Page 1
STM8L001J3
SO8N
4.9x6 mm or 150 mils body width
8-bit ultra-low-power microcontroller with up to 8-Kbyte
Flash memory, multifunction timers, comparators, UART, SPI, I2C
Datasheet - production data
Features
• Main microcontroller features
– Supply voltage range 1.8 V to 3.6 V
– Low power consumption (Halt: 0.3 µA,
Active-halt: 0.8 µA, Dynamic Run:
150 µA/MHz)
– STM8 Core with up to 16 CISC MIPS
throughput
– Temp. range: -40 to 125 °C
• Memories
– 8 Kbytes of Flash program including up to
2 Kbytes of data EEPROM
– Error correction code (ECC)
– Flexible write and read protection modes
– In-application and in-circuit programming
– Data EEPROM capability
– 1.5 Kbytes of static RAM
• Clock management
– Internal 16 MHz RC with fast wakeup time
(typ. 4 µs)
– Internal low consumption 38 kHz RC
driving both the IWDG and the AWU
• Reset and supply management
– Ultra-low power POR/PDR
– Three low-power modes: Wait, Active-halt,
Halt
• Interrupt management
– Nested interrupt controller with software
priority control
– Up to 6 external interrupt sources
• I/Os
– Up to 6 I/Os, all mappable on external
interrupt vectors
– I/Os with programmable input pull-ups, high
sink/source capability and one LED driver
infrared output
• Peripherals
– Two 16-bit general purpose timers (TIM2
and TIM3) with up and down counter and 1
channel (used as IC, OC, PWM)
– One 8-bit timer (TIM4) with 7-bit prescaler
– Infrared remote control (IR)
– Independent watchdog
– Auto-wakeup unit
– Beeper timer with 1, 2 or 4 kHz frequencies
– SPI synchronous serial interface
– Fast I2C Multimaster/slave 400 kHz
– UART with fractional baud rate generator
– 2 comparators with 1 input each
• Development support
– Hardware single wire interface module
(SWIM) for fast on-chip programming and
non intrusive debugging
September 2020 DS12153 Rev 4 1/58
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com
Page 2

STM8L001J3
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 Product overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.1 Central processing unit STM8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.2 Development tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.3 Single wire data interface (SWIM) and debug module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.4 Interrupt controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.5 Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.6 Low power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.7 Voltage regulators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.8 Clock control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.9 Independent watchdog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.10 Auto-wakeup counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.11 General purpose and basic timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.12 Beeper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.13 Infrared (IR) interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.14 Comparators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.15 USART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.16 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.17 I2C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5 Memory and register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6 Interrupt vector mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7 Option bytes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8 Electrical parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.1 Parameter conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.1.1 Minimum and maximum values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.1.2 Typical values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.1.3 Typical curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 3

STM8L001J3
8.1.4 Loading capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
8.1.5 Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8.2 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8.3 Operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.3.1 General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.3.2 Power-up / power-down operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.3.3 Supply current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.3.4 Clock and timing characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.3.5 Memory characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.3.6 I/O port pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.3.7 Communication interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.3.8 Comparator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.3.9 EMC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
8.4 Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
9 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
9.1 SO8N package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
10 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
11 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
DS12153 Rev 4 3/58
3
Page 4

List of tables STM8L001J3
List of tables
Table 1. STM8L001J3 device feature summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 2. Legend/abbreviation for table 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 3. STM8L001J3 pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 4. Flash and RAM boundary addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 5. I/O Port hardware register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 6. General hardware register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 7. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 8. Interrupt mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 9. Option bytes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 10. Option byte description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 11. Voltage characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 12. Current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 13. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 14. General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 15. Operating conditions at power-up / power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 16. Total current consumption in Run mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 17. Total current consumption in Wait mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 18. Total current consumption and timing in Halt and Active-halt mode at
VDD = 1.8 V to 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 19. Peripheral current consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 20. HSI oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 21. LSI oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 22. RAM and hardware registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 23. Flash program memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 24. I/O static characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 25. Output driving current (High sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 26. Output driving current (true open drain ports). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 27. Output driving current (PA0 with high sink LED driver capability). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 28. SPI characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 29. I2C characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 30. Comparator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 31. EMS data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 32. EMI data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 33. ESD absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 34. Electrical sensitivities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 35. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 36. SO8N – 8-lead 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width,
package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 37. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 38. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 5

STM8L001J3 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. STM8L001J3 device block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 2. STM8L001J3 SO8N pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 3. Memory map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 4. Pin loading conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 5. Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 6. IDD(RUN) vs. VDD, fCPU = 2 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 7. IDD(RUN) vs. VDD, fCPU = 16 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 8. IDD(WAIT) vs. VDD, fCPU = 2 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 9. IDD(WAIT) vs. VDD, fCPU = 16 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 10. Typ. IDD(Halt) vs. VDD, fCPU = 2 MHz and 16 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 11. Typical LSI RC frequency vs. VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 12. Typical VIL and VIH vs. VDD (High sink I/Os) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 13. Typical VIL and VIH vs. VDD (true open drain I/Os). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 14. Typical pull-up resistance R
Figure 15. Typical pull-up current I
Figure 16. Typ. VOL at VDD = 3.0 V (High sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 17. Typ. VOL at VDD = 1.8 V (High sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 18. Typ. VOL at VDD = 3.0 V (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 19. Typ. VOL at VDD = 1.8 V (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 20. Typ. VDD - VOH at VDD = 3.0 V (High sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 21. Typ. VDD - VOH at VDD = 1.8 V (High sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 22. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 23. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 1
Figure 24. SPI timing diagram - master mode
Figure 25. Typical application with I2C bus and timing diagram (1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 26. SO8N – 8-lead, 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package outline . 53
Figure 27. SO8N – 8-lead 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width,
package recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 28. Example of SO8N marking (package top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
vs. VDD with VIN=VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
PU
vs. VDD with VIN=VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
PU
(1)
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
DS12153 Rev 4 5/58
5
Page 6

Introduction STM8L001J3
1 Introduction
This datasheet provides the STM8L001J3 pinout, ordering information, mechanical and
electrical device characteristics.
For complete information on the STM8L001J3 microcontroller memory, registers and
peripherals, please refer to the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx microcontroller family reference
manual (RM0013).
The STM8L001J3 devices are members of the STM8L low-power 8-bit family. They are
referred to as low-density devices in the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx microcontroller family
reference manual (RM0013) and in the How to program STM8L and STM8AL Flash
program memory and data EEPROM programming manual (PM0054).
All devices of the SM8L Series provide the following benefits:
• Reduced system cost
– 8 Kbytes of low-density embedded Flash program memory including up to
2 Kbytes of data EEPROM
– High system integration level with internal clock oscillators and watchdogs.
– Smaller battery and cheaper power supplies.
• Low power consumption and advanced features
– Up to 16 MIPS at 16 MHz CPU clock frequency
– Less than 150 µA/MHz, 0.8 µA in Active-halt mode, and 0.3 µA in Halt mode
– Clock gated system and optimized power management
•
Short development cycles
– Application scalability across a common family product architecture with
compatible pinout, memory map and modular peripherals.
– Full documentation and a wide choice of development tools
•
Product longevity
– Advanced core and peripherals made in a state-of-the art technology
– Product family operating from 1.8 V to 3.6 V supply.
6/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 7
STM8L001J3 Description
2 Description
The STM8L001J3 low-power microcontroller features the enhanced STM8 CPU core
providing increased processing power (up to 16 MIPS at 16 MHz) while maintaining the
advantages of a CISC architecture with improved code density, a 24-bit linear addressing
space and an optimized architecture for low power operations.
The family includes an integrated debug module with a hardware interface (SWIM) which
allows non-intrusive in-application debugging and ultra fast Flash programming.
All STM8L001J3 microcontrollers feature low power low-voltage single-supply program
Flash memory. The 8-Kbyte devices embed data EEPROM.
The STM8L001J3 low power microcontroller is based on a generic set of state-of-the-art
peripherals. The modular design of the peripheral set allows the same peripherals to be
found in different ST microcontroller families including 32-bit families. This makes any
transition to a different family very easy, and simplified even more by the use of a common
set of development tools.
All STM8L low power products are based on the same architecture with the same memory
mapping and a coherent pinout.
Table 1. STM8L001J3 device feature summary
Features STM8L001J3
Flash
RAM 1.5 Kbytes
Peripheral functions
Timers Two 16-bit timers, one 8-bit timer
Operating voltage 1.8 to 3.6 V
Operating temperature -40 to +125 °C
Packages SO8N
Universal synchronous / asynchronous receiver / transmitter (USART),
8 Kbytes of Flash program memory including up to
2 Kbytes of Data EEPROM
Independent watchdog (IWDG), Auto-wakeup unit (AWU), Beep,
Serial peripheral interface (SPI), Inter-integrated circuit (I2C),
2 comparators, Infrared (IR) interface
DS12153 Rev 4 7/58
16
Page 8
Product overview STM8L001J3
MS32610V1
16 MHz int RC
Clock
controller
Clocks
AWU
Beeper
Address and data bus
38 kHz int RC
Debug module
I²C1
SPI
USART
Up to 8 Kbytes
Flash memory
controller
1.5 Kbytes
to core and
peripherals
IWDG
16-bit Timer 2
(SWIM)
Nested interrupt
up to 6 external
multimaster
8-bit Timer 4
SRAM
interrupts
(including
up to 2 Kbytes
data EEPROM)
Power
Volt. reg.
POR/PDR
Reset
COMP1
COMP2
Port A
Port B
Port C
Port D
RX, TX
SDA, SCL
PA
PB
PC
PD
MOSI, MISO,
SCK
BEEP
SWIM
COMP1_CH3
COMP_REF
Infrared interface
IR_TIM
16-bit Timer 3
IR_TIM
TIM3_CH2
COMP2_CH2
V
DD18
@ V
DD
STM8
Core
up to 16 MHz
V
DD
= 1.8V to 3.6V
V
SS
3 Product overview
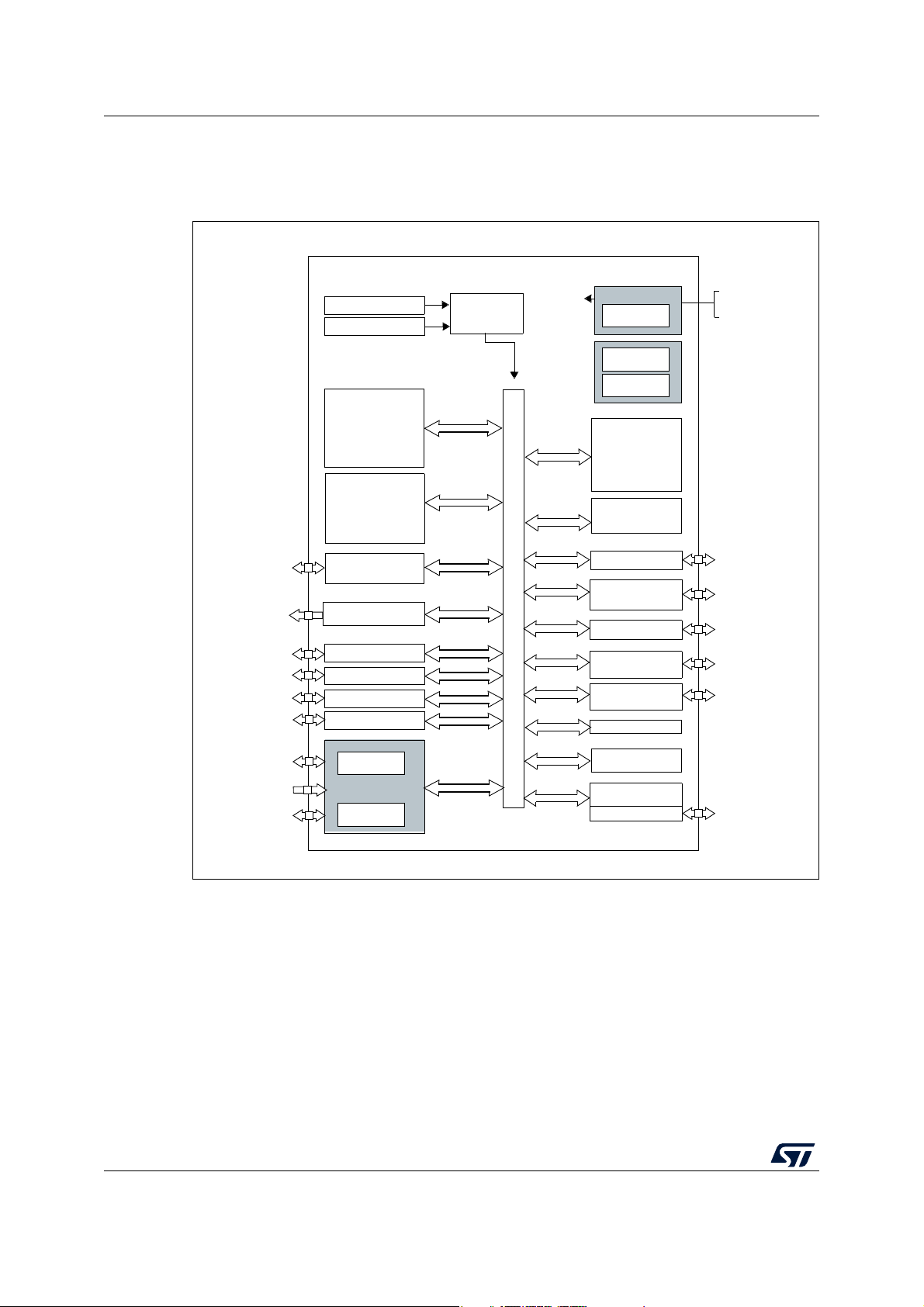
Figure 1. STM8L001J3 device block diagram
Legend:
AWU: Auto-wakeup unit
Int. RC: internal RC oscillator
I2C: Inter-integrated circuit multimaster interface
POR/PDR: Power on reset / power down reset
SPI: Serial peripheral interface
SWIM: Single wire interface module
USART: Universal synchronous / asynchronous receiver / transmitter
IWDG: Independent watchdog
8/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 9

