Page 1
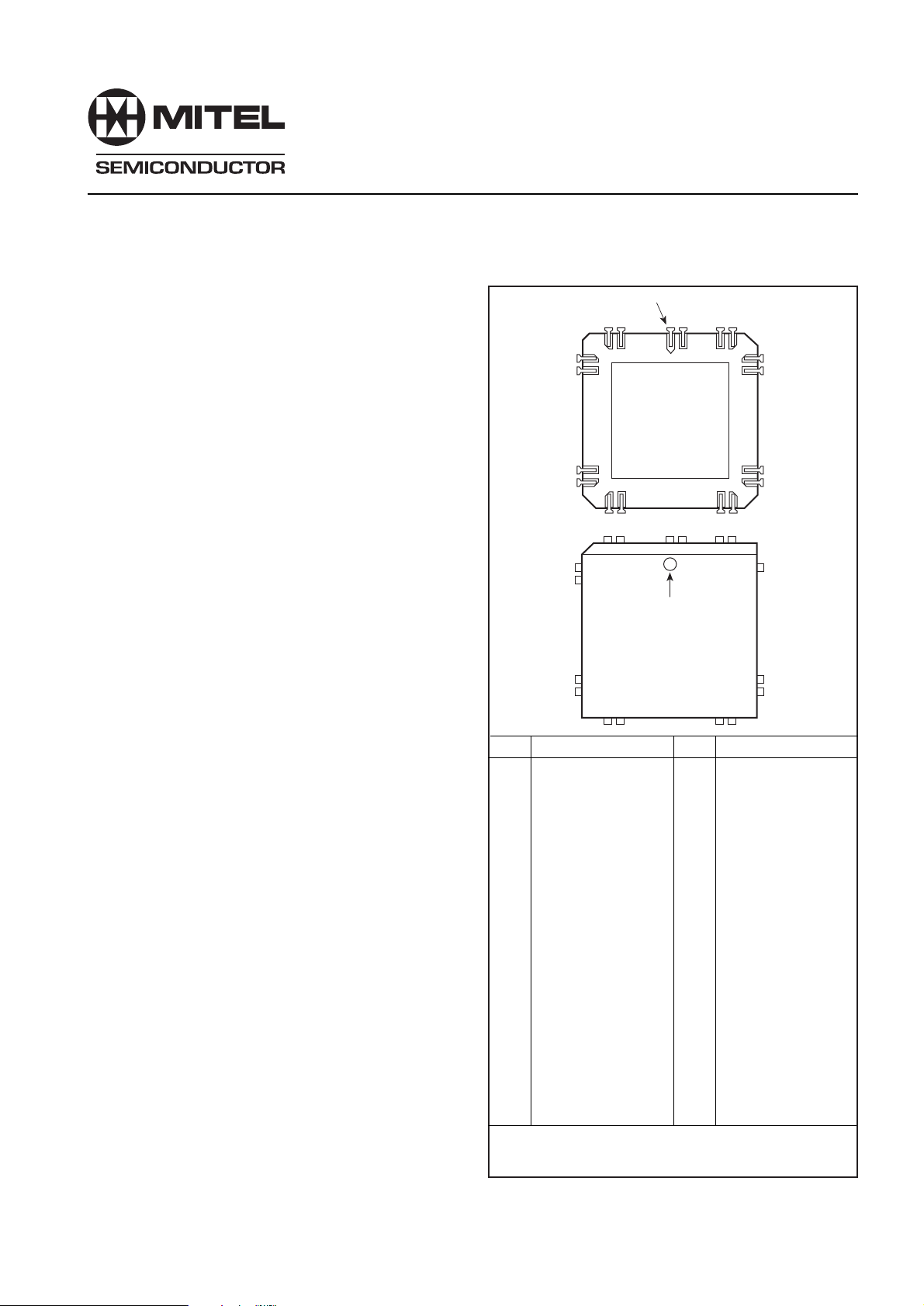
PIN 1
SP8855E
2.8GHz Parallel Load Professional Synthesiser
Advance Information
Supersedes version in January 1996 Professional Products IC Hanbook, HB2480-3.0 DS4239 - 3.0 March 1999
The SP8855E is one of a family of parallel load
synthesisers containing all the elements apart from the loop
amplifier to fabricate a PLL synthesis loop. Other devices in
the series are the SP8852E which is a fully programmable
device requiring two 16 bit words to set the RF and reference
counters, and the SP8854E which has hard wired reference
counter programming and requires a single bit word to program the RF divider. The SP8855E replaces the existing
SP8855D.
The SP8855E is intended for applications where a fixed
synthesiser frequency is required although it can also be used
where frequency selection is set by switches. In general the
device will be programmed by connecting the programming
pins to either V
be used to control the F
direction of the loop and select the phase detector gain.
Another input may be used to disable the phase detector
output.
The device is available in both plastic (HP) and ceramic
(HC) J-leaded 44-lead chip carrier. Ambient temperature
ranges available are shown in the ordering information.
or ground. Additional hard wired inputs can
CC
and F
pd
outputs set the control
ref
OPTIONAL
PIN 1
REFERENCE
HC44
FEATURES
■ 2.8GHz Operating Frequency (IG GRADE)
■ Single 5V Supply Operation
■ High Comparison Frequency 50MHz
■ High Gain Phase Detector 1mA/rad
■ Programmable Phase Detector Gain
■ Zero "Dead Band" Phase Detector
■ Wide range of RF and Reference Divide Ratios
■ Programming by Hard Wired Inputs
■ Low cost plastic package option
■ GPS HI-REL level a screened option
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply voltage -0.3V to 6V
Storage temperature -65 °C to +150°C
Operating temperature -55°C to +100°C
Prescaler & reference Input Voltage 2.5V p-p
Data Inputs VCC +0.3V
V
-0.3V
Junction temperature + 175°C (HC package)
+ 150°C (HP package)
EE
HP44
Pin Description Pin Description
1 Input bus bit 10 23 Control Direction
2 Input bus bit 9 24 F
3 Input bus bit 8 25 F
4 Input bus bit 7 26 +5V
5 Input bus bit 6 27 Ref. osc capacitor
6 Input bus bit 5 28 Ref in/XTAL
7 Input bus bit 4 29 Reference bit 9
8 Input bus bit 3 30 Reference bit 8
9 Input bus bit 2 31 Reference bit 7
10 Input bus bit 1 32 Reference bit 6
11 Input bus bit 0 33 Reference bit 5
12 0V (prescaler) 34 Reference bit 4
13 RF input 35 Reference bit 3
14 RF input 36 Reference bit 2
15 VCC + 5V (prescaler) 37 Reference bit 1
16 V
17 Lock detect output 39 Phase Detect Enable
18 C-lock detect 40 Phase Detect Gain 1
19 Rset 41 Phase Detect Gain 0
20 Charge pump output 42 Input bus bit 13
21 Charge pump ref. 43 Input bus bit 12
22 F
*Fpd and Fref outputs are reversed using the Control Direction
input. The table above is correct when pin 23 is high.
