Page 1
T R I Q U I N T S E M I C O N D U C T O R , I N C .
1
SYSTEM TIMING
PRODUCTS
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
TQ1090
11-Output
Configurable
Clock Buffer
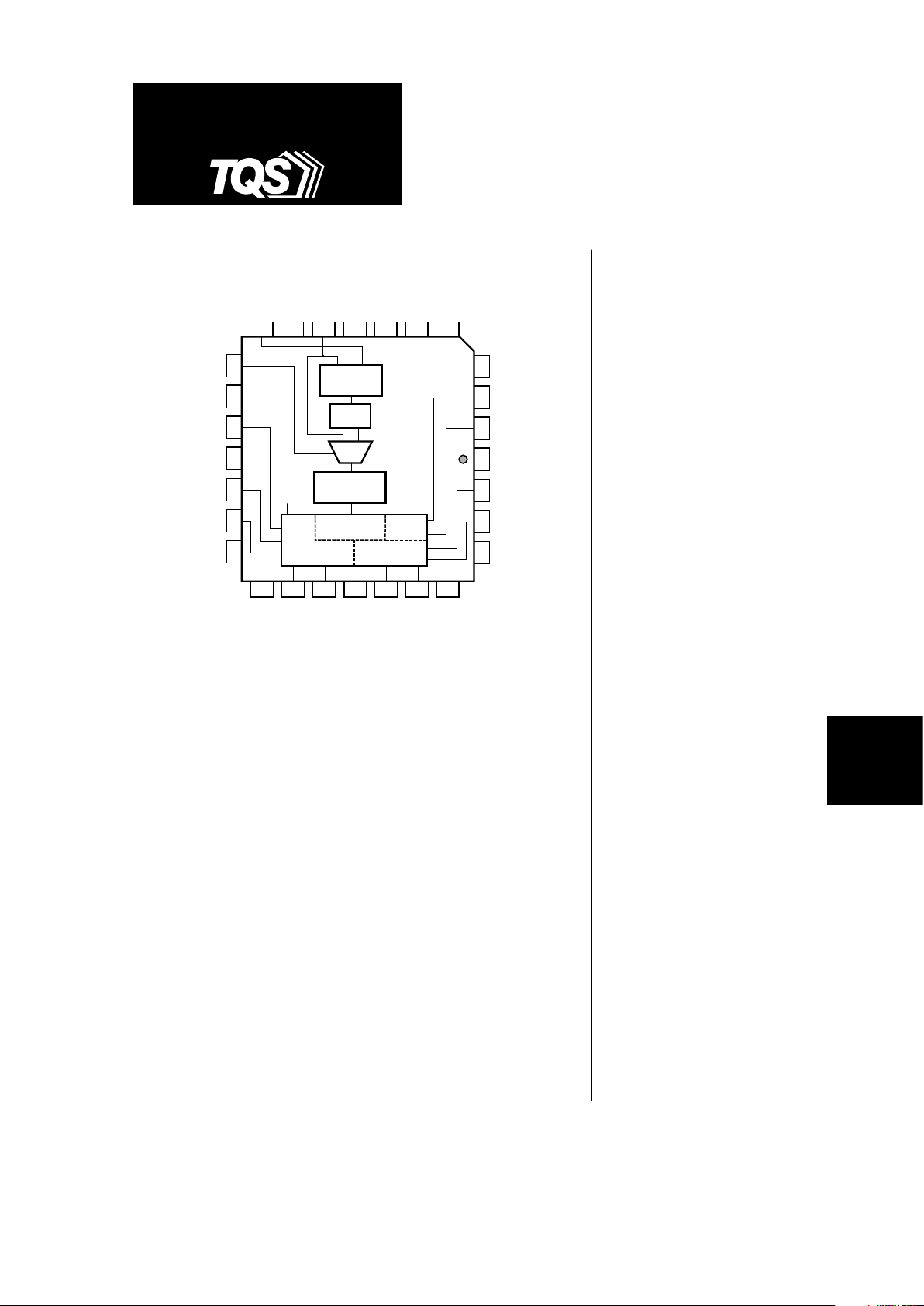
Figure 1. Block Diagram
Output Buffers
VCO
Phase
Detector
VDD
Q10
Q9
GND
Q8
Q7
VDD
TEST
VDD
Q0
GND
Q1
Q2
VDD
FBIN S1 REFCLK S0 GND GND GND
GND Q3 Q4 VDD Q5 Q6 GND
1
2
14
13
12
11 10
9
8765
4
3
22212019
18
17
16
15
27
28
252423
26
MUX
Divide Logic
÷ 2
Group A
Group C
Group B
S1 S0
TriQuint’s TQ1090 is a configurable clock buffer which generates 11
outputs, operating over a wide range of frequencies from 33 MHz to
45MHz, 65 MHz to 90 MHz and 130 MHz to 180 MHz. The outputs are
available at 1x, 2x and 4x, or at
1
/2x, 1x and 2x, or at 1/4 x, 1/2 x and
1x the reference clock frequency, f
REF
.