STM8L001J3 Product overview
3.1 Central processing unit STM8
The 8-bit STM8 core is designed for code efficiency and performance.
It features 21 internal registers, 20 addressing modes including indexed, indirect and
relative addressing, and 80 instructions.
3.2 Development tools
Development tools for the STM8 microcontrollers include:
• The STVD high-level language debugger including C compiler, assembler and
integrated development environment
• The STVP Flash programming software
The STM8 also comes with starter kits, evaluation boards and low-cost in-circuit
debugging/programming tools.
3.3 Single wire data interface (SWIM) and debug module
The debug module with its single wire data interface (SWIM) permits non-intrusive real-time
in-circuit debugging and fast memory programming.
The Single wire interface is used for direct access to the debugging module and memory
programming. The interface can be activated in all device operation modes.
The non-intrusive debugging module features a performance close to a full-featured
emulator. Beside memory and peripherals, also CPU operation can be monitored in realtime by means of shadow registers.
Recommendations for SWIM pin (pin#1)
As the NRST pin is not available on this device, if the SWIM pin should be used with the I/O
pin functionality, it is recommended to add a ~5 seconds delay in the firmware before
changing the functionality on the pin with SWIM functions. This action allows the user to set
the device into SWIM mode after the device power on and to be able to reprogram the
device. If the pin with SWIM functionality is set to I/O mode immediately after the device
reset, the device is unable to connect through the SWIM interface and it gets locked forever.
This initial delay can be removed in the final (locked) code.
If the initial delay is not acceptable for the application there is the option that the firmware
reenables the SWIM pin functionality under specific conditions such as during firmware
startup or during application run. Once that this procedure is done, the SWIM interface can
be used for the device debug/programming.
3.4 Interrupt controller
The STM8L001J3 features a nested vectored interrupt controller:
• Nested interrupts with 3 software priority levels
• 26 interrupt vectors with hardware priority
• Up to 6 external interrupt sources on 6 vectors
• Trap and reset interrupts.
DS12153 Rev 4 9/58
16
Page 10

Product overview STM8L001J3
3.5 Memory
The STM8L001J3 devices have the following main features:
• 1.5 Kbytes of RAM
• The EEPROM is divided into two memory arrays (see the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx
microcontroller family reference manual (RM0013) for details on the memory mapping):
– 8 Kbytes of low-density embedded Flash program including up to 2 Kbytes of data
EEPROM. Data EEPROM and Flash program areas can be write protected
independently by using the memory access security mechanism (MASS).
– 64 option bytes (one block) of which 5 bytes are already used for the device.
Error correction code is implemented on the EEPROM.
Recommendation for the device's programming:
The device's 8 Kbytes program memory is not empty on virgin devices; there is code loop
implemented on the reset vector. It is recommended to keep valid code loop in the device to
avoid the program execution from an invalid memory address (which would be any memory
address out of 8 Kbytes program memory space).
If the device's program memory is empty (0x00 content), it displays the behavior described
below:
• After the power on, the “empty” code is executed (0x0000 opcodes = instructions: NEG
(0x00, SP)) until the device reaches the end of the 8 Kbytes program memory (the end
address = 0x9FFF).
It takes around 4 milliseconds to reach the end of the 8 Kbytes memory space @2 MHz
HSI clock.
• Once the device reaches the end of the 8 Kbytes program memory, the program
continues and code from a non-existing memory is fetched and executed.
The reading of non-existing memory is a random content which can lead to the execution of
invalid instructions.
The execution of invalid instructions generates a software reset and the program starts
again. A reset can be generated every 4 milliseconds or more.
Only the “connect on-the-fly” method can be used to program the device through the SWIM
interface. The “connect under-reset” method cannot be used because the NRST pin is not
available on this device.
The “connect on-the-fly” mode can be used while the device is executing code, but if there is
a device reset (by software reset) during the SWIM connection, this connection is aborted
and it must be performed again from the debug tool. Note that the software reset occurrence
can be of every 4 milliseconds, making it difficult to successfully connect to the device's
debug tool (there is practically only one successful connection trial for every 10 attempts).
Once that a successful connection is reached, the device can be programmed with a valid
firmware without problems; therefore it is recommended that device is never erased and
that is contains always a valid code loop.
10/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 11

STM8L001J3 Product overview
3.6 Low power modes
To minimize power consumption, the product features three low power modes:
• Wait mode: CPU clock stopped, selected peripherals at full clock speed.
• Active-halt mode: CPU and peripheral clocks are stopped. The programmable wakeup
time is controlled by the AWU unit.
• Halt mode: CPU and peripheral clocks are stopped, the device remains powered on.
The RAM content is preserved. Wakeup is triggered by an external interrupt.
3.7 Voltage regulators
The STM8L001J3 embeds an internal voltage regulator for generating the 1.8 V power
supply for the core and peripherals.
This regulator has two different modes: main voltage regulator mode (MVR) and low power
voltage regulator mode (LPVR). When entering Halt or Active-halt modes, the system
automatically switches from the MVR to the LPVR in order to reduce current consumption.
3.8 Clock control
The STM8L001J3 embeds a robust clock controller. It is used to distribute the system clock
to the core and the peripherals and to manage clock gating for low power modes. This
system clock is a 16-MHz High Speed Internal RC oscillator (HSI RC), followed by a
programmable prescaler.
In addition, a 38 kHz low speed internal RC oscillator is used by the independent watchdog
(IWDG) and Auto-wakeup unit (AWU).
3.9 Independent watchdog
The independent watchdog (IWDG) peripheral can be used to resolve processor
malfunctions due to hardware or software failures.
It is clocked by the 38 kHz LSI internal RC clock source, and thus stays active even in case
of a CPU clock failure.
3.10 Auto-wakeup counter
The auto-wakeup (AWU) counter is used to wakeup the device from Active-halt mode.
3.11 General purpose and basic timers
STM8L001J3 devices contain two 16-bit general purpose timers (TIM2 and TIM3) and one
8-bit basic timer (TIM4).
DS12153 Rev 4 11/58
16
Page 12

Product overview STM8L001J3
16-bit general purpose timers
The 16-bit timers consist of 16-bit up/down auto-reload counters driven by a programmable
prescaler. They perform a wide range of functions, including:
• Time base generation
• Measuring the pulse lengths of input signals (input capture)
• Generating output waveforms (output compare, PWM and One pulse mode)
• Interrupt capability on various events (capture, compare, overflow, break, trigger)
8-bit basic timer
The 8-bit timer consists of an 8-bit up auto-reload counter driven by a programmable
prescaler. It can be used for timebase generation with interrupt generation on timer
overflow.
3.12 Beeper
The STM8L001J3 devices include a beeper function used to generate a beep signal in the
range of 1, 2 or 4 kHz when the LSI clock is operating at a frequency of 38
kHz.
3.13 Infrared (IR) interface
The STM8L001J3 devices contain an infrared interface which can be used with an IR LED
for remote control functions. Two timer output compare channels are used to generate the
infrared remote control signals.
3.14 Comparators
The STM8L001J3 features two zero-crossing comparators (COMP1 and COMP2) sharing
the same current bias and voltage reference. The voltage reference can be internal
(comparison with ground) or external (comparison to a reference pin voltage).
Each comparator is connected to 4 channels, which can be used to generate interrupt, timer
input capture or timer break. Their polarity can be inverted.
3.15 USART
The USART interface (USART) allows full duplex, asynchronous communications with
external devices requiring an industry standard NRZ asynchronous serial data format. It
offers a very wide range of baud rates.
3.16 SPI
The serial peripheral interface (SPI) provides half/ full duplex synchronous serial
communication with external devices. It can be configured as the master and in this case it
provides the communication clock (SCK) to the external slave device. The interface can
also operate in multi-master configuration.
12/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 13

