Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA9800
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL
detector
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
July 1994
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
FEATURES
• Suitable for negative vision modulation
• Applicable for IF frequencies of 38.9 MHz, 45.75 MHz
and 58.75 MHz
• Gain controlled wide band VIF amplifier (AC coupled)
• True synchronous demodulation with active carrier
regeneration (ultra-linear demodulation, good
intermodulation figures, reduced harmonics and
• AGC output voltage for tuner; adjustable take-over point
(TOP)
• AFC detector without extra reference circuit
• Alignment-free FM-PLL detector with high linearity
• Stabilizer circuit for ripple rejection and to achieve
constant output signals
• 5 to 8 V positive supply voltage range, low power
consumption (300 mW at +5 V supply voltage).
excellent pulse response)
• Peak sync AGC for negative modulation
• Video amplifier to match sound trap and sound filter
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA9800 is a monolithic integrated circuit for vision
and sound IF signal processing in TV and VTR sets.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
P
V
i IF
positive supply voltage (pin 20) 4.5 5 8.8 V
supply current 51 60 69 mA
vision IF input signal sensitivity (RMS value, pins 1 and 2) − 50 90 µV
maximum vision IF input signal (RMS value, pins 1 and 2) 70 150 − mV
G
v
V
o CVBS
IF gain control 64 70 73 dB
CVBS output signal on pin 7 (peak-to-peak value) 1.7 2.0 2.3 V
B −3 dB video bandwidth on pin 7 6 8 − MHz
S/N (W) signal-to-noise ratio weighted; for video 56 59 − dB
α
0.92/1.1
α
2.76/3.3
α
H
V
o AF
T
amb
intermodulation attenuation 56 62 − dB
56 62 − dB
suppression of harmonics in video signal 35 40 − dB
maximum AF output signal for THD < 1.5% (RMS value, pin 9) 0.8 −− V
operating ambient temperature −20 −+70 °C
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED TYPE
NUMBER
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
TDA9800 20 DIL plastic SOT146
TDA9800T 20 mini-pack plastic SOT163A
Note
1. SOT146-1; 1996 December 6.
2. SOT163-1; 1996 December 6.
July 1994 2
PACKAGE
(1)
(2)
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
handbook, full pagewidth
VP = 5 V (9 V)
2f
PC
IF input
V
i PC
V
i VIF1
V
i VIF2
GND
CCS
18
1
2
4
takeover
point
V
P VCO2 VCO1
20
INTERNAL
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
3-STAGE
IF-AMPLIFIER
TUNER
AGC
3
tuner AGC
output
T
PLL
17
TRAVELLING
WAVE
DIVIDER
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
AND PHASE
DETECTOR
6
DEMODULATOR
16
VCO
VIDEO
TDA9800
IF
AGC
12
TAGCTOP
19
C
DETECTOR
AGC
C
AGC
AGC
5
MUTE
sound
MUTE
8
n.c.
AFC
15
AFC
VIDEO
AMPLIFIER
13
V
o(vid)
1 V (p-p)
sound
mute
BUFFER AND
NOISE
CLIPPING
14
V
i(vid)
SOUND
TRAP
AF
AMPLIFIER
FM-PLL
11
V
i IC
SOUND
FILTER
9
10
7
video and
intercarrier
V
o AF
C
AF
V
o CVBS
2 V (p-p)
MED329
C
AF
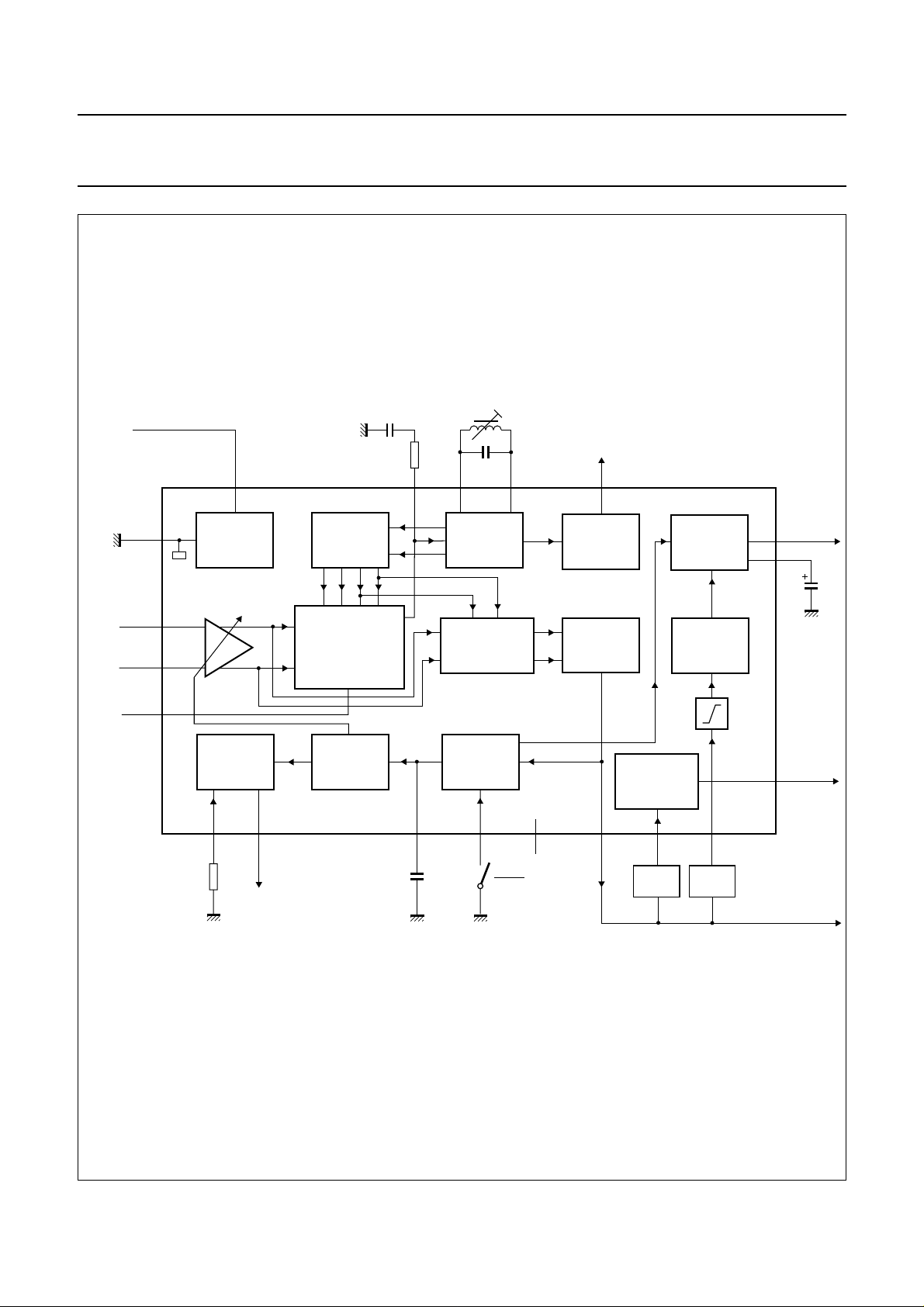
Fig.1 Block diagram.
