Datasheet SN74LS193D, SN74LS193DR2, SN74LS193M, SN74LS193MEL, SN74LS193ML1 Datasheet (MOTOROLA)
...Page 1
5-1
FAST AND LS TTL DAT A
PRESETTABLE BCD/DECADE
UP/ DOWN COUNTER
PRESETTABLE 4-BIT BINARY
UP/ DOWN COUNTER
The SN54/74LS192 is an UP/DOWN BCD Decade (8421) Counter and the
SN54/74LS193 is an UP/DOWN MODULO-16 Binary Counter. Separate
Count Up and Count Down Clocks are used and in either counting mode the
circuits operate synchronously. The outputs change state synchronous with
the LOW-to-HIGH transitions on the clock inputs.
Separate Terminal Count Up and Terminal Count Down outputs are
provided which are used as the clocks for a subsequent stages without extra
logic, thus simplifying multistage counter designs. Individual preset inputs
allow the circuits to be used as programmable counters. Both the Parallel
Load (PL
) and the Master Reset (MR) inputs asynchronously override the
clocks.
• Low Power . . . 95 mW Typical Dissipation
• High Speed . . . 40 MHz Typical Count Frequency
• Synchronous Counting
• Asynchronous Master Reset and Parallel Load
• Individual Preset Inputs
• Cascading Circuitry Internally Provided
• Input Clamp Diodes Limit High Speed Termination Effects
NOTE:
The Flatpak version
has the same pinouts
(Connection Diagram) as
the Dual In-Line Package.
CONNECTION DIAGRAM DIP (TOP VIEW)
14 13 12 11 10 9
123456
7
16 15
8
V
CC
P
1
P0MR TC
DTCU
P
2
PL
P
3
Q1Q0CPDCPUQ2Q3GND
PIN NAMES LOADING (Note a)
HIGH
LOW
CP
U
CP
D
MR
PL
P
n
Q
n
TC
D
TC
U
Count Up Clock Pulse Input
Count Down Clock Pulse Input
Asynchronous Master Reset (Clear) Input
Asynchronous Parallel Load (Active LOW) Input
Parallel Data Inputs
Flip-Flop Outputs (Note b)
Terminal Count Down (Borrow) Output (Note b)
Terminal Count Up (Carry) Output (Note b)
0.5 U.L.
0.5 U.L.
0.5 U.L.
0.5 U.L.
0.5 U.L.
10 U.L.
10 U.L.
10 U.L.
0.25 U.L.
0.25 U.L.
0.25 U.L.
0.25 U.L.
0.25 U.L.
5 (2.5) U.L.
5 (2.5) U.L.
5 (2.5) U.L.
NOTES:
a. 1 TTL Unit Load (U.L.) = 40 µA HIGH/1.6 mA LOW.
b. The Output LOW drive factor is 2.5 U.L. for Military (54) and 5 U.L. for Commercial (74)
b. T emperature Ranges.