STM8L001J3 Product overview
3.17 I2C
The inter-integrated circuit (I2C) bus interface is designed to serve as an interface between
the microcontroller and the serial
I2C bus-specific sequencing, protocol, arbitration and timing. It manages standard and fast
speed modes.
I2Cbus. It provides multi-master capability, and controls all
DS12153 Rev 4 13/58
16
Page 14
Pin description STM8L001J3
MSv46315V1
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
PC1/I2C_SCL/
PC2/USART_RX
PB7/SPI_MISO/
PC0/I2C_SDA
PB6/SPI_MOSI
PB3/TIM2_ETR/COMP2_CH2/
PB5/SPI_SCK/
PD0/TIM3_CH2/COMP1_CH3
PA0/SWIM/BEEP/IR_TIM/
PC3/USART_TX/
PC4/USART_CK/CCO
PA2/
PA4/TIM2_BKIN/
PA6/COMP_REF
VSS
VDD
STM8L
4 Pin description
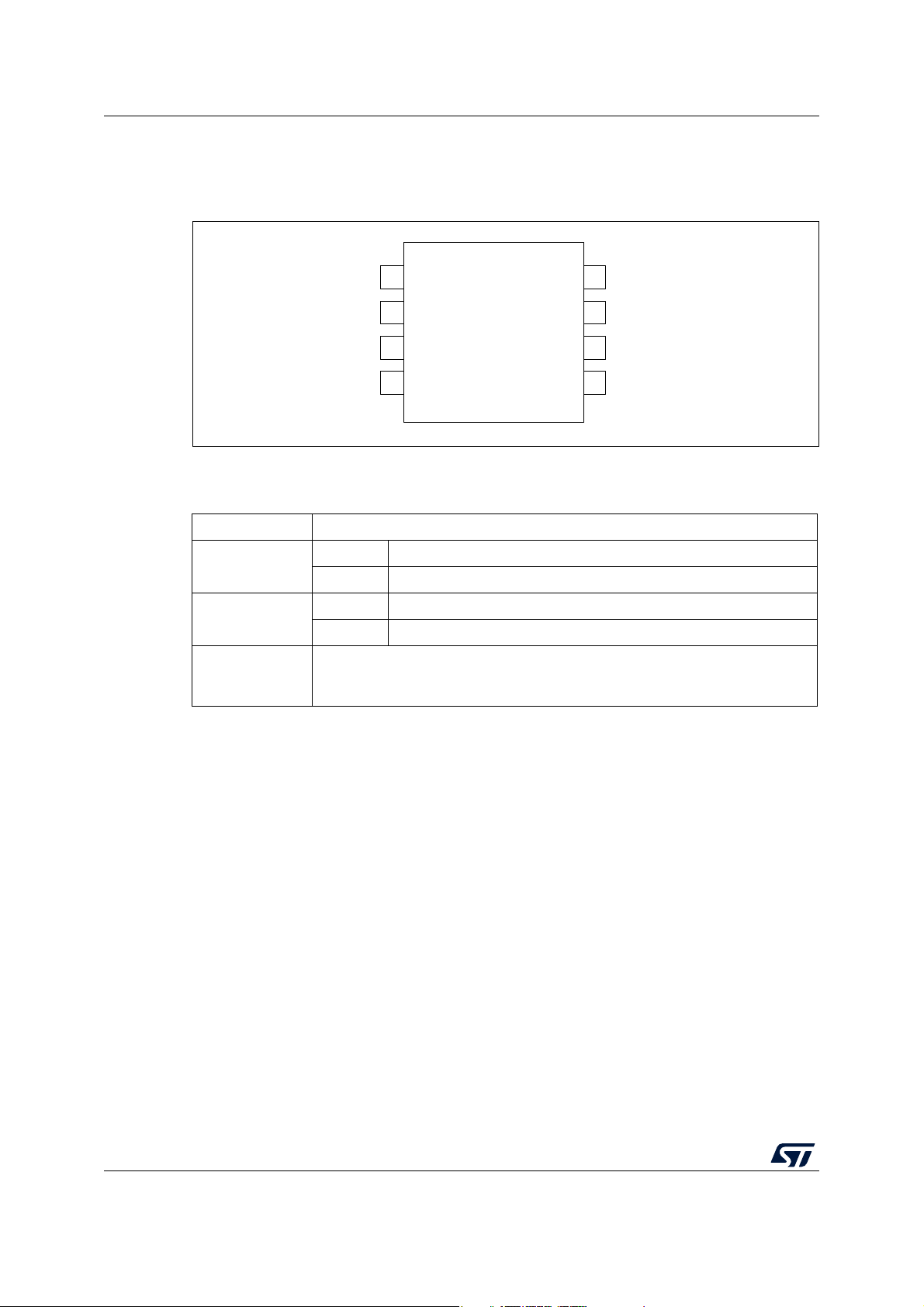
Figure 2. STM8L001J3 SO8N pinout
Table 2. Legend/abbreviation for table 4
Type I= input, O = output, S = power supply
Input CM = CMOS
Level
Output HS = high sink/source (20 mA)
Port and control
configuration
Input float = floating, wpu = weak pull-up
Output T = true open drain, OD = open drain, PP = push pull
Bold X (pin state after reset release).
Reset state
Unless otherwise specified, the pin state is the same during the reset phase (i.e.
“under reset”) and after internal reset release (i.e. at reset state).
14/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 15
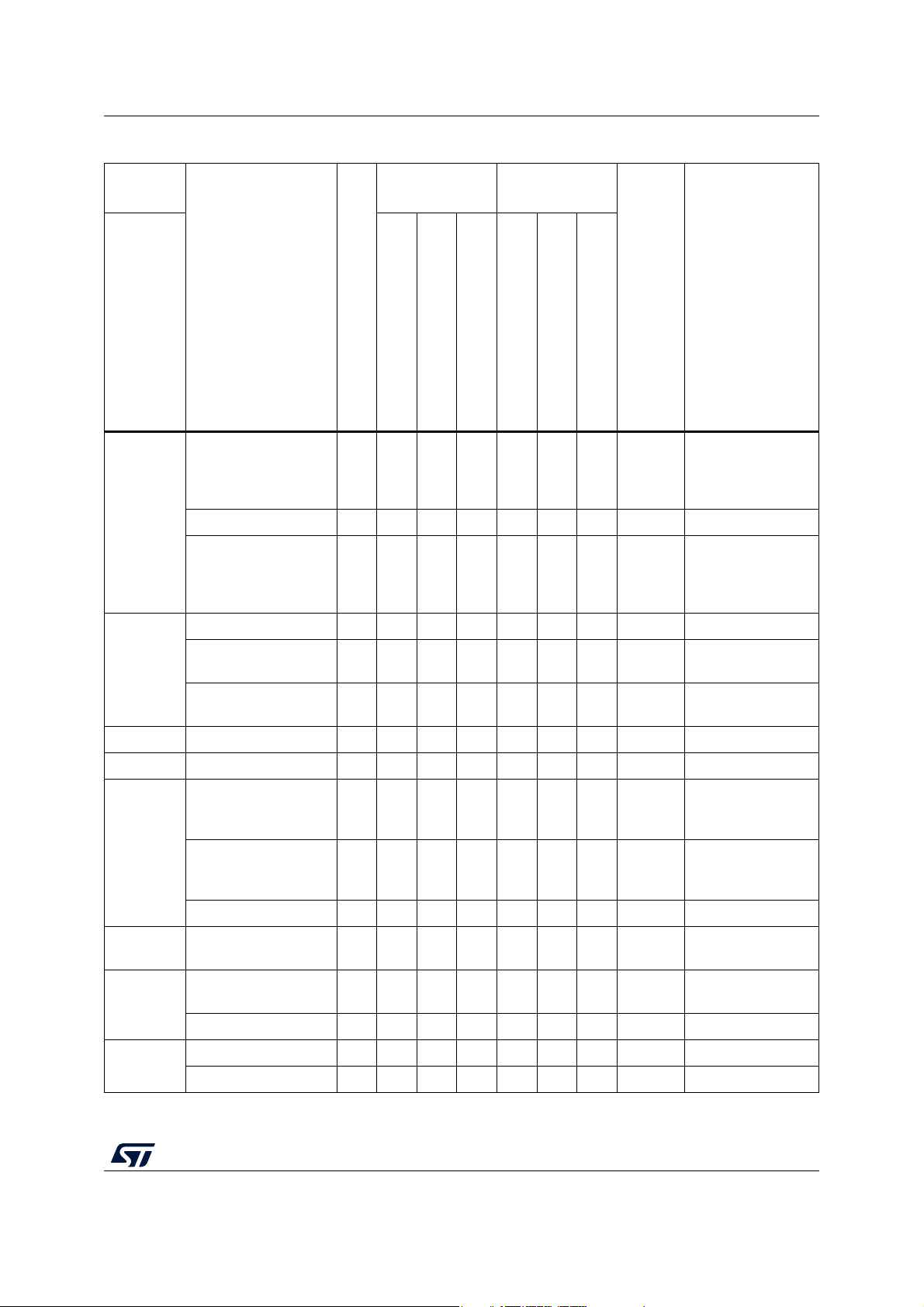
STM8L001J3 Pin description
Pin
number
SO8N
1
Table 3. STM8L001J3 pin description
Input Output
Main
Pin name
Type
OD
Floating
WPU
function
PP
(after
reset)
Alternate function
Ext. interrupt
High sink / source
(1)
PA0
IR_TIM
/SWIM/BEEP/
(2)
I/O X X
(1)
HS
C
XXPort A0
(2)
SWIM input and
output / Beep
output/ Timer
infrared output
(1)
PC3/USART_TX I/O X
X X HS X X Port C3 USART transmit
USART
PC4/USART_CK/
CCO
I/O X
(1)
XXHSXXPort C4
synchronous clock /
Configurable clock
output
PA2 I/O X XXHSXXPort A2-
2
PA4/TIM2_BKIN I/O X XXHSXXPort A4
PA6/COMP_REF I/O X XXHSXXPort A6
3V
4V
SS
DD
PD0/TIM3_CH2/
COMP1_CH3
5
PB3/TIM2_ETR/
COMP2_CH2
S - ----- -Ground
S - ----- -Power supply
I/O X XXHSXXPort D0
I/O X XXHSXXPort B3
Timer 2 - break
input
Comparator
external reference
Timer 3 - Channel 2
/ Comparator 1 -
Channel 3
Timer 2 - trigger /
Comparator 2 -
Channel 2
PB5/SPI_SCK I/O X X X HS X X Port B5 SPI clock
6 PB6/SPI_MOSI I/O X XXHSXXPort B6
PB7/SPI_MISO I/O X XXHSXXPort B7
7
(3)
PC0/I2C_SDA I/O X -X-T
PC1/I2C_SCL I/O X -X-T
- Port C0 I2C data
(3)
- Port C1 I2C clock
SPI master out /
slave in
SPI master in /
slave out
8
PC2/USART_RX I/O X X X HS X X Port C2 USART receive
DS12153 Rev 4 15/58
16
Page 16