July 1994 3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
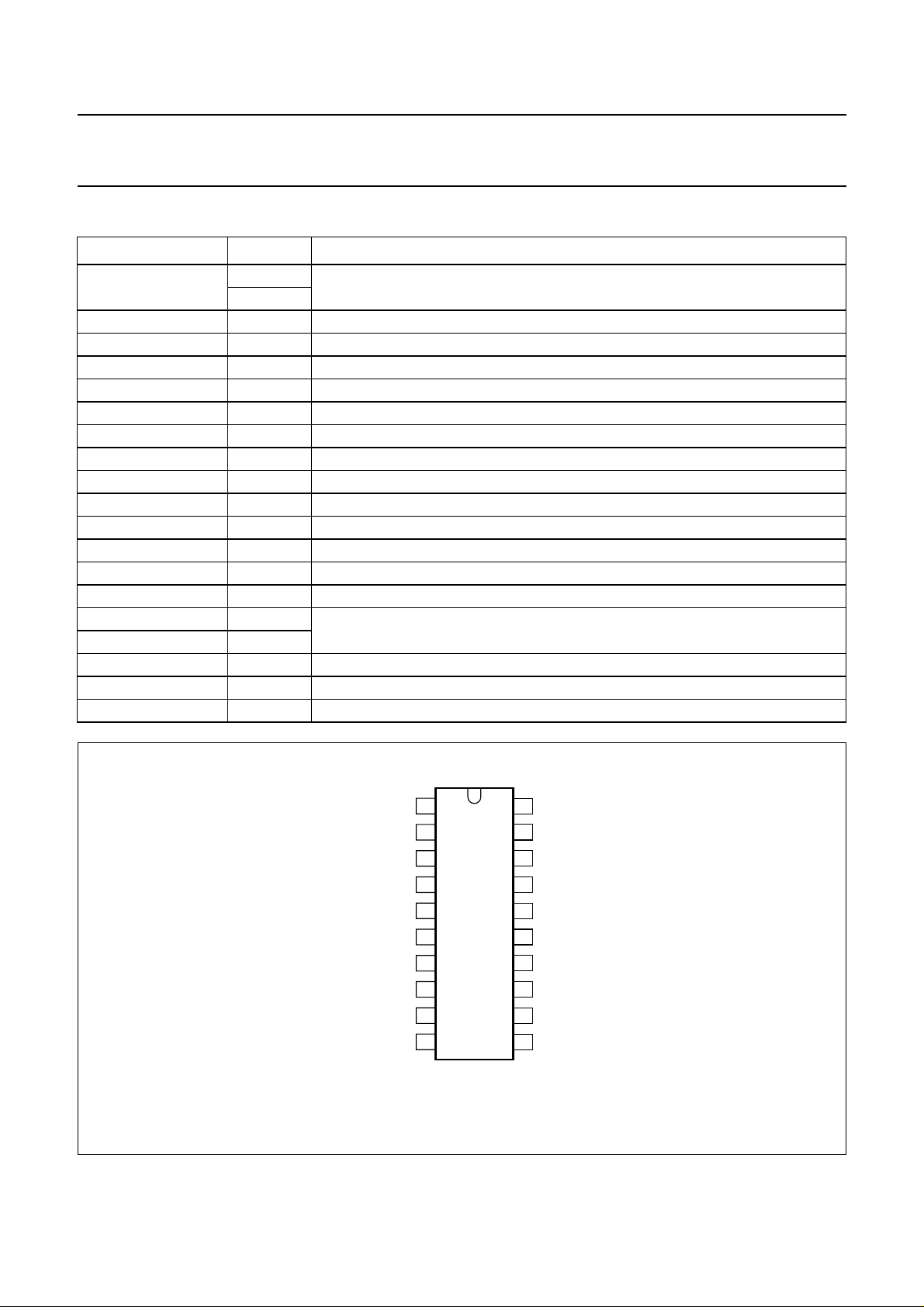
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
V
i IF
TADJ 3 tuner AGC take-over adjust (TOP)
φADJ 4 phase detector adjust
MUTE 5 sound mute switch
T
PLL
V
o CVBS
n.c. 8 not connected
V
o AF
C
AF
V
i IC
TAGC 12 tuner AGC output
V
o VID
V
i VID
AFC 15 automatic frequency control output
VCO1 16 VCO reference circuit for 2 f
VCO2 17
GND 18 ground (0 V)
C
AGC
V
P
1 vision IF differential input signal
2
6 PLL time constant of phase detector
7 CVBS (positive) output signal
9 audio frequency output signal
10 decoupling capacitor of audio frequency amplifier
11 sound intercarrier input signal
13 video and sound intercarrier output signal
14 video input signal to buffer amplifier
PC
19 AGC capacitor
20 positive supply voltage
handbook, halfpage
V
i VIF1
V
i VIF2
MUTE
V
o CVBS
Vo
TOP
CCS
T
PLL
C
n.c.