SN54/74LS192
SN54/74LS193
PRESETTABLE BCD/DECADE
UP/DOWN COUNTER
PRESETTABLE 4-BIT BINARY
UP/DOWN COUNTER
LOW POWER SCHOTTKY
J SUFFIX
CERAMIC
CASE 620-09
N SUFFIX
PLASTIC
CASE 648-08
16
1
16
1
ORDERING INFORMATION
SN54LSXXXJ Ceramic
SN74LSXXXN Plastic
SN74LSXXXD SOIC
16
1
D SUFFIX
SOIC
CASE 751B-03
LOGIC SYMBOL
VCC = PIN 16
GND = PIN 8
5
4
326
7
12
91011511
CP
D
Q0Q1Q2Q
3
TC
D
P
3
P2P1P
0
PL
CP
U
TC
U
13
MR
14
Page 2
5-2
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
SN54/74LS192 • SN54/74LS193
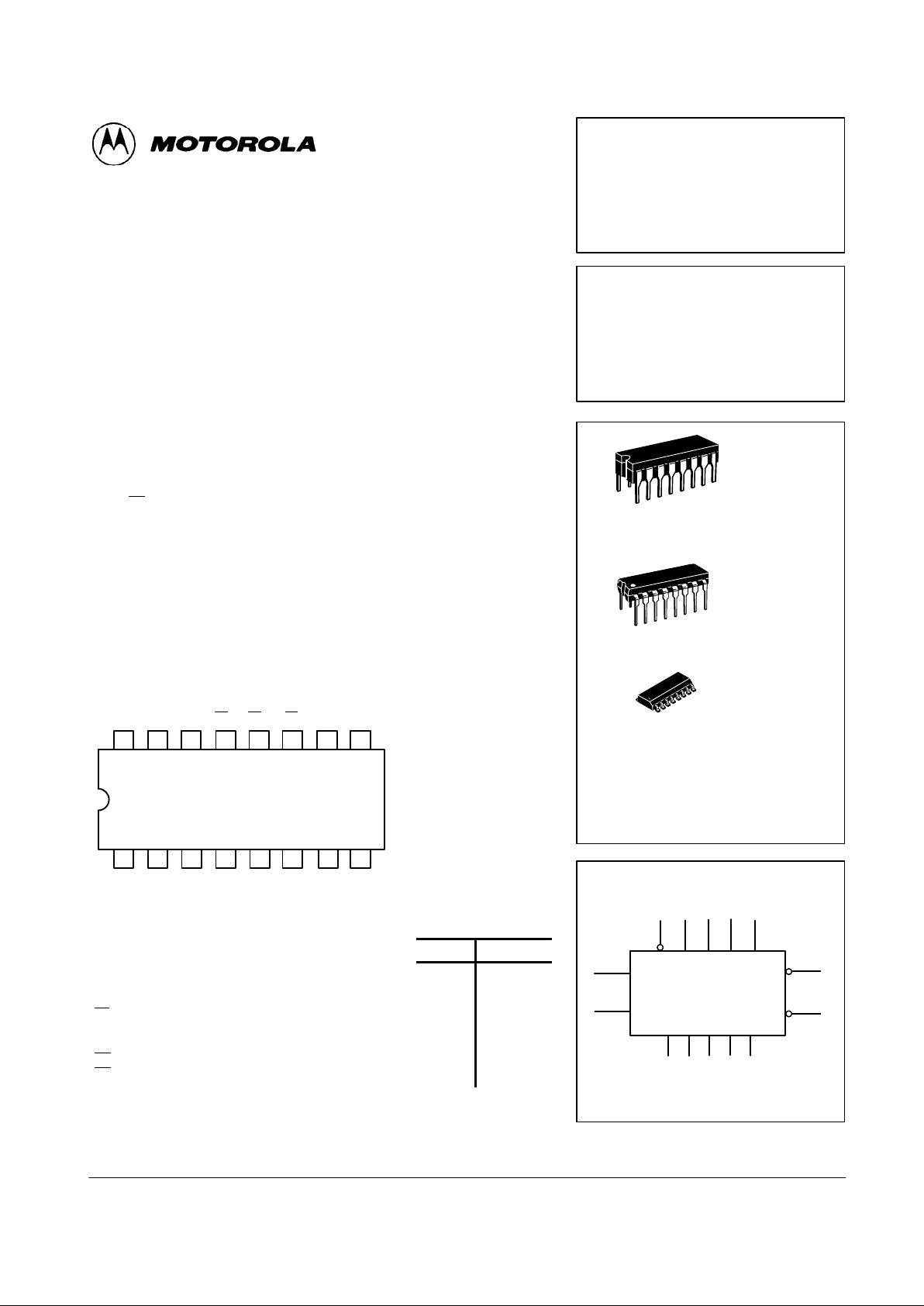
STATE DIAGRAMS
LS192 LOGIC EQUATIONS
FOR TERMINAL COUNT
LS192
LS193
COUNT UP
COUNT DOWN
0123
4
5
6
7
891011
12
13
14
15
0123
4
5
6
7
891011
12
13
14
15
TC
U
= Q0 ⋅ Q3 ⋅ CP
U
TCD = Q0 ⋅ Q1 ⋅ Q2 ⋅ Q3 ⋅ CP
D
LS193 LOGIC EQUATIONS
FOR TERMINAL COUNT
TCU = Q0 ⋅ Q1⋅ Q2⋅ Q3 ⋅ CP
U
TCD = Q0 ⋅ Q1 ⋅ Q2 ⋅ Q3 ⋅ CP
D
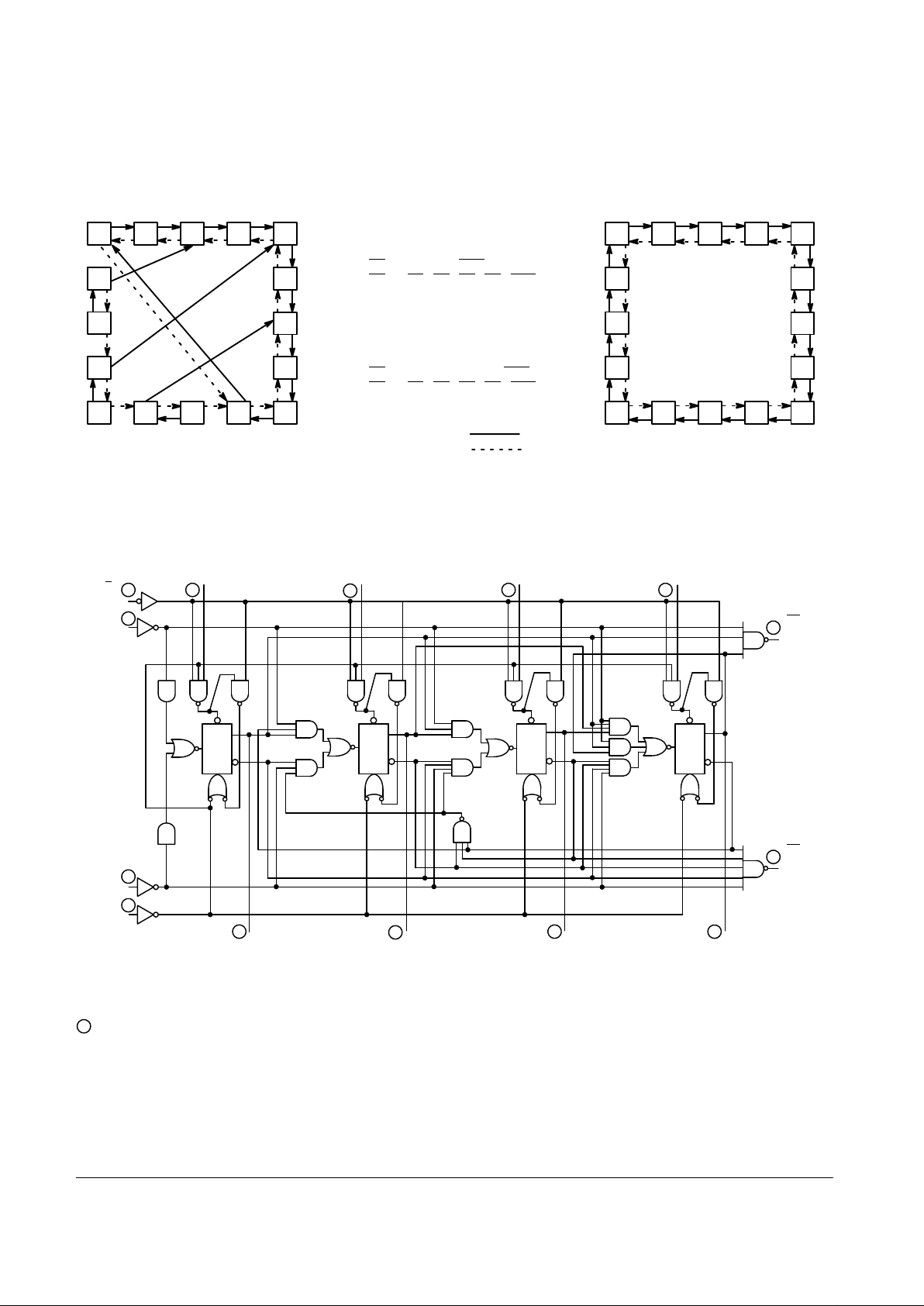
LOGIC DIAGRAMS
VCC = PIN 16
GND = PIN 8
= PIN NUMBERS
LS192
P
0
P
1
P
2
P
3
TC
U
(CARRY
OUTPUT)
Q
0
Q
1
Q
2
Q
3
MR
(CLEAR)
(DOWN
COUNT)
CP
D
(UP COUNT)
CP
U
(LOAD)
P
L
1
2
67
3
4
5
911
12
10
13
15
14
TC
