Page 1

TS472
Very low noise microphone preamplifier with
2.0 V bias output and active low standby mode
Features
■ Low noise: 10 nV/√Hz typ. equivalent input
noise at F = 1 kHz
■ Fully-differential input/output
■ 2.2 to 5.5 V single supply operation
■ Low power consumption at 20 dB: 1.8 mA
■ Fast start up time at 0 dB: 5 ms typ.
■ Low distortion: 0.1% typ.
■ 40 kHz bandwidth regardless of the gain
■ Active low standby mode function (1 μA max)
■ Low noise 2.0 V microphone bias output
■ Available in flip-chip lead-free package and in
QFN24 4 x 4 mm package
■ ESD protection (2 kV)
Applications
■ Video and photo cameras with sound input
■ Sound acquisition and voice recognition
■ Video conference systems
■ Notebook computers and PDAs
Flip-chip - 12 bumps
Pin connections (top view)
QFN24
Description
Pin connections (top view)
The TS472 is a differential-input microphone
GND STBY VCC
preamplifier optimized for high-performance PDA
and notebook audio systems.
This device features an adjustable gain from 0 to
40 dB with excellent power-supply and commonmode rejection ratios. In addition, the TS472 has
a very low noise microphone bias generator of
2V.
It also includes a complete shutdown function,
with active low standby mode.
August 2009 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 1/25
BYP
GND
1
NC
2
3
NC
4
5
IN-
6
NC
8 9 10 11 12
7
IN+ GS BIAS
NC NC NC
NCNCNC
192021222324
18
NC
OUT+
17
OUT-
16
C2
15
14
C1
13
NC
www.st.com
25
Page 2