AF
AF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TDA9800
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
July 1994 4
MED330
V
20
P
19
C
AGC
18
GND
17
VCO2
16
VCO1
AFC
15
V
14
i(vid)
V
13
o(vid)
TAGC
12
V
11
i IC
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Vision IF input
The vision IF amplifier consists of three AC-coupled
differential amplifier stages; each stage comprises a
controlled feedback network by means of emitter
degeneration.
IF and tuner AGC
The automatic control voltage to maintain the video output
signal at a constant level is generated according to the
transmission standard. Since the TDA9800 is suitable for
negative modulation only the peak-sync level is detected.
The AGC detector charges and discharges the capacitor
on pin 19 to set the IF gain and the tuner gain. The AGC
capacitor voltage is transferred to an internal IF control
signal, and is fed to the tuner AGC to generate the tuner
AGC output current on pin 12 (open-collector output). The
tuner AGC voltage take over point is adjusted on pin 3.
This allows the tuner and the IF SAW filter to be matched
to achieve the optimum IF input level.
Frequency detector, phase detector and video demodulator
The IF amplifier output signal is fed to a frequency detector
and to a phase detector. During acquisition the frequency
detector produces a DC current which is proportional to the
frequency difference between the input and the VCO
signal. After frequency lock-in the phase detector
produces a DC current proportional to the phase
difference between the VCO and the input signal. Via the
loop filter the DC current of either frequency detector or
phase detector is converted into a DC voltage, which
controls the VCO frequency.
The video demodulator is a linear multiplier, designed for
low distortion and wide bandwidth. The vision IF input
signal is multiplied by the in-phase component of the VCO
output. The demodulated output signal is fed via an
integrated low-pass filter (f
amplifier for suppression of the carrier harmonics.
= 12 MHz) to the video
g
with 90 degree phase difference independent of
frequency.
Video amplifier, buffer and noise clipping
The video amplifier is a wide bandwidth operational
amplifier with internal feedback. A nominal positive
modulated video signal of 1 V (p-p) is present on the
composite video output (pin 13). The input impedance of
the 7 dB wideband buffer amplifier (with internal feedback)
is suitable for ceramic sound trap filters. The CVBS output
(pin 7) provides a positive video signal of 2 V (p-p). Noise
clipping is provided internally.
Sound demodulation
The FM sound intercarrier signal is fed to pin 11 and
through a limiter amplifier before it is demodulated. This
achieves high sensitivity and high AM suppression. The
limiter amplifier consists of seven internal AC-coupled
stages, minimizing the DC offset.
The FM-PLL demodulator consists of an RC-oscillator,
loop filter and phase detector. The oscillator frequency is
locked on the FM intercarrier signal from the limiter
amplifier. As a result of this locking, the RC-oscillator is
frequency-modulated.
The modulating signal voltage (AF signal) is used to
control the oscillator frequency. By this, the FM-PLL
operates as an FM demodulator.
The audio frequency amplifier with internal feedback is
designed for high gain and high common mode rejection.
The low-level AF signal output from the FM-PLL
demodulator is amplified and buffered in a low-ohmic
audio signal output stage (pin 9). An external decoupling
capacitor on pin 10 removes the DC voltage from the audio
amplifier input.
By using the sound mute switch (pin 5) the AF amplifier is
set to mute state.
VCO and travelling wave divider
The VCO operates with a symmetrically-connected
reference LC-circuit, operating at double vision carrier
frequency. Frequency control is performed by an internal
varicap diode. The voltage to set the VCO frequency to the
actual frequency of double vision carrier frequency, is also
amplified and converted for the AFC output current.