D
(BORROW
OUTPUT)
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
Page 3
5-3
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
SN54/74LS192 • SN54/74LS193
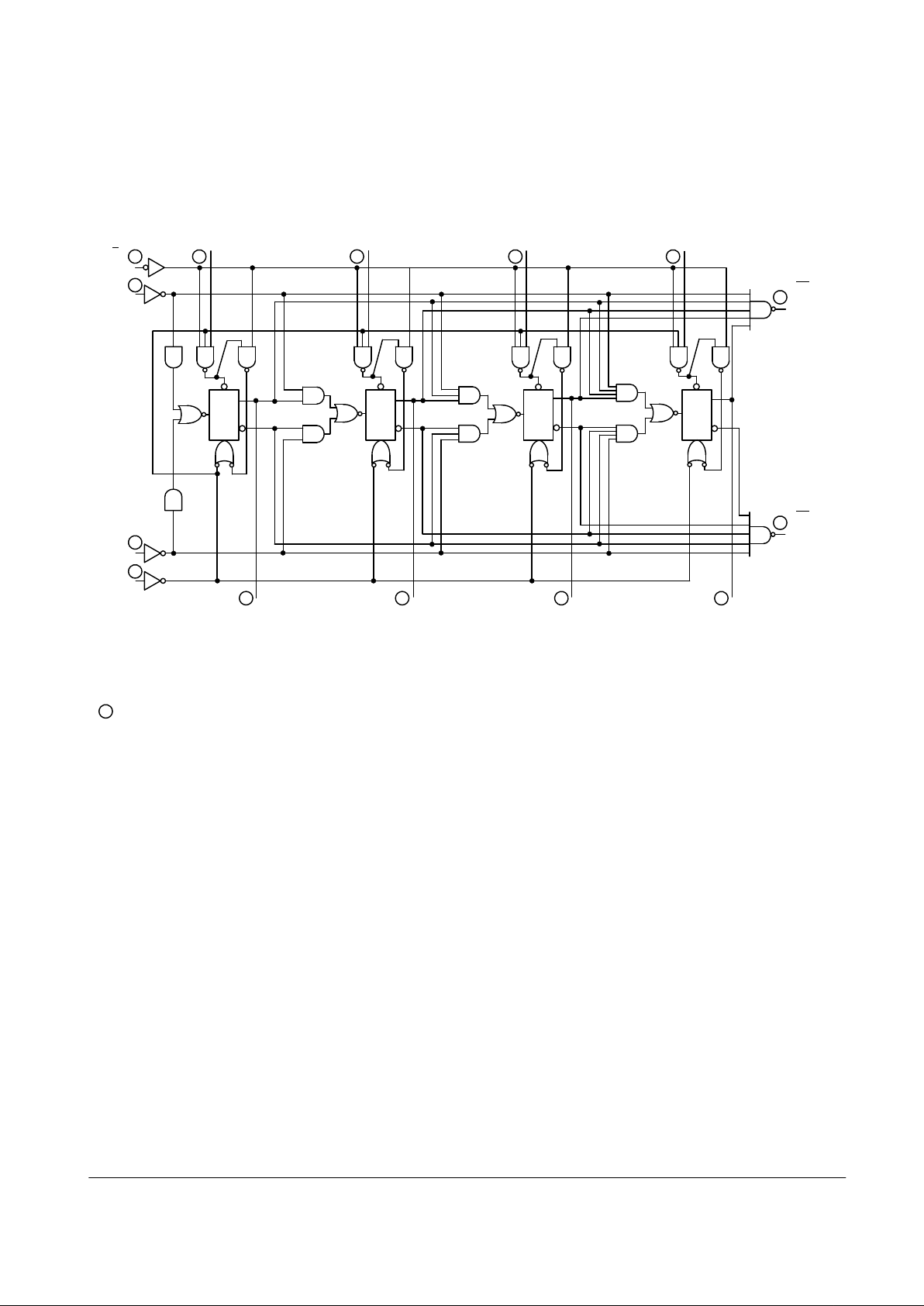
LOGIC DIAGRAMS (continued)
VCC = PIN 16
GND = PIN 8
= PIN NUMBERS
LS193
P
0
P
1
P
2
P
3
Q
0
Q
1
Q
2
Q
3
MR
(CLEAR)
(DOWN
COUNT)
CP
D
(UP COUNT)
CP
U
(LOAD)
P
L
1
2
67
3
4
5
911
12
10
13
15
14
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
S
D
Q
Q
C
D
T
TC
U
(CARRY
OUTPUT)
TC
D
(BORROW
OUTPUT)
Page 4

5-4
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
SN54/74LS192 • SN54/74LS193
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The LS192 and LS193 are Asynchronously Presettable
Decade and 4-Bit Binary Synchronous UP/ DOWN (Reversable) Counters. The operating modes of the LS192 decade
counter and the LS193 binary counter are identical, with the
only difference being the count sequences as noted in the
State Diagrams. Each circuit contains four master/slave
flip-flops, with internal gating and steering logic to provide
master reset, individual preset, count up and count down
