Datasheet TSB80C188EB20, TSB80C188EB13, TSB80C186EB20, TSB80L186EB8, TSB80L186EB13 Datasheet (Intel Corporation)
...Page 1
*Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, including infringement of any patent or
copyright, for sale and use of Intel products except as provided in Intel’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products. Intel retains the right to make
changes to these specifications at any time, without notice. Microcomputer Products may have minor variations to this specification known as errata.
October 1995
COPYRIGHT
©
INTEL CORPORATION, 1995
Order Number: 272433-004
80C186EB/80C188EB AND 80L186EB/80L188EB
16-BIT HIGH-INTEGRATION EMBEDDED PROCESSORS
X
Full Static Operation
X
True CMOS Inputs and Outputs
Y
Integrated Feature Set
Ð Low-Power Static CPU Core
Ð Two Independent UARTs each with
an Integral Baud Rate Generator
Ð Two 8-Bit Multiplexed I/O Ports
Ð Programmable Interrupt Controller
Ð Three Programmable 16-Bit
Timer/Counters
Ð Clock Generator
Ð Ten Programmable Chip Selects with
Integral Wait-State Generator
Ð Memory Refresh Control Unit
Ð System Level Testing Support (ONCE
Mode)
Y
Direct Addressing Capability to 1 Mbyte
Memory and 64 Kbyte I/O
Y
Speed Versions Available (5V):
Ð 25 MHz (80C186EB25/80C188EB25)
Ð 20 MHz (80C186EB20/80C188EB20)
Ð 13 MHz (80C186EB13/80C188EB13)
Y
Available in Extended Temperature
Range (
b
40§Ctoa85§C)
Y
Speed Versions Available (3V):
Ð 16 MHz (80L186EB16/80L188EB16)
Ð 13 MHz (80L186EB13/80L188EB13)
Ð 8 MHz (80L186EB8/80L188EB8)
Y
Low-Power Operating Modes:
Ð Idle Mode Freezes CPU Clocks but
keeps Peripherals Active
Ð Powerdown Mode Freezes All
Internal Clocks
Y
Supports 80C187 Numeric Coprocessor
Interface (80C186EB PLCC Only)
Y
Available In:
Ð 80-Pin Quad Flat Pack (QFP)
Ð 84-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
(PLCC)
Ð 80-Pin Shrink Quad Flat Pack (SQFP)
The 80C186EB is a second generation CHMOS High-Integration microprocessor. It has features that are new
to the 80C186 family and include a STATIC CPU core, an enhanced Chip Select decode unit, two independent
Serial Channels, I/O ports, and the capability of Idle or Powerdown low power modes.
272433– 1
1
Page 2

80C186EB/80C188EB and 80L186EB/80L188EB
16-Bit High-Integration Embedded Processors
CONTENTS PAGE
INTRODUCTION ААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 4
CORE ARCHITECTURE ААААААААААААААААААА 4
Bus Interface Unit АААААААААААААААААААААААААА 4
Clock Generator ААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 4
80C186EC PERIPHERAL
ARCHITECTURE АААААААААААААААААААААААА 5
Interrupt Control Unit ААААААААААААААААААААААА 5
Timer/Counter Unit АААААААААААААААААААААААА 5
Serial Communications Unit АААААААААААААААА 7
Chip-Select Unit АААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 7
I/O Port Unit ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 7
Refresh Control Unit ААААААААААААААААААААААА 7
Power Management Unit ААААААААААААААААААА 7
80C187 Interface (80C186EB Only) ААААААААА 7
ONCE Test Mode АААААААААААААААААААААААААА 7
PACKAGE INFORMATION АААААААААААААААА 8
Prefix Identification ААААААААААААААААААААААААА 8
Pin Descriptions АААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 8
80C186EB PINOUT ААААААААААААААААААААААА 14
PACKAGE THERMAL
SPECIFICATIONS
АААААААААААААААААААААА 22
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ААААААААА 23
Absolute Maximum Ratings ААААААААААААААА 23
CONTENTS PAGE
Recommended Connections
АААААААААААААА 23
DC SPECIFICATIONS АААААААААААААААААААА 24
ICCversus Frequency and Voltage ААААААААА 27
PDTMR Pin Delay Calculation ААААААААААААА 27
AC SPECIFICATIONS АААААААААААААААААААА 28
AC CharacteristicsÐ80C186EB25 ААААААААА 28
AC CharacteristicsÐ80C186EB20/13 ААААА 30
AC CharacteristicsÐ80L186EB16 ААААААААА 32
Relative Timings АААААААААААААААААААААААААА 36
Serial Port Mode 0 Timings АААААААААААААААА 37
AC TEST CONDITIONS АААААААААААААААААА 38
AC TIMING WAVEFORMS ААААААААААААААА 38
DERATING CURVES ААААААААААААААААААААА 41
RESET ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 42
BUS CYCLE WAVEFORMS АААААААААААААА 45
EXECUTION TIMINGS ААААААААААААААААААА 52
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY АААААААААА 53
ERRATA ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА 59
REVISION HISTORY ААААААААААААААААААААА 59
2
2
Page 3
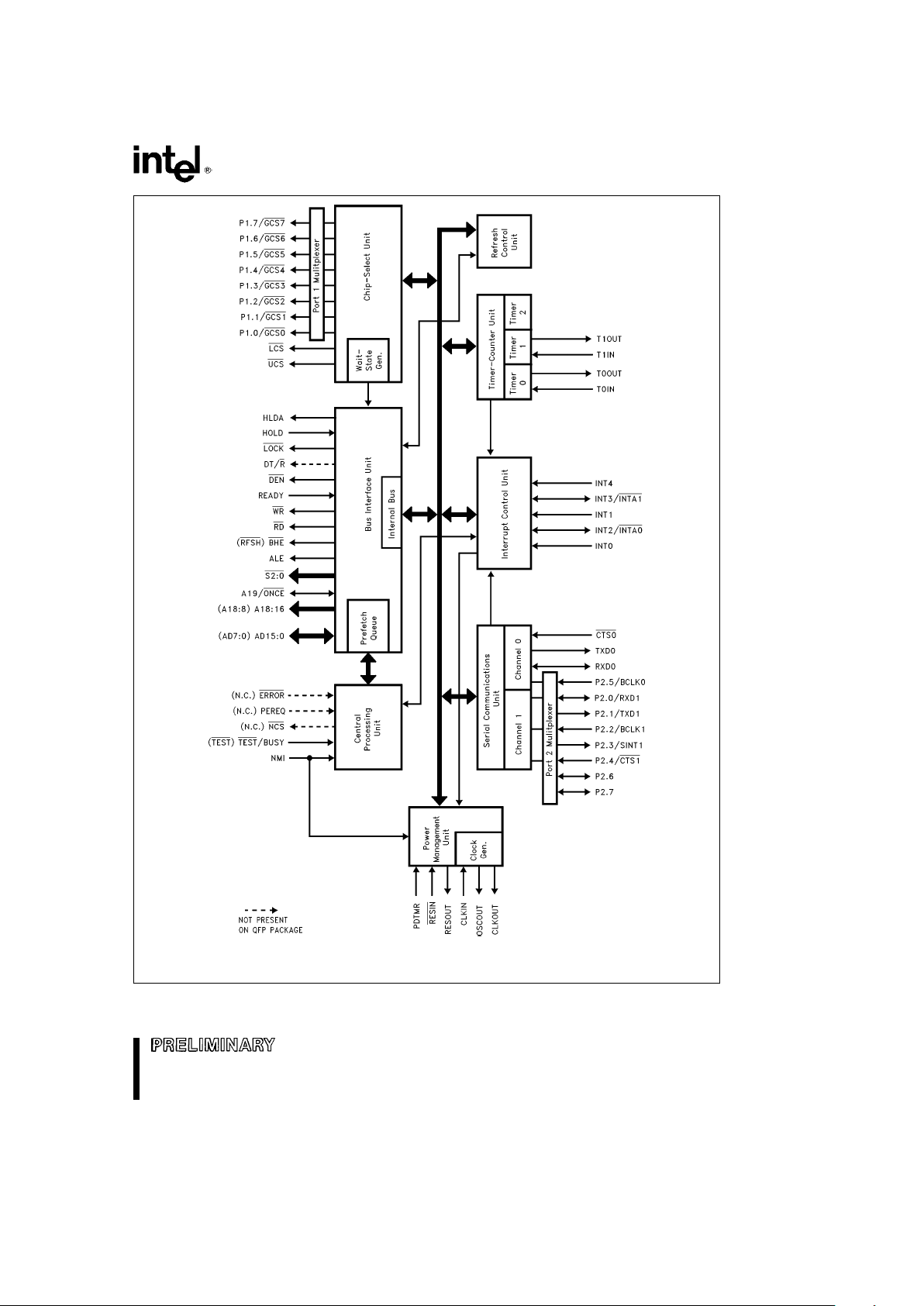
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 2
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 1. 80C186EB/80C188EB Block Diagram
3
3
Page 4

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INTRODUCTION
Unless specifically noted, all references to the
80C186EB apply to the 80C188EB, 80L186EB, and
80L188EB. References to pins that differ between
the 80C186EB/80L186EB and the 80C188EB/
80L188EB are given in parentheses. The ‘‘L’’ in the
part number denotes low voltage operation. Physically and functionally, the ‘‘C’’ and ‘‘L’’ devices are
identical.
The 80C186EB is the first product in a new generation of low-power, high-integration microprocessors.
It enhances the existing 186 family by offering new
features and new operating modes. The 80C186EB
is object code compatible with the 80C186XL/
80C188XL microprocessors.
The 80L186EB is the 3V version of the 80C186EB.
The 80L186EB is functionally identical to the
80C186EB embedded processor. Current
80C186EB users can easily upgrade their designs to
use the 80L186EB and benefit from the reduced
power consumption inherent in 3V operation.
The feature set of the 80C186EB meets the needs
of low power, space critical applications. Low-Power
applications benefit from the static design of the
CPU core and the integrated peripherals as well as
low voltage operation. Minimum current consumption is achieved by providing a Powerdown mode
that halts operation of the device, and freezes the
clock circuits. Peripheral design enhancements ensure that non-initialized peripherals consume little
current.
Space critical applications benefit from the integration of commonly used system peripherals. Two
serial channels are provided for services such as
diagnostics, inter-processor communication, modem
interface, terminal display interface, and many others. A flexible chip select unit simplifies memory and
peripheral interfacing. The interrupt unit provides
sources for up to 129 external interrupts and will prioritize these interrupts with those generated from
the on-chip peripherals. Three general purpose timer/counters and sixteen multiplexed I/O port pins
round out the feature set of the 80C186EB.
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the 80C186EB/
80C188EB. The Execution Unit (EU) is an enhanced
8086 CPU core that includes: dedicated hardware to
speed up effective address calculations, enhance
execution speed for multiple-bit shift and rotate instructions and for multiply and divide instructions,
string move instructions that operate at full bus
bandwidth, ten new instruction, and fully static operation. The Bus Interface Unit (BIU) is the same as
that found on the original 186 family products, ex-
cept the queue status mode has been deleted and
buffer interface control has been changed to ease
system design timings. An independent internal bus
is used to allow communication between the BIU
and internal peripherals.
CORE ARCHITECTURE
Bus Interface Unit
The 80C186EB core incorporates a bus controller
that generates local bus control signals. In addition,
it employs a HOLD/HLDA protocol to share the local
bus with other bus masters.
The bus controller is responsible for generating 20
bits of address, read and write strobes, bus cycle
status information, and data (for write operations) information. It is also responsible for reading data off
the local bus during a read operation. A READY input pin is provided to extend a bus cycle beyond the
minimum four states (clocks).
The local bus controller also generates two control
signals (DEN
and DT/R) when interfacing to exter-
nal transceiver chips. (Both DEN
and DT/R are
available on the PLCC devices, only DEN
is available on the QFP and SQFP devices.) This capability
allows the addition of transceivers for simple buffering of the multiplexed address/data bus.
Clock Generator
The processor provides an on-chip clock generator
for both internal and external clock generation. The
clock generator features a crystal oscillator, a divideby-two counter, and two low-power operating
modes.
The oscillator circuit is designed to be used with either a parallel resonant fundamental or third-overtone mode crystal network. Alternatively, the oscillator circuit may be driven from an external clock
source. Figure 2 shows the various operating modes
of the oscillator circuit.
The crystal or clock frequency chosen must be twice
the required processor operating frequency due to
the internal divide-by-two counter. This counter is
used to drive all internal phase clocks and the external CLKOUT signal. CLKOUT is a 50% duty cycle
processor clock and can be used to drive other system components. All AC timings are referenced to
CLKOUT.
4
4
Page 5
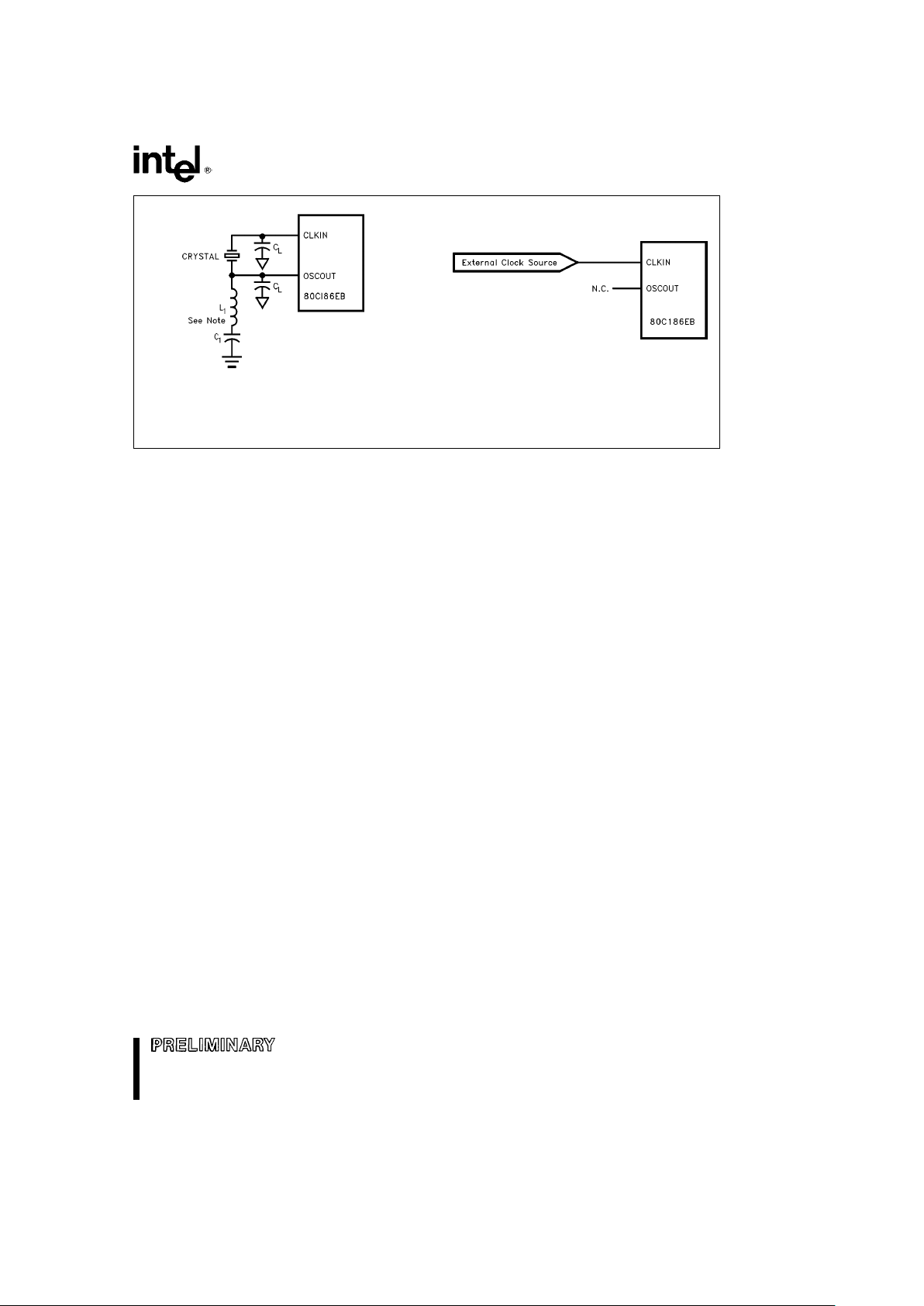
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 3
(A) Crystal Connection
NOTE:
The L
1C1
network is only required when using a third-
overtone crystal.
272433– 4
(B) Clock Connection
Figure 2. Clock Configurations
The following parameters are recommended when
choosing a crystal:
Temperature Range: Application Specific
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance): 40X max
C0 (Shunt Capacitance of Crystal): 7.0 pF max
C
L
(Load Capacitance): 20 pFg2pF
Drive Level: 1 mW max
80C186EB PERIPHERAL
ARCHITECTURE
The 80C186EB has integrated several common system peripherals with a CPU core to create a compact, yet powerful system. The integrated peripherals are designed to be flexible and provide logical
interconnections between supporting units (e.g., the
interrupt control unit supports interrupt requests
from the timer/counters or serial channels).
The list of integrated peripherals includes:
#
7-Input Interrupt Control Unit
#
3-Channel Timer/Counter Unit
#
2-Channel Serial Communications Unit
#
10-Output Chip-Select Unit
#
I/O Port Unit
#
Refresh Control Unit
#
Power Management Unit
The registers associated with each integrated periheral are contained within a 128 x 16 register file
called the Peripheral Control Block (PCB). The PCB
can be located in either memory or I/O space on
any 256 Byte address boundary.
Figure 3 provides a list of the registers associated
with the PCB. The Register Bit Summary at the end
of this specification individually lists all of the registers and identifies each of their programming attributes.
Interrupt Control Unit
The 80C186EB can receive interrupts from a number of sources, both internal and external. The interrupt control unit serves to merge these requests on
a priority basis, for individual service by the CPU.
Each interrupt source can be independently masked
by the Interrupt Control Unit (ICU) or all interrupts
can be globally masked by the CPU.
Internal interrupt sources include the Timers and Serial channel 0. External interrupt sources come from
the five input pins INT4:0. The NMI interrupt pin is
not controlled by the ICU and is passed directly to
the CPU. Although the Timer and Serial channel
each have only one request input to the ICU, separate vector types are generated to service individual
interrupts within the Timer and Serial channel units.
Timer/Counter Unit
The 80C186EB Timer/Counter Unit (TCU) provides
three 16-bit programmable timers. Two of these are
highly flexible and are connected to external pins for
control or clocking. A third timer is not connected to
any external pins and can only be clocked internally.
However, it can be used to clock the other two timer
channels. The TCU can be used to count external
events, time external events, generate non-repetitive waveforms, generate timed interrupts. etc.
5
5
Page 6