0V 38 Reference bit 0
EE
enable 44 Input bus bit 11
ref/Fpd
pd*
ref*
Fig.1 Pin connections - top view
Page 2
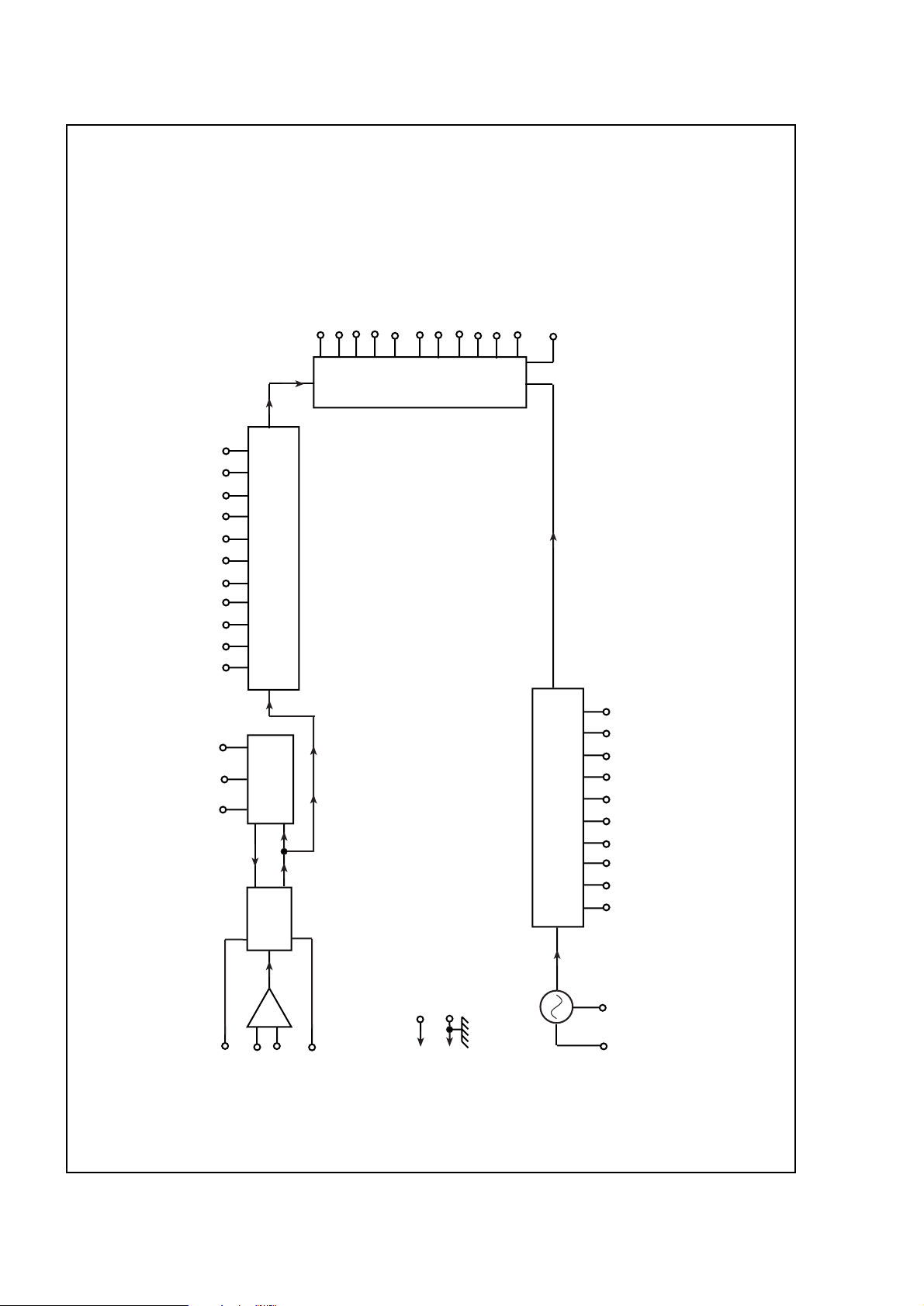
SP8855E
0V PRESCALER
Vcc + 5V
PRESCALER
RF INPUT
÷ 8/9
MODULS
CONTROL
B0
B2
11 10 9
3 BIT
A
COUNTER
11 BIT
M
COUNTER
B3 B13
PHASE
DETECTOR
876543 2
1
44 43
42
Fpd
20
V
EE
0V
211719
182425
222340
41
39
CHARGE PUMP OUTPUT
CHARGE PUMP REFERENCE
LOCK DET O/P
R set
C - LOCK DETECT
Fpd *
Fref *
Fpd / Fref ENABLE
CONTROL DIRECTION
PHASE DETECTOR GAIN 1
PHASE DETECTOR GAIN 0
PHASE DETECTOR ENABLE
Fref
10 BIT REFERENCE DIVIDER
38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29
BIT 9BIT 0
REFERENCE
DIVIDER
PROGRAMMING
27
28
REFERENCE
CAPACITOR
REFERENCE
CRYSTAL
26
26
+5V
* Fpd and Fref outputs are reversed using the Control
Direction input. Diagram is correct when pin 23 is high.