The VCO signal is divided-by-two in a travelling wave
divider, which generates two differential output signals
July 1994 5
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
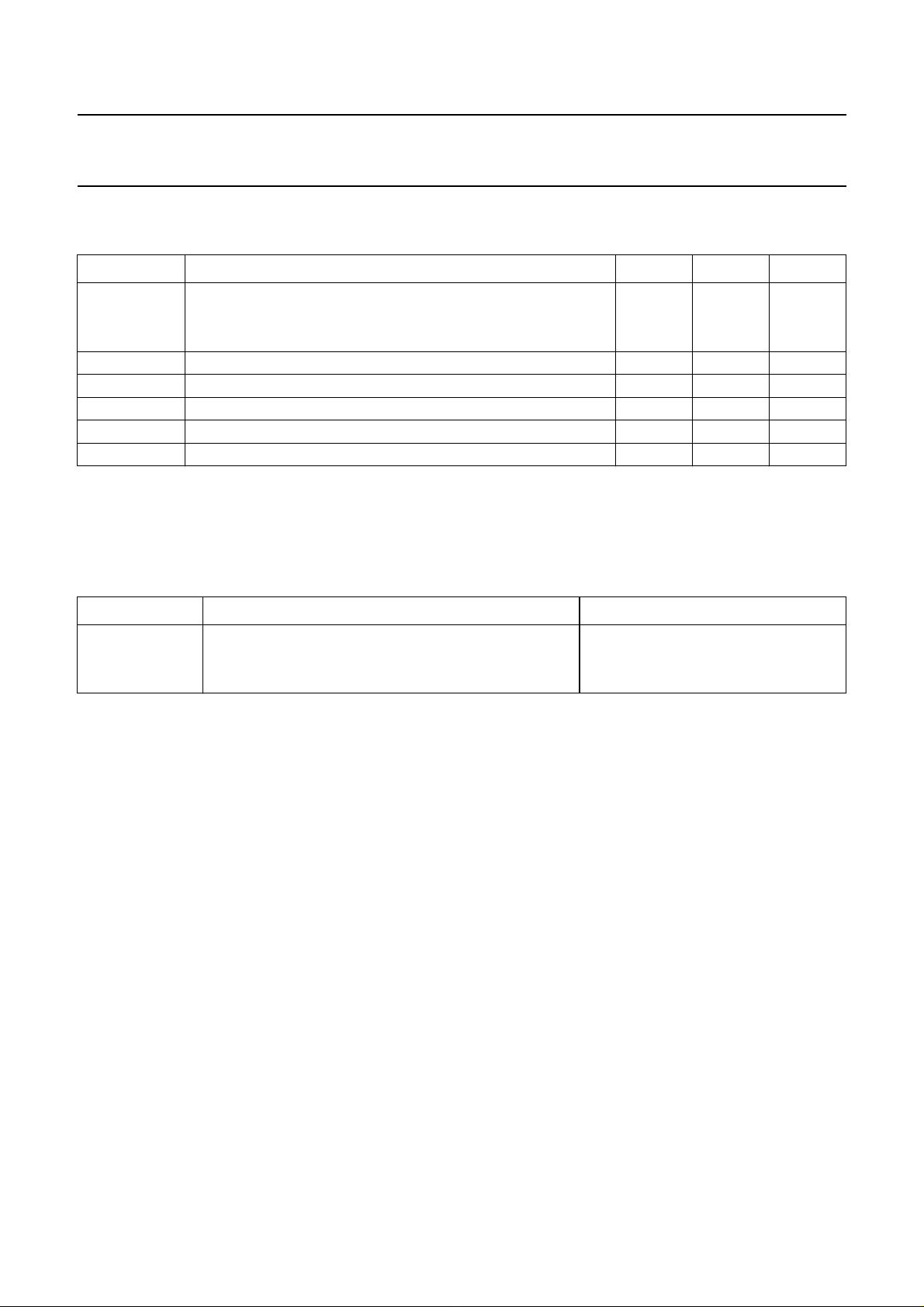
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
V
I
t
s max
V
12
T
stg
V
ESD
Notes
1. Supply current I
2. Equivalent to discharging a 200 pF capacitor through a 0 Ω series resistor (negative and positive voltage).
supply voltage (pin 20) for a maximum chip temperature (note 1)
SOT146 at +120 °C 0 8.8 V
SOT163A at +100 °C 0 5.5 V
voltage on pins 1, 2, 7, 11, 13, 14, 15 and 19 0 V
P
V
short-circuit time − 10 s
tuner AGC output voltage − 13.2 V
storage temperature range −25 +150 °C
electrostatic handling for all pins (note 2) −±300 V
= 69 mA at T
P
amb
= +70 °C.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
SYMBOL PARAMETER THERMAL RESISTANCE
R
th j-a
from junction to ambient in free air
SOT146 73 K/W
SOT163A 85 K/W
July 1994 6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
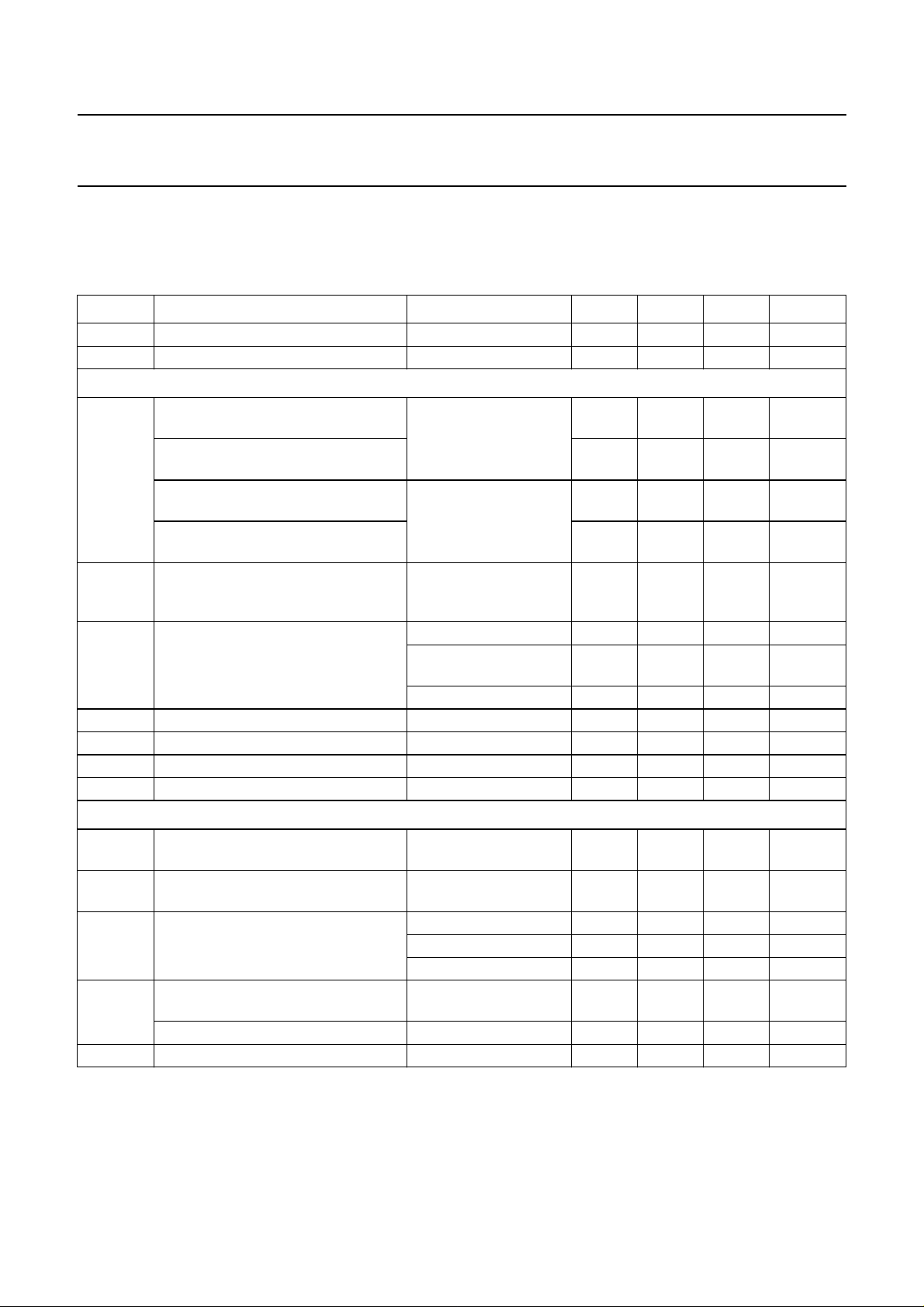
CHARACTERISTICS
The following characteristics apply for V
ratios; V
= 10 mV RMS value (sync level); video modulation DSB; residual carrier: 10%; video signal in accordance
ilF
= 5 V; T
P
with CCIR line 17 or NTC-7 Composite; measurements taken in Fig.3 unless otherwise specified
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
P
supply voltage (pin 20) note 1 4.5 5 8.8 V
supply current 51 60 69 mA
Vision IF input (pins 1 and 2)
V
i
input sensitivity (RMS value) at
38.9 MHz and 45.75 MHz
input sensitivity (RMS value) at
58.75 MHz
maximum input signal (RMS value) at
38.9 MHz and 45.75 MHz
maximum input signal (RMS value) at
58.75 MHz
∆V
o int.