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
PCB
Function
Offset
00H Reserved
02H End Of Interrupt
04H Poll
06H Poll Status
08H Interrupt Mask
0AH Priority Mask
0CH In-Service
0EH Interrupt Request
10H Interrupt Status
12H Timer Control
14H Serial Control
16H INT4 Control
18H INT0 Control
1AH INT1 Control
1CH INT2 Control
1EH INT3 Control
20H Reserved
22H Reserved
24H Reserved
26H Reserved
28H Reserved
2AH Reserved
2CH Reserved
2EH Reserved
30H Timer0 Count
32H Timer0 Compare A
34H Timer0 Compare B
36H Timer0 Control
38H Timer1 Count
3AH Timer1 Compare A
3CH Timer1 Compare B
3EH Timer1 Control
PCB
Function
Offset
40H Timer2 Count
42H Timer2 Compare
44H Reserved
46H Timer2 Control
48H Reserved
4AH Reserved
4CH Reserved
4EH Reserved
50H Port 1 Direction
52H Port 1 Pin
54H Port 1 Control
56H Port 1 Latch
58H Port 2 Direction
5AH Port 2 Pin
5CH Port 2 Control
5EH Port 2 Latch
60H Serial0 Baud
62H Serial0 Count
64H Serial0 Control
66H Serial0 Status
68H Serial0 RBUF
6AH Serial0 TBUF
6CH Reserved
6EH Reserved
70H Serial1 Baud
72H Serial1 Count
74H Serial1 Control
76H Serial1 Status
78H Serial1 RBUF
7AH Serial1 TBUF
7CH Reserved
7EH Reserved
PCB
Function
Offset
80H GCS0 Start
82H GCS0 Stop
84H GCS1 Start
86H GCS1 Stop
88H GCS2 Start
8AH GCS2 Stop
8CH GCS3 Start
8EH GCS3 Stop
90H GCS4 Start
92H GCS4 Stop
94H GCS5 Start
96H GCS5 Stop
98H GCS6 Start
9AH GCS6 Stop
9CH GCS7 Start
9EH GCS7 Stop
A0H LCS Start
A2H LCS Stop
A4H UCS Start
A6H UCS Stop
A8H Relocation
AAH Reserved
ACH Reserved
AEH Reserved
B0H Refresh Base
B2H Refresh Time
B4H Refresh Control
B6H Reserved
B8H Power Control
BAH Reserved
BCH Step ID
BEH Reserved
PCB
Function
Offset
C0H Reserved
C2H Reserved
C4H Reserved
C6H Reserved
C8H Reserved
CAH Reserved
CCH Reserved
CEH Reserved
D0H Reserved
D2H Reserved
D4H Reserved
D6H Reserved
D8H Reserved
DAH Reserved
DCH Reserved
DEH Reserved
E0H Reserved
E2H Reserved
E4H Reserved
E6H Reserved
E8H Reserved
EAH Reserved
ECH Reserved
EEH Reserved
F0H Reserved
F2H Reserved
F4H Reserved
F6H Reserved
F8H Reserved
FAH Reserved
FCH Reserved
FEH Reserved
Figure 3. Peripheral Control Block Registers
6
6
Page 7

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Serial Communications Unit
The Serial Control Unit (SCU) of the 80C186EB contains two independent channels. Each channel is
identical in operation except that only channel 0 is
supported by the integrated interrupt controller
(channel 1 has an external interrupt pin). Each
channel has its own baud rate generator that is independent of the Timer/Counter Unit, and can be
internally or externally clocked at up to one half the
80C186EB operating frequency.
Independent baud rate generators are provided for
each of the serial channels. For the asynchronous
modes, the generator supplies an 8x baud clock to
both the receive and transmit register logic. A 1x
baud clock is provided in the synchronous mode.
Chip-Select Unit
The 80C186EB Chip-Select Unit (CSU) integrates
logic which provides up to ten programmable chipselects to access both memories and peripherals. In
addition, each chip-select can be programmed to
automatically insert additional clocks (wait-states)
into the current bus cycle and automatically terminate a bus cycle independent of the condition of the
READY input pin.
I/O Port Unit
The I/O Port Unit (IPU) on the 80C186EB supports
two 8-bit channels of input, output, or input/output
operation. Port 1 is multiplexed with the chip select
pins and is output only. Most of Port 2 is multiplexed
with the serial channel pins. Port 2 pins are limited to
either an output or input function depending on the
operation of the serial pin it is multiplexed with.
Refresh Control Unit
The Refresh Control Unit (RCU) automatically generates a periodic memory read bus cycle to keep
dynamic or pseudo-static memory refreshed. A 9-bit
counter controls the number of clocks between refresh requests.
A 12-bit address generator is maintained by the RCU
and is presented on the A12:1 address lines during
the refresh bus cycle. Address bits A19:13 are programmable to allow the refresh address block to be
located on any 8 Kbyte boundary.
Power Management Unit
The 80C186EB Power Management Unit (PMU) is
provided to control the power consumption of the
device. The PMU provides three power modes: Active, Idle, and Powerdown.
Active Mode indicates that all units on the
80C186EB are functional and the device consumes
maximum power (depending on the level of peripheral operation). Idle Mode freezes the clocks of the
Execution and Bus units at a logic zero state (all
peripherals continue to operate normally).
The Powerdown mode freezes all internal clocks at
a logic zero level and disables the crystal oscillator.
All internal registers hold their values provided V
CC
is maintained. Current consumption is reduced to
just transistor junction leakage.
80C187 Interface (80C186EB Only)
The 80C186EB (PLCC package only) supports the
direct connection of the 80C187 Numerics Coprocessor.
ONCE Test Mode
To facilitate testing and inspection of devices when
fixed into a target system, the 80C186EB has a test
mode available which forces all output and input/
output pins to be placed in the high-impedance
state. ONCE stands for ‘‘ON Circuit Emulation’’. The
ONCE mode is selected by forcing the A19/ONCE
pin LOW (0) during a processor reset (this pin is
weakly held to a HIGH (1) level) while RESIN
is ac-
tive.
7
7
Page 8
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
PACKAGE INFORMATION
This section describes the pins, pinouts, and thermal
characteristics for the 80C186EB in the Plastic
Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) package, Shrink Quad
Flat Pack (SQFP), and Quad Flat Pack (QFP) package. For complete package specifications and information, see the Intel Packaging Outlines and Dimensions Guide (Order Number: 231369).
Prefix Identification
With the extended temperature range, operational
characteristics are guaranteed over the temperature
range corresponding to
b
40§Ctoa85§C ambient.
Package types are identified by a two-letter prefix to
the part number. The prefixes are listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Prefix Identification
Prefix Note
Package Temperature
Type Type
TN PLCC Extended
TS QFP (EIAJ) Extended
SB 1 SQFP Extended/Commercial
N 1 PLCC Commercial
S 1 QFP (EIAJ) Commercial
NOTE:
1. The 5V 25 MHz and 3V 16 MHz versions are only avail-
able in commercial temperature range corresponding to
0
§
Ctoa70§C ambient.
Pin Descriptions
Each pin or logical set of pins is described in Table
3. There are three columns for each entry in the Pin
Description Table.
The Pin Name column contains a mnemonic that
describes the pin function. Negation of the signal
name (for example, RESIN
) denotes a signal that is
active low.
The Pin Type column contains two kinds of information. The first symbol indicates whether a pin is power (P), ground (G), input only (I), output only (O) or
input/output (I/O). Some pins have multiplexed
functions (for example, A19/S6). Additional symbols
indicate additional characteristics for each pin. Table
2 lists all the possible symbols for this column.
The Input Type column indicates the type of input
(Asynchronous or Synchronous).
Asynchronous pins require that setup and hold times
be met only in order to guarantee
recognition
at a
particular clock edge. Synchronous pins require that
setup and hold times be met to guarantee proper
operation.
For example, missing the setup or hold
time for the SRDY pin (a synchronous input) will result in a system failure or lockup. Input pins may also
be edge- or level-sensitive. The possible characteristics for input pins are S(E), S(L), A(E) and A(L).
The Output States column indicates the output
state as a function of the device operating mode.
Output states are dependent upon the current activity of the processor. There are four operational
states that are different from regular operation: bus
hold, reset, Idle Mode and Powerdown Mode. Appropriate characteristics for these states are also indicated in this column, with the legend for all possible characteristics in Table 2.
The Pin Description column contains a text description of each pin.
As an example, consider AD15:0. I/O signifies the
pins are bidirectional. S(L) signifies that the input
function is synchronous and level-sensitive. H(Z)
signifies that, as outputs, the pins are high-impedance upon acknowledgement of bus hold. R(Z) signifies that the pins float during reset. P(X) signifies
that the pins retain their states during Powerdown
Mode.
8
8
Page 9

