Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8580J
Multi-purpose power amplifier
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Feb 25
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
2000 Apr 18
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
FEATURES
General
• Supply voltage range from 8 to 24 V
• Low distortion
• Few external components, fixed gain
• High output power
• Can be used as a stereo amplifier in Bridge-Tied Load
(BTL) or quad Single-Ended (SE) amplifiers
• Single-ended mode without loudspeaker capacitor
• Mute and standby mode with one- or two-pin operation
• Diagnostic information for Dynamic Distortion Detector
(DDD), high temperature (145 °C) and short-circuit
• No switchon/off plops when switching between standby
and mute or mute and on; an external RC-network is
prescribed to ensure plop-free operation
• Low offset variation at outputs between mute and on
• Fast mute on supply voltage drops.
ORDERING INFORMATION
Protection
• Short-circuitproofto ground, positivesupplyvoltageand
across load; the supply voltage ranges where the
different short circuit conditions are guaranteed are
given in Chapter “Limiting values”
• ESD protected on all pins
• Thermal protection against temperatures exceeding
150 °C.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8580J is a stereo Bridge-Tied Load (BTL) or a
quad Single-Ended (SE) amplifier that operates over a
wide supply voltage range from 8 to 24 V. This makes it
suitable for applications such as television, home-sound
systems and active speakers.
Because of an internal voltage buffer, this device can be
used withouta capacitor connected in series with the load
(SE application). A combined BTL and 2 × SE application
can also be configured (one chip stereo and subwoofer
application).
TYPE
NUMBER
TDA8580J DBS17P plastic DIL-bent-SIL power package; 17 leads (lead length 12 mm) SOT243-1
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