RF DIVIDER PROGRAMMING
Fig. 2 SP8855E block diagram
2
Page 3
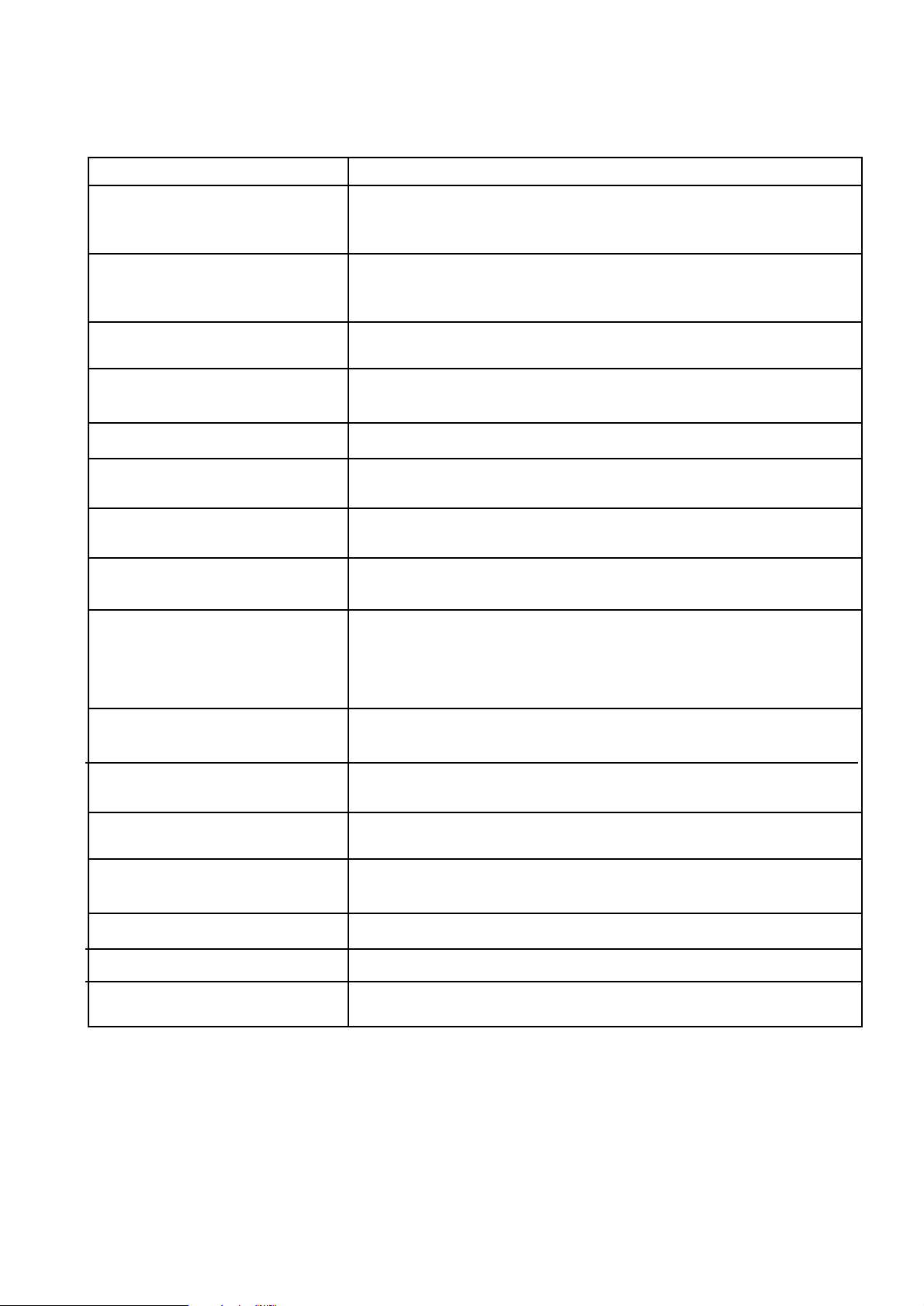
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN DESCRIPTION
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,42,43,44 These pins are the data inputs used to set the RF divider ratio
(M.N+A). Open circuit = 1 (high) on these pins. Inputs are transparent into
the data buffers.
13, 14 (RF INPUT) Balanced inputs to the RF pre-amplifier. For single ended operation the
signal is AC coupled into pin 13 with pin 14 AC decoupled to ground (or
vice -versa). Pins 13 and 14 are internally DC biased.
17 (LOCK DETECT INPUT) A current sink into this pin is enabled when the lock detect circuit indicates
lock. Used to give an external indication of phase lock.
18 (C-LOCK DETECT) A capacitor connected to this point determines the lock detect integrator time
constant and can be used to vary the sensitivity of the phase lock indicator.
19 (Rset) An external resistor from Pin 19 to VCC sets the charge pump output current
20 (CP OUTPUT) The phase detector output is a single ended charge pump sourcing or
sinking current to the inverting input of an external loop filter.
21 (CP REF) Connected to the non-inverting input of the loop filter to set the optimum DC
bias.
SP8855E
22 (F
ENABLE Part of the data input bus. When this pin is logic HI the F
ref/Fpd
are enabled. Open circuit = HI
and F
ref
outputs
pd
23 (CONTROL DIRECTION) This pin controls charge pump output direction. For Pin 23 HI the output
sinks current when F
23 LO the relationship is reversed. (see table 2).
> F
or when the RF phase leads Ref phase. For Pin
pd
ref
Changing the state of pin 23 reverses the pins on which Fref and Fpd output
occur. See pin 24 and Pin 25 below for details. Open circuit = HI.
24 = Fpd if Pin 23 is HI RF divider output pulses. Fpd = RF input frequency /(M.N+A). Pulse width =
= F
25 = F
if Pin 23 is LO 8 RF input cycles (1 cycle of the divide by 8 prescaler output).
ref
if Pin 223 is HI Reference divider output pulses. Fref = Reference input frequency/R. Pulse
ref
width = high period of Ref input.
27 (Reference Oscillator Capacitor) Leave open circuit if an external reference is used. See fig. 5 for typical
connection for use as an onboard crystal oscillator.
28 (Ref IN/XTAL) This pin is the input buffer amplifier for an external reference signal. This
amplifier provides the active element if an onboard crystal oscillator is used.
29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38 These pins set the Reference divider ratio R. Open circuit = HI.
39 (Phase Detector ENABLE) When this pin is HI the phase detector output is enable. Open circuit = HI.
40, 41 (PD Gain) These pins set the charge pump current multiplication factor (see table 1). Open
circuit = HI.
