Page 1
®
STEERING
CONTROL
GENERATOR
LEFT
RIGHT
INPUTS
RIGHT
SURROUND
LEFT
SURROUND
CENTER
RIGHT
LEFT
RESET
SERIAL BUS
OUTPUTS
L+R FOR
SUBWOOFER
STEERING MATRIX
AND OUTPUT
AMPLIFIERS
ANALOG
SIGNAL
PROCESSING
MODE CONTROL
LOGIC AND NOISE
GENERATOR
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
SSM2005
CENTER OUT
R FILTER IN
R FILTER OUT
L FILTER IN
L FILTER OUT
L OUT
L OUT A
L IN
R OUT
R OUT A
R IN
V
EE
ACOM AUDIO GND
GND
V
CC
(L+R) OUT
(L–R) OUT
(L–R) HIGH IN
(L–R) LOW IN
R HIGH BAND DET.
L HIGH BAND DET.
HIGH BAND DET. OUT
R LOW BAND DET.
L LOW BAND DET.
LOW BAND DET. OUT
LF OUT
RF OUT
LS OUT
RS OUT
NOISE IN
NOISE OUT
LOAD
RESET
DATA IN
V
CC
ACOM AUDIO GND
GND
V
EE
WRITE
CLOCK IN
FRONT/REAR TC FILTER
LOW BAND TC FILTER
HIGH BAND TC FILTER
FRONT/REAR DET.
FRONT/REAR (L–R) DET.
FRONT/REAR (L+R) DET.
AUTOBALANCE LOCKOUT
AUTOBALANCE TC
Decoder
a
FEATURES
Generates 5.1-Channel Soundfield from All Stereo Sources
No Pre-Encoding Required
Excellent Decoding of Pre-Encoded Sources
4- or 5-Speaker Operation
Subwoofer Output
Full Bandwidth on All Channels
Optimized Modes for Video and Music
Excellent Surround Image at All Positions
Independent Left and Right Surround Steering
No Surround Channel Delay Required
Built-In White Noise Generator
APPLICATIONS
Home Theater Receivers
VCD/DVD Players
Auto Sound Receivers and Amplifiers
Surround Sound Decoders
Karaoke
Computer Audio Boards
Video Games
5.1-Channel Soundfield Generator
SSM2005
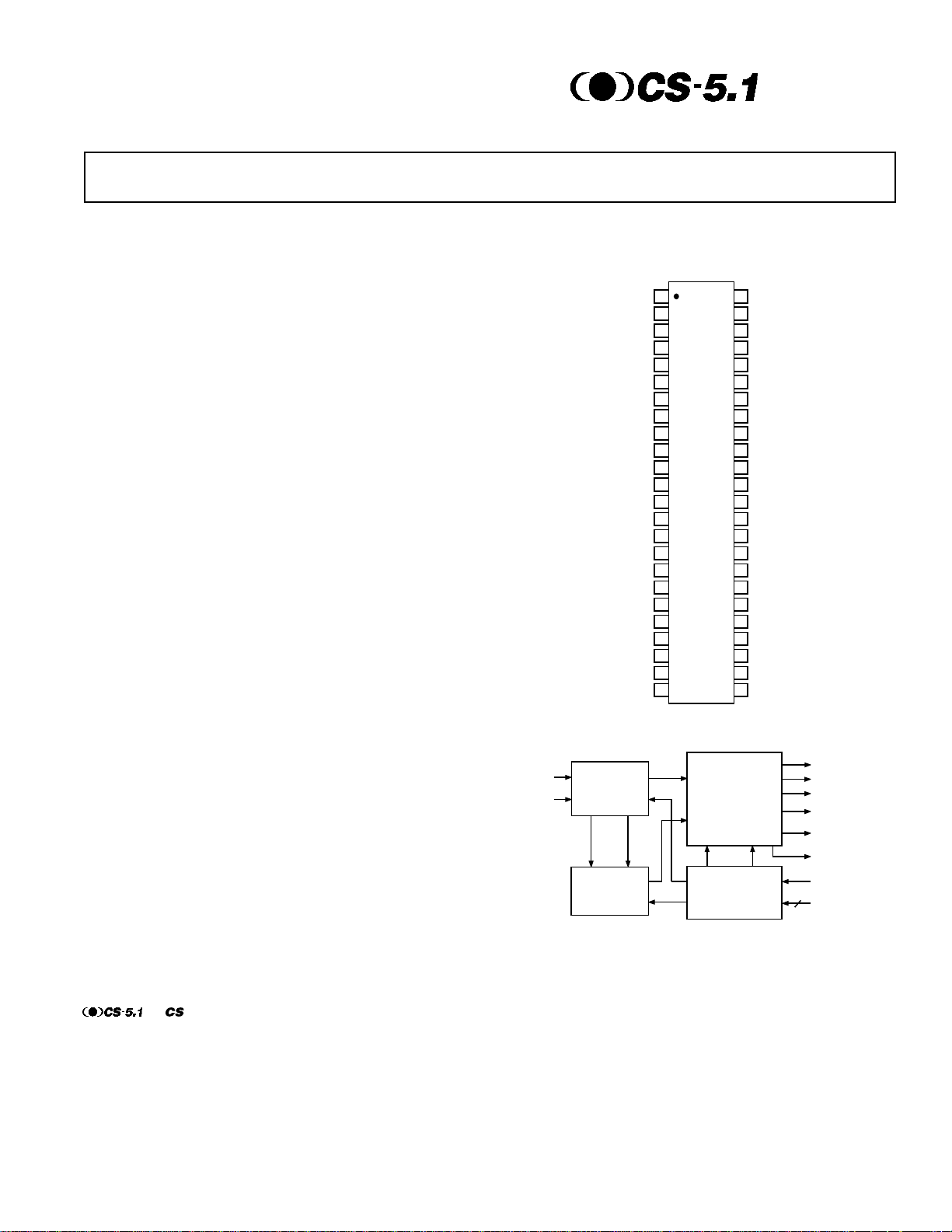
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
48-Lead SSOP
(RS Suffix)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM2005 Circle Surround® decoder produces true 5.1-channel
surround soundfield from any stereo source, including VCD, DVD,
VCR, CD and FM stereo broadcasts. The SSM2005 is also compatible with encoded sources, such as Dolby ProLogic
Surround
encoded movies and music. External delays and noise
®
and Circle
reduction processors are not required for the surround channels.