2000 Apr 18 2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
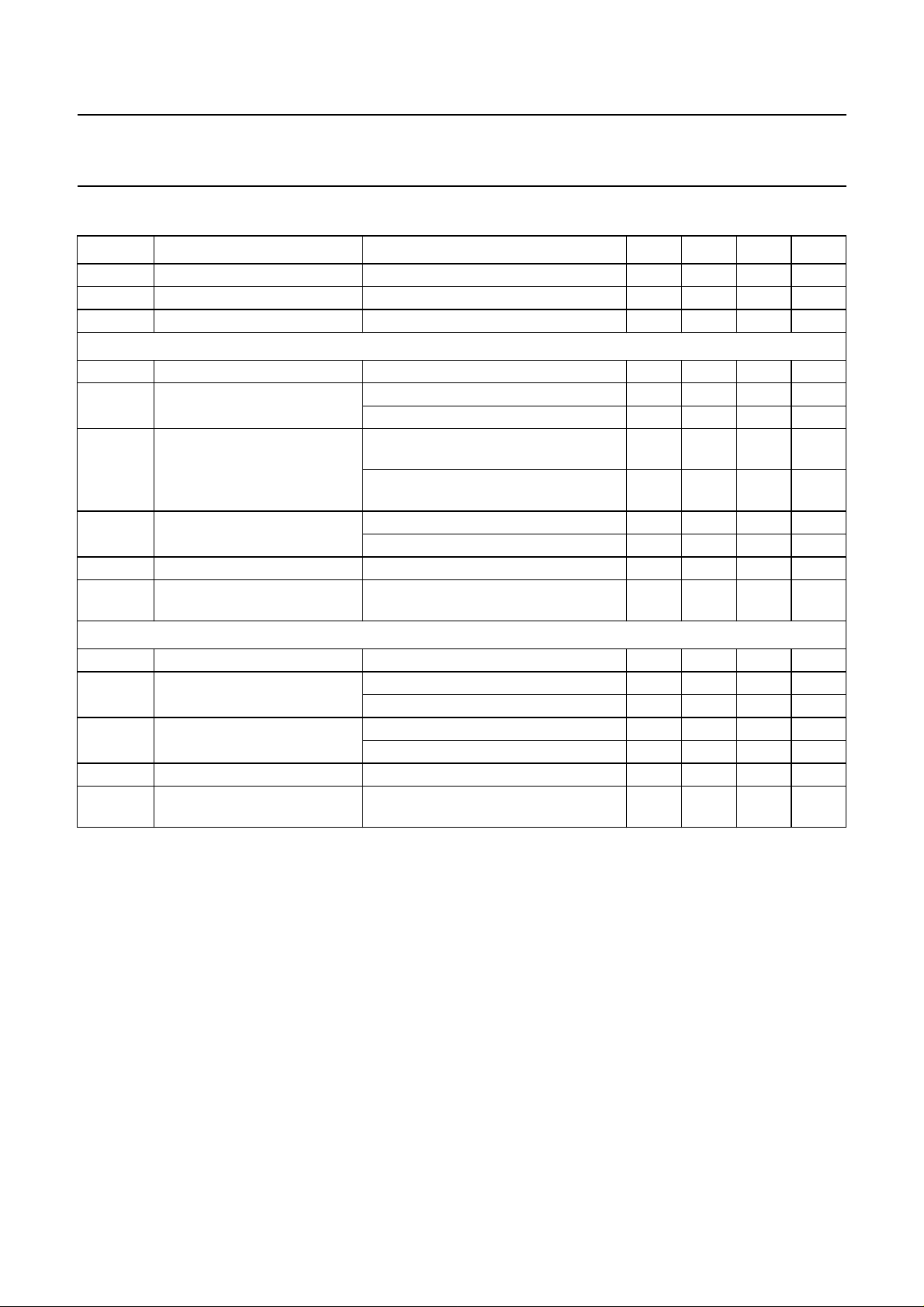
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
q(tot)
I
stb
Bridge-tied load application
G
v
P
o
THD total harmonic distortion f
V
offset(DC)
V
no
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection f
Single-ended application
G
v
P
o
V
offset(DC)
V
no
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection f
operating supply voltage 8.0 14.4 24 V
total quiescent current VP= 14.4 V − 140 170 mA
standby supply current VP= 14.4 V − 150µA
voltage gain 31 32 33 dB
output power THD = 0.5%; VP= 14.4 V; RL=4Ω 14 15 − W
THD = 0.5%; V
= 1 kHz; Po= 1 W; VP= 14.4 V;
i
= 24 V; RL=8Ω 21 23 − W
P
− 0.05 0.1 %
RL=4Ω
f
= 1 kHz; Po= 10 W; VP=24V;
i
− 0.02 0.05 %
RL=8Ω
DC output offset voltage VP= 14.4 V; mute condition; RL=4Ω− 10 20 mV
V
= 14.4 V; on condition − 0 140 mV
P
noise output voltage Rs=1kΩ; VP= 14.4 V − 100 150 µV
= 1 kHz; V
i
ripple(p-p)
= 2 V; on or mute
50 60 − dB
condition; Rs=0Ω
voltage gain 25 26 27 dB
output power THD = 0.5%; VP= 14.4 V; RL=4Ω 3.8 4.0 − W
THD = 0.5%; V
= 24 V; RL=4Ω 10.5 11.5 − W
P
DC output offset voltage VP= 14.4 V; mute condition; RL=4Ω− 10 20 mV
= 14.4 V; on condition − 0 100 mV
V
P
noise output voltage Rs=1kΩ; VP= 14.4 V − 80 120 µV
= 1 kHz; V
i
ripple(p-p)
= 2 V; on or mute
40 45 − dB
condition; Rs=0Ω
2000 Apr 18 3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
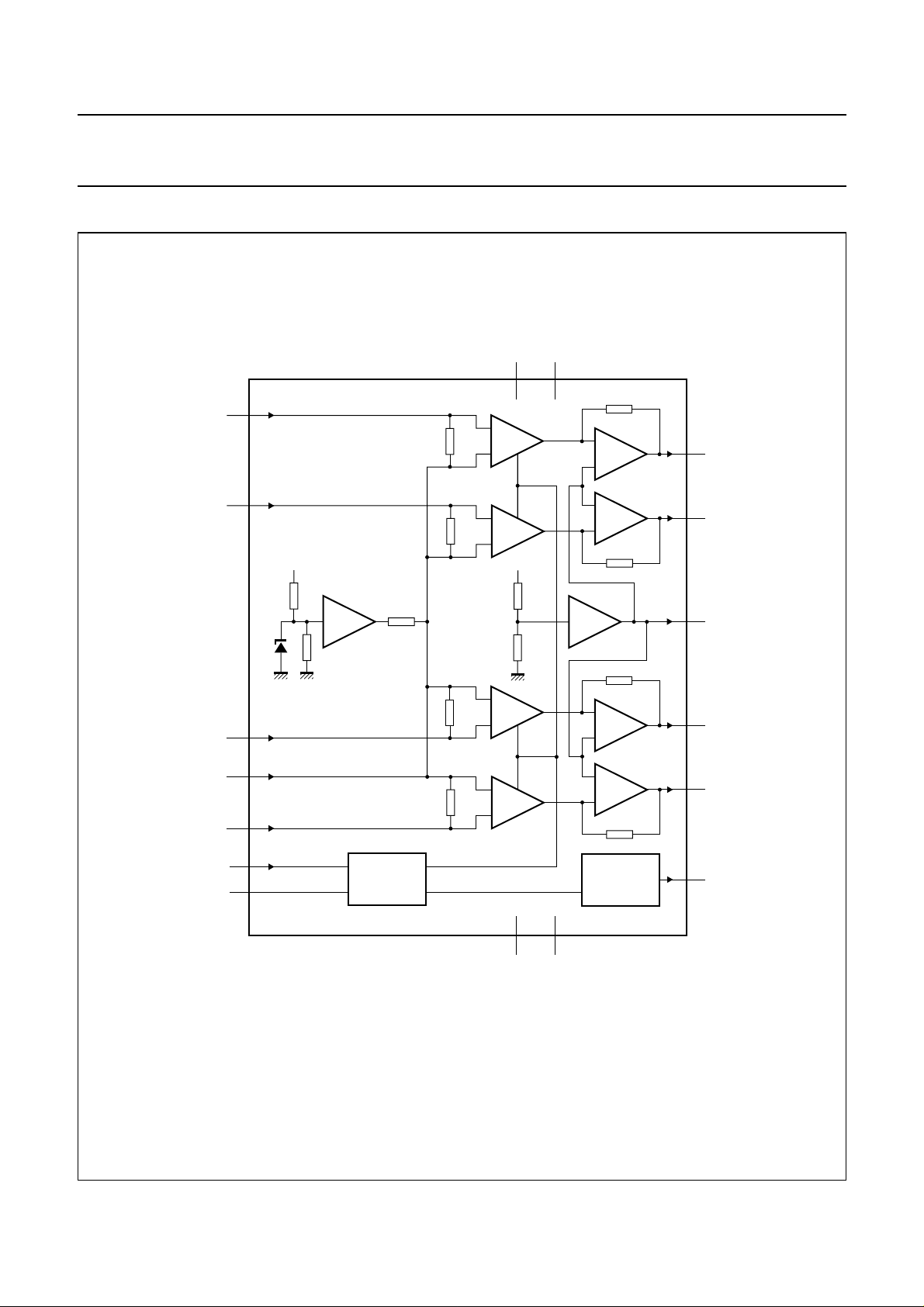
BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
P1VP2
handbook, full pagewidth
IN1
7
60
kΩ
TDA8580J
3
15
−
V/I
+
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
1
OUT1+
IN2
IN3
IN5
IN4
MUTE
STANDBY
8
+
60
V/I
kΩ
−
V
px
30 kΩ
BUFFER
60
10
12
11
13
5
INTERFACE
kΩ
60
kΩ
V
px
45
kΩ
45
kΩ
−
V/I
+
+
V/I
−
216
PGND1 PGND2
+
OA
−
45 kΩ
BUFFER
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
OA
−
45 kΩ
DIAGNOSTIC
4
9
14
17
6
MGE010
OUT2−
BUFFER
OUT3−
OUT4+
DIAG
Fig.1 Block diagram.