3
Page 4
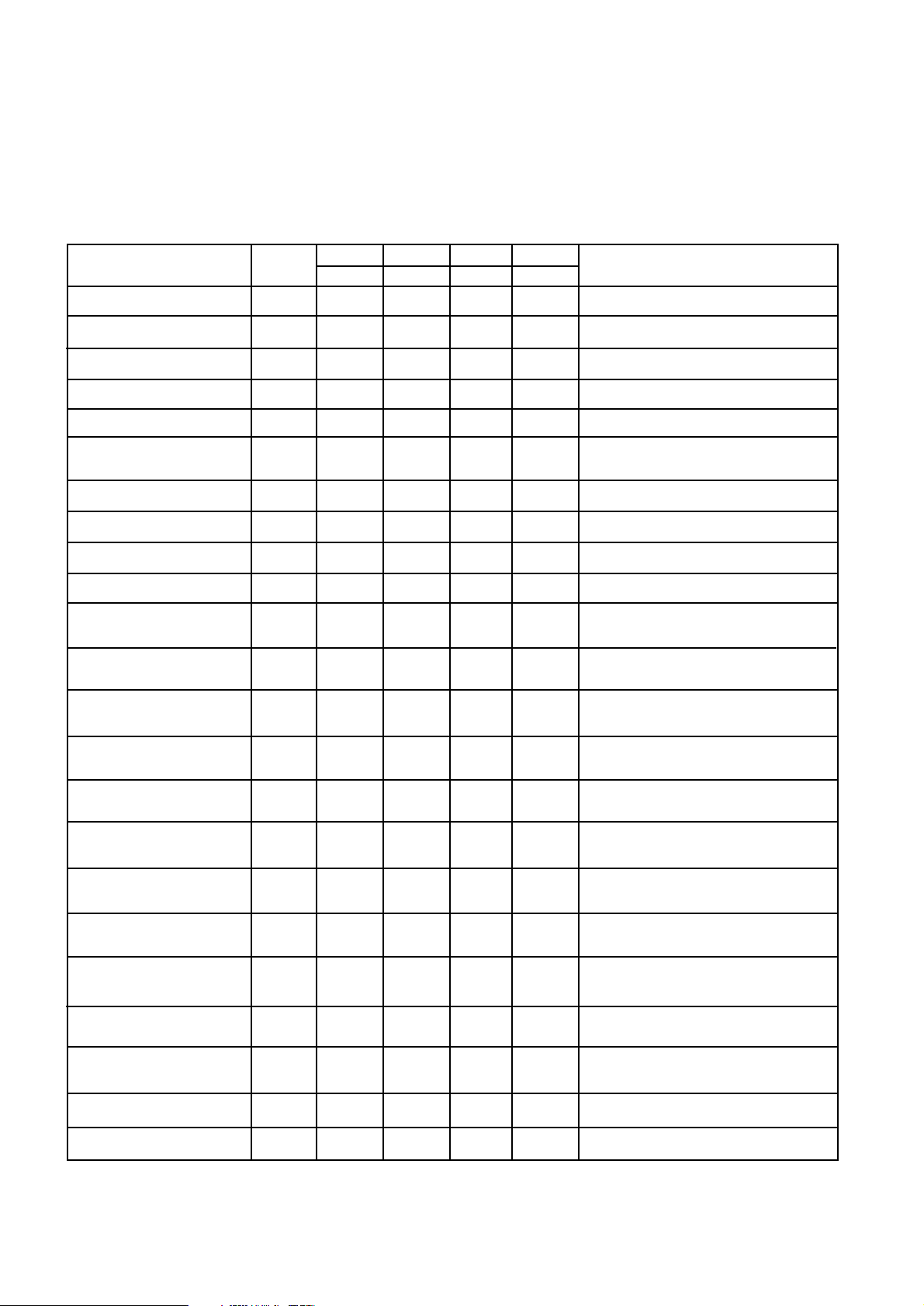
SP8855E
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Guaranteed over the full temperature and supply voltage range (unless otherwise stated)
Temperature T
MA part -55°C and +125°C Supply Voltage = 4.75V and 5.25V
Characteristics Pin Value Units Conditions
Supply current15, 26 180 240 mA
RF input sensitivity 13, 14 -5.0 +7.0 dBm 100MHz to 2.8/2.7GHz See Fig. 3
RF division ratio 13,14,24 56 16383
Reference division ratio 28, 25 1 1023
Comparison frequency 28,24,25 50 MHz
for KG parts -55°C and +100°C, Temperature T
amb
Min Typ Max
for IG parts -40°C and +85°, Temperature T
amb
case
for
Reference input frequency 28 10 100 MHz Reference division ratio ≥ 2 at frequencies
>50MHz also see Note 1.
Reference input voltage 28 630 1200 2000 mV p-p Sine Wave 10-100MHz
F
output voltage high 24, 25 - 0.8 Vwrt V
ref/Fpd
F
output voltage low 24, 25 - 1.4 Vwrt V
red/Fpd
Lock detect output voltage 17 300 500 mV I
Charge pump current at 19,20,21 ±1.4 ±1.5 ±1.7 mA V
multiplication factor = 1 I
Charge pump current at 19,20,21 ±2.0 ±2.3 ±2.5 mA V
multiplication factor = 1.5 I
Charge pump current at 19,20,21 ±3.4 ±3.8 ±4.6 mA V
multiplication factor = 2.5 I
Charge pump current at 19,20,21 ±5.4 ±6.1 ±6.5 mA V
multiplication factor = 4.0 I
CC
CC
2.2K to 0V
2.2K to 0V
= 3mA
OUT
= V
pin 20
= 1.6mA
pin 19
= V
pin 20
= 1.6mA
pin 19
= V
pin 20
= 1.6mA
pin 19
= V
pin 20
= 1.6mA
pin 19
pin 21,
pin 21,
pin 21,
pin 21,
Input bus high logic level 1-11, 22 3.5 V
23, 29-44
Input bus low logic level 1-11, 22 1 V
23,29-44
Input bus current source 1-11,22 -200 µAV
23,29-44
= 0V
IN
Input bys current sink 1-11, 22 10 µAV
23,29-44
Up down current matching 20 ±5%V
Charge pump reference 21 VCC-0.5 V I
voltage multiplication factor = 1
Charge pump reference 21 VCC-1.6 V I
voltage multiplication factor = 4
R
current 19 0.5 2 mA See Note 2
set
R
Voltage 19 1.6 V I
set
= V
IN
CC
= V
pin 20
I
pin 19
pin 19
pin 19
pin 19
pin 21,
= 1.6mA
=1.6mA current
=1.6mA current
= 1.6mA
Notes: 1. Lower reference frequencies may be used if slew rates are maintained.
