Page 1
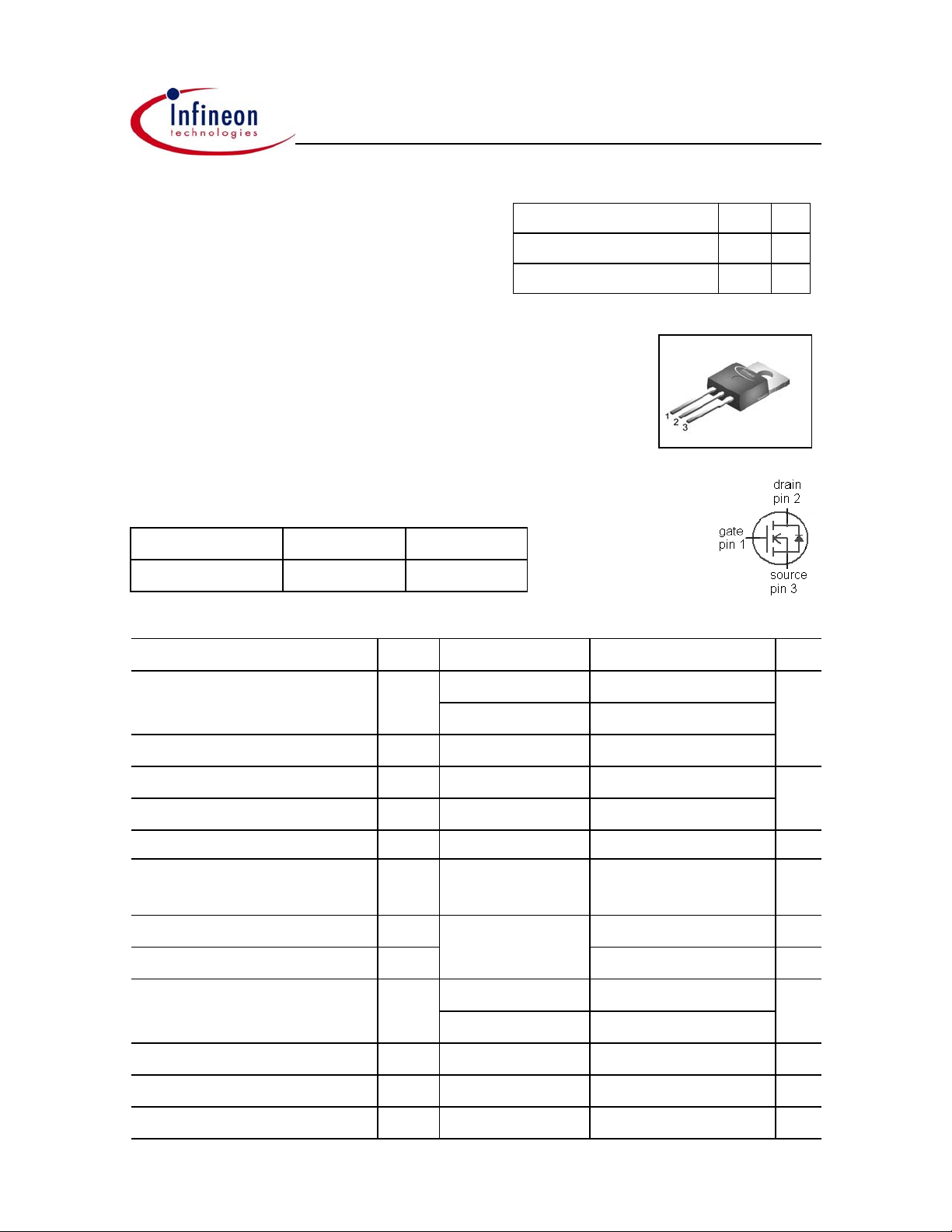
SPP24N60CFD
CoolMOSTM Power Transistor
Features
• Intrinsic fast-recovery body diode
• Extremely low reverse recovery charge
• Ultra low gate charge
• Extreme dv /dt rated
• High peak current capability
• Qualified according to JEDEC
• CoolMOS CFD designed for
• Softswitching PWM Stages
• LCD & CRT TV
Type Package Marking
Type Package Marking
SPP24N60CFD TO-220 24N60CFD
SPP24N60CFD PG-TO220 24N60CFD
Maximum ratings, at T
1)
for target applications
=25 °C, unless otherwise specified
j
Product Summary
V
@ Tjmax 650 V
DS
R
DS(on),max
I
D
PG-TO220
0.185
21.7 A
Ω
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
Continuous drain current
Pulsed drain current
2)
Avalanche energy, single pulse
Avalanche energy, repetitive
Avalanche current, repetitive
2),3)
2),3)
I
D
I
D,pulse
E
AS
E
AR
I
AR
Drain source voltage slope dv /dt
Reverse diode dv /dt dv /dt V/ns
Maximum diode commutation speed di /dt A/µs
Gate source voltage
V
GS
TC=25 °C
T
=100 °C
C
TC=25 °C
ID=10A, VDD=50 V
ID=20A, VDD=50 V
=21.7A, VDS=480V,
I
D
T
=125°C
j
=21.7A, VDS=480 V,
I
S
T
=125°C
j
static V
AC (f >1 Hz)
Power dissipation
Operating and storage temperature
P
tot
, T
T
j
TC=25 °C
stg
Value
21.7
13.7
55
780 mJ
1
20
80
40
600
±20
±30
240
-55 ... 150
A
A
V/ns
W
°C
Mounting torque M3 & M3.5 screws 60 Ncm
Rev. 1.2 page 1 2007-08-28
Page 2
SPP24N60CFD
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
Values
min. typ. max.
Thermal characteristics
Thermal resistance, junction - case
Thermal resistance, junction ambient
Soldering temperature, wave
soldering only allowed at leads
Electrical characteristics, at T
R
thJC
R
thJA
T
sold
=25 °C, unless otherwise specified
j
leaded - - 62
1.6 mm (0.063 in.)
from case for 10 s
- - 0.52 K/W
- - 260 °C
Static characteristics
Drain-source breakdown voltage
Avalanche breakdown voltage
Gate threshold voltage
V
(BR)DSSVGS
V
(BR)DSVGS
V
GS(th)
=0 V, ID=250 µA
=0 V, ID=21.7 A
VDS=VGS, ID=1.2 mA
600 - - V
- 700 -
345
Zero gate voltage drain current
Gate-source leakage current