When one of the Group A outputs (Q0–Q4) is used as feedback to the PLL,
all Group A outputs will be at f
REF
, all Group B outputs (Q5–Q8) will be at
2x f
REF
and all Group C outputs (Q9,Q10) will be at 4x f
REF
. When one of the
Group B outputs is used as feedback to the PLL, all Group A outputs will
be at
1
/2 x f
REF
, all Group B outputs will be at f
REF
and all Group C outputs
will be at 2x f
REF
. When one of the Group C outputs is used as feedback to
the PLL, all Group A outputs will be at
1
/4 x f
REF
, all Group B outputs will be
at
1
/2 x f
REF
and all Group C outputs will be at f
REF
.
A very stable internal Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) provides low-jitter operation
.
This completely self-contained PLL requires no external capacitors or
resistors. The PLL’s Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) has a frequency
range from 260 MHz to 360 MHz. By feeding back one of the output clocks
to FBIN, the PLL continuously maintains frequency and phase synchronization between the reference clock (REFCLK) and each of the outputs.
Features
• Wide frequency range:
33 MHz to 45 MHz
65 MHz to 90 MHz and
130 MHz to 180 MHz
• Output configurations:
four outputs at f
REF
four outputs at 2x f
REF
two output at 4x f
REF
or
five outputs at
1
/2 x f
REF
three outputs at f
REF
two outputs at 2x f
REF
• Selectable Phase Shift:
–2t, –t, 0, +t (t = 1/f
vco
)
• Low output-to-output skew:
150 ps (max) within a group
• Near-zero propagation delay
–350 ps
±
500 ps (max) or
–350 ps
±
700 ps (max)
• TTL-compatible I/O with 30 mA
output drive
• Ideal for Power PC
™
designs
• 28-pin J-lead surface-mount
package
Page 2

2
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
TQ1090
Table 1. Frequency Mode Selection
Output Reference Clock ␣ Output Frequency Range
Test Feedback Mode Frequency Range Group A: Q0–Q4 Group B: Q5,Q08 Group c: Q9,Q10
0 Group A ÷8 35 MHz – 45 MHz 35 MHz – 45 MHz 65 MHz – 90 MHz 130 MHz – 180 MHz
0 Group B ÷4 65 MHz – 90 MHz 35 MHz – 45 MHz 65 MHz – 90 MHz 130 MHz – 180 MHz
0 Group C ÷2 130 MHz – 180 MHz 35 MHz – 45 MHz 65 MHz – 90 MHz 130 MHz – 180 MHz
The phase relationship of the Group A outputs to Group
B and C are controlled by the phase-select pins S0 and
S1. The phase difference can be varied from –2t, –t, 0
or +t, where t = 1/fvco.
TriQuint’s patented output buffer design delivers a very
low output-to-output skew of 150 ps (max). The
TQ1090’s symmetrical TTL outputs are capable of
sourcing and sinking 30 mA.