2. Pin 19 current x multiplication factor must be less than 5mA if charge pump accuracy is to be maintained.
4
Page 5
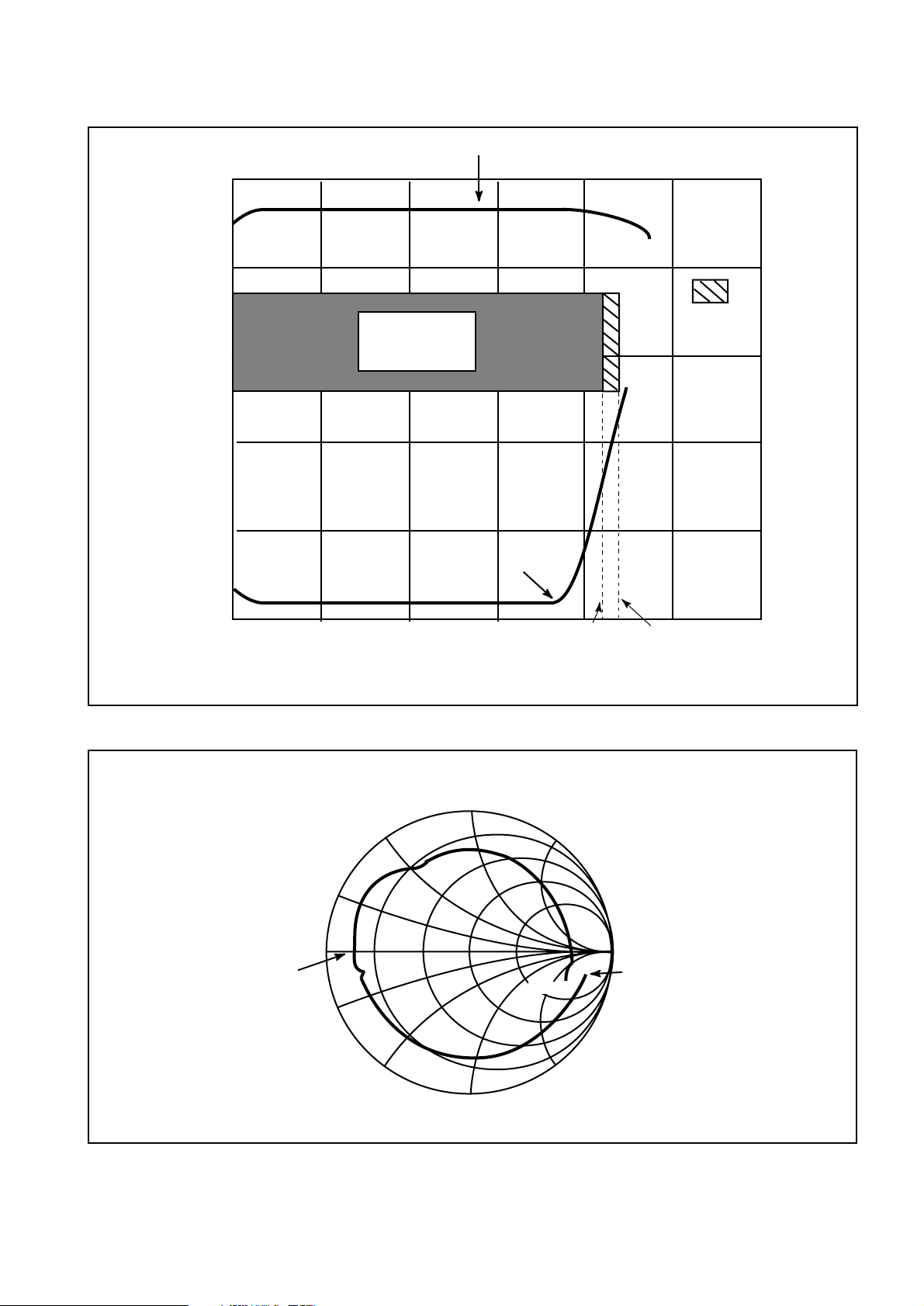
+20
+10
+7
-5
-10
-20
TYPICAL OVERLOAD
GUARANTEED
OPERTAING
WINDOW
OPERATING
AREA FOR
'IG' PARTS
ONLY
SP8855E
-30
100MHz
+j0.2
1.1GHz
-j0.2
+j0.5
0.2 0.5 1
0
TYPICAL SENSITIVITY
1GHz
2.7GHz
2GHz
INPUT DRIVE REQUIREMENTS
Fig. 3 SP8855E
+j1
+j2
2.5GHz
2.8GHz
Zo = 50Ω
50MHz
10GHz
-j0.5
-j1
Fig. 4 R.F. input impedance
-j2
5
Page 6

SP8855E
VCC
+5V
* VALUES DEPEND
ON APPLICATION
RF COUNTER
PROGRAMMING
APPLICATION USING
CRYSTAL REFERENCE
27
100p
SP8855
28
33p
10MHz
CRYSTAL
VCO
1k
1n
1n 10n
2k2
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
4
6
5
202122
18
19
*100n
Fig. 5 Typical application diagram
3
2
1
232425
Fpd Fref
1µ
4443424140
26
27
10n
Ref in
REFERENCE COUNTER
PROGRAMMING
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
1n
*
VCC
-
+
LOOP
FILTER
*
OP27
ETC
*
+30V
100n
DESCRIPTION
Prescaler and AM counter
The programmable divider chain is of AM counter
construction and therefore contains a dual modulus front end
prescaler, an A counter which controls the dual modulus ratio
and an M counter which performs the bulk multi-modulus
division. A programmable divider of this construction has a
division ratio of MN+A and a minimum integer steppable
division ratio of N(N-1), where N is the prescaler ratio.
Programming
The device is programmed by connecting the
programming pins to either VCC or ground. The programming
inputs will go high if left open circuit but for best noise immunity
a wired connection to VCC is preferable. The programming
inputs can be driven from TTL or CMOS logic levels if required.
Reference input
The reference source can be either driven from an external
sine or square wave source of up to 100MHz or a crystal can
be connected as shown in Fig. 5.
6
Phase Comparator and Charge pump
The SP8855E has a digital phase/frequency comparator
driving a charge pump with programmable current output.
The charge pump current level at the minimum gain setting
is approximately equal to the current fed into the R
se
input
t
pin 19 and can be increased by programming pins 40 and
41 according to Table 1 by up to 4 times.
Pin 40 Pin 41 Current Multiplication
Factor
0 0 1.0
0 1 1.5
1 0 2.5
1 1 4.0
Table 1
Page 7

V
- 1.6V
Pin 19 current .