Pin description STM8L001J3
1. The PA0 pin is in input pull-up during the reset phase and after internal reset release. This PA0 default state influences all
the GPIOs connected in parallel on pin number 1 (PC3, PC4).
2. High sink LED driver capability available on PA0.
3. In the open-drain output column, ‘T’ defines a true open-drain I/O (P-buffer, weak pull-up and protection diode to V
not implemented). Although PC0/PC1 itself is a true open drain GPIO with its respective internal circuitry and
characteristics, V
also bonded to the same pin number.
maximum of the pin number 7 and pin number 8 is limited by the standard GPIO (PB7 or PC2) which is
IN
DD
are
Slope control of all GPIO pins can be programmed except true open drain pins which by
default is limited to 2 MHz.
Note: The PA1, PA3, PA5, PB0, PB1, PB2, PB4, PC5, PC6, PD1, PD2, PD3, PD4, PD5, PD6 and
PD7 GPIOs should be configured after device reset, by user software into the in output
push-pull mode with output-low state to reduce device consumption and to improve EMC
immunity. Those GPIOs are not connected to pins and after device reset are in input floating
mode. To configure PA1 pin in output push-pull mode refer to Section “Configuring
NRST/PA1 pin as general purpose output” in the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx
microcontroller family reference manual (RM0013).
Note: As several pins provide a connection to multiple GPIOs, the mode selection for any of those
GPIOs impacts all the other GPIOs connected to the same pin. The user is responsible for
the proper setting of the GPIO modes in order to avoid conflicts between GPIOs bonded to
the same pin (including their alternate functions). For example, pull-up enabled on PA0 is
also seen on PC3 and PC4. Push-pull configuration of PA2 is also seen on PA4 and PA6,
etc.
16/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 17
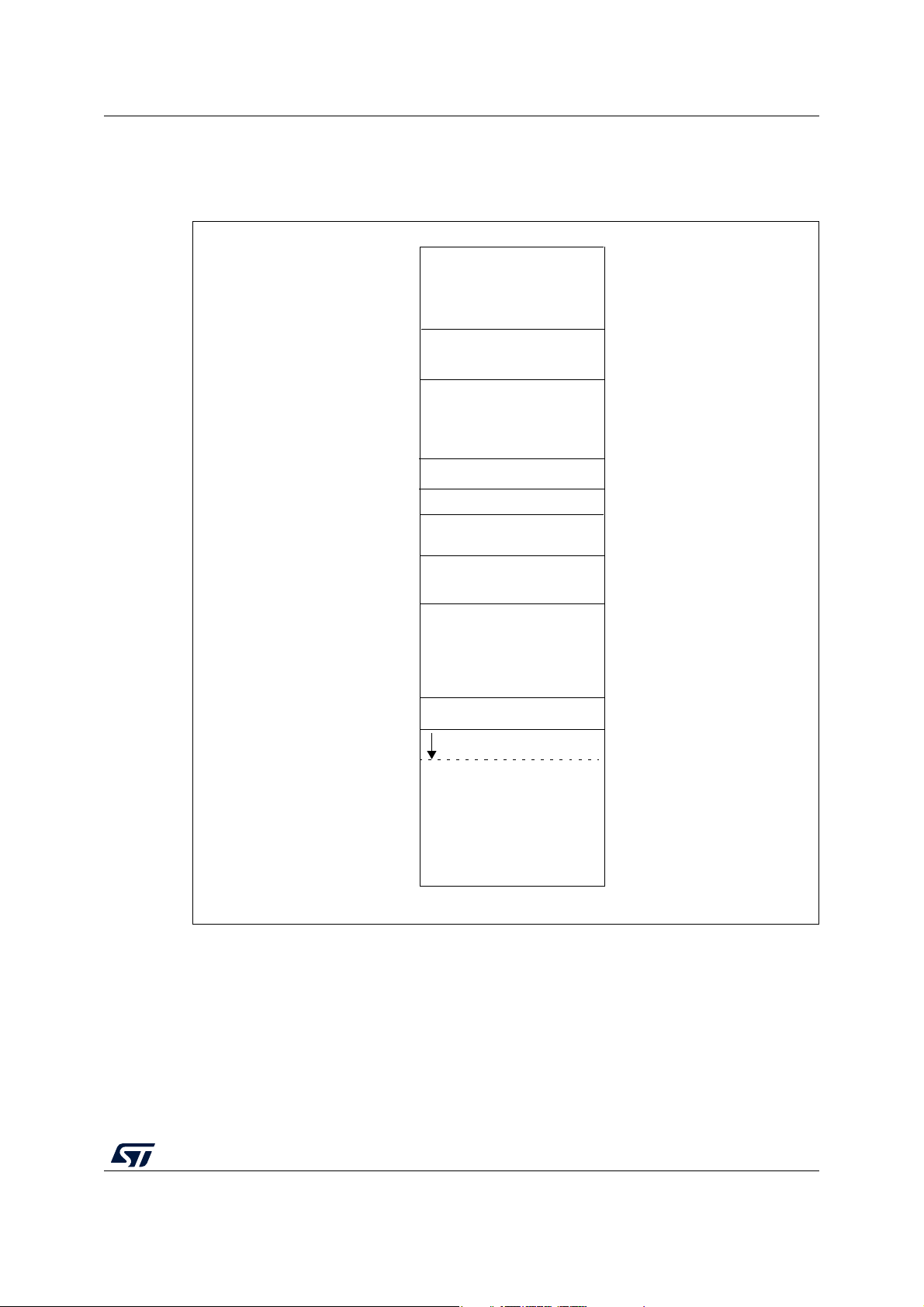
STM8L001J3 Memory and register map
GPIO and peripheral registers
(2)
0x00 0000
Reserved
Flash program memory
(up to 8 Kbytes)
(1)
Interrupt vectors
0x00 4800
0x00 48FF
RAM
0x00 05FF
(1.5 Kbytes)
(1)
(up to 513 bytes)
(1)
0x 004900
Option bytes
0x00 5000
0x00 57FF
0x00 5800
0x00 7FFF
0x00 8000
0x00 9FFF
0x00 0600
0x00 47FF
0x00 49FF
0x00 7EFF
0x00 8080
0x00 807F
CPU/SWIM/Debug/ITC
Registers
0x00 7F00
Reserved
Reserved
including
Stack
including
Data EEPROM
(up to 2 Kbytes)
0x 004925
0x 004931
0x 004924
0x 004930
Unique ID
Reserved
Low-density
MS32621V1
5 Memory and register map
Figure 3. Memory map
1. Table 4 lists the boundary addresses for each memory size. The top of the stack is at the RAM end
address.
2. Refer to Table 6 for an overview of hardware register mapping, to Table 5 for details on I/O port hardware
registers, and to Table 7 for information on CPU/SWIM/debug module controller registers.
DS12153 Rev 4 17/58
27
Page 18
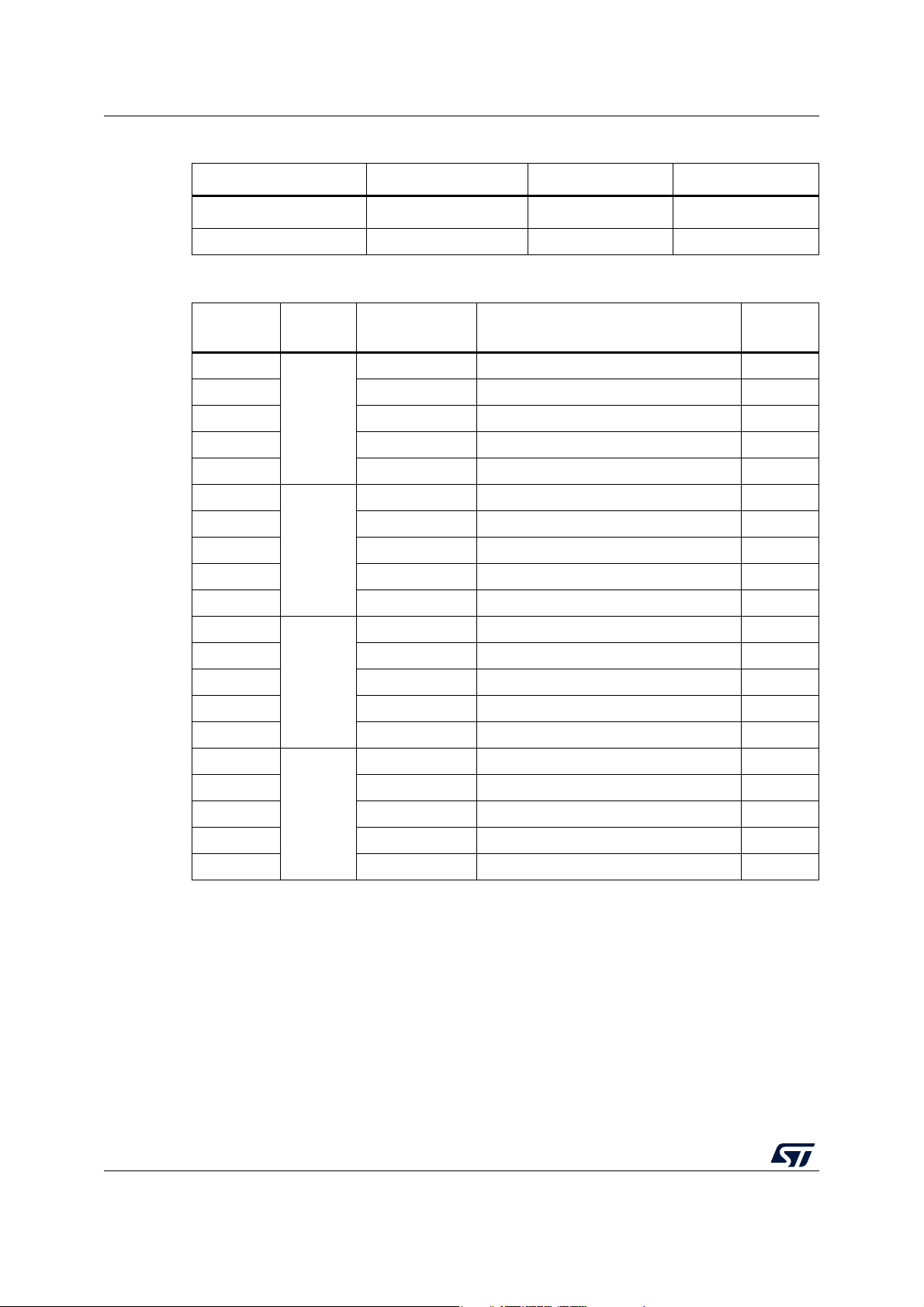
Memory and register map STM8L001J3
Table 4. Flash and RAM boundary addresses
Memory area Size Start address End address
RAM 1.5 Kbytes 0x00 0000 0x00 05FF
Flash program memory 8 Kbytes 0x00 8000 0x00 9FFF
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 5000
Table 5. I/O Port hardware register map
Reset
status
PA_ODR Port A data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5001 PA_IDR Port A input pin value register 0xxx
0x00 5002 PA_DDR Port A data direction register 0x00
Port A
0x00 5003 PA_CR1 Port A control register 1 0x00
0x00 5004 PA_CR2 Port A control register 2 0x00
0x00 5005
PB_ODR Port B data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5006 PB_IDR Port B input pin value register 0xxx
0x00 5007 PB_DDR Port B data direction register 0x00
Port B
0x00 5008 PB_CR1 Port B control register 1 0x00
0x00 5009 PB_CR2 Port B control register 2 0x00
0x00 500A
PC_ODR Port C data output latch register 0x00
0x00 500B PC_IDR Port C input pin value register 0xxx
0x00 500C PC_DDR Port C data direction register 0x00
Port C
0x00 500D PC_CR1 Port C control register 1 0x00
0x00 500E PC_CR2 Port C control register 2 0x00
0x00 500F
PD_ODR Port D data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5010 PD_IDR Port D input pin value register 0xxx
0x00 5011 PD_DDR Port D data direction register 0x00
Port D
0x00 5012 PD_CR1 Port D control register 1 0x00
0x00 5013 PD_CR2 Port D control register 2 0x00
18/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 19

STM8L001J3 Memory and register map
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 5050
Table 6. General hardware register map
Reset
status
FLASH_CR1 Flash control register 1 0x00
0x00 5051 FLASH_CR2 Flash control register 2 0x00
0x00 5052 FLASH _PUKR
Flash
Flash Program memory unprotection
register
0x00
0x00 5053 FLASH _DUKR Data EEPROM unprotection register 0x00
0x00 5054 FLASH _IAPSR
Flash in-application programming status
register
0x00 5055
to
Reserved area (75 bytes)
0x00 509F
0x00 50A0
EXTI_CR1 External interrupt control register 1 0x00
0x00 50A1 EXTI_CR2 External interrupt control register 2 0x00
0x00 50A2 EXTI_CR3 External interrupt control register 3 0x00
ITC-EXTI
0x00 50A3 EXTI_SR1 External interrupt status register 1 0x00
0x00 50A4 EXTI_SR2 External interrupt status register 2 0x00
0x00 50A5 EXTI_CONF External interrupt port select register 0x00
0xX0
0x00 50A6
WFE_CR1 WFE control register 1 0x00
WFE
0x00 50A7 WFE_CR2 WFE control register 2 0x00
0x00 50A8
to
Reserved area (8 bytes)
0x00 50AF
0x00 50B0
RST_CR Reset control register 0x00
RST
0x00 50B1 RST_SR Reset status register 0x01
0x00 50B2
to
Reserved area (14 bytes)
0x00 50BF
0x00 50C0
CLK_CKDIVR Clock divider register 0x03
0x00 50C1
to
0x00 50C2
CLK
Reserved area (2 bytes)
0x00 50C3 CLK_PCKENR Peripheral clock gating register 0x00
0x00 50C4 Reserved (1 byte)
0x00 50C5 CLK_CCOR Configurable clock control register 0x00
0x00 50C6
to
Reserved area (25 bytes)
0x00 50DF
DS12153 Rev 4 19/58
27
Page 20

Memory and register map STM8L001J3
Table 6. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 50E0
0x00 50E1 IWDG_PR IWDG prescaler register 0x00
0x00 50E2 IWDG_RLR IWDG reload register 0xFF
0x00 50E3
to
0x00 50EF
0x00 50F0
0x00 50F1 AWU_APR
0x00 50F2 AWU_TBR AWU timebase selection register 0x00
0x00 50F3 BEEP BEEP_CSR BEEP control/status register 0x1F
0x00 50F4
to
0x00 51FF
0x00 5200
0x00 5201 SPI_CR2 SPI control register 2 0x00
0x00 5202 SPI_ICR SPI interrupt control register 0x00
0x00 5203 SPI_SR SPI status register 0x02
0x00 5204 SPI_DR SPI data register 0x00
0x00 5205
to
0x00 520F
0x00 5210
IWDG
AWU
SPI
IWDG_KR IWDG key register 0xXX
Reserved area (13 bytes)
AWU_CSR AWU control/status register 0x00
AWU asynchronous prescaler buffer
register
Reserved area (268 bytes)
SPI_CR1 SPI control register 1 0x00
Reserved area (11 bytes)
I2C_CR1 I2C control register 1 0x00
Reset
status
0x3F
0x00 5211 I2C_CR2 I2C control register 2 0x00
0x00 5212 I2C_FREQR I2C frequency register 0x00
0x00 5213 I2C_OARL I2C own address register low 0x00
0x00 5214 I2C_OARH I2C own address register high 0x00
0x00 5215 Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 5216 I2C_DR I2C data register 0x00
0x00 5217 I2C_SR1 I2C status register 1 0x00
0x00 5218 I2C_SR2 I2C status register 2 0x00
0x00 5219 I2C_SR3 I2C status register 3 0x00
0x00 521A I2C_ITR I2C interrupt control register 0x00
0x00 521B I2C_CCRL I2C Clock control register low 0x00
0x00 521C I2C_CCRH I2C Clock control register high 0x00
0x00 521D I2C_TRISER I2C TRISE register 0x02
20/58 DS12153 Rev 4
I2C
Page 21

STM8L001J3 Memory and register map
Table 6. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
Reset
status
0x00 521E
to
Reserved area (18 bytes)
0x00 522F
0x00 5230
USART_SR USART status register 0xC0
0x00 5231 USART_DR USART data register 0xXX
0x00 5232 USART_BRR1 USART baud rate register 1 0x00
0x00 5233 USART_BRR2 USART baud rate register 2 0x00
USART
0x00 5234 USART_CR1 USART control register 1 0x00
0x00 5235 USART_CR2 USART control register 2 0x00
0x00 5236 USART_CR3 USART control register 3 0x00
0x00 5237 USART_CR4 USART control register 4 0x00
0x00 5238
to
Reserved area (18 bytes)
0x00 524F
DS12153 Rev 4 21/58
27
Page 22

