Page 1
The mark ★ shows major revised points.
DESCRIPTION
The µPD75512(A) is a 4-bit single-chip microcomputer which employs 75X series architecture, and its
performance is comparable to that of an 8-bit microcomputer.
In addition to its high-speed processing capabilities, the
µ
PD75512(A) is also capable of processing data in
units of 1, 4, or in 8-bits. With its internally provided A/D converter and serial interface, the
µ
PD75512(A) provides
the highest performance in its class.
Detailed functions are described in the following user‘s manual. Be sure to read it for designing.
µ
PD75516 User‘s Maual: IEM-5049
FEATURES
• Higher reliability than µPD75512
• Adequate I/O lines: 64
(can be provided with pull-up/pull-down resistors: 47)
• Built-in 8-bit serial interface: 2-ch
NEC standard serial bus interface (SBI) internally provided
• Built-in 8-bit A/D converter: 8-ch
• Variable instruction execution time function which is convenient for high-speed operation and power saving
· 0.95
µ
s/1.95 µs/15.3 µs (at 4.19 MHz operation),
· 122
µ
s (at 32.768 kHz operation)
• Program memory (ROM) size: 12,160 × 8 bits
• Data memory (RAM) size: 512 × 4 bits
• High-performance timer function: 4-ch
· 8-bit timer/event counter
· Watch timer
· 8-bit basic interval timer
· Timer/pulse generator: Capable of outputting 14-bit PWM
• Clock operation for reduced power consumption possible
(5
µ
A TYP. at 3 V operation)
• PROM version (
µ
PD75P516) available
APPLICATIONS
Switable for automotive and transportation equipments, etc.
NEC Corporation 1991
Document No. IC-2815A
(O. D. No. IC-8265A)
Date Published January 1994 P
Printed in Japan
DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD75512(A)
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
4-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER
Page 2
µ
PD75512(A)
2
Electrical
Specifications
Item
Product
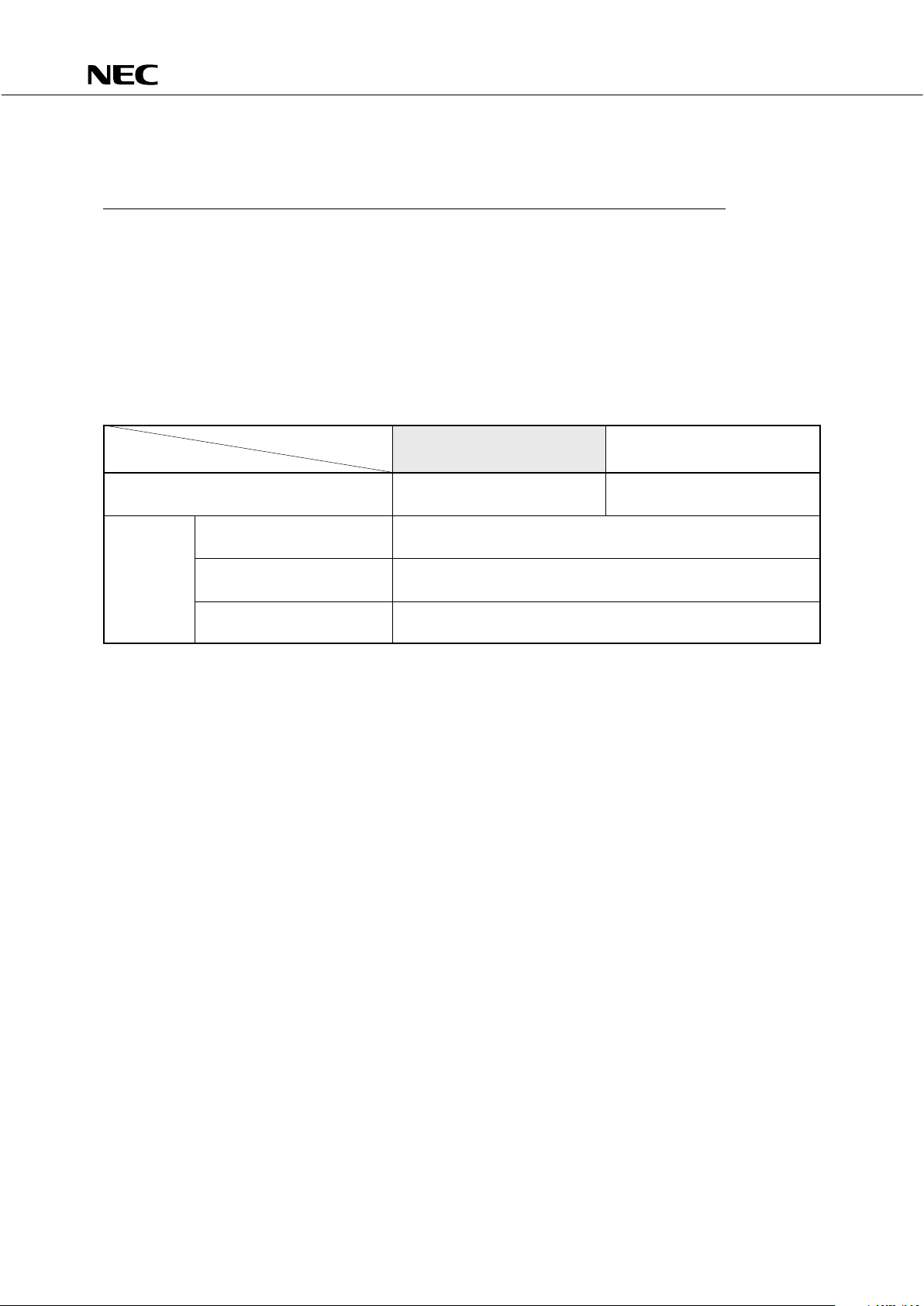
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number Package Quality Grade
µ
PD75512GF(A)-xxx-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP Special
(14 × 20mm)
Remarks: xxx is ROM code number.
Please refer to “Quality Grade on NEC Semiconductor Devices” (Document number IEI-1209) published by NEC
Corporation to know the specification of quality grade on the devices and its recommended applications.
Difference between
µ
PD75512(A) and µPD75512
µ
PD75512(A)
µ
PD75512
Quality Grade Special Standard
Absolute Maximum Ratings Differ in high-level and low-level output current
DC Characteristics Differ in low-level output voltage
A/D Converter Characteristics Differ in ambient temperature range and absolute accuracy
Page 3
µ
PD75512(A)
3
µ
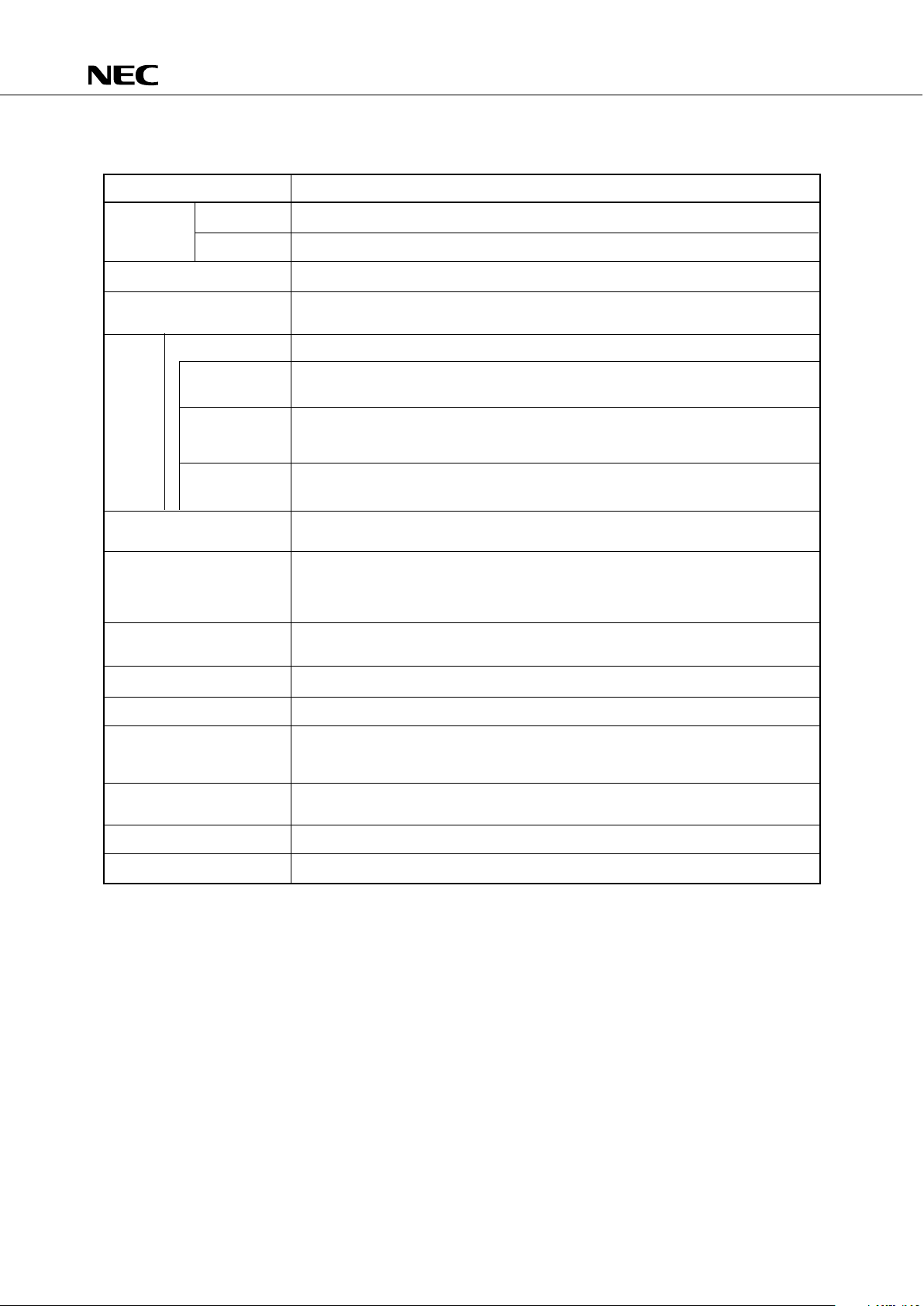
PD75512(A) FUNCTIONS
Item Function
Internal ROM 12160 × 8 bits
Memory
Size RAM 512 × 4 bits
Genearl-Purpose Register (4 bits × 8 or 8 bits × 4) × 4 banks
Instruction Cycle • 0.95 µs/1.91 µs/15.3 µs (Main system clock: at 4.19 MHz)
• 122 µs (Subsystem clock: at 32.768 kHz)
Total 64 lines
CMOS Inputs 16 lines (also serve as INT, SIO, PPO, analog input; can be pulled up by software: 7
lines)
Input/
Output CMOS 28 lines
Ports Input/Outputs • Can be pulled up by software: 16 lines
• Can be pulled down by mask option: 4 lines
N-ch Open-Drain 20 lines (10 V withstand voltage; pins that can be pulled up by mask option: 20)
Input/Outputs
A/D Converter 8-bit resolution × 8 channels (successive approxmation type)
• Operation voltage: VDD = 3.5 to 6.0 V
• Timer/event counter
• Basic interval timer
• Timer/pulse generator (capable of outputting 14-bit PWM)
• Watch timer
• NEC standard serial bus interface (SBI)/3-line SIO: 1 channel
• Normal clock synchronized serial interface (3-line SIO): 1 channel
Vector Interrupt External: 3, Internal: 4
Test Input External: 1, Internal: 1
• Bit data set/reset/test/boolean operation instruction
Instruction Set • 4-bit data transfer/operation/increment/decrement /compare instructions
• 8-bit data transfer/operation/increment/decrement /compare instructions
• Ceramic/crystal oscillator for main system clock: 4.19 MHz
• Crystal oscillator for subsystem clock: 32.768 kHz
Operation Voltage VDD = 2.7 V to 6.0 V
Package 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20mm)
System Clock Generator
Timer/Counter 4 channels
Serial Interface 2 channels
★
Page 4

µ
PD75512(A)
4
CONTENTS
1. PIN CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................................................... 6
2. INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ......................................................................................................... 7
3. PIN FUNCTIONS .............................................................................................................................. 8
3.1 PORT PINS ............................................................................................................................................. 8
3.2 NON-PORT PINS ................................................................................................................................... 10
3.3 PIN INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUITS ............................................................................................................ 11
3.4 RECOMMENDED CONDITIONS FOR UNUSED PINS.......................................................................... 14
3.5 MASK OPTION SELECTION ................................................................................................................. 15
4. MEMORY CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................... 16
5. PERIPHERAL HARDWARE FUNCTIONS ........................................................................................ 19
5.1 PORT ...................................................................................................................................................... 19
5.2 CLOCK GENERATOR CIRCUIT ............................................................................................................. 20
5.3 CLOCK OUTPUT CIRCUIT..................................................................................................................... 21
5.4 BASIC INTERVAL TIMER ...................................................................................................................... 22
5.5 WATCH TIMER ...................................................................................................................................... 23
5.6 TIMER/EVENT COUNTER ..................................................................................................................... 23
5.7 TIMER/PULSE GENERATOR ................................................................................................................. 25
5.8 SERIAL INTERFACE............................................................................................................................... 26
5.9 A/D CONVERTER ................................................................................................................................... 30
5.10 BIT SEQUENTIAL BUFFER ................................................................................................................... 31
6. INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................................ 31
7. STANDBY FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................................... 33
8. RESET FUNCTIONS......................................................................................................................... 34
9. INSTRUCTION SET.......................................................................................................................... 36
10. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................................................... 44
11. PACKAGE DRAWINGS .................................................................................................................... 57
12. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ................................................................................ 58
Page 5