Contents TS472
Contents
1 Typical application schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1 Differential configuration principle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.2 Higher cut-off frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.3 Lower cut-off frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.4 Low-noise microphone bias source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.5 Gain settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.6 Wake-up time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.7 Standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.8 Layout considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.9 Single-ended input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.10 Demonstration board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.1 Flip-chip package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.2 QFN24 package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 3
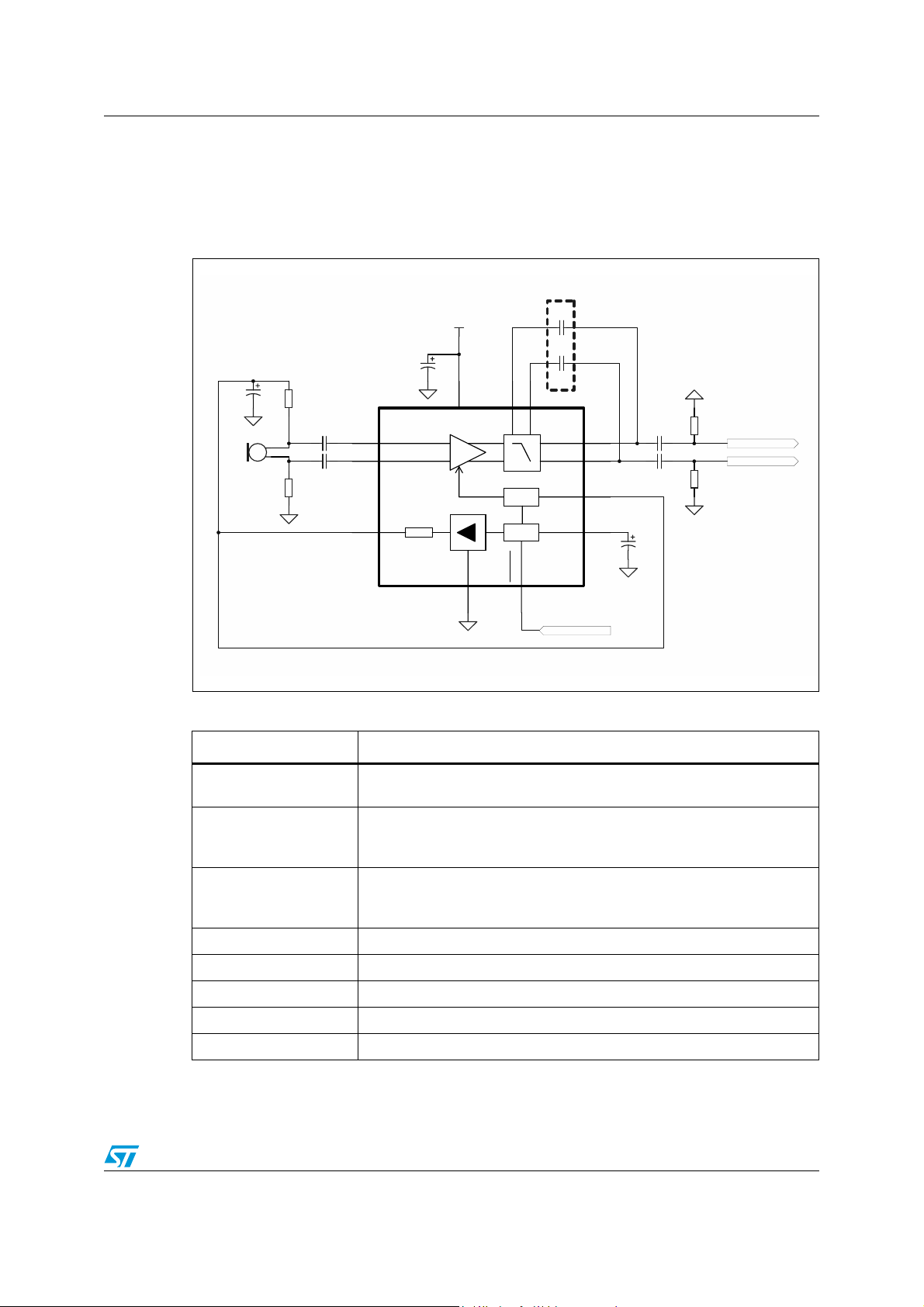
TS472 Typical application schematic
1 Typical application schematic
Figure 1 shows a typical application schematic for the TS472.
Figure 1. Application schematic (flip-chip)
Optional
VCC
C1
Cs
1uF
C3
Rpos
1uF
Cin+
+
Electret Mic
Table 1. Description of external components
Cin-
Rneg
U1 TS472_FC
Vcc
IN+
IN-
BIAS
2.0V
GND
C1
G
Bias
STDBY
C2
GAIN
SELECT
BYPASS
Standby Control
C2
OUT+
OUT-
Components Functional description
C
, C
in+
in-
Input coupling capacitors that block the DC voltage at the amplifier input
terminal.
Output coupling capacitors that block the DC voltage coming from the
, C
C
out+
out-
amplifier output terminal (pins C2 and D2) and determine the lower cut-off
frequency (see Section 4.3: Lower cut-off frequency).
Output load resistors used to charge the output coupling capacitors C
, R
R
out+
out-
These output resistors can be represented by an input impedance of a
following stage.
, R
R
pos
neg
C
s
C
b
, C
C
1
2
C
3
Polarizing resistors for biasing of a microphone.
Supply bypass capacitor that provides power supply filtering.
Bypass pin capacitor that provides half-supply filtering.
Low pass filter capacitors allowing to cut the high frequency.
Bias output filtering capacitor.
Cb
1uF
Cout+
Cout-
Rout+
Rout-
Positive Output
Negative Output
out
.
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 3/25
Page 4
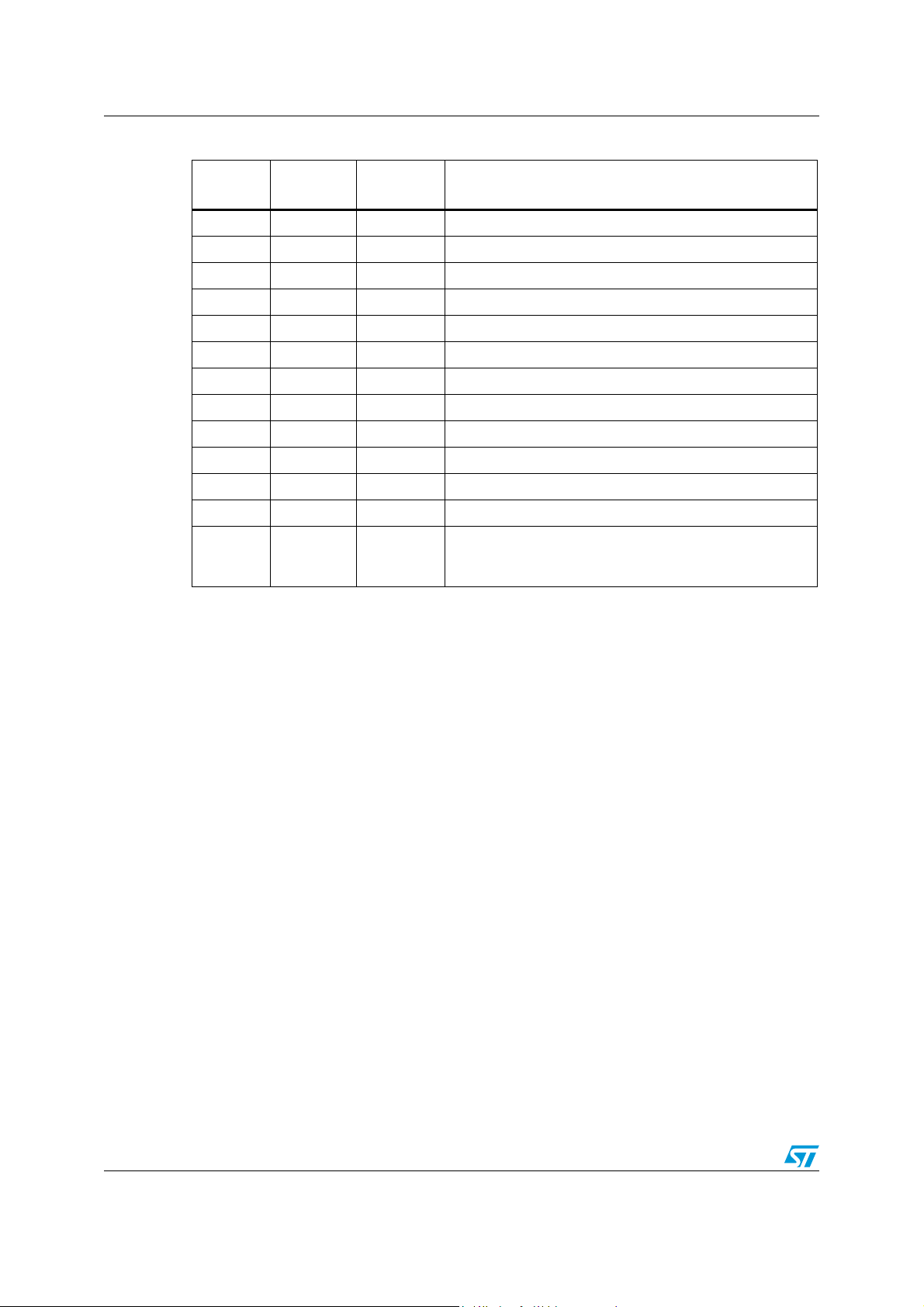
Typical application schematic TS472
Table 2. Pin descriptions
Pin name
IN+ A1 8 Positive differential input
IN- B1 5 Negative differential input
BIAS A2 10 2 V bias output
GND C1 4, 22 Ground
STBY C3 21 Standby
BYP D1 2 Bypass
GS B2 9 Gain select
OUT- D2 16 Negative differential output
OUT+ C2 17 Positive differential output
C1 A3 14 Low-pass filter capacitor
C2 B3 15 Low-pass filter capacitor
Vcc D3 20 Power supply
NC ---
Flip-chip
designator
QFN
designator
3, 6, 7, 11,
12, 13, 18,
19, 23, 24
Not connected, floating pins
Pin description
4/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 5
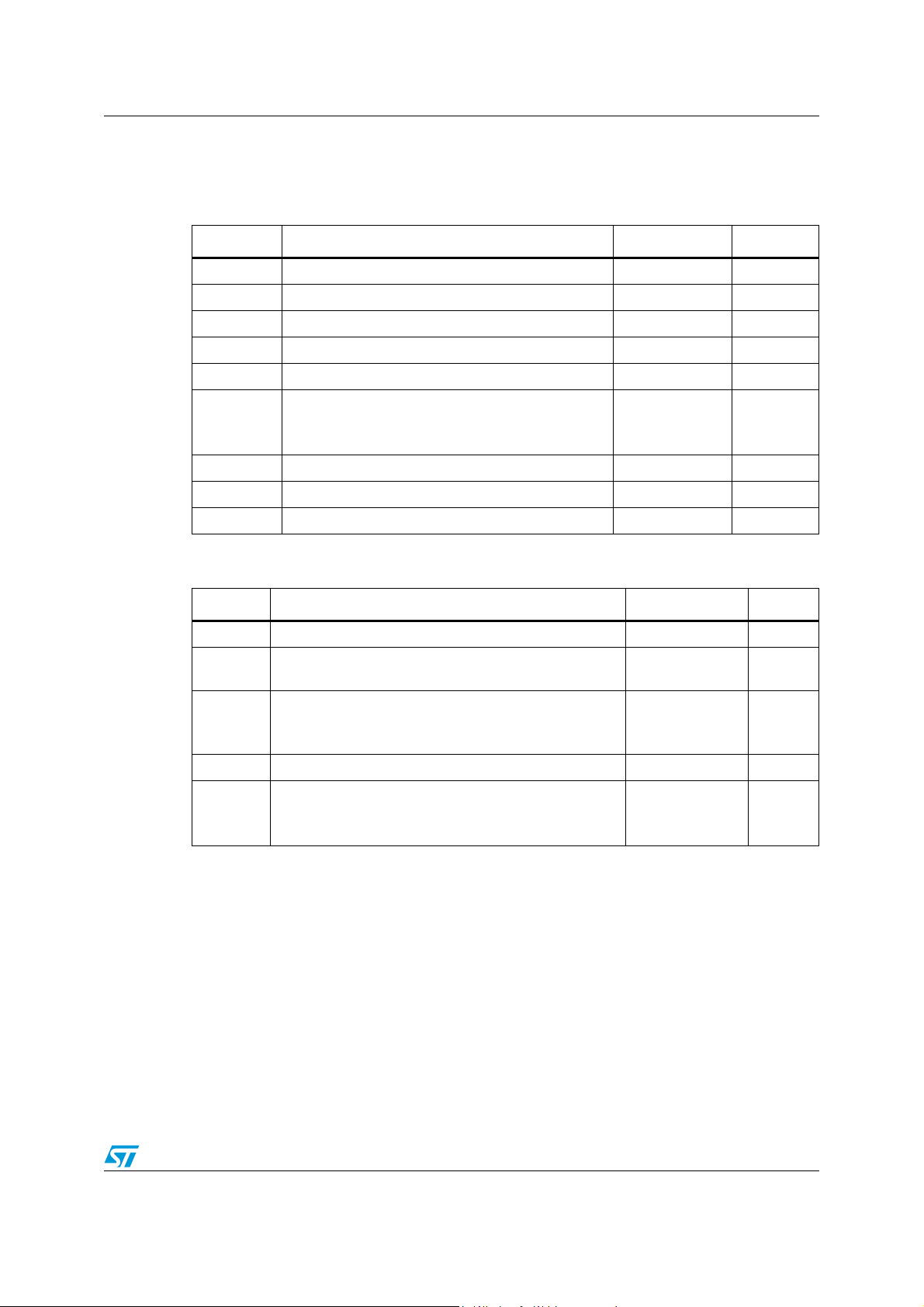
TS472 Absolute maximum ratings
2 Absolute maximum ratings
Table 3. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
T
T
CC
V
oper
stg
T
Supply voltage
Input voltage -0.3 to VCC+0.3 V
i
Operating free air temperature range -40 to + 85 °C
Storage temperature -65 to +150 °C
Maximum junction temperature 150 °C
j
Thermal resistance junction to ambient:
R
thja
Flip-chip
QFN24
ESD Human body model 2 kV
ESD Machine model 200 V
Lead temperature (soldering, 10sec) 250 °C
1. All voltage values are measured with respect to the ground pin.
Table 4. Operating conditions
(1)
6V
180
110
°C/W
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
CC
A
Supply voltage 2.2 to 5.5 V
Typical differential gain
(GS connected to 4.7 kΩ or bias)
20 dB
Standby voltage input:
V
R
STBY
T
op
thja
Device ON
Device OFF
1.5 ≤ V
GND ≤ V
STBY
STBY
≤ V
CC
≤ 0.4
Operational free air temperature range -40 to +85 °C
Thermal resistance junction to ambient:
Flip-chip
QFN24
150
60
V
°C/W
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 5/25
Page 6
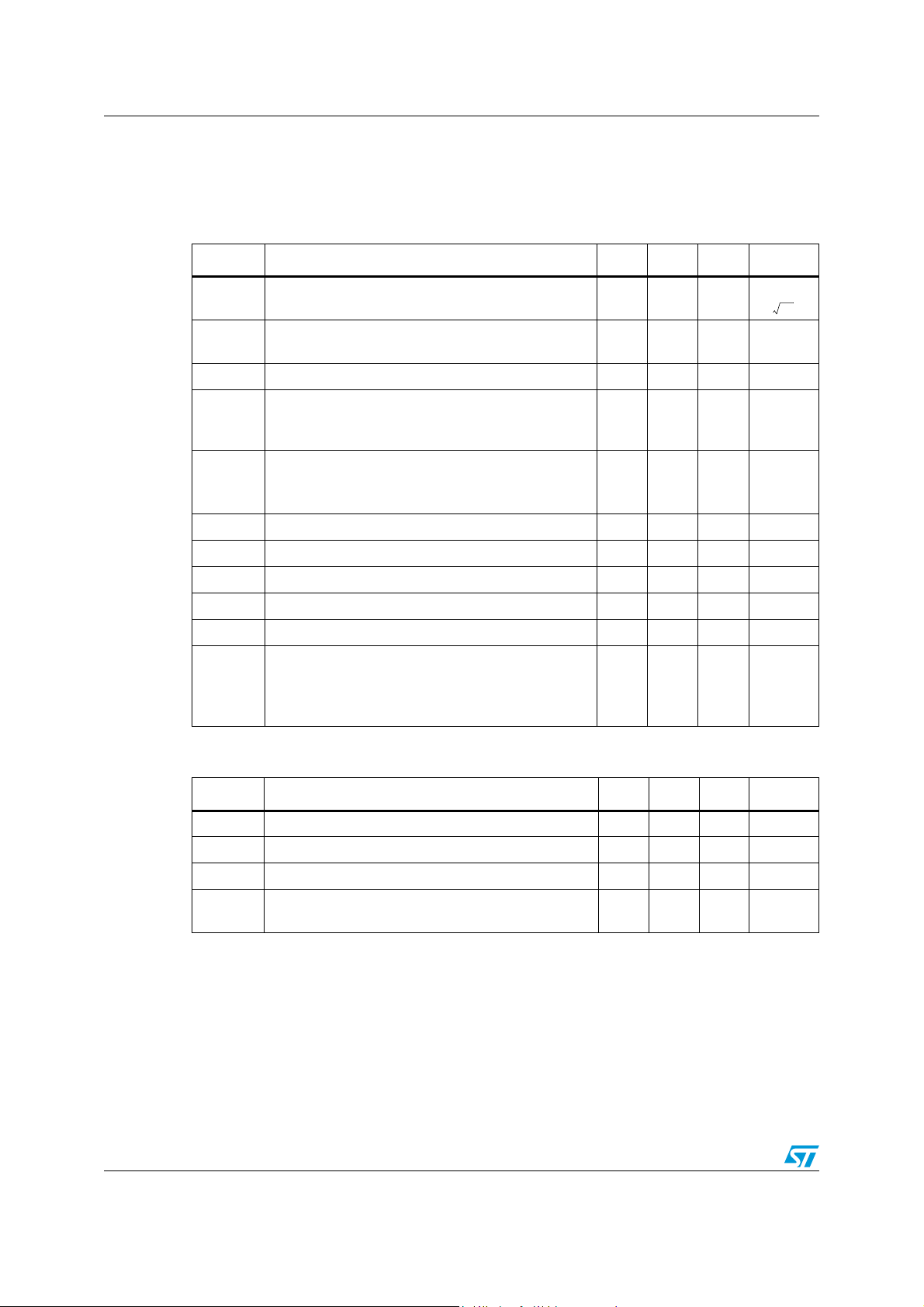
Electrical characteristics TS472
3 Electrical characteristics
Table 5. Electrical characteristics at VCC = 3 V with GND = 0 V, T
(unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
amb
= 25° C
e
THD+N
V
Equivalent input noise voltage density
n
=100Ω at 1 kHz
R
EQ
Total harmonic distortion + noise
20 Hz ≤F ≤ 20 kHz, gain = 20 dB, V
Input voltage, gain = 20 dB 10 70 mV
in
=50mV
in
Bandwidth at -3 dB
B
Bandwidth at -1 dB
W
pin A3, B3 floating
Overall output voltage gain (Rgs variable):
G
Minimum gain, Rgs infinite
Maximum gain, Rgs = 0
Input impedance referred to GND 80 100 120 kΩ
in
Resistive load 10 kΩ
Capacitive load 100 pF
Supply current, gain = 20 dB 1.8 2.4 mA
Standby current 1 μA
R
LOAD
C
LOAD
I
I
STBY
Z
CC
Power supply rejection ratio, gain = 20 dB,
PSRR
F = 217 Hz, V
Differential output
= 200 mVpp, inputs grounded
ripple
Single-ended outputs,
Table 6. Bias output: VCC = 3 V, GND = 0 V, T
(unless otherwise specified)
RMS
amb
39.5
= 25° C
-3
nV
10
------------
0.1 %
40
20 kHz
-1.5
dB
41042.5
-70
dB
-46
Hz
RMS
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
R
I
out
PSRR
No load condition 1.9 2 2.1 V
out
Output resistance 80 100 120 W
out
Output bias current 2 mA
Power supply rejection ratio, F = 217 Hz,
= 200 mVpp
V
ripple
6/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
70 80 dB
Page 7
TS472 Electrical characteristics
Table 7. Differential RMS noise voltage
Gain
Input referred noise voltage
(μV
)
RMS
Output noise voltage
(μV
)
RMS
(dB)
Unweighted filter A-weighted filter Unweighted filter A-weighted filter
015 10 15 10
20 3.4 2.3 34 23
40 1.4 0.9 141 91
Table 8. Bias output RMS noise voltage
(1)
C
3
(μF)
Unweighted filter
RMS
)
(μV
154.4
10 2.2 1.2
1. Bias output filtering capacitor.
Table 9. SNR (signal to noise ratio), THD+N < 0.5%
Unweighted filter 20 Hz - 20 kHz
Gain
(dB)
(dB)
=2.2V VCC=3V VCC=5.5V VCC=2.2V VCC=3V VCC=5.5V
V
CC
0 75 76 76798080
A-weighted filter
(μV
RMS
A-weighted filter
(dB)
)
20 82 83 83 89 90 90
40 70 72 74 80 82 84
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 7/25
Page 8
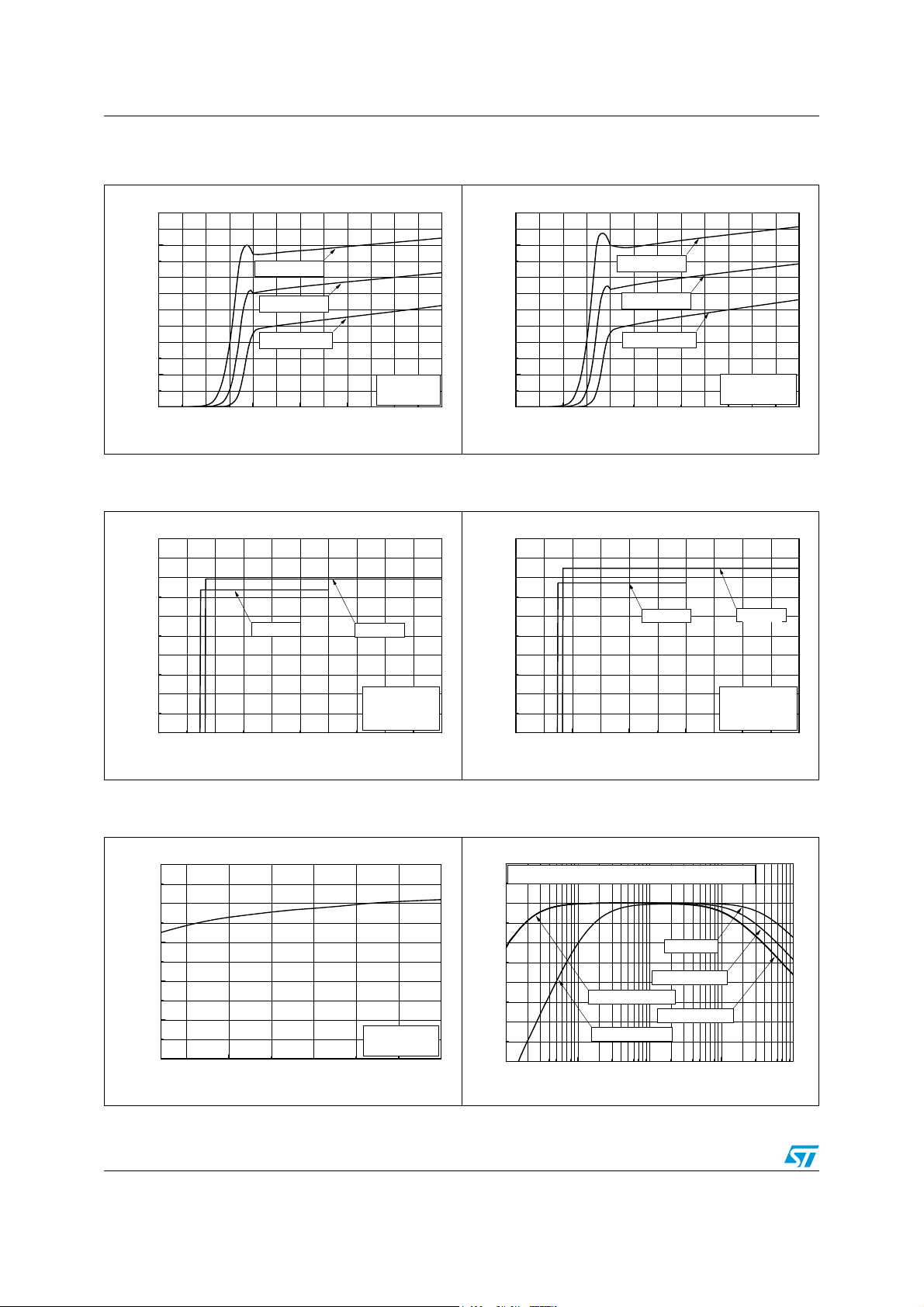
Electrical characteristics TS472
Figure 2. Current consumption vs. power
supply voltage
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
Current Consumption (mA)
0.0
0123456
Tamb=85°C
Tamb=25°C
Tamb=-40°C
No Loads
GS floating
Power Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 4. Current consumption vs. standby
voltage
2.5
2.0
Figure 3. Current consumption vs. power
supply voltage
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
Current Consumption (mA)
0.0
0123456
Tamb=85°C
Tamb=25°C
Tamb=-40°C
No Loads
GS grounded
Power Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 5. Current consumption vs. standby
voltage
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
Current Consumption (mA)
0.0
012345
Vcc=3V
Standby Voltage (V)
Vcc=5V
No Loads
GS floating
Tamb = 25°C
Figure 6. Standby threshold voltage vs.
power supply voltage
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
Standby Treshold Voltage (V)
0.0
2.2
345
Power Supply V oltage (V)
No Loads
Tamb = 25°C
1.5
1.0
0.5
Current Consumption (mA)
0.0
012345
Standby Voltage (V)
Figure 7. Frequency response
30
5.5
Cb=1μF, T
20
10
PSRR (dB)
0
-10
-20
10 100 1000 10000 100000
=25°C, Gain=20dB, Rout=100k
AMB
Cin,Cout=100nF
Cin,Cout=10nF
Frequency (Hz)
Vcc=3V
no C1,C2
C1,C2=100pF
C1,C2=220pF
Vcc=5V
No Loads
GS grounded
Tamb = 25°C
Ω
8/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 9

