Page 1
IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
Bipolar IC
Features
● Push-pull outputs (open collector)
● Double pulse suppression
● Dynamic current limitation
● Overvoltage protection
● IC undervoltage protection
● Reference voltage source
● Reference overload protection
● Soft start
● Feed-forward control
● Operational amplifier (TDA 4716 C)
TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
P-DIP-14-1
P-DIP-16-1
Type Ordering Code Package
■ TDA 4714 C Q67000-A8312 P-DIP-14-1
■ TDA 4716 C Q67000-A8313 P-DIP-16-1
■ Not for new design
These versatile SMPS ICs comprise digital and analog functions which are required to
design high-quality flyback, single-ended, and push-pull converters in normal, halfbridge and full-bridge configurations. The components can also be used in single-ended
voltage multipliers and speed-controlled motors. Malfunctions in electrical operation are
recognized by the integrated op amps which activate protective functions.
Semiconductor Group 1 09.94
Page 2
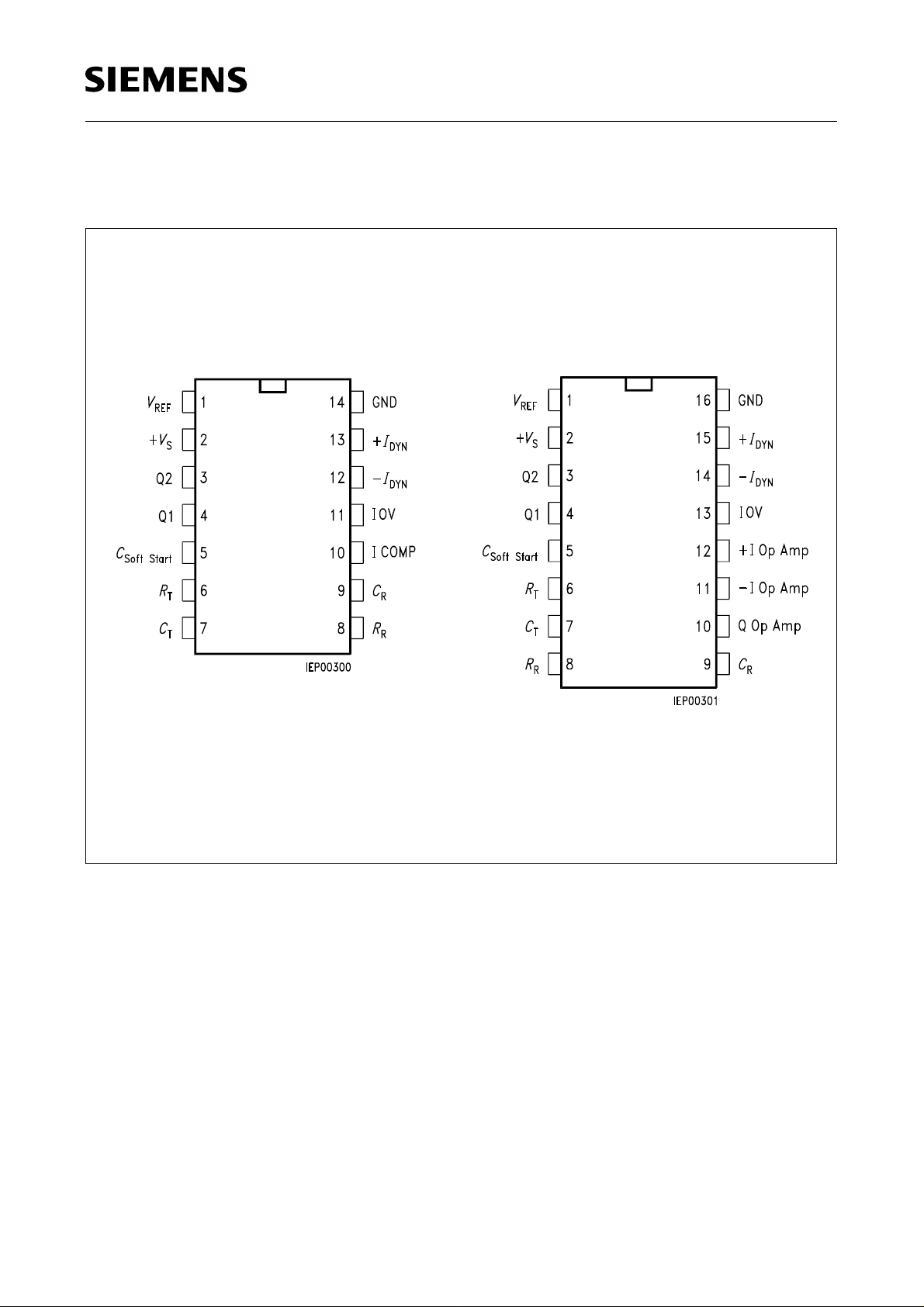
Pin Configurations
(top view)
TDA 4714 C TDA 4716 C
TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Semiconductor Group 2
Page 3
TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Pin Definitions and Functions
(TDA 4714 C)
Pin Symbol Function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
V
REF
+ V
Q2
Q1
C
soft start
R
T
C
T
R
R
C
R
Reference voltage
S
Supply voltage
Output Q2
Output Q1
Soft start
VCO R
VCO C
T
T
Ramp generator R
Ramp generator C
10 I COMP Input comparator
11 I OV Input overvoltage
1213–
I
DYN
Dynamic current
limitation (–)
+ I
DYN
Dynamic current
limitation (+)
Pin Definitions and Functions
(TDA 4716 C)
Pin Symbol Function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
R
R
8
9
10
V
REF
V
S
Q2
Q1
C
soft start
R
T
C
T
R
R
C
R
Q op amp
Reference voltage V
Supply voltage V
S
Output Q2
Output Q1
Soft start
VCO R
VCO C
Ramp generator R
Ramp generator C
T
T
R
R
Operational amplifier
REF
output
11
– I op amp
Operational amplifier
input (–)
12
+ I op amp
Operational amplifier
input (+)
13 I OV Input overvoltage
14 GND Ground
Semiconductor Group 3
1415–
I
DYN
Dynamic current
limitation (–)
+ I
DYN
Dynamic current
limitation (+)
16 GND Ground
Page 4