Circle Surround encoded stereo signals will produce a full 360º
soundfield when played through the SSM2005. Recording engineers can encode sounds to any of the five speakers surrounding
the listener. Left Front, Right Front, Center, and differentiated
Left and Right surround channels are generated, providing a realistic ambiance effect with either 4- or 5-speaker configurations.
The SSM2005 is available from Analog Devices, subject to the
License and Royalty requirements as described on the following
page of the data sheet.
and are registered trademarks of SRS Labs, Inc. and ValenceTechnology Ltd.
Circle Surround is a registered trademark of SRS Labs, Inc. and Valence Technology Ltd.
Dolby ProLogic
Circle Surround technology is protected under one or more of the following U.S. Patents and corresponding patents
worldwide: 5,319,713; 5,333,201; 5,638,452; 5,771,295.
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
is a registered trademark of Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation, San Francisco, California.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1999
Figure 1. Simplified Block Diagram
Page 2
SSM2005–SPECIFICATIONS
(V
= ±6.0 V, T
S
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Autobalance Off, Noise Off)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS␣
1
Level
Input Impedance Z
VL, V
IN
R
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Level
Left Front L
Right Front R
Center L
Left Rear, Right Rear L
Channel Separation
Left Front and Right Front / Center L
Left Rear and Right Rear / Center L
Left Rear, Left Front L
Left Rear, Right Rear L
Output Impedance Z
OUT
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE␣
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise THD+N All Channels 0.04 %
Signal-to-Noise Ratio SNR 88 dB
Dynamic Range, Output DR Noise Floor to 1% THD 100 dB
Headroom HR All Channels 12 dB
NOISE GENERATOR␣
Output Level
2
Matching All Channels 0.5 1.5 dB
AUTOBALANCE
Capture Range |
Capture Time V
CONTROL LOGIC␣
Logic Thresholds Logic Levels Referenced to ACOM
High (1) 2.4 V
Low (0) 0.8 V
Input Current 1 µA
Timing Characteristics See Timing Diagrams
POWER SUPPLIES␣
Operating Voltage Range
Current I
NOTES
1
0 dBd = 300 mV rms
2
With filter shown in Figure 8.
3
Specifications apply for V
Specifications subject to change without notice.
.
= ±6 V.
S
3
V
+V
S
S
–V
S,
S
LICENSING INFORMATION
= ⴙ25ⴗC, f = 2 kHz, Modes: Video, 5-2-5, Center On, Sound Spread Off,
A
Z
< 10 Ω 0 dBd
SOURCE
L and R Inputs 10 kΩ
= 0 dBd, RT = Off 0 dBd
T
= 0 dBd, LT = Off 0 dBd
T
= RT = 0 dBd, In Phase,
T
Video Mode +6 dBd
= RT = 0 dBd, Out of Phase +3 dBd
T
= RT, In Phase, Video Mode 30 dBd
T
= RT, Out of Phase 40 dBd
T
= RT, Out of Phase 30 dBd
T
= RT, Out of Phase 30 dBd
T
10 Ω
Noise Mode On, A-Weighted –10 dBd
| – |
V
H
= VR > –10 dBd,
L
|V
LEFT
| ±4dB
V
L
– V
| < 3 dB 5 s
RIGHT
Single Supply +10 +12 V
Dual Supply ±5 ±6V
VL = VR = ACOM, VS = 12 V 18 30 mA
The CIRCLE SURROUND® TECHNOLOGY rights incorporated in the SSM2005 are owned by SRS Labs, Inc. and by Valence Technology Ltd., and licensed
to Analog Devices, Inc.
Users of any SSM2005 Circle Surround decoder must first sign a free use license to purchase OEM quantities for consumer electronics applications which
may be granted upon submission of a preproduction sample to, and the satisfactory passing of performance verification tests performed by SRS Labs, Inc.
or Valence Technology Ltd. SRS Labs, Inc. and Valence Technology Ltd. reserve the right to decline a use license for any submission that does not pass
performance specifications or is not in the consumer electronics classification.
All equipment manufactured using any SSM2005 Circle Surround decoder must carry the Circle Surround logo on the front panel in a manner approved
in writing by SRS Labs, Inc. or Valence Technology Ltd. If the Circle Surround logo is printed in users manuals, service manuals or advertisements, it
must appear in a form approved in writing by SRS Labs, Inc. or Valence Technology Ltd. The rear panel of Circle Surround products, users manuals,
service manuals, and all advertisements must all carry the Circle Surround legend as specified in the Circle Surround trademark manual published by SRS
Labs, Inc. and Valence Technology Ltd.
–2– REV. 0
Page 3

SSM2005
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Supply Voltage, V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±8 V or +16 V
S
Logic Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . –20°C to +70°C
Package Type
48-Lead SSOP (RS) 100 50 °C/W
S
NOTE
1
θ
is specified for worst case conditions.