2000 Apr 18 4
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
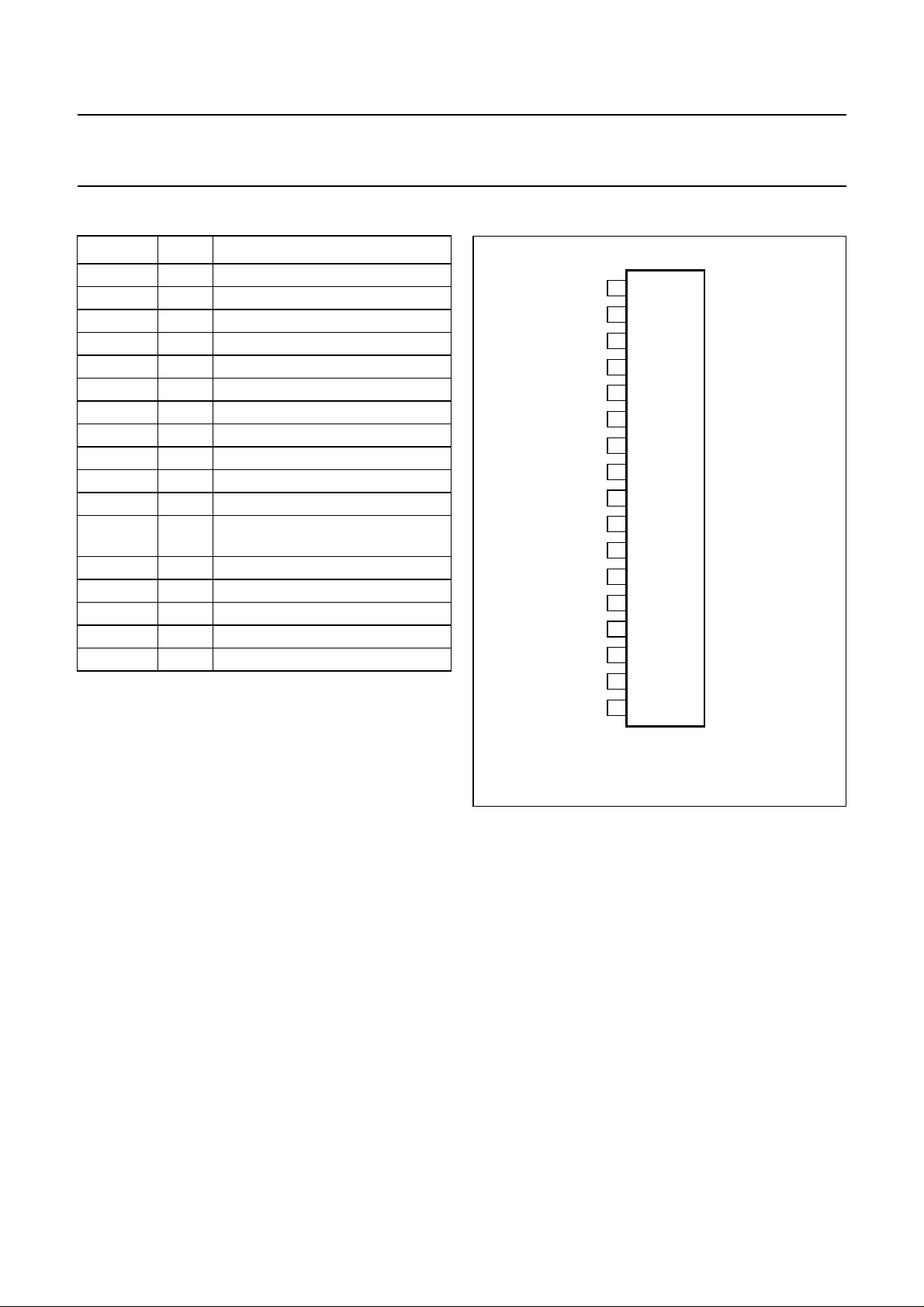
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
OUT1+ 1 non-inverting output 1
PGND1 2 power ground 1
V
P1
3 supply voltage 1
OUT2− 4 inverting output 2
STANDBY 5 standby/mute/on selection input
DIAG 6 diagnostic output
IN1 7 input 1
IN2 8 input 2
BUFFER 9 single-ended buffer output
IN3 10 input 3
IN4 11 input 4
IN5 12 input 5; signal ground capacitor
connection
MUTE 13 mute/on selection input
OUT3− 14 inverting output 3
V
P2
15 supply voltage 2
PGND2 16 power ground 2
OUT4+ 17 non-inverting output 4
handbook, halfpage
STANDBY
OUT1+
PGND1
V
P1
OUT2−
DIAG
IN1
IN2
BUFFER
IN3
IN4
IN5
MUTE
OUT3−
V
P2
PGND2
OUT4+
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
TDA8580J
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
MGE009
2000 Apr 18 5
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
TheTDA8580J is amulti-purposepoweramplifier with four
amplifiers which can be connected in the following
configurationswith high outputpowerandlow distortion (at
minimum quiescent current):
• Dual bridge-tied load amplifiers
• Quad single-ended amplifiers
• Dual single-ended amplifiers and one bridge-tied load
amplifier.
The amplifier can be switched in on, mute and off
(standby)by the MUTEandSTANDBYpins (for interfacing
directly with a microcontroller). One-pin operation is also
possible by applying a voltage greater than 8 V to the
STANDBY pin to switch the amplifier in on mode.
Special attention is given to the dynamic behaviour as
follows:
• Slow offset change between mute and on(controlled by
• Low noise levels, which are independent of the supply
voltage.
Protections are includedto avoidthe IC beingdamaged at:
• Over temperature: Tj> 150 °C
• Short-circuit of the output pin(s) to ground or supply rail;
when short-circuited, the power dissipation is limited
• ESD protection (Human Body Model 3000 V, Machine
Model 300 V)
• Energy handling. A DC voltage of 6 V can be connected
to the output of any amplifier while the supply pins are
short-circuited to ground.
Diagnostics are available for the following conditions
(see Figs 3, 4 and 5):
• Chip temperature above 145 °C
• Distortion over 2% due to clipping
• Short-circuit protection active.
MUTE and STANDBY pins)
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
supply voltage operating − 24 V
no signal condition − 28 V
V
DIAG
I
OSM
I
ORM
V
P(scol)
V
P(scg)
voltage on pin DIAG − 18 V
non-repetitive peak output current − 6A
repetitive peak output current − 4.5 A
supply voltage with short-circuit across load − 28 V
supply voltage with short-circuit from output
− 26 V
to ground
V
P(scs)
supply voltage with short-circuit from output
− 16 V
to supply
V
P(rp)
P
tot
T
j
T
stg
T
amb
reverse polarity − 6V
total power dissipation − 75 W
junction temperature − 150 °C
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
ambient temperature −40 +85 °C
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
R
th(j-a)
th(j-c)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 40 K/W
thermal resistance from junction to case 1.5 K/W
2000 Apr 18 6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
CHARACTERISTICS
VP= 14.4 V; T
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
P
I
q(tot)
I
stb
V
O
V
P(mute)
V
I
Control pins
TANDBY PIN (see Table 1)
S
V
5(stb)
V
hys(5)(stb)
V
5(mute)
V
5(on)
MUTE PIN (see Table 1)
V
13(mute)
V
13(on)
Diagnostic; output buffer (open-collector); see Figs 3, 4 and 5
V
OL
I
LI
CD clip detector V
T
j(diag)
Stereo BTL application; see Figs 6, 7, 10, 11, 14, 15, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26 and 28
THD total harmonic distortion f
P
o
G
v
=25°C; fi= 1 kHz; RL= ∞; measured in test circuit of Fig.28; unless otherwise specified.