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 2. Pin Description Nomenclature
Symbol Description
P Power Pin (ApplyaVCCVoltage)
G Ground (Connect to V
SS
)
I Input Only Pin
O Output Only Pin
I/O Input/Output Pin
S(E) Synchronous, Edge Sensitive
S(L) Synchronous, Level Sensitive
A(E) Asynchronous, Edge Sensitive
A(L) Asynchronous, Level Sensitive
H(1) Output Driven to VCCduring Bus Hold
H(0) Output Driven to V
SS
during Bus Hold
H(Z) Output Floats during Bus Hold
H(Q) Output Remains Active during Bus Hold
H(X) Output Retains Current State during Bus Hold
R(WH) Output Weakly Held at VCCduring Reset
R(1) Output Driven to V
CC
during Reset
R(0) Output Driven to V
SS
during Reset
R(Z) Output Floats during Reset
R(Q) Output Remains Active during Reset
R(X) Output Retains Current State during Reset
I(1) Output Driven to VCCduring Idle Mode
I(0) Output Driven to V
SS
during Idle Mode
I(Z) Output Floats during Idle Mode
I(Q) Output Remains Active during Idle Mode
I(X) Output Retains Current State during Idle Mode
P(1) Output Driven to VCCduring Powerdown Mode
P(0) Output Driven to V
SS
during Powerdown Mode
P(Z) Output Floats during Powerdown Mode
P(Q) Output Remains Active during Powerdown Mode
P(X) Output Retains Current State during Powerdown Mode
9
9
Page 10
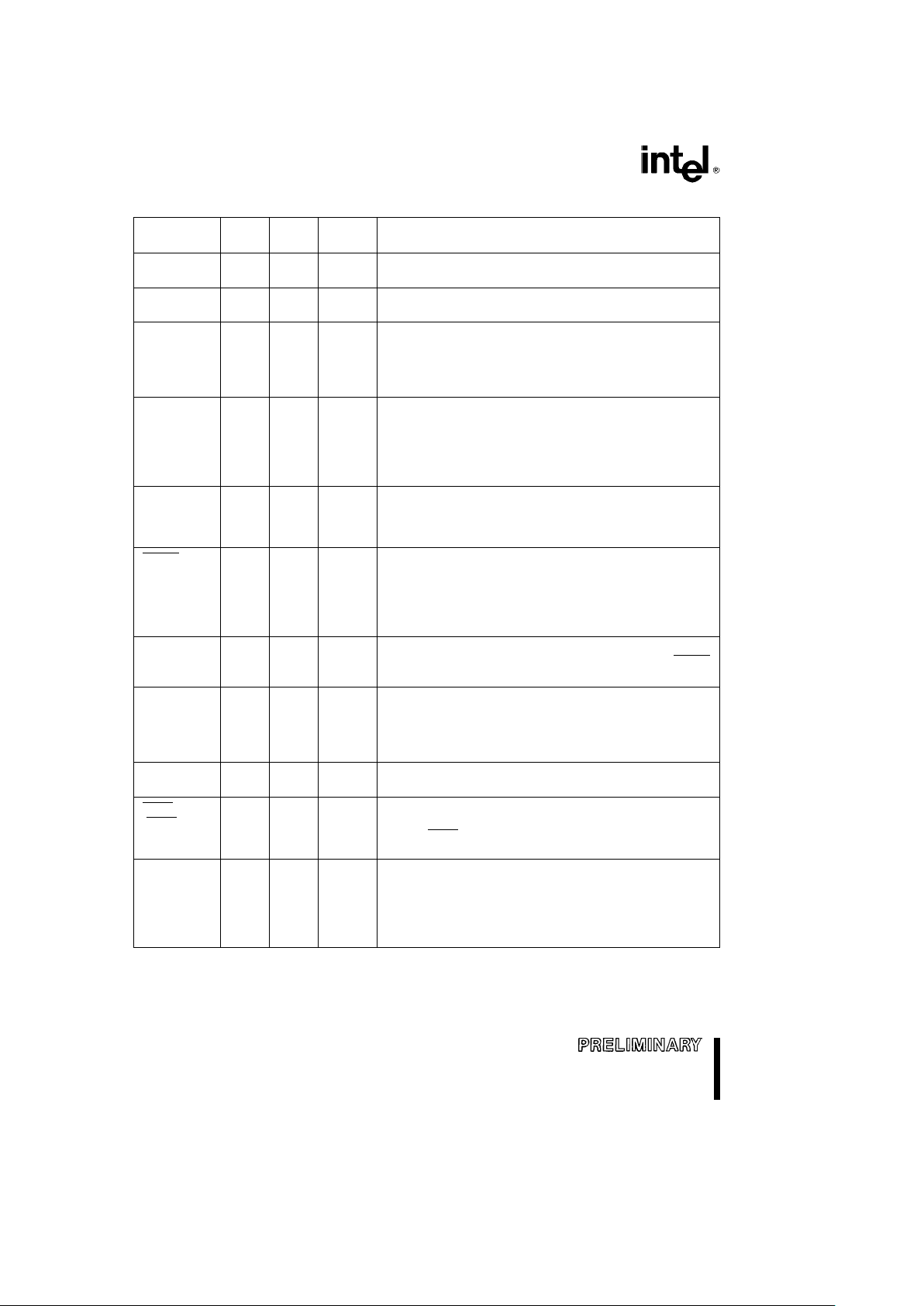
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 3. Pin Descriptions
Pin Pin Input Output
Description
Name Type Type States
V
CC
PÐ ÐPOWER connections consist of four pins which must be
shorted externally to a V
CC
board plane.
V
SS
GÐ ÐGROUND connections consist of six pins which must be
shorted externally to a V
SS
board plane.
CLKIN I A(E) Ð CLocK INput is an input for an external clock. An external
oscillator operating at two times the required processor
operating frequency can be connected to CLKIN. For crystal
operation, CLKIN (along with OSCOUT) are the crystal
connections to an internal Pierce oscillator.
OSCOUT O Ð H(Q) OSCillator OUTput is only used when using a crystal to
generate the external clock. OSCOUT (along with CLKIN)
R(Q)
are the crystal connections to an internal Pierce oscillator.
P(Q)
This pin is not to be used as 2X clock output for non-crystal
applications (i.e., this pin is N.C. for non-crystal applications).
OSCOUT does not float in ONCE mode.
CLKOUT O Ð H(Q) CLocK OUTput provides a timing reference for inputs and
outputs of the processor, and is one-half the input clock
R(Q)
(CLKIN) frequency. CLKOUT has a 50% duty cycle and
P(Q)
transistions every falling edge of CLKIN.
RESIN I A(L) Ð RESet IN causes the processor to immediately terminate
any bus cycle in progress and assume an initialized state. All
pins will be driven to a known state, and RESOUT will also
be driven active. The rising edge (low-to-high) transition
synchronizes CLKOUT with CLKIN before the processor
begins fetching opcodes at memory location 0FFFF0H.
RESOUT O Ð H(0) RESet OUTput that indicates the processor is currently in
the reset state. RESOUT will remain active as long as RESIN
R(1)
remains active.
P(0)
PDTMR I/O A(L) H(WH) Power-Down TiMeR pin (normally connected to an external
capacitor) that determines the amount of time the processor
R(Z)
waits after an exit from power down before resuming normal
P(1)
operation. The duration of time required will depend on the
startup characteristics of the crystal oscillator.
NMI I A(E) Ð Non-Maskable Interrupt input causes a TYPE-2 interrupt to
be serviced by the CPU. NMI is latched internally.
TEST/BUSY I A(E) Ð TEST is used during the execution of the WAIT instruction to
suspend CPU operation until the pin is sampled active
(TEST
)
(LOW). TEST is alternately known as BUSY when interfacing
with an 80C187 numerics coprocessor (80C186EB only).
AD15:0 I/O S(L) H(Z) These pins provide a multiplexed Address and Data bus.
During the address phase of the bus cycle, address bits 0
(AD7:0) R(Z)
through 15 (0 through 7 on the 80C188EB) are presented on
P(X)
the bus and can be latched using ALE. 8- or 16-bit data
information is transferred during the data phase of the bus
cycle.
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
10
10
Page 11
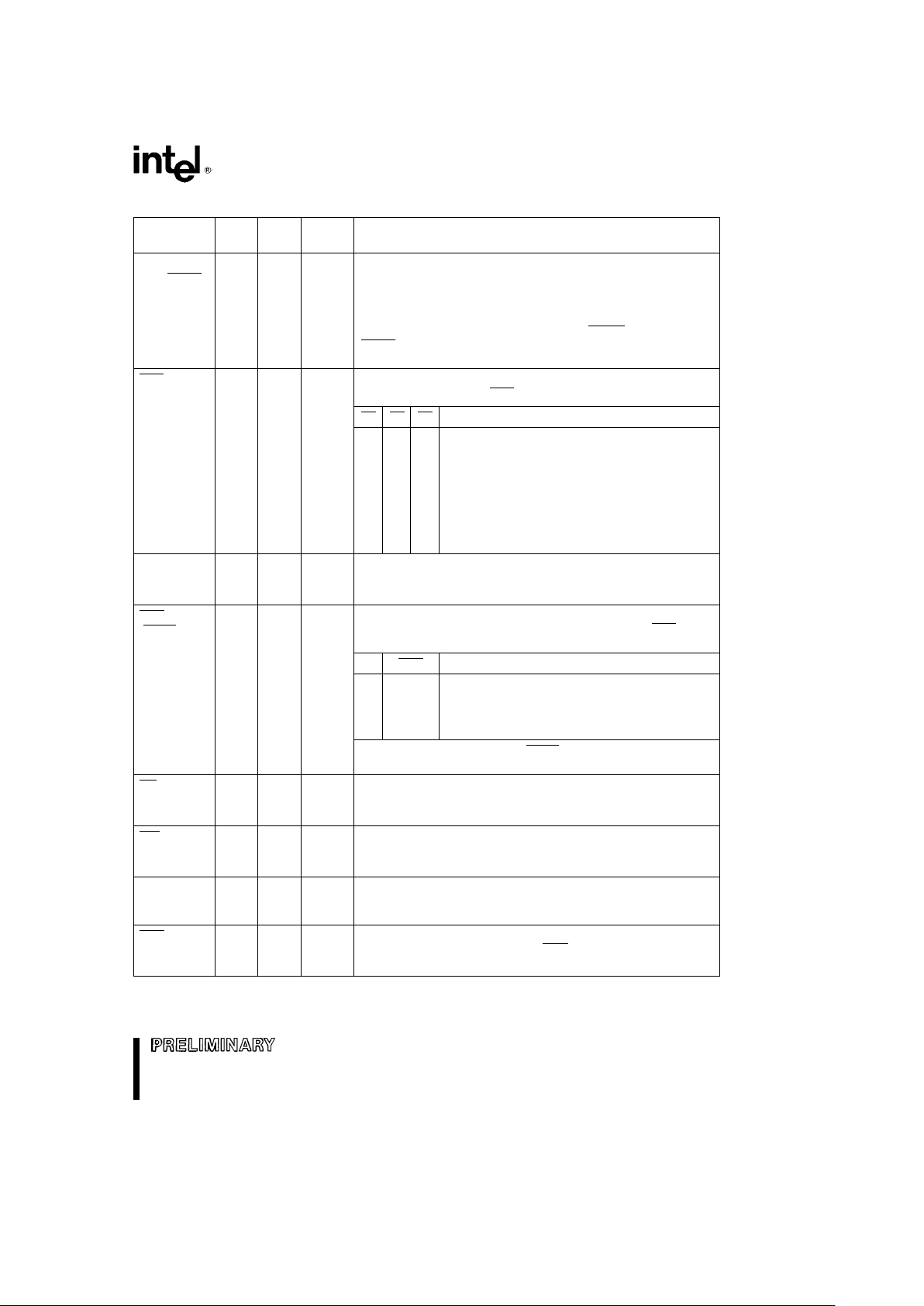
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 3. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Pin Input Output
Description
Name Type Type States
A18:16 I/O A(L) H(Z) These pins provide multiplexed Address during the address
phase of the bus cycle. Address bits 16 through 19 are presented
A19/ONCE
R(WH)
on these pins and can be latched using ALE. These pins are
(A15:A8) P(X)
driven to a logic 0 during the data phase of the bus cycle. On the
(A18:16)
80C188EB, A15 –A8 provide valid address information for the
(A19/ONCE)
entire bus cycle. During a processor reset (RESIN
active), A19/
ONCE
is used to enable ONCE mode. A18:16 must not be driven
low during reset or improper operation may result.
S2:0 O Ð H(Z) Bus cycle Status are encoded on these pins to provide bus
transaction information. S2:0
are encoded as follows:
R(Z)
P(1)
S2
S1 S0 Bus Cycle Initiated
0 0 0 Interrupt Acknowledge
0 0 1 Read I/O
0 1 0 Write I/O
0 1 1 Processor HALT
1 0 0 Queue Instruction Fetch
1 0 1 Read Memory
1 1 0 Write Memory
1 1 1 Passive (no bus activity)
ALE O Ð H(0) Address Latch Enable output is used to strobe address
information into a transparent type latch during the address phase
R(0)
of the bus cycle.
P(0)
BHE O Ð H(Z) Byte High Enable output to indicate that the bus cycle in progress
is transferring data over the upper half of the data bus. BHE
and
(RFSH
) R(Z)
A0 have the following logical encoding
P(X)
A0 BHE Encoding (for the 80C186EB/80L186EB only)
0 0 Word Transfer
0 1 Even Byte Transfer
1 0 Odd Byte Transfer
1 1 Refresh Operation
On the 80C188EB/80L188EB, RFSH is asserted low to indicate a
refresh bus cycle.
RD O Ð H(Z) ReaD output signals that the accessed memory or I/O device
must drive data information onto the data bus.
R(Z)
P(1)
WR O Ð H(Z) WRite output signals that data available on the data bus are to be
written into the accessed memory or I/O device.
R(Z)
P(1)
READY I A(L) Ð READY input to signal the completion of a bus cycle. READY
must be active to terminate any bus cycle, unless it is ignored by
S(L)
correctly programming the Chip-Select Unit.
DEN O Ð H(Z) Data ENable output to control the enable of bi-directional
transceivers in a buffered system. DEN
is active only when data is
R(Z)
to be transferred on the bus.
P(1)
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
11
11
Page 12
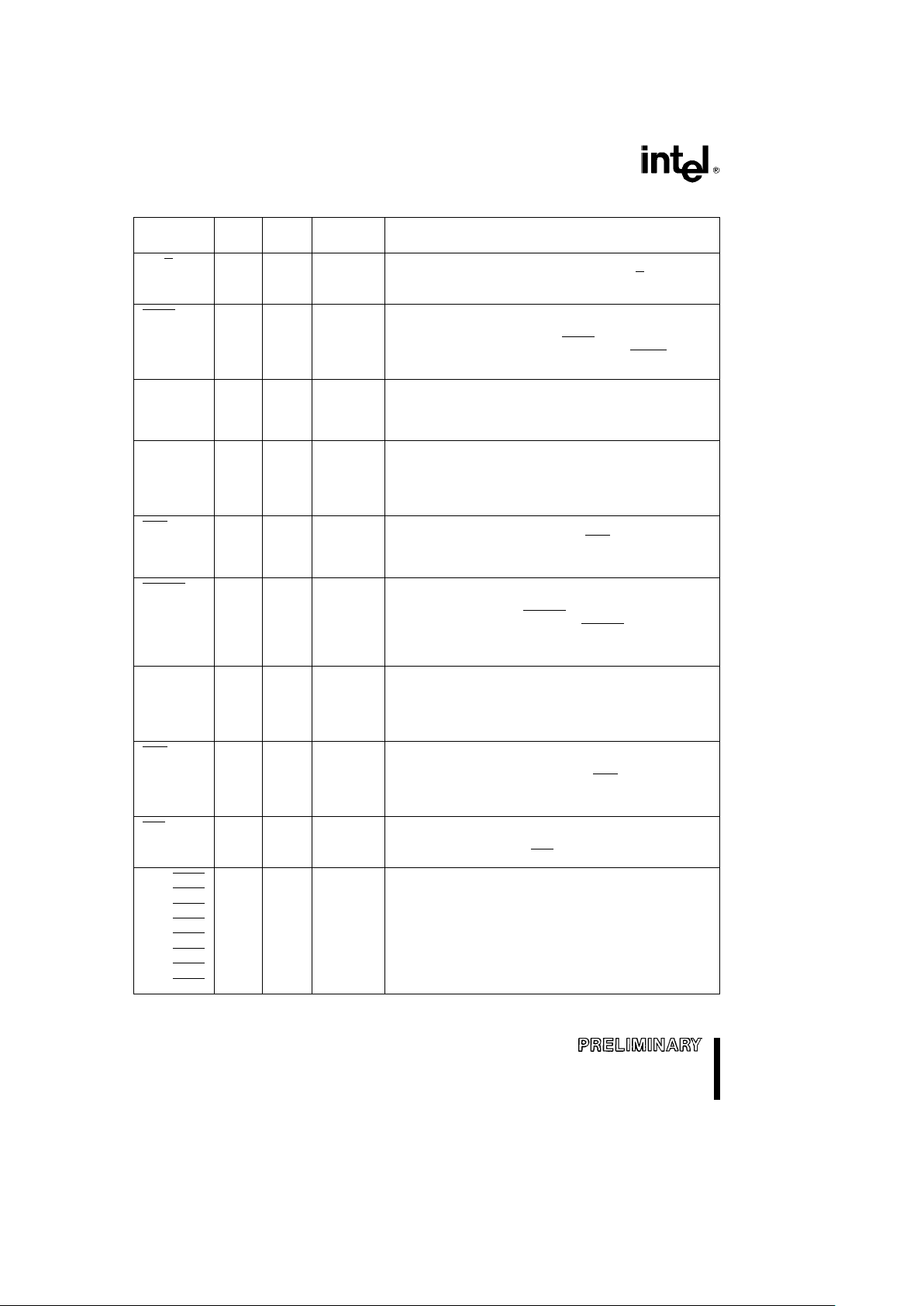
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 3. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Pin Input Output
Description
Name Type Type States
DT/R O Ð H(Z) Data Transmit/Receive output controls the direction of a
bi-directional buffer in a buffered system. DT/R
is only
R(Z)
available for the PLCC package.
P(X)
LOCK O Ð H(Z) LOCK output indicates that the bus cycle in progress is not
to be interrupted. The processor will not service other bus
R(WH)
requests (such as HOLD) while LOCK
is active. This pin is
P(1)
configured as a weakly held high input while RESIN
is
active and must not be driven low.
HOLD I A(L) Ð HOLD request input to signal that an external bus master
wishes to gain control of the local bus. The processor will
relinquish control of the local bus between instruction
boundaries not conditioned by a LOCK prefix.
HLDA O Ð H(1) HoLD Acknowledge output to indicate that the processor
has relinquished control of the local bus. When HLDA is
R(0)
asserted, the processor will (or has) floated its data bus
P(0)
and control signals allowing another bus master to drive the
signals directly.
NCS O Ð H(1) Numerics Coprocessor Select output is generated when
accessing a numerics coprocessor. NCS is not provided on
(N.C.) R(1)
the QFP or SQFP packages. This signal does not exist on
P(1)
the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
ERROR I A(L) Ð ERROR input that indicates the last numerics coprocessor
operation resulted in an exception condition. An interrupt
(N.C.)
TYPE 16 is generated if ERROR
is sampled active at the
beginning of a numerics operation. ERROR
is not provided
on the QFP or SQFP packages. This signal does not exist
on the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
PEREQ I A(L) Ð CoProcessor REQuest signals that a data transfer
between an External Numerics Coprocessor and Memory is
(N.C.)
pending. PEREQ is not provided on the QFP or SQFP
packages. This signal does not exist on the 80C188EB/
80L188EB.
UCS O Ð H(1) Upper Chip Select will go active whenever the address of
a memory or I/O bus cycle is within the address limitations
R(1)
programmed by the user. After reset, UCS
is configured to
P(1)
be active for memory accesses between 0FFC00H and
0FFFFFH.
LCS O Ð H(1) Lower Chip Select will go active whenever the address of
a memory bus cycle is within the address limitations
R(1)
programmed by the user. LCS
is inactive after a reset.
P(1)
P1.0/GCS0 O Ð H(X)/H(1) These pins provide a multiplexed function. If enabled, each
pin can provide a Generic Chip Select output which will go
P1.1/GCS1
R(1)
active whenever the address of a memory or I/O bus cycle
P1.2/GCS2
P(X)/P(1)
is within the address limitations programmed by the user.
P1.3/GCS3
When not programmed as a Chip-Select, each pin may be
P1.4/GCS4
used as a general purpose output Port. As an output port
P1.5/GCS5
pin, the value of the pin can be read internally.
P1.6/GCS6
P1.7/GCS7
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
12
12
Page 13
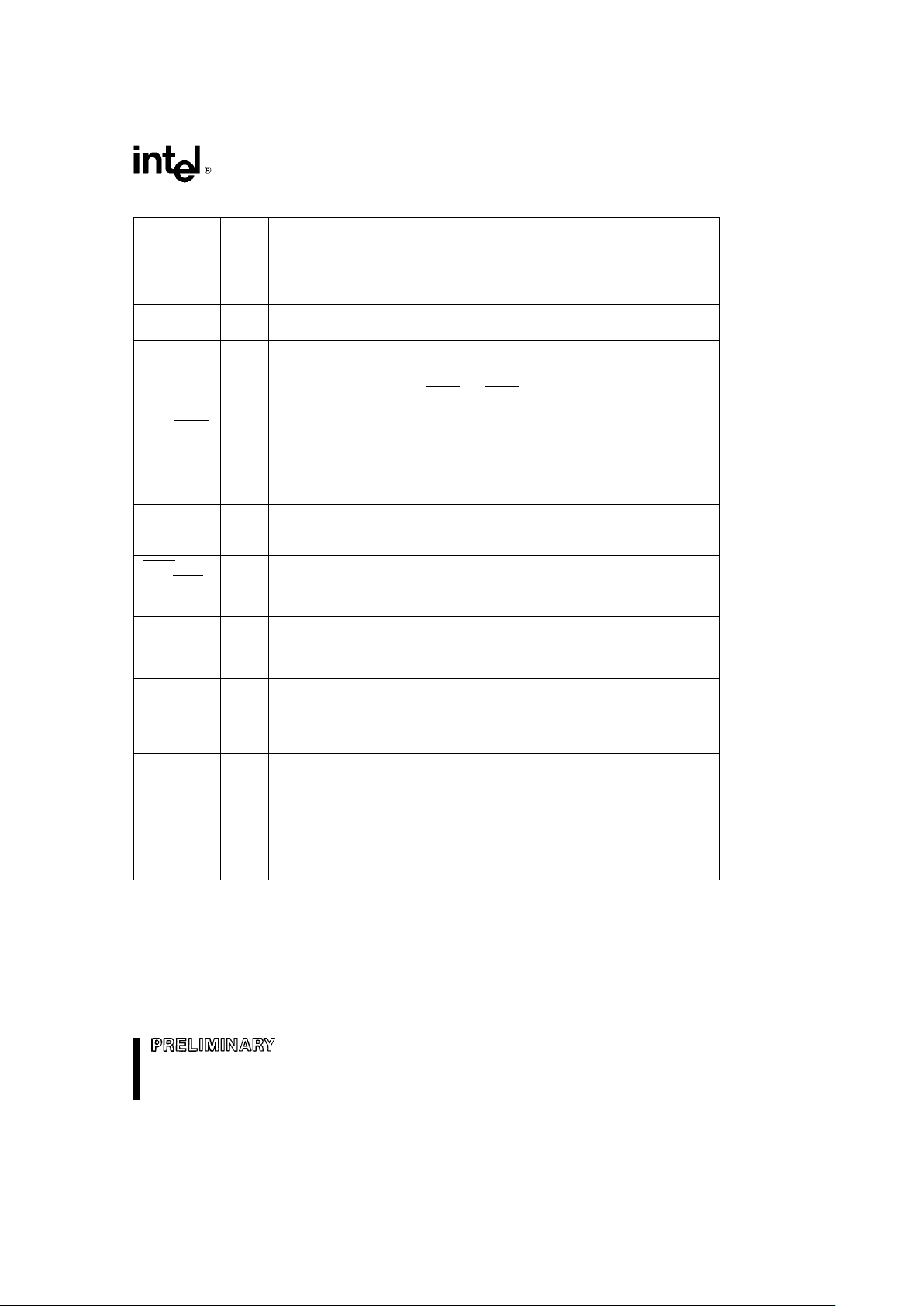
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 3. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Pin Input Output
Description
Name Type Type States
T0OUT O Ð H(Q) Timer OUTput pins can be programmed to provide a
single clock or continuous waveform generation,
T1OUT R(1)
depending on the timer mode selected.
P(Q)
T0IN I A(L) Ð Timer INput is used either as clock or control signals,
depending on the timer mode selected.
T1IN A(E)
INT0 I A(E,L) Ð Maskable INTerrupt input will cause a vector to a
specific Type interrupt routine. To allow interrupt
INT1
expansion, INT0 and/or INT1 can be used with
INT4
INTA0
and INTA1 to interface with an external slave
controller.
INT2/INTA0 I/O A(E,L) H(1) These pins provide a multiplexed function. As inputs,
they provide a maskable INTerrupt that will cause
INT3/INTA1
R(Z)
the CPU to vector to a specific Type interrupt routine.
P(1)
As outputs, each is programmatically controlled to
provide an INTERRUPT ACKNOWLEDGE
handshake signal to allow interrupt expansion.
P2.7 I/O A(L) H(X) BI-DIRECTIONAL, open-drain Port pins.
P2.6 R(Z)
P(X)
CTSO I A(L) Ð Clear-To-Send input is used to prevent the
transmission of serial data on their respective TXD
P2.4/CTS1
signal pin. CTS1 is multiplexed with an input only port
function.
TXD0 O Ð H(X)/H(Q) Transmit Data output provides serial data
information. TXD1 is multiplexed with an output only
P2.1/TXD1 R(1)
Port function. During synchronous serial
P(X)/P(Q)
communications, TXD will function as a clock output.
RXD0 I/O A(L) R(Z) Receive Data input accepts serial data information.
RXD1 is multiplexed with an input only Port function.
P2.0/RXD1 H(Q)
During synchronous serial communications, RXD is
P(X)
bi-directional and will become an output for
transmission or data (TXD becomes the clock).
P2.5/BCLK0 I A(L)/A(E) Ð Baud CLocK input can be used as an alternate clock
source for each of the integrated serial channels.
P2.2/BCLK1
BCLKx is multiplexed with an input only Port function,
and cannot exceed a clock rate greater than one-half
the operating frequency of the processor.
P2.3/SINT1 O Ð H(X)/H(Q) Serial INTerrupt output will go active to indicate
serial channel 1 requires service. SINT1 is
R(0)
multiplexed with an output only Port function.
P(X)/P(X)
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
13
13
Page 14