TS472 Electrical characteristics
Figure 8. Bias output voltage vs. bias output
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
Bias Output Voltage (V)
1.4
Figure 9. Bias output voltage vs. power
current
Vcc=2.5-6V
Tamb=85°C
Tamb=-40°C
Tamb=25°C
01234
Bias Output Current (mA)
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
Bias Output Voltage (V)
1.4
supply voltage
Tamb=25°C
2.2
Ibias=0mA
Ibias=2mA
Ibias=4mA
345
Power Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 10. Bias PSRR vs. frequency Figure 11. Bias PSRR vs. frequency
0
Vripple=200mVpp
Vcc=3V
-20
Cb=1μF
Tamb =25°C
-40
Bias floating or 1kΩ to GND
0
Vripple=200mVpp
Vcc=5V
-20
Cb=1μF
Tamb=25°C
-40
Bias = 1kΩ to GND
5.5
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
50 20k
100 1000 10000
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 12. Differential output PSRR vs.
frequency
0
Vripple=200mVpp
Inputs grounded
-10
Vcc=3V
-20
Cb=1μF
Cin=100nF
-30
Tamb=25°C
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-80
50 20k
GS=bias
100 1000 10000
GS grounded
GS floating
Frequency (Hz)
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
50 20k
100 1000 10000
Frequency (Hz)
Bias floating
Figure 13. Differential output PSRR vs.
frequency
0
Vripple=200mVpp
Inputs grounded
-10
Vcc=5V
-20
Cb=1μF
Cin=100nF
-30
Tamb=25°C
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-80
50 20k
GS grounded
100 1000 10000
GS=bias
GS floating
Frequency (Hz)
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 9/25
Page 10