µ
PD75512(A)
5
APPENDIX A. FUNCTIONAL DIFFERENCES AMONG µPD755XX(A) SERIES PRODUCTS ............. 59
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS ................................................................................................ 60
APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS ................................................................................................ 61
Page 6
µ
PD75512(A)
6
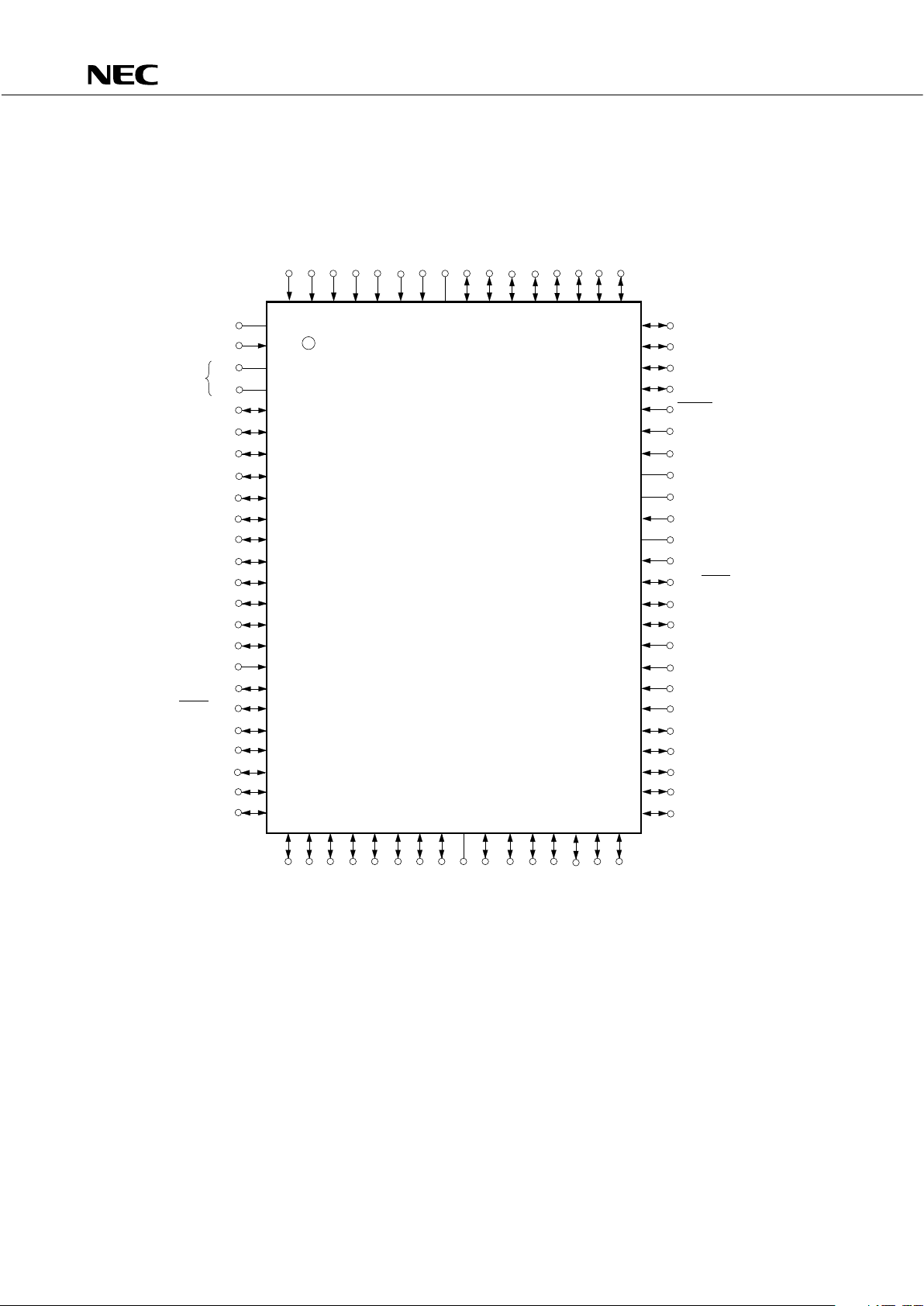
1. PIN CONFIGURATION
IC: Internally Connected (Connect directly to VSS)
*: Power must be supplied to both VDD pins.
AN0
PD75512GF(A)
– –3B9×××
µ
AN4/P150
P120
AV
SS
AN1
1
80
21
22
23
24
25 26
P93
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
64
27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39
40
AN2
AN3
AN5/P151
AN6/P152
AN7/P153
P121
P122
P123
P130
P131
P132
P133
AV
REF
V
DD
V
DD
*
P113
P112
P111
P110
P103
P102
P101
P100
P92
P91
P90
SI1/P83
SO1/P82
SCK1/P81
PPO/P80
KR7/P73
KR6/P72
KR5/P71
KR4/P70
KR3/P63
KR2/P62
KR1/P61
KR0/P60
P53
P52
P51
P50
V
SS
P43
P42
P41
P40
P33
P32
P31
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
P140
P141
P142
P143
RESET
X2
X1
IC
XT2
XT1
V
SS
P00/INT4
P01/SCK0
P02/SO0/SB0
P03/SI0/SB1
P10/INT0
P11/INT1
P12/INT2
P13/TI0
P20/PTO0
P21
P22/PCL
P23/BUZ
P30
79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65
Page 7
µ
PD75512(A)
7
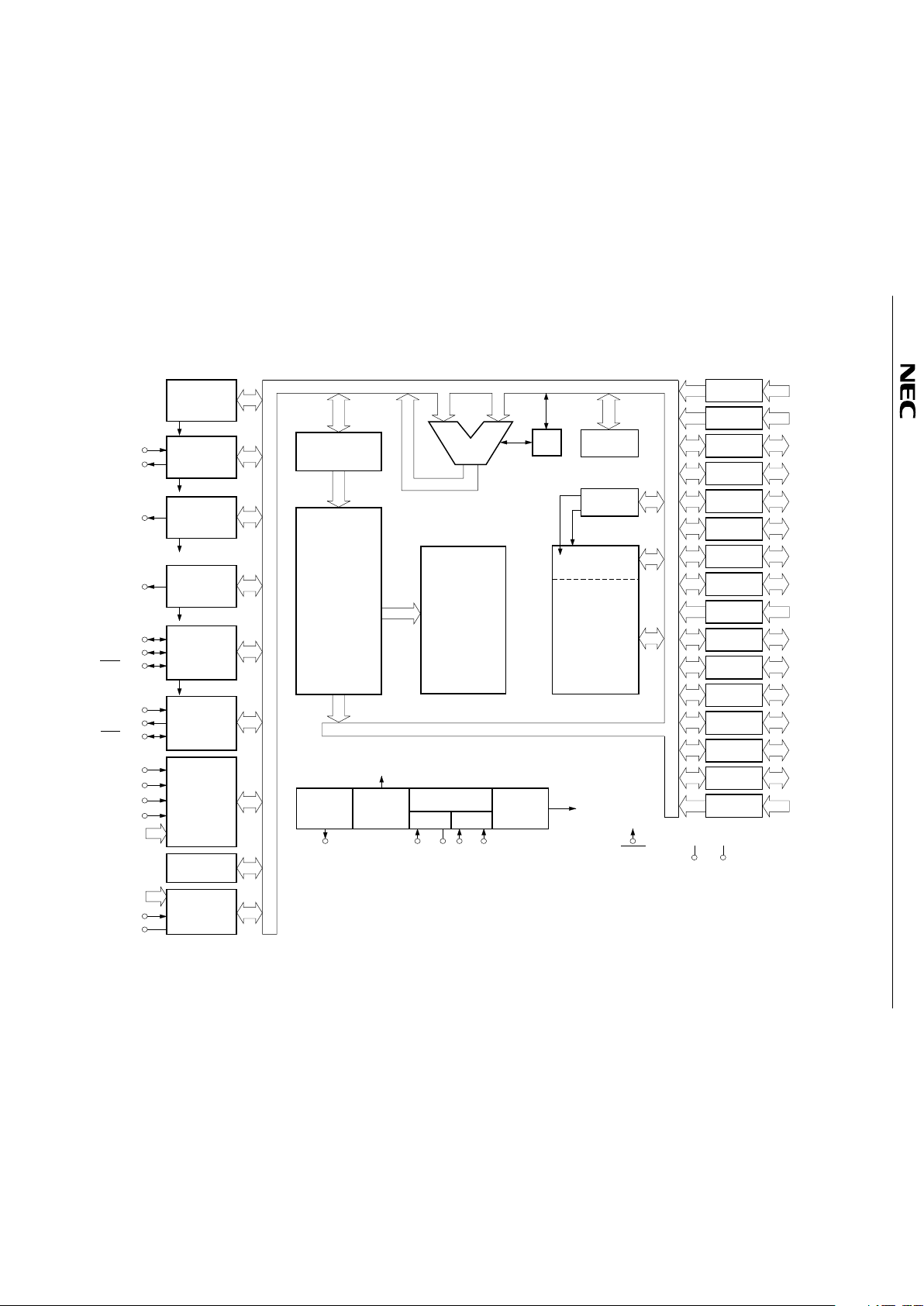
2. INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
PORT 0
PORT 1
PORT 2
PORT 3
PORT 4
PORT 5
PORT 6
PORT 7
PORT 8
PORT 9
PORT10
PORT11
PORT12
PORT13
PORT14
PORT15
44P10-P13
P00-P03
4 P20-P23
4
4 P30-P33
4 P40-P43*
4 P50-P53*
4 P60-P63
4 P70-P73
P80-P83
4 P90-P93
4 P100-P103
4 P110-P113
4 P120-P123*
4 P130-P133*
4 P140-P143*
P150-P153
4
SP (8)
BANK
GENERAL REG.
CY
ALU
PROGRAM
COUNTER (14)
ROM
PROGRAM
MEMORY
12160 × 8 BITS
DECODE
AND
CONTROL
RAM
DATA MEMORY
512 x 4 BITS
TI0/P13
TIMER/EVENT
COUNTER
#0
INTT0
PTO0/P20
BUZ/P23
WATCH
TIMER
INTW
INTCSI
SERIAL
INTERFACE0
SI0/SB1/P03
SO0/SB0/P02
SCK0/P01
INT0/P10
INT1/P11
INT2/P12
INT4/P00
KR0/P60
–KR7/P73
8
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
BIT SEQ.
BUFFER (16)
BASIC
INTERVAL
TIMER
INTBT
PPO/P80
TIMER/PULSE
GENERATOR
INTTPG
SERIAL
INTERFACE1
SI1/P83
SO1/P82
SCK1/P81
A/D
CONVERTER
AV
REF
AV
SS
AN0-AN3
AN4
/P150-AN7/P15
f /2
X
N
VDDV
SS
RESET
PCL/P22 XT1 XT2 X1 X2
SUB MAIN
CLOCK
OUTPUT
CONTROL
CLOCK
DIVIDER
CLOCK
GENERATOR
STAND BY
CONTROL
CPU CLOCK
4
Φ
*: PORTs 4, 5, and 12 to 14 are 10 V middle voltage, N-ch open-drain input/output ports.
Page 8
µ
PD75512(A)
8
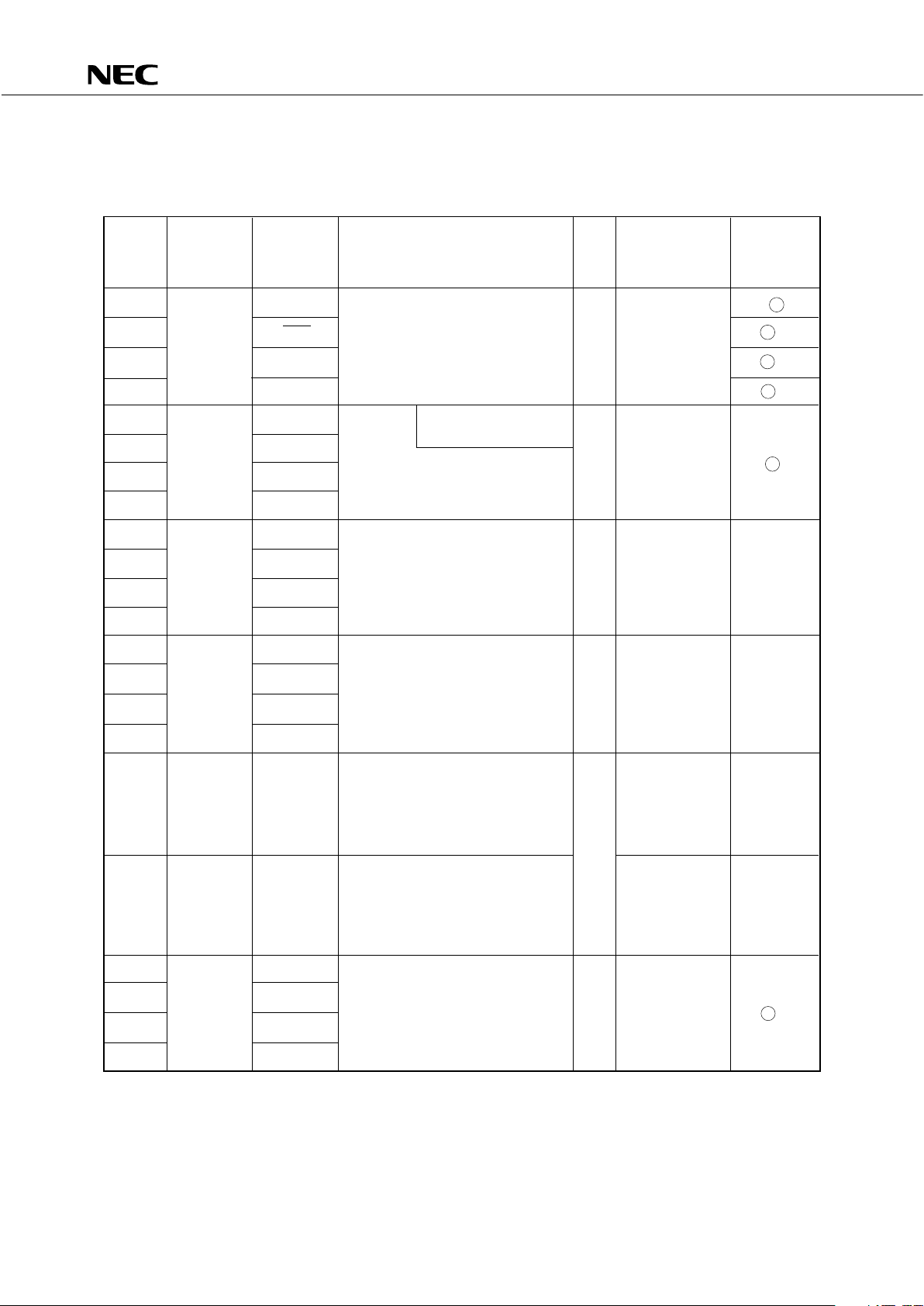
3. PIN FUNCTIONS
3.1 PORT PINS (1/2)
Input/
Pin Input/ Shared Function 8-bit When Reset Output
Name Output Pin I/O Circuit
Type*
P00 INT4 4-bit input port (PORT0). B
For P01 to P03, built-in pull-up
P01 SCK0 resistors can be specified in 3-bit F -A
Input units by software. x Input
P02 SO0/SB0 F -B
P03 SI0/SB1 M -C
P10 INT0 With noise
elimination function
P11 INT1
Input 4-bit input port (PORT1). x Input B -C
P12 INT2 Built-in pull-up resistors can be
specified by software in 4-bit units.
P13 TI0
P20 PTO0
4-bit input/output port (PORT2).
P21 Input/ — Built-in pull-up resistors can be
output specified by software in 4-bit units. x Input E-B
P22 PCL
P23 BUZ
P30 — Programmable 4-bit input/output
port (PORT3).
P31 Input/ — Input/output can be specified in
output bit units. x Input E-C
P32 — Built-in pull-up resistors can be
specified by software in 4-bit unit.
P33 —
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output High level
port (PORT4). (when pull-up
P40 to Input/ — A pull-up resistor can be provided resistor is M
P43 output in bit units (mask option). provided) or
10V withstanding voltage in the high impedance
open-drain mode.
O
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output High level
port (PORT5). (when pull-up
P50 to Input/ — A pull-up resistor can be provided resistor is M
P53 output in bit units (mask option). provided) or
10V withstanding voltage in the high impedance
open-drain mode.
P60 KR0 Programmable 4-bit input/ output
port (PORT6).
P61 Input/ KR1 Input/output can be specified in
output bit units. O Input F -C
P62 KR2 Built-in pull-up resistors can be
specified by software in 4-bit units.
P63 KR3
*: The number enclosed with a circle indicates Schmitt trigger input.
Page 9
µ
PD75512(A)
9
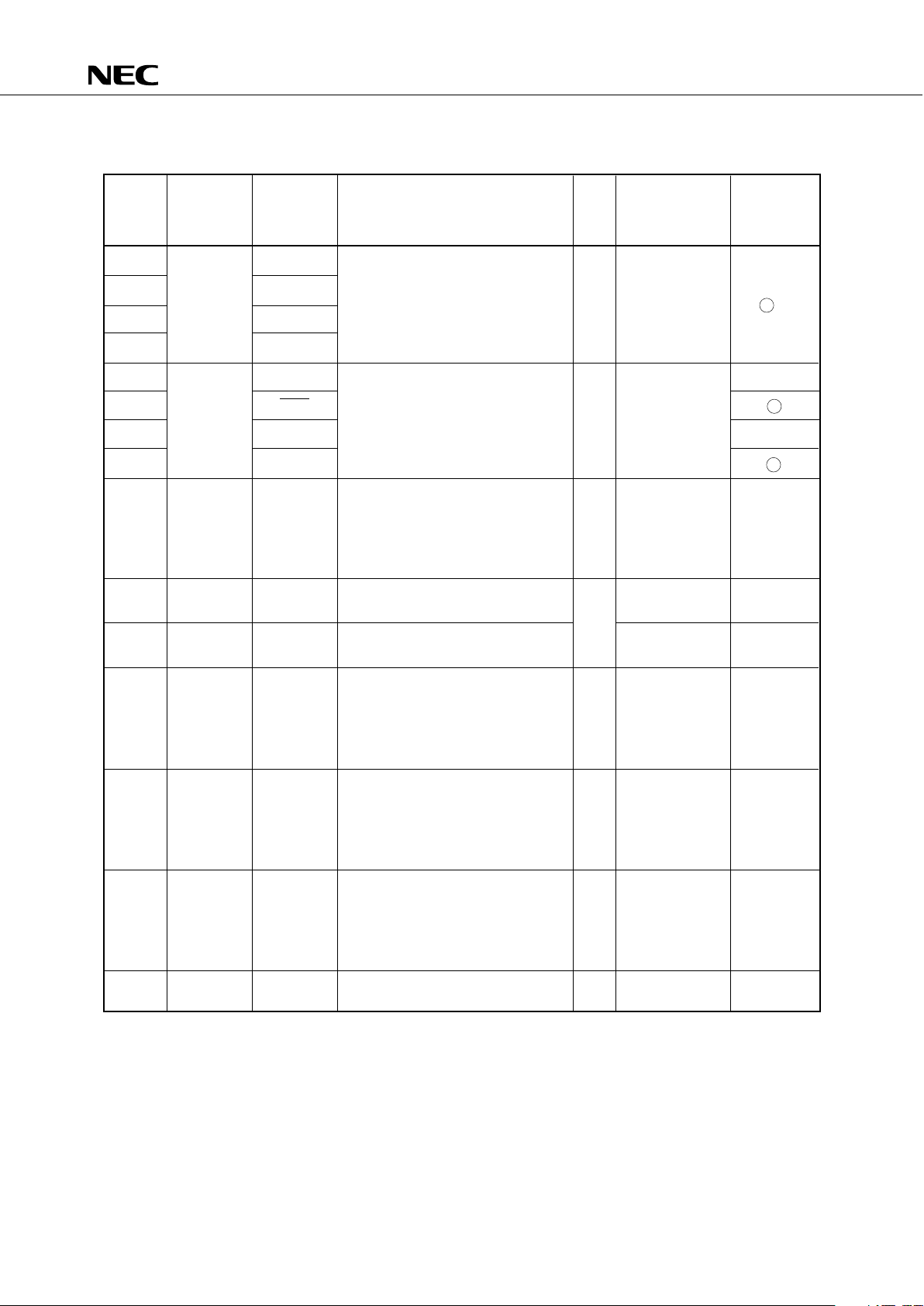
3.1 PORT PINS (2/2)
Input/
Pin Input/ Shared Function 8-bit When Reset Output
Name Output Pin I/O Circuit
Type*
P70 KR4
4-bit input/output port (PORT7).
P71 Input/ KR5 Built-in pull-up resistor can be
output specified in 4-bit units by software. O Input F -A
P72 KR6
P73 KR7
P80 PPO E
P81 SCK1 F
Input 4-bit input port (PORT8). x Input
P82 SO1 E
P83 SI1 B
Low level
4-bit input/output port (PORT9). (when pullP90 to Input/ — Built-in pull-up resistors can be x down resistor V
P93 output specified in bit units by mask is provided)
option. or high
impedance
P100 to Input/ — 4-bit input/output port (PORT10). Input E
P103 output
x
P110 to Input/ — 4-bit input/output port (PORT11). Input E
P113 output
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output High level
port (PORT12). (when pull-up
P120 to Input/ — A pull-up resistor can be provided resistor is M
P123 output in bit units (mask option). x provided) or
10V withstanding voltage in the high impedance
open-drain mode.
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output High level
port (PORT13). (when pull-up
P130 to Input/ — A pull-up resistor can be provided x resistor is M
P133 output in bit units (mask option). provided) or
10V withstanding voltage in the high impedance
open-drain mode.
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output High level
port (PORT14). (when pull-up
P140 to Input/ — A pull-up resistor can be provided x resistor is M
P143 output in bit units (mask option). provided) or
10V withstanding voltage in the high impedance
open-drain mode.
P150 to Input AN4 to AN7 4-bit input port (PORT15). x Input Y-A
P153
*: The number enclosed with a circle indicates Schmitt trigger input.
Page 10
µ
PD75512(A)
10
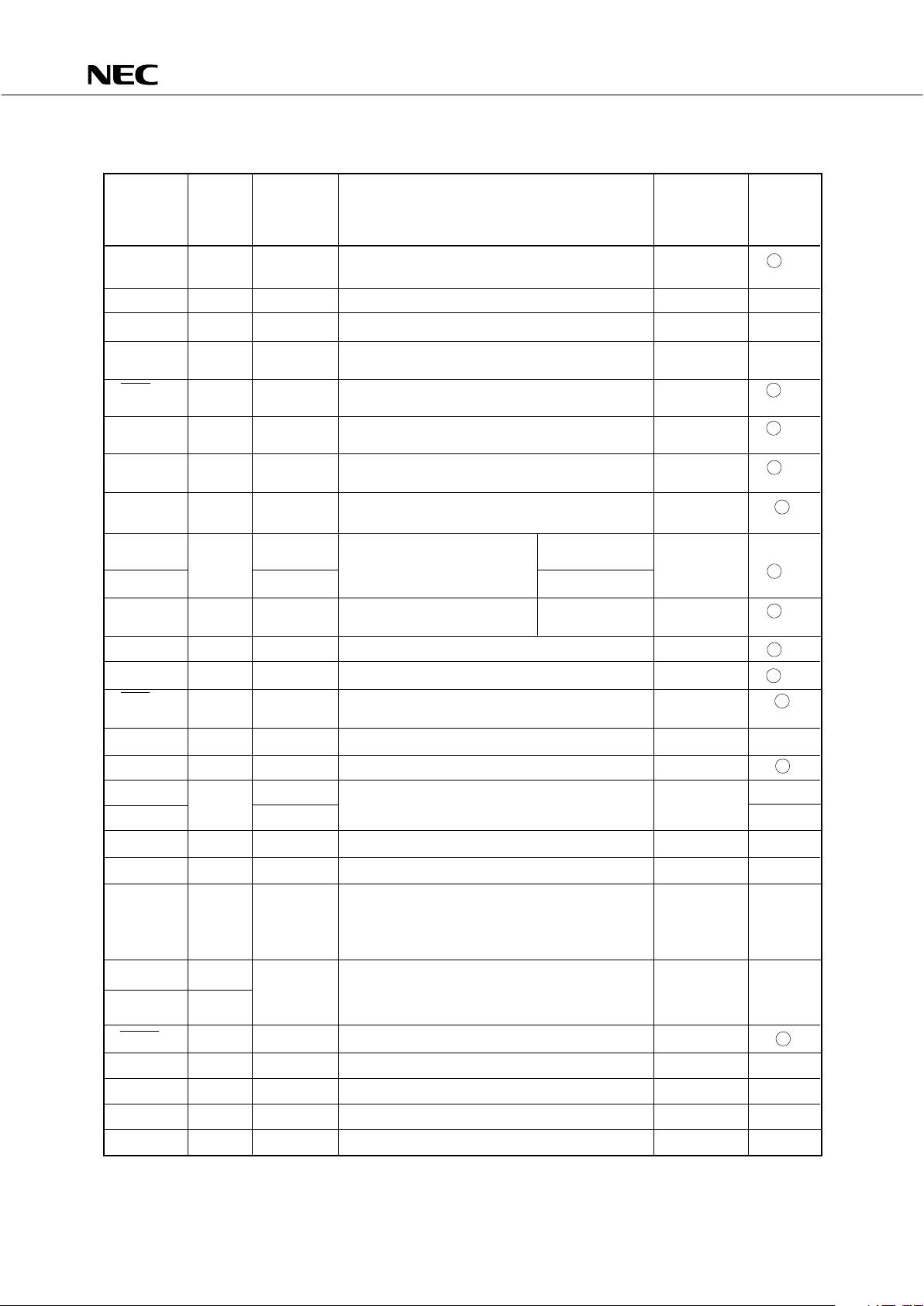
3.2 NON-PORT PINS
Input/
Pin Input/ Shared Function When Reset Output
Name Output Pin Circuit
Type*