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
80C186EB PINOUT
Tables 4 and 5 list the 80C186EB/80C188EB pin
names with package location for the 84-pin Plastic
Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) component. Figure 5
depicts the complete 80C186EB/80C188EB pinout
(PLCC package) as viewed from the top side of the
component (i.e., contacts facing down).
Tables 6 and 7 list the 80C186EB/80C188EB pin
names with package location for the 80-pin Quad
Flat Pack (QFP) component. Figure 6 depicts the
complete 80C186EB/80C188EB (QFP package) as
viewed from the top side of the component (i.e., contacts facing down).
Tables 8 and 9 list the 80186EB/80188EB pin
names with package location for the 80-pin Shrink
Quad Flat Pack (SQFP) component. Figure 7 depicts
the complete 80C186EB/80C188EB (SQFP package) as viewed from the top side of the component
(i.e., contacts facing down).
Table 4. PLCC Pin Names with Package Location
Address/Data Bus
Name Location
AD0 61
AD1 66
AD2 68
AD3 70
AD4 72
AD5 74
AD6 76
AD7 78
AD8 (A8) 62
AD9 (A9) 67
AD10 (A10) 69
AD11 (A11) 71
AD12 (A12) 73
AD13 (A13) 75
AD14 (A14) 77
AD15 (A15) 79
A16 80
A17 81
A18 82
A19/ONCE
83
Bus Control
Name Location
ALE 6
BHE
(RFSH)7
S0
10
S1
9
S2 8
RD 4
WR
5
READY 18
DEN
11
DT/R
16
LOCK 15
HOLD 13
HLDA 12
Power
Name Location
V
SS
2, 22, 43
63, 65, 84
V
CC
1, 23
42, 64
Processor Control
Name Location
RESIN 37
RESOUT 38
CLKIN 41
OSCOUT 40
CLKOUT 44
TEST/BUSY 14
NCS
(N.C.) 60
PEREQ (N.C.) 39
ERROR
(N.C.) 3
PDTMR 36
NMI 17
INT0 31
INT1 32
INT2/INTA0
33
INT3/INTA1
34
INT4 35
I/O
Name Location
UCS 30
LCS
29
P1.0/GCS0
28
P1.1/GCS1
27
P1.2/GCS2 26
P1.3/GCS3 25
P1.4/GCS4
24
P1.5/GCS5
21
P1.6/GCS6
20
P1.7/GCS7
19
T0OUT 45
T0IN 46
T1OUT 47
T1IN 48
RXD0 53
TXD0 52
P2.5/BCLK0 54
CTS0
51
P2.0/RXD1 57
P2.1/TXD1 58
P2.2/BCLK1 59
P2.3/SINT1 55
P2.4/CTS1
56
P2.6 50
P2.7 49
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
14
14
Page 15

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 5. PLCC Package Locations with Pin Name
Location Name
1V
CC
2V
SS
3 ERROR (N.C.)
4RD
5WR
6 ALE
7 BHE
(RFSH)
8S2
9S1
10 S0
11 DEN
12 HLDA
13 HOLD
14 TEST
/BUSY
15 LOCK
16 DT/R
17 NMI
18 READY
19 P1.7/GCS7
20 P1.6/GCS6
21 P1.5/GCS5
Location Name
22 V
SS
23 V
CC
24 P1.4/GCS4
25 P1.3/GCS3
26 P1.2/GCS2
27 P1.1/GCS1
28 P1.0/GCS0
29 LCS
30 UCS
31 INT0
32 INT1
33 INT2/INTA0
34 INT3/INTA1
35 INT4
36 PDTMR
37 RESIN
38 RESOUT
39 PEREQ (N.C.)
40 OSCOUT
41 CLKIN
42 V
CC
Location Name
43 V
SS
44 CLKOUT
45 T0OUT
46 T0IN
47 T1OUT
48 T1IN
49 P2.7
50 P2.6
51 CTS0
52 TXD0
53 RXD0
54 P2.5/BCLK0
55 P2.3/SINT1
56 P2.4/CTS1
57 P2.0/RXD1
58 P2.1/TXD1
59 P2.2/BCLK1
60 NCS
(N.C.)
61 AD0
62 AD8 (A8)
63 V
SS
Location Name
64 V
CC
65 V
SS
66 AD1
67 AD9 (A9)
68 AD2
69 AD10 (A10)
70 AD3
71 AD11 (A11)
72 AD4
73 AD12 (A12)
74 AD5
75 AD13 (A13)
76 AD6
77 AD14 (A14)
78 AD7
79 AD15 (A15)
80 A16
81 A17
82 A18
83 A19/ONCE
84 V
SS
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
15
15
Page 16
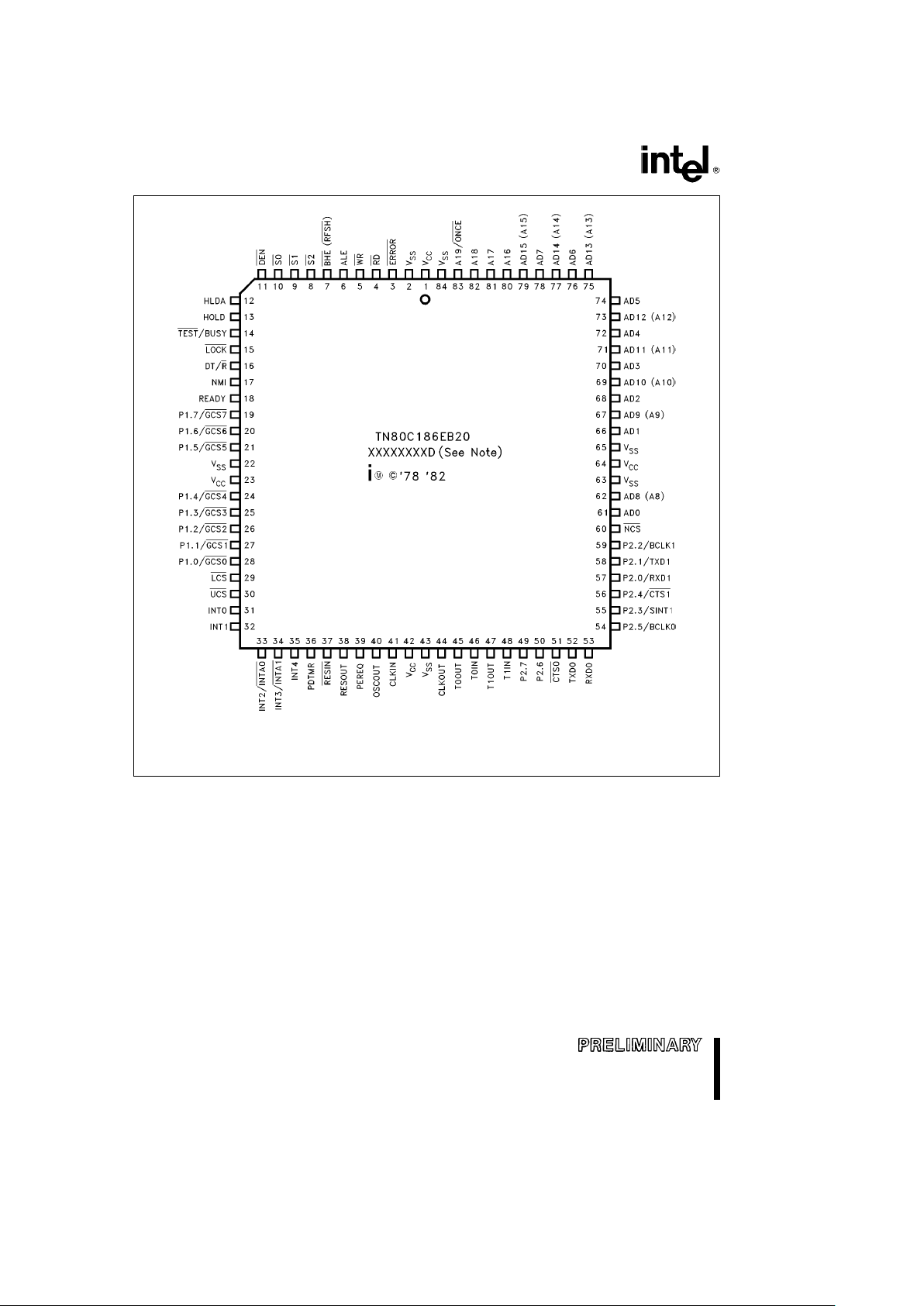
80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 5
NOTE:
This is the FPO number location (indicated by X’s).
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
Figure 4. 84-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier Pinout Diagram
16
16
Page 17