Electrical characteristics TS472
Figure 14. Differential output PSRR vs.
frequency
0
V
=200mVPP, Inputs grounded
RIPPLE
VCC=3V, Minimum Gain, Cin=1μF, T
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
No Cb
Cb=100nF
=25°C
AMB
Cb=1μF
-80
-100
100 1k 10k
50 20k
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 16. Single-ended output PSRR vs.
frequency
0
Vripple=200mVpp
Inputs grounded
-10
Cb=1μF
-20
Cin=100nF
Tamb=25°C
-30
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-80
Vcc=2.2V
50 20k
100 1000 10000
Vcc=3V
Vcc=5V
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 15. Differential output PSRR vs.
frequency
0
V
=200mVPP, Inputs grounded
RIPPLE
VCC=3V, Gain=20dB, Cin=1μF, T
-20
AMB
=25°C
-40
Cb=1μF
No Cb
PSRR (dB)
-60
-80
Cb=100nF
-100
100 1k 10k
50 20k
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 17. Equivalent input noise voltage
density
1000
Cin=100nF
REQ=100
T
=25°C
100
)
Hz
√
nV/
(
n
e
10
1
10 100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
AMB
Ω
Figure 18. Δgain vs. power supply voltage Figure 19. Δgain vs. ambient temperature
1.0
F=1kHz
Vin=5mV
0.8
Tamb=25°C
Maximum Gain
0.6
0.4
0.2
Gain (dB)
Δ
0.0
-0.2
-0.4
2.2
345
Power Supply Voltage (V)
Minimum Gain
Gain=20dB
5.5
10/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
0.50
F=1kHz
VIN=5mV
0.25
0.00
-0.25
Gain (dB)
Δ
-0.50
-0.75
-1.00
-40-20 0 20406080
Minimum Gain
Ambient Temperature (°C)
Maximum Gain
Gain=20dB
Page 11