internal IF amplitude difference
between picture and sound carrier
G
IF
IF gain control see Fig.4
B −3 dB IF bandwidth upper cut-off frequency 70 100 − MHz
R
i
C
i
V
1, 2
input resistance (differential) 1.7 2.2 2.7 kΩ
input capacitance (differential) 1.2 1.7 2.5 pF
DC input voltage 3.0 3.4 3.8 V
True synchronous video demodulator
f
VCO
maximum oscillator frequency for
carrier regeneration
∆f
VCO
oscillator drift (free running) as a
function of temperature
V
o ref
oscillator swing at pins 16 and 17
(RMS value)
∆f
PC
vision carrier capture range
(negative)
vision carrier capture range (positive) 1.5 2 − MHz
t
acqu
acquisition time BL = 60 kHz; note 4 −−30 ms
= +25 °C; see Table 1 for input frequencies and picture to sound
amb
−1 dB video at output − 50 90 µV
− 60 100 µV
+1 dB video at output 70 150 − mV
80 160 − mV
within AGC range;
− 0.7 1 dB
B/G: ∆f = 5.5 MHz;
M/N: ∆f = 4.5 MHz
38.9 MHz and
64 70 − dB
45.75 MHz
58.75 MHz 62 68 − dB
note 2
f=2f
PC
I
= 0; note 3 −−±20 ppm/K
AFC
125 130 − MHz
fPC= 38.9 MHz − 120 − mV
f
= 45.75 MHz − 100 − mV
PC
f
= 58.75 MHz − 80 − mV
PC
1.5 2 − MHz
July 1994 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
i IF
I
loop
Composite video amplifier (pin 13)
V
0 vid
V
13
V
0 FM
R
13
I
int13
I
13
B −3 dB video bandwidth C13< 50 pF; RL>1kΩ 710−MHz
α
H
RR ripple rejection on pin 13 see Fig.9 32 35 − dB
IF input signal sensitivity
(RMS value, pins 1 and 2)
for PLL still locked maximum IF gain;
− 50 90 µV
note 5
for C/N = 10 dB note 6 − 100 140 µV
FPLL loop offset current at pin 6 note 7 −−±4.5 µA
sound carrier off
output signal (peak-to-peak value) see Fig.7 0.9 1.0 1.1 V
sync level 1.4 1.5 1.6 V
zero carrier level − 2.6 − V
upper video clipping level VP− 1.1 VP− 1.0 − V
lower video clipping level − 0.3 0.4 V
IF intercarrier level (RMS value) sound carrier on; note 8 − 170 − mV
output resistance −−10 Ω
internal bias current for emitter
DC 1.8 2.5 − mA
follower
maximum output sink current DC and AC 1.4 −−mA
maximum output source current 2.0 −−mA
suppression of video signal
harmonics
C13< 50 pF; RL>1kΩ;
note 9
35 40 − dB
CVBS buffer amplifier and noise clipper (pins 7 and 14)
R
14
C
14
V
14
G
v
V
o CVBS
input resistance 2.6 3.3 4.0 kΩ
input capacitance 1.4 2 3.0 pF
DC voltage at input pin 14 not connected 1.5 1.8 2.1 V
voltage gain note 10 6 7 7.5 dB
CVBS output signal on pin 7
(peak-to-peak value)
sound carrier off;
see Fig.3
1.7 2.0 2.3 V
CVBS output level upper video clipping 3.9 4.0 − V
lower video clipping − 1.0 1.1 V
sync level − 1.35 − V
R
I
7
int7
output resistance −−10 Ω
internal bias current for emitter
DC 1.8 2.5 − mA
follower
I
7
maximum output sink current DC and AC 1.4 −−mA
maximum output source current 2.4 −−mA
B −3 dB video bandwidth C7< 20 pF; RL> 1kΩ 811−MHz
July 1994 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Measurements from IF input to CVBS output (pin 7) 330 Ω between pins 13 and 14, sound carrier off
V
o CVBS
CVBS output signal on pin 7
(peak-to-peak value)
∆V
o
deviation of CVBS output signal at
B/G
50 dB gain control −−0.5 dB
30 dB gain control −−0.1 dB
black level tilt note 11 −−1%
∆G differential gain CCIR line 330 or
∆ϕ differential phase − 1 3 deg
B −3 dB video bandwidth C
NTC-7 Composite
< 20 pF; RL> 1kΩ 68−MHz
L
S/N(W) signal-to-noise ratio; weighted see Fig.5 and note 12 56 59 − dB
α
0.92/1.1
α
2.76/3.3
α
C
intermodulation at ‘blue’ f = 0.92 or 1.1 MHz;
intermodulation at ‘yellow’ 58 64 − dB
see Fig.6 and note 13
intermodulation at ‘blue’ f = 2.76 or 3.3 MHz;
intermodulation at ‘yellow’ 57 63 − dB
see Fig.6 and note 13
residual vision carrier (RMS value) fundamental wave − 110mV
harmonics − 110mV
α
H
suppression of video signal
note 9 35 40 − dB
harmonics
RR ripple rejection on pin 7 see Fig.9 25 28 − dB
1.7 2.0 2.3 V
−25%
56 62 − dB
56 62 − dB
AGC detector (pin 19)
t
resp
response to an increasing amplitude
step of 50 dB in input signal
response to a decreasing amplitude
step of 50 dB in input signal
I
19
charging current note 11 0.85 1.1 1.35 mA
discharging current 17 22 27 µA
V
19
AGC voltage maximum gain 0 see
− 110ms
− 50 100 ms
Fig.4
minimum gain − see
Fig.4
− V
V
− 0.7 V
P
July 1994 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Tuner AGC (pin 12)
V
i