TI0 Input P13 The external event pulse input for the timer/event — B -C
counter.
PTO0 Output P20 Timer/event counter output Input E-B
PCL Output P22 Clock output Input E-B
BUZ Output P23 Fixed frequency output (for buzzer output or Input E-B
system clock trimming)
SCK0 Input/ P01 Serial clock input/output Input F -A
output
SO0/SB0 Input/ P02 Serial data output Input F -B
output Serial bus input/output
SI0/SB1 Input/ P03 Serial data input Input M -C
output Serial bus input/output
INT4 Input P00 Edge detection vector interrupt input (both rising — B
edge and falling edge detection)
INT0 P10 Edge detection vector Synchronized
interrupt input with clock
Input (detection edge selectable) — B -C
INT1 P11 Asynchronous
INT2 Input P12 Edge detection testable input Asynchronous — B -C
(rising edge detection)
KR0-KR3 Input P60-P63 Parallel falling edge detection testable input Input F -C
KR4-KR7 Input P70-P73 Parallel falling edge detection testable input Input F -A
SCK1 Input/ P81 Serial clock input/output Input F
output
SO1 Output P82 Serial data output Input E
SI1 Input P83 Serial data input Input B
AN0-AN3 — Y
Input A/D converter analog input —
AN4-AN7 P150-P153 Y-A
AVREF Input — A/C converter reference voltage input — Z
AVSS — — A/D converter reference ground — —
Pins for connecting the crystal ceramic oscillator
to the main system clock generator. When
X1, X2 Input — inputting the external clock, input the external — —
clock to pin X1, and the reverse phase of the
external clock to pin X2.
XT1 Input Pins for connecting the crystal oscillator to the
— subsystem clock generator. When the external — —
clock is used, inputs the external clock to pin
XT1. In this case, pin XT2 must be left open.
RESET Input — System reset input — B
PPO Output P80 Timer/pulse generator pulse output Input E
IC — — Internally Connected. Connect directly to VSS.——
VDD — — Positive power supply — —
VSS — — GND — —
*: The number enclosed with a circle indicates Schmidt trigger input.
XT2 —
Page 11
µ
PD75512(A)
11
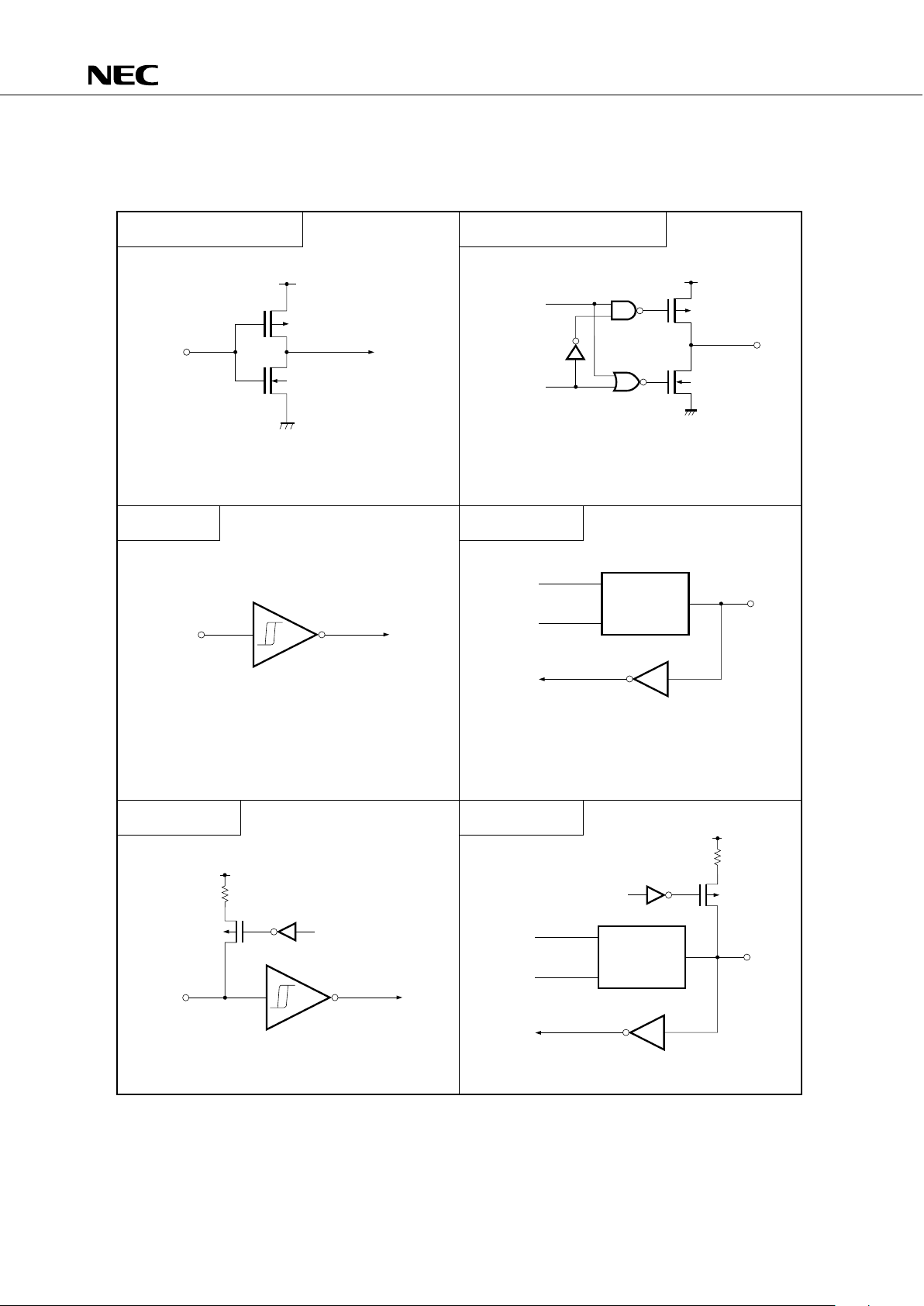
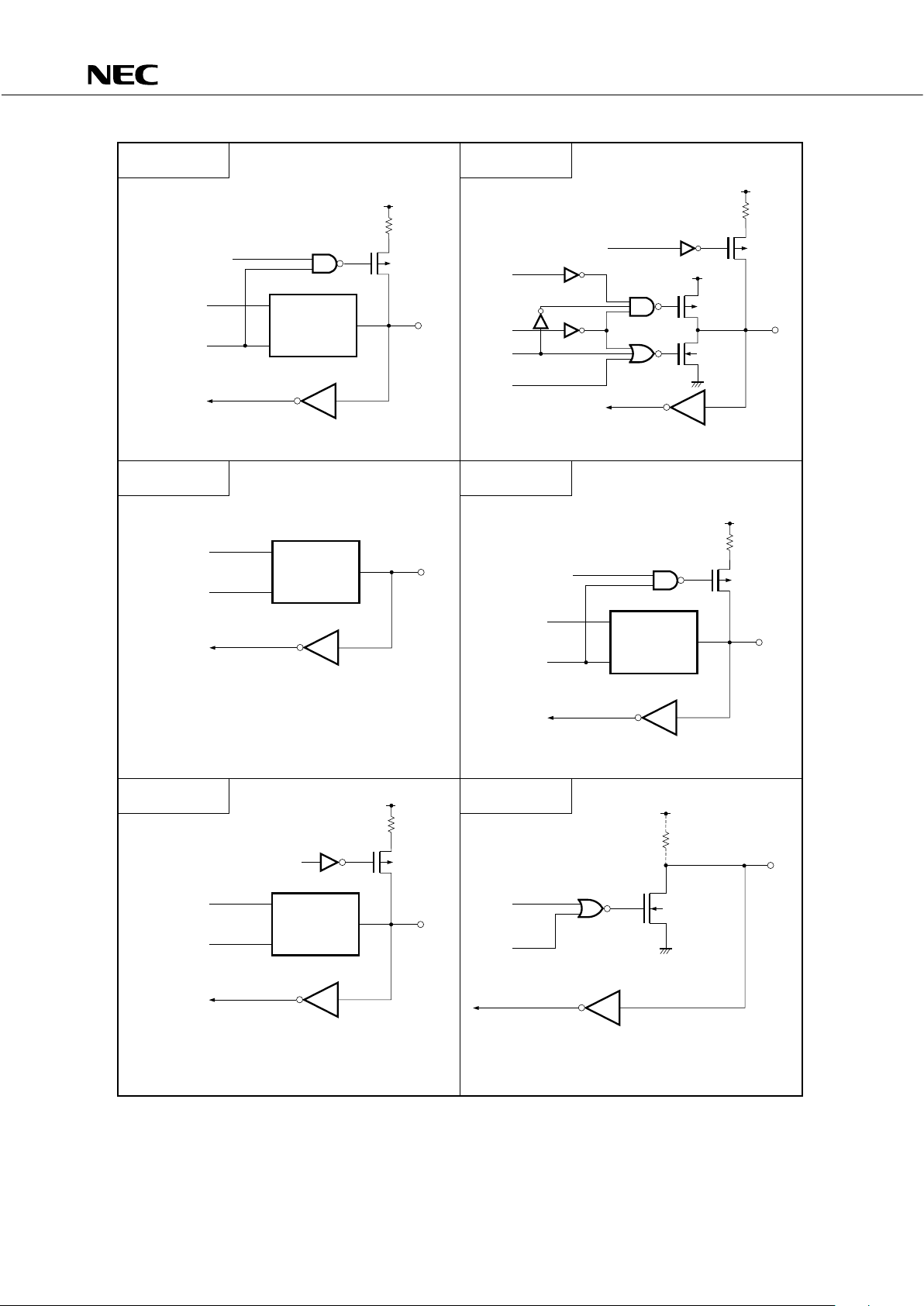
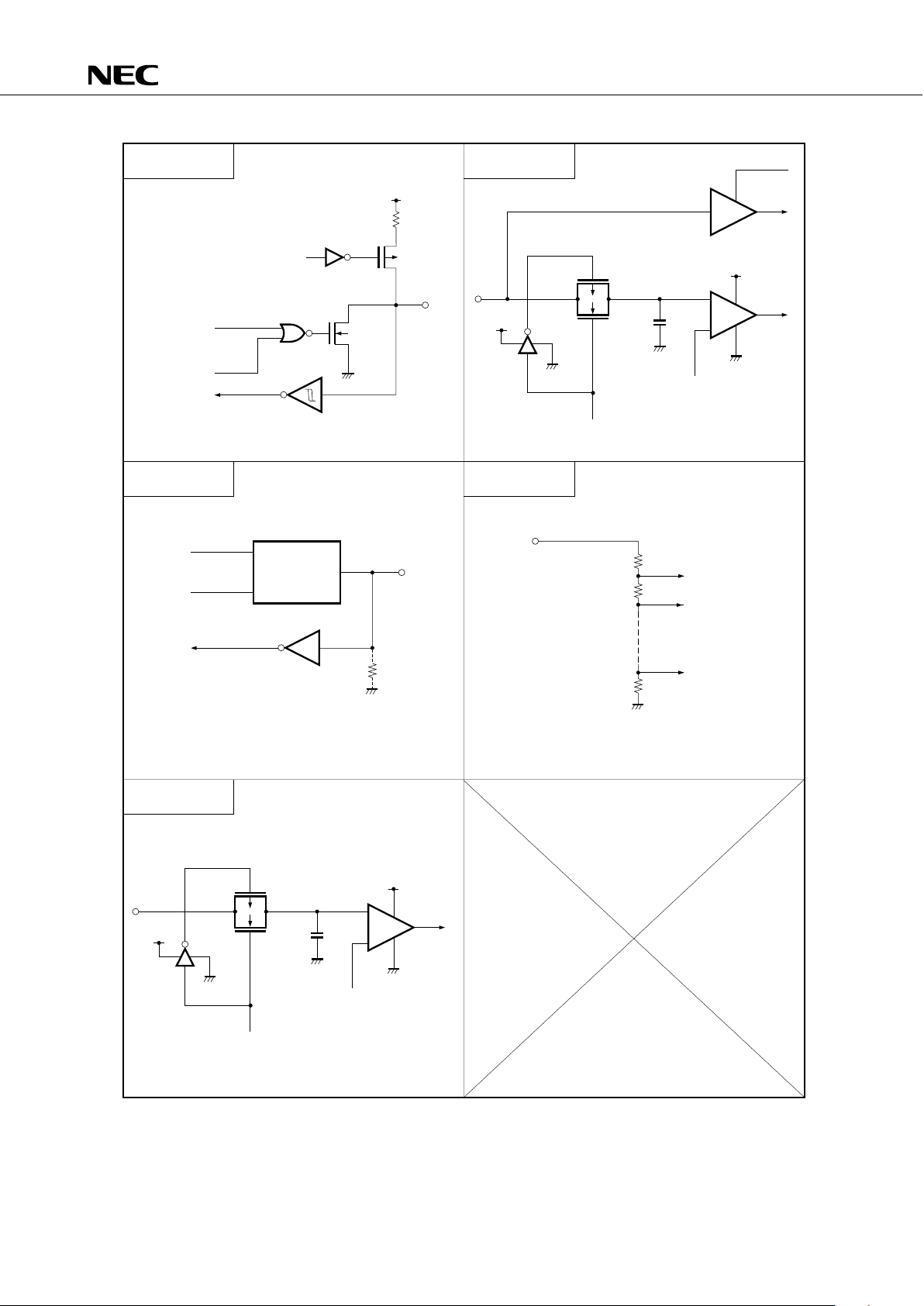
3.3 PIN INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUITS
The following shows a simplified input/output circuit diagram for each pin of the
µ
PD75512(A).
TYPE A
TYPE D
TYPE B
TYPE E
IN
V
DD
Input buffer of CMOS standard
data
output
disable
OUT
P–ch
N–ch
Push-pull output that can be set in a output
high-impedance state (both P-ch and N-ch are off)
IN
Schmitt trigger input with hysteresis characteristics
data
output
disable
Type D
Type A
IN/OUT
This input/output circuit consists of D-type push-pull
outputs and Type A input buffers.
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
TYPE B–C
TYPE E
–
B
IN
data
output
disable
Type D
Type A
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
IN/OUT
Schmitt trigger input with hysteresis characteristics
VDD
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P–ch
N–ch
Fig. 3-1 Pin Input/Output Circuits (1/3)
Page 12
µ
PD75512(A)
12
Type E-C
data
output
disable
Type D
Type A
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
IN/OUT
Type F-B
data
output
disable
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
N-ch
P-ch
output
disable
(P-ch)
output
disable
(N-ch)
V
DD
IN/OUT
Type B
Type F Type F-C
data
output
disable
Type D
Type B
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
IN/OUT
data
output
disable
Type D
Type B
IN/OUT
This input/output circuit consists of D-type push-pull
outputs and Type B Schmitt trigger inputs.
Type F-A Type M
data
output
disable
V
DD
P.U.R.
IN/OUT
N-ch
Middle-voltage input buffer
(can withstand up to +10 V)
data
output
disable
Type D
Type B
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
IN/OUT
(can withstand
up to +10 V)
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
(Mask Option)
Fig. 3-1 Pin Input/Output Circuits (2/3)
Page 13
µ
PD75512(A)
13
Type M-C
Type Y-A
Type V
Type Z
data
output
disable
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
IN/OUT
P–ch
N-ch
N–ch
IN
P–ch
AV
SS
V
DD
V
DD
AV
SS
Sampling
C
+
–
input
enable
Reference voltage
(from a voltage tap of series
resistor string)
IN instruction
data
output
disable
Type D
Type A
IN/OUT
AV
AV
SS
Reference voltage
REF
P.D.R
(Mask Option)
N–ch
IN
P–ch
AV
SS
V
DD
V
DD
AV
SS
Sampling
C
+
–
Input
enable
Reference voltage
(from a voltage tap of series
resistor string)
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.D.R. : Pull-Down Resistor
Type Y
Fig. 3-1 Pin Input/Output Circuits (3/3)
Page 14
µ
PD75512(A)
14
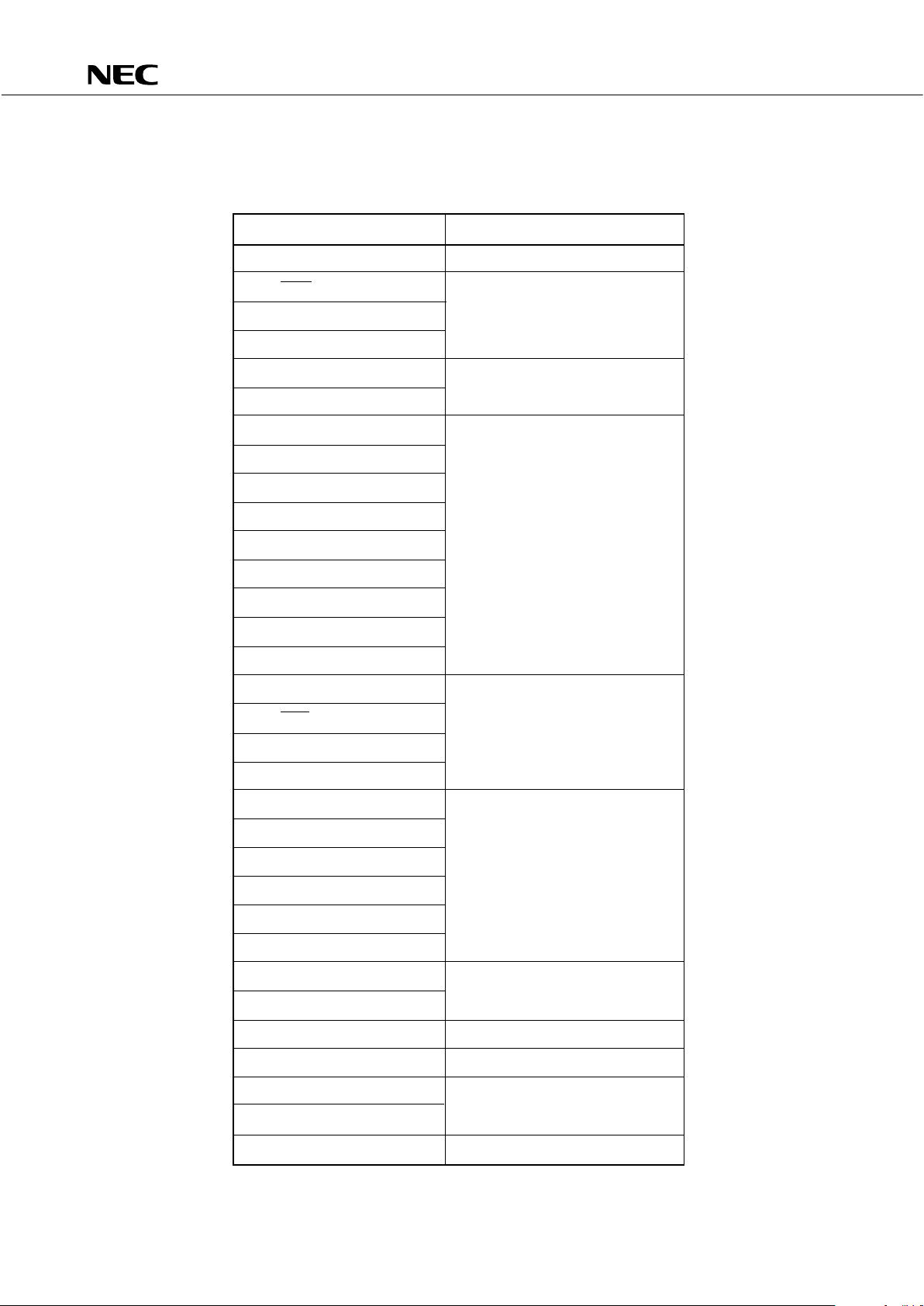
3.4 RECOMMENDED CONDITIONS FOR UNUSED PINS
Table 3-1 Recommended Conditions for Unused Pins
Pin Recommended Conditions
P00/INT4 Connect to VSS
P01/
SCK0
P02/SO0/SB0 Connect to VSS or VDD
P03/SI1/SB1
P10/INT0-P12/INT2
Connect to VSS
P13/TI0
P20/PTO0
P21
P22/PCL
P23/BUZ
Input state: Connect to VSS or VDD
P30-P33
Output state: Open
P40-P43
P50-P53
P60/KR0-P63/KR3
P70/KR4-P73/KR7
P80/PPO
P81/
SCK1
Connect to VSS or VDD
P82/SO1
P83/SI1
P90-P93
P100-P103
P110-P113 Input state: Connect to VSS or VDD
P120-P123 Output state: Open
P130-P133
P140-P143
P150/AN4-P153/AN7
Connect to VSS
AN0-AN3
XT1 Connect to VSS or VDD
XT2 Open
AVREF
Connect to VSS
AVSS
IC Connect directly to VSS
★
Page 15
µ
PD75512(A)
15
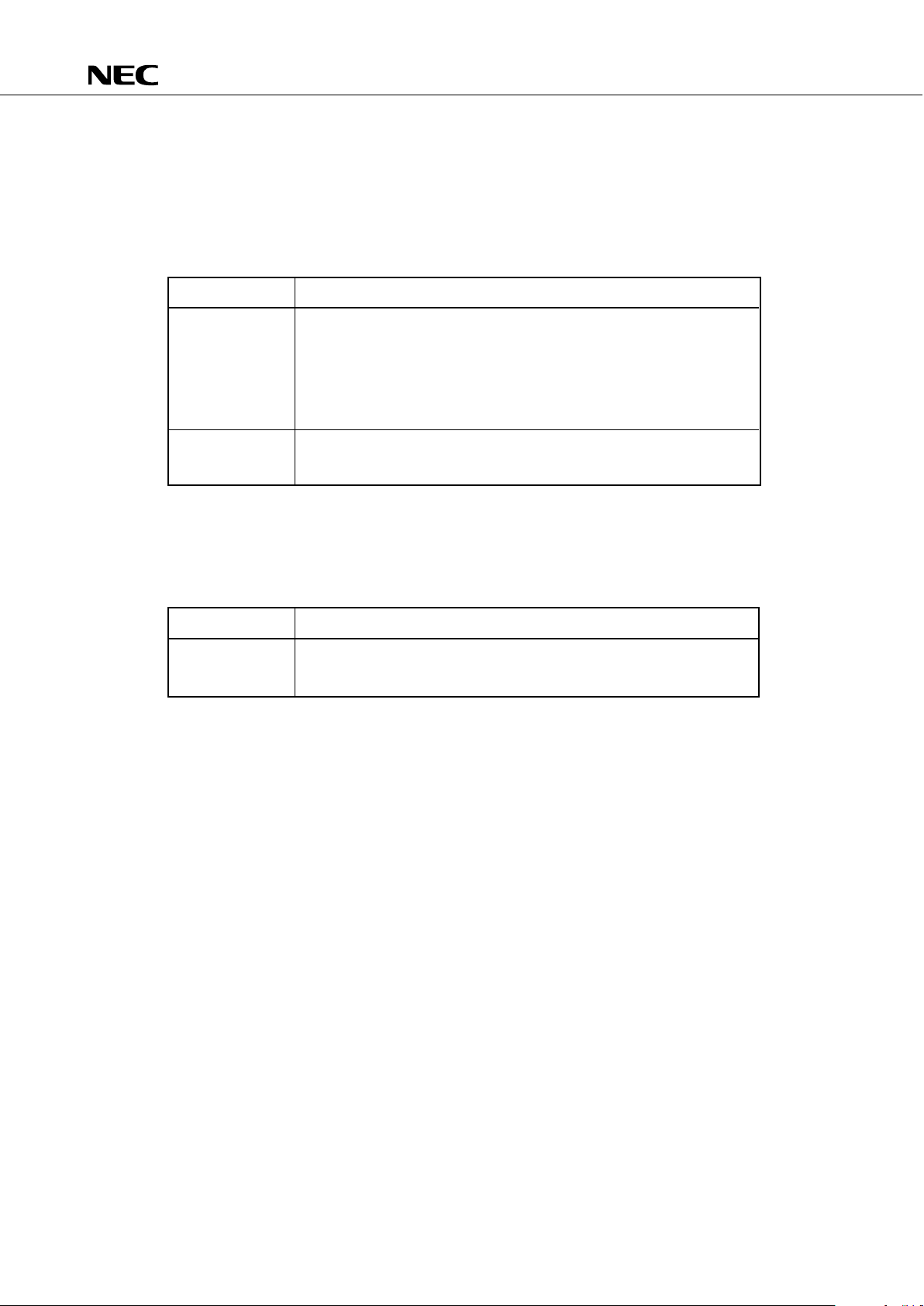
3.5 MASK OPTION SELECTION
The following mask options are provided with the pins.
(1) Pull-up/pull-down resistor selection
Table 3-2 Pull-up/Pull-down Resistor Selection
Pins Mask Option
P40-P43 (1) With pull-up resistor (2) Without pull-up resistor
P50-P53 (Can be specified in bit units) (Can be specified in bit units)
P120-P123
P130-P133
P140-P143
P90-P93 (1) With pull-down resistor (2) Without pull-down resistor
(Can be specified in bit units) (Can be specified in bit units)
(2) Feedback resistor selection for the subsystem clock oscillation
Table 3-3 Feedback Resistor Selection
Pins Mask Option
XT1, XT2 (1) With feedback resistor (2) Without feedback resistor
(When the subsystem clock (When the subsystem clock
is used) is not used)
Note: The operation is not affected if the feedback resistor is selected when the subsystem
clock is not used. However, the supply current I
DD is increased.
★
Page 16