CC
R
set
Phase detector gain =
(mA) X multiplication factor
I
pin 19
mA/radian
2π
To allow for control direction changes introduced by the
design of the PLL, pin 23 can be programmed to reverse the
control direction of the loop by transposing the Fpd and F
connections. In order that any external phase detector will also
be reversed by this function, the Fpd and F
outputs are also
ref
interchanged as shown in Table 2.
Output for RF Phase Lag
Control direction pin 23 pin 20
1 Current Source
0 Current Sink
Table 2
The charge pump connections to the loop amplifier consist
of the charge pump output and the charge pump reference.
The matching of the charge pump up and down currents will
only be maintained if the charge pumps output is held at a
voltage equal to the charge pump reference using an
operational amplifier to produce a virtual earth condition at pin
20.
The lock detect circuit can drive an LED to give visual
indication of phase lock or provide an indication to the control
system if a pull-up resistor is used in place of the LED. A small
capacitor connected from the C-lock detector pin to ground
may be used to delay lock detect indication and remove
ref
glitches produced by momentary phase coincidence during
lock up. The phase detector can be disabled by pulling pin 39
to logic low.
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 PIN
2928272625242322212
TEN BIT REFERENCE COUNTER
REFERENCE DIVIDER PROGRAMMING PIN ALLOCATION
SP8855E
0
The Fpd and Fref signals to the phase detector are available
on pin 24 and 25 and may be used to monitor the frequency
input to the phase detector or used in conjunction with an
external phase detector. When the Fpd/Fref outputs are to be
used at high frequencies, an external pull down resistor of
minimum value 330Ω may be used connected to ground to
reduce the fall time of the output pulse.
40 41 42 43 44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 PIN
PHASE
DETECTOR
GAIN
CONTROL
see Table 1
13 212 211 210
2
REFERENCE DIVIDER PROGRAMMING PIN ALLOCATION
2928272625242322212
M COUNTER
RF
3 BIT A
COUNTER
Fig. 6 Programming data format
0
7
Page 8

SP8855E
Vcc
40k 5k
40k
INPUT
Fig. 7a RF and reference divider programming bits, F
enable, control direction and phase detector gain control
inputs
5k
50µA
0V
pd/Fref
RF
INPUT
RF
INPUT
14
13
4k
3k
325
500
500
Fig. 7b RF inputs
Vcc
325
3mA
0V
C-LOCK DETECT (HIGH WHEN LOCKED)
18
3k
50k
20µA
3k
100µA
Fig. 7c Lock detect decouple
R
set
19
Vcc
Vcc
V
REF
4.7V
0V
400µA
2k52k5
LOW
WHEN
LOCKED
3k
100
3k
100
Fig. 7d Lock detect output
CHARGE PUMP
OUTPUT REFERENCE
20 21
450
Vcc
17
LOCK
DETECT
OUTPUT
1k 11
0V
Vcc
450
CHARGE PUMP
CURRENT SOURCES
130
Fig. 7e R
UP
Vcc
DOWN
2mA
pin Fig. 7f Charge pump circuit
set
83 83
Fig. 7 Interface circuit diagrams
8
Page 9

SP8855E
Vcc
3.3mA
296
outputs
ref
24, 25
F
pd,Fref,
OUTPUTS
0V
296
296
Fig. 7g Fpd, and F
APPLICATIONS
RF Layout
The SP8855E can operate with input frequencies up to
2.8GHz but to obtain optimum performance, good RF layout
practices should be used. A suitable layout technique is to use
double sided printed circuit board with through plated holes.
Wherever possible the top surface on which the SP8855E is
mounted should be left as a continuous sheet of copper to form
a low impedance earth plane. The ground pins 12 and 16
should be connected directly to the earth plane. Pins such as
and the unused RF input should be decoupled with chip
V
cc
capacitors mounted as close to the device pin as possible with
a direct connection to the earth plane, suitable values are
10nF for the power supplies and <1nF for the RF input pin. (a
lower value should be used sufficient to give good decoupling
at the RF frequency of operation). A larger decoupling
capacitor mounted as close as possible to pin 26 should be
used to prevent modulation of V
The R
resistor should also be mounted close to the R
set
by the charge pump pulses.
CC
pin
set
to prevent noise pick-up, and the capacitor connected from the
charge pump output should be a chip component with short
connections to the SP8855E.
When the reference is derived from a crystal connected to
pins 27 and 28 as shown in Fig.5 the oscillator components are
best mounted close to the SP8855E.
All signals such as the programming inputs, RF in
reference in and the connections to the op-amp are best taken
through the pc board adjacent to the SP8855E with through
plated holes allowing connections to remote points without
fragmenting the earth plane.
Programming inputs
The input pins are designed to be compatible with TTL or
CMOS logic with a switching threshold set at about 2.4V by
three forward biased base emitter diodes. The inputs will be
taken high by an internal pull up resistor if left open circuit but
for best noise immunity it is better to connect unused inputs
directly to VCC or ground.
Vcc
40k
OSCILLATOR
CRYSTAL
28
27
60k
OSCILLATOR
CAPACITOR
100µA
3k
3k
50µA
50µA
100µA 100µA
40k
60k
0V
Fig. 7h Reference oscillator
RF inputs
The prescaler has a differential input amplifier to improve
input sensitivity. Generally the input drive will be single ended
and the RF signal should be AC coupled to either of the inputs
using a chip capacitor. The remaining input should be
decoupled to ground , again using a chip capacitor. The inputs
can be driven differentially but the input circuit should not
provide DC path between inputs or to ground.
Lock detect circuit
The lock detect circuit uses the up and down correction
pulses from the phase detector to determine whether the loop
is in or out of lock. When the loop is locked, both up and down
pulses are very narrow compared to the reference frequency,
but the pulse width in the out of lock condition continuously
varies, depending on the phase difference between the
outputs of the reference and RF counters. The logical AND of
the up and down pulses is used to switch a 20µA current sink
to pin 18 and a 50k resistor provides a load to VCC. The circuit
is shown in Fig.7c. When lock is established, the narrow
pulses from the phase detector ensure that the current source
is off for the majority of the time and so pin18 will be pulled high
by the 50k resistor. A voltage comparator with a switching
threshold at abount 4.7V monitors the voltage at pin 18 and
switches pin 17 low when pin 18 is more positive than the 4.7V
threshold. When the loop is unlocked, the frequency
difference at the counter outputs will produce a cyclic change
in pulse width from the phase detector outputs with a
frequency equal to the difference in frequency at the reference
and RF counter outputs. A small capacitor connected to pin 18
prevents the indication of a false phase lock conditions at pin
17 for momentaary phase coincidence. Because of the
variable width pulse nature of the signal at pin 18 the
calculation of a suitable capacitor value is complex, but if an
indication with a delay amounting to several times the
expected lock up time is acceptable, the delay will be
approximately equal to the time constant of the capacitor on
pin 18 and the internal 50k resistor.