operations.
Each flip-flop contains JK feedback from slave to master
such that a LOW-to-HIGH transition on its T input causes the
slave, and thus the Q output to change state. Synchronous
switching, as opposed to ripple counting, is achieved by
driving the steering gates of all stages from a common Count
Up line and a common Count Down line, thereby causing all
state changes to be initiated simultaneously. A LOW -to-HIGH
transition on the Count Up input will advance the count by one;
a similar transition on the Count Down input will decrease the
count by one. While counting with one clock input, the other
should be held HIGH. Otherwise, the circuit will either count by
twos or not at all, depending on the state of the first flip-flop,
which cannot toggle as long as either Clock input is LOW.
The Terminal Count Up (TC
U
) and Terminal Count Down
(TC
D
) outputs are normally HIGH. When a circuit has reached
the maximum count state (9 for the LS192, 15 for the LS193),
the next HIGH-to-LOW transition of the Count Up Clock will
cause TC
U
to go LOW. TCU will stay LOW until CPU goes
HIGH again, thus effectively repeating the Count Up Clock,
but delayed by two gate delays. Similarly, the TC
D
output will
go LOW when the circuit is in the zero state and the Count
Down Clock goes LOW. Since the TC outputs repeat the clock
waveforms, they can be used as the clock input signals to the
next higher order circuit in a multistage counter.
Each circuit has an asynchronous parallel load capability
permitting the counter to be preset. When the Parallel Load
(PL
) and the Master Reset (MR) inputs are LOW, information
present on the Parallel Data inputs (P0, P3) is loaded into the
counter and appears on the outputs regardless of the
conditions of the clock inputs. A HIGH signal on the Master
Reset input will disable the preset gates, override both Clock
inputs, and latch each Q output in the LOW state. If one of the
Clock inputs is LOW during and after a reset or load operation,
the next LOW-to-HIGH transition of that Clock will be
interpreted as a legitimate signal and will be counted.
MODE SELECT TABLE
MR PL CP
U
CP
D
MODE
H X X X Reset (Asyn.)
L L X X Preset (Asyn.)