µ
PD75512(A)
16
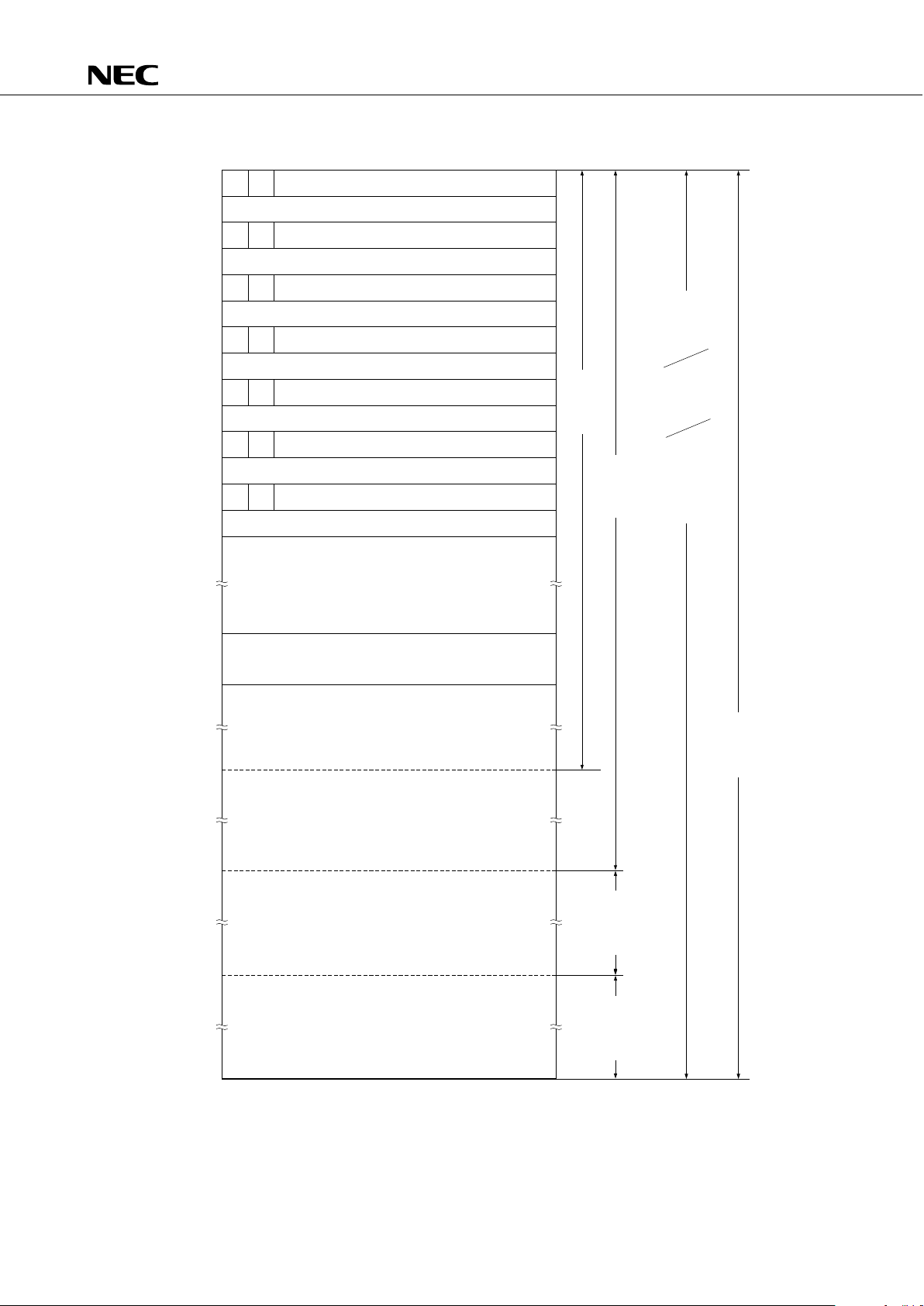
4. MEMORY CONFIGURATION
• Program memory (ROM) ... 12160 × 8 bits (0000H-2F7FH)
• 0000H, 0001H : Vector table to which address from which program is started is written after reset
• 0002H-000DH : Vector table to which address from which program is started is written after
interrupt
• 0020H-007FH: Table area referenced by GETI instruction
• Data memory
• Data area .... 512 × 4 bits (000H–1FFH)
• Peripheral hardware area .... 128 × 4 bits (F80H–FFFH)
★
Page 17
µ
PD75512(A)
17
76
MBE
MBE
MBE
MBE
MBE
MBE
Internal reset start address (upper 6 bits)
Internal reset start address (lower 8 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (lower 8 bits)
INT0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
INT1 start address (upper 6 bits)
INT1 start address (lower 8 bits)
INTCSIO0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTCSIO0 start address (lower 8 bits)
INTT0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
0000H
0002H
0004H
0006H
0008H
000AH
0020H
007FH
0080H
007FH
0800H
0FFFH
1000H
1FFFH
GETI instruction reference table
0
CALLF
!faddr
instruction
entry
address
Address
2000H
2F7FH
BRCB
!caddr
instruction
branch
address
BRCB
!caddr
instruction
branch
address
RBE
RBE
RBE
RBE
RBE
RBE
MBE
INTTPG start address (upper 6 bits)000CH
RBE
INTTPG start address (lower 8 bits)
BR !addr
instruction
branch address
CALL !addr
instruction
subroutine
entry address
BR $addr
instruction
relational
branch address
(–15 to –1,
+2 to +16)
Branch destination
address and
subroutine entry
address for
GETI instruction
BRCB
!caddr
instruction
branch
address
Remarks: In addition to the above, branching to an address, for which only the lower 8 bits of the PC are
modified, is possible by the BR PCDE and BR PCXA instructions.
Fig. 4-1 Program Memory Map
Page 18
µ
PD75512(A)
18
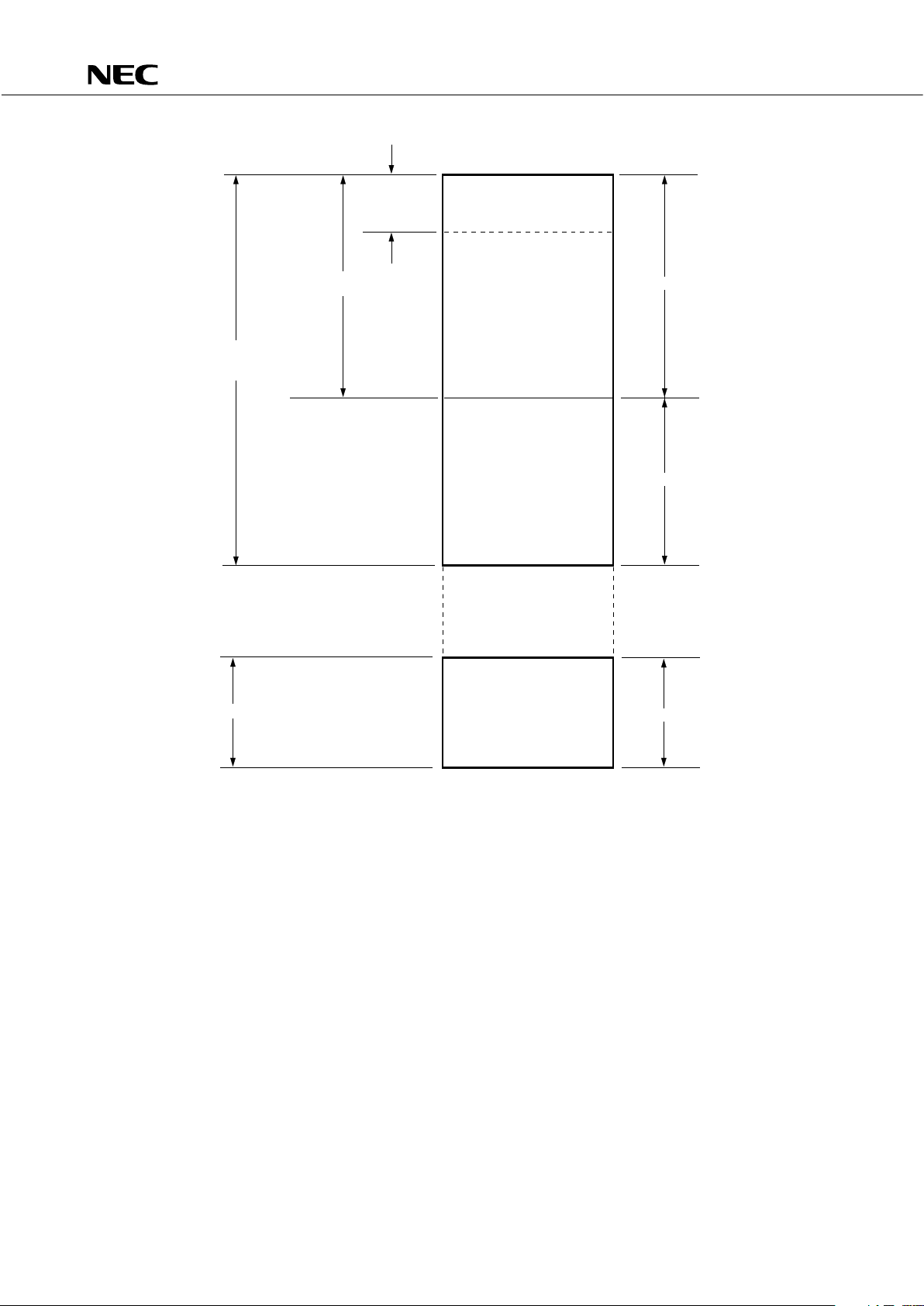
Data memory
Memory bank
General
purpose
register
area
000H
01FH
008H
(32 × 4)
256× 4
Stack
area
100H
0FFH
Data area
Static RAM
(512× 4)
1FFH
256× 4
Unmapped
F80H
128× 4
FFFH
Peripheral hardware area
15
1
0
Fig. 4-2 Data Memory Map
Page 19
µ
PD75512(A)
19
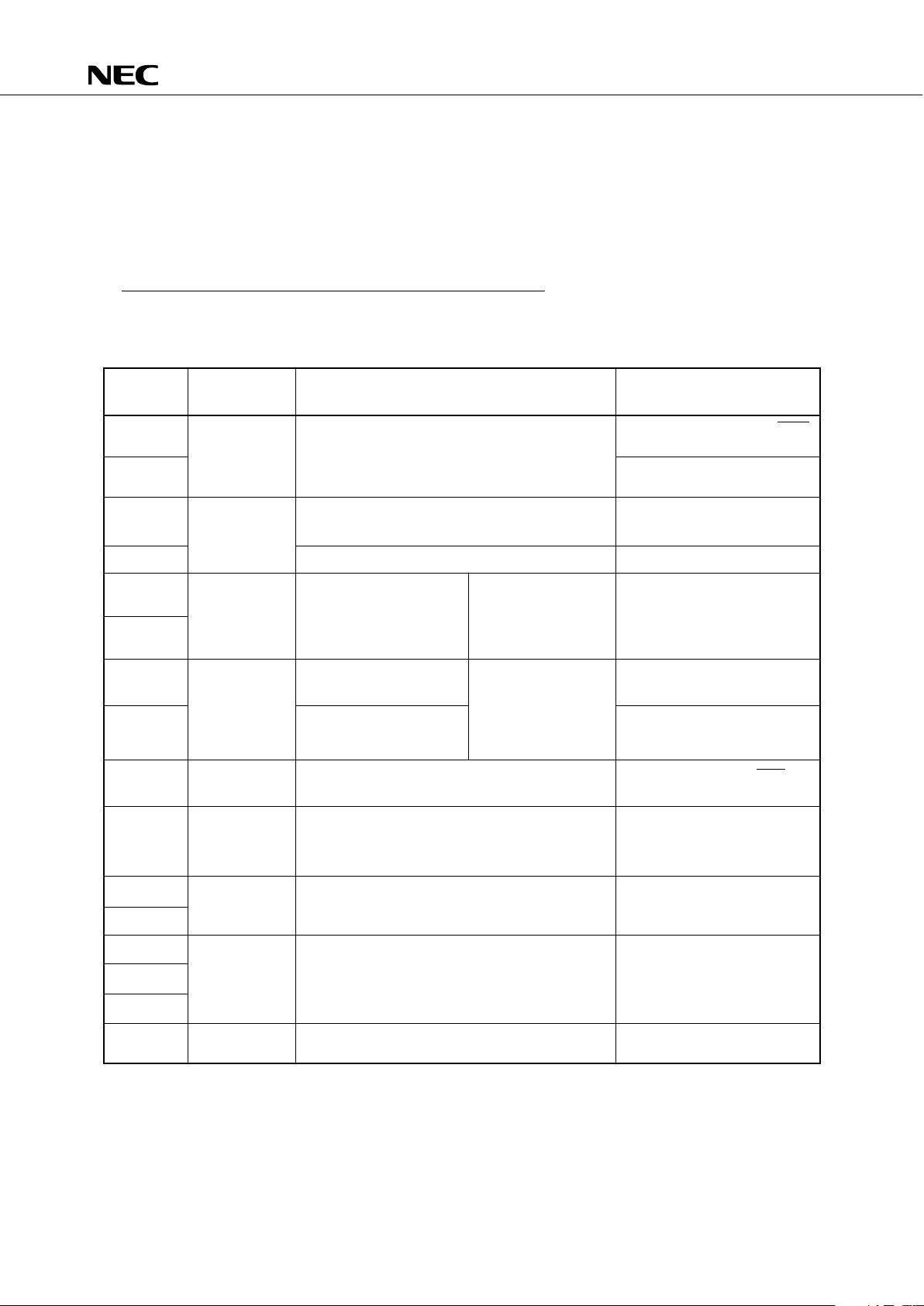
5. PERIPHERAL HARDWARE FUNCTIONS
5.1 PORT
I/O ports are classified into following kinds:
• CMOS input (PORTS 0, 1, 8, 15) : 16
• CMOS input/output (PORTS 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11) : 28
• N-ch open-drain input/output (PORTS 4, 5, 12, 13, 14) : 20
Total : 64
Table 5-1 Port Functions
Port
Function Operation/Feature Remarks
(Pin Name)
Also serves as the INT4,
SCK0
,
Can be read or tested regardless of the operation SO0/SB0, and SI0/SB1 pins
4-bit input mode of the shared pin.
Also serves as INT0 to 2, and
TIO pins
Can be specified for I/O in 4-bit units Also serves as PTO0, PCL and
4-bit I/O BUZ pins.
Can be specified for I/O in 1/4-bit units. —
4-bit I/O Whether or not the internal
(N-ch Can be specifiedfor pull-up resistor is provided
open-drain, I/O in 4-bit units can be specified for each bit
can sustain by mask option
with 10V)
Can be specified
for I/O in 1/4-bit units Ports 6 and 7 can Also serves as KR0-3.
4-bit I/O be paired to I/O
Can be specified data in 8-bit units
I/O in 4-bit Also serves as KR4-7.
units
4-bit Can be read or tested regardless of the operation Also serves as PPO,
SCK1
,
input mode of the shared pin. SO1, and SI1 pins.
Whether or not the internal
pull-up resistor is provided
can be specified for each bit
by mask option.
PORT10
4-bit I/O Can be specified for I/O in 4-bit units. —
PORT11
PORT12 4-bit I/O Whether or not the internal
(N-ch pull-up resistor is provided
PORT13 open-drain, Can be specified for I/O in 4-bit units. can be specified for each
can sustain bit by mask option.
PORT14 with 10V)
PORT15 4-bit Can be read or tested regardless of the operation Also serves as AN4-7 pins.
Input mode of the shared pins
PORT9 4-bit I/O Can be specified for I/O in 4-bit units.
PORT8
PORT0
PORT1
PORT2
PORT4
PORT3
PORT5
PORT7
PORT6
Ports 4 and 5 can
be paired to I/O
data in 8-bit units
★
Page 20
µ
PD75512(A)
20
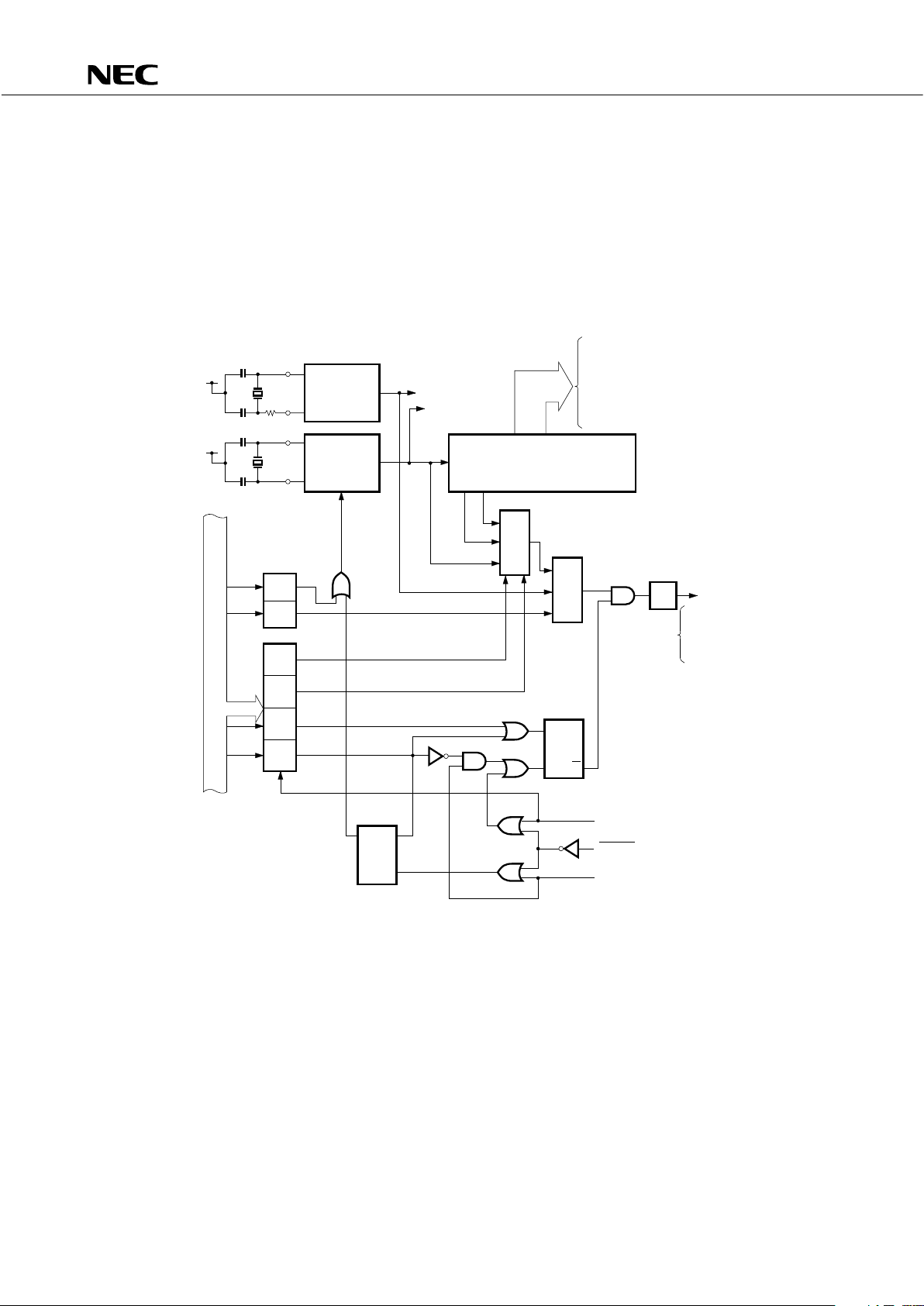
6.2 CLOCK GENERATOR CIRCUIT
The operation of the clock generator circuit is determined by the processor clock control regiser (PPC) and
system clock control register (SCC).
This circuit can generate two types of clocks: main system clock and subsystem clock.
In addition, it can also change the instruction execution time.
• 0.95
µ
s, 1.91 µs, 15.3 µs (main system clock: 4.19 MHz)
• 122
µ
s (subsystem clock: 32.768 kHz)
*: instruction execution.
Remarks 1: f
X = Main system clock frequency
2: f
XT = Subsystem clock frequency
3: Φ= CPU clock
4: PCC: Processor clock control register
5: SCC: System clock control register
6: One clock cycle (tCY) of Φ is one machine cycle of an instruction. For tCY, refer to AC
characteristics in 10. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS.
Fig. 5-1 Clock Generator Block Diagram
V
DD
V
DD
XT1
XT2
X1
X2
f
XT
f
X
Watch timer
Subsystem
clock
oscillator
Main system
clock
oscillator
1/2 1/16
1/8 to 1/4096
Frequency divider
· Basic interval timer (BT)
· Timer/event counter
· Serial interface
· Watch timer
· Clock output circuit
· A/D converter
· INT0 noise rejecter circuit
Internal bus
WM.3
SCC
SCC3
SCC0
PCC
PCC0
PCC1
PCC2
PCC3
HALT*
STOP*
4
PCC2, PCC3
clear signal
STOP F/F
QS
R
Q
S
R
HALT F/F
Oscillator
disable
signal
Frequency
divider
1/4
Selector
Φ
· CPU
· Clock output
circuit
· INT0 noise
rejecter circuit
Wait release
signal from BT
RESET signal
Standby release
signal from interrupt
control circuit
Timer/pulse
generator
Selector
Page 21