The Shift Select pins, S0 and S1, control the phase
shift of the Group A outputs (Q0 – Q4), relative to the
other outputs. The user can select from four
incremental phase shifts as shown in Table 2 (Phase
Selection). The phase shift increment (t) is calculated
using the following equation, where
n
is the divide
mode:
t =
In the test mode, the PLL is bypassed and REFCLK is
connected directly to the Divide Logic block via the
MUX, as shown in Figure 1. This mode is useful for
debug and test purposes. The test mode is outlined
in Table 3.
The maximum rise and fall time at the output pins is 1.4
ns. All outputs of the TQ1090 are TTL-compatible with
30 mA symmetric drive and a minimum V
OH
of 2.4 V.
Power-Up/Reset Synchronization
After power-up or reset, the PLL requires time before it
achieves synchronization lock. The maximum time
required for synchronization (TSYNC) is 500 ms.
Functional Description
The core of the TQ1090 is a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
that continuously compares the reference clock
(REFCLK) to the feedback clock (FBIN), maintaining a
zero frequency difference between the two. Since one
of the outputs is always connected to FBIN, the PLL
keeps the propagation delay between the outputs and
the reference clock within –350 ps
+500 ps for the
TQ1090-MC500, and within –350 ps
+700 ps for the
TQ1090-MC700.
The internal Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO), has an
operating range of 260 MHz to 360 MHz, as shown in
Table 1. The combination of the VCO and the Divide
Logic enables the TQ1090 to operate between 33 MHz
and 45 MHz, 65 MHz and 90 MHz, and from 130 MHz
to 180 MHz.
1
(f
REF
) (n)
Page 3
TQ1090
3
SYSTEM TIMING
PRODUCTS
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Table 2. Test Mode Selection
Group A Group B Group C
Test Mode Ref. Clock Outputs Q0–Q4 Outputs Q5–Q18 Outputs Q9–Q10
1 ÷2f
REF
f
REF
÷ 8f
REF
÷ 4f
REF
÷ 2
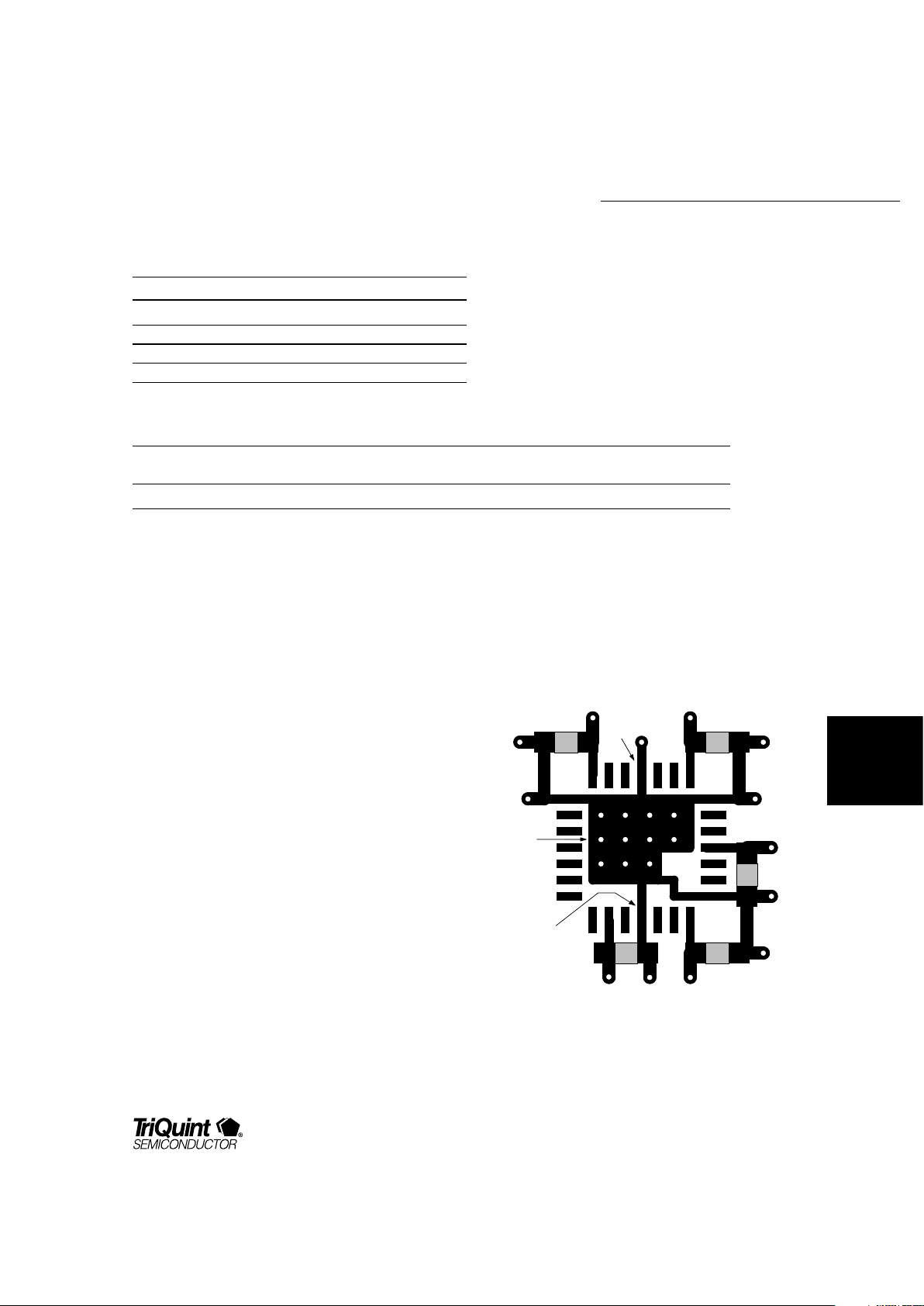