Memory and register map STM8L001J3
Table 6. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 5250
0x00 5251 TIM2_CR2 TIM2 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5252 TIM2_SMCR TIM2 slave mode control register 0x00
0x00 5253 TIM2_ETR TIM2 external trigger register 0x00
0x00 5254 TIM2_IER TIM2 interrupt enable register 0x00
0x00 5255 TIM2_SR1 TIM2 status register 1 0x00
0x00 5256 TIM2_SR2 TIM2 status register 2 0x00
0x00 5257 TIM2_EGR TIM2 event generation register 0x00
0x00 5258 TIM2_CCMR1 TIM2 capture/compare mode register 1 0x00
0x00 5259 TIM2_CCMR2 TIM2 capture/compare mode register 2 0x00
0x00 525A TIM2_CCER1 TIM2 capture/compare enable register 1 0x00
TIM2
0x00 525B TIM2_CNTRH TIM2 counter high 0x00
0x00 525C TIM2_CNTRL TIM2 counter low 0x00
0x00 525D TIM2_PSCR TIM2 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 525E TIM2_ARRH TIM2 auto-reload register high 0xFF
0x00 525F TIM2_ARRL TIM2 auto-reload register low 0xFF
0x00 5260 TIM2_CCR1H TIM2 capture/compare register 1 high 0x00
TIM2_CR1 TIM2 control register 1 0x00
Reset
status
0x00 5261 TIM2_CCR1L TIM2 capture/compare register 1 low 0x00
0x00 5262 TIM2_CCR2H TIM2 capture/compare register 2 high 0x00
0x00 5263 TIM2_CCR2L TIM2 capture/compare register 2 low 0x00
0x00 5264 TIM2_BKR TIM2 break register 0x00
0x00 5265 TIM2_OISR TIM2 output idle state register 0x00
0x00 5266
to
0x00 527F
Reserved area (26 bytes)
22/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 23

STM8L001J3 Memory and register map
Table 6. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 5280
TIM3_CR1 TIM3 control register 1 0x00
Reset
status
0x00 5281 TIM3_CR2 TIM3 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5282 TIM3_SMCR TIM3 slave mode control register 0x00
0x00 5283 TIM3_ETR TIM3 external trigger register 0x00
0x00 5284 TIM3_IER TIM3 interrupt enable register 0x00
0x00 5285 TIM3_SR1 TIM3 status register 1 0x00
0x00 5286 TIM3_SR2 TIM3 status register 2 0x00
0x00 5287 TIM3_EGR TIM3 event generation register 0x00
0x00 5288 TIM3_CCMR1 TIM3 capture/compare mode register 1 0x00
0x00 5289 TIM3_CCMR2 TIM3 capture/compare mode register 2 0x00
0x00 528A TIM3_CCER1 TIM3 capture/compare enable register 1 0x00
TIM3
0x00 528B TIM3_CNTRH TIM3 counter high 0x00
0x00 528C TIM3_CNTRL TIM3 counter low 0x00
0x00 528D TIM3_PSCR TIM3 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 528E TIM3_ARRH TIM3 auto-reload register high 0xFF
0x00 528F TIM3_ARRL TIM3 auto-reload register low 0xFF
0x00 5290 TIM3_CCR1H TIM3 capture/compare register 1 high 0x00
0x00 5291 TIM3_CCR1L TIM3 capture/compare register 1 low 0x00
0x00 5292 TIM3_CCR2H TIM3 capture/compare register 2 high 0x00
0x00 5293 TIM3_CCR2L TIM3 capture/compare register 2 low 0x00
0x00 5294 TIM3_BKR TIM3 break register 0x00
0x00 5295 TIM3_OISR TIM3 output idle state register 0x00
0x00 5296
to
Reserved area (74 bytes)
0x00 52DF
0x00 52E0
TIM4_CR1 TIM4 control register 1 0x00
0x00 52E1 TIM4_CR2 TIM4 control register 2 0x00
0x00 52E2 TIM4_SMCR TIM4 Slave mode control register 0x00
0x00 52E3 TIM4_IER TIM4 interrupt enable register 0x00
0x00 52E4 TIM4_SR1 TIM4 Status register 1 0x00
TIM4
0x00 52E5 TIM4_EGR TIM4 event generation register 0x00
0x00 52E6 TIM4_CNTR TIM4 counter 0x00
0x00 52E7 TIM4_PSCR TIM4 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 52E8 TIM4_ARR TIM4 auto-reload register low 0xFF
DS12153 Rev 4 23/58
27
Page 24

Memory and register map STM8L001J3
Table 6. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 52E9
to
0x00 52FE
0x00 52FF IRTIM IR_CR Infra-red control register 0x00
0x00 5300
0x00 5301 COMP_CSR Comparator status register 0x00
0x00 5302 COMP_CCS Comparator channel selection register 0x00
COMP
COMP_CR Comparator control register 0x00
Reserved area (23 bytes)
Reset
status
Table 7. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 7F00
0x00 7F01 PCE Program counter extended 0x00
0x00 7F02 PCH Program counter high 0x80
0x00 7F03 PCL Program counter low 0x00
0x00 7F04 XH X index register high 0x00
0x00 7F05 XL X index register low 0x00
0x00 7F06 YH Y index register high 0x00
CPU
A Accumulator 0x00
Reset
status
0x00 7F07 YL Y index register low 0x00
0x00 7F08 SPH Stack pointer high 0x05
0x00 7F09 SPL Stack pointer low 0xFF
0x00 7F0A CC Condition code register 0x28
0x00 7F0B
to
0x00 7F5F
0x00 7F60 CFG CFG_GCR Global configuration register 0x00
0x00 7F61
0x00 7F6F
0x00 7F70
0x00 7F71 ITC_SPR2 Interrupt Software priority register 2 0xFF
0x00 7F72 ITC_SPR3 Interrupt Software priority register 3 0xFF
0x00 7F73 ITC_SPR4 Interrupt Software priority register 4 0xFF
0x00 7F74 ITC_SPR5 Interrupt Software priority register 5 0xFF
0x00 7F75 ITC_SPR6 Interrupt Software priority register 6 0xFF
0x00 7F76 ITC_SPR7 Interrupt Software priority register 7 0xFF
0x00 7F77 ITC_SPR8 Interrupt Software priority register 8 0xFF
ITC-SPR
(1)
ITC_SPR1 Interrupt Software priority register 1 0xFF
Reserved area (85 bytes)
Reserved area (15 bytes)
24/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 25

STM8L001J3 Memory and register map
Table 7. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
Reset
status
0x00 7F78
to
Reserved area (2 bytes)
0x00 7F79
0x00 7F80 SWIM SWIM_CSR SWIM control status register 0x00
0x00 7F81
to
Reserved area (15 bytes)
0x00 7F8F
0x00 7F90
DM_BK1RE Breakpoint 1 register extended byte 0xFF
0x00 7F91 DM_BK1RH Breakpoint 1 register high byte 0xFF
0x00 7F92 DM_BK1RL Breakpoint 1 register low byte 0xFF
0x00 7F93 DM_BK2RE Breakpoint 2 register extended byte 0xFF
0x00 7F94 DM_BK2RH Breakpoint 2 register high byte 0xFF
0x00 7F95 DM_BK2RL Breakpoint 2 register low byte 0xFF
DM
0x00 7F96 DM_CR1 Debug module control register 1 0x00
0x00 7F97 DM_CR2 Debug module control register 2 0x00
0x00 7F98 DM_CSR1 Debug module control/status register 1 0x10
0x00 7F99 DM_CSR2 Debug module control/status register 2 0x00
0x00 7F9A DM_ENFCTR Enable function register 0xFF
1. Refer to Table 6: General hardware register map on page 19 (addresses 0x00 50A0 to 0x00 50A5) for a list
of external interrupt registers.
DS12153 Rev 4 25/58
27
Page 26

Interrupt vector mapping STM8L001J3
6 Interrupt vector mapping
IRQ
No.
Source
block
Description
Table 8. Interrupt mapping
Wakeup
from Halt
mode
Wakeup
from
Active-halt
mode
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFI
mode)
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFE
mode)
Vector
address
- RESET Reset Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8000
- TRAP Software interrupt - - - - 0x00 8004
0 - Reserved - - - - 0x00 8008
1 FLASH EOP/WR_PG_DIS - - Yes Yes
(1)
2-3-Reserved ----
4 AWU Auto wakeup from Halt - Yes Yes Yes
(1)
0x00 800C
0x00 8010
-0x00 8017
0x00 8018
5 - Reserved - - - - 0x00 801C
6 EXTIB External interrupt port B Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8020
7 EXTID External interrupt port D Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8024
8 EXTI0 External interrupt 0 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8028
9 EXTI1 External interrupt 1 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 802C
10 EXTI2 External interrupt 2 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8030
11 EXTI3 External interrupt 3 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8034
12 EXTI4 External interrupt 4 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8038
13 EXTI5 External interrupt 5 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 803C
14 EXTI6 External interrupt 6 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8040
15 EXTI7 External interrupt 7 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8044
16 - Reserved - - - - 0x00 8048
17 - Reserved - - - -
18 COMP Comparators - - Yes Yes
19 TIM2
Update
/Overflow/Trigger/Break
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8054
(1)
0x00 804C
-0x00 804F
0x00 8050
20 TIM2 Capture/Compare - - Yes Yes 0x00 8058
21 TIM3 Update /Overflow/Break - - Yes Yes
22 TIM3 Capture/Compare - - Yes Yes
23-
24
-Reserved ----
25 TIM4 Update /Trigger - - Yes Yes
26 SPI End of Transfer Yes Yes Yes Yes
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
0x00 805C
0x00 8060
0x00 8064-
0x00 806B
0x00 806C
0x00 8070
26/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 27

STM8L001J3 Interrupt vector mapping
Table 8. Interrupt mapping (continued)
IRQ
Source
No.
block
27 USART
Description
Transmission
complete/transmit data
Wakeup
from Halt
mode
Wakeup
from
Active-halt
mode
--YesYes
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFI
mode)
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFE
mode)
(1)
Vector
address
0x00 8074
register empty
28 USART
Receive Register DATA
FULL/overrun/idle line
--YesYes
(1)
0x00 8078
detected/parity error
29 I2C I2C interrupt
1. In WFE mode, this interrupt is served if it has been previously enabled. After processing the interrupt, the processor goes
back to WFE mode. Refer to Section Wait for event (WFE) mode in the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx microcontroller family
reference manual (RM0013).
2. The device is woken up from Halt or Active-halt mode only when the address received matches the interface address.
(2)
Yes Yes Yes Ye s
(1)
0x00 807C
DS12153 Rev 4 27/58
27
Page 28

Option bytes STM8L001J3
7 Option bytes
Option bytes contain configurations for device hardware features as well as the memory
protection of the device. They are stored in a dedicated row of the memory.
All option bytes can be modified only in ICP mode (with SWIM) by accessing the EEPROM
address. See
Refer to the How to program STM8L and STM8AL Flash program memory and data
EEPROM programming manual (PM0054) and the STM8 SWIM communication protocol
and debug module user manual (UM0470) for information on SWIM programming
procedures.
Tab le 9 for details on option byte addresses.
Table 9. Option bytes
Option
Addr. Option name
Read-out
0x4800
0x4807 - - Reserved 0x00
0x4802
0x4803 DATASIZE OPT3 DATASIZE[7:0] 0x00
0x4808
protection
(ROP)
UBC (User
Boot code size)
Independent
watchdog
option
OPT1
OPT2
byte
No.
OPT1 ROP[7:0] 0x00
OPT2 UBC[7:0] 0x00
OPT4
[1:0]
7654 3 2 1 0
Reserved
Table 10. Option byte description
ROP[7:0] Memory readout protection (ROP)
0xAA: Enable readout protection (write access via SWIM protocol)
Refer to Read-out protection section in the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx
microcontroller family reference manual (RM0013) for details.
UBC[7:0] Size of the user boot code area
0x00: no UBC
0x01-0x02: UBC contains only the interrupt vectors.
0x03: Page 0 and 1 reserved for the interrupt vectors. Page 2 is available to
store user boot code. Memory is write protected
...
0x7F - Page 0 to 126 reserved for UBC, memory is write protected
Refer to User boot area (UBC) section in the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx
microcontroller family reference manual (RM0013) for more details.
UBC[7] is forced to 0 internally by HW.
Option bits Factory
default
setting
IWDG
_HALT
IWDG
_HW
0x00
28/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 29