µ
PD75512(A)
21
5.3 CLOCK OUTPUT CIRCUIT
The clock output circuit outputs clock pulse from the P22/PCL pin. This clock pulse is used for the remote control
output, peripheral LSIs, etc.
• Clock output (PCL): Φ, 524 kHz, 262 kHz, 65.5 kHz (operating at 4.19 MHz)
Fig. 5-2 Clock Output Circuit Configuration
Remarks:
A measures to prevent outputting narrow width pulse when selecting clock output enable/
disable is taken.
Selector
Output
buffer
PCL/P22
Bit 2 of PMGBPORT2.2
Port 2 input/
output mode
specification
bit
P22 output
latch
Internal bus
CLOM3 CLOM2 CLOM1 CLOM0 CLOM
4
Φ
f
X
/2
3
fX/2
4
fX/2
6
From the
clock
generator
Page 22

µ
PD75512(A)
22
5.4 BASIC INTERVAL TIMER
The basic interval timer has these functions:
• Interval timer operation which generates a reference time interrupt
• Watchdog timer application which detects a program runaway
• Selects the wait time for releasing the standby mode and counts the wait time
• Reads out the count value
From the
clock generator
fX/2
5
fX/2
7
fX/2
9
fX/2
12
MPX
Clear
Basic interval timer
(8-bit frequency divider circuit)
3
4
8
BT
Clear
Set
signal
BT
interrupt
request flag
IRQBT
Wait release signal
for standby release
Vector
interrupt
request
signal
Internal bus
BTM3 BTM2 BTM1 BTM0 BTM
SET1*
*: Instruction execution
Fig. 5-3 Basic Interval Timer Configuration
Page 23

µ
PD75512(A)
23
5.5 WATCH TIMER
The
µ
PD75512(A) has a built-in 1-ch watch timer. The watch timer has these functions.
• Sets the test flag (IRQW) with 0.5 sec interval.
The standby mode can be released by IRQW.
• 0.5 second interval can be generated either from the main system clock or subsystem clock.
• Time interval can be advanced to 128 times faster (3.91 ms) by setting the fast mode. This is convenient
for program debugging, test, etc.
• Fixed frequency (2.048 kHz) can be output to the P23/BUZ pin. This can be used for beep and system clock
frequency trimming.
• The frequency divider circuit can be cleared so that zero second watch start is possible.
WM70000WM2WM1WM0
Selector Frequency divider
f
W
2
7
(256 Hz: 3.91 ms)
INTW
(IRQW
set signal)
f
W
2
14
(2 Hz
0.5 sec)
Selector
f
W
(32.768
kHz)
f
W
16
(2.048
kHz)
Clear
f
X
128
(32.768 kHz)
f
XT
(32.768 kHz)
From the
clock
generator
WM PORT2.3 Bit 2 of PMGB
Output buffer
P23/BUZ
P23
output
latch
Port 2
input/output
mode
Bit test
instruction
8
Internal bus
Remarks: ( ) is for fX = 4.194304 MHz, fXT = 32.768 kHz.
Fig. 5-4 Watch Timer Block Diagram
5.6 TIMER/EVENT COUNTER
The
µ
PD75512(A) has a built-in 1-ch timer/event counter. The timer/event counter has these functions:
• Programmable interval timer operation
• Outputs square-wave signal of an arbitrary frequency to the PTO0 pin.
• Event counter operation
• Divides the TI0 pin input in N and outputs to the PTO0 pin (frequency divider operation).
• Supplies serial shift clock to the serial interface circuit.
• Count condition read out function
Page 24