amb
operating supply voltage 8.0 14.4 24 V
total quiescent current − 140 170 mA
standby current − 150µA
DC output voltage − 7.0 − V
low supply voltage mute 6.0 7.0 8.0 V
DC input voltage − 4.0 − V
voltageat STANDBY pin forstandby
0 − 0.8 V
condition
hysteresis voltage at STANDBY pin
note 1 − 0.2 − V
for standby condition
voltage at STANDBY pin for mute
V13< 0.8 V 2.0 − 5.3 V
condition
voltage at STANDBY pin for on
VP> 9 V; note 2 8.0 − 18 V
condition
voltage at MUTE pin for mute
V5=5V 0 − 0.8 V
condition
voltage at MUTE pin for on condition V5=5V 2.5 − 5.3 V
LOW-level output voltage I
leakage current V
junction temperature for high
=1mA − 0.2 0.8 V
sink
= 14.4 V −−1µA
DIAG
<0.8V 124%
DIAG
V
< 0.8 V − 145 −°C
DIAG
temperature warning
= 10 kHz; Po= 1 W; RL=4Ω;
i
− 0.2 0.3 %
filter: 22 Hz < f < 30 kHz
= 1 kHz; Po= 1 W; VP= 14.4 V;
f
i
− 0.05 0.1 %
RL=4Ω
f
= 1 kHz; Po= 10 W; VP=24V;
i
− 0.02 0.05 %
RL=8Ω
output power THD = 0.5%; VP= 14.4 V; RL=4Ω 14 15 − W
voltage gain V
THD = 0.5%; V
THD = 10%; V
THD = 10%; V
= 3 V 31 32 33 dB
o(rms)
= 24 V; RL=8Ω 21 23 − W
P
= 14.4 V; RL=4Ω 18 20 − W
P
= 24 V; RL=8Ω 28 30 − W
P
2000 Apr 18 7
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
α
cs
∆G
v
V
offset(DC)
V
no
V
no(mute)
V
o(mute)
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection R
Z
i
CMRR common mode rejection ratio R
Quad SE application; see Figs 8, 9, 12, 13, 16, 17, 20, 25, 27 and 29
THD total harmonic distortion f
P
o
G
v
α
cs
∆G
v
V
offset(DC)
V
no
V
no(mute)
V
o(mute)
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection f
Z
i
CMRR common mode rejection ratio V
Notes
1. Hysteresis between the rise and fall voltage when pin STANDBY is controlled with low ohmic voltage source.
2. At lower VP the voltage at the STANDBY pin for on condition will be adjusted automatically to maintain an
on condition at low battery voltage (down to 8 V) when using one-pin operation.
3. The noise output is measured in a bandwidth of 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
channel separation Po= 2 W; fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω 60 65 − dB
channel unbalance −−1dB
DC output offset voltage on condition − 0 140 mV
mute condition; R
=4Ω−10 20 mV
L
noise output voltage Rs=1kΩ; VP= 14.4 V; note 3 − 100 150 µV
noise output voltage mute note 3 − 020µV
output voltage mute V
=1V − 3 500 µV
i(rms)
=0Ω; fi= 1 kHz;
s
V
ripple(p-p)
= 2 V; on or mute
50 60 − dB
condition
input impedance 23 30 37 kΩ
=0Ω; V
s
= 1 kHz; Po= 1 W; RL=4Ω−0.05 0.1 %
i
= 10 kHz; Po= 1 W; RL=4Ω;
f
i
= 0.5 V; fi= 1 kHz − 60 − dB
i(rms)
− 0.2 0.3 %
filter: 22 Hz < f < 30 kHz
f
= 1 kHz; Po= 1 W; VP=24V,
i
− 0.05 0.1 %
RL=4Ω; filter: 22 Hz<f<30kHz
output power THD = 0.5%; VP= 14.4 V; RL=4Ω 3.8 4.0 − W
voltage gain V
THD = 0.5%; V
THD = 10%; V
THD = 10%; V
= 3 V 25 26 27 dB
o(rms)
= 24 V; RL=4Ω 10.5 11.5 − W
P
= 14.4 V; RL=4Ω 4.9 5.2 − W
P
= 24 V; RL=4Ω 14 15 − W
P
channel separation Po= 2 W; fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω 40 46 − dB
channel unbalance −−1dB
DC output offset voltage VP= 14.4 V; on condition − 0 100 mV
V
= 14.4 V; mute condition;
P
− 10 20 mV
RL=4Ω
noise output voltage Rs=1kΩ; VP= 14.4 V; note 3 − 80 120 µV
noise output voltage mute note 3 − 020µV
output voltage mute V
=1V − 3 500 µV
i(rms)
= 1 kHz; V
i
ripple(p-p)
= 2 V, on or
40 45 − dB
mute condition; Rs=0Ω
input impedance 46 60 74 kΩ
= 0.5 V; fi= 1 kHz; Rs=0Ω− 60 − dB
i(rms)
2000 Apr 18 8
Page 9
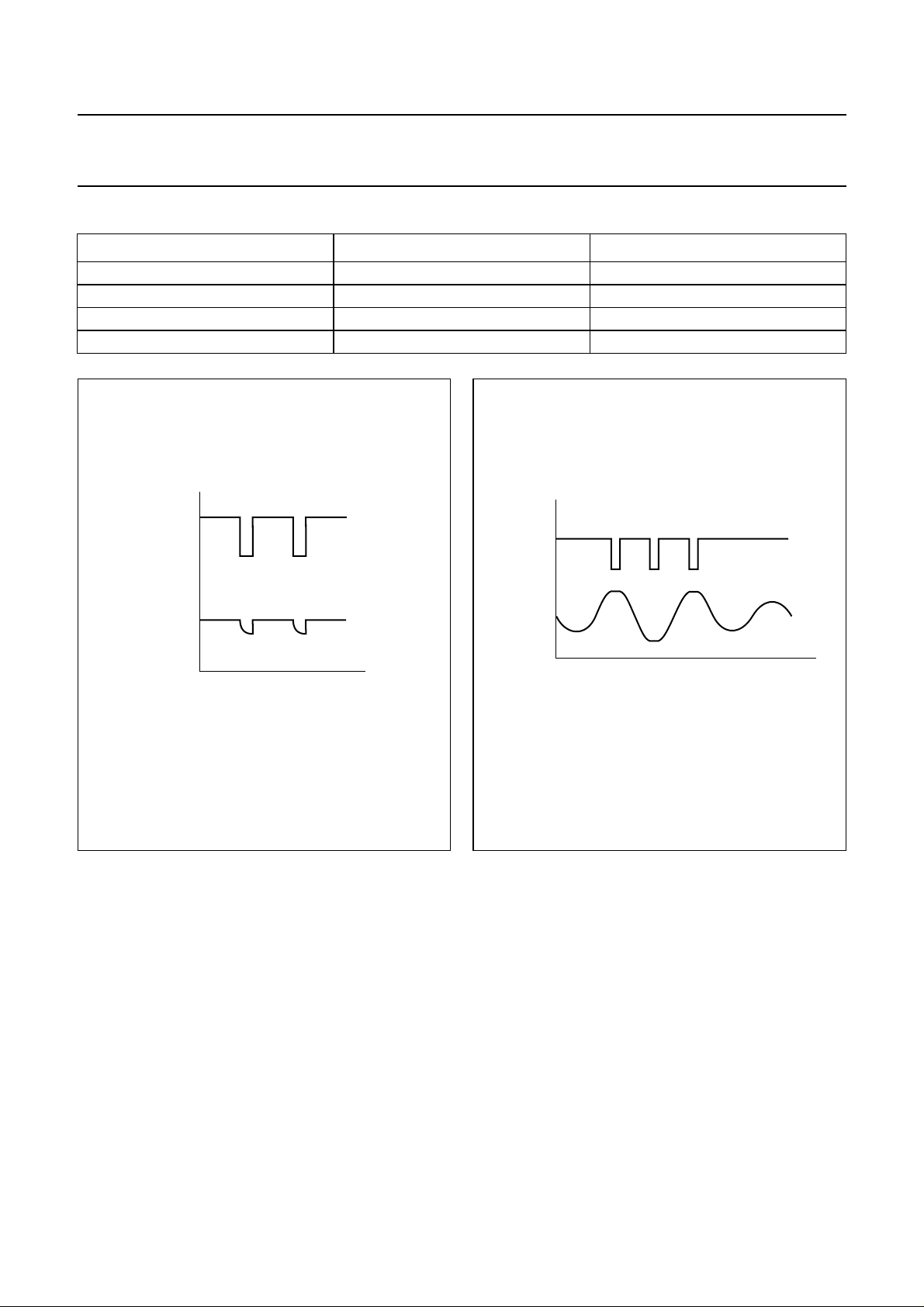
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
Table 1 Selection of standby, mute and on
VOLTAGE AT PIN STANDBY VOLTAGE AT PIN MUTE FUNCTION
< 0.8 V don’t care standby (off)
2 to 5.3 V < 0.8 V mute (DC settled)
2 to 5.3 V 2.5 to 5.3 V on (AC operating)
≥ 8.0 V don’t care on (AC operating)
handbook, halfpage
DIAG
amplifier
output
temperature
overload
MGE020
Fig.3 Diagnostic waveform: temperature overload.