Drain-source on-state resistance
Gate resistance
Transconductance
I
I
R
R
g
DSS
GSS
DS(on)
G
fs
VDS=600 V, VGS=0 V,
T
=25 °C
j
V
=600 V, VGS=0 V,
DS
T
=150 °C
j
VGS=20 V, VDS=0 V
VGS=10 V, ID=15.4 A,
T
=25 °C
j
V
=10 V, ID=15.4 A,
GS
T
=150 °C
j
- 2.5 - µA
- 2600 -
- - 100 nA
- 0.15 0.185
- 0.42 -
f =1 MHz, open drain - 0.8 -
|VDS|>2|ID|R
I
=15.4 A
D
DS(on)max
,
- 14.0 - S
Ω
Rev. 1.2 page 2 2007-08-28
Page 3
SPP24N60CFD
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
Values
min. typ. max.
Dynamic characteristics
Input capacitance
Output capacitance
Reverse transfer capacitance
Effective output capacitance, energy
4)
related
Effective output capacitance, time
5)
related
Turn-on delay time
Rise time
Turn-off delay time
Fall time
C
C
C
C
C
t
t
t
t
iss
oss
rss
o(er)
o(tr)
d(on)
r
d(off)
f
=0 V, VDS=25 V,
V
GS
f =1 MHz
=0 V, VDS=0 V
V
GS
to 480 V
V
=400 V,
DD
V
=10 V, ID= 21.7A,
GS
=6.8 Ω
R
G
- 3160 - pF
- 900 -
-34-
- 103 -
- 188 -
-50-ns
-24-
- 100 -
-9-
Gate Charge Characteristics
Gate to source charge
Gate to drain charge
Gate charge total
Gate plateau voltage
1)
J-STD20 and JESD22
2)
Pulse width tp limited by T
3)
Repetitive avalanche causes additional power losses that can be calculated as PAV=EAR*f.
4)
C
is a fixed capacitance that gives the same stored energy as C
o(er)
5)
C
is a fixed capacitance that gives the same charging time as C
o(tr)
j,max
Q
Q
Q
V
gs
gd
g
plateau
=480 V,
V
DD
I
=21.7 A,
D
V
=0 to 10 V
GS
while VDS is rising from 0 to 80% V
oss
while VDS is rising from 0 to 80% V
oss
-15-nC
-67-
- 110 143
- 7.3 - V
DSS.
DSS.
Rev. 1.2 page 3 2007-08-28
Page 4
SPP24N60CFD
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
Values
min. typ. max.
Reverse Diode
Diode continuous forward current
Diode pulse current
2)
Diode forward voltage
Reverse recovery time
Reverse recovery charge
Peak reverse recovery current
I
S
I
S,pulse
V
SD
t
rr
Q
I
rrm
=25 °C
T
C
--55
- - 21.7 A
VGS=0 V, IF=IS,
T
=25 °C
j
- 1.0 1.2 V
- 140 - ns
V
=480 V, IF=IS,
rr
R
di
/dt =100 A/µs
F
- 0.9 - µC
-11-A
Rev. 1.2 page 4 2007-08-28
Page 5