Figure 2. Top Layer Layout of Power Pins
(approx. 3.3x)
Layout Guidelines
Multiple ground and power pins on the TQ1090 reduce
ground bounce. Good layout techniques, however, are
necessary to guarantee proper operation and to meet
the specifications across the full operating range. We
recommend bypassing each of the V
DD
supply pins to
the nearest ground pin, as close to the chip as possible.
Figure 2 shows the recommended power layout for the
TQ1090. The bypass capacitors should be located on
the same side of the board as the TQ1090. The V
DD
traces connect to an inner-layer VDD plane. All of the
ground pins (GND) are connected to a small ground
plane on the surface beneath the chip. Multiple
through-holes connect this small surface plane to an
inner-layer ground plane. The capacitors (C1–C5) are
0.1 mF. TriQuint’s test board uses X7R temperaturestable capacitors in 1206 SMD cases.
C4
C5
C1
C2
C3
Pin 1
Pin 15
Ground
Plane
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
S0 S1 Phase Shift (Group A: Q0 – Q4)
00 +t
10 0
01 –t
1 1 –2t
Table 2. Phase Shift Selection
Page 4

4
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
TQ1090
Limits
4
Symbol Description Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
OHT
Output HIGH voltage VDD= Min IOH= –30 mA 2.4 3.4 V
VIN= VIH or V
IL
V
OHC
Output HIGH voltage VDD= Min IOH= –1 mA 3.2 4.1 V
VIN= VIH or V
IL
V
OL
Output LOW voltage VDD= Min IOL = 30 mA 0.27 0.5 V
VIN= VIH or V
IL
V
IH
5
Input HIGH level Guaranteed input logical HIGH 2.0 V
Voltage for all Inputs
V
IL
5
Input LOW level Guaranteed input logical LOW 0.8 V
Voltage for all inputs
I
IL
Input LOW current VDD= Max VIN = 0.40 V –156 –400 µ A
I
IH
Input HIGH current VDD= Max VIN = 2.7 V 0 25 µA
I
I
Input HIGH current VDD= Max VIN = 5.5 V 2 1000 µA
I
DDS
6
Power supply current VDD= Max 119 170 mA
V
I
Input clamp voltage VDD= Min IIN = –18 mA –0.70 –1.2 V
Notes: 1. Exceeding these parameters may damage the device.