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 6. QFP Pin Name with Package Location
Address/Data Bus
Name Location
AD0 10
AD1 15
AD2 17
AD3 19
AD4 21
AD5 23
AD6 25
AD7 27
AD8 (A8) 11
AD9 (A9) 16
AD10 (A10) 18
AD11 (A11) 20
AD12 (A12) 22
AD13 (A13) 24
AD14 (A14) 26
AD15 (A15) 28
A16 29
A17 30
A18 31
A19/ONCE
32
Bus Control
Name Location
ALE 38
BHE
(RFSH)39
S0
42
S1
41
S2 40
RD 36
WR
37
READY 49
DEN
43
LOCK
47
HOLD 45
HLDA 44
Power
Name Location
V
SS
12, 14, 33
35, 53, 73
V
CC
13, 34
54, 72
Processor Control
Name Location
RESIN 68
RESOUT 69
CLKIN 71
OSCOUT 70
CLKOUT 74
TEST 46
PDTMR 67
NMI 48
INT0 62
INT1 63
INT2/INTA0
64
INT3/INTA1 65
INT4 66
I/O
Name Location
UCS 61
LCS
60
P1.0/GCS0
59
P1.1/GCS1
58
P1.2/GCS2 57
P1.3/GCS3 56
P1.4/GCS4
55
P1.5/GCS5
52
P1.6/GCS6
51
P1.7/GCS7
50
T0OUT 75
T0IN 76
T1OUT 77
T1IN 78
RXD0 3
TXD0 2
P2.5/BCLK0 4
CTS0
1
P2.0/RXD1 7
P2.1/TXD1 8
P2.2/BCLK1 9
P2.3/SINT1 5
P2.4/CTS1
6
P2.6 80
P2.7 79
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
17
17
Page 18

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 7. QFP Package Location with Pin Names
Location Name
1 CTS0
2 TXD0
3 RXD0
4 P2.5/BCLK0
5 P2.3/SINT1
6 P2.4/CTS1
7 P2.0/RXD1
8 P2.1/TXD1
9 P2.2/BCLK1
10 AD0
11 AD8 (A8)
12 V
SS
13 V
CC
14 V
SS
15 AD1
16 AD9 (A9)
17 AD2
18 AD10 (A10)
19 AD3
20 AD11 (A11)
Location Name
21 AD4
22 AD12 (A12)
23 AD5
24 AD13 (A13)
25 AD6
26 AD14 (A14)
27 AD7
28 AD15 (A15)
29 A16
30 A17
31 A18
32 A19/ONCE
33 V
SS
34 V
CC
35 V
SS
36 RD
37 WR
38 ALE
39 BHE
(RFSH)
40 S2
Location Name
41 S1
42 S0
43 DEN
44 HLDA
45 HOLD
46 TEST
47 LOCK
48 NMI
49 READY
50 P1.7/GCS7
51 P1.6/GCS6
52 P1.5/GCS5
53 V
SS
54 V
CC
55 P1.4/GCS4
56 P1.3/GCS3
57 P1.2/GCS2
58 P1.1/GCS1
59 P1.0/GCS0
60 LCS
Location Name
61 UCS
62 INT0
63 INT1
64 INT2/INTA0
65 INT3/INTA1
66 INT4
67 PDTMR
68 RESIN
69 RESOUT
70 OSCOUT
71 CLKIN
72 V
CC
73 V
SS
74 CLKOUT
75 T0OUT
76 T0IN
77 T1OUT
78 T1IN
79 P2.7
80 P2.6
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
18
18
Page 19

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 6
NOTE:
This is the FPO number location (indicated by X’s).
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
Figure 5. Quad Flat Pack Pinout Diagram
19
19
Page 20

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Table 8. SQFP Pin Functions with Location
AD Bus
AD0 47
AD1 52
AD2 54
AD3 56
AD4 58
AD5 60
AD6 62
AD7 64
AD8 (A8) 48
AD9 (A9) 53
AD10 (A10) 55
AD11 (A11) 57
AD12 (A12) 59
AD13 (A13) 61
AD14 (A14) 63
AD15 (A15) 65
A16 66
A17 67
A18 68
A19/ONCE 69
Bus Control
ALE 75
BHE
Ý
(RFSHÝ)76
S0
Ý
79
S1
Ý
78
S2
Ý
77
RD
Ý
73
WR
Ý
74
READY 6
DEN
Ý
80
LOCK
Ý
4
HOLD 2
HLDA 1
Processor Control
RESIN
Ý
25
RESOUT 26
CLKIN 28
OSCOUT 27
CLKOUT 31
TESTÝ/BUSY 3
NMI 5
INT0 19
INT1 20
INT2/INTA0
Ý
21
INT3/INTA1
Ý
22
INT4 23
PDTMR 24
Power and Ground
V
CC
11
V
CC
29
V
CC
50
V
CC
71
V
SS
10
V
SS
30
V
SS
49
V
SS
51
V
SS
70
V
SS
72
I/O
UCS
Ý
18
LCS
Ý
17
P1.0/GCS0
Ý
16
P1.1/GCS1
Ý
15
P1.2/GCS2
Ý
14
P1.3/GCS3
Ý
13
P1.4/GCS4
Ý
12
P1.5/GCS5
Ý
9
P1.6/GCS6
Ý
8
P1.7/GCS7
Ý
7
P2.0/RXD1 44
P2.1/TXD1 45
P2.2/BCLK1 46
P2.3/SINT1 42
P2.4/CTS1
Ý
43
P2.5/BCLK0 41
P2.6 37
P2.7 36
CTS0
Ý
38
TXD0 39
RXD0 40
T0IN 33
T1IN 35
T0OUT 32
T1OUT 34
Table 9. SQFP Pin Locations with Pin Names
1 HLDA
2 HOLD
3 TEST
Ý
4 LOCK
Ý
5 NMI
6 READY
7 P1.7/GCS7
Ý
8 P1.6/GCS6
Ý
9 P1.5/GCS5
Ý
10 V
SS
11 V
CC
12 P1.4/GCS4
Ý
13 P1.3/GCS3
Ý
14 P1.2/GCS2
Ý
15 P1.1/GCS1
Ý
16 P1.0/GCS0
Ý
17 LCS
Ý
18 UCS
Ý
19 INT0
20 INT1
21 INT1/INTA0
Ý
22 INT3/INTA1
Ý
23 INT4
24 PDTMR
25 RESIN
Ý
26 RESOUT
27 OSCOUT
28 CLKIN
29 V
CC
30 V
SS
31 CLKOUT
32 T0OUT
33 T0IN
34 T1OUT
35 T1IN
36 P2.7
37 P2.6
38 CTS0
Ý
39 TXD0
40 RXD0
41 P2.5/BCLK0
42 P2.3/SINT1
43 P2.4/CTS1
Ý
44 P2.0/RXD1
45 P2.1/TXD1
46 P2.2/BCLK1
47 AD0
48 AD8 (A8)
49 V
SS
50 V
CC
51 V
SS
52 AD1
53 AD9 (A9)
54 AD2
55 AD10 (A10)
56 AD3
57 AD11 (A11)
58 AD4
59 AD12 (A12)
60 AD5
61 AD13 (A13)
62 AD6
63 AD14 (A14)
64 AD7
65 AD15 (A15)
66 A16
67 A17
68 A18
69 A19/ONCE
70 V
SS
71 V
CC
72 V
SS
73 RD
Ý
74 WR
Ý
75 ALE
76 BHEÝ(RFSHÝ)
77 S2
Ý
78 S1
Ý
79 S0
Ý
80 DEN
Ý
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
20
20
Page 21

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 7
NOTE:
XXXXXXXXC indicates Intel FPO number.
Pin names in parentheses apply to the 80C188EB/80L188EB.
Figure 6. SQFP Package
21
21
Page 22

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
PACKAGE THERMAL
SPECIFICATIONS
The 80C186EB/80L186EB is specified for operation
when T
C
(the case temperature) is within the range
of
b
40§Ctoa100§C (PLCC package) orb40§Cto
a
114§C (QFP package). TCmay be measured in
any environment to determine whether the processor is within the specified operating range. The case
temperature must be measured at the center of the
top surface.
T
A
(the ambient temperature) can be calculated
from i
CA
(thermal resistance from the case to ambi-
ent) with the following equation:
T
A
e
T
C
b
P*i
CA
Typical values for iCAat various airflows are given
in Table 10. P (the maximum power consumption,
specified in watts) is calculated by using the maximum ICC as tabulated in the DC specifications and
V
CC
of 5.5V.
Table 10. Thermal Resistance (i
CA
) at Various Airflows (in§C/Watt)
Airflow Linear ft/min (m/sec)
0 200 400 600 800 1000
(0) (1.01) (2.03) (3.04) (4.06) (5.07)
iCA(PLCC) 30 24 21 19 17 16.5
iCA(QFP) 58 47 43 40 38 36
iCA(SQFP) 70 TBD TBD TBD TBD TBD
22
22
Page 23

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Storage Temperature ААААААААААb65§Ctoa150§C
Case Temp under Bias АААААААААb65§Ctoa120§C
Supply Voltage
with Respect to V
SS
АААААААААААb0.5V toa6.5V
Voltage on other Pins
with Respect to V
SS
ААААААb0.5V to V
CC
a
0.5V
NOTICE: This data sheet contains preliminary information on new products in production. It is valid for
the devices indicated in the revision history. The
specifications are subject to change without notice.
*
WARNING: Stressing the device beyond the ‘‘Absolute
Maximum Ratings’’ may cause permanent damage.
These are stress ratings only. Operation beyond the
‘‘Operating Conditions’’ is not recommended and extended exposure beyond the ‘‘Operating Conditions’’
may affect device reliability.
Recommended Connections
Power and ground connections must be made to
multiple V
CC
and VSSpins. Every 80C186EB-based
circuit board should include separate power (V
CC
)
and ground (V
SS
) planes. Every VCCpin must be
connected to the power plane, and every V
SS
pin
must be connected to the ground plane. Pins identified as ‘‘NC’’ must not be connected in the system.
Liberal decoupling capacitance should be placed
near the processor. The processor can cause transient power surges when its output buffers transition, particularly when connected to large capacitive loads.
Low inductance capacitors and interconnects are
recommended for best high frequency electrical performance. Inductance is reduced by placing the decoupling capacitors as close as possible to the processor V
CC
and VSSpackage pins.
Always connect any unused input to an appropriate
signal level. In particular, unused interrupt inputs
(INT0:4) should be connected to V
CC
through a pull-
up resistor (in the range of 50 KX). Leave any un-
used output pin or any NC pin unconnected.
23
23
Page 24

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
DC SPECIFICATIONS (80C186EB/80C188EB)
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
V
CC
Supply Voltage 4.5 5.5 V
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
b
0.5 0.3 V
CC
V
V
IH
Input High Voltage 0.7 V
CCVCC
a
0.5 V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage 0.45 V I
OL
e
3 mA (Min)
V
OH
Output High Voltage V
CC
b
0.5 V I
OH
eb
2 mA (MIn)
V
HYR
Input Hysterisis on RESIN 0.50 V
I
LI1
Input Leakage Current for Pins:
g
15 mA0VsV
IN
s
V
CC
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY, HOLD,
RESIN
, CLKIN, TEST, NMI, INT4:0,
T0IN, T1IN, RXD0, BCLK0
, CTS0,
RXD1, BCLK1, CTS1, P2.6, P2.7
I
LI2
Input Leakage Current for Pins:
g
0.275
g
7mA0V
s
V
IN
k
V
CC
ERROR, PEREQ
I
LI3
Input Leakage Current for Pins:
b
0.275
b
5.0 mA V
IN
e
0.7 VCC(Note 1)
A19/ONCE
, A18:16, LOCK
I
LO
Output Leakage Current
g
15 mA 0.45sV
OUT
s
V
CC
(Note 2)
I
CC
Supply Current Cold (RESET)
80C186EB25 115 mA (Notes 3, 7)
80C186EB20 108 mA (Note 3)
80C186EB13 73 mA (Note 3)
I
ID
Supply Current Idle
80C186EB25 91 mA (Notes 4, 7)
80C186EB20 76 mA (Note 4)
80C186EB13 48 mA (Note 4)
I
PD
Supply Current Powerdown
80C186EB25 100 mA (Notes 5, 7)
80C186EB20 100 mA (Note 5)
80C186EB13 100 mA (Note 5)
C
IN
Input Pin Capacitance 0 15 pF T
F
e
1 MHz
C
OUT
Output Pin Capacitance 0 15 pF T
F
e
1 MHz (Note 6)
NOTES:
1. These pins have an internal pull-up device that is active while RESIN
is low and ONCE Mode is not active. Sourcing more
current than specified (on any of these pins) may invoke a factory test mode.
2. Tested by outputs being floated by invoking ONCE Mode or by asserting HOLD.
3. Measured with the device in RESET and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with ALL outputs loaded as
specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
4. Measured with the device in HALT (IDLE Mode active) and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with ALL
outputs loaded as specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
5. Measured with the device in HALT (Powerdown Mode active) and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with
ALL outputs loaded as specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
6. Output Capacitance is the capacitive load of a floating output pin.
7. Operating temperature for 25 MHz is 0
§
Cto70§C, V
CC
e
5.0g10%.
24
24
Page 25

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
DC SPECIFICATIONS (80L186EB16) (operating temperature, 0
§
Cto70§C)
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
V
CC
Supply Voltage 3.0 5.5 V
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
b
0.5 0.3 V
CC
V
V
IH
Input High Voltage 0.7 V
CCVCC
a
0.5 V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage 0.45 V I
OL
e
1.6 mA (Min) (Note 1)
V
OH
Output High Voltage V
CC
b
0.5 V I
OH
eb
1 mA (Min) (Note 1)
V
HYR
Input Hysterisis on RESIN 0.50 V
I
LI1
Input Leakage Current for pins:
g
15 mA0VsV
IN
s
V
CC
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY, HOLD,
RESIN
, CLKIN, TEST, NMI,
INT4:0, T0IN, T1IN, RXD0,
BCLK0, CTS0, RXD1, BCLK1,
CTS1
, SINT1, P2.6, P2.7
I
LI2
Input Leakage Current for Pins:
b
0.275
b
2mAV
IN
e
0.7 VCC(Note 2)
A19/ONCE
, A18:16, LOCK
I
LO
Output Leakage Current
g
15 mA 0.45sV
OUT
s
VCC(Note 3)
I
CC3
Supply Current (RESET, 3.3V)
80L186EB16 54 mA (Note 4)
I
ID3
Supply Current Idle (3.3V)
80L186EB16 38 mA (Note 5)
I
PD3
Supply Current Powerdown (3.3V)
80L186EB16 40 mA (Note 6)
C
IN
Input Pin Capacitance 0 15 pF T
F
e
1 MHz
C
OUT
Output Pin Capacitance 0 15 pF T
F
e
1 MHz (Note 7)
NOTES:
1. I
OL
and IOHmeasured at V
CC
e
3.0V.
2. These pins have an internal pull-up device that is active while RESIN
is low and ONCE Mode is not active. Sourcing more
current than specified (on any of these pins) may invoke a factory test mode.
3. Tested by outputs being floated by invoking ONCE Mode or by asserting HOLD.
4. Measured with the device in RESET and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with ALL outputs loaded as
specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
5. Measured with the device in HALT (IDLE Mode active) and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with ALL
outputs loaded as specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
6. Measured with the device in HALT (Powerdown Mode active) and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with
ALL outputs loaded as specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
7. Output Capacitance is the capacitive load of a floating output pin.
25
25
Page 26