IF input signal for minimum starting
point of tuner take over (RMS value)
IF input signal for maximum starting
point of tuner take over (RMS value)
V
12
allowable voltage from external source −−13.2 V
saturation voltage I
∆V
12
variation of take over point by
temperature
I
12
∆G
IF
sink current see Fig.4
IF slip by automatic gain control tuner gain current from
AFC circuit (pin 15)
S control steepness ∆I15/∆f note 15
∆f
V
IF
15
frequency variation by temperature I
output voltage upper limit see Fig.8 VP− 0.5 VP− 0.3 − V
output voltage lower limit − 0.3 0.5 V
I
15
output current source 160 200 240 µA
output current sink 160 200 240 µA
∆I
15
residual video modulation current
(peak-to-peak value)
Sound mute switch (pin 5)
V
V
I
IL
α
∆V
IL
IH
mute
5
input voltage for MUTE-ON 0 − 0.8 V
input voltage for MUTE-OFF 1.5 − V
LOW level input current V5=0V −−300 −360 µA
audio attenuation V5= 0 V 70 80 − dB
DC offset voltage at switching (plop) switching to MUTE-ON − 100 500 mV
input at pins 1 and 2;
R
= 22 kΩ
TOP
input at pins 1 and 2;
R
=0Ω
TOP
= 1.7 mA −−0.2 V
12
−−5mV
50 −−mV
I12= 0.4 mA − 0.02 0.06 dB/K
no tuner gain reduction − 0.1 0.3 µA
maximum tuner gain
1.7 2.0 2.6 mA
reduction
− 68dB
20 to 80%
see Fig.8 and note 14
38.9 MHz −0.6 −0.72 −0.84 µA/kHz
45.75 MHz −0.45 −0.6 −0.75 µA/kHz
58.75 MHz −0.38 −0.5 −0.62 µA/kHz
= 0; note 3 −−±20 ppm/K
AFC
− 20 30 µA
note 16
P
V
July 1994 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
FM sound limiter amplifier (pin 11)
V
i FM
input signal (RMS value, pin 11) CCIR468-4
for S/N = 40 dB see Fig.11 − 200 300 µV
for AM suppression α
= 40 dB AM: f = 1 kHz; m = 0.3 − 1 − mV
AM
maximum input signal handling
(RMS value)
α
AM
R
11
AM suppression see Fig.10;
input resistance 480 600 720 Ω
B −3 dB IF frequency response of
sound IF
V
11
DC voltage 2.3 2.6 2.9 V
FM-PLL sound demodulator and AF output (pin 9) note 17
f
i FM
catching range of PLL 4 − 7 MHz
holding range of PLL 3.5 − 8 MHz
t
acqu
V
o AF
acquisition time −−4µs
AF output signal (RMS value, pin 9) ∆fAF= ±27 kHz;
maximum output signal handling THD<1.5% 0.8 −−V
∆V
o
∆f
AF
V
10
R
9
R
L
V
9
temperature drift of AF output signal − 3710
frequency deviation THD < 1.5%; note 18 −−±50 kHz
DC voltage at decoupling capacitor voltage dependent on
output resistance − 100 −Ω
load resistance (pin 9) 2.2 −−kΩ
DC voltage 1.6 2.0 2.4 V
B −3 dB audio frequency bandwidth 95 120 − kHz
THD total harmonic distortion without ceramic filter − 0.1 0.5 %
S/N (W) signal-to-noise ratio, weighted CCIR468-4; see Fig.11 50 55 − dB
V
SC
residual sound carrier and
harmonics (RMS value)
RR ripple rejection on pin 9 see Fig.9 26 30 − dB
note 17
AM: f = 1 kHz; m = 0.3
lower and upper
cut-off frequency
see Fig.11
VCO frequency;
note 19
200 −−mV
46 50 − dB
3.5 − 10 MHz
280 350 420 mV
-3
1.2 − 2.2 V
−−75 mV
dB/K
Measurements from IF input to audio output (pin 9) 560 Ω between pins 13 and 11; note 20
S/N (W) weighted signal-to-noise ratio 27 kHz FM deviation; CCIR468-4; 50 µs (75 µs at standard M)
de-emphasis; with offset alignment on pin 4
6 kHz sinusoidal waveform black-to-white 39 46 − dB
black picture sync only 40 48 − dB
white picture 39 46 − dB
colour bar 39 46 − dB
July 1994 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
Notes
1. Values of video and sound parameters are decreased at VP= 4.5 V.
2. Loop bandwidth BL = 60 kHz (natural frequency fn= 15 kHz; damping factor d = 2 calculated with grey level and
FPLL input signal level). Resonance circuit of VCO: Qo> 50; C
3. Temperature coefficient of external LC-circuit is equal to zero.
4. V
= 10 mV (RMS value); ∆f = 1 MHz (VCO frequency offset related to picture carrier frequency); white picture
i IF
video modulation.
5. V
signal for nominal video signal.
i IF
6. Transformer at IF input (Fig.3). The C/N ratio at IF input for ‘lock-in’ is defined as the vision IF input signal (sync level,
RMS value) in relation to a superimposed, 5 MHz band-limited white noise signal (RMS value); video modulation:
white picture.
7. Offset current measured between pin 6 and half of supply voltage (V = 2.5 V) under the following conditions: no input
signal at IF input (pins 1 and 2) and IF amplifier gain at minimum (V19=VP), pin 4 (phase adjust) open-circuit.