STM8L001J3 Option bytes
Table 10. Option byte description (continued)
DATASIZE[7:0] Size of the data EEPROM area
0x00: no data EEPROM area
0x01: 1 page reserved for data storage from 0x9FC0 to 0x9FFF
0x02: 2 pages reserved for data storage from 0x9F80 to 0x9FFF
OPT3
OPT4
...
0x20: 32 pages reserved for data storage from 0x9800 to 0x9FFF
Refer to Data EEPROM (DATA) section in the STM8L001xx, STM8L101xx
microcontroller family reference manual (RM0013) for more details.
DATASIZE[7:6] are forced to 0 internal by HW.
IWDG_HW: Independent watchdog
0: Independent watchdog activated by software
1: Independent watchdog activated by hardware
IWDG_HALT: Independent window watchdog reset on Halt/Active-halt
0: Independent watchdog continues running in Halt/Active-halt mode
1: Independent watchdog stopped in Halt/Active-halt mode
Caution: After a device reset, read access to the program memory is not guaranteed if address
0x4807 is not programmed to 0x00.
DS12153 Rev 4 29/58
29
Page 30

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
50 pF
STM8L PIN
MS32617V1
8 Electrical parameters
8.1 Parameter conditions
Unless otherwise specified, all voltages are referred to VSS.
8.1.1 Minimum and maximum values
Unless otherwise specified the minimum and maximum values are guaranteed in the worst
conditions of ambient temperature, supply voltage and frequencies by tests in production on
100% of the devices with an ambient temperature at T
the selected temperature range).
Data based on characterization results, design simulation and/or technology characteristics
are indicated in the table footnotes and are not tested in production. Based on
characterization, the minimum and maximum values refer to sample tests and represent the
mean value plus or minus three times the standard deviation (mean±3
8.1.2 Typical values
= 25 °C and TA = TA max (given by
A
∑).
Unless otherwise specified, typical data are based on TA = 25 °C, V
only as design guidelines and are not tested.
8.1.3 Typical curves
Unless otherwise specified, all typical curves are given only as design guidelines and are
not tested.
8.1.4 Loading capacitor
The loading conditions used for pin parameter measurement are shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Pin loading conditions
= 3 V. They are given
DD
30/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 31

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
MS32618V1
V
IN
STM8L PIN
8.1.5 Pin input voltage
The input voltage measurement on a pin of the device is described in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Pin input voltage
8.2 Absolute maximum ratings
Stresses above the absolute maximum ratings listed in Tab le 11: Voltage characteristics,
Tab le 12: Current characteristics and Table 13: Thermal characteristics may cause
permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of
the device at these conditions is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability. The device mission profile is compliant with
the JEDEC JESD47 qualification standard; extended mission profiles are available on
demand.
Table 11. Voltage characteristics
Symbol Ratings Min Max Unit
- V
V
DD
SS
V
IN
External supply voltage -0.3 4.0
Input voltage on any pin
(1)
VSS-0.3 VDD+0.3
see Absolute maximum
V
ESD
Electrostatic discharge voltage
ratings (electrical sensitivity)
on page 51
1. I
must never be exceeded. This is implicitly insured if VIN maximum is respected. If VIN maximum
INJ(PIN)
cannot be respected, the injection current must be limited externally to the I
injection is induced by V
while a negative injection is induced by VIN<VSS.
IN>VDD
value. A positive
INJ(PIN)
V
-
DS12153 Rev 4 31/58
52
Page 32

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Table 12. Current characteristics
Symbol Ratings Max. Unit
I
VDD
I
VSS
I
IO
Total current into V
Total current out of V
Output current sunk by IR_TIM pin (with high sink LED
driver capability)
power line (source) 80
DD
ground line (sink) 80
SS
80
Output current sunk by any other I/O and control pin 25
Output current sourced by any I/Os and control pin -25
I
INJ(PIN)
ΣI
INJ(PIN)
1. I
2. When several inputs are submitted to a current injection, the maximum ΣI
must never be exceeded. This is implicitly insured if VIN maximum is respected. If VIN maximum
INJ(PIN)
cannot be respected, the injection current must be limited externally to the I
injection is induced by VIN>VDD while a negative injection is induced by VIN<VSS.
positive and negative injected currents (instantaneous values). These results are based on characterization
with ΣI
INJ(PIN)
Injected current on any pin
Total injected current (sum of all I/O and control pins)
maximum current injection on four I/O port pins of the device.
Table 13. Thermal characteristics
(1)
(2)
value. A positive
INJ(PIN)
is the absolute sum of the
INJ(PIN)
±5
±25
Symbol Ratings Value Unit
T
STG
T
Storage temperature range -65 to +150
Maximum junction temperature 150
J
mA
° C
32/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 33

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
8.3 Operating conditions
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA.
8.3.1 General operating conditions
Table 14. General operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
(1)
f
MASTER
V
DD
(2)
P
D
T
A
T
J
1. f
2. To calculate P
= f
MASTER
Θ
JA
CPU
in table “Thermal characteristics”
Master clock frequency 1.8 V ≤ V
Standard operating voltage - 1.8 3.6 V
Power dissipation at TA= 125 °C
for suffix 3 devices
Temperature range
Junction temperature range
) use the formula given in thermal characteristics P
Dmax(TA
1.8 V ≤ V
(3 suffix version)
-40 °C ≤ T
(3 suffix version)
< 3.6 V 0 16 MHz
DD
SO8N - 49 mW
< 3.6 V
DD
A
Dmax
≤ 125 °C
=(T
-TA)/ΘJA with T
Jmax
− 40 125 °C
- 40 130 °C
in this table and
Jmax
DS12153 Rev 4 33/58
52
Page 34

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
8.3.2 Power-up / power-down operating conditions
Table 15. Operating conditions at power-up / power-down
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
t
VDD
t
TEMP
V
POR
V
PDR
1. Guaranteed by characterization results.
2. Correct device reset during power on sequence is guaranteed when t
circuit is recommended to ensure correct device reset during power down, when V
3. Tested in production.
VDD rise time rate - 20 - 1300 µs/V
Reset release delay VDD rising - 1 - ms
Power on reset
(1)(2)
threshold
Power down reset
(1)(2)
threshold
8.3.3 Supply current characteristics
Total current consumption
The MCU is placed under the following conditions:
• All I/O pins in input mode with a static value at VDD or VSS (no load)
• All peripherals are disabled except if explicitly mentioned.
- 1.35 - 1.65
(3)
- 1.40 - 1.60 V
is respected. External reset
VDD[max]
< VDD < V
PDR
DD[min]
.
V
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA.
34/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 35

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
1. Based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
2. All peripherals off, VDD from 1.8 V to 3.6 V, HSI internal RC osc., f
3. Maximum values are given for TA = − 40 to 125 °C.
4. CPU executing typical data processing.
5. An approximate value of I
6. Tested in production.
Figure 6. I
Table 16. Total current consumption in Run mode
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Code executed from
RAM
Supply
I
DD (Run)
I
DD(Run)
DD(RUN)
current in
Run
mode
= f
MASTER
vs. V
(4) (5)
Code executed from
can be given by the following formula:
DD(Run)
x 150 µA/MHz +215 µA.
DD, fCPU
= 2 MHz Figure 7. I
Flash
(2)
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
(1)
Typ M ax
= 2 MHz 0.39 0.60
= 4 MHz 0.55 0.70
= 8 MHz 0.90 1.20
= 16 MHz 1.60 2.10
= 2 MHz 0.55 0.70
= 4 MHz 0.88 1.80
= 8 MHz 1.50 2.50
= 16 MHz 2.70 3.50
CPU=fMASTER
DD(RUN)
vs. VDD, f
= 16 MHz
CPU
(3)
(6)
Unit
mA
1. Typical current consumption measured with code executed from Flash.
DS12153 Rev 4 35/58
52
Page 36

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
I
1. Based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
2. Maximum values are given for TA = -40 to 125 °C.
Figure 8. I
Table 17. Total current consumption in Wait mode
(1)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ Max
= 2 MHz 245 400
= 4 MHz 300 450
= 8 MHz 380 600
= 16 MHz 510 800
DD(WAIT)
vs. VDD, f
= 16 MHz
CPU
DD (Wait)
DD(WAIT)
Supply
current in
Wait mode
vs. VDD, f
CPU not clocked,
all peripherals off,
HSI internal RC osc.
= 2 MHz Figure 9. I
CPU
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
f
MASTER
(2)
Unit
µA
1. Typical current consumption measured with code executed from Flash.
36/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 37

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
Table 18. Total current consumption and timing in Halt and Active-halt mode at
V
= 1.8 V to 3.6 V
DD
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ Max Unit
I
DD(AH)
I
DD(WUFAH)
t
WU(AH)
I
DD(Halt)
I
DD(WUFH)
Supply current in Active-halt
mode
Supply current during
wakeup time from Active-halt
mode
Wakeup time from Active-
(3)
halt mode to Run mode
Supply current in Halt mode
Supply current during
wakeup time from Halt mode
LSI RC osc.
(at 37 kHz)
--2-mA
= 16 MHz 4 6.5 μs
f
CPU
TA = -40 °C to 25 °C 0.35 1.2
T
= 55 °C 0.6 1.8 μA
A
= 85 °C 1 2.5
T
A
= 105 °C 2.5 6.5 μA
T
A
T
= 125 °C 5.4 12
A
(1)(2)
T
= -40 °C to 25 °C 0.8 2 μA
A
= 55 °C 1 2.5 μA
T
A
= 85 °C 1.4 3.2 μA
T
A
T
= 105 °C 2.9 7.5 μA
A
= 125 °C 5.8 13 μA
T
A
(4)
(4)
(4)
2-mA
μA
μA
μA
Wakeup time from Halt mode
t
1. T
2. Guaranteed by characterization results.
3. Measured from interrupt event to interrupt vector fetch.
4. Tested in production.
(3)
WU(Halt)
= -40 to 125 °C, no floating I/O, unless otherwise specified.
A
To get tWU for another CPU frequency use tWU(FREQ) = tWU(16 MHz) + 1.5 (T
The first word of interrupt routine is fetched 5 CPU cycles after t
to Run mode
Figure 10. Typ. I
DD(Halt)
= 16 MHz 4 6.5 μs
f
CPU
.
WU
vs. V
DD, fCPU
= 2 MHz and 16 MHz
FREQ-T16 MHz
).
1. Typical current consumption measured with code executed from Flash.
DS12153 Rev 4 37/58
52
Page 38

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Current consumption of on-chip peripherals
Measurement made for f
MASTER
Table 19. Peripheral current consumption
= from 2 MHz to 16 MHz
Symbol Parameter Typ. V
I
DD(TIM2)
I
DD(TIM3)
I
DD(TIM4)
I
DD(USART)
I
DD(SPI)
I
DD(I2C1)
I
DD(COMP)
1. Data based on a differential IDD measurement between all peripherals off and a timer counter running at
16 MHz. The CPU is in Wait mode in both cases. No IC/OC programmed, no I/O pin toggling. not tested in
production.
2. Data based on a differential IDD measurement between the on-chip peripheral when kept under reset and
not clocked and the on-chip peripheral when clocked and not kept under reset. The CPU is in Wait mode in
both cases. No I/O pin toggling. Not tested in production.
TIM2 supply current
TIM3 supply current
TIM4 timer supply current
USART supply current
SPI supply current
I2C supply current
Comparator supply current
(1)
(1)
9
(1)
(2)
(2)
(2)
8.3.4 Clock and timing characteristics
Internal clock sources
= 3.0 V Unit
DD
9
4
µA/MHz
7
4
4
(2)
20 µA
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA.
High speed internal RC oscillator (HSI)
Table 20. HSI oscillator characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
f
Frequency VDD = 3.0 V - 16 - MHz
HSI
= 3.0 V, TA = 25 °C -5 - 5 %
V
ACC
Accuracy of HSI
HSI
oscillator
(factory calibrated)
I
DD(HSI)
1. V
2. Guaranteed by characterization results.
HSI oscillator power
consumption
= 3.0 V, TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
DD
DD
1.8 V ≤ V
-40 °C ≤ T
≤ 3.6 V,
DD
≤ 125 °C
A
- - 70 100
-7.5
(1)
(2)
-7.5
(2)
(2)
µA
%
38/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 39