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
DC SPECIFICATIONS (80L186EB13/80L188EB13, 80L186EB8/80L188EB8)
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
V
CC
Supply Voltage 2.7 5.5 V
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
b
0.5 0.3 V
CC
V
V
IH
Input High Voltage 0.7 V
CCVCC
a
0.5 V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage 0.45 V I
OL
e
1.6 mA (Min) (Note 1)
V
OH
Output High Voltage V
CC
b
0.5 V I
OH
eb
1 mA (Min) (Note 1)
V
HYR
Input Hysterisis on RESIN 0.50 V
I
LI1
Input Leakage Current for pins:
g
15 mA0VsV
IN
s
V
CC
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY, HOLD,
RESIN
, CLKIN, TEST, NMI,
INT4:0, T0IN, T1IN, RXD0,
BCLK0, CTS0, RXD1, BCLK1,
CTS1
, SINT1, P2.6, P2.7
I
LI2
Input Leakage Current for Pins:
b
0.275
b
2mAV
IN
e
0.7 VCC(Note 2)
A19/ONCE
, A18:16, LOCK
I
LO
Output Leakage Current
g
15 mA 0.45sV
OUT
s
VCC(Note 3)
I
CC5
Supply Current (RESET, 5.5V)
80L186EB13 73 mA (Note 4)
80L186EB8 45 mA (Note 4)
I
CC3
Supply Current (RESET, 2.7V)
80L186EB13 36 mA (Note 4)
80L186EB8 22 mA (Note 4)
I
ID5
Supply Current Idle (5.5V)
80L186EB13 48 mA (Note 5)
80L186EB8 31 mA (Note 5)
I
ID3
Supply Current Idle (2.7V)
80L186EB13 24 mA (Note 5)
80L186EB8 15 mA (Note 5)
I
PD5
Supply Current Powerdown (5.5V)
80L186EB13 100 mA (Note 6)
80L186EB8 100 mA (Note 6)
I
PD3
Supply Current Powerdown (2.7V)
80L186EB13 30 mA (Note 6)
80L186EB8 30 mA (Note 6)
C
IN
Input Pin Capacitance 0 15 pF T
F
e
1 MHz
C
OUT
Output Pin Capacitance 0 15 pF T
F
e
1 MHz (Note 7)
NOTES:
1. I
OL
and IOHmeasured at V
CC
e
2.7V.
2. These pins have an internal pull-up device that is active while RESIN
is low and ONCE Mode is not active. Sourcing more
current than specified (on any of these pins) may invoke a factory test mode.
3. Tested by outputs being floated by invoking ONCE Mode or by asserting HOLD.
4. Measured with the device in RESET and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with ALL outputs loaded as
specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
5. Measured with the device in HALT (IDLE Mode active) and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with ALL
outputs loaded as specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
6. Measured with the device in HALT (Powerdown Mode active) and at worst case frequency, V
CC
, and temperature with
ALL outputs loaded as specified in AC Test Conditions, and all floating outputs driven to V
CC
or GND.
7. Output Capacitance is the capacitive load of a floating output pin.
26
26
Page 27

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
ICCVERSUS FREQUENCY AND VOLTAGE
The current (ICC) consumption of the processor is
essentially composed of two components; I
PD
and
I
CCS
.
I
PD
is the quiescent current that represents internal
device leakage, and is measured with all inputs or
floating outputs at GND or V
CC
(no clock applied to
the device). I
PD
is equal to the Powerdown current
and is typically less than 50 mA.
I
CCS
is the switching current used to charge and
discharge parasitic device capacitance when changing logic levels. Since I
CCS
is typically much greater
than I
PD,IPD
can often be ignored when calculating
I
CC
.
I
CCS
is related to the voltage and frequency at which
the device is operating. It is given by the formula:
PowereVcIeV
2
c
C
DEV
c
f
... I
e
I
CC
e
I
CCS
e
VcC
DEV
c
f
Where: VeDevice operating voltage (VCC)
C
DEV
e
Device capacitance
f
e
Device operating frequency
I
CCS
e
I
CC
e
Device current
Measuring C
DEV
on a device like the 80C186EB
would be difficult. Instead, C
DEV
is calculated using
the above formula by measuring I
CC
at a known V
CC
and frequency (see Table 11). Using this C
DEV
val-
ue, I
CC
can be calculated at any voltage and fre-
quency within the specified operating range.
EXAMPLE: Calculate the typical I
CC
when operating
at 10 MHz, 4.8V.
I
CC
e
I
CCS
e
4.8c0.583c10&28 mA
PDTMR PIN DELAY CALCULATION
The PDTMR pin provides a delay between the assertion of NMI and the enabling of the internal
clocks when exiting Powerdown. A delay is required
only when using the on-chip oscillator to allow the
crystal or resonator circuit time to stabilize.
NOTE:
The PDTMR pin function does not apply when
RESIN
is asserted (i.e., a device reset during Pow-
erdown is similar to a cold reset and RESIN
must
remain active until after the oscillator has stabilized).
To calculate the value of capacitor required to provide a desired delay, use the equation:
440cteCPD(5V, 25§C)
Where: tedesired delay in seconds
C
PD
e
capacitive load on PDTMR in microfarads
EXAMPLE: To get a delay of 300 ms, a capacitor
value of C
PD
e
440c(300c10
b
6
)e0.132 mFis
required. Round up to standard (available) capacitive values.
NOTE:
The above equation applies to delay times greater
than 10 ms and will compute the TYPICAL capacitance needed to achieve the desired delay. A delay
variance of
a
50% orb25% can occur due to
temperature, voltage, and device process extremes. In general, higher V
CC
and/or lower tem-
perature will decrease delay time, while lower V
CC
and/or higher temperature will increase delay time.
Table 11. Device Capacitance (C
DEV
) Values
Parameter Typ Max Units Notes
C
DEV
(Device in Reset) 0.583 1.02 mA/V*MHz 1, 2
C
DEV
(Device in Idle) 0.408 0.682 mA/V*MHz 1, 2
1. Max C
DEV
is calculated atb40§C, all floating outputs driven to VCCor GND, and all
outputs loaded to 50 pF (including CLKOUT and OSCOUT).
2. Typical C
DEV
is calculated at 25§C with all outputs loaded to 50 pF except CLKOUT and
OSCOUT, which are not loaded.
27
27
Page 28

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80C186EB25
Symbol Parameter
25 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max
INPUT CLOCK
T
F
CLKIN Frequency 0 50 MHz 1
T
C
CLKIN Period 20
%
ns 1
T
CH
CLKIN High Time 8
%
ns 1, 2
T
CL
CLKIN Low Time 8
%
ns 1, 2
T
CR
CLKIN Rise Time 1 7 ns 1, 3
T
CF
CLKIN Fall Time 1 7 ns 1, 3
OUTPUT CLOCK
T
CD
CLKIN to CLKOUT Delay 0 16 ns 1, 4
T CLKOUT Period 2*T
C
ns 1
T
PH
CLKOUT High Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PL
CLKOUT Low Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PR
CLKOUT Rise Time 1 6 ns 1, 5
T
PF
CLKOUT Fall Time 1 6 ns 1, 5
OUTPUT DELAYS
T
CHOV1
ALE, S2:0, DEN, DT/R, BHE (RFSH), LOCK, A19:16 3 17 ns 1, 4, 6, 7
T
CHOV2
GCS0:7, LCS, UCS, NCS,RD,WR 3 20 ns 1,4,6,8
T
CLOV1
BHE (RFSH), DEN, LOCK, RESOUT, HLDA, T0OUT, 3 17 ns 1, 4, 6
T1OUT, A19:16
T
CLOV2
RD,WR, GCS7:0, LCS, UCS, AD15:0 (AD7:0, A15:8), 3 20 ns 1, 4, 6
NCS
, INTA1:0, S2:0
T
CHOF
RD,WR, BHE (RFSH), DT/R, LOCK, S2:0, A19:16 0 20 ns 1
T
CLOF
DEN, AD15:0 (AD7:0, A15:8) 0 20 ns 1
28
28
Page 29

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80C186EB25
(Continued)
Symbol Parameter
25 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max
SYNCHRONOUS INPUTS
T
CHIS
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, BCLK1:0, T1:0IN, READY, CTS1:0, P2.6, P2.7 10 ns 1, 9
T
CHIH
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, BCLK1:0, T1:0IN, READY, CTS1:0 3ns1,9
T
CLIS
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY 10 ns 1, 10
T
CLIH
READY, AD15:0 (AD7:0) 3 ns 1, 10
T
CLIS
HOLD, PEREQ, ERROR 10 ns 1, 9
T
CLIH
HOLD, PEREQ, ERROR 3ns1,9
NOTES:
1. See AC Timing Waveforms, for waveforms and definition.
2. Measure at V
IH
for high time, VILfor low time.
3. Only required to guarantee I
CC
. Maximum limits are bounded by TC,TCHand TCL.
4. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 13 for capacitive derating information.
5. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 14 for rise and fall times outside 50 pF.
6. See Figure 14 for rise and fall times.
7. T
CHOV1
applies to BHE (RFSH), LOCK and A19:16 only after a HOLD release.
8. T
CHOV2
applies to RD and WR only after a HOLD release.
9. Setup and Hold are required to guarantee recognition.
10. Setup and Hold are required for proper operation.
29
29
Page 30

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80C186EB20/80C186EB13
Symbol Parameter
20 MHz 13 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max Min Max
INPUT CLOCK
T
F
CLKIN Frequency 0 40 0 26 MHz 1
T
C
CLKIN Period 25
%
38.5
%
ns 1
T
CH
CLKIN High Time 10
%
12
%
ns 1, 2
T
CL
CLKIN Low Time 10
%
12
%
ns 1, 2
T
CR
CLKIN Rise Time 1818ns1,3
T
CF
CLKIN Fall Time 1818ns1,3
OUTPUT CLOCK
T
CD
CLKIN to CLKOUT Delay 0 17 0 23 ns 1, 4
T CLKOUT Period 2*T
C
2*T
C
ns 1
T
PH
CLKOUT High Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5 (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PL
CLKOUT Low Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5 (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PR
CLKOUT Rise Time 1616ns1,5
T
PF
CLKOUT Fall Time 1616ns1,5
OUTPUT DELAYS
T
CHOV1
ALE, S2:0, DEN, DT/R, 3 22 3 25 ns 1,4,6,7
BHE (RFSH), LOCK,
A19:16
T
CHOV2
GCS0:7, LCS, UCS, NCS, 3 27 3 30 ns 1,4,6,8
RD
,WR
T
CLOV1
BHE (RFSH), DEN, LOCK, 3 22 3 25 ns 1,4,6
RESOUT, HLDA, T0OUT,
T1OUT, A19:16
T
CLOV2
RD,WR, GCS7:0, LCS, 3 27 3 30 ns 1,4,6
UCS
, AD15:0 (AD7:0,
A15:8), NCS
, INTA1:0, S2:0
T
CHOF
RD,WR, BHE (RFSH), 025025ns1
DT/R
, LOCK, S2:0, A19:16
T
CLOF
DEN, AD15:0 (AD7:0, 0 25 0 25 ns 1
A15:8)
30
30
Page 31

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80C186EB20/80C186EB13
(Continued)
Symbol Parameter
20 MHz 13 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max Min Max
SYNCHRONOUS INPUTS
T
CHIS
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, BCLK1:0, T1:0IN, 10 10 ns 1, 9
READY, CTS1:0
, P2.6, P2.7
T
CHIH
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, BCLK1:0, T1:0IN, 3 3 ns 1, 9
READY, CTS1:0
T
CLIS
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY 10 10 ns 1, 10
T
CLIH
READY, AD15:0 (AD7:0) 3 3 ns 1, 10
T
CLIS
HOLD, PEREQ, ERROR 10 10 ns 1, 9
T
CLIH
HOLD, PEREQ, ERROR 3 3 ns 1, 9
NOTES:
1. See AC Timing Waveforms, for waveforms and definition.
2. Measure at V
IH
for high time, VILfor low time.
3. Only required to guarantee I
CC
. Maximum limits are bounded by TC,TCHand TCL.
4. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 13 for capacitive derating information.
5. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 14 for rise and fall times outside 50 pF.
6. See Figure 14 for rise and fall times.
7. T
CHOV1
applies to BHE (RFSH), LOCK and A19:16 only after a HOLD release.
8. T
CHOV2
applies to RD and WR only after a HOLD release.
9. Setup and Hold are required to guarantee recognition.
10. Setup and Hold are required for proper operation.
31
31
Page 32

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80L186EB16
Symbol Parameter
16 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max
INPUT CLOCK
T
F
CLKIN Frequency 0 32 MHz 1
T
C
CLKIN Period 31.25
%
ns 1
T
CH
CLKIN High Time 13
%
ns 1, 2
T
CL
CLKIN Low Time 13
%
ns 1, 2
T
CR
CLKIN Rise Time 1 8 ns 1, 3
T
CF
CLKIN Fall Time 1 8 ns 1, 3
OUTPUT CLOCK
T
CD
CLKIN to CLKOUT Delay 0 30 ns 1, 4
T CLKOUT Period 2*T
C
ns 1
T
PH
CLKOUT High Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PL
CLKOUT Low Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PR
CLKOUT Rise Time 1 9 ns 1, 5
T
PF
CLKOUT Fall Time 1 9 ns 1, 5
OUTPUT DELAYS
T
CHOV1
DT/R, LOCK, A19:16, R
FSH
3 22 ns 1,4,6,7
T
CHOV2
GCS0:7, LCS, UCS, NCS,RD,WR 3 27 ns 1,4,6,8
T
CHOV3
BHE, DEN 325ns1,4
T
CHOV4
ALE 3 30 ns 1, 4
T
CHOV5
S2:0 333ns1,4
T
CLOV1
LOCK, RESOUT, HLDA, T0OUT, T1OUT, A19:16 3 22 ns 1, 4, 6
T
CLOV2
RD,WR, GCS7:0, LCS, UCS, NCS, INTA1:0, AD15:0 3 27 ns 1, 4, 6
(AD7:0, A15:8)
T
CHOF
RD,WR, BHE (RFSH), DT/R, LOCK, S2:0, A19:16 0 25 ns 1
T
CLOF
DEN, AD15:0 (AD7:0, A15:8) 0 25 ns 1
T
CLOV3
BHE, DEN 3 25 ns 1,4,6
T
CLOV5
S2:0 3 33 ns 1,4,6
32
32
Page 33