9
Page 10

SP8855E
If a faster indication is required, comparable with the loop
lock up time, the capacitor will need to be 2-3 times smaller
than the time constant calculation suggests. The time to
respond to an out of lock conditions is 2-3 times less than that
required to indicate lock.
Charge pump circuit
The charge pump circuit converts the variable width up and
down pulses from the phase detector into adjustable current
pulses which can be directly connected to the loop amplifier.
The magnitude of the current and therefore the phase detector
gain can be modified when new frequency data is entered to
compensate for change in the VCO gain characteristics over
its frequency band. The charge pump pulse current is
determined by the current fed into pin 19 and is approximately
equal to pin 19 current when the programmed multiplication
ratio is one. The circuit diagram Fig. 7e shows the internal
components on pin 19 which mirror the input current into the
charge pump. The voltage at pin 19 will be approximately 1.6V
above ground due to two Vbe drops in the current mirror. This
voltage will exhibit a negative temperature coefficient, causing
the charge pump current to change with chip temperature by
up to 10% over the full military temperature range if the current
programming resistor is connected to V
application diagram Fig. 5. In critical applications where this
change in charge pump current would be too large the resistor
to pin 19 could be increased in value and connected to a higher
supply to reduce the effect of Vbe variation on the current level.
A suitable resistor connected to a 30V supply would reduce
the variation in pin 19 current due to temperature to less than
1.5%. Alternatively a stable current source could be used to
set pin 19 current.
The charge pump output on pin 20 will only produce
symmetrical up and down currents if the voltage is equal to that
on the voltage reference pin 21. In order to ensure that this
voltage relationship is maintained, an operational amplifier
must be used as shown in the typical application Fig. 5. Using
this configuration pin 20 voltage will be forced to be equal to
that pin 21 since the operational amplifier differential input
voltage will be no more than a few millivolts (the input offset
voltage of the amplifier). When the synthesiser is first switched
on or when a frequency outside VCO range is programmed the
amplifier output will limit, allowing pin 20 voltage to differ from
that on pin 21. As soon as an achievable frequency value is
programmed and the amplifier output starts to slew the correct
voltage relationship between pin 20 and 21 will be restored.
Because of the importance of voltage equality between the
charge pump reference and output pins, a resistor should
never be connected in series with the operational amplifier
inverting input and pin 20 as is the case with a phase detector
giving voltage outputs. Any current drawn from the charge
pump reference pin should be limited to the few micro amps
input current of a typical operational amplifier. A resistor
between the charge pump reference and the non inverting
input could be added to provide isolation but the value should
not be so high that more than a few millivolts drop are
produced by the amplifier input current.
as shown in the
CC
When selecting a suitable amplifier for the loop filter, a
number of parameters are important; input offset voltage in
most designs is only a few millivolts and an offset of 5mV will
produce a mismatch in the up and down currents of about 4%
with the charge pump multiplication factor set at 1. The
mismatch in up down currents caused by input offset voltage
will be reduced in proportion to the charge pump multiplication
factor in use. If the linearity of the phase detector about the
normal phase locked operating point is critical, the input offset
voltage of most amplifiers can be adjusted to near zero by
means of a potentiometer.
The charge pump reference voltage on pin 21 is about 1.3V
below the positive supply and will change with the temperature
and with the programmed charge pump multiplication factor.
In many cases it is convenient to operate the amplifier with the
negative power supply pin connected to 0V as this removes
the need for an additional power supply. The amplifier
selected must have a common mode range to within 3.4V
(minimum charge pump reference voltage) of the negative
supply pin to operate correctly without a negative supply. Most
popular amplifiers can be operated from a 30V positive supply
to give a wide VCO voltage drive range and have adequate
common mode range to operate with inputs at +3.4V with
respect to the negative supply. Input bias and offset current
levels to most operational amplifiers are unlikely to be high
enough to significantly affect the accuracy of the charge pump
circuit currents but the bias current can be important in
reducing reference side bands and local oscillator drift during
frequency changes. When the loop is locked, the charge pump
produces only very narrow pulses of sufficient width to make
up for any charge lost from the loop filter components during
the reference cycle. The charge lost will be due to leakage
from the charge pump output pin and to the amplifier input
bias current the latter usually being more significant. The
result of the lost charge is a sawtooth ripple on the VCO control
line which frequency modulates the phase locked oscillator at
the reference frequency and its harmonics.
It is possible to disable the charge pump by taking pin 39
low. In this case any leakage current will cause the oscillator
to drift off frequency. This feature may be useful where having
achieved lock an external phase detector of the user's choice
can be employed to suit a specific application.
Fpd and F
These outputs provide access to the outputs from the RF
and reference dividers and are provided for monitoring
purposes during product development or test, and for
connection of an external phase detector if required. The
output circuit is of ECL type, the circuit diagram being shown
in Fig. 7g. The outputs are enabled when pin 22 is high and
disabled when pin22 is low, but are best left in the disabled
state when not required as the fast edge speeds on the output
can increase the level of reference sidebands on the
synthesised oscillator.
The emitter follower outputs have no internal pull down
resistor to save current and if the outputs are required an
external pull down resistor should be fitted. The value should
be kept as high as possible to reduce supply current, about
2.2k. being suitable for monitoring with a high impedance
oscilloscope probe or for driving an AC coupled 50 Ohm load.
outputs
ref
10
Page 11

A minimum value for the pull down resistor is 330 Ohms. When
the Fpd and F
the logic low level of about 3.5V so that the additional supply
outputs are disabled the output level will be at
ref
current due to the load resistors will be present even when the
outputs are disabled.