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
Low speed internal RC oscillator (LSI)
Table 21. LSI oscillator characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
(1)
f
f
drift(LSI)
1. V
2. For each individual part, this value is the frequency drift from the initial measured frequency.
Frequency - 26 38 56 kHz
LSI
LSI oscillator frequency
(2)
drift
= 1.8 V to 3.6 V, TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
DD
Figure 11. Typical LSI RC frequency vs. V
8.3.5 Memory characteristics
0 °C ≤ TA ≤ 85 °C -12 - 11 %
DD
TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
Table 22. RAM and hardware registers
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
RM
1. Minimum supply voltage without losing data stored in RAM (in Halt mode or under Reset) or in hardware
registers (only in Halt mode). Guaranteed by characterization results.
Data retention mode
(1)
Halt mode (or Reset) 1.65 - - V
Flash memory
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
V
Operating voltage
DD
(all modes, read/write/erase)
Programming time for 1- or 64-byte (block)
erase/write cycles (on programmed byte)
t
prog
Programming time for 1- to 64-byte (block)
write cycles (on erased byte)
Table 23. Flash program memory
f
MASTER
DS12153 Rev 4 39/58
= 16 MHz 1.8 - 3.6 V
--6-ms
--3-ms
Max
(1)
Unit
52
Page 40

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Table 23. Flash program memory (continued)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
TA=+25 °C, VDD = 3.0 V -
I
t
N
1. Guaranteed by characterization results.
2. Retention guaranteed after cycling is 10 years at 55 °C.
3. Retention guaranteed after cycling is 1 year at 55 °C.
4. Data based on characterization performed on the whole data memory (2 Kbytes).
Programming/ erasing consumption
prog
Data retention (program memory)
after 10k erase/write cycles
= +85 °C
at T
A
Data retention (data memory)
after 10k erase/write cycles
RET
at T
= +85 °C
A
Data retention (data memory)
after 300k erase/write cycles
= +125 °C
at T
A
Erase/write cycles (program memory) See notes
RW
Erase/write cycles
(data memory) See notes
=+25 °C, VDD = 1.8 V - -
T
A
100
100
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)(4)
T
= 55 °C 20
RET
T
= 55 °C 20
RET
T
= 85 °C 1
RET
(1)(2)
(1)(3)
8.3.6 I/O port pin characteristics
Max
(1)
Unit
-
0.7
mA
--
--
years
--
- - cycles
- - kcycles
General characteristics
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA unless otherwise specified. All
unused pins must be kept at a fixed voltage: using the output mode of the I/O for example or
an external pull-up or pull-down resistor.
Table 24. I/O static characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
V
V
V
Input low level voltage
IL
Input high level voltage
IH
Schmitt trigger voltage hysteresis
hys
(2)
(2)
All I/Os VSS-0.3 - 0.3 x V
All I/Os 0.70 x V
Standard I/Os - 200 -
(3)
True open drain I/Os - 250 -
V
≤ VIN ≤ V
SS
DD
Standard I/Os
V
≤ VIN ≤ V
Input leakage current
I
lkg
(4)
SS
True open drain I/Os
V
≤ VIN ≤ V
SS
DD
DD
PA0 with high sink LED
driver capability
R
C
Weak pull-up equivalent resistor
PU
(7)
I/O pin capacitance - - 5
IO
(6)
V
= V
IN
SS
(1)
DD
-VDD+0.3 V
- - 50
- - 200
- - 200
30 45 60 kΩ
(8)
Max Unit
V
DD
mV
(5)
(5)
nA
(5)
-pF
40/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 41

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
1. VDD = 3.0 V, TA = -40 to 85 °C unless otherwise specified.
2. Guaranteed by characterization results.
3. Hysteresis voltage between Schmitt trigger switching levels. Guaranteed by characterization results.
4. The max. value may be exceeded if negative current is injected on adjacent pins.
5. Not tested in production.
pull-up equivalent resistor based on a resistive transistor (corresponding I
6. R
PU
Figure 14).
7. Guaranteed by design.
8. Capacitance per one GPIO on pin. Complete pin capacitance depends on how many GPIOs are connected on a given pin
(see Table 3). Total pin capacitance is then N x C
(where N = number of GPIOs on a given pin).
IO
current characteristics described in
PU
Figure 12. Typical VIL and V
Figure 13. Typical V
and V
IL
vs. VDD (High sink I/Os)
IH
vs. VDD (true open drain I/Os)
IH
DS12153 Rev 4 41/58
52
Page 42

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Figure 14. Typical pull-up resistance RPU vs. VDD with VIN=V
Figure 15. Typical pull-up current IPU vs. VDD with VIN=V
SS
SS
42/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 43

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
Output driving current
Subject to general operating conditions for V
I/O
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
Type
(1)
V
OL
Standard
(2)
V
OH
1. The IIO current sunk must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the sum
of I
(I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
IO
2. The IIO current sourced must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the
sum of I
(I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
IO
Table 25. Output driving current (High sink ports)
Output low level voltage for an I/O pin
Output high level voltage for an I/O pin
and TA unless otherwise specified.
DD
= +2 mA,
I
VSS
.
VDD
.
IO
V
= 3.0 V
DD
I
= +2 mA,
IO
V
= 1.8 V
DD
= +10 mA,
I
IO
= 3.0 V
V
DD
I
= -2 mA,
IO
V
= 3.0 V
DD
I
= -1 mA,
IO
V
= 1.8 V
DD
= -10 mA,
I
IO
V
= 3.0 V
DD
-0.45V
-0.45V
-1.2V
V
-0.45 - V
DD
-0.45 - V
V
DD
-1.2 - V
V
DD
Table 26. Output driving current (true open drain ports)
I/O
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
Typ e
I
= +3 mA,
IO
V
= 3.0 V
(1)
V
Output low level voltage for an I/O pin
OL
Open drain
1. The IIO current sunk must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the sum
of IIO (I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
VSS
.
DD
= +1 mA,
I
IO
= 1.8 V
V
DD
-0.45V
-0.45V
Table 27. Output driving current (PA0 with high sink LED driver capability)
I/O
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
Typ e
= +20 mA,
(1)
V
IR
1. The IIO current sunk must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the sum
of IIO (I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
Output low level voltage for an I/O pin
OL
VSS
.
I
IO
V
DD
= 2.0 V
-0.9V
DS12153 Rev 4 43/58
52
Page 44

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Figure 16. Typ. VOL at VDD = 3.0 V (High sink
ports)
Figure 18. Typ. VOL at VDD = 3.0 V (true open
drain ports)
Figure 17. Typ. VOL at VDD = 1.8 V (High sink
ports)
Figure 19. Typ. VOL at VDD = 1.8 V (true open
drain ports)
Figure 20. Typ. V
DD
- V
at VDD = 3.0 V (High
OH
Figure 21. Typ. V
sink ports)
44/58 DS12153 Rev 4
- V
DD
at VDD = 1.8 V (High
OH
sink ports)
Page 45

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
8.3.7 Communication interfaces
Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
Unless otherwise specified, the parameters given in Tab le 28 are derived from tests
performed under ambient temperature, f
conditions summarized in
Section 8.3.1. Refer to I/O port characteristics for more details on
MASTER
the input/output alternate function characteristics (NSS, SCK, MOSI, MISO).
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Table 28. SPI characteristics
frequency and VDD supply voltage
(1)
Min Max Unit
f
SCK
1/t
c(SCK)
t
r(SCK)
t
f(SCK)
t
su(NSS)
t
h(NSS)
t
w(SCKH)
t
w(SCKL)
t
su(MI)
t
su(SI)
t
h(MI)
t
h(SI)
t
a(SO)
t
dis(SO)
t
v(SO)
t
v(MO)
t
h(SO)
t
h(MO)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)(3)
(2)(4)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
SPI clock frequency
Master mode 0 8
Slave mode 0 8
SPI clock rise and fall time Capacitive load: C = 30 pF - 30
NSS setup time Slave mode 4 x T
MASTER
NSS hold time Slave mode 80 -
(2)
SCK high and low time
(2)
Master mode,
MASTER
= 8 MHz, f
f
SCK
= 4 MHz
105 145
Master mode 30 -
Data input setup time
Slave mode 3 -
Master mode 15 -
Data input hold time
Slave mode 0 -
Data output access time Slave mode - 3x T
Data output disable time Slave mode 30 -
Data output valid time Slave mode (after enable edge) - 60
Data output valid time
Master mode
(after enable edge)
-20
Slave mode (after enable edge) 15 -
Data output hold time
Master mode
(after enable edge)
1-
MHz
-
ns
MASTER
1. Parameters are given by selecting 10-MHz I/O output frequency.
2. Values based on design simulation and/or characterization results, and not tested in production.
3. Min time is for the minimum time to drive the output and max time is for the maximum time to validate the data.
4. Min time is for the minimum time to invalidate the output and max time is for the maximum time to put the data in Hi-Z.
DS12153 Rev 4 45/58
52
Page 46

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
ai14135b
NSS input
t
SU(NSS)
tc(SCK)
th(NSS)
SCK input
CPHA=1
CPOL=0
CPHA=1
CPOL=1
t
w(SCKH)
tw(SCKL)
ta(SO)
tv(SO)
th(SO)
tr(SCK)
tf(SCK)
tdis(SO)
MISO
OUTPUT
MOSI
INPUT
t
su(SI)
th(SI)
MSB OUT
MSB IN
BIT6 OUT
LSB OUT
LSB IN
BIT 1 IN
Figure 22. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 0
Figure 23. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 1
1. Measurement points are done at CMOS levels: 0.3V
and 0.7V
DD
(1)
DD.
46/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 47

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
ai14136d
SCK Output
CPHA=0
MOSI
OUTPUT
MISO
INP U T
CPHA=0
LSB OUT
LSB IN
CPOL=0
CPOL=1
B I T1 OUT
NSS input
t
c(SCK)
t
w(SCKH)
t
w(SCKL)
t
r(SCK)
t
f(SCK)
t
h(MI)
High
SCK Output
CPHA=1
CPHA=1
CPOL=0
CPOL=1
t
su(MI)
t
v(MO)
t
h(MO)
MSB IN
BIT6 IN
MSB OUT
Figure 24. SPI timing diagram - master mode
(1)
1. Measurement points are done at CMOS levels: 0.3V
and 0.7V
DD
DD.
DS12153 Rev 4 47/58
52
Page 48

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Inter IC control interface (I2C)
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD,
f
MASTER
, and TA unless otherwise
specified.
The STM8L I2C interface meets the requirements of the Standard I2C communication
protocol described in the following table with the restriction mentioned below:
Refer to I/O port characteristics for more details on the input/output alternate function
characteristics (SDA and SCL).
Symbol Parameter
t
w(SCLL)
t
w(SCLH)
t
su(SDA)
t
h(SDA)
t
r(SDA)
t
r(SCL)
t
f(SDA)
t
f(SCL)
t
h(STA)
t
su(STA)
t
su(STO)
t
w(STO:STA)
C
1. f
SCK
Data based on standard I
2.
The maximum hold time of the START condition has only to be met if the interface does not stretch the low
3.
period of SCL signal.
The device must internally provide a hold time of at least 300 ns for the SDA signal in order to bridge the
4.
undefined region of the falling edge of SCL
SCL clock low time 4.7 - 1.3 -
SCL clock high time 4.0 - 0.6 -
SDA setup time 250 - 100 -
SDA data hold time 0
SDA and SCL rise time - 1000 - 300
SDA and SCL fall time - 300 - 300
START condition hold time 4.0 - 0.6 -
Repeated START condition setup
time
STOP condition setup time 4.0 - 0.6 - μs
STOP to START condition time
(bus free)
Capacitive load for each bus line - 400 - 400 pF
b
must be at least 8 MHz to achieve max fast I2C speed (400 kHz).
2
Table 29. I2C characteristics
Standard mode
I2C
(2)
Min
4.7 - 0.6 -
4.7 - 1.3 - μs
C protocol requirement, not tested in production.
).
(3)
Max
-0
Fast mode I2C
(2)
Min
(4)
(2)
Max
900
(1)
(2)
(3)
Unit
μs
ns
μs
Note: For speeds around 200 kHz, achieved speed can have ± 5% tolerance
For other speed ranges, achieved speed can have ± 2% tolerance
The above variations depend on the accuracy of the external components used.
48/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 49