TS472 Electrical characteristics
Figure 20. Maximum input voltage vs. gain,
150
)
RMS
mV
(
100
THD+N<1%
VCC=5.5V
T
=25°C
AMB
F=1kHz
THD+N<1%
Figure 21. Maximum input voltage vs. power
supply voltage, THD+N<1%
T
)
mV
(
140
RMS
120
100
=25°C, F=1kHz, THD+N<1%
AMB
80
60
50
Maximum Input Voltage
0
0 10203040
VCC=3V
VCC=2.2V
Gain (dB)
Maximum Input Voltage
40
Gain=40dB
20
0
2.2
345
Power Supply Voltage (V)
Gain=30dB
Figure 22. THD+N vs. input voltage Figure 23. THD+N vs. input voltage
10
GS floating
GS=bias
1
10
GS floating
1
GS=bias
Gain=0dB
Gain=20dB
5.5
THD+N (%)
0.1
GS grounded
Tamb=25°C, Vcc=3V, F=100Hz,
0.01
Cb=1μF, RL=10kΩ, BW=100Hz-120kHz
1E-3 0.01 0.1
Input Voltage (V)
0.3
THD+N (%)
0.1
GS grounded
Tamb=25°C, Vcc=5V, F=100Hz,
0.01
Cb=1μF, RL=10kΩ, BW=100Hz-120kHz
1E-3 0.01 0.1
Input Voltage (V)
Figure 24. THD+N vs. input voltage Figure 25. THD+N vs. input voltage
10
GS floating
GS=bias
1
THD+N (%)
0.1
GS grounded
Tamb=25°C, Vcc=3V, F=1kHz,
0.01
Cb=1μF, RL=10kΩ, BW=100Hz-120kHz
1E-3 0.01 0.1
Input Voltage (V)
0.3
10
GS floating
GS=bias
1
THD+N (%)
0.1
GS grounded
Tamb=25°C, Vcc=5V, F=1kHz,
0.01
Cb=1μF, RL=10kΩ, BW=100Hz-120kHz
1E-3 0.01 0.1
Input Voltage (V)
0.3
0.3
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 11/25
Page 12