JA
Junction Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . .+300°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option
SSM2005RS-Reel –20°C to +70°C 48-Lead SSOP RS-48
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the SSM2005 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
1
JA
JC
Units
–3–REV. 0
Page 4
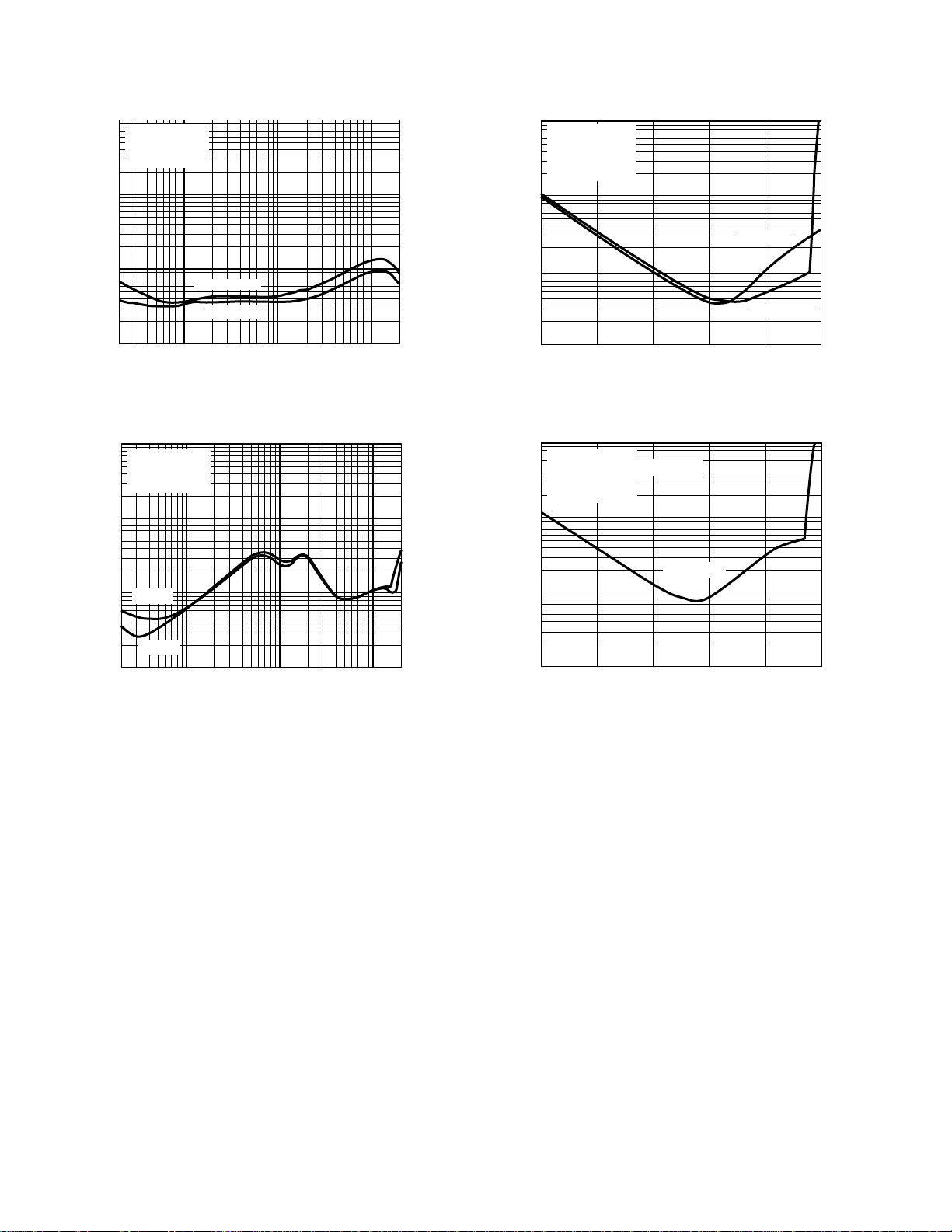
SSM2005
–Typical Performance Characteristics
10
VSY = ±6V
V
= 300mV
IN
RL = 100kV
1
THD + N – %
0.1
0.01
20 20k100
rms
CENTER OUT
LF, RF OUT
FREQUENCY – Hz
1k
10k
Figure 2. THD + N vs. Frequency; Front Channels
10
VSY = ±6V
V
= 300mV
IN
RL = 100kV
1
THD + N – %
0.1
LS OUT
rms
10
VSY = ±6V
V
= 1kHz
IN
= 100kV
R
L
0dBr = 300mV
1
THD + N – %
0.1
0.01
235
225
rms
215 25
AMPLITUDE – dBr A
LF, RF OUT
CENTER OUT
5
15
Figure 4. THD + N vs. Amplitude; Front Channels
10
VSY = ±6V
L
= RT = 1kHz; OUT OF PHASE
T
= 100kV
R
L
0dBr = 300mV
1
THD + N – %
0.1
rms
LS, RS OUT
RS OUT
0.01
20 20k100
FREQUENCY – Hz
1k
10k
Figure 3. THD + N vs. Frequency; Surround Channels
0.01
235
225
215 25
FREQUENCY – dBr A
5
15
Figure 5. THD + N vs. Frequency; Surround Channels
–4– REV. 0
Page 5
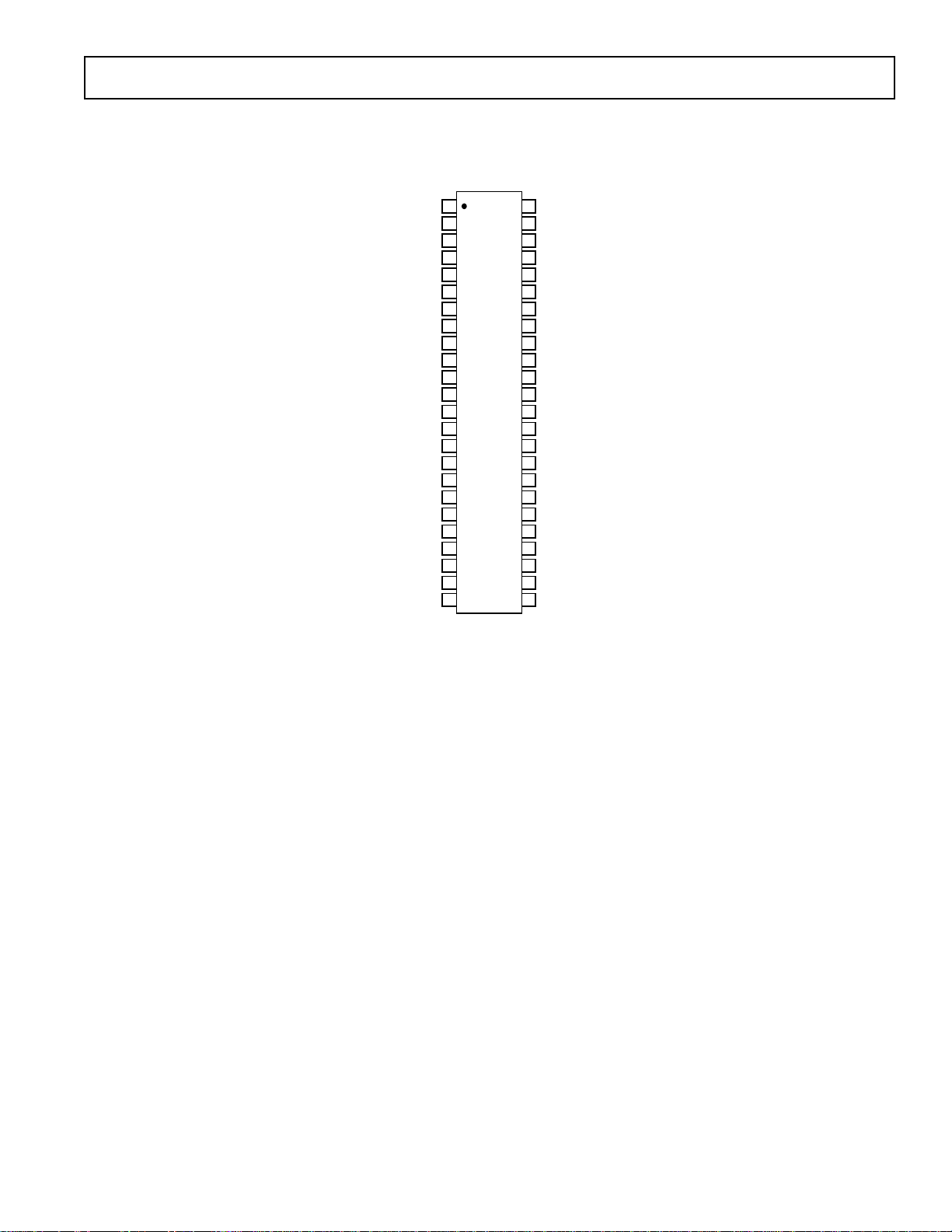
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
48-Lead SSOP
(RS Suffix)
SSM2005
R FILTER IN
R FILTER OUT
L FILTER IN
L FILTER OUT
L OUT
L OUT A
L IN
R OUT
R OUT A
R IN
V
ACOM AUDIO GND
GND
V
(L+R) OUT
(L–R) OUT
(L–R) HIGH IN
(L–R) LOW IN
R HIGH BAND DET.
L HIGH BAND DET.
HIGH BAND DET. OUT
R LOW BAND DET.
L LOW BAND DET.
LOW BAND DET. OUT
EE
CC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
SSM2005
12
TOP VIEW
13
(Not to Scale)
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
48
CENTER OUT
47
LF OUT
46
RF OUT
45
LS OUT
44
RS OUT
43
NOISE IN
42
NOISE OUT
41
LOAD
40
RESET
39
DATA IN
38
V
CC
37
ACOM AUDIO GND
36
GND
35
V
EE
34
WRITE
33
CLOCK IN
32
FRONT/REAR TC FILTER
31
LOW BAND TC FILTER
30
HIGH BAND TC FILTER
29
FRONT/REAR DET.
28
FRONT/REAR (L–R) DET.
27
FRONT/REAR (L+R) DET.
26
AUTOBALANCE LOCKOUT
25
AUTOBALANCE TC
–5–REV. 0
Page 6

SSM2005
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Pin # Name Connected to / Function:
1 R Filter In 3-Pole Active Low-Pass Filter Output; used for Center Cancelling Correction
2 R Filter Out 3-Pole Active Low-Pass Filter Input
3 L Filter In 3-Pole Active Low-Pass Filter Output; used for Center Cancelling Correction
4 L Filter Out 3-Pole Active Low-Pass Filter Input
5 L Out Connect to Pin 6
6 L Out A Connect to Pin 5
7 L In Left Stereo Source Line Input; Should be 0 dBd (300 mV rms)
8 R Out Connect to Pin 9
9 R Out A Connect to Pin 8
10 R In Right Stereo Source Line Input; Should be 0 dBd (300 mV rms)
11 V
EE
12 ACOM Audio GND Audio Ground