µ
PD75512(A)
24
Internal bus
88 SET1*
TM07 TM06 TM05 TM04 TM03 TM02 TM01 TM00
TM0
PORT1.3
Input
buffer
P13/TI0
From the
clock
generator
MPX
*:Instruction execution
Timer operation start signal
CP
8
8
Modulo register (8)
Comparator (8)
Count register (8)
Clear
T0
TMOD0
Reset
TOE0 PORT2.0
Bit 2 of PGMB
To serial interface
P20/PTO0
INTT0
IRQT0
set signal
()
RESET
IRQT0
clear signal
Output
buffer
TOUT
F/F
TO
enable
flag
P20
output
latch
Port 2
input/
output
mode
Coincidence
8
Fig. 5-5 Timer/Event Counter Block Diagram
Page 25

µ
PD75512(A)
25
5.7 TIMER/PULSE GENERATOR
The
µ
PD75512(A) contains a timer/pulse generator, that can be used as the timer or the pulse generator. Timer/
pulse generator has the following functions.
(a) Function, when used in the timer mode
• 8-bit interval timer operation (IRQTPG generation), for which the clock source can be changed in 5
steps.
• Square waveform output to the PPO pin
(b) Function, when used in the PWM pulse generation mode
• 14-bit accuracy PWM pulse output to PPO pin (can be used as a D/A converter for electronics tuning).
• Fixed time interval interrupt generation (2
15
/fX = 7.81ms: fX = 4.19 MHz)
When no pulse output is required, the PPO pin can be used as 1-bit output port.
Note: When setting the STOP mode, if the timer pulse generator is in operating mode, erroneous operation
may occur. Therefore, the timer/pulse generator must be set in no-operation state by the mode
register, before setting the STOP mode.
Internal bus
8
8
TPGM3
(Set to1 )
MODH
Modulo register L (8) Modulo register H (8)
Frequency
divider
f
x
1/2
TPGM1
Prescaler select latch (5)
Clear
CP
Clear
8
Count register (8)
Comparator (8)
T F/F
Set
Coincidence
Modulo latch H (8)
8
TPGM4 TPGM5 TPGM7
PPO
Output buffer
INTTPG
(IRQTPG
set signal)
Selector
MODL
Fig. 5-6 Timer/Pulse Generator Block Diagram (Timer Mode)
Page 26

µ
PD75512(A)
26
Internal bus
Modulo register H (8)
MODL
MODH
Modulo register L (8)
TPGM3
TPGM1
f
x
1/2
Frequency divider
MODH(8) MODL (6)
7-2
Modulo latch (14)
PWM pulse generator
IRQTPG set signal
( = 7.8 ms: f at 4.19MHz)
x
2
15
f
x
INTTPG TPGM5
TPGM7
Selector
Output buffer
PPO
Fig. 5-7 Timer/Pulse Generator Block Diagram (PWM Pulse Generation Mode)
5.8 SERIAL INTERFACE
The
µ
PD75512(A) is provided with two serial interface channels. Table 5-2 indicates differences between channel
0 and channel 1.
Table 5-2 Differences Between Channel 0 and Channel 1
Serial Transfer Mode, Funciton Channel 0 Channel 1
Clock Selection fX/24, fX/23, TOUT F/F, external clock fX/24, fX/23 external clock
3-Line Transfer Method MSB first/LSB first selectable MSB first
Serial I/O
Transfer Completion Serial transfer completion interrupt Serial transfer completion flag (EOT)
Flag request flag (IRQCSI0)
2-Line Serial I/O
Usable Unprovided
Serial Bus Interface (SBI)
(1) Serial interface function (Channel 0)
The
µ
PD75512(A) is equipped with the following four modes:
• Operation stop mode
• Three-line serial I/O mode
• Two-line serial I/O mode
• SBI mode (serial bus interface mode)
Page 27

µ
PD75512(A)
27
Internal bus
8/4
8
88
P03/SI/SB1
P02/SO/SB0
P01/SCK0
P01
output
latch
Selector Selector
Bit
test
Slave address register
(SVA)
Address comparator
Shift register (SIO0)
SET CLR
Bit manipulation
(8)
(8)
Coincidence
signal
SBIC
RELT
CMDT
SO0 latch
Bit test
ACKT
ACKE
BSYE
Busy/
acknowledge
output
circuit
Bus release/
command/
acknowledge
detector
circuit
RELD
CMDD
ACKD
Serial clock
counter
Serial clock
control
circuit
INTCSI0
control
circuit
MPX
I
NTCSI0
IRQCSI0
set signal
(
)
DQ
f
X
/2
3
fX/2
4
fX/2
6
TOUT F/F
(from timer/
event counter)
External SCK0
(8)
Fig. 5-8 Serial Interface (Channel 0) Block Diagram
CSIM0
Page 28

µ
PD75512(A)
28
(2) Serial interface (Channel 1) configuration
µ
PD75512(A) serial interface (channel 1) has following two modes.
• Operation stop mode
• 3-line serial I/O mode
Page 29

µ
PD75512(A)
29
Fig. 5-9 Serial Interface (Channel 1) Block Diagram
Bit
manipulation
0
CSIM1
Clear
Set
Serial transfer
completion flag
(EOT)
f /2
x
3
f /2
x
4
MPX
8
Bit
manipulation
bit 7
Serial operation mode (8)
register 1 (8)
Internal bus
8
SIO1 write signal (serial start signal)
SIO1
7bit 0
Shift register 1 (8)
P83/SI1
P82/SO1
P81/SCK1
Serial clock
counter (3)
Overflow
Clear
QRS
Page 30

µ
PD75512(A)
30
5.9 A/D CONVERTER
The
µ
PD75512(A) is provided with an 8-bit resolution analog-to-digital (A/D) converter with eight channels
of analog inputs (AN0-AN7).
This A/D converter is of a successive approximation type.
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
AN4
AN5
AV
REF
AV
SS
Multiplexer
Sample hold circuit
+
–
Tap decoder
R/2 R/2RR R
8
8
SA register (8)
Control circuit
Internal bus
0
ADM6 ADM5 ADM4 SOC EOC
ADM1 0 ADM
Comparator
8
AN6
AN7
Fig. 5-10 Block Diagram of A/D Converter
Page 31

µ
PD75512(A)
31
Address bit
Symbol
L register
32103210 32103210
L = F L = C L = B L = 8 L = 7 L = 4 L = 3 L = 0
BSB3 BSB2 BSB1 BSB0
DECS L
INCS L
FC3H FC2H FC1H FC0H
5.10 BIT SEQUENTIAL BUFFER ..... 16 BITS
The bit sequential buffer is a data memory specifically provided for bit manipulation. With this buffer,
addresses and bit specifications can be sequentially up-dated in bit manipulation operation. Therefore, this
buffer is very useful for processing long data in bit units.
Remarks:
For the pmem.@L addressing, the specification bit is shifted according to the L register.
Fig. 5-11 Bit Sequential Buffer Format
6. INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS
The µPD75512(A) has 7 different interrupt sources and multiplexed interrupt with priority order.
In addition to that, the
µ
PD75512 is also provided with two types of test sources, of which INT2 has two types
of edge detection testable inputs.
The interrupt control circuit of the µPD75512(A) has these functions:
• Hardware controlled vector interrupt function which can control whether or not to accept an interrupt by
using the interrupt flag (IExxx) and interrupt master enable flag (IME).
• The interrupt start address can be arbitrarily set.
• Interrupt request flag (IRQxxx) test function (an interrupt generation can be confirmed by means of
software).
• Standby mode release (Interrupts to be released can be selected by the interrupt enable flag).
Page 32

µ
PD75512(A)
32
Internal bus
222
IM2 IM1 IM0
IRQBT
INT4
/P00
INT0
/P10
INT1
/P11
INT2
/P12
KR0/P60
KR7/P73
Noise
elimination
circuit
INT
BT
INTCSI0
INTT0
INTTPG
Selector
Both edge
detection
circuit
Edge
detection
circuit
Edge
detection
circuit
Rising edge
detection
circuit
Falling edge
detection
circuit
IRQ4
IRQ0
IRQ1
IRQCSI0
IRQT0
IRQTPG
IM2
Interrupt enable flag (IExxx)
(IME)
VRQn
Decoder
IST
Priority control
circuit
Vector table
address
generator
Standby
release signal
Fig. 6-1 Interrupt Control Block Diagram
IRQ2
INTW
IRQW
4
2
IPS
Page 33

µ
PD75512(A)
33
Can operate only when the external
SCK0 input is selected as the serial
clock
Instruction for Setting STOP instrtuction HALT instruction
Can be set only when operating on
the main system clock
Can be set when operating either on
the main system clock or the subsystem clock
Item
Mode
STOP Mode
HALT Mode
Clock Oscillator Only the main system clock can stop
its operation.
Only the CPU clock Φ stops its
operation. (oscillation continues)
Basic Interval
Timer
Does not operate Operates (Sets IRQBT with the
reference time interval)
System Clock at the Time of
Setting
Serial Interface
(Channel 0)
Operates when the timer system
clock is operating or external SCK0 is
selected
Serial Interface
(Channel 1)
Can operate only when the external
SCK1 input is selected as the serial
clock
Operates only when the main system
clock is operating
Timer/Event
Counter
Can only operate when the TI0 pin
input is selected as system clock
Operates only when the main system
clock is operating
Clock Timer Operates when fXT is selected as the
count clock
Can operate
A/D Converter Does not operate
Timer/Pulse
Generator
Operates only when the main system
clock is operating
Does not operate
Operates only when the main system
clock is operating
Release Signal
CPU Does not operate
Timer/Pulse
Generator
INT1, INT2, and INT4 can operate, but INT0 cannot operate
An interrupt request signal from a piece of hardware, whose operation is
enabled by the interrupt enable flag, or the RESET signal input
Operation
Status
7. STANDBY FUNCTIONS
In order to fully exploit the µPD75512(A) low power dissipation, CPU operation can be stopped by setting the unit
to the standby mode, thus, further reducing power dissipation. The
µ
PD75512(A) features two standby modes, a
STOP mode and a HALT mode.
Table 7-1 Status in Standby Mode
Page 34

µ
PD75512(A)
34
8. RESET FUNCTIONS
When the
RESET
signal is input, the µPD75512(A) is reset and each hardware is initialized as indicated in
Table 8-1. Fig. 8-1 shows the reset operation timing.
RESET input
Wait
(31.3ms/4.19MHz)
Operation mode
or standby mode
HALT mode Operation mode
Internal reset operation
Fig. 8-1 Reset Operation by RESET Input
Table 8-1 Status of Each Hardware after Reset (1/2)
Hardware RESET Input in Standby Mode RESET Input during Operation
Program Counter (PC) The contents of the lower 6 bits
of address 0000H of the program
memory are set to PC13-8, and
the contents of address 0001H
are set to PC7-0.
Same as left
PSW Carry Flag (CY) Retained Undefined
Skip Flag (SK0-2) 0 0
Interrupt Status Flag (IST0, 1) 0 0
Bank Enable Flag (MBE, RBE) The contents of bit 6 of address
0000H of the program memory
are set to RBE and those of bit 7
are set to MBE.
Same as left
Stack Pointer (SP) Undefined Undefined
Data Memory (RAM) Retained * Undefined
General-Purpose Register
(X, A, H, L, D, E, B, C)
Retained Undefined
Bank Selection Register (MBS, RBS) 0, 0 0, 0
Basic Interval
Timer
Counter (BT) Undefined Undefined
Timer/Event
Counter
Counter (T0) 0 0
Modulo Register
(TMOD0)
FFH
FFH
Mode Register (TM0) 0 0
TOE0, TOUT F/F 0, 0 0, 0
Mode Register (BTM) 0 0
Timer/Pulse
Generator
Modulo Register
0Mode Register 0
Mode Register (WM) 0
Watch Timer
0
Retained
Retained
*: Data of address 0F8H to 0FDH of the data memory becomes undefined when a
RESET
signal is input.
Page 35

µ
PD75512(A)
35
Shift Register (SIO0) Retained Undefined
Operation Mode 0 0
Register (CSIM0)
SBI Control Register 0 0
(SBIC)
Slave Address Register Retained Undefined
(SVA)
P01/SCK0 Output 1 1
Latch
A/D Converter Mode Regiseter (ADM), 04H (EOC = 1) 04H (EOC = 1)
EOC
SA Register 7FH 7FH
Clock Processor Clock Control 0 0
Generator, Register (PCC)
Clock Output
System Clock Control 0 0
Circuit
Register (SCC)
Clock Output Mode 0 0
Register (CLOM)
Serial Shift Register Retained Undefined
Interface (SIO1)
(Channel 1)
Operation Mode 0 0
Register 1 (CSIM1)
Serial Transfer End 0 0
Flag (EOT)
Interrupt Interrupt Request Flag Reset (0) Reset (0)
Function (IRQxxx)
Interrupt Enable Flag 0 0
(IExxx)
Interrupt Master Enable 0 0
Flag (IME)
INT0, INT1, INT2 Mode 0, 0, 0 0, 0, 0
Registers (IM0, 1, 2)
Digital Port Output Buffer Off Off
Output Latch Clear (0) Clear (0)
Input/Output Mode 0 0
Register (PMGA, B, C)
Pull-Up Resistor 0 0
Specification Register
(POGA)
Bit Sequential Buffer (BSB0-3) Retained Undefined
Hardware RESET Input during OperationRESET Input in Standby Mode
Table 8-1 Status of Each Hardware after Reset (2/2)
Serial
Interface
(Channel 0)
Page 36

µ
PD75512(A)
36
9. INSTRUCTION SET
(1) Operand representation and description
Describe one or more operands in the operand field of each instruction according to the operand
representation and description methods of the instruction (for details, refer to RA75X Assembler Package
User's Manual - Language (EEU-730)). With some instructions, only one operand should be selected from
several operands. The uppercase characters, +, and – are keywords and must be described as is.
Describe an appropriate numeric value or label as immediate data.
Representation Description
reg X, A, B, C, D, E, H, L
reg1 X, B, C, D, E, H, L
rp XA, BC, DE, HL
rp1 BC, DE, HL
rp2 BC, DE
rp' XA, BC, DE, HL, XA', BC', DE', HL'
rp'1 BC, DE, HL, XA', BC', DE', HL'
rpa HL, HL+, HL–, DE, DL
rpa1 DE, DL
n4 4-bit immediate data or label
n8 8-bit immediate data or label
mem 8-bit immediate data or label*
bit 2-bit immediate data or label
fmem FB0H to FBFH,FF0H to FFFH immediate data or label
pmem FC0H to FFFH immediate data or label
addr 0000H to 2F7FH immediate data or label
caddr 12-bit immediate data or label
faddr 11-bit immediate data or label
taddr 20H to 7FH immediate data (where bit0 = 0) or label
PORTn PORT0 to PORT15
IExxx IEBT, IECSI0, IET0, IE0, IE1, IE2, IE4, IEW, IETPG
RBn RB0-RB3
MBn MB0, MB1, MB15
*: Only even addresses can be described in mem when processing
8-bit data.
Page 37

µ
PD75512(A)
37
(2) Legend of operation field
A : A register; 4-bit accumulator
B : B register; 4-bit accumulator
C : C register; 4-bit accumulator
D : D register; 4-bit accumulator
E : E register; 4-bit accumulator
H : H register; 4-bit accumulator
L : L register; 4-bit accumulator
X : X register; 4-bit accumulator
XA : Register pair (XA); 8-bit accumulator
BC : Register pair (BC); 8-bit accumulator
DE : Register pair (DE); 8-bit accumulator
HL : Register pair (HL); 8-bit accumulator
XA' : Expanded register pair (XA')
BC' : Expanded register pair (BC')
DE' : Expanded register pair (DE')
HL' : Expanded register pair (HL')
PC : Program counter
SP : Stack pointer
CY : Carry flag; or bit accumulator
PSW : Program status word
MBE : Memory bank enable flag
RBE : Register bank enable flag
PORTn : Port n (n = 0 to 15)
IME : Interrupt mask enable flag
IPS : Interrupt priority selector register
IExxx : Interrupt enable flag
RBS : Memory bank selector register
MBS : Memory bank selector register
PCC : Processor clock control register
.
: Delimiter of address and bit
(xx) : Contents addressed by xx
xxH : Hexadecimal data
Page 38

µ
PD75512(A)
38
(3) Symbols in addressing area field
*1 MB = MBE . MBS
(MBS = 0, 1, 15)
*2 MB = 0
*3 MBE = 0 : MB = 0 (00H-7FH) Data memory
MB = 15 (80H-FFH) addressing
MBE = 1 : MB = MBS (MBS = 0, 1, 15)
*4 MB = 15, fmem = FB0H-FBFH,
FF0H-FFFH
*5 MB = 15, pmem = FC0H-FFFH
*6 addr = 0000H-2F7FH
*7 addr = (Current PC) – 15 to (Current PC) – 1
(Current PC) + 2 to (Current PC) + 16
Program
*8 caddr = 0000H-0FFFH (PC13, 12 = 00B) or memory
1000H-1F7FH (PC13, 12 = 01B) or addressing
2000H-2F7FH (PC13, 12 = 10B)
*9 faddr = 0000H-07FFH
*10 taddr = 0020H-007FH
Remarks 1: MB indicates memory bank that can be accessed.
2: In *2, MB = 0 regardless of MBE and MBS.
3: In *4 and *5, MB = 15 regardless of MBE and MBS.
4: *6 to *10 indicate areas that can be addressed.
(4) Machine cycle field
In this field, S indicates the number of machine cycles required when an instruction having a skip
function skips. The value of S varies as follows:
• When no instruction is skipped ····························································· S = 0
• When 1-byte or 2-byte instruction is skipped······································ S = 1
• When 3-byte instruction (BR ! addr or CALL ! addr) is skipped ······· S = 2
Note
: The GETI instruction is skipped in one machine cycle.
One machine cycle equals to one cycle of the CPU clock Φ, (=tCY), and can be changed in three steps
depending on the setting of the processor clock control register (PCC).
Page 39