Electrical characteristics TS472
Figure 26. THD+N vs. input voltage Figure 27. THD+N vs. input voltage
10
GS floating
GS=bias
1
THD+N (%)
0.1
GS grounded
Tamb=25°C, Vcc=3V, F=20kHz,
0.01
Cb=1μF, RL=10kΩ, BW=100Hz-120kHz
1E-3 0.01 0.1
Input Voltage (V)
0.3
10
GS floating
GS grounded
1
THD+N (%)
0.1
Tamb=25°C, Vcc=5V, F=20kHz,
0.01
Cb=1μF, RL=10kΩ, BW=100Hz-120kHz
GS=bias
1E-3 0.01 0.1
Input Voltage (V)
Figure 28. THD+N vs. frequency Figure 29. THD+N vs. frequency
10
Tamb=25°C
Vcc=3V
RL=10k
Cb=1μF
BW=100Hz-120kHz
GS grounded, Vin=20mV
1
THD + N (%)
Ω
GS=bias, Vin=100mV
10
Tamb=25°C
Vcc=5V
RL=10k
Ω
Cb=1μF
BW=100Hz-120kHz
1
GS grounded, Vin=20mV
THD + N (%)
GS=bias, Vin=100mV
0.3
0.1
100 1000 10000
GS floating, Vin=100mV
Frequency (Hz)
20k50
0.1
GS floating, Vin=100mV
100 1000 10000
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 30. Transient response Figure 31. Common mode rejection ratio
(CMRR) vs frequency
0
Δ
Vicm=200mVpp, VCC=3V
CIN=1μF, T
-20
-40
-60
CMRR (dB)
-80
-100
20 20k
=25°C
AMB
Maximum Gain
Gain=20dB
Minimum Gain
100 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
20k50
12/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 13