13 GND Power Ground
14 V
CC
15 (L+R) Out RC to Front/Rear Detector Input
16 (L–R) Out RC to Front/Rear Detector Input and Input of Crossover
17 (L–R) High In Output of High-Pass Crossover
18 (L–R) Low In Output of Low-Pass Crossover
19 R High Band Det. RC Network Fed by Right Stereo Source Line Input
20 L High Band Det. RC Network Fed by Left Stereo Source Line Input
21 High Band Det. Out Capacitor to ACOM; Controls Rear High Frequency Output Steering
22 R Low Band Det. Right Input, used for Autobalance and Low Band Steering
23 L Low Band Det. Left Input, used for Autobalance and Low Band Steering
24 Low Band Det. Out Capacitor to ACOM; Controls Left-to-Right Output Steering
25 Autobalance TC RC Network to ACOM
26 Autobalance Lockout RC Network to ACOM
27 Front/Rear (L+R) Det. RC Network Fed by (L+R) Out (Pin 15)
28 Front/Rear (L–R) Det. RC Network Fed by (L-R) Out (Pin 16)
29 Front/Rear Det. Capacitor to ACOM; Controls Front-to-Back Output Steering
30 High Band TC Filter RC Network to ACOM
31 Low Band TC Filter RC Network to ACOM
32 Front/Rear TC Filter RC Network to ACOM
33 Clock In Clock from Serial Bus
34 WRITE Chip Select from Serial Bus
35 V
EE
36 GND Power Ground
37 ACOM Audio GND Audio Ground
38 V
CC
39 Data In Data from Serial Bus
40 Reset Reset from Serial Bus
41 LOAD Load from Serial Bus
42 Noise Out Connect to RC Filter; White Noise Output
43 Noise In Connect to RC Filter Output; Filtered White Noise
44 RS Out Connect to Right Surround (Rear) Amplifier Input
45 LS Out Connect to Left Surround (Rear) Amplifier Input
46 RF Out Connect to Right Front Amplifier Input
47 LF Out Connect to Left Front Amplifier Input
48 Center Out Connect to Center Amplifier Input
Negative Supply
Positive Supply
Negative Supply
Positive supply
–6– REV. 0
Page 7

L Left
R Right
Surround Encoded Left Input
L
T
Surround Encoded Right Input
R
T
Table I. Abbreviations and Notations Used in the Text
LF Left Front Output
RF Right Front Output
LS Left Surround Output
RS Right Surround Output
C Center Output
dBd 0 dBd = 300 mV rms
ACOM Quality Audio Ground
VCA Voltage Controlled Amplifier
SSM2005
SIMPLIFIED THEORY OF OPERATION
General
The SSM2005 Circle Surround decoder processes stereo input
signals, and outputs 5 channels of surround sound, plus an L+R
output for a subwoofer low-pass filter. The SSM2005 provides
signal processing, steering control, input autobalance, and a digital
interface for mode control. This device uses analog circuits such as
amplifiers, rms detectors, VCAs and digital logic to carry out the
circle surround algorithm in real time. No artificial reverberation
or delay effects are used, preserving the natural sound of the
original stereo recording.