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Circuit Description
The following is a description of the individual functional units and their interaction.
Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
The VCO generates a sawtooth voltage. The duration of the falling edge is determined
C
by the value of
approximately the frequency, is determined by the value of
VCO provides a trigger signal for the ramp generator, as well as an L signal for a number
of IC parts to be controlled.
Ramp Generator
The ramp generator is triggered by the VCO and oscillates at the same frequency. The
duration of the falling edge of the ramp generator waveform is to be shorter than the fall
time of the VCO. To control the pulse width at the output, the voltage of the rising edge
of the ramp generator signal is compared with a DC voltage at comparator K2. The slope
of the rising edge of the ramp generator signal is controlled by the current through
This offers the possibility of an additional, superimposed control of the output duty cycle.
This additional control capability, called “feed-forward control”, is utilized to compensate
for known interference such as ripple on the input voltage.
. The duration of the rising edge of the waveform and, therefore,
T
R
. During the fall time, the
T
R
R
.
Push-Pull Flipflop
The push-pull flipflop is switched by the falling edge of the VCO. This ensures that only
one output of the two push-pull outputs is enabled at a time.
Comparator K2
The two plus inputs of the comparator are switched such that the lower plus level is
always compared with the level of the minus input. As soon as the voltage of the rising
sawtooth edge exceeds the lower of the two plus levels, both outputs are disabled via
the pulse turn-OFF flipflop. The period during which the respective, active output is low
can be infinitely varied. As the frequency remains constant, this process corresponds to
a change in duty cycle.
Operational Amplifier K1 (TDA 4716 C)
The op amp K1 is a high-quality amplifier. Fluctuations in the output voltage of the power
supply are amplified by K1 and applied to the free positive input of comparator K2.
Variations in output voltage are, in this way, converted to a corresponding change in
output duty cycle. K1 has a common-mode input voltage range between 0 V and + 5 V.
Semiconductor Group 4
Page 5