handbook, halfpage
normal
DIAG
amplifier
output
active
DDD
Fig.4 Diagnostic waveform: DDD function.
normal
MGE021
2000 Apr 18 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, halfpage
short-circuit to
GND
V
P
DIAG
amplifier
output
MGE022
Fig.5 Diagnostic waveform: short-circuit to GND
or VP.
handbook, halfpage
1
MGS700
THD
(%)
−1
10
−2
10
10 10
2
(1)
(2)
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V; 2 channel driven.
(1) Po=1W.
(2) Po=10W.
Fig.6 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
frequency; BTL mode.
5
10
handbook, halfpage
1
MGS701
THD
(%)
−1
10
(1)
(2)
−2
10
10 10
2
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
RL=8Ω; VP= 24 V; 2 channel driven.
(1) Po=1W.
(2) Po=10W.
Fig.7 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
frequency; BTL mode.
handbook, halfpage
1
MGS702
THD
(%)
−1
10
−2
5
10
10
10 10
2
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
5
10
Po= 1 W; RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V; 4 channel driven.
Fig.8 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
frequency; SE mode.
2000 Apr 18 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, halfpage
1
MGS703
THD
(%)
−1
10
(1)
(2)
−2
10
10 10
2
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
RL=4Ω; VP= 24 V; 4 channel driven.
(1) Po=5W.
(2) Po=1W.
Fig.9 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
frequency; SE mode.
2
10
handbook, halfpage
MGS704
THD
(%)
(2)
10
(1)
(3)
1
(1)
−1
10
−2
5
10
10
−1
10
(2)
(3)
11010
Po (W)
2
RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V; 2 channel driven.
(1) fi= 10 kHz.
(2) fi= 1 kHz.
(3) fi= 100 Hz.
Fig.10 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
output power; BTL mode.
2
10
handbook, halfpage
MGS705
THD
(%)
10
(2)
(3)
(1)
1
−1
10
−2
10
−1
10
(1)
(2)
(3)
11010
Po (W)
RL=8Ω; VP= 24 V; 2 channel driven.
(1) fi= 10 kHz.
(2) fi= 1 kHz.
(3) fi= 100 Hz.
Fig.11 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
output power; BTL mode.
2
2
10
handbook, halfpage
MGS706
THD
(%)
10
(2)
(1)
(3)
1
(1)
−1
10
−2
10
−1
10
(2)
(3)
1
Po (W)
RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V; 4 channel driven
(1) fi= 10 kHz.
(2) fi= 1 kHz.
(3) fi= 100 Hz.
Fig.12 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
output power; SE mode.
10
2000 Apr 18 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
2
10
handbook, halfpage
THD
(%)
10
1
(1)
−1
10
−2
10
−1
10
RL=4Ω; VP= 24 V; 4 channel driven.
(1) fi= 10 kHz.
(2) fi= 1 kHz.
(3) fi= 100 Hz.
(2)
(3)
11010
(3)
MGS707
(2)
(1)
P
(W)
o
Fig.13 Total harmonic distortion as a function of
output power; SE mode.
2
30
handbook, halfpage
P
d
(W)
20
10
0
0 102030
fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V; 2 channel driven.
MGS708
Po (W)
Fig.14 Power dissipation as a function of output
power; BTL mode.
30
MGS709
Po (W)
40
handbook, halfpage
P
d
(W)
30
20
10
0
01020 40
fi= 1 kHz; RL=8Ω; VP= 24 V; 2 channel driven.
Fig.15 Power dissipation as a function of output
power; BTL mode.
16
handbook, halfpage
P
d
(W)
12
8
4
0
0246
fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V; 4 channel driven.
MGS710
Po (W)
Fig.16 Power dissipation as a function of output
power; SE mode.
2000 Apr 18 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
12
MGS711
Po (W)
40
handbook, halfpage
P
d
(W)
30
20
10
0
048 16
fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω; VP= 24 V; 4 channel driven.
Fig.17 Power dissipation as a function of output
power; SE mode.
40
handbook, halfpage
P
o
(W)
30
20
(1)
10
0
8 121620
fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω; 2 channel driven.
(1) THD = 10%.
(2) THD = 0.5%.
(2)
VP (V)
Fig.18 Output power as a function of supply
voltage; BTL mode.
MGS712
40
handbook, halfpage
P
o
(W)
30
20
(1)
10
(2)
0
81216 24
fi= 1 kHz; RL=8Ω; 2 channel driven.
(1) THD = 10%.
(2) THD = 0.5%
20
Fig.19 Output power as a function of supply
voltage; BTL mode.