8. The intercarrier output signal is superimposed to the video signal at pin 13 and can be calculated by the following
V
formula: = sound to picture carrier ratio at IF
20
13 interc.
log
--------------------------------------- -
1V p-p()
p-p()
V
iSC
dB 6.9 dB 2 dB with
----------- V
iPC
input (pins 1 and 2 in dB and ±2 dB = tolerance of intercarrier output amplitude V
9. Measurements taken with SAW filter G1962; modulation: VSB, f
10. The 7 dB buffer gain accounts for 1 dB loss in the sound trap. Buffer output signal is typical 2 V (p-p). If no sound
trap is applied a 330 Ω resistor must be connected from output to input (from pin 13 to pin 14).
11. The leakage current of the AGC capacitor has to be < 1 µA to avoid larger tilt.
12. S/N is the ratio of black-to-white amplitude to the black level noise voltage (RMS value, pin 7). B = 5 MHz weighted
in accordance with CCIR-567 at a source impedance of 50 Ω.
13. α
= 20 log (Vo at 4.4 (3.58) MHz / Vo at 0.92 (1.1) MHz) + 3.6 dB; α
0.92/1.1
black/white signal.
α
= 20 log (Vo at 4.4 (3.58) MHz / Vo at 2.76 (3.3) MHz); α
2.76/3.3
carrier.
14. To match the AFC output signal to different tuning systems a current source output is provided (Fig.8).
15. Depending on the ratio ∆C/Co of the LC resonance circuit of VCO (Qo> 50; Co=C
C
≈ 8.5 pF).
int
16. No mute state is also valid for pin not connected.
17. Input level for second IF from an external generator with 50 Ω source impedance, AC coupled with 10 nF capacitor,
f
= 1 kHz, 27 kHz (54% FM deviation) of audio reference. A VIF/SIF input signal is not permitted. Pin 19 has to
mod
be connected to positive supply voltage. S/N and THD measurements are taken at 50 µs (75 µs at standard M)
de-emphasis.
18. To allow higher frequency deviation, the resistor Rx on pin 10 (see Fig.12) has to be increased to a value which does
not exceed the AF output signal of nominally 0.35 V for THD = 0.1% (Rx = 4.7 kΩ provides −6 dB amplification).
19. The leakage current of the 2.2 µF capacitor is < 100 nA.
20. For all S/N measurements the used vision IF modulator has to meet the following specification:
- Incidental phase modulation for black-to-white jump less than 0.5 degree.
= 8.2 pF; C
ext
V
iSC
----------- V
iPC
> 0.5 MHz, loop bandwidth BL = 60 kHz.
video
value at 2.76 (3.3) MHz related to colour
2.76/3.3
≈ 8.5 pF (loop voltage about 2.7 V).
int
dB±+=
.
o FM
value at 0.92 (1.1) MHz related to
0.92/1.1
+ C
int
ext; Cext
= 8.2 pF;
July 1994 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
Table 1 Input frequencies and carrier ratios.
B/G STANDARD M/N STANDARD M STANDARD UNIT
picture carrier f
sound carrier f
PC
SC
picture to sound carrier ratio SC 13 7 7 dB
VP = 5 V (9 V)
10 µF
10 nF
38.9 45.75 58.75 MHz
33.4 41.25 54.25 MHz
22 kΩ
(62 kΩ)
22 kΩ
(62 kΩ)
0.1 µF
1 V (p-p)
video and intercarrier
AFC
tuner AGC
vision
IF
50 Ω
1:1
V
P
20
19
1
V
i VIF1Vi VIF2
2
330 Ω
V
i(vid)
14 13 12
2.2 µF
C
AGC
18
GND
see
(1)
table
VCO2 VCO1
17 16
AFC
15
TDA9800
3456789
13 kΩ
takeover
point
CCSTOP MUTE T
sound
mute
PLL
390 Ω
0.1 µF
V
o CVBS
V
o(vid)
n.c.
560 Ω
11
10
V
o AFCAF
V
i ICTAGC
2.2 µF
MED331
V
o AF
CVBS
2 V (p-p)
Fig.3 Test circuit.
July 1994 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
70
handbook, full pagewidth
60
G
IF
(dB)
50
40
30
20
10
0
−10
0
(2) (3) (4)
(1)
1234
V19 (V)
Fig.4 IF AGC (dashed) and tuner AGC as a function of take over point adjustment.
MED332
5
I
12
(mA)
0
0.2
0.6
1.0
1.4
1.8
2.0
0
V
i IF(rms)
V
i IF(rms)
MED333
(dB)
(mV)
80
handbook, halfpage
S/N
(dB)
60
40
20
0
−60 −40 −20 20
0.06 0.6 6 60060
10
Fig.5 Typical signal-to-noise ratio as a function of
IF input signal.
July 1994 14
handbook, halfpage
−13.2 dB
−24 dB
SC CC PC SC CC PC
SC = sound carrier level ; with respect to TOP sync level.
CC = chrominance carrier level ; with respect to TOP sync level.
PC = picture carrier level ; with respect to TOP sync level.
Sound shelf attenuation: 17 dB.
−3.2 dB
−13.2 dB
−24 dB
BLUE YELLOW
Fig.6 Input conditions for intermodulation
measurements.
−10 dB
MED334
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
handbook, halfpage
2.6 V
2.5 V
1.8 V
1.5 V
Fig.7 Video signal levels on output pin 13.
zero carrier
level
white level
sync level
MED335
Fig.8 Measurement conditions and typical AFC characteristic.
handbook, full pagewidth
V
P
TDA9800
VP = 5 V
Fig.9 Ripple rejection condition.
July 1994 15
100 mV
(f
ripple
= 70 Hz)
MED337
t
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
α
AM
(dB)
−20
−40
−60
−80
−100
370
V
o AF
(mV RMS)
360
0
−1
10
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
1
10 10
2
Fig.10 Typical AM suppression of FM sound demodulator.
(1)
MED338
3
V
(mV)
i IC
10
MED339
60
S/N (W)
(dB)
50
350
340
330
−1
10
11010
Fig.11 Typical AF output signal and signal-to-noise ratio.