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Pulse Turn-OFF Flipflop
The pulse turn-OFF flipflop enables the outputs at the start of each half cycle. If an error
signal from comparator K7 or a turn-off signal from K2 is present, the outputs will
immediately be switched off.
Comparator K3
Comparator K3 limits the voltage of capacitance
C
(and also at K2!) to a maximum
soft start
of + 5 V. The voltage at the ramp generator output may, however, rise to 5.5 V. With a
corresponding slope of the rising ramp generator edge, the duty cycle can be limited to
a desired maximum value.
Comparator K4
The comparator has its switching threshold at 1.5 V and sets the error flipflop with its
output if the voltage at capacitance
C
soft start
is below 1.5 V. However, the error flipflop
accepts the set signal only if no reset pulse (error) is applied. In this way the outputs
cannot be turned on again as long as an error signal is present.
Soft Start
The lower one of the two voltages at the plus inputs of K2 is a measure for the duty cycle
at the output. At the instant of turning on the component, the voltage at capacitor
C
soft start
equals 0 V. As long as no error is present, this capacitor is charged with a current of 6 µA
at the maximum value of 5 V. In case of an error,
C
soft start
is discharged with a current of
2 µA. A set signal is pending at the error flipflop below a charge of 1.5 V and the outputs
are enabled if no reset signal is pending simultaneously. As the minimum ramp
generator voltage, however, is 1.8 V, the duty cycle at the outputs is actually increased
slowly and continuously not before the voltage at
C
soft start
exceeds 1.8 V.
Error Flipflop
Error signals, which are led to input
R of the error flipflop cause an immediate disabling
of the outputs, and after the error has been eliminated, the component to switch on again
by the soft start.
Comparator K5, K8, V
Overcurrent Load
REF
These are error detectors which cause immediate disabling of the outputs via the error
flipflop when an error occurs. After elimination of the error, the component switches on
again by the soft start.
Semiconductor Group 5
Page 6

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Comparator K7
K7 serves to recognize overcurrents. This is the reason why both inputs of the
operational amplifier have been brought out. Turning on is resumed after error recovery
at the beginning of the next half period but without using the soft start. K7 has a commonmode input voltage range between 0 V and + 4 V. The delay time between occurrence
of an error and disabling of the outputs is only 250 ns.
Outputs
Both outputs are transistors with open collectors and operate in a push-pull
arrangement. They are actively low. The time in which only one of the two outputs is
conductive can be varied infinitely. The length of the falling edge at VCO is equal to the
minimum time during which both outputs are disabled simultaneously. The minimum
L voltage is 0.7 V.
Reference Voltage
The reference voltage source is a highly constant source with regard to its temperature
behavior. It can be utilized in the external wiring of the op amp, the error comparators,
the ramp generator, or other external components.
Semiconductor Group 6
Page 7

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Block Diagram (TDA 4714 C)
Semiconductor Group 7
Page 8

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Block Diagram (TDA 4716 C)
Semiconductor Group 8
Page 9

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test
Condition
min. max.
Supply voltage
Voltage at Q1, Q2
Current at Q1, Q2
Input
Input C
Input R
Input C
R
T
T
R
R
Input comparator
K2, K5, K7
Output K5
Input op amp TDA 4716 C
Output op amp TDA 4716 C
Reference voltage
V
S
V
Q
I
Q
V
IRT
V
ICT
V
IRR
I
ICR
V
I K2, 5, 7
V
Q K5
V
I Op Amp
V
Q Op Amp
V
Q REF
– 0.3
– 0.3
33
33
V
V Q1, Q2 high
70 mA Q1, Q2 low
– 0.3
– 0.3
– 0.3
–10
– 0.3
7
7
7
10
33
V
V
V
mA
V
– 0.3 33 V
– 0.3 33 V
– 0.3 VS –1
max. 7
– 0.3 V
REF
V
V
V
Input
C
soft start
Junction temperature
Storage temperature
Thermal resistance
system - air
Operating Range
Supply voltage
Ambient temperature
Frequency
VCO frequency
Ramp generator frequency
V
I soft start
T
j
T
stg
R
th SA
V
S
T
A
f
f
VCO
f
RG
– 0.3 7 V
–55
150
125
°C
°C
70 K/W
10.5 30 V
–25 85 °C
40
40
40
100
250
250
kHz
kHz
kHz
Semiconductor Group 9
Page 10

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Characteristics
11 V <
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
V
<30V; –25°C< TA <85°C
S
min. typ. max.
Supply current
C
= 1 nF
T
f
= 100 kHz
VCO
Reference
Reference voltage,
I
= 1 mA, VS = 12 V
REF
T
A
Voltage change
V
= 14 V ± 20 %
S
Voltage change
V
= 25 V ± 20 %
S
Voltage change
0 mA < I
REF
1)
< 5 mA
Temperature coefficient
Response threshold
of
I
overcurrent
REF
Oscillator (VCO)
= 25 °C
I
S
V
REF
∆V
∆V
∆V
TC
I
REF
REF
REF
REF
820mA
2.475 2.500
8
15
0.25
10
2.525
15
0.4
V
mV
mV
mV
mV/K
mA
Frequency range
Frequency change
V
= 14 V ± 20 %
S
Frequency change
V
= 25 V ± 20 %
S
Tolerance
∆
R
= 0; ∆CT = 0
T
Fall time sawtooth
C
= 1 nF
T
C
= 10 nF
T
RC combination
VCO
1)
Between 0 °C and 70 °C ambient temp. ∆V
f
40
∆f/f
∆f/f
∆f/f
C
T
R
T
is reduced to max. 5 mV.
REF
–1
–7
0.82
5
0.5
1
10
100
1
7
47
700
kHz
%
%
%
µs
µs
nF
kΩ
Semiconductor Group 10
Page 11