1 Power dissipation 2 Safe operating area
P
=f(TC) ID=f(VDS); TC=25 °C; D =0
tot
parameter: t
250
10
2
p
limited by on-state
resistance
SPP24N60CFD
1 µs
200
1
10
150
[W]
tot
P
[A]
D
I
100
0
10
50
-1
0
0 40 80 120 160
TC [°C]
10
10
0
10
1
VDS [V]
3 Max. transient thermal impedance 4 Typ. output characteristics
I
=f(VDS); Tj=25 °C ID=f(VDS); Tj=25 °C
D
parameter: D=t
0
10
/T parameter: V
p
50
45
GS
20 V
10 V
10 µs
100 µs
1 ms
DC
10 ms
10
2
10
3
40
0.5
8 V
35
30
25
[A]
D
I
20
15
7 V
6.5 V
10
6 V
5
0
5.5 V
5 V
0 5 10 15 20
VDS [V]
[K/W]
10
thJC
Z
10
-1
-2
10
0.1
0.05
0.02
0.01
single pulse
-5
0.2
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
tp [s]
Rev. 1.2 page 5 2007-08-28
Page 6

SPP24N60CFD
5 Typ. output characteristics 6 Typ. drain-source on-state resistance
I
=f(VDS); Tj=150 °C R
D
parameter: V
GS
=f(ID); Tj=150 °C
DS(on)
parameter: V
GS
35
30
20 V
10 V
8 V
1.2
1
25
[A]
D
I
20
15
10
7 V
6.5 V
6 V
5.5 V
]
Ω
[
R
DS(on)
0.8
0.6
0.4
5 V
5.5 V
6 V
5
5 V
0
0 5 10 15 20
VDS [V]
0.2
0 5 10 15 20 25
ID [A]
7 Drain-source on-state resistance 8 Typ. transfer characteristics
R
=f(Tj); ID=15.4 A; VGS=10 V ID=f(VGS); |VDS|>2|ID|R
DS(on)
parameter: T
j
DS(on)max
6.5 V
7 V
10 V
20 V
0.6
80
25 °C
0.5
60
0.4
]
Ω
[
R
DS(on)
0.3
98 %
[A]
D
I
40
150 °C
0.2
typ
20
0.1
0
-60 -20 20 60 100 140 180
Tj [°C]
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
VGS [V]
Rev. 1.2 page 6 2007-08-28
Page 7