TS472 Application information
4 Application information
4.1 Differential configuration principle
The TS472 is a fully-differential input/output microphone preamplifier. The TS472 also
includes a common-mode feedback loop that controls the output bias value to average it at
V
/2. This allows the device to always have a maximum output voltage swing, and by
CC
consequence, maximize the input dynamic voltage range.
The advantages of a fully-differential amplifier are:
● Very high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio).
● High common mode noise rejection.
● In theory, the filtering of the internal bias by an external bypass capacitor is not
necessary. However, to reach maximum performance in all tolerance situations, it is
better to keep this option.
4.2 Higher cut-off frequency
The higher cut-off frequency F
capacitors C
, C2.
1
of the microphone preamplifier depends on the external
CH
TS472 has an internal first order low-pass filter (R = 40 kΩ, C = 100 pF) to limit the highest
cut-off frequency on 40 kHz (with a 3 dB attenuation). By connecting C
decrease F
by applying the following formula.
CH
CH
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
2π 40
× 10 C
F
1
3
100
12,
12–
× 10+()⋅⋅
, C2 you can
1
Figure 32 represents the higher cut-off frequency in Hz versus the value of the output
capacitors C
, C2 in nF.
1
Figure 32. Higher cut-off frequency vs. output capacitors
40
10
Higher Cut-off Frequency (kHz)
1
200 400 600 800 1000
C1, C2 (pF)
For example, F
is almost 20 kHz with C
CH
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 13/25
=100 pF.
1,2
Page 14

Application information TS472
4.3 Lower cut-off frequency
The lower cut-off frequency FCL of the microphone preamplifier depends on the input
capacitors C
in an application because of DC voltage blocking.
and output capacitors C
in
. These input and output capacitors are mandatory
out
The input capacitors C
in series with the input impedance of the TS472 (100 kΩ) are
in
equivalent to a first order high-pass filter. Assuming that F
amplified (with a 3 dB attenuation), the minimum value of C
C
in
The capacitors C
in series with the output resistors R
out
next stage) are also equivalent to a first order high-pass filter. Assuming that F
lowest frequency to be amplified (with a 3 dB attenuation), the minimum value of C
C
Figure 33. Lower cut-off frequency vs. input
capacitors
1000
ZinMAX
Typical Zin
100
is the lowest frequency to be
CL
is:
in
------------------------------------------------------=
2π F
out
1
CL
1
------------------------------------------ -=
⋅⋅
2π F
CLRout
1003× 10⋅⋅
(or an input impedance of the
out
is the
CL
Figure 34. Lower cut-off frequency vs. output
capacitors
1000
Rout=10k
100
out
Ω
is:
ZinMIN
Lower Cut-off frequency (Hz)
10
1 10 100
Cin (nF)
Lower Cut-off frequency (Hz)
10
1 10 100 1000
Figure 33 and Figure 34 give directly the lower cut-off frequency (with 3 dB attenuation)
versus the value of the input or output capacitors.
Note: If F
is kept the same for calculation purposes, take into account that the 1st order high-
CL
pass filter on the input and the 1st order high-pass filter on the output create a 2nd order
high-pass filter in the audio signal path with an attenuation of 6 dB on F
40 dB/decade.
4.4 Low-noise microphone bias source
The TS472 provides a very low noise voltage and power supply rejection BIAS source
designed for biasing an electret condenser microphone cartridge. The BIAS output is
typically set at 2.0 V
drop-out, determined by the internal 100 Ω resistance (for detailed load regulation curves
see Figure 8).
(no load conditions), and can typically source 2 mA with respect to
DC
Rout=100k
Ω
Cout (nF)
and a roll-off of
CL
14/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 15

TS472 Application information
4.5 Gain settings
The gain in the application depends mainly on:
● the sensitivity of the microphone,
● the distance to the microphone,
● the audio level of the sound,
● the desired output level.
The sensitivity of the microphone is generally expressed in dB/Pa, referenced to 1 V/Pa. For
example, the microphone used in testing had an output voltage of 6.3 mV for a sound
pressure of 1 Pa (where Pa is the pressure unit, Pascal). Expressed in dB, the sensitivity is:
20Log(0.0063) = -44 dB/Pa
To facilitate the first approach, Ta bl e 1 0 gives voltages and gains used with a low-cost omnidirectional electret condenser microphone of -44 dB/Pa.
Table 10. Typical TS472 gain vs. distance to the microphone (sensitivity -44 dB/Pa)
Distance to microphone Microphone output voltage TS472 gain
1cm 30mV
20 cm 3 mV
RMS
RMS
20
100
The gain of the TS472 microphone preamplifier can be set as follows.
1. From -1.5 dB to 41 dB by connecting an external grounded resistor R
to the GS pin.
GS
This enables the gain to be adapted more precisely to each application.
Table 11. Selected gain vs. gain select resistor
Gain (dB) 010203040
R
(Ω) 470k 27k 4k7 1k 68
GS
Figure 35. Gain in dB vs. gain select resistor Figure 36. Gain in V/V vs. gain select resistor
50
40
30
20
Gain (dB)
10
0
-10
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M
RGS
(Ω)
Tamb=25°C
100
10
Gain (V/V)
1
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M
RGS
(Ω)
Tamb=25°C
2. To 20 dB by applying V
> 1VDC on the gain select (GS) pin. This setting can help to
GS
reduce a number of external components in an application, because 2.0 V
provided by the TS472 itself on the BIAS pin.
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 15/25
DC
is
Page 16

Application information TS472
Figure 37 gives other values of the gain vs. voltage applied on the GS pin.
Figure 37. Gain vs. gain select voltage
40
20
0
-20
Gain (dB)
-40
-60
-80
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 4 5
VGS (V
)
Tamb=25°C
Note: In the case of a single-ended output configuration (either positive or negative output is used
for the following signal processing) the overall gain is half. One must also take into account
that all advantages of the differential configuration principles are lost (see the difference in
PSRR in Ta bl e 5 ).
4.6 Wake-up time
When the standby mode is released to switch the device to ON, a signal appears on the
output a few microseconds later, and the bypass capacitor C
milliseconds. As C
properly until the C
is directly linked to the bias of the amplifier, the bias will not work
b
voltage is correct.
b
In a typical application, when a biased microphone is connected to the differential input via
the input capacitors (C
), (and the output signal is in line with the specification), the wake-up
in
time will depend upon the values of the input capacitors C
lower than 0 dB, the wake-up time is determined only by the bypass capacitor C
described above. For a gain superior to 0 dB, refer to Figure 38.
is charged within a few
b
and the gain. When the gain is
in
, as
b
Figure 38. Wake-up time in a typical application vs. input capacitors
60
Tamb = 25°C
Vcc=3V
50
Cb=1μF
40
30
20
Wake-up Time (ms)
10
0
Gain=20dB
20 40 60 80 100
16/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Maximum Gain
Input capacitors CIN (nF)
Page 17