MGS713
VP (V)
16
handbook, halfpage
P
o
(W)
12
8
(1)
4
0
81216 24
fi= 1 kHz; RL=4Ω; 2 channel driven.
(1) THD = 0.5%.
(2) THD = 10%
(2)
20
Fig.20 Output power as a function of supply
voltage; SE mode.
MGS714
VP (V)
2000 Apr 18 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
34
handbook, halfpage
G
v
(dB)
33
32
31
30
10 10
2
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
Ci= 470 nF.
Fig.21 Gain as a function of input frequency;
BTL mode.
MGS717
MGS715
∆P
0.8
o
(W)
0.4
0
−0.4
5
10
−0.8
10 10
2
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
5
10
THD = 0.5%; RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V.
Fig.22 Power bandwidth as a function of
frequency; BTL mode.
0.8
handbook, halfpage
∆P
o
(W)
0.4
0
−0.4
−0.8
10 10
THD = 0.5%; R
2
=8Ω; VP=24V.
L
3
10
Fig.23 Power bandwidth as a function of
frequency; BTL mode.
MGS716
−50
handbook, halfpage
α
cs
MGS718
(dB)
−54
−58
−62
(1)
−66
4
10
fi (Hz)
5
10
−70
10 10
2
(2)
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
5
10
Po= 2 W; RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V.
(1) Channels 3 and 4 to channels 1 and 2.
(2) Channels 1 and 2 to channels 3 and 4.
Fig.24 Channel separation as a function of
frequency; BTL mode.
2000 Apr 18 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
−20
handbook, halfpage
α
cs
(dB)
−30
−40
(1)
(2)
(3)
−50
−60
10 10
2
3
10
10
Po= 2 W; RS=0Ω; RL=4Ω; VP= 14.4 V.
(1) Channel 1 to channel 2.
(2) Channel 1 to channel 3.
(3) Channel 1 to channel 4.
Fig.25 Channel separation as a function of
frequency; SE mode.
4
MGS719
fi (Hz)
−20
handbook, halfpage
MGS720
SVRR
(dB)
−40
(1)
−60
5
10
−80
10 10
Rs=0Ω;V
ripple(p-p)
2
=2V.
(2)
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
5
10
(1) Vp= 14.4 V.
(2) Vp=24V.
Fig.26 SVRR as a function of frequency;
BTL mode.
−20
handbook, halfpage
MGS721
SVRR
(dB)
−30
−40
(1)
(2)
−50
−60
10 10
Rs=0Ω;V
ripple(p-p)
2
=2V.
3
10
4
10
fi (Hz)
10
(1) Vp= 14.4 V.
(2) Vp=24V.
Fig.27 SVRR as a function of frequency; SE mode.
5
2000 Apr 18 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
APPLICATION INFORMATION
The application circuit depends on the supply voltage
used. For supply voltages below 18 V the application
circuits are shown in Figs 28, 29 and 30.
The typical application circuits for the different supply
voltage ranges are shown in Figs 31, 32 and 33.
Additional information for the applications shown in
Figs 28, 29 and 30
The RC-network connected to pin 5 determines the
amplifier switch on/off behaviour as follows;
• Switched from STANDBY to MUTE when V
switching
(typically 9 V) is enabled and the switch SW1 is closed.
During MUTE there is no output noise and no offset.
• Switched from MUTE to ON when the switch SW1 is
opened. During switching ON the offset and noise are
gradually built up. The time constant is fixed by R1 × C1.
Theinputs can betiedtogether andconnectedto one input
capacitor. Becausethe input resistanceis decreased bya
factor of 2, the low frequency roll-off is shifted to a higher
frequency when Ci is kept the same value.
The low frequency cut-off is determined by;
12π( RiCi)××⁄
=
f
3dB–
==
---------------------------------------------------------------------2π60 10
1
3
× 220 109–×××
12 Hz.
The Boucherot network connected to the buffer (pin 9) is
necessary to guarantee a low output resistance at high
frequencies when the buffer is loaded (only in SE
applications).
Additional information for the applications shown in
Figs 31, 32 and 33
Short circuit behaviour at high supply voltages (V
> 18 V):
p
• When Vp> 18 V it is advisable to use the applications
given in Figs 32 and 33. In these applications the
diagnostics output is tied to pin 5 (one pin operation) or
pin 13 (two pin operation). During a fault condition the
amplifier is soft-muted and the amplitude of the output
signal is reduced at:
– over temperature (still large dynamic range)
– short to ground and over load (output current
reduced)
• The 4.7 µF capacitor and the 10 kΩ resistor connected
to pin 5 or to pin 13 are used to:
– provide a stable loop
– control the switch on/off behaviour
– minimize the effect due to clip detection.
Use of common buffer
In SE applications the buffer output is used in place of a
SE capacitor. To minimize the crosstalk (high channel
separation) and distortion it is advised to connect the
speaker wires as closelyas possibleto pin9 without using
a shared wire. Internally in the IC all the efforts have been
taken to minimize the crosstalk by locating the feedback
loops as close as possible to pin 9.
If a common wire is shared by all the speakers, the series
resistance of this shared wire will introduce added signal
voltages resulting from the currents flowing through this
wire when a connected amplifier is driven by a signal.
Optimize the THD performance
The TDA8580J application can be optimized to gain the
lowest THD possible by applying the following guidelines:
• SE application: minimize the shared wires to pin 9 (see
section “Use of common buffer”).
• Because the inputs are quasi differential, ground loops
can be avoided by connecting the negative terminal of
the 100 µF signal ground capacitor (connected to
pin 12) to the ground pin of the signal processor.
Note: do not leave the inputs in the open condition to
prevent HF oscillation.
• Increase the value of electrolytic supply capacitor
(typical value 1000 µF) to the maximum possible to
minimize cross talk and distortion at low signal
frequencies, due to the PSRR (power supply rejection
ratio). Forsuppressing high frequency transients on the
supply line a capacitor (typical value 100 nF) with a low
ESR is required to be connected in parallel with the
electrolytic capacitor. The capacitor combination must
be placed as close as possible to the IC (using short
interconnection tracks).
Headroom
A typical CD requires at least 12 dB dynamic headroom
(a factor of 15.85), compared with the average power
output, for passing the loudest parts without distortion.
2000 Apr 18 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
For BTL application at Vp= 24 V, RL=8Ω and Po at
THD = 0.5% (see Fig.15), the Average Listening
Level (ALL) for music power without distortion yields:
P
oALL()
Table 2 P
23
-------------- -
15.85
as a function ofheadroom (music signals) for
d
=2×23 W (THD = 0.5%).