2. Maximum ambient temperature with device not switching and unloaded.
3. These values apply to both TQ1089-MC500 and TQ1089-MC700.
4. Typical limits are at V
DD
= 5.0 V and TA = 25 °C.
5. These are absolute values with respect to device ground and all overshoots due to system or tester noise are included.
6. This parameter is measured with device not switching and unloaded.
7. These parameters are not 100% tested, but are periodically sampled.
Symbol Description Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
C
IN
3
Input capacitance VIN = 2.0 V at f = 1 MHz 6 pF
(VDD = +5 V + 5%, TA = 0 °C to +70 °C)
3
Absolute Maximum Ratings
1
DC Characteristics
Capacitance
Storage temperature –65 °C to +150 °C
Ambient temperature with power applied
2
–55 °C to +100 °C
Supply voltage to ground potential –0.5 V to +7.0 V
DC input voltage –0.5 V to +(VDD + 0.5)V
DC input current –30 mA to +5 mA
Package thermal resistance (MQuad) θJA = 45 °C/W
Die junction temperature TJ = 150 °C␣ ␣
Page 5

TQ1090
5
SYSTEM TIMING
PRODUCTS
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Symbol Input Clock (REFCLK) Test Conditions (Figure 3)
1
Min Typ Max Unit
t
CPWH
CLK pulse width HIGH Figure 4 2 --- — ns
t
CPWL
CLK pulse width LOW Figure 4 2 --- — ns
t
IR
Input rise time (0.8 V - 2.0V) — — 2.0 ns
AC Characteristics
Symbol Output Clocks (Q0–Q10) Test Conditions (Figure 3)
1
Min Typ Max Unit
t
OR,t OF
Rise/fall time (0.8 V – 2.0V) Figure 4 350 — 1400 ps
t
PD1
2
CLK ↑ to FBIN ↑ (TQ1090-MC500) Figure 4 –850 –350 +150 ps
t
PD2
2
CLK ↑ to FBIN ↑ (TQ1090-MC700) Figure 4 –1050 –350 +350 ps
t
SKEW1
3
Rise–rise, fall–fall (within group) Figure 5 — 60 150 ps
t
SKEW2
3
Rise–rise, fall–fall (group-to-group, aligned) Figure 6 (skew2 takes into account skew1) — 75 350 ps
t
SKEW3
3
Rise–rise, fall–fall (group-to-group, non-aligned) (skew3 takes into account skews1, 2) — — 650 ps
t
SKEW4
3
Rise–fall, fall–rise (skew4 takes into account skew3) — — 1200 ps
t
CYC
4
Duty-cycle Variation Figure 4 –1000 0 +1000 ps
t JP
5
Period-to-Period Jitter Figure 4 — 80 200 ps
t JR
5
Random Jitter Figure 4 — 190 400 ps
t
SYNC
6Synchronization Time — 10 500 µs
(VDD = +5 V + 5%, TA = 0 °C to +70 °C)
Notes:
Q0
Q1
Q2
•
•
•
•
Q10
FBIN
CLK
•
•
•
•
R1
R2
+5 V
R1
R2
+5 V
R1
R2
+5 V
R1
R2
+5 V
R1
R2
+5 V
Y
X
50 Ω
Z
Z
R1 = 160 Ω
R2 = 71 Ω
Y + Z = X
Figure 3. AC Test Circuit
Notes: 1. All measurements are tested with a REFCLK having a rise time of 0.5 ns (0.8 V to 2.0 V).
2. The PLL maintains alignment of CLK and FBIN at all times. This specification applies to the rising edge only because the input duty
cycle can vary while the output duty cycle is typically 50/50. The delay t
PD
is measured at the 1.5 V level between CLK and FBIN.
3. Skew
specifies the width of the window in which outputs switch, and is measured at 1.5 V.
Skew 1 is a subset of skew 2. Skew 2 is a subset of skew 3. Skew 3 is a subset of skew 4.
Definition of skew terms:
Rise–rise: Skew between rising edges (low to high transitions).
Fall–fall: Skew between falling edges (high to low transitions).
Rise–fall, fall–rise: Skew between rising-to-falling and falling-to-rising edges.