The SSM2005 can decode any existing media including CD,
VCD, DVD, cassette tapes, VHS, FM radio and television stereo
broadcasts. For convenience in balancing the system, an on-chip
digital noise generator is available. The net result is outstanding
5.1 channel surround sound from all stereo sources, which reveals the hidden ambiance already contained in existing music
and cinematic recordings. The listening experience is greatly
enhanced and made more enjoyable when compared to ordinary
stereo. In the following description, please refer to Figure 6.
Input Signal Processing
Stereo inputs L and R are fed to both the Steering Control
Generator, and the Autobalance circuitry. The balanced signals
are passed through the Center Channel Cancel circuitry to the
Channel Steering VCAs.
The autobalance output signals also feed the Precision Sum and
Difference Amplifiers. The sum (L+R) and difference (L–R)
signals form the basis for the center and surround channels,
respectively. The center channel signal is fed to the center channel cancel circuitry, and to the channel steering VCAs. The
surround channel signal is separated by an external Crossover
Network into the Surround High and Surround Low bands and
fed to the channel steering VCAs.
Steering Control Generator
The purpose of the steering control generator is to analyze the dynamic characteristics of music, dialog, or special effects, using proprietary high speed analog computing circuits. Control voltages for
all VCAs are then computed, and the soundfield expansion performed in accordance with the circle surround decoding algorithm.
The control signals depend upon the SSM2005 modes selected, and
will differ for video mode vs. music mode, 5.2.5 mode vs. 4.2.4
mode, etc.
Channel Steering VCAs
Command signals from the steering control generator are fed to
the channel steering VCAs, which control the amplitude of the
five output channels. High performance, low distortion VCAs
with typically 12 dBd headroom are used for all channels.
Output Amplifier
The Output Amplifiers receive signals from the VCAs and the
internal Noise Generator. Each amplifier has a multiplexer switch
which will enable it to output a white noise waveform under
control of the Serial Bus. This simplifies balancing of the listening
system. The output amplifiers provide load drive capability with
typically 12 dBd of headroom. The overall gain from L and R
inputs to Circle Surround Outputs is unity; the Noise Generator
gives an output level of –10 dBd (100 mV rms).
Mode Control Logic
The various SSM2005 modes are shown in Figure 7. There are
modes for different types of source material, such as video sound
tracks or music. Other modes include 5.2.5/4.2.4, Sound Spread,
Phantom Center mode, autobalance, and Noise Generation. Each
mode’s status is stored in the Mode Control Logic, as determined
by the data sent via the serial bus. Refer to the Typical Outputs In
Various Modes section for a more detailed explanation of the various modes.
Applying a logic low to the Reset input will override the Mode
Control Logic and put the SSM2005 into its Default mode. Default modes for the device are video/5.2.5/center active/sound
spread on/autobalance on/noise off. See Figure 9 for logic timing
diagrams.
Autobalance Feature
The autobalance circuitry is activated when the SSM2005 is placed
into autobalance On Mode. In this mode, the device will adjust the
gains of its input amplifiers to balance the stereo inputs to equal
loudness. With a mono input signal, the autobalance circuitry will
typically balance L and R to within ±0.5 dB. A 22 µF external ca-
pacitor connected to Pin 25 sets a 5 second averaging period for
comparing the levels between the stereo inputs.
Using autobalance will slightly degrade the maximum channel
separation from the SSM2005. The autobalance mode can be
left off without fear of degrading the soundfield, unless the
stereo input signal is expected to be off balance by more than
±1.5 dB. Most CD, VCD and DVD player outputs are specified
to within ±0.25 dB balance.
Noise Generator
When the noise mode is selected, the audio inputs are muted.
Noise will be available from the output of the channel determined
by the mode control logic. The noise generator uses a feedback
shift register that generates a pseudo-random digital output waveform with a repeat time of three seconds. This digital noise waveform is band-pass filtered externally to approximate white noise.
Power Supplies
The SSM2005 may be operated from regulated ±5 V to ±6 V
supplies that can supply 45 mA each. The recommended operating
voltage is ± 6 V, which will give a typical headroom of 12 dBd.
–7–REV. 0
Page 8

SSM2005
Power-Up
The SSM2005 will be in an undefined mode on power-up. Reset
should be applied to the SSM2005, or the mode control logic
should be loaded to put the device into a definite mode state.
Serial Data Control Inputs
The SSM2005 provides a simple 3- or 4-wire serial interface to
control the mode settings for the device. Data is input on the
DATA IN pin, while CLOCK IN is the serial clock. Data can be
shifted into the SSM2005 at clock rates up to 1 MHz.