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80L186EB16
(Continued)
Symbol Parameter
16 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max
SYNCHRONOUS INPUTS
T
CHIS
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, BCLK1:0, T1:0IN, READY, CTS1:0, P2.6, P2.7 15 ns 1, 9
T
CHIH
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, T1:0IN, BCLK1:0, READY, CTS1:0 3ns1,9
T
CLIS
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY 15 ns 1, 10
T
CLIH
READY, AD15:0 (AD7:0) 3 ns 1, 10
T
CLIS
HOLD 15 ns 1, 9
T
CLIH
HOLD 3 ns 1, 9
NOTES:
1. See AC Timing Waveforms, for waveforms and definition.
2. Measure at V
IH
for high time, VILfor low time.
3. Only required to guarantee I
CC
. Maximum limits are bounded by TC,TCHand TCL.
4. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 13 for capacitive derating information.
5. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 14 for rise and fall times outside 50 pF.
6. See Figure 14 for rise and fall times.
7. T
CHOV1
applies to BHE (RFSH), LOCK and A19:16 only after a HOLD release.
8. T
CHOV2
applies to RD and WR only after a HOLD release.
9. Setup and Hold are required to guarantee recognition.
10. Setup and Hold are required for proper operation.
33
33
Page 34

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80L186EB13/80L186EB8
Symbol Parameter
13 MHz 8 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max Min Max
INPUT CLOCK
T
r
CLKIN Frequency 0 26 0 16 MHz 1
T
C
CLKIN Period 38.5
%
62.5
%
ns 1
T
CH
CLKIN High Time 15
%
15
%
ns 1, 2
T
CL
CLKIN Low Time 15
%
15
%
ns 1, 2
T
CR
CLKIN Rise Time 1 8 1 8 ns 1, 3
T
CF
CLKIN Fall Time 1 8 1 8 ns 1, 3
OUTPUT CLOCK
T
CD
CLKIN to CLKOUT Delay 0 10 0 50 ns 1, 4
T CLKOUT Period 2*T
C
2*T
C
ns 1
T
PH
CLKOUT High Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5 (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
TPLCLKOUT Low Time (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5 (T/2)b5 (T/2)a5ns 1
T
PR
CLKOUT Rise Time 1 10 1 15 ns 1, 5
T
PF
CLKOUT Fall Time 1 10 1 15 ns 1, 5
OUTPUT DELAYS
T
CHOV1
ALE, S2-0, DEN, DT/R, 3 25 3 30 ns 1,4,6,7
BHE
(RFSH), LOCK,
A19:16
T
CHOV2
GCS0:7, LCS, UCS, 3 30 3 35 ns 1, 4,6, 8
NCS
,RD,WR
T
CLOV1
BHE (RFSH), DEN, 3 25 3 30 ns 1,4,6
LOCK, RESOUT, HLDA,
T0OUT, T1OUT, A19:16
T
CLOV2
S2:0,RD,WR, GCS7:0, 3 30 3 35 ns 1,4,6
LCS, UCS, NCS,
INTA1:0
, AD15:0 (AD7:0,
A15:8)
T
CHOF
RD,WR
, BHE (RFSH), 0 30 0 30 ns 1
DT/R, LOCK, S2:0,
A19:16
T
CLOF
DEN, AD15:0 0 30 0 35 ns 1
(AD7:0, A15:8)
34
34
Page 35

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CharacteristicsÐ80L186EB13/80L186EB8
(Continued)
Symbol Parameter
13 MHz 8 MHz
Units Notes
Min Max Min Max
SYNCHRONOUS INPUTS
T
CHIS
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, 20 25 ns 1, 9
BCLK1:0, T1:0IN, READY
CTS1:0
, P2.6, P2.7
T
CHIH
TEST, NMI, INT4:0, T1:0IN, 3 3 ns 1, 9
BCLK1:0, READY, CTS1:0
T
CLIS
AD15:0 (AD7:0), READY 20 25 ns 1, 10
T
CLIH
READY, AD15:0 (AD7:0) 3 3 ns 1, 10
T
CLIS
HOLD 20 25 ns 1, 9
T
CLIH
HOLD 3 3 ns 1, 9
NOTES:
1. See AC Timing Waveforms, for waveforms and definition.
2. Measured at V
IH
for high time, VILfor low time.
3. Only required to guarantee I
CC
. Maximum limits are bounded by TC,TCHand TCL.
4. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 13 for capacitive derating information.
5. Specified for a 50 pF load, see Figure 14 for rise and fall times outside 50 pF.
6. See Figure 14 for rise and fall times.
7. T
CHOV1
applies to BHE (RFSH), LOCK and A19:16 only after a HOLD release.
8. T
CHOV2
applies to RD and WR only after a HOLD release.
9. Setup and Hold are required to guarantee recognition.
10. Setup and Hold are required for proper operation.
35
35
Page 36

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Relative Timings (80C186EB25, 20, 13/80L186EB16, 13, 8)
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
RELATIVE TIMINGS
T
LHLL
ALE Rising to ALE Falling Tb15 ns
T
AVLL
Address Valid to ALE Falling (/2Tb10 ns
T
PLLL
Chip Selects Valid to ALE Falling (/2Tb10 ns 1
T
LLAX
Address Hold from ALE Falling (/2Tb10 ns
T
LLWL
ALE Falling to WR Falling (/2Tb15 ns 1
T
LLRL
ALE Falling to RD Falling (/2Tb15 ns 1
T
WHLH
WR Rising to ALE Rising (/2Tb10 ns 1
T
AFRL
Address Float to RD Falling 0 ns
T
RLRH
RD Falling to RD Rising (2*T)b5ns2
T
WLWH
WR Falling to WR Rising (2*T)b5ns2
T
RHAV
RD Rising to Address Active Tb15 ns
T
WHDX
Output Data Hold after WR Rising Tb15 ns
T
WHPH
WR Rising to Chip Select Rising (/2Tb10 ns 1
T
RHPH
RD Rising to Chip Select Rising (/2Tb10 ns 1
T
PHPL
CS Inactive to CS Active (/2Tb10 ns 1
T
OVRH
ONCE Active to RESIN Rising T ns 3
T
RHOX
ONCE Hold from RESIN Rising T ns 3
NOTES:
1. Assumes equal loading on both pins.
2. Can be extended using wait states.
3. Not tested
36
36
Page 37

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Serial Port Mode 0 Timings (80C186EB25, 20, 13/80L186EB16, 13, 8)
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
T
XLXL
TXD Clock Period T (na1) ns 1, 2
T
XLXH
TXD Clock Low to Clock High (nl1) 2Tb35 2Ta35 ns 1
T
XLXH
TXD Clock Low to Clock High (ne1) Tb35 Ta35 ns 1
T
XHXL
TXD Clock High to Clock Low (nl1) (nb1) Tb35 (nb1) Ta35 ns 1, 2
T
XHXL
TXD Clock High to Clock Low (ne1) Tb35 Ta35 ns 1
T
QVXH
RXD Output Data Setup to TXD Clock High (nl1) (nb1) Tb35 ns 1, 2
T
QVXH
RXD Output Data Setup to TXD Clock High (ne1) Tb35 ns 1
T
XHQX
RXD Output Data Hold after TXD Clock High (nl1) 2Tb35 ns 1
T
XHQX
RXD Output Data Hold after TXD Clock High (ne1) Tb35 ns 1
T
XHQZ
RXD Output Data Float after Last TXD Clock High Ta20 ns 1
T
DVXH
RXD Input Data Setup to TXD Clock High Ta20 ns 1
T
XHDX
RXD Input Data Hold after TXD Clock High 0 ns 1
NOTES:
1. See Figure 12 for waveforms.
2. n is the value of the BxCMP register ignoring the ICLK Bit (i.e., ICLK
e
0).
37
37
Page 38

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
AC TEST CONDITIONS
The AC specifications are tested with the 50 pF load
shown in Figure 7. See the Derating Curves section
to see how timings vary with load capacitance.
Specifications are measured at the V
CC
/2 crossing
point, unless otherwise specified. See AC Timing
Waveforms, for AC specification definitions, test
pins, and illustrations.
272433– 8
C
L
e
50 pF for all signals.
Figure 7. AC Test Load
AC TIMING WAVEFORMS
272433– 9
Figure 8. Input and Output Clock Waveform
38
38
Page 39

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 10
NOTE:
20% V
CC
k
Floatk80% V
CC
Figure 9. Output Delay and Float Waveform
272433– 11
Figure 10. Input Setup and Hold
39
39
Page 40

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 12
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 11. Relative Signal Waveform
272433– 13
Figure 12. Serial Port Mode 0 Waveform
40
40
Page 41

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
DERATING CURVES
TYPICAL OUTPUT DELAY VARIATIONS VERSUS LOAD CAPACITANCE
272433– 14
Figure 13
TYPICAL RISE AND FALL VARIATIONS VERSUS LOAD CAPACITANCE
272433– 15
Figure 14
41
41
Page 42

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
RESET
The processor will perform a reset operation any
time the RESIN
pin active. The RESIN pin is actually
synchronized before it is presented internally, which
means that the clock must be operating before a
reset can take effect. From a power-on state, RESIN
must be held active (low) in order to guarantee correct initialization of the processor. Failure to pro-
vide RESIN
while the device is powering up will
result in unspecified operation of the device.
Figure 14 shows the correct reset sequence when
first applying power to the processor. An external
clock connected to CLKIN must not exceed the V
CC
threshold being applied to the processor. This is normally not a problem if the clock driver is supplied
with the same V
CC
that supplies the processor.
When attaching a crystal to the device, RESIN
must
remain active until both V
CC
and CLKOUT are stable
(the length of time is application specific and depends on the startup characteristics of the crystal
circuit). The RESIN
pin is designed to operate correctly using an RC reset circuit, but the designer
must ensure that the ramp time for V
CC
is not so
long that RESIN
is never really sampled at a logic
low level when V
CC
reaches minimum operating
conditions.
Figure 16 shows the timing sequence when RESIN
is applied after VCCis stable and the device has
been operating. Note that a reset will terminate all
activity and return the processor to a known operating state. Any bus operation that is in progress at the
time RESIN
is asserted will terminate immediately
(note that most control signals will be driven to their
inactive state first before floating).
While RESIN is active, bus signals LOCK, A19/
ONCE
, and A18:16 are configured as inputs and
weakly held high by internal pullup transistors. Only
19/ONCE
can be overdriven to a low and is used to
enable ONCE
Mode. Forcing LOCK or A18:16 low at
any time while RESIN
is low is prohibited and will
cause unspecified device operation.
42
42
Page 43

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Figure 15. Cold Reset Waveforms
272433– 16
NOTE:
CLKOUT synchronization occurs on the rising edge of RESIN
. If RESIN is sampled high while CLKOUT is high (solid line), then CLKOUT will remain
low for two CLKIN periods. If RESIN
is sampled high while CLKOUT is low (dashed line), then CLKOUT will not be affected.
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
43
43
Page 44

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
Figure 16. Warm Reset Waveforms
272433– 17
NOTE:
CLKOUT synchronization occurs on the rising edge of RESIN
. If RESIN is sampled high while CLKOUT is high (solid line), then CLKOUT will remain
low for two CLKIN periods. If RESIN
is sampled high while CLKOUT is low (dashed line), then CLKOUT will not be affected.
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
44
44
Page 45

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
BUS CYCLE WAVEFORMS
Figures 17 through 23 present the various bus cycles that are generated by the processor. What is
shown in the figure is the relationship of the various
bus signals to CLKOUT. These figures along with
the information present in AC Specifications allow
the user to determine all the critical timing analysis
needed for a given application.
272433– 18
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 17. Read, Fetch, and Refresh Cycle Waveforms
45
45
Page 46

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 19
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 18. Write Cycle Waveforms
46
46
Page 47

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 20
NOTE:
The address driven is typically the location of the next instruction prefetch. Under a majority of instruction sequences the
AD15:0 (AD7:0) bus will float, while the A19:16 (A19:8) bus remains driven and all bus control signals are driven to their
inactive state.
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 19. Halt Cycle Waveforms
47
47
Page 48

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 21
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 20. Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Waveform
48
48
Page 49

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 22
NOTE:
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 21. HOLD/HLDA Waveforms
49
49
Page 50

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 23
NOTES:
1. READY
must be low by either edge to cause a wait state.
2. Lighter lines indicate READ cycles, darker lines indicate WRITE cycles.
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 22. Refresh during Hold Acknowledge
50
50
Page 51

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
272433– 24
NOTES:
1. READY
must be low by either edge to cause a wait state.
2. Lighter lines indicate READ cycles, darker lines indicate WRITE cycles.
Pin names in parentheses apply to 80C188EB/80L188EB
Figure 23. Ready Waveforms
51
51
Page 52

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
EXECUTION TIMINGS
A determination of program execution timing must
consider the bus cycles necessary to prefetch instructions as well as the number of execution unit
cycles necessary to execute instructions. The following instruction timings represent the minimum
execution time in clock cycles for each instruction.
The timings given are based on the following assumptions:
#
The opcode, along with any data or displacement
required for execution of a particular instruction,
has been prefetched and resides in the queue at
the time it is needed.
#
No wait states or bus HOLDs occur.
#
All word-data is located on even-address boundaries (80C186EB only).
All jumps and calls include the time required to fetch
the opcode of the next instruction at the destination
address.
All instructions which involve memory accesses can
require one or two additional clocks above the minimum timings shown due to the asynchronous handshake between the bus interface unit (BIU) and execution unit.
With a 16-bit BIU, the 80C186EB has sufficient bus
performance to ensure that an adequate number of
prefetched bytes will reside in the queue (6 bytes)
most of the time. Therefore, actual program execution time will not be substantially greater than that
derived from adding the instruction timings shown.
The 80C188EB 8-bit BIU is limited in its performance
relative to the execution unit. A sufficient number of
prefetched bytes may not reside in the prefetch
queue (4 bytes) much of the time. Therefore, actual
program execution time will be substantially greater
than that derived from adding the instruction timings
shown.
52
52
Page 53

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY
80C186EB 80C188EB
Function Format Clock Clock Comments
Cycles Cycles
DATA TRANSFER
MOV
e
Move:
Register to Register/Memory 1000100w modreg r/m 2/12 2/12*
Register/memory to register 1000101w modreg r/m 2/9 2/9*
Immediate to register/memory 1100011w mod000 r/m data data if we1 12/13 12/13 8/16-bit
Immediate to register 1011w reg data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
Memory to accumulator 1010000w addr-low addr-high 8 8*
Accumulator to memory 1010001w addr-low addr-high 9 9*
Register/memory to segment register 10001110 mod0reg r/m 2/9 2/13
Segment register to register/memory 10001100 mod0reg r/m 2/11 2/15
PUSHePush:
Memory 11111111 mod110 r/m 16 20
Register 01010 reg 10 14
Segment register 000reg110 9 13
Immediate 011010s0 data data if se01014
PUSHAePush All 01100000 36 68
POPePop:
Memory 10001111 mod000 r/m 20 24
Register 01011 reg 10 14
Segment register 000reg111 (regi01) 8 12
POPAePopAll 01100001 51 83
XCHGeExchange:
Register/memory with register 1000011w modreg r/m 4/17 4/17*
Register with accumulator 10010 reg 3 3
INeInput from:
Fixed port 1110010w port 10 10*
Variable port 1110110w 8 8*
OUTeOutput to:
Fixed port 1110011w port 9 9*
Variable port 1110111w 7 7*
XLATeTranslate byte to AL 11010111 11 15
LEAeLoad EA to register 10001101 modreg r/m 6 6
LDSeLoad pointer to DS 11000101 modreg r/m (modi11) 18 26
LESeLoad pointer to ES 11000100 modreg r/m (modi11) 18 26
LAHFeLoad AH with flags 10011111 2 2
SAHFeStore AH into flags 10011110 3 3
PUSHFePush flags 10011100 9 13
POPFePop flags 10011101 8 12
Shaded areas indicate instructions not available in 8086/8088 microsystems.
NOTE:
*Clock cycles shown for byte transfers. For word operations, add 4 clock cycles for all memory transfers.
53
53
Page 54