SP8855E
Loop Filter Design
Generally the third order filter configuration shown in Fig.8
gives better results than the more commonly used second
order because the reference sidebands are reduced. Three
equations are required to determine values for the three
constants where;
Reference input
The reference input circuit functions as an input amplifier or
crystal oscillator. When an external reference signal is used
this is simply AC coupled to pin 28, the base of the input
emitter follower. When a low phase noise synthesiser is
required the reference signal is critical since any noise present
here will be multiplied by the loop. To obtain the lowest
possible phase noise from the SP8855E it is best to use the
highest possible reference input frequency and to divide this
down internally to obtain the required frequency at the phase
detector. The amplitude of the reference input is also
important, and a level close to the maximum will give the
lowest noise. When the use of a low reference input frequency
say 4-10MHz is essential some advantage may be gained by
using a limiting amplifier such as a CMOS gate to square up
the reference input.
In cases where a suitable reference signal is not available,
it may be more convenient to use the input buffer as a crystal
oscillator in this case the emitter follower input transistor is
connected as a Colpitts oscillator with the crystal connected
from the base to ground and with the feedback necessary for
oscillation provided by a capacitor tap at the emitter. The
arrangement is shown inset in Fig. 5.
C
1
C
2
τ1 = C
1
τ2 = R2 (C1 + C2)
τ3 = C2 R
2
The equations are
1/2
2
2
τ
n
2
2
2
τ
n
3
φ
ο
1 τ1 =
2 τ
=
2
3 τ3 =
Kφ K
Nω
n
1
2
ω
τ
n
- tan φ
1 + ω
0
2
1 + ω
3
1
+
ο
cos
ω
n
Where;
Kφis the phase detector gain factor in mA/radian
K0is theVCO gain factor in radian/second/Volt
N is the total division ratio from VCO to reference
frequency
is the natural loop bandwidth
ω
n
is the phase margin normally set to 45°
φ
ο
Since the phase detector is linear over a range of 2π radian,
Kφ can be calculated from
FROM
CHARGE
PUMP
OUTPUT
FROM
CHARGE
PUMP
REFERENCE
-
+
Fig. 8 third order loop filter circuit diagram
Kφ = Phase comparator current setting/2π mA/radian
R
2
TO
VCO
These values can now be substituted in equation 1 to obtain
a value for C1 and equation 2 and 3 used to determine values
for C2 and R
2
EXAMPLE
Calculate values for a loop with the following parameters
Frequency to be synthesised: 1000MHz
Reference frequency 10MHz
Division ratio 1000MHz/10MHz = 100
natural loop frequency 100KHz
ω
n
K0 VCO gain factor 2π x 10MHz/Volt
φ0 phase margin 45°
Phase comparator current 6.3mA
The phase detector gain factor K
= 6.3mA /2π = 1mA/radian
φ
11
Page 12

SP8855E
From equation 3:
- tan 45° +
τ
=
3
100kHz x 2π
τ
= 659 x 10
3
cos 45°
-9
From equation 2:
τ
=
2
(100kHz x 2π)
τ2 = 3.844 x 10
-6
Using these values in equation 1:
1 x 10 -3 x 2π x 10MHz/V
τ1 =
100 x (2π x 100kHz)
1
=
1
2
x 659 x 10
2
0.4142
628319
-9
[A]
1/2
Where A is:
2
2
1 + ω
1 + ω
τ
1 + (2π x 100kHz) x (3.844 x 10 -6)
2
n
=
2
2
τ
1 + (2π x 100kHz) x (659 x 10 -9)
3
n
τ1 =
62832
39.48 x 10
τ1 = 1.59 x 10
= 3.84 x 10
τ
1
Now τ1 = C1 ∴ C1 = 3.84nF
τ2 = R2 (C1 + C2)
= C2 R
τ
3
Substituting for C
τ2 = R
∴ R2 =
τ
2
2
2 C1
- τ
C
1
2
+
3
=
22
6.833
12
1.1714
-9
x 2.415
-9
τ
3
∴ τ2 = R2 C1 + τ
R
2
3.844 x 10
9.61 x 10
22
1/2
3
-6
- 659 x 10
-9
-9
R2 = 829.4Ω
= C2 R
τ
3
2
C2 = 0.794nF
∴ C2 =
R
τ
3
2
=
659 x 10
829.4
-9
12
Page 13

Page 14

http://www.mitelsemi.com
World Headquarters - Canada
Tel: +1 (613) 592 2122
Fax: +1 (613) 592 6909
North America Asia/Pacific Europe, Middle East,
Tel: +1 (770) 486 0194 Tel: +65 333 6193 and Africa (EMEA)
Fax: +1 (770) 631 8213 Fax: +65 333 6192 Tel: +44 (0) 1793 518528
Fax: +44 (0) 1793 518581
Information relating to products and services furnished herein by Mitel Corporation or its subsidiaries (collectively “Mitel”) is believed to be reliable. However, Mitel assumes no
liability for errors that may appear in this publication, or for liability otherwise arising from the application or use of any such information, product or service or for any infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights owned by third parties which may result from such application or use. Neither the supply of such information or purchase of product or
service conveys any license, either express or implied, under patents or other intellectual property rights owned by Mitel or licensed from third parties by Mitel, whatsoever.
Purchasers of products are also hereby notified that the use of product in certain ways or in combination with Mitel, or non-Mitel furnished goods or services may infringe patents or
other intellectual property rights owned by Mitel.
This publication is issued to provide information only and (unless agreed by Mitel in writing) may not be used, applied or reproduced for any purpose nor form par t of any order or
contract nor to be regarded as a representation relating to the products or services concerned. The products, their specifications, services and other information appearing in this
publication are subject to change by Mitel without notice. No warranty or guarantee express or implied is made regarding the capability, performance or suitability of any product or
service. Information concerning possible methods of use is provided as a guide only and does not constitute any guarantee that such methods of use will be satisfactory in a specific
piece of equipment. It is the user’s responsibility to fully determine the performance and suitability of any equipment using such information and to ensure that any publication or
data used is up to date and has not been superseded. Manufacturing does not necessarily include testing of all functions or parameters. These products are not suitable for use in
any medical products whose failure to perform may result in significant injury or death to the user. All products and materials are sold and services provided subject to Mitel’s
conditions of sale which are available on request.
M Mitel (design) and ST-BUS are registered trademarks of MITEL Corporation
Mitel Semiconductor is an ISO 9001 Registered Company
Copyright 1999 MITEL Corporation
All Rights Reserved
Printed in CANADA
TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION - NOT FOR RESALE
 Loading...
Loading...