STEREO
INPUTS
L
R
AUTO BALANCE
AND MUTE
PRECISION
SUM AND
DIFFERENCE
AMPLIFIERS
STEERING CONTROL GENERATOR
L+R = CENTER
L–R = SURROUND
CENTER CHANNEL
CANCEL
CROSSOVER
NETWORK
The shift register clock at CLOCK IN is enabled when the
WRITE input is low. The WRITE pin can therefore be used as a
chip select input. However, the shift register contents are not
transferred into the register banks until the rising edge of LOAD.
For a traditional 3-wire serial interface, WRITE and LOAD
should be tied together. Figure 7 shows the timing diagram and
minimum timing requirements for the digital interface.
To enable a data transfer, the WRITE and LOAD inputs are
driven low. The 8-bit serial data, formatted MSB first, should
be fed to DATA IN and clocked into the shift register on the
rising edge of CLOCK IN. The new mode setting will then
activate on the rising edge of WRITE and LOAD.
CIRCLE
SURROUND
LEFT
RIGHT
CENTER
SURROUND
HIGH BAND
SURROUND
LOW BAND
7X
CHANNEL
STEERING
VCAs
OUTPUT
AMPLIFIERS
OUTPUTS
L
R
AMPLIFIERS
C
L
S
R
S
MODE CONTROL LOGIC
RESET
CLOCK
DATA
SELECT
LOAD
SERIAL BUS
TO SUBWOOFER
FILTER
NOISE
GENERATOR
+V GND 2VACOM
INPUT POWER
Figure 6. Block Diagram
Table II. Modes List
Modes Effect
Video Center Channel Cancellation Active
Music Center Cancel Cancellation Off; Center Reduced by –4 dB.
5-2-5 5-Channel Circle Surround Enabled
4-2-4 4-Channel Matrix Enabled
Center On Center Channel Output On
Phantom Center Center Channel Output Off; Divided and Added to LF and RF
Sound Spread On Hard Panned Input Steered to Front and Rear Side
Sound Spread Off Hard Panned Input Steered to Front Side Only
Autobalance On Balances L
and R to ±1 dB
Autobalance Off Autobalance Disabled
Noise Off Noise Generator Disabled
Noise On Noise Generator On; Inputs Muted
–8– REV. 0
Page 9

SSM2005
Table III. Data Decoding Truth Table
MSB LSB
Reset D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 Mode
1 0 0 1 XXXXX C Noise On
1 1 0 1 XXXXX LF Noise On
1 1 1 0 XXXXX RF Noise On
1 0 1 0 XXXXX LS Noise On
1 1 0 0 XXXXX RS Noise On
1 0 0 0 XXXXX All Mute
1 1111XXXX Autobalance On
1 1110XXXX Autobalance Off
1 111X1XXX Center Active
1 111X0XXX Phantom Center
1 1 1 1 X X 1 X X Sound Spread On
1 1 1 1 X X 0 X X Sound Spread Off
1 1 1 1 XXX1 X 5.2.5 Mode
1 1 1 1 XXX0 X 4.2.4 Mode
1 1 1 1 XXXX1 Video Mode
1 1 1 1 XXXX0 Music Mode
0 XXXXXXXX Noise Off, Autobalance On, Center Active,
Sound Spread On, 5.2.5 Mode, Video Mode
–9–REV. 0
Page 10

SSM2005
Table IV. Timing Description
Timing Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
t
CL
t
CH
t
DS
t
DH
t
CW
t
WC
t
LW
t
WL
t
L
t
W3
NOTES:
1. An idle HI (CLK-HI) or idle LO (CLK-LO) clock may be used. Data is latched on the positive edge.
2. For SPITM or MICROWIRETM 3-wire bus operation, tie LD to WRITE and use WRITE pulse to drive both pins. (This generates an automatic
internal LD signal.)
3. If an idle HI clock is used, tCW and tWL are measured from the final negative transition to the idle state.
4. The first data byte selects an address (MSB HI), and subsequent MSB LO states set gain levels. Refer to the Address/Data Decoding Truth Table.
5. Data must be sent MSB first.
1
CLK
0
Input Clock Pulsewidth 50 ns
Input Clock Pulsewidth 50 ns
Data Setup Time 25 ns
Data Hold Time 35 ns
Positive CLK Edge to End of Write 25 ns
Write to Clock Setup Time 35 ns
End of Load Pulse to Next Write (4-Wire Mode) 20 ns
End of Write to Start of Load (4-Wire Mode) 20 ns
Load Pulsewidth (4-Wire Mode) 250 ns
Load Pulsewidth (3-Wire Mode) 250 ns
DATA
WRITE & LOAD
CLK
DATA
WRITE & LOAD
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
t
CL
t
DS
t
WC
t
CH
t
DH
t
CW
t
W3
Figure 7. Logic Timing Diagram
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
MICROWIRE is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
–10– REV. 0
Page 11

SSM2005
TYPICAL OUTPUTS IN VARIOUS MODES
The SSM2005 Circle Surround decoder uses ambiance and
directional information already present in a stereo signal, and
does not require the audio signal to be encoded. The device
requires no delay generators or noise reduction. Fully differentiated rear channels provide rear stereo separation for enhanced
spatial perception, a feature unique to Circle Surround.
Video mode provides the highest degree of channel separation
between the front and center speakers. Video mode cancels common center channel material from the left and right front channels. This restores a wide stereo image to matrix encoded sound
tracks, while maintaining a solid center channel for dialogue and
mono information.
The Music mode is optimized for unencoded stereo music reproduction, with full bandwidth on all channels. The steering for the
LF and RF channels is deactivated to prevent any stereo image
wandering. The independent two-band rear channel steering
provides excellent surround imaging, even in car audio applications. Well balanced sound is obtained everywhere within a 4- or
5-speaker setup.
