Load Regulation (note 1) Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.1V,Io=10mA
to 7.5A,Vadj=0V 5 mV
Dropout Voltage (note 2) Vadj=0V for all conditions below.
(Vctrl - Vout) Vin=2.05V,Io=1.5A 0.95 V
Vin=2.05V,Io=3A 1.00
Vin=2.05V,Io=4A 1.05
Vin=2.05V,Io=7.5A 1.15
Dropout Voltage (note 2) Vadj=0V for all conditions below.
(Vin - Vout) Vctrl=2.75V,Io=1.5A 0.075 V
Vctrl=2.75V,Io=3A 0.150
Vctrl=2.75V,Io=4A 0.200
Vctrl=2.75V,Io=7.5A 0.375
Current Limit Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.05V,
dVo=100mV Vadj=0V 7.7 9 A
Minimum Load Current (note 3) Vctrl=5V,Vin=3.3V,Vadj=0V, 5 10 mA
Thermal Regulation 30 mS Pulse 0.01 0.02 %/W
Ripple Rejection Vctrl=5V,Vin=5V,Io=4A,Vadj=0V 60 70 dB
Tj=25,Vripple=1Vpp at 120Hz
S.D Threshold Voltage Vctrl - 1.4 Vctrl - 2.2 V
S.D Input Current Vctrl=5V, S.D=0V 94 130 uA
2-2
Rev. 1.1
9/24/99
Page 3

US1176
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONSELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
PARAMETER SYM TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Control Pin Current Vadj=0V for all below conditions.
Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.05V,Io=1.5A mA
Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.05V,Io=3A
Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.05V,Io=4A
Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.05V,Io=7.5A
Adjust Pin Current Iadj Vctrl=2.75V,Vin=2.05V,Vadj=0V, 50 120 uA
Note 1 : Low duty cycle pulse testing with Kelvin connections are required in order to maintain accurate data.
Note 2 : Drop-out voltage is defined as the minimum
differential between Vin and Vout required to maintain
regulation at Vout. It is measured when the output voltage drops 1% below its nominal value.
PIN DESCRIPTIONSPIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN # PIN SYMBOL
1 Vsense
2 S.D
3 Adj
4 Vout
5 Vctrl
6,7 Vin
PIN DESCRIPTION
This pin is the positive side of the reference which allows remote load sensing
to achieve excellent load regulation.
When this pin is pulled lower than 1.4V with respect to the Vctrl pin the device is shutdown.
To enable the operation leave this pin open. Internal to device, there is a pull up resistor.
A resistor divider from this pin to the Vout pin and ground sets the output voltage.
The output of the regulator. A minimum of 10uF capacitor must be connected from this
pin to ground to insure stability.
This pin is the supply pin for the internal control circuitry as well as the base drive for
the pass transistor.This pin must always be higher than the Vout pin in order for
the device to regulate.(see specifications)
The input pin of the regulator. Typically a large storage capacitor is connected from this
pin to ground to insure that the input voltage does not sag below the minimum drop
out voltage during the load transient response. This pin must always be higher than
Vout in order for the device to regulate.(see specifications)
Note 3 : Minimum load current is defined as the minimum current required at the output in order for the output voltage to maintain regulation. Typically the resistor
dividers are selected such that it automatically maintains this current.
Rev. 1.1
9/24/99
2-3
Page 4

US1176
BLOCK DIAGRAMBLOCK DIAGRAM
Vin
Vctrl
CURRENT
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
SD
+
LIMIT
OUTPUT
SHUTDOWN
Figure 1 - Simplified block diagram of the US1176
APPLICATION INFORMATIONAPPLICATION INFORMATION
Introduction
The US1176 adjustable regulator is a 5 terminal device
designed specificaly to provide extremely low dropout
voltages comparable to the PNP type without the disadvantage of the extra power dissipation due to the base
current associated with PNP regulators.This is done by
bringinging out the control pin of the regulator that provides the base current to the power NPN and connecting it to a voltage that is grater than the voltage present
at the Vin pin.This flexebility makes the US1176 ideal
for applications where dual inputs are available such as
a computer motherboard with an ATX style power supply that provides 5V and 3.3V to the board.One such
application is the new graphic chip sets that require anywhere from 2.4V to 2.7V supply such as the Intel I740
chip set. The US1176 can easily be programmed with
the addition of two external resistors to any voltages
within the range of 1.25 to 5.5 V. Another major requirement of these graphic chips is the need to switch the
load current from zero to several amps in tens of nanoseconds at the processor pins ,which translates to an
approximately 300 to 500 nS of current step at the regulator . In addition, the output voltage tolerances are also
extremely tight and they include the transient response
as part of the specification.
Vout
Vsense
1.25V
1176blk1-1.0
+
Adj
The US1176 is specifically designed to meet the fast
current transient needs as well as providing an accurate
initial voltage , reducing the overall system cost with the
need for fewer number of output capacitors.Another feature of the device is its true remote sensing capability
which allows accurate voltage setting at the load rather
than at the device.
Output Voltage Setting
The US1176 can be programmed to any voltages in the
range of 1.25V to 5.5V with the addition of R1 and R2
external resistors according to the following formula:
R
2
V V
OUT REF ADJ
= +
Wehre : V V Typically
I lly
ADJ
=50 uA Typica
R in figure
1 2
& R as shown
Vin
Vctrl
REF
= .
Vin
Vctrl
R
1
125
US1176
SD
Open
+ ×1
I R
Vout
Vsense
Adj
IAdj = 50uA
2
Vref
2
Vout
R1
R2
1176app2-1.0
2-4
Figure 2 - Typical application of the US1176 for
programming the output voltage.
Rev. 1.1
9/24/99
Page 5