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
Typical application with I2C bus and timing diagram
VDD
4.7kΩ 4.7kΩ
VDD
100Ω
100Ω
SDA
SCL
STM8L
I2C BUS
SDA
tf(SDA)
SCL
Figure 25.
Start
tr(SDA) tsu(SDA) th(SDA)
1. Measurement points are done at CMOS levels: 0.3 x VDD and 0.7 x V
8.3.8 Comparator characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
Table 30. Comparator characteristics
DD.
tsu(STA)
tsu(STO)th(STA) tw(SCLH) tw(SCLL) tr(SCL) tf(SCL)
(1)
(1)
Repeated start
tw(STO:STA)
Stop
Typ Max
Start
MS32620V2
(1)
Unit
V
IN(COMP_REF)
V
IN
(2)
V
offset
t
START
I
DD(COMP)
(2)
t
propag
Comparator external reference - -0.1 - VDD-1.25 V
Comparator input voltage range - -0.25 - VDD+0.25 V
Comparator offset error - - - ± 20 mV
Startup time (after BIAS_EN) - - - 3
Analog comparator consumption - - - 25
Analog comparator consumption
during power-down
---60
100-mV input step
Comparator propagation delay
with 5-mV overdrive,
--2
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
input rise time = 1 ns
1. Guaranteed by design.
2. The comparator accuracy depends on the environment. In particular, the following cases may reduce the accuracy of the
comparator and must be avoided:
- Negative injection current on the I/Os close to the comparator inputs
- Switching on I/Os close to the comparator inputs
- Negative injection current on not used comparator input.
- Switching with a high dV/dt on not used comparator input.
These phenomena are even more critical when a big external serial resistor is added on the inputs.
µs
µA
nA
µs
DS12153 Rev 4 49/58
52
Page 50

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
8.3.9 EMC characteristics
Susceptibility tests are performed on a sample basis during product characterization.
Functional EMS (electromagnetic susceptibility)
Based on a simple running application on the product (toggling 2 LEDs through I/O ports),
the product is stressed by two electromagnetic events until a failure occurs (indicated by the
LEDs).
• ESD: Electrostatic discharge (positive and negative) is applied on all pins of the device
until a functional disturbance occurs. This test conforms with the IEC 61000-4-2
standard.
• FTB: A burst of fast transient voltage (positive and negative) is applied to V
through a 100 pF capacitor, until a functional disturbance occurs. This test conforms
with the IEC 61000-4-4 standard.
A device reset allows normal operations to be resumed. The test results are given in the
table below based on the EMS levels and classes defined in application note AN1709.
Designing hardened software to avoid noise problems
EMC characterization and optimization are performed at component level with a typical
application environment and simplified MCU software. It should be noted that good EMC
performance is highly dependent on the user application and the software in particular.
and VSS
DD
Therefore it is recommended that the user applies EMC software optimization and
prequalification tests in relation with the EMC level requested for his application.
Prequalification trials:
To complete these trials, ESD stress can be applied directly on the device, over the range of
specification values. When unexpected behavior is detected, the software can be hardened
to prevent unrecoverable errors occurring. Refer to application note Software techniques for
improving microcontrollers EMC performance (AN1015).
Symbol Parameter Conditions
V
V
FESD
Voltage limits to be applied on any I/O pin to
induce a functional disturbance
Fast transient voltage burst limits to be
applied through 100 pF on VDD and V
EFTB
pins to induce a functional disturbance
Table 31. EMS data
SO8N, V
SO8N, V
SS
SO8N, V
= 3.3 V TBD
DD
= 3.3 V, f
DD
= 3.3 V, f
DD
HSI
/2 TBD
HSI
Level/
Class
TBD
50/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 51

STM8L001J3 Electrical parameters
Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Based on a simple application running on the product (toggling 2 LEDs through the I/O
ports), the product is monitored in terms of emission. This emission test is in line with the
norm SAE J 1752/3 which specifies the board and the loading of each pin.
Table 32. EMI data
(1)
Max vs.
Unit
16 MHz
dBμV30 MHz to 130 MHz TBD
Symbol Parameter Conditions
V
= 3.6 V,
DD
TA = +25 °C,
EMI
Peak level
S
SO8N
conforming to
IEC61967-2
1. Not tested in production.
Monitored
frequency band
0.1 MHz to 30 MHz TBD
130 MHz to 1 GHz TBD
SAE EMI Level TBD -
Absolute maximum ratings (electrical sensitivity)
Based on two different tests (ESD and LU) using specific measurement methods, the
product is stressed in order to determine its performance in terms of electrical sensitivity.
For more details, refer to the application note AN1181.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharges (a positive then a negative pulse separated by 1 second) are
applied to the pins of each sample according to each pin combination. The sample size
depends on the number of supply pins in the device (3 parts*(n+1) supply pin).
This test conforms to the JESD22-A114A/A115A standard.
Table 33. ESD absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Ratings Conditions
V
ESD(HBM)
V
ESD(CDM)
1. Guaranteed by characterization results.
Electrostatic discharge voltage
(human body model)
Electrostatic discharge voltage
(charge device model)
= +25 °C
T
A
DS12153 Rev 4 51/58
Maximum
(1)
value
TBD
TBD
Unit
V
52
Page 52

Electrical parameters STM8L001J3
Static latch-up
• LU: 2 complementary static tests are required on 10 parts to assess the latch-up
performance. A supply overvoltage (applied to each power supply pin) and a current
injection (applied to each input, output and configurable I/O pin) are performed on each
sample. This test conforms to the EIA/JESD 78 IC latch-up standard. For more details,
refer to the application note AN1181.
Symbol Parameter Class
LU Static latch-up class TBD
Table 34. Electrical sensitivities
8.4 Thermal characteristics
The maximum chip junction temperature (T
) must never exceed the values given in
Jmax
Tab le 14: General operating conditions on page 33.
The maximum chip-junction temperature, T
, in degrees Celsius, may be calculated
Jmax
using the following equation:
T
Jmax
= T
Amax
+ (P
Dmax
x ΘJA)
Where:
• T
•Θ
• P
• P
is the maximum ambient temperature in °C
Amax
is the package junction-to-ambient thermal resistance in °C/W
JA
is the sum of P
Dmax
is the product of I
INTmax
INTmax
DD
and P
I/Omax (PDmax
= P
INTmax
+ P
and VDD, expressed in watts. This is the maximum chip
I/Omax
)
internal power.
• P
represents the maximum power dissipation on output pins
I/Omax
where:
P
I/Omax =
taking into account the actual V
Σ (VOL*IOL) + Σ((VDD-V
OH)*IOH
OL/IOL and VOH/IOH
),
of the I/Os at low and high level in
the application.
Table 35. Thermal characteristics
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
Θ
JA
1. Thermal resistances are based on JEDEC JESD51-2 with 4-layer PCB in a natural convection
environment.
Thermal resistance junction-ambient SO8N 102 °C/W
(1)
52/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 53

STM8L001J3 Package information
SO-A_V2
E1
8
ccc
b
D
c
1
E
h x 45˚
A2
k
0.25 mm
L
A1
GAUGE PLANE
e
A
L1
9 Package information
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at:
ECOPACK® is an ST trademark.
Failure analysis and guarantee
The small number of pins available induces limitations on failure analysis depth in case of
isolated symptom, typically with an impact lower than 0.1%. Please contact your sales office
for additional information for any failure analysis. STMicroelectronics will make a feasibility
study for investigation based on failure rate and symptom description prior to responsibility
endorsement.
9.1 SO8N package information
Figure 26. SO8N – 8-lead, 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width,
package outline
www.st.com.
1. Drawing is not to scale.
Table 36. SO8N – 8-lead 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width,
package mechanical data
millimeters inches
Symbol
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A - - 1.750 - - 0.0689
A1 0.100 - 0.250 0.0039 - 0.0098
A2 1.250 - - 0.0492 - -
b 0.280 - 0.480 0.0110 - 0.0189
c 0.170 - 0.230 0.0067 - 0.0091
DS12153 Rev 4 53/58
(1)
56
Page 54

Package information STM8L001J3
O7_FP_V1
1.27
0.6 (x8)
3.9
6.7
Table 36. SO8N – 8-lead 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width,
package mechanical data (continued)
millimeters inches
Symbol
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
D 4.800 4.900 5.000 0.1890 0.1929 0.1969
E 5.800 6.000 6.200 0.2283 0.2362 0.2441
E1 3.800 3.900 4.000 0.1496 0.1535 0.1575
e - 1.270 - - 0.0500 -
h 0.250 - 0.500 0.0098 - 0.0197
k 0° - 8° 0° - 8°
L 0.400 - 1.270 0.0157 - 0.0500
L1 - 1.040 - - 0.0409 -
ccc - - 0.100 - - 0.0039
1. Values in inches are converted from mm and rounded to four decimal digits.
(1)
Figure 27. SO8N – 8-lead 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils body width,
package recommended footprint
1. Dimensions are expressed in millimeters.
2. Drawing is not to scale.
54/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 55

STM8L001J3 Package information
MSv46327V1
8L001J3
R Y WW
Product identification
Additional information
Date code
Unmarkable surface
PIN1 reference
Device marking for SO8N – 8-lead 4.9 x 6 mm, plastic small outline, 150 mils
body width
The following figure gives an example of topside marking orientation versus pin 1 identifier
location.
The printed markings may differ depending on the supply chain.
Other optional marking or inset/upset marks, which identify the parts throughout supply
chain operations, are not indicated below.
Figure 28. Example of SO8N marking (package top view)
1. Parts marked as ES or E or accompanied by an Engineering Sample notification letter are not yet qualified
and therefore not approved for use in production. ST is not responsible for any consequences resulting
from such use. In no event will ST be liable for the customer using any of these engineering samples in
production. ST's Quality department must be contacted prior to any decision to use these engineering
samples to run a qualification activity.
DS12153 Rev 4 55/58
56
Page 56

Ordering information STM8L001J3
10 Ordering information
Table 37. Ordering information scheme
Example: STM8 L 001 J 3 M 3
Device family
STM8 microcontroller
Family type
L = Low power
Sub family type
00x = Value line sub-family
001 = Low density
Pin count
J = 8 pins
Program memory size
3 = 8 Kbytes
Package
M = SO8N
Temperature range
3 = -40°C to 125°C
1. For a list of available options (e.g. memory size, package) and order-able part numbers or for further
information on any aspect of this device, please go to www.st.com or contact the ST Sales Office nearest to
you.
56/58 DS12153 Rev 4
Page 57

STM8L001J3 Revision history
11 Revision history
Table 38. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
06-Jun-2017 1 Initial release.
Updated:
– Document’s confidentiality level to public
– Section 1: Introduction
04-Oct-2017 2
– Section 2: Description
– Section 9: Package information
– Figure 23: SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 1
– Figure 24: SPI timing diagram - master mode
– Figure 25: Typical application with I2C bus and timing diagram (1)
Updated:
04-Jul-2018 3
– Recommendations for SWIM pin (pin#1) on Section 3.3: Single wire
data interface (SWIM) and debug module
Deleted:
– Figure: Typical HSI frequency vs. VDD
10-Sep-2020 4
– Figure: Typical HSI accuracy vs. temperature, VDD = 3 V
– Figure: Typical HSI accuracy vs. temperature, VDD = 1.8 V to 3.6 V
Updated:
– Table 20: HSI oscillator characteristics
(1)
(1)
DS12153 Rev 4 57/58
57
Page 58

STM8L001J3
IMPORTANT NOTICE – PLEASE READ CAREFULLY
STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, enhancements, modifications, and
improvements to ST products and/or to this document at any time without notice. Purchasers should obtain the latest relevant information on
ST products before placing orders. ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale in place at the time of order
acknowledgment.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection, and use of ST products and ST assumes no liability for application assistance or
the design of Purchasers’ products.
No license, express or implied, to any intellectual property right is granted by ST herein.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the information set forth herein shall void any warranty granted by ST for such product.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks of ST. For additional information about ST trademarks, please refer to www.st.com/trademarks. All other
product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces information previously supplied in any prior versions of this document.
© 2020 STMicroelectronics – All rights reserved
58/58 DS12153 Rev 4
 Loading...
Loading...