The 5.2.5 mode provides the maximum channel separation to
the surround channels, and should be used with any encoded
stereo input signal. The 4.2.4 mode can be used to reduce the
dynamic steering of the surround channels, allowing the
SSM2005 to simulate a 4-channel surround sound decoder.
Sound Spread OFF allows the maximum channel separation
between the surround and front speakers. With Sound Spread
OFF, a hard panned left input signal will produce an output
only in the left front output. In Sound Spread ON mode, a hard
panned left input signal will produce equal output from the left
front and left surround outputs.
The following tables demonstrate the differences between the
modes of the SSM2005 under various input conditions. The L
T
and RT inputs are at 2 kHz, and are shown in terms of their
differences in magnitude (in dB) and phase (in degrees). For
example, a 0␣ ⬔ 180° input means L
tude, but opposite in phase to R
is exactly equal in magni-
T
.
T
Table VI. Video/5.2.5/Sound Spread ON/Center ON
Input Output
|LT| – |RT| (dB)
dB ⬔ φ |LF| |RF| |C| |LS| |RS|
0 ⬔ 0° – 30 –30 +6 –40 –40
0 ⬔ 180° –35 –35 –45 +6 +6
L
Only 0 –60 –30 0 –30
T
R
Only –60 0 –30 –30 0
T
–6 ⬔ 0° 0 –15 –4 0 –25
–6 ⬔ 180° –30 –36 –26 0 –15
Table VII. Music/5.2.5/Sound Spread ON/Center ON
Input Output
|LT| – |RT| (dB)
dB ⬔ φ |LF| |RF| |C| |LS| |RS|
0 ⬔ 0° 0 0 +2 –40 –40
0 ⬔ 180° 0 0 –45 +6 +6
L
Only 0 –60 –30 0 –30
T
Only –60 0 –30 –30 0
R
T
–6 ⬔ 0° 0 –6–40 –25
–6 ⬔ 180° 0 –6 –26 0 –15
Table VIII. Video/5.2.5/Sound Spread ON/Phantom Center
Input Output
|LT| – |RT| (dB)
dB ⬔ φ |LF| |RF| |C| |LS| |RS|
0 ⬔ 0° +3 +3 Off –40 –40
0 ⬔ 180° –35 –35 Off +6 +6
Only 0 –60 Off 0 –30
L
T
R
Only –60 0 Off –30 0
T
–6 ⬔ 0° 0 –15 Off 0 –25
–6 ⬔ 180° –30 –36 Off 0 –15
Table V. Video/5.2.5/Sound Spread OFF/Center ON
Input Output
|LT| – |RT| (dB)
dB ⬔ φ |LF| |RF| |C| |LS| |RS|
0 ⬔ 0° – 30 –30 +6 –40 –40
0 ⬔ 180° –35 –35 –45 +6 +6
L
Only 0 –60 –30 –30 –35
T
R
Only –60 0 –30 –35 –30
T
–6 ⬔ 0° 0 –15 –4 –25 –30
–6 ⬔ 180° –30 –36 –26 0 –15
Table IX. Video/4.2.4/Sound Spread OFF/Center ON
Input Output
|LT| – |RT| (dB)
dB ⬔ φ |LF| |RF| |C| |LS| |RS|
0 ⬔ 0° – 30 –30 +6 –40 –40
0 ⬔ 180° –35 –35 –45 +6 +6
L
Only 0 –60 –30 –32 –32
T
Only –60 0 –30 –32 –32
R
T
–6 ⬔ 0° 0 –15 –4 –26 –26
–6 ⬔ 180° –30 –36 –26 0 –2
–11–REV. 0
Page 12

SSM2005
TO SUBWOOFER FILTER
5.9kV
0.1mF
5.9kV
0.1mF
L 1 R OUT
(OPTIONAL)
0.01mF
48.7kV
105kV
4.7nF
0.01mF
48.7kV
105kV
4.7nF
LEFT IN
RIGHT IN
40.2kV
0.1mF
787V
787V
7.87kV
0.1mF
453V 453V
162kV
0.01mF
787kV
100pF
909V
0.1mF
100V
100V
0.1mF
0.1mF
10mF
10mF
10mF
+
+
0.1mF
0.1mF
+
10mF
+
0.1mF
1mF
1mF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
SSM2005
+
22mF
4.7MV
48
47
46
45
44
0.47mF
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
1mF
1mF
3.82kV
1kV
10kV
C
OUT
LF
OUT
RF
OUT
LS
OUT
RS
OUT
LOAD
RESET
DATA
16V
26V
WRITE
CLK IN
1mF
1mF
33.2kV
274kV
0.1mF 0.22mF
100kV
1mF
274kV
0.1mF 0.22mF
DENOTES CONTROL
GROUND
DENOTES SIGNAL
GROUND
DENOTES CONNECTION
1mF
SSM2275-A
SSM2275-B
10mF
+
10mF
+
26V
16V
1nF1nF
SSM2275-A
SSM2275-B
0.1mF
1mF
453V
0.1mF
0.1mF
1mF
909V
453V
1kV
Figure 8. Typical Application Schematic
–12– REV. 0
Page 13

48
47
46
45
44
7
10
39
SSM2005*
LEFT IN
RIGHT IN
10mF
10mF
CENTER
L
F
R
F
L
S
R
S
OUTPUTS
*ADDITIONAL PINS
OMITTED FOR CLARITY
SSM2275
2.05kV 4.23kV
1mF
SUBWOOFER
0.47mF
f
C
= 100Hz
APPLICATION NOTES
Figure 8 shows a typical SSM2005 application schematic. The
stereo source signal is connected to the SSM2005 audio signal
inputs at Pins 7 and 10, as well as the Left/Right level detectors
at Pins 19, 20, 22, and 23. The input signal goes through the
autobalance circuitry and can be accessed at Pins 6 and 9.
A sum (L+R) and difference (L–R) signal is available at Pins 15
and 16, respectively. These signals are fed into the Front/Rear
level detector at Pins 27 and 28.