µ
PD75512(A)
39
Ma- Ad-
Instruc- Mne-
Operand Bytes
chine
Operation
dress- Skip
tions monics Cyc- ing Conditions
les Area
Transfer MOV A, #n4 1 1 A ← n4 String effect A
reg1, #n4 2 2 reg1 ← n4
XA, #n8 2 2 XA ← n8 String effect A
HL, #n8 2 2 HL ← n8 String effect B
rp2, #n8 2 2 rp2 ← n8
A, @HL 1 1 A ← (HL) *1
A, @HL+ 1 2+S A ← (HL), then L ← L+1 *1 L = 0
A, @HL– 1 2+S A ← (HL), then L ← L–1 *1 L = FH
A, @rpa1 1 1 A ← (rpa1) *2
XA, @HL 2 2 XA ← (HL) *1
@HL, A 1 1 (HL) ← A*1
@HL, XA 2 2 (HL) ← XA *1
A,mem 2 2 A ← (mem) *3
XA, mem 2 2 XA ← (mem) *3
mem, A 2 2 (mem) ← A*3
mem, XA 2 2 (mem) ← XA *3
A, reg 2 2 A ← reg
XA, rp' 2 2 XA ← rp'
reg1, A 2 2 reg1 ← A
rp'1, XA 2 2 rp'1 ← XA
XCH A, @HL 1 1 A ↔ (HL) *1
A, @HL+ 1 2+S A ← (HL), then L ← L+1 *1 L = 0
A, @HL– 1 2+S A ← (HL), then L ← L–1 *1 L = FH
A, @rpa1 1 1 A ↔ (rpa1) *2
XA, @HL 2 2 XA ↔ (HL) *1
A, mem 2 2 A ↔ (mem) *3
XA, mem 2 2 XA ↔ (mem) *3
A, reg1 1 1 A ↔ reg1
XA, rp' 2 2 XA ↔ rp'
Table MOVT XA, @PCDE 1 3 XA ← (PC13-8+DE)ROM
Reference
XA, @PCXA 1 3 XA ← (PC13-8+XA)ROM
Page 40

µ
PD75512(A)
40
Ma- Ad-
Instruc- Mne-
Operand Bytes
chine
Operation
dress- Skip
tions monics Cyc- ing Conditions
les Area
MOV1 CY, fmem.bit 2 2 CY ← (fmem.bit) *4
CY, pmem.@L 2 2 CY ← (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) *5
CY, @H+mem. 2 2 CY ← (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
bit
fmem.bit, CY 2 2 (fmem.bit) ← CY *4
pmem.@L, CY 2 2 (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) ← CY *5
@H+mem.bit, 2 2 (H+mem3-0.bit) ← CY *1
CY
ADDS A,#n4 1 1+S A ← A+n4 carry
XA,#n8 2 2+S XA ← XA+n8 carry
A,@HL 1 1+S A ← A+(HL) *1 carry
XA,rp’ 2 2+S XA ← XA+rp’ carry
rp’1,XA 2 2+S rp’1 ← rp’1+XA carry
ADDC A,@HL 1 1 A,CY ← A+(HL)+CY *1
XA,rp’ 2 2 XA,CY ← XA+rp’+CY
rp’1,XA 2 2 rp’1,CY ← rp’1+XA+CY
SUBS A,@HL 1 1+S A ← A-(HL) *1 borrow
XA,rp’ 2 2+S XA ← XA-rp’ borrow
rp’1,XA 2 2+S rp’1 ← rp’1-XA borrow
SUBC A,@HL 1 1 A,CY ← A-(HL)-CY *1
XA,rp’ 2 2 XA,CY ← XA-rp’-CY
rp’1,XA 2 2 rp’1,CY ← rp’1-XA-CY
AND A,#n4 2 2 A ← A ∧ n4
A,@HL 1 1 A ← A ∧ (HL) *1
XA,rp’ 2 2 XA ← XA-rp’
rp’1,XA 2 2 rp’1 ← rp’1 ∧ XA
OR A,#n4 2 2 A ← A ∨ n4
A,@HL 1 1 A ← A ∨ (HL) *1
XA,rp’ 2 2 XA ← XA ∨ rp’
rp’1,XA 2 2 rp’1 ← rp’1 ∨ XA
XOR A,#n4 2 2 A ← A ∨ n4
A,@HL 1 1 A ← A ∨ (HL) *1
XA,rp’ 2 2 XA ← XA ∨ rp’
rp’1,XA 2 2 rp’1 ← rp’1 ∨ XA
Bit
Transfer
Arithmetic
Operation
Page 41

µ
PD75512(A)
41
Ma- Ad-
Instruc- Mne-
Operand Bytes
chine
Operation
dress- Skip
tions monics Cyc- ing Conditions
les Area
RORC A 1 1 CY ← A0, A3 ← CY, An-1 ← An
NOT A 2 2 A ←
A
Incre- INCS reg 1 1+S reg ← reg+1 reg = 0
ment/ rp1 1 1+S rp1 ← rp1+1 rp1 = 00H
Decre- @HL 2 2+S (HL) ← (HL)+1 *1 (HL) = 0
ment mem 2 2+S (mem) ← (mem)+1 *3 (mem) = 0
DECS reg 1 1+S reg ← reg-1 reg = FH
rp’ 2 2+S rp’ ← rp’-1 rp’ = FFH
Compari- SKE reg,#n4 2 2+S Skip if reg = n4 reg = n4
son @HL,#n4 2 2+S Skip if (HL) = n4 *1 (HL) = n4
A,@HL 1 1+S Skip if A = (HL) *1 A = (HL)
XA,@HL 2 2+S Skip if XA = (HL) *1 XA = (HL)
A,reg 2 2+S Skip if A = reg A = reg
XA,rp’ 2 2+S Skip if XA = rp’ XA = rp’
SET1 CY 1 1 CY ← 1
CLR1 CY 1 1 CY ← 0
SKT CY 1 1+S Skip if CY = 1 CY = 1
NOT1 CY 1 1 CY ←
CY
Carry
Flag
Manipulation
Accumulator
Manipulation
Page 42

µ
PD75512(A)
42
Ma- Ad-
Instruc- Mne-
Operand Bytes
chine
Operation
dress- Skip
tions monics Cyc- ing Conditions
les Area
Memory/ SET1 mem.bit 2 2 (mem.bit) ← 1*3
Bit fmem.bit 2 2 (fmem.bit) ← 1 *4
Manipu- pmem.@L 2 2 (pmem7-2 + L3-2.bit(L1-0)) ← 1*5
lation @H+mem.bit 2 2 (H + mem3-0.bit) ← 1*1
CLR1 mem.bit 2 2 (mem.bit) ← 0 *3
fmem.bit 2 2 (fmem.bit) ← 0 *4
pmem.@L 2 2 (pmem7-2 + L3-2.bit(L1-0)) ← 0*5
@H+mem.bit 2 2 (H+mem3-0.bit) ← 0*1
SKT mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (mem.bit) = 1 *3 (mem.bit) = 1
fmem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (fmem.bit) = 1 *4 (fmem.bit) = 1
pmem.@L 2 2+S
Skip if (pmem
7-2+L3-2
.bit (L
1-0
)) = 1
*5 (pmem.@L) = 1
@H+mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (H + mem3-0.bit) = 1 *1
(@H+mem.bit) = 1
SKF mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (mem.bit) = 0 *3 (mem.bit) = 0
fmem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (fmem.bit) = 0 *4 (fmem.bit) = 0
pmem.@L 2 2+S
Skip if (pmem7-2 +L3-2.bit (L1-0)) = 0
*5 (pmem.@L) = 0
@H+mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (H + mem3-0.bit) = 0 *1
(@H+mem.bit) = 0
SKTCLR
fmem.bit 2 2+S Skip if (fmem.bit) = 1 and clear *4 (fmem.bit) = 1
pmem.@L 2 2+S Skip if (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit *5 (pmem.@L) = 1
(L1-0)) = 1 and clear
@H+mem.bit 2 2+S
Skip if (H+mem3-0.bit) = 1 and clear
*1
(@H+mem.bit) = 1
AND1 CY,fmem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY ∧ (fmem.bit) *4
CY,pmem.@L 2 2
CY ← CY ∧ (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0))
*5
CY,@H+mem.bit
2 2 CY
←
CY ∧ (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
OR1 CY,fmem.bit 2 2 CY
←
CY ∨ (fmem.bit) *4
CY,pmem.@L 2 2
CY ← CY ∨ (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit (L1-0))
*5
CY,@H+mem.bit
2 2 CY
←
CY ∨ (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
XOR1 CY,fmem.bit 2 2 CY
←
CY ∨ (fmem.bit) *4
CY,pmem.@L 2 2
CY ← CY ∨ (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit (L1-0))
*5
CY,@H+mem.bit
2 2 CY
←
CY ∨ (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
Branch BR addr — — PC13-0 ← addr *6
(The most suitable instruction
is selectable from among BR
!addr, BRCB !caddr, and BR
$addr depending on the
assembler.)
!addr 3 3 PC13-0 ← addr *6
$addr 1 2 PC13-0 ← addr *7
BRCB !caddr 2 2 PC13-0 ← PC13,12+caddr11-0 *8
BR PCDE 2 3 PC13-0 ← PC13-8+DE
PCXA 2 3 PC13-0 ← PC13-8+XA
Page 43

µ
PD75512(A)
43
Ma- Ad-
Instruc- Mne-
Operand Bytes
chine
Operation
dress- Skip
tions monics Cyc- ing Conditions
les Area
CALL !addr 3 3 (SP-4)(SP-1)(SP-2) ← PC11-0 *6
(SP-3) ← MBE, RBE, PC13,12
PC13-0 ← addr, SP ← SP-4
CALLF !faddr 2 2 (SP-4)(SP-1)(SP-2) ← PC11-0 *9
(SP-3) ← MBE, RBE, PC13,12
PC13-0 ← 00, faddr, SP ← SP-4
RET 1 3 MBE, RBE, PC13,12 ← (SP+1)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
SP ← SP+4
RETS 1 3+S MBE, RBE, PC13,12 ← (SP+1) Undefined
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
SP ← SP+4,
then skip unconditionally
RETI 1 3 PC13,12 ← (SP+1)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
PSW ← (SP+4)(SP+5), SP ← SP+6
PUSH rp 1 1 (SP-1)(SP-2) ← rp, SP ← SP-2
BS 2 2
(SP-1) ← MBS, (SP-2) ← RBS, SP ← SP-2
POP rp 1 1 rp ← (SP+1)(SP), SP ← SP+2
BS 2 2
MBS ← (SP+1), RBS ← (SP), SP ← SP+2
Inter- EI 2 2 IME (IPS.3) ← 1
rupt IExxx 2 2 IExxx ← 1
Control DI 2 2 IME (IPS.3) ← 0
IExxx 2 2 IExxx ← 0
I/O IN *1A,PORTn 2 2 A ← PORTn (n = 0-15)
XA,PORTn 2 2
XA
←
PORTn+1,PORTn
(n = 4, 6)
OUT *1PORTn,A 2 2 PORTn ← A (n = 2-7, 9-14)
PORTn,XA 2 2 PORTn+1,PORTn ← XA (n = 4, 6)
CPU HALT 2 2 Set HALT Mode (PCC.2 ← 1)
Control STOP 2 2 Set STOP Mode (PCC.3 ← 1)
NOP 1 1 No Operation
Special SEL RBn 2 2 RBS ← n (n = 0-3)
MBn 2 2 MBS ← n (n = 0, 1, 15)
GETI *2taddr 1 3
.
Where TBR instruction, *10
PC13-0 ← (taddr)4-0+(taddr+1)
.
Where TCALL instruction,
(SP-4)(SP-1)(SP-2) ← PC11-0
(SP-3) ← MBE, RBE, PC13,12
PC13-0 ← (taddr)5-0+(taddr+1)
SP ← SP-4
.
Except for TBR and TCALL Depends on
instructions, referenced
Instruction execution of instruction
(taddr)(taddr+1)
*1: When executing the IN/OUT instruction, MBE = 0, or MBE = 1, and MBS = 15.
*2: The TBR, and TCALL instructions are the assembler pseudo-instructions for the table definition of
GETI instruction.
Subroutine/
Stack
Control
......................................................... .............................
......................................................... .............................
Page 44

µ
PD75512(A)
44
10. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (Ta = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Supply Voltage VDD -0.3 to +7.0 V
VI1 Other than ports 4, 5, 12-14 -0.3 to VDD+0.3 V
Input Voltage VI2 Ports 4, 5, 12-14 w/pull-up -0.3 to VDD+0.3
V
resistor
Open drain -0.3 to +11 V
Output Voltage VO -0.3 to VDD+0.3 V
High-Level Output IOH* 1 pin Peak -10 mA
Current rms -5 mA
All pins Peak -30 mA
rms -15 mA
Low-Level Output IOL* 1 pin Peak 10 mA
Current rms 5 mA
Total of ports 0, 2, 3, 4 Peak 100 mA
rms 60 mA
Total of ports 5-11 Peak 100 mA
rms 60 mA
Total of ports 12-14 Peak 40 mA
rms 25 mA
Operating Temperature Topt -40 to +85 °C
Storage Temperature Tstg -65 to +150 °C
*: rms = Peak value x √Duty
OPERATING SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. MAX. Unit
A/D Converter Supply voltage VDD 3.5 6.0 V
Ambient temperature Ta -40 +85 °C
Timer/Pulse Supply voltage VDD 4.5 6.0 V
Generator Ambient temperatuare Ta -40 +85 °C
Other Circuits Supply voltage VDD 2.7 6.0 V
Ambient temperatuare Ta -40 +85 °C
CAPACITANCE (Ta = 25°C, VDD = 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input Capacitance CI f = 1 MHz 15 pF
Output Capacitance CO Pins other than thosemeasured are at 0 V 15 pF
Input/Output CIO
15 pF
Capacitance
Page 45

µ
PD75512(A)
45
MAIN SYSTEM CLOCK OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT CHARACTERISTICS
(T
a = -40 to +85°C, VDD = 2.7 to 6.0 V)
Oscillator
Recommended
Item Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Constants
Ceramic Oscillation VDD = osccillation
1.0 5.0
*
3
MHz
frequency(fX)*
1
voltage range
Oscillation stabiliza- After VDD came to
tion time*
2
MIN. value of
oscillation voltage
4ms
range
Crystal Oscillation
1.0 4.19 5.0
*
3
MHz
frequency (fX)*
1
Oscillation stabiliza- VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 10 ms
tion time*
2
30 ms
External Clock X1 input frequency
1.0 5.0
*
3
MHz
(fX)*
1
X1 input high-,
low-level widths
(tXH, tXL) 100 500 ns
SUBSYSTEM CLOCK OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT CHARACTERISTICS
(T
a = -40 to +85°C, VDD = 2.7 to 6.0 V)
Oscillator
Recommended
Item Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Constants
Crystal Oscillation*
1
32 32.768 35 kHz
frequency (fXT)
Oscillation stabiliza- VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 1.0 2 s
tion time*
2
10 s
External Clock XT1 input frequency
32 100 kHz
(fXT)*
1
XT1 input high-,
low-level widths 5 15
µ
s
(tXTH, tXTL)
*1: Only to express the characteristics of the oscillator circuit. For instruction execution time, refer to AC
Characteristics.
2: Time required for oscillation to stabilize after VDD reaches the minimum value of the oscillation voltage
range or the STOP mode has been released.
3: When the oscillation frequency is 4.19 MHz < fx ≤ 5.0 MHz, do not select PCC = 0011 as the instruction
execution time: otherwise, one machine cycle is set to less than 0.95
µ
s, falling short of the rated
minimum value of 0.95
µ
s.
X1 X2
C1 C2
X1 X2
C1 C2
X1 X2
PD74HCU04
µ
XT1 XT2
R
C3 C4
XT1 XT2
Open
★
Page 46

µ
PD75512(A)
46
Note: When using the oscillation circuit of the main system clock and subsystem clock, wire the portion
enclosed in dotted line in the figures as follows to avoid adverse influences on the wiring capacity:
• Keep the wiring length as short as possible.
• Do not cross the wiring over the other signal lines. Do not route the wiring in the vicinity of lines
through which a high alternating current flows.
• Always keep the ground point of the capacitor of the oscillator circuit at the same potential as V
SS.
Do not connect the ground pattern through which a high current flows.
• Do not extract signals from the oscillation circuit.
The amplification factor of the subsystem clock oscillation circuit is designed to be low to reduce the
current dissipation and therefore, the subsystem clock oscillation circuit is influenced by noise more
easily than the main system clock oscillation circuit. When using the subsystem clock, therefore,
exercise utmost care in wiring the circuit.
★
Page 47

µ
PD75512(A)
47
DC CHARACTERISTICS (Ta = -40 to +85°C, VDD = 2.7 to 6.0 V)
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
High-Level Input VIH1 Ports 2, 3, 9-11, P80, P82 0.7VDD VDD V
Voltage
VIH2 Ports 0, 1, 6, 7, 15, P81, P83,
RESET
0.8VDD VDD V
VIH3 Ports 4, 5, 12-14 w/pull-up resistor 0.7VDD VDD V
Open-drain 0.7VDD 10 V
VIH4 X1, X2, XT1 VDD-0.5 VDD V
Low-level Input VIL1 Ports 2-5, 9-14, P80, P82 0 0.3VDD V
Voltage VIL2 Ports 0, 1, 6, 7, 15, P81, P83,
RESET
0 0.2VDD V
VIL3 X1, X2, XT1 0 0.4 V
High-Level Output VOH VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V, IOH = -1 mA VDD-1.0 V
Voltage IOH = -100 µAVDD-0.5 V
Low-Level Output VOL Ports 3, 4, and 5 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V, 0.2 1.0 V
Voltage IOL = 5 mA
VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V, IOL = 1.6 mA 0.4 V
IOL = 400 µA 0.5 V
SB0, 1 Open-drain Pull-up
0.2VDD V
resistor ≥ 1 kΩ
High-Level Input ILIH1 VI = VDD Other than below 3
µ
A
Leakage Current
ILIH2 X1, X2, XT1 20
µ
A
ILIH3 VI = 9 V Ports 4, 5, 12-14
20
µ
A
(open-drain)
Low-Level Input ILIL1 VI = 0 V Other than below -3
µ
A
Leakage Current
ILIL2 X1, X2, XT1 -20
µ
A
High-Level Output ILOH1 VO = VDD Other than below 3
µ
A
Leakage Current
ILOH2 VO = 9 V Ports 4, 5, 12-14
20
µ
A
(open-drain)
Low-Level Output ILOL VO = 0 V
-3
µ
A
Leakage Current
Internal Pull-Up Resistor RU1
Ports 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 7
VDD = 5.0 V±10% 15 40 80 kΩ
(except P00) VI = 0V
VDD = 3.0 V±10% 30 300 kΩ
RU2 Ports 4, 5, 12-14 VDD = 5.0 V±10% 15 40 70 kΩ
VO = VDD-2.0 V
VDD = 3.0 V±10% 10 60 kΩ
Internal Pull-Down RD VO = 2 V Port 9 20 70 140 kΩ
Resistor
Page 48