SPP24N60CFD
9 Typ. gate charge 10 Forward characteristics of reverse diode
V
=f(Q
GS
parameter: V
); ID=21.7 A pulsed IF=f(VSD)
gate
DD
10
120 V
parameter: T
2
10
j
[V]
GS
V
8
6
480 V
[A]
F
I
10
1
150 °C
4
0
10
2
-1
0
0 25 50 75 100 125
Q
[nC]
gate
10
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
11 Avalanche SOA 12 Avalanche energy
I
=f(tAR) EAS=f(Tj); ID=10 A; VDD=50 V
AR
parameter: T
20
j(start)
800
150 °C, 98%
25 °C
25 °C, 98%
VSD [V]
700
16
600
500
400
[mJ]
AS
E
300
[A]
AV
I
12
125 °C
25 °C
8
200
4
100
0
10
-3
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
4
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
tAR [µs]
0
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200
Tj [°C]
Rev. 1.2 page 7 2007-08-28
Page 8

13 Drain-source breakdown voltage 14 Typ. capacitances
SPP24N60CFD
V
BR(DSS)
=f(Tj); ID=10 mA C =f(VDS); VGS=0 V; f =1 MHz
700
660
[V]
620
BR(DSS)
V
580
540
-60 -20 20 60 100 140 180
Tj [°C]
4
10
3
10
2
10
C [pF]
1
10
0
10
0 100 200 300 400 500
Ciss
Coss
Crss
VDS [V]
15 Typ. C
E
= f(VDS)Q
oss
[µJ]
oss
E
stored energy 16 Typ. reverse recovery charge
oss
=f(Tj);parameter: ID =21.7 A
rr
18
15
12
9
6
3
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
1.2
1.1
1
[µC]
rr
Q
0.9
0.8
25 50 75 100 125
VDS [V]
Tj [°C]
Rev. 1.2 page 8 2007-08-28
Page 9

17 Typ. reverse recovery charge 18 Typ. reverse recovery charge
Q
=f(IS); parameter: di/ dt =100 A/µs Qrr=f(di /dt ); parameter: ID=21.7 A
rr
SPP24N60CFD
1.2
1
125 °C
0.8
[µC]
rr
Q
0.6
0.4
5 9 13 17 21
25 °C
IS [A]
2.4
2
1.6
[µC]
rr
Q
1.2
0.8
100 200 300 400 500 600
125 °C
25 °C
d i/d t [A/µs]
Rev. 1.2 page 9 2007-08-28
Page 10

Definition of diode switching characteristics
SPP24N60CFD
Rev. 1.2 page 10 2007-08-28
Page 11

PG-TO-220-3-1; -3-21
SPP24N60CFD
Dimension in mm/ inches
Rev. 1.2 page 11 2007-08-28
Page 12

SPP24N60CFD
A
s
(
s
.
s
o
r
e
.
Published by
Infineon Technologies AG
81726 München, Germany
© Infineon Technologies AG 2006.
ttention please!
The information given in this data sheet shall in no event be regarded as a guarantee of conditions o
characteristics (“Beschaffenheitsgarantie”). With respect to any examples or hints given herein, any typica
values stated herein and/or any information regarding the application of the device, Infineon Technologie
hereby disclaims any and all warranties and liabilities of any kind, including without limitation warranties o
non-infringement of intellectual property rights of any third party
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your neares
Infineon Technologies Office
Warnings
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the type
in question please contact your nearest Infineon Technologies Office
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the expres
written approval of Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasonably be expected t
cause the failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device or
system. Life support devices or systems are intended to be implanted in the human body, or to support and/o
maintain and sustain and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of th
user or other persons may be endangered
www.infineon.com ).
Rev. 1.2 page 12 2007-08-28
 Loading...
Loading...