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Characteristics (cont’d)
11 V <
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
Ramp Generator
V
<30V; –25°C< TA <85°C
S
min. typ. max.
Frequency range
Maximum voltage at
Minimum voltage at C
Input current through R
C
R
R
R
Current transformation ratio
Comparator K2
Input current
Turn-OFF delay time
1)
Input voltage
Duty cycle
D = 0
D = max
Common-mode input voltage range
Soft Start K3, K4
Charge current for
Discharge current for C
Upper limiting voltage
Switching voltage K4
C
soft start
soft start
f
RG
V
H
V
L
I
RR
I
RR/ICR
–
I
K2
t
D OFF
V
IK2
V
IC
I
ch
I
dch
V
lim
V
K4
40
0
0
5.5
1.8
1/4
1.8
5
6
2
5
1.5
100
400
2
500
5.5
kHz
V
V
µA
µA
ns
V
V
V
µA
µA
V
V
Operational Amplifier (TDA 4716 C)
Open-loop voltage gain
Input offset voltage
Temperature coefficient of
V
IO
Input current
Common-mode input voltage range
Output current
Rise time of output voltage
Transition frequency
Phase of
f
T
Output voltage
– 3 mA <
1)
At the input: step function ∆V = – 100 mV ∆V = + 100 mV
I < 1.5 mA
G
V0
V
IO
TC
– I
I
V
IC
I
Q
∆V/∆t
f
T
ϕ
T
V
Q H/L
60
–10
–30
0
–3
1.5
Semiconductor Group 11
80
1
3
120
10
30
2
5
1.5
5.5
dB
mV
µV/K
µA
V
mA
V/µs
MHz
degr.
V
Page 12

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Characteristics (cont’d)
11 V <
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
Output Stages Q1, Q2
V
<30V; –25°C< TA <85°C
S
min. typ. max.
Output voltage
I
= 20 mA
Q
Output leakage current
V
= 30 V
QH
Dynamic Current
Limitation K7
Common-mode input voltage range
Input offset voltage
Input current
Turn-OFF delay time
Error detection time
2)
2)
Overvoltage K5
Switching voltage
Input current
Turn-OFF delay time
Error detection time
1)
1)
V
QH
V
QL
I
Q
V
IC
V
IO
– I
t
D OFF
t
V
– I
t
D OFF
t
30
1.1
2
0
–10
I
4
10
2
250
50
– 0.03
V
REF
I
V
2
+ 0.03
REF
250
V
V
µA
V
mV
µA
ns
ns
V
µA
ns
ns
Supply Undervoltage
Turn-ON threshold for
V
, rising
S
V
S
8.8
Turn-ON threshold
for
V
, rising (0 °C < TA <70 °C)
S
Turn-OFF threshold for
V
, falling
S
V
V
S
S
8.5
Turn-ON threshold
for
V
, falling (0 °C < TA <70 °C)
S
1)
At the input: step function V
2)
At the input: step function ∆V = – 100 mV ∆V = + 100 mV
= – 100 mV V
REF
V
S
= + 100 mV
REF
Semiconductor Group 12
11
10.5
10.5
10
V
V
V
V
Page 13

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Dimensioning Notes for RC Network
1. Determination of the minimum time during which both outputs must be disabled
C
→ selection of
2. Determination of the VCO frequency = 2 x output frequency
→ selection of
3. Determination of the rated slope of the rising ramp generator voltage, which the
maximum possible turn-on period per half wave depends on
→ selection of
4. Duration of the soft start process
→ selection of
5. Wiring of the operational amplifier according to the dynamic requirements
(TDA 4716 C).
; selection of CR ≤ CT.
T
R
.
T
R
.
R
C
soft start
Semiconductor Group 13
Page 14

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Pulse Diagram
Semiconductor Group 14
Page 15

TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
VCO Frequency versus RT and C
T
Semiconductor Group 15
Page 16

VCO Temperature Response
V
= 12 V; D = max.
S
∆f
VCO
----------------
f
K×
K
1 K⁄[]
with
C
as parameter
T
TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Semiconductor Group 16
Page 17

Supply Current versus Temperature Output Current versus
L-Output Voltage
TDA 4714 C
TDA 4716 C
Semiconductor Group 17
 Loading...
Loading...