July 1994 16
(2)
2
Vi FM (mV)
40
30
20
3
10
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
handbook, full pagewidth
22 kΩ
VP = 5 V (9 V)
(62 kΩ)
330 Ω
sound
trap
15
µH
V
i(vid)
14 13 12
1 V (p-p)
560
Ω
sound
filter
V
o(vid)
video and intercarrier
(2) (2)
TAGC
11
see
table
(1)
16
22 kΩ
(62 kΩ)
0.1 µF
AFCVCO2 VCO1GND
15
10 µF
10 nF
2.2 µF
V
20
C
P
AGC
19
18
17
tuner AGC
12 V (9 V)
(2)
V
i IC
AFC
vision
IF
50 Ω
(1) depends on tuner
SAW
filter
G1962
1
IF input
2
V
i VIF1Vi VIF2
TDA9800
34567 8910
o CVBS
n.c.
22 nF
V
o AFCAF
2.2
k
Ω
C
AF
13 kΩ
takeover
point
CCSTOP MUTE
sound
mute
T
PLL
390 Ω
0.1 µF
V
(3)
R
x
2.2 µF
CVBS
2 V (p-p)
V
o AF
MED340
Fig.12 Application circuit.
July 1994 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
handbook, full pagewidth
antenna input
(dBµV)
120
100
80
60
40
20
(1)
tuner gain
control range
TOP
VHF/UHF
40 dB
RF gain
IF
SAW insertion
loss 20 dB
6 dB IF slip
SAW insertion
loss 20 dB
IF gain range
64 (<70) dB
64 dB
IF AGC
IF amplifier, demodulator
and video
video
1 V (p-p)
−1
10
0.66 × 10
−2
10
−3
10
0.66 × 10
−4
10
0.66 × 10
−5
10
0.66 × 10
IF signals
(RMS value)
(V)
−1
−3
−4
−5
tuner
SAW filter TDA9800
(1) depends on TOP
Fig.13 Front end level diagram.
July 1994 18
MED341
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL
detector
i IC
V
11
+
Ω
670
3.6 V
2.5 mA
10
pF
kΩ
2 kΩ
5
kΩ
1
kΩ
5.5
kΩ
5.5
15
pF
kΩ
ull pagewidth
TAGC
o(vid)
V
i(vid)
V
12
13
14
+
3.6 V
2
mA
2
kΩ
11.5 kΩ
20
kΩ
6.6
+
+
57 kΩ
2.5 kΩ 5 kΩ
TDA9800
TDA9800
AF
C
10
++
190 µA
6.4
VCO
+
1.5 pF
kΩ
+
40 µA
50 µA
o AF
V
9
MED342
2 mA
2.5 mA
8
n.c.
7
o CVBS
V
6
PLL
T
100 Ω
+
+
AFC
VCO1
VCO2
GND
AGC
C
200 µA
+
15
1
16
++
17
18
+
19
kΩ
1
kΩ
+
+
+
1
kΩ
3 V
1 mA
1
i VIF1
V
1.1
2.5 µA
kΩ
3.6 V
5 kΩ
kΩ
1.1
+
2
++
mute
+
+
20
P
V
i VIF2
V
+
3.65 V
+
3.6 V
+
25 µA
5
MUTE
18
kΩ
16 kΩ
4
CCS
20
kΩ
9 kΩ
3
TOP
Fig.14 Internal circuits.
July 1994 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
PACKAGE OUTLINES
DIP20: plastic dual in-line package; 20 leads (300 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
20
pin 1 index
e
b
SOT146-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
11
E
c
(e )
1
M
H
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
mm
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT146-1
1 2
min.
max.
1.73
1.30
0.068
0.051
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
b
b
1
0.53
0.38
0.021
0.015
0.014
0.009
REFERENCES
cD E e M
0.36
0.23
(1) (1)
26.92
26.54
1.060
1.045
SC603
July 1994 20
6.40
6.22
0.25
0.24
10
(1)
M
e
L
1
3.60
8.25
3.05
7.80
0.14
0.32
0.12
0.31
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
H
E
10.0
0.2542.54 7.62
8.3
0.39
0.010.10 0.30
0.33
ISSUE DATE
92-11-17
95-05-24
Z
w
max.
2.04.2 0.51 3.2
0.0780.17 0.020 0.13
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
SO20: plastic small outline package; 20 leads; body width 7.5 mm
D
c
y
Z
20
pin 1 index
1
e
11
A
2
10
w M
b
p
SOT163-1
E
H
E
Q
A
1
L
p
L
detail X
(A )
A
X
v M
A
A
3
θ
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
UNIT
mm
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included.
A
max.
2.65
0.10
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT163-1
A
1
0.30
0.10
0.012
0.004
A2A
2.45
2.25
0.096
0.089
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
075E04 MS-013AC
0.25
0.01
b
3
p
0.49
0.32
0.36
0.23
0.019
0.013
0.014
0.009
(1)E(1) (1)
cD
13.0
7.6
7.4
0.30
0.29
1.27
0.050
12.6
0.51
0.49
REFERENCES
July 1994 21
eHELLpQ
10.65
10.00
0.419
0.394
1.4
0.055
1.1
0.4
0.043
0.016
1.1
1.0
0.043
0.039
PROJECTION
0.25
0.25 0.1
0.01
0.01
EUROPEAN
ywv θ
Z
0.9
0.4
8
0.004
ISSUE DATE
0.035
0.016
95-01-24
97-05-22
0
o
o
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
“IC Package Databook”
our
(order code 9398 652 90011).
DIP
SOLDERING BY DIPPING OR BY WAVE
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact
time of successive solder waves must not exceed
5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
stg max
). If the
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
R
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the
lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not
more than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the
soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in
contact for up to 10 seconds. If the bit temperature is
between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
SO
REFLOW SOLDERING
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all SO
packages.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
AVE SOLDERING
W
Wave soldering techniques can be used for all SO
packages if the following conditions are observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave) soldering
technique should be used.
• The longitudinal axis of the package footprint must be
parallel to the solder flow.
• The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves at
the downstream end.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
R
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonally-
opposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
July 1994 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
VIF-PLL demodulator and FM-PLL detector TDA9800
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
July 1994 23
 Loading...
Loading...