The L+R signal is also fed internally to the center channel VCA
to produce the center channel output at Pin 48. In addition, the
L–R signal is fed into two external filters, creating a low-band and
high-band signal with a crossover frequency of 2 kHz. The crossover filters are both 3
rd
order Bessel filters, providing a minimum
group delay to the surround channels. The L–R high-band signal
is connected to Pin 17, and the L–R low-band signal is connected
to Pin 18. These two pins provide the multiband steering to the
two surround outputs.
Low-pass filters are inserted between Pins 1 and 2, and Pins 3
and 4. These filters are used for the center-canceling circuitry,
which removes center channel information from the left front
and right front outputs. This circuitry is only active in Video
mode, providing maximum channel separation between the
center and front outputs. In an application that will only use
Music mode, these active filters can be removed and replaced
with a 1 µF capacitor between Pins 1 and 2, and Pins 3 and 4.
The capacitors and resistors connected to Pins 21, 24, 25, 26, 29,
30, 31 and 32 are used to create the time constants for the steering circuitry. The values shown in Figure 8 are strongly recommended. Variation from these values will result in improper
operation of the Circle Surround decoder, and may result in the
assembled unit failing SRS Labs approval.
The noise generator output is at Pin 42, and the input to the noise
steering circuit is at Pin 43. The R-C network connected between
Pins 42 and 43 is used to remove dc voltage and high frequencies,
which could damage speakers. Other noise-shaping circuitry could
be used here to create noise patterns other than white, or to further
attenuate the noise output with a resistor divider.
Adding a Subwoofer Output
The SSM2005 provides an output of the summed Left In and
Right In signals. This L+R signal is used to drive the center channel output, and it can also be used to provide a subwoofer channel by connecting the output from Pin 15 to a low-pass filter. The
schematic for such a configuration is shown in Figure 9.
Here, Pin 15 is connected to a 2nd order Bessel low-pass filter.
The circuit uses the SSM2275, a low noise audio op amp that
can run from the same ±6 V that power the SSM2005. Using
the component values shown in Figure 9, the filter’s cutoff
frequency is 100 Hz.
SSM2005
Figure 9. Adding a Subwoofer Output
Implementing a Stereo Bypass Mode
Figure 10 shows a schematic for implementing a clickless stereo
bypass around the SSM2005. The stereo bypass mode allows
the user to defeat the Circle Surround decoding and listen to
two-channel stereo from the left front and right front speakers.
The SSM2402 is a clickless dual audio single-pole single-throw
(SPST) switch. When the control voltage, V
+0.8 V) the switch is open, and the five channel outputs are
connected to the outputs of the SSM2005. When V
high (above +2.0 V) the SSM2402 switch closes, connecting the
LF and RF outputs to Left In and Right In respectively. At the
same time, a data byte should be loaded into the SSM2005,
placing the Circle Surround decoder into Mute Mode. The data
byte required for Mute Mode can be found in Table III, and the
logic timing diagrams can be found in Figure 7.
SSM2402
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
48
47
46
45
44
V
BYP
V
HIGH =
BYP
STEREO MODE
V
LOW = CIRCLE
BYP
SURROUND MODE
LEFT IN
RIGHT IN
DATA IN
26V
10mF
10mF
LOW = CS MODE
V
BYP
0 0 0 x x x xx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SSM2005*
7
10
39
Figure 10. Implementing a Clickless Stereo Bypass Mode
, is low (below
BYP
goes
BYP
+6V
OUTPUTS
CENTER
L
F
R
F
L
S
R
S
*ADDITIONAL PINS
OMITTED FOR CLARITY
x DENOTES A DON'T CARE BIT
–13–REV. 0
Page 14

SSM2005
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SSM2402
+6V
26V
SSM2005*
FOR KARAOKE, LOAD DATA
BYTE: 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1
LEFT IN
RIGHT IN
10mF
10mF
CENTER
L
F
R
F
L
S
R
S
OUTPUTS
*ADDITIONAL PINS OMITTED
FOR CLARITY
+5V
KARAOKE
MODE
CIRCLE
SURROUND
MODE
SW-2
7404
26V
OP179
+6V
0.1mF
1kV
MIC
2.2kV
10kV
+6V
48
47
46
45
44
7
10
39
Using the SSM2005 for Karaoke
In Video mode, the SSM2005 removes centered vocal information from the LF and RF speakers. This allows the device to be
used in Karaoke applications, where the user can sing along with
any music recording. Figure 11 shows a circuit diagram for such
an application.
The OP179 is the microphone preamplifier with a gain of +20 dB.
A 2.2 kΩ resistor connects the microphone to the +6 V supply rail,
providing proper biasing for an electret microphone.
The SSM2402 is used as a clickless switch, connecting the
center output to either the center out from the SSM2005 or the
microphone. In Circle Surround mode, the control voltages to
the SSM2402 connect the output from the SSM2005 to the
center output.
In Karaoke Mode, this connection is opened, and the microphone is directed to the center output. At the same time, the
SSM2005 should be loaded with data byte (MSB first):
1␣ 1␣ 1␣ 0␣ 1␣ 0␣ 1␣ 1. This activates the center canceling circuitry in
the SSM2005, removing centered vocal information from the
left front and right front speakers.
The overall result is the microphone output comes out of the
center speaker, with the vocals-removed music coming from the
remaining speakers.
Figure 11. Using the SSM2005 for Karaoke
–14– REV. 0
Page 15

OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
48-Lead SSOP
(RS Suffix)
0.630 (16.00)
0.620 (15.75)
SSM2005
0.092 (2.34)
0.088 (2.24)
0.016 (0.41)
0.008 (0.20)
PIN 1
48
0.025 (0.635)
BSC
0.0135 (0.343)
0.008 (0.203)
25
241
0.110 (2.79)
0.095 (2.41)
SEATING
PLANE
0.299 (7.59)
0.292 (7.42)
0.410 (10.41)
0.400 (10.16)
0.010 (0.254)
0.005 (0.127)
C3628–8–7/99
88
08
0.040 (1.02)
0.024 (0.61)
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
–15–REV. 0
 Loading...
Loading...