TS472 Application information
4.7 Standby mode
When the standby command is set, it takes a few microseconds to set the output stages
(differential outputs and 2.0 V bias output) to high impedance and the internal circuitry to
shutdown mode
.
4.8 Layout considerations
The TS472 has sensitive pins to connect C1, C2 and Rgs. To obtain high power supply
rejection and low noise performance, it is mandatory that the layout track to these
components be as short as possible.
Decoupling capacitors on V
and bypass pin are needed to eliminate power supply drops.
CC
In addition, the capacitor location for the dedicated pin should be as close to the device as
possible.
4.9 Single-ended input configuration
It is possible to use the TS472 in a single-ended input configuration. The schematic in
Figure 39 provides an example of this type of configuration.
Figure 39. Typical single-ended input application
VCC
Cs
1uF
C3
1uF
+
Electret Mic
Rpos
Cin+
Cin-
U1 TS472
IN+
A1
IN-
B1
BIAS
A2
2.0V
Vcc
D3
GND
C1
A3
C1
G
Bias
STDBY
C3
B3
C2
Optional
C1
C2
OUT+
OUT-
GAIN
SELECT
BYPASS
Rout+
Positive Output
Negative Output
Rout-
Cb
1uF
Cout+
Cout-
C2
D2
B2
D1
Standby Control
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 17/25
Page 18

Application information TS472
4.10 Demonstration board
A demonstration board for the TS472 is available. For more information about this
demonstration board, refer to application note AN
Figure 40. PCB top layer Figure 41. PCB bottom layer
Figure 42. Component location
2240 on www.st.com.
18/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 19

TS472 Package information
5 Package information
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
®
is an ST trademark.
5.1 Flip-chip package information
Figure 43. TS472 footprint recommendation
500μm
500μm
Φ=250μm
Φ=250μm
Φ=400μm typ.
Φ=400μm typ.
Φ=340μm min.
Φ=340μm min.
500μm
500μm
500μm
500μm
Non Solder mask opening
Non Solder mask opening
Pad in Cu 18μm with Flash NiAu (2-6μm, 0.2μm max.)
Pad in Cu 18μm with Flash NiAu (2-6μm, 0.2μm max.)
500μm
500μm
75µm min.
75µm min.
100μm max.
100μm max.
150μm min.
150μm min.
Track
Track
Figure 44. Pinout (top view)
3
3
2
2
1
1
C1
C1
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
BIAS
BIAS
IN+
IN+
A
A
C2
C2
GS
GS
IN- GND
IN- GND
B
B
Balls are underneath
STDBY
STDBY
STDBY
OUT+
OUT+
C
C
VCC
VCC
OUT-
OUT-
BYPASS
BYPASS
D
D
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 19/25
Page 20

Package information TS472
Figure 45. Marking (top view)
■ ST logo
■ Part number: 472
■ E Lead free bumps
■ Three digits datecode: YWW
■ The dot indicates pin A1
Figure 46. Flip-chip - 12 bumps
2.1 mm
2.1 mm
0.5mm
0.5mm
0.5mm
0.5mm
∅ 0.315mm
∅ 0.315mm
1.6 mm
1.6 mm
600µm600µm
E
E
472
472
YWW
YWW
● Die size: 2.1 mm x 1.6 mm ± 30 µm
● Die height (including bumps): 600 µm
● Bumps diameter: 315 µm ±50 µm
● Bump diameter before reflow: 300 µm
±10 µm
● Bump height: 250 µm ±40 µm
● Die height: 350 µm ±20 µm
● Pitch: 500 µm ±50 µm
● Coplanarity: 50 µm max
Figure 47. Tape & reel specification (top view)
4
4
1
1
A
A
8
8
Die size Y + 70µm
Die size Y + 70µm
Die size X + 70µm
Die size X + 70µm
4
4
All dimensions are in mm
All dimensions are in mm
User direction of feed
User direction of feed
1.5
1.5
1
1
A
A
20/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 21

TS472 Package information
A
5.2 QFN24 package information
Figure 48. QFN24 package mechanical drawing
D
A1
A2
D1
Nd
0.50 DIA.
0
SEATING
PLANE
L
1
2
3
Ne
b
D2
R
Q
e
E1
P
1
2
3
E2
E
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 21/25
Page 22

Package information TS472
Table 12. QFN24 package mechanical data
Dimensions
Ref.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A 0.80 1.00 0.031 0.040
A1 0.05 0.002
A2 0.65 0.80 0.026 0.031
D 4.00 0.158
D1 3.75 0.148
E 4.00 0.158
E1 3.75 0.148
P 0.24 0.42 0.60 0.009 0.017 0.024
R 0.13 0.17 0.23 0.005 0.007 0.009
e 0.50 0.020
N 24.00 0.945
Nd 6.00 0.236
Ne 6.00 0.236
L 0.30 0.40 0.50 0.012 0.016 0.020
b 0.18 0.30 0.007 0.012
Q 0.20 0.45 0.008 0.018
D2 1.95 2.10 2.25 0.077 0.083 0.089
E2 1.95 2.10 2.25 0.077 0.083 0.089
Ø 12°
22/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 23

TS472 Ordering information
6 Ordering information
Table 13. Order codes
Order code
TS472EIJT -40°C, +85°C Flip-chip Tape & reel 472
TS472IQT -40°C, +85°C QFN24 4x4mm Tape & reel K472
Temperature
range
Package Packing Marking
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 23/25
Page 24

Revision history TS472
7 Revision history
Table 14. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
01-Jul-05 1 Initial release corresponding to product preview version.
01-Oct-05 2 First release of fully mature product datasheet.
01-Dec-05 3
Added single-ended input operation in Section 4: Application
information.
12-Sep-2006 4
02-Mar-2009 5
25-Aug-2009 6 Corrected QFN package pinout on cover page.
Added QFN package information. Updated curves, added new ones
in Section 3: Electrical characteristics.
Corrected error on C1 and C2 caps.
Added Table 2: Pin descriptions.
Updated QFN24 package information in Section 5.2.
24/25 Doc ID 11015 Rev 6
Page 25

TS472
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
Doc ID 11015 Rev 6 25/25
 Loading...
Loading...