µ
PD75512(A)
48
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Supply Current *1IDD1 4.19 MHz*2 crystal Ooperation VDD = 5 V±10%*
3
39mA
oscillator mode
VDD = 3 V±10%*
4
0.55 1.5 mA
IDD2
C1 = C2 = 22pF
HALT mode VDD = 5 V±10% 600 1800
µ
A
VDD = 3 V±10% 200 600
µ
A
IDD3 32.768 kHz*5 crystal Operation VDD = 3 V±10%
40 120
µ
A
oscillator mode
IDD4 HALT mode VDD = 3 V±10% 5 15
µ
A
IDD5 XT1 = 0 V VDD = 5 V±10% 0.5 20
µ
A
STOP mode
V
DD
= 3 V±10%
0.3 10
µ
A
Ta = 25°C5
µ
A
*1: Currents for the built-in pull-up resistor are not included.
2: Including when the subsystem clock is operated.
3: When operand in the high-speed mode with the processor clock control register (PCC) set to 0011.
4: When operated in the low-speed mode with the PCC set to 0000.
5: When operated with the subsystem clock by setting the system clock control register (SCC) to 1001 to
stop the main system clock operation.
Page 49

µ
PD75512(A)
49
AC CHARACTERISTICS (Ta = -40 to +85°C, VDD = 2.7 to 6.0 V)
(1) Basic Operation
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
tCY w/main system clock VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 0.95 64
µ
s
3.8 64
µ
s
w/sub-system clock 114 122 125
µ
s
TI0 Input Frequency fTI VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 0 1 MHz
0 275 kHz
TI0 Input High-, tTIH,VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 0.48
µ
s
Low-Level Widths t
TIL
1.8
µ
s
Interrupt Input High-, tINTH, INT0 *2
µ
s
Low-Level Widths t
INTL
INT1, 2, 4 10
µ
s
KR0-7 10
µ
s
RESET Low-Level Width tRSL 10
µ
s
*1: The CPU clock (Φ) cycle time is
determined by the oscillation frequency
of the connected oscillator, system clock
control register (SCC), and processor
clock control register (PCC). The figure
on the right is cycle time t
CY vs. supply
voltage V
DD characteristics at the main
system clock.
2: 2tCY or 128/fX depending on the setting
of the interrupt mode register (IM0).
0123 456
0.5
1
2
3
4
5
6
60
Supply voltage V
DD
[V]
Cycle time t
CY
[ s]
tCY vs V
DD
(with main system clock)
µ
64
70
Guaranteed operating range
CPU Clock Cycle Time*
1
(Minimum Instruction
Execution Time
= 1 Machine Cycle)
Page 50

µ
PD75512(A)
50
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK Cycle Time tKCY1 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 1600 ns
3800 ns
SCK High-, Low-Level tKL1 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V (tKCY1/2)-50 ns
Widths
tKH1 (tKCY1/2)
-150
ns
SI Set-Up Time (vs. SCK ↑)tSIK1 150 ns
SI Hold Time (vs. SCK ↑ )tKSI1 400 ns
SCK ↓→ SO Output tKSO1 RL = 1 kΩ,VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 250 ns
Delay Time CL = 100 pF*
1000 ns
*: RL and CL are load resistance and load capacitance of the SO output line.
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK Cycle Time tKCY2 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 800 ns
3200 ns
SCK High-, Low-Level tKL2 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 400 ns
Widths
tKH2 1600 ns
SI Set-Up Time (vs. SCK ↑)tSIK2 100 ns
SI Hold Time (vs. SCK ↑)tKSI2 400 ns
SCK ↓→ SO Output tKSO2 RL = 1 kΩ, CL = 100 pF* VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 300 ns
Delay Time
1000 ns
*: RL and CL are load resistance and load capacitance of the SO output line.
(2) Serial Transfer Operation
(a) Two-Line and Three-Line Serial I/O Modes (SCK: internal clock output)
(b) Two-Line and Three-Line Serial I/O Modes (SCK: external clock input)
Page 51

µ
PD75512(A)
51
(c) SBI Mode (SCK: internal clock output (master))
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK Cycle Time tKCY3 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 1600 ns
3800 ns
SCK High-, Low-Level tKL3 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V tKCY3/2-50 ns
Widths t
KH3
tKCY3/2-150 ns
SB0, 1 Set-Up Time tSIK3
150 ns
(vs. SCK ↑ )
SB0, 1 Hold Time tKSI3
tKCY3/2 ns
(vs. SCK ↑ )
SCK ↓→ SB0, 1 Output tKSO3 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 0 250 ns
Delay Time
0 1000 ns
SCK ↑→ SB0, 1 ↓ tKSB tKCY3 ns
SB0,1 ↓→ SCK tSBK tKCY3 ns
SB0, 1 Low-Level Width tSBL tKCY3 ns
SB0, 1 High-Level Width tSBH tKCY3 ns
(d) SBI Mode (SCK: external clock input (slave))
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK Cycle Time tKCY4 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 800 ns
3200 ns
SCK High-, Low-Level tKL4 VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 400 ns
Widths tKH4
1600 ns
SB0, 1 Set-Up Time tSIK4
100 ns
(vs. SCK ↑ )
SB0, 1 Hold Time tKSI4
tKCY4/2 ns
(vs. SCK ↑ )
SCK ↓→ SB0, 1 Output tKSO4 RL = 1 kΩ,VDD = 4.5 to 6.0 V 0 300 ns
Delay Time CL = 100 pF*
0 1000 ns
SCK ↑→ SB0, 1 ↓ tKSB tKCY4 ns
SB0,1 ↓→ SCK ↓ tSBK tKCY4 ns
SB0, 1 Low-Level Width tSBL tKCY4 ns
SB0, 1 High-Level Width tSBH tKCY4 ns
*: RL and CL are load resistance and load capacitance of the SO output line.
Page 52

µ
PD75512(A)
52
(3) A/D Converter (Ta = -40 to +85°C, VDD = 3.5 to 6.0 V, AVSS = VSS = 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Resolution 8 8 8 bit
Absolute Accuracy*
1
2.5 V ≤ AVREF ≤ VDD*
2
±2.0 LSB
Conversion Time*
3
tCONV 168/fXµs
Sampling Time*
4
tSAMP 44/fX
µ
s
Analog Input Voltage VIAN AVSS AVREF V
Analog Input Impedance RAN 1000 MΩ
AVREF Current AIREF 1.0 2.0 mA
*1: Absolute accuracy excluding quantization error (±1–2LSB)
2: Set ADM1 as follows, in respect to the reference voltage of the AD converter (AV
REF).
ADM1 can be set to either 0 or 1 when 0.6V
DD ≤ AVREF ≤ 0.65VDD
3: Time since execution of conversion start instruction until EOC = 1 (40.1 µs: fX = 4.19 MHz)
4: Time since execution of conversion start instruction until end of sampling (10.5
µ
s: fX = 4.19 MHz)
2.5 V 0.6 V
DD
0.65 V
DD
VDD(3.5 to 6.0 V)
ADM1=0
ADM1=1
AV
REF
Page 53

µ
PD75512(A)
53
AC TIMING TEST POINT (excluding X1 and XT1 inputs)
X1 input
V
DD
–0.5V
0.4 V
t
XL
t
XH
1/f
X
XT1 input
V
DD
–0.5V
0.4 V
t
XTL
t
XTH
1/f
XT
TI0
t
TIL
t
TIH
1/f
TI
CLOCK TIMING
TI0 TIMING
Test points
0.8 V
DD
0.2 V
DD
0.8 V
DD
0.2 V
DD
Page 54

µ
PD75512(A)
54
SERIAL TRANSFER TIMING
THREE-LINE SERIAL I/O MODE:
SCK
t
KL1
t
KH1
t
KCY1
Output data
t
SIK1
t
KSI1
t
KSO1
Input data
SI
SO
TWO-LINE SERIAL I/O MODE:
SCK
tKL2
tKH2
tKCY2
tSIK2 tKSI2
tKSO2
SB0,1
Page 55

µ
PD75512(A)
55
SERIAL TRANSFER TIMING
BUS RELEASE SIGNAL TRANSFER:
SCK
t
KL3,4
t
KCY3,4
t
SIK3,4
t
KSI3,4
t
KSO3,4
SB0,1
t
KH3,4
t
SBK
t
SBH
t
SBL
t
KSB
COMMAND SIGNAL TRANSFER:
SCK
t
KL3,4
t
KCY3,4
t
SIK3,4
t
KSI3,4
t
KSO3,4
SB0,1
t
KH3,4
t
SBK
t
KSB
INTERRUPT INPUT TIMING
INT0, 1, 2, 4
KR0-7
t
INTL
t
INTH
RESET INPUT TIMING:
RESET
t
RSL
Page 56

µ
PD75512(A)
56
LOW-VOLTAGE DATA RETENTION CHARACTERISTICS OF DATA MEMORY IN STOP MODE
(T
a = –40 to +85°C)
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Data Retention Supply VDDDR
2.0 6.0 V
Voltage
Data Retention Supply IDDDR VDDDR = 2.0 V
0.1 10
µ
A
Current*
1
Release Signal Set Time tSREL 0
µ
s
Oscillation Stabilization tWAIT Released by RESET 217/fX ms
Wait Time*
2
Released by interrupt *3 ms
*1: Does not include current flowing through internal pull-up resistor
2: The oscillation stabilization wait time is the time during which the CPU is stopped to prevent
unstable operation when oscillation is started.
3: Depends on the setting of the basic interval timer mode register (BTM) as follows:
BTM3 BTM2 BTM1 BTM0 WAIT time ( ): fX = 4.19 MHz
–0002
20
/fX (approx. 250 ms)
–0112
17
/fX (approx. 31.3 ms)
–1012
15
/fX (approx. 7.82 ms)
–1112
13
/fX (approx. 1.95 ms)
DATA RETENTION TIMING (releasing STOP mode by RESET)
DATA RETENTION TIMING (standby release signal: releasing STOP mode by interrupt)
STOP mode
Data retention mode
STOP instruction
execution
V
DD
RESET
V
DDDR
t
SREL
t
WAIT
Operation
mode
Internal reset operation
HALT mode
STOP mode
Data retention mode
STOP instruction execution
V
DD
V
DDDR
t
SREL
t
WAIT
Operation
mode
HALT mode
Standby release signal
(interrupt request)
Page 57

µ
PD75512(A)
57
11. PACKAGE DRAWINGS
N
A
M
F
B
64
65
40
K
L
80 PIN PLASTIC QFP (14×20)
80
1
25
24
41
G
D
C
P
detail of lead end
S
Q
5°±5°
M
I
H
J
P80GF-80-3B9-2
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A
B
C
D
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
23.6±0.4
14.0±0.2
0.8
0.35±0.10
0.15
20.0±0.2
0.929±0.016
0.039
0.031
0.006
0.031 (T.P.)
0.795
NOTE
M
N
0.15
0.15
1.8±0.2
0.8 (T.P.)
0.006
0.006
+0.004
–0.003
Each lead centerline is located within 0.15
mm (0.006 inch) of its true position (T.P.) at
maximum material condition.
0.071
0.014
0.551
0.8±0.2
0.031
P 2.7 0.106
0.693±0.016
17.6±0.4
1.0
+0.009
–0.008
Q
0.1±0.1
0.004±0.004
S 3.0 MAX. 0.119 MAX.
+0.10
–0.05
+0.009
–0.008
+0.004
–0.005
+0.009
–0.008
+0.008
–0.009
Page 58

µ
PD75512(A)
58
12. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS
It is recommended that µPD75512(A) be soldered under the following conditions.
For details on the recommended soldering conditions, refer to Information Document "Semiconductor
Devices Mounting Manual" (IEI-616).
For other soldering methods and conditions, consult NEC.
Table 12-1 Soldering Conditions of Surface Mount Type
µ
PD75512GF(A)-xxx-3B9: 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm)
Soldering Method Soldering Conditions
Symbol for Recommended
Condition
Infrared Reflow Package peak temperature: 230°C, IR30-00-1
time: 30 seconds max. (210°C min.),
number of times: 1
VPS Package peak temperature: 215°C, VP15-00-1
time: 40 seconds max. (200°C min.),
number of times: 1
Wave Soldering Soldering bath temperature: 260°C max., WS60-00-1
time: 10 seconds max., number of times: 1,
pre-heating temperature: 120°C max. (package surface
temperature)
Pin Partial Heating Pin temperature: 300°C max., —
time: 3 seconds max. (per side)
Caution: Do not use two or more soldering methods in combination (except the pin partial heating
method).
A model that can be soldered under the more stringent conditions (infrared reflow peak
temperature: 235°C, number of times: 2, and an extended number of days) is also available.
For details, consult NEC.
Notice
Page 59

µ
PD75512(A)
59
APPENDIX A. FUNCTIONAL DIFFERENCES AMONG µPD755XX(A) SERIES PRODUCTS
µ
PD75512(A)
µ
PD75516(A)
µ
PD75P516
ROM Configuration Mask ROM EPROM/One-time PROM
ROM (Bit) 12160 x 8 16256 x 8 16256 x 8
RAM (Bit) 512 x 4
Mask Option • Ports 4, 5, 12, 14 are provided with internal pull-up
resistors. Not provided
• Port 9 is provided with an internal pull-down resistor.
VPP, PROM, Pins for programming Not provided Provided
LED Direct Drive Not offered Offered
Supply Voltage Range 2.7 to 6.0 V 4.75 to 5.5 V
Absolute Maximum Differ in high-level / low-level output current
Ratings
DC Characteristics Differ in low-level output voltage
A/D Converter Differ in ambient temperature range and absolute accuracy
Characteristics
Quality Grade Special Standard
Package 80-pin plastic QFP (14 x 20 mm) • 80-pin plastic QFP
(14 x 20 mm)
• 80-pin ceramic WQFN
Electrical
Specifi-
cations
Product
Item
Page 60

µ
PD75512(A)
60
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
The following development support tools are readily available to support development of systems using
µ
PD75512(A):
Hardware IE-75000-R *
1
In-circuit emulator for 75X series
IE-75001-R
IE-75000-R-EM *
2
Emulation board for IE-75000-R and IE-75001-R
EP-75516GF-R Emulation prove for µPD75512(A), provided with 80-pin conversion socket
EV-9200G-80.
PG-1500 PROM programmer
PA-75P516GF PROM programmer adapter solely used for µPD75P516GF. It is connected
to PG-1500.
Software IE Control Program
PG-1500 Controller
RA75X Relocatable
Assembler
*1: Maintenance product
2: Not provided with IE-75001-R.
3: Ver.5.00/5.00A has a task swap function, but this function cannot be used with this software.
Remarks: For development tools from other companies, refer to 75X Series Selection Guide (IF-151).
EV-9200G-80
Host machine
PC-9800 series (MS-DOSTM Ver.3.30 to Ver.5.00A*3)
IBM PC/ATTM (PC DOSTM Ver.3.1)
Page 61

µ
PD75512(A)
61
APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS
★
Page 62

µ
PD75512(A)
62
[MEMO]
Page 63

µ
PD75512(A)
63
➀
STATIC ELECTRICITY (ALL MOS DEVICES)
Exercise care so that MOS devices are not adversely influenced by static electricity while being
handled.
The insulation of the gates of the MOS device may be destroyed by a strong static charge.
Therefore, when transporting or storing the MOS device, use a conductive tray, magazine case,
or conductive buffer materials, or the metal case NEC uses for packaging and shipment, and use
grounding when assembling the MOS device system. Do not leave the MOS device on a plastic
plate and do not touch the pins of the device.
Handle boards on which MOS devices are mounted similarly .
➁
PROCESSING OF UNUSED PINS (CMOS DEVICES ONLY)
Fix the input level of CMOS devices.
Unlike bipolar or NMOS devices, if a CMOS device is operated with nothing connected to its
input pin, intermediate level input may be generated due to noise, and an inrush current may flow
through the device, causing the device to malfunction. Therefore, fix the input level of the device
by using a pull-down or pull-up resistor. If there is a possibility that an unused pin serves as an
output pin (whose timing is not specified), each pin should be connected to V
DD or GND through
a resistor.
Refer to “Processing of Unused Pins” in the documents of each devices.
➂
STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION (ALL MOS DEVICES)
The initial status of MOS devices is undefined upon power application.
Since the characteristics of an MOS device are determined by the quantity of injection at the
molecular level, the initial status of the device is not controlled during the production process. The
output status of pins, I/O setting, and register contents upon power application are not guaranteed.
However, the items defined for reset operation and mode setting are subject to guarantee after
the respective operations have been executed.
When using a device with a reset function, be sure to reset the device after power application.
GENERAL NOTES ON CMOS DEVICES
Page 64

µ
PD75512(A)
64
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior
written consent of NEC Corporation. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors which
may appear in this document.
NEC Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other
intellectual property rights of third parties b y or arising from use of a device described herein or any
other liability arising from use of such device. No license, either express, implied or otherwise, is granted
under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Corporation or others.
The devices listed in this document are not suitable for uses in aerospace equipment, submarine cables,
nuclear reactor control systems and life support systems. If customers intend to use NEC devices for
above applications or they intend to use "Standard" quality grade NEC devices for the applications not
intended by NEC, please contact our sales people in advance.
Application examples recommended by NEC Corporation
Standard: Computer, Office equipment, Communication equipment, Test and Measurement equipment,
Machine tools, Industrial robots, Audio and Visual equipment, Other consumer products, etc.
Special: Automotive and Transportation equipment, Traffic control systems, Antidisaster systems,
Anticrime system, etc.
MS-DOS is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
PC DOS and PC/AT are trademarks of IBM Corporation.
[MEMO]
M4 92.6
 Loading...
Loading...