P
o
HEADROOM P
1.45 W.==
d
0dB 32W
12 dB 16 W
So for the average music listening level a total power
dissipation of 16 W can be used for calculating the
optimum heat sink thermal resistance.
Heatsink calculation
The measured thermalresistance ofthis package R
th(j-c)
a maximum of 1.5 K/W. For a maximum ambient
temperature of 60oC the required heatsink thermal
resistance can be calculated as shown in the following
example.
EXAMPLE
Measured or given values:
=24V
V
p
RL=8Ω (2 × BTL)
Measured worst case Pd (sine wave) = 32 W
T
= 150oC
j(max)
T
amb(max)
R
R
th hs()
150 60–
----------------------
th(j-c)
=60oC
= 1.5 K/W
T
--------------------------------------------------
32
–
j max()
1.5 1.3 K/W=–=
T
amb max()
P
d
R
–=
th j c–()
Table 3 Heatsink thermal resistance as a function of
headroom for P
is
HEAD ROOM P
=2×23 W (THD = 0.5%).
o
d
0 dB 32 W 1.3 K/W
12 dB 16 W 4.12 K/W
R
th(hs)
2000 Apr 18 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, full pagewidth
220 nF
V
inL
220 nF
V
inR
V
switching
(9 V typical)
R1
(1)
R2
SW1
100 µF
10 V
MUTE
STANDBY
4.7 µF
IN1
IN2
IN5
IN3
IN4
V
1000 µF
16/40 V
V
P1VP2
3
15
7
−
60
V/I
kΩ
60
kΩ
60
kΩ
+
+
V/I
−
V
px
45
kΩ
45
kΩ
−
V/I
+
TDA8580J
8
V
px
30 kΩ
BUFFER
12
10
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
OA
−
45 kΩ
BUFFER
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
+
60
V/I
kΩ
11
13
5
INTERFACE
−
216
PGND1 PGND2
OA
−
45 kΩ
DIAGNOSTIC
100 nF
1
4
9
14
17
6
MGU075
OUT1+
OUT2−
BUFFER
OUT3−
OUT4+
DIAG
P
+
4 or 8 Ω
−
+
4 or 8 Ω
−
+5 V
10
kΩ
(1) R1 and R2 values depend on V
applied; the value of R1 and R2 connected in parallel should be minimum 10 kΩ.
switching
Fig.28 Stereo bridge-tied load application; VP≤ 18 V.
2000 Apr 18 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, full pagewidth
220 nF
V
inR
FRONT
V
V
REAR
V
(9 V typical)
SW1
inL
inR
inL
V
switching
(1)
220 nF
100 µF
220 nF
220 nF
R1
R2
10 V
STANDBY
IN1
IN2
IN5
IN3
IN4
MUTE
4.7 µF
V
1000 µF
16/40 V
VP1V
P2
3
15
7
−
60
V/I
kΩ
60
kΩ
60
kΩ
+
+
V/I
−
V
px
45
kΩ
45
kΩ
−
V/I
+
TDA8580J
8
V
px
30 kΩ
BUFFER
12
10
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
OA
−
45 kΩ
BUFFER
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
+
60
V/I
kΩ
11
13
5
INTERFACE
−
216
PGND1 PGND2
OA
−
45 kΩ
DIAGNOSTIC
100 nF
1
9
14
17
6
MGU077
4
OUT1+
OUT2−
BUFFER
OUT3−
OUT4+
DIAG
P
+
4 or 8 Ω
−
−
4 or 8 Ω
+
2 Ω
220 nF
+
4 or 8 Ω
−
−
4 or 8 Ω
+
+5 V
10
kΩ
(1) R1 and R2 values depend on V
applied; the value of R1 and R2 connected in parallel should be minimum 10 kΩ.
switching
Fig.29 Quad single-ended application; VP≤ 18 V.
2000 Apr 18 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, full pagewidth
220 nF
V
inR
100 µF
10 V
220 nF
V
inR
220 nF
V
inL
STANDBY
V
switching
(9 V typical)
R1
(1)
R2
SW1
IN1
IN2
IN5
IN3
IN4
MUTE
4.7 µF
V
1000 µF
16/40 V
V
P1VP2
3
15
7
−
60
V/I
kΩ
60
kΩ
60
kΩ
+
+
V/I
−
V
px
45
kΩ
45
kΩ
−
V/I
+
TDA8580J
8
V
px
30 kΩ
BUFFER
12
10
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
OA
−
45 kΩ
BUFFER
45 kΩ
−
OA
+
+
+
60
V/I
kΩ
11
13
5
INTERFACE
−
216
PGND1 PGND2
OA
−
45 kΩ
DIAGNOSTIC
100 nF
14
17
MGU076
1
4
9
6
OUT1+
OUT2−
BUFFER
OUT3−
OUT4+
DIAG
P
+
4 or 8 Ω
−
2 Ω
220 nF
+
4 or 8 Ω
−
−
4 or 8 Ω
+
+5 V
10
kΩ
(1) R1 and R2 values depend on V
applied; the value of R1 and R2 connected in parallel should be minimum 10 kΩ.
switching
Fig.30 Dual single-ended and one bridge-tied load application; VP≤ 18 V.
2000 Apr 18 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, full pagewidth
V
P
100 nF
1000 µF
IN1
IN2
inputs
V
switching
(9 V typical)
R1
(3)
45 kΩ
IN3
IN4
IN5
100 µF
STANDBY
R2
(3)
15 kΩ
V
P1
315
7
8
10
11
TDA8580J
12
5
216
V
P2
OUT1+
1
OUT2−
4
OUT3−
14
OUT4+
17
BUFFER
9
DIAG
6
PGND2PGND1
4.7 µF
SW1
(1) Load conditions: quad SE (4 x 4 Ω), or dual BTL (2 x 8 Ω), or dual SE (2 x 4 Ω) and one BTL (1 x 8 Ω).
(2) RC combination not required in BTL mode.
(3) R1 and R2 values depend on V
applied; the value of R1 and R2 connected in parallel should be minimum 10 kΩ.
switching
Fig.31 Application 1; supply voltage range 8 V < VP≤ 18 V; 1-pin and 2-pin operation.
10 kΩ
(1)
2 Ω
+5 V
(2)
MGS699
220 nF
(2)
handbook, full pagewidth
V
P
V
switching
(9 V typical)
(3)
(3)
100 nF
R1
45 kΩ
R2
15 kΩ
1000 µF
inputs
100 µF
4.7 µF
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
IN5
MUTE
STANDBY
3.6 V
V
P1
3
7
8
10
11
TDA8580J
12
13
5
216
V
P2
15
OUT1+
1
OUT2−
4
OUT3−
14
OUT4+
17
BUFFER
9
DIAG
6
PGND2PGND1
SW1
MGS697
(1) Load conditions: quad SE (4 x 4 Ω), or dual BTL (2 x 8 Ω), or dual SE (2 x 4 Ω) and one BTL (1 x 8 Ω).