US1176
The US1176 keeps a constant 1.25V between the Vsense
pin and the Vadj pin. By placing a resistor R1 across
these two pins and connecting the Vsense and Vout pin
together , a constant current flows through R1, adding
to the Iadj current and into the R2 resistor producing a
voltage equal to the (1.25/R1)*R2 + Iadj*R2 .This voltage
is then added to the 1.25V to set the output voltage.
This is summarized in the above equation. Since the
minimum load current requirement of the US1176 is 10
mA , R1 is typically selected to be a 121Ω resistor so
that it automatically satisfies this condition. Notice that
since the Iadj is typically in the range of 50uA it only
adds a small error to the output voltage and should be
considered when very precise output voltage setting is
required.
Load Regulation
Since the US1176 has separate pins for the output (Vout)
and the sense (Vsense), it is ideal for providing true remote sensing of the output voltage at the load.This
means that the voltage drops due to parasitic resistance
such as PCB traces between the regulator and the load
are compensated for using remote sensing. Figure 3
shows a typical application of the US1176 with remote
sensing.
Adj
Vout
Vsense
1176app3-1.0
R1
R2
R
L
Vin
Vctrl
Vin
US1176
Vctrl
Figure 3 - Schematic showing connection for best
load regulation
Stability
The US1176 requires the use of an output capacitor as
part of the frequency compensation in order to make the
regulator stable. Typical designs for the microprocessor applications use standard electrolytic capacitors with
typical ESR in the range of 50 to 100 mΩ and an output
capacitance of 500 to 1000uF. Fortunately as the capacitance increases, the ESR decreases resulting in a
fixed RC time constant. The US1176 takes advantage of
this phenomena in making the overall regulator loop
stable.
For most applications a minimum of 100uF aluminum
electrolytic capacitor such as Sanyo, MVGX series
,Panasonic FA series as well as the Nichicon PL series
insures both stability and good transient response.
Shutdown Operation
The US1176 can be disabled by pulling the S.D pin low
using an open collector device such as a low cost 2N3904
general purpose transistor as shown in the application
circuit. The current sink of the pin is equal to:
Isink=(Vctrl-1.4)/R where, R=50 kΩ typ.
Thermal Design
The US1176 incorporates an internal thermal shutdown
that protects the device when the junction temperature
exceeds the allowable maximum junction temperature.
Although this device can operate with junction temperatures in the range of 150°C ,it is recommended that the
selected heat sink be chosen such that during maximum continuos load operation the junction temperature
is kept below this number. The example below shows
the steps in selecting the proper surface mount package.
Assuming, the following conditions:
Vout=2.7V
Vin=3.3V
Vctrl=5V
Iout=2A DC Avg
Calculate the maximum power dissipation using the following equation:
Pd=Iout*(Vin-Vout) + (Iout/60)*(Vctrl - Vout)
Pd=2*(3.3-2.7) + (2/60)*(5-2.7)=1.28 W
Using table below select the proper package and the
amount of copper board needed.
Pkg Copper θJA(°C/W) Max Pd Max Pd
Area (Ta=25°C) (Ta=45°C)
M or P 1.4"X1.4" 25 4.4W 3.6W
M or P 1.0"X1.0" 30 3.7W 3.0W
M or P 0.7"X0.7" 35 3.1W 2.6W
M or P Pad Size 45 2.4W 2.0W
Note: Above table is based on the maximum junction
temperature of 135°C.
As shown in the above table, any of the two packages
will do the job. For lower cost applications the Power
Flex package is recommended.
Rev. 1.1
9/24/99
2-5
 Loading...
Loading...