L H H H No Change
L H H Count Up
L H H Count Down
L = LOW Voltage Level
H = HIGH Voltage Level
X = Don’t Care
= LOW-to-HIGH Clock Transition
Page 5

5-5
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
SN54/74LS192 • SN54/74LS193
GUARANTEED OPERATING RANGES
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
V
CC
Supply Voltage 54
74
4.5
4.75
5.0
5.0
5.5
5.25
V
T
A
Operating Ambient Temperature Range 54
74
–55
0
25
25
125
70
°C
I
OH
Output Current — High 54, 74 –0.4 mA
I
OL
Output Current — Low 54
74
4.0
8.0
mA
DC CHARACTERISTICS OVER OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE (unless otherwise specified)
Limits
Symbol Parameter
Min Typ Max
Unit Test Conditions
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage 2.0 V
Guaranteed Input HIGH Voltage for
All Inputs
54 0.7
Guaranteed Input LOW Voltage for
VILI
nput
LOW Volt
age
74 0.8
V
pg
All Inputs
V
IK
Input Clamp Diode Voltage –0.65 –1.5 V VCC = MIN, IIN = –18 mA
54 2.5 3.5 V
VCC = MIN, IOH = MAX, VIN = V
IH
VOHOutput HIGH Volt
age
74 2.7 3.5 V
CC
,
OH
,
IN IH
or VIL per Truth Table
54, 74 0.25 0.4 V IOL = 4.0 mA
VCC = VCC MIN,
VOLOutput LOW Volt
age
74 0.35 0.5 V IOL = 8.0 mA
V
IN
=
V
IL
or
V
IH
per Truth Table
20 µA VCC = MAX, VIN = 2.7 V
IIHI
nput
HIGH C
urren
t
0.1 mA VCC = MAX, VIN = 7.0 V
I
IL
Input LOW Current –0.4 mA VCC = MAX, VIN = 0.4 V
I
OS
Short Circuit Current (Note 1) –20 –100 mA VCC = MAX
I
CC
Power Supply Current 34 mA VCC = MAX
Note 1: Not more than one output should be shorted at a time, nor for more than 1 second.
AC CHARACTERISTICS (T
A
= 25°C)
Limits
Symbol Parameter
Min Typ Max
Unit Test Conditions
f
MAX
Maximum Clock Frequency 25 32 MHz
t
PLH
t
PHL
CPU Input to
TC
U
Output
17
18
26
24
ns
t
PLH
t
PHL
CPD Input to
TCD Output
16
15
24
24
ns
VCC = 5.0 V
t
PLH
t
PHL
Clock to Q
27
30
38
47
ns
CC
CL = 15 pF
t
PLH
t
PHL
PL to Q
24
25
40
40
ns
t
PHL
MR Input to Any Output 23 35 ns
Page 6

5-6
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
SN54/74LS192 • SN54/74LS193
AC SETUP REQUIREMENTS (T
A
= 25°C)
Limits
Symbol Parameter
Min Typ Max
Unit Test Conditions
t
W
Any Pulse Width 20 ns
t
s
Data Setup Time 20 ns
t
h
Data Hold Time 5.0 ns
V
CC
=
5.0 V
t
rec
Recovery Time 40 ns
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS
SETUP TIME (ts) is defined as the minimum time required for
the correct logic level to be present at the logic input prior to the
PL
transition from LOW-to-HIGH in order to be recognized and
transferred to the outputs.
HOLD TIME (th) is defined as the minimum time following the
PL
transition from LOW-to-HIGH that the logic level must be
maintained at the input in order to ensure continued recogni-
tion. A negative HOLD TIME indicates that the correct logic
level may be released prior to the PL
transition from
LOW-to-HIGH and still be recognized.
RECOVERY TIME (t
rec
) is defined as the minimum time
required between the end of the reset pulse and the clock
transition from LOW-to-HIGH in order to recognize and
transfer HIGH data to the Q outputs.
Page 7

5-7
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
SN54/74LS192 • SN54/74LS193
AC WAVEFORMS
Figure 1
Figure 2 Figure 3
Figure 4 Figure 5
Figure 6 Figure 7
1.3 V
CPU or CP
D
CPU or CP
D
CPU or CP
D
Q
Q
Q
t
w
CPU or CP
D
TC
U
or TC
D
PL
PL
P
n
Q
n
MR
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PLH
P
n
Q
n
NOTE: PL = LOW
t
W
t
PHL
P
n
PL
Q
n
t
s(H)
t
s(L)
t
h(H)
t
h(L)
* The shaded areas indicate when the input is permitted
* to change for predictable output performance
Q = P Q = P
t
PLH
t
rec
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PHL
t
W
t
PHL
t
PHL
t
W
1.3 V
1.3 V 1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
1.3 V
t
rec
 Loading...
Loading...