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY (Continued)
80C186EB 80C188EB
Function Format Clock Clock Comments
Cycles Cycles
DATA TRANSFER (Continued)
SEGMENT
e
Segment Override:
CS 00101110 2 2
SS 00110110 2 2
DS 00111110 2 2
ES 00100110 2 2
ARITHMETIC
ADD
e
Add:
Reg/memory with register to either 000000dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate to register/memory 100000sw mod000 r/m data data if s we01 4/16 4/16*
Immediate to accumulator 0000010w data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
ADCeAdd with carry:
Reg/memory with register to either 000100dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate to register/memory 100000sw mod010 r/m data data if s we01 4/16 4/16*
Immediate to accumulator 0001010w data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
INCeIncrement:
Register/memory 1111111w mod000 r/m 3/15 3/15*
Register 01000 reg 3 3
SUBeSubtract:
Reg/memory and register to either 001010dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate from register/memory 100000sw mod101 r/m data data if s we01 4/16 4/16*
Immediate from accumulator 0010110w data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
SBBeSubtract with borrow:
Reg/memory and register to either 000110dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate from register/memory 100000sw mod011 r/m data data if s we01 4/16 4/16*
Immediate from accumulator 0001110w data data if we1 3/4 3/4* 8/16-bit
DECeDecrement
Register/memory 1111111w mod001 r/m 3/15 3/15*
Register 01001 reg 3 3
CMPeCompare:
Register/memory with register 0011101w modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Register with register/memory 0011100w modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate with register/memory 100000sw mod111 r/m data data if s we01 3/10 3/10*
Immediate with accumulator 0011110w data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
NEGeChange sign register/memory 1111011w mod011 r/m 3/10 3/10*
AAAeASCII adjust for add 00110111 8 8
DAAeDecimal adjust for add 00100111 4 4
AASeASCII adjust for subtract 00111111 7 7
DASeDecimal adjust for subtract 00101111 4 4
MULeMultiply (unsigned): 1111011w mod100 r/m
Register-Byte 26–28 26–28
Register-Word 35–37 35–37
Memory-Byte 32–34 32–34
Memory-Word 41–43 41–43*
Shaded areas indicate instructions not available in 8086/8088 microsystems.
NOTE:
*Clock cycles shown for byte transfers. For word operations, add 4 clock cycles for all memory transfers.
54
54
Page 55

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY (Continued)
80C186EB 80C188EB
Function Format Clock Clock Comments
Cycles Cycles
ARITHMETIC (Continued)
IMULeInteger multiply (signed): 1111011w mod101 r/m
Register-Byte 25–28 25–28
Register-Word 34–37 34–37
Memory-Byte 31–34 31–34
Memory-Word 40–43 40–43*
IMULeInteger Immediate multiply 011010s1 modreg r/m data data if se0 22– 25/ 22– 25/
(signed)
29–32 29–32
DIVeDivide (unsigned): 1111011w mod110 r/m
Register-Byte 29 29
Register-Word 38 38
Memory-Byte 35 35
Memory-Word 44 44*
IDIVeInteger divide (signed): 1111011w mod111 r/m
Register-Byte 44–52 44–52
Register-Word 53–61 53–61
Memory-Byte 50–58 50–58
Memory-Word 59–67 59–67*
AAMeASCII adjust for multiply 11010100 00001010 19 19
AADeASCII adjust for divide 11010101 00001010 15 15
CBWeConvert byte to word 10011000 2 2
CWDeConvert word to double word 10011001 4 4
LOGIC
Shift/Rotate Instructions:
Register/Memory by 1 1101000w modTTTr/m 2/15 2/15
Register/Memory by CL 1101001w modTTTr/m
5an/17an5an/17an
Register/Memory by Count 1100000w modTTTr/m count
5an/17an5an/17an
TTT Instruction
000 ROL
001 ROR
010 RCL
011 RCR
1 0 0 SHL/SAL
101 SHR
111 SAR
AND
e
And:
Reg/memory and register to either 001000dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate to register/memory 1000000w mod100 r/m data data if we1 4/16 4/16*
Immediate to accumulator 0010010w data data if we1 3/4 3/4* 8/16-bit
TESTeAnd function to flags, no result:
Register/memory and register 1000010w modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate data and register/memory 1111011w mod000 r/m data data if we1 4/10 4/10*
Immediate data and accumulator 1010100w data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
OReOr:
Reg/memory and register to either 000010dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate to register/memory 1000000w mod001 r/m data data if we1 4/16 4/16*
Immediate to accumulator 0000110w data data if we1 3/4 3/4* 8/16-bit
Shaded areas indicate instructions not available in 8086/8088 microsystems.
NOTE:
*Clock cycles shown for byte transfers. For word operations, add 4 clock cycles for all memory transfers.
55
55
Page 56

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY (Continued)
80C186EB 80C188EB
Function Format Clock Clock Comments
Cycles Cycles
LOGIC (Continued)
XOR
e
Exclusive or:
Reg/memory and register to either 001100dw modreg r/m 3/10 3/10*
Immediate to register/memory 1000000w mod110 r/m data data if we1 4/16 4/16*
Immediate to accumulator 0011010w data data if we1 3/4 3/4 8/16-bit
NOTeInvert register/memory 1111011w mod010 r/m 3/10 3/10*
STRING MANIPULATION
MOVSeMove byte/word 1010010w 14 14*
CMPSeCompare byte/word 1010011w 22 22*
SCASeScan byte/word 1010111w 15 15*
LODSeLoad byte/wd to AL/AX 1010110w 12 12*
STOSeStore byte/wd from AL/AX 1010101w 10 10*
INSeInput byte/wd from DX port 0110110w 14 14
OUTSeOutput byte/wd to DX port 0110111w 14 14
Repeated by count in CX (REP/REPE/REPZ/REPNE/REPNZ)
MOVSeMove string 11110010 1010010w 8a8n 8a8n*
CMPSeCompare string 1111001z 1010011w 5a22n 5a22n*
SCASeScan string 1111001z 1010111w 5a15n 5a15n*
LODSeLoad string 11110010 1010110w 6a11n 6a11n*
STOSeStore string 11110010 1010101w 6a9n 6a9n*
INSeInput string 11110010 0110110w 8a8n 8a8n*
OUTSeOutput string 11110010 0110111w 8a8n 8a8n*
CONTROL TRANSFER
CALL
e
Call:
Direct within segment 11101000 disp-low disp-high 15 19
Register/memory 11111111 mod010 r/m 13/19 17/27
indirect within segment
Direct intersegment 10011010 segment offset 23 31
segment selector
Indirect intersegment 11111111 mod011 r/m (modi11) 38 54
JMPeUnconditional jump:
Short/long 11101011 disp-low 14 14
Direct within segment 11101001 disp-low disp-high 14 14
Register/memory 11111111 mod100 r/m 11/17 11/21
indirect within segment
Direct intersegment 11101010 segment offset 14 14
segment selector
Indirect intersegment 11111111 mod101 r/m (modi11) 26 34
Shaded areas indicate instructions not available in 8086/8088 microsystems.
NOTE:
*Clock cycles shown for byte transfers. For word operations, add 4 clock cycles for all memory transfers.
56
56
Page 57

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY (Continued)
80C186EB 80C188EB
Function Format Clock Clock Comments
Cycles Cycles
CONTROL TRANSFER (Continued)
RET
e
Return from CALL:
Within segment 11000011 16 20
Within seg adding immed to SP 11000010 data-low data-high 18 22
Intersegment 11001011 22 30
Intersegment adding immediate to SP 11001010 data-low data-high 25 33
JE/JZeJump on equal/zero 01110100 disp 4/13 4/13 JMP not
JL/JNGEeJump on less/not greater or equal 01111100 disp 4/13 4/13
taken/JMP
JLE/JNGeJump on less or equal/not greater 01111110 disp 4/13 4/13
taken
JB/JNAEeJump on below/not above or equal 01110010 disp 4/13 4/13
JBE/JNAeJump on below or equal/not above 01110110 disp 4/13 4/13
JP/JPEeJump on parity/parity even 01111010 disp 4/13 4/13
JOeJump on overflow 01110 000 disp 4/13 4/13
JSeJump on sign 01111000 disp 4/13 4/13
JNE/JNZeJump on not equal/not zero 01110101 disp 4/13 4/13
JNL/JGEeJump on not less/greater or equal 01111101 disp 4/13 4/13
JNLE/JGeJump on not less or equal/greater 01111111 disp 4/13 4/13
JNB/JAEeJump on not below/above or equal 01110011 disp 4/13 4/13
JNBE/JAeJump on not below or equal/above 01110111 disp 4/13 4/13
JNP/JPOeJump on not par/par odd 01111011 disp 4/13 4/13
JNOeJump on not overflow 01110001 disp 4/13 4/13
JNSeJump on not sign 01111001 disp 4/13 4/13
JCXZeJump on CX zero 11100011 disp 5/15 5/15
LOOPeLoop CX times 11100010 disp 6/16 6/16 LOOP not
LOOPZ/LOOPEeLoop while zero/equal 11100001 disp 6/16 6/16
taken/LOOP
LOOPNZ/LOOPNEeLoop while not zero/equal 11100000 disp 6/16 6/16
taken
ENTEReEnter Procedure 11001000 data-low data-high L
Le0 15 19
L
e
1 25 29
L
l
1
22a16(nb1) 26a20(nb1)
LEAVEeLeave Procedure 11001001 8 8
INTeInterrupt:
Type specified 11001101 type 47 47
Type 3 11001100 45 45 ifINT. taken/
INTOeInterrupt on overflow 11001110 48/4 48/4
if INT. not
taken
IRETeInterrupt return 11001111 28 28
BOUNDeDetect value out of range 01100010 modreg r/m 33–35 33–35
Shaded areas indicate instructions not available in 8086/8088 microsystems.
NOTE:
*Clock cycles shown for byte transfers. For word operations, add 4 clock cycles for all memory transfers.
57
57
Page 58

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY (Continued)
80C186EB 80C188EB
Function Format Clock Clock Comments
Cycles Cycles
PROCESSOR CONTROL
CLCeClear carry 11111000 2 2
CMCeComplement carry 11110101 2 2
STCeSet carry 11111001 2 2
CLDeClear direction 11111100 2 2
STDeSet direction 11111101 2 2
CLIeClear interrupt 11111010 2 2
STIeSet interrupt 11111011 2 2
HLTeHalt 11110100 2 2
WAITeWait 10011011 6 6 ifTESTe0
LOCKeBus lock prefix 11110000 2 2
NOPeNo Operation 10010000 3 3
(TTT LLL are opcode to processor extension)
Shaded areas indicate instructions not available in 8086/8088 microsystems.
NOTE:
*Clock cycles shown for byte transfers. For word operations, add 4 clock cycles for all memory transfers.
FOOTNOTES
The Effective Address (EA) of the memory operand
is computed according to the mod and r/m fields:
if mod
e
11 then r/m is treated as a REG field
if mod
e
00 then DISPe0*, disp-low and disphigh are absent
if mod
e
01 then DISPedisp-low sign-extended to 16-bits, disp-high is absent
if mod
e
10 then DISPedisp-high: disp-low
if r/m
e
000 then EAe(BX)a(SI)aDISP
if r/m
e
001 then EAe(BX)a(DI)aDISP
if r/m
e
010 then EAe(BP)a(SI)aDISP
if r/m
e
011 then EAe(BP)a(DI)aDISP
if r/m
e
100 then EAe(SI)aDISP
if r/m
e
101 then EAe(DI)aDISP
if r/m
e
110 then EAe(BP)aDISP*
if r/m
e
111 then EAe(BX)aDISP
DISP follows 2nd byte of instruction (before data if
required)
*except if mod
e
00 and r/me110 then EA
e
disp-high: disp-low.
EA calculation time is 4 clock cycles for all modes,
and is included in the execution times given whenever appropriate.
Segment Override Prefix
0 0 1 reg 1 1 0
reg is assigned according to the following:
Segment
reg Register
00 ES
01 CS
10 SS
11 DS
REG is assigned according to the following table:
16-Bit (w
e
1) 8-Bit (we0)
000 AX 000 AL
001 CX 001 CL
010 DX 010 DL
011 BX 011 BL
100 SP 100 AH
101 BP 101 CH
110 SI 110 DH
111 DI 111 BH
The physical addresses of all operands addressed
by the BP register are computed using the SS segment register. The physical addresses of the destination operands of the string primitive operations
(those addressed by the DI register) are computed
using the ES segment, which may not be overridden.
58
58
Page 59

80C186EB/80C188EB, 80L186EB/80L188EB
ERRATA
An 80C186EB/80L186EB with a STEPID value of
0001H has the following known errata. A device with
a STEPID of 0001H can be visually identified by the
presence of an ‘‘A’’ alpha character next to the
FPO number. The FPO number location is shown in
Figures 4, 5 and 6.
1. A19/ONCE
is not latched by the rising edge of
RESIN
. A19/ONCE must remain active (LOW) at
all times to remain in the ONCE Mode. Removing
A19/ONCE
after RESIN is high will return all output pins to a driving state, however, the
80C186EB will remain in a reset state.
2. During interrupt acknowledge (INTA) bus cycles,
the bus controller will ignore the state of the
READY pin if the previous bus cycle ignored the
state of the READY pin. This errata can only occur if the Chip-Select Unit is being used. All active
chip-selects must be programmed to use READY
(RDY bit must be programmed to a 1) if waitstates are required for INTA bus cycles.
3. CLKOUT will transition off the rising edge of
CLKIN rather than the falling edge of CLKIN. This
does not affect any bus timings other than T
CD
.
4. RESIN has a hysterisis of only 130 mV. It is recommended that RESIN
be driven by a Schmitt
triggered device to avoid processor lockup during
reset using an RC circuit.
5. SINT1 will only go active for one clock period
when a receive or transmit interrupt is pending
(i.e., it does not remain active until the S1STS
register is read). If SINT1 is to be connected to
any of the processor interrupt lines (INT0–INT4),
then it must be latched by user logic.
An 80C186EB/80L186EB with a STEPID value of
0001H or 0002H has the following known errata. A
device with a STEPID of 0002H can be visually identified by noting the presence of a ‘‘B’’, ‘‘C’’, ‘‘D’’, or
‘‘E’’ alpha character next to the FPO number. The
FPO number location is shown in Figures 4, 5 and 6.
1. An internal condition with the interrupt controller
can cause no acknowledge cycle on the INTA1
line in response to INT1. This errata only occurs
when Interrupt 1 is configured in cascade mode
and a higher priority interrupt exists. This errata
will not occur consistantly, it is dependent on interrupt timing.
REVISION HISTORY
This data sheet replaces the following data sheets:
270803-004 80C186EB
270885-003 80C188EB
270921-003 80L186EB
270920-003 80L188EB
272311-001 SB80C188EB/SB80L188EB
272312-001 SB80C186EB/SB80L186EB
59
59
 Loading...
Loading...