Within a group: Skew between outputs of the same group (for example, skew among Group A outputs)
Group-to-group: Skew between outputs of any group (for example, skew between Group A to Group B outputs)
Aligned: Skew between outputs that are in phase.
Non-aligned: Skew between outputs that are not in phase.
4. This specification represents the deviation from 50/50 on the outputs.
5. Jitter specifications refer to peak-to-peak value. t
JR
is the jitter on the output with respect to the reference clock. tJP is the jitter on the
output with respect to the same output’s previous rising edge.
6. t
SYNC
is the time required for the PLL to synchronize; this assumes the presence of a CLK signal and a connection from one of the
outputs to FBIN.
Page 6

6
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
TQ1090
Figure 5. t
SKEW1
Switching Waveforms
Figure 4. General Timing
Figure 6. t
SKEW2
Page 7

TQ1090
7
SYSTEM TIMING
PRODUCTS
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
28-Pin MQuad Pin Description
Pin # Pin Name Description I/O
1 GND Ground —
2 Q9 Output Clock 9 (C1) O
3 Q10 Output Clock 10 (C2) O
4 VDD +5 V —
5 GND Ground —
6 GND Ground —
7 GND Ground —
8 GND Ground —
9 REFCLK Reference Clock I
10 GND Ground —
11 FBIN Feedback In I
12 TEST Test I
13 VDD +5 V —
14 Q0 Output Clock 0 (A1) O
Pin # Pin Name Description I/O
15 GND Ground —
16 Q1 Output Clock 1 (A2) O
17 Q2 Output Clock 2 (A3) O
18 VDD +5 V —
19 GND Ground —
20 Q3 Output Clock 3 (A4) O
21 Q4 Output Clock 4 (A5) O
22 VDD +5 V —
23 Q5 Output Clock 5 (B1) O
24 Q6 Output Clock 6 (B2) O
25 GND Ground —
26 VDD +5 V —
27 Q7 Output Clock 7 (B3) O
28 Q8 Output Clock 8 (B4) O
28-Pin MQuad J-Leaded Package Mechanical Specification
(All dimensions in inches)
PIN 1
.050 TYP.
NON-ACCUM.
.445 ±.005
.490 ±.005
.445
±.005
.490
±.005
.045
X 45°°
.132 ±.005
.050 TYP.
.410
±.015
.018
.104
±.005
.172 ±.005
8
15
22
.445
±.005
.040 MIN
.015
X 45°°
0.125
VENT PLUG
.028
.060
Page 8

8
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
TQ1090
Figure 10. IOL vs.V
OL
V
OL
IOL min (mA) IOL max (mA)
–2.5 –145 –435
–2.0 –135 –410
–1.5 –115 –350
–1.0 –90 –265
–0.5 –40 –120
0.0 0 0
0.5 37 97
1.0 49 140
1.5 53 155
2.0 54 157
2.5 54 159
3.0 54 160
3.5 54 160
4.0 54 160
4.5 54 160
5.0 54 160
10.0 54 160
Table 5. IOL vs.V
OL
These output characteristics are provided for modelling
purposes only. TriQuint does not guarantee the
information in these tables and figures.
Output Characteristics
The IV characteristics, transition times, package
characteristics, device and bond wire characteristics
for the TQ1090 are describedin Tables 4 through 9 and
Figures 9 through 11.
Figure 9. IOH vs.V
OH
Table 4. IOH vs.V
OH
V
OH
IOH min (mA) IOH max (mA)
0.0 –70 –160
0.5 –70 –157
1.0 –68 –152
1.5 –65 –142
2.0 –59 –130
2.5 –48 –106
3.0 –29 –79
3.5 0 –42
4.0 0 0
4.5 0 0
5.0 0 0
5.5 40 120
6.0 90 265
6.5 115 350
7.0 135 410
7.5 145 435
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0
Volts
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
I (mA)
OL
V max
OL
V min
OL
LOW
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0
Volts
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
-140
-160
I (mA)
OH
V max
OH
V min
OH
HIGH
Notes: 1. These are worst-case corners for process, voltage,
and temperature.