(2) RC combination not required in BTL mode.
(3) R1 and R2 valuesdepend on V
applied; the value of R1 and R2 connectedin parallel shouldbe minimum 10 kΩ.
switching
Fig.32 Application 2; supply voltage range 18 V < VP≤ 24 V; 1-pin operation.
(1)
2 Ω
(2)
(2)
220 nF
2000 Apr 18 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
handbook, full pagewidth
(1) Load conditions: quad SE (4 x 4 Ω), or dual BTL (2 x 8 Ω), or dual SE (2 x 4 Ω) and one BTL (1 x 8 Ω)
(2) RC combination not required in BTL mode.
V
P
100 nF
10 kΩ
MSB
1000 µF
inputs
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
IN5
100 µF
STANDBY
4.7 µF
V
P1
315
7
8
10
11
TDA8580J
12
5
216
V
P2
OUT1+
1
OUT2−
4
OUT3−
14
OUT4+
17
BUFFER
9
MUTE
13
DIAG
6
PGND2PGND1
Fig.33 Application 3; supply voltage range 18 V < VP≤ 24 V; 2-pin operation.
4.7 µF
(1)
(2)
2 Ω
(2)
220 nF
10 kΩ
MUTE
MGS698
INTERNAL PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN NAME EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
7, 8, 10, 11
Inputs
and 12
1, 4, 9, 14
Outputs
and 17
7, 8, 10 and 11
V
int
0.5 V
V
int
12
MGS723
V
P
1, 4, 9, 14, and 17
P
MGL849
2000 Apr 18 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
PIN NAME EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
5 STANDBY
5
V
P
MGL848
13 MUTE
6 DIAG
V
int
13
4 V
MGS724
6
MGS722
2000 Apr 18 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
PACKAGE OUTLINE
DBS17P: plastic DIL-bent-SIL power package; 17 leads (lead length 12 mm)
SOT243-1
non-concave
D
d
j
x
E
h
view B: mounting base side
A
B
L
3
L
Q
D
h
2
E
A
117
e
Z
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
UNIT A e
mm
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT243-1
A2bpcD
17.0
4.6
4.4
0.75
0.60
15.5
1
e
(1)
deD
0.48
24.0
23.6
20.0
19.6
0.38
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
w M
b
p
(1)
E
h
12.2
10 2.54
11.8
REFERENCES
0 5 10 mm
scale
1
1.27
2000 Apr 18 24
e
5.08
c
2.4
1.6
PROJECTION
e
2
4.3
EUROPEAN
m
E
2
h
6
LL3m
3.4
12.4
3.1
11.0
2.1
1.8
v M
(1)
v
Qj
0.8
0.4w0.03
ISSUE DATE
97-12-16
99-12-17
Z
x
2.00
1.45
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
SOLDERING
Introduction to soldering through-hole mount
packages
This text gives a brief insight to wave, dip and manual
soldering.A more in-depthaccount of solderingICs can be
found in our
Packages”
Wave soldering is the preferred method for mounting of
through-hole mount IC packages on a printed-circuit
board.
Soldering by dipping or by solder wave
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joints for more than 5 seconds.
Suitability of through-hole mount IC packages for dipping and wave soldering methods
DBS, DIP, HDIP, SDIP, SIL suitable suitable
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
PACKAGE
Thetotal contact timeofsuccessive solder wavesmustnot
exceed 5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may benecessary immediately aftersoldering to keepthe
temperature within the permissible limit.
Manual soldering
Apply the soldering iron (24 V or less) to the lead(s) of the
package, either below the seating plane or not more than
2 mm above it. If the temperature of the soldering iron bit
is less than 300 °C it may remain in contact for up to
10 seconds. If the bit temperature is between
300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
SOLDERING METHOD
DIPPING WAVE
(1)
stg(max)
). If the
Note
1. For SDIP packages, the longitudinal axis must be parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board.
2000 Apr 18 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
DATA SHEET STATUS
DATA SHEET STATUS
Objective specification Development This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for
Preliminary specification Qualification This data sheet contains preliminary data, andsupplementary data will be
Product specification Production This data sheet contains final specifications. Philips Semiconductors
Note
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting valuesgiven are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
atthese or atany other conditionsabovethose giveninthe
Characteristics sectionsof the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentation or warrantythat suchapplicationswill be
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
PRODUCT
STATUS
DEFINITIONS
product development. Specification may change in any manner without
notice.
published at a later date. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to
make changes at any time without notice in order to improve design and
supply the best possible product.
reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice in order to
improve design and supply the best possible product.
DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expectedto resultin personalinjury. Philips
Semiconductorscustomers using orselling theseproducts
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
theuse of anyofthese products, conveysnolicence or title
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products,and makesnorepresentations or warrantiesthat
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
(1)
2000 Apr 18 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multi-purpose power amplifier TDA8580J
NOTES
2000 Apr 18 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 3 Figtree Drive, HOMEBUSH, NSW 2140,
Tel. +61 2 9704 8141, Fax. +61 2 9704 8139
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101 1248, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 20 0733, Fax. +375 172 20 0773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 68 9211, Fax. +359 2 68 9102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Sydhavnsgade 23, 1780 COPENHAGEN V,
Tel. +45 33 29 3333, Fax. +45 33 29 3905
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615 800, Fax. +358 9 6158 0920
France: 51 Rue Carnot, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 4099 6161, Fax. +33 1 4099 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 2353 60, Fax. +49 40 2353 6300
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: PT Philips Development Corporation, Semiconductors Division,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext. 2501, Fax. +62 21 794 0080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Via Casati, 23 - 20052 MONZA(MI),
Tel. +39 039 203 6838, Fax +39 039 203 6800
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku,
TOKYO 108-8507, Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5057
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381, Fax +9-5 800 943 0087
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Al.Jerozolimskie 195 B, 02-222 WARSAW,
Tel. +48 22 5710 000, Fax. +48 22 5710 001
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 58088 Newville 2114,
Tel. +27 11 471 5401, Fax. +27 11 471 5398
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 93 301 6312, Fax. +34 93 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 8 5985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2886, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Yukari Dudullu, Org. San. Blg., 2.Cad. Nr. 28 81260 Umraniye,
ISTANBUL, Tel. +90 216 522 1500, Fax. +90 216 522 1813
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 208 730 5000, Fax. +44 208 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 3341 299, Fax.+381 11 3342 553
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing & Sales Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218,
5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. SCA
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
2000
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
69
Printed in The Netherlands 753503/25/03/pp28 Date of release: 2000 Apr 18 Document order number: 9397 750 05478
 Loading...
Loading...