2. Includes diode to ground current.
Page 9

TQ1090
9
SYSTEM TIMING
PRODUCTS
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
Diode to GND␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣␣ Diode Stack to VDD
V I (mA) V I (mA)
0.0 0 5.0 0
–0.4 0 5.4 0
–0.5 0 5.5 0
–0.6 –5 5.6 5
–0.7 –15 5.7 15
–0.8 –35 5.8 35
–0.9 –55 5.9 55
–1.0 –75 6.0 75
–2.0 –300 7.0 300
–2.5 –350 7.5 350
–3.0 –360 8.0 360
Note: TriQuint does not guarantee diode operation for purposes
other than ESD protection.
Table 6. Above-VDD and Below-Ground Characteristics Table 9. Rise and Fall Times
Figure 11. Output Model
Time (ns) TR min (V) TR max (V) TF min (V) TF max (V)
0.0 0.15 0.32 3.20 3.04
0.1 0.15 0.32 3.20 3.04
0.2 0.16 0.32 3.06 2.95
0.3 0.18 0.32 2.86 2.90
0.4 0.23 0.32 2.62 2.68
0.5 0.26 0.32 2.38 2.50
0.6 0.34 0.32 2.17 2.36
0.7 0.46 0.34 2.00 2.22
0.8 0.67 0.39 1.85 2.09
0.9 0.89 0.49 1.69 1.95
1.0 1.12 0.63 1.52 1.86
1.1 1.32 0.86 1.38 1.68
1.2 1.50 1.09 1.26 1.59
1.3 1.73 1.27 1.12 1.49
1.4 1.93 1.45 0.96 1.36
1.5 2.15 1.64 0.83 1.23
1.6 2.75 2.23 0.52 0.95
1.7 2.58 2.00 0.61 1.00
1.8 2.75 2.23 0.52 0.95
1.9 2.90 2.41 0.45 0.91
2.0 3.02 2.50 0.39 0.86
2.1 3.12 2.64 0.33 0.77
2.2 3.17 2.77 0.29 0.73
2.3 3.19 2.86 0.24 0.68
2.4 3.20 2.95 0.21 0.64
2.5 3.20 2.99 0.19 0.59
2.6 3.20 3.02 0.17 0.55
2.7 3.20 3.02 0.16 0.53
2.8 3.20 3.04 0.16 0.50
2.9 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.45
3.0 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.41
3.1 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.40
3.2 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.37
3.3 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.36
3.4 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.32
3.5 3.20 3.04 0.15 0.32
L1 C1
2 nH 10 pF
Table 7. Device and Bond Wire Characteristics
(Estimated)
L2 C2
1.85 nH 0.40 pF
Table 8. 28-Pin MQuad Package Characteristics
(Into 0 pF, 50 Ohms to 1.5 V)
C2
DIE
C1
L2L1
OUTPUT
Page 10

10
For additional information and latest specifications, see our website: www.triquint.com
TQ1090
Additional Information
For latest specifications, additional product information,
worldwide sales and distribution locations, and information about TriQuint:
Web: www.triquint.com Tel: (503) 615-9000
Email: sales@tqs.com Fax: (503) 615-8900
For technical questions and additional information on specific applications:
Email: applications@tqs.com
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; TriQuint assumes no liability for inaccuracies or
omissions. TriQuint assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all such information
shall be entirely at the user's own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change without notice.
No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party.
TriQuint does not authorize or warrant any TriQuint product for use in life-support devices and/or systems.
Copyright © 1997 TriQuint Semiconductor, Inc. All rights reserved.
Revision 1.1.A November 1997
Ordering Information
To order, please specify as shown below:
TQ1090-MC nnn
11-Output Configurable Clock Buffer
Propagation delay skew:
500
–350 ps ± 500 ps
700
–350 ps ± 700 ps
Temperature range: 0 °C to 70 °C (Commercial)
Package: MQuad
Note: All parts are marked as
MC500. MC700 parts have a “2”
added to the marking